
Data Services Management Console:
Administrator Guide
BusinessObjects Data Services XI 3.1 (12.1.0)

Copyright
© 2008 Business Objects, an SAP company. All rights reserved. Business Objects
owns the following U.S. patents, which may cover products that are offered and
licensed by Business Objects: 5,295,243; 5,339,390; 5,555,403; 5,590,250;
5,619,632; 5,632,009; 5,857,205; 5,880,742; 5,883,635; 6,085,202; 6,108,698;
6,247,008; 6,289,352; 6,300,957; 6,377,259; 6,490,593; 6,578,027; 6,581,068;
6,628,312; 6,654,761; 6,768,986; 6,772,409; 6,831,668; 6,882,998; 6,892,189;
6,901,555; 7,089,238; 7,107,266; 7,139,766; 7,178,099; 7,181,435; 7,181,440;
7,194,465; 7,222,130; 7,299,419; 7,320,122 and 7,356,779. Business Objects and
its logos, BusinessObjects, Business Objects Crystal Vision, Business Process
On Demand, BusinessQuery, Cartesis, Crystal Analysis, Crystal Applications,
Crystal Decisions, Crystal Enterprise, Crystal Insider, Crystal Reports, Crystal
Vision, Desktop Intelligence, Inxight and its logos , LinguistX, Star Tree, Table
Lens, ThingFinder, Timewall, Let There Be Light, Metify, NSite, Rapid Marts,
RapidMarts, the Spectrum Design, Web Intelligence, Workmail and Xcelsius are
trademarks or registered trademarks in the United States and/or other countries
of Business Objects and/or affiliated companies. SAP is the trademark or registered
trademark of SAP AG in Germany and in several other countries. All other names
mentioned herein may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Third-party
Contributors
Business Objects products in this release may contain redistributions of software
licensed from third-party contributors. Some of these individual components may
also be available under alternative licenses. A partial listing of third-party
contributors that have requested or permitted acknowledgments, as well as required
notices, can be found at: http://www.businessobjects.com/thirdparty
2008-08-26

Contents
Introduction 9Chapter 1
Welcome to Data Services........................................................................10
Overview of this guide...............................................................................15
Administrator User Interface 17Chapter 2
Installation and configuration.....................................................................18
About the Management Console...............................................................20
Administrator navigation............................................................................23
Welcome..............................................................................................10
Documentation set for Data Services...................................................10
Accessing documentation....................................................................13
Business Objects information resources..............................................14
About this guide....................................................................................15
Who should read this guide..................................................................16
Logging in.............................................................................................21
Management Console navigation.........................................................22
Navigation tree.....................................................................................23
Pages...................................................................................................27
Administrator Management 29Chapter 3
Adding repositories....................................................................................30
Connecting repositories to the Administrator.......................................31
Changing repository connection allocation..........................................34
Adapter considerations.........................................................................34
Managing user roles..................................................................................35
To add users and their roles.................................................................36
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 3

Contents
Adding Access Servers..............................................................................37
To connect an Access Server to the Administrator..............................38
Centralizing administration........................................................................38
To group administration by job type.....................................................39
Setting the status interval..........................................................................39
To set the status interval.......................................................................39
Setting the log retention period..................................................................40
To delete log information......................................................................40
Managing database account changes.......................................................41
Updating local repository login parameters..........................................42
Updating datastore connection parameters.........................................43
Central Repository Management 45Chapter 4
Setting up users and groups......................................................................46
To add the secure central repository to the Administrator....................46
To add a group to a central repository..................................................47
To add users.........................................................................................47
To add or remove a user from a group.................................................49
Deleting groups..........................................................................................49
To delete a group..................................................................................50
Viewing reports..........................................................................................50
Object state report................................................................................50
Change report......................................................................................51
Server groups 53Chapter 5
Server group architecture..........................................................................54
Load balance index..............................................................................56
Job execution.......................................................................................56
Job launcher.........................................................................................57
Working with server groups and Designer options...............................57
4 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Contents
Editing and removing a server group.........................................................59
To edit a server group...........................................................................60
To remove a server group....................................................................60
Monitoring Job Server status in a server group.........................................61
Executing jobs using server groups...........................................................62
Batch Jobs 63Chapter 6
Executing batch jobs..................................................................................64
To execute a job...................................................................................64
Scheduling jobs.........................................................................................65
Using the Data Services job scheduler................................................65
Scheduling jobs in BusinessObjects Enterprise...................................77
Using a third-party scheduler...............................................................80
Data Services job launcher..................................................................86
Monitoring jobs..........................................................................................89
Overall status.......................................................................................89
Statistics...............................................................................................91
Ignore error status................................................................................94
Deleting batch job history data.............................................................94
Stopping a running job.........................................................................95
Trace, monitor, and error logs..............................................................95
Real-Time Jobs 97Chapter 7
Supporting real-time jobs...........................................................................98
Configuring and monitoring real-time services........................................101
Creating services and service providers............................................101
Starting and stopping services...........................................................107
Updating service providers.................................................................110
Monitoring services............................................................................111
Creating and monitoring client interfaces................................................113
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 5

Contents
RFC clients.........................................................................................114
Adding IDoc configurations to an RFC client.....................................117
Message Broker clients......................................................................119
Monitoring clients...............................................................................119
Real-Time Performance 123Chapter 8
Configuring Access Server output...........................................................124
To configure an Access Server...........................................................125
Service configuration parameters............................................................127
Service startup behavior.....................................................................128
High traffic behavior...........................................................................129
Response time controls......................................................................130
Service statistics......................................................................................131
Service provider statistics........................................................................133
Using statistics and service parameters..................................................134
Profile Server Management 137Chapter 9
Defining the profiler repository.................................................................138
To define a profiler repository.............................................................138
Connecting repositories to the Administrator ..........................................139
To add a local, central, or profiler repository connection to the
Administrator......................................................................................139
To view the list of repositories connected to the Administrator..........141
Defining profiler users..............................................................................141
To define a profiler user......................................................................142
Configuring profiler task parameters.......................................................143
To configure profiler task parameters ................................................144
Task execution parameters................................................................144
Task management parameters...........................................................146
Monitoring profiler tasks using the Administrator ....................................148
6 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Contents
To monitor a profiler task in the Data Services Administrator............149
Adapters 155Chapter 10
Overview of adapters...............................................................................156
To create an adapter datastore connection in the Designer...............157
Adding and configuring adapter instances..............................................158
To add an adapter instance................................................................158
To edit an adapter's configuration......................................................159
Adapter instance configuration information........................................159
Starting and stopping adapter instances.................................................163
To start an adapter instance...............................................................163
To stop an adapter instance...............................................................163
To start or stop an adapter operation instance...................................163
Monitoring adapter instances..................................................................164
To monitor the adapter instances and operations..............................164
To monitor adapter instance statistics................................................165
Support for Web Services 167Chapter 11
Support for HTTP 169Chapter 12
Overview..................................................................................................170
Adapter installation and configuration.....................................................171
URL for HTTP requests to Data Services..........................................171
Configuring the HTTP adapter...........................................................171
Configuring an operation instance.....................................................174
Defining the HTTP adapter datastore................................................177
Configuring SSL with the HTTP adapter............................................180
Troubleshooting 185Chapter 13
Reestablishing network connections.......................................................186
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 7

Contents
To reestablish network connections for your repository.....................186
Reinstalling the Web Server service........................................................186
To reinstall the Web Server service....................................................187
Finding problems.....................................................................................187
To determine which object is not operating properly..........................188
To determine the cause of the error...................................................189
Error and trace logs.................................................................................189
Batch job logs.....................................................................................189
Service provider logs..........................................................................191
Access Server logs.............................................................................193
Adapter logs.......................................................................................195
Resolving connectivity problems.............................................................196
Restarting the Access Server..................................................................198
To perform a controlled restart of the Access Server.........................198
To perform an abort and restart of the Access Server.......................199
Index 201
8 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Introduction
1

Introduction
1
Welcome to Data Services
Welcome to Data Services
Welcome
Data Services XI Release 3 provides data integration and data quality
processes in one runtime environment, delivering enterprise performance
and scalability.
The data integration processes of Data Services allow organizations to easily
explore, extract, transform, and deliver any type of data anywhere across
the enterprise.
The data quality processes of Data Services allow organizations to easily
standardize, cleanse, and consolidate data anywhere, ensuring that end-users
are always working with information that's readily available, accurate, and
trusted.
Documentation set for Data Services
You should become familiar with all the pieces of documentation that relate
to your Data Services product.
What this document providesDocument
Documentation Map
Release Summary
Release Notes
Getting Started Guide
Installation Guide for Windows
10 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide
Information about available Data Services books,
languages, and locations
Highlights of key features in this Data Services release
Important information you need before installing and
deploying this version of Data Services
An introduction to Data Services
Information about and procedures for installing Data
Services in a Windows environment.
Introduction
Welcome to Data Services
What this document providesDocument
1
Installation Guide for UNIX
Advanced Development Guide
Designer Guide
Integrator's Guide
Management Console: Administrator
Guide
Management Console: Metadata Reports Guide
Migration Considerations
Data Quality to Data Services Migration
Guide
Performance Optimization Guide
Information about and procedures for installing Data
Services in a UNIX environment.
Guidelines and options for migrating applications including information on multi-user functionality and
the use of the central repository for version control
Information about how to use Data Services Designer
Information for third-party developers to access Data
Services functionality
Information about how to use Data Services Administrator
Information about how to use Data Services Metadata
Reports
Release-specific product behavior changes from
earlier versions of Data Services to the latest release
Information about how to migrate from Data Quality
to Data Services
Information about how to improve the performance
of Data Services
Reference Guide
Detailed reference material for Data Services Designer
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 11
Introduction
1
Welcome to Data Services
Technical Manuals
What this document providesDocument
A compiled “master” PDF of core Data Services books
containing a searchable master table of contents and
index:
•
Getting Started Guide
•
Installation Guide for Windows
•
Installation Guide for UNIX
•
Designer Guide
•
Reference Guide
•
Management Console: Metadata Reports Guide
•
Management Console: Administrator Guide
•
Performance Optimization Guide
•
Advanced Development Guide
•
Supplement for J.D. Edwards
•
Supplement for Oracle Applications
•
Supplement for PeopleSoft
•
Supplement for Siebel
•
Supplement for SAP
Tutorial
A step-by-step introduction to using Data Services
In addition, you may need to refer to several Adapter Guides and
Supplemental Guides.
What this document providesDocument
JMS Adapter Interface
Salesforce.com Adapter
Interface
Supplement for J.D. Edwards
Supplement for Oracle Applications
12 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide
Information about how to install, configure, and use the Data
Services Adapter for JMS
Information about how to install, configure, and use the Data
Services Salesforce.com Adapter Interface
Information about license-controlled interfaces between Data
Services and J.D. Edwards World and J.D. Edwards OneWorld
Information about the license-controlled interface between Data
Services and Oracle Applications

Introduction
Welcome to Data Services
What this document providesDocument
1
Supplement for PeopleSoft
Supplement for SAP
Supplement for Siebel
Information about license-controlled interfaces between Data
Services and PeopleSoft
Information about license-controlled interfaces between Data
Services, SAP ERP and R/3, and SAP BI/BW
Information about the license-controlled interface between Data
Services and Siebel
Accessing documentation
You can access the complete documentation set for Data Services in several
places.
Accessing documentation on Windows
After you install Data Services, you can access the documentation from the
Start menu.
1. Choose Start > Programs > BusinessObjects XI 3.1 >
BusinessObjects Data Services > Data Services Documentation.
Note:
Only a subset of the documentation is available from the Start menu. The
documentation set for this release is available in LINK_DIR\Doc\Books\en.
2. Click the appropriate shortcut for the document that you want to view.
Accessing documentation on UNIX
After you install Data Services, you can access the online documentation by
going to the directory where the printable PDF files were installed.
1. Go to LINK_DIR/doc/book/en/.
2. Using Adobe Reader, open the PDF file of the document that you want
to view.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 13

Introduction
1
Welcome to Data Services
Accessing documentation from the Web
You can access the complete documentation set for Data Services from the
Business Objects Customer Support site.
1.
Go to http://help.sap.com.
2. Cick Business Objects at the top of the page.
You can view the PDFs online or save them to your computer.
Business Objects information resources
A global network of Business Objects technology experts provides customer
support, education, and consulting to ensure maximum business intelligence
benefit to your business.
Useful addresses at a glance:
ContentAddress
Customer Support, Consulting, and
Education services
http://service.sap.com/
Online Developer Community
https://boc.sdn.sap.com/EIM
14 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide
Information about Customer Support programs, as well as links to technical articles,
downloads, and online forums. Consulting
services can provide you with information
about how Business Objects can help
maximize your business intelligence investment. Education services can provide information about training options and modules.
From traditional classroom learning to targeted e-learning seminars, Business Objects can offer a training package to suit
your learning needs and preferred learning
style.
An online resource for sharing and learning
about Data Services with your developer
colleagues.
Introduction
Overview of this guide
ContentAddress
1
Blueprints
https://boc.sdn.sap.com/dataser
vices/blueprints
http://help.sap.com/
Documentation mailbox
documentation@businessob
jects.com
Blueprints for you to download and modify
to fit your needs. Each blueprint contains
the necessary Data Services project, jobs,
data flows, file formats, sample data, template tables, and custom functions to run
the data flows in your environment with
only a few modifications.
Business Objects product documentation.Product documentation
Send us feedback or questions about your
Business Objects documentation. Do you
have a suggestion on how we can improve
our documentation? Is there something that
you particularly like or have found useful?
Let us know, and we will do our best to ensure that your suggestion is considered for
the next release of our documentation.
Note:
If your issue concerns a Business Objects
product and not the documentation, please
contact our Customer Support experts.
Overview of this guide
About this guide
The guide covers the BusinessObjects™ Data Services Administrator, a
web-based application written entirely in Java. You can install the Data
Services Administrator on a separate computer from the other Data Services
components. It runs on the Data Services Web Server, which is supported
by the Data Services Web Server service. The Administrator uses a JDBC
connection to repositories.
Use the Administrator to:
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 15

Introduction
1
Overview of this guide
• Set up users and their roles
• Add connections to Access Servers and repositories
• Manage the retention of Job Server and Access Server logs
• Access job data published for Web Services
• Schedule and monitor batch jobs
• Configure and monitor:
• Access Server status
• Real-time services
• Client interfaces including SAP ERP and R/3 client interfaces (to read
IDocs) and message traffic moving in and out of an Access Server
• Adapter instances (a prerequisite for creating adapter datastores)
Who should read this guide
This and other Data Services product documentation assume the following:
• You are an application developer, consultant or database administrator
working on data extraction, data warehousing, data integration, or data
quality.
• You understand your source and target data systems, DBMS, legacy
systems, business intelligence, and messaging concepts.
• You understand your organization's data needs.
• You are familiar with SQL (Structured Query Language).
• If you are interested in using this product to design real-time processing
you are familiar with:
• DTD and XML Schema formats for XML files
• Publishing Web Services (WSDL, HTTP/S and SOAP protocols, etc.)
• You are familiar with Data Services installation environments: Microsoft
Windows or UNIX.
16 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Administrator User Interface
2

Administrator User Interface
2
Installation and configuration
This section describes the Administrator and how to navigate through its
browser-based, graphical user interface.
Related Topics
• Installation and configuration on page 18
• About the Management Console on page 20
• Administrator navigation on page 23
Installation and configuration
• General information about the components and architecture of Data
Services
• Complete installation instructions for all Data Services components
including connectivity testing for Data Services real-time functionality.
A summary of the connections used in Data Services is included here for
your reference. You must create the connections in the first four rows of the
following table before you can log in to the Administrator.
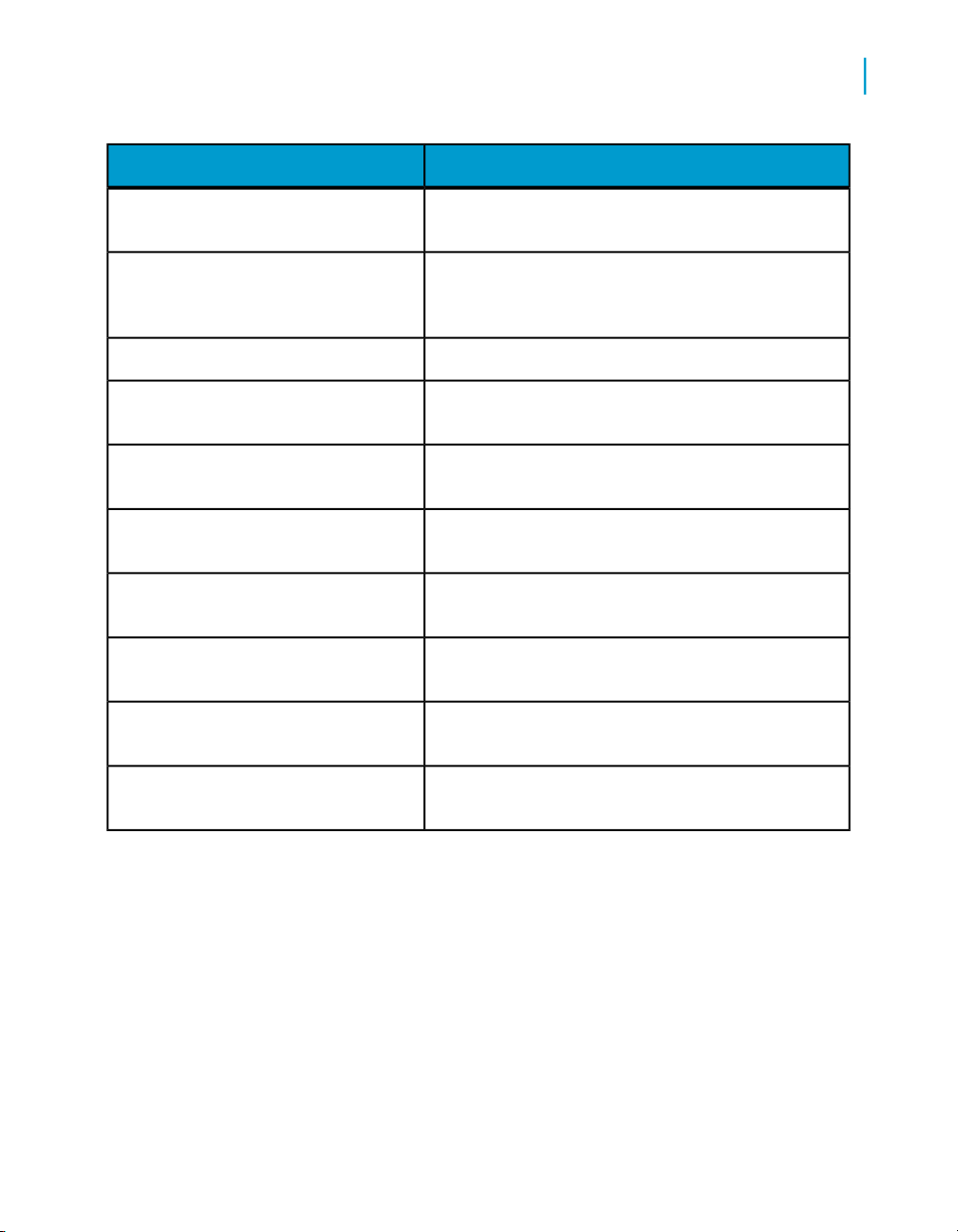
Custom connectionRepository ManagerRepository(s)
18 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide
Purpose of this connectionConnection TypeConnection ToolComponent
•
Connects Designer and
repositories.
•
Provides location for
storage of Data Services tables and job
metadata.
•
Connection information
is based on the
database you use for a
repository.

Administrator User Interface
Installation and configuration
Purpose of this connectionConnection TypeConnection ToolComponent
Connects a Job Server to
the Data Services Service
and repository you specify.
2
Server ManagerJob Server(s)
Server ManagerAccess Server(s)
InstallerAdministrator
Default (3500) or
custom port
Default (4000) or
custom port
Automatically assigned ports
You can also set a Job
Server to support adapters
via a separate communication port (default 4001).
Required to use the
Adapter Instance node in
the Administrator.
Connects an Access Server to the Data Services
Service and provides a port
for Message Client libraries
(allows applications to
communicate with Data
Services).
Provides an HTTP port
(28080) for connection between Administrator and all
Access Servers.
Includes an automatically
assigned shutdown port
(22828) which is not displayed. It is used by the
Tomcat service to start and
stop the application server,
which supports the Administrator.
For web application servers
other than the packaged
Tomcat server, the ports
may vary.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 19

Administrator User Interface
2
About the Management Console
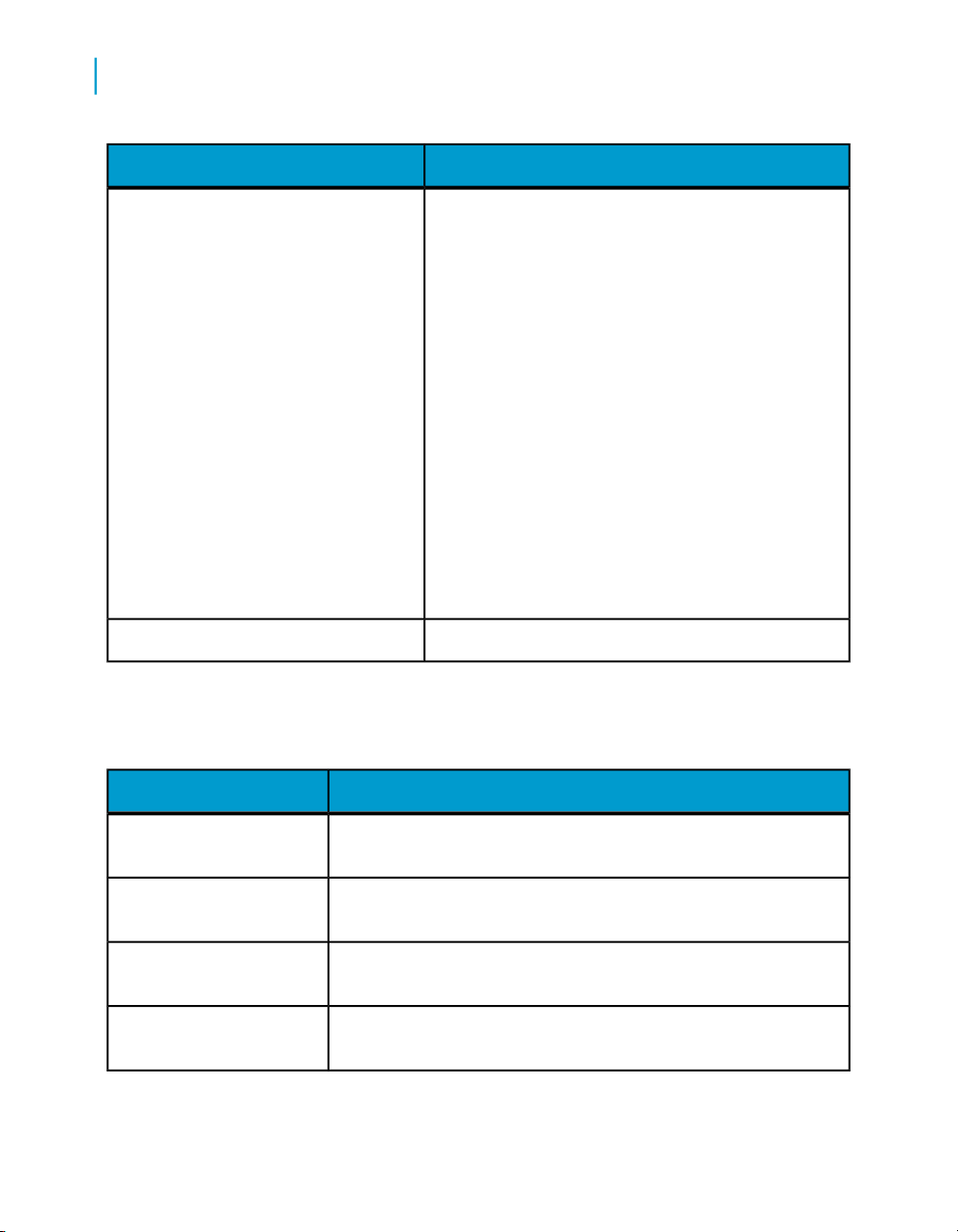
Purpose of this connectionConnection TypeConnection ToolComponent
Computer name on
which an Access
Server is installed
AdministratorAccess Server(s)
AdministratorRepository(s)
and port (you specified in Server Manager). For example:
AT589:4000
Settings based on
each repository's
database
Connects Access Server
(s) to the Administrator
Connects repositories to
the Administrator. Job
Servers (previously connected to each repository
using the Server Manager)
also link to the Administrator with this connection.
For more information, see the BusinssObjects Data Services Designer Guide.
About the Management Console
The Management Console is a collection of Web-based applications for
administering Data Services jobs and services, viewing object relationships,
and evaluating job execution performance and data quality.
These applications include:
• Administrator — Manage your production environment including batch
job execution, real-time services, Web services, adapter instances, server
groups, central and profiler repositories, and more. This guide describes
the Administrator.
• Impact and Lineage Analysis — Analyze the end-to-end impact and
lineage for Data Services tables and columns and BusinessObjects
Enterprise objects such as universes, business views, and reports.
• Operational Dashboards — View dashboards of Data Services job
execution statistics to see at a glance the status and performance of your
job executions for one or more repositories over a given time period.
20 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Administrator User Interface
About the Management Console
• Data Quality Dashboards — Evaluate the reliability of your target data
based on the validation rules you created in your Data Services batch
jobs to quickly review, assess, and identify potential inconsistencies or
errors in source data.
• Auto Documentation — View, analyze, and print graphical
representations of all objects as depicted in Data Services Designer
including their relationships, properties, and more.
Related Topics
• Management Console—Metadata Reports Guide: Impact and Lineage
Analysis Reports
• Management Console—Metadata Reports Guide: Operational Dashboard
Reports
• Management Console—Metadata Reports Guide: Data Validation
Dashboard Reports
• Management Console—Metadata Reports Guide: Auto Documentation
Reports
2
Logging in
To access the Administrator, first log in to the Data Services Management
Console. The first time you log in to the Management Console, use the default
user name and password (admin/admin). Business Objects recommends
that you change the defaults thereafter.
Related Topics
• Managing user roles on page 35
To log in to the Management Console
1. The first step depends on your operating system:
• On Windows, click the Start menu and select Programs > Business
Objects XI 3.1 > BusinessObjects Data Services > Data Services
Management Console.
If you encounter an error, check to see if your web application server
is installed and running.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 21

Administrator User Interface
2
About the Management Console
2. Enter the default user name (admin) and password (admin) and click Log
3. To launch the Administrator, click the Administrator icon (or name).
If you are logged in to the Designer, you can also access the Management
Console home page as follows:
• From the Start page, click Management Console.
• From the Tools menu, click Management Console.
• Click the Management Console tool bar icon.
• On UNIX, open a browser, enter the following case-sensitive URL,
then press Enter:
http://hostname:28080/DataServices
in.
The Management Console home page opens.
The Administrator Status page displays a status overview of all jobs.
Management Console navigation
After logging in to the Management Console and launching one of the
applications, the application name appears under the Management Console
banner.
The upper-right side of the main window includes the following links:
• Home—Click to return to the Management Console home page (for
example to select another application).
• Logout—Click to exit the application and the Management Console and
return to the login page.
• Settings—The metadata reporting applications also include a Settings
control panel for changing a variety of options depending on the
application.
As you navigate around the applications, notice the top of the right-hand
pane often displays a "bread crumb" path to indicate where you are in the
application. Depending on the page displayed, sometimes you can click on
the bread crumbs to navigate to a different part of the application.
22 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

The Administrator, Impact and Lineage Analysis, and Auto Documentation
applications also use a navigation tree in the left-hand pane.
Data Services Management Console sessions time out after 120 minutes (2
hours) of inactivity.
Administrator navigation
The layout of the Data Services Administrator consists of a window with a
navigation tree on the left and pages with tabs on the right.
Navigation tree
The navigation tree is divided into nine nodes: Status, Batch, Real-Time,
Web Services, Adapter Instances, Server Groups, Central Repositories,
Profiler Repositories, and Management.
Status node
Administrator User Interface
Administrator navigation
2
When the Administrator opens, it displays the Status page. The Status page
displays the status of the following items (after you have connected them to
the Administrator). The red, green, and yellow icons indicate the overall
status of each item based on the jobs, services, and other objects they
support.
• Batch—Contains the name of the repository associated with Job Server
on which you run the batch jobs. To see batch jobs status, connect the
repository to the Administrator.
Click the repository name to display a list of batch jobs and their status.
• Real-time—Contains the name of the Access Servers associated with a
real-time service. To see real-time jobs status, connect the Access Server
to the Administrator.
Click the Access Server name to display a list of real-time services and
their client interfaces.
• Adapters—Contains the name of the repository associated with Job
Server on which you run the adapter. To see an adapter's status, enable
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 23

Administrator User Interface
2
Administrator navigation
Batch node
a Job Server for adapters, then add the repository associated with that
Job Server.
• Profiler—Contains the name of the repository associated with the Profiler
Server. To see a profiler repository, connect the profiling repository to the
Administrator.
Click the repository name to display a list of profiler tasks and their status.
After you add at least one repository connection to the Administrator, you
can expand the Batch node. Then click a repository name to display its Batch
Job Status page.
Click the All Repositories option to see jobs in all repositories connected
to this Administrator (only appears if more than one repository is connected).
Each repository under the Batch node includes the following tabs:
• Batch Job Status—View the status of the last execution and in-depth
information about each job
• Batch Job Configuration—Configure execution and scheduling options
for individual jobs
• Repository Schedules—View and configure schedules for all jobs in the
repository
• Datastore Configurations—Edit some options for a datastore or a
particular datastore configuration rather than using the Designer.
• Resource Management—Manage data transfer and communication
resources that Data Services uses to distribute data flow execution.
Related Topics
• Batch Jobs on page 63
Real-Time node
After you add a connection to an Access Server in the Administrator, you
can expand the Real-Time node. Expand an Access Server name under the
Real-Time node to view the options.
24 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Administrator User Interface
Administrator navigation
2
Access Server node
options
Status
Real-time Services
Client Interfaces
Logs - Current
Logs - History
Related Topics
• Real-Time Jobs on page 97
• Real-Time Performance on page 123
Description
View status of real-time services and client interfaces
supported by this Access Server. Control, restart, and
set a service provider interval for this Access Server.
View status for services and service providers, start
and stop services, add or remove a service, configure
Job Servers for a service.
View status for client interfaces, start and stop interfaces, add or remove an interface.
View list of current Access Server logs, content of
each log, clear logs, configure content of logs for
display, enable or disable tracing for each Access
Server.
View list of historical Access Server logs, view content
of each log, delete logs.
Web Services node
Use this node to select real-time and batch jobs that you want to publish as
Web service operations and to monitor the status of those operations. You
can also use the node to set security for jobs published as Web service
operations and view the WSDL file that Data Services generates.
Related Topics
• Support for Web Services on page 167
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 25

Administrator User Interface
2
Administrator navigation
Adapter Instances node
Use this node to configure a connection between Data Services and an
external application by creating an adapter instance and dependent
operations. This is a prerequisite requirement for creating a datastore for
adapters in the Designer.
After you create a datastore, import data through the adapter and create
jobs. Then use this node to view the status of Adapter instances. Options
are listed by Job Server under the Adapter Instance node.
Related Topics
• Adapters on page 155
Server Groups node
The Server Groups node allows you to group Job Servers that are associated
with the same repository into a server group.
Use a server group if you want Data Services to automatically use the Job
Server on a computer with the lightest load when a batch job is executed.
This functionality improves load balancing (throughput) in production
environments and also provides a hot backup method. When a job is
launched, if a Job Server is down, another Job Server in the same group
executes the job.
Related Topics
• Server groups on page 53
Central Repositories node
The Central Repositories node has configuration options for secure central
repositories including:
• Users and groups — Use to configure groups and users for secure
access to central repository objects
• Reports — Use to generate reports about central repository objects such
as which objects a user currently has checked out or the changes made
to an object over a specified time frame
26 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Related Topics
• Central Repository Management on page 45
Profiler Repositories node
After you connect a profiler repository to the Administrator, you can expand
Profiler Repositories node. Click a repository name to open the Profiler
Tasks Status page.
Related Topics
• Profile Server Management on page 137
Management node
The Management node contains the configuration options for the
Administrator application. Before you can use the Administrator, you must
add connections to other Data Services components using the Management
node. For example, expand the management node and:
• Click Repositories to add a connection to the repositories that contain
the jobs and data profiler tables with which you want to work.
Administrator User Interface
Administrator navigation
2
Pages
• Click Access Servers to add a connection to your Access Servers (for
real-time jobs).
Related Topics
• Administrator Management on page 29
The top of the page indicates the currently selected node. Once you select
a branch on the navigation tree to go to a page, use the tab row on the page
to navigate further.
As you drill into various pages, a "bread crumb" trail often indicates where
you are in the Administrator application. Depending on the page displayed,
sometimes you can click on the bread crumb links to navigate to a different
page.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 27

Administrator User Interface
2
Administrator navigation
A dark blue (shaded) tab signifies the active page. Click a light blue tab to
go to that page. Some pages do not include a tab row.
28 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Administrator Management
3

Administrator Management
3
Adding repositories
Configuring the Administrator
Use the Management features to configure the Data Services Administrator.
Related Topics
• Adding repositories on page 30
• Managing user roles on page 35
• Adding Access Servers on page 37
• Centralizing administration on page 38
• Setting the status interval on page 39
• Setting the log retention period on page 40
Adding repositories
The Administrator allows you to manage batch jobs, real-time jobs, and
profiling tasks. You must first add a repository connection to the Administrator
so that you can view the jobs. Similarly, you must add a profiling repository
connection before you can view the tasks in that repository. After adding a
repository connection:
• Jobs and logs (stored on a Job Server computer) appear in the
Administrator.
• From the Batch Job Configuration page, you can execute batch jobs.
• Repositories become available to Metadata Reports users.
• From the Profiler Configuration page, change parameter settings for the
Data Profiler.
• From the Profiler Task Status page, you can view and manage Profiler
tasks.
Related Topics
• Connecting repositories to the Administrator on page 31
• Changing repository connection allocation on page 34
• Adapter considerations on page 34
30 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Administrator Management
Adding repositories
Connecting repositories to the Administrator
Use the List of Repositories page to connect a repository to an Administrator.
To add a local, central, or profiler repository connection to the Administrator
1. Select Management > Repositories on the navigation tree.
2. Click Add on the List of Repositories page.
3. Enter the following information for the repository.
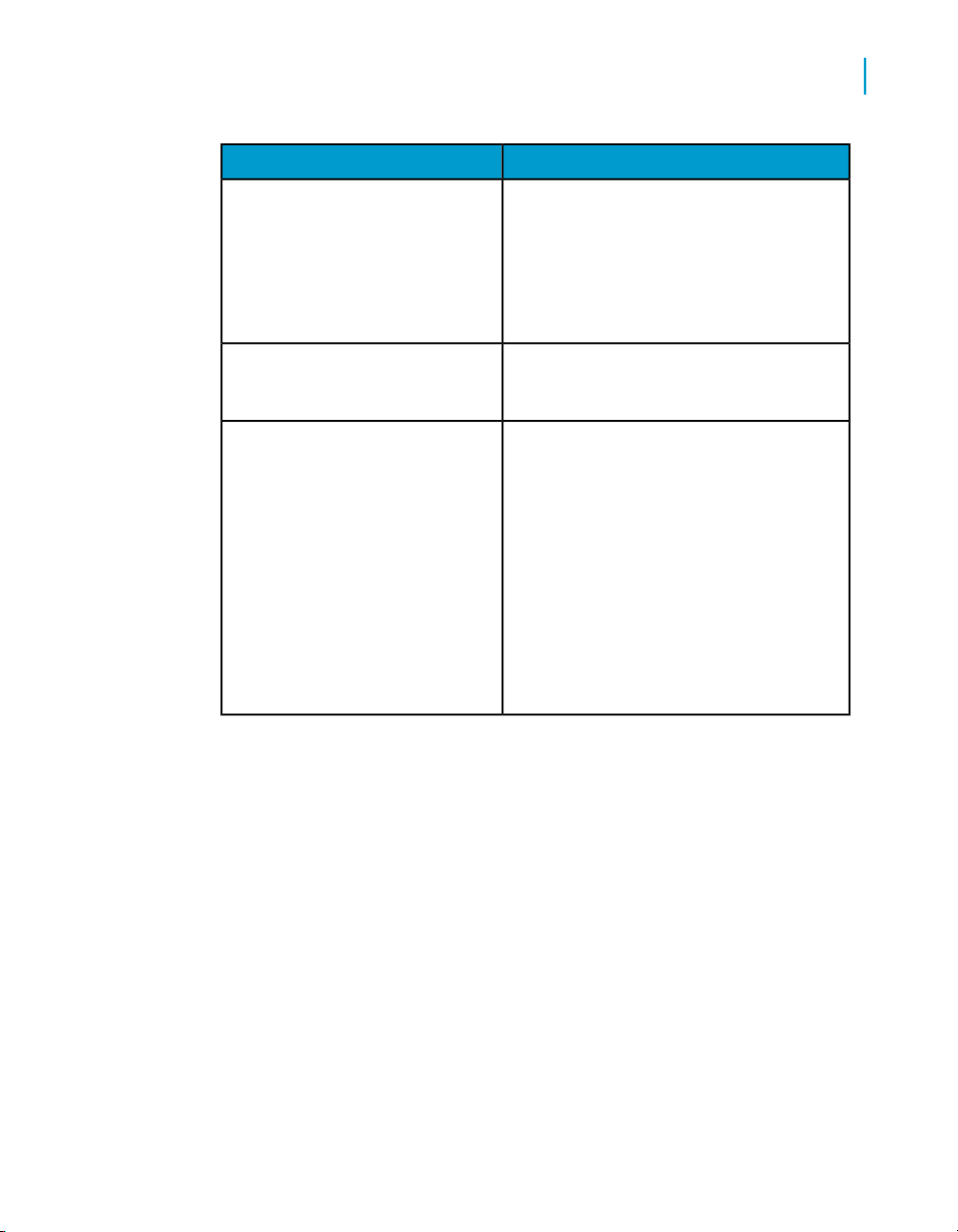
DescriptionOption
3
Repository Name
Database type
Logical name for a repository (used in the Administrator
only).
The type of database storing your local, central, or
profiler repository. Select one of the following database
types:
• DB2
• Informix
• Microsoft SQL Server
• Oracle
• Sybase ASE
• MySQL
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 31

Administrator Management
3
Adding repositories
Oracle RAC
DescriptionOption
Select if your repository is an Oracle database that is
part of an Oracle Real Application Clusters (RAC) system. If you select this option, specify the complete
connection string that corresponds to the Oracle RAC
in the Connection string option. Obtain this RAC
connection information from the Oracle TNSNames.ora
file, starting from (DESCRIPTION= until the end of the
entry:
ARMSTRONG.ACCT =
(DESCRIPTION =
(ADDRESS_LIST=
(FAILOVER = ON)
(LOAD_BALANCE = ON)
(ADDRESS= (PROTOCOL = TCP) (HOST = SERVER1)
(PORT = 1521))
(ADDRESS= (PROTOCOL = TCP) (HOST = SERVER2)
(PORT = 1521))
(ADDRESS= (PROTOCOL = TCP) (HOST = SERVER3)
(PORT = 1521))
)
(CONNECT_DATA=
(SERVICE_NAME = acct.us.yourcompany.com)
)
)
Select to have Microsoft SQL Server validate the login
account name and password using the information from
the Windows operating system. Clear to use the existing
Windows authentication
Microsoft SQL Server login account and password. For
more information on how to use Windows authentication
with Microsoft SQL Server, refer to the Microsoft SQL
Server documentation.
Host name on which the database server is running.Machine Name
Port number of the database or data source.Database Port
32 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Administrator Management
Adding repositories
DescriptionOption
3
Service Name/SID, Database
name, Server name, or Data
source
User name
Password
4. (Optional) If you want to test the database information you have specified
for the repository, before attempting to register it with the Administrator,
you can click Test.
5. Click Apply.
The Administrator validates repository connection information, and displays
it on the List of Repositories page.
This field requires additional information based on the
Database Type you select.
The user or owner name for the database or data
source.
The user's account password for the database or data
source.
To view the list of repositories connected to the Administrator
Select Management > Repositories.
The List of Repositories page lists the repositories that are connected to the
Administrator. The repository type column shows which type of repository
you created in the Repository Manager.
You can also remove a connection to a repository from this page.
Note:
If you create a clean repository with the same name as a repository you had
previously connected to the Administrator, you must reconnect the repository.
To do this, go to the List of Repositories page, click the repository's name
to open the Edit Repository page, then click Apply.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 33

Administrator Management
3
Adding repositories
Changing repository connection allocation
The Administrator allocates four repository connections per user as a default.
However, you can override the default value before starting the Administrator.
For Windows, modify the wrapper cmd_line section of LINK_DIR
/ext/WebServer/conf by adding DCNX_POOL_LIMIT:
wrapper.cmd_line=$ (wrapper.javabin)
-Dcatalina.home=$ (wrapper.tomcat_home)
-DLINK_DIR=$ (ACTAHOME) -DCNX_POOL_LIMIT=1
-classpath $ (wrapper.class_path)
For UNIX, modify the catalina.sh script found in LINK_DIR
/ext/WebServer/bin by adding -DCNX_POOL_LIMIT=1 in the 'start' section (not
the 'security' section) as follows:
if [ "$1" = "start" ] ; then
if [ "$1" = "-security" ] ; then
echo "Using Security Manager"
...
else
"$_RUNJAVA" $JAVA_OPTS $CATALINA_OPTS \
-DCNX_POOL_LIMIT="1" \
-Djava.endorsed.dirs="$JAVA_
Adapter considerations
To access adapter instances, you must associate a repository with a Job
Server that is:
• Installed on the same computer as the adapter instance.
• Configured with the following adapter-related properties: Support Adapter
and SNMP communication check box selected and the Communication
Port number set. Configure these properties using the Server Manager
utility.
If these conditions have not been met, you will not be able to use the Adapter
Instance node of the Administrator.
34 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Managing user roles
The Administrator allows you to add multiple user accounts with different
roles:
Administrator Management
Managing user roles
DescriptionRole
3
Administrator
Multiuser administrator
Monitor
Provides access to all Administrator functionality.
Limited to managing secure central repositories, this role is a subset of the Administrator
role. Multiuser administrators can:
•
Add and remove secure central repositories.
•
Manage users and groups.
•
View secure central repository reports.
Provides access limited to options available
from the Status tabs. For example, a Monitor
can abort batch jobs but cannot execute or
schedule them. A monitor can restart, abort or
shut down an Access Server, service, adapter
instance, or client interface but cannot add or
remove them.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 35

Administrator Management
3
Managing user roles
Profiler administrator
DescriptionRole
Limited to managing profiler repositories, this
role is a subset of the Administrator role. Profiler administrators can:
•
Define profiler repositories.
•
Add and remove profiler users.
•
Manage profiler tasks in any profiler repository.
•
Manage the Profiler configuration.
Profiler user
Operator
Limited to managing profiler tasks in the profiler
repository that is configured for the user.
Has all Administrator privileges except cannot
modify repository, access, or CMS servers nor
update datastore settings.
To add users and their roles
1. Select Management > Users.
2. Click Add to open the Add Users page.
3. In the User name box, enter a new user ID.
User names and passwords for the Administrator do not need to match
those for your system or repository.
4. In the Password box, enter the new password.
5. In the Display Name box, enter another identifier for the user such as
the full name. If you have trouble recognizing a login name, you can use
this value to label the account.
6. In the Role list, select a user role.
7. In the Status list, select a status for this account.
36 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Administrator Management
Adding Access Servers
You can select active or suspended. If you want to delete the user, go to
the User Management page.
8. In the Profiler repository list, select a profiler repository for this account.
You can assign a profiler repository to users with Administrator, Profiler
Administrator, and Profiler User roles.
• A user with a Profiler User role is authorized to manage tasks only in
this profiler repository.
• For a user with an Administrator or Profiler Administrator role, the
repository you specify in this option is the default repository for this
account. These administrators can also manage tasks in any profiler
repository.
9. Click Apply.
View the new user in the Users table on the User Management page.
You can also edit or delete user IDs using from the User Management
page.
3
Adding Access Servers
The Administrator acts as a front end for Access Servers connected to it.
Use the Administrator to:
• Configure real-time jobs as real-time services.
• Configure real-time services with service providers.
• Monitor Access Servers, real-time services, and service providers.
You first must connect an Access Server to the Administrator so that you
can use the Administrator to create a real-time service from a real-time job.
After a service starts, the Access Server brokers messages between external
applications and Data Services.
When a message request comes in, the Access Server communicates with
the Job Server to get the repository data needed to run a real-time service
and process the message. A reply comes back through the Access Server
to the message originator and the Access Server log records the event, which
you can monitor from the Administrator.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 37

Administrator Management
3
Centralizing administration
Use the List of Access Servers page to connect an Administrator to a
repository.
To connect an Access Server to the Administrator
1. Select Access Servers from the Management menu.
2. Click Add.
3. Enter the following information.
DescriptionOption
Machine name
Communication Port
4. (Optional) Before attempting to register the Access Server with the
Administrator, click Ping to see if the Access Server is available and
exists on the computer and port you specified.
5. Click Apply.
The Administrator registers the Access Server, validates the Access
Server connection information, and shows that information on the List of
Access Servers page.
To view a list of Access Servers connected to the Administrator, select
Access Servers from the Management menu.
The List of Access Servers page lists the Access Servers that are connected
to the Administrator. You can also remove a connection to an Access Server
from this page.
Host name of the computer on which the Access
Server is installed.
Port assigned to this Access Server in the Server
Manager utility.
Centralizing administration
You can connect any number of repositories and Access Servers to an
Administrator, which allows you to administrate all jobs from a single, central
location.
38 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Alternatively, you can set up an Administrator to manage the jobs from an
individual developer, the test repository, or different types of production jobs
(batch and real-time). You can connect repositories to one Administrator,
providing convenient access to a particular set of real-time jobs (for example,
a set that serves a unique function such as development). However,
Administrators cannot connect to each other.
To group administration by job type
1. Configure Administrators that will process a particular type of job.
For example, in your production environment you can configure one
Administrator to process batch jobs and a different Administrator to
process real-time jobs.
2. Connect each Administrator to the repositories that contain that type of
job.
You might want to name repositories so that you can easily see the types
of jobs stored on them.
3. Connect Access Servers to any Administrators that process or manage
real-time jobs.
Administrator Management
Setting the status interval
3
Setting the status interval
Use the Status Interval page to specify the time period for which the
Administrator displays the status (using the red, yellow, and green status
icons) on the Batch Job Status page.
To set the status interval
1. Select Status Interval from the Management menu.
2. On the Status Interval page, specify the time period.
You can filter the information on this page in three ways:
• By the last execution of each job
• By number of days
• By range of dates
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 39

Administrator Management
3
Setting the log retention period
3. Click Apply.
The Administrator updates the list of job executions and the status interval
displays in the table title on the Batch Job Status page. The following
example lists the jobs that have executed in the last 5 days.
Setting the log retention period
The log retention period provides an automatic way to delete log files.
To delete log information
1. Select Log Retention Period > Management.
2. In the Log Retention Period box, enter the number of days you want to
retain:
• Historical batch job error, trace, and monitor logs
• Current service provider trace and error logs
• Current and historical Access Server logs
The Administrator deletes all log files beyond this period. For example:
40 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Administrator Management
Managing database account changes
• If you enter 1 then the Administrator displays the logs for today only.
After 12:00 AM, these logs clear and the Administrator begins saving
logs for tomorrow.
• If you enter -1 Data Services will not delete logs.
• If you enter 1095 Data Services deletes logs older than approximately
three years.
You can also delete Access Server logs manually using the Access Server
Current Logs and Access Server History Logs pages.
3. Click Apply.
Changes you make to the log retention period occur as a background
clean-up process so they do not interrupt more important message
processing. Therefore, you might not see logs deleted immediately when
you select Apply. Changes can take up to an hour to take effect.
4. Choose a repository to view a list of executed batch job logs. When you
select repository name from the Batch Jobs menu, the Administrator
lists the most recent job first, providing a link to each job's log.
3
Related Topics
• Monitoring jobs on page 89
Managing database account changes
Data Services uses several types of user accounts and associated
passwords. For various reasons, database account parameters such as user
names or passwords change. For example, perhaps your company's
compliance and regulations policies require periodically changing account
passwords for security.
Related Topics
• Updating local repository login parameters on page 42
• Updating datastore connection parameters on page 43
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 41

Administrator Management
3
Managing database account changes
Updating local repository login parameters
If the login information, particularly the password, for a repository has
changed, Data Services provides an optional password file that all schedules
or exported execution commands use. In other words, Data Services uses
this password file to store and update connection information in one location
that multiple schedules or exported execution commands share for that
repository.
Note:
This description does not apply to central repositories.
The password file:
• Specifies the connection information for the repository
• Can be stored in a central location for access by others who run jobs in
that repository.
• Gets created when you create or update a job schedule to minimize
associated maintenance
Related Topics
• Using a third-party scheduler on page 80
To update the repository connection information and use a password file
1. Expand the Management node.
2. Click Repositories.
3. Click the repository name to configure.
The "Add/Edit Repository" page displays.
4. Edit the connection information as necessary.
5. Click Apply.
6. Click Generate password file to create or update the password file.
The default name and location of the file are %LINK_DIR%\conf\reposi
toryname.txt.
42 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Administrator Management
Managing database account changes
Updating job schedules
When database account information for your repository changes, the Data
Services job schedules associated with that account must also be updated.
When you use a password file, the job schedules access it at run time to
automatically retrieve the updated account information.
Related Topics
• Scheduling jobs on page 65
Updating datastore connection parameters
If the information associated with a datastore connection changes, particularly
passwords, you can update the changes using the Administrator.
Note:
Only users with Administrator role privileges can edit datastore parameters.
3
To edit the connection information for an individual configuration in a datastore
1. Select Datastore Configurations from the Management menu.
2. Click the configuration name to configure.
3. Edit the enabled fields as necessary:
4. Click Apply.
Clicking Reset returns all fields to the last set of values applied.
To edit the connection information for multiple configurations in a datastore
1. Select Datastore Configurations from the Management menu.
2. Click the datastore name to configure.
All configurations for that datastore display.
3. Edit the enabled fields as necessary.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 43

Administrator Management
3
Managing database account changes
Click More to display the page for that individual configuration, which
includes more options specific to it.
4. Click Apply.
Clicking Reset returns all fields to the last set of values applied.
44 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Central Repository Management
4

Central Repository Management
4
Setting up users and groups
About this section
This section describes how to manage your secure central repositories using
the Administrator.
When you create a secure central repository, the repository name appears
under the Central Repositories node. Links under this node include:
• Users and groups — Use to add, remove, and configure users and groups
for secure object access.
• Reports — Use to generate reports for central repository objects such as
viewing the change history of an object.
Setting up users and groups
The process for setting up users and groups is as follows:
1. Add the secure central repository to the Administrator.
2. Add groups.
3. Add users.
4. Associate users with groups.
The following sections describes these procedures.
Note:
The concept of users in the Administrator refers to setting up users to access
the Data Services Administrator application. By contrast, the Users and
Groups link under the Central Repositories node in the Administrator is
for setting up rights and access to a specific central repository.
Related Topics
• Managing user roles on page 35
• Advanced Development Guide: Implementing Central Repository Security
To add the secure central repository to the Administrator
1. Log in to the Administrator.
2. Select Management > Central repositories.
46 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

3. Add the secure central repository.
The repository appears on the List of Repositories page.
Related Topics
• Logging in on page 21
• Connecting repositories to the Administrator on page 31
To add a group to a central repository
Groups are specific to a repository and are not visible in any other local or
central repository.
1. Expand the Central Repositories node in the navigation tree, expand
the repository to configure, and click Users and Groups.
The Groups and Users page displays.
2. On the Groups tab, click Add.
3. Type a Name for the group.
4. Optionally, type a Description for the group.
5. Click Apply.
Central Repository Management
Setting up users and groups
4
The group appears on the Groups tab.
To add users
1. Expand the Central Repositories node in the navigation tree, expand
the repository to configure, and click Users and Groups.
2. Click the Users tab.
3. Click Add.
On the Add/Edit User page, enter the following information.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 47

Central Repository Management
4
Setting up users and groups
DescriptionOption
Type a new user name.
User name
Display name
Default group
Status
User names and passwords in the Administrator do not need to match those for your
system or repository.
Type a new password for the user.Password
Retype the password.Confirm password
Enter another identifier for the user such as
the full name. If you have difficulty recognizing a user name, you can use this value to
label the account.
The default group to which the user belongs. You can change the default by selecting another from the drop-down list.
Select a value from the drop-down list:
Active — Enables the user's account for
normal activities.
Suspended — Select to disable the login
for that user.
Optionally, type a description for the user.Description
The User is a member of list on the left shows the groups to which this
user belongs.
4. Click Apply.
48 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Clicking Reset returns all fields to the last set of values applied.
To add or remove a user from a group
1. Expand the Central Repositories node in the navigation tree, expand
the repository to configure, and click Users and Groups.
2. Click the Group tab.
3. Click the group name.
4. The Member users list on the left shows the users in this group.
To add users to a group, click the user names from the Other users list
and click Add users. Select multiple user names using the Ctrl or Shift
keys.
To remove a user from the group, select a user name from the Member
users list and click Remove users. Select multiple user names using the
Ctrl or Shift keys.
5. Click Apply.
Central Repository Management
Deleting groups
4
Clicking Reset returns all fields to the last set of values applied.
Alternately, click the Users tab, click the user name, and associate the user
with one or more groups by selecting group names and adding or removing
them.
Related Topics
• Advanced Development Guide: Implementing Central Repository Security
Deleting groups
You cannot delete a group in the following instances.
• It is the default group for any user (whether or not they are active).
• It is the only group with full permissions for an object.
• A member of the group is untertaking any central repository tasks using
the Designer.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 49

Central Repository Management
4
Viewing reports
To delete a group
1. Expand the Central Repositories node in the navigation tree, expand
the repository to configure, and click Users and Groups.
2. Click the Group tab.
3. Select the check box for the group.
4. Click Remove.
Viewing reports
You can generate reports about objects in a central repository such as which
objects a user currently has checked out or the changes made to an object
over a specified time frame.
Expand the central repository to view and expand the Reports link.
Related Topics
• Object state report on page 50
• Change report on page 51
Object state report
Use the object state report to view details on one or more objects such as
whether the objects are checked out and by whom.
Click the Object State Report link to display a search page with the following
criteria (all fields are optional):
• Object name — Type an object name. You can use the % symbol as a
wildcard.
• Object type — For example select Batch job, Table, or Stored
procedure
• State — For example select Checked out
• User — Select a central repository user name
Click Search to generate the report. The report has the following columns.
50 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

• Object name
• Object type
• State
• User name — User account associated with the check-out or check-in
• Associated repository — The repository to which the object belongs
• Time — Check-out or check-in date and time
• Comments — Comments added when user checked out or checked in
the object
Click the object name to display the object's history.
Related Topics
• Advanced Development Guide: Viewing object history
Change report
Central Repository Management
Viewing reports
4
Use the change report to view the change history for an object over a
specified period of time.
Click the Change Report link to display a search page with the following
criteria:
• Start date — Enter a date or click the calendar icon to select a start date.
• End date — Enter a date or click the calendar icon to select an end date.
• Object type — Optionally select an object type; for example batch job,
table, or stored procedure.
• State — Optionally select an object state; for example Checked out
• User — Optionally select a central repository user name
Click Search to generate the report. The report has following columns.
• Object name
• Object type
• State
• Version — The version number of the object
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 51

Central Repository Management
4
Viewing reports
• User name — User account associated with the check-out or check-in
• Associated repository — The repository to which the object belongs
• Time — Check-out or check-in date and time
• Comments — Comments added when user checked out or checked in
the object
52 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Server groups
5

Server groups
5
Server group architecture
About this section
Use the Administrator to create and maintain server groups.
This section describes how to work with server groups.
Related Topics
• Server group architecture on page 54
• To add a server group on page 58
• Editing and removing a server group on page 59
• Monitoring Job Server status in a server group on page 61
• Executing jobs using server groups on page 62
Server group architecture
You can group Job Servers on different computers into a logical Data Services
component called a server group. A server group automatically measures
resource availability on each Job Server in the group and distributes
scheduled batch jobs to the Job Server with the lightest load at runtime.
There are two rules for creating server groups:
• All the Job Servers in an individual server group must be associated with
the same repository, which must be defined as a default repository. The
Job Servers in the server group must also have:
• Identical Data Services versions
• Identical database server versions
• Identical locale
• Each computer can only contribute one Job Server to a server group
54 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Server groups
Server group architecture
.The requirement that all Job Servers in a server group be associated with
the same repository simply allows you to more easily track which jobs are
associated with a server group. Business Objects recommends that you use
a naming convention for server groups that includes the name of the
repository. For example, for a repository called DEV, a server group might
be called SG_DEV.
5
On startup, all Job Servers check the repository to find out if they must start
as part of a server group.
Compared to normal Job Servers, Job Servers in a server group each:
• Collect a list of other Job Servers in their server group
• Collect system load statistics every 60 seconds:
• Number of CPUs (on startup only)
• Average CPU load
• Available virtual memory
• Service requests for system load statistics
• Accept server group execution requests
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 55

Server groups
5
Server group architecture
Load balance index
All Job Servers in a server group collect and consolidate system load statistics
and convert them into a load balance index value for each Job Server. A Job
Server's load balance index value allows Data Services to normalize statistics
taken from different platforms. The Job Server with the lowest index value
is selected to execute the current job. Data Services polls all Job Server
computers every 60 seconds to refresh the load balance index.
Job execution
After you create a server group, you can select a server group to execute a
job from the Designer's Execution Properties window or from the
Administrator's Execute Batch Job, Schedule Batch Job, and Export Batch
Job pages.
When you execute a job using a server group, the server group executes
the job on the Job Server in the group that is running on the computer that
has the lightest load. The Administrator will also resynchronize a Job Server
with its repository if there are changes made to the server group configuration
settings.
You can execute parts of your job on different Job Servers in a server group.
You can select the following distribution levels from the Designer's Execution
Properties window or from the Administrator's Execute Batch Job, Schedule
Batch Job, and Export Batch Job pages:
• Job level - A job can execute on an available Job Server.
• Data flow level - Each data flow within a job can execute on an available
Job Server.
• Sub data flow level - A resource-intensive operation (such as a sort, table
comparison, or table lookup) within a data flow can execute on an available
Job Server.
Related Topics
• Performance Optimization Guide: Using grid computing to distribute data
flows execution
56 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Server groups
Server group architecture
Job launcher
The Job Launcher, exported as part of a job's execution commands, includes
a specific command line option for server groups. You can use this option
to change the Job Servers in a server group.
Related Topics
• Data Services job launcher on page 86
Working with server groups and Designer options
Some Designer options assume paths are relative to a Job Server. If your
Job Servers are on different machines from your Designer (typically the case
in a production environment) you must ensure that connections and directory
paths point to the Job Server host that will run the job. Such options include:
• Source and target directories for files
• Bulk load directories
• Source and target connection strings to databases
• Path to repositories
5
When using server groups consider the additional layer of complexity for
connections. For example, if you have three Job Servers in a server group:
• Use the same directory structure across your three host computers for
source and target file operations and use relative paths for file names.
• Use the same connection strings to your databases for all three Job Server
hosts.
If you use job distribution levels, the Job Servers in the server group must
have:
• Identical Data Services versions
• Identical database server versions
• Identical locale
• Identical operating systems
Thoroughly test the Job Server job options when working with server groups.
Adding a server group:
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 57

Server groups
5
Server group architecture
• In the Administrator, use the Server Groups node to create and add a
server group.
To add a server group
1. Select Server Groups > All Server Groups.
2. Click the Server Group Configuration tab.
3. Click Add.
4. Follow the instructions on the Add Server Group page to create a server
group.
• When you select a repository, all Job Servers registered with that
repository display. You can create one server group per repository.
• Notice that the Administrator provides a default server group name.
It is the name of your repository with the prefix SG_ (for server group).
You can change the default name, however, labeling a server group
with the repository name is recommended.
• One Job Server on a computer can be added to a server group. Use
the Host and Port column to verify that the Job Servers you select
are each installed on a different host.
• When you select a repository, all Job Servers registered with that
repository display. You can create one server group per repository.
• Notice that the Administrator provides a default server group name.
It is the name of your repository with the prefix SG_ (for server group).
58 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Server groups
Editing and removing a server group
You can change the default name, however, labeling a server group
with the repository name is recommended.
• One Job Server on a computer can be added to a server group. Use
the Host and Port column to verify that the Job Servers you select
are each installed on a different host.
5. After you select the Job Servers for a server group, click Apply.
5
The display returns to the Server Group Configuration page.
Related Topics
• Monitoring Job Server status in a server group on page 61
Editing and removing a server group
You can select a new set of Job Servers for an existing server group or
remove a server group.
Trace messages are written for a change in Job Server status when you
create, edit, or remove server groups.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 59

Server groups
5
Editing and removing a server group
• When a Job Server is upgraded to membership in a server group, the
trace message is:
Collecting system load statistics, maintaining list of Job
Server(s) for this server group, and accepting Job Server
execution requests.
• When a Job Server is downgraded out of a server group, the trace
message is:
Deleting current system load statistics, and not collecting
more. Not accepting job execution requests from a server
group.
To edit a server group
1. In the Server Group Status page, click the Configuration tab.
2. In the Server Group Configuration page, click the server group that you
want to edit.
3. In the Edit Server Group page, select a new set of Job Servers.
4. Click Apply.
Your edited server group is saved and the display returns to the Server
Groups Configuration page.
To remove a server group
1. In the Server Group Status page, click the Configuration tab.
2. In the Server Group Configuration page, select the check box for a the
server group(s) that you want to remove.
3. Click Remove.
The selected server group is removed as shown in the display.
Note:
If you delete Job Servers from a repository, so as to delete all the Job Servers
in a server group, the Administrator displays an invalid status for the server
group.
60 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Server groups
Monitoring Job Server status in a server group
Monitoring Job Server status in a server
group
If Job Servers are in a server group, you can view their status in the
Administrator.
• To monitor the status of these Job Servers, select Server Groups > All
Server Groups.
The Server Group Status page opens. All existing server groups are
displayed with the Job Servers they contain.
DescriptionIndicator
A green indicator signifies that a Job Server is running.
A yellow indicator signifies that a Job Server is not running.
A red indicator signifies that the Job Server cannot connect
to the repository.
5
If a server group contains Job Servers with a mix of green, yellow, or red
indicators, then its indicator appears yellow:
Otherwise, a server group indicator displays the same color indicator as
its Job Servers.
• To view the status for a single server group, select its name.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 61

Server groups
5
Executing jobs using server groups
Executing jobs using server groups
After you create a server group, you can select a server group to execute a
job from the Designer's Execution Properties window or from the
Administrator's Execute Batch Job and Schedule Batch Job pages.
Related Topics
• Batch Jobs on page 63
62 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Batch Jobs
6

Batch Jobs
6
Executing batch jobs
About this section
This section describes how to execute, schedule, and monitor batch jobs
from the Administrator.
Before you can manage batch jobs with the Administrator, add repository
connections.
Related Topics
• Executing batch jobs on page 64
• Scheduling jobs on page 65
• Monitoring jobs on page 89
• Adding repositories on page 30
Executing batch jobs
You can execute batch jobs from the Administrator if their repositories are
connected to the Administrator.
To execute a job
1. Select Batch > repository.
The Administrator opens the Batch Job Status page, which lists all the
jobs in the repository you just selected.
To view jobs in all repositories from this page, select Batch > All
Repositories. (The All Repositories option appears under the Batch Job
node if more than one repository is connected to the Administrator.)
2. Click the Batch Job Configuration tab.
3. To the right of the job you want to run, click Execute.
The Administrator opens the Execute Batch Job page.
4. Under Execution options, set the parameters for the execution of this
job.
5. Under Trace options, set the trace properties for this execution of the
job.
6. Click Execute to run the job.
64 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

The Administrator returns to the Batch Job Status page.
Related Topics
• Reference Guide: Data Services Objects, Batch Job, Parameters
• Reference Guide: Data Services Objects, Batch Job, Trace properties
Scheduling jobs
There are three ways to manage job schedules.
Related Topics
• Using the Data Services job scheduler on page 65
• Scheduling jobs in BusinessObjects Enterprise on page 77
• Using a third-party scheduler on page 80
Using the Data Services job scheduler
Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
6
When you schedule batch jobs using the Data Services job scheduler, it
creates an entry in the operating system's scheduling utility on the Job Server
computer. Windows uses the Task Scheduler and UNIX systems use the
CRON utility. (Note that if you make changes to a schedule directly through
these utilities, the Data Services job scheduler will not reflect those changes.)
Related Topics
• Adding a job schedule on page 65
• Activating or deactivating job schedules on page 74
• Updating a job schedule on page 76
• Removing a job schedule on page 76
• Migration considerations on page 77
Adding a job schedule
To add a job schedule
1. Select Batch > repository.
2. Click the Batch Job Configuration tab.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 65

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
3. For the job to configure, click Add Schedule.
4. On the Schedule Batch Job page, enter the desired options
DescriptionOption
Enter a job schedule
Enter a unique name that describes
this schedule.
Schedule name
Active
Note:
You cannot rename a schedule after
creating it.
Select this box to enable (activate)
this schedule; then click Apply.
This option allows you to create
several schedules for a job and
then activate the one(s) you want
to run.
Select a scheduler
Select where to schedule the job:
Data Services scheduler
or
BOE scheduler
Select scheduled day(s) for executing the job
66 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide
Data Services scheduler—Creates the schedule on the Job Server computer
BOE scheduler—Creates the
schedule on the selected central
management server (CMS)

Calendar
Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
DescriptionOption
From the drop-down list on the calendar, select:
•
Day of Week to schedule the
job by the day of the week. You
can select one or more days.
Click again to deselect.
•
Day of Month to schedule the
job by date. You can select one
or more dates. Click again to
deselect.
If Recurring is selected, then
the Administrator schedules this
job to repeat every week or
month on the selected day. Note
that if you select multiple days
of the week or month, the job
will run on a recurring basis by
default.
6
Select scheduled time for executing the jobs
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 67

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
Once a day at
or
Multiple times a day
DescriptionOption
Select the job execution frequency:
Only once a day—Enter the time
for the scheduler to start the job
(hours, minutes, and either AM or
PM).
Multiple times a day:
•
For the Data Services scheduler, enter the time (hours, minutes, and either AM or PM) for
the scheduler to repeatedly run
the job for the selected duration
(in minutes) at the selected interval (in minutes).
•
For the BOE scheduler, enter
(in minutes) the repeat interval
to run the job. You must also
select all days in the calendar
(for weekly or monthly).
Select job execution parameters
68 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide
Select a time when all of the required resources are available.
Typically, you want to schedule
jobs to ensure they finish before
the target database or data
warehouse must be available to
meet increased demand.

System configuration
Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
DescriptionOption
Select the system configuration to
use when executing this job. A
system configuration defines a set
of datastore configurations, which
define the datastore connections.
For more information, see "Creating
and managing multiple datastore
configurations" in the Data Services
Designer Guide.
If a system configuration is not
specified, Data Services uses the
default datastore configuration for
each datastore.
This option is a run-time property.
This option is only available if there
are system configurations defined
in the repository.
6
Job Server or server group
Use password file
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 69
Select the Job Server or a server
group to execute this schedule.
Select to create or update the
password file that the job schedule
accesses for current repository
connection information. Clear to
generate the batch file with a hardcoded repository information.

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
Enable auditing
Disable data validation statistics
collection
DescriptionOption
Clear this check box if you do not
want to collect audit statistics for
this specific job execution. (The
default is selected.)
For more information about auditing, see “Using Auditing” in the Da-
ta Services Designer Guide.
Select this check box if you do not
want to collect data validation
statistics for any validation transforms in this job. (The default is
cleared.)
Enable recovery
Recover from last failed execution
Collect statistics for optimization
Select this check box to enable the
Recovery mode when this job runs.
Select this check box if an execution of this job has failed and you
want to enable the Recovery mode.
Select this check box if you want to
collect statistics that the Data Services optimizer will use to choose
an optimal cache type (in-memory
or pageable). This option is not selected by default.
See “Using statistics for cache selftuning” in the Data Services Perfor-
mance Optimization Guide.
70 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Collect statistics for monitoring
Use collected statistics
Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
DescriptionOption
Select this check box if you want to
display cache statistics in the Performance Monitor in the Administrator. (The default is cleared.)
See “Monitoring and tuning cache
types” in the Data Services Perfor-
mance Optimization Guide.
Select this check box if you want
the Data Services optimizer to use
the cache statistics collected on a
previous execution of the job. (The
default is selected.)
For more information, see “Using
statistics for cache self-tuning” in
the Data Services Performance
Optimization Guide.
6
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 71

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
Distribution level
DescriptionOption
Select the level within a job that you
want to distribute to multiple job
servers for processing:
•
Job—The whole job will execute
on an available Job Server.
•
Data flow—Each data flow
within the job can execute on an
available Job Server.
•
Sub data flow—Each sub data
flow (can be a separate transform or function) within a data
flow can execute on an available
Job Server.
For more information, see “Using grid computing to distribute
data flows execution” in the Da-
ta Services Performance Optimization Guide.
5. Click Apply. Clicking Reset returns all fields to the last set of values
applied.
72 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
6
Related Topics
• Designer Guide: Datastores, Creating and managing multiple datastore
configurations
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 73

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
• Managing database account changes on page 41
• Reference Guide: Data Services Objects, Batch Job, Parameters
• Designer Guide: Data Assessment, Using Auditing
• Management Console—Metadata Reports Guide: Data Validation
Dashboard Reports
• Performance Optimization Guide: Using Caches, Using statistics for cache
self-tuning
• Performance Optimization Guide: Using Caches, To monitor and tune
in-memory and pageable caches
• Performance Optimization Guide: Distributing Data Flow Execution, Using
grid computing to distribute data flows execution
Activating or deactivating job schedules
In order for a job schedule to run, it must be active.
To change an existing job schedule, you must first deactivate it, make the
changes, then reactivate it.
Related Topics
• Updating a job schedule on page 76
To activate or deactivate one or more job schedules
1. Select Batch > repository .
2. Click the Repository Schedules tab.
The Repository Schedules tab lists all schedules for all jobs in the
repository and you can remove, activate, or deactivate one or more
schedules.
74 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
Alternately, you can click the Batch Job Configuration tab, then for a
particular job, click the Schedules link. The Batch Job Schedules tab lists
all schedules for that particular job. Here you can add, remove, activate,
or deactivate one or more schedules:
6
The Job Server column listed next to each schedule indicates which Job
Server will execute it.
If there is a server group icon in the Job Server column, this indicates the
schedule will be executed by the server group, and the schedule is stored
on the indicated Job Server. To see which server group is associated
with the schedule, roll your cursor over the server group icon.
If there is CMS icon in the Job Server column, this indicates the job
schedule is managed by a CMS.
Click the System Configuration names, if configured, to open a page that
lists the datastore configurations in that system configuration.
3. On either the Repository Schedules tab or the Batch Job Schedules
tab, select one or more check boxes for a schedule.
4. Click Activate (or Deactivate).
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 75

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
Updating a job schedule
To edit a job schedule, you must first deactivate it, make the changes, then
reactivate it.
To update a job schedule
1. Select Batch > repository.
2. Click the Batch Job Configuration tab.
3. Click the Schedules link for the desired job.
4. Click the schedule name to edit.
5. The "Schedule Batch Job" page displays.
6. If the schedule is currently active, deactivate it by clearing the Active
check box and click Apply.
Note:
You do not need to deactivate the schedule to update most of the job
execution parameters at the bottom of the page. Only the schedule-related
parameters require deactivation in order to update them.
7. Edit the schedule parameters as required.
8. To reactivate the schedule now, select the Active check box.
9. Click Apply.
The status bar at the top of the page confirms that the schedule has been
created and/or activated.
Related Topics
• Adding a job schedule on page 65
Removing a job schedule
To remove a job schedule
1. Select Batch > repository
2. Click the Repository Schedules tab.
3. Select one or more check boxes for a schedule.
4. Click Remove.
The Administrator deletes the information about this job schedule.
76 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Migration considerations
Changes made to the Job Server, such as an upgrade, do not affect
schedules created in Data Services as long as:
• The new version of Data Services is installed in the same directory as
the original version (Data Services schedulers use a hard-coded path to
the Job Server).
• The new installation uses the Job Server name and port from the previous
installation. (This occurs automatically when you install over the existing
DSConfig file.)
When you export a repository via an .atl file, jobs and their schedules (created
in Data Services) automatically export as well.
You can also import a repository .atl file including jobs and their associated
schedules (previously created in Data Services) back in to Data Services.
Remember that once imported, you must reactivate job schedules to use
them. If the job schedule uses a password file, then reactivating it will
automatically generate the password file.
Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
6
Related Topics
• Advanced Development Guide: Importing from a File
Scheduling jobs in BusinessObjects Enterprise
If you are using BusinessObjects Enterprise and you want to manage your
Data Services job schedules in that application, first create a connection to
a Central Management Server (CMS), then configure the schedule to use
that server.
Related Topics
• To add a CMS connection on page 78
• To create a job schedule in BusinessObjects Enterprise on page 79
• To remove a CMS connection on page 80
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 77

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
To add a CMS connection
1. Select Management > CMS Connection.
2. Click Add.
3. On the CMS Connections page, enter the connection information.
The parameters in the top section are the same as when logging in to
BusinessObjects Central Management Console (CMC) or InfoView. For
details, refer to the BusinessObjects Enterprise InfoView User's Guide.
The parameters in the bottom section (User account credentials for
executing the program) depend on how the CMS server is set up. For
details, refer to "Authentication and program objects" in the
BusinessObjects Enterprise Administrator's Guide.
System
DescriptionOption
Type the computer name that hosts the Central Management Server (CMS), a colon, and
the port number.
Type the CMC/InfoView user name.User name
Type the CMC/InfoView user password.Password
Select the authentication type for the serverAuthentication
User account credentials for executing the program (optional)
Note:
If you do not have the following option cleared in the Business Objects
Central Management Console, you will be required to enter user account
credentials in order for your schedules to run:
In the CMC, select Objects tab > Objects Settings button > Program
objects tab, clear the Use Impersonation option.
78 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

DescriptionOption
The CMS computer might require operating
User name
Password
4. Click Apply.
system login credentials to run the schedule.
If so, type the user name (and password) for
the applicable account.
The CMS computer might require operating
system login credentials to run the schedule.
If so, type the (user name and) password for
the applicable account.
To create a job schedule in BusinessObjects Enterprise
Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
6
1. Select Batch > repository
2. Click the Repository Schedules tab.
3. Click the schedule name to configure.
4. If the schedule is currently active, deactivate it by clearing the Active
check box and click Apply.
5. Edit the schedule parameters as necessary.
Note:
Time-sensitive parameters reflect the time zone of the computer where
the Administrator is installed, not where the CMS is installed.
6. Under the Select a scheduler section, select BOE scheduler.
7. From the drop-down list, select a CMS name.
8. To reactivate the schedule now, select the Active check box.
9. Click Apply.
The status bar at the top of the page confirms that the schedule has been
created and/or activated.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 79

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
If it doesn't already exist, BusinessObjects Enterprise creates a folder
called Data Services and stores the schedule file and a parameters file
(called schedulename.txt).
For a BOE schedule with the option Use password file selected, then
Data Services also creates a password file in the Data Services folder
(called repositoryname.txt)
Note:
When you deactivate a schedule created on a CMS, BusinessObjects
Enterprise deletes the object. Therefore, any changes made to the calendar,
etc. will be lost.
To remove a CMS connection
1. Select Management > CMS Connection.
2. Select the check box for the connection to remove from the administrator.
3. Click Remove.
Using a third-party scheduler
When you schedule jobs using third-party software:
• The job initiates outside of Data Services.
• The job runs from an executable batch file (or shell script for UNIX),
exported from Data Services.
Note:
When a third-party scheduler invokes a job, the corresponding Job Server
must be running.
Related Topics
• Data Services job launcher on page 86
To execute a job with a third-party scheduler
1. Export the job's execution command to an executable batch file (.bat file
for Windows or .sh file for UNIX environments).
80 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
2. Ensure that the Data Services Service is running (for that job's Job Server)
when the job begins to execute.
The Data Services Service automatically starts the Job Server when you
restart the computer on which you installed the Job Server.
• You can also verify whether a Job Server is running at any given time
using the Designer. Log in to the repository that contains your job and
view the Designer's status bar to verify that the Job Server connected
to this repository is running.
• You can verify whether all Job Servers in a server group are running
using the Administrator. In the navigation tree select Server Groups
> All Server Groups to view the status of server groups and the Job
Servers they contain.
3. Schedule the batch file from the third-party software.
Note:
To stop a Data Services job launched by a third-party scheduling application,
press CTRL+C on the application's keyboard.
Related Topics
• To export a job for scheduling on page 81
• Data Services job launcher on page 86
6
To export a job for scheduling
1. Select Batch > repository.
2. Click the Batch Job Configuration tab.
3. For the batch job to configure, click the Export Execution Command
link.
4. On the Export Execution Command page, enter the desired options
for the batch job command file you want the Administrator to create:
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 81

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
File name
System configuration
DescriptionOption
The name of the batch file or script containing
the job. The third-party scheduler executes
this file. The Administrator automatically appends the appropriate extension:
•
.sh for UNIX
•
.bat for Windows
Select the system configuration to use when
executing this job. A system configuration
defines a set of datastore configurations,
which define the datastore connections.
For more information, see “Creating and
managing multiple datastore configurations”
in the Data Services Designer Guide.
If a system configuration is not specified,
Data Services uses the default datastore
configuration for each datastore.
This option is a run-time property. This option
is only available if there are system configurations defined in the repository.
Job Server or server
group
Enable auditing
82 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide
Select the Job Server or a server group to
execute this schedule.
Clear this check box if you do not want to
collect audit statistics for this specific job execution. (The default is selected.)

Disable data validation
statistics collection
Enable Recovery
Recover from last failed
execution
Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
DescriptionOption
Select this check box if you do not want to
collect data validation statistics for any validation transforms in this job. (The default is
cleared.)
Select this check box to enable the automatic
recovery feature. When enabled, Data Services saves the results from completed steps
and allows you to resume failed jobs.
See “Automatically recovering jobs” in the
Data Services Designer Guide for information
about the recovery options.
Select this check box to resume a failed job.
Data Services retrieves the results from any
steps that were previously executed successfully and re-executes any other steps. This
option is a run-time property. This option is
not available when a job has not yet been
executed or when recovery mode was disabled during the previous run.
6
Use password file
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 83
Select to create or update a password file
that automatically updates job schedules after
changes in database or repository parameters. Clear to generate the batch file with a
hard-coded repository user name and password.

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
Collect statistics for optimization
Collect statistics for monitoring
DescriptionOption
Select this check box if you want to collect
statistics that the Data Services optimizer will
use to choose an optimal cache type (inmemory or pageable). This option is not selected by default.
See “Using statistics for cache self-tuning” in
the Data Services Performance Optimization
Guide.
Select this check box if you want to display
cache statistics in the Performance Monitor
in the Administrator. (The default is cleared.)
For more information, see “Monitoring and
tuning cache types” in the Data Services
Performance Optimization Guide.
Select this check box if you want the Data
Services optimizer to use the cache statistics
collected on a previous execution of the job.
Use collected statistics
84 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide
(The default is selected.)
See “Using statistics for cache self-tuning” in
the Data Services Performance Optimization
Guide.

Distribution level
Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
DescriptionOption
Select the level within a job that you want to
distribute to multiple job servers for processing:
•
Job—The whole job will execute on one
job server.
•
Data flow—Each data flow within the job
will execute on a separate job server.
•
Sub data flow—Each sub data flow (can
be a separate transform or function) within
a data flow will execute on a separate job
server.
For more information, see “Using grid
computing to distribute data flows execution” in the Data Services Performance
Optimization Guide.
6
5. Click Export.
The Administrator creates command files filename.txt (the default for
filename is the job name) and a batch file for the job and writes them to
the local LINK_DIR\log directory.
Note:
You can relocate the password file from the LINK_DIR\conf directory, but
you must edit the filename.txt file so that it refers to the new location of
the password file. Open the file in a text editor and add the relative or absolute
file path to the new location of the password file in the argument -R "
repositoryname.txt".
Related Topics
• Designer Guide: Datastores, Creating and managing multiple datastore
configurations
• Reference Guide: Data Services Objects, Batch Job, Parameters
• Designer Guide: Data Assessment, Using Auditing
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 85

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
• Management Console—Metadata Reports Guide: Data Validation
Dashboard Reports
• Managing database account changes on page 41
• Performance Optimization Guide: Using Caches, Monitoring and tuning
cache types
• Performance Optimization Guide: Using Caches, Using statistics for cache
self-tuning
• Performance Optimization Guide: Distributing Data Flow Execution, Using
grid computing to distribute data flows execution
Data Services job launcher
Data Services exports job execution command files as batch files on Windows
or CRON files on UNIX. These files pass parameters and call
AL_RWJobLauncher. Then, AL_RWJobLauncher executes the job, sends it to
the appropriate Data Services Job Server, and waits for the job to complete.
Caution:
Do not modify the exported file without assistance from Business Objects
Customer Assurance.
The following shows a sample Windows NT batch file created when Data
Services exports a job. ROBOT is the host name of the Job Server computer.
All lines after inet:ROBOT:3513 are AL_Engine arguments, not
AL_RWJobLancher arguments.
D:\Data Services\bin\AL_RWJobLauncher.exe
"inet:ROBOT:3513"
"-SrepositoryServer
-Uusername
-Ppassword
-G"b5751907_96c4_42be_a3b5_0aff44b8afc5"
-r100 -T14
-CTBatch -CmROBOT -CaROBOT
-CjROBOT -Cp3513"
Job launcher flag values and arguments
The following table lists job launcher flags and their values.
86 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

-w
-t
-s
Batch Jobs
Scheduling jobs
ValueFlag
The job launcher starts the job(s) and then waits before
passing back the job status. If -w is not specified, the
launcher exits immediately after starting a job.
The time, in milliseconds, that the Job Server waits before
checking a job's status. This is a companion argument for
-w.
Status or return code. 0 indicates successful completion,
non-zero indicates an error condition.
Combine -w, -t, and -s to execute the job, wait for completion, and return the status.
6
-C
-S
-R
Name of the engine command file (path to a file which contains the Command line arguments to be sent to the engine).
Prints AL_RWJobLauncher version number.-v
Lists the server group and Job Servers it contains using the
following syntax:
"SvrGroupName;JobSvr1Name:JobSvr1Host:Job
Svr1Port;JobSvr2Name:JobSvr2Host:JobSvr2Port";
For example:
"SG_DEV;JS1:HPSVR1:3500;JS2:WINSVR4:3505";
The location and name of the password file. Replaces the
hard-coded repository connection values for -S, -N, -U,
-P.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 87

Batch Jobs
6
Scheduling jobs
There are two arguments that do not use flags:
• inet address—The host name and port number of the Job Server. The
string must be in quotes. For example:
"inet:HPSVR1:3500"
If you use a server group, inet addresses are automatically rewritten using
the -S flag arguments. On execution, the first Job Server in the group
checks with the others and the Job Server with the lightest load executes
the job.
• server log path—The fully qualified path to the location of the log files.
The server log path must be in quotes. The server log path argument
does not appear on an exported batch job launch command file. It appears
only when Data Services generates a file for an active job schedule and
stores it in the following directory: LINK_DIR/Log/JobServerName/Repos
itoryName/JobInstanceName
You cannot manually edit server log paths.
Job launcher error codes
The job launcher also provides error codes to help debug potential problems.
The error messages are:
Error messageError number
Network failure.180002
180003
180004
88 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide
The service that will run the schedule has not started.
LINK_DIR is not defined.
The trace message file could not be created.180005

180007
Error messageError number
The error message file could not be created.180006
The GUID could not be found.
The status cannot be returned.
No command line arguments were found.180008
Invalid command line syntax.180009
Cannot open the command file.180010
Batch Jobs
Monitoring jobs
6
Monitoring jobs
Using the Administrator, you can monitor job execution of any batch job in
a connected repository. You can monitor jobs that you run from the
Administrator or from the Designer.
This section discusses how you can use the Administrator to view a batch
job's overall status and statistics.
Related Topics
• Overall status on page 89
• Statistics on page 91
Overall status
The Batch Job Status page lists each batch job execution. Use this list to
view the overall status of each execution and to access more detailed
statistics and log files.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 89

Batch Jobs
6
Monitoring jobs
To view overall status of executed jobs
1. Select Batch > repository.
The Batch Job Status page shows each instance of job execution on the
selected repository. The list shows jobs that ran during the time period
specified in the table title.
2. Find the overall status of a batch job execution by examining the indicator
in the Status column.
DescriptionIndicator
A green indicator means the batch job ran without
error.
A red indicator means the batch job experienced an
error.
Check the End Time column to see if or when the job completed.
3. If a batch job execution has a red status, examine the trace, monitor, and
error logs for more information.
4. To view detailed information about a particular job execution, look at the
data on the Batch Job Status page.
If the job includes a server group icon in the Job Server column, this
indicates that the job was executed by a server group. You can roll your
cursor over the server group icon to view the name of the server group.
The Job Server listed is the Job Server in the server group that executed
the job.
90 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Batch Jobs
Monitoring jobs
Note:
All jobs can be executed by an explicitly selected Job Server or by a
server group. If you choose to execute a job using a server group, you
can use this page to see which Job Server actually executed the job. If
you explicitly select a Job Server to execute a job, then even if it is also
part of a server group, the server group icon does not appear for the job
in the Job Server column on this page.
6
Related Topics
• Setting the status interval on page 39
Statistics
For each job execution, the Administrator shows statistics. Statistics quantify
the activities of the components of the job. You can view the following types
of statistics:
• Job statistics such as time spent in a given component of a job and the
• Data flow object statistics such as the cache size used by a transform
Job statistics
To help tune the performance of a job, review job statistics.
number of data rows that streamed through the component.
within a data flow.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 91

Batch Jobs
6
Monitoring jobs
To view job statistics
1. Select Batch > repository
2. On the Batch Job Status page, find a job execution instance.
Identify an instance using the page sub-title (which provides the name of
the repository on which Data Services stores the job) and the following
column headings on this page:
See Overall Status.Status
Name you gave the job in the DesignerJob Name
Name of a set of datastore configurations that
the job uses to connect to source and target
databases when it executes. Each value in
this column is a link. Click the link to view the
System Configuration
set of datastore configurations in the system
configuration. To change the system configuration, click the Configuration tab, then use
the Execute, Add Schedule or Export Exe-
cution Command pages.
Server that ran this jobJob Server
Date and time this instance startedStart Time
Date and time this instance stoppedEnd Time
Time (in seconds) the job took to completeDuration
Times this instance ran before completingRun #
3. Under Job Information for an instance, click Monitor.
92 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Batch Jobs
Monitoring jobs
The Administrator opens the Job Server Monitor Log Viewer page. This
page shows several statistics about this instance of job execution starting
with the name of the monitor log file.
After the file name, each line in the log provides the following information:
6
• Path Name — Indicates which object (step in a data flow) is executing.
• State — Indicates the run time order of the processes in the execution
of the transform object and the states of each process. These are not
error status states. However, if a process state is Proceed and it never
changes to Stop, this indicates the process ran with errors.
• Initializing — Job is initializing
• Optimizing — Job is optimizing
• Proceed — Process is executing
• Stop — Process ends without error
• Row Count — Indicates the number of rows processed through this
object. This value updates based on the Monitor sample rate (# of
rows) set as an execution option on the Execute Batch Job page.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 93

Batch Jobs
6
Monitoring jobs
• Elapsed Time — Indicates the time (in seconds) since this object
• Absolute time — Indicates the time (in seconds) since the execution
Related Topics
• Overall status on page 89
Data flow statistics
To help tune the performance of a data flow, review data flow statistics.
Related Topics
• Performance Optimization Guide: Measuring performance of Data Services
jobs
Ignore error status
received its first row of data.
of this entire data flow (including all of the transforms) began.
The Batch Job Status page includes an option to Ignore Error Status (button
at end of page). Use this option if you are working through jobs with warnings
or errors on this page and you want to mark a row so that you know you are
finished looking at its logs.
To ignore error status
1. Select the job or jobs that you want to ignore.
2. Click the Ignore Error Status button.
The page refreshes and the rows you selected now display a green status
icon.
Deleting batch job history data
The Batch Job Status page includes an option to delete information about
how a job ran. If you want to manually delete rows from this page, select the
94 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

rows that you want to delete, then select Delete. You can also manage this
information by setting the Administrator's log retention period.
Note:
When you delete this job information, it also clears data validation statistics
from Data Validation Metadata Reports.
Stopping a running job
The Batch Job Status page includes an option to abort batch jobs. If a batch
job is running and you need to stop it, select the check box before the job
name and click Abort.
Trace, monitor, and error logs
You can view and delete trace, monitor, and error logs for job instances from
the "Batch Job Status" page. The corresponding Job Server must be up and
running to view or delete these logs.
Batch Jobs
Monitoring jobs
6
You can set trace log options on the "Execute Batch Job" page.
You can use the Delete button on the "Batch Job Status" page to delete a
set of batch log history files from a Job Server computer and its corresponding
repository.
Related Topics
• Batch job logs on page 189
• Statistics on page 91
• Reference Guide: Data Services Objects, Log
To delete trace, monitor, and error logs for a batch job
1. Select Batch > repository.
2. Select the job or jobs for which you want to delete logs.
Alternately, you can click Select All.
3. Click Delete.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 95

Batch Jobs
Monitoring jobs
6
96 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Real-Time Jobs
7

Real-Time Jobs
7
Supporting real-time jobs
This section describes how to support real-time jobs using the Administrator.
Before configuring services, add real-time job repository and Access Server
connections to the Administrator.
Related Topics
• Supporting real-time jobs on page 98
• Configuring and monitoring real-time services on page 101
• Creating and monitoring client interfaces on page 113
Supporting real-time jobs
The Access Server manages real-time communication between Data Services
and external applications (such as ERP or web applications). The Access
Server determines how to process incoming and outgoing messages based
on the settings you choose for each real-time job in the Administrator.
In particular you use the Administrator to define:
• Services — A service is a name that identifies a task. The Access Server
receives requests for a service. You associate a service with a real-time
job. The real-time job contains the real-time processing loop that can
process requests for this service and generate a response.
• Service providers — A service provider is the computer process that
performs a service; the service provider completes the tasks in a real-time
job. A service provider is controlled by a Job Server. A Job Server can
control several service providers—each service provider is a unique
process or instance.
The Access Server uses services and service providers to process message
requests.
• For example, suppose an external application sends a request to the
Access Server.
• The Access Server determines the appropriate service for the request.
• Next, the Access Server finds the associated service providers and
dispatches the request to the next available service provider.
• Under the control of a Job Server, that service provider completes the
processing for the request. A different Job Server might control each
service provider.
98 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide

Real-Time Jobs
Supporting real-time jobs
The Access Server manages the entire set of service providers, implementing
configuration changes and telling the appropriate Job Servers to start and
stop service providers. At a prescribed interval, the Access Server updates
service providers, balancing loads and implementing configuration changes.
To balance loads, the Access Server monitors requests for services to ensure
that no service provider is over-used or under-used. Based on the number
of requests for a service, the Access Server tells Job Servers to start or stop
service providers.
7
To support real-time jobs, you must:
• Create any number of Access Servers using the Server Manager utility,
then add a connection to each local or remote Access Server using the
Management node in the Administrator.
Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide 99

Real-Time Jobs
7
Supporting real-time jobs
• In the Real-Time node of the Administrator, create a service for each
real-time job under each Access Server's node.
• Create one or more service providers for each service.
100 Data Services Management Console: Administrator Guide
 Loading...
Loading...