
Management Console Guide
■ SAP BusinessObjects Data Services XI 4.0 (14.0.0)
2010-12-02

Copyright
© 2010 SAP AG. All rights reserved.SAP, R/3, SAP NetWeaver, Duet, PartnerEdge, ByDesign, SAP
Business ByDesign, and other SAP products and services mentioned herein as well as their respective
logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of SAP AG in Germany and other countries. Business
Objects and the Business Objects logo, BusinessObjects, Crystal Reports, Crystal Decisions, Web
Intelligence, Xcelsius, and other Business Objects products and services mentioned herein as well
as their respective logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of Business Objects S.A. in the
United States and in other countries. Business Objects is an SAP company.All other product and
service names mentioned are the trademarks of their respective companies. Data contained in this
document serves informational purposes only. National product specifications may vary.These materials
are subject to change without notice. These materials are provided by SAP AG and its affiliated
companies ("SAP Group") for informational purposes only, without representation or warranty of any
kind, and SAP Group shall not be liable for errors or omissions with respect to the materials. The
only warranties for SAP Group products and services are those that are set forth in the express
warranty statements accompanying such products and services, if any. Nothing herein should be
construed as constituting an additional warranty.
2010-12-02

Contents
Introduction.............................................................................................................................9Chapter 1
1.1
1.1.1
1.1.2
1.1.3
1.1.4
1.2
1.2.1
1.2.2
2.1
3.1
3.1.1
3.1.2
3.2
3.2.1
3.2.2
3.2.3
3.2.4
3.2.5
3.3
3.3.1
3.3.2
3.4
3.4.1
3.4.2
3.4.3
3.4.4
3.5
Welcome to SAP BusinessObjects Data Services...................................................................9
Welcome.................................................................................................................................9
Documentation set for SAP BusinessObjects Data Services...................................................9
Accessing documentation......................................................................................................12
SAP BusinessObjects information resources.........................................................................13
Overview of this guide............................................................................................................14
About this guide.....................................................................................................................15
Who should read this guide....................................................................................................16
Logging into the Management Console................................................................................17Chapter 2
Management Console navigation...........................................................................................17
Administrator.........................................................................................................................19Chapter 3
Administrator navigation.........................................................................................................19
Navigation tree.......................................................................................................................19
Pages.....................................................................................................................................24
Administrator Management....................................................................................................24
Managing database account changes.....................................................................................24
Configuring the report server.................................................................................................26
Adding Access Servers..........................................................................................................27
Setting the status interval.......................................................................................................28
Exporting certification logs.....................................................................................................29
Central Repository management............................................................................................32
Setting up users and groups..................................................................................................32
Viewing reports......................................................................................................................35
Server Groups.......................................................................................................................37
Server group architecture.......................................................................................................37
Editing and removing a server group.......................................................................................41
Monitoring Job Server status in a server group......................................................................42
Executing jobs using server groups........................................................................................42
Batch Jobs.............................................................................................................................43
2010-12-023

Contents
3.5.1
3.5.2
3.5.3
3.6
3.6.1
3.6.2
3.6.3
3.7
3.7.1
3.7.2
3.7.3
3.7.4
3.7.5
3.8
3.8.1
3.8.2
3.8.3
3.9
3.9.1
3.9.2
3.9.3
3.9.4
3.9.5
3.10
3.10.1
3.10.2
3.10.3
3.10.4
3.11
3.12
3.12.1
3.12.2
3.13
3.13.1
3.13.2
3.13.3
3.13.4
3.13.5
Executing batch jobs..............................................................................................................43
Scheduling jobs......................................................................................................................44
Monitoring jobs......................................................................................................................57
Real-Time Jobs......................................................................................................................62
Supporting real-time jobs.......................................................................................................62
Configuring and monitoring real-time services........................................................................65
Creating and monitoring client interfaces................................................................................74
Real-Time Performance..........................................................................................................79
Configuring Access Server output..........................................................................................80
Service configuration parameters...........................................................................................82
Service statistics....................................................................................................................85
Service provider statistics......................................................................................................86
Using statistics and service parameters.................................................................................88
Profile Server Management....................................................................................................89
To define a profiler repository.................................................................................................90
Configuring profiler task parameters......................................................................................90
Monitoring profiler tasks using the Administrator ...................................................................94
RFC Server Management.......................................................................................................96
64-bit platform prerequisites...................................................................................................96
Adding an RFC server interface..............................................................................................96
Starting or stopping an RFC server interface connection........................................................97
Monitoring RFC server interfaces...........................................................................................98
Removing one or more RFC server interfaces........................................................................99
Adapters..............................................................................................................................100
Overview of adapters...........................................................................................................100
Adding and configuring adapter instances............................................................................102
Starting and stopping adapter instances...............................................................................107
Monitoring adapter instances...............................................................................................108
Support for Web Services....................................................................................................109
Support for HTTP.................................................................................................................110
Overview..............................................................................................................................110
Adapter installation and configuration...................................................................................111
Troubleshooting the Administrator........................................................................................120
Reestablishing network connections....................................................................................121
Finding problems..................................................................................................................121
Error and trace logs..............................................................................................................122
Resolving connectivity problems..........................................................................................127
Restarting the Access Server..............................................................................................129
4.1
Metadata Reports ...............................................................................................................131Chapter 4
Requirements.......................................................................................................................131
2010-12-024

Contents
4.2
4.2.1
4.3
4.4
4.4.1
5.1
5.1.1
5.1.2
5.2
5.3
5.4
5.4.1
5.4.2
5.4.3
6.1
6.2
6.2.1
6.2.2
6.3
6.3.1
6.3.2
6.3.3
Adding Metadata Integrator..................................................................................................131
To run the Metadata Integrator ............................................................................................132
Repository reporting tables and views..................................................................................133
Logging into the Management Console................................................................................136
Management Console navigation.........................................................................................136
Impact and Lineage Analysis Reports.................................................................................139Chapter 5
Navigation............................................................................................................................139
To increase the java heap memory in Windows....................................................................140
To increase the java heap memory in UNIX..........................................................................141
Analysis options...................................................................................................................141
Table-level and column-level analysis....................................................................................145
Impact and Lineage Analysis Settings control panel.............................................................146
Settings tab.........................................................................................................................147
Refresh Usage Data tab.......................................................................................................147
About tab.............................................................................................................................148
Operational Dashboard Reports.........................................................................................149Chapter 6
Dashboards home page.......................................................................................................149
Job execution statistics........................................................................................................150
Current (snapshot) pie chart.................................................................................................150
Historical (trend) bar chart....................................................................................................151
Job Execution Duration........................................................................................................152
Configuring the Job Execution Duration dashboard..............................................................152
Current (snapshot) speedometer.........................................................................................153
Historical (trend) line chart...................................................................................................156
7.1
7.1.1
7.1.2
7.1.3
7.2
7.3
7.3.1
7.3.2
7.4
7.5
7.5.1
7.5.2
Data Validation Dashboard Reports....................................................................................159Chapter 7
Configuring Data Validation dashboards...............................................................................159
Creating functional areas......................................................................................................160
Creating business rules........................................................................................................161
Enabling data validation statistics collection..........................................................................164
Viewing Data Validation dashboards....................................................................................165
Functional area view.............................................................................................................165
Functional area pie chart......................................................................................................165
History line chart..................................................................................................................166
Business rule view...............................................................................................................167
Validation rule view..............................................................................................................168
Validation rule bar chart........................................................................................................168
History line chart..................................................................................................................169
2010-12-025

Contents
7.6
7.6.1
7.6.2
7.7
7.7.1
7.7.2
7.7.3
8.1
8.1.1
8.1.2
8.1.3
8.1.4
8.1.5
8.1.6
8.2
8.2.1
8.3
Sample data view.................................................................................................................169
Sample data table................................................................................................................170
History line chart..................................................................................................................170
Data Validation dashboards Settings control panel...............................................................170
Repository tab.....................................................................................................................171
Functional area tab...............................................................................................................171
Business rule tab.................................................................................................................171
Auto Documentation Reports..............................................................................................173Chapter 8
Navigation............................................................................................................................173
To search for a specific object..............................................................................................174
Repository...........................................................................................................................175
Project.................................................................................................................................175
Job......................................................................................................................................175
Work flow............................................................................................................................176
Data flow.............................................................................................................................176
Generating documentation for an object...............................................................................177
To print Auto Documentation for an object...........................................................................177
Auto Documentation Settings control panel.........................................................................178
9.1
9.2
9.3
9.4
9.5
9.6
9.7
9.8
9.8.1
9.9
9.9.1
9.9.2
9.9.3
9.9.4
9.9.5
9.9.6
9.9.7
9.10
9.11
Data Quality Reports...........................................................................................................179Chapter 9
Lists of available reports......................................................................................................180
List of reports by job............................................................................................................181
Data Quality Reports Settings control panel.........................................................................182
Report options.....................................................................................................................182
Troubleshooting reports.......................................................................................................183
USA CASS report: USPS Form 3553..................................................................................183
NCOALink Processing Summary Report..............................................................................184
Delivery Sequence Invoice report.........................................................................................186
Contents of report...............................................................................................................186
US Addressing Report.........................................................................................................187
To enable the report ............................................................................................................188
Percent calculation...............................................................................................................188
Information in the US Addressing report .............................................................................188
DPV sections.......................................................................................................................189
Information in the DSF2 sections.........................................................................................189
LACSLink sections..............................................................................................................190
SuiteLink sections................................................................................................................191
DSF2 Augment Statistics log file .........................................................................................191
US Regulatory Locking Report.............................................................................................192
2010-12-026

Contents
9.12
9.13
9.14
9.15
9.16
9.17
9.18
9.19
9.20
9.21
9.22
9.23
9.24
9.25
9.26
9.27
9.28
9.29
Index 211
Canadian SERP report: Statement of Address Accuracy......................................................193
Australian AMAS report: Address Matching Processing Summary.......................................194
New Zealand Statement of Accuracy (SOA) report..............................................................196
Address Information Codes Sample report...........................................................................198
Address Information Code Summary report.........................................................................198
Address Validation Summary report.....................................................................................199
Address Type Summary report.............................................................................................200
Address Standardization Sample report...............................................................................201
Address Quality Code Summary report................................................................................201
Geocoder Summary report...................................................................................................202
Overview of match reports ..................................................................................................203
Best Record Summary report...............................................................................................203
Match Contribution report....................................................................................................204
Match Criteria Summary report............................................................................................206
Match Duplicate Sample report............................................................................................207
Match Input Source Output Select report.............................................................................207
Match Multi-source Frequency report...................................................................................208
Match Source Statistics Summary report.............................................................................209
2010-12-027

Contents
2010-12-028
Introduction
Introduction
1.1 Welcome to SAP BusinessObjects Data Services
1.1.1 Welcome
SAP BusinessObjects Data Services delivers a single enterprise-class solution for data integration,
data quality, data profiling, and text data processing that allows you to integrate, transform, improve,
and deliver trusted data to critical business processes. It provides one development UI, metadata
repository, data connectivity layer, run-time environment, and management console—enabling IT
organizations to lower total cost of ownership and accelerate time to value. With SAP BusinessObjects
Data Services, IT organizations can maximize operational efficiency with a single solution to improve
data quality and gain access to heterogeneous sources and applications.
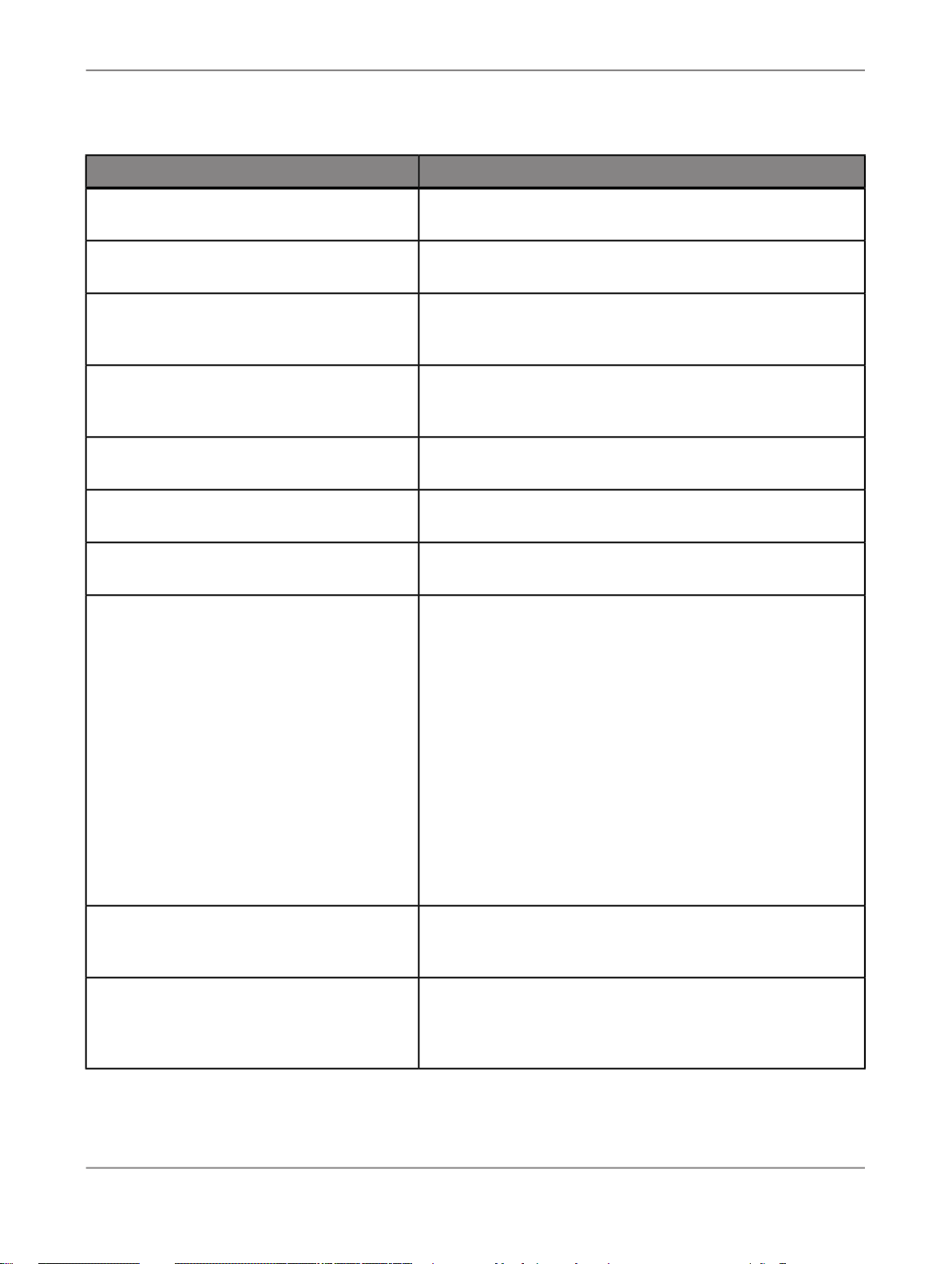
1.1.2 Documentation set for SAP BusinessObjects Data Services
You should become familiar with all the pieces of documentation that relate to your SAP BusinessObjects
Data Services product.
What this document providesDocument
Administrator's Guide
Customer Issues Fixed
Designer Guide
Information about administrative tasks such as monitoring,
lifecycle management, security, and so on.
Information about customer issues fixed in this release.
Information about how to use SAP BusinessObjects Data
Services Designer.
Documentation Map
Information about available SAP BusinessObjects Data Services books, languages, and locations.
2010-12-029
Introduction
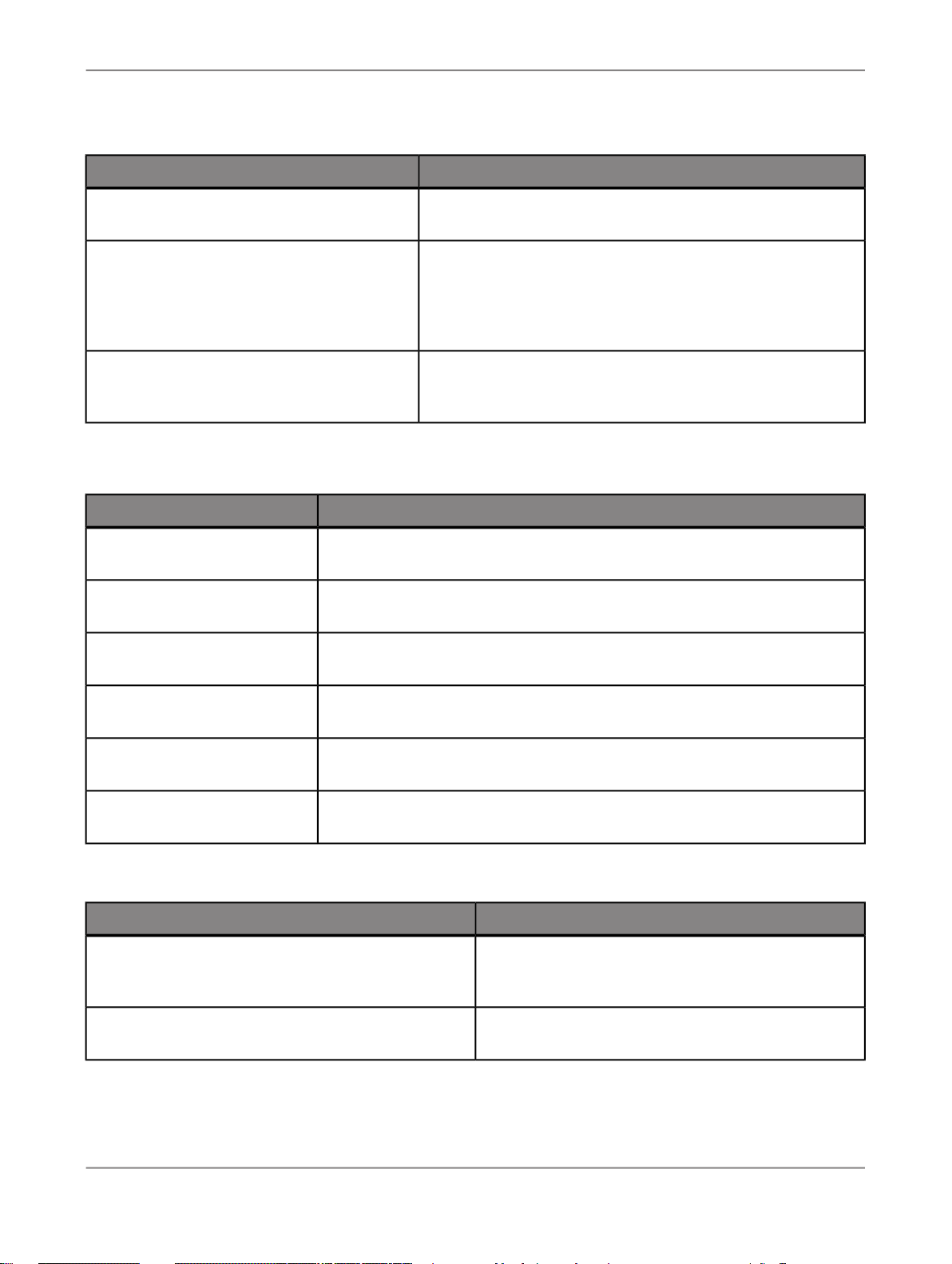
What this document providesDocument
Installation Guide for Windows
Installation Guide for UNIX
Integrator's Guide
Management Console Guide
Performance Optimization Guide
Reference Guide
Release Notes
Technical Manuals
Information about and procedures for installing SAP BusinessObjects Data Services in a Windows environment.
Information about and procedures for installing SAP BusinessObjects Data Services in a UNIX environment.
Information for third-party developers to access SAP BusinessObjects Data Services functionality using web services and
APIs.
Information about how to use SAP BusinessObjects Data
Services Administrator and SAP BusinessObjects Data Services Metadata Reports.
Information about how to improve the performance of SAP
BusinessObjects Data Services.
Detailed reference material for SAP BusinessObjects Data
Services Designer.
Important information you need before installing and deploying
this version of SAP BusinessObjects Data Services.
A compiled “master” PDF of core SAP BusinessObjects Data
Services books containing a searchable master table of contents and index:
•
Administrator's Guide
•
Designer Guide
•
Reference Guide
•
Management Console Guide
•
Performance Optimization Guide
•
Supplement for J.D. Edwards
•
Supplement for Oracle Applications
•
Supplement for PeopleSoft
•
Supplement for Salesforce.com
•
Supplement for Siebel
•
Supplement for SAP
Text Data Processing Extraction Customization Guide
Text Data Processing Language Reference
Guide
Information about building dictionaries and extraction rules to
create your own extraction patterns to use with Text Data
Processing transforms.
Information about the linguistic analysis and extraction processing features that the Text Data Processing component provides, as well as a reference section for each language supported.
2010-12-0210
Introduction
What this document providesDocument
Tutorial
Upgrade Guide
What's New
In addition, you may need to refer to several Adapter Guides and Supplemental Guides.
Supplement for J.D. Edwards
Supplement for Oracle Applications
Supplement for PeopleSoft
A step-by-step introduction to using SAP BusinessObjects
Data Services.
Release-specific product behavior changes from earlier versions of SAP BusinessObjects Data Services to the latest release. This manual also contains information about how to
migrate from SAP BusinessObjects Data Quality Management
to SAP BusinessObjects Data Services.
Highlights of new key features in this SAP BusinessObjects
Data Services release. This document is not updated for support package or patch releases.
What this document providesDocument
Information about interfaces between SAP BusinessObjects Data Services
and J.D. Edwards World and J.D. Edwards OneWorld.
Information about the interface between SAP BusinessObjects Data Services
and Oracle Applications.
Information about interfaces between SAP BusinessObjects Data Services
and PeopleSoft.
Supplement for Salesforce.com
Supplement for SAP
Supplement for Siebel
Information about how to install, configure, and use the SAP BusinessObjects
Data Services Salesforce.com Adapter Interface.
Information about interfaces between SAP BusinessObjects Data Services,
SAP Applications, and SAP NetWeaver BW.
Information about the interface between SAP BusinessObjects Data Services
and Siebel.
We also include these manuals for information about SAP BusinessObjects Information platform services.
Information platform services Administrator's Guide
Information platform services Installation Guide for
UNIX
What this document providesDocument
Information for administrators who are responsible for
configuring, managing, and maintaining an Information
platform services installation.
Installation procedures for SAP BusinessObjects Information platform services on a UNIX environment.
2010-12-0211

Introduction
What this document providesDocument
Information platform services Installation Guide for
Windows
1.1.3 Accessing documentation
You can access the complete documentation set for SAP BusinessObjects Data Services in several
places.
1.1.3.1 Accessing documentation on Windows
After you install SAP BusinessObjects Data Services, you can access the documentation from the Start
menu.
1.
Choose Start > Programs > SAP BusinessObjects Data Services XI 4.0 > Data Services
Documentation.
Installation procedures for SAP BusinessObjects Information platform services on a Windows environment.
Note:
Only a subset of the documentation is available from the Start menu. The documentation set for this
release is available in <LINK_DIR>\Doc\Books\en.
2.
Click the appropriate shortcut for the document that you want to view.
1.1.3.2 Accessing documentation on UNIX
After you install SAP BusinessObjects Data Services, you can access the online documentation by
going to the directory where the printable PDF files were installed.
1.
Go to <LINK_DIR>/doc/book/en/.
2.
Using Adobe Reader, open the PDF file of the document that you want to view.
1.1.3.3 Accessing documentation from the Web
2010-12-0212

Introduction
You can access the complete documentation set for SAP BusinessObjects Data Services from the SAP
BusinessObjects Business Users Support site.
1.
Go to http://help.sap.com.
2.
Click SAP BusinessObjects at the top of the page.
3.
Click All Products in the navigation pane on the left.
You can view the PDFs online or save them to your computer.
1.1.4 SAP BusinessObjects information resources
A global network of SAP BusinessObjects technology experts provides customer support, education,
and consulting to ensure maximum information management benefit to your business.
Useful addresses at a glance:
2010-12-0213
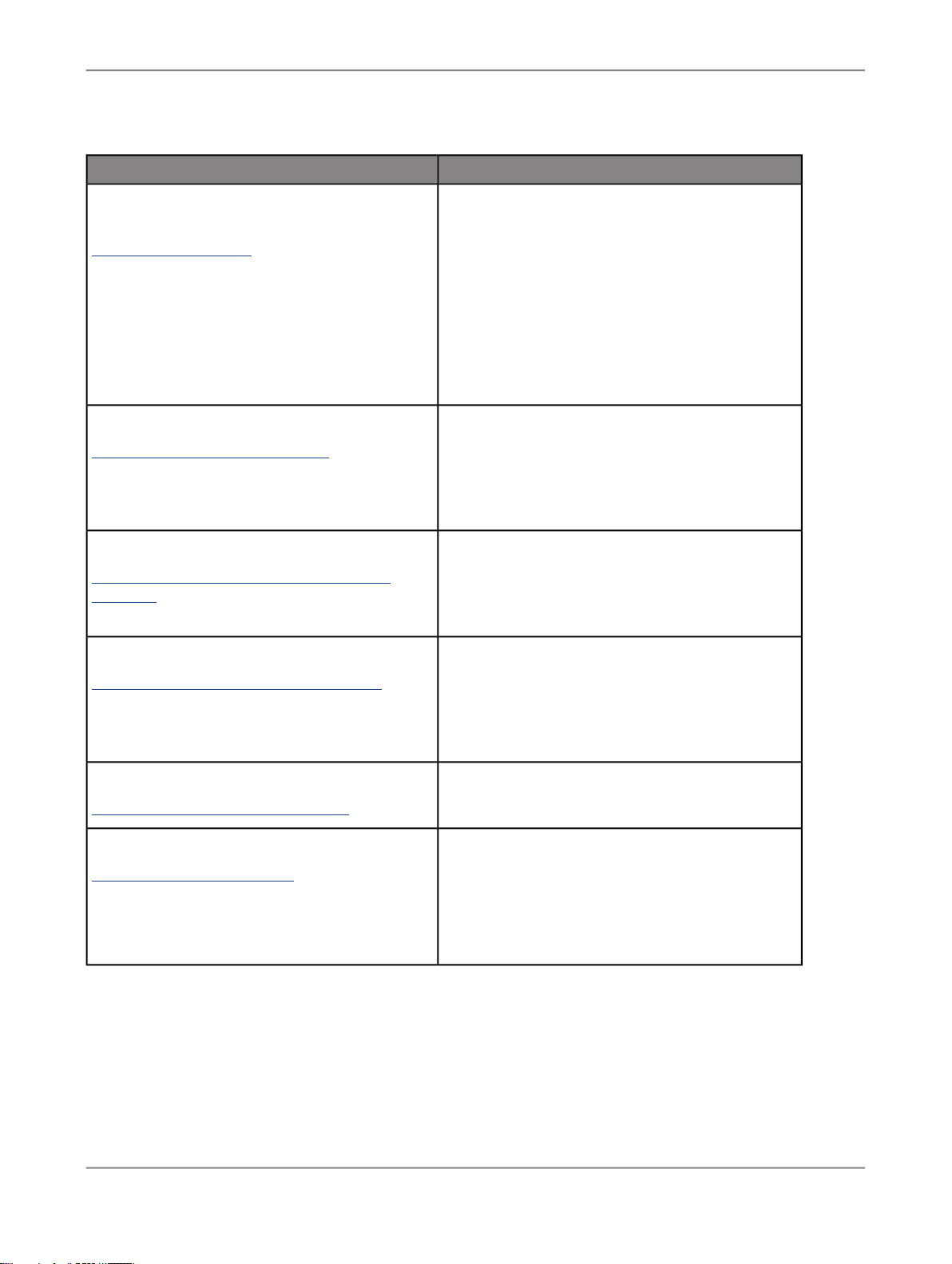
Introduction
ContentAddress
Customer Support, Consulting, and Education
services
http://service.sap.com/
SAP BusinessObjects Data Services Community
http://www.sdn.sap.com/irj/sdn/ds
Forums on SCN (SAP Community Network )
http://forums.sdn.sap.com/forum.jspa?foru
mID=305
Blueprints
http://www.sdn.sap.com/irj/boc/blueprints
Information about SAP Business User Support
programs, as well as links to technical articles,
downloads, and online forums. Consulting services
can provide you with information about how SAP
BusinessObjects can help maximize your information management investment. Education services
can provide information about training options and
modules. From traditional classroom learning to
targeted e-learning seminars, SAP BusinessObjects
can offer a training package to suit your learning
needs and preferred learning style.
Get online and timely information about SAP BusinessObjects Data Services, including tips and tricks,
additional downloads, samples, and much more.
All content is to and from the community, so feel
free to join in and contact us if you have a submission.
Search the SAP BusinessObjects forums on the
SAP Community Network to learn from other SAP
BusinessObjects Data Services users and start
posting questions or share your knowledge with the
community.
Blueprints for you to download and modify to fit your
needs. Each blueprint contains the necessary SAP
BusinessObjects Data Services project, jobs, data
flows, file formats, sample data, template tables,
and custom functions to run the data flows in your
environment with only a few modifications.
http://help.sap.com/businessobjects/
Supported Platforms (Product Availability Matrix)
https://service.sap.com/PAM
1.2 Overview of this guide
SAP BusinessObjects product documentation.Product documentation
Get information about supported platforms for SAP
BusinessObjects Data Services.
Use the search function to search for Data Services.
Click the link for the version of Data Services you
are searching for.
2010-12-0214

Introduction
1.2.1 About this guide
The guide includes information about the SAP BusinessObjects Data ServicesManagement Console,
a collection of Web-based applications for administering Data Services jobs and services, viewing object
relationships, evaluating job execution performance and data validity, and generating data quality
reports.
You can install the Management Console on a separate computer from other Data Services components.
It runs on your web application server. The Management Console is written in Java and uses a JDBC
connection to repositories.
The Management Console includes the following applications:
• Administrator
Use to manage your production environment including batch job execution, real-time services, Web
services, adapter instances, server groups, central and profiler repositories, and more.
• Impact and Lineage Analysis
Use to analyze the end-to-end impact and lineage for Data Services tables and columns and SAP
BusinessObjects Enterprise objects such as universes, business views, and reports.
• Operational Dashboard
Use to view dashboards of job execution statistics to see at a glance the status and performance
of your job executions for one or more repositories over a given time period.
• Data Validation Dashboard
Use to evaluate the reliability of your target data based on the validation rules you created in your
batch jobs to quickly review, assess, and identify potential inconsistencies or errors in source data.
• Auto Documentation
Use to view, analyze, and print graphical representations of all objects as depicted in the Designer
including their relationships, properties, and more.
• Data Quality Reports
Use to view and export reports for batch and real-time jobs such as job summaries and data quality
transform-specific reports.
Related Topics
• Administrator
• Impact and Lineage Analysis Reports
• Operational Dashboard Reports
• Data Validation Dashboard Reports
• Auto Documentation Reports
• Data Quality Reports
2010-12-0215

Introduction
1.2.2 Who should read this guide
This and other SAP BusinessObjects Data Services documentation assume the following:
• You are an application developer, consultant or database administrator working on data extraction,
data warehousing, data integration, or data quality.
• You understand your source and target data systems, DBMS, legacy systems, business intelligence,
and messaging concepts.
• You understand your organization's data needs.
• You are familiar with SQL (Structured Query Language).
• If you are interested in using this software to design real-time processing, you are familiar with:
• DTD and XML Schema formats for XML files
• Publishing Web Services (WSDL, HTTP/S and SOAP protocols, etc.)
• You are familiar with SAP BusinessObjects Data Services installation environments: Microsoft
Windows or UNIX.
2010-12-0216

Logging into the Management Console
Logging into the Management Console
When you log in to the Management Console, you must log in as a user defined in the Central
Management Server (CMS).
1.
Navigate to the Management Console address in a supported web browser:
http://hostname:28080/DataServices
where hostname is the name of the computer hosting the web application server.
Note:
If you are logged in to the Designer, you can also access the Management Console home page in
several ways:
• From the Start page, click Data Services Management Console.
• From the Tools menu, click Data Services Management Console.
• Click the Data Services Management Console tool bar icon.
2.
Enter your user credentials for the CMS.
• System
Specify the server name and optionally the port for the CMS.
• User name
Specify the user name to use to log into CMS.
• Password
Specify the password to use to log into the CMS.
• Authentication
Specify the authentication type used by the CMS.
3.
Click Log on.
The software attempts to connect to the CMS using the specified information. When you log in
successfully, the list of local repositories that are available to you is displayed.
The Management Console home page opens.
2.1 Management Console navigation
2010-12-0217

Logging into the Management Console
After logging in to the Management Console and launching one of the applications, the application
name appears under the Management Console banner.
The upper-right side of the main window includes the following links:
• Home
Click to return to the Management Console home page (for example, to select another application).
• Settings
The metadata reporting applications also include a Settings control panel for changing a variety of
options depending on the selected application.
• Logout
Click to exit the application and the Management Console and return to the login page.
• Help icon
Opens the
Management Console Guide
.
As you navigate around the applications, notice that the top of the right pane often displays a “bread
crumb” path to indicate where you are in the application. Depending on the page displayed, sometimes
you can click on the bread crumbs to navigate to a different part of the application.
The Administrator, Impact and Lineage Analysis, and Auto Documentation applications also use a
navigation tree in the left pane.
Management Console sessions time out after 120 minutes (2 hours) of inactivity.
2010-12-0218

Administrator
Administrator
This section describes the Administrator and how to navigate through its browser-based, graphical user
interface.
Use the Administrator to:
• Set up users and their roles
• Add connections to Access Servers and repositories
• Manage the retention of Job Server and Access Server logs
• Access job data published for Web Services
• Schedule and monitor batch jobs
• Configure and monitor:
• Access Server status
• Real-time services
• Client interfaces including SAP application client interfaces (to read IDocs) and message traffic
moving in and out of an Access Server
• Adapter instances (a prerequisite for creating adapter datastores)
Related Topics
• Logging into the Management Console
• Administrator navigation
3.1 Administrator navigation
The layout of the Administrator consists of a window with a navigation tree on the left and pages with
tabs on the right.
3.1.1 Navigation tree
The navigation tree is divided into several nodes, including:
• Status
• Batch
2010-12-0219

Administrator
• Real-Time
• Web Services
• SAP Connections
• Server Groups
• Profiler Repositories
• Management
Note:
The nodes displayed depend on the permissions granted to the user you use to log in to the Management
Console. For example, the Profiler Repositories node only appears if you have access to view or manage
a profiler repository, as defined in the Central Management Console (CMC).
3.1.1.1 Status node
When the Administrator opens, it displays the Status page. The Status page displays the status of the
following items (after you have connected them to the Administrator). The red, green, and yellow icons
indicate the overall status of each item based on the jobs, services, and other objects they support.
• Batch
Contains the name of the repository associated with the Job Server on which you run the batch jobs.
To see batch jobs status, connect the repository to the Administrator.
Click the repository name to display a list of batch jobs and their status.
• Real-Time
Contains the name of the Access Servers associated with a real-time service. To see real-time jobs
status, connect the Access Server to the Administrator.
Click the Access Server name to display a list of real-time services and their client interfaces.
• Adapters
Contains the name of the repository associated with the Job Server on which you run the adapter.
To see an adapter's status, enable a Job Server for adapters, and then add the repository associated
with that Job Server.
• Profiler
Contains the name of the repository associated with the Profiler Server. To see a profiler repository,
connect the profiling repository to the Administrator.
Click the repository name to display a list of profiler tasks and their status.
2010-12-0220
Administrator
3.1.1.2 Batch node
After you add at least one repository connection to the Administrator, you can expand the Batch node.
Then click a repository name to display its Batch Job Status page.
Click the All Repositories option to see jobs in all repositories connected to this Administrator (this
node only appears if more than one repository is connected).
Each repository under the Batch node includes the following tabs:
• Batch Job Status
View the status of the last execution and in-depth information about each job.
• Batch Job Configuration
Configure execution and scheduling options for individual jobs.
• Repository Schedules
View and configure schedules for all jobs in the repository.
Related Topics
• Batch Jobs
3.1.1.3 Real-Time node
After you add a connection to an Access Server in the Administrator, you can expand the Real-Time
node. Expand an Access Server name under the Real-Time node to view the options.
DescriptionAccess Server node options
View status of real-time services and client interfaces supported by
Status
Real-time Services
this Access Server. Control, restart, and set a service provider interval for this Access Server.
View status for services and service providers, start and stop services, add or remove a service, configure Job Servers for a service.
Client Interfaces
View status for client interfaces, start and stop interfaces, add or
remove an interface.
2010-12-0221
Administrator
Logs - Current
DescriptionAccess Server node options
View list of current Access Server logs, content of each log, clear
logs, configure content of logs for display, enable or disable tracing
for each Access Server.
Logs - History
View list of historical Access Server logs, view content of each log,
delete logs.
Related Topics
• Real-Time Jobs
• Real-Time Performance
3.1.1.4 Web Services node
Use this node to select real-time and batch jobs that you want to publish as Web service operations
and to monitor the status of those operations. You can also use the node to set security for jobs published
as Web service operations and view the WSDL file that SAP BusinessObjects Data Services generates.
Related Topics
• Support for Web Services
3.1.1.5 Adapter Instances node
Use this node to configure a connection between SAP BusinessObjects Data Services and an external
application by creating an adapter instance and dependent operations. This is a prerequisite requirement
for creating a datastore for adapters in the Designer.
After you create a datastore, import data through the adapter and create jobs. Then use this node to
view the status of Adapter instances. Options are listed by Job Server under the Adapter Instance node.
Related Topics
• Adapters
2010-12-0222

Administrator
3.1.1.6 Server Groups node
The Server Groups node allows you to group Job Servers that are associated with the same repository
into a server group.
Use a server group if you want SAP BusinessObjects Data Services to automatically use the Job Server
on a computer with the lightest load when a batch job is executed. This functionality improves load
balancing (throughput) in production environments and also provides a hot backup method. When a
job is launched, if a Job Server is down, another Job Server in the same group executes the job.
Related Topics
• Server Groups
3.1.1.7 Profiler Repositories node
After you connect a profiler repository to the Administrator, you can expand the Profiler Repositories
node. Click a repository name to open the Profiler Tasks Status page.
Related Topics
• Profile Server Management
3.1.1.8 Management node
The Management node contains the configuration options for the Administrator application. Before you
can use some features of the Administrator, you must add connections to other SAP BusinessObjects
Data Services components using the Management node. For example, expand the management node
and:
• Expand Datastore and click a repository to manage datastore configurations for that repository.
• Click Access Servers to add a connection to your Access Servers (for real-time jobs).
Related Topics
• Administrator Management
2010-12-0223

Administrator
3.1.2 Pages
The top of the page indicates the currently selected node. Once you select a branch on the navigation
tree to go to a page, use the tab row on the page to navigate further.
As you drill into various pages, a “bread crumb” trail often indicates where you are in the Administrator
application. Depending on the page displayed, sometimes you can click on the bread crumb links to
navigate to a different page.
A dark blue (shaded) tab signifies the active page. Click a light blue tab to go to that page. Some pages
do not include a tab row.
3.2 Administrator Management
Use the Management features to configure the Administrator.
Related Topics
• Managing database account changes
• Configuring the report server
• Adding Access Servers
• Setting the status interval
• Exporting certification logs
3.2.1 Managing database account changes
SAP BusinessObjects Data Services uses several types of user accounts and associated passwords.
For various reasons, database account parameters such as user names or passwords change. For
example, perhaps your company's compliance and regulations policies require periodically changing
account passwords for security.
Related Topics
• Updating local repository login parameters
• Updating datastore connection parameters
2010-12-0224

Administrator
3.2.1.1 Updating local repository login parameters
If the login information, particularly the password, for a repository has changed, SAP BusinessObjects
Data Services provides an optional password file that all schedules or exported execution commands
use. In other words, the software uses this password file to store and update connection information in
one location that multiple schedules or exported execution commands share for that repository.
Note:
This description does not apply to central repositories.
The password file:
• Specifies the connection information for the repository.
• Can be stored in a central location for access by others who run jobs in that repository.
• Is created when you create or update a job schedule to minimize associated maintenance.
Related Topics
• Using a third-party scheduler
3.2.1.1.1 To update the CMS connection information and use a password file
1.
Expand the Management node.
2.
Click CMS Connection.
3.
Edit the connection information as necessary.
4.
Click Apply.
5.
Click Generate password file to create or update the password file.
The default name and location of the file are <LINK_DIR>\conf\repositoryname.txt.
3.2.1.1.2 Updating job schedules
When database account information for your repository changes, the SAP BusinessObjects Data
Services job schedules associated with that account must also be updated. When you use a password
file, the job schedules access it at runtime to automatically retrieve the updated account information.
Related Topics
• Scheduling jobs
3.2.1.2 Updating datastore connection parameters
2010-12-0225
Administrator
If the information associated with a datastore connection changes, particularly passwords, you can
update the changes using the Administrator.
Note:
Only users with Administrator role privileges can edit datastore parameters.
3.2.1.2.1 To edit the connection information for an individual configuration in a datastore
1.
Select Management > Datastore, and select the repository that contains the datastore configuration
that you want to edit.
2.
Click the configuration name to configure.
3.
Edit the enabled fields as necessary.
4.
Click Apply. To return all fields to the last set of values applied, click Reset.
3.2.1.2.2 To edit the connection information for multiple configurations in a datastore
1.
Select Management > Datastore, and select the repository that contains the datastore configurations
that you want to edit.
2.
Click the datastore name to configure.
All configurations for that datastore display.
3.
Edit the enabled fields as necessary.
Click More to display the page for that individual configuration, which includes more options specific
to it.
4.
Click Apply. To return all fields to the last set of values applied, click Reset.
3.2.2 Configuring the report server
For each repository registered in the Central Management Console (CMC), a report server configuration
is automatically created with default parameters. The Report Server Configuration node in the
Management Console Administrator lets you edit the default parameters, including the location where
job reports are written upon execution.
1.
Select Management > Report Server Configuration > repository.
The Report Server Configuration page opens and displays the report export configuration parameters.
If the configuration has not yet been saved for the selected repository, the page displays default
parameters.
2.
Enter the appropriate configuration information.
DescriptionOption
Host name
The name of the machine that the report server is running on. By default,
the current web application server name is used. Localhost is not a valid
name.
2010-12-0226

Administrator
Export location
Overwrite
DescriptionOption
The port number of the machine that the report server is running on.Communication port
The path where the reports will be exported to. The default path is
<LINK_DIR>\DataQuality\reports\. Upon execution, the repository name and job name folders are appended to the path. If the Overwrite
option is not selected, a run ID folder is also appended to the path.
Note:
If you export reports to a location other than a local drive, such as a
network drive, before you execute the job you must start the web application server with an account that has access rights to that location.
The format in which the reports can be exported (PDF or RTF).Export type
Specifies whether existing reports will be overwritten when the reports
are exported. If this option is not selected, the reports are exported to a
subfolder with the run ID, which specifies a unique identification of an
instance of the executed job.
The supported language that the reports are generated in. Note that
Language
some reports, such as country-specific certification reports, are designed
only to support English, so changing the option for those reports has no
effect.
3.
Click Apply to save the configuration. To return all fields to the last set of values applied, clicking
Reset.
4.
Verify that the security setting for this operation is disabled. Select Administrator > Web Services
and click the Web Services Configuration tab. If the Select the Export_DQReport operation is
enabled (displays a check in the Session Security column), select the checkbox next to it, select
Disable Session Security from the pull-down menu, and click the Apply button.
To generate and export all of the job reports to the specified location at runtime, select the Export Data
Quality Reports option when you execute the job.
Related Topics
• To add a job schedule
• Reference Guide: Data Services Objects, Batch Job, Parameters
• Integrator's Guide: To configure web service information using the Administrator
3.2.3 Adding Access Servers
The Administrator acts as a front end for Access Servers connected to it. Use the Administrator to:
2010-12-0227
Administrator
• Configure real-time jobs as real-time services.
• Configure real-time services with service providers.
• Monitor Access Servers, real-time services, and service providers.
You first must connect an Access Server to the Administrator so that you can use the Administrator to
create a real-time service from a real-time job. After a service starts, the Access Server brokers messages
between external applications and SAP BusinessObjects Data Services.
When a message request comes in, the Access Server communicates with the Job Server to get the
repository data needed to run a real-time service and process the message. A reply comes back through
the Access Server to the message originator and the Access Server log records the event, which you
can monitor from the Administrator.
Use the Access Servers page to connect an Administrator to a repository.
1.
Select Management > Access Servers.
2.
Click Add.
3.
Enter the following information.
DescriptionOption
Machine Name
Communication Port
4.
(Optional) Before attempting to register the Access Server with the Administrator, click Ping to see
if the Access Server is available and exists on the computer and port you specified.
5.
Click Apply.
The Administrator registers the Access Server, validates the Access Server connection information,
and displays the information on the Access Servers page.
To view a list of Access Servers connected to the Administrator, select Management > Access Servers.
The Access Servers page lists the Access Servers that are connected to the Administrator. You can
also remove a connection to an Access Server from this page.
3.2.4 Setting the status interval
Host name of the computer on which the Access Server is installed.
Port assigned to the Access Server in the Server Manager
utility.
Use the Status Interval page to specify the time period for which the Administrator displays the status
(using the red, yellow, and green status icons) on the Batch Job Status page.
1.
Select Management > Status Interval.
2.
On the Status Interval page, specify the time period.
You can filter the information on this page in three ways:
2010-12-0228

Administrator
• By the last execution of each job
• By number of days
• By range of dates
3.
Click Apply.
The Administrator updates the list of job executions and the status interval displays in the table title
on the Batch Job Status page. The following example lists the last execution of all jobs.
3.2.5 Exporting certification logs
When you run address cleanse jobs with the appropriate options set, you can generate reports to qualify
for mailing discounts with certain countries' postal authorities. In the Management Console, you can
generate the certification log files required for those certifications.
The Certification Logs page is available to users who are assigned either the Administrator or Operator
role.
Related Topics
• Exporting NCOALink certification logs
• Exporting New Zealand SOA certification logs
• Exporting DSF2 certification log
3.2.5.1 Exporting NCOALink certification logs
Before you export the certification log, you must have run a job containing a USA Regulatory Address
Cleanse transform with the NCOA certification options set appropriately. You must also configure your
repository in the Central Management Console (CMC).
You can export the certification log for the data in one repository or in all repositories.
Caution:
If you select all repositories and have more than one connection to the same repository, your results
may contain duplicate records.
1.
Select Management > Certification Logs, and select the repository that contains the certification
log that you want to export.
2.
Click the NCOALink tab.
3.
Select the date range that contains the data that you want to export.
4.
Select the NCOALink licensee ID for the logs that you want to export, or select All NCOA Licensee
IDs.
2010-12-0229

Administrator
5.
Specify the location where the certification logs will be exported.
Note:
The location that you specify is relative to the web application server.
To reset the export location to the default, click the Reset button. The default location is
<LINK_DIR>\DataQuality\certifications\CertificationLogs\repository\.
6.
If you want to overwrite an existing log file, click the Overwrite option.
7.
Click the Search button. The page displays the available log files with the specified criteria. You
can sort the log files using the column headers.
The "Data Available" column has a Yes status when there is data for at least one of the log types
(PAF, Bala, or CSL). A No status indicates that no data is available and will result in an empty log
file for each type.
8.
Select the log file(s) that you want to export or select the checkbox next to "Select All".
9.
Click the Export button.
After the log file is exported, a confirmation message is displayed at the top of the page.
Related Topics
• Administrator Guide: Repository management, To register a repository in the CMC
• NCOALink Processing Summary Report
• Designer Guide: Data Quality, Address Cleanse, NCOALink (USA Regulatory Address Cleanse)
• Reference Guide: Transforms, NCOALink options
3.2.5.2 Exporting New Zealand SOA certification logs
Before you export the certification log, you must have run a job containing a Global Address Cleanse
transform with the New Zealand SOA certification options set appropriately. You must also configure
your repository in the CMC.
You can export the certification log for the data in one repository or in all repositories.
Caution:
If you select all repositories and have more than one connection to the same repository, your results
may contain duplicate records.
1.
Select Management > Certification Logs, and select the repository that contains the certification
log that you want to export.
2.
Click the New Zealand SOA tab.
3.
Select whether you want to export all certification log data that is in the selected repository or just
the data within a specified date range.
The Year list contains the current year and the two previous years, because certification logs are
required to be retained for two years.
2010-12-0230

Administrator
4.
Specify the location where the certification logs will be exported.
The default location is <LINK_DIR>\DataQuality\certifications\Certification
Logs\repository\. To reset the export location to the default, click the Reset button.
5.
If you want to overwrite an existing log file, click the Overwrite option.
6.
Click the Export button.
After the log file is exported, a confirmation message is displayed at the top of the page.
Related Topics
• New Zealand Statement of Accuracy (SOA) report
• Designer Guide: Data Quality, Address Cleanse, New Zealand Certification
• Reference Guide: Transforms, Global Address engine
• Reference Guide: Transforms, Report options for New Zealand
3.2.5.3 Exporting DSF2 certification log
Before you export the certification log, you must have run a job containing a USA Regulatory Address
Cleanse transform with the DSF2 certification options set appropriately. You must also configure your
repository in the Central Management Console (CMC).
You can export the certification log for the data in one repository or in all repositories.
Caution:
If you select all repositories and have more than one connection to the same repository, your results
may contain duplicate records.
1.
Open the Data Services Management Console.
2.
Click the Administrator icon.
3.
Select Management > Certification Logs, and select the repository that contains the certification
log that you want to export.
4.
Click the DSF2 tab.
5.
Select the date range that contains the data that you want to export.
6.
Select the DSF2 licensee ID drop list and select the logs that you want to export, or select All DSF2
Licensee IDs.
7.
Specify the location where the certification logs will be exported.
Note:
The location that you specify is relative to the web application server.
To reset the export location to the default, click the Reset button. The default location is
<LINK_DIR>\DataQuality\certifications\CertificationLogs\repository\.
8.
If you want to overwrite an existing log file, click the Overwrite option.
2010-12-0231

Administrator
10.
11.
9.
Click the Search button. The page displays the available log files with the specified criteria. You
can sort the log files using the column headers.
The "Data Available" column has a Yes status when there is data for the log file. A No status indicates
that no data is available and will result in an empty log file.
Select the log file(s) that you want to export or select the checkbox next to "Select All".
Click the Export button.
After the log file is exported, a confirmation message is displayed at the top of the page.
Related Topics
• US Addressing Report
• Designer Guide: DSF2 overview
• Reference Guide: Transforms, DSF2 Walk Sequencer
3.3 Central Repository management
This section describes how to manage your secure central repositories using the Administrator.
When you log into the Management Console as a user with the appropriate rights, the name of each
secure central repository appears under the Central Repositories node. Links under this node include:
• Users and groups
Use to add, remove, and configure users and groups for secure object access.
• Reports
Use to generate reports for central repository objects such as viewing the change history of an
object.
Note:
Before you can manage a secure central repository, it must be registered in the Central Management
Console (CMC) and have appropriate user access applied.
Related Topics
• Administrator's Guide: To register a repository in the CMC
3.3.1 Setting up users and groups
The general process for setting up secure central repository users and groups is as follows:
2010-12-0232

Administrator
1.
Register the secure central repository in the Central Management Console (CMC).
2.
Add central repository groups.
3.
Associate users with groups.
The following sections describe these procedures.
Related Topics
• Designer Guide: Implementing Central Repository Security
3.3.1.1 To add a group to a central repository
Groups are specific to a secure central repository and are not visible in any other local or central
repository.
1.
Expand the Central Repositories node in the navigation tree and expand the repository to configure.
2.
Click Users and Groups.
The Groups and Users page displays.
3.
On the Groups tab, click Add.
4.
Type a Name for the group.
5.
Optionally, type a Description for the group.
6.
Click Apply.
The group appears on the Groups tab.
3.3.1.2 To add users
1.
Expand the Central Repositories node in the navigation tree and expand the repository to configure.
2.
Click Users and Groups.
The Groups and Users page displays.
3.
Click the Users tab.
4.
Click Add.
On the Add/Edit User page, enter the following information.
2010-12-0233

Administrator
DescriptionOption
Select the user to add to the group.
User name
Note:
The list of available users includes all users defined in the
Central Management Console (CMC).
The default central repository group to which the user be-
Default group
longs. You can change the default by selecting another
from the drop-down list.
Select a value from the drop-down list:
• Active
Status
Enables the user's account for normal activities.
• Suspended
Select to disable the login for that user.
Optionally, type a description for the user.Description
The User is a member of list on the left shows the groups to which this user belongs.
5.
Click Apply.
Clicking Reset returns all fields to the last set of values applied.
3.3.1.3 To add or remove a user from a group
1.
Expand the Central Repositories node in the navigation tree and expand the repository to configure.
2.
Click Users and Groups.
3.
Click the Group tab.
4.
Click the group name.
5.
The Members list on the left shows the users in this group.
To add users to a group, click the user names from the Not Members list and click Add Users.
Select multiple user names using the Ctrl or Shift keys.
To remove a user from the group, select a user name from the Members list and click Remove
Users. Select multiple user names using the Ctrl or Shift keys.
6.
Click Apply.
Clicking Reset returns all fields to the last set of values applied.
2010-12-0234

Administrator
Alternately, click the Users tab, click the user name, and associate the user with one or more groups
by selecting group names and adding or removing them.
Related Topics
• Designer Guide: Implementing Central Repository Security
3.3.1.4 To delete a group
1.
Expand the Central Repositories node in the navigation tree, expand the repository to configure,
and click Users and Groups.
2.
Click the Group tab.
3.
Select the check box for the group.
4.
Click Remove.
Note:
You cannot delete a group in the following instances:
• It is the default group for any user (whether or not they are active).
• It is the only group with full permissions for an object.
• A member of the group is undertaking any central repository tasks using the Designer.
3.3.2 Viewing reports
You can generate reports about objects in a central repository such as which objects a user currently
has checked out or the changes made to an object over a specified time frame.
Expand the central repository to view and expand the Reports link.
Related Topics
• Object state report
• Change report
3.3.2.1 Object state report
2010-12-0235

Administrator
Use the object state report to view details on one or more objects such as whether the objects are
checked out and by whom.
Click the Object State Report link to display a search page with the following criteria (all fields are
optional):
• Object name—Type an object name. You can use the % symbol as a wildcard.
• Object type—For example select Batch job, Table, or Stored procedure.
• State—For example select Checked out.
• User—Select a central repository user name.
Click Search to generate the report. The report has the following columns:
• Object name
• Object type
• State
• User name—The user account associated with the check-out or check-in.
• Associated repository—The repository to which the object belongs.
• Time—Check-out or check-in date and time.
• Comments—Comments added when user checked out or checked in the object.
Click the object name to display the object's history.
Related Topics
• Designer Guide: Viewing object history
3.3.2.2 Change report
Use the change report to view the change history for an object over a specified period of time.
Click the Change Report link to display a search page with the following criteria:
• Start date—Enter a date or click the calendar icon to select a start date.
• End date—Enter a date or click the calendar icon to select an end date.
• Object type—Optionally select an object type; for example batch job, table, or stored procedure.
• State—Optionally select an object state; for example Checked out.
• User—Optionally select a central repository user name.
Click Search to generate the report. The report has the following columns:
• Object name
• Object type
• State
• Version—The version number of the object.
• User name—The user account associated with the check-out or check-in.
• Associated repository—The repository to which the object belongs.
2010-12-0236

Administrator
• Time—Check-out or check-in date and time.
• Comments—Comments added when user checked out or checked in the object.
3.4 Server Groups
About this section
Use the Administrator to create and maintain server groups.
This section describes how to work with server groups.
Related Topics
• Server group architecture
• To add a server group
• Editing and removing a server group
• Monitoring Job Server status in a server group
• Executing jobs using server groups
3.4.1 Server group architecture
You can group Job Servers on different computers into a logical SAP BusinessObjects Data Services
component called a server group. A server group automatically measures resource availability on each
Job Server in the group and distributes scheduled batch jobs to the Job Server with the lightest load at
runtime.
There are two rules for creating server groups:
• All the Job Servers in an individual server group must be associated with the same repository, which
must be defined as a default repository. The Job Servers in the server group must also have:
• Identical SAP BusinessObjects Data Services versions
• Identical database server versions
• Identical locale
• Each computer can only contribute one Job Server to a server group.
2010-12-0237

Administrator
The requirement that all Job Servers in a server group be associated with the same repository simply
allows you to more easily track which jobs are associated with a server group. It is recommended that
you use a naming convention for server groups that includes the name of the repository. For example,
for a repository called DEV, a server group might be called SG_DEV.
On startup, all Job Servers check the repository to find out if they must start as part of a server group.
Compared to normal Job Servers, Job Servers in a server group each:
• Collect a list of other Job Servers in their server group
• Collect system load statistics every 60 seconds:
• Number of CPUs (on startup only)
• Average CPU load
• Available virtual memory
• Service requests for system load statistics
• Accept server group execution requests
3.4.1.1 Load balance index
All Job Servers in a server group collect and consolidate system load statistics and convert them into
a load balance index value for each Job Server. A Job Server's load balance index value allows the
software to normalize statistics taken from different platforms. The Job Server with the lowest index
value is selected to execute the current job. The software polls all Job Server computers every 60
seconds to refresh the load balance index.
2010-12-0238

Administrator
3.4.1.2 Job execution
After you create a server group, you can select a server group to execute a job from the Designer's
Execution Properties window or from the Administrator's Execute Batch Job, Schedule Batch Job, and
Export Batch Job pages.
When you execute a job using a server group, the server group executes the job on the Job Server in
the group that is running on the computer that has the lightest load. The Administrator will also
resynchronize a Job Server with its repository if there are changes made to the server group configuration
settings.
You can execute parts of your job on different Job Servers in a server group. You can select the following
distribution levels from the Designer's Execution Properties window or from the Administrator's Execute
Batch Job, Schedule Batch Job, and Export Batch Job pages:
• Job level
A job can execute on an available Job Server.
• Data flow level
Each data flow within a job can execute on an available Job Server.
• Sub data flow level
A resource-intensive operation (such as a sort, table comparison, or table lookup) within a data flow
can execute on an available Job Server.
Related Topics
• Performance Optimization Guide: Using grid computing to distribute data flows execution
3.4.1.3 Job launcher
The Job Launcher, exported as part of a job's execution commands, includes a specific command line
option for server groups. You can use this option to change the Job Servers in a server group.
Related Topics
• About the job launcher
2010-12-0239

Administrator
3.4.1.4 Working with server groups and Designer options
Some Designer options assume paths are relative to a Job Server. If your Job Servers are on different
machines from your Designer (typically the case in a production environment) you must ensure that
connections and directory paths point to the Job Server host that will run the job. Such options include:
• Source and target directories for files
• Bulk load directories
• Source and target connection strings to databases
• Path to repositories
When using server groups consider the additional layer of complexity for connections. For example, if
you have three Job Servers in a server group:
• Use the same directory structure across your three host computers for source and target file
operations and use relative paths for file names.
• Use the same connection strings to your databases for all three Job Server hosts.
If you use job distribution levels, the Job Servers in the server group must have:
• Identical SAP BusinessObjects Data Services versions
• Identical database server versions
• Identical locale
• Identical operating systems
Thoroughly test the Job Server job options when working with server groups.
Adding a server group:
• In the Administrator, use the Server Groups node to create and add a server group.
3.4.1.4.1 To add a server group
1.
Select Server Groups > All Server Groups.
2.
Click the Server Group Configuration tab.
3.
Click Add.
4.
Follow the instructions on the Add Server Group page to create a server group.
• When you select a repository, all Job Servers registered with that repository display. You can
create one server group per repository.
• Notice that the Administrator provides a default server group name. It is the name of your repository
with the prefix SG_ (for server group). You can change the default name, however, labeling a
server group with the repository name is recommended.
• One Job Server on a computer can be added to a server group. Use the Host and Port column
to verify that the Job Servers you select are each installed on a different host.
5.
After you select the Job Servers for a server group, click Apply.
2010-12-0240

Administrator
The display returns to the Server Group Configuration page.
Related Topics
• Monitoring Job Server status in a server group
3.4.2 Editing and removing a server group
You can select a new set of Job Servers for an existing server group or remove a server group.
Trace messages are written for a change in Job Server status when you create, edit, or remove server
groups.
• When a Job Server is upgraded to membership in a server group, the trace message is:
Collecting system load statistics, maintaining list of Job Server(s) for
this server group, and accepting Job Server execution requests.
• When a Job Server is downgraded out of a server group, the trace message is:
Deleting current system load statistics, and not collecting more. Not ac
cepting job execution requests from a server group.
3.4.2.1 To edit a server group
1.
In the Server Group Status page, click the Server Group Configuration tab.
2.
In the Server Group Configuration page, click the server group that you want to edit.
3.
In the Edit Server Group page, select a new set of Job Servers.
4.
Click Apply.
Your edited server group is saved and the display returns to the Server Groups Configuration page.
3.4.2.2 To remove a server group
1.
In the Server Group Status page, click the Server Group Configuration tab.
2.
In the Server Group Configuration page, select the check box for the server group(s) that you want
to remove.
2010-12-0241

Administrator
3.
Click Remove.
The selected server group is removed as shown in the display.
Note:
If you delete Job Servers from a repository, so as to delete all the Job Servers in a server group, the
Administrator displays an invalid status for the server group.
3.4.3 Monitoring Job Server status in a server group
If Job Servers are in a server group, you can view their status in the Administrator.
• To monitor the status of these Job Servers, select Server Groups > All Server Groups.
The Server Group Status page opens. All existing server groups are displayed with the Job Servers
they contain.
DescriptionIndicator
A green icon indicates that a Job Server is running.
A yellow icon indicates that a Job Server is not running.
A red icon indicates that the Job Server cannot connect to the repository.
If a server group contains Job Servers with a mix of green, yellow, or red indicators, then its indicator
appears yellow:
Otherwise, a server group indicator displays the same color indicator as its Job Servers.
• To view the status for a single server group, select its name.
3.4.4 Executing jobs using server groups
After you create a server group, you can select a server group to execute a job from the Designer's
Execution Properties window or from the Administrator's Execute Batch Job and Schedule Batch Job
pages.
Related Topics
• Batch Jobs
2010-12-0242

Administrator
3.5 Batch Jobs
About this section
This section describes how to execute, schedule, and monitor batch jobs from the Administrator.
Before you can manage batch jobs with the Administrator, add repository connections.
Related Topics
• Executing batch jobs
• Scheduling jobs
• Monitoring jobs
• Adding repositories
3.5.1 Executing batch jobs
You can execute batch jobs from the Administrator if their repositories are registered in the Central
Management Console (CMC) and your user has the appropriate rights.
1.
Select Batch > repository.
The Administrator opens the Batch Job Status page, which lists all of the jobs in the selected
repository.
To view jobs in all repositories from this page, select Batch > All Repositories. (The All Repositories
option appears under the Batch Job node if more than one repository is connected to the
Administrator.)
2.
Click the Batch Job Configuration tab.
3.
To the right of the job you want to run, click Execute.
The Administrator opens the Execute Batch Job page.
4.
Under Enter Execution Options, set the parameters for the execution of this job.
5.
Under Select Trace Options, set the trace properties for this execution of the job.
6.
Click Execute to run the job.
The Administrator returns to the Batch Job Status page.
Related Topics
• Reference Guide: Objects, Batch Job, Parameters
• Reference Guide: Objects, Batch Job, Trace properties
2010-12-0243

Administrator
3.5.2 Scheduling jobs
There are three ways to manage job schedules.
Related Topics
• Using the job scheduler
• Scheduling jobs in SAP BusinessObjects Enterprise
• Using a third-party scheduler
3.5.2.1 Using the job scheduler
When you schedule batch jobs using the SAP BusinessObjects Data Services job scheduler, it creates
an entry in the operating system's scheduling utility on the Job Server computer. Windows uses the
Task Scheduler and UNIX systems use the CRON utility. (Note that if you make changes to a schedule
directly through these utilities, the job scheduler will not reflect those changes.)
Related Topics
• To add a job schedule
• Activating or deactivating one or more job schedules
• To update a job schedule
• To remove a job schedule
• Migration considerations
3.5.2.1.1 To add a job schedule
1.
Select Batch > repository.
2.
Click the Batch Job Configuration tab.
3.
For the job to configure, click Add Schedule.
4.
On the Schedule Batch Job page, enter the desired options:
Enter a job schedule
DescriptionOption
Schedule name
Enter a unique name that describes this schedule.
Note:
You cannot rename a schedule after you create it.
2010-12-0244

Administrator
Active
Select a scheduler
DescriptionOption
Select this box to enable (activate) this schedule, then click Apply.
This option allows you to create several schedules for a job and
then activate the one(s) you want to run.
Creates the schedule on the Job Server computer.Data Services scheduler
BOE scheduler
Creates the schedule on the selected central management server
(CMS).
Select scheduled day(s) for executing the job
From the drop-down list on the calendar, select:
• Day of Week to schedule the job by the day of the week. You
can select one or more days. Click again to deselect.
• Day of Month to schedule the job by date. You can select one
Calendar
or more dates. Click again to deselect.
If Recurring is selected, then the Administrator schedules this job
to repeat every week or month on the selected day. Note that if you
select multiple days of the week or month, the job will run on a recurring basis by default.
Select scheduled time for executing the jobs
Once a day
Enter the time for the scheduler to start the job (hours, minutes, and
either AM or PM).
• For the Data Services scheduler, enter the time (hours, minutes,
and either AM or PM) for the scheduler to repeatedly run the job
for the selected duration (in minutes) at the selected interval (in
minutes).
• For the BOE scheduler, enter (in minutes) the repeat interval to
Multiple times a day
run the job. You must also select all days in the calendar (for
weekly or monthly).
Select job execution parameters
Select a time when all of the required resources are available.
Typically, you want to schedule jobs to ensure they finish before the
target database or data warehouse must be available to meet increased demand.
2010-12-0245

Administrator
System configuration
Use password file
DescriptionOption
Select the system configuration to use when executing this job. A
system configuration defines a set of datastore configurations, which
define the datastore connections.
For more information, see "Creating and managing multiple datastore
configurations" in the
Designer Guide
.
If a system configuration is not specified, the software uses the default datastore configuration for each datastore.
This option is a run-time property. This option is only available if
there are system configurations defined in the repository.
Select the Job Server or a server group to execute this schedule.Job Server or server group
Select to create or update the password file that the job schedule
accesses for current repository connection information. Deselect
the option to generate the batch file with a hard-coded repository
information.
Enable auditing
Disable data validation statistics collection
Recover from last failed execution
Collect statistics for optimization
Note:
This option is disabled if you have not set up a CMS connection.
Select this option if you want to collect audit statistics for this specific
job execution. This option is selected by default.
For more information about auditing, see “Using Auditing” in the
Designer Guide
.
Select this option if you do not want to collect data validation
statistics for any validation transforms in this job. This option is not
selected by default.
Select this option to enable the recovery mode when this job runs.Enable recovery
Select this option if an execution of this job has failed and you want
to enable the recovery mode.
Select this option to collect statistics that the optimizer will use to
choose an optimal cache type (in-memory or pageable). This option
is not selected by default.
See “Using statistics for cache self-tuning” in the
mization Guide
.
Performance Opti-
2010-12-0246

Administrator
Collect statistics for monitoring
Use collected statistics
Export Data Quality reports
DescriptionOption
Select this option to display cache statistics in the Performance
Monitor in the Administrator. This option is not selected by default.
See “Monitoring and tuning cache types” in the
mization Guide
.
Performance Opti-
Select this option if you want the optimizer to use the cache statistics
collected on a previous execution of the job. The option is selected
by default.
For more information, see “Using statistics for cache self-tuning” in
the
Performance Optimization Guide
.
Generates and exports all specified job reports to the location
specified in the Management > Report Server Configuration
node. By default, the reports are exported to
<LINK_DIR>\DataQuality\reports\repository\job.
Distribution level
5.
Click Apply. Clicking Reset returns all fields to the last set of values applied.
Related Topics
• Designer Guide: Datastores, Creating and managing multiple datastore configurations
• Managing database account changes
• Reference Guide: Objects, Batch Job, Parameters
• Designer Guide: Data Assessment, Using Auditing
• Data Validation Dashboard Reports
• Configuring the report server
• Performance Optimization Guide: Using Caches, Using statistics for cache self-tuning
• Performance Optimization Guide: Using Caches, To monitor and tune in-memory and pageable caches
• Performance Optimization Guide: Distributing Data Flow Execution, Using grid computing to distribute
data flows execution
Select the level within a job that you want to distribute to multiple
Job Servers for processing:
• Job: The whole job will execute on an available Job Server.
• Data flow: Each data flow within the job can execute on an
available Job Server.
• Sub data flow: Each sub data flow (can be a separate transform
or function) within a data flow can execute on an available Job
Server.
For more information, see “Using grid computing to distribute data
flows execution” in the
Performance Optimization Guide
.
2010-12-0247

Administrator
Activating or deactivating one or more job schedules
In order for a job schedule to run, it must be active.
To change an existing job schedule, you must first deactivate it, make the changes, then reactivate it.
1.
Select Batch > repository .
2.
Click the Repository Schedules tab.
In order for a job schedule to run, it must be active.
The Repository Schedules tab lists all schedules for all jobs in the repository, and you can remove,
activate, or deactivate one or more schedules.
Alternately, click the Batch Job Configuration tab, then for a particular job, click the Schedules link.
The Batch Job Schedules tab lists all schedules for that particular job. Here you can add, remove,
activate, or deactivate one or more schedules:
The Job Server column listed next to each schedule indicates which Job Server will execute it.
If there is a server group icon in the Job Server column, this indicates the schedule will be executed
by the server group, and the schedule is stored on the indicated Job Server. To see which server
group is associated with the schedule, roll your cursor over the server group icon.
If there is CMS icon in the Job Server column, this indicates the job schedule is managed by a
Central Management Server.
Click the System Configuration names, if configured, to open a page that lists the datastore
configurations in that system configuration.
3.
On either the Repository Schedules tab or the Batch Job Schedules tab, select one or more
check boxes for a schedule.
4.
Click Activate (or Deactivate).
Related Topics
• To update a job schedule
3.5.2.1.2 To update a job schedule
To edit a job schedule, you must first deactivate it, make the changes, then reactivate it.
1.
Select Batch > repository.
2.
Click the Batch Job Configuration tab.
3.
Click the Schedules link for the desired job.
4.
Click the schedule name to edit.
5.
The "Schedule Batch Job" page displays.
6.
If the schedule is currently active, deactivate it by clearing the Active check box and click Apply.
2010-12-0248

Administrator
Note:
You do not need to deactivate the schedule to update most of the job execution parameters at the
bottom of the page. Only the schedule-related parameters require deactivation in order to update
them.
7.
Edit the schedule parameters as required.
8.
To reactivate the schedule now, select the Active check box.
9.
Click Apply.
The status bar at the top of the page confirms that the schedule has been created and/or activated.
Related Topics
• To add a job schedule
3.5.2.1.3 To remove a job schedule
1.
Select Batch > repository.
2.
Click the Repository Schedules tab.
3.
Select one or more check boxes for a schedule.
4.
Click Remove.
The Administrator deletes the information about this job schedule.
3.5.2.1.4 Migration considerations
Changes made to the Job Server, such as an upgrade, do not affect schedules created in SAP
BusinessObjects Data Services as long as:
• The new version of the software is installed in the same directory as the original version (SAP
BusinessObjects Data Services schedulers use a hard-coded path to the Job Server).
• The new installation uses the Job Server name and port from the previous installation. (This occurs
automatically when you install over the existing DSConfig file.)
When you export a repository via an .atl file, jobs and their schedules (created in SAP BusinessObjects
Data Services) automatically export as well.
You can also import a repository .atl file including jobs and their associated schedules (previously
created in SAP BusinessObjects Data Services) back into SAP BusinessObjects Data Services.
Remember that once imported, you must reactivate job schedules to use them. If the job schedule uses
a password file, then reactivating it will automatically generate the password file.
Related Topics
• Designer Guide: Importing from a File
2010-12-0249

Administrator
3.5.2.2 Scheduling jobs in SAP BusinessObjects Enterprise
If you are using SAP BusinessObjects Enterprise and you want to manage your SAP BusinessObjects
Data Services job schedules in that application, first create a connection to a Central Management
Server (CMS), then configure the schedule to use that server.
3.5.2.2.1 To add a CMS connection
1.
Select Management > CMS Connection.
2.
Click Add.
3.
On the CMS Connections page, enter the connection information.
The parameters in the top section are the same as when logging in to an SAP BusinessObjects
EnterpriseCentral Management Console (CMC) or InfoView. For details, refer to the
BusinessObjects Enterprise InfoView User's Guide
.
SAP
The parameters in the bottom section (User account credentials for executing the program) depend
on how the CMS server is set up. For details, refer to "Authentication and program objects" in the
SAP BusinessObjects Enterprise Administrator's Guide
DescriptionOption
System
Type the computer name that hosts the Central Management
Server (CMS), a colon, and the port number.
.
Type the CMC/InfoView user name.User name
Type the CMC/InfoView user password.Password
Select the authentication type for the serverAuthentication
User account credentials for executing the program (optional)
Note:
If you do not have the following option cleared in the Central Management Console, you will be
required to enter user account credentials in order for your schedules to run:
In the CMC, select Objects > Objects Settings > Program objects and clear the Use Imper-
sonation option.
The CMS computer might require operating system login
User name
credentials to run the schedule. If so, type the user name (and
password) for the applicable account.
Password
The CMS computer might require operating system login
credentials to run the schedule. If so, type the (user name
and) password for the applicable account.
2010-12-0250

Administrator
4.
Click Apply.
3.5.2.2.2 To create a job schedule in SAP BusinessObjects Enterprise
1.
Select Batch > repository.
2.
Click the Repository Schedules tab.
3.
Click the schedule name to configure.
4.
If the schedule is currently active, deactivate it by clearing the Active check box and click Apply.
5.
Edit the schedule parameters as necessary.
Note:
Time-sensitive parameters reflect the time zone of the computer where the Administrator is installed,
not where the CMS is installed.
6.
Under the Select a scheduler section, select BOE scheduler.
7.
From the drop-down list, select a CMS name.
8.
To reactivate the schedule now, select the Active check box.
9.
Click Apply.
The status bar at the top of the page confirms that the schedule has been created and/or activated.
If it doesn't already exist, SAP BusinessObjects Enterprise creates a folder called Data Services
and stores the schedule file and a parameters file (called schedulename.txt).
For a BOE schedule with the Use password file option selected, then SAP BusinessObjects Data
Services also creates a password file in the Data Services folder (called repositoryname.txt)
Note:
When you deactivate a schedule created on a CMS, SAP BusinessObjects Enterprise deletes the
object. Therefore, any changes made to the calendar will be lost.
3.5.2.2.3 To remove a CMS connection
1.
Select Management > CMS Connection.
2.
Select the check box for the connection to remove from the administrator.
3.
Click Remove.
3.5.2.3 Using a third-party scheduler
When you schedule jobs using third-party software:
• The job initiates outside of SAP BusinessObjects Data Services.
• The job runs from an executable batch file (or shell script for UNIX) exported from SAP
BusinessObjects Data Services.
2010-12-0251

Administrator
Note:
When a third-party scheduler invokes a job, the corresponding Job Server must be running.
Related Topics
• About the job launcher
3.5.2.3.1 To execute a job with a third-party scheduler
1.
Export the job's execution command to an executable batch file (.bat file for Windows or .sh file for
UNIX environments).
2.
Ensure that the Data Services Service is running (for that job's Job Server) when the job begins to
execute.
The Data Services Service automatically starts the Job Server when you restart the computer on
which you installed the Job Server.
• You can also verify whether a Job Server is running at any given time using the Designer. Log
in to the repository that contains your job and view the Designer's status bar to verify that the
Job Server connected to this repository is running.
• You can verify whether all Job Servers in a server group are running using the Administrator. In
the navigation tree select Server Groups > All Server Groups to view the status of server
groups and the Job Servers they contain.
3.
Schedule the batch file from the third-party software.
Note:
To stop an SAP BusinessObjects Data Services job launched by a third-party scheduling application,
press CTRL+C on the application's keyboard.
3.5.2.3.2 To export a job for scheduling
1.
Select Batch > repository.
2.
Click the Batch Job Configuration tab.
3.
For the batch job to configure, click the Export Execution Command link.
4.
On the Export Execution Command page, enter the desired options for the batch job command
file that you want the Administrator to create:
DescriptionOption
The name of the batch file or script containing the job. The
third-party scheduler executes this file. The Administrator
File name
automatically appends the appropriate extension:
• .sh for UNIX
• .bat for Windows
2010-12-0252

Administrator
System configuration
DescriptionOption
Select the system configuration to use when executing this
job. A system configuration defines a set of datastore configurations, which define the datastore connections.
For more information, see “Creating and managing multiple
datastore configurations” in the
Designer Guide
.
If a system configuration is not specified, the software uses
the default datastore configuration for each datastore.
This option is a run-time property. This option is only available
if there are system configurations defined in the repository.
Job Server or server group
Enable auditing
Disable data validation statistics
collection
Enable recovery
Recover from last failed execution
Select the Job Server or a server group to execute this
schedule.
Select this option if you want to collect audit statistics for this
specific job execution. The option is selected by default.
For more information about auditing, see “Using Auditing” in
the
Designer Guide
.
Select this option if you do not want to collect data validation
statistics for any validation transforms in this job. The option
is not selected by default.
Select this option to enable the automatic recovery feature.
When enabled, the software saves the results from completed
steps and allows you to resume failed jobs.
See “Automatically recovering jobs” in the
Designer Guide
for information about the recovery options.
Select this option to resume a failed job. The software retrieves the results from any steps that were previously executed successfully and re-executes any other steps. This
option is a run-time property. This option is not available when
a job has not yet been executed or when recovery mode was
disabled during the previous run.
Use password file
Select to create or update a password file that automatically
updates job schedules after changes in database or repository
parameters. Deselect the option to generate the batch file
with a hard-coded repository user name and password.
2010-12-0253

Administrator
Collect statistics for optimization
Collect statistics for monitoring
Use collected statistics
DescriptionOption
Select this option to collect statistics that the optimizer will
use to choose an optimal cache type (in-memory or pageable). This option is not selected by default.
See “Using statistics for cache self-tuning” in the
Optimization Guide
.
Performance
Select this option to display cache statistics in the Performance Monitor in the Administrator. The option is not selected
by default.
For more information, see “Monitoring and tuning cache types”
in the
Performance Optimization Guide
.
Select this check box if you want the optimizer to use the
cache statistics collected on a previous execution of the job.
The option is selected by default.
See “Using statistics for cache self-tuning” in the
Optimization Guide
.
Performance
Generates and exports all specified job reports to the location
Export Data Quality reports
specified in the Management > Report Server Configura-
tion node. By default, the reports are exported to
<LINK_DIR>\DataQuality\reports\repository\job.
Select the level within a job that you want to distribute to
multiple Job Servers for processing:
• Job: The whole job will execute on one Job Server.
• Data flow: Each data flow within the job will execute on
a separate Job Server.
Distribution level
• Sub data flow: Each sub data flow (can be a separate
transform or function) within a data flow can execute on
a separate Job Server.
For more information, see “Using grid computing to distribute
5.
Click Export.
data flows execution” in the
Performance Optimization Guide
The Administrator creates command files filename.txt (the default for filename is the job name)
and a batch file for the job and writes them to the local <LINK_DIR>\log directory.
Note:
You can relocate the password file from the <LINK_DIR>\conf directory, but you must edit the
filename.txt file so that it refers to the new location of the password file. Open the file in a text editor
.
2010-12-0254

Administrator
and add the relative or absolute file path to the new location of the password file in the argument -R
"repositoryname.txt".
Related Topics
• Designer Guide: Datastores, Creating and managing multiple datastore configurations
• Reference Guide: Objects, Batch Job, Parameters
• Designer Guide: Data Assessment, Using Auditing
• Data Validation Dashboard Reports
• Managing database account changes
• Configuring the report server
• Performance Optimization Guide: Using Caches, Monitoring and tuning cache types
• Performance Optimization Guide: Using Caches, Using statistics for cache self-tuning
• Performance Optimization Guide: Distributing Data Flow Execution, Using grid computing to distribute
data flows execution
3.5.2.4 About the job launcher
SAP BusinessObjects Data Services exports job execution command files as batch files on Windows
or CRON files on UNIX. These files pass parameters and call AL_RWJobLauncher. Then,
AL_RWJobLauncher executes the job, sends it to the appropriate Job Server, and waits for the job to
complete.
Caution:
Do not modify the exported file without assistance from SAP Business User Support.
The following shows a sample Windows NT batch file created when the software exports a job. ROBOT
is the host name of the Job Server computer. All lines after inet:ROBOT:3513 are AL_Engine
arguments, not AL_RWJobLauncher arguments.
D:\Data Services\bin\AL_RWJobLauncher.exe
"inet:ROBOT:3513"
"-SCMSServer
-Uusername
-Ppassword
-G"b5751907_96c4_42be_a3b5_0aff44b8afc5"
-r100 -T14
-CTBatch -CmROBOT -CaROBOT
-CjROBOT -Cp3513"
Related Topics
• Administrator's Guide: Configuring SSL for Data Services components
• Administrator's Guide: Configuring SSL for the CMS connection
2010-12-0255

Administrator
3.5.2.4.1 Job launcher flag values and arguments
The following table lists job launcher flags and their values.
ValueFlag
-w
-t
-s
-C
-S
-R
The job launcher starts the job(s) and then waits before passing back the job
status. If -w is not specified, the launcher exits immediately after starting a job.
The time, in milliseconds, that the Job Server waits before checking a job's status.
This is a companion argument for -w.
Status or return code. 0 indicates successful completion, non-zero indicates an
error condition.
Combine -w, -t, and -s to execute the job, wait for completion, and return the
status.
Name of the engine command file (path to a file which contains the Command
line arguments to be sent to the engine).
Prints AL_RWJobLauncher version number.-v
Lists the server group and Job Servers that it contains using the following syntax:
"SvrGroupName;inet:JobSvr1Name:JobSvr1Host:JobSvr1Port;inet:JobSvr2Name:JobSvr2Host:Job
Svr2Port";
For example: "SG_DEV;inet:HPSVR1:3500;inet:WINSVR4:3505";
The location and name of the password file. Replaces the hard-coded repository
connection values for -S, -N, -U, -P.
Generates and exports all specified job reports to the location specified in the
Management > Report Server Configuration node. By default, the reports are
exported to <LINK_DIR>\DataQuality\reports\repository\job.
-xCR
In order to use this flag, you must disable the security for the Export_DQReport
operation in the Administrator > Web Services > Web Services Configuration
tab.
There are two arguments that do not use flags:
• inet address: The host name and port number of the Job Server. The string must be in quotes.
For example:
"inet:HPSVR1:3500"
If you use a server group, inet addresses are automatically rewritten using the -S flag arguments.
On execution, the first Job Server in the group checks with the others and the Job Server with the
lightest load executes the job.
2010-12-0256

Administrator
• server log path: The fully qualified path to the location of the log files. The server log path must
be in quotes. The server log path argument does not appear on an exported batch job launch
command file. It appears only when Data Services generates a file for an active job schedule and
stores it in the following directory: <LINK_DIR>/Log/JobServerName/RepositoryName/JobIn
stanceName.
You cannot manually edit server log paths.
Related Topics
• Integrator's Guide: To configure web service information using the Administrator
3.5.2.4.2 Job launcher error codes
The job launcher also provides error codes to help debug potential problems. The error messages are:
Error messageError number
Network failure.180002
180004
180007
3.5.3 Monitoring jobs
Using the Administrator, you can monitor job execution of any batch job in a connected repository. You
can monitor jobs that you run from the Administrator or from the Designer.
The service that will run the schedule has not started.180003
LINK_DIR is not defined.
The trace message file could not be created.180005
The error message file could not be created.180006
The GUID could not be found.
The status cannot be returned.
No command line arguments were found.180008
Invalid command line syntax.180009
Cannot open the command file.180010
This section discusses how you can use the Administrator to view a batch job's overall status and
statistics.
2010-12-0257

Administrator
3.5.3.1 To view overall status of executed jobs
The "Batch Job Status" page lists each batch job execution. Use this list to view the overall status of
each execution and to access more detailed statistics and log files.
1.
Select Batch > repository.
To view jobs in all repositories from this page, select Batch > All Repositories. (The All Repositories
option appears under the Batch Job node if more than one repository is connected to the
Administrator.)
The "Batch Job Status" page shows each instance of job execution for the selected repository.
2.
You can filter the list of batch jobs displayed by selecting a job name and/or when the job executed.
To filter by job, select the job name from the drop-down Job name list. Or type the name, or type
part of the name and a wildcard character (% or *), into the wildcard search string box and click
Search. The Search field is not case sensitive and spaces are allowed.
To filter by when the job(s) executed, select one of the following options:
• Show last execution of a job.
• Show status relative to today—Select the number of previous days over which to view job
executions.
• Show status as a set period—Type the date range or select the dates by clicking the calendar
icons.
3.
Click Search to update the list.
4.
To sort the values in each column in ascending or descending order, click the column heading.
5.
Find the overall status of a batch job execution by examining the indicator in the Status column.
DescriptionIndicator
A green icon indicates that the batch job ran without error.
A yellow icon indicates that the batch job has one or more warnings.
A red icon indicates that the batch job experienced an error.
Check the End Time column to see if or when the job completed.
6.
If a batch job execution has a red status, examine the trace, monitor, and error logs for more
information.
7.
To view detailed information about a particular job execution, look at the data on the Batch Job
Status page.
If the job includes a server group icon in the Job Server column, this indicates that the job was
executed by a server group. You can roll your cursor over the server group icon to view the name
of the server group. The Job Server listed is the Job Server in the server group that executed the
job.
2010-12-0258

Administrator
Note:
All jobs can be executed by an explicitly selected Job Server or by a server group. If you choose to
execute a job using a server group, you can use this page to see which Job Server actually executed
the job. If you explicitly select a Job Server to execute a job, then even if it is also part of a server
group, the server group icon does not appear for the job in the Job Server column on this page.
Related Topics
• Setting the status interval
3.5.3.2 Statistics
For each job execution, the Administrator shows statistics. Statistics quantify the activities of the
components of the job. You can view the following types of statistics:
• Job statistics such as time spent in a given component of a job and the number of data rows that
streamed through the component.
• Data flow object statistics such as the cache size used by a transform within a data flow.
3.5.3.2.1 To view job statistics
To help tune the performance of a job, review job statistics.
1.
Select Batch > repository.
2.
On the Batch Job Status page, find a job execution instance.
Identify an instance using the page sub-title (which provides the name of the repository on which
SAP BusinessObjects Data Services stores the job) and the following column headings on this page:
DescriptionColumn
See Overall Status.Status
The name that you gave the job in the Designer.Job Name
2010-12-0259

Administrator
System Configuration
DescriptionColumn
Name of a set of datastore configurations that the job uses to connect to
source and target databases when it executes. Each value in this column is
a link. Click the link to view the set of datastore configurations in the system
configuration. To change the system configuration, click the Batch Job
Configuration tab, then use the Execute, Add Schedule or Export Execution Command pages.
The server that ran this job.Job Server
The date and time that the job execution instance started.Start Time
The date and time that this job execution instance stopped.End Time
The time (in seconds) that the job took to complete.Duration
The number of times that this instance ran before completing.Run #
3.
Under Job Information for an instance, click Monitor.
The Administrator opens the Job Server Monitor Log Viewer page. This page shows several statistics
about this instance of job execution starting with the name of the monitor log file.
After the file name, each line in the log provides the following information:
DescriptionColumn
Indicates which object (step in a data flow) is executing.Path Name
Indicates the run-time order of the processes in the execution of the transform
State
object and the states of each process. These are not error status states. However,
if a process state is Proceed and it never changes to Stop, this indicates the process ran with errors.
Indicates that the job is initializing.Initializing
Indicates that the job is optimizing.Optimizing
Indicates that the process is executing.Proceed
Indicates that the process ended without error.Stop
Indicates the number of rows processed through this object. This value updates
Row Count
based on the Monitor sample rate (# of rows) set as an execution option on the
Execute Batch Job page.
Elapsed
Time
Absolute
Time
Indicates the time (in seconds) since the object received its first row of data.
Indicates the time (in seconds) since the execution of this entire data flow (including
all of the transforms) began.
2010-12-0260

Administrator
Related Topics
• To view overall status of executed jobs
3.5.3.2.2 Data flow statistics
To help tune the performance of a data flow, review data flow statistics.
Related Topics
• Performance Optimization Guide: Measuring performance of jobs
3.5.3.3 To ignore error status
The "Batch Job Status" page includes an option to Ignore Error Status. Use this option if you are
working through jobs with warnings or errors on this page and you want to mark a row so that you know
you are finished looking at its logs.
1.
On the "Batch Job Status" page, select the job or jobs that you want to ignore.
2.
Click the Ignore Error Status button.
The page refreshes and the rows you selected now display a green status icon.
3.5.3.4 Deleting batch job history data
The "Batch Job Status" page includes an option to delete information about how a job ran. If you want
to manually delete rows from this page, select the rows that you want to delete, then select Delete.
You can also manage this information by setting the Administrator's log retention period.
Note:
When you delete this job information, the software also clears data validation statistics from Data
Validation Metadata Reports.
3.5.3.5 Stopping a running job
The "Batch Job Status" page includes an option to abort batch jobs. If a batch job is running and you
need to stop it, select the check box next to the job name and click Abort.
2010-12-0261

Administrator
3.5.3.6 To delete trace, monitor, and error logs for a batch job
You can view and delete trace, monitor, and error logs for job instances from the "Batch Job Status"
page. The corresponding Job Server must be up and running to view or delete these logs.
You can set trace log options on the "Execute Batch Job" page.
You can use the Delete button on the "Batch Job Status" page to delete a set of batch log history files
from a Job Server computer and its corresponding repository.
1.
Select Batch > repository.
2.
Select the job or jobs for which you want to delete logs.
Alternately, you can click Select All.
3.
Click Delete.
The batch log history files are deleted from the Job Server computer and its corresponding repository.
Related Topics
• Batch job logs
• Statistics
• Reference Guide: Objects, Log
3.6 Real-Time Jobs
This section describes how to support real-time jobs using the Administrator.
Before configuring services, add real-time job repository and Access Server connections to the
Administrator.
Related Topics
• Supporting real-time jobs
• Configuring and monitoring real-time services
• Creating and monitoring client interfaces
3.6.1 Supporting real-time jobs
2010-12-0262

Administrator
The Access Server manages real-time communication between SAP BusinessObjects Data Services
and external applications (such as ERP or web applications). The Access Server determines how to
process incoming and outgoing messages based on the settings you choose for each real-time job in
the Administrator.
In particular you use the Administrator to define:
• Services—A service is a name that identifies a task. The Access Server receives requests for a
service. You associate a service with a real-time job. The real-time job contains the real-time
processing loop that can process requests for this service and generate a response.
• Service providers—A service provider is the engine process that performs a service; the service
provider completes the tasks in a real-time job. A service provider is controlled by a Job Server. A
Job Server can control several service providers—each service provider is a unique process instance.
The Access Server uses services and service providers to process message requests. The following
is an example:
1.
An external application sends a request to the Access Server.
2.
The Access Server determines the appropriate service for the request.
3.
The Access Server finds the associated service providers and dispatches the request to the next
available service provider.
4.
Under the control of a Job Server, that service provider completes the processing for the request.
A different Job Server might control each service provider.
The Access Server manages the entire set of service providers, implementing configuration changes
and telling the appropriate Job Servers to start and stop service providers. At a prescribed interval, the
Access Server updates service providers, balancing loads and implementing configuration changes.
To balance loads, the Access Server monitors requests for services to ensure that no service provider
is over-used or under-used. Based on the number of requests for a service, the Access Server tells
Job Servers to start or stop service providers.
To support real-time jobs, you must:
2010-12-0263

Administrator
• Create any number of Access Servers using the Server Manager utility, then add a connection to
each local or remote Access Server using the Management node in the Management Console
Administrator.
• In the Real-Time node of the Administrator, create a service for each real-time job under each
Access Server's node.
• Create one or more service providers for each service.
• Start the services.
• Monitor the services.
Related Topics
• Creating services and service providers
• Starting and stopping services
• Monitoring services
2010-12-0264

Administrator
3.6.2 Configuring and monitoring real-time services
To enable an Access Server to support real-time jobs, you must configure and monitor real-time services
and service providers for it.
• Configure services by specifying a real-time job and other operational parameters.
• Configure service providers by specifying a Job Server and indicating the maximum and minimum
number of instances that you want the Job Server to control. Each service provider is a unique
process or instance controlled by a Job Server.
Related Topics
• Creating services and service providers
• Starting and stopping services
• Updating service providers
• Monitoring services
3.6.2.1 Creating services and service providers
In the Administrator, you create a service that processes requests for each real-time job. You also
create the service providers to perform that service. A service provider is the process that completes
the tasks in a real-time job.
3.6.2.1.1 To add a service
1.
Select Real-time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
2.
Click the Real-Time Services Configuration tab.
3.
Click the Add button.
4.
In the "Service configuration" section, enter information that describes this service.
DescriptionParameter
A unique name for this service.Service name
2010-12-0265

Administrator
Job name
DescriptionParameter
Click Browse Jobs to view a list of all the real-time jobs
available in the repositories that you connected to the Administrator. Select a job name to fill the service configuration
form.
Repository name
Processing retry count max
Enable job tracing
Startup timeout
Queuing timeout
Processing timeout
Recycle request count max
Logical name for a repository (used in the Administrator
only).
The number of times that the Access Server attempts to
restart a job that fails to respond.
A flag that indicates whether the service will write trace
messages.
Select Enable for the job to write trace messages.
The maximum time that the Access Server waits for the
service to register after startup (in seconds).
The maximum time that the Access Server waits for the
service to process the request (in seconds).
The maximum time that the Access Server waits for a response from the service (in seconds).
The number of requests that the Access Server sends to a
given real-time service before automatically recycling the
flow.
System Configuration
If configured, select the system configuration to use when
executing this service.
This option is available only if there are system configurations defined in the repository. For more information, see
“Parameters” in the
Reference Guide
.
2010-12-0266

Administrator
DescriptionParameter
A flag that indicates whether the Access Server attempts
to automatically start this service when the Access Server
restarts.
Select Enable if you want to automatically start this service
Enable
when the Access Server restarts. This is the default setting.
If you clear the Enable option, when the Access Server
restarts, it does not automatically start this service. If you
manually attempt to start a disabled service, an error message appears in the Service's Status column.
5.
Add one or more job servers to start this service provider. In the "Service provider" section, click the
Add button to insert a new Job Server.
6.
In the Job Server list, select a Job Server to control the service provider. Job Servers are defined
by host name and port number.
You may not select a Job Server more than one time.
7.
In the Min instances and Max instances fields, enter a minimum and a maximum number of service
providers that you want this Job Server to control for this service.
8.
The job server is enabled by default. To configure but not start the service providers controlled by
this Job Server, select the checkbox next to the Job Server, and click the Disable button.
9.
To add a substitution parameter, click the Add Overridden Parameter link.
10.
From the drop-down list, select the substitution parameter to override, and enter the override value.
11.
Click Apply.
The Administrator updates the configuration parameters for this service. These configuration
parameters apply to all providers of this service.
When you are ready for the Access Server to process requests, start the service.
Related Topics
• Service startup behavior
• High-traffic behavior
• Response time controls
• To start a service
• Reference Guide: Objects, Batch Job, Parameters
3.6.2.1.2 To add or change a service provider for a service
1.
Select Real-time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
2.
Click the Real-Time Services Configuration tab.
2010-12-0267

Administrator
3.
Click the name of the service for which you want to change the service provider.
4.
In the "Service provider" section, click the Add button.
5.
In the Job Server list, select a Job Server to control the service provider. Job Servers are defined
by host name and port number.
You may not select a Job Server more than one time.
6.
In the Min instances and Max instances fields, enter a minimum and a maximum number of service
provider instances that you want this Job Server to control.
7.
The job server is enabled by default. To configure but not start the service providers controlled by
this Job Server, select the checkbox next to the Job Server, and click the Disable button.
8.
Click the Apply button.
If the service has already started, the Access Server adds this service provider to the available list
when it next updates the service providers.
If the service has not yet started, the Access Server starts enabled service providers when the
service starts.
Related Topics
• Updating service providers
3.6.2.1.3 To set the service provider update interval
The Provider update interval for services option sets the time interval, in seconds, between service
provider updates. Valid values range from 10 to 120 seconds. The default is 30 seconds. When updating
service providers, the Access Server balances loads and implements any configuration changes you
have applied to a service provider.
If the provider update interval is too small, performance can decrease because the Access Server must
frequently check for events and collect statistics. It's recommended that you set the Provider update
interval for services to 30 seconds. On systems with heavy loads and production systems with fewer
start and stop events, you can increase the interval.
1.
Select Real-Time > Access Server > Status.
This is the time interval, in seconds, between service provider updates. Valid values range from 10
to 120 seconds. The default is 30 seconds. When updating service providers, the Access Server
balances loads and implements any configuration changes you have applied to a service provider.
If the provider update interval is too small, performance can decrease because the Access Server
must frequently check for events and collect statistics. It's recommended that you set the Provider
update interval for services option to 30 seconds. On systems with heavy loads and production
systems with fewer start and stop events, you can increase the interval.
2.
Click the Access Server Configuration tab.
3.
Enter the desired Provider update interval for services.
Related Topics
• Updating service providers
2010-12-0268

Administrator
3.6.2.2 Starting and stopping services
After you create the required services and service providers, you can start them. After you start a service
or service provider, SAP BusinessObjects Data Services ensures that it continues to run. You can also
use the Administrator to stop a service (such as for maintenance). Similarly, use the Administrator to
remove, enable, or disable services and service providers.
3.6.2.2.1 To start a service
1.
Select Real-Time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
2.
In the Real-Time Services Status tab, select the check box next to the service or services that you
want to start.
3.
Click Start.
The Access Server starts the minimum number of service providers for this service.
3.6.2.2.2 To enable a service
1.
Select Real-Time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
2.
Click the Real-Time Services Configuration tab. The table of services displays the status in the
Enabled column.
3.
Select the check box next to the service or services that you want to enable.
4.
Click the Enable button.
The Access Server enables the minimum number of service providers for this service, and the
"Enabled" column displays Yes.
This change does not start the service. Instead, the service is enabled the next time that the Access
Server attempts to start the service, such as after the Access Server restarts.
3.6.2.2.3 To disable a service
1.
Select Real-Time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
2.
Click the Real-Time Services Configuration tab. The table of services displays the status in the
Enabled column.
3.
Select the check box next to the service or services that you want to disable.
4.
Click the Disable button.
This change does not have an immediate effect on the service. Instead, the service is disabled the next
time that the Access Server attempts to start the service, such as after the Access Server restarts. If
you attempt to start a disabled real-time service, an error message displays in the service's status.
3.6.2.2.4 To abort or shut down a service
1.
Select Real-Time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
2010-12-0269

Administrator
2.
In the Real-Time Services Status tab, select the check box next to the service or services that you
want to abort or shut down.
DescriptionOption
Abort
Shuts down all service providers for this service without waiting for them to
complete processing. The Access Server responds to current and new requests
for this service with an error.
Shutdown
Shuts down all service providers for this service after they complete processing
any current requests. The Access Server responds to new requests for this
service with an error.
3.
Click Abort or Shutdown.
Related Topics
• To start a service
• To disable a service
3.6.2.2.5 To remove a service
1.
Select Real-Time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
2.
Click the Real-Time Services Configuration tab.
3.
Select the check box next to the service or services that you want to remove.
4.
Click Remove.
The Administrator stops processing this service. The Access Server shuts down each of the service
providers defined for this service and removes the service from the list.
3.6.2.2.6 To remove, enable, or disable a service provider
1.
Select Real-Time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
2.
Click the Real-Time Services Configuration tab.
3.
If you want to change a Job Service's service providers, select the check box next to a Job Server.
4.
Click one of the buttons below the list of Job Servers to perform the appropriate action:
2010-12-0270

Administrator
DescriptionOption
Enable
Start the service providers controlled by the selected Job Servers. Each Job
Server starts the minimum number of service providers. The Access Server
now includes the selected Job Servers in the set of available service providers.
If a Job Server is already enabled, this choice has no effect.
Remove
Discontinue using the service providers controlled by the selected Job Servers
to process requests for this service. The Access Server shuts down the service
providers and removes the Job Server from the list.
5.
Shut down the service providers controlled by the selected Job Servers. The Access Server finishes
processing any current requests and no longer includes the selected Job Servers in the set of service
providers available to process requests for this service.
The Administrator completes this action during the next service provider update.
Related Topics
• Updating service providers
3.6.2.2.7 To restart a service provider
1.
Select Real-Time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
2.
Select the service that you want to restart the service provider for. The "Service Provider Status"
page opens.
Note:
Select Restart only if the service providers controlled by this Job Server are currently enabled. To
verify the status, select the Real-Time Services Configuration tab and view service provider status
in the Job Servers for Service section.
3.
Click Restart.
The Administrator completes this action during the next service provider update. The Administrator
shuts down any service providers controlled by the selected Job Servers and immediately restarts
the minimum number of service providers. For example, you might restart a service provider after
a computer running its Job Server reboots following a crash.
3.6.2.3 Updating service providers
At a specified provider update interval, the Access Server updates service providers. When updating
service providers, the Access Server balances the work load—starting or stopping service providers
as necessary—and implements other events that you initiated since the last update.
2010-12-0271

Administrator
When balancing the work load, the Access Server checks the number of requests in a service queue
and the minimum idle time for a service. If the number of requests in a service queue is greater than
the number of service providers started, the Access Server tries to start a new service provider.
Conversely, if the minimum idle time for a service is more than 10 minutes, the Access Server will shut
down a service provider. However, the number of service providers cannot exceed the maximum number
of instances configured nor can it be less than the minimum number of instances configured.
When implementing events that you initiated, the Access Server does the following:
• Enables service providers
• Disables service providers
• Reconfigures service providers
• Restarts service providers
• Adds service providers
• Removes service providers
Related Topics
• To set the service provider update interval
3.6.2.4 Monitoring services
Use the Administrator to monitor services. With the Administrator you can do the following:
• View service status—From the Access Server Status page or the Real-Time Services Status page,
view whether a service is running or not. Based on this information, you can begin troubleshooting
problems.
• View service provider status—From the Real-Time Services Status page, click a service name to
view:
• The statistics for a particular service.
• Detailed statistics about each service provider. Using this information, you can monitor and
evaluate system performance.
• The status of all service providers in that service.
• View logs—The Access Server node provides access to current and historical service provider trace
and error logs.
Related Topics
• To view the status of services
• Service statistics
• Service provider statistics
• To view the statistics for a service provider
• To view the logs for a service provider
2010-12-0272

Administrator
3.6.2.4.1 To view the status of services
1.
Select Real-Time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
The Administrator opens the Real-Time Services Status page. For each service, this page shows
the overall status and statistics about the number of available service providers and the number of
started service providers.
2.
Verify that the services are working.
DescriptionIndicator
A green icon indicates that the service is operating properly.
A yellow icon indicates that some aspect of the service is not working,
and that the Access Server is attempting to reestablish the service
using error handling.
A red icon indicates that one or more aspects of the service is not
working, and the Access Server cannot reestablish the service.
3.
If a service shows a yellow or red status, click the service name to see more information.
Related Topics
• Service statistics
• Troubleshooting the Administrator
3.6.2.4.2 To view the statistics for a service provider
1.
Select Real-Time > Access Server > Real-Time Services.
2.
Click the name of the service.
This page shows the overall statistics for the service, the service providers for the service (listed by
Job Server), and the status of each service provider. Start a service to see its service provider status
information.
3.
Under Service Provider Status Information, click the Process ID of a service provider to view its
statistics.
The Administrator opens the Service Provider Status page.
Under Service Provider Status Information, the page shows the statistics for this service provider.
Related Topics
• Service provider statistics
2010-12-0273

Administrator
• To view the logs for a service provider
3.6.3 Creating and monitoring client interfaces
A client is an external application that communicates with SAP BusinessObjects Data Services through
the Access Server.
There are two types of client interfaces in the Administrator:
• Remote Function Call (RFC) clients
• Message broker clients
Configure RFC clients in the Administrator for real-time jobs that use SAP IDocs. To support these jobs,
create an RFC client interface and attach IDoc configuration information to it.
SAP BusinessObjects Data Services creates message broker client interfaces when communication
occurs between the Access Server and an external application that uses SAP BusinessObjects Data
Services message client libraries. To monitor message statistics, view the message broker clients of
each Access Server as needed.
This section describes configuration and monitoring for each type of client.
For more information about using the Message Client library, see the
Services Integrator's Guide
.
SAP BusinessObjects Data
3.6.3.1 RFC clients
You can configure IDoc message sources in the Administrator as well as in the Designer. You can
configure other IDoc sources and targets using the Designer.
Note:
Using the Administrator, create a service for your real-time job that contains an IDoc as a message
source before you configure an RFC client.
An RFC client uses the SAP RFC protocol to communicate with the Access Server. An RFC client
requires connection information so that an Access Server can register to receive IDocs from an SAP
application server. An RFC client can process one or more IDoc types. An RFC client specifies which
service will process a particular IDoc type and whether or not the RFC client connection can process
an IDoc type in parallel.
The process of creating an RFC client interface for IDocs has two parts:
• Adding an RFC client
2010-12-0274

Administrator
• Adding IDoc configurations to an existing RFC client
Configure one RFC client per Access Server. This means that you can process IDocs from one instance
of SAP. To process IDocs from more than one instance, configure more than one Access Server.
Note:
SAP application function modules are responsible for IDoc processing. In SAP BusinessObjects Data
Services, the RFC client might fail if multiple IDocs are sent from SAP and you previously set the SAP
packet size to 1. Therefore:
• Do not enable the option of immediate IDoc dispatch in SAP unless the volume of produced IDocs
is very low (no more than one IDoc per minute).
• For batch processing of IDocs, the packet size should never be smaller than 5 or larger than 1000.
The following table provides estimates for this parameter:
Packet sizeIDocs per dayIDoc Processing Volume
51 to 300Light
20301 to 1000Medium
For more information, see the
SAP BusinessObjects Data Services Supplement for SAP
3.6.3.1.1 Adding an RFC client
1.
Select Real-time > Access Server > Client Interfaces.
2.
Click the Client Interface Configuration tab.
3.
Click Add.
The Administrator opens the RFC Client Configuration page.
4.
Enter the client configuration information.
DescriptionField
The registered server program ID from transaction SM59.RFC program ID
User name
Password
The user name through which SAP BusinessObjects Data Services connects to this SAP application server.
The password for the user account through which SAP BusinessObjects Data Services connects to this SAP application server.
80301 to 1000Heavy
800more than 5000Very Heavy
.
SAP application server name
The domain name or IP address of the computer where the SAP
application server is running.
The SAP application client number.Client number
2010-12-0275

Administrator
DescriptionField
The SAP application system number.System number
SAP gateway host name
The domain name or IP address of the computer where the SAP
RFC gateway is located.
The TCP/IP service name for the SAP application server gate-
SAP gateway service name
way. Typically, this value is SAPGW and the system number.
It can also be a service number, for example 3301.
Select to use an sapnwrfc.ini file, which overrides the datastore
Use sapnwrfc.ini
settings associated with this RFC client. The default location to
place the sapnwrfc.ini file is in the current directory of the process being executed (%LINK_DIR/bin).
Destination name
5.
Click Apply.
For more information, see the
SAP BusinessObjects Data Services Supplement for SAP
If using an sapnwrfc.ini file, enter the destination name to reference.
Related Topics
• Supplement for SAP: Using the sapnwrfc.ini file
.
3.6.3.2 Adding IDoc configurations to an RFC client
After you create an RFC client, you can list the IDoc types that you want to receive.
3.6.3.2.1 To add an IDoc configuration to an RFC client
1.
Select Real-time > Access Server > Client Interfaces.
2.
Click the Client Interface Configuration tab.
3.
Click the name of an existing RFC client interface.
The RFC Client Configuration page opens.
4.
Click the Supported IDocs link.
5.
Click Add.
6.
Enter IDoc information:
a. In the IDoc Type box, enter the IDoc type that this SAP application server will send to the Access
Server.
b. In the Service Name box, enter the name of the service that will process this IDoc.
2010-12-0276

Administrator
The service identifies the job that processes this IDoc.
c. If you want the Access Server to read IDocs (of this type and from the specified SAP source) in
parallel, check the Parallel Processing check box.
Real-time services that contain an IDoc message source can be processed one at a time or in
parallel. The Parallel Processing option allows you to increase the number of IDoc source
messages processed per minute for the IDoc type specified. This option is disabled by default.
The option allows the Access Server to send an IDoc to a service queue (where it waits for a
service provider) and continue with the next IDoc without waiting for reply. The maximum number
of outstanding IDoc requests in the queue is the number of IDocs received or four, whichever is
smaller.
Note:
Where a strict IDoc processing sequence is required, do not use the Parallel Processing option.
7.
Click Apply.
8.
(Optional) Select Real-time > Access Server > Client Interfaces.
9.
From the Client Interface Status page, select the check box next to the new RFC client and click
Start.
The Administrator starts the RFC client. A green indicator signifies that the client is running. Detailed
status information is provided in the Status column.
Related Topics
• Configuring and monitoring real-time services
3.6.3.2.2 To close connections to an RFC client interface
1.
Select Real-time > Access Server > Client Interfaces.
2.
Select the check box next to the RFC client you want to disconnect.
If you choose Shut down, the Access Server allows the clients to finish processing any active
requests before closing the connection. The Access Server responds with an error to any new
requests that arrive during that interval.
If you choose Abort, the Access Server closes the connection to the client without responding to
requests currently being processed.
3.
Click Shut down or Abort.
3.6.3.3 Message Broker clients
A Message Broker client uses an XML message to communicate with an Access Server.
Message Broker clients include:
2010-12-0277

Administrator
• External applications
• Adapters
• Service providers
Use the Administrator to monitor Message Broker clients.
3.6.3.4 Monitoring client interfaces
From the Client Interface Status page, you can view the overall status of all client connections.
3.6.3.4.1 To view the overall status of client connections
1.
Select Real-time > Access Server > Client Interfaces.
2.
Verify that the RFC client connections are working.
DescriptionIndicator
A green icon indicates that each client of this type has an open connection with
Access Server.
A yellow icon indicates that at least one client of this type is disconnecting.
A red icon indicates that the Access Server could not reserve the specified port to
listen for client requests.
If an RFC client interface has a red status:
a. View the Status column and click the name of the client to view statistics about the particular
client connection with a problem.
b. If you want to restart, abort, or shut down a client interface, click the Back button in the navigation
bar. The Administrator returns to the Client Interface Status page.
c. Click Start, Abort, or Shutdown.
Related Topics
• Finding problems
3.6.3.4.2 To monitor Message Broker clients
Select Real-time > Access Server > Client Interfaces.
2010-12-0278

Administrator
Under Message Broker Clients, this page lists each message broker client that has registered with
the Access Server along with statistics for that client.
Note:
The first client in this list is the Administrator. You registered with the Access Server when you added
connection information to the Administrator.
Message broker client interface information includes:
DescriptionItem
The name of the client.Name
Time Connected
Last Message Received
Last Message Sent
Received Messages
Sent Messages
3.7 Real-Time Performance
About this section
This section discusses the Access Server parameters, statistics for services and service providers, and
how to tune the performance of services and service providers.
The total time that this client has been connected to the Access Server.
The length of time since the Access Server has received a
message from this client.
The length of time since the Access Server has sent a message to this client.
The number of messages that the Access Server has received
from this client.
The number of messages that the Access Server has sent
to this client.
Related Topics
• Configuring Access Server output
• Service configuration parameters
• Service statistics
• Service provider statistics
• Using statistics and service parameters
2010-12-0279

Administrator
3.7.1 Configuring Access Server output
You can configure the Access Server to control its operation and output such as sending specific event
information to its trace log.
SAP BusinessObjects Data Services installation includes a server configuration utility called the Server
Manager. The Server Manager allows you to view and change the following Access Server information:
DescriptionOption
The location of the configuration and log files for this instance of the Access
Directory
Server.
Do not change this value after the initial configuration.
Communication Port
Parameters
Enable Access
Server
The port on this computer the Access Server uses to communicate with the
Administrator and through which you can add additional configuration information to an Access Server.
Make sure that this port number is not used by another application on this
computer.
Command-line parameters used by the Data Services Service to start this
Access Server.
For development, consider including the following parameters:
-P -T16
where -P indicates that trace messages are recorded, and -T16 indicates
that the Access Server collects events for services and service providers.
These parameters are described in the next table.
An option to control the automatic start of the Access Server when the Data
Services Service starts.
3.7.1.1 To configure an Access Server
2010-12-0280

Administrator
1.
Select Start > Programs > SAP BusinessObjects Data Services XI 4.0 > Data Services Server
Manager.
2.
In the Server Manager, click Edit Access Server Config.
The Access Server Configuration Editor opens.
3.
Click Add to configure a new Access Server or select an existing Access Server, then click Edit to
change the configuration for that Access Server.
4.
Make the appropriate changes in the Access Server Properties window.
5.
Click OK to return to the Access Server Configuration Editor.
6.
Click OK to return to the Server Manager.
7.
Click Restart to stop and start the Data Services Service with the new Access Server configuration.
The following parameters are available to control the operation and output of an Access Server:
DescriptionParameter
-A
-C
-H
-P
-Rroot_directo
ry
-Tvalue
Specifies the communication port for an Access Server. The default value is
-A4000.
Disables display output.
Prints the parameter list to the console.
Enables trace messages to the console and log.
Indicates the location of the Access Server directory.
Determines the type of tracing information displayed in the console and the
Access Server log. Use any value or any combination of values:
1
system
real-time service flow2
client4
transaction8
service16
2010-12-0281

Administrator
DescriptionParameter
administration64
request128
For example, to enable tracing for both system-level and service-level operations, include the value 17 after the T parameter.
-V
-VC
-X
Displays the version number of the Access Server.
Displays communication protocol and version number.
Validates the Access Server configuration without launching the Access Server.
The -A and -R parameters can also be set using the Server Manager.
The -P and -T parameters can be set using the Administrator. Select Real-Time > Access Server
> Logs-Current, and click the Access Server Log Configuration tab.
3.7.2 Service configuration parameters
Each service contains configuration parameters that control how the Access Server dispatches requests
to the assigned real-time job. These parameters determine how the system handles errors that occur
during operation.
Often, requirements during development differ from requirements during production. Therefore, the
values of your configuration parameters differ during development and production. To ensure that the
system works as expected, test the values before committing the Access Server configuration to
production use.
Parameters control different categories of Access Server operation:
• Service startup behavior
• High-traffic behavior
• Response time controls
Related Topics
• To add a service
• Service startup behavior
2010-12-0282

Administrator
• High-traffic behavior
• Response time controls
3.7.2.1 Service startup behavior
Use two parameters to configure how the Access Server starts service providers associated with a
particular service:
• Startup timeout—The maximum time that the Access Server waits for a flow (service and its
providers) to register after startup.
• Recycle request count max—The number of requests that the Access Server sends to a given
flow before automatically recycling.
When the Access Server starts, it immediately starts the service providers for each service. If you want
the Access Server to start more than one instance of a service to process a particular type of message,
you must define more than one service provider for the service.
The Job Servers launch the jobs, which in turn initiate their corresponding real-time services. The first
operation of each real-time service is to register with the Access Server.
If an error occurs and a real-time service fails to register, the Access Server instructs the Job Server
to restart the job. The Access Server waits the length of time that you configure as the startup timeout
before instructing the Job Server to start the job again. The startup timeout is in seconds. The Access
Server continues to instruct the Job Server to restart the job until the real-time service registers.
You can also control how many requests a particular service provider processes. After a provider
processes the number of requests specified by the Recycle request count max parameter, the Access
Server automatically recycles the service provider—that is, the Access Server automatically stops the
2010-12-0283

Administrator
current instance of the real-time service and starts a new instance of that service. Setting this parameter
to a higher value increases the time that the service provider is available to accept requests for
processing. Setting this parameter to a lower value refreshes any data cached in the real-time service
more often.
3.7.2.2 High-traffic behavior
Use the Queuing Timeout parameter to specify the maximum amount of time the client application must
wait for a request to be processed.
If the number of requests the Access Server receives for a particular service exceeds the number of
registered service providers that can process those requests, the Access Server queues the requests
in the order they are received. When a service provider completes processing a request and responds
to the Access Server, the Access Server dispatches the next request in the queue for that service to
the open service provider.
If there are many requests and the queue causes requests to exceed the queuing timeout, the Access
Server removes the oldest request from the queue and responds to the client with an error indicating
that the request failed. You can use the queuing timeout to ensure that the client receives a timely
response, even during high-traffic periods.
The queuing timeout is in seconds.
A service experiences high traffic when the available resources cannot process the received requests
efficiently. High traffic occurs when the time messages wait to be processed exceeds the time required
to process them.
Related Topics
• Using statistics and service parameters
2010-12-0284

Administrator
3.7.2.3 Response time controls
Use two parameters to configure how long the Access Server waits for responses from service providers
for a particular service:
• Processing timeout
• Processing retry count max
After the Access Server sends a request to a service provider to process, the Access Server waits for
the response. If the response does not arrive within the specified processing timeout, the Access Server
sends the request to another waiting service provider. The Processing timeout is in seconds.
If the first attempt fails, the Access Server will attempt to process the request as many times as you
specify in the Processing retry count max parameter.
If Processing retry count max is set to zero, the maximum response time is equal to the queuing
timeout plus the processing timeout.
3.7.3 Service statistics
The Real-Time Services Status page for a particular service shows overall statistics.
2010-12-0285

Administrator
DescriptionStatistic
Number of processed requests
Number of requests in queue
Maximum queuing time (milliseconds)
Average queuing time (milliseconds)
Queuing timeout
Maximum processing time
(milliseconds)
The number of requests for this service from any client that the Access
Server received and responded to since the last time the Access
Server started.
The number of messages that the Access Server has received from a
client for this service but has not sent to a service provider for processing.
This value reflects the current state of the Access Server.
The maximum time any request for this service waited after the Access
Server received the message and before the Access Server sent the
request to a service provider for processing.
The average time that requests for this service waited after the Access
Server received the request and before the Access Server sent the
request to a service provider for processing.
The number of requests to which the Access Server replied to the client
with an error indicating that there was no service provider available to
process the request.
The maximum time required to process a request for this service. It is
the difference between the time the Access Server sent the request to
a service provider and the time that the Access Server responded to
the client. The processing time does not include time the request spent
in a queue waiting to be sent to a service provider.
Average processing time (milliseconds)
Processing timeouts
3.7.4 Service provider statistics
The Service Provider Status page shows the statistics for an instance of a real-time service.
The average time required to process a request for this service. It is
the difference between the time the Access Server sent the request to
a service provider and the time that the Access Server responded to
the client. The processing time does not include time the request spent
in a queue waiting to be sent to a service provider.
The number of requests that the Access Server sent to a service
provider and did not receive a response before exceeding the processing timeout. These requests are either successfully processed by another service provider, or if they are left unprocessed beyond the time
indicated by the queuing timeout parameter, the Access Server returns
an error to the client.
2010-12-0286

Administrator
When SAP BusinessObjects Data Services measures a statistic "from the start," the value does not
restart when the Access Server restarts the service provider. The value restarts when the Access Server
restarts.
When the software measures a statistic "for the current service provider," the value restarts when the
Access Server restarts the service provider, either due to error or when the service provider reaches
the maximum number of requests defined for the service.
DescriptionStatistic
Max processing time (milliseconds)
Average processing time (milliseconds)
Processed requests (for the current
service provider)
Processed requests (since start)
Error replies received from the start
Communication errors encountered from
the start
The longest time it took between when the Access Server
sent a message to this service provider and when the service
provider returned a response.
The average time it took between when the Access Server
sent a message to this service provider and when the service
provider returned a response.
If you are running more than one service provider for this
service, compare this statistic with the same statistic from the
other instances. If this instance is significantly different, look
for processing constraints on the computer where this instance runs.
The number of requests that the Access Server sent to this
service provider to which the service provider responded.
The number of requests that the Access Server sent to this
service provider to which the service provider responded.
The number of requests that the Access Server sent to this
service provider to which the service provider responded with
an error.
The number times that the communication link between the
Access Server and this service provider failed.
Timeout errors encountered from the
start
Service provider connections (restarts)
from the start
The number of times the Access Server sent requests to this
service provider and did not receive a response within the
time specified by the processing timeout.
The number of times the Access Server restarted this service
provider when it did not receive a response from the service
provider.
2010-12-0287

Administrator
DescriptionStatistic
The last time of a successful flow launch
The system time when the Access Server last started the
real-time service associated with this service provider. If the
Access Server never successfully started an instance of this
service provider, the value is "N/A."
This time is from the computer running the Access Server.
Time since start attempt
The amount of time since the Access Server last attempted
to start this service provider. This value reflects successful
and unsuccessful attempts.
Time since last request start
The amount of time since the Access Server last sent a request to this service provider. This value reflects successful
and unsuccessful attempts.
3.7.5 Using statistics and service parameters
You can use the statistics for a service to tune the service parameters.
2010-12-0288

Administrator
DescriptionStatistic
Average and maximum processing time
Maximum queuing time
If the average or maximum processing time for a service provider is
equal or close to the processing timeout value resulting in processing
timeouts, consider increasing the processing timeout parameter for the
service.
In a tuned system, the maximum and average queuing times should be
close together, the difference being an indication of the traffic distribution
for this service. Values should not approach the value of the queuing
timeout parameter listed for the service.
If the maximum queuing time for a service provider is equal or close to
the queuing timeout parameter and there are queuing timeouts listed,
consider the following changes:
• Increase the queuing timeout parameter for the service.
• Increase the number of service providers available, either controlled
by the same Job Server host or by a different Job Server.
If you find that the average time in the queue is longer than the average
processing time, the traffic for this service is too high for the resources
provided. Consider running multiple service providers to process the
same message type. You can add the same job many times in the service
list, or you can add the same job controlled by a different Job Server on
a separate computer to the service list.
If you find that the average queuing time is growing, consider increasing
the queuing timeout or adding processing resources.
Processing timeouts
If you see processing timeouts and service providers restarting successfully, consider increasing the number of processing retries allowed for
the service.
3.8 Profile Server Management
This section describes how to use the Administrator to manage the data in the profiler repository and
manage tasks on the profiler server.
The Data Profiler executes on a profiler server to provide the following data profiler information that
multiple users can view:
• Column analysis—This information includes minimum value, maximum value, average value,
minimum string length, and maximum string length. You can also generate detailed column analysis
such as distinct count, distinct percent, median, median string length, pattern count, and pattern
percent.
2010-12-0289

Administrator
• Relationship analysis—This information identifies data mismatches between any two columns for
which you define a relationship, including columns that have an existing primary key and foreign
key relationship.
You can execute the Data Profiler on data contained in databases and flat files. Databases include
DB2, Oracle, SQL Server, Sybase, and Attunity Connector for mainframe databases. See the
Notes
for the complete list of sources that the Data Profiler supports.
This section assumes that you have already installed SAP BusinessObjects Data Services, which
includes the Data Profiler.
Related Topics
• Designer Guide: Data Assessment, Using the Data Profiler
3.8.1 To define a profiler repository
Release
The Data Profiler repository is a set of tables that holds information about your data that the Data Profiler
generates.
1.
Create a database to use as your profiler repository.
The profiler repository can be one of the following database types: DB2, MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server,
or Sybase.
2.
Create a profiler repository with the Repository Manager.
Select Profiler in the Repository type option.
3.
Associate the profiler repository with a Job Server with the Server Manager.
Related Topics
• Administrator's Guide: Using the Repository Manager
• Administrator's Guide: Using the Server Manager on Windows
• Administrator's Guide: Using the Server Manager on UNIX systems
3.8.2 Configuring profiler task parameters
Set configuration parameters to control the amount of resources that profiler tasks use to calculate and
generate profiler statistics.
Note:
If you plan to use Detailed profiling or Relationship profiling, ensure that you use the Server Manager
to specify a pageable cache directory that:
• Contains enough disk space for the amount of data you plan to profile.
2010-12-0290

Administrator
• Is on a separate disk or file system from the system where SAP BusinessObjects Data Services is
installed.
Related Topics
• Administrator's Guide: Using the Server Manager on Windows
• Administrator's Guide: Using the Server Manager on UNIX systems
3.8.2.1 To configure profiler task parameters
1.
Select Management > Profiler Configuration to access the Profiler Configuration page.
2.
Keep or change the parameters values listed on the Profiler Configuration page.
The Profiler Configuration page groups the parameters into the following categories:
• Task execution parameters
• Task management configuration parameters
Related Topics
• Task execution parameters
• Task management configuration parameters
3.8.2.2 Task execution parameters
The Profiler Configuration page groups the Task execution parameters into subcategories Reading Data, Saving
Data, and Performance.
Task execution subcategory
AllProfiling sizeReading Data
DescriptionDefault valueParameter
The maximum number of rows to
profile.
You might want to specify a maximum number of rows to profile if
the tables you profile are very large
and you want to reduce memory
consumption.
2010-12-0291

Administrator
Task execution subcategory
Saving Data
Number of days to keep results
1Sampling rowsReading Data
100Number of distinct valuesSaving Data
100Number of patternsSaving Data
90
DescriptionDefault valueParameter
Profiles the first row of the specified
number of sampling rows.
For example, if you set Profiling
size to 1000000 and set Sampling
rows to 100, the Profiler profiles
rows number 1, 101, 201, and so
forth until 1000000 rows are profiled. Sampling rows throughout the
table can give you a more accurate
representation rather than profiling
just the first 1000000 rows.
The number of distinct values to
save in the profiler repository.
The number of patterns to save in
the profiler repository.
The number of days to keep the
profiler results in the profiler
repository.
The number of records to save in
100Number of records to saveSaving Data
the profiler repository for each attribute.
5000Rows per commitSaving Data
The number of rows to save before
a commit is issued.
The number of parallel processing
2Degree of ParallelismPerformance
threads that the profiler task can
use.
2File processing threadsPerformance
The number of file processing
threads for file sources.
3.8.2.3 Task management configuration parameters
The Profiler Configuration page groups the Task management configuration parameters into subcategories,
basic and advanced.
2010-12-0292

Administrator
Task management
subcategory
DescriptionDefault valueParameter
10Maximum concurrent tasksBasic
The maximum number of profiler
tasks to run simultaneously.
The number of days that must
elapse before a profiler task is rerun
for the same table or key columns
when the user clicks the Submit
option. The Submit option is on the
Submit Column Profile Request
and Submit Relationship Profile
Request windows in the Designer.
The default is 0, which is to always
0Refresh interval (days)Basic
rerun the profiler task when the user
clicks the Submit option. In other
words, there is no limit to the number of Data Profiler tasks that can
be run per day.
To override this interval, use the
Update option on the Profile tab of
the View Data window in the Design
er.
Advanced
Advanced
Invoke sleep interval (seconds)
Submit sleep interval (seconds)
5
10
2Inactive interval (minutes)Advanced
The number of seconds to sleep
before the Data Profiler checks for
completion of an invoked task.
Invoked tasks run synchronously,
and the Data Profiler must check for
their completion.
The number of seconds to sleep
before the Data Profiler attempts to
start pending tasks.
Pending tasks have not yet started
because the maximum number of
concurrent tasks was reached.
The number of minutes a profiling
task can be inactive before the Data
Profiler cancels it.
2010-12-0293

Administrator
3.8.3 Monitoring profiler tasks using the Administrator
You can monitor your profiler task by name in either the Designer or the Administrator.
On the Administrator, you can see the status of profiler tasks, cancel profiler tasks, or delete a profiler
task with its generated profile statistics.
1.
Expand the Profiler Repositories node.
2.
Click the profiler repository name.
3.
The Profiler Tasks Status window displays.
This status window contains the following columns:
DescriptionColumn
If you want to cancel a profiler task that is currently running, select this
check box and click Cancel.
Select
Status
Task Name
Last Update
Status Message
If you want to delete a profiler task and its profiler data from the profiler
repository, select this check box and click Delete.
If you click Delete on a running task, the Profiler cancels the task before
it deletes the data.
The status of a profiler task can be:
• Done—The task completed successfully.
• Pending—The task is on the wait queue because the maximum
number of concurrent tasks has been reached or another task is
profiling the same table.
• Running—The task is currently executing.
• Error—The task terminated with an error.
The name of the profiler task. The name is a link to the Profiler Task
Items report.
The names of the tables on which the profiler task was run.Description
The identification number for this profiler task instance.Run #
The date and time that this profiler task last performed an action (such
as submitted or attributes calculations completed for a column).
Is blank if the profiler task completed successfully. Displays an error
message if the profiler task failed.
4.
Click the task name to display the Profiler Task Items report, which displays the profiling type that
was done for each column:
2010-12-0294

Administrator
This Profiler Task Items report contains the following columns:
DescriptionColumn
The status for each column on which the profiler task executed. The
status can be:
• Done—The task completed successfully.
• Pending—The task is on the wait queue because the maximum
Status
number of concurrent tasks has been reached or another task is
profiling the same table.
• Running—The task is currently executing.
• Error—The task terminated with an error.
Item
Job Server
Profiling Type
Last Update
The column number in the data source on which this profiler task
executed.
The machine name and port number of the Job Server where the
profiler task executed.
The process ID that executed the profiler task.Process ID
Indicates what type of profiling was done on each column. The Profiling Type can be:
• Single Table Basic—Column profile with default profile statistics.
• Single Table Detailed—Column profile with detailed profile
statistics.
• Relational Basic—Relational profile with only key column data.
• Relational Detailed—Relational profile with data saved from all
columns.
The name of the datastore.Datastore
The name of the data source (table, flat file, or XML file).Source
The name of the column on which the profiler task executed.Column
The date and time that this profiler task last performed an action
(such as submitted or profile calculations completed for a column).
Status Message
Is blank if the profiler task completed successfully. Displays an error
message if the profiler task failed.
Related Topics
• Designer Guide: Data Assessment, Monitoring profiler tasks using the Designer
2010-12-0295

Administrator
3.9 RFC Server Management
Data Services uses the SAP RFC Server Interface for the following tasks:
• Scheduling SAP jobs
• Reading from SAP Open Hub destinations
• Loading SAP NetWeaver BW
• Viewing Data Services logs from SAP NetWeaver BW
This section describes how to use the RFC Server Interface in the Administrator.
To access the RFC Server Interface, in the Administrator expand the SAP Connections node and click
RFC Server Interface. Two tabs display: RFC Server Interface Status and RFC Server Interface
Configuration.
3.9.1 64-bit platform prerequisites
To use the RFC Server Interface on 64-bit UNIX platforms, first confirm that your environment is
configured correctly:
1.
Ensure that the 64-bit Java Development Kit (JDK) is installed.
2.
Ensure that SAP BusinessObjects Data Services is correctly installed with a supported web application
server.
3.
Export the JAVA_HOME environment variable, pointing to the location of the 64-bit JDK.
4.
Restart your web application server.
For the latest update of these configuration steps, see SAP Note 1394367.
3.9.2 Adding an RFC server interface
1.
Select SAP Connections > RFC Server Interface.
2.
Click the RFC Server Interface Configuration tab.
3.
Click Add.
The Administrator opens the RFC Server Configuration page.
4.
Enter the configuration information.
All options except the RFC Program ID, SAP Gateway Host Name, and SAP Gateway Service
Name must match the SAP Applications datastore settings.
2010-12-0296

Administrator
DescriptionField
RFC program ID
User name
Password
SAP application server name
SAP gateway host name
The registered server program ID in the SAP RFC destination
to which this RFC Server will connect.
The user name through which SAP BusinessObjects Data Services connects to this SAP application server. Use the same
user name used to create the SAP BW Source datastore.
The password for the user account through which SAP BusinessObjects Data Services connects to this SAP application server.
The domain name or IP address of the computer where the SAP
application server is running.
The SAP application client number.Client number
The SAP application system number.System number
The domain name or IP address of the computer where the SAP
RFC gateway is located.
The TCP/IP service name or service number for the SAP appli-
SAP gateway service name
cation server gateway. Typically, this value is SAPGW plus the
system number.
The number of TCP/IP connections to the SAP gateway host.SAP gateway connection count
5.
Click Apply.
The Administrator adds the RFC server interface definition and returns to the RFC Server Interface
Status page.
After adding the interface, you must manually start it from the RFC Server Interface Status page.
3.9.3 Starting or stopping an RFC server interface connection
After adding an interface, you must start it manually. To start the interface connection, on the RFC
Server Interface Status page, select the check box for the interface to start and click Start.
2010-12-0297

Administrator
To stop an interface connection:
1.
Select the check box for the RFC server to disconnect.
2.
Click Abort or Shut down.
• If you choose Abort, the RFC server closes the connection to SAP BW without responding to
requests currently being processed.
• If you choose Shut down, the RFC server finishes processing any active requests before closing
the connection. Any new requests to this RFC server will result in an error.
3.9.4 Monitoring RFC server interfaces
From the RFC Server Interface Status page (expand SAP Connections and click RFC Server Interface),
you can access the status, statistics, and logs for all interface connections.
3.9.4.1 Viewing the status of interface connections
The following tables describes the status icons.
DescriptionIndicator
A green icon indicates that each client of this type has an open connection with SAP
BW server.
A yellow icon indicates that at least one client of this type is disconnecting.
A red icon indicates that there was a problem starting the RFC server or processing
an SAP BW request.
If an RFC server interface has a red status, view the "Status" column and click the name of the interface
to view the log details.
To restart, abort, or shut down an interface, click the Back button in the navigation bar to return to the
RFC Server Interface Status page.
Related Topics
• Finding problems
2010-12-0298

Administrator
3.9.4.2 Monitoring interface statistics
The "RFC Server Interface Statistics" section lists each configured interface and statistics for that
interface:
DescriptionItem
The name of the RFC server interface.Name
Time connected
Last message received
Last message sent
Received messages
Sent messages
The total time that this interface has been connected to the
SAP BW server.
The length of time since the RFC server has received a
message from SAP BW.
The length of time since the RFC server has sent a message
to SAP BW.
The number of messages that the RFC server has received
from SAP BW.
The number of messages that the RFC server has sent to
SAP BW.
3.9.4.3 Viewing RFC server interface logs
You can view the last three logs for an interface, each of which is 500 Kb in size. To view the logs for
an interface, from the RFC Server Interface Status page, click the name of the interface. A page with
two tabs displays:
• RFC Server Log Viewer: This tab displays the most recent log for the interface with the log path
displayed at the top of the window.
• RFC Server History Log: This tab displays the previous two logs for the interface. Click a log name
to view it.
3.9.5 Removing one or more RFC server interfaces
2010-12-0299

Administrator
1.
Under the SAP Connections node, click RFC server Interface.
2.
On the RFC Server Interface Configuration tab, select the check box for one or more interfaces.
3.
Click Remove.
3.10 Adapters
About this section
This section describes how to add an adapter to the SAP BusinessObjects Data Services system, how
to start an adapter instance, and how to monitor an adapter's operation instances.
Related Topics
• Overview of adapters
• Adding and configuring adapter instances
• Starting and stopping adapter instances
• Monitoring adapter instances
3.10.1 Overview of adapters
An SAP BusinessObjects Data Services adapter is a Java program that allows SAP BusinessObjects
Data Services to communicate with front-office and back-office applications. Depending on the adapter
implementation, adapter capabilities include the ability to:
• Browse application metadata.
• Import application metadata into the repository.
• Move batch and real-time data between SAP BusinessObjects Data Services and information
resource applications.
Adapters can handle the following types of metadata: tables, documents, functions, outbound messages,
and message functions. Each of these can be used in real-time or batch jobs. Outbound messages
and message functions are the only objects that include operations.
An adapter can process several predefined operations. An operation is a unit of work or set of tasks
that the adapter completes. Operations include:
• Taking messages from an application and send them to a real-time service for processing, possibly
returning a response to the application.
• Taking messages from a real-time service and send them to an application for processing, possibly
returning a response to the real-time service.
2010-12-02100
 Loading...
Loading...