Page 1
FILE NO.
REFERENCE NO. TI5110LCD
Training Manual
Principle of LCD Display
CONTENTS
Pages
1. Construction of LCD Display ----------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 - 5
1-1 Principle of LCD Display ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2
1-2 Construction of LCD Display --------------------------------------------------------------------- 2 - 3
1-3 Main Component of LCD Display --------------------------------------------------------------- 4 - 5
2. Principle of Liquid Crystal --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6 - 8
2-1 Liquid Crystal --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6
2-2 Rubbing-process------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 6 - 7
2-3 Operation of Liquid Crystal ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 8
3. Principle of LCD --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9 - 11
3-1 Operation of Polarized Board for LCD Panel (Shutter)----------------------------------------- 9
3-2 Operation of Alignment Film------------------------------------------------------------------------- 10
3-3 Operation of LCD Panel ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 10 - 11
3-4 Transparent Electrode -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 11
4. Type of LCD Display Construction ------------------------------------------------------------ 12 - 13
4-1 Twisted Nematic (TN) Type -------------------------------------------------------------------- 12- 13
4-2 Super TN (STN) Type---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 12- 13
4-3 Triple STN (TSTN) Type / Film STN (FSTN) Type --------------------------------------- 12- 13
5. System of LCD Display ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 14 - 20
5-1 Dot-Matrix System ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 14
5-2 Colorization ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 15
5-3 Drive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 16
5-4 Passive Matrix System-------------------------------------------------------------------------- 16 - 17
5-5 Active Matrix System---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 18 - 19
5-6 Drive of Active Matrix System----------------------------------------------------------------- 19 - 20
6. Improvement Technology of LCD Display -------------------------------------------------- 21 - 27
6-1 Subject of LCD Display ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 21
6-1-1 Angle of View----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 21
6-1-2 Response Characteristic--------------------------------------------------------------------------- 21
6-2 Angle of View-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 22
6-3 Multi-Domain System --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 23
6-4 MVA (Multi-domain Vertical Alignment) System ----------------------------------------------- 24
6-5 IPS (In-Plain Switching) System ------------------------------------------------------------------- 25
6-6 Optically Compensated Film ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 26
6-7 OCB (Optically Compensated Birefringence) System ---------------------------------------- 26
6-8 Improvement of Response Speed ----------------------------------------------------------------- 27
6-8-1 Inpulse System--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 27
6-8-2 FFD (Feed Forward Driving) System----------------------------------------------------------- 27
7. Appendix ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 28 - 31
7-1 Backlight-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 28
7-2 LVDS Circuit--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 29
7-3 Block Diagram Example------------------------------------------------------------------------ 30 - 31
Page 2

-2-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
■ Construction of LCD Display
1. Construction of LCD Display
1-1 Principle of LCD Display
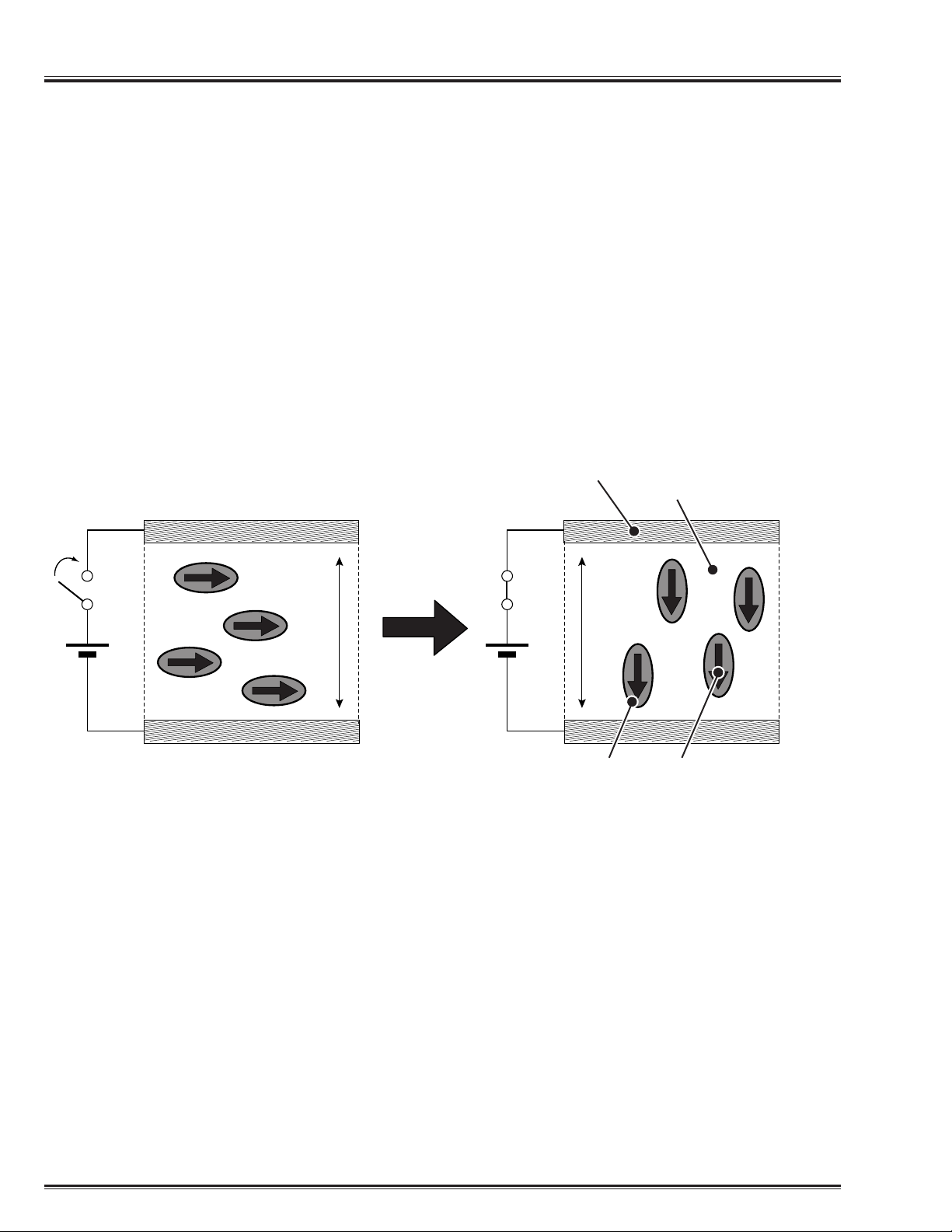
The LCD (Liquid Crystal Device) Display is used to display the electric signal, converted from picture
data similar to a CRT display. The transistor (TFT) switched by the electric signal changes the transmis-
sion to light in small picture elements (pixels) of the LCD. The LCD display makes the picture by grouping
these elements of each RGB color.
1-2 Construction of LCD Display
LCD Display
Liquid Crystal is packed between the board modules (TFT and Common) and the LCD panel (or LCD
shutter) is constructed. A back light is attached to the LCD panel for LCD Display.
Board Module (Common Electrode)
The Common Electrode consists of a polarized board, a color filter, and a transparent electrode on a
glass plate. An alignment film is formed on the transparent electrode.
Board Module (TFT Electrode)
The TFT Electrode consists of a polarized board and a transparent electrode (pixel electrode and drive
transistor) on a glass plate. An alignment film is formed on the transparent electrode.
Backlight
A fluorescent light is used for the Backlight.
✐ TFT:
Thin Film Transistor
✐ LCD Panel and LCD Shutter: They are the same things, but in the explanation LCD panel is used
for structure and LCD shutter is used for function.
Page 3
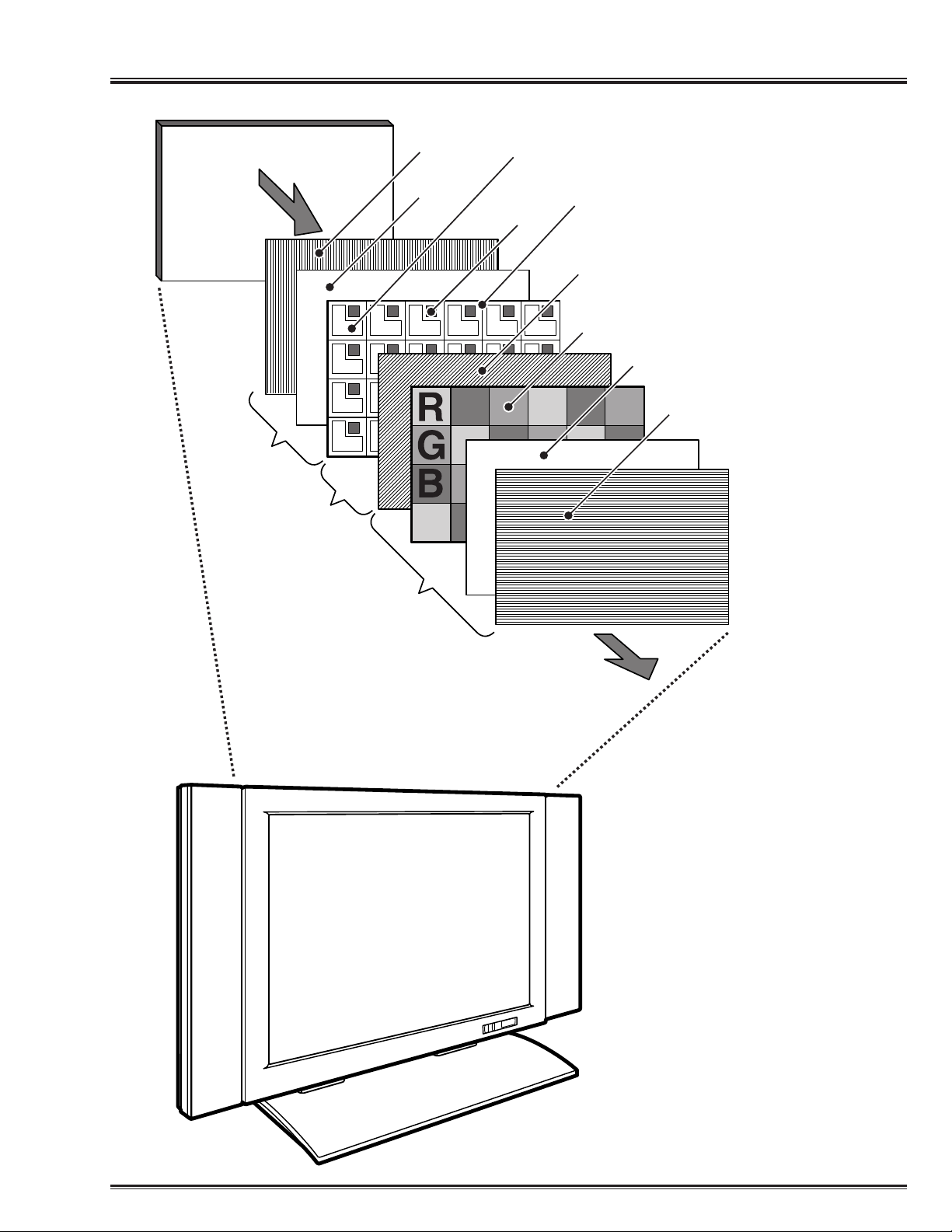
-3-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Construction of LCD Display
Note: Alignment film is not
shown in this figure.
Fig. 1 Construction of LCD Display
(Transparent Type TFT LCD)
Backlight
Board
Module
(TFT side)
Polarized
Board
Glass
Plate
Pixel
(Picture Element)
Transparent
TFT
Electrode
(Pixel, TFT)
Transparent
Electrode
(Common)
Color Filter
Glass
Plate
Polarized
Board
LCD Layer
Board Module
(Common side)
The light of each picture element is transmitted
by switching the drive transistor (TFT) on and off.
Page 4

-4-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Construction of LCD Display
1-3 Main component of LCD Display
LCD Shutter
Supplying voltage to the transparent electrodes between the pixel and common sides changes the
arrangement of liquid crystal. By assembling two polarized boards, the transfer of light from the backlight
can be controlled by the transparent ratio of the LCD Shutter.
Liquid Crystal
Liquid Crystal is a material whose state is between a solid and a liquid. It has both characteristics of
solids and liquids, and generally it is a white turbid liquid. Its molecules are normally arranged compara-
tively opaque and change to transparent with the application of voltage or heat.
Transparent Electrode (Film)
An LCD shutter is operated by supplying voltage derived from the video signal. Transparent film is used
for its electrode.
Alignment Film
This is a film for arranging liquid crystal molecules and is made of Polymid resin.
Polarized Board
The light with a specified direction passes through a polarized board.
Drive Transistor
The thin film transistor (TFT) is used to drive the LCD shutter of each pixel.
Color Filter
It is a filter with three colors (R, G, B) arranged for each pixel.
Backlight
Liquid crystal does not emit light. A light source is needed for display. The light source placed on the
reverse side of the LCD panel is called “Backlight.”
Page 5
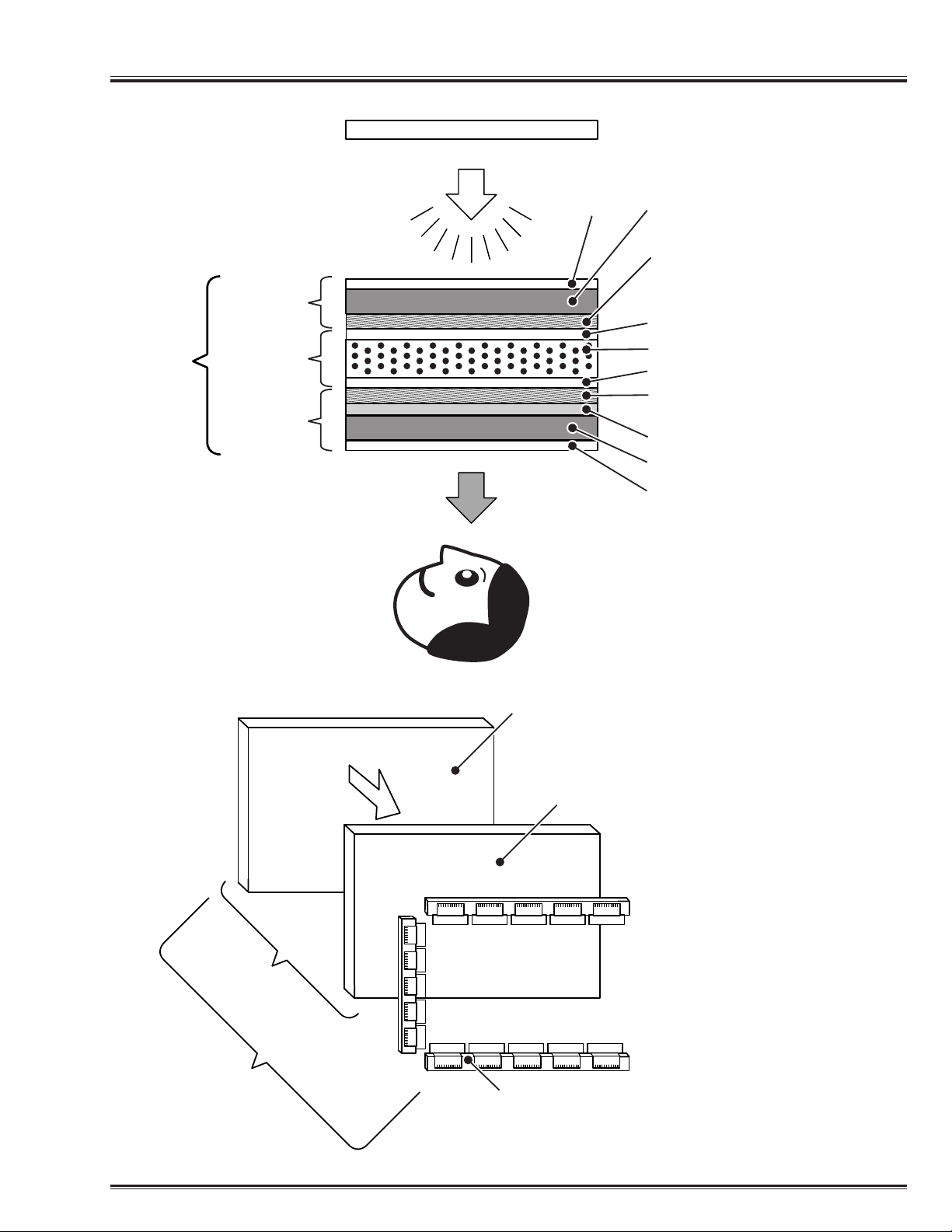
-5-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Construction of LCD Display
Fig. 2 Construction of LCD Display
(Cross Section)
Fig. 3 Assembly of LCD Display
Backlight
LCD
Shutter
Module
(Back)
LCD Layer
Module
(Front)
Polarized
Board
Glass
Plate
Transparent Electrode
(Pixel, TFT)
Alignment Film
Liquid Crystal
Alignment Film
Transparent Electrode
(Common)
Color Filter
Glass Plate
Polarized
Board
LCD
Display
LCD
Module
Backlight
LCD Panel
(LCD Shutter)
TFT Display
Drive Circuit
(with IC)
Page 6

-6-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
2. Principle of Liquid Crystal
2-1 Liquid Crystal
What is Liquid Crystal?
Liquid Crystal is a material whose state is between a solid and liquid. It has characteristics of both solids
and liquids, and generally is a white turbid liquid. Its molecules are normally arranged comparatively
opaque and change to transparent with the application of voltage or heat.
Almost all the materials consist of an organic compound taking the form of a slender stick or a flat plate.
There are three types of liquid crystal as shown in Fig. 4, and they depend on the construction and
arrangement of molecules.
Generally Nematic liquid crystal is used for the display apparatus.
(a) Smectic
Molecules are in layers and arranged parallel to each other. The center of gravity is arranged at random
in the layer.
(b) Nematic
Molecules are not in layers. They are arranged parallel. The center of gravity is able to move freely to the
major axis.
(c) Cholesteric
Molecules are in layers and arranged parallel. The arranging direction of the major axis for the neighbor-
ing layers is shifted gradually.
In order to use liquid crystal for display, it is necessary to regularly arrange the molecules of Nematic
(Rubbing-process).
2-2 Rubbing-process
After chemicals for arranging are put on the glass plate, they are hardened, and then the surface on the
plate is rubbed with a cloth to fix the direction of the gaps that are made. The arranging direction of mole-
cules is settled in the gaps.
This process is used to change the characteristics so the molecules that touch the rubbed surface are
arranged to the major axis of the rubbed direction.
This thin film on the glass plate is called “Alignment film.”
■ Principle of Liquid Crystal
Page 7
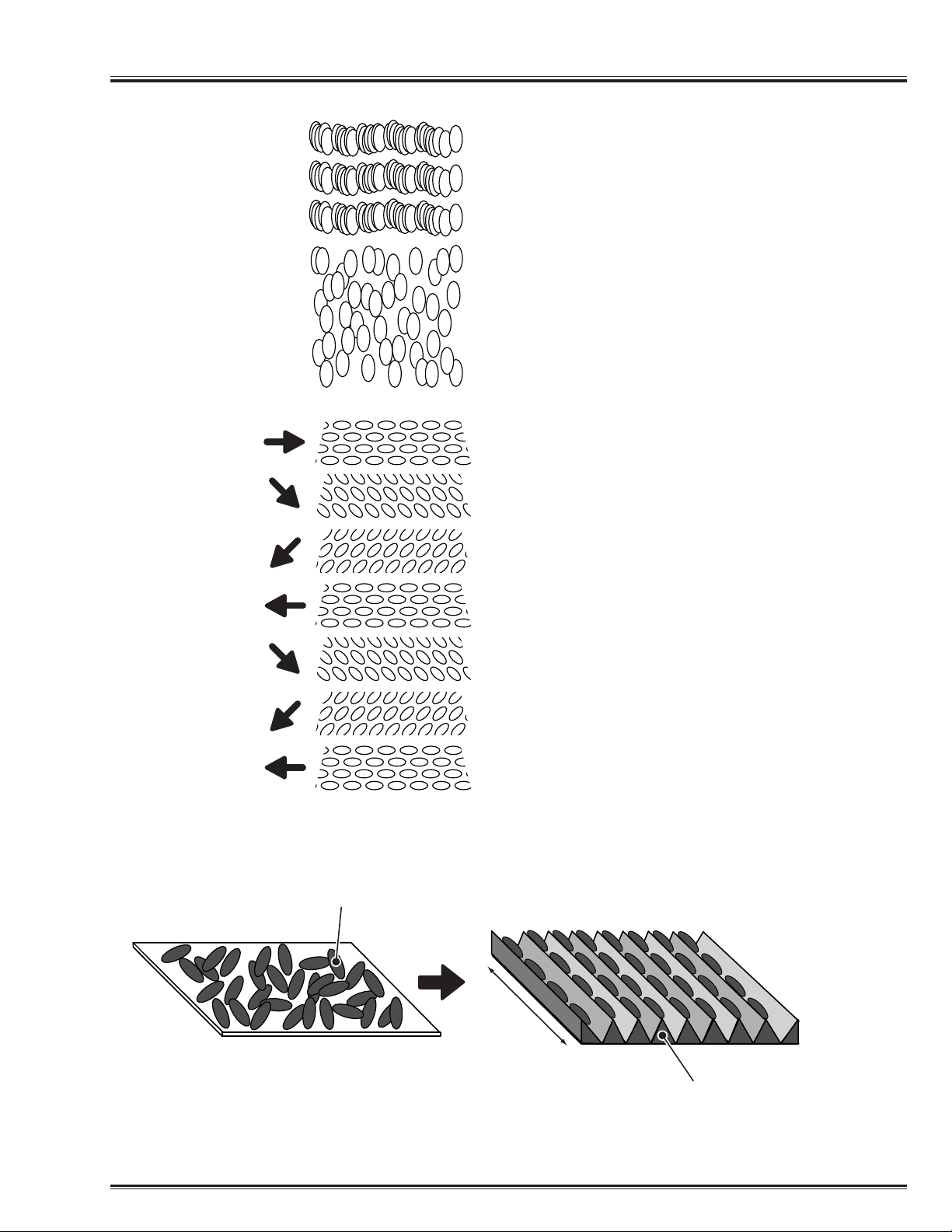
-7-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Principle of Liquid Crystal
Fig. 4 Liquid Crystal
(a) Smectic
(c) Cholesteric
(b) Nematic
Fig. 5 Rubbing-Process
Natural Condition
Liquid Crystal Molecule
Arranging
Rubbing
Direction
Alignment Film
Page 8
-8-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Principle of Liquid Crystal
2-3 Operation of Liquid Crystal
The chemistry substance required for liquid crystal material is one that reacts so that the arrangement
direction is changed according to an applied electric field.
In the LCD display, a liquid crystal is placed between two electrodes. When the voltage is supplied
between them, an electric field is generated in the liquid crystal, and liquid crystal molecules are moved
and arranged. The Backlight applied to the liquid crystal is either passed or blocked according to the
arrangement of the molecules.
If an electric field from an external source is applied to liquid crystal, electric dipoles will be generated
that will react to the intensity and direction of the electric field. Through the operation of these electric
dipoles and the electric field, the power changing direction of liquid crystal molecules is generated.
Therefore, according to an external electric field, liquid crystal molecules move and change direction
from horizontal to vertical.
Fig. 6 Operation of Liquid Crystal
Electric
Field
Transparent
Electrode
Liquid Crystal
Electric
Field
Liquid Crystal
Molecule
Electric
Dipole
Page 9
-9-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
3. Principle of LCD
3-1 Operation of Polarized Board for LCD Panel (Shutter)
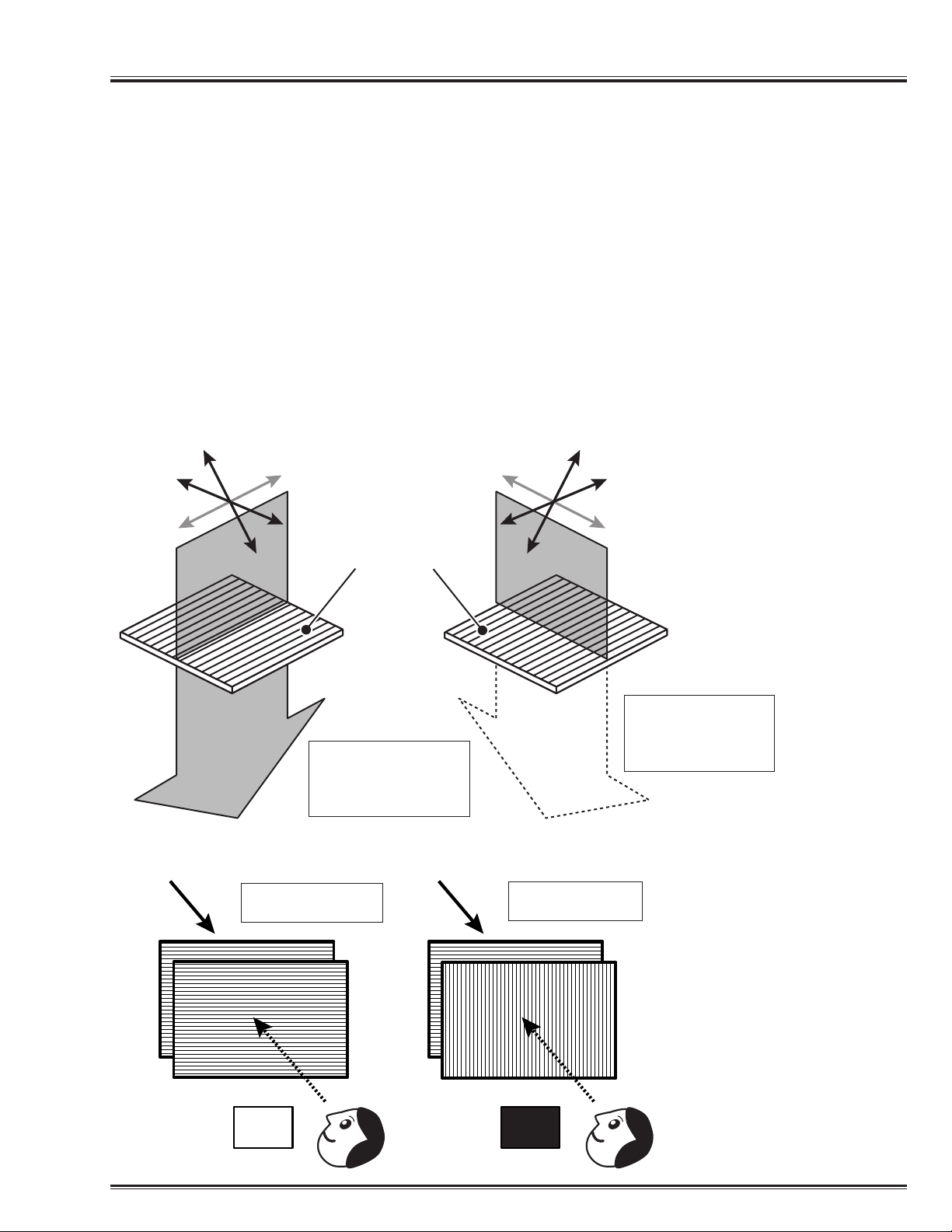
Light is an electromagnetic wave that is oscillating at right angles to the direction of advance. In fact, the
oscillating directions of all light is mixed. A polarized board can let only the light in the specific direction
pass from the light with which these various oscillating directions were mixed. Therefore, only the light of
the same direction as the polarization direction of a polarized board can be taken out by letting the light
pass through this polarized board. That is, if the oscillating direction of light and the direction of a polarized board are in agreement, the light will pass through a polarized board. Moreover, if the direction of a
polarized board differs from the oscillating direction of light, the light cannot pass through a polarized
board. When the oscillating direction of a polarized board and light are shifted 90º(right-angled), the light
is blocked completely. The light passes and looks bright if the two boards are in the same direction when
looking at two polarized boards in piles, however, if shifted at right-angles, the light is blocked and looks
dark.
■ Principle of LCD
Fig. 7 Operation of
Polarized Board
Fig. 8 Operation of
Polarized Board
Oscillating direction of light
Oscillating direction of light
The oscillating direction
of light and the direction
of a polarized board are
in agreement.
The direction of a
polarized board differs
from the oscillating
direction of light
Passage Interception
The two boards are
the same directions.
The two boards are
shifted right-angled.
Polarized
Board
Light
Light
White
Black
Page 10
-10-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
3-2 Operation of Alignment Film
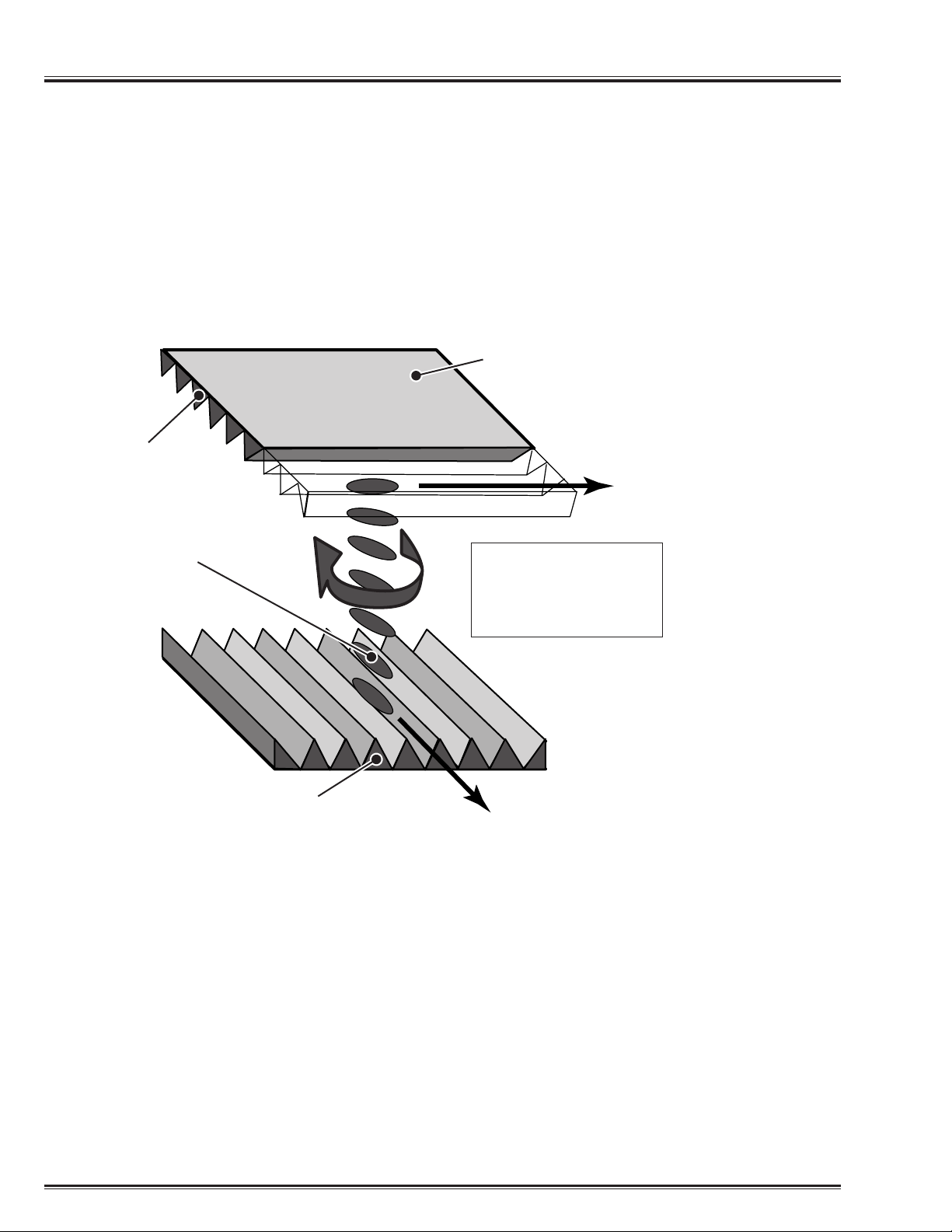
Liquid crystal is inserted into alignment films of an upper and lower plate that have the direction of
grooves shifted by 90º on the LCD display. The liquid crystal molecules of upper alignment plate are
arranged along with the upper alignment film. The liquid crystal molecules of lower alignment plate are
arranged along with the lower alignment film. The liquid crystal layer between these alignment films is
twisted little by little and is arranged so that a spiral is formed. Light entering through the first alignment
plate will have its oscillating direction twisted 90º by the liquid crystal layer between the alignment films.
Now the direction of oscillation is aligned with the second alignment plate and the light will pass through.
Principle of Liquid Crystal
Fig. 9
Operation of
Alignment Film
By the upper-and-lower
alignment films, spirally, a
liquid crystal molecules are
twisted 90º and arranged.
3-3 Operation of LCD Panel
In the LCD panel, a liquid crystal is inserted and enclosed between two glass plates. The polarized
board, transparent electrode, and the alignment film are formed on these glass plates. The light can be
passed or blocked by supplying voltage or not to this LCD panel.
In the condition (Switch-Off) that the voltage is not supplied, the liquid crystal molecules are twisted 90º
sideways and arranged spirally. The oscillating direction of the light that passed the upper polarized
board is changed by the twisted liquid crystal molecule arrangement. Therefore, the direction of a polar-
ized board and the oscillating direction of the light which is shifted 90º and arranged become the same,
and this light can now pass through a polarized board. This is the liquid crystal shutter-on condition and
an LCD panel (LCD shutter) passes the light.
Alignment
Plate
Alignment
Film
Direction
of Groove
Liquid
Crystal
Molecule
Alignment
Film
Direction
of Groove
Page 11

-11-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Principle of Liquid Crystal
Fig. 10 Operation of
LCD Panel
Passage
Interception
3-4 Transparent Electrode
In order to generate an electric field in liquid crystal, voltage is supplied to the upper-and-lower electrodes. If metal is used for these electrodes, the light is interrupted by this metal and cannot pass into the
liquid crystal. Therefore, a transparent electrode that passes light is used for the electrode of the LCD
shutter.
On the contrary, in the condition (Switch-On) that voltage is supplied, the liquid crystal molecules are
arranged in a line at right angles to a glass plate. Since vertical liquid crystal molecules do not affect the
oscillating direction of light, the light that passed the upper polarized board passes as it is without changing the oscillating direction. Since the oscillating direction of this light differs from direction of the lower
polarized board which is shifted 90º and arranged, the light collides with this polarized board and cannot
pass. This is the liquid crystal shutter-off condition and the LCD panel (LCD shutter) blocks the light.
This is the basic structure (On—Off of the light by the LCD shutter) of an LCD panel. It is a sandwich
structure of the upper and lower sides of transparent electrodes, alignment films, and polarized boards,
with an enclosed liquid crystal material between them.
The LCD panel shown in Fig. 10 is a type of panel that changes the light into a passage condition when
voltage is not supplied between the upper-and-lower polarized boards that are arranged at 90º. This type
of panel has the advantage that black contrast is improved, and it usually works well. This mode is called
“Normally White Mode.”
An LCD panel that passes light when voltage is not supplied is referred to as “Normally Black Mode.” In
practice, with this type (when the upper-and-lower polarized boards are arranged in the same direction),
displaying perfect black becomes difficult due to the leakage of light caused by variations in the arrangement of the liquid crystal molecules.
Polarized
Board
Transparent
Electrode
(Upper)
Alignment
Film
Liquid
Crystal
Alignment
Film
Transparent
Electrode
(Lower)
Polarized
Board
Light
Light
Polarized
Board
Transparent
Electrode
(Upper)
Alignment
Film
Liquid
Crystal
Alignment
Film
Transparent
Electrode
(Lower)
Polarized
Board
Page 12

-12-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
■ Type of LCD Display Construction
4 Type of LCD Display Construction
4-1 Twisted Nematic (TN) Type
A Nematic type of LCD Display where the liquid crystal molecules are twisted 90º between upper and
lower boards is called a Twisted Nematic type (TN type) liquid crystal.
Most LCD displays are of this type and feature high contrast (ratio) under low voltage and power.
4-2 Super TN (STN) Type
Super TN type (STN type) LCD Displays are used for LCD televisions, personal computer monitors, cel-
lular phones, etc. A liquid crystal material developed to improve visual characteristics, such as contrast
ratio is used.
In this STN type liquid crystal molecules are twisted 180º to 270º and arranged between upper and lower
electrodes. By supplying voltage to this liquid crystal, the transparent ratio of light changes more steeply.
Therefore, with the STN type as compared to the TN type, contrast and rise characteristic of the voltage
(response of switch On and Off) are improved, and a clearer picture on larger screens becomes possible.
4-3 Triple STN (TSTN) Type / Film STN (FSTN) Type
A fault of the STN type is that the display colors during On and Off of the LCD shutter become yellowish
green and navy blue. (In TN type, they are white and black.) This is because light of a specific wave-
length is reflected and scattered by the thickness of the LCD panel. Therefore, even if a color filter of
RGB is attached to an STN type liquid crystal, bluish green is mixed with the colors from black, gray to
white, and a natural color picture cannot be displayed. The triple STN type (TSTN type) and the film STN
type (FSTN type) have been developed as an advanced type of STN.
In the TSTN type, optically compensated films (high polymer films) which sandwich the upper and lower
LCD panels are used. They compensate for the twist of the light crystal cell, and the display colors of yel-
lowish green and navy blue are changed to the correct white and black. The “FSTN” type uses a single
optically compensated film
Page 13

-13-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Type of LCD Display Construction
Fig. 11 Type of LCD Display Construction
Twist of molecule
(90º)
Twist of molecule
(180º - 270º)
TSTN Type
STN Type
TN Type
Module
LCD Layer
Module
Module
LCD Layer
Module
Optically
Compensated
Film
Module
LCD Layer
Module
Optically
Compensated
Film
Page 14

-14-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
5 System of LCD Display
5-1 Dot-Matrix System
LCD displays have two drive systems, Segment and Dot-Matrix. The Dot-Matrix system is used for LCD
television displays.
The picture elements (pixels) of the display unit are arranged horizontally (X line) and vertically (Y row)
by this Dot-Matrix system, and various characteristics and figures can be displayed.
Fig. 12 shows a matrix of “X x Y = 10 (pixels)” with the character “Y” displayed. In this Dot-Matrix system,
by making the size of a pixel smaller and increasing the whole number of pixels, the big screen with fine
character or picture becomes possible.
With the present liquid crystal manufacture technology, the number of pixels per inch has reached
200ppi*, and very high definition screen display is possible. Moreover, the number of pixels of an LCD
display panel corresponding to bigger screen sizes can be specified and manufactured. For example, the
number of pixels of the SXGA* panel is about 1,300,000 (1,280 x 1,024 = 1,310,720 pixels).
✐ ppi: pixel per inch
✐ SXGA: Super eXtended Graphics Array
■ System of LCD Display
Fig. 12 Dot-Matrix System
In colorization of LCD panel,
one pixel consists of 3 RGB
dots (sub-pixels).
A character or a figure is
displayed by making the
pixel of each X and Y inter-
section turn on (or off).
X
Y
RGB
Page 15

-15-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
5-2 Colorization
Since an LCD shutter only passes or blocks light, in itself it cannot display a color picture. The color pic-
ture is made by mixing the three colors of RGB (three primary colors of light) respectively, like the CRT
color television. The color LCD panel has a color filter of RGB attached to the monochrome panel. See
Fig. 13. In this color LCD panel, by controlling the voltages and the waveforms that are supplied at each
RGB pixel, the transparent ratio is controlled and hue and brightness are adjusted. Therefore, smaller
pixels and more numbers of pixels are required for the color LCD Display. For example, although the
SXGA panel described before has about 1,300,000 pixels, in colorization, there are about 4 million dots
(sub-pixels).
System of LCD Display
Fig. 13 Colorization of LCD Display
Color Panel Monochrome Panel
R
Backlight
White
Color
G
White
Monochrome
B
Color Filter
LCD Shutter
Backlight
LCD Shutter
Page 16

-16-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
5-3 Drive System
The drive systems for LCD display are divided into the following classifications:
The Static Drive System, which is seldom used;
The Passive Matrix System, which is used for still pictures, such as calculators and notebook PCs;
The Active Matrix System, which is suitable for high definition and the high-speed response needed for
big screen LCD television.
System of LCD Display
Drive System Static Drive System
Dynamic Drive System Passive Matrix System
Active Matrix System
Classification of LCD Drive System
5-4 Passive Matrix System
In the structure of a passive matrix system, Y electrodes of the vertical direction (Y-direction) are formed
in upper glass plate, and X electrodes of the horizontal direction (X direction) are formed in lower glass
plate as a matrix. The liquid crystal molecules are sandwiched between these electrodes. By supplying
voltage between the Y electrode and the X electrode in sequence, at a certain time, an electric field is
generated in the liquid crystal where the selected Y electrode and X electrode cross. Therefore, the liquid
crystal molecules of this pixel address (X, Y electrode intersection) change arrangement and an LCD
shutter is turned On or Off.
Fig. 14 Passive Matrix System
These electrodes are
transparent electrodes.
Y Electrode
0 Y1 Y2 Y3 Y4
Y
Glass
Plate
Liquid
Crystal
Layer
Glass
Plate
X0
X1
X2
X Electrode
X3
X4
Page 17

-17-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
System of LCD Display
Fig. 15
Passive Matrix System
LCD shutter is turned on
or turned off in this
address (X2, Y1).
In the dynamic drive system, since the electric signal (voltage) is supplied to the Y electrode and the X
electrode in sequence, the number of pixels which makes all pixels (the total number of pixels are “X x
Y”) turn on or off becomes “X+Y”. Therefore, compared with the static drive system that has an indepen-
dent electrode for each pixel, the number of electrodes of the dynamic drive system is very few.
However, with this dynamic drive system, since the electrode itself is the wiring, it has resistance that
cannot be disregarded in the big screens. This resistance causes the speed of the shutter to become
slower. Therefore, when displaying moving pictures etc., an afterimage is generated.
This passive matrix system is not suitable for LCD televisions with big screens that require moving pic-
tures and high resolution.
The active matrix system was developed in order to overcome these faults.
Y1
Y0 Y1 Y2
X0
X1
Liquid
X2
Crystal
X3
X2
Page 18

-18-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
5-5 Active Matrix System
In the active matrix system, a switch element is attached for every pixel at the intersection of the X and Yelectrodes of a passive matrix system. Each pixel is now controlled by the switch element (active element). Since the switch for each pixel is turned On and Off independently, the response speed is
increased. Thin Film Transistor (TFT) is used for the switch element and is attached on the glass board.
The LCD display using this TFT is called “TFT LCD display”.
The upper electrode for the whole pattern is formed on the upper glass plate and is called the “Common
Electrode”. A pixel electrode (pixel pattern), TFT (switch element) which drives a pixel electrode, and X
electrode for gate input and Y electrode for source input of TFT are formed on the lower glass plate. In
this structure, the electric field is generated in the area between the pixel electrode and the common
electrode, and the LCD shutter for 1 pixel is operated.
When an electric signal (voltage) is supplied to the Y and X electrode of TFT, TFT is turned On, and the
liquid crystal molecules are operated as a light switch. Refer to Fig. 17 (Address X1 and Y0).
System of LCD Display
Fig. 16 Structure of Active
Matrix System
Fig. 17 Equivalent Circuit of
Active Matrix System
By TFT, the shutter of a pixel at the
address (X1, Y0) is turned On or Off.
Glass Plate
(Upper)
COMMON
Electrode
Liquid
Crystal
Liquid
Crystal
Layer
0
Y
TFT
Glass Plate
(Lower)
COMMON
Electrode
Y Electrode
Y1
X1
X Electrode
X2
Pixel Electrode
Y Electrode
COMMON
Electrode
Electrode
X1
Gate
TFT
(Switch Element)
Equivalent Circuit
(TFT)
COMMON
Pixel
Source
Y0
Pixel Electrode
(Pixel Pattern)
X Electrode
Liquid
Crystal
Drain
TFT
X1
Gate
Equivalent Circuit
(Switch)
COMMON
Source
Switch
0
Y
(On / Off)
Drain
Page 19

-19-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
System of LCD Display
Fig. 18 Structure of TFT Matrix
The LCD shutter is operated by
TFT at the address (X1, Y0).
The amplification operation of a transistor is used for the TFT switch in the active matrix system. In this
system, switching speed is unified over the whole display, increasing drive response speed as compared
with the passive matrix system. Therefore, TFT LCD display (active matrix system) is adopted for the
highly efficient display, which can provide the response speed required for big screens or quickly moving
pictures. However, further response speed is needed for high definition LCD television. This will be
described later.
5-6 Drive of Active Matrix System
The TFT LCD display consists of a matrix of n lines of X direction (X0 - Xn-1) and of n rows of Y direction
(Y0 - Yn-1). The line of X direction is called the “gate line” and the line (row) of Y direction is called the
“data line.”
First, the scan is started from the pixel address
(X0, Y0), and when the address (X0, Yn-1) is
selected the scan of X0 line is completed. Next, all
the pixels from X1 line to Xn-1 line are scanned in
sequence, and the final address is (Xn-1, Yn-1).
The operation of selected pixel address (X1, Y2)
is explained below.
First, (signal) voltage is supplied to X1 line (gate
of TFT), next voltage is supplied to Y2 row (source
of TFT), and the address of the intersection of X1
line and Y2 row is selected and its TFT is turned
On or Off. However, just switching the TFT on and
off will not change the brightness of the screen.
The brightness of a screen is changed by controlling the voltage of a data line (Y row). Fig. 19
shows the voltage characteristic of the matrix system.
Fig. 19 Voltage Characteristic of Matrix System
Since the time for the drive voltage to reach its
required value is shorter in the active matrix system,
the response time of the display becomes quicker.
Y0 Y1 Y2 Y3
X0
TFT (Switch)
Liquid Crystal
COMMON Electrode
X1
X2
X3
Active Matrix System
Passive Matrix System
Voltage to liquid crystal
Time
Page 20

-20-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
In Fig. 20, the voltage of the data line (Y2) is supplied in the positive direction to a common electrode
(DC drive). In practice a uniform AC voltage is supplied to the common electrode (AC drive) to prolong
the life of the liquid crystal.
Fig. 20 LCD Drive Circuit (Normally White Type)
In practice, driven by AC signal
to COMMON. (AC Drive)
System of LCD Display
Data Line Drive Circuit (Y row)
TFT
Pixel
Electrode
Glass Plate
(Common)
Liquid
Crystal
Glass Plate
(TFT)
Variable
Voltage
Y0
Video Data
Processor
Y1 Y2 Y3
X Direction
Y Direction
• • •
Timming Controller
(Scan Converter)
Yn-1
X0
X1
X2
X3
Xn-1
COMMON
Power
Circuit
• • •
Gate Line Drive Circuit (X line)
X1
Y2
TFT: On (X1, Y2)
Y2
Y2
Y2
Y2
COMMON
Brightness
of Screen
COMMON
TFT: On
TFT: Off
Page 21

-21-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
6 Improvement Technology of LCD Display
6-1 Subject of LCD Display
6-1-1 Angle of View
Angle of view means the normal visible range (angle) of a screen.
In an LCD display, the angle of view is narrow compared with a CRT or PDP (Plasma Display Panel). The
viewing angle of the typical TN type LCD display is about 100º. However with the new improved technolo-
gy that has been developed the angle of view for LCD display has increased to 160º or 170º. This
improved system will be described later. (The angle of view for a CRT or PDP is 180º.)
■ Improvement Technology of LCD Display
6-1-2 Response Characteristic
The response characteristic of the LCD display is the speed at which the display is refreshed by the input
signal (video data signal).
If this response characteristic is slow, an afterimage will appear on the screen. Therefore, in large screen
LCD television, improving this response characteristic becomes very important.
Fig. 21 Angle of View
Vertical
Angle of View
Horizontal
Angle of View
Page 22

-22-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
6-2 Angle of View (TN Type)
The principle of optical penetration and the interception of the LCD shutter by the arranged direction of
cylindrical liquid crystal molecules controls the direction of light. Therefore, brightness, hue, and contrast
depend on the direction of view of the LCD display. The range (angle) where these look normal is called
the “angle of view.” The fault of the TN LCD display is that this angle of view is narrow.
Fig. 22 shows that brightness changes depending on the angle the screen with a gray picture is viewed.
In this figure, the liquid crystal molecule leans diagonally. Therefore, the amount of optical penetration will
change depending on the angle when watching the screen from the front or the side.
Fig. 22 Angle of View (TN type)
Improvement Technology of LCD Display
The brightness becomes
different depending on the
angle of view.
Glass
Plate
Glass
Plate
Polarized
Board
Transparent Electrode
(Common)
Alignment Film
Liquid Crystal Molecule
Alignment Film
Transparent Electrode
(Pixel, TFT)
Polarized
Board
Page 23

-23-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
6-3 Multi-Domain System
The arrangement of the TN LCD display is one directional. In this Multi-Domain System, one pixel is
divided into two or more different arranged domains.
Fig. 23 shows the example of Multi-Domain System with two domains. The quantity of the light per pixel
from various angles is equalized by this system. Moreover, the angle of view becomes even wider by
increasing the number of divisions. However, manufacturing is difficult in the rubbing process*.
✐ Refer to 2-2 Rubbing-process.
Improvement Technology of LCD Display
Fig. 23
Multi-Domain System
The brightness of a screen
is equalized as macro view.
Polarized
Board
Glass
Plate
Transparent Electrode
(Common)
Alignment Film
Glass
Plate
Alignment Film
(Left)
Alignment Film
(Right)
Liquid Crystal Molecule
Transparent Electrode
(Pixel, TFT)
Polarized
Board
Page 24

-24-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Improvement Technology of LCD Display
6-4 MVA (Multi-domain Vertical Alignment) System
In the MVA system, the (alignment) film is arranged so that the liquid crystal molecules are stood vertical-
ly. The MVA system combines vertical alignment with the Multi-domain system. By vertically aligning the
liquid crystal molecules, the influence of optical interception is lost, and the angle of view and contrast
are improved.
A type of material is used that causes the liquid crystal molecules to become vertical to the glass plate
without supplying voltage. (Nega-Nematic liquid crystal*)
In the MVA system, attaching the boss by resin and making the liquid crystal molecules stand diagonally
on the transparent electrode make multiple alignment domains. Therefore, since the rubbing process can
be skipped at the alignment film production, manufacturing becomes easier compared with the multi-
domain system.
✐ Generally, a Posi-Nematic system is used that aligns the liquid crystal molecules by supplying voltage.
Fig. 24 MVA (Multi-domain Vertical Alignment) System
Glass
Plate
(Left)
Glass
Plate
Polarized
Board
Transparent Electrode
(Common)
Alignment Film
Liquid Crystal Molecule
(Nega-Nematic)
Alignment Film
Boss
(Right)
Transparent Electrode
(Pixel, TFT)
Polarized
Board
Page 25

-25-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Improvement Technology of LCD Display
6-5 IPS (In-Plain Switching) System
The structure of an IPS system is shown in Fig. 25. The pixel and common electrodes are mounted to
the transparent film (drive transistor) side and the electric field is generated horizontally to the glass
plate. With this electric field, the alignment direction of liquid crystal molecules is rotated 90º in parallel to
the glass plate.
In the IPS system, liquid crystal molecules rotate all at once in the horizontal direction. Since these liquid
crystal molecules do not lean like the TN type, there is little change in the picture characteristics (contrast, brightness, hue, etc.) and the angle of view becomes wider. However, there are a few problems.
The quantity of transparent light is reduced, slower response speed, and a white picture becomes a little
bluish or yellowish depending on the viewing direction. The S-IPS (Super-IPS) type was developed to
improve upon these problems. In the S-IPS type, the structure of the electrode for driving the liquid crystal molecules becomes a zigzag form, which reduces the change of color, increases the viewing angle to
about 160º and has high definition equivalent to a CRT.
Fig. 25 IPS (In-Plain Switching) System
Basic Structure of IPS System
Normally Black Mode
Polarized
Board
Transparent Electrode
(Pixel)
Liquid Crystal Molecule
(Vertical)
Electric
Field
Glass Plate
(Without Transparent Electrode)
Alignment Film
Alignment Film
Transparent Electrode
(Common)
Glass Plate
Polarized
Board
Polarized
Board
Alignment Film
Dark (Switch Off) Bright (Switch On)
Liquid Crystal
Molecule
(Vertical)
Page 26

-26-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Improvement Technology of LCD Display
6-6 Optically Compensated Film
By using the optically compensated film, the phase shift of the STN type of LCD display is corrected, and
the angle of view and contrast are improved.
(Refer to 4-3 Triple STN Type.)
Three methods for attaching the optically compensated film are shown in Fig. 26.
Fig. 26
Optically Compensated Film
1 sheet / 1 side 2 sheets / 1 side 2 sheets / 2 sides
6-7 OCB (Optically Compensated Birefringence) System
The OCB system combines the bend-alignment system where the liquid crystal molecules are bent and
aligned between the upper and lower boards and optically compensation film. This system has the features of increased angle of view and quicker response speeds. However, bend-alignment is difficult to
make uniform and stable.
Fig. 27 OCB System
Polarized Board
Compensated
Film
Liquid Crystal
Polarized
Board
Polarized Board
Compensated Film 1
Compensated Film 2
Liquid Crystal
Polarized
Board
Polarized Board
Compensated
Film 1
Liquid Crystal
Polarized
Board
Compensated
Film 2
Polarized Board
Glass
Plate
Glass
Plate
Optically Compensated
Film
Transparent Electrode
(Common)
Alignment Film
Liquid Crystal Molecule
Alignment Film
Transparent Electrode
(Pixel, TFT)
Polarized
Board
Page 27

-27-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
6-8 Improvement of Response Speed
6-8-1 Inpulse System
In order to reduce afterimage and dim outline, there is the system that has the backlight blinked for every
writing of one picture or an all black picture in inserted in the fixed cycle. It is called the “Inpulse System.”
For example, with the system called “Super Inpulse System,” the black data is written in every 1/60 second, and the afterimage and the ghosts are reduced.
Improvement Technology of LCD Display
With the usual LCD panel, since the
picture is displayed continuously,
the front picture becomes dim as
the afterimage.
In the inpulse system, by inserting
black data between the picture
data, the afterimage is reduced and
the high-speed response is
improved.
Fig. 28 Inpulse System
6-8-2 FFD (Feed Forward Driving) System
The response speed of LCD brightness can be improved by adding over-shoot characteristic to the data
line voltage. Fig. 29 shows the actual overdrive circuit used in a digital drive system.
Fig. 29
Overdrive Circuit
Waveform (Normal)
Waveform with Over-Shoot
Drive Circuit (Normal)
Overdrive Circuit
Picture Data
Black Data
Over-Shoot
Time
Response Time
(By Overdrive Circuit)
Voltage
Brightness
Voltage
Time
Response
Time
Brightness
Voltage
Time
Time
Voltage
Time
Time
Page 28

-28-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
7 Appendix
7-1 Backlight
An LCD panel does not emit light itself. For the display, a light source is required, and normally fluores-
cent lights are used for the backlight of the LCD television.
The backlight consists of fluorescent lights, a reflective plate, and a diffusion sheet (or board). Fig. 30
shows the structure and photograph of 30V and 15V LCD televisions backlights.
Fig. 30
Backlight
30V Type
15V Type
■ Appendix
LCD Panel
Fluorescent Lights
(30V: 16pcs)
LCD Panel
Fluorescent Lights
(15V: 2pcs, 20V:3pcs)
Diffusion Sheet (Board)
Reflective Plate
Diffusion Sheet
Reflective Plate
Page 29

-29-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
7-2 LVDS Circuit
(1) LVDS Interface
For transmitting the video signal information, an interface circuit with an LVDS (Low Noise Differential
Signaling) standard is used, which has the merit of low noise, high speed operation by a small amplitude,
and low power consumption.
The LVDS cable connects the transmitter in the driving circuit and the receiver in the module.
(2) Driving Circuit
Fig. 32 shows the block diagrams of a panel driving circuit. The final video information (signal) from the
video processor (for example pixelworks) is transmitted to the LCD panel module through an LVDS cable.
1.2V
345/200mV
100Ω
Terminated
3.5mA
Receiver
(LCD Panel)
Transmitter
(Driving
Circuit)
LVDS Cable
Fig. 31
LVDS Interface
LVDS Transmitter
LVDS Receiver
Video Processor (pixelworks)
LCD Module
Part of (Panel) Driving Circuit Part of Panel Display (in the module)
Fig. 32
Block Diagrams of Panel Driving Circuit
Appendix
TxCLKIN
TxIN
8
R
8
G
8
B
VsyncVsync
Hsync
BLANK
PARITY
DCLK
TxOUT
DATA (LVDS)
CLOCK (LVDS)
LVDS
PDWN
RxOUTRxIN
8
R
8
G
8
B
VsyncVsync
Hsync
BLANK
PARITY
DCLK
RxCLKOUT
Page 30

-30-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
7-3 Block Diagram Example
(1) CLT-1583
Appendix
(2) CLT-2053
Fig. 33 Block Diagram: CLT-1583
Fig. 34
Block Diagram: CLT-2053
Tuner Board
Sub CPU
M37272M6
U101
+CONTROL
TU201
Tuner / IF
TMQJ8
47
+9V
34
CVBS_OUT
L_OUT
LVR
Monitor Output
IIC
V_TV
3033
R_OUT
R_TV
48 46
32
6717
L_TV
+12V
AV Switch U46
CXA2089Q
SY1
SC1
S1
S
AV1 Input
+9V
4
16
Audio Processor
CC_R
CC_G
CC_B
CVBS1
L1
L
V
Audio AMP
LA4263
108
L
R
238
NJW1138M
301
AUDIO_R
AUDIO_L
41
R1
R
U45
R
3
L
1
Headphone (J26)
U44
Main Board
S_CLK / SIN_OUT/ ENABLE_IN / ENABLE_OUT
V33D
Video Decoder
VPC3230D
717472 5 4 6
SELECTED_C
SELECTED_Y
CVBS
43
4539
9842735 1
11
L2
R2
R
L
AV2 Input
U19
INPUT_Y
INPUT_Cr/Pr
INPUT_Cb/Pb
18
16
YCbCr
Component
VY [0-7]
VUV [0-7]
R_PC
L_PC
3
2
1
40
CVBS2
V
R
L
U36
Main Scaler / (Main)CPU
PW113-10Q
PIXELWORKS
GRE [0-7]
GGE [0-7]
U6
Graphic A/D
AD9883
54
30 31
48 43
Red_PC
HS_PC
RHG
PC Input
GBE [0-7]
V33D
G_PC
VS_PC
V
Speaker (R)
Speaker (L)
VCPU 33/18
MENORY
DATA
Flash ROM
8Mbits
AVDD
PVDD
B_PC
B
D-SUB
LCD Panel
V33
RX CLK+/-
RX IN+/-[0-3]
IC1
DRO [0-7]
DGO [0-7]
DBO [0-7]
VCPU 33
37
LVDS
Interface
THC63LVDM83A
U30
Tuner Board
Sub CPU
M37272M6
U101
TU201
Tuner / IF
TMQJ8
+9V
34
CVBS_OUT
Monitor Output
IIC
+CONTROL
V_TV
47
48 46
3033
L_OUT
R_OUT
LVR
6717
R_TV
32
L_TV
S1
+14V
+9V
16
AV Switch U46
CXA2089Q
SY1
SC1
CVBS1
V
S
AV1 Input
Audio AMP
4
LA4263
Audio Processor
NJW1138M
CC_R
CC_G
CC_B
41
L1
R1
R
L
108
L
R
238
301
AUDIO_R
AUDIO_L
U45
R
3
L
1
Headphone (J26)
U44
Main Board
S_CLK / SIN_OUT/ ENABLE_IN / ENABLE_OUT
V33D
3
2
1
40
CVBS2
V
AV2 Input
U19
Video Decoder
VPC3230D
717472 5 4 6
SELECTED_C
SELECTED_Y
CVBS
43
4539
18
16
9842735 1
11
L2
R2
RLR
L
INPUT_Y
INPUT_Cr/Pr
INPUT_Cb/Pb
L3
Audio
Board
VY [0-7]
VUV [0-7]
R3
AV3 Input
R
L
Main Scaler / (Main)CPU
PW113-10Q
PIXELWORKS
U36
U30
YCbCr
Component
MENORY
DATA
Flash ROM
VCPU 33/18
8Mbits
Speaker (R)
Speaker (L)
DRO [0-7]
DGO [0-7]
DBO [0-7]
VCPU 33
37
LCD Panel
Page 31

-31-
Training Manual Principle of LCD
Appendix
(3) CLT1554 / CLT2054
Fig. 35 Block Diagram: CLT1554 / CLT2054
AV1
S Video
Composite Video
Audio
AV2
Composite Video
Audio
AV3
Component Video
Audio
TV (A201)
Tuner
IF
Sound Multiplex
3
AV1_Y
IC1001
1
AV1_CV
Video SW
5
TV_CV
AV1/TV_Y/CV
AV2_V
1
3
AV3_Y
90 85
AV1_C
92
AV3_Cr
Digital Decoder
94
AV3_Cb
AD_Cb
(480i)
AD_Y
AD_Cr
Y/C Separation
48
54
A/D Converter
43
(480p)
AD_HS
7
5
IC1002
Video SW
IC2001
with
IC4101
30
AD_VS
16
36 37
(For Caption)
SEL_Y/CV
7
DEC_Y/C (0-7)
AD_R/G (0-7)
38
31
AD_CLAMP
28
5V
3.3V
IIC Bus
(Y/UV)
IIC Bus
IIC Bus
IC1701
26
AD_Y
Sync Separation
R: 1
AV1_L/R
L: 30
R: 2
L: 29
R: 3
L: 28
R: 4
L: 27
IC001
Audio SW
Audio Control
Surround
AV2_L/R
AV3_L/R
TV_L/R
IIC Bus IIC Bus
15
10
21
SEL_R
SEL_L
IC801
CPU
22
OSD_HD
12 10
IC871
DD Converter
13 11
OSD_HD
154
SDRAM
13
IC101
Audio AMP
9
23 18
VD
VD
153
19G20B21Y16
R
OSD_CC
152R151G150B148Y149
IC301
IP Converter
Screen Controller
IC361
16
R-OUT (+)
15
R-OUT (-)
24
L-OUT (+)
25
L-OUT (-)
I
I
IIC Bus
R/G/B (0-7)
R/G/B (0-7)
SPEAKER
(Right)
SPEAKER
(Left)
(For 20V)
(For 15V)
IC781
LVDS
Transmitter
LCD PANEL
(20V)
LCD PANEL
(15V)
Page 32

SEP / 2004 Printed in Japan SANYO Electric Co., Ltd.
 Loading...
Loading...