SANYO LC876694B, LC876662B Datasheet

Ordering number : ENN*6843
LC876694B/78B/62B
8-Bit Single-Chip Microcontroller
Preliminary
Overview
The LC876694B/LC876678B/LC876662B are 8 bit single chip microcontrollers with the following on-chip functional
blocks :
- CPU: operable at a minimum bus cycle time of 100ns
- On-chip ROM Maximum Capacity : LC876694B 96K bytes
LC876678B 80K bytes
LC876662B 64K bytes
- On-chip RAM: 2048 bytes
- VFD automatic display controller / driver
- 16 bit timer / counter (can be divided into two 8 bit timers)
- 16 bit timer / PWM (can be divided into two 8 bit timers)
- timer for use as date / time clock
- High speed clock counter
- System clock divider function
- synchronous serial I/O port (with automatic block transmit / receive function)
- asynchronous / synchronous serial I/O port
- 12-channel × 8-bit AD converter
- Weak signal detector
- 15-sour ce 10-vec tored in terrupt syst em
All of the above functions are fabricated on a single chip.
Features
(1) Read-Only Memory (ROM): LC876694B 98304 × 8 bits
LC876678B 81920 × 8 bits
LC876662B 65536
(2) Random Access Memory (RAM): LC876694B/78B/62B 2048 × 9 bits
(3) Minimum Bus Cycle Time: 100ns (10MHz)
Note: The bus cycle time indicates ROM read time.
(4) Minimum Instruction Cycle Time: 300ns (10MHz)
8 bits
×
CMOS IC
Ver.1.01
51000
11901 RM (IM) SK No.6843-1/23

LC876694B/78B/62B
(5) Ports
- Input/output ports
Data direction programmable for each bit individually : 20 (P1n, P70 to P73, P8n)
- 15V withstand input/output ports
Data direction programmable in nibble units : 8 (P0n)
(When N-channel open drain output is selected, data can be input in bit units.)
Data direction programmable for each bit individually : 8 (P3n)
- Input ports : 2 (XT1,XT2)
- VFD output ports
Large current outputs for digits : 9 (S0 / T0 to S8 / T8)
Large current outputs for digits / segments : 7 (S9 / T9 to S15 / T15)
digit / segment outputs : 8 (S16 to S23)
segment outputs : 28 (S24 to S51)
Other functions
Input/output ports : 12(PFn, PG0 to 3)
Input ports : 24 (PCn, PDn, PEn)
- Oscillator pins : 2 (CF1,CF2)
- Reset pin : 1 (RES#)
- Power supply : 6 (VSS1 to 2, VDD1 to4)
- VFD power supply : 1 (VP)
(6) VFD automatic display controller
- Programmable segment/digit output pattern
Output can be switched between digit/segment waveform output (pins 9 to 24 can be used for output of digit
waveforms).
parallel-drive available for large current VFD.
- 16-step dimmer function available
(7) Weak signal detection (MIC signals etc)
- Counts pulses with width greater than a preset value
- 2 bit counter
(8) Timers
- Timer 0: 16 bit timer / counter with capture register
Mode 0: 2 channel 8-bit timer with programmable 8 bit prescaler and 8 bit capture register
Mode 1: 8 bit timer with 8 bit programmable prescaler and 8 bit capture register + 8 bit
Counter with 8-bit capture register
Mode 2: 16 bit timer with 8 bit programmable prescaler and 16 bit capture register
Mode 3: 16 bit counter with 16 bit capture register
- Timer 1: PWM / 16 bit timer toggle output
Mode 0: 2 channel 8 bit timer (with toggle output)
Mode 1: 2 channel 8 bit PWM
Mode 2: 16 bit timer (with toggle output) Toggle output also possible using lower order 8 bits.
Mode 3: 16 bit timer (with toggle output) Lower order 8 bits can be used as PWM output.
- Base Timer
1) The clock signal can be selected from any of the following :
Sub-clock (32.768kHz crystal oscillator), system clock, and prescaler output from timer 0
2) Interrupts can be selected to occur at one of five different times.
(9) High speed clock counter
1) Capable of counting maximum : 20MHz clock (Using main clock 10MHz)
2) Real time output
No.6843-2/23

LC876694B/78B/62B
(10) Serial-interface
- SIO 0: 8 bit synchronous serial Interface
1) LSB first / MSB first function availa ble
2) Internal 8 bit baud-rate generator (maximum transmit clock period 4 / 3 Tcyc)
3) Continuous automatic data communication (1-256 bits)
- SIO 1: 8 bit asynchronous / synchronous serial interface
Mode 0: Synchronous 8 bit serial IO (2-wire or 3-wire, transmit clock 2–512 Tcyc)
Mode 1: Asynchronous serial IO (half duplex, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, baud rate 8–2048Tcyc)
Mode 2: Bus mode 1 (start bit, 8 data bits, transmit clock 2–512 Tcyc)
Mode 3: Bus mode 2 (start detection, 8 data bits, stop detection)
(11) AD converter
-8 bits × 12 channels
(12) Remote control receiver circuit (connected to P73 / INT3 / T0IN terminal)
-Noise rejection function (noise rejection filter time constant can selected from 1 / 32 / 128 Tcyc)
(13) Watchdog timer
- The watching timer period is set using an external RC.
- Watchdog timer can produce interrupt, system reset
(14) Interrupts: 15-source, 10-vectored interrupts
1) Three priority (low, high and highest) multiple interrupts are supported. During interrupt handling, an equal or
lower priority interrupt request is refused.
2) If interrupt requests to two or more vector addresses occur at once, the higher priority interrupt takes precedence.
In the case of equal priority levels, the vector with the lowest address takes precedence.
(15) Subroutine stack levels: 1024 levels max. Stack is located in RAM.
(16) Multiplication and division
- 16 bit × 8 bit (executed in 5 cycles)
- 24 bit × 16 bit (12 cycles)
- 16 bit ÷ 8 bit (8 cycles)
- 24 bit ÷ 16 bit (12 cycles)
(17) Oscillation circuits
- On-chip RC oscillation circuit for system clock use.
- On-chip CF oscillation circuit for system clock use. (R
- On-chip Crystal oscillation circuit low speed system clock use. (Rd, R
built in)
f
external)
f
(18) System clock divider function
- Able to reduce current consumption
Available minimum instruction cycle time: 300ns, 600ns, 1.2µs, 4.8µs, 9.6µs, 19.2µs, 38.4µs, 76.8µs.
(Using 10MHz main clock)
No.6843-3/23

LC876694B/78B/62B
(19) Standby function
- HALT mode
HALT mode is used to reduce power consumption. Program execution is stopped. Peripheral circuits still
operate but VFD display and some serial transfer operations stop.
1) Oscillation circuits are not stopped automatically.
2) Release occurs on system reset or by interrupt.
-HOLD mode
HOLD mode is used to reduce power consumption. Both program execution and peripheral circuits are
stopped.
1)CF, RCand crystal oscillation circuits stop automatically.
2) Release occurs on any of the following conditions.
(1) input to the reset pin goes low
(2) a specified level is input at least one of INT0, INT1, INT2
(3) an interrupt condition arises at port 0
-X’tal HOLD made
X’tal HOLD mode is used to reduce power consumption. Program execution is stopped.
All peripheral circuits except the base timer are stopped.
1) CF and RC oscillation circuits stop automatically.
2) Crystal oscillator is maintained in its state at HOLD mode inception.
3) Release occurs on any an any of the following conditions
(1) input to the reset pin goes low
(2) a specified level is input to at least one of INT0, INT1, INT2
(3) an interrupt condition arises at port 0
(4) an interrupt condition arises at the base-timer
(20) Factory shipment
-delivery form QIP100E
(21) Development tools
- Evaluation chip: LC876095
- Emulator: EVA62S + ECB876600 (Evaluation chip board) + SUB876500 + POD100QFP
- Flash ROM version: LC87F66C8A
No.6843-4/23
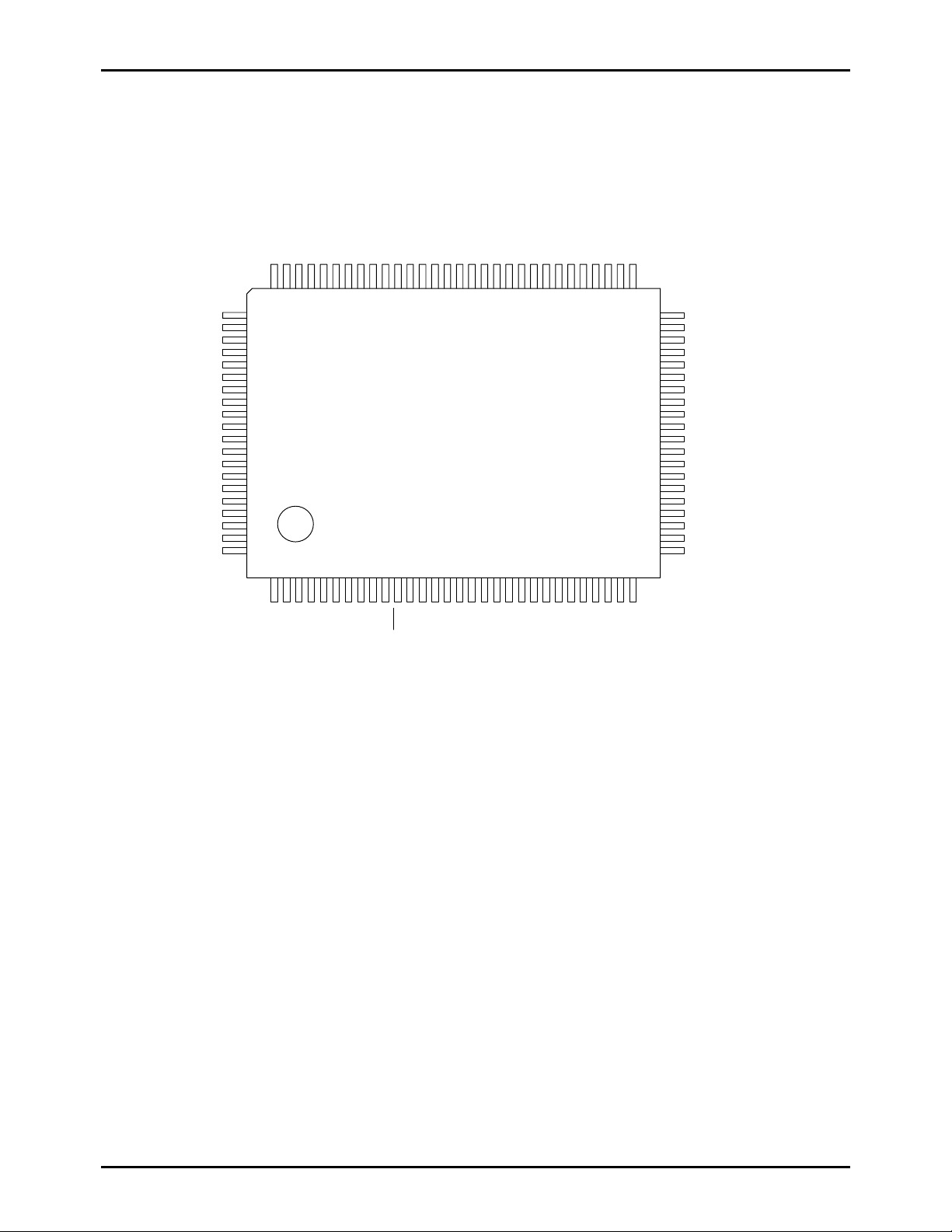
Pin Assignment
Z
S48/PG0
S49/PG1
S50/PG2
S51/PG3
P00
P01
P02
P03
VSS2
VDD2
P04
P05
P06
P07
P10/SO0
P11/SI0/SB0
P12/SCK0
P13/SO1
P14/SI1/SB1
P15/SCK1
LC876694B/78B/62B
S47/PF7
S46/PF6
S45/PF5
S44/PF4
S43/PF3
S42/PF2
S41/PF1
S40/PF0
VDD4
S39/PE7
S38/PE6
S37/PE5
S36/PE4
S35/PE3
S34/PE2
S33/PE1
S32/PE0
S31/PD7
S30/PD6
S29/PD5
S28/PD4
S27/PD3
S26/PD2
S25/PD1
8079787776757473727170696867666564636261605958575655545352
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
P30
P31
P32
P33
P16/T1PWML
P17/T1PWMH/BU
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
P34
P35
P36
P37
RES
CF1
CF2
VSS1
VDD1
P80/AN0
P81/AN1
P82/AN2
P83/AN3
P84/AN4
P85/AN5
XT1/AN10
XT2/AN11
P86/AN6
S24/PD0
25
P87/AN7/MICIN
S23/PC7
26
P70/INT0/T0LCP/AN8
S22/PC6
27
P71/INT1/T0HCP/AN9
S21/PC5
28
P72/INT2/T0IN/NKIN
S20/PC4
29
P73/INT3/T0IN
VP
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
S0/T0
S19/PC3
S18/PC2
S17/PC1
S16/PC0
VDD3
S15/T15
S14/T14
S13/T13
S12/T12
S11/T11
S10/T10
S9/T9
S8/T8
S7/T7
S6/T6
S5/T5
S4/T4
S3/T3
S2/T2
S1/T1
SANYO: QIP100E
No.6843-5/23
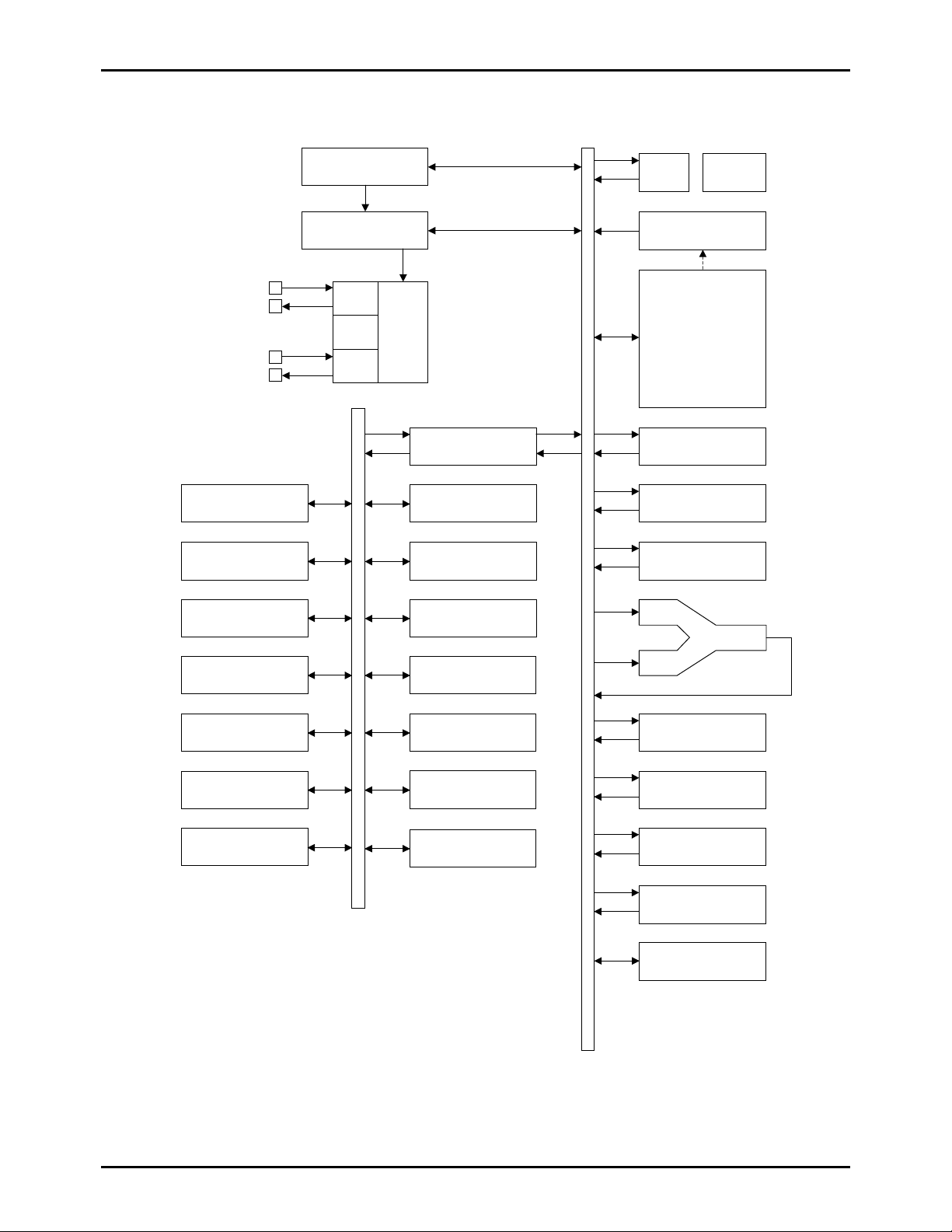
System Bl ock Diagram
Interrupt Control
LC876694B/78B/62B
IR PLA
SIO0
SIO1
Timer 0
(High speed clock
Timer 1
counter)
Stand-by C ontr ol
CF
RC
X’tal
Clock
Generator
Bus Interface
Port 0
Port 1
Port 3
Port 7
ROM
PC
ACC
B Register
C Register
ALU
Base Timer
VFD Controller
INT0-3
Noise Rejection Filter
Port 8
ADC
Weak Signa Detector
PSW
RAR
RAM
Stack Pointer
Watch Do g Timer
No.6843-6/23

LC876694B/78B/62B
Pin Assignment
Pin name I/O Function Option
VSS1
VSS2
VDD1
VDD2
VDD3
VDD4
VP - • Power supply (-) No
PORT0
P00 to P07
PORT1
P10 to P17
PORT3
P30 to P33
PORT7
P70 to P73
- • Power supply (-) No
- • Power supply (+) No
I/O • 8bit input/output port
• data direction programmable in nibble units
• Use of pull-up resistor can be specified in nibble units
• Input for HOLD release
• Input for port 0 interrupt
• 15V withstand at N-channel open drain output
I/O • 8bit input/output port
• data direction programmable for each bit
• Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
• Other pin functions
P10 SIO0 data output
P11 SIO0 data input/bus input/output
P12 SIO0 clock input/output
P13 SIO1 data output
P14 SIO1 data input/bus input/output
P15 SIO1 clock input/output
P16: Timer 1 PWML output
P17: Timer 1 PWMH output/Buzzer output
I/O • 8bit Input/output port
• Data direction can b e specified for each bit
• Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
• 15V withstand at N-channel open drain output
• 4bit Input/output port
I/O
• Data direction can b e specified for each bit
• Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
• Other func tions
P70: INT0 input/HOLD release input/Timer0L capture Input/output for watc h dog timer
P71: INT1 input/HOLD release input/Timer0H capture input
P72: INT2 input/HOLD release input/timer 0 event input/Timer0L capture input/High
speed clock counter input
P73: INT3 input(noise rejection filter attached input)/timer 0 event input/Timer 0H
capture input
AD input port: AN8(P70), AN9(P71)
The following types of interrupt detection are possible:
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
INT0
INT1
INT2
INT3
Rising Falling Rising/
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
falling
No
No
Yes
Yes
H level L level
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Yes
No
No
No.6843-7/23
 Loading...
Loading...