Page 1
Ordering number : ENN7022
60401TN (OT) No. 7022-1/14
Overview
The LC72317, 72318 and 72319 are low-voltage
electronic tuning radio microcontrollers that include a PLL
that operates up to 250 MHz and a 1/4 duty 1/2 bias LCD
driver on chip. These ICs include an on-chip DC-DC
converter, making it is easy to create the supply voltages
required for tuning and allowing cost reductions in end
products.
These ICs are optimal for use in low-voltage portable
audio equipment that includes a radio receiver.
Function
• Program memory (ROM):
— 6144 × 16 bits (12K bytes) LC72317
— 8192 × 16 bits (16K bytes) LC72318/319
• Data memory (RAM):
— 256 × 4 bits LC72317/318
— 512 × 4 bits LC72319
• Cycle time: 40 µs (all 1-word instructions) at 75kHz
crystal oscillation
• Stack: 8 levels
• LCD driver: 48 to 112 segments (1/4 duty, 1/2 bias
drive)
• Interrupts: Two external interrupts
Timer interrupts (1, 5, 10, and 50 ms)
• A/D converter: Three input channels
(5-bit successive approximation
conversion)
• Input ports: 9 ports (of which three can be switched for
use as A/D converter inputs)
• Output ports: 6 ports (of which 1 can be switched for use
as the beep tone output and 2 are opendrain ports)
Continued on next page.
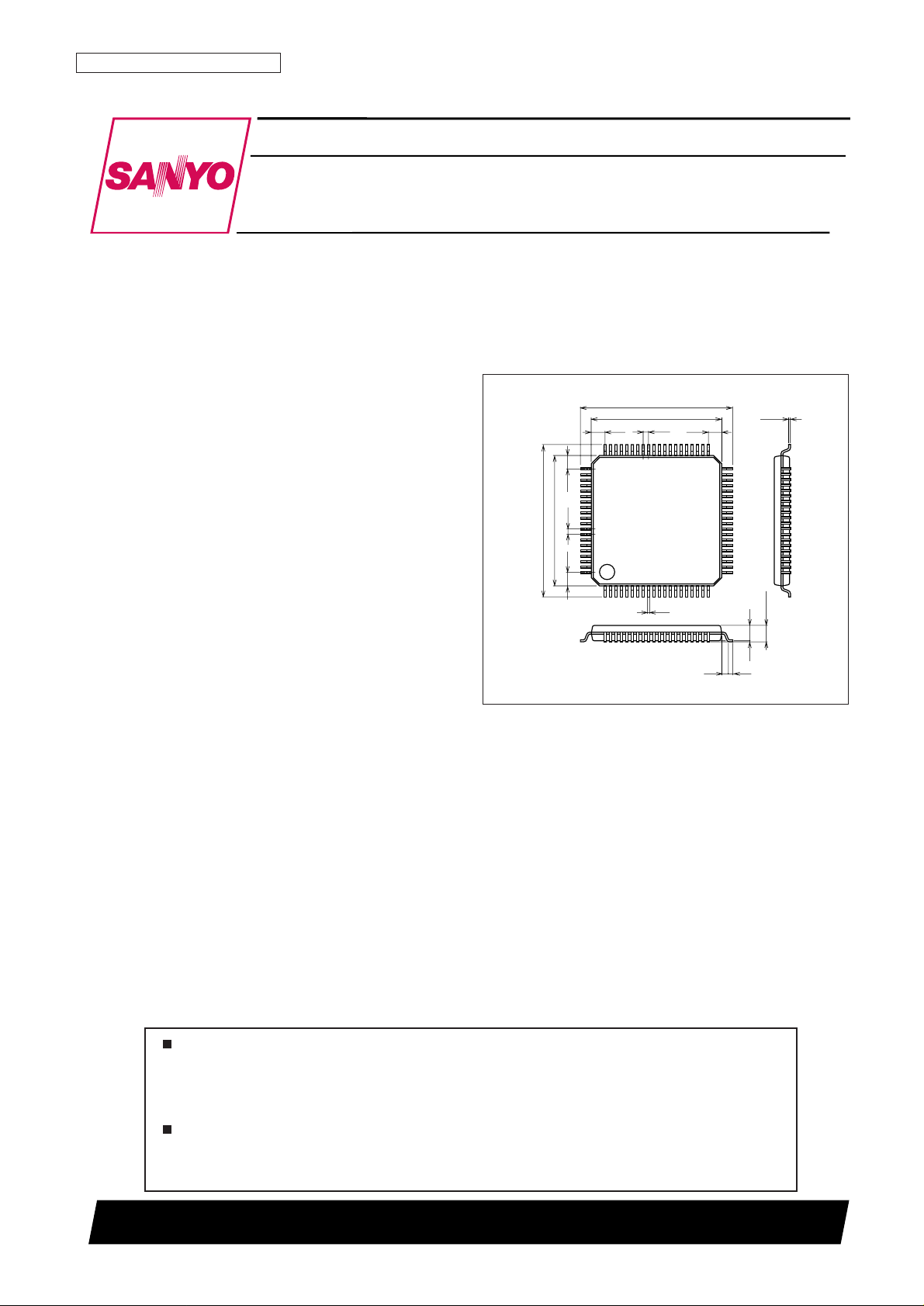
Package Dimensions
unit: mm
3220-SQFP80
14.0
12.0
1.25 1.25
0.5
14.0
12.0
1.25
1.25
0.5
120
21
40
41
60
61
80
0.1
0.5
1.6max
1.4
0.5
0.2
0.135
SANYO: SQFP80
[LC72317, 72318, 72319]
LC72317, 72318, 72319
SANYO Electric Co.,Ltd. Semiconductor Company
TOKYO OFFICE Tokyo Bldg., 1-10, 1 Chome, Ueno, Taito-ku, TOKYO, 110-8534 JAPAN
Low-Voltage ETR-Controller
CMOS IC
Any and all SANYO products described or contained herein do not have specifications that can handle
applications that require extremely high levels of reliability, such as life-support systems, aircraft’s
control systems, or other applications whose failure can be reasonably expected to result in serious
physical and/or material damage. Consult with your SANYO representative nearest you before using
any SANYO products described or contained herein in such applications.
SANYO assumes no responsibility for equipment failures that result from using products at values that
exceed, even momentarily, rated values (such as maximum ratings, operating condition ranges, or other
parameters) listed in products specifications of any and all SANYO products described or contained
herein.
Page 2
No. 7022-2/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
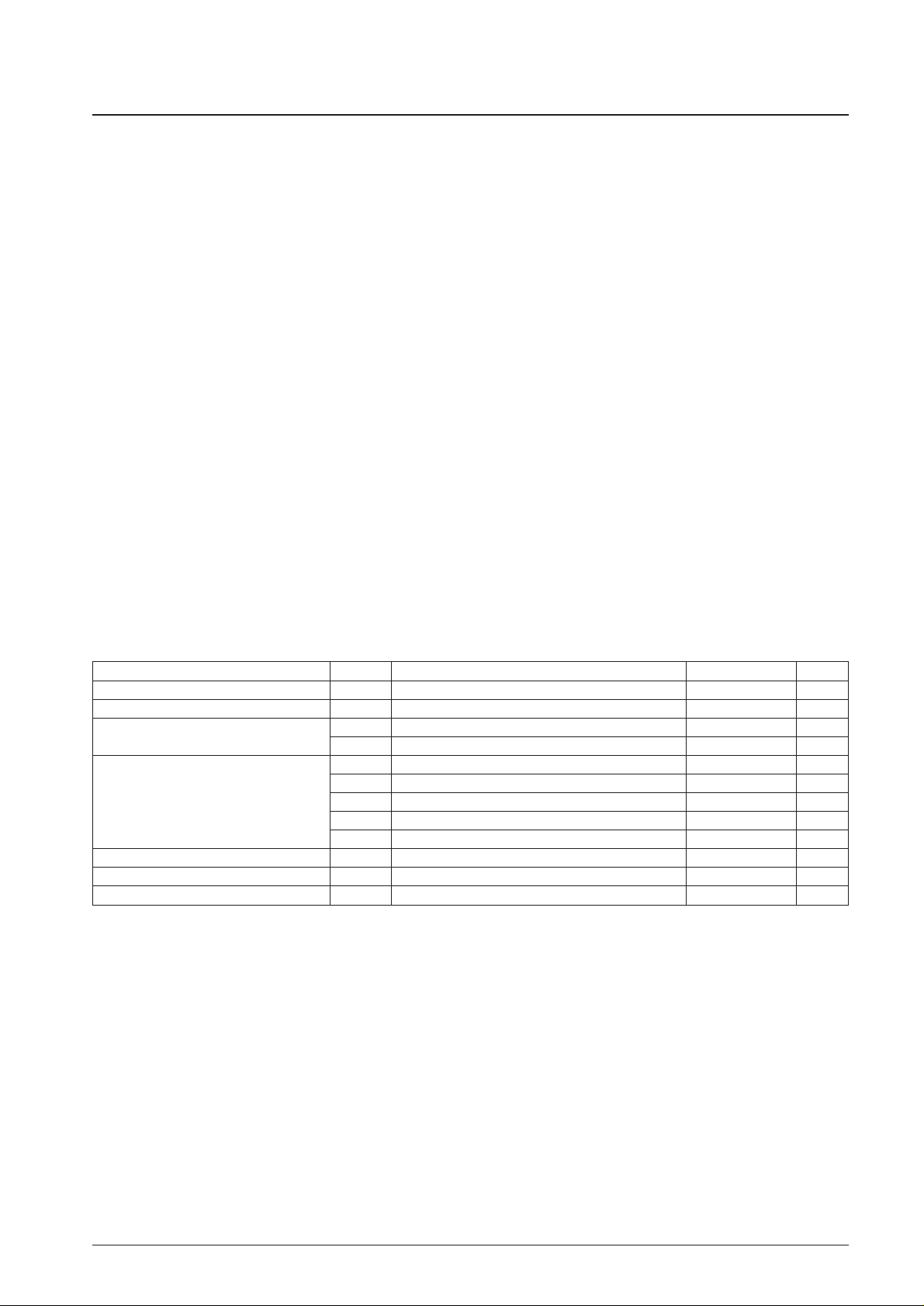
Parameter Symbol Conditions Ratings Unit
Maximum supply voltage V
DD
max VDD –0.3 to +4.0 V
Input voltage V
IN
All input pins –0.3 to VDD+0.3 V
Output voltage
V
OUT
(1) AOUT, PE –0.3 to +15 V
V
OUT
(2) All output pins except V
OUT
(1) –0.3 to VDD+ 0.3 V
I
OUT
(1) PC, PD, PG, PH, PI, PJ, PK, PL, EO 0 to 3 mA
I
OUT
(2) PB 0 to 1 mA
Output current I
OUT
(3) AOUT, PE 0 to 2 mA
I
OUT
(4) S1 to S28 300 µA
I
OUT
(5) COM1 to COM4 3 mA
Allowable power dissipation Pdmax Ta = –20 to +70°C 300 mW
Operating temperature Topr –20 to +70 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –45 to +125 °C
Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings at Ta = 25°C, VSS= 0 V
Continued from preceding page.
I/O ports: 29 pins (Of these 16 can be switched over to
function as LCD ports as a mask options, and
3 ports can be switched over for use with
serial I/O.)
• Serial I/O: One system
• Reference frequencies: 1, 3, 3.125, 5, 6.25, 12.5,
and 25 kHz
• Input frequencies: FM band: 10 to 250 MHz
AM band: 0.5 to 20 MHz
• Input sensitivity:
FM band: 35 mVrms (50 mVrms at 130 MHz or higher
frequency)
AM band: 35 mVrms
• IF counting: Using the HCTR input pin for 0.4 to
12 MHz signals
• External reset input: During CPU and PLL operations,
instruction execution is started from
location 0.
• Built-in power-on reset circuit:
The CPU starts execution from location 0 when power is
first applied.
• Halt mode: The controller-operating clock is stopped.
• Backup mode: The crystal oscillator is stopped.
• Static power-on function: Backup state is cleared with
the PF port
• Beep tone: 1.5 and 3.1 kHz
• Built-in tuner voltage generating circuit:
Cost reduced in tuner-use power supply circuit
• Memory retention voltage: 0.9 V at least
• VDDvoltage
— PLL: 1.8 to 3.6 V
— CPU and ADC: 1.6 to 3.6 V
• Optional function switches:
— PH0 to PH3 (open-drain output/general-purpose
input and output/S13 to S16)
— PG0 to PG3 (open-drain output/general-purpose
input and output/S17 to S20)
— PI0 to PI3 (open-drain output/general-purpose input
and output/S21 to S24)
— PJ0 to PJ3 (open-drain output/general-purpose input
and output/S25 to S28)
— VSENSE circuit (provided/not provided)
— FM DC/DC clock (1/256, 75 kHz)
• Package: SQFP-80 (0.5-mm pitch)
Page 3
No. 7022-3/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
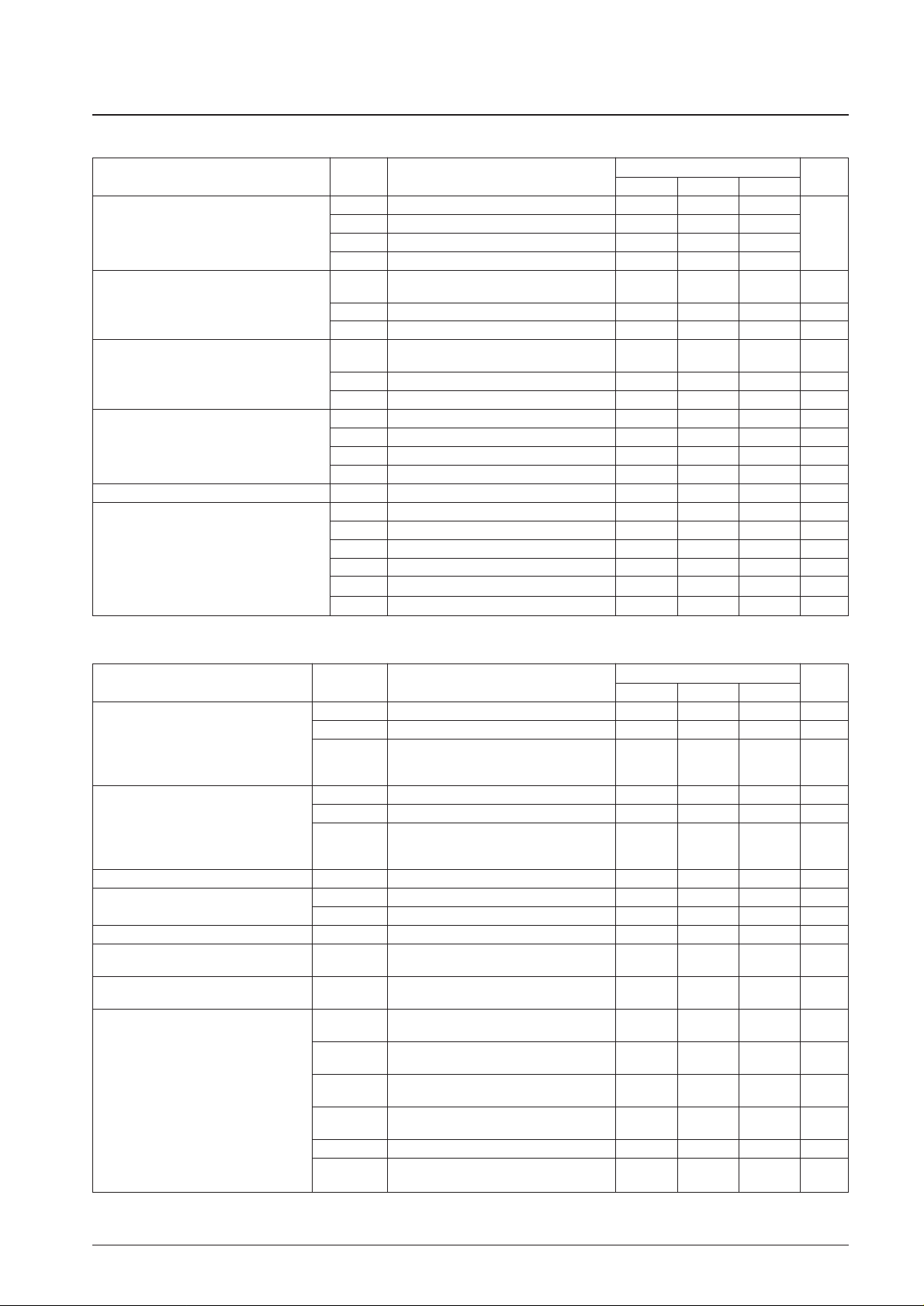
Parameter Symbol Conditions
Ratings
Unit
min typ max
V
DD
(1) PLL operating voltage 1.8 3.0 3.6
Supply voltage
V
DD
(2) Memory retention voltage 1.0
V
V
DD
(3) CPU operating voltage 1.4 3.0 3.6
V
DD
(4) A/D converter operating voltage 1.6 3.0 3.6
V
IH
(1)
Input ports other than V
IH
(2), VIH(3), AMIN,
0.7 V
DD
V
DD
V
Input high-level voltage
FMIN, HCTR, and XIN
V
IH
(2) BRES port 0.8 V
DD
V
DD
V
V
IH
(3) Port PF 0.6 V
DD
V
DD
V
V
IL
(1)
Input ports other than V
IL
(2), VIL(3), AMIN,
0 0.3 V
DD
V
Input low-level voltage
FMIN, HCTR, and XIN
V
IL
(2) BRES port 0 0.2 V
DD
V
V
IL
(3) Port PF 0 0.2 V
DD
V
V
IN
(1) XIN 0.5 0.6 Vrms
Input amplitude
V
IN
(2) FMIN, AMIN 0.035 0.35 Vrms
V
IN
(3) FMIN 0.05 0.35 Vrms
V
IN
(4) HCTR 0.035 0.35 Vrms
Input voltage range V
IN
(5) ADIO, ADI1, ADI3 0 V
DD
V
F
IN
(1) XIN: CI ≤ 35 kΩ 70 75 80 kHz
F
IN
(2) FMIN: VIN(2), VDD(1) 10 130 MHz
Input frequency
F
IN
(3) FMIN: VIN(3), VDD(1) 130 250 MHz
F
IN
(4) AMIN(H): VIN(3), VDD(1) 2 40 MHz
F
IN
(5) AMIN(L): VIN(3), VDD(1) 0.5 10 MHz
F
IN
(6) HCTR: VIN(3), VDD(1) 0.4 12 MHz
Allowable Operating Ranges at Ta = –20 to +70°C, VDD= 1.8 to 3.6 V
Parameter Symbol Conditions
Ratings
Unit
min typ max
I
IH
(1) XIN: VI= VDD= 3.0 V 3 µA
Input high-level current
I
IH
(2) FMIN, AMIN, HCTR: VI= VDD= 3.0 V 3 8 20 µA
PA/PF (without pull-down resistors), the PC,
IIH(3) PD, PG, PH, PI, PJ, PK, and PL ports, 3 µA
and BRES: V
I
= VDD= 3.0 V
I
IL
(1) XIN: V
DD(1)
= V
SS
–3 µA
Input low-level current
I
IL
(2) FMIN, AMIN, HCTR: VI= VDD= V
SS
–3 –8 –20 µA
PA/PF (without pull-down resistors), the PC,
IIL(3) PD, PG, PH, PI, PJ, PK, and PL ports, –3 µA
and BRES: V
I
= VDD= V
SS
Input floating voltage V
IF
PA/PF (with pull-down resistors) 0.05 V
DD
V
Pull-down resistor values
R
PD
(1) PA/PF (with pull-down resistors), VDD= 3.0 V 75 100 200 kΩ
R
PD
(2) TEST1, TEST2 (with pull-down resistors) 10 kΩ
Hysteresis V
H
BRES 0.1 V
DD
0.2 V
DD
V
Voltage doubler reference voltage
DBR4
Referenced to V
DD
, C(3) = 0.47 µF,
1.3 1.5 1.7 V
Ta = 25°C *
1
Voltage doubler step-up voltage DBR1, 2, 3
C(1) = 0.47 µF
2.7 3.0 3.3 V
C(2) = 0.47 µF, without loading, Ta = 25°C *
1
VOH(1) PB: IO= –1 mA
V
DD
– VDD– V
0.7 V
DD
0.3 V
DD
VOH(2) PC, PD, PG, PH, PI, PJ, PK, PL: IO= –1 mA
V
DD
–
V
0.3 V
DD
VOH(3) EO: IO= –500 µA
V
DD
–
V
Output high-level voltage 0.3 V
DD
VOH(4) XOUT: IO= –1 µA
V
DD
–
V
0.3 V
DD
VOH(5) S1 to S28: IO= –20 µA *
1
2.0 V
V
OH
(6)
COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4:
2.0 V
I
O
= –100 µA *
1
Electrical Characteristics within the allowable operating ranges
Continued on next page.
Page 4
No. 7022-4/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
Parameter Symbol Conditions
Ratings
Unit
min typ max
V
OL
(1) PB: IO= –1 mA 0.3 V
DD
0.7 V
DD
V
V
OL
(2)
PC, PD, PG, PH, PI, PJ, PK, PL: IO= –1 mA
0.3 V
DD
V
V
OL
(3) EO: IO= –500 µA 0.3 V
DD
V
V
OL
(4) XOUT: IO= –1 µA 0.3 V
DD
V
Output low-level voltage V
OL
(5) S1 to S28: IO= –20 µA *
1
1.0 V
V
OL
(6)
COM1, COM2, COM3, COM4:
1.0 V
I
O
= –100 µA *
1
VOL(7) PE: IO= 2 mA 1.0 V
V
OL
(8)
AOUT, TU: IO= 1 mA, AIN = 1.3 V (AOUT), VDD= 3 V
0.5 V
Output off leakage current
I
OFF
(1)
Ports PB, PC, PD, PG, PH, PI, PJ, PK, PL, and EO
–3 +3 µA
I
OFF
(2) AOUT, TU and port PE –100 +100 nA
A/D converter error ADI0, ADI1, ADI3 –1/2 +1/2 LSB
Supply voltage drop detection voltage V
SENSE
(1) Ta = 25°C *
2
1.6 1.75 1.9 V
Supply voltage rise detection voltage V
SENSE
(2) Ta = 25°C *
2
(1)min (1)max
V
+0.1 +0.2
I
DD
(1) VDD(1): FIN(2) 130 MHz, Ta = 25°C 5 15 mA
I
DD
(2) VDD(1): In HALT mode, Ta = 25°C *
3
0.1 mA
Current drain I
DD
(3)
V
DD
= 3.6 V, with the oscillator stopped,
0.1 mA
Ta = 25°C *
4
IDD(4)
V
DD
= 1.8 V, with the oscillator stopped,
1 µA
Ta = 25°C *
4
Note: The halt mode current is due to the CPU executing 20 instruction steps every 125 ms.
Continued from preceding page.
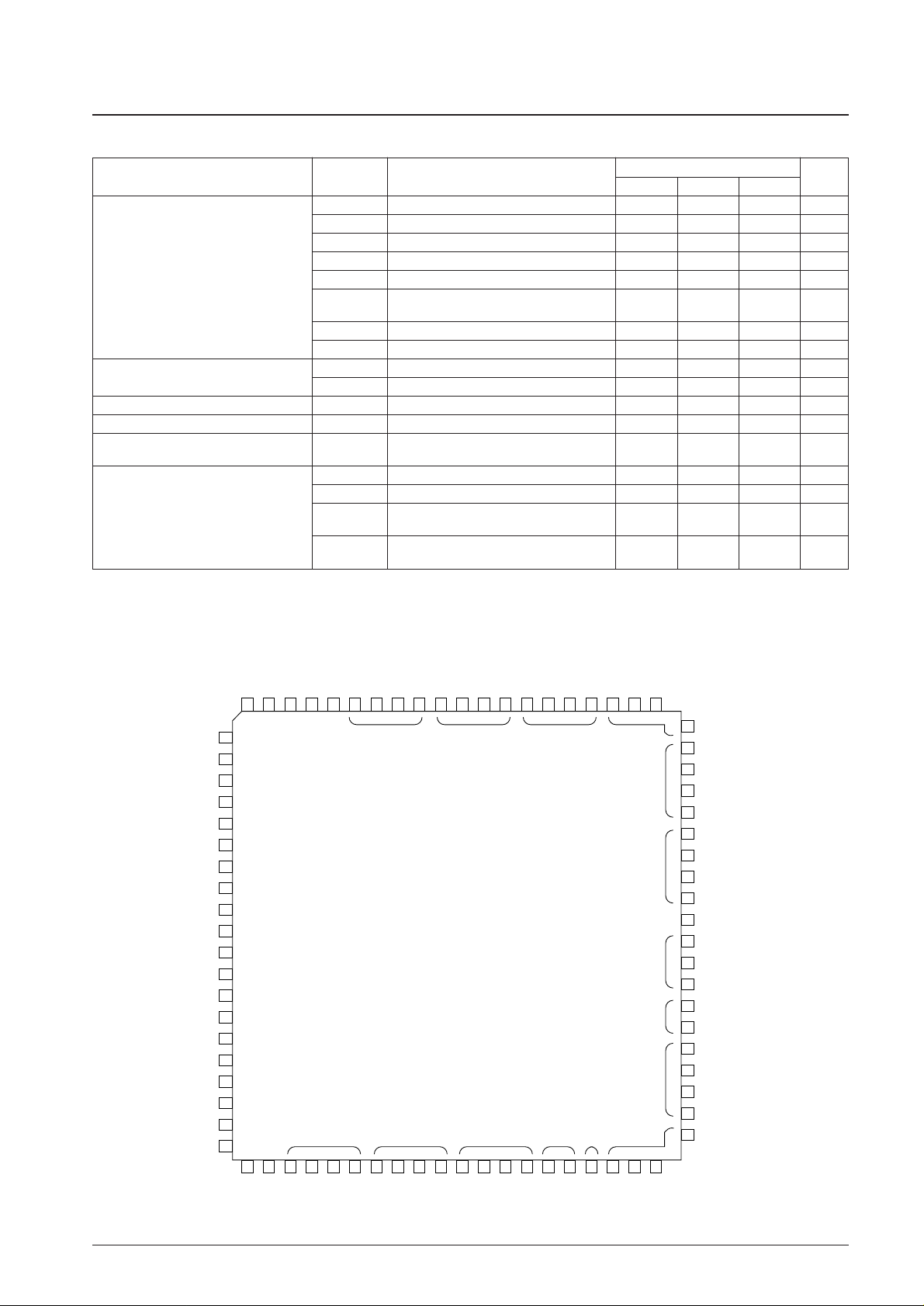
Pin Assignment
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
COM4S1S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
S7
S8
S9
S10
S11
S12
S13/PH0
S14/PH1
S15/PH2
S16/PH3
S17/PG0
S18/PG1
S19/PG2
XOUT
I
I
I
O
I / O I / O
I / O
I / O
I / O
I / OI / OI / OI / O
I / O
O (OD)
TEST2
PA3
PA2
PA1
PA0
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
PC3
PC2
PC1
PC0
PL2
PL1
PL0
PD3
PD2
INT1/PD1
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
INT0/PD0
SI1/PK3
SO1/PK2
SCK1/PK1
PK0
PE1
BEEP/PE0
ADI3/PF2
ADI1/PF1
ADI0/ PF0
VSS
S28/PJ3
S27/PJ2
S26/PJ1
S25/PJ0
S24/PI3
S23/PI2
S22/PI1
S21/PI0
S20/PG3
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
70
69
68
67
66
65
64
63
62
61
XIN
TEST1
AGND
AOUT
AIN
EO
VSS
AMIN
FMIN
VDD
HCTR
TU
BRES
DBR1
DBR2
DBR3
DBR4
COM1
COM2
COM3
Page 5
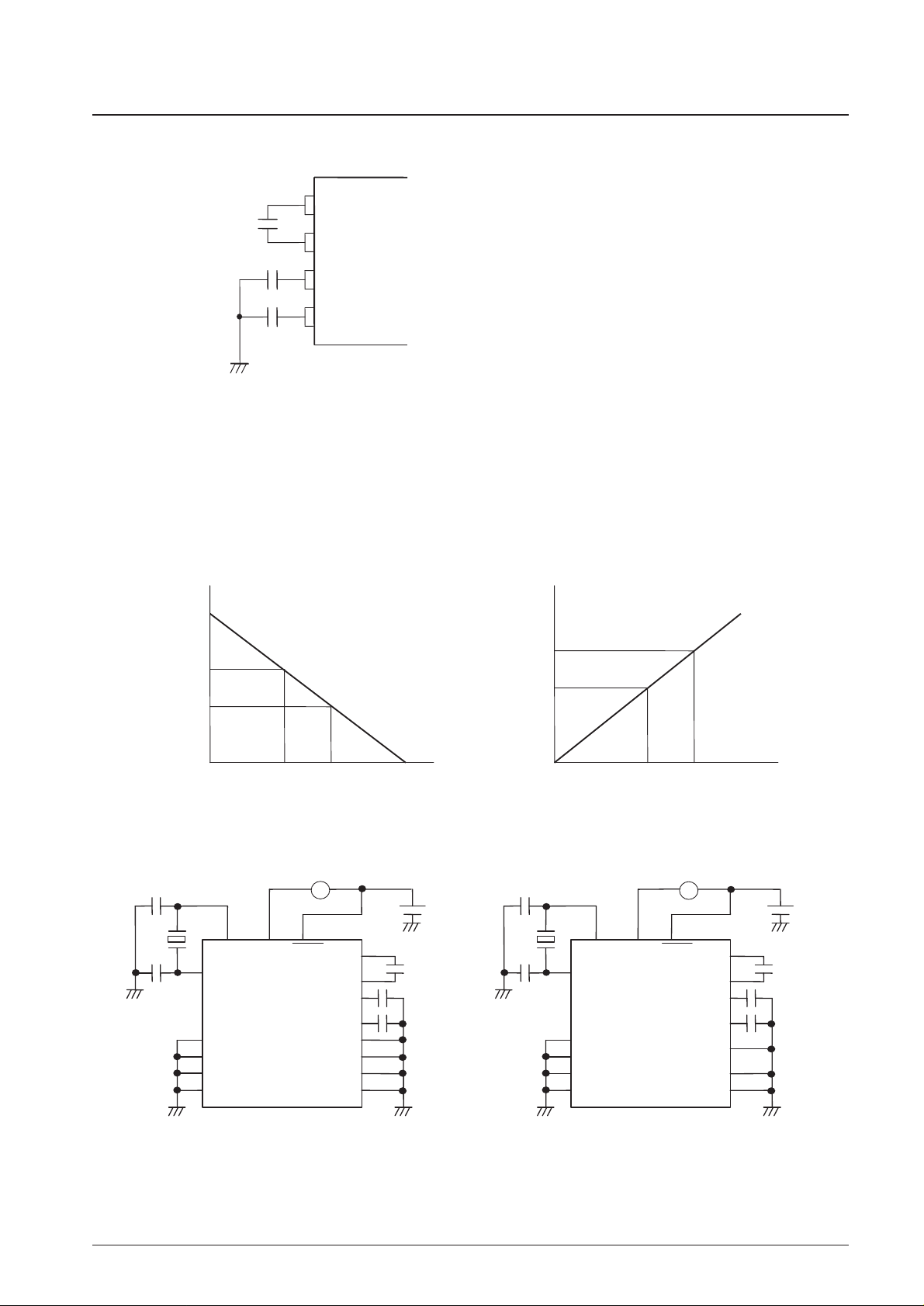
Note: * C(1), C(2), and C(3) must be connected even if an LCD is not used.
No. 7022-5/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
DBR1
DBR2
DBR3
0.1 to 1 µF
0.1 to 1 µF
0.1 to 1 µF
C(C1)
C(C2)
DBR4
C(C3)
Notes: *1. The capacitors C(1), C(2), and C(3) must be connected to the DBR pins.
*2. V
SENSE
When the VDDvoltage drops, the V
SENSE
flag is set when that voltage is 1.75 V (typical). Applications can
check the V
SENSE
flag using the TST instruction. Battery or other power source depletion can be easily
measured by monitoring this flag.
Note that the voltage for V
SENSE
detection differs for the falling and rising directions. Thus, after the V
SENSE
flag has been set due to a voltage drop, it will not be reset if the voltage rises by under 0.1 V.
V
DD
t
1.9 V
1.6 V
→ SETRESET←
V
DD
t
2.1 V
1.7 V
→RESETSET←
A A
7 pF 7 pF
FMIN
XIN
AMIN
TEST1, 2
HCTR
XOUT
VDD
DBR2
DBR1
DBR1
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
0.1 µF
DBR3
DBR4
RESRES
VSS
PA, PF, PL
AGND
AIN
FMIN
XIN
AMIN
TEST1, 2
HCTR
XOUT VDD
VSS
AGND
AIN
7pF
75 kHz 75 kHz
7pF
DBR2
DBR3
DBR4
V
SENSE
(1)
For a falling voltage
*3. Halt mode current measurement circuit *4. Backup mode current measurement circuit
With all ports other than those specified above left open.
With output mode selected for PC and PD.
With segments S13 to S28 selected.
With all ports other than those specified above left open.
With output mode selected for PC and PD.
With segments S13 to S28 selected.
V
SENSE
(2)
For a rising voltage
Page 6

Block Diagram
No. 7022-6/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
PHASE
DETECTOR
REFERENCE DIVIDER
SYSTEM CLOCK
GENERATOR
PROGRAMMBLE DIVIDER
1/16,1/17
V
SENSE
SEG
LA
P-ON
RESET
TIME BASE
CONTROL
UNIVERSAL
COUNTER (20bits)
BANK
COUNT
END
ADDRESS
DECODER
DATA BUS
TIMER 0
JUDGE
ALU
CF
SKIP
BANK
LATCH
A
STACK
4
14
14
ADDRESS COUNTER
ADDRESS DECODER
ROM
12k × 16bits
(LC72317)
16k × 16bits
(LC72318)
16k × 16bits
(LC72319)
RAM
256××4bits(LC72317)
512×4bits(LC72319)
256 4bits(LC72318)
BUS
CONTROL
JMP
CAL
RETURN
INTERRUPT
RESET
INSTRUCTION
DECODER
PLL DATA LATCH
PLL CONTROL
FM LOCAL 1/256
AM LOCAL 1/2
DATA
LATCH
BUS
DRIVER
DATA
LATCH
BUS
DRIVER
BUS
DRIVER
XIN
XOUT
FMIN
PC2
PC1
PC0
PC3
PA3
PA2
PA1
PA0
TEST2
TEST1
RES
*
AMIN
S16/PH3
S15/PH2
S13/PH0
S14/PH1
LCD
PORT
DRIVER
LCPA/B
LCDA/B
EO
S12
S1
HCTR
VSS
VDD
PB2
PB1
PB0
PB3
*
LATCH
BUS
DRIVER
PD2
INT1/PD1
INT0/PD0
AGND
AOUT
AIN
PD3
LATCH
B
PE0/BEEP
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4
DBR4
DBR3
DBR2
DBR1
MPX
(5bits)
MPX
MPX
BEEP TONE
COMMON
DRIVER
DOUBLER
CIRCUIT
LATCH
BUS
DRIVER
LATCH
/
/
BUS
DRIVER
7
122
PF1/ADI1
PF0/ADI0
PE1
PF2/ADI3
TU
75kHz
S20/PG3
S19/PG2
S17/PG0
S18/PG1
S24/PI3
S23/PI2
S21/PI0
S22/PI1
S28/PJ3
S27/PJ2
S25/PJ0
S26/PJ1
/
/
/
LATCH
BUS
DRIVER
PK0
SCK1/PK1
SO1/PK2
SI1/PK3
/
DIVIDER
1/2
1/2
DATA
DATA
1/2
DATA
LATCH
/
BUS
DRIVER
DATA
LATCH
/
BUS
DRIVER
DATA
LATCH
/
BUS
DRIVER
DATA
LATCH
/
BUS
DRIVER
DATA
DATA
Page 7

No. 7022-7/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
Pin Functions
Pin No. Pin I/O Function I/O circuit
75 kHz oscillator connections
80
1
XIN
XOUT
I
O
IC testing. These pins must be connected to ground during normal operation. —
79
2
TEST1
TEST2
I
I
Special-purpose key return signal input ports designed with a low threshold voltage.
When used in conjunction with port PB to form a key matrix, up to 3 simultaneous key
presses can be detected. The four pull-down resistors are selected together in a
single operation using the IOS instruction; they cannot be specified individually. Input
is disabled in backup mode, and the pull-down resistors are disabled after a reset.
6
5
4
3
PA0
PA1
PA2
PA3
I
General-purpose CMOS and n-channel open-drain output shared-function ports.
The IOS instruction (Pwn = 2) is used for function switching.
(b0: PB0, b2: PB1, b3: PB2, PB3) (0: general-purpose CMOS, 1: n-channel open-
drain)
Special-purpose key source signal output ports. Since unbalanced CMOS output
transistor circuits are used, diodes to prevent short-circuits when multiple keys are
pressed are not required. These ports go to the output high-impedance state in
backup mode. These ports go to the output high-impedance state after a reset and
remain in that state until an output instruction (OUT, SPB, or RPB) is executed.
*: Verify the output impedance conditions carefully if these pins are used for functions
other than key source outputs.
10
9
8
7
PB0
PB1
PB2
PB3
O
General-purpose I/O ports.
PD0 and PD1 can be used as an external interrupt port. Input or output mode can be
set individually using the IOS instruction by the bit . A value of 0 specifies input, and 1
specifies output. These ports go to the input disabled high-impedance state in backup
mode. They are set to function as general-purpose input ports after a reset.
14
13
12
11
21
20
19
18
17
PC0
PC1
PC2
PC3
INT0/PD0
INT1/PD1
PD2
PD3
PL0
*
2
I/O
General-purpose output ports with shared beep tone output function (pin 27 only).
The BEEP instruction is used to switch pin 27 between the general-purpose output
port and beep tone output functions. To use pin 27 as a general-purpose output port,
execute a BEEP instruction with b2 set to 0. Set b2 to 1 to use pin 27 as the beep
tone output port. The b0 and b1 bits are used to select the beep tone frequency.
There are two beep tone frequencies supported.
*: When pin 27 is set up as the beep tone output, executing an output instruction to
pin 27 only changes the state of the internal output latch, it does not affect the beep
tone output in any way. Only pin 27 can be switched between the general-purpose
output function and the beep tone output function; the PE1 pin only functions as a
general-purpose output. These pins go to the high-impedance state in backup
mode and remain in that state until an output instruction or a BEEP instruction is
executed. Since these ports are open-drain ports, resistors must be inserted
between these pins and V
DD
. These ports are set to general-purpose output port
function after a reset.
27
26
BEEP/PE0
PE1
Input with built-in
pull-down resistor
Unbalanced CMOS pushpull/n-channel open-drain
N-channel open-drain
CMOS push-pull
Continued on next page.
O
Page 8

No. 7022-8/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
Continued from preceding page.
Pin No. Pin I/O Function I/O circuit
General-purpose input and A/D converter input shared function ports. The IOS
instruction is used to switch between the general-purpose input and A/D converter
port functions. The general-purpose input and A/D converter port functions can be
switched by the bit, with 0 specifying general-purpose input, and 1 specifying the A/D
converter input function. To select the A/D converter function, set up the A/D
converter pin with an IOS instruction with Pwn set to 1. The A/D converter is started
with the UCC instruction (b3 = 1, b2 = 1). The ADCE flag is set when the conversion
completes. The INR instruction is used to read in the data.
*: If an input instruction is executed for one of these pins which is set up for analog
input, the read in data will be at the low level since CMOS input is disabled. In
backup mode these pins go to the input disabled high-impedance state. These
ports are set to their general-purpose input port function after a reset. The A/D
converter is a 5-bit successive approximation type converter, and features a
conversion time of 1.28 ms. Note that the full-scale A/D converter voltage (1FH) is
(63/96) 3 V.
30
29
28
PF0/ADI0
PF1/ADI1
PF2/ADI3
I
CMOS input/analog input
Shared function ports that function either as LCD driver segment outputs or generalpurpose I/O ports.
The IOS instruction is used to switch between the segment output and the generalpurpose I/O port functions. It is also used to switch the direction of pins functioning as
general-purpose I/O ports.
• When used as segment output ports
The IOS (Pwn=8) instruction is used to set the following 4 pins to function as
segment output ports.
b0 to b3 correspond to S17 to S20/PG0 to PG3
(0: Segment output, 1: PG0 to PG3)
The IOS (Pwn=9) instruction is used to set the following 4 pins to function as
segment output ports.
b0 to b3 correspond to S13 to S16/PH0 to PH3
(0: Segment output, 1: PH0 to PH3)
The IOS (Pwn=D) instruction is used to set the following 4 pins to function as
segment output ports.
b0 to b3 correspond to S21 to S24/PI0 to PI3
(0: Segment output, 1: PG0 to PG3)
The IOS (Pwn=E) instruction is used to set the following 4 pins to function as
segment output ports.
b0 to b3 correspond to S25 to S28/PJ0 to PJ3
(0: Segment output, 1: PH0 to PH3)
• When used as general-purpose I/O ports
The IOS instruction is used to switch the I/O direction. The directions of these
pins can be set individually in 1-bit units.
b0 = PG0 b0 = PH0 b0 = PI0 b0 = PJ0
b1 = PG1 b1 = PH1 b1 = PI1 b1 = PJ1 0: Input
b2 = PG2 b2 = PH2 b2 = PI2 b2 = PJ2 1: Output
b3 = PG3 b3 = PH3 b3 = PI3 b3 = PJ3
In backup mode, if used as general-purpose I/O ports, they will be in the input
disabled high-impedance state. If used as segment outputs, they will be held fixed at
the low level.
After a reset, these pins function as segment output ports.
Although the general-purpose port/LCD port setting is a mask option, the setup with
the IOS instruction described above is also necessary.
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
PJ3/S28
PJ2/S27
PJ1/S26
PJ0/S25
PI3/S24
PI2/S23
PI1/S22
PI0/S21
PG3/S20
PG2/S19
PG1/S18
PG0/S17
PH3/S16
PH2/S15
PH1/S14
PH0/S13
*2
O
CMOS push-pull
Continued on next page.
CMOS input
CMOS push-pull
General-purpose input ports, general-purpose I/O ports, and serial I/O port.
The general-purpose I/O port is switched using the IOS instruction; the direction (input
or output) is set in a 1-bit unit. Switching between the general-purpose input port and
the serial I/O port function is also performed with the IOS instruction.
In backup mode, these ports go to the input disabled high-impedance state.
After a reset, these pins are set to function as general-purpose input ports.
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
PK0
SCK1/PK1
SO1/PK2
SI1/PK3
25
24
23
22
Page 9

No. 7022-9/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
Continued from preceding page.
Pin No. Pin I/O Function I/O circuit
General-purpose input ports
In backup mode, these ports go to the input disabled high-impedance state.
16
15
PL1
PL2
I
CMOS input
LCD driver segment output pins.
A 1/4-duty 1/2-bias drive technique is used.
The frame frequency is 75 Hz.
In backup mode, the outputs are fixed at the low level.
After a reset, the outputs are fixed at the low level.
48 to
59
S12 to S1 O
LCD driver common output pins.
A 1/4-duty 1/2-bias drive technique is used.
The frame frequency is 75 Hz.
In backup mode, the outputs are fixed at the low level.
After a reset, the outputs are fixed at the low level.
60
61
62
63
COM4
COM3
COM2
COM1
O
LCD power supply step-up voltage inputs.
64
65
66
67
DBR4
DBR3
DBR2
DBR1
I
CMOS push-pull
Continued on next page.
System reset input.
In CPU operating mode or halt mode, applications must apply a low level for at least
one full machine cycle to reset the system and restart execution with the PC set to
location 0. This pin is connected in parallel with the internal power on reset circuit.
68 RES I
Tuning voltage generation circuit outputs.
These pins include a transistor, and a tuning voltage (12 to 17 V) can be generated by
connecting external coil, diode, and capacitor components.
69 TU O
N-channel open-drain
FM VCO (local oscillator) input.
This pin is selected with the PLL instruction CW1.
The input must be capacitor coupled.
Input is disabled in backup mode, in halt mode, after a reset, and in PLL stop mode.
72 FMIN I
CMOS amplifier input
AM VCO (local oscillator) input.
This pin and the bandwidth are selected with the PLL instruction CW1.
The input must be capacitor coupled.
Input is disabled in backup mode, in halt mode, after a reset, and in PLL stop mode.
73 AMIN I
CMOS amplifier input
CW1 b1, b0 Bandwidth
1 1 0.5 to 10 MHz (MW, LW)
Page 10

No. 7022-10/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
Continued from preceding page.
Pin No. Pin I/O Function I/O circuit
Special-purpose universal counter input port
• To measure a frequency, set up HCTR frequency measurement mode and the
measurement time with a UCS instruction (b3=0, b2=0) and start the count with a
UCC instruction.
70
HCTR I
CMOS amplifier input
Connections for the built-in transistor used to form a low-pass filter.
AGND is connected to ground.
76
77
78
AIN
AOUT
AGND
I
O
–
Main charge pump output. When the local oscillator frequency divided by N is higher
than the reference frequency a high level is output, when lower, a low level is output.
The pin is set to the high-impedance state when the frequencies match.
Output goes to the high-impedance state in backup mode, in halt mode, after a reset,
and in PLL stop mode.
75 EO O
Power supply pin. This pin must be connected to ground.
This pin must be connected to ground.
This pin must be connected to V
DD
.
—
74
31
71
V
SS
V
SS
V
DD
—
CMOS push-pull
UCS b1 b0 Measurement time
Measurement
UCS b3 b2 Input pin mode 0 0 1 ms
0 0 HCTR
Frequency
0 1 4 ms
measurement
0 1 – 1 0 8 ms
1 0 – 1 1 32 ms
Note 2: When a pin in an I/O switching port is used as an output, applications must first set up the data with an OUT, SPB, or RPB instruction and then set
up output mode with an IOS instruction.
The CNTEND flag is set when the count completes. Since the input circuit functions
as an AC amplifier in this mode, the input must be capacitance coupled.
This pin goes to the input disabled state in backup mode, halt mode, PLL stop mode,
and after a reset.
Page 11

LC72317, 72318 and 72319 Series Instruction Set
Terminology
ADDR : Program memory address
b : Borrow
C : Carry
DH : Data memory address High (Row address) [2 bits]
DL : Data memory address Low (Column address) [4 bits]
I : Immediate data [4 bits]
M : Data memory address
N : Bit position [4 bits]
Rn : Resister number [4 bits]
Pn : Port number [4 bits]
PW : Port control word number [4 bits]
r : General register (One of the addresses from 00H to 0FH of BANK0)
( ), [ ] : Contents of register or memory
M (DH, DL) : Data memory specified by DH, DL
No. 7022-11/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
Mnemonic
Operand
Function Operations function
Instruction format
1st 2nd
AD r M Add M to r r ← (r) + (M)
ADS r M Add M to r, then skip if carry r ← (r) + (M), skip if carry
AC r M Add M to r with carry r ← (r) + (M) + C
ACS r M
Add M to r with carry, r ← (r) + (M) + C
then skip if carry skip if carry
AI M I Add I to M M ← (M) + I
AIS M I Add I to M, then skip if carry M ← (M) + I, skip if carry
AIC M I Add I to M with carry M ← (M) + I + C
AICS M I
Add I to M with carry, M ← (M) + I + C,
then skip if carry skip if carry
SU r M Subtract M from r r ← (r) – (M)
SUS r M
Subtract M from r, r ← (r) – (M),
then skip if borrow skip if borrow
SB r M Subtract M from r with borrow r ← (r) – (M) – b
SBS r M
Subtract M from r with borrow, r ← (r) – (M) – b,
then skip if borrow skip if borrow
SI M I Subtract I from M M ← (M) – I
SIS M I
Subtract I from M, M ← (M) – I,
then skip if borrow skip if borrow
SIB M I Subtract I from M with borrow M ← (M) – I – b
SIBS M I
Subtract I from M with borrow, M ← (M) – I – b,
then skip if borrow skip if borrow
f e d c b a 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 DH DL r
0 1 0 0 0 1 DH DL r
0 1 0 0 1 0 DH DL r
0 1 0 0 1 1 DH DL r
0 1 0 1 0 0 DH DL I
0 1 0 1 0 1 DH DL I
0 1 0 1 1 0 DH DL I
0 1 0 1 1 1 DH DL I
0 1 1 0 0 0 DH DL r
0 1 1 0 0 1 DH DL r
0 1 1 0 1 0 DH DL r
0 1 1 0 1 1 DH DL r
0 1 1 1 0 0 DH DL I
0 1 1 1 0 1 DH DL I
0 1 1 1 1 0 DH DL I
0 1 1 1 1 1 DH DL I
Instructions
Continued on next page.
Addition instructionsSubtraction instructions
Page 12

No. 7022-12/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
Continued from preceding page.
Mnemonic
Operand
Function Operations function
Instruction format
1st 2nd
SEQ r M Skip if r equal to M (r) – (M), skip if zero
SEQI M I Skip if M equal to I (M) – I, skip if zero
SNEI M I Skip if M not equal to I (M) – I, skip if not zero
SGE r M
Skip if r is greater than or (r) – (M),
equal to M skip if not borrow
SGEI M I
Skip if M is greater than
(M) – I, skip if not borrow
equal to I
SLEI M I Skip if M is less than I (M) – I, skip if borrow
AND r M AND M with r r ← (r) AND (M)
ANDI M I AND I with M M ← (M) AND I
OR r M OR M with r r ← (r) OR (M)
ORI M I OR I with M M ← (M) OR I
EXL r M Exclusive OR M with r r ← (r) XOR (M)
EXLI M I Exclusive OR M with M M ← (M) XOR I
SHR r Shift r right with carry
LD r M Load M to r r ← (M)
ST M r Store r to M M ← (r)
MVRD r M
Move M to destination M
[DH, Rn] ← (M)
referring to r in the same row
MVRS M r
Move source M referring to r
M ← [DH, Rn]
to M in the same row
MVSR M1 M2 Move M to M in the same row [DH, DL1] ← [DH, DL2]
MVI M I Move I to M M ← I
TMT M N
Test M bits, then skip if all bits
if M (N) = all 1s, then skip
specified are true
TMF M N
Test M bits, then skip if all bits
if M (N) = all 0s, then skip
specified are false
JMP ADDR Jump to the address PC ← ADDR
CAL ADDR Call subroutine
PC ← ADDR
Stack ← (PC) + 1
RT Return from subroutine PC ←Stack
PC ← Stack,
RTI Return from interrupt BANK ← Stack,
CARRY ← Stack
f e d c b a 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 DH DL r
0 0 0 1 1 0 DH DL I
0 0 0 0 0 1 DH DL I
0 0 0 1 1 0 DH DL r
0 0 0 1 1 1 DH DL I
0 0 0 0 1 1 DH DL I
0 0 1 0 0 0 DH DL r
0 0 1 0 0 1 DH DL I
0 0 1 0 1 0 DH DL r
0 0 1 0 1 1 DH DL I
0 0 1 1 0 0 DH DL r
0 0 1 1 1 0 DH DL I
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 r
1 1 0 1 0 0 DH DL r
1 1 0 1 0 1 DH DL r
1 1 0 1 1 0 DH DL r
1 1 0 1 1 1 DH DL r
1 1 1 0 0 0 DH DL1 DL2
1 1 1 0 0 1 DH DL I
1 1 1 1 0 0 DH DL N
1 1 1 1 0 1 DH DL N
1 0 0 ADDR (13 bits)
1 0 1 ADDR (13 bits)
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
Bit test
instructions
Jump and subroutine
call instructions
carry
(r)
Comparison instructionsLogic instructionsTransfer instructions
Continued on next page.
Instructions
Page 13

No. 7022-13/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
Continued from preceding page.
Mnemonic
Operand
Function Operations function
Instruction format
1st 2nd
SS SWR N Set status register (Status W-reg) N ← 1
RS SWR N Reset status register (Status W-reg) N ← 0
TST SRR N Test status register true if (Status R-reg) N = all
TSF SRR N Test status register false if (Status R-reg) N = all
TUL N Test Unlock F/F
if Unlock F/F (N) = all 0s,
then skip
PLL M Load M to PLL register PLL reg ← PLL data
SIO I1 SIO reg ← I1, I2
UCS I Set I to UCCW1 UCCW1 ← I
UCC I Set I to UCCW2 UCCW2 ← I
BEEP I Beep control BEEP reg ← I
DZC I Dead zone control DZC reg ← I
TMS I Set timer register Timer reg ← I
IOS PWn N Set port control word IOS reg PWn ← N
IN M Pn Input port data to M M ← (Pn)
OUT M Pn Output contents of M to port P1n ← M
INR M Pn Input port data to M M ← (Pn)
SPB P1n N Set port1 bits (Pn)N ← 1
RPB P1n N Reset port1 bits (Pn)N ← 0
TPT P1n N
Test port1 bits, then skip if all bits
if (Pn)N = all 1s, then skip
specified are true
TPF P1n N
Test port1 bits, then skip if all bits
if (Pn)N = all 0s, then skip
specified are false
BANK I Select Bank BANK ← I
LCDA M I
Output segment pattern to LCD
LCD (DIGIT) ← M
LCDB M I
digit direct
LCPA M I
Output segment pattern to LCD
LCD (DIGIT) ← LA ← M
LCPB M I
digit through LA
HALT I Halt mode control
HALT reg ← I,
then CPU clock stop
CKSTP Clock stop Stop x’tal OSC
NOP No operation No operation
f e d c b a 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
SWR N
0 0
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
SWR N
0 1
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 SRR N
1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 SRR N
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 N
1 1 1 1 1 0 DH DL r
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 I1 I2
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 I
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 I
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 I
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 I
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 I
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 PWn N
1 1 1 0 1 0 DH DL Pn
1 1 1 0 1 1 DH DL Pn
0 0 1 1 1 0 DH DL Pn
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 Pn N
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 Pn N
1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 Pn N
1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 Pn N
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 I
1 1 0 0 0 0 DH DL DIGIT
1 1 0 0 0 1 DH DL DIGIT
1 1 0 0 1 0 DH DL DIGIT
1 1 0 0 1 1 DH DL DIGIT
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 I
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Bank switching
instructions
Status register
instructions
Hardware control
instructions
LCD
instructions
Other
instructions
I/O instructions
Instructions
Page 14

PS No. 7022-14/14
LC72317, 72318, 72319
This catalog provides information as of June, 2001. Specifications and information herein are subject to
change without notice.
Specifications of any and all SANYO products described or contained herein stipulate the performance,
characteristics, and functions of the described products in the independent state, and are not guarantees
of the performance, characteristics, and functions of the described products as mounted in the customer’s
products or equipment. To verify symptoms and states that cannot be evaluated in an independent device,
the customer should always evaluate and test devices mounted in the customer’s products or equipment.
SANYO Electric Co., Ltd. strives to supply high-quality high-reliability products. However, any and all
semiconductor products fail with some probability. It is possible that these probabilistic failures could
give rise to accidents or events that could endanger human lives, that could give rise to smoke or fire,
or that could cause damage to other property. When designing equipment, adopt safety measures so
that these kinds of accidents or events cannot occur. Such measures include but are not limited to protective
circuits and error prevention circuits for safe design, redundant design, and structural design.
In the event that any or all SANYO products (including technical data, services) described or contained
herein are controlled under any of applicable local export control laws and regulations, such products must
not be exported without obtaining the export license from the authorities concerned in accordance with the
above law.
No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or
mechanical, including photocopying and recording, or any information storage or retrieval system,
or otherwise, without the prior written permission of SANYO Electric Co., Ltd.
Any and all information described or contained herein are subject to change without notice due to
product/technology improvement, etc. When designing equipment, refer to the “Delivery Specification”
for the SANYO product that you intend to use.
Information (including circuit diagrams and circuit parameters) herein is for example only; it is not
guaranteed for volume production. SANYO believes information herein is accurate and reliable, but
no guarantees are made or implied regarding its use or any infringements of intellectual property rights
or other rights of third parties.
 Loading...
Loading...