
• 15P0078B1 •
ASAB
ADVANCED SOFT STARTER
INSTALLATION AND PROGRAMMING
INSTRUCTIONS
Issued on 22/05/13
R. 03
English
• This manual is integrant and essential to the product. Carefully read the instructions contained herein as
they provide important hints for use and maintenance safety.
• This device is to be used only for the purposes it has been designed to. Other uses should be considered
improper and dangerous. The manufacturer is not responsible for possible damages caused by improper,
erroneous and irrational uses.
• Elettronica Santerno is responsible for the device in its original setting.
• Any changes to the structure or operating cycle of the device must be performed or authorized by the
Engineering Department of Elettronica Santerno.
• Elettronica Santerno assumes no responsibility for the consequences resulting from the use of non-original
spare parts.
• Elettronica Santerno reserves the right to make any technical changes to this manual and to the device
without prior notice. If printing errors or similar are detected, corrections will be included in new releases of
the manual.
• The information contained herein is the property of Elettronica Santerno and cannot be reproduced.
Elettronica Santerno enforces its rights on the drawings and catalogues according to the law.
Elettronica Santerno S.p.A.
S.S. Selice, 47 – 40026 Imola (BO) Italy
Tel. +39 0542 489711 – Fax +39 0542 489722
www.santerno.com sales@santerno.com

ASAB
1/66
Contents
1 About This Manual ..................................................................................................................................................... 3
2 Caution Statements.................................................................................................................................................... 3
2.1 Electrical Shock Risk .....................................................................................................................................................................3
2.2 System Design and Safety of Personnel.......................................................................................................................................3
2.3 Disposal Instructions .....................................................................................................................................................................4
3 Introduction ................................................................................................................................................................ 5
3.1 Feature List ...................................................................................................................................................................................5
3.2 Specifications ................................................................................................................................................................................5
4 Installation ................................................................................................................................................................ 11
4.1 Physical Installation .....................................................................................................................................................................11
4.2 Control Terminals ........................................................................................................................................................................11
4.3 Control Voltage............................................................................................................................................................................12
4.4 Control Wiring..............................................................................................................................................................................12
4.5 Relay Outputs..............................................................................................................................................................................12
4.6 Motor Thermistors .......................................................................................................................................................................12
4.7 Power Terminations ....................................................................................................................................................................13
4.8 Power Input and Output Configurations ......................................................................................................................................14
4.9 Schematic Diagrams ...................................................................................................................................................................15
5 Power Circuits .......................................................................................................................................................... 16
5.1 Motor Connection ........................................................................................................................................................................16
5.2 Bypass Contactor ........................................................................................................................................................................19
5.3 Main Contactor ............................................................................................................................................................................19
5.4 Circuit Breaker.............................................................................................................................................................................19
5.5 Earth Terminals ...........................................................................................................................................................................19
5.6 Power Factor Correction .............................................................................................................................................................19
5.7 Power Supply Fuses ...................................................................................................................................................................19
6 Operation .................................................................................................................................................................. 24
6.1 Keypad and Feedback ................................................................................................................................................................24
6.2 Start, Stop and Reset Commands ..............................................................................................................................................26
6.3 Soft Start Methods.......................................................................................................................................................................26
6.4 Stop Methods ..............................................................................................................................................................................29
6.5 Jog Operation ..............................................................................................................................................................................31
6.6 Inside Delta Operation ................................................................................................................................................................32
7 Programming Menu.................................................................................................................................................. 33
7.1 Quick Setup .................................................................................................................................................................................34
7.2 Standard Menu ............................................................................................................................................................................35
7.3 Extended Menu ...........................................................................................................................................................................36
7.4 Parameter Descriptions ...............................................................................................................................................................38
7.5 Adjustment Lock ..........................................................................................................................................................................49
7.6 Access Code ...............................................................................................................................................................................49
7.7 Setup Tools .................................................................................................................................................................................49
8 Logs Menu ................................................................................................................................................................ 51
8.1 Trip Log .......................................................................................................................................................................................51
8.2 Event Log ....................................................................................................................................................................................51
8.3 Performance Counters ................................................................................................................................................................51
9 Application Examples .............................................................................................................................................. 52
9.1 Installation with Main Contactor ..................................................................................................................................................52
9.2 Installation with Bypass Contactor ..............................................................................................................................................53
9.3 Emergency Run Operation ..........................................................................................................................................................54
9.4 Auxiliary Trip Circuit ....................................................................................................................................................................55
9.5 DC Brake with External Zero Speed Sensor ...............................................................................................................................56
9.6 Soft Braking .................................................................................................................................................................................57
9.7 Two Speed Motor ........................................................................................................................................................................58
10 Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................................................... 59

2/66
ASAB
10.1 Protection Responses .................................................................................................................................................................59
10.2 Trip Messages .............................................................................................................................................................................59
10.3 General Faults .............................................................................................................................................................................62
11 Accessories .............................................................................................................................................................. 64
11.1 Communication Modules .............................................................................................................................................................64
11.2 Remote Control Panel (RCP) ......................................................................................................................................................64
11.3 Finger Guard Kit ..........................................................................................................................................................................64
11.4 PC Software ................................................................................................................................................................................64
12 Busbar Adjustment Procedure ............................................................................................................................... 65

ASAB
3/66
WARNING
Indicates a hazard that may cause personal injury or death.
CAUTION
Indicates a hazard that may damage the equipment or installation.
NOTE
Provides helpful information.
This symbol is used throughout this manual to draw attention to topics of special importance to the installation and
operation of equipment.
NOTE
The ASAB soft starter is not user serviceable. The unit should only be serviced by authorised service personnel.
Unauthorised tampering with the unit will void the product warranty.
WARNING - ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
Models ASAB-0500B~ASAB-1600C: The busbar and heatsink must be treated as live whenever the unit has mains voltage
connected (including when the starter is tripped or waiting for a command).
SHORT CIRCUIT
The ASAB is not short circuit proof. After severe overload or short circuit, the operation of the ASAB should be fully tested by
an authorised service agent.
GROUNDING AND BRANCH CIRCUIT PROTECTION
It is the responsibility of the user or person installing the ASAB to provide proper grounding and branch circuit protection
according to local electrical safety codes.
1 About This Manual
The examples and diagrams in this manual are included solely for illustrative purposes. The information contained in this manual is
subject to change at any time and without prior notice. In no event will responsibility or liability be accepted for direct, indirect or
consequential damages resulting from the use or application of this equipment.
2 Caution Statements
Caution Statements cannot cover every potential cause of equipment damage but can highlight common causes of damage. It is the
installer's responsibility to read and understand all instructions in this manual prior to installing, operating or maintaining the equipment,
to follow good electrical practice including applying appropriate personal protective equipment and to seek advice before operating this
equipment in a manner other than as described in this manual.
2.1 Electrical Shock Risk
The voltages present in the following locations can cause severe electric shock and may be lethal:
AC supply cables and connections
Output cables and connections
Many internal parts of the starter, and external option units
The AC supply must be disconnected from the starter using an approved isolation device before any cover is removed from the starter or
before any servicing work is performed.
2.2 System Design and Safety of Personnel
The starter is intended as a component for professional incorporation into complete equipment or a system. If installed incorrectly, the
starter may present a safety hazard.
The starter uses high voltages and currents, carries stored electrical energy, and is used to control equipment which can cause injury.
Close attention is required to the electrical installation and the system design to avoid hazards either in normal operation or in the event
of equipment malfunction. System design, installation, commissioning and maintenance must be carried out by personnel who have the
necessary training and experience. They must read this safety information and this guide carefully.
None of the starter functions must be used to ensure safety of personnel, ie they must not be used for safety-related functions.
Careful consideration must be given to the functions of the starter which might result in a hazard, either through their intended behaviour
or through incorrect operation due to a fault. In any application where a malfunction of the starter or its control system could lead to or
allow damage, loss or injury, a risk analysis must be carried out, and where necessary, further measures taken to reduce the risk.

4/66
ASAB
Equipment containing electrical components may not be disposed of together with domestic
waste.
It must be collected separately as electrical and electronic waste according to local and
currently valid legislation.
The system designer is responsible for ensuring that the complete system is safe and designed correctly according to the relevant safety
standards.
2.2.1 STOP function
The STOP function does not remove dangerous voltages from the starter, the motor or any external option units.
2.3 Disposal Instructions

ASAB
5/66
Extensive starting and stopping options
Adaptive control
Constant current
Current ramp
Timed voltage ramp soft stop
Brake
Models for all connection requirements
23 A to 1600 A (nominal)
200 VAC to 525 VAC
380 VAC to 690 VAC
Internally bypassed options
In-line or inside delta connection (auto-detect)
Inputs and outputs
Remote control inputs
(3 x fixed, 1 x programmable)
Relay outputs
(3 x programmable)
Analog output
DeviceNet, Modbus, Profibus, Ethernet (Ethernet IP, Modbus
TCP, Profinet) or USB communication modules (optional)
Easy-to-read display with comprehensive feedback
Multi-language feedback
Multiple status screens and performance graphs
Date and time stamped event logging
Operational counters (number of starts, hours run,
kWh)
Performance monitoring (current, voltage, power
factor, kWh)
User-programmable monitoring screen
Customisable protection
Motor overload
Excess start time
Undercurrent
Instantaneous overcurrent
Current imbalance
Mains frequency
Input trip
Motor thermistor
Power circuit
Phase sequence
ASAB-
–
– –
Control voltage
12 = 110~120 VAC or 220~240 VAC
14 = 24 VAC/VDC
Mains voltage
5 = 200 ~ 525 VAC
7 = 380 ~ 690 VAC
Bypass
B = internally bypassed
C = non-bypassed (continuous connection)
Nominal current rating
80 A : AC-53b
3.5 - 15 : 345
Off time (seconds)
Start time (seconds)
Start current (multiple of motor full load current)
Starter current rating (amperes)
NOTE
Models ASAB-0255C~ASAB-1600C must be externally bypassed.
3 Introduction
The ASAB is an advanced digital soft start solution for motors from 11 kW to 850 kW. ASAB soft starters provide a complete range of
motor and system protection features and have been designed for reliable performance in the most demanding installation situations.
3.1 Feature List
3.2 Specifications
3.2.1 Model Code
3.2.2 Current Ratings
Contact your local supplier for ratings under operating conditions not covered by these ratings charts.
Current Ratings for Bypass Operation

6/66
ASAB
AC53b 3.0-10:350
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 3.5-15:345
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 4.0-20:340
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 4.5-30:330
40 ºC <1000 metres
ASAB-0023B
23 A
20 A
17 A
15 A
ASAB-0043B
43 A
37 A
31 A
26 A
ASAB-0053B
53 A
53 A
46 A
37 A
AC53b 3.0-10:590
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 3.5-15:585
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 4.0-20:580
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 4.5-30:570
40 ºC <1000 metres
ASAB-0076B
76 A
64 A
55 A
47 A
ASAB-0097B
97 A
82 A
69 A
58 A
ASAB-0100B
100 A
88 A
74 A
61 A
ASAB-0105B
105 A
105 A
95 A
78 A
ASAB-0145B
145 A
123 A
106 A
90 A
ASAB-0170B
170 A
145 A
121 A
97 A
ASAB-0200B
200 A
189 A
160 A
134 A
ASAB-0220B
220 A
210 A
178 A
148 A
ASAB-0255B
255 A
231 A
201 A
176 A
ASAB-0255C
255 A
231 A
201 A
176 A
ASAB-0350B
350 A
329 A
284 A
244 A
ASAB-0380C
380 A
380 A
359 A
299 A
ASAB-0425B
425 A
411 A
355 A
305 A
ASAB-0430C
430 A
430 A
368 A
309 A
ASAB-0500B
500 A
445 A
383 A
326 A
ASAB-0580B
580 A
492 A
425 A
364 A
ASAB-0620C
620 A
620 A
540 A
434 A
ASAB-0650C
650 A
650 A
561 A
455 A
ASAB-0700B
700 A
592 A
512 A
438 A
ASAB-0790C
790 A
790 A
714 A
579 A
ASAB-0820B
820 A
705 A
606 A
516 A
ASAB-0920B
920 A
804 A
684 A
571 A
ASAB-0930C
930 A
930 A
829 A
661 A
ASAB-1000B
1000 A
936 A
796 A
664 A
ASAB-1200C
1200 A
1200 A
1200 A
1071 A
ASAB-1410C
1410 A
1410 A
1319 A
1114 A
ASAB-1600C
1600 A
1600 A
1600 A
1353 A
AC53b 3.0-10:350
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 3.5-15:345
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 4.0-20:340
40 ºC <1000 40 ºC <1000
metres
AC53b 4.5-30:330
40 ºC <1000 metres
ASAB-0023B
34 A
30 A
26 A
22 A
ASAB-0043B
64 A
59 A
51 A
44 A
ASAB-0053B
79 A
79 A
69 A
55 A
AC53b 3.0-10:590
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 3.5-15:585
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 4.0-20:580
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53b 4.5-30:570
40 ºC <1000 metres
ASAB-0076B
114 A
96 A
83 A
70 A
ASAB-0097B
145 A
123 A
104 A
87 A
ASAB-0100B
150 A
132 A
112 A
92 A
ASAB-0105B
157 A
157 A
143 A
117 A
ASAB-0145B
218 A
184 A
159 A
136 A
ASAB-0170B
255 A
217 A
181 A
146 A
ASAB-0200B
300 A
283 A
241 A
200 A
ASAB-0220B
330 A
315 A
268 A
223 A
ASAB-0255B
382 A
346 A
302 A
264 A
ASAB-0255C
382 A
346 A
302 A
264 A
ASAB-0350B
525 A
494 A
427 A
366 A
ASAB-0380C
570 A
570 A
539 A
449 A
ASAB-0425B
638 A
617 A
533 A
458 A
ASAB-0430C
645 A
645 A
552 A
464 A
ASAB-0500B
750 A
668 A
575 A
490 A
In-line connection
Inside delta connection

ASAB
7/66
ASAB-0580B
870 A
738 A
637 A
546 A
ASAB-0620C
930 A
930 A
810 A
651 A
ASAB-0650C
975 A
975 A
842 A
683 A
ASAB-0700B
1050 A
889 A
768 A
658 A
ASAB-0790C
1185 A
1185 A
1071 A
868 A
ASAB-0820B
1230 A
1058 A
910 A
774 A
ASAB-0920B
1380 A
1206 A
1026 A
857 A
ASAB-0930C
1395 A
1395 A
1244 A
992 A
ASAB-1000B
1500 A
1404 A
1194 A
997 A
ASAB-1200C
1800 A
1800 A
1800 A
1606 A
ASAB-1410C
2115 A
2115 A
1979 A
1671 A
ASAB-1600C
2400 A
2400 A
2400 A
2030 A
351 A : AC-53a
3.5 - 15 : 50 - 6
Starts per hour
On-load duty cycle (%)
Start time (seconds)
Start current (multiple of motor full load current)
Starter current rating (amperes)
AC53a 3-10:50-6
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53a 3.5-15:50-6
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53a 4-20:50-6
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53a 4.5-30:50-6
40 ºC <1000 metres
ASAB-0255C
255 A
222 A
195 A
171 A
ASAB-0380C
380 A
380 A
348 A
292 A
ASAB-0430C
430 A
413 A
355 A
301 A
ASAB-0620C
620 A
614 A
515 A
419 A
ASAB-0650C
650 A
629 A
532 A
437 A
ASAB-0790C
790 A
790 A
694 A
567 A
ASAB-0930C
930 A
930 A
800 A
644 A
ASAB-1200C
1200 A
1200 A
1135 A
983 A
ASAB-1410C
1410 A
1355 A
1187 A
1023 A
ASAB-1600C
1600 A
1600 A
1433 A
1227 A
AC53a 3-10:50-6
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53a 3.5-15:50-6
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53a 4-20:50-6
40 ºC <1000 metres
AC53a 4.5-30:50-6
40 ºC <1000 metres
ASAB-0255C
382 A
334 A
293 A
257 A
ASAB-0380C
570 A
570 A
522 A
437 A
ASAB-0430C
645 A
620 A
533 A
451 A
ASAB-0620C
930 A
920 A
773 A
628 A
ASAB-0650C
975 A
943 A
798 A
656 A
ASAB-0790C
1185 A
1185 A
1041 A
850 A
ASAB-0930C
1395 A
1395 A
1200 A
966 A
ASAB-1200C
1800 A
1800 A
1702 A
1474 A
ASAB-1410C
2115 A
2033 A
1780 A
1535 A
ASAB-1600C
2400 A
2400 A
2149 A
1840 A
Current Ratings for Continuous Operation (Not bypassed)
In-line connection
Inside delta connection

8/66
ASAB
In-line connection
Inside delta connection
Model
Minimum
Maximum
Minimum
Maximum
ASAB-0023B
5 A
23 A
5 A
34 A
ASAB-0043B
9 A
43 A
9 A
64 A
ASAB-0053B
11 A
53 A
11 A
79 A
ASAB-0076B
15 A
76 A
15 A
114 A
ASAB-0097B
19 A
97 A
19 A
145 A
ASAB-0100B
20 A
100 A
20 A
150 A
ASAB-0105B
21 A
105 A
21 A
157 A
ASAB-0145B
29 A
145 A
29 A
217 A
ASAB-0170B
34 A
170 A
34 A
255 A
ASAB-0200B
40 A
200 A
40 A
300 A
ASAB-0220B
44 A
220 A
44 A
330 A
ASAB-0255B
51 A
255 A
51 A
382 A
ASAB-0255C
51 A
255 A
51 A
382 A
ASAB-0350B
70 A
350 A
70 A
525 A
ASAB-0380C
76 A
380 A
76 A
570 A
ASAB-0425B
85 A
425 A
85 A
638 A
ASAB-0430C
86 A
430 A
86 A
645 A
ASAB-0500B
100 A
500 A
100 A
750 A
ASAB-0580B
116 A
580 A
116 A
870 A
ASAB-0620C
124 A
620 A
124 A
930 A
ASAB-0650C
130 A
650 A
130 A
975 A
ASAB-0700B
140 A
700 A
140 A
1050 A
ASAB-0790C
158 A
790 A
158 A
1185 A
ASAB-0820B
164 A
820 A
164 A
1230 A
ASAB-0920B
184 A
920 A
184 A
1380 A
ASAB-0930C
186 A
930 A
186 A
1395 A
ASAB-1000B
200 A
1000 A
200 A
1500 A
ASAB-1200C
240 A
1200 A
240 A
1800 A
ASAB-1410C
282 A
1410 A
282 A
2115 A
ASAB-1600C
320 A
1600 A
320 A
2400 A
Minimum and Maximum Current Settings
The ASAB's minimum and maximum full load current settings depend on the model:

ASAB
9/66
E
087 1 8 . E
A
C
D
B
E
A B
C
D
Model
A
mm (inch)
B
mm (inch)
C
mm (inch)
D
mm (inch)
E
mm (inch)
Weight
kg (lb)
ASAB-0023B
183
4.3
ASAB-0043B
(7.2)
(9.5)
ASAB-0053B
295
278
150
124
ASAB-0076B
(11.6)
(10.9)
(5.9)
(4.9)
4.5 (9.9)
ASAB-0097B
213
5.0
ASAB-0100B
(8.4)
(11.0)
ASAB-0105B
ASAB-0145B
ASAB-0170B
438
380
275
250
250
15
ASAB-0200B
(17.2)
(15.0)
(10.8)
(9.8)
(9.8)
(33.0)
ASAB-0220B
ASAB-0255B
440
392
424
376
296
26 (57.2)
ASAB-0350B
(17.3)
(15.4)
(16.7)
(14.8)
(11.7)
30.2
ASAB-0425B
(66.58)
ASAB-0500B
49.5
ASAB-0580B
(109.13)
ASAB-0700B
640
600
433
320
295
ASAB-0820B
(25.2)
(23.6)
(17.0)
(12.6)
(11.6)
60.0
ASAB-0920B
(132.3)
ASAB-1000B
ASAB-0255C
460 (18.1)
400 (15.7)
390 (15.4)
320 (12.6)
280 (11.0)
24 (52.9)
ASAB-0380C
ASAB-0430C
45.0
ASAB-0620C
689
522
430
320
300
(98.1)
ASAB-0650C
(27.1)
(20.6)
(16.9)
(12.6)
(11.8)
ASAB-0790C
ASAB-0930C
53.0 (116.8)
ASAB-1200C
856
727
585
500
364
117
ASAB-1410C
(33.7)
(28.6)
(23.0)
(19.7)
(14.3)
(257.9)
ASAB-1600C
130 (286.6)
3.2.3 Dimensions and Weights
3.2.4 Specifications
Supply
Mains voltage (L1, L2, L3)
5 ......................................................................................................................................................... 200 VAC ~ 525 VAC (± 10%)
7 .................................................................................................. 380 VAC ~ 600 VAC (± 10%) (in-line or inside delta connection)
7 ................................................................................................... 380 VAC ~ 690 VAC (± 10%) (earthed star supply system only)
Control voltage (A4, A5, A6)
12 ......................................................................................................... 110 ~ 120 VAC or 220 ~ 240 VAC (+ 10% / -15%), 600mA
14 ............................................................................................................................................................. 24 VAC/VDC ±20%, 2.8A

10/66
ASAB
Mains frequency ................................................................................................................................................................. 45 Hz ~ 66 Hz
Rated insulation voltage to earth ................................................................................................................................................. 600 VAC
Rated impulse withstand voltage ........................................................................................................................................................ 4 kV
Form designation ...................................................................................... Bypassed or continuous, semiconductor motor starter form 1
Short circuit capability
Coordination with semiconductor fuses ............................................................................................................................................. Type 2
Coordination with HRC fuses ............................................................................................................................................................. Type 1
ASAB-0023B ~ ASAB-0220B .................................................................................................................. prospective current 65 kA
ASAB-0255B ~ ASAB-1000B .................................................................................................................. prospective current 85 kA
ASAB-0255C ~ ASAB-0930C .................................................................................................................. prospective current 85 kA
ASAB-1200C ~ ASAB-1600C ................................................................................................................ prospective current 100 kA
Electromagnetic capability (compliant with EU Directive 89/336/EEC)
EMC Emissions ............................................................................................. IEC 60947-4-2 Class B and Lloyds Marine No 1 Specification
EMC Immunity ....................................................................................................................................................................... IEC 60947-4-2
Inputs
Input rating ................................................................................................................................................... Active 24 VDC, 8 mA approx
Start (54, 55) ...................................................................................................................................................................... Normally Open
Stop (56, 57) .................................................................................................................................................................... Normally Closed
Reset (58, 57) .................................................................................................................................................................. Normally Closed
Programmable input (53, 55) ............................................................................................................................................. Normally Open
Motor thermistor (64, 65) ............................................................................................................................... Trip >3.6 k, reset <1.6k
Outputs
Relay outputs ....................................................................................................... 10A @ 250 VAC resistive, 5A @ 250 VAC AC15 pf 0.3
Programmable outputs
Relay A (13, 14) ..................................................................................................................................................... Normally Open
Relay B (21, 22, 24) ..................................................................................................................................................... Changeover
Relay C (33, 34) .......................................................................................................................................................... Normally Open
Analog output (40, 41) ........................................................................................................................... 0-20 mA or 4-20 mA (selectable)
Maximum load .......................................................................................................................................... 600 (12 VDC @ 20 mA)
Accuracy ................................................................................................................................................................................... ± 5%
24 VDC output (55, 41)
Maximum load .......................................................................................................................................................................... 200 mA
Accuracy ................................................................................................................................................................................. ± 10%
Environmental
Protection
ASAB-0023B ~ ASAB-0105B .................................................................................................................................................... IP20
ASAB-0145B ~ ASAB-1600C ..................................................................................................................................................... IP00
Operating temperature ............................................................................................................. -10 ˚C to 60 ˚C, above 40 ˚C with derating
Storage temperature ...................................................................................................................................................... -25 °C to + 60 °C
Operating Altitude ....................................................................................................................... 0 - 1000 m, above 1000 m with derating
Humidity ....................................................................................................................................................... 5% to 95% Relative Humidity
Pollution degree ............................................................................................................................................................ Pollution Degree 3
Vibration (ASAB-0023B ~ ASAB-1000B) ......................................................................................................................... IEC 60068-2-6
Heat Dissipation
During Start .............................................................................................................................................................. 4.5 watts per ampere
During Run
ASAB-0023B ~ ASAB-0053B ................................................................................................................................ ≤ 39 watts approx
ASAB-0076B ~ ASAB-0105B .............................................................................................................................. ≤ 51 watts approx
ASAB-0145B ~ ASAB-0220B ............................................................................................................................ ≤ 120 watts approx
ASAB-0255B ~ ASAB-0500B ............................................................................................................................ ≤ 140 watts approx
ASAB-0580B ~ ASAB-1000B ............................................................................................................................ ≤ 357 watts approx
ASAB-0255C ~ ASAB-1600C ............................................................................................................. 4.5 watts per ampere approx
Certification
C ....................................................................................................................................................................................... IEC 60947-4-2
CCC .................................................................................................................................................... GB 14048.6 (CNCA-01C-011:2007)
CE ..................................................................................................................................................................................... IEC 60947-4-2
GOST .................................................................................................................................................................... GOST R 50030.4.1-2002
RoHS ........................................................................................................................................ Compliant with EU Directive 2002/95/EC
UL / C-UL .......................................................................................................................................................................................... UL 508
ASAB-0023B ~ ASAB-0105B ............................................................................................................ IP20 & NEMA1, UL Indoor Type 1
ASAB-0145B ~ ASAB-1600C .................................................................................................................... IP00, UL Indoor Open Type
Marine .................................................................................................................................................. Lloyds Marine No 1 Specification

ASAB
11/66
1
ASAB-0023B ~ ASAB-0220B: Allow 100 mm (3.94 inches)
between soft starters.
ASAB-0255B ~ ASAB-1000B: Allow 200 mm (7.88 inches)
between soft starters.
ASAB-0255C: Allow 100 mm (3.94 inches) between soft
starters.
ASAB-0380C ~ ASAB-1600C: Allow 200 mm (7.88 inches)
between soft starters.
2
ASAB-0023B ~ ASAB-0220B: Allow 50 mm (1.97 inches)
between the soft starter and solid surfaces.
ASAB-0255B ~ ASAB-1000B: Allow 200 mm (7.88 inches)
between the soft starter and solid surfaces.
ASAB-0255C: Allow 100 mm (3.94 inches) between the soft
starter and solid surfaces.
ASAB-0380C ~ ASAB-1600C: Allow 200 mm (7.88 inches)
between the soft starter and solid surfaces.
3
Soft starters may be mounted side by side with no clearance
(that is, if mounted without communications modules).
4
The soft starter may be mounted on its side. Derate the soft
starter's rated current by 15%.
13 14 21 22 2 4 33 34
40 41 53 5 4 5 5 5 6 57 58 64 65A4 A5 A 6
5 4 3 2 1
9 8 7 6
A4 A5 A 6 40 41 5 3 54 55 56 57 58 64 65
13 14 21 22 24 33 34
1 3 1 4 2 1 2 2 2 4 3 3 3 4
4 0 4 1 5 3 5 4 5 5 5 6 5 7 58 6 4 6 5
A 4 A 5 A 6
5 4 3 2 1
9 8 7 6
5 4 3 2 1
9 8 7 6
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
1
Relay outputs 4
Inputs and outputs
13, 14
Relay output A
54, 55
Start
21, 22, 24
Relay output B
56, 57
Stop
33, 34
Relay output C
58, 57
Reset
2
Control voltage (model dependent)
53, 55
Programmable input A
A5, A6
110~120 VAC
64, 65
Motor thermistor input
A4, A6
220~240 VAC
40, 41
Analog output
A5, A6
24 VAC/VDC
55, 41
24 VDC output
3
DB9 connector for remote control panel
NOTE
If you are not using a thermistor, do not short terminals 64, 65.
NOTE
The DB9 connector on the soft starter should only be used to connect to a remote control panel. Connecting other
equipment to this port can damage the soft starter or the equipment.
1
4
3
2
2
1/L 1 5/ L33/L 2
2/T 1 6/ T34/T 2
1/L 1 5/ L33/L 2
2/T 1 6/ T34/T 2
B
1
/
L
1
5
/
L
3
3
/L
2
2
/
T
1
6
/
T
3
4
/T
2
1/ L 1 5 / L33 /L 2
4 Installation
4.1 Physical Installation
4.2 Control Terminals
Control terminations use 2.5mm2 plug-in terminal blocks. Unplug each block, complete the wiring, then reinsert the block.

12/66
ASAB
1
A
B
A B
C
A
B
C
C
2 3
5 7
5 6
5 5
5 4
5 8
5 7
5 6
5 5
5 4
5 8
5 7
5 6
5 5
5 4
5 8
0 872 1.B
1
Two-wire control
2
Three-wire control
3
Four-wire control
A
Start B Stop
C
Reset
CAUTION
Do not apply voltage to the control input terminals. These are active 24 VDC inputs and must be controlled with
potential free contacts.
Cables to the control inputs must be segregated from mains voltage and motor cabling.
CAUTION
Some electronic contactor coils are not suitable for direct switching with PCB mount relays. Consult the contactor
manufacturer/supplier to confirm suitability.
No motor thermistors
Motor thermistors
65
64
65
64
0 8 7 2 2 .A
Thermistor input
NOTE
If no motor thermistors are connected to the ASAB thermistor input terminals 64, 65 must be open. If 64, 65 are shorted,
the ASAB will trip.
The thermistor circuit should be run in screened cable and must be electrically isolated from earth and all other power and
control circuits.
4.3 Control Voltage
Different models require control voltage to different terminals:
12 (110~120 VAC) A5, A6
12 (220~240 VAC) A4, A6
14 (24 VAC/VDC) A5, A6
4.4 Control Wiring
The ASAB has three fixed inputs for remote control. These inputs should be controlled by contacts rated for low voltage, low current
operation (gold flash or similar).
4.5 Relay Outputs
The ASAB has three programmable relay outputs.
Operation of the programmable outputs is determined by the settings of parameters 7A~7I.
If assigned to Main Contactor, the output activates as soon as the soft starter receives a start command and remains active
while the soft starter is controlling the motor (until the motor starts a coast to stop, or until the end of a soft stop).
If assigned to Run, the output activates when the soft start is complete (when the starting current falls below 120% of the
programmed motor full load current) and remains closed until the beginning of a stop (either soft stop or coast to stop).
If assigned to a trip function, the output activates when a trip occurs.
If assigned to a flag, the output activates when the specified flag is active (parameters 7J~7L).
4.6 Motor Thermistors
Motor thermistors can be connected directly to the ASAB. The soft starter will trip when the resistance of the thermistor circuit exceeds
approximately 3.6 kor falls below 20 .

ASAB
13/66
NOTE
For personnel safety, the power terminals on models up to ASAB-0105B are protected by snap-off tabs. When using
large cables, it may be necessary to break off these tabs.
NOTE
Some units use aluminium busbars. When connecting power terminations, we recommend cleaning the surface contact
area thoroughly (using an emery or stainless steel brush) and using an appropriate jointing compound to prevent
corrosion.
ASAB-0023B~ASAB-0105B
05 9 66 .E
Cable size:
6-50 mm2 (AWG 10-1/0)
Torque: 4 Nm (2.9 ft-lb)
1 12 90 .A
14 mm (0.55 inch)
Torx T20 x 150
Flat 7 mm x 150
ASAB-0145B
ASAB-0170B~ASAB-0220B
ASAB-0255B
19 Nm (14.0 ft-lb)
38 Nm (28.0 ft-lb)
38 Nm (28.0 ft-lb)
ASAB-0350B~ASAB-0425B
ASAB-0500B~ASAB-1000B
ASAB-0255C
38 Nm (28.0 ft-lb)
38 Nm (28.0 ft-lb)
38 Nm (28.0 ft-lb)
ASAB-0380C~ASAB-0930C
ASAB-1200C~ASAB-1600C
38 Nm (28.0 ft-lb)
66 Nm (48.7 ft-lb)
6 m m1 9 m m
8 .5 m m
(M 8 )
0 83 5 1. B
0 83 5 2. B
6 m m1 9 m m
1 0. 5 m m
(M 1 0 )
5 m m
2 8 m m
11 m m
(M 1 0 )
13 1 8 1. B
6 m m
2 8 m m
11 m m
(M 1 0 )
1 45 4 3. A
1 3 m m
3 2 m m
11 m m
(M 1 0 )
0 9 8 6 6 .B
6 m m
3 2 m m
1 0. 5 m m
(M 1 0 )
0 83 53 .B
1 3 m m3 2 m m
1 0. 5 m m
(M 1 0 )
0 83 5 4. B
1 6 m m5 1 m m
1 2. 5 m m
(M 1 2 )
0 83 55 . B
4.7 Power Terminations
Use only copper stranded or solid conductors, rated for 75 ºC or higher.

14/66
ASAB
ASAB-0023B~
ASAB-0105B
ASAB-0145B~ASAB-0220B
ASAB-0255B~ASAB-0425B
ASAB-0500B~ASAB-1000B
ASAB-0255C has dedicated bypass terminals at the bottom of the unit.
The bypass terminals are T1B, T2B, T3B.
( L1 B L 2B L 3 B )
1 /L 1 3 / L2 5 /L 3
2 /T 1 4/ T 2 6 /T 3
1 /L 1 3 / L2 5 /L 3
( L1 B L2 B L 3 B )
2 /T 1 4 / T 2 6 /T 3
(L 1 B L2 B L 3 B )
1 /L 1 3 / L2 5 /L 3
2 /T 1 4/ T 2 6 /T 3
1 /L 1 3 / L2 5 /L 3
(L 1 B L2 B L 3 B )
2 /T 1 4/ T 2 6 /T 3
0 87 2 3. D
1 /L 1 , 3 /L 2 , 5 /L 3
2 /T 1 , 4 / T2 , 6 /T 3
1 /L 1 3/ L2 5 /L 3
2 /T 1 4 /T 2 6 /T 3
1 /L 1 3 /L 2 5 /L 3
2 /T 1 4 /T 2 6 /T 3
1 /L 1 3 /L 2 5 /L 3
2 /T 1 4 /T 2 6 /T 3
1 /L 1 3 /L 2 5 /L 3
1 /L 1 3 /L 2 5 /L 3
2 /T 1 4/ T 2 6 /T 3
14 7 6 0 .A
StatusGraphs Logs
Exit Enter
Menu
Local
Remote
Local
Ready
Run
Trip
Start
Reset
Stop
RemoteInputs
InputA Start Stop Reset
Status Graphs Logs
Exit Enter
Menu
Local
Remote
Local
Ready
Run
Trip
Start
Reset
Stop
RemoteInputs
InputA Start Stop Reset
StatusGraphs Logs
Exit Enter
Menu
Local
Remote
Local
Ready
Run
Trip
Start
Reset
Stop
RemoteInpu ts
InputA Start Stop Reset
StatusGraphs Logs
Exit Enter
Menu
Local
Remote
Local
Ready
Run
Trip
Start
Reset
Stop
RemoteInpu ts
InputA Start Stop Reset
1 49 8 8. A
StatusGraphs L ogs
Exit Enter
Menu
Local
Remote
Local
Ready
Run
Trip
Start
Reset
Stop
RemoteInput s
InputA Start Stop Reset
1 /L 1 3 /L 2 5 /L 3
T 1B T 2B T 3B
2 /T 1 4 /T 2 6 /T 3
4.8 Power Input and Output Configurations
4.8.1 Internally Bypassed Models (ASAB-0023B~ASAB-1000B)
Models ASAB-0023B ~ ASAB-0220B have power inputs at the top of the unit and outputs at the bottom of the unit.
Internally bypassed models ASAB-0255B ~ ASAB-0425B have output busbars at the bottom of the unit and input busbars at both the top
and bottom of the unit. The AC supply can be connected 'Top in, Bottom out' or 'Bottom in, Bottom out'.
Internally bypassed models ASAB-0500B ~ ASAB-1000B have input and output busbars at the top and bottom of the unit. The AC
supply can be connected 'Top in, Bottom out', 'Top in, Top out', 'Bottom in, Bottom out' or 'Bottom in, Top out'.
4.8.2 ASAB-0255C
4.8.3 ASAB-0380C~ASAB-1600C
ASAB-0380C~ASAB-1600C have dedicated bypass terminals, on the input busbars. The bypass terminals are L1B, L2B, L3B.
The busbars on non-bypassed models ASAB-0380C ~ ASAB-1600C can be adjusted for top or bottom input and output as required.
Refer to Busbar Adjustment Procedure for step-by-step instructions. All units are manufactured top in/bottom out.

ASAB
15/66
Internally bypassed models
Non-bypassed models
1
Control voltage (model dependent)
54, 55
Start 2 Remote control inputs
56, 57
Stop 3 Motor thermistor input
58, 57
Reset
4
Relay outputs
53, 55
Programmable input A
40, 41
Analog output
13, 14
Relay output A
55, 41
24 VDC output
21, 22, 24
Relay output B
33, 34
Relay output C
NOTE
Different models require control voltage to different terminals:
12 (110~120 VAC) A5, A6
12 (220~240 VAC) A4, A6
14 (24 VAC/VDC) A5, A6
NOTE
* ASAB-0255C current transformers are located on the output. Bypass terminals are labelled T1B, T2B and T3B.
2 2
2 1
6 /T 3
2 /T 1
13
14
4 /T 2
24
3 3
3 4
6 5
6 4
4 1
4 0
56
57
58
53
54
A 6
A 5
A 4
5/ L3
3/ L2
55
P E
1/ L1
2 4 V DC
20 0 m A
08 7 24 .B
+
4
1
2
3
+
A
6 /T 3
2 /T 1
4 /T2
5 /L3
3 /L2
1 /L1
L 3B
L 2B
L 1B
4
1
2
3
P E
55
A 4
A 5
A 6
54
53
58
57
56
4 0
4 1
6 4
6 5
3 4
3 3
24
14
13
2 1
2 2
A
0 87 2 5. A
*
*
*
+
+
2 4 V DC
20 0 m A
4.9 Schematic Diagrams

16/66
ASAB
NOTE
When testing the soft starter with a small motor, set parameter 1A Motor Full Load Current to the minimum allowable
value.
6 /T 3
2 /T 1
5 /L 3
3 /L 2
1 /L 1
1 3
1 4
4 /T 2
E
K M 1
K M 1 F 1
M
3
KM1
Main contactor (optional)
F1
Semiconductor fuses (optional)
5 Power Circuits
5.1 Motor Connection
ASAB soft starters can be connected to the motor in-line or inside delta (also called three-wire and six-wire connection). When
connecting in inside delta, enter the motor full load current (FLC) for parameter 1A. The ASAB will automatically detect whether the
motor is connected in-line or inside delta and will calculate the correct inside delta current level.
5.1.1 Testing the Installation
The ASAB can be connected to a small motor for testing. During this test, the soft starter's control input and relay output protection
settings can be tested. This test mode is not suitable for testing soft starting or soft stopping performance.
The FLC of the test motor must be at least 2% of the soft starter's minimum FLC (refer to Minimum and Maximum Current Settings on
page 8).
Models which are internally bypassed do not require an external bypass contactor.
5.1.2 In-line installation, internally bypassed

ASAB
17/66
KM1
Main contactor
KM2
Bypass contactor (external)
F1
Semiconductor fuses (optional)
NOTE
The bypass terminals on ASAB-0255C are T1B, T2B, T3B. The bypass terminals on ASAB-0380C ~ ASAB-1600C are
L1B, L2B, L3B.
The fuses can be installed on the input side if required.
6 /T 3
2 /T 1
5 /L 3
3 /L 2
1 /L 1
1 3
1 4
4 /T 2
E
K M 1
K M 1 F 1
M
3
KM1
Main contactor (optional)
F1
Semiconductor fuses (optional)
5.1.3 In-line installation, externally bypassed
Non-bypassed models have dedicated bypass terminals, which allow the ASAB to continue providing protection and monitoring functions
even when bypassed via an external bypass contactor.
The bypass contactor must be connected to the bypass terminals and controlled by a programmable output configured to Run (refer to
parameters 7A~7I).
5.1.4 In-line installation, non-bypassed

18/66
ASAB
04 4 7 9 .C
M
3
6 /T 3
2/ T 1
13
14
4 /T 2
K M 1
U 1( 1 ) U 2( 4 )
V 1( 2 )
V 2( 5)
W 1 (3 ) W 2 (6 )
5 /L 3
3 /L 2
1 /L 1
E
K M 1 F 1
KM1
Main contactor
F1
Semiconductor fuses (optional)
CAUTION
When connecting the ASAB in inside delta configuration, always install a main contactor or shunt trip circuit breaker.
M
3
6/T 3
2/T 1
5/L 3
3/L 2
1/L 1
13
14
4/T 2
E
KM 1
KM 1 F1
U1 (1) U 2( 4)
V1 (2)
V2 (5)
W 1(3) W2 (6)
L2 B*
L1 B*
L3 B*
KM 2
34
33
KM 2
KM1
Main contactor
KM2
Bypass contactor (external)
F1
Semiconductor fuses (optional)
NOTE
The bypass terminals on ASAB-0255C are T1B, T2B, T3B. The bypass terminals on ASAB-0380C ~ ASAB-1600C are
L1B, L2B, L3B.
The fuses can be installed on the input side if required.
CAUTION
When connecting the ASAB in inside delta configuration, always install a main contactor or shunt trip circuit breaker.
5.1.5 Inside delta installation, internally bypassed
5.1.6 Inside delta installation, externally bypassed
Non-bypassed models have dedicated bypass terminals, which allow the ASAB to continue providing protection and monitoring functions
even when bypassed via an external bypass contactor.
The bypass contactor must be connected to the bypass terminals and controlled by a programmable output configured to Run (refer to
parameters 7A~7I).

ASAB
19/66
6/ T3
2/ T1
5/ L3
3/ L2
1/ L1
13
14
4/ T2
K M1
K M1 F 1
U1 (1 ) U 2 (4 )
V 1(2 )
V 2(5 )
W 1( 3) W 2( 6)
M
3
0 4 4 83 . C
KM1
Main contactor
F1
Semiconductor fuses (optional)
CAUTION
When connecting the ASAB in inside delta configuration, always install a main contactor or shunt trip circuit breaker.
CAUTION
Power factor correction capacitors must be connected to the input side of the soft starter. Connecting power factor
correction capacitors to the output side will damage the soft starter.
CAUTION
Adaptive Control controls the motor's speed profile, within the programmed time limit. This may result in a higher level
of current than traditional control methods.
5.1.7 Inside delta installation, non-bypassed
5.2 Bypass Contactor
Some ASAB soft starters are internally bypassed and do not require an external bypass contactor.
Non-bypassed soft starters may be installed with an external bypass contactor. Select a contactor with an AC1 rating greater than or
equal to the full load current rating of the connected motor.
5.3 Main Contactor
A main contactor must be installed if the ASAB is connected to the motor in inside delta format and is optional for in-line connection.
Select a contactor with an AC3 rating greater than or equal to the full load current rating of the connected motor.
5.4 Circuit Breaker
A shunt trip circuit breaker may be used instead of a main contactor to isolate the motor circuit in the event of a soft starter trip. The
shunt trip mechanism must be powered from the supply side of the circuit breaker or from a separate control supply.
5.5 Earth Terminals
Earth terminals are located at the back of the soft starter.
ASAB-0023B ~ ASAB-0105B have one terminal on the input side (top).
ASAB-0145B ~ ASAB-1000B and ASAB-0255C ~ ASAB-1600C have two terminals, one on the input side (top) and one on
the output side (bottom).
5.6 Power Factor Correction
If power factor correction is used, a dedicated contactor should be used to switch in the capacitors.
5.7 Power Supply Fuses
Semiconductor fuses can be used for Type 2 coordination (according to IEC 60947-4-2 standard) and to reduce the risk of damage to
SCRs from transient overload currents.
HRC fuses (such as Ferraz AJT fuses) can be used for Type 1 coordination according to IEC 60947-4-2 standard.
For applications using Adaptive Control to soft stop the motor with stop times greater than 30 seconds, motor branch protection should
be selected as follows:
standard HRC line fuses: minimum 150% motor full load current
motor rated line fuses: minimum rating 100/150% motor full load current
motor control circuit breaker minimum long time setting: 150% motor full load current
motor control circuit breaker minimum short time setting: 400% motor full load current for 30 seconds

20/66
ASAB
NOTE
Fuse selection is based on a 400% FLC start for 20 seconds in conjunction with standard published starts per hour, duty
cycle, 40°C ambient temperature and up to 1000 m altitude. For installations operating outside these conditions,
consult your local supplier.
These fuse tables contain recommendations only. Always consult your local supplier to confirm the selection for your
particular application.
Model
SCR I2T (A2S)
Supply Voltage
(< 440 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 575 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 690 VAC)
ASAB-0023B
1150
170M1314
170M1314
170M1314
ASAB-0043B
8000
170M1316
170M1316
170M1316
ASAB-0053B
15000
170M1318
170M1318
170M1318
ASAB-0076B
15000
170M1319
170M1319
170M1318
ASAB-0097B
51200
170M1321
170M1321
170M1319
ASAB-0100B
80000
170M1321
170M1321
170M1321
ASAB-0105B
125000
170M1321
170M1321
170M1321
ASAB-0145B
125000
170M1321
170M1321
170M1321
ASAB-0170B
320000
170M2621
170M2621
170M2621
ASAB-0200B
320000
170M2621
170M2621
170M2621
ASAB-0220B
320000
170M2621
170M2621
170M2621
ASAB-0255B
320000
170M2621
170M2621
170M2621
ASAB-0255C
320000
170M2621
170M2621
170M2621
ASAB-0350B
202000
170M5011
170M5011
––
ASAB-0380C
320000
170M6011
170M6011
––
ASAB-0425B
320000
170M6011
––
––
ASAB-0430C
320000
170M6011
170M6011
––
ASAB-0500B
320000
170M6008*
––
––
ASAB-0580B
781000
170M6013
170M6013
170M6013
ASAB-0620C
1200000
170M6015
170M6015
170M6014
ASAB-0650C
1200000
170M6015
170M6015
170M6014
ASAB-0700B
781000
170M5015
170M5015
––
ASAB-0790C
2530000
170M6017
170M6017
170M6016
ASAB-0820B
1200000
170M5017
170M6015
––
ASAB-0920B
2530000
170M6017
170M6017
––
ASAB-0930C
4500000
170M6019
170M6019
170M6019
ASAB-1000B
2530000
170M6018
170M6013*
––
ASAB-1200C
4500000
170M6021
––
––
ASAB-1410C
6480000
––
––
––
ASAB-1600C
12500000
170M6019*
––
––
Model
SCR I2T (A2S)
Supply Voltage
(< 440 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 575 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 690 VAC)
ASAB-0023B
1150
63FE
63FE
63FE
ASAB-0043B
8000
120FEE
120FEE
120FEE
ASAB-0053B
15000
200FEE
200FEE
200FEE
ASAB-0076B
15000
200FEE
200FEE
200FEE
ASAB-0097B
51200
200FEE
200FEE
200FEE
ASAB-0100B
80000
280FM
280FM
280FM
ASAB-0105B
125000
280FM
280FM
280FM
ASAB-0145B
125000
280FM
280FM
280FM
ASAB-0170B
320000
450FMM
450FMM
450FMM
ASAB-0200B
320000
450FMM
450FMM
450FMM
ASAB-0220B
320000
450FMM
450FMM
450FMM
ASAB-0255B
320000
450FMM
450FMM
450FMM
ASAB-0255C
320000
450FMM
450FMM
450FMM
ASAB-0350B
202000
315FM*
––
––
ASAB-0380C
320000
––
––
––
5.7.2 Bussman Fuses - Square Body (170M)
* Two parallel connected fuses required per phase.
5.7.3 Bussman Fuses - British Style (BS88)

ASAB
21/66
ASAB-0380C
320000
400FMM*
400FMM
400FMM*
ASAB-0425B
320000
400FMM*
––
––
ASAB-0430C
320000
––
––
––
ASAB-0500B
320000
450FMM*
––
––
ASAB-0580B
781000
500FMM*
500FMM*
500FMM*
ASAB-0620C
1200000
630FMM*
630FMM*
––
ASAB-0650C
1200000
630FMM*
630FMM*
––
ASAB-0700B
781000
630FMM*
––
––
ASAB-0790C
2530000
––
––
––
ASAB-0820B
1200000
––
––
––
ASAB-0920B
2530000
––
––
––
ASAB-0930C
4500000
––
––
––
ASAB-1000B
2530000
––
––
––
ASAB-1200C
4500000
––
––
––
ASAB-1410C
6480000
––
––
––
ASAB-1600C
12500000
––
––
––
Model
SCR I2T (A2S)
Supply Voltage
(< 440 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 575 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 690 VAC)
ASAB-0023B
1150
HSJ40**
HSJ40**
ASAB-0043B
8000
HSJ80**
HSJ80**
ASAB-0053B
15000
HSJ110**
HSJ110**
ASAB-0076B
15000
HSJ125**
HSJ125**
ASAB-0097B
51200
HSJ175
HSJ175**
ASAB-0100B
80000
HSJ175
HSJ175
ASAB-0105B
125000
HSJ225
HSJ225
ASAB-0145B
125000
HSJ250
HSJ250**
ASAB-0170B
320000
HSJ300
HSJ300
ASAB-0200B
320000
HSJ350
HSJ350
ASAB-0220B
320000
HSJ400**
HSJ400**
Not suitable
ASAB-0255B
320000
HSJ450**
HSJ450**
ASAB-0255C
320000
HSJ450**
HSJ450**
ASAB-0350B
202000
HSJ500**
ASAB-0380C
320000
ASAB-0425B
320000
ASAB-0430C
320000
ASAB-0500B
320000
ASAB-0580B
781000
ASAB-0620C
1200000
Not suitable
Not suitable
ASAB-0650C
1200000
ASAB-0700B
781000
ASAB-0790C
2530000
ASAB-0820B
1200000
ASAB-0920B
2530000
ASAB-0930C
4500000
ASAB-1000B
2530000
ASAB-1200C
4500000
ASAB-1410C
6480000
ASAB-1600C
12500000
Model
SCR I2T (A2S)
Supply Voltage
(< 440 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 575 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 690 VAC)
ASAB-0023B
1150
A070URD30XXX0063
A070URD30XXX0063
––
ASAB-0043B
8000
A070URD30XXX0125
A070URD30XXX0125
A070URD30XXX0125
ASAB-0053B
15000
A070URD30XXX0125
A070URD30XXX0125
A070URD30XXX0125
* Two parallel connected fuses required per phase.
5.7.4 Ferraz Fuses - HSJ
5.7.5 Ferraz Fuses - North American Style (PSC 690)
** Two series connected fuses required per phase.

22/66
ASAB
ASAB-0076B
15000
A070URD30XXX0160
A070URD30XXX0160
A070URD30XXX0160
ASAB-0097B
51200
A070URD30XXX0200
A070URD30XXX0200
A070URD30XXX0200
ASAB-0100B
80000
A070URD30XXX0200
A070URD30XXX0200
A070URD30XXX0200
ASAB-0105B
125000
A070URD30XXX0315
A070URD30XXX0315
A070URD30XXX0315
ASAB-0145B
125000
A070URD30XXX0315
A070URD30XXX0315
A070URD30XXX0315
ASAB-0170B
320000
A070URD30XXX0315
A070URD30XXX0315
A070URD30XXX0315
ASAB-0200B
320000
A070URD30XXX0450
A070URD30XXX0450
A070URD30XXX0450
ASAB-0220B
320000
A070URD30XXX0450
A070URD30XXX0450
A070URD30XXX0450
ASAB-0255C
320000
A070URD30XXX0450
A070URD30XXX0450
A070URD30XXX0450
ASAB-0255B
320000
A070URD30XXX0450
A070URD30XXX0450
A070URD30XXX0450
ASAB-0255C
320000
A070URD30XXX0450
A070URD30XXX0450
A070URD30XXX0450
ASAB-0350B
202000
A070URD31XXX0550
––
––
ASAB-0380C
320000
A070URD33XXX0700
A070URD33XXX0700
––
ASAB-0425B
238000
A070URD32XXX0630
––
––
ASAB-0430C
320000
A070URD33XXX0700
A070URD33XXX0700
––
ASAB-0500B
320000
A070URD32XXX0700
–-
–-
ASAB-0580B
781000
A070URD32XXX0800
–-
–-
ASAB-0620C
1200000
A070URD33XXX1000
A070URD33XXX1000
A070URD33XXX1000
ASAB-0650C
1200000
A070URD33XXX1000
A070URD33XXX1000
A070URD33XXX1000
ASAB-0700B
781000
A070URD33XXX0900
–-
––
ASAB-0790C
2530000
A070URD33XXX1400
A070URD33XXX1400
A070URD33XXX1400
ASAB-0820B
1200000
A070URD33XXX1100
––
––
ASAB-0920B
2530000
A070URD33XXX1250
––
––
ASAB-0930C
4500000
A070URD33XXX1400
A070URD33XXX1400
A070URD33XXX1400
ASAB-1000B
2530000
A070URD33XXX1400
––
––
ASAB-1200C
4500000
A055URD33XXX2250
––
––
ASAB-1410C
6480000
A055URD33XXX2250
––
––
ASAB-1600C
12500000
––
––
––
Model
SCR I2T (A2S)
Supply Voltage
(< 440 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 575 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 690 VAC)
ASAB-0023B
1150
6.9URD30D11A0050
6.9URD30D11A0050
6.9URD30D11A0050
ASAB-0043B
8000
6.9URD30D11A0125
6.9URD30D11A0125
6.9URD30D11A0125
ASAB-0053B
15000
6.9URD30D11A0125
6.9URD30D11A0125
6.9URD30D11A0125
ASAB-0076B
15000
6.9URD30D11A0160
6.9URD30D11A0160
6.9URD30D11A0160
ASAB-0097B
51200
6.9URD30D11A0200
6.9URD30D11A0200
6.9URD30D11A0200
ASAB-0100B
80000
6.9URD30D11A0200
6.9URD30D11A0200
6.9URD30D11A0200
ASAB-0105B
125000
6.9URD30D11A0315
6.9URD30D11A0315
6.9URD30D11A0315
ASAB-0145B
125000
6.9URD30D11A0315
6.9URD30D11A0315
6.9URD30D11A0315
ASAB-0170B
320000
6.9URD30D11A0315
6.9URD30D11A0315
6.9URD30D11A0315
ASAB-0200B
320000
6.9URD31D11A0450
6.9URD31D11A0450
6.9URD31D11A0450
ASAB-0220B
320000
6.9URD31D11A0450
6.9URD31D11A0450
6.9URD31D11A0450
ASAB-0255B
320000
6.9URD31D11A0450
6.9URD31D11A0450
6.9URD31D11A0450
ASAB-0255C
320000
6.9URD31D11A0450
6.9URD31D11A0450
6.9URD31D11A0450
ASAB-0350B
202000
6.9URD31D11A0550
––
––
ASAB-0380C
320000
6.9URD33D11A0700
6.9URD33D11A0700
6.9URD33D11A0700
ASAB-0425B
320000
6.9URD32D11A0630
––
––
ASAB-0430C
320000
6.9URD33D11A0700
6.9URD33D11A0700
6.9URD33D11A0700
ASAB-0500B
320000
6.9URD32D11A0700
––
––
ASAB-0580B
781000
6.9URD32D11A0800
––
––
ASAB-0620C
1200000
6.9URD33D11A1000
6.9URD33D11A1000
6.9URD33D11A1000
ASAB-0650C
1200000
6.9URD33D11A1000
6.9URD33D11A1000
6.9URD33D11A1000
ASAB-0700B
781000
6.9URD33D11A0900
––
––
ASAB-0790C
2530000
6.6URD33D11A1400
6.6URD33D11A1400
––
ASAB-0820B
1200000
6.9URD33D11A1100
––
––
ASAB-0920B
2530000
6.9URD33D11A1250
––
––
ASAB-0930C
4500000
6.6URD33D11A1400
6.6URD33D11A1400
––
XXX = blade type. Refer to Ferraz catalog for details.
5.7.6 Ferraz Fuses - European Style (PSC 690)

ASAB
23/66
ASAB-1000B
2530000
6.9URD33D11A1400
––
––
ASAB-1200C
4500000
6URD233PLAF2200
6URD233PLAF2200
––
ASAB-1410C
6480000
6URD233PLAF2200
6URD233PLAF2200
––
ASAB-1600C
12500000
6URD233PLAF2800
6URD233PLAF2800
––
Model
SCR I2T (A2S)
Supply Voltage
(< 440 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 575 VAC)
Supply Voltage
(< 690 VAC)
ASAB-0023B
1150
AJT25
AJT25
ASAB-0043B
8000
AJT50
AJT50
ASAB-0053B
15000
AJT60
AJT60
ASAB-0076B
15000
AJT80
AJT80
ASAB-0097B
512000
AJT100
AJT100
ASAB-0100B
80000
AJT100
AJT100
ASAB-0105B
125000
AJT125
AJT125
ASAB-0145B
125000
AJT150
AJT150
ASAB-0170B
320000
AJT175
AJT175
ASAB-0200B
320000
AJT200
AJT200
ASAB-0220B
320000
AJT250
AJT250
ASAB-0255C
320000
AJT300
AJT300
ASAB-0255B
202000
AJT300
AJT300
ASAB-0350B
202000
AJT400
AJT400
Not suitable
ASAB-0380C
320000
AJT450
AJT450
ASAB-0425B
238000
AJT450
AJT450
ASAB-0430C
320000
AJT450
AJT450
ASAB-0500B
320000
AJT500
AJT500
ASAB-0580B
781000
A4BQ800
A4BQ800
ASAB-0620C
1200000
A4BQ800
A4BQ800
ASAB-0650C
1200000
A4BQ800
A4BQ800
ASAB-0700B
781000
A4BQ800
A4BQ800
ASAB-0790C
2530000
A4BQ1200
A4BQ1200
ASAB-0820B
1200000
A4BQ1200
A4BQ1200
ASAB-0920B
2530000
A4BQ1200
A4BQ1200
ASAB-0930C
4500000
A4BQ1200 / A4BT1100
A4BQ1200 / A4BT1100
ASAB-1000B
2530000
A4BQ1200
A4BQ1200
ASAB-1200C
4500000
A4BQ1600
A4BQ1600
ASAB-1410C
6480000
A4BQ2000
A4BQ2000
ASAB-1600C
12500000
A4BQ2500 / A4BT1800
A4BQ2500 / A4BT1800
5.7.7 Ferraz Fuses - AJT

24/66
ASAB
Sta tu s Gr ap hs L og s
E xi t E n te r
M en u
L oc a l
Re m o t e
L oc a l
Re a d y
Ru n
Tr ip
S ta r t
R e s e t
S to p
5
1
2
3
4
6
Re m ot e I n p u ts
In pu t A S t ar t St o p Re s et
1
Four-line display for status and programming details.
2
LOCAL/REMOTE: Toggle between Local and Remote control
STATUS: Open the status displays and scroll between different status
screens
GRAPHS: Open the performance graphs and scroll between different
graph screens
LOGS: Open the logs
3
Soft starter local control buttons:
START: Start the motor
STOP: Stop the motor
RESET: Reset a trip (Local mode only).
4
Status LEDs (see below for details)
5
Menu navigation buttons:
EXIT: Exit the menu or parameter, or cancel a parameter change.
MENU/ENTER: Enter a menu or parameter, or save a parameter
change.
: Scroll to the next or previous menu or parameter, change the setting
of the current parameter or scroll through the status or graph screens.
6
Remote input LEDs. When on:
INPUT A: Programmable input A is active
START: The remote start input is active
STOP: The remote stop input is active
RESET: The remote reset input is active
LED name
On
Flashing
Ready
The motor is stopped and the starter is ready to start.
The motor is stopped and the starter is waiting for the
Restart Delay (parameter 5A) or Motor Temperature
Check (parameter 4F).
Run
The motor is in run state (receiving full voltage).
The motor is starting or stopping.
Trip
The starter has tripped.
The starter is in warning state.
Local
The starter is in Local control mode.
–
Status
The status screens are active.
–
Graphs
The graph screens are active.
The graph has been paused.
Logs
The logs menu is open.
–
NOTE
Screens shown here are with the default settings.
6 Operation
6.1 Keypad and Feedback
6.1.1 The Keypad
Starter Status LEDs
If the starter is in remote control mode, the Local LED will be off.
If all LEDs are off, the starter is not receiving control voltage.
6.1.2 Displays
The keypad displays a wide range of performance information about the soft starter. The bottom half of the screen shows real-time
information on current or motor power (as selected in parameter 10J). Use the STATUS button or and buttons to select the
information shown on the top half of the screen.
Starter status
Motor temperature
Current
Motor power
Last start information
Date and time
SCR conduction

ASAB
25/66
Ready
M1 000% 000.0kW
Ready
0000 hrs
Primary Motor Set
M1 000% M2 000%
Phase Currents
000.0A 000.0A 000.0A
000.0kW 0000HP
0000kVA -. - - pf
Last start 010 s
350 % FLC Temp 5%
L1 Cond
L2 Cond
L3 Cond
Starter Status
The starter status screen shows details of the starter's operating status, motor temperature and motor power.
Programmable screen
The ASAB's user-programmable screen can be configured to show the most important information for the particular application. Use
parameters 10B to 10E to select which information to display.
Motor Temperature
The temperature screen shows which motor data set is in use, and the temperature of both motors as a percentage of total thermal
capacity. If the ASAB is configured for use on one motor, the temperature for the secondary motor (M2) will always show 0%.
Current
The current screen shows real-time line current on each phase.
Motor Power
The motor power screen shows motor power (kW, HP and kVA) and power factor.
Last Start Information
The last start information screen shows details of the most recent successful start:
start duration (seconds)
maximum start current drawn (as a percentage of motor full load current)
calculated rise in motor temperature
Date and Time
The date/time screen shows the current system date and time (24 hour format). For details on setting the date and time, refer to Set
Date and Time on page 49.
SCR Conduction Bargraph
The SCR conduction bargraph shows the level of conduction on each phase.
6.1.3 Graphs
The ASAB can display real-time performance information for:
current
motor temperature
motor kW
motor kVA
motor power factor
The newest information is displayed at the right hand edge of the screen. Older data is not stored.
To access the graphs or to change which graph is shown, press the GRAPHS button.
The graph can also be paused, to allow past performance to be analysed. To pause the graph, press and hold the GRAPHS button
for more than 0.5 seconds. To unpause the graph, press the GRAPHS button again.

26/66
ASAB
NOTE
The ASAB will not collect data while the graph is paused. When graphing resumes, a small gap will be shown between
the old data and the new data.
Soft Start Method
Parameter Controlled
Performance Parameters Influenced
Timed Voltage Ramp
Voltage
Start current, start torque, acceleration
Constant Current
Current
Start torque, acceleration
Torque Control
Torque
Start current, acceleration
Adaptive Control
Acceleration
Start current, start torque
To Control
Use
Motor Start Current
Constant Current
Motor/Load Acceleration
Adaptive Control
6.2 Start, Stop and Reset Commands
The soft starter can be controlled in three ways:
using the buttons on the keypad
via remote inputs
via a serial communication link
The LOCAL/REMOTE button controls whether the ASAB will respond to local control (via the keypad) or remote control (via the
remote inputs). The ASAB can also be set to allow local control only or remote control only, using parameter 6A Local/Remote. The
Local LED on the keypad is on when the soft starter is in local control mode and off when the soft starter is in remote control mode.
The STOP button on the keypad is always enabled.
Control via the serial communication network is always enabled in local control mode, and can be enabled or disabled in remote control
mode (parameter 6B Comms in Remote). Control via the serial communication network requires an optional communication module.
6.2.1 Using the Soft Starter to Control a Motor
To soft start the motor, press the START button on the keypad or activate the Start remote input. The motor will start using the start
mode selected in parameter 2A.
To stop the motor, press the STOP button on the keypad or activate the Stop remote input. The motor will stop using the stop mode
selected in parameter 2H.
To reset a trip on the soft starter, press the RESET button on the keypad or activate the Reset remote input.
To stop the motor with a coast to stop, regardless of the setting of parameter 2H Stop Mode, press the local STOP and RESET
buttons at the same time. The soft starter will remove power from the motor and open the main contactor, and the motor will coast to
stop.
6.3 Soft Start Methods
Soft starters offer a variety of methods to control motor starting. Each soft start method uses a different primary control parameter.
Best results are obtained by selecting the soft start method that directly controls the parameter of most importance for the application.
Typically soft starters are used to limit motor start current or control load acceleration and/or deceleration. The ASAB can be set to
either Constant Current or Adaptive Control.

ASAB
27/66
Current (%motor full load current)
700%
600%
500%
300%
100%
400%
200%
10% 20% 3 0% 40% 50% 60% 70% 8 0% 9 0% 100 %
1
3
2
1: Initial current (parameter 2C)
2: Current limit (parameter 2B)
3: Full voltage current
Rotor speed (% full speed)
Current (%motor full load current)
700%
600%
500%
300%
100%
400%
200%
1
4
3
2
1: Initial current (parameter 2C)
2: Start ramp time (parameter 2D)
3: Current limit (parameter 2B)
4: Full voltage current
Time
CAUTION
Adaptive Control cannot start the motor faster than a direct on-line (DOL) start. If the start ramp time (parameter 2D) is
shorter than the motor's DOL start time, starting current may reach DOL levels.
6.3.1 Constant Current
Constant current is the traditional form of soft starting, which raises the current from zero to a specified level and keeps the current
stable at that level until the motor has accelerated.
Constant current starting is ideal for applications where the start current must be kept below a particular level.
6.3.2 Current Ramp
Current ramp soft starting raises the current from a specified starting level (1) to a maximum limit (3), over an extended period of time
(2).
Current ramp starting can be useful for applications where:
the load can vary between starts (for example a conveyor which may start loaded or unloaded). Set the initial current
(parameter 2C) to a level that will start the motor with a light load, and the current limit (parameter 2B) to a level that will start
the motor with a heavy load.
the load breaks away easily, but starting time needs to be extended (for example a centrifugal pump where pipeline pressure
needs to build up slowly).
the electricity supply is limited (for example a generator set), and a slower application of load will allow greater time for the
supply to respond.
6.3.3 Adaptive Control for Starting
In an adaptive control soft start, the ASAB adjusts the current in order to start the motor within a specified time and using a selected
acceleration profile.
Every application has a particular starting profile, based on characteristics of the load and the motor. Adaptive Control offers three
different starting profiles, to suit the requirements of different applications. Selecting a profile that matches the inherent profile of the
application can help smooth out acceleration across the full start time. Selecting a dramatically different Adaptive Control profile can
somewhat neutralise the inherent profile.
The ASAB monitors the motor's performance during each start, to improve control for future soft starts.
Adaptive Control
To use Adaptive Control to control starting performance:
1. Select Adaptive Control from the Start Mode menu (parameter 2A)
2. Set the desired Start Ramp Time (parameter 2D)

28/66
ASAB
Speed
0
10 %
20 %
30 %
40 %
50 %
60 %
70 %
80 %
90 %
10 0%
0 48 27 . C
1
2
3
4
Adaptive start profile (parameter 2J):
1. Early acceleration
2. Constant acceleration
3. Late acceleration
4. Start ramp time (parameter 2D)
Time
NOTE
Adaptive Control will control the load according to the programmed profile. Start current will vary according to the
selected acceleration profile and the programmed start time.
If replacing a motor connected to a ASAB programmed for Adaptive Control starting or stopping, or if the starter has
been tested on a different motor prior to actual installation, the starter will need to learn the characteristics of the new
motor. The ASAB will automatically re-learn the motor's characteristics if parameter 1A Motor Full Load Current or
parameter 2L Adaptive Control Gain is changed.
CAUTION
Adaptive Control controls the motor's speed profile, within the programmed time limit. This may result in a higher level
of current than traditional control methods.
NOTE
Changing the gain setting resets the starter's adaptive control learning. The first start after changing the gain will use
constant current.
Current (%motor full load current)
1
2
6
4
5
3
1: Kickstart level (parameter 2E)
2: Kickstart time (parameter 2F)
3: Initial current (parameter 2C)
4: Start ramp time (parameter 2D)
5: Current limit (parameter 2B)
6: Full voltage current
Rotor speed (% full speed)
3. Select the desired Adaptive Start Profile (parameter 2J)
4. Set a start Current Limit (parameter 2B) sufficiently high to allow a successful start. The first Adaptive Control start will be a
Constant Current start. This allows the ASAB to learn the characteristics of the connected motor. This motor data is used by the
ASAB during subsequent Adaptive Control starts.
How to Select the Adaptive Control Start Profile
The best profile will depend on the exact details of each application.
Some loads, such as submersible pumps, should not be run at slow speeds. An early acceleration profile will raise the speed quickly,
then control acceleration through the rest of the start.
Fine-tuning Adaptive Control
If the motor does not start or stop smoothly, adjust the adaptive control gain (parameter 2L). The gain setting determines how much the
ASAB will adjust future adaptive control starts and stops, based on information from the previous start. The gain setting affects both
starting and stopping performance.
If the motor accelerates or decelerates too quickly at the end of a start or stop, increase the gain setting by 5%~10%.
If the motor speed fluctuates during starting or stopping, decrease the gain setting slightly.
6.3.4 Kickstart
Kickstart provides a short boost of extra torque at the beginning of a start, and can be used in conjunction with current ramp or constant
current starting.
Kickstart can be useful to help start loads that require high breakaway torque but then accelerate easily (for example flywheel loads such
as presses).

ASAB
29/66
Stop Method
Performance Result
Coast To Stop
Natural load run down
TVR Soft Stop
Extended run down time
Adaptive Control
Extended run down time according to selected deceleration profile
Brake
Reduced run down time
Voltage (% full voltage)
1
1: Stop time (parameter 2I)
Time
NOTE
Adaptive control does not actively slow the motor down and will not stop the motor faster than a coast to stop. To
shorten the stopping time of high inertia loads, use brake.
CAUTION
Adaptive Control controls the motor's speed profile, within the programmed time limit. This may result in a higher level
of current than traditional control methods.
6.4 Stop Methods
Soft starters offer a variety of methods for the control of motor stopping.
Soft starters are often used in pumping applications to eliminate the damaging effects of fluid hammer. Adaptive Control should be the
preferred stop method for these applications.
6.4.1 Coast to Stop
Coast to stop lets the motor slow at its natural rate, with no control from the soft starter. The time required to stop will depend on the
type of load.
6.4.2 TVR Soft Stop
Timed voltage ramp reduces the voltage to the motor gradually over a defined time. The load may continue to run after the stop ramp is
complete.
Timed voltage ramp stopping can be useful for applications where the stop time needs to be extended, or to avoid transients on
generator set supplies.
6.4.3 Adaptive Control for Stopping
In an adaptive control soft stop, the ASAB controls the current in order to stop the motor within a specified time and using a selected
deceleration profile. Adaptive Control can be useful in extending the stopping time of low inertia loads.
Every application has a particular stopping profile, based on characteristics of the load and the motor. Adaptive Control offers three
different stopping profiles. Choose the adaptive control profile that best matches your application requirements.
Adaptive Control
To use Adaptive Control to control stopping performance:
1. Select Adaptive Control from the Stop Mode menu (parameter 2H)
2. Set the desired Stop Time (parameter 2I)
3. Select the required Adaptive Stop Profile (parameter 2K)

30/66
ASAB
Speed
10 0%
9 0%
8 0%
7 0%
6 0%
5 0%
4 0%
3 0%
2 0%
1 0%
0
04 8 3 5.C
1 2 3
4
Adaptive Control stop profile (parameter 2K):
1. Early deceleration
2. Constant deceleration
3. Late deceleration
4. Stop time (parameter 2I)
Time
Adaptive Stop Profile
Application
Late Deceleration
High head systems where even a small decrease in motor/pump speed results in a rapid transition
between forward flow and reverse flow.
Constant Deceleration
Low to medium head, high flow applications where the fluid has high momentum.
Early Deceleration
Open pump systems where fluid must drain back through the pump without driving the pump in reverse.
NOTE
Adaptive Control will control the load according to the programmed profile. Stopping current will vary according to the
selected deceleration profile and stop time.
If replacing a motor connected to a ASAB programmed for Adaptive Control starting or stopping, or if the starter has been
tested on a different motor prior to actual installation, the starter will need to learn the characteristics of the new motor. The
ASAB will automatically re-learn the motor's characteristics if parameter 1A Motor Full Load Current or parameter 2L Adaptive
Control Gain is changed.
CAUTION
If the brake torque is set too high, the motor will stop before the end of the brake time and the motor will suffer unnecessary heating
which could result in damage. Careful configuration is required to ensure safe operation of the starter and motor.
A high brake torque setting can result in peak currents up to motor DOL being drawn while the motor is stopping. Ensure protection
fuses installed in the motor branch circuit are selected appropriately.
CAUTION
Brake operation causes the motor to heat faster than the rate calculated by the motor thermal model. If you are using
brake, install a motor thermistor or allow sufficient restart delay (parameter 5A).
Pump stopping
The hydraulic characteristics of pump systems vary considerably. This variation means the ideal deceleration profile and stop time will
vary from application to application. The table provides guidelines on selecting between Adaptive Control deceleration profiles, but we
recommend testing the three profiles to identify the best profile for the application.
The first Adaptive Control stop will be a normal soft stop. This allows the ASAB to learn the characteristics of the connected motor. This
motor data is used by the ASAB during subsequent Adaptive Control stops.
6.4.4 Brake
Brake reduces the time the motor requires to stop.
During braking an increased noise level from the motor may be audible. This is a normal part of motor braking.
When brake is selected, the ASAB uses DC injection to slow the motor.
ASAB braking:
Does not require the use of a DC brake contactor
Controls all three phases so that the braking currents and associated heating are evenly distributed through the motor.
Braking has two stages:
Pre-brake: provides an intermediate level of braking to slow motor speed to a point where full brake can be operated
successfully (approximately 70% speed).
Full brake: brake provides maximum braking torque but is ineffective at speeds greater than approximately 70%.

ASAB
31/66
Speed
10 0%
75 %
0%
50 %
25 %
1
2
3
1: Stop time (parameter 2I)
2: Brake time (parameter 15H)
3: Coast to stop time
Time
CAUTION
When using DC brake, the mains supply must be connected to the soft starter (input terminals L1, L2, L3) in positive phase
sequence and parameter 4B Phase Sequence must be set to Positive Only.
NOTE
For loads which may vary between braking cycles, install a zero speed sensor to ensure that the soft starter ends DC
braking when the motor stops. This avoids unnecessary heating of the motor.
For more information on using the ASAB with an external speed sensor (eg for applications with variable load during the
braking cycle), refer to DC Brake with External Zero Speed Sensor on page 56.
NOTE
Setting parameter 15F above 50% may cause increased shaft vibration.
Available torque
0%
10 0%
90 %
80 %
20 %
40 %
10 %
30 %
50 %
60 %
70 %
05 723 .D
1. Motor FLT
2. Jog forward maximum torque
3. Jog reverse maximum torque
NOTE
Soft start and soft stop are not available during jog operation.
Jog is only available for the primary motor.
CAUTION
Slow speed running is not intended for continuous operation due to reduced motor cooling.
Jog operation causes the motor to heat faster than the rate calculated by the motor thermal model. If you are using jog,
install a motor thermistor or allow sufficient restart delay (parameter 5A)
To configure the ASAB for brake operation:
1. Set parameter 2I for the desired stopping time duration (1). This is the total braking time and must be set sufficiently longer than
the brake time (parameter 15H) to allow the pre-braking stage to reduce motor speed to approximately 70%. If the stop time is too
short, braking will not be successful and the motor will coast to stop.
2. Set Brake Time (parameter 15H) to approximately one quarter of the programmed Stop Time. This sets the time for the Full Brake
stage (2).
3. Adjust the Brake Torque (parameter 15G) so that the desired stopping performance is achieved. If set too low, the motor will not
stop completely and will coast to stop by the end of the braking period.
6.5 Jog Operation
Jog runs the motor at reduced speed, to allow alignment of the load or to assist servicing. The motor can be jogged in either forward or
reverse direction.
The maximum available torque for jog forward is approximately 50%~75% of motor full load torque (FLT) depending on the motor. The
torque when the motor is jogged in reverse is approximately 25% to 50% of FLT.
Parameter 15F Jog Torque controls how much of the maximum available jog torque the soft starter will apply to the motor.
To activate jog operation, use a programmable input (parameter 6D). If any other command is received when jogging the starter will
stop and await a new command.

32/66
ASAB
Adaptive Control Start
The starter performs a constant current start.
Adaptive Control Stop
The starter performs a TVR soft stop if parameter 2I Stop Time is >0 secs. If parameter 2I is set to 0
secs the starter performs a coast to stop.
Jog
The starter issues a warning with the error message Unsupported Option.
Brake
The starter performs a coast to stop.
PowerThrough
The starter trips with the error message Lx-Tx Shorted.
NOTE
When connected in inside delta, current imbalance is the only phase loss protection that is active during run. Do not
disable current imbalance protection (parameter 4A) during inside delta operation.
CAUTION
Inside delta operation is only possible with mains voltage 600 VAC.
6.6 Inside Delta Operation
Adaptive Control, Jog, Brake and PowerThrough functions are not supported with inside delta (six-wire) operation. If these functions
are programmed when the starter is connected inside delta the behaviour is as given below:

ASAB
33/66
Quick Setup Menu
Provides access to quick setup options for common applications.
Standard Menu
The Standard Menu provides access to commonly used parameters, allowing you to configure the
ASAB to suit your application.
Extended Menu
The Extended Menu provides access to all the ASAB's programmable parameters, allowing
experienced users to take advantage of advanced features.
Setup Tools
Setup Tools includes maintenance options to configure the ASAB's date and time or load a
standard parameter set.
7 Programming Menu
The Programming Menu lets you view and change programmable parameters that control how the ASAB operates.
To open the Programming Menu, press the MENU/ENTER button while viewing the status or graph screens.
To navigate through the Programming Menu:
to scroll through parameter groups, press the or button.
to open a submenu, press the MENU/ENTER button.
to view the parameters in a group, press the MENU/ENTER button.
to return to the previous level, press the EXIT button.
to close the Programming Menu, press EXIT repeatedly or press the STATUS or GRAPHS button.
To change a parameter value:
scroll to the appropriate parameter in the Programming Menu and press MENU/ENTER to enter edit mode.
to alter the parameter setting, use the and buttons. Pressing or once will increase or decrease the value
by one unit. If the button is held for longer than five seconds, the value will increase or decrease at a faster rate.
to save changes, press MENU/ENTER. The setting shown on the display will be saved and the keypad will return to the
parameter list.
to cancel changes, press EXIT. The keypad will ask for confirmation, then return to the parameter list without saving
You can access the Programming Menu at any time, including while the soft starter is running. Any changes to the start profile take
effect immediately.
The Programming Menu contains four sub-menus:
changes.
34/66
ASAB
Application
Parameter
Suggested value
Pump Centrifugal
Motor Full Load Current
Start Mode
Adaptive Start Profile
Start Ramp Time
Stop Mode
Adaptive Stop Profile
Stop Time
Model dependent
Adaptive Control
Early Acceleration
10 seconds
Adaptive Control
Late Deceleration
15 seconds
Pump Submersible
Motor Full Load Current
Start Mode
Adaptive Start Profile
Start Ramp Time
Stop Mode
Adaptive Stop Profile
Stop Time
Model dependent
Adaptive Control
Early Acceleration
5 seconds
Adaptive Control
Late Deceleration
5 seconds
Fan Damped
Motor Full Load Current
Start Mode
Current Limit
Model dependent
Constant Current
350%
Fan Undamped
Motor Full Load Current
Start Mode
Adaptive Start Profile
Start Ramp Time
Excess Start Time
Locked Rotor Time
Model dependent
Adaptive Control
Constant Acceleration
20 seconds
30 seconds
20 seconds
Compressor Screw
Motor Full Load Current
Start Mode
Start Ramp Time
Current Limit
Model dependent
Constant Current
5 seconds
400%
Compressor Recip
Motor Full Load Current
Start Mode
Start Ramp Time
Current Limit
Model dependent
Constant Current
5 seconds
450%
Conveyor
Motor Full Load Current
Start Mode
Start Ramp Time
Current Limit
Stop Mode
Adaptive Stop Profile
Stop Time
Model dependent
Constant Current
5 seconds
400%
Adaptive Control
Constant Deceleration
10 seconds
Crusher Rotary
Motor Full Load Current
Start Mode
Start Ramp Time
Current Limit
Excess Start Time
Locked Rotor Time
Model dependent
Constant Current
10 seconds
400%
30 seconds
20 seconds
Crusher Jaw
Motor Full Load Current
Start Mode
Start Ramp Time
Current Limit
Excess Start Time
Locked Rotor Time
Model dependent
Constant Current
10 seconds
450%
40 seconds
30 seconds
7.1 Quick Setup
The Quick Setup Menu makes it easy to configure the ASAB for common applications. The ASAB selects the parameters relevant to the
application and suggests a typical setting, and you can adjust each parameter to suit your exact requirements.
Always set parameter 1A Motor Full Load Current to match the motor's nameplate full load current. The suggested value is the starter's
minimum full load current.
On the display, the highlighted values are suggested values and the values enclosed in a box are the loaded values.

ASAB
35/66
Default Setting
1
Motor Details
1A Motor Full Load Current
Model dependent
2
Primary Start/Stop
2A Start Mode
Constant Current
2B Current Limit
350%
2C Initial Current
350%
2D Start Ramp Time
00:10 mm:ss
2G Excess Start Time
00:20 mm:ss
2H Stop Mode
Coast To Stop
2I Stop Time
00:00 mm:ss
4
Protection Levels
4B Phase Sequence
Any Sequence
4C Undercurrent
20% FLC
4D Instantaneous Overcurrent
400% FLC
4E Input A Trip
Always Active
5
Protection Delays
5C Undercurrent Delay
00:05 mm:ss
5D Instantaneous Overcurrent Delay
00:00 mm:ss
5E Input A Trip Delay
00:00 mm:ss
5F Input A Initial Delay
00:00 mm:ss
6
Inputs
6D Input A Function
Motor Set Select
6E Input A Name
Input Trip
7
Relay Outputs
7A Relay A Function
Main Contactor
7B Relay A On Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7C Relay A Off Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7D Relay B Function
Run 7E Relay B On Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7F Relay B Off Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7G Relay C Function
Trip 7H Relay C On Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7I Relay C Off Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7J Low Current Flag
50% FLC
7K High Current Flag
100% FLC
7L Motor Temperature Flag
80% FLC
10
Display
10A Language
English
10B User Screen - Top Left
Starter State
10C User Screen - Top Right
Blank
10D User Screen - Bottom Left
Hours Run
10E User Screen - Bottom Right
Blank
10J Display A or kW
Current
7.2 Standard Menu
The standard menu provides access to commonly used parameters, allowing the user to configure the ASAB as required for the
application.

36/66
ASAB
Default Setting
1
Motor Details
1A Motor Full Load Current
Model dependent
1B Locked Rotor Time
00:10 mm:ss
1C Motor FLC-2
Model dependent
1D Locked Rotor Time-2
00:10 mm:ss
1E Dual Thermal Model
Single
2
Primary Start/Stop
2A Start Mode
Constant Current
2B Current Limit
350% FLC
2C Initial Current
350% FLC
2D Start Ramp Time
00:10 mm:ss
2E Kickstart Level
500% FLC
2F Kickstart Time
0 ms 2G Excess Start Time
00:20 mm:ss
2H Stop Mode
Coast To Stop
2I Stop Time
00:00 mm:ss
2J Adaptive Start Profile
Constant Acceleration
2K Adaptive Stop Profile
Constant Deceleration
2L Adaptive Control Gain
75%
3
Secondary Start/Stop
3A Start Mode-2
Constant Current
3B Current Limit-2
350% FLC
3C Initial Current-2
350% FLC
3D Start Ramp-2
00:10 mm:ss
3E Kickstart Level-2
500% FLC
3F Kickstart Time-2
0 ms 3G Excess Start Time-2
00:20 mm:ss
3H Stop Mode-2
Coast To Stop
3I Stop Time-2
00:00 mm:ss
3J Adaptive Start Profile-2
Constant Acceleration
3K Adaptive Stop Profile-2
Constant Deceleration
3L Adaptive Control Gain-2
75%
4
Protection Levels
4A Current Imbalance
30% 4B Phase Sequence
Any Sequence
4C Undercurrent
20% FLC
4D Instantaneous Overcurrent
400% FLC
4E Input A Trip
Always Active
4F Motor Temperature Check
Do Not Check
4G Frequency Check
Start/Run
4H Frequency Variation
±5 Hz
5
Protection Delays
5A Restart Delay
00:10 mm:ss
5B Current Imbalance Delay
00:03 mm:ss
5C Undercurrent Delay
00:05 mm:ss
5D Instantaneous Overcurrent Delay
00:00 mm:ss
5E Input A Trip Delay
00:00 mm:ss
5F Input A Initial Delay
00:00 mm:ss
5G Frequency Delay
00:01 mm:ss
6
Inputs
6A Local/Remote
LCL/RMT Anytime
6B Comms in Remote
Enable Control in RMT
6C Remote Reset Logic
Normally Closed (N/C)
6D Input A Function
Motor Set Select
6E Input A Name
Input Trip
7.3 Extended Menu
The Extended Menu provides access to all the ASAB's programmable parameters.

ASAB
37/66
7
Relay Outputs
7A Relay A Function
Main Contactor
7B Relay A On Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7C Relay A Off Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7D Relay B Function
Run 7E Relay B On Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7F Relay B Off Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7G Relay C Function
Trip 7H Relay C On Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7I Relay C Off Delay
00:00 mm:ss
7J Low Current Flag
50% FLC
7K High Current Flag
100% FLC
7L Motor Temperature Flag
80%
8
Analog Output
8A Analog Output A
Current (% FLC)
8B Analog A Scale
4-20 mA
8C Analog A Maximum Adjustment
100%
8D Analog A Minimum Adjustment
0%
9
Auto-Reset
9A Auto-Reset Action
Do Not Auto-Reset
9B Maximum Resets
1 9C Reset Delay Groups A&B
00:05 mm:ss
9D Reset Delay Group C
5 minutes
10
Display
10A Language
English
10B User Screen - Top Left
Starter State
10C User Screen - Top Right
Blank
10D User Screen - Bottom Left
Hours Run
10E User Screen - Bottom Right
Blank
10F Graph Timebase
10 seconds
10G Graph Maximum Adjustment
400%
10H Graph Minimum Adjustment
0% 10I Mains Reference Voltage
400 V
10J Display A or kW
Current
15
Restricted
15A Access Code
0000 15B Adjustment Lock
Read & Write
15C Emergency Run
Disable
15D Current Calibration
100%
15E Shorted SCR Action
3-Phase Control Only
15F Jog Torque
50%
15G Brake Torque
20%
15H Brake Time
00:01 mm:ss
15I Brake Torque-2
20%
15J Brake Time-2
00:01 mm:ss
16
Protection Action
16A Motor Overload
Trip Starter
16B Current Imbalance
Trip Starter
16C Undercurrent
Trip Starter
16D Instantaneous Overcurrent
Trip Starter
16E Input A Trip
Trip Starter
16F Frequency
Trip Starter
16G Motor Thermistor
Trip Starter
16H Excess Start Time
Trip Starter
16I Starter Communication
Trip Starter
16J Heatsink Overtemperature
Trip Starter
16K Battery/Clock
Trip Starter
16L Network Communication
Trip Starter
16M Low Control Volts
Trip Starter

38/66
ASAB
NOTE
Parameter 1B determines the trip current for motor overload protection. The default setting of parameter 1B provides
Motor Overload Protection: Class 10, Trip Current 105% of FLA (full load amperage) or equivalent.
NOTE
The second thermal model is only active if parameter 1E Dual Thermal Model is set to 'Dual' and the starter is using the
secondary motor set (a programmable input is set to 'Motor Set Select' and the input is active).
7.4 Parameter Descriptions
7.4.1 1 Motor Details
1A – Motor FLC
Range: Model dependent
Description: Matches the starter to the connected motor's full load current. Set to the full load current (FLC) rating shown on
1B – Locked Rotor Time
Range: 0:01 - 2:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 10 seconds
Description: Sets the maximum length of time the motor can sustain locked rotor current from cold before reaching its
1C – Motor FLC-2
Range: Model dependent
Description: Sets the secondary motor's full load current.
1D – Locked Rotor Time-2
Range: 0:01 - 2:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 10 seconds
Description: Sets the maximum length of time the motor can sustain locked rotor current from cold before reaching its
the motor nameplate.
maximum temperature. Set according to the motor datasheet.
maximum temperature. Set according to the motor datasheet.
1E – Dual Thermal Model
Options: Single (default)
Description: Activates dual thermal modelling. The dual thermal model is required only if the ASAB is controlling two
7.4.2 2 Primary Start/Stop
2A – Start Mode
Options: Constant Current (default)
Description: Selects the soft start mode.
2B – Current Limit
Range: 100% - 600% FLC Default: 350%
Description: Sets the current limit for constant current and current ramp soft starting, as a percentage of motor full load current.
2C – Initial Current
Range: 100% - 600% FLC Default: 350%
Description: Sets the initial start current level for current ramp starting, as a percentage of motor full load current. Set so that
Dual
physically separate motors.
Adaptive Control
the motor begins to accelerate immediately after a start is initiated.
If current ramp starting is not required, set the initial current equal to the current limit.
2D – Start Ramp Time
Range: 1 - 180 (seconds) Default: 10 seconds
Description: Sets the total start time for an Adaptive Control start or the ramp time for current ramp starting (from the initial
current to the current limit).

ASAB
39/66
CAUTION
Kickstart subjects the mechanical equipment to increased torque levels. Ensure the motor, load and couplings can handle
the additional torque before using this feature.
NOTE
We recommend leaving the gain setting at the default level unless performance is not satisfactory.
If the motor accelerates or decelerates too quickly at the end of a start or stop, increase the gain setting by 5%~10%. If
the motor speed fluctuates during starting or stopping, decrease the gain setting slightly.
2E – Kickstart Level
Range: 100% - 700% FLC Default: 500%
Description: Sets the level of the kickstart current.
2F – Kickstart Time
Range: 0 – 2000 milliseconds Default: 0000 milliseconds
Description: Sets the kickstart duration. A setting of 0 disables kickstart.
2G – Excess Start Time
Excess start time is the maximum time the ASAB will attempt to start the motor. If the motor does not transition to Run mode within the
programmed limit, the starter will trip. Set for a period slightly longer than required for a normal healthy start. A setting of 0 disables
excess start time protection.
Range: 0:00 - 4:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 20 seconds
Description: Set as required.
2H – Stop Mode
Options: Coast To Stop (default)
TVR Soft Stop
Adaptive Control
Brake
Description: Selects the stop mode.
2I – Stop Time
Range: 0:00 - 4:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 0 second
Description: Sets the time for soft stopping the motor using timed voltage ramp or Adaptive Control.
If a main contactor is installed, the contactor must remain closed until the end of the stop time. Use a
programmable output configured to Run to control the main contactor. Sets the total stopping time when using
brake.
2J – Adaptive Start Profile
Options: Early Acceleration
Constant Acceleration (default)
Late Acceleration
Description: Selects which profile the ASAB will use for an Adaptive Control soft start.
2K – Adaptive Stop Profile
Options: Early Deceleration
Constant Deceleration (default)
Late Deceleration
Description: Selects which profile the ASAB will use for an Adaptive Control soft stop.
2L – Adaptive Control Gain
Range: 1% - 200% Default: 75%
Description: Adjusts the performance of Adaptive Control. This setting affects both starting and stopping control.

40/66
ASAB
7.4.3 3 Secondary Start/Stop
Refer to the Primary Start/Stop parameters for parameter details.
3A – Start Mode-2
Options: Constant Current (default)
Adaptive Control
Description: Selects the soft start mode.
3B – Current Limit-2
Range: 100% - 600% FLC Default: 350%
Description: Sets the current limit for constant current and current ramp soft starting, as a percentage of motor full load current.
3C – Initial Current-2
Range: 100% - 600% Default: 350%
Description: Sets the initial start current level for current ramp starting, as a percentage of motor full load current. Set so that
the motor begins to accelerate immediately after a start is initiated.
If current ramp starting is not required, set the initial current equal to the current limit.
3D – Start Ramp Time-2
Range: 1 - 180 (seconds) Default: 10 seconds
Description: Sets the total start time for an Adaptive Control start or the ramp time for current ramp starting (from the initial
current to the current limit).
3E – Kickstart Level-2
Range: 100% - 700% FLC Default: 500%
Description: Sets the level of the kickstart current.
3F – Kickstart Time-2
Range: 0 - 2000 (milliseconds) Default: 0000 milliseconds
Description: Sets the kickstart duration. A setting of 0 disables kickstart.
3G – Excess Start Time-2
Range: 0:00 - 4:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 20 seconds
Description: Set as required.
3H – Stop Mode-2
Options: Coast To Stop (default)
TVR Soft Stop
Adaptive Control
Brake
Description: Selects the stop mode.
3I – Stop Time-2
Range: 0:00 - 4:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 0 second
Description: Sets the stop time.
3J – Adaptive Start Profile-2
Options: Early Acceleration
Constant Acceleration (default)
Late Acceleration
Description: Selects which profile the ASAB will use for an Adaptive Control soft start.

ASAB
41/66
Options:
Always Active (default)
A trip can occur at any time when the soft starter is receiving power.
Operating Only
A trip can occur while the soft starter is running, stopping or starting.
Run Only
A trip can only occur while the soft starter is running.
3K – Adaptive Stop Profile-2
Options: Early Deceleration
Description: Selects which profile the ASAB will use for an Adaptive Control soft stop.
3L – Adaptive Control Gain-2
Range: 1% - 200% Default: 75%
Description: Adjusts the performance of Adaptive Control. This setting affects both starting and stopping control.
7.4.4 4 Protection Levels
4A – Current Imbalance
Range: 10% - 50% Default: 30%
Description: Sets the trip point for current imbalance protection.
4B – Phase Sequence
Options: Any Sequence (default)
Description: Selects which phase sequences the soft starter will allow at a start. During its pre-start checks, the starter
Constant Deceleration (default)
Late Deceleration
Positive Only
Negative Only
examines the sequence of the phases at its input terminals and trips if the actual sequence does not match the
selected option.
4C – Undercurrent
Range: 0% - 100% Default: 20%
Description: Sets the trip point for undercurrent protection, as a percentage of motor full load current. Set to a level between
the motor's normal working range and the motor's magnetising (no load) current (typically 25% to 35% of full load
current). A setting of 0% disables undercurrent protection.
4D – Instantaneous Overcurrent
Range: 80% - 600% FLC Default: 400%
Description: Sets the trip point for instantaneous overcurrent protection, as a percentage of motor full load current.
4E – Input A Trip
Description: Selects when an input trip can occur.
4F – Motor Temperature Check
Options: Do Not Check (default)
Check
Description: Selects whether the ASAB will verify the motor has sufficient thermal capacity for a successful start. The soft
starter compares the motor's calculated temperature with the temperature rise from the last motor start and only
operates if the motor is cool enough to start successfully.
4G – Frequency Check
Options: Do Not Check
Start Only
Start/Run (default)
Run Only
Description: Determines when and if the starter will monitor for a frequency trip.

42/66
ASAB
Options:
LCL/RMT Anytime
LOCAL/REMOTE button is always enabled.
LCL/RMT When Off
LOCAL/REMOTE button is enabled when the starter is off.
Local Control Only
All remote inputs are disabled.
Remote Control Only
Local control buttons (START, RESET, LOCAL/REMOTE) are disabled.
4H – Frequency Variation
Options: ± 2 Hz
Description: Selects the soft starter's tolerance for frequency variation.
7.4.5 5 Protection Delays
5A – Restart Delay
Range: 00:01 - 60:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 10 seconds
Description: The ASAB can be configured to force a delay between the end of a stop and the beginning of the next start.
5B – Current Imbalance Delay
Range: 0:00 - 4:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 3 seconds
Description: Slows the ASAB's response to current imbalance, avoiding trips due to momentary fluctuations.
5C – Undercurrent Delay
Range: 0:00 - 4:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 5 seconds
Description: Slows the ASAB's response to undercurrent, avoiding trips due to momentary fluctuations.
± 5 Hz (default)
± 10 Hz
± 15 Hz
During the restart delay period, the display shows the time remaining before another start can be attempted.
5D – Instantaneous Overcurrent Delay
Range: 0:00 - 1:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 0 second
Description: Slows the ASAB's response to overcurrent, avoiding trips due to momentary overcurrent events.
5E – Input A Trip Delay
Range: 0:00 - 4:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 0 second
Description: Sets a delay between the input activating and the soft starter tripping.
5F – Input A Initial Delay
Range: 00:00 - 30:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 0 second
Description: Sets a delay before an input trip can occur. The initial delay is counted from the time a start signal is received.
5G – Frequency Delay
Range: 0:01 - 4:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 1 second
Description: Slows the ASAB's response to frequency disturbances, avoiding trips due to momentary fluctuations.
7.4.6 6 Inputs
6A – Local/Remote
The state of the input is ignored until the initial delay has elapsed.
Description: Selects when the LOCAL/REMOTE button can be used to switch between local and remote control, and
enables or disables the local control buttons and remote control inputs.
The STOP button on the keypad is always enabled.
6B – Comms in Remote
Options: Disable Control in RMT
Enable Control in RMT (default)
Description: Selects whether the starter will accept Start and Stop commands from the serial communication network when in
Remote mode. The Reset, Force Comms Trip and Local/Remote Control commands are always enabled.

ASAB
43/66
Options:
Motor Set Select (default)
The ASAB can be configured with two separate sets of motor data.
To use the secondary motor data, parameter 6D must be set to 'Motor Set Select'
and 53, 55 must be closed when a start command is given. The ASAB checks
which motor data to use at a start, and will use that motor data for the entire
start/stop cycle.
Input Trip (N/O)
Input A can be used to trip the soft starter. When parameter 6D is set to Input Trip
(N/O), a closed circuit across 53, 55 trips the soft starter.
Input Trip (N/C)
When parameter 6D is set to Input Trip (N/C), an open circuit across 53, 55 trips the
soft starter.
Local/Remote Select
Input A can be used to select between local and remote control, instead of using the
LOCAL/REMOTE button on the keypad. When the input is open, the starter is
in local mode and can be controlled via the keypad. When the input is closed, the
starter is in remote mode. The START and LOCAL/REMOTE buttons are
disabled, and the soft starter will ignore any Local/Remote select command from
the serial communications network.
To use Input A to select between local and remote control, parameter 6A must be
set to 'LCL/RMT Anytime' or 'LCL/RMT When Off'.
Emergency Run
In emergency run the soft starter continues to run until stopped, ignoring all trips
and warnings (refer to parameter 15C for details).
Closing the circuit across 53, 55 activates emergency run.
Opening the circuit ends emergency run and the ASAB stops the motor.
Starter Disable
The ASAB can be disabled via the control inputs. An open circuit across 53, 55 will
disable the starter. The ASAB will not respond to start commands. If running, the
soft starter will allow the motor to coast to stop, ignoring the soft stop mode set in
parameter 2H.
Jog Forward
Activates jog operation in a forward direction (will operate only in Remote mode).
Jog Reverse
Activates jog operation in reverse direction (will operate only in Remote mode).
Options:
Off
Relay A is not used.
Main Contactor (default)
The relay closes when the ASAB receives a start command, and remains closed as
long as the motor is receiving voltage.
Run
The relay closes when the starter changes to run state.
Trip
The relay closes when the starter trips (refer to parameter 16A to 16M).
Warning
The relay closes when the starter issues a warning (refer to parameter 16A to 16M).
Low Current Flag
The relay closes when the low current flag activates (refer to parameter 7J Low
Current Flag, while the motor is running).
High Current Flag
The relay closes when the high current flag activates (refer to parameter 7K High
Current Flag, while the motor is running).
Motor Temperature Flag
The relay closes when the motor temperature flag activates (refer to parameter 7L
Motor Temperature Flag).
6C – Remote Reset Logic
Options: Normally Closed (default)
Normally Open
Description: Selects whether the ASAB's remote reset input (terminals 58, 57) is normally open or normally closed.
6D – Input A Function
Description: Selects the function of Input A.
6E – Input A Name
Options: Input Trip (default) No Flow
Description: Selects a message for the keypad to display when Input A is active.
7.4.7 7 Relay Outputs
7A – Relay A Function
Description: Selects the function of Relay A (normally open).
Low Pressure Starter Disable
High Pressure Controller
Pump Fault PLC
Low Level Vibration Alarm
High Level

44/66
ASAB
Options:
Current (% FLC) (default)
Current as a percentage of motor full load current.
Motor Temp (%)
Motor temperature as a percentage of the motor's thermal capacity.
Motor kW (%)
Measured motor kilowatts, as a percentage of maximum kW.
Motor kVA (%)
Measured motor kilovolt amperes, as a percentage of maximum kVA.
Motor pf
Motor power factor, measured by the soft starter.
Measured motor kW:
3 x average current x mains reference voltage x measured power factor
Maximum motor kW:
3 x motor FLC x mains reference voltage. Power factor is assumed to be 1
Measured motor kVA:
3 x average current x mains reference voltage
Maximum motor kVA:
3 x motor FLC x mains reference voltage
7B, 7C – Relay A Delays
The ASAB can be configured to wait before opening or closing Relay A.
Parameter 7B Relay A On Delay
Range: 0:00 - 5:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 0 second
Description: Sets the delay for closing Relay A.
Parameter 7C Relay A Off Delay
Range: 0:00 - 5:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 0 second
Description: Sets the delay for re-opening Relay A.
7D~7I – Output Relays B & C
Parameters 7D~7I configure the operation of Relays B and C in the same way as parameters 7A~7C configure Relay A. Refer to Relay
A for details.
Relay B is a changeover relay.
7D Relay B Function Default: Run
7E Relay B On Delay
7F Relay B Off Delay
Relay C is normally open.
7G Relay C Function Default: Trip
7H Relay C On Delay
7I Relay C Off Delay
7J, 7K – Low Current Flag and High Current Flag
The ASAB has low and high current flags to give early warning of abnormal operation. The current flags can be configured to indicate
an abnormal current level during operation, between the normal operating level and the undercurrent or instantaneous overcurrent trip
levels. The flags can signal the situation to external equipment via one of the programmable outputs. The flags clear when the current
returns within the normal operating range by 10% of the programmed motor full load current.
Parameter 7J Low Current Flag
Range: 1% - 100% FLC Default: 50%
Description: Sets the level at which the low current flag operates, as a percentage of motor full load current.
Parameter 7K High Current Flag
Range: 50% - 600% FLC Default: 100%
Description: Sets the level at which the high current flag operates, as a percentage of motor full load current.
7L – Motor Temperature Flag
The ASAB has a motor temperature flag to give early warning of abnormal operation. The flag can indicate that the motor is operating
above its normal operating temperature but lower than the overload limit. The flag can signal the situation to external equipment via one
of the programmable outputs.
Range: 0% - 160% Default: 80%
Description: Sets the level at which the motor temperature flag operates, as a percentage of the motor's thermal capacity.
7.4.8 8 Analog Output
The ASAB has an analog output, which can be connected to associated equipment to monitor motor performance.
8A – Analog Output A
Description: Selects which information will be reported via the analog output.

ASAB
45/66
Group
A
Current imbalance
Phase Loss
Power loss / Power circuit
Frequency
B Undercurrent
Instantaneous overcurrent
Input A Trip
C Motor overload (thermal model)
Motor thermistor
Heatsink Overtemperature
NOTE
If the starter is manually reset, the resets counter will return to zero.
8B – Analog A Scale
Range: 0-20 mA
Description: Selects the range of the analog output.
8C – Analog A Maximum
Range: 0% - 600% Default: 100%
Description: Calibrates the upper limit of the analog output to match the signal measured on an external current measuring
8D – Analog A Minimum
Range: 0% - 600% Default: 0%
Description: Calibrates the lower limit of the analog output to match the signal measured on an external current measuring
7.4.9 9 Auto-Reset
The ASAB can be programmed to automatically reset certain trips, which can help minimise operating downtime. Trips are divided into
three categories for auto-reset, depending on the risk to the soft starter:
4-20 mA (default)
device.
device.
Other trips cannot be automatically reset.
This function is ideal for remote installations using 2-wire control in Remote mode. If the 2-wire start signal is present after an
auto-reset, the ASAB will restart.
9A – Auto-Reset Action
Options: Do Not Auto-Reset (default)
Reset Group A
Reset Group A & B
Reset Group A, B & C
Description: Selects which trips can be auto-reset.
9B – Maximum Resets
Range: 1 - 5 Default: 1
Description: Sets how many times the soft starter will auto-reset, if it continues to trip. The reset counter increases by one
each time the soft starter auto-resets, and decreases by one after each successful start/stop cycle.
9C – Reset Delay Groups A&B
Range: 00:05 - 15:00 (minutes:seconds) Default: 5 seconds
Description: Sets the delay before resetting Group A and Group B trips.
9D – Reset Delay Group C
Range: 5 - 60 (minutes) Default: 5 minutes
Description: Sets the delay before resetting Group C trips.

46/66
ASAB
Options:
Blank
Displays no data in the selected area, allowing long messages to be shown without
overlapping.
Starter State
The starter's operating state (starting, running, stopping or tripped). Only available for
top left and bottom left positions on the screen.
Motor Current
The average current measured on three phases.
Motor pf
The motor's power factor, measured by the soft starter.
Mains Frequency
The average frequency measured on three phases.
Motor kW
The motor's running power in kilowatts.
Motor HP
The motor's running power in horsepower.
Motor Temp
The motor's temperature, calculated by the thermal model.
kWh
The number of kilowatt hours the motor has run via the soft starter.
Hours Run
The number of hours the motor has run via the soft starter.
7.4.10 10 Display
10A – Language
Options: English (default) Português
Description: Selects which language the keypad will use to display messages and feedback.
10B, 10C, 10D, 10E – User-Programmable Screen
Description: Selects which information will be displayed on the programmable monitoring screen.
Chinese Français
Español Italiano
Deutsch Russian
10B User Screen - Top Left Default: Starter State
10C User Screen - Top Right Default: Blank
10D User Screen - Bottom Left Default: Hours Run
10E User Screen - Bottom Right Default: Blank
10F – Graph Timebase
Options: 10 seconds (default)
30 seconds
1 minute
5 minutes
10 minutes
30 minutes
1 hour
Description: Sets the graph time scale. The graph will progressively replace the old data with new data.
10G – Graph Maximum
Range: 0% – 600% Default: 400%
Description: Adjusts the upper limit of the performance graph.
10H – Graph Minimum
Range: 0% – 600% Default: 0%
Description: Adjusts the lower limit of the performance graph.
10I – Mains Reference Voltage
Range: 100 – 690 V Default: 400 V
Description: Sets the nominal mains voltage for the keypad's monitoring functions. This is used to calculate motor kilowatts
and kilovolt amperes (kVA) but does not affect the ASAB's motor control or protection.
10J – Display A or kW
Options: Current (default)
Motor kW
Description: Selects whether the ASAB will display current (amperes) or motor kilowatts on the main monitoring screen.

ASAB
47/66
NOTE
In the event of a lost access code, contact your supplier for a master access code that allows you to re-program a new
access code.
Options:
Read & Write (default)
Allows users to alter parameter values in the Programming Menu.
Read Only
Prevents users altering parameter values in the Programming Menu.
Parameter values can still be viewed.
CAUTION
Continued use of Emergency Run is not recommended. Emergency Run may compromise the starter life as all protections
and trips are disabled.
Using the starter in Emergency Run mode will void the product warranty.
Calibration (%) =
Current shown on ASAB display
Current measured by external device
eg 102% =
66A
65A
NOTE
This adjustment affects all current-based functions and protections.
CAUTION
PowerThrough uses a two-phase soft start technology and additional care is required when sizing circuit breakers and
protection. Contact your local supplier for assistance.
NOTE
PowerThrough remains active until '3-Phase Control Only' is reselected.
PowerThrough operation does not support Adaptive Control soft starting or soft stopping. In PowerThrough, the ASAB will
automatically select constant current soft starting and timed voltage ramp soft stopping. If PowerThrough is enabled,
parameters 2C and 2B must be set appropriately.
PowerThrough can only operate with internally bypassed soft starters.
7.4.11 15 Restricted
15A – Access Code
Range: 0000 - 9999 Default: 0000
Description: Sets the access code to control access to restricted sections of the menus.
15B – Adjustment Lock
Description: Selects whether the keypad will allow parameters to be changed via the Programming Menu.
15C – Emergency Run
Options: Disable (default)
Description: Selects whether the soft starter will permit emergency run operation. In emergency run, the soft starter will start
Use the EXIT and MENU/ENTER buttons to select which digit to alter and use the and buttons to
change the value.
Enable
(if not already running) and continue to operate until emergency run ends, ignoring stop commands and trips.
Emergency run is controlled using a programmable input.
15D – Current Calibration
Range: 85% - 115% Default: 100%
Description: Calibrates the soft starter's current monitoring circuits to match an external current metering device.
Use the following formula to determine the necessary adjustment:
15E – Shorted SCR Action
Options: 3-Phase Control Only (default)
PowerThrough
Description: Selects whether the soft starter will allow PowerThrough operation. For critical applications this allows the soft
starter to control the motor with two-phase control, if the soft starter is damaged on one phase. PowerThrough
only operates after the soft starter has tripped on "Lx-Tx Shorted" and has been reset.

48/66
ASAB
NOTE
PowerThrough is only available with in-line installations. If the starter is installed inside delta, PowerThrough will not
operate.
The starter will trip on Lx-Tx Shorted on the first start attempt after control power is applied. PowerThrough will not
operate if control power is cycled between starts.
NOTE
Parameter 15H is used in conjunction with parameter 2I. Refer to Brake for details.
CAUTION
Defeating the protection may compromise the starter and motor, and should only be done in the case of emergency.
16A Motor Overload
16B Current Imbalance
16C Undercurrent
16D Instantaneous Overcurrent
16E Input A Trip
16F Frequency
16G Motor Thermistor
16H Excess Start Time
16I Starter Communication
16J Heatsink Overtemperature
16K Battery/Clock
16L Network Communication
16M Low Control Volts
15F – Jog Torque
The ASAB can jog the motor at a reduced speed, which allows precise positioning of belts and flywheels. Jog can be used for either
forward or reverse operation.
Range: 20% - 100% Default: 50%
Description: Sets the current limit for jog operation.
15G – Brake Torque
Range: 20% - 100% Default: 20%
Description: Sets the amount of brake torque the ASAB will use to slow the motor.
15H – Brake Time
Range: 1 - 30 (seconds) Default: 1 second
Description: Sets the duration for DC injection during a braking stop.
<
15I – Brake Torque-2
Range: 20% - 100% Default: 20%
Description: Sets the amount of brake torque the ASAB will use to slow the motor.
15J – Brake Time-2
Range: 1 - 30 (seconds) Default: 1 second
Description: Sets the duration for DC injection during a braking stop.
7.4.12 16 Protection Action
16A~16M – Protection Action
Options: Trip Starter (default)
Description: Selects the soft starter's response to each protection.
Warn and Log
Log Only

ASAB
49/66
Access Denied
Adj Lock is On
Enter Access Code
0###
MENU/ENTER
Access Allowed
SUPERVISOR
7.5 Adjustment Lock
You can lock the Programming Menu to prevent users from altering parameter settings. The adjustment lock can be turned on and off
using parameter 15B.
To lock the programming menu:
1. Open the Programming Menu.
2. Open the Extended Menu.
3. Select 'Restricted'.
4. Enter the Access Code.
5. Select parameter 15B Adjustment Lock
6. Select and store 'Read Only'.
If a user attempts to change a parameter value when the adjustment lock is active, an error message is displayed:
7.6 Access Code
Critical parameters (parameter group 15 and higher) are protected by a four-digit security access code, preventing unauthorised users
from viewing or modifying parameter settings.
When a user attempts to enter a restricted parameter group, the keypad prompts for an access code. The access code is requested
once for the programming session, and authorisation continues until the user closes the menu.
To enter the access code, use the EXIT and MENU/ENTER buttons to select a digit, and the and buttons to change the
value. When all four digits match your access code, press MENU/ENTER. The keypad will display an acknowledgement message
before continuing.
To change the access code, use parameter 15A.
The default access code is 0000.
7.7 Setup Tools
Setup Tools includes maintenance options to configure the ASAB's date and time, reset the thermal models or load a standard
parameter set.
To access the Setup Tools, open the Programming Menu then select Setup Tools.
7.7.1 Set Date and Time
To set the date and time:
1. Open the Setup Tools.
2. Scroll to the date/time screen.
3. Press the MENU/ENTER button to enter edit mode.
4. Press the MENU/ENTER and EXIT buttons to select which part of the date or time to edit.
5. Use the and buttons to change the value.
6. To save changes, press the MENU/ENTER button. The ASAB will confirm the changes.
To cancel changes, press the EXIT button.

50/66
ASAB
1. Open the Setup Tools.
2. Scroll to Load/Save Settings and press the MENU/ENTER button.
3. Scroll to the required function and press the MENU/ENTER button.
Load/Save Settings
Load Defaults
Load User Set 1
Load User Set 2
4. At the confirmation prompt, select YES to confirm or NO to cancel and then
MENU/ENTER to load/save the selection.
Load Defaults
No
Yes
When the action has been completed, the screen will briefly display a
confirmation message, then return to the status screens.
NOTE
This function is protected by the security access code.
1. Open the Setup Tools.
2. Scroll to Reset Thermal Models and press MENU/ENTER.
Reset Thermal Models
M1 X%
M2 X%
MENU/ENTER to Reset
3. Use to select Reset and press MENU/ENTER to confirm.
Do Not Reset
Reset
4. When the thermal model has been reset, the screen will display a confirmation message
then return to the previous screen.
CAUTION
Resetting the motor thermal model may compromise motor life and should only be done in the case of emergency.
7.7.2 Load/Save Settings
The Load/Save Settings menu requires an access code and allows users to:
Load the ASAB's parameters with default values
Reload previously saved parameter settings from an internal file
Save the current parameter settings to an internal file
In addition to the factory default values file, the ASAB can store two user-defined parameter files. These files contain default values
until a user file is saved.
To load or save parameter settings:
7.7.3 Reset Thermal Models
The ASAB's advanced thermal modelling software constantly monitors the motor's performance. This allows the ASAB to calculate the
motor's temperature and ability to start successfully at any time. If the ASAB is configured for use on two motors, each motor's
temperature is modelled separately.
The thermal model for the active motor can be reset if required.

ASAB
51/66
NOTE
The reset counters function is protected by the access code.
8 Logs Menu
The Logs Menu provides information on events, trips and starter performance.
Press the LOGS button to open the Logs Menu.
To navigate through the Logs Menu:
to open a log, press the MENU/ENTER button.
to scroll through the entries in each log, press the and buttons.
to view details of a log entry, press the MENU/ENTER button.
to return to the previous level, press the EXIT button.
to close the Logs Menu, press LOGS.
8.1 Trip Log
The Trip Log stores details of the eight most recent trips, including the date and time the trip happened. Trip 1 is the most recent and
trip 8 is the oldest stored trip.
To open the Trip Log:
1. Open the Logs Menu.
2. Scroll to Trip Log and press MENU/ENTER.
3. Use the and buttons to select a trip to view, and press MENU/ENTER to display details.
To close the log and return to the main display, press LOGS.
8.2 Event Log
The Event Log stores time-stamped details of the starter's 99 most recent events (actions, warnings and trips), including the date and
time of the event. Event 1 is the most recent and event 99 is the oldest stored event.
To open the Event Log:
1. Open the Logs Menu.
2. Scroll to Event Log and press MENU/ENTER.
3. Use the and buttons to select an event to view, and press MENU/ENTER to display details.
To close the log and return to the main display, press LOGS.
8.3 Performance Counters
The performance counters store statistics on the starter's operation:
Hours run (lifetime and since counter last reset)
Number of starts (lifetime and since counter last reset)
Motor kWh (lifetime and since counter last reset)
Number of times the thermal model has been reset
To view the counters:
1. Open the Logs Menu.
2. Scroll to counters and press MENU/ENTER.
3. Use the and buttons to scroll through the counters. Press MENU/ENTER to view details.
4. To reset a counter, press MENU/ENTER then use the and buttons to select Reset/Do Not Reset. Press
MENU/ENTER to confirm the action.
To close the counter and return to the Logs Menu, press MENU/ENTER.

52/66
ASAB
K M 1
K M 1
F1
2 2
2 1
6 /T3
2 /T1
13
14
4 /T2
24
3 3
3 4
5 /L3
3 /L2
S 1
S 2
E
1 /L1
6 5
6 4
4 1
4 0
5 6
5 7
5 8
5 3
5 5
A 6
A 5
A 4
5 4
A
08 8 77 .A
6
3
1 2
4
5
+
+
1 Three-phase supply
2
Motor terminals
3
Control voltage (model dependent)
4
Remote control inputs
5
Motor thermistor input
6
Relay outputs
KM1
Main contactor
F1
Semiconductor fuses (optional)
S1
Start/stop contact
S2
Reset contact
13, 14
Relay output A
21, 22, 24
Relay output B
33, 34
Relay output C
9 Application Examples
A selection of Application Notes are available describing advanced installation or configuration of the ASAB for situations with specific
performance requirements. Application notes are available for situations including brake and jog operation, pumping and advanced
protection options.
9.1 Installation with Main Contactor
The ASAB is installed with a main contactor (AC3 rated). Control voltage must be supplied from the input side of the contactor.
The main contactor is controlled by the ASAB Main Contactor output, which by default is assigned to Output Relay A (terminals 13, 14).
Parameter settings:
Parameter 7A Relay A Function
Select 'Main Contactor' - assigns the Main Contactor function to Relay Output A (default setting)
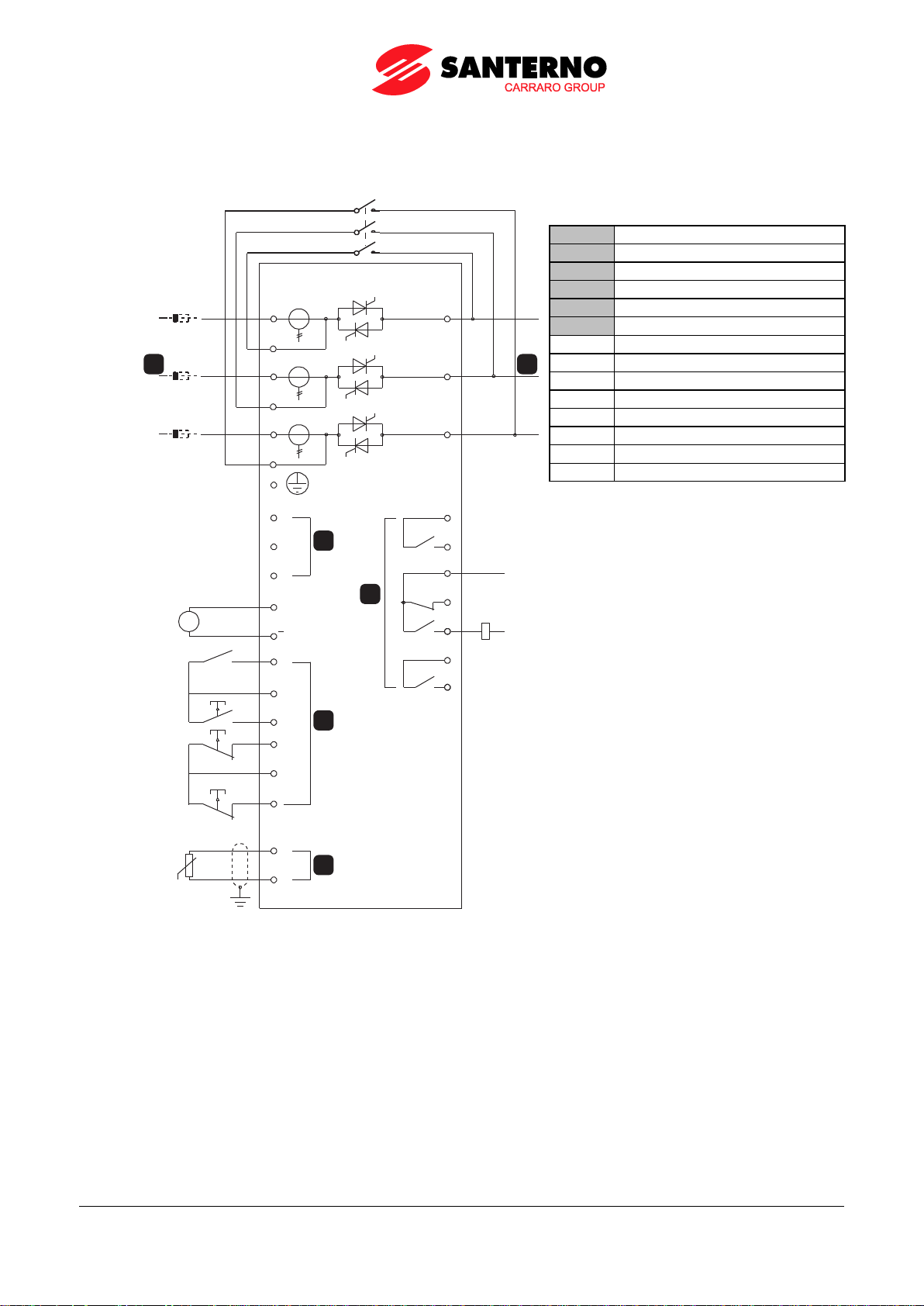
ASAB
53/66
K M 1
2 2
2 1
13
14
24
3 3
3 4
S 1
S 2
S 3
E
6 /T3
2/ T1
4/ T2
5 /L3
3 /L2
1 /L1
L3 B
L 1B
L2 B
K M 1
F 1
65
64
41
40
5 6
5 7
5 8
5 3
5 5
A 6
A 5
A 4
5 4
A
08 8 7 8.A
6
3
1 2
4
5
+
+
1 Three-phase supply
2
Motor terminals
3
Control voltage (model dependent)
4
Remote control inputs
5
Motor thermistor input
6
Relay outputs
KM1
Bypass contactor (external)
F1
Semiconductor fuses (optional)
S1
Start contact
S2
Stop contact
S3
Reset contact
13, 14
Relay output A
21, 22, 24
Relay output B
33, 34
Relay output C
9.2 Installation with Bypass Contactor
The ASAB is installed with a bypass contactor (AC1 rated). The bypass contactor is controlled by the ASAB Run Output which by default
is assigned to Output Relay B (terminals 21, 22, 24).
Parameter settings:
Parameter 7D Relay B Function
Select 'Run' - assigns the run output function to Relay Output B (default value).

54/66
ASAB
KM 1 F1
2 2
2 1
6 /T3
2 /T1
1 3
1 4
4 /T2
24
3 3
3 4
5/ L3
3/ L2
S 3
S 1
S 2
E
1/ L1
6 5
6 4
4 1
4 0
5 6
5 7
5 8
5 3
5 5
A 6
A 5
A 4
5 4
A
08 8 79 .A
6
3
1 2
4
5
+
+
1
Three-phase supply
2
Motor terminals
3
Control voltage (model dependent)
4
Remote control inputs
5
Motor thermistor input
6
Relay outputs
S1
Start/stop contact
S2
Reset contact
S3
Emergency Run Contact
13, 14
Relay output A
21, 22, 24
Relay output B
33, 34
Relay output C
NOTE
Although the Emergency Run satisfies the functionality requirements of Fire Mode, Santerno does not recommend its
use in situations that require testing and/or compliance with specific standards as it is not certified.
9.3 Emergency Run Operation
In normal operation the ASAB is controlled via a remote two-wire signal (terminals 56, 57).
Emergency Run is controlled by a two-wire circuit connected to Input A (terminals 53, 55). Closing Input A causes the ASAB to run the
motor and ignore certain trip conditions.
Parameter settings:
Parameter 6D Input A Function
Select 'Emergency Run' - assigns Input A for Emergency Run function.
Parameter 15C Emergency Run
Select 'Enable' - Enables Emergency Run mode.

ASAB
55/66
K M 1 F 1
2 2
2 1
6 /T3
2 /T1
13
14
4 /T2
24
3 3
3 4
5 /L3
3 /L2
S 3
S 1
S 2
E
1 /L1
6 5
6 4
4 1
4 0
5 6
5 7
5 8
5 3
5 5
A 6
A 5
A 4
5 4
A
08 8 80 .A
6
3
1 2
4
5
+
+
1
Three-phase supply
2
Motor terminals
3
Control voltage (model dependent)
4
Remote control inputs
5
Motor thermistor input
6
Relay outputs
S1
Start/stop contact
S2
Reset contact
S3
Auxiliary trip contact
13, 14
Relay output A
21, 22, 24
Relay output B
33, 34
Relay output C
9.4 Auxiliary Trip Circuit
In normal operation the ASAB is controlled via a remote two-wire signal (terminals 56, 57).
Input A (terminals 53, 55) is connected to an external trip circuit (such as a low pressure alarm switch for a pumping system). When the
external circuit activates, the soft starter trips, which stops the motor.
Parameter settings:
Parameter 6D Input A Function
Select 'Input Trip (N/O)'. Assigns the Input A to Auxiliary Trip (N/O) function.
Parameter 6E Input A Name
Select a name, eg Low Pressure. Assigns a name to Input A.
Parameter 4E Input A Trip
Set as required. For example, 'Run Only' limits the input trip to when the soft starter is running only.
Parameter 5E Input A Trip Delay
Parameter 5F Input A Initial Delay
Set as required. Sets a delay between the input activating and the soft starter tripping.
Set at around 120 seconds. Limits operation of the input trip to 120 seconds after the start signal. This allows time for
pressure to build up in the piping before the low pressure input becomes active.

56/66
ASAB
12 7 89 .B
-F 1
L 3L 2L 1 N E
-K A 1
L1 L2 L 3 E
T 1 T 2 T 3
A 5A 4 A 6
5 4 5 5 5 6 5 7 5 8
53 5 5
-K A 1-K A 2
-K A 1
-K A 2
T 3T 2T1
M
3
-K A 2
-K A 1
-A 2
1
Control voltage
A Off (Ready)
54, 55
Start B
Start
56, 57
Stop C
Run
58, 57
Reset D
Stop 2 Motor terminals
E Zero speed
3
Three-phase supply
5 Start signal (2, 3, or 4-wire)
4
Starter Disable (shown on starter display)
6 Zero speed sensor
CAUTION
When using DC brake, the mains supply must be connected to the soft starter (input terminals L1, L2, L3) in positive phase
sequence and parameter 4B Phase Sequence must be set to Positive Only.
9.5 DC Brake with External Zero Speed Sensor
For loads which may vary between braking cycles, there are benefits in using an external zero-speed sensor to interface with the ASAB
for brake shut-off. This control method ensures that the ASAB braking will always shut off when the motor has reached a standstill, thus
avoiding unnecessary motor heating.
The following schematic diagram shows how you can use a zero-speed sensor with the ASAB to turn the brake function off at motor
standstill. The zero-speed sensor (A2) is often referred to as an under-speed detector. Its internal contact is open at zero-speed and
closed at any speed above zero-speed. Once the motor has reached a standstill, 53, 55 will open and the starter will be disabled.
When the next start command is given (ie next application of KA1), 53, 55 closes and the ASAB is enabled.
The ASAB must be operated in remote mode and parameter 6D Input A Function must be set to 'Starter Disable'.
For details on configuring DC Brake, refer to Brake (page 30).

ASAB
57/66
3
6
5 3
5
6
1
2
3
4
1
Control voltage (model dependent)
A2
Zero speed sensor
2
Remote control inputs
KA1
Run relay
3
Motor thermistor input
KA2
Start relay
4
Relay outputs
KA3
Brake relay
5
Three-phase supply
KA4
Zero speed sensor relay
6
Motor terminals
KM1
Line contactor (Run)
KM2
Line contactor (Brake)
KT1
Run delay timer
KT2
Brake delay timer
S1
Start contact
S2
Stop contact
S3
Reset contact
NOTE
If the ASAB trips on supply frequency (parameter 16F Frequency) when the braking contactor KM2 opens, modify the
frequency protection settings.
9.6 Soft Braking
For applications with high inertia and/or a variable load, the ASAB can be configured for soft braking.
In this application the ASAB is employed with forward run and braking contactors. When the ASAB receives a start signal (pushbutton
S1), it closes the forward run contactor (KM1) and controls the motor according to the programmed primary motor settings.
When the ASAB receives a stop signal (pushbutton S2), it opens the forward run contactor (KM1) and closes the braking contactor
(KM2) after a delay of approximately 2-3 seconds (KT1). KA3 is also closed to activate the secondary motor settings, which should be
user programmed for the desired stopping performance characteristics.
When motor speed approaches zero, the zero speed sensor (A2) stops the soft starter and opens the braking contactor (KM2).
Parameter settings:
Parameter 6D Input A Function (terminals 53, 55)
Select 'Motor Set Select' - assigns Input A for Motor set selection.
Set starting performance characteristics using the primary motor set.
Set braking performance characteristics using the secondary motor settings.
Parameter 7G Relay C Function
Select 'Trip' - assigns Trip function to Relay Output C.

58/66
ASAB
NOTE
Pole Amplitude Modulated (PAM) motors alter the speed by effectively changing the stator frequency using external
winding configuration. Soft starters are not suitable for use with this type of two-speed motor.
08 88 2. A
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
2/T1
4/T2
6/T3
E
T4
T5
T6
T1
T2
T3
A6
A4
A5
1/L1
3/L2
5/L3
24
22
21
KA1
KA2
KA1
KA2
KM3
KA1
KM2KA2
KM1
KM2
KM3
KM1
KM3
KM1
KM3
KM2
S1
KM2
KM1
KA1
56
57
58
53
55
54
1
Control voltage (model dependent)
KA1
Remote start relay (low speed)
2
Remote control inputs
KA2
Remote start relay (high speed)
3
Relay outputs
KM1
Line contactor (high speed)
4
Three-phase supply
KM2
Line contactor (low speed)
5
Motor terminals
KM3
Star contactor (high speed)
6
Remote low speed start input
S1
Reset contact
7
Remote high speed start input
21, 22, 24
Relay output B
NOTE
Contactors KM2 and KM3 must be mechanically interlocked.
NOTE
If the ASAB trips on supply frequency (parameter 16F Frequency) when the high-speed start signal (7) is removed,
modify the frequency protection settings.
9.7 Two Speed Motor
The ASAB can be configured for control of dual speed Dahlander type motors, using a high speed contactor (KM1), low speed contactor
(KM2) and a star contactor (KM3).
When the soft starter receives a high speed start signal, it closes the high speed contactor (KM1) and star contactor (KM3), then controls
the motor according to the primary motor settings.
When the soft starter receives a low speed start signal, it closes the low speed contactor (KM2). This closes Input A and the ASAB
controls the motor according to the secondary motor settings.
Parameter settings:
Parameter 6D Input A Function
Select 'Motor Set Select' - assigns Input A for Motor set selection.
Set high speed performance characteristics using the primary motor settings.
Set low speed performance characteristics using the secondary motor settings.
Parameter 7D Relay B Function
Select 'Trip' - assigns Trip function to Relay Output B

ASAB
59/66
Display
Possible cause/Suggested solution
Battery/clock
A verification error has occurred on the real time clock, or the backup battery voltage is low. If the battery
is low and the power is off, date/time settings will be lost. Reprogram the date and time.
Related parameters: 16K
Controller
This is a name selected for a programmable input. Refer to Input trip.
Current imbalance
Current imbalance can be caused by problems with the motor, the environment or the installation, such
as:
An imbalance in the incoming mains voltage
A problem with the motor windings
A light load on the motor
A phase loss on input terminals L1, L2 or L3 during Run mode
An SCR that has failed open circuit. A failed SCR can only be definitely diagnosed by replacing the
SCR and checking the starter's performance.
Related parameters: 4A, 5B, 16B
Current Read Err
Lx
Where 'X' is 1, 2 or 3.
Internal fault (PCB fault). The output from the CT circuit is not close enough to zero when the SCRs are
turned off. Contact your local supplier for advice.
This trip is not adjustable.
Related parameters: None
Excess start time
Excess start time trip can occur in the following conditions:
parameter 1A Motor Full Load Current is not appropriate for the motor
parameter 2B Current Limit has been set too low
parameter 2D Start Ramp Time has been set greater than the setting for 2G Excess Start Time
setting
parameter 2D Start Ramp Time is set too short for a high inertia load when using Adaptive Control
Related parameters: 1A, 1C, 2B, 2D, 2G, 3B, 3D, 3G, 16H
Firing Fail Px
Where 'X' is phase 1, 2 or 3.
The SCR did not fire as expected. The SCR may be faulty or there may be an internal wiring fault.
This trip is not adjustable.
Related parameters: None
FLC too high (FLC
out of range)
The ASAB can support higher motor full load current values when connected to the motor using inside
delta configuration rather than in-line connection. If the soft starter is connected in-line but the
programmed setting for parameter 1A Motor Full Load Current is above the in-line maximum, the soft
starter will trip at start (see Minimum and Maximum Current Settings on page 8).
If the soft starter is connected to the motor using inside delta configuration, the soft starter may not be
correctly detecting the connection. Contact your local supplier for advice.
Related parameters: 1A, 1C
Frequency (Mains
supply)
The mains frequency has gone beyond the specified range.
Check for other equipment in the area that could be affecting the mains supply, particularly variable speed
drives and switch mode power supplies (SMPS).
If the ASAB is connected to a generator set supply, the generator may be too small or could have a speed
regulation problem.
Related parameters: 4G, 4H, 5G, 16F
10 Troubleshooting
10.1 Protection Responses
When a protection condition is detected, the ASAB will write this to the event log and may also trip or issue a warning. The soft starter's
response depends on the Protection Action setting (parameter group 16).
Some protection responses cannot be adjusted by the user. These trips are usually caused by external events (such as phase loss) or
by a fault within the soft starter. These trips do not have associated parameters and cannot be set to Warn or Log.
If the ASAB trips you will need to identify and clear the condition that triggered the trip, then reset the soft starter before restarting. To
reset the starter, press the RESET button on the keypad or activate the Reset remote input.
If the ASAB has issued a warning, the soft starter will reset itself once the cause of the warning has been resolved.
10.2 Trip Messages
This table lists soft starter's protection mechanisms and the probable cause of the trip. Some of these can be adjusted using parameter
group 4 Protection Levels and parameter group 16 Protection Action, other settings are built-in system protections and cannot be set or
adjusted.

60/66
ASAB
Heatsink
overtemperature
Check if cooling fans are operating. If mounted in an enclosure, check if ventilation is adequate.
Fans operate during Start, Run and for 10 minutes after the starter exits the Stop state.
NOTE
Models ASAB-0023B to ASAB-0053B and ASAB-0170B do not have a cooling fan.
Models with fans will operate the cooling fans from a Start until 10 minutes after a Stop.
Related parameters: 16J
High Level
This is a name selected for a programmable input. Refer to Input trip.
High Pressure
This is a name selected for a programmable input. Refer to Input trip.
Input trip
The soft starter's programmable input is set to a trip function and has activated. Resolve the trigger
condition.
Related parameters: 4E, 5E, 5F, 6D, 6E, 16E
Instantaneous
overcurrent
There has been a sharp rise in motor current, probably caused by a locked rotor condition (shearpin)
while running. This may indicate a jammed load.
Related parameters: 4D, 5D, 16D
Internal fault X
The ASAB has tripped on an internal fault. Contact your local supplier with the fault code (X).
Related parameters: None
L1 phase loss
L2 phase loss
L3 phase loss
During pre-start checks the starter has detected a phase loss as indicated.
In run state, the starter has detected that the current on the affected phase has dropped below 3.3% of
the programmed motor FLC for more than 1 second, indicating that either the incoming phase or
connection to the motor has been lost.
Check the supply and the input and output connections at the starter and at the motor end.
Phase loss can also be caused by a failed SCR, particularly an SCR that has failed open circuit. A failed
SCR can only be definitely diagnosed by replacing the SCR and checking the starter's performance.
Related parameters: None
L1-T1 shorted
L2-T2 shorted
L3-T3 shorted
During pre-start checks the starter has detected a shorted SCR or a short within the bypass contactor as
indicated. If the starter is connected in-line with the motor, consider using PowerThrough to allow
operation until the starter can be repaired.
NOTE
PowerThrough is only available with in-line installations. If the starter is installed
inside delta, PowerThrough will not operate.
The starter will trip on Lx-Tx Shorted on the first start attempt after control power is
applied. PowerThrough will not operate if control power is cycled between starts.
Related parameters: 15E
Low Control Volts
The ASAB has detected a drop in the control voltage.
Check the external control supply (terminals A4, A5, A6) and reset the starter.
If the external control supply is stable:
the 24 V supply on the main control PCB may be faulty; or
the bypass driver PCB may be faulty (internally bypassed models only). Contact your local supplier
for advice.
This protection is not active in Ready state.
Related parameters: 16M
Low Level
This is a name selected for a programmable input. Refer to Input trip.
Low Pressure
This is a name selected for a programmable input. Refer to Input trip.
Motor overload
(thermal model)
Motor 2 overload
The motor has reached its maximum thermal capacity. Overload can be caused by:
The soft starter protection settings not matching the motor thermal capacity
Excessive starts per hour
Excessive throughput
Damage to the motor windings
Resolve the cause of the overload and allow the motor to cool.
Related parameters: 1A, 1B, 1C, 1D, 2A, 2B, 3A, 3B, 16A
Motor Connection
Tx
Where 'X' is 1, 2 or 3.
The motor is not connected correctly to the soft starter for in-line or inside delta use.
Check individual motor connections to the soft starter for power circuit continuity.
Check connections at the motor terminal box.
This trip is not adjustable.
Related parameters: None

ASAB
61/66
Motor thermistor
The motor thermistor input has been enabled and:
The resistance at the thermistor input has exceeded 3.6 kΩ for more than one second.
The motor winding has overheated. Identify the cause of the overheating and allow the motor to cool
before restarting.
The motor thermistor input has been opened.
NOTE
If a valid motor thermistor is no longer used, a 1.2 kΩ resistor must be fitted across
terminals 64, 65.
Related parameters: 16G
Network
communication
(between module
and network)
The network master has sent a trip command to the starter, or there may be a network communication
problem.
Check the network for causes of communication inactivity.
Related parameters: 16L
No Flow
This is a name selected for a programmable input. Refer to Input trip.
Parameter out of
Range
A parameter value is outside the valid range.
The starter will load the default value for all affected parameters. Press RESET to go to the first invalid
parameter and adjust the setting.
Related parameters: None
Phase sequence
The phase sequence on the soft starter's input terminals (L1, L2, L3) is not valid.
Check the phase sequence on L1, L2, L3 and ensure the setting in parameter 4B is suitable for the
installation.
Related parameters: 4B
PLC
This is a name selected for a programmable input. Refer to Input trip.
Power loss / Power
circuit
The starter is not receiving mains supply on one or more phases when a Start Command is given.
Check that the main contactor closes when a start command is given, and remains closed until the end of
a soft stop. Check the fuses. If testing the soft starter with a small motor, it must draw at least 2% of its
minimum FLC setting on each phase.
Related parameters: None
Pump Fault
This is a name selected for a programmable input. Refer to Input trip.
Starter
communication
(between module
and soft starter)
There is a problem with the connection between the soft starter and the optional communications
module. Remove and reinstall the module. If the problem persists, contact your local distributor.
There is an internal communications error within the soft starter. Contact your local distributor.
Related parameters: 16I
Starter Disable
This is a name selected for a programmable input. Refer to Input trip.
Thermistor circuit
The thermistor input has been enabled and:
The resistance at the input has fallen below 20 Ω (the cold resistance of most thermistors will be
over this value) or
A short circuit has occurred. Check and resolve this condition.
Related parameters: None
Check that a PT100 (RTD) is not connected to 64, 65.
Related parameters: None
Time-overcurrent
The ASAB is internally bypassed and has drawn high current during running. (The 10A protection curve
trip has been reached or the motor current has risen to 600% of the motor FLC setting.)
Related parameters: None
Undercurrent
The motor has experienced a sharp drop in current, caused by loss of load. Causes can include broken
components (shafts, belts or couplings), or a pump running dry.
Related parameters: 4C, 5C, 16C
Unsupported
option (function
not available in
inside delta)
The selected function is not available (eg jog is not supported in inside delta configuration).
Related parameters: None
Vibration Alarm
This is a name selected for a programmable input. Refer to Input trip.
VZC Fail Px
Where 'X' is 1, 2 or 3.
Internal fault (PCB fault). Contact your local supplier for advice.
This trip is not adjustable.
Related parameters: None

62/66
ASAB
Symptom
Probable Cause
Starter "Not Ready"
Check Input A (53, 55). The starter disable function may be active. If parameter 6D
is set to Starter Disable and there is an open circuit on 53, 55, the ASAB will not start.
The soft starter does not respond to the
START or RESET button on the
keypad.
The soft starter may be in Remote control mode. When the soft starter is in Remote
control mode, the Local LED on the starter is off. Press the LOCAL/REMOTE
button once to change to Local control.
The soft starter does not respond to
commands from the control inputs.
The soft starter may be in Local control mode. When the soft starter is in Local
control mode, the Local LED on the starter is on. Press the LOCAL/REMOTE
button once to change to Remote control.
The control wiring may be incorrect. Check that the remote start, stop and reset
inputs are configured correctly (refer to Control Wiring on page 12 for details).
The signals to the remote inputs may be incorrect. Test the signalling by activating
each input signal in turn. The appropriate remote control input LED should activate
on the starter.
The soft starter does not respond to a start
command from either the local or remote
controls.
The soft starter may be waiting for the restart delay to elapse. The length of the
restart delay is controlled by parameter 5A Restart Delay.
The motor may be too hot to permit a start. If parameter 4F Motor Temperature
Check is set to Check, the soft starter will only permit a start when it calculates that
the motor has sufficient thermal capacity to complete the start successfully. Wait for
the motor to cool before attempting another start.
The starter may be disabled via a programmable input. If parameter 6D is set to
Starter Disable and there is an open circuit on 53, 55, the ASAB will not start. If
there is no further need to disable the starter, close the circuit on the input.
NOTE
Parameter 6A Local/Remote controls when the LOCAL/REMOTE
button is enabled.
A reset does not occur after an Auto-Reset,
when using a remote two-wire control.
The remote 2-wire start signal must be removed and reapplied for a re-start.
Non-resettable Thermistor Cct trip, when
there is a link between the thermistor input
64, 65 or when the motor thermistor
connected between 64, 65 is permanently
removed.
The thermistor input is enabled once a link is fitted and short circuit protection has
activated.
- Remove the link then load the default parameter set. This will
disable the thermistor input and clear the trip.
- Place a 1k2 resistor across the thermistor input.
- Turn thermistor protection to 'Log only' (parameter 16G).
The soft starter does not control the motor
correctly during starting.
Start performance may be unstable when using a low Motor Full Load Current setting
(parameter 1A). This can affect use on a small test motor with full load current
between 5 A and 50 A.
Power factor correction (PFC) capacitors must be installed on the supply side of the
soft starter. To control a dedicated PFC capacitor contactor, connect the contactor
to run relay terminals.
Motor does not reach full speed.
If the start current is too low, the motor will not produce enough torque to accelerate
to full speed. The soft starter may trip on excess start time.
NOTE
Make sure the motor starting parameters are appropriate for the application
and that you are using the intended motor starting profile. If parameter 6D is
set to Motor Set Select, check that the corresponding input is in the expected
state.
The load may be jammed. Check the load for severe overloading or a locked rotor
situation.
Erratic motor operation.
The SCRs in the ASAB require at least 5 A of current to latch. If you are testing the
soft starter on a motor with full load current less than 5 A, the SCRs may not latch
correctly.
Erratic and noisy motor operation.
If the soft starter is connected to the motor using inside delta configuration, the soft
starter may not be correctly detecting the connection. Contact your local supplier for
advice.
Soft stop ends too quickly.
The soft stop settings may not be appropriate for the motor and load. Review the
settings of parameters 2H, 2I, 3H and 3I.
If the motor is very lightly loaded, soft stop will have limited effect.
Adaptive Control, brake, jog and
PowerThrough functions not working.
These features are only available with in-line installation. If the ASAB is installed
inside delta, these features will not operate.
10.3 General Faults
This table describes situations where the soft starter does not operate as expected but does not trip or give a warning.

ASAB
63/66
After selecting Adaptive Control the motor
used an ordinary start and/or the second
start was different to the first.
The first Adaptive Control start is actually 'Constant Current' so that the starter can
learn from the motor characteristics. Subsequent starts use Adaptive Control.
PowerThrough does not operate when
selected.
The starter will trip on Lx-Tx Shorted on the first start attempt after control power is
applied. PowerThrough will not operate if control power is cycled between starts.
Parameter settings cannot be stored.
Make sure you are saving the new value by pressing the MENU/ENTER button
after adjusting a parameter setting. If you press EXIT, the change will not be saved.
Check that the adjustment lock (parameter 15B) is set to Read & Write. If the
adjustment lock is set to Read Only, settings can be viewed but not changed. You
need to know the security access code to change the adjustment lock setting.
The EEPROM may be faulty on the keypad. A faulty EEPROM will also trip the soft
starter, and the keypad will display the message Parameter out of Range. Contact
your local supplier for advice.
Remote keypad shows message "awaiting
data"
The keypad is not receiving data from the control PCB. Check the cable connection.

64/66
ASAB
NOTE
Finger guards can be used on soft starter models ASAB-0145B~ASAB-1000B (internally bypassed models only). Different
kits are required for different models.
11 Accessories
11.1 Communication Modules
ASAB soft starters support network communication via easy-to-install communications modules. Each soft starter can support one
communications module at a time.
Available protocols:
Ethernet (Profinet, Modbus TCP, Ethernet IP), Profibus, DeviceNet, Modbus RTU, and USB.
11.2 Remote Control Panel (RCP)
A remote mounted keypad can be installed with the ASAB. The keypad can be mounted up to 3 metres away from the starter, for
control and monitoring.
The starter can be controlled and programmed from either the remote keypad or the keypad on the starter. Both displays show the
same information.
The remote keypad also allows parameter settings to be copied between soft starters.
11.3 Finger Guard Kit
Finger guards may be specified for personnel safety. Finger guards fit over the soft starter terminals to prevent accidental contact with
live terminals. Finger guards provide IP20 protection when correctly installed.
11.4 PC Software
WinMaster PC software provides monitoring, programming and control of up to 99 soft starters.
A Modbus or USB communication module is required for each starter to use WinMaster.

ASAB
65/66
NOTE
Many electronic components are sensitive to static electricity. Voltages so low that they cannot be felt, seen or heard, can
reduce the life, affect performance, or completely destroy sensitive electronic components. When performing service,
proper ESD equipment should be used to prevent possible damage from occurring.
0 92 75 . B
1. Remove all wiring and links from the soft starter before
dismantling the unit.
2. Remove the unit cover (4 screws).
3. Remove the keypad faceplate, then gently remove the
keypad (2 screws).
4. Remove the control terminal plugs.
5. Gently fold the main plastic away from the starter (12
screws).
6. Unplug the keypad loom from CON 1 (see note).
7. Label each SCR firing loom with the number of the
corresponding terminal on the backplane PCB, then unplug
the looms.
8. Unplug the thermistor, fan and current transformer wires
from the model board.
9. Remove the plastic tray from the starter (four screws).
NOTE
Remove the main plastic slowly to avoid damaging the keypad wiring loom which runs between the main plastic and the
backplane PCB.
08 60 5. A
10. Unscrew and remove the magnetic bypass plates (models
ASAB-0620C to ASAB-1600C only).
11. Remove the current transformer assembly (three screws).
12. Identify which busbars are to be moved. Remove the bolts
holding these busbars in place then slide the busbars out
through the bottom of the starter (four bolts per busbar).
08 6 06 .A
13. Slide the busbars in through the top of the starter. For input
busbars, the short curved end should be outside the starter.
For output busbars, the unthreaded hole should be outside
the starter.
14. Replace the dome washers with the flat face towards the
busbar, then tighten the bolts holding the busbars in place to
20 Nm.
15. Place the current transformer assembly over the input
busbars and screw the assembly to the body of the starter
(see note).
16. Run all wiring to the side of the starter and secure with cable
ties.
12 Busbar Adjustment Procedure
The busbars on non-bypassed models ASAB-0380C ~ ASAB-1600C can be adjusted for top or bottom input and output as required.
All units are manufactured with input and output busbars at the bottom of the unit as standard. The input and/or output busbars can be
moved to the top of the unit if required.

66/66
ASAB
NOTE
If moving the input busbars, the current transformers (CTs) must also be reconfigured.
1. Label the CTs L1, L2 and L3 (L1 is leftmost when looking from the front of the starter). Remove the cable ties and
unscrew the CTs from the bracket.
2. Move the CT bracket to the top of the starter. Position the CTs for the correct phases, then screw the CTs to the
bracket. For models ASAB-0380C ~ ASAB-0930C, the CTs must be placed on an angle (the left hand legs of each
CT will be on the top row of holes and the right hand legs will be on the bottom tabs).

15P0078B1
710-08733-00D
È710-08733-00DpËÍ
 Loading...
Loading...