Page 1

SanDisk® SSD Dashboard
User Manual
Page 2

Accessing Online Support
Visit our product support website at kb.sandisk.com and choose from these topics:
▪ Downloads — Download software and updates for your SanDisk product
▪ Registration — Register your SanDisk product to get the latest updates and special
▪ SanDisk Community — Share your thoughts and connect with other SanDisk users
oers.
Page 3

Table of Contents
_________
Accessing Online Support........................................................................................... ii
_________
1 Introduction ....................................................................................................................1
Minimum System Requirements.................................................................................................1
Supported Operating Systems................................................................................................... 1
Supported Languages.....................................................................................................................1
Installation.............................................................................................................................................1
Usage .................................................................................................................................................... 2
_________
2 Status............................................................................................................................... 4
Status Section....................................................................................................................................4
Capacity................................................................................................................................................5
Volumes.................................................................................................................................................5
Life Remaining................................................................................................................................... 5
Temperature........................................................................................................................................5
Interface Speed................................................................................................................................. 5
_________
3 Performance..................................................................................................................7
Performance Chart...........................................................................................................................7
Transfer Speed MB/s.......................................................................................................................7
Transfer IOPS......................................................................................................................................7
TRIM........................................................................................................................................................8
_________
4 Tools..................................................................................................................................9
Firmware Update..............................................................................................................................9
Check for Updates.........................................................................................................................10
Update Using Bootable USB Drive..........................................................................................11
Update Using File on My Computer...................................................................................... 12
Erase Drive—Secure Erase..........................................................................................................13
Delete User Data with Secure Erase......................................................................................14
Create a Bootable USB Drive for Secure Erase............................................................... 14
Sanitize.................................................................................................................................................15
Delete User Data with Sanitize.................................................................................................15
Create a Bootable USB Drive with Sanitize....................................................................... 16
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
i
Page 4

Erase Drive......................................................................................................................................... 17
Bootable USB Drive for Erase Drive...................................................................................... 17
PSID Revert........................................................................................................................................18
S.M.A.R.T.............................................................................................................................................. 19
Diagnostic Short Test.................................................................................................................. 20
Diagnostic Extended Test..........................................................................................................20
Drive Details.......................................................................................................................................21
System Details.................................................................................................................................22
_________
5 Settings.........................................................................................................................23
Application Update.......................................................................................................................23
Starting SanDisk SSD Dashboard with Windows Startup.........................................24
Select Language............................................................................................................................ 24
_________
6 Help................................................................................................................................ 26
Online Support................................................................................................................................26
Generate Report.............................................................................................................................26
About SanDisk SSD Dashboard..............................................................................................27
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
ii
Page 5

1
Introduction
Introduction
This chapter contains the following sections.
▪ Minimum System Requirements
▪ Supported Operating Systems
▪ Supported Languages
▪ Installation
▪ Usage
Minimum System Requirements
The SanDisk SSD Dashboard is a Microsoft Windows application.
Administrative rights are required for installation and execution of the
application.
Supported Operating Systems
▪ Windows 10 (32/64 bit)
▪ Windows 8.1 (32/64 bit)
▪ Windows 7 (32/64 bit)
◦ Windows 7 requires a Microsoft
Hotfix 2990941
MS
◦ Windows 7 requires the support of a graphics driver that supports
OpenGL 2.1 or higher.
Hotfix to support NVMe, see:
Supported Languages
Seventeen languages are supported:
Czech
▪
Danish
▪
Dutch
▪
English
▪
French
▪
German
▪
Italian
▪
Japanese
▪
Korean
▪
Polish
▪
Portuguese
▪
Russian
▪
Simplified Chinese
▪
Spanish
▪
Swedish
▪
Traditional Chinese
▪
Turkish
▪
Installation
You can download the current version of the SanDisk SSD Dashboard software from
kb.sandisk.com.
After the file has been downloaded, follow these steps to install the application.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
1
Page 6
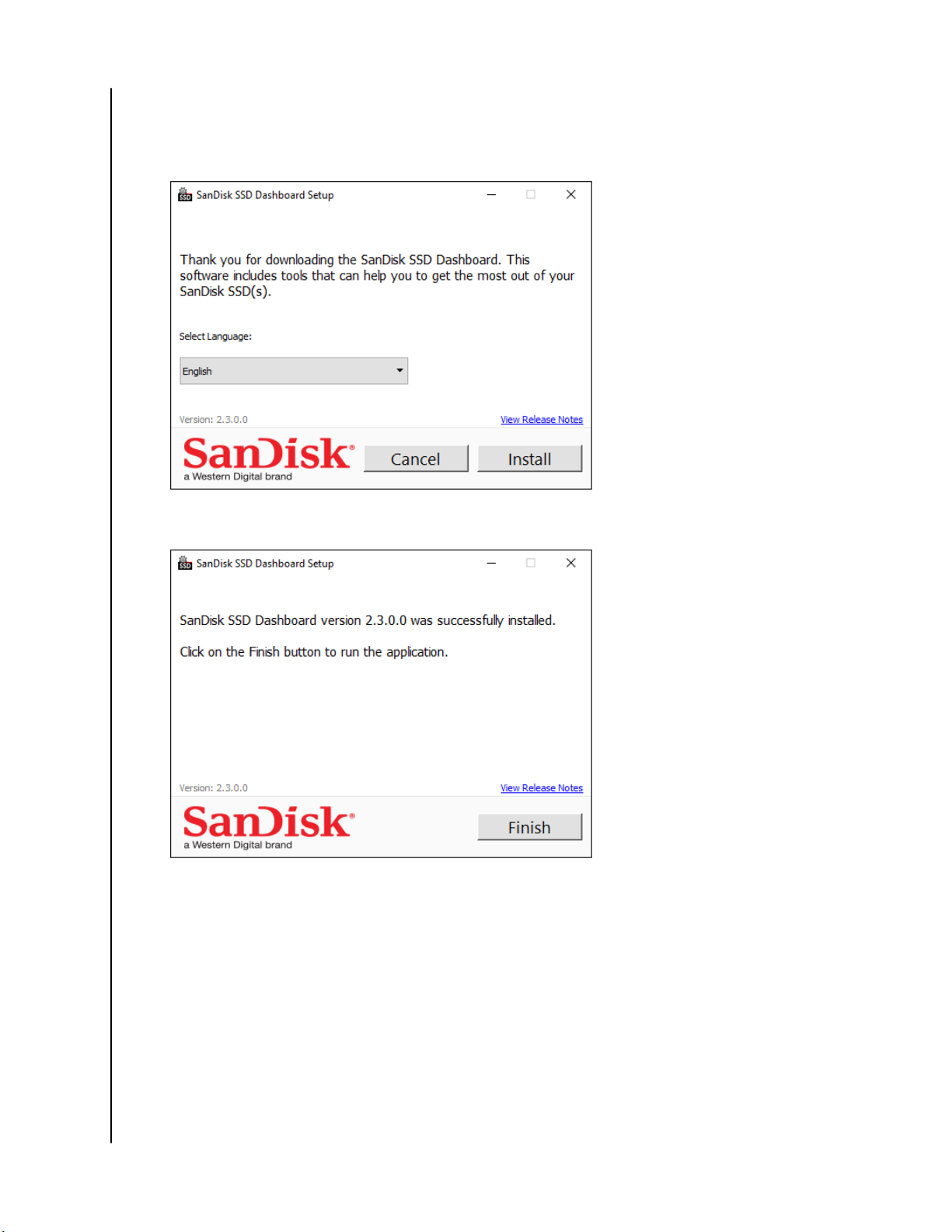
1. Double-click on the SanDiskSSDDashboardSetup.exe file icon to launch the
installation.
Note:
To cancel the installation, click on the X in the upper-right corner of the dialog
box.
Introduction
2. When the installation is complete, click Finish. The SanDisk SSD Dashboard
launches and populates the Status section.
When the installation has completed successfully, click on the Finish button.
This will automatically launch the SanDisk SSD Dashboard and load the
Status section.
Note:
To perform an application update, see Application Update.
Usage
The SanDisk SSD Dashboard automatically scans for SanDisk SSDs after it
launches.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
2
Page 7
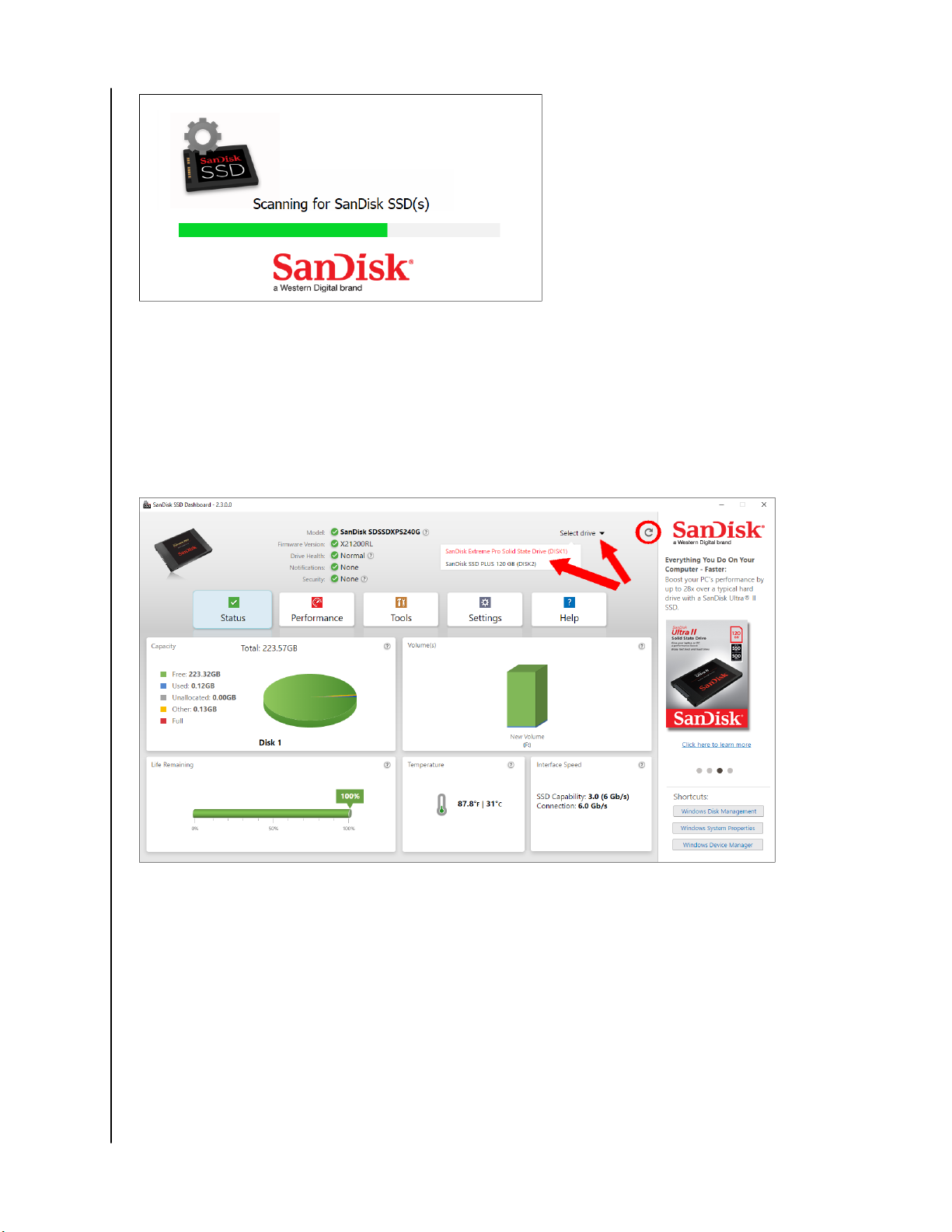
If a SanDisk SSD is connected to the system after Dashboard is launched, the
Dashboard will automatically scan the system. It will add the drive as the
current model if this is the only SanDisk drive in the system, or add it to the list
of drives in the Select Drive drop-down. If, for some reason, you do not see the
drive, click the Refresh icon in the upper right corner of the screen to rescan
the system for SanDisk SSDs.
Introduction
When all SSD drives have been detected, you can select a
clicking on the Select drive drop-down menu.
specific drive by
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
3
Page 8

2
Status
Status
This chapter contains the following sections.
▪ Status Section
▪ Capacity
▪ Volumes
▪ Life Remaining
▪ Temperature
▪ Interface Speed
Status Section
The Status section displays the overall state and health of the selected drive.
Note:
To select an SSD drive, click the Select drive drop-down menu.
The following information is listed at the top of the Status screen:
▪ Model - The product model name of the selected SanDisk SSD.
▪ Firmware Version - The version number of the firmware installed on the
selected SanDisk SSD. Notifications of updates also appear in this section.
▪ Drive Health - Drive Health summarizes the current condition of the selected
SSD based on Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology
(S.M.A.R.T.) attributes.
◦ Normal: The drive is in good condition.
◦ Poor: The number of spare blocks has reached the minimum threshold or
the drive is overheating. In the case of low spare-block count, replace this
drive with a new SanDisk SSD.
Notifications - Notifications, such as software or S.M.A.R.T. attribute
▪
warnings, will be displayed in this area.
▪ Security - If the selected drive supports security, this area will be visible.
◦ “Not Activated” displays if the security protocol is not active.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
4
Page 9

◦ If the security protocol is active, the name of the active security protocol
displays, for example, “Activated, TCG Opal 2.0/eDrive”.
Capacity
As used for storage capacity on our packaging and device label, one gigabyte
(GB) = one billion bytes and one terabyte (TB) = one trillion bytes. On the
SanDisk SSD Dashboard and within Windows folders, total accessible capacity
varies depending on operating environment and the capacity displayed is
based on the Windows operating system's calculation method for totalreported capacity.
▪ Green - Free space
▪ Blue - Used space
▪ Gray - Unallocated space
▪ Yellow - Other
▪ Red - Full
Status
Volumes
The chart displays any drive volumes recognized by Windows.
▪ Green - Free space
▪ Blue - Used space
▪ Red - No free space
Life Remaining
The Life Remaining percentage represents the remaining writes the selected
drive can perform in its lifetime.
Note:
If this feature is not supported by the drive, a “Not Supported”
message will be displayed.
Temperature
The temperature reported by the SSD. The thermometer graphic displays one
of two colors, as follows.
▪ Green - Normal operation
▪ Yellow - The SSD is currently overheating
Interface Speed
▪ SSD Capability - The fastest speed supported by the drive.
▪ Connection - The port connecting the SSD to the system.
Note:
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
For SATA SSD, the connection speed is the actual speed negotiated
with the system. If the connection speed is lower than the SSD
5
Page 10

Capability speed, the following message appears in red: For best
performance, connect your SSD to a 6.0 Gb/s-capable port.
Status
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
6
Page 11

3
Performance
Performance
This chapter contains the following sections.
▪ Performance Chart
▪ Transfer Speed MB/s
▪ Transfer IOPS
▪ TRIM
Performance Chart
The Performance chart provides two dierent real time performance metrics:
transfer speed MB/s (megabytes per second) and transfer IOPS (I/O operation
count per second).
The chart scrolls from right to left and shows moving, 5-minute time line
increments on the horizontal axis. The vertical axis of the chart will show either
Transfer Speed MB/s or Transfer IOPS.
Transfer Speed MB/s
The SSD MB/s write and read speeds are shown in the chart with blue and
green indicators, respectively.
Transfer IOPS
The SSD I/O write and read speeds are shown in the chart with purple and
orange indicators, respectively.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
7
Page 12

Performance
TRIM
(This feature will be displayed if the operating system supports it.) The TRIM
function frees up space on the SSD that was used by files that have been
deleted.
Note:
▪ Click the Enable Windows TRIM checkbox to automatically run TRIM.
▪ Select Weekly, for the frequency, if available.
▪ Click Run TRIM Now to manually run TRIM.
SanDisk recommends that TRIM be run on a weekly basis.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
8
Page 13

4
Tools
Tools
This chapter contains the following sections.
▪ Firmware Update
▪ Check for Updates
▪ Update Using Bootable
USB Drive
▪ Update Using File on My
Computer
▪ Erase Drive—Secure Erase
▪ Delete User Data with
Secure Erase
▪ Create a Bootable USB
Drive for Secure Erase
▪ Sanitize
▪ Delete User Data with
Sanitize
▪ Create a Bootable USB
Drive with Sanitize
▪ Erase Drive
▪ Bootable USB Drive for
Erase Drive
▪ PSID Revert
▪ S.M.A.R.T.
▪ Diagnostic Short Test
▪ Diagnostic Extended Test
▪ Drive Details
▪ System Details
Firmware Update
Note:
Click Update SSD Firmware to initiate a firmware update, or click on the Show
More Options drop-down menu to choose from additional firmware update
methods.
To avoid data loss, it is strongly recommended that you backup your
data before updating the firmware.
When you click the Update SSD Firmware button, a confirmation dialog box
appears.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
9
Page 14

After the firmware has been downloaded to the SSD, a full-system shutdown is
required to complete the firmware update process for SATA SSDs. This is
typically done by shutting the computer down, and then turning it back on.
A dialog box appears that provides the option to shut the computer down
now, or later.
Tools
Check for Updates
Click Check for Updates to manually check if a firmware update is available for
the selected drive.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
10
Page 15

Tools
If a firmware update is found, the status message will change to “There is new
firmware available for this drive,” and the update options will be displayed.
Update Using Bootable USB Drive
Note:
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
The USB device must be formatted in order for the Dashboard to
recognize it. During USB creation, it will automatically be reformatted to FAT32. All data will be permanently erased from the
USB device.
11
Page 16

Tools
1. Insert a formatted USB drive. If the USB drive is added to the system after
the Dashboard is launched, it won't be recognized automatically. Click the
refresh icon next to the "No USB Drive Found" drop-down.
2. Before proceeding, backup any existing data on the USB drive.
3. Click the drop-down list to select the USB drive.
Note: If the USB drive is not listed, click the Refresh icon next to the drop-down list to
scan for the USB drive.
4. Click Create USB Drive.
Update Using File on My Computer
Note:
If you have already downloaded the specific firmware file that should be used
for the update, click Select File.
Only use compatible firmware update files for this process.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
12
Page 17

Tools
A confirmation dialog box appears.
Erase Drive—Secure Erase
Secure Erase permanently destroys all user data on the selected SSD.
Note:
Secure Erase deletes the mapping table on the selected SSD, but it
does not erase all blocks that have been written to. This makes
Secure Erase a faster “erase” option than the Sanitize function (also
see Sanitize).
Secure Erase can only be performed on an SSD that is not the boot drive.
However, if the SSD is the boot drive, the Secure Erase function can be
performed from a formatted USB. See
Create a Bootable USB Drive for Secure Erase.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
13
Page 18

Delete User Data with Secure Erase
Tools
Note:
Ensure that the correct SSD is selected on a system with more than
one SSD. The Secure Erase function permanently destroys all user
data on the selected SSD.
1. In the blue section at the top of the Dashboard, click the Select drive drop-
down menu to select the SSD on which all user data will be permanently
deleted.
Note:
If the SSD to be deleted is not listed, click the Refresh icon next to the Select
drive drop-down menu to scan for the SSD.
The name of the selected SSD appears next to Model.
2. Click Erase Now next to Secure Erase to delete all user data and leave the
drive in an unformatted state.
Create a Bootable USB Drive for Secure Erase
1. Insert a formatted USB drive.
2. Before proceeding, backup any existing data on the USB drive.
3. Click the drop-down list to select the USB drive.
Note:
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
If the USB drive is not listed, click the Refresh icon next to the drop-down list
to scan for the USB drive.
14
Page 19

Tools
4. Click Create USB Drive.
Sanitize
Sanitize permanently destroys all user data on the SSD.
Note:
Sanitize deletes the mapping table and erases all blocks that have
been written to on the selected SSD. This makes Sanitize a slower
“erase” option than the Secure Erase function (also see
Secure Erase).
Sanitize can only be performed on an SSD that is not the boot drive. However,
if the SSD is the boot drive, the Sanitize function can be performed from a
formatted USB. See Create a Bootable USB Drive with Sanitize.
Delete User Data with Sanitize
Note:
1. In the blue section at the top of the Dashboard, click the Select drive drop-
down menu to select the SSD on which all user data will be permanently
deleted.
Note:
Ensure that the correct SSD is selected on a system with more than
one SSD. The Sanitize function permanently destroys all user data on
the selected SSD.
If the SSD to be deleted is not listed, click the Refresh icon next to the Select
drive drop-down menu to scan for the SSD.
The name of the selected SSD appears next to Model.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
15
Page 20

2. Click Erase Now next to Sanitize to delete all user data and leave the drive in
an unformatted state.
Tools
Create a Bootable USB Drive with Sanitize
1. Insert a formatted USB drive.
2. Before proceeding, backup any existing data on the USB drive.
3. Click the drop-down list to select the USB drive.
Note:
If the USB drive is not listed, click the Refresh icon next to the drop-down list
to scan for the USB drive.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
16
Page 21

Tools
4. Click Create USB Drive.
Erase Drive
Erase Drive permanently destroys all user data on the selected SSD.
Note:
Erase Drive deletes the mapping table on the selected SSD, but it
does not erase all blocks that have been written to.
Bootable USB Drive for Erase Drive
Note:
1. Insert a formatted USB drive.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
The USB drive must be formatted as a FAT or FAT32 file system.
17
Page 22

2. Before proceeding, backup any existing data on the USB drive.
3. Click the drop-down list to select the USB drive. Note: If the USB drive is
not listed, click the Refresh icon next to the drop-down list to scan for the
USB drive.
4. Click Create USB Drive.
Tools
PSID Revert
PSID (Physical Security ID) is a unique 32-character alphanumeric identifier for
SanDisk security-capable SSDs, which is required to restore the drive to a
clean state. It is printed on the SSD label (for encrypted drives) as a 32character string, as well as a 2D barcode.
The PSID revert function is useful if the drive is locked and needs to be repurposed. It allows users to regain use of the drive by restoring factory
settings. Note that this function will erase all user data and leave the drive in
an unformatted state.
Note:
The drive must be locked and encrypted.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
18
Page 23

Tools
If the SSD is the boot drive, you may create a bootable USB drive with PSID
Revert tool on it. The bootable USB drive can also be used as portable tool to
erase SSDs on multiple systems.
Click on the Select USB Drive dropdown to choose the desired USB drive and
then click Create USB Drive. If it is not listed, click the Refresh icon next to the
dropdown menu to scan for the USB drive. It is recommended to backup any
existing data on the USB drive before proceeding.
S.M.A.R.T.
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis and Reporting Technology) is an industrystandard drive monitoring system.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
19
Page 24

Tools
Diagnostic Short Test
The S.M.A.R.T. Diagnostic Short Test runs automatically run every time the
SanDisk SSD Dashboard application is launched. It is a quick, drive health test
defined by the S.M.A.R.T. specification.
as
Diagnostic Extended Test
The S.M.A.R.T. Diagnostic Extended Test is an extended drive health test as
defined by the S.M.A.R.T. specification. The SanDisk SSD Dashboard cannot be
used while the test is running. However, you can cancel the test at any time.
If the test is successful, the progress status changes to a green, test complete
message.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
20
Page 25

If the test is unsuccessful, click the provided link to go to the test details.
Drive Details
Tools
Drive Details displays the following information for the selected drive:
▪ Model Name
▪ Model String
▪ NVMe Revision / SATA Revision
▪ NVMe Link Speed / SATA Link Speed
▪ Serial Number
▪ Maximum LBA
▪ World Wide Name (a unique
identifier used for storage technologies)
▪ 4K Alignment
For additional information, click Show Advanced Details.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
21
Page 26

System Details
System Details displays information about the operating system, computer
hardware, and ATA controller(s) used in the system on which SanDisk SSD
Dashboard is installed.
Tools
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
22
Page 27

5
Settings
Settings
This chapter contains the following sections.
▪ Application Update
▪ Starting SanDisk SSD Dashboard with
Windows Startup
▪ Select Language
Application Update
If a newer version of the application is available, a message will be displayed in
Notifications area.
the
Clicking on the New Application Available link will take you to the Settings
section, which will display the number of the new version available. Click on
Update SanDisk SSD Dashboard to initiate the update.
Click OK to confirm and proceed with the application update. After the update
finished downloading, the installation process will begin.
has
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
23
Page 28

Starting SanDisk SSD Dashboard with Windows Startup
Settings
To launch the SanDisk SSD Dashboard at Windows startup, check Start SSD
Dashboard with Windows startup.
To open the SanDisk SSD Dashboard in Windows’ system tray on the
taskbar, check Start minimized.
Select Language
Click the Select Language drop-down menu to select the display language of
the SanDisk SSD Dashboard.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
24
Page 29

Settings
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
25
Page 30

6
Help
This chapter contains the following sections.
▪ Online Support
▪ Generate Report
▪ About SanDisk SSD Dashboard
Online Support
The Online Support section contains links to the SanDisk Support website,
where you’ll
Knowledge Base, and the SanDisk Community forum.
The Software & Downloads link takes you to the latest product and application
software and firmware versions, and when specialized support is required, use
the Get Help - Create a Support Case form.
find product-specific information and user guides, a searchable
Help
Generate Report
Click Generate Report to create and save a full system report that provides the
detailed information required for certain support cases.
The Generate Report function generates two files:
▪ SSD_Dashboard_Report.csv
▪ SSD_Dashboard_Report_msinfo.txt.
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
26
Page 31

About SanDisk SSD Dashboard
The About SSD Dashboard section contains the current version number of the
SanDisk SSD Dashboard software, as well as links to the End User License
Agreement (EULA), Third Party Notices, and the SanDisk Privacy Statement.
Help
SanDisk SSD Dashboard
User Manual
27
Page 32

SanDisk and the SanDisk logo are registered trademarks or trademarks of Western
Digital Corporation or its affiliates in the U.S. and/or other countries. Microsoft and
Windows are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation
in the United States and/or other countries. All other marks that may be mentioned
herein are the property of their respective owners. As used for storage capacity,
one gigabyte (GB) = one billion bytes and one terabyte (TB) = one trillion bytes.
Total accessible capacity varies depending on operating environment. Pictures
shown may vary from actual products. Not all products are available in all regions of
the world.
©
2018 Western Digital Corporation or its
SanDisk
5601 Great Oaks Parkway
San Jose, California 95119 U.S.A.
aliates.
02-02-WW-02-00005-P6 April 2018
 Loading...
Loading...