Samsung TT17J Series Service Manual
COLOR MONITOR
TT17J*
Manual
SERVICE
COLOR MONITOR CONTENTS
1. Precautions
2. Product Specifications
3. Disassembly & Reassembly
4. Alignment & Adjustments
5. Troubleshooting
6. Exploded View & Parts List
7. Electrical Parts List
8. Block Diagram
9. Wiring Diagram
10. Schematic Diagrams
WARNINGS
1. For continued safety, do not attempt to modify the
circuit board.
2. Disconnect the AC power before servicing.
3. When the chassis is operating, semiconductor
heatsinks are potential shock hazards.
1-1-1 Servicing the High Voltage VR
and CRT :
WARNING: A high voltage VR replaced in the wrong
direction may cause excessive X-ray
emissions.
Caution: When replacing the high voltage
adjustment VR, it must be fixed by a
soldering iron after it is properly set.
1. When servicing the high voltage system, remove
the static charge by connecting a 10 kohm resistor
in series with an insulated wire (such as a test
probe) between the chassis and the anode lead.
2. If the HV VR requires adjustment, (a) Replace the
VR and adjust the high voltage to the specification.
(b) Use a soldering iron to melt the adjustment cap
on the HV VR to prevent any movement.
3. When troubleshooting a monitor with excessively
HV, avoid being unnecessarily close to the monitor.
Do not operate the monitor for longer than is
necessary to locate the cause of excessive voltage.
4. High voltage should always be kept at the rated
value, no higher. Only when high voltage is
excessive are X-rays capable of penetrating the shell
of the CRT, including the lead in glass material.
Operation at high voltages may also cause failure of
the CRT or high voltage circuitry.
5. When the HV regulator is operating properly, there
is no possibility of an X-ray problem. Make sure the
HV does not exceed its specified value and that it is
regulating correctly.
6. The CRT is especially designed to prohibit
X-ray emissions. To ensure continued X-ray
protection, replace the CRT only with one that is
the same or equivalent type as the original.
7. Handle the CRT only when wearing shatterproof
goggles and after completely discharging the high
voltage anode.
8. Do not lift the CRT by the neck.
1-1-2 Fire and Shock Hazard :
Before returning the monitor to the user, perform the
following safety checks:
1. Inspect each lead dress to make certain that the
leads are not pinched or that hardware is not
lodged between the chassis and other metal parts in
the monitor.
2. Inspect all protective devices such as nonmetallic
control knobs, insulating materials, cabinet backs,
adjustment and compartment covers or shields,
isolation resistor-capacitor networks, mechanical
insulators, etc.
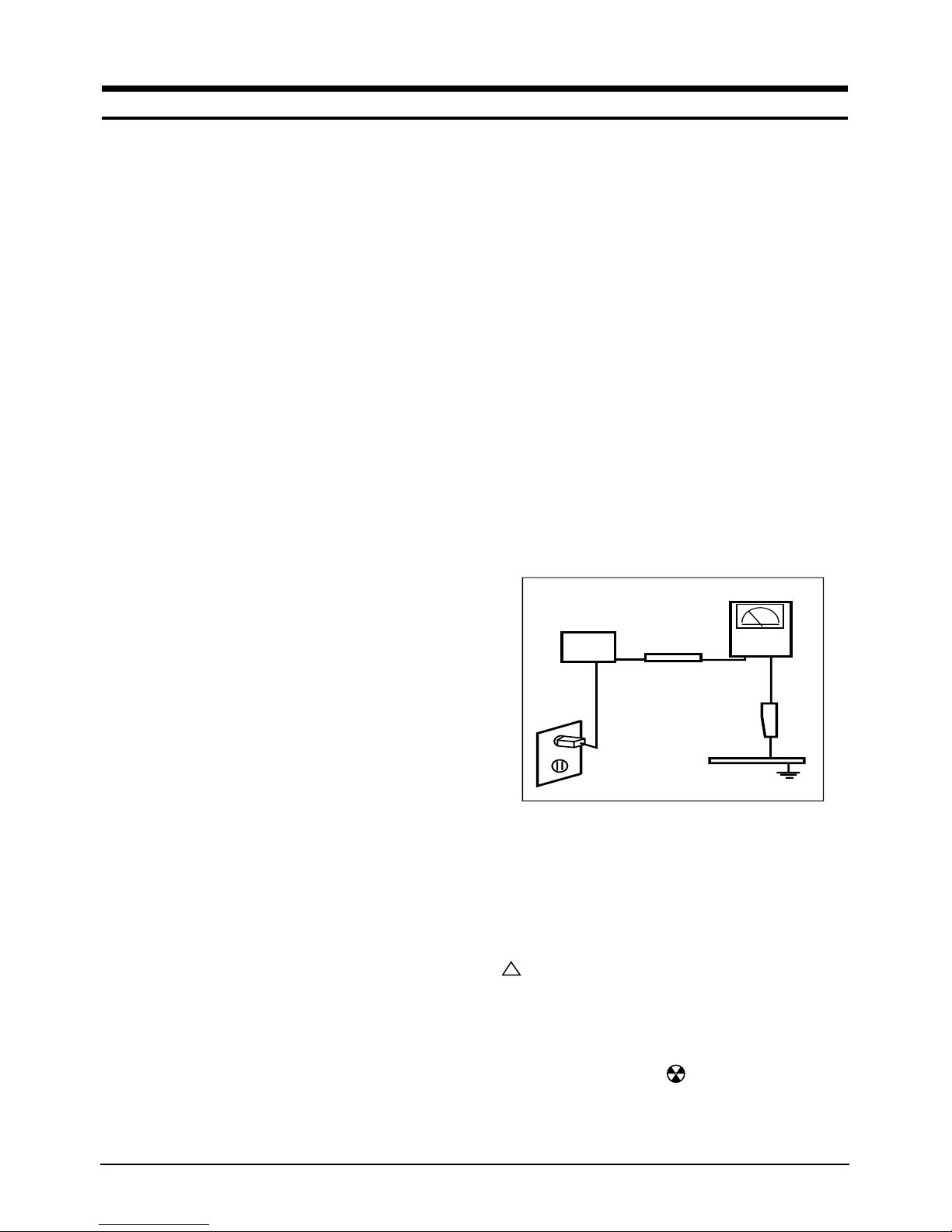
3. Leakage Current Hot Check (Figure 1-1):
WARNING: Do not use an isolation transformer during
this test.
Use a leakage current tester or a metering system
that complies with American National Standards
Institute (ANSI C101.1, Leakage Current for
Appliances), and Underwriters Laboratories (UL
Publication UL1410, 59.7).
4. With the unit completely reassembled, plug the AC
line cord directly into a 120V AC outlet. With the
unit’s AC switch first in the ON position and then
OFF, measure the current between a known earth
ground (metal water pipe, conduit, etc.) and all
exposed metal parts, including: metal cabinets,
screwheads and control shafts. The current
measured should not exceed 0.5 milliamp. Reverse
the power-plug prongs in the AC outlet and repeat
the test.
Figure 1-1. Leakage Current Test Circuit
1-1-3 Product Safety Notices
Some electrical and mechanical parts have special
safety-related characteristics which are often not
evident from visual inspection. The protection they give
may not be obtained by replacing them with
components rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc. Parts
that have special safety characteristics are identified by
on schematics and parts lists. A substitute
replacement that does not have the same safety
characteristics as the recommended replacement part
might create shock, fire and / or other hazards. Product
safety is under review continuously and new
instructions are issued whenever appropriate.
Components identified by on schematics and parts
lists must be sealed by a soldering iron after
replacement and adjustment.
1. Servicing precautions are printed on the cabinet,
TT17J* 1-1
1 Precautions
1-1 Safety Precautions
!
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
TEST ALL
EXPOSED METAL
SURFACES
(READING SHOULD
NOT BE ABOVE 0.5mA)
LEAKAGE
CURRENT
TESTER
2-WIRE CORD
ALSO TEST WITH
PLUG REVERSED
(USING AC ADAPTER
PLUG AS REQUIRED)
EARTH
GROUND

and should be followed closely.
2. Always unplug the unit’s AC power cord from the
AC power source before attempting to: (a) remove
or reinstall any component or assembly, (b)
disconnect PCB plugs or connectors, (c) connect all
test components in parallel with an electrolytic
capacitor.
3. Some components are raised above the printed
circuit board for safety. An insulation tube or tape
is sometimes used. The internal wiring is
sometimes clamped to prevent contact with
thermally hot components. Reinstall all such
elements to their original position.
4. After servicing, always check that the screws,
components and wiring have been correctly
reinstalled. Make sure that the area around the
serviced part has not been damaged.
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor
components or assemblies, drain the electrostatic
charge from your body by touching a known earth
ground. Alternatively, wear a discharging wriststrap device. To avoid a shock hazard, be sure to
remove the wrist strap before applying power to
the monitor.
2. After removing an ESD-equipped assembly, place it
on a conductive surface such as aluminum foil to
prevent accumulation of an electrostatic charge.
3. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can
generate electrical charges sufficient to damage
ESDs.
4. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or
desolder ESDs.
5. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some
solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static”
can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage
ESDs.
5. Check the insulation between the blades of the AC
plug and accessible conductive parts (examples:
metal panels, input terminals and earphone jacks).
6. Insulation Checking Procedure: Disconnect the
power cord from the AC source and turn the power
switch ON. Connect an insulation resistance meter
(500 V) to the blades of the AC plug.
The insulation resistance between each blade of the
AC plug and accessible conductive parts (see
above) should be greater than 1 megohm.
7. Never defeat any of the +B voltage interlocks. Do
not apply AC power to the unit (or any of its
assemblies) unless all solid-state heat sinks are
correctly installed.
8. Always connect a test instrument’s ground lead to
the instrument chassis ground before connecting the
positive lead; always remove the instrument’s
ground lead last.
6. Do not remove a replacement ESD from its
protective package until you are ready to install it.
Most replacement ESDs are packaged with leads
that are electrically shorted together by conductive
foam, aluminum foil or other conductive materials.
7. Immediately before removing the protective
material from the leads of a replacement ESD,
touch the protective material to the chassis or
circuit assembly into which the device will be
installed.
Caution: Be sure no power is applied to the
chassis or circuit and observe all
other safety precautions.
8. Minimize body motions when handling
unpackaged replacement ESDs. Motions such as
brushing clothes together, or lifting your foot from
a carpeted floor can generate enough static
electricity to damage an ESD.
9. Indicates ESDs on the Schematic Diagram in
this manual.
1 Precautions
1-2 TT17J*
1-3 Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESD) Precautions
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be easily damaged by static electricity. Such components are commonly
called Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESD). Examples of typical ESD devices are integrated circuits and some fieldeffect transistors. The following techniques will reduce the incidence of component damage caused by static electricity.
1-2 Servicing Precautions
WARNING1: First read the “Safety Precautions” section of this manual. If unforeseen circumstances
create conflict between the servicing precautions and safety precautions, always
follow the safety precautions.
WARNING2: A high voltage VR replaced in the wrong direction may cause excessive X-ray
emissions.
WARNING3: An electrolytic capacitor installed with the wrong polarity might explode.
TT17J* 2-1
2 Product Specifications
2-1 Specifications
Picture Tube: 17-Inch (43 cm): 16-inch (40.6 cm) viewable,
Flat-face, 90˚ Deflection, 0.20 mm (Horizontal) / 0.25 mm (Diagonal) Dot pitch,
Silica coated with anti-electrostatic properties (TCO: Multilayer coating),
Medium-short persistence phosphor
Scanning Frequency Horizontal : 30 kHz to 85 kHz
Vertical : 50 Hz to 160 Hz
Display Colors Unlimited colors
Maximum Resolution Horizontal : 1600 Dots, Vertical : 1200 Lines
Input Video Signal Analog, 0.7 Vp-p positive at 75 Ω, internally terminated
Input Sync Signal Separate Sync : TTL level, positive/negative
Maximum Pixel Clock rate 135 MHz
Video Signal 1.0 Vpp, 75Ω, NTSC/PAL/SECAM
Audio Signal 500 mVrms over than 47
kΩ
Active Display Horizontal : 312 mm ± 4 mm, Vertical : 234 mm ± 4 mm
Input Voltage AC 90 to 264 Volts, 60 Hz / 50 Hz ± 3 Hz
Power Consumption 100 Watt (max)
Dimensions (W x D x H)
Unit (Without Speakers) 16.53 x 16.81 x 15.03 Inches (420 x 427 x 382 mm)
(With Speakers) 20.19 x 16.81 x 15.03 Inches (513 x 427 x 382 mm)
Carton 20.19 x 22.51 x 21.02 Inches (513 x 572 x 534 mm)
Weight (Net/Gross)
(Without Speakers) 37.4 lbs (17.0 kg) / 44.1 lbs (20.0 kg)
(With Speakers) 39.7 lbs (18.0 kg) / 46.3 lbs (21.0 kg)
Environmental Considerations Operating Temperature : 32°F to 104°F (0°C to 40°C)
Humidity : 10 % to 80 %
Storage Temperature : -4°F to 113°F (-20°C to 45°C)
Humidity : 5 % to 95 %
• Above models comply with SWEDAC (MPR II) recommendations for reduced electromagnetic fields.
• Designs and specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
Item
Description
2 Product Specifications
2-2 TT17J*
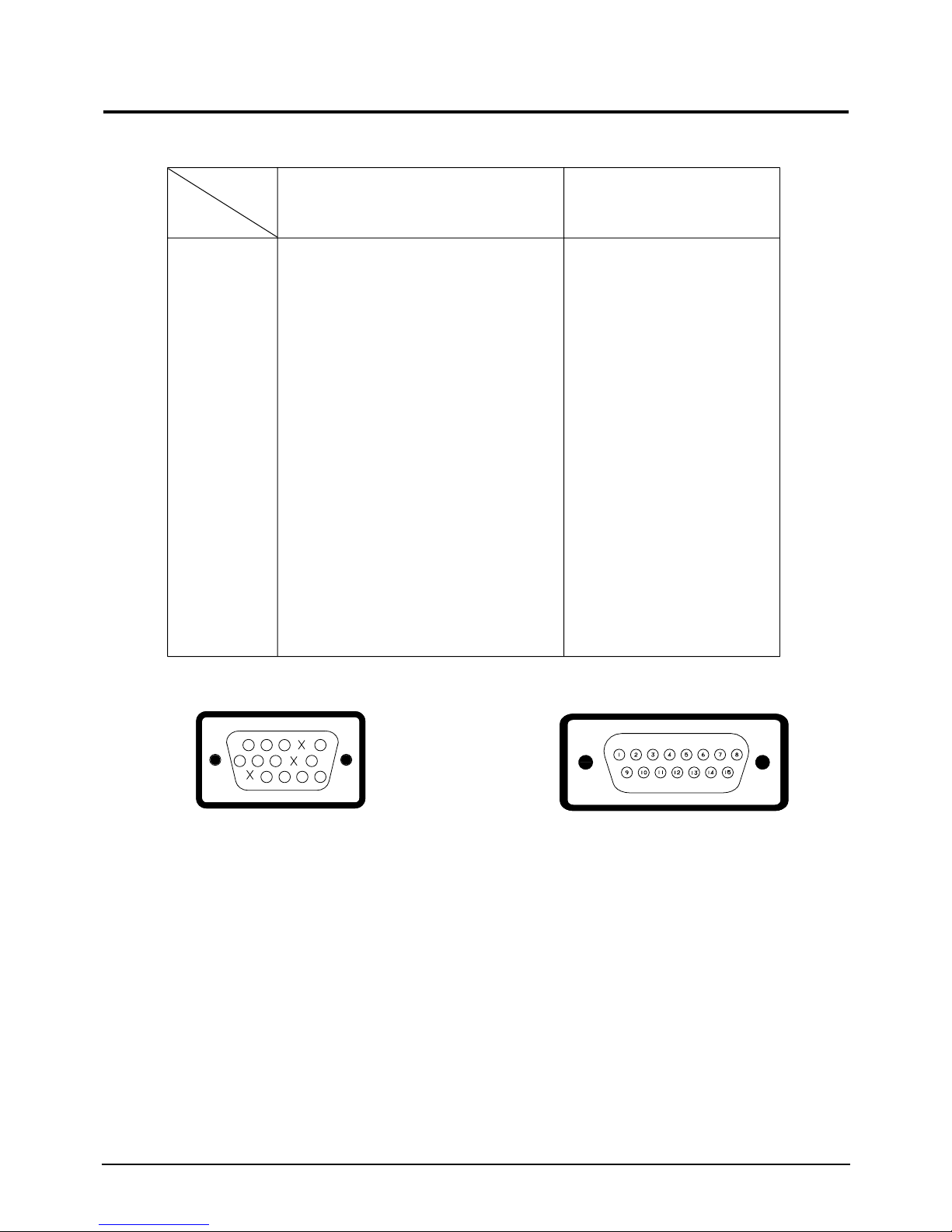
2-2 Pin Assignments
5
10
15
3
2
8
12 13 14
716
Figure 2-1. Male Type Figure 2-2. Male Type
Sync
Type
Pin No.
Macintosh
Separate
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Red
Green
Blue
N-C
DDC Return
GND-R
GND-G
GND-B
N-C
GND-Sync. /Self-raster
N-C
DDC Data
H-Sync.
V-Sync.
DDC Clock
GND-R
Red
H/V Sync.
Sense 0
Green
GND-G
Sense 1
Reserved
Blue
Sense 2
GND
V-Sync.
GND-B
GND
H-Sync.
2 Product Specifications
TT17J* 2-3
QRS
P
O
Video
Sync
Sync
Horizontal
Vertical
CDE
P
O
B
A
Video
Sync
Sync
Separate Sync
2-3 Timing Chart
This section of the service manual describes the timing that the computer industry recognizes as standard
for computer-generated video signals.
C D
A
O
E
B
P
Video
Sync
Sync
Video
Q R S
A : Line time total B : Horizontal sync width O : Frame time total P : Vertical sync width
C : Back porch D : Active time Q : Back porch R : Active time
E : Front porch S : Front porch
fH (kHz)
A µsec
B µsec
C µsec
D µsec
E µsec
fV (Hz)
O msec
P msec
Q msec
R msec
S msec
Clock
Frequency
(MHz)
Polarity
H.Sync
V.Sync
Remark
IBM
VESA
800/85 Hz
800 x 600
1024/75 Hz
1024 x 768
1024/85 Hz
1024 x 768
VGA3/60 Hz
640 x 480
VGA2/70 Hz
720 x 400
31.469
31.777
3.813
1.907
25.422
0.636
70.087
14.268
0.064
1.080
12.711
0.413
28.322
Negative
Positive
Separate
31.469
31.778
3.813
1.907
25.422
0.636
59.940
16.683
0.064
1.048
15.253
0.318
25.175
Negative
Negative
Separate
37.500
26.667
2.032
3.810
20.317
0.508
75.000
13.333
0.080
0.427
12.800
0.027
31.500
Negative
Negative
Separate
43.269
23.111
1.556
2.222
17.778
1.556
85.008
11.764
0.671
0.578
11.093
0.023
36.000
Negative
Negative
Separate
46.875
21.333
1.616
3.232
16.162
0.323
75.000
13.333
0.064
0.448
12.800
0.021
49.500
Positive
Positive
Separate
53.674
18.631
1.138
2.702
14.222
0.569
85.061
11.756
0.056
0.503
11.179
0.019
56.250
Positive
Positive
Separate
60.023
16.660
1.219
2.235
13.003
0.203
75.029
13.328
0.050
0.466
12.795
0.017
78.750
Positive
Positive
Separate
68.677
14.561
1.016
2.201
10.836
0.508
84.997
11.765
0.044
0.524
11.183
0.015
94.500
Positive
Positive
Separate
800/75 Hz
800 x 600
640/75 Hz
640 x 480
640/85 Hz
640 x 480
Table 2-1. Timing Chart
Mode
Timing
1280/75 Hz
1280 x 1024
79.976
12.504
1.067
1.837
9.481
0.119
75.025
13.329
0.038
0.475
12.804
0.013
135.000
Positive
Positive
Separate

2 Product Specifications
2-4 TT17J*
Memo

3-1-1 Cabinet Disassembly
1. With a pad beneath it, stand the monitor on its
front with the screen facing downward and
the base closest to you. Make sure nothing will
damage the screen.
2. Remove the Stand from the monitor.
(Refer to Stand manual)
3. Incline the monitor by lifting the rear of the
monitor.
4. Push the Opening jig each groove along the
top of the monitor till it makes a “ttak” sound.
(2 grooves : Left and Right, Make sure each
snap is disengaged.)
5. Squeeze the hold-snap on bottom of the
monitor using your hand.
6. Insert the Opening jig into the groove then
release the hold-snap.
7. When the hold-snap release, lift the Rear
Cover slightly to make sure it doesn’t reengage while you release the snap on the
other side.
8. In a similar manner, Release the hold-snap on
the opposite side.
9. Pull the Rear Cover up off the monitor.
10. Using pinch-nose pliers or ling-nose pliers,
acrefully disconnect the Anode Cap from the
CRT.
Warning: Do not touch the Anode contact
on the CRT (High Voltage may
remain).
Note : If the hold-snap on the bottom of the
Front Cover is broken, secure the
cabinet by applying a 4x16 screw in
the extra holes on each side of the
cabinet.
3-1-2 Removing the CRT Socket PCB
1. Complete all previous steps.
2. Lift up the Video Spring and remove the CRT
Socket PCB from the CRT.
TT17J* 3-1
3 Disassembly and Reassembly
This section of the service manual describes the disassembly and reassembly procedures for the
TT17J* monitor.
WARNING: This monitor contains electrostatically sensitive devices. Use with caution when
handling these components.
3-1 Disassembly
Cautions:1. Disconnect the monitor from the power source before disassembly.
2. To remove the Rear Cover, you must use the special opening jig tool.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3

3. Disconnect all connectors on the CRT Socket
PCB.
4. Using a solder iron, disconnect Ground (G2)
on the back of the Video Shield and remove
the Shield Cap.
5. Remove the screw on the front of the Shield
Socket.
6. Desolder the 4 tabs on the CRT Socket PCB
and remove Shield.
7. Place the Video PCB on a flat, level surface
that is protected from static electricity.
3-1-3 Removing the Main PCB
1. Complete all previous steps.
2. Disconnect the Degaussing Coil at GT601 and
GT602 on the Main PCB.
3. Disconnect all easily accessible ground wires
on the Main PCB and Bottom Chassis.
4. Disconnect the DY connector at the CN303
connector on the Main .
5. Remove 2 screws the Main PCB then lift up
the Bottom to separate the two Shield.
6. Remove the screws on the back and along
each side of the Bottom Chassis.
7. Carefully lift the Main PCB Ass’y and remove
the remaining ground wires.
8. Place the Main PCB Ass’y on a flat, level
surface that is protected from static electricity.
3-1-4 CRT Ass’y Disassembly
1. Complete all previous steps.
2. Straighten the Degaussing Coil Assembly
coated metal ties and lift the Coil Ass’y from
the CRT.
3. Remove the four corner screws and lift the
CRT up and away from the Front Cover
Assembly and place it on a padded surface.
Caution: Do not lift the CRT by the neck.
If you will be returning this CRT to
the monitor, be sure to place the CRT
face downward on a protective pad.
3 Disassembly and Reassembly
3-2 TT17J*
Figure 4
3-2 Reassembly
Reassembly procedures are in the reverse order of Disassembly procedures.

4-1-1 Before Making Adjustments
4-1-1 (a) ORIENTATION
When servicing, always face the monitor to the
east.
4-1-1 (b) MAGNETIC FIELDS
Whenever possible, use magnetic field isolation
equipment such as a Helmholtz field to surround
the monitor. If a Helmholtz field is not available,
frequently degauss the unit under test.
Caution: Other electrical equipment may cause
external magnetic fields which may
interfere with monitor performance.
Use an external degaussing coil to limit magnetic
build up on the monitor. If an external degaussing
coil is not available, use the internal degaussing
circuit. However, do not use the internal
degaussing circuit more than once per 30 minutes.
4-1-1 (c) WARM-UP TIME
The monitor must be on for 30 minutes before
starting alignment. Warm-up time is especially
critical in color temperature and white balance
adjustments.
4-1-1 (d) SIGNAL
Analog, 0.7 Vp-p positive at 75 ohm, internal
termination
Sync: Separate
(TTL level negative/positive)
4-1-1 (e) SCANNING FREQUENCY
Horizontal : 30 kHz to 85 kHz (Automatic)
Vertical : 50 Hz to 160 Hz (Automatic)
Unless otherwise specified, adjust at the
1024 x 768 mode (68 kHz/85 Hz),
Refer to Table 2-1 on page 2-3.
4-1-2 Required Equipment
The following equipment may be necessary for
adjustment procedures:
4-1-2 (a) DISPLAY CONTROL ADJUSTMENT
1. Non-metallic (–) screwdriver:
1.5, 2.5, 3 mm
2. Non-metallic (+) screwdriver:
1.5, 2.5, 3 mm
3. Digital Multimeter (DMM), or
Digital Voltmeter
4. Signal generator, or
DM200 software
5. Software: Softjig or DM200
6. Interface Board Ver. 2.0 Code No.
BH81-90001K
7. Parallel communications cable (25-pin to
25-pin); Code No. BH81-90001H
8. Signal cable (15-pin to 15-pin cable with
additional 3-pin connector); Code No.
BH81-90001J
9. 5 V DC adapter, not supplied
10. Personal computer
Note: Softjig Ass’y (includes items 6, 7 and 9)
Code No. BH81-90001L
4-1-2 (b) COLOR ADJUSTMENTS
1. All equipment listed in 4-1-2 (a), above
2. Color analyzer, or any luminance
measurement equipment
TT17J* 4-1
4 Alignment and Adjustments
This section of the service manual explains how to make permanent adjustments to the monitor. Directions
are given for adjustments using the monitor Interface Board Ver. 2.0 and software (Softjig).
4-1 Adjustment Conditions
Caution: Changes made without the Softjig are saved only to the user mode settings. As such, the
settings are not permanently stored and may be inadvertently deleted by the user.
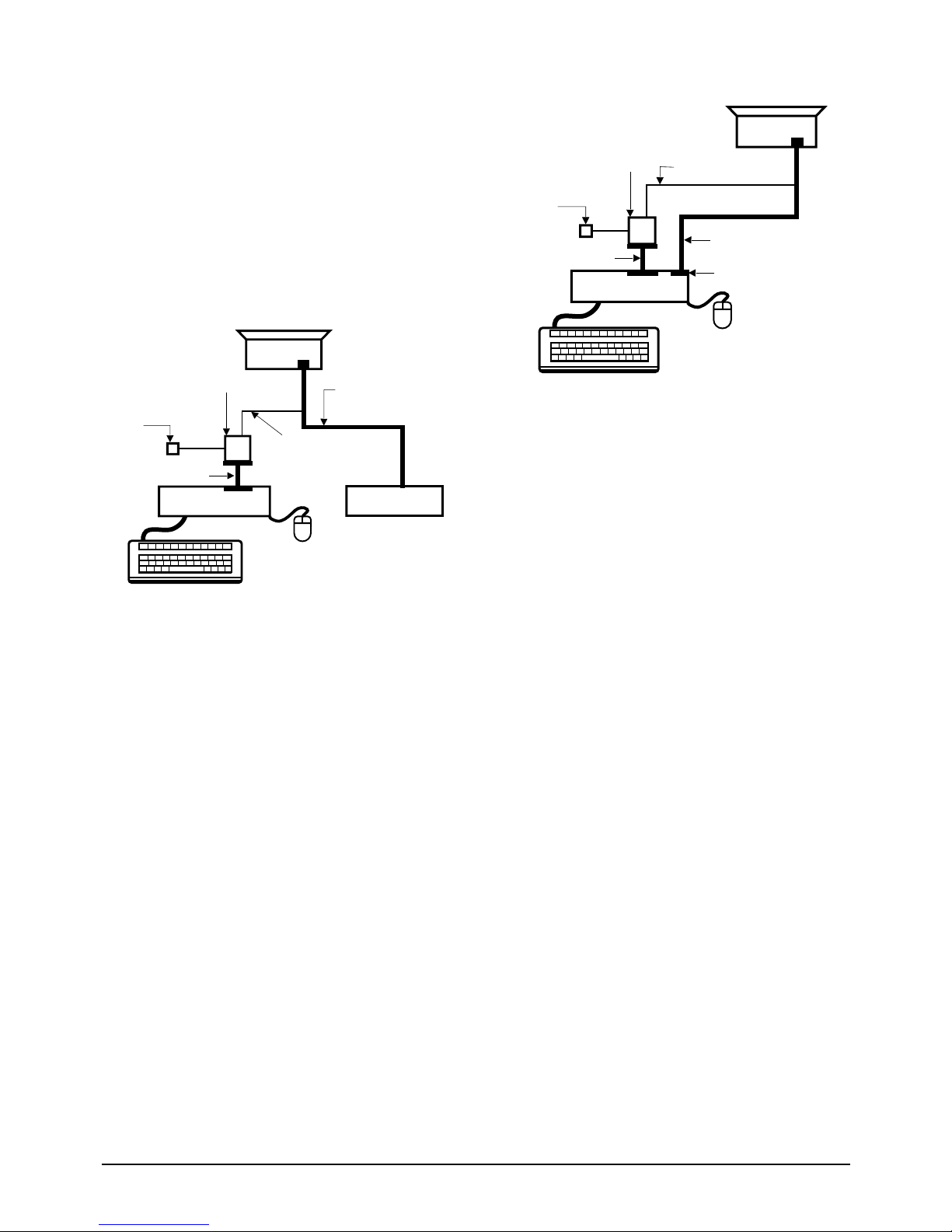
4-1-3 Connecting the SoftJig
Connect the monitor to the signal generator and/
or PC as illustrated in Figures 4-1 and 4-2.
Note: The signal cable connector which includes
the 3-wire cable must connect to the
monitor. If you use Setup 2 (PC only, no
signal generator) you can only make
adjustments to the signal timing available
on that computer system. To make
corrections to all factory timings requires
the use of an additional signal generator.
4 Alignment and Adjustments
4-2 TT17J*
MONITOR
INTERFACE
BOARD VER. 2.0
PC
SIGNAL
GENERATOR
3-WIRE
CABLE
SIGNAL CABLE
5V DC
ADAPTOR
PARALLEL CABLE
Figure 4-1. Setup 1, With Signal Generator
MONITOR
INTERFACE
BOARD VER. 2.0
PC
3-WIRE CABLE
SIGNAL CABLE
PARALLEL CABLE
D-SUB
CONNECTOR
5V DC
ADAPTOR
Figure 4-2. Setup 2, Without Signal Generator
Signal: 1024 x 768 (68 kHz/85 Hz)
Display image: Don’t care
Contrast: Minimum
Brightness: Minimum
Limit: 26.0 kV ± 0.3 kV
Measure the hight voltage level at the anode cap.
High voltage should be within the limit as above.
If the high voltage needs adjustment use the
following procedure.
PROCEDURE
1. Turn the power off and disconnect the AC line
cord from the power source.
2. Turn the power on after connecting high
voltage Probe.
3. Using the jig, adjust the high voltage to the
specification.
* High Voltage Adjustment PROCEDURE using Softjig
① Select matching model name in “Model” field.
➁ Select “ @7: Zero Beam” in menu after
selecting “Extra 1”
➂ Adjust high voltage using control bar after
selecting “HV MIN”
➃ Turn the power off/on after adjustment
finished.
➄ Check the high voltage has been fixed with
adjusted value after reselecting “@7: Zero Beam”.
4-2-2 SCREEN VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Signal: 1024 x 768 (68 kHz/85 Hz)
Display image: Don’t care
Contrast: Minimum
Brightness: Minimum
Limit: 520 V ± 10 V
Screen Voltage adjustment procedure using softjig
is all the same as 4-2-1 but selecting “G2 CONT”
on the contrary to “HV MIN”.
4-2-3 CENTER RASTER
Adjust SW401 so that the back raster comes to the
center when you apply basic mode for 17”.
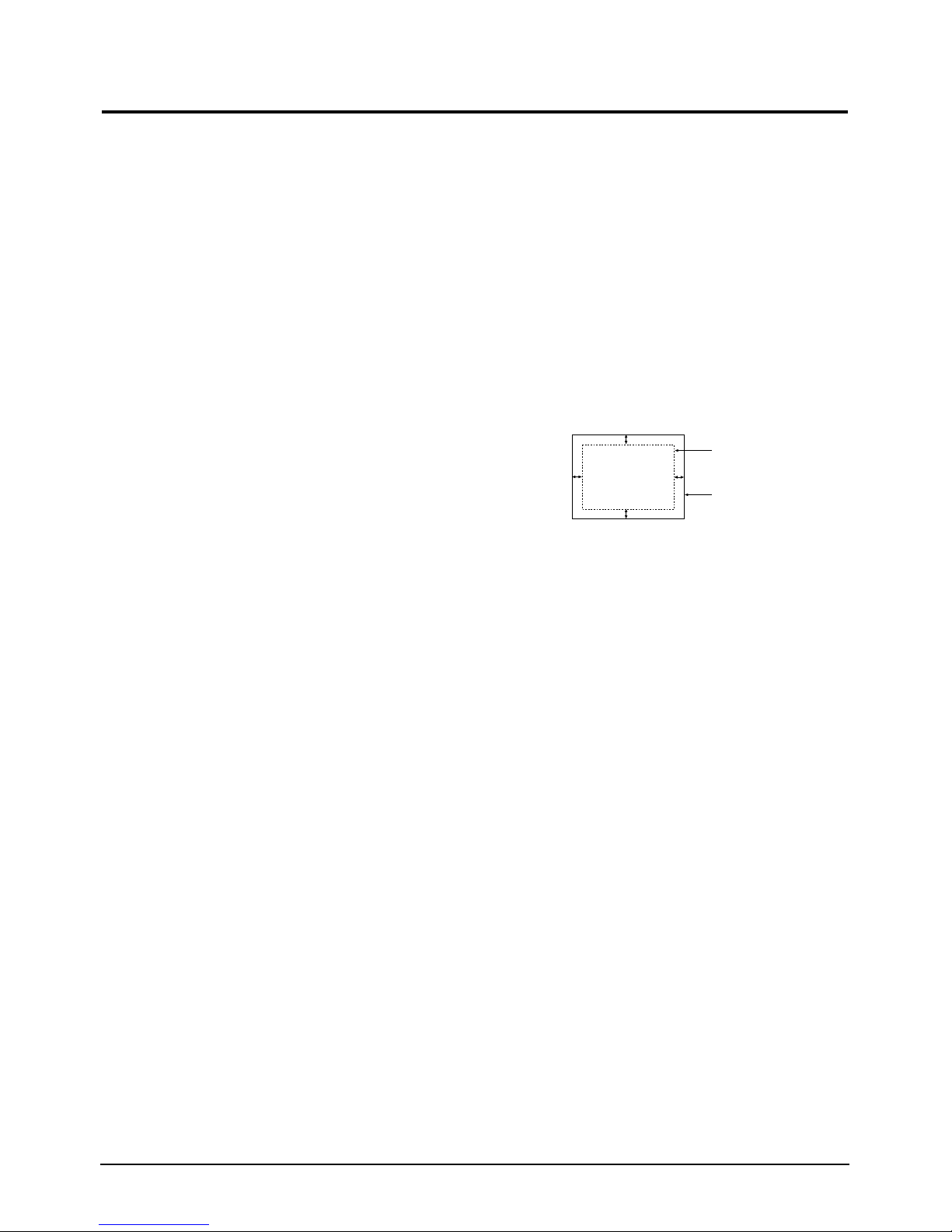
4-2-4 Centering
Centering means to position the center point of
the display in the middle of the display area.
Horizontal size and position and vertical size and
position control the centering of the display.
Adjust the horizontal size and vertical size to their
optimal settings: 312 mm (H) x 234 mm (V).
Adjust the horizontal position and vertical
position to ≤ 5.0 mm of the center point of the
screen.
|A-B| ≤ 5.0 mm. |C-D| ≤ 5.0 mm.
Figure 4-3. Centering
* In Softjig window, “Geometry” has to be
selected for GD adjustment.
4-2-4 (a) HORIZONTAL SIZE ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
Use control bar after selecting “H-SIZE” in left
menu to adjust the horizontal size of the display
pattern to 312 mm.(Tolerance: ± 3 mm.)
If “H-SIZE” is not enough to adjust it, select
“SIZE B+” by turns.
4-2-4 (b) VERTICAL SIZE ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
Use control bar after selecting “V-SIZE” in left
menu to adjust the vertical size of the display
pattern to 234 mm.(Tolerance: ± 3 mm.)
4 Alignment and Adjustments
TT17J* 4-3
4-2 Display Control Adjustments
4-2-1 HIGH VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT
C
A
DISPLAY AREA
EDGE OF BEZEL
B
D
4-2-4 (c) HORIZONTAL POSITION ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Use control bar after selecting “H-POSITION” in
left menu to center the horizontal image on the
raster.
4-2-4 (d) VERTICAL POSITION ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Use control bar after selecting “V-POSITION” in
left menu to center the vertical image on the
raster.
4-2-5 Linearity
Linearity affects the symmetry of images as they
appear on the screen. Unless each row or column
of blocks in a crosshatch pattern is of equal size,
or within the tolerances shown in Table 4-1 , an
image appears distorted, elongated or squashed.
Horizontal Linearity = 2x x100
Vertical Linearity = 2x x100
Table 4-1
❈ Preset Mode : 68KHz / 85Hz
Pre-load Mode : Refer to Timing Chart
4-2-5 (a) HORIZONTAL LINEARITY ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
To adjust the Horizontal Linearity, refer to Table
4-1 for the tolerance range.
Increase or decrease H_LIN to optimize the
image.
4-2-5 (b) VERTICAL LINEARITY ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
To adjust the Vertical Linearity, refer to Table 4-1
for the tolerance range.
Use control bar after selecting “V-LINEARITY
BAL” in left menu to optimize the image.
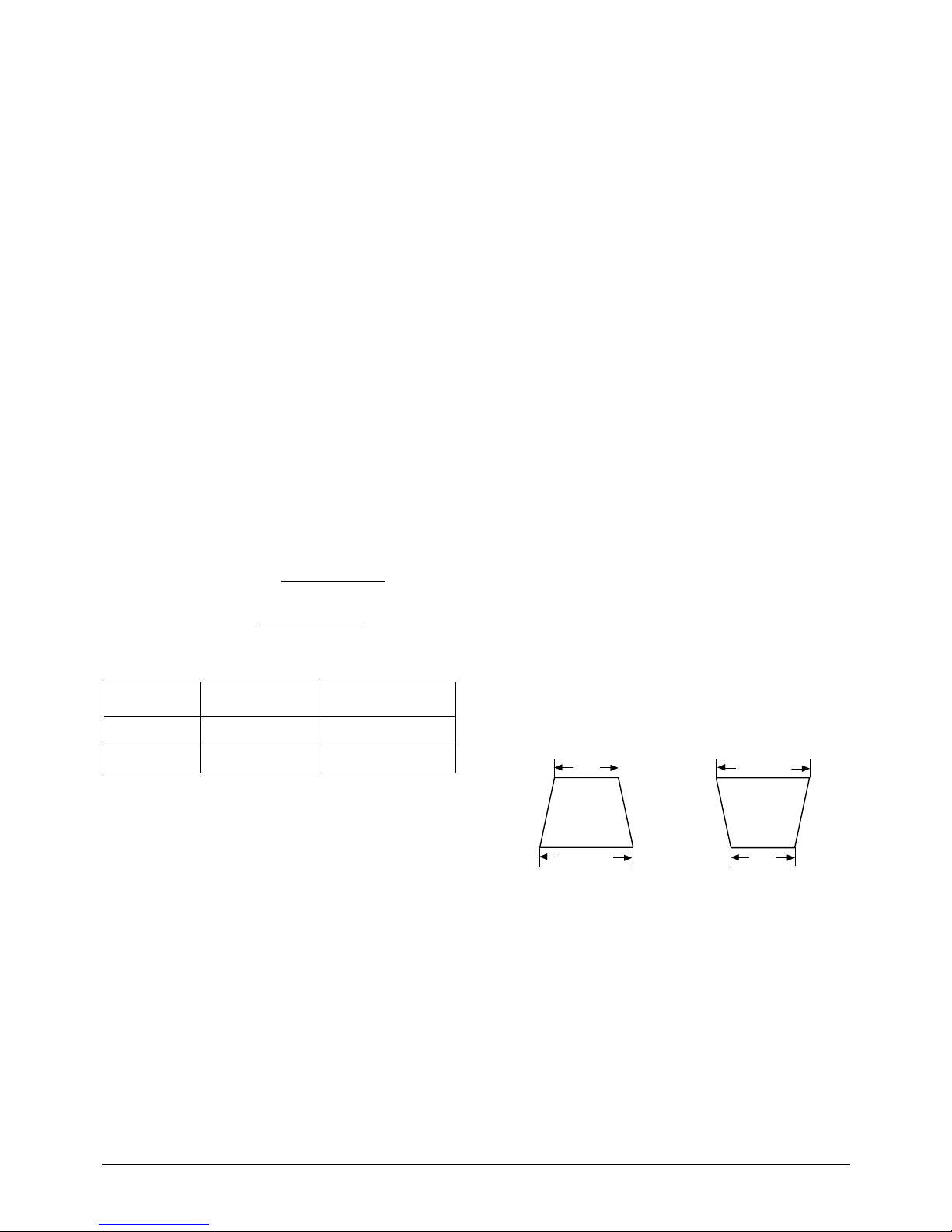
4-2-6 Trapezoid Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
Use control bar after selecting “TRAPEZOID” in
left menu to make the image area rectangular.
Figure 4-4. Trapezoid
4 Alignment and Adjustments
4-4 TT17J*
| A - B | < 4 mm
A
B
B
A
X max-X min
X max+X min
Y max-Y min
Y max+Y min
Preset mode ≤ 4% ≤ 10%
Adjacent Linearity
Entire Linearity
Pre-load mode ≤ 5% ≤ 14%
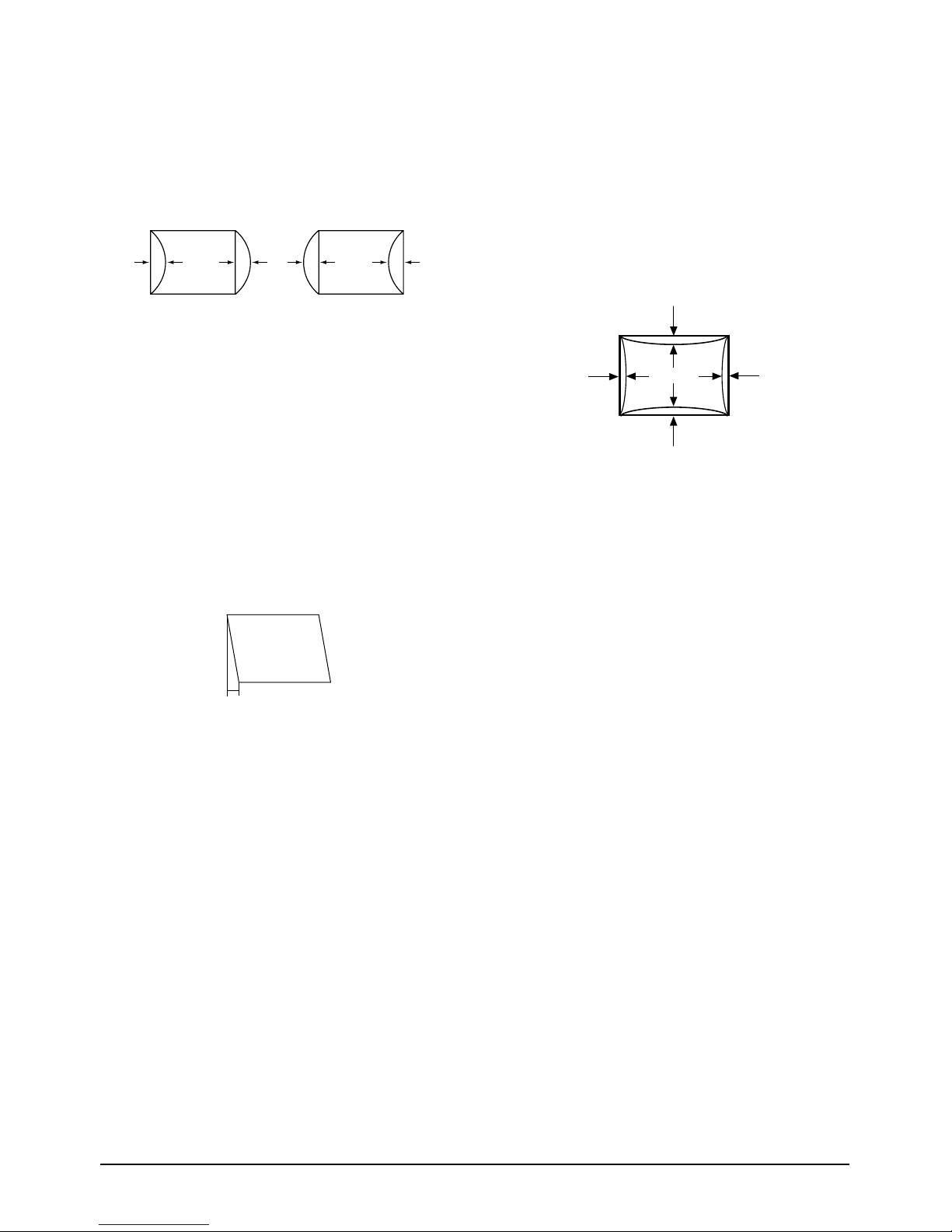
4-2-7 Pinbalance Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
Figure 4-5. Pinbalance
Use control bar after selecting “PINBALANCE” in
left menu to optimize the image.
4-2-8 Parallelogram Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning Frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
Use control bar after selecting “PARALLEL” in
left menu to make the image area rectangular.
Figure 4-6. Parallelogram
4-2-9 Side Pincushion Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Use control bar after selecting “PINCUSHION” in
left menu to straighten the sides of the image area.
4-2-10 Tilt Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning Frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
Use control bar after selecting “ROTATION” in
left menu to correct the tilt of the display.
4-2-11 Degauss
No adjustments are available for the degaussing
circuit. The degaussing circuit can effectively
function only once per 30 minutes.
4-2-12 To Delete the User Mode Data
To delete the adjustment data from the user
modes, click “@4: USER DELETE” in right ment.
4-2-13 Save the Data
To save the adjustment data for a mode, press
“@3: ALL MODE SAVE” in right ment.
4 Alignment and Adjustments
TT17J* 4-5
4 mm
D1 D2 D1
| C1 |, | C2 | ≤ 2.0 mm, | D1 |, | D2 | ≤ 2.0 mm.
Figure 4-7. Pincushion
C2
C1
D1 D2
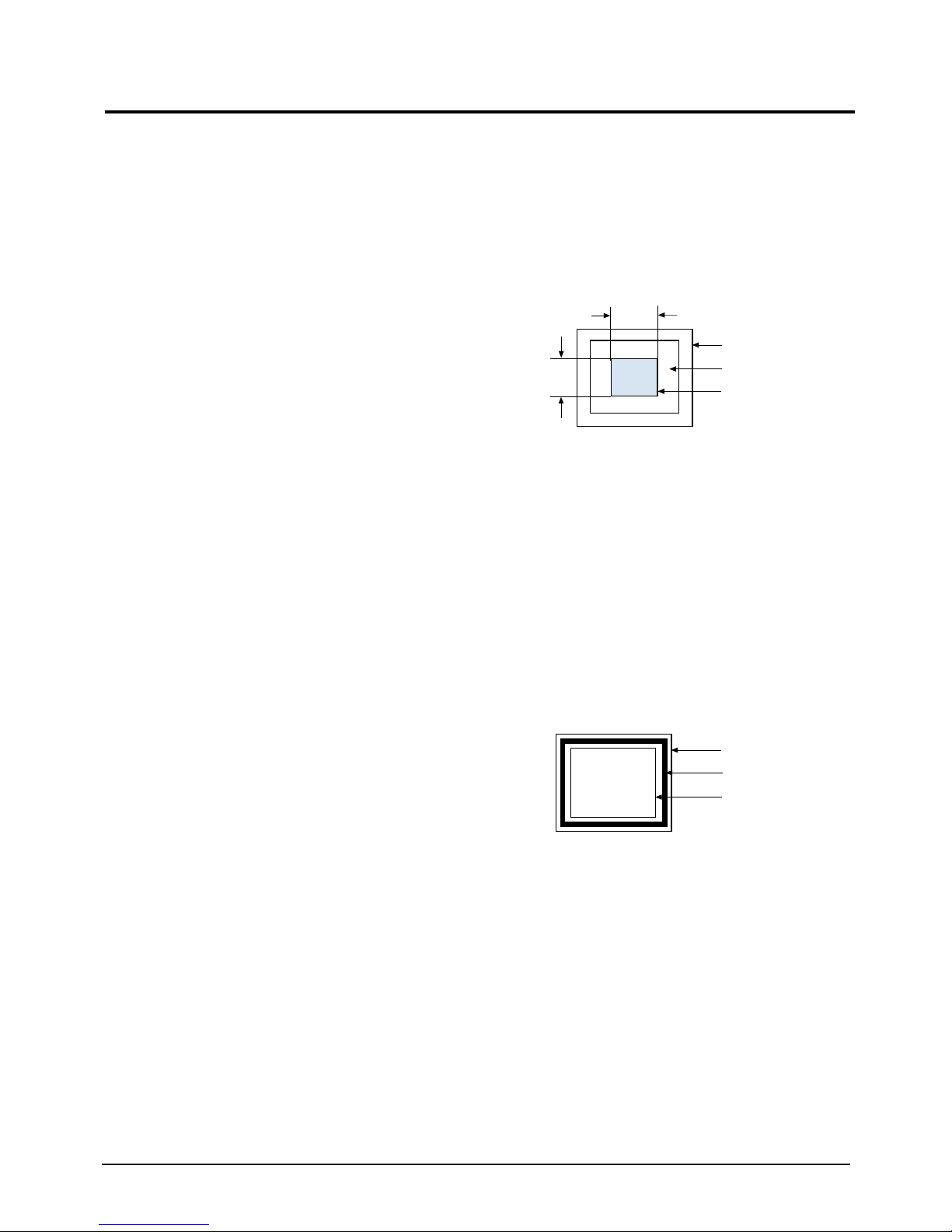
CAUTION:Check below condition before color
adjustment
Video signal : Analog 0.7 Vp-p (at 75 Ω)
Sync : TTL level (H, V seperate signal)
* Select “Color” in Softjig menu for color adjustment.
4-3-1 Color Coordinates (Temperature)
Color temperature is a measurement of the
radiant energy transmitted by a color. For
computer monitors, the color temperature refers
to the radiant energy transmitted by white. Color
coordinates are the X and Y coordinates on the
chromaticity diagram of wavelengths for the
visible spectrum.
CONDITIONS
Measurement instrument: Color analyzer
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: White flat field at
center of display area
Luminance: Maximum
PROCEDURE
Use the directions in sections 4-3-2 through 4-3-3
to adjust the color coordinates for:
9300K to x = 0.283 ± 0.02, y = 0.298 ± 0.02
6500K to x = 0.313 ± 0.03, y = 0.329 ± 0.03
Video Mode to x= 0.270 ± 0.03, y = 0.270 ± 0.03
4-3-2 Color Adjustments
4-3-2 (a) BACK RASTER COLOR ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Back raster pattern
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
1. Select “@1: CHANNEL 1” in right menu to
control the color for 9300K.
2. Adjust the luminance of the back raster to
between 0.5 to 0.7 ft-L using contron bar after
selecting “GREEN CUTOFF” in the menu.
3. Use control bar after selecting “BLUE
CUTOFF” in left menu to set the “y”
coordinate to 0.298 ± 0.02.
4. Use control bar after selecting “RED
CUTOFF” in left menu to 0.283 ± 0.02.
* If color values would not be matched desirable
values, repeat sequence 3 and 4 after readjusting
“GREEN CUTOFF” control a little different.
4-3-2 (b) WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: White box pattern
Brightness: 0.06ft-L at Back Raster
Pattern Display
Contrast: Maximum
Figure 4-8. White Box Pattern
1. Use control bar after selecting “RED GAIN”,
“GREEN GAIN” and “BLUE GAIN” to adjust
the luminance to 40 ft-L with the color
coordinates ranged for
9300K to x = 0.283 ± 0.02, y = 0.298 ± 0.02.
4-3-2 (c) ABL ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Full white pattern
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
Figure 4-9. Full White Pattern
1. Check the ABL. If it is not within the
specifications, use the ABL controls to adjust
it. (29 ± 1 ft-L )
2. Select “@4: COLOR SAVE” to save the data.
3. Select “@6: ALL COLOR SAVE” to save the
CH2.
4 Alignment and Adjustments
4-6 TT17J*
4-3 Color Adjustments
1/3H-1/2H
1/3V-1/2V
FRONT BEZEL OPENING
BACK RASTER
WHITE WINDOW
FRONT BEZEL OPENING
BACK RASTER
WHITE WINDOW

4 Alignment and Adjustments
TT17J* 4-7
4-3-2 (d) WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT VERIFICATION
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Back raster pattern
Full White Pattern
X-Y Coordinates: x = 0.283 ± 0.02,
y = 0.298 ± 0.02
ABL Luminance Refer to 4-3-2(c)
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: 5 ft-L, 24 ft-L
1. Check whether the color coordinates of the
back raster satisfy the above spec.
If they do not, return to 4-3-2 (a) and readjust
all settings.
2. Display a full white pattern.
3. Select “Geometry” in softjig menu.
4. Select “@7: 5-ft “ in right menu.
5. Check whether the white coordinates of the
video meet the above coordinates spec.
6. Select “@8: 24-ft “ in right menu.
7. Check whether the white coordinates of the
video satisfies the above spec.
If they do not, return to 4-3-2 (a) and readjust
all settings.
Select “Color” and click “@2: CHANNEL 2”
for color ajdustment for 6500K
Repeat the sequence of 9300K adjustment.
The luminance values the same as 9300K, but
the color coordinated of back raster and white
box are : x = 0.313 ± 0.03 y = 0.329 ± 0.03
Select “Color” and click “@3: CHANNEL 3”
for color ajdustment for Video Mode.
The color coordinated of back raster and white
box are : x=270 ± 0.03 y = 270± 0.03
1 Adjust the luminance is 0.5~0.7 ft-L cut-off.
2 Adjust the luminance is 43ft-L at white Box
pattern.
3 ABL control to adjust 31ft-L at Full white
pattern.
4-3-3 Luminance Uniformity Check
Luminance is considered uniform only if the ratio
of lowest to highest brightness areas on the screen
is not less than 7.5:10.
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
(1024 x 768)
Display image: White flat field
Brightness: Cut off point at 24 ft-L
Contrast: Maximum
PROCEDURE
Measure luminance at nine points on the display
screen (see figure below).
4-3-4 Focus Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
(1024 x 768)
Display image: “H” character pattern
Brightness: Cut off point
Contrast: Maximum
PROCEDURE
1. Adjust the Focus VR on the FBT to display the
sharpest image possible.
2. Use Locktite to seal the Focus VR in position.
Figure 4-10. Luminance Uniformity Check Locations

4 Alignment and Adjustments
4-8 TT17J*
4-3-5 Color Purity Adjustment
Color purity is the absence of undesired color.
Conspicuous mislanding (unexpected color in a
uniform field) within the display area shall not be
visible at a distance of 50 cm from the CRT
surface.
CONDITIONS
Orientation: Monitor facing east
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: White flat field
Luminance: Cut off point at the center
of the display area
Note: Color purity adjustments should only be
attempted by qualified personnel.
PROCEDURE
For trained and experienced service technicians
only.
Use the following procedure to correct minor
color purity problems:
1. Make sure the display is not affected by
external magnetic fields.
2. Make sure the spacing between the PCM
assembly and the CRT stem is 29 mm ± 1 mm.
3. Display a green pattern over the entire display
area.
4. Adjust the purity magnet rings on the PCM
assembly to display a pure green pattern.
(Optimum setting: x = 0.295 ± 0.015,
y = 0.594 ± 0.015)
5. Repeat steps 4 and 5 using a red pattern and
then again, using a blue pattern.
Table 4-4. Color Purity Tolerances
(For 9300K color adjustment: x = 0.283 ± 0.02, y = 0.298 ± 0.02)
6. When you have the PCMs properly adjusted,
carefully glue them together to prevent their
movement during shipping.
Red: x = 0.640 ± 0.015 y = 0.323 ± 0.015
Green: x = 0.295 ±0.015 y = 0.594 ± 0.015
Blue: x = 0.142 ± 0.015 y = 0.066 ±0.015
TT17J* 5-1
5 Troubleshooting
5-1 Parts Level Troubleshooting
Notes: 1. If a picture does not appear, fully rotate the brightness and contrast controls clockwise and reinspect.
2. Check the following circuits.
• No raster appears: Power circuit, Horizontal output circuit.
• High voltage develops but no raster appears: Video output circuits.
• High voltage does not develop: Horizontal output circuits.
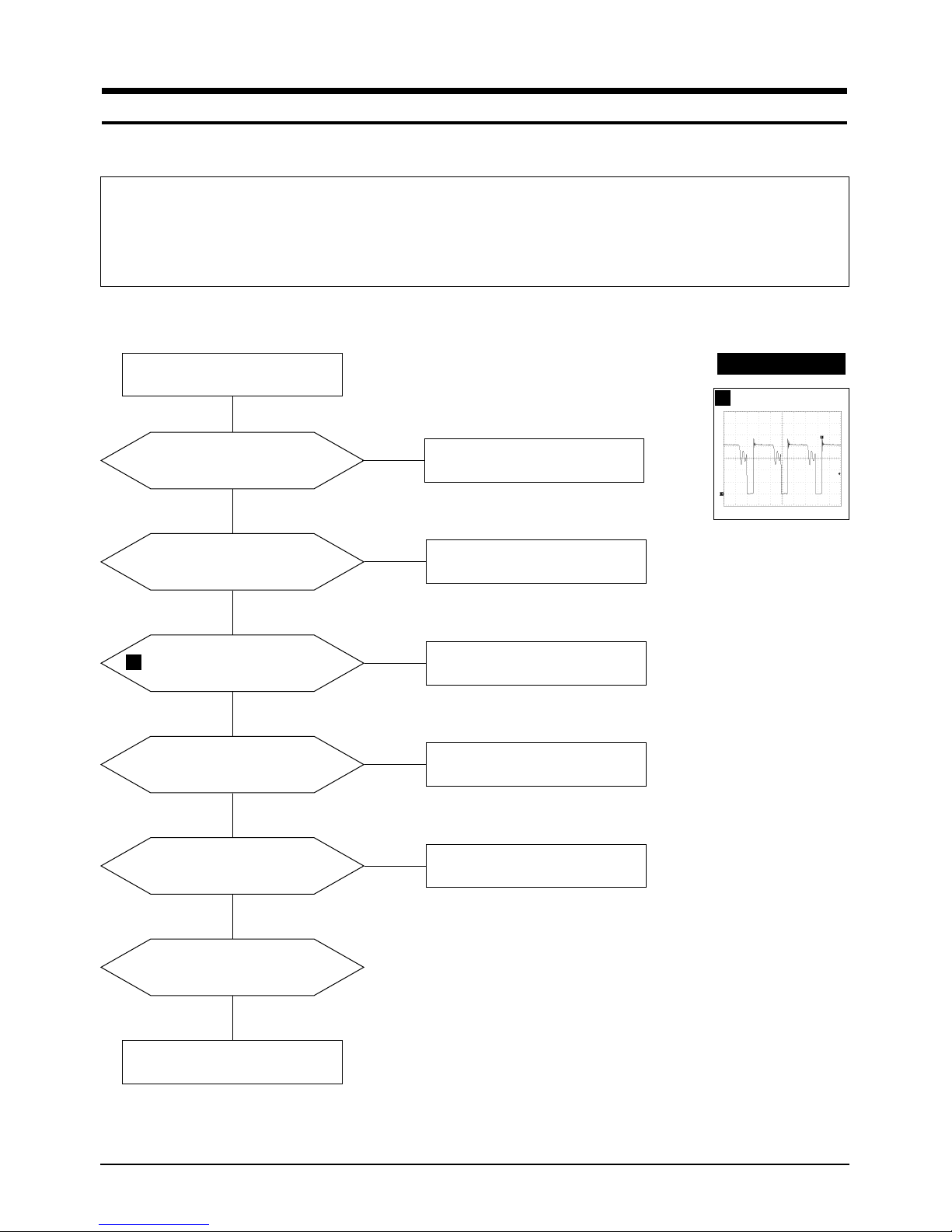
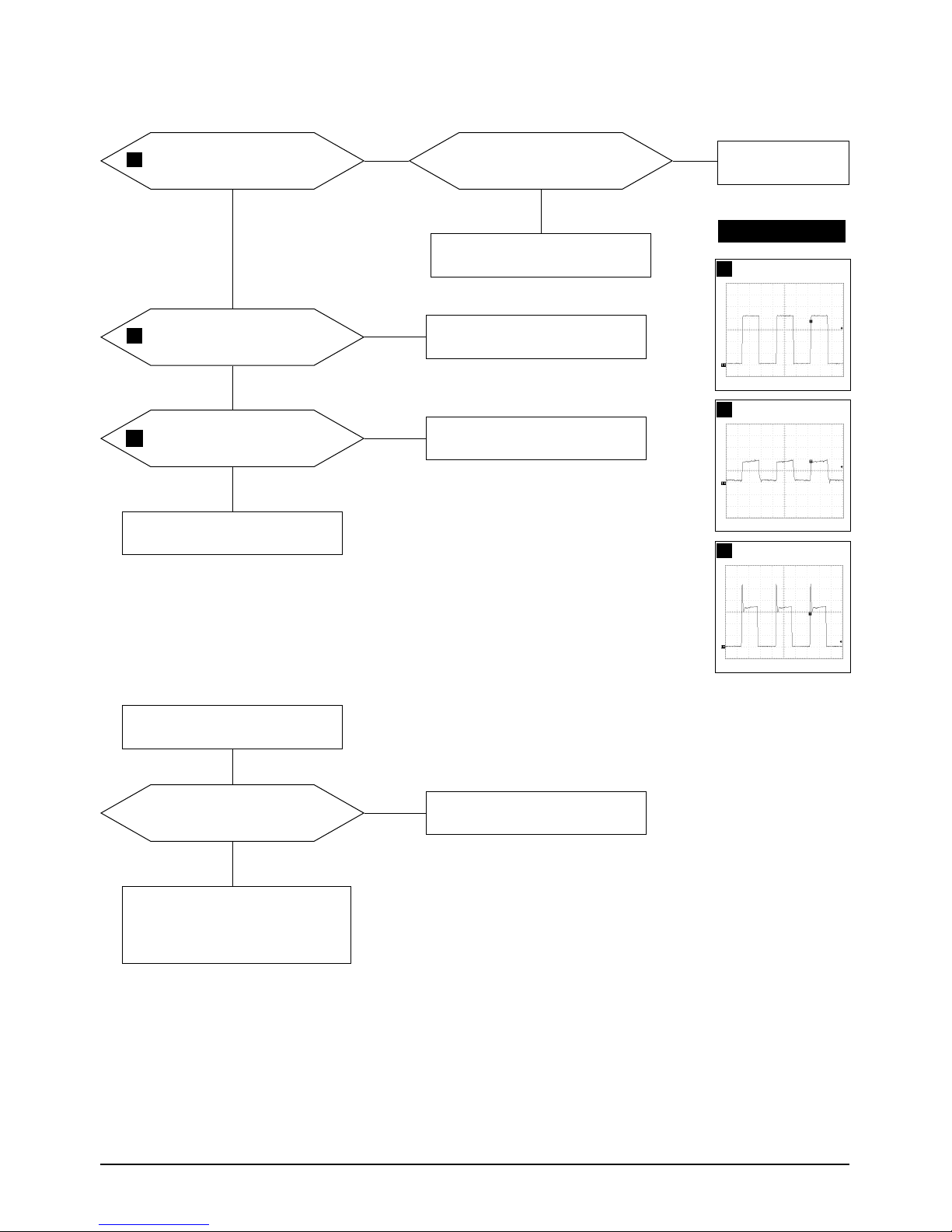
5-1-1 No Power Supply
Chirping noise exists?
Check and replace IC601.
Check and replace D601 and FH1
Done.
No
Yes
Repeating start?
Check and replace D606.
No
Yes
IC601 Pin 1 waveform is right?
Check and replace D614, IC601,
Q602, and ZD601.
Yes
No
C622 Voltage is 13 V ± 0.5V?
Check and replace IC201, IC301,
IC401, Q402, and Q404.
Yes
No
Operate normally?
Replace Main board.
Yes
Verify voltages.
Yes
No
WAVEFORMS
1
1
100 V (IC601, #1)
CH1 P-P = 100 V CH1 RMS = 350.2 V
5 Troubleshooting
5-2 TT17J*
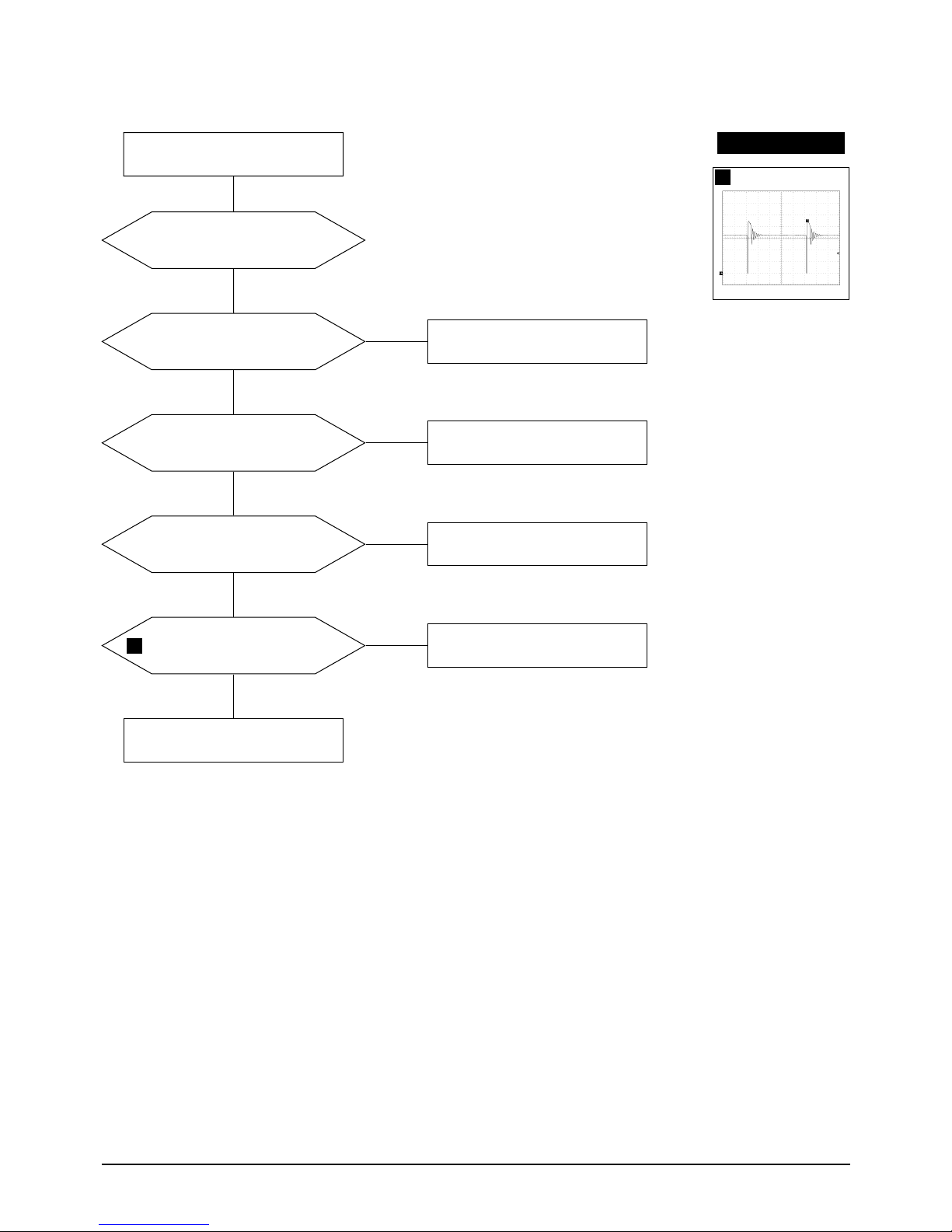
5-1-2 DPMS Failure
Make No H/V sync. (power off
mode)
Check signal source
H/V sync. video level.
LED blinks?
Check IC201 Pin 40.
Yes
No
+12 V line off?
Check IC201 Pin 6.
Yes
No
IC602 Pin 4
voltage exists?
Check IC201 Pin 6.
Check and replace IC602.
No
Yes
IC601 Pin 1 output
voltage exists?
Refer to 5-1-1 No Power Supply.
Done
Yes
No
WAVEFORMS
2
2
100V (IC601, #1)
CH1 P-P = 100V CH1 RMS = 325.8 V
5 Troubleshooting
TT17J* 5-3
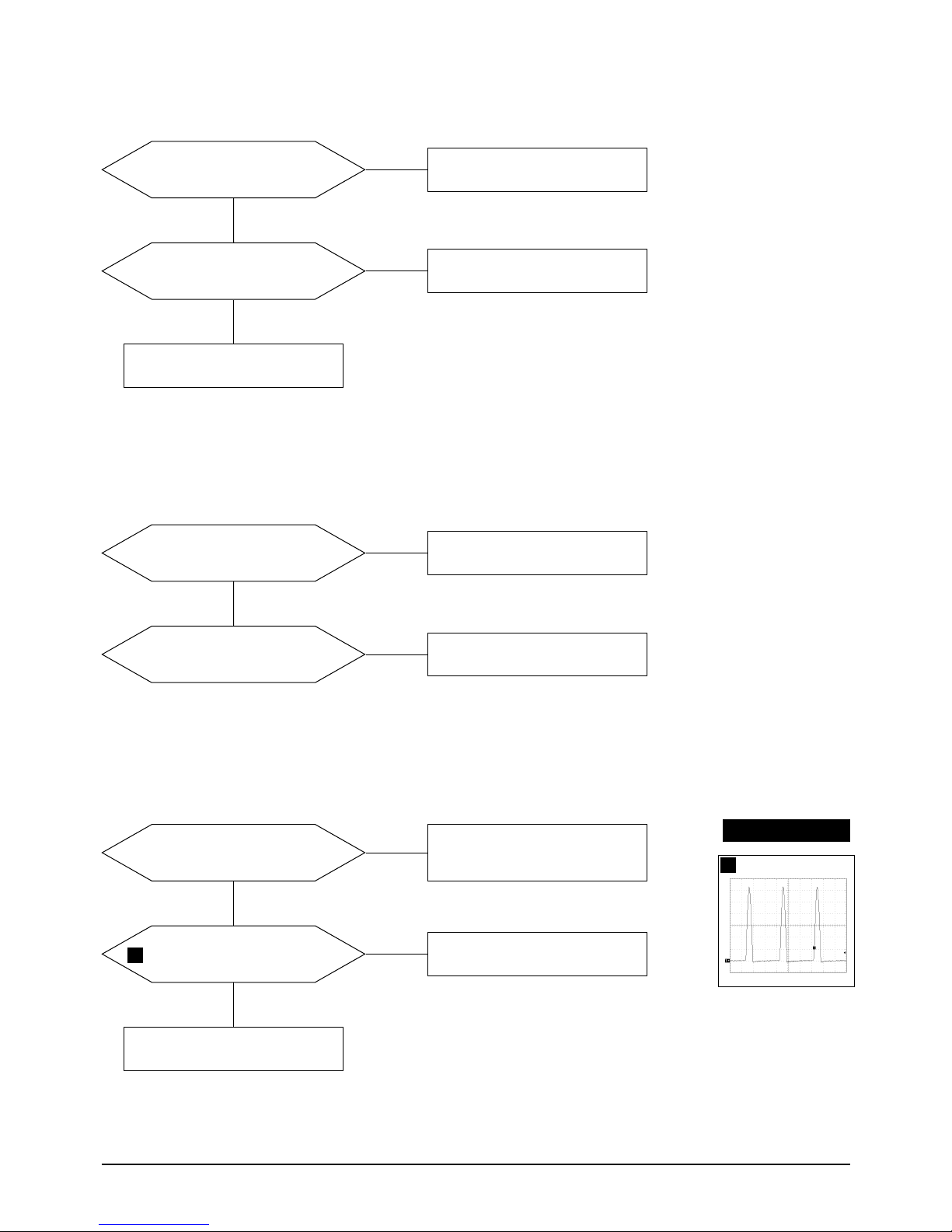
5-1-3 H_Deflection Failure
Does Horizontal paluse signal
appear at Pin 8 of IC401?
Check IC401.
Yes
No
Does 110 Vp-p signal appear
at Collector of Q403?
Check Q403.
No
No
Check Q402, Q404 and T401.
WAVEFORMS
4
3
2.00 V (IC401, #6)
CH1 P-P = 2.00V CH1 RMS = 5.868V
4
1.00V (IC401, #8)
CH1 P-P = 1.00V CH1 RMS = 1.298V
5
20.0 V (Q403, Collector)
CH1 P-P = 20.0 V CH1 RMS = 46.80V
Does PWM output signal appear
at Pin 6 (H_out) of IC401?
Check IC401.
Check 12 V line.
Yes
No
Does DC 12V appear at
Pin 10 of IC401?
Yes
No
3
5-1-4 S Correction Failure
S1~S4 signals are right at each
frequency block?
Check S1 ~ S4 signal.
Check and replace Q404, Q409, Q410,
Q411, Q414, Q415, Q416, Q420,
and Q421.
Yes
Check and replace IC201.
No
5
5 Troubleshooting
5-4 TT17J*
5-1-5 H_Lin. Failure
IC201 Pin 21 voltage varies with
different H_Lin. DAC values?
IC603 Pin 9 voltage varies with
different H_Lin. DAC values?
Check +13 V, –10 V line.
Check some parts around IC603.
Check Q412, Q413 and T402.
Yes
Yes
No
Replace IC201.
No
5-1-6 Invariable H_Size
IC401 Pin 6 voltage varies with
different B_Out DAC values?
Q402 Gate output duty varies with
different B_Out DAC values?
Check some parts around Q402,
IC401 Pin 3 ~ 6.
Yes
No
Check and replace IC401.
No
5-1-7 Abnormal H_Size
IC401 Pin 11 output duty
varies with different B+ offset
DAC values?
Q404 Collector waveform is
right?
Check and replace Q405,
Q406, Q407, and Q408.
Check some parts
around D409 and L401.
Yes
Yes
No
Check and replace IC201.
No
WAVEFORMS
6
6
200 V (Q404, Collector)
CH1 P-P = 200V CH1 RMS = 387.2V
 Loading...
Loading...