Samsung SPI-2210022502 User Manual

EPBD-001884
Ed. 05
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210
100RAS Outdoor Premium RAS
System Description

COPYRIGHT
This manual is proprietary to SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. and is protected by copyright.
No information contained herein may be copied, translated, transcribed or duplicated for any commercial
purposes or disclosed to the third party in any form without the prior written consent of SAMSUNG Electronics
Co., Ltd.
TRADEMARKS
Product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective
companies.
This manual should be read and used as a guideline for properly installing and operating the product.
This manual may be changed for the system improvement, standardization and other technical reasons without prior
notice.
If you need updated manuals or have any questions concerning the contents of the manuals, contact our Document
Center at the following address or Web site:
Address: Document Center 3rd Floor Jeong-bo-tong-sin-dong. Dong-Suwon P.O. Box 105, 416, Maetan-3dong
Yeongtong-gu, Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea 442-600
Homepage: http://www.samsungdocs.com
©2007~2009 SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.

INTRODUCTION
Purpose
This description describes the characteristics, functions and structures of the Outdoor
Premium RAS of Mobile WiMAX, also referred to as the outdoor SPI-2210. Throughout
this document the SPI-2210 designation will be used.
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description
Document Content and Organization
This description is composed of five Chapters, an Abbreviation and Index as follows:
CHAPTER 1. Overview of Mobile WiMAX System
Mobile WiMAX System Introduction
Characteristics of Mobile WiMAX System
Components of Mobile WiMAX Network
Functions of Mobile WiMAX System
CHAPTER 2. Overview of Outdoor SPI-2210
Outdoor SPI-2210 Introduction
Major functions
Resources
System Configuration
Interface between the Systems
CHAPTER 3. Outdoor SPI-2210 Architecture
System Configuration
Hardware Structure
Software Structure
Redundancy
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. I
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
CHAPTER 4. Message Flow
Call Processing Message Flow
Network Synchronization Message Flow
Alarm Message Flow
Loading Message Flow
Operation and Maintenance Message Flow
CHAPTER 5. Additional Functions and Tools
TTLNA
Web-EMT
ABBREVIATION
Describes the acronyms used in this description.
INDEX
Index provides main searching keywords to be found.
Conventions
The following types of paragraphs contain special information that must be carefully read
and thoroughly understood. Such information may or may not be enclosed in a rectangular
box, separating it from the main text, but is always preceded by an icon and/or a bold title.
NOTE
Indicates additional information as a reference.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. II
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
Revision History
EDITION DATE OF ISSUE REMARKS
00 10. 2007. First Draft
01 11. 2007. Cabinet configuration is changed.
02 01. 2008. - Delete the information related DHCP Server
- sFTP SFTP
- Modify the 'PSMR/PSFMR' information
- Modify the external interface (3.2.7)
- Modify the figure 3.1 and figure 4.15
- Modify the ‘4.1’
- Modify the beamforming explanation
03 06. 2008. - Abbreviations are changed.
- Rel. 5 information is added.
04 03. 2009. - The RADIUS protocol support for interfacing with the AAA
server is added. (1.3, 2.5.1, 4.1)
- ‘Disabling ZCS’ function is added. (2.2.5)
- Figure 3.5 is changed.
- The alarm port specification is changed from 10 Tx UDA to
6 Tx UDA. (3.2.5, 3.2.6)
- The path test-related content is modified. (3.3.3.13)
- The failure alarm types are modified. (4.3)
- The acronyms in The ABBREVIATION section are modified.
05 06. 2009. - Modify Figures 1.1, 1.2, 2.4, 4.1 to 4.4, 4.6 to 4.8, and 4.13
to 4.15
- Add Figures 4.9
- Modify Sections 1.3, 3.3.3.6, 4.1.1 to 4.1.4, and 4.1.6
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. III
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
This page is intentionally left blank.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. IV
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION I
Purpose.......................................................................................................................................I
Document Content and Organization .......................................................................................... I
Conventions................................................................................................................................ II
Revision History......................................................................................................................... III
CHAPTER 1. Overview of Mobile WiMAX System 1-1
1.1 Introduction to Mobile WiMAX.............................................................................................. 1-1
1.2 Characteristics of the Mobile WiMAX System..................................................................... 1-3
1.3 Mobile WiMAX Network Configuration................................................................................. 1-4
1.4 Mobile WiMAX System Functions........................................................................................ 1-6
CHAPTER 2. Overview of Outdoor SPI-2210 2-1
2.1 Introduction to Outdoor SPI-2210......................................................................................... 2-1
2.2 Main Functions ...................................................................................................................... 2-3
2.2.1 Physical Layer Processing Function........................................................................... 2-3
2.2.2 Call Processing Function............................................................................................2-5
2.2.3 IP Processing Functions.............................................................................................2-8
2.2.4 Auxiliary Device Interface Function............................................................................. 2-9
2.2.5 Maintenance Function .............................................................................................. 2-10
2.2.6 Function of Supporting the Outdoor Environment..................................................... 2-13
2.3 Specifications ...................................................................................................................... 2-14
2.4 System Configuration.......................................................................................................... 2-17
2.5 Interface between Systems................................................................................................. 2-18
2.5.1 Interface Structure.................................................................................................... 2-18
2.5.2 Protocol Stack........................................................................................................... 2-19
2.5.3 Physical Interface Operation Method........................................................................ 2-20
CHAPTER 3. Outdoor SPI-2210 Architecture 3-1
3.1 System Configuration............................................................................................................3-1
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. V
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
3.2 Detailed Structure...................................................................................................................3-3
3.2.1 Digital Main Block (DMB).............................................................................................3-3
3.2.2 RF Block (RFB)...........................................................................................................3-7
3.2.3 PDP-PO.....................................................................................................................3-10
3.2.4 Direct Air Cooling System (DACS)............................................................................3-12
3.2.5 Universal Control Module (UCM) and Sensor ...........................................................3-16
3.2.6 I/O Module.................................................................................................................3-18
3.2.7 External Interface Structure.......................................................................................3-19
3.3 Software Structure ...............................................................................................................3-21
3.3.1 Basic Structure..........................................................................................................3-21
3.3.2 Call Control (CC) Block .............................................................................................3-23
3.3.3 Operation And Maintenance (OAM) Block.................................................................3-26
3.4 Redundancy Structure.........................................................................................................3-43
3.4.1 MMA-S Redundancy Structure..................................................................................3-43
3.4.2 MRA-S Redundancy Structure..................................................................................3-44
3.4.3 Backhaul Redundancy Structure...............................................................................3-44
CHAPTER 4. Message Flow 4-1
4.1 Call Processing Message Flow .............................................................................................4-1
4.1.1 Initial Access................................................................................................................4-1
4.1.2 Authentication..............................................................................................................4-4
4.1.3 Status Change.............................................................................................................4-7
4.1.4 Location Update........................................................................................................4-11
4.1.5 Paging.......................................................................................................................4-16
4.1.6 Handover...................................................................................................................4-17
4.1.7 Access Termination ...................................................................................................4-23
4.2 Network Synchronization Message Flow...........................................................................4-25
4.3 Alarm Signal Flow................................................................................................................4-26
4.4 Loading Message Flow........................................................................................................4-28
4.5 Operation and Maintenance Message Flow.......................................................................4-30
CHAPTER 5. Additional Functions and Tools 5-1
5.1 TTLNA/RET .............................................................................................................................5-1
5.2 Web-EMT.................................................................................................................................5-2
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. VI

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
ABBREVIATION I
A ~ C............................................................................................................................................ I
D ~ I............................................................................................................................................ II
L ~ P.......................................................................................................................................... III
Q ~ T .........................................................................................................................................IV
U ~ W .........................................................................................................................................V
INDEX I
A ~ E............................................................................................................................................ I
F ~ M..........................................................................................................................................II
N ~ S ......................................................................................................................................... III
T ~ W.........................................................................................................................................IV
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. VII

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1.1 Mobile WiMAX Network Configuration...................................................................1-4
Figure 1.2 Configuration of Mobile WiMAX System Functions (Based on Profile C)...............1-6
Figure 2.1 IPv4/IPv6 Dual Stack Operation.............................................................................2-8
Figure 2.2 SMOR Configuration............................................................................................2-17
Figure 2.3 Structure of Outdoor SPI-2210 Interface..............................................................2-18
Figure 2.4 Protocol Stack between NEs................................................................................2-19
Figure 2.5 Protocol Stack between Outdoor SPI-2210 and WSM.........................................2-19
Figure 3.1 Internal Configuration of Outdoor SPI-2210...........................................................3-2
Figure 3.2 DMB Configuration.................................................................................................3-4
Figure 3.3 RFB Configuration .................................................................................................3-7
Figure 3.4 PDP-PO Configuration.........................................................................................3-10
Figure 3.5 Power Structure...................................................................................................3-11
Figure 3.6 DACS Configuration.............................................................................................3-12
Figure 3.7 Heat Radiation Structure of the Outdoor SPI-2210..............................................3-14
Figure 3.8 Heating Structure of the Outdoor SPI-2210 .........................................................3-15
Figure 3.9 UCM and Sensor Configuration ...........................................................................3-16
Figure 3.10 UCM Configuration Diagram of the Outdoor SPI-2210 ......................................3-17
Figure 3.11 I/O Module Configuration ...................................................................................3-18
Figure 3.12 External Interfaces of Outdoor SPI-2210...........................................................3-19
Figure 3.13 Software Structure of Outdoor SPI-2210............................................................3-21
Figure 3.14 CC Block Structure.............................................................................................3-23
Figure 3.15 OAM Software Structure....................................................................................3-26
Figure 3.16 Interface between OAM Blocks..........................................................................3-26
Figure 3.17 SNMPD Block ....................................................................................................3-28
Figure 3.18 OAGS Block....................................................................................................... 3-29
Figure 3.19 Web-EMT Block.................................................................................................3-30
Figure 3.20 CLIM Block ........................................................................................................3-31
Figure 3.21 PAM Block..........................................................................................................3-32
Figure 3.22 UFM Block .........................................................................................................3-34
Figure 3.23 Loader Block......................................................................................................3-35
Figure 3.24 ULM Block .........................................................................................................3-37
Figure 3.25 OPM Block.........................................................................................................3-38
Figure 3.26 OSSM Block ......................................................................................................3-38
Figure 3.27 OER/OEV Block.................................................................................................3-39
Figure 3.28 OCM Block.........................................................................................................3-40
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. VIII

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
Figure 3.29 RDM Block ........................................................................................................ 3-42
Figure 3.30 Redundancy Structure of OAM Block (MMA-S)................................................. 3-43
Figure 3.31 Redundancy Structure of UCCM (MMA-S)........................................................ 3-43
Figure 3.32 MRA-S Redundancy Structure .......................................................................... 3-44
Figure 3.33 Load Sharing Structure of Backhaul.................................................................. 3-44
Figure 4.1 Initial Access Process............................................................................................ 4-2
Figure 4.2 Authentication Procedure (At the time of initial access) ........................................ 4-4
Figure 4.3 Authentication Procedure (At the time of the Authenticator Relocation)................ 4-6
Figure 4.4 Awake Mode Idle Mode Status Change Procedure .......................................... 4-7
Figure 4.5 Awake Mode Sleep Mode Status Change Procedure ....................................... 4-8
Figure 4.6 Idle Mode Awake Mode (QCS) Procedure........................................................ 4-9
Figure 4.7 Inter-RAS Location Update Procedure.................................................................4-11
Figure 4.8 Inter-ACR Location Update Procedure (CMIP/PMIP Case) ................................ 4-12
Figure 4.9 Inter-ACR Location Update Procedure (Simple IP Case).................................... 4-14
Figure 4.10 Paging Procedure.............................................................................................. 4-16
Figure 4.11 Inter-RAS Handover Procedure......................................................................... 4-17
Figure 4.12 Inter-ASN Handover (ASN-Anchored Mobility).................................................. 4-19
Figure 4.13 Inter-ASN Handover (CSN-Anchored Mobility).................................................. 4-21
Figure 4.14 Access Termination (Awake Mode) ................................................................... 4-23
Figure 4.15 Access Termination (Idle Mode) ........................................................................ 4-24
Figure 4.16 Network Synchronization Flow of Outdoor SPI-2210 ........................................ 4-25
Figure 4.17 Alarm Signal Flow of Outdoor SPI-2210............................................................ 4-26
Figure 4.18 Alarm and Control Structure of Outdoor SPI-2210 ............................................ 4-27
Figure 4.19 Loading Message Flo w ..................................................................................... 4-29
Figure 4.20 Operation and Maintenance Signal Flow........................................................... 4-30
Figure 5.1 TTLNA/RET Interface............................................................................................ 5-1
Figure 5.2 Web-EMT Interface ............................................................................................... 5-2
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. IX
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
This page is intentionally left blank.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. X
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description
CHAPTER 1. Overview of Mobile
WiMAX System
1.1 Introduction to Mobile WiMAX
The Mobile WiMAX system is the wireless network system that supports IEEE 802.16e2005 base service. The IEEE 802.16 standard constitutes the basis for Mobile WiMAX, and
includes IEEE Std 802.16-2004 which defines the fixed wireless Internet connection
service, and IEEE Std 802.16, P802.16-2004/Cor/D3 which defines mobility technology
such as handover or paging.
Mobile WiMAX Sta nda rd
In this description, the entire Mobile WiMAX standard is expressed IEEE 802.16.
The wireless LAN (WLAN, Wireless Local Area Network) can provide high speed data
services, but its radio wave is short and covers only small areas, and also gives limited user
mobility. It is difficult for WLAN to ensure Quality of Service (QoS) for data service.
On the contrary, the present mobile communication networks support the mobility of the
users, but the service charge and the cost of system operations are high due to the limited
wireless resources. To provide faster service in the existing mobile communication
networks, it requires a separate wireless communication technology such as High Speed
Packet Access (HSPA) for the data services.
Mobile WiMAX can, therefore, overcome the limitations of the WLAN and present mobile
communication networks, and accommodate only the advantages of the system.
Mobile WiMAX can ultimately provide the high speed wireless internet services with low
cost at any time and in anyplace.
Samsung Mobile WiMAX System provides high speed data services using the transmission
technology of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) by the Time
Division Duplex (TDD), and can give wider coverage compared to the existing WLAN.
The system performance and the capacity have been expanded by the high performance
hardware, and thus, it can easily give various functions and services to the users.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-1
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
The Mobile WiMAX system consists of Radio Access Station (RAS), Access Control
Router (ACR) and Mobile WiMAX System Manager (WSM). RAS manages 802.16
Medium Access Control (MAC)/Physical Layer (PHY) function for Mobile Station (MS),
ACR manages various control functions and interworking function between Mobile
WiMAX ASN system and CSN system.
System Support Standards
Network Working Group (NWG) of Mobile WiMAX Forum defines the Mobile
WiMAX network as Access Service Network (ASN) and Connectivity Service
Network (CSN). Samsung’s RAS is Base Station (BS) and ACR is ASN-GW
(Gateway) of ASN, respectively.
RAS and ACR are based on ASN Profile C and Wave 2 Profile defined in the
Mobile WiMAX Forum and the Wave 2 Profile contains Wave 1 Profile.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-2

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
1.2 Characteristics of the Mobile WiMAX System
The major characteristics of Mobile WiMAX system are listed below.
High Compatibility and Cross-Interworking
The Mobile WiMAX system is based on IEEE 802.16 standard and complies with Wave 2
Profile and ASN Profile C of the Mobile WiMAX Forum. Therefore, the Mobile WiMAX
system provides high compatibility and excellent cross-interworking.
High Performance Module Structure
The Mobile WiMAX system has high performance by using high-performance processor
and provides the module structure that it is easy to upgrade hardware and software.
High System Stability
The Mobile WiMAX system provides the redundancy structure for main modules to ensure
higher stability.
Variant Advance RF and Antenna Solution Support
The Mobile WiMAX system supports Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) and applies
the power amplifier to support wideband operation bandwidth. In addition, it can readily
support 4-branch diversity and beamforming.
Evolution Possibility into Next Generation Networking
The Mobile WiMAX system complies with the structure of the Mobile WiMAX ASN
Profile C network and the ASN Profile C network composition is similar to the network
structure considered in 3GPP Long Term Evolution (LTE)/Service Architecture Evolution
(SAE). Therefore, the Mobile WiMAX system can easily evolve into the next generation
network.
Maintenance Function with Strengthened Security
The Mobile WiMAX system provides the security function (SNMPv3, SSH, SFTP and
HTTPs) to all channels for operation and maintenance. The Mobile WiMAX system
provides the operator Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) function to
authenticate the operator and assign the right for system access and store the operation
history in a log.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-3
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
A
A
A
A
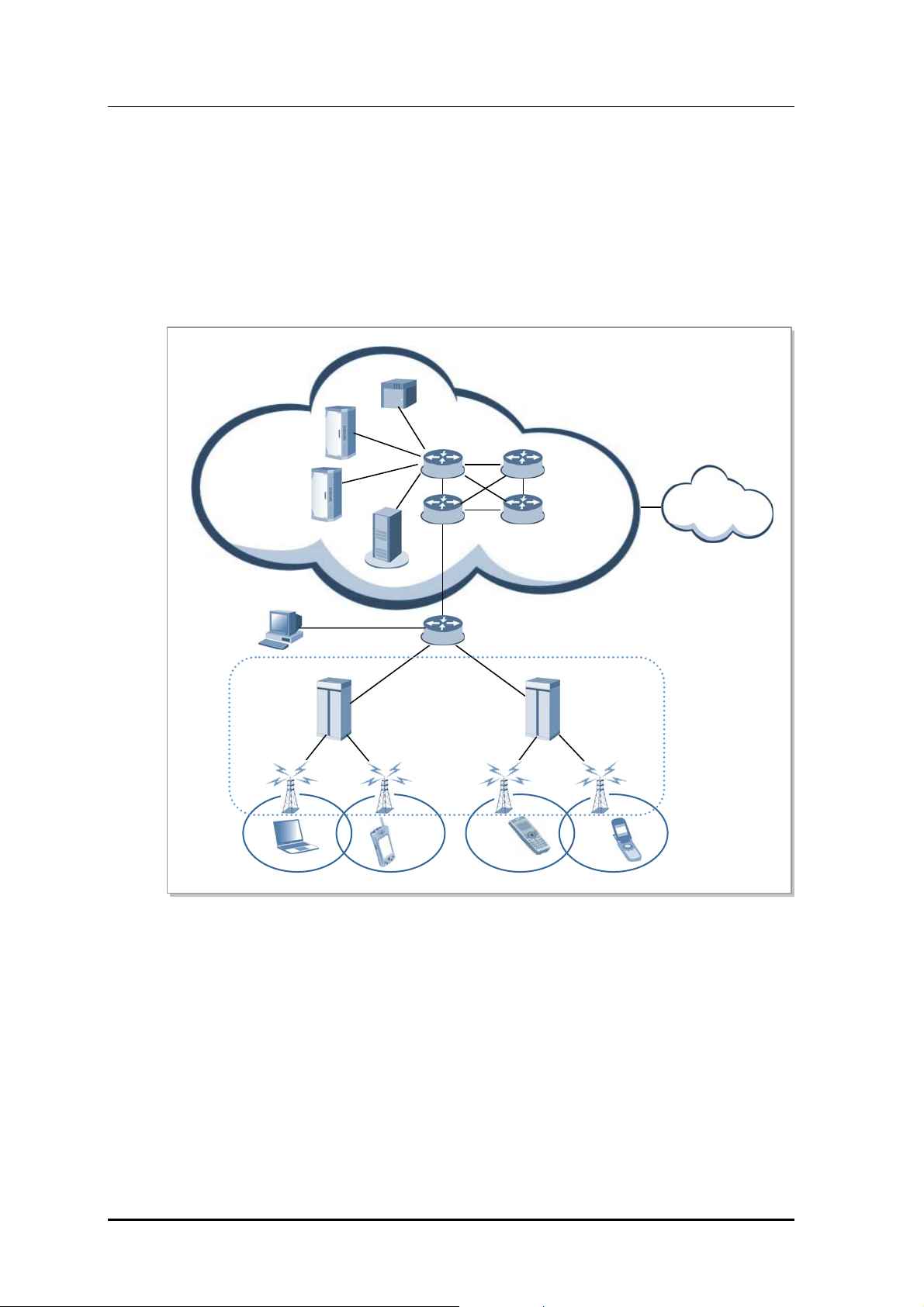
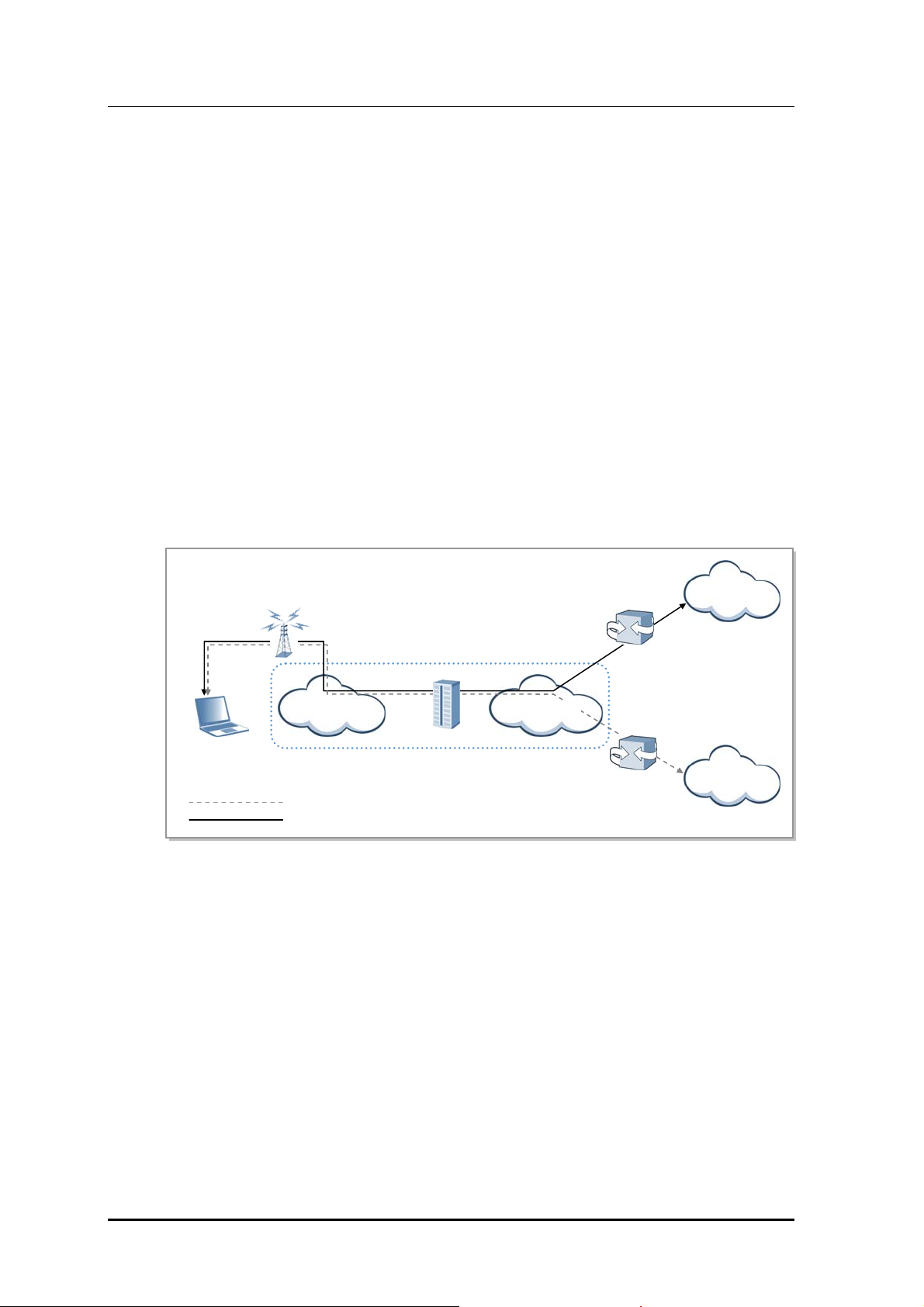
1.3 Mobile WiMAX Network Configuration
Mobile WiMAX network is composed of ASN and CSN. ACR and RAS are involved in
ASN and WSM is the Network Element (NE) to manage ACR and RAS. CSN is composed
of AAA server, HA, and PCRF server. ASN is connected with CSN by router and switch.
The following diagram shows the composition of Mobile WiMAX network.
AA
H
Core Router/Switch
WSM
RAS
DHCP
MS
PCRF
CSN
Edge Router/Switch
SN
ACR
Figure 1.1 Mobile WiMAX Network Configura tion
…
RAS
MS MS MS
RAS
CR
RAS
Internet
Radio Access Station (RAS)
RAS as the system between ACR and MS has the interface with ACR and provides the
wireless connection to MS under IEEE 802.16 standards to support wireless
communication service for subscribers.
RAS carries out wireless signal exchange with MS, modulation/demodulation signal
processing for packet traffic signal, efficient use of wireless resources, packet scheduling
for Quality of Service (QoS) assurance, Admission Control, assignment of wireless
bandwidth, Automatic Repeat request (ARQ) processing and ranging function. In addition,
RAS controls the connection for packet calls and handover.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-4
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
Access Control Router (ACR)
ACR, which is the system between CSN and RAS, enables several RASs to interwork with
IP network, sends/receives traffic between external network and MS, and controls QoS.
The ACR interfaces with the Authentication, Authorization and Accounting (AAA) server
using the DIAMETER/RADIUS protocols and with the Policy & Charging Rules Function
(PCRF) server using the Diameter protocol. For Mobile IP services the ACR interacts with
the Home Agent.
Mobile WiMAX System Manager (WSM)
WSM provides the management environment for the operator to operate and maintain ACR
and RAS.
Home Agent (HA)
HA accesses other networks or private networks and enables Mobile IP (MIP) users to
access internet. HA interworks with ACR that performs Foreign Agent (FA) function for
Mobile IPv4 and interworks with MS to exchange data for Mobile IPv6.
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server
The DHCP server allocates IP addresses to simple IP users. When an MS requests an IP
address to be allocated, the DHCP server allocates an IP address by interacting with the
ACR that functions as a DHCP relay agent and sends it to the ACR.
Authorization, Authentication and Accounting (AAA) Server
AAA server interfaces with ACR and carries out subscriber authentication and accounting
functions. The AAA server interfaces with ACR via Diameter/RADIUS protocol and
provides Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) certification.
Policy & Charging Rules Function (PCRF) Server
The PCRF server is the server that manages the service policy and interfaces with ACR via
Diameter protocol. The PCRF server sends QoS setting information for each user session
and accounting rule information to ACR.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-5
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
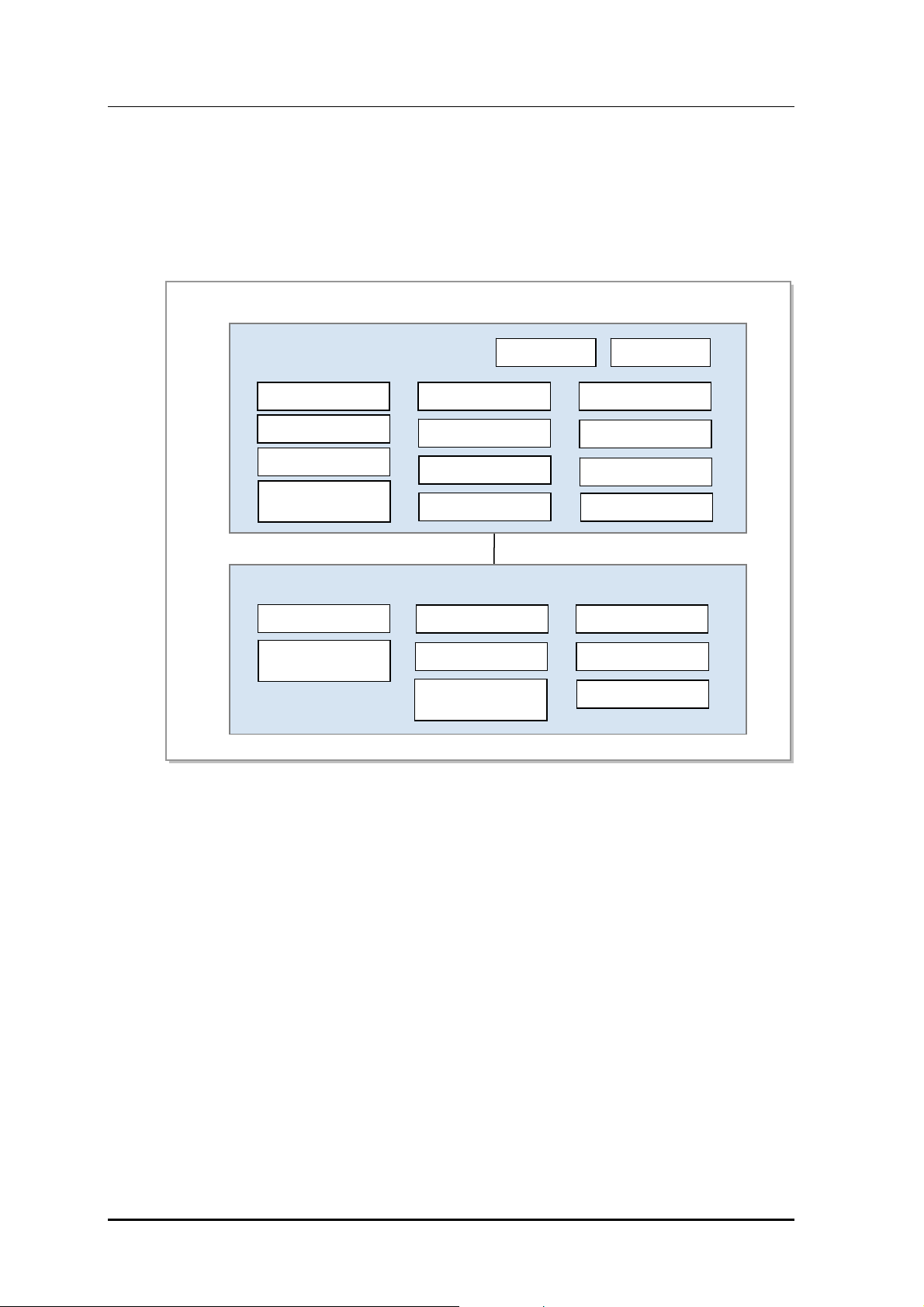
1.4 Mobile WiMAX System Functions
The figure below shows the functions of the ASN systems (ACR and RAS) based on
Profile C.
Each block name complies with the standard of Mobile WiMAX NWG.
ASN
ASN-GW (ACR)
Paging Controller
Location Register
Context Function
Handover Function
(Handover Relay)
BS (RAS)
Context Function
Handover Function
(Handover Control)
Figure 1.2 Configuration of Mobile WiMA X Sys tem F unct ions (Base d on Prof ile C)
Authenticator
Key Distributor
SFA
AAA Client
Key Receiver
RRC & RRA
SFM
(Admission Control)
MIP FA PMIP client
IP Packet Forwarding
Header Compression
Packet Classification
DHCP relay agent
R6
ARQ Operation
MAC PDU
Encapsulation/PHY
The ACR supports the Convergence Sublayer (CS) and performs the packet classification
and Packet Header Suppression (PHS) functions. When the ACR carries out the header
compression function, it supports ROHC defined in the NWG standard.
In addition, the ACR performs the paging controller and location register functions for a
MS in Idle Mode.
In authentication, the ACR performs the authenticator function and carries out the key
distributor function to manage the higher security key by interworking with the AAA server
as an AAA client. At this time, RAS performs the key receiver function to receive the
security key from the key distributor and manage it.
The ACR interworks with the AAA server of CSN for authentication and charging services
and with the HA of CSN for Mobile IP (MIP) service. The ACR as FA of MIP supports
Proxy MIP (PMIP).
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-6
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
The RAS performs the Service Flow Management (SFM) function to create/change/release
connections for each Service Flow (SF) and the admission control function while
creating/changing connections. In regard to the SFM function of the RAS, the ACR carries
out the SF Authentication (SFA) and SFID management functions. The ACR carries out the
SFA function to obtain the QoS information from Policy Function (PF) and apply it in the
SF creation and performs the SFID management function to create/change/release SFID
and map SF according to the packet classification.
In handover, the RAS performs the handover control function to determine the execution of
the handover and deal with corresponding handover signaling. The ACR confirms the
neighbor BS list and relays the handover signaling message to the target system.
At this time, the ACR and the RAS carries out the context function to exchange the context
information between the target system and the serving system.
The RAS provides admission control to collect/manage the MS's radio resource
information and the RAS's own radio resource information (e.g., BSID). When load
balancing is required based on admission control results, it performs resource management
through FA overriding and BS init HO (Handover).
ASN System Function
For the detailed description about the RAS functions, refer to Chapter 2 of this
system description. For the description about the ACR functions, refer to the
system description for ACR provided by Samsung.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-7

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
This page is intentionally left blank.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-8

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description
CHAPTER 2. Overview of Outdoor
SPI-2210
2.1 Introduction to Outdoor SPI-2210
The outdoor SPI-2210, RAS of Mobile WiMAX, is controlled by ACR and connects
Mobile WiMAX calls to MS.
The outdoor SPI-2210 interfaces with MS via a wireless channel observing the Mobile
WiMAX standard (IEEE 802.16) and provides high-speed data service and multimedia
service in wireless broadband.
To this end, the outdoor SPI-2210 provides the following functions:
modulation/demodulation of packet traffic signal, scheduling and radio bandwidth
allocation to manage air resources efficiently and ensure Quality of Service (QoS),
Automatic Repeat request (ARQ) processing, ranging function, connection control function
to transmit the information on the outdoor SPI-2210 and set/hold/disconnect the packet call
connection, handover control and ACR interface function and system operation
management function.
The outdoor SPI-2210 interfaces with ACR in one way of Fast Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet
and can exchange various control signals and traffic signals stably.
The outdoor SPI-2210 is installed in the outdoor environment and managed in the omni or
sector method according to the property of the installed area. In addition, the outdoor SPI2210 supports the capacity of the maximum 3Carrier/3Sector and MIMO only with the
basic cabinet.
The characteristics of the outdoor SPI-2210 are as follows:
Application of the OFDMA Method
OFDMA is used to transmit data to several users simultaneously by using the sub-carrier
allocated to each user and transmit data by allocating one or more sub-carriers to a specific
subscriber according to the channel status and the transmission rate requested by a user.
In addition, since it can select the sub-carriers with excellent features for each subscriber
and allocate them to the subscribers when some subscribers divide and use the whole subcarrier, it can raise the data throughput by distributing the resources efficiently.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-1
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
Support of Broadband Channel Bandwidth
The outdoor SPI-2210 supports wide bandwidth of 5/10 MHz per carrier and high-speed
and high capacity packet service.
Support of 3Carrier/3Sector
The outdoor SPI-2210 can support 3Carrier/3Sector by the basic cabinet.
Support of MIMO
The outdoor SPI-2210 basically supports MIMO of 2Tx/2Rx RF path. There are methods
of MIMO as follows;
Downlink
Space Time Coding (STC): method for raising reliability of link
Spatial Multiplexing (SM): method for raising data transmission rate
Uplink
Collaborative SM (CSM): Doubled frequency efficiency
Support of Frequency Reuse Pattern (FRP)
The outdoor SPI-2210 supports FRP N=1 that provides the service to 3-sector by using a
carrier and FRP N=3 that provides the service to 3-sector by using different carriers.
A service provider can efficiently operate its own frequency resources by using the FRP
function.
Support of 4-Branch Rx Diversity (Optional)
The outdoor SPI-2210 supports 4-branch Rx diversity providing four Rx paths to each
sector to raise the Rx performance. In the outdoor SPI-2210, Mobile WiMAX base station
RF Receiver (MRR), an Rx module, should be additionally mounted to support 4-branch
Rx diversity.
Support of Various Frequency Allocation
The outdoor SPI-2210 supports various frequency allocation methods such as contiguous
carrier, noncontiguous carrier, FRP N=1 or FRP N=3. The outdoor SPI-2210 can apply RF
combiner optionally to such frequency allocation methods.
Support of Beamforming (Option)
The outdoor SPI-2210 is designed as the structure to support beamforming later.
The outdoor SPI-2210 mitigates the interference efficiently by uplink and downlink
beamforming to raises the average capacity and expand the data coverage. Also the outdoor
SPI-2210 needs the process to calibrate the reciprocity between uplink channel and
downlink channel.
Schedule to Provide the System Feature
For the schedule to provide the features described in this system description, see
separate document.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-2

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
2.2 Main Functions
The main functions of the outdoor SPI-2210 are as follows:
Physical layer processing function
Call processing function
IP processing function
Auxiliary device interface function
Convenient operation and maintenance function
Function of supporting the outdoor environment
2.2.1 Physical Layer Processing Function
OFDMA Ranging
The ranging supported by the OFDMA system is roughly divided by the uplink timing
synchronization method and the contention based bandwidth request method.
Uplink Timing Synchronization
In the uplink timing synchronization method, the outdoor SPI-2210 detects the timing
error of the uplink signal by using the ranging code transmitted from MS and transmits
the timing correction command to each MS to correct the transmission timing of the
uplink. The uplink timing synchronization method has initial ranging, periodic ranging,
handover ranging, etc.
Contention Based Bandwidth Request
In the contention based bandwidth request method, the outdoor SPI-2210 receives the
bandwidth request ranging code from each MS and allocates uplink resources to the
corresponding MS to enable to transmit the bandwidth request header.
The contention based bandwidth request method has bandwidth request ranging or
something.
Channel Encoding/Decoding
The outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the Forward Error Correction (FEC) encoding for the
downlink packet created in the upper layer by using Convolutional Turbo Code (CTC).
On the contrary, it decodes the uplink packet received from the MS after demodulating.
Modulation/Demodulation
The outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the FEC encoding for the downlink packet created in the
upper layer and modulates the encoded packet into the QAM signal. In addition, the
outdoor SPI-2210 demodulates and decodes the uplink packet received from MS.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-3

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
OFDMA Sub-carrier Allocation
The subchannelization is the process to tie the sub-carriers of OFDMA as a transmission
unit after grouping them by a certain rule. The outdoor SPI-2210 performs the
subchannelization to mitigate the interference between cells.
The outdoor SPI-2210 maps the column of the modulated downlink QAM symbol structure
with each sub-carrier and carries out the subchannelization when the column of the QAM
symbol structure is transmitted to the MS over the wireless line.
In such way, the outdoor SPI-2210 transmits the column of the QAM symbol structure to
the MS via the sub-carriers pertained to each subchannel.
DL/UL MAP Construction
The outdoor SPI-2210 informs the air resources for the uplink and the downlink to the MS
by using DL/UL MAP. The DL/UL MAP consists of the scheduling information of the
outdoor SPI-2210 and includes various control information for the MS.
Power Control
The outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the power control function for the uplink signal received
from multiple MSs and then set the power intensity of the uplink signal to a specific level.
The outdoor SPI-2210 transmits the power correction command to each MS and then
makes the MS power intensity be the level required in the outdoor SPI-2210 when the MS
transmits the modulated uplink signal in a specific QAM modulation method.
Hybrid-ARQ (H-ARQ) Operation
H-ARQ is the physical layer retransmission method using the stop-and-wait protocol.
The outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the H-ARQ function and raises data throughput by retransmitting or combining the frame from the physical layer to minimize the effect
attending to the change of wireless channel environment or the change in the interference
signal level.
MIMO
The outdoor SPI-2210 provides the MIMO function as follows according to Mobile
WiMAX Wave 2 Profile:
Downlink
Matrix A (STC)
Transmission ratio of the Matrix A or (STC) is 1 and equal to that of Single Input
Single Output (SISO). However The Matrix A or the STC reduces the error of the
signal received from the MS by raising the stability of the signal received from the
MS by means of the Tx diversity. This technology is, also, effective in low Signal
to Noise Ratio (SNR) and provides excellent performance even when the MS
moves in high speed.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-4

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
Matrix B (SM, vertical encoding)
Matrix B or SM method raises the effectiveness of the frequency by raising the
transmission ratio in proportion to the number of antenna in comparison with SISO.
This technology is effective when the reception SNR is high.
Uplink
Collaborative SM (CSM)
CSM is the technology that doubles the frequency efficiency in view of the outdoor
SPI-2210 as two MSs with each individual antenna send data simultaneously by
using the same channel.
Beamforming
The outdoor SPI-2210 can carry out the following beamforming function later according to
Mobile WiMAX Wave 2 Profile: For the beamforming, the outdoor SPI-2210 is designed
on the basis of 4Tx and 4Rx.
Downlink
DL dedicated pilots for Partial Usage of Subchannels (PUSC) and B-AMC (2 3)
Uplink
UL sounding channel (type A) with decimation and cyclic shift
UL PUSC and B-AMC (2 3)
The beamforming operation method following the Wave 2 Profile is as follows:
1) If an MS in a specific area transmits the sounding signal to the outdoor SPI-2210, the
outdoor SPI-2210 analyzes this signal.
2) The outdoor SPI-2210 estimates an appropriate beamforming coefficient on the basis
of the result analyzed in step 1).
3) The outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the beamforming for the uplink and the downlink.
Since the uplink and downlink channels have the high correlation in TDD method, the
beamforming can be supported.
2.2.2 Call Processing Function
Cell Initialization Function
The outdoor SPI-2210 announces the MAC Management message such as DCD/UCD/
MOB_NBR-ADV to the cell area in service periodically to enable the MS receiving the
message to carry out the appropriate call processing function.
Call Control and Wireless Resource Allocation Function
The outdoor SPI-2210 enables an MS to enter to or exit from the network. When an MS
enters to or exit from the network, the outdoor SPI-2210 transmits/receives the signaling
message required for call processing via R1 interface with the MS or R6 interface with
ACR.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-5
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
The outdoor SPI-2210 allocates various management/transport Connection Identifier (CID)
required for the network entry and service to a MS. When the MS exit from the network,
the outdoor SPI-2210 collects and release the allocated CID.
Handover
The outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the signaling and bearer processing for inter-sector HO
(Handover), inter-ACR HO and inter-carrier HO. At this time, ACR relays the handover
message between serving RAS and target RAS through the R6 interface.
To minimize the traffic disconnection in inter-RAS HO, the outdoor SPI-2210 performs the
data switching function. In handover, the outdoor SPI-2210 enables the serving RAS to
switch the user data in queuing to the target RAS and, therefore, the MS to recover the
traffic without loss.
Handover Procedure
For the detailed handover procedure, refer to Chapter 4 ‘Message Flow’.
Support of Sleep Mode
Sleep mode is the mode defined to save the MS power under IEEE 802.16 standard and
indicates the status that air resources allocated to an MS are released when the MS does not
need traffic reception/transmission temporarily. If the MS in Sleep Mode needs the traffic
reception/transmission, the MS returns to the normal status immediately.
Both Idle Mode and Sleep Mode are modes to save the MS power. The Idle Mode release
all service flows allocated to an MS, while the Sleep Mode releases only the air resources
between the MS and RAS temporarily, continuously keeping the service flow information
allocated to the MS.
The outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the related call processing function by receiving/sending
the signaling message required for the MS's status transition into Sleep Mode and the MS
return from the Sleep Mode to Awake Mode.
Admission Control (AC) Function
If the outdoor SPI-2210 receives the call setup request, such as network entry, Quick
Connection Setup (QCS) and handover, from an MS, it monitors the traffic and signaling
load for each subcell and the number of user in Active/Sleep Mode and performs the AC
function to prevent the system overload.
AC can be roughly divided into AC by MS and AC by service flow.
AC by MS
If the number of users who the subcell is in Active/Sleep Mode exceeds the threshold
when the outdoor SPI-2210 receives the call setup request from an MS, it rejects the
call setup request of the MS.
AC by service flow
When service flow is added, the outdoor SPI-2210 checks if the air resources of the
requested subcell exceed the threshold and determines the creation of the service
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-6

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
MAC ARQ Function
The outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the ARQ function of the MAC layer. In packet data
exchange, the transmission side transmits ARQ block which SDU is divided into, and
retransmits the packet according to the ARQ feedback information received from the
reception side to raise the reliability of data communication.
The outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the following function for the service flows applying
ARQ:
MAC Management creation and transmission concerned with ARQ operation
Feedback processing depending on ARQ types
Block processing (fragmentation/reassemble/retransmission) depending on ARQ types
ARQ timer/window management
QoS Support Function
The packet traffic exchanged between ACR and Outdoor SPI-2210 is delivered to the
modem in the outdoor SPI-2210. At this time, the outdoor SPI-2210 allocates the queue in
the modem to each service flow that QoS type is specified to observe the QoS constraint
given for each QoS class or service flow and performs the strict-priority scheduling
according to the priority.
The modem that receives the packet traffic performs the scheduling by using the
uplink/downlink algorithm, such as Proportional Fair (PF) or Round Robin (RR) and
transmits the scheduled allocation information to an MS through DL/UL MAP.
The MS receiving the DL/UL MAP checks the air resources allocated to the MS and
modulates/demodulates the downlink packet or transmits the uplink packet from the
allocated uplink area.
Since the outdoor SPI-2210 provides the QoS monitoring function, it can compile statistics
on packets unsatisfying the latency requested from the QoS parameter according to TDD
frames and report the statistics to an operator via the OAM interface.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-7
Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
A
2.2.3 IP Processing Functions
IP QoS Function
Since the outdoor SPI-2210 supports Differentiated Services (DiffServ), it can provide the
backhaul QoS in the communication with ACR.
It supports 8-class DiffServ and supports the mapping between the DiffServ service class
and the service class of the user traffic received from an MS. In addition, the outdoor SPI2210 supports between Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) and 802.3 Ethernet
MAC service class.
Simultaneous Support of IPv4/IPv6
ACR communicates with the outdoor SPI-2210 through the GRE tunnel and the backhaul
IP version between the outdoor SPI-2210 and ACR is managed independently from the
service IP version for the MS.
Even if, therefore, IPv4 is used in backhaul between the outdoor SPI-2210 and ACR, all of
IPv4, IPv6 and IPv4/IPv6 dual stack services can be supported.
IPv6 Network
IPv4 Network
Dual Stack MS
(IPv4/IPv6)
RAS
Access Network
IPv4
IPv6
Figure 2.1 IPv4/IPv6 Dual St ack Operation
Gateway
Dual Stack Processing
Core Network
CR
Gateway
IP Routing Function
Since the outdoor SPI-2210 provides several Ethernet interfaces, it stores the routing table
with the information on the Ethernet interface to route IP packets. The routing table of the
outdoor SPI-2210 is configured depending on operator’s setting and the configuration and
the setting of the routing table are similar to the standard setting of the router.
The outdoor SPI-2210 supports the static routing configuration only and not the router
function for the traffic received from the outside. When the outdoor SPI-2210 connects an
auxiliary device, it supports the IP packet routing function for the auxiliary device by using
Network Address Translation (NA T).
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-8

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
Ethernet/VLAN Interface Function
The outdoor SPI-2210 provides the Ethernet interface and supports the static link grouping
function, Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) function and Ethernet CoS function under
IEEE 802.3ad for the Ethernet interface. At this time, the MAC bridge function defined in
IEEE 802.1D is excluded.
The outdoor SPI-2210 enables several VLAN IDs to be set in one Ethernet interface and
maps the DSCP value of IP header with the CoS value of Ethernet header in Tx packet to
support Ethernet CoS.
2.2.4 Auxiliary Device Interface Function
The outdoor SPI-2210 can support better performance service and convenience by
supporting various auxiliary devices.
Wireless Backhaul Interface
Auxiliary device part of the outdoor SPI-2210 can mount a wireless backhaul device
provided by a service provider. The outdoor SPI-2210 supplies the power to the wireless
backhaul device.
When the server that manages the wireless backhaul device exist, the outdoor SPI-2210
supports the User Define Ethernet (UDE) port to provide path for maintenance traffic
between that server and wireless backhaul device.
UDA Support
The outdoor SPI-2210 receives or sends alarm history from/to outside through UDA.
The outdoor SPI-2210 provides a total of 24 UDA Rx ports and 10 UDA Tx ports.
The outdoor SPI-2210 provides UDA Tx 1 port to AICU for interoperation with TTLNA.
When subcell output of RAS is blocked by an operator command for the TTLNA receiver
test, the UDA informs the AICU that TTLNA becomes Rx only mode.
An operator uses UDA control commands to expand UDA ports, name UDA ports, and
transmit UDA Tx signals.
Auxiliary Device Interface
The outdoor SPI-2210 provides the Ethernet interface to connect auxiliary devices such as
TTLNA and allocates IP addresses by operating as a DHCP server for the auxiliary devices.
In addition, the outdoor SPI-2210 provides the traffic path to transmit/receive the
maintenance traffic between an auxiliary device and the remote auxiliary device
monitoring server.
If the auxiliary device uses a private IP address, the outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the NAT
function to change the address into a public IP address (i.e., the IP address of the outdoor
SPI-2210) for the communication with an external monitoring server.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-9

Mobile WiMAX Outdoor RAS SPI-2210 System Description/Ed.05
2.2.5 Maintenance Function
The outdoor SPI-2210 interworking with the management system carries out the following
maintenance functions: system initialization and restart, management for system
configuration, management for the operation parameters, failure and status management for
system resources and services, statistics management for system resources and various
performance data, diagnosis management for system resources and services and security
management for system access and operation.
Graphic and Text-based Console Interface
WSM manages the entire Mobile WiMAX system by using Database Management System
(DBMS) and Outdoor SPI-2210 interworks with this WSM. Moreover, the outdoor SPI2210 interoperates with the console terminal so that the operator can connect to an NE
directly without using the WSM to perform the operational and maintenance functions.
For operator’s convenience and working purpose, the operator can select graphic-based
console interface (Web-based Element Maintenance T erminal, Web-EMT) or text-based
console interface (Integrated Management Interface Shell, IMISH).
The operator can access the console interface with no separate software and log in to WebEMT through Internet Explore and IMISH through Secure Shell (SSH) on the command
window.
The operator can carry out the retrieval and setup of the configuration and the operation
information and monitoring about faults, status and statistics via consol terminal.
However, the operator can carry out grow/degrow of resources and setting of the neighbor
list and paging group which have correlation between several NEs only via the WSM.
Operator Authentication Function
The outdoor SPI-2210 provides the authentication and the permission management
functions for the operator who manages the Mobile WiMAX system. The operator accesses
the outdoor SPI-2210 by using the operator’s ID and password via Web-EMT or IMISH
and the outdoor SPI-2210 assigns the operation right in accordance with the operator’s
level.
The outdoor SPI-2210 carries out the logging function for successful access, access failure
and login history.
Maintenance Function with Enhanced Security Function
For the security, the outdoor SPI-2210 supports Simple Network Management Protocol
version 3 (SNMPv3) and SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP) in the communication with
WSM and Hyper Text Transfer Protocol over SSL (HTTPs) and Secure Shell (SSH) in the
communication with console terminals.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-10
 Loading...
Loading...