Samsung SMM-2CR0480800 User Manual

EPB
ED.
Smart MBS
System Des cr ip t ion /Int rod uc ti on

Copyright
All text and images in this document are subject to the copyright of SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.
This docum ent ma y not be r eproduc ed, distr ibut ed, or modi fied with out th e writt en permi ssion of SAMSUNG
Electronics Co., L td.
Trademark
The marks appearing on this document are trademarks of SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd, its subsidiaries,
or affiliates.
This manual should be read and used as a guideline for properly installing and operating the product.
This m anual ma y be c han ged f or t he s yst em im prov emen t, s tand ard izati on an d ot her tech nic al r eas ons with out pri or
notice.
If you need updated manu als or have any questions c oncerning the contents of the manuals, c ontact our Document
Center at the following address or Web site:
Address: Document Center 3rd Floor Jeong-bo-tong-sin-dong. Dong-Suwon P.O. Box 105, 416, Maetan-3dong
Homepage: http://www.samsungdocs.com
©2011 SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
Yeongtong-gu, Suwon-si, Gyeonggi-do, Korea 442-600

INTRODUCTION
Smart MBS System Description
Purpose
This document introduces characteristics, features, and structure for Smart MBS Base Station of the
Samsung Multi-Mo d al Syste m.
Docu ment Content and Organization
This document consists of 4 CHAPTERS, APPENDIX, and ACRONYMS.
Chapter 1. Samsung Multimodal System Abstract
Explains the following…
Smart MBS System Introduction
Samsung Multimodal System Network Configuration
Samsung Multimodal System Feature
Chapter 2. Smart MBS Abstract
Explains the following…
Smart MBS System’s Characteristics
Smart MBS ‘s Main Feature
Smart MBS ‘s Specification
Operat ion manual o n Backhaul Interface
Chapter 3. HW Architecture of Smart MBS
Explains the following…
System Internal Structure
UADU (Universal Platform Digital Unit)
RRH (Remote Radio Hea d)
Thermal Radiation Structure
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. I
INTRODUCTION
Chapter 4. SW Architecture of Smart MBS
Explains the following…
Smart MBS SW Structure
Loading Flow
ABBREVIATION
Provide s d efinition for acrony ms u se d in this document.
Conventions
Following symbols are used in this document. The information provided along with this symbol should
be familiarized for safe operation/ha ndli ng of the system.
Additional Reference
Provides reference in addition to the main contents.
Reference
Revi sion Hist ory
Rev. Date Note
1.0 2011.10 First Edition
II © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

Smart MBS System Description
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION I
Purpose ....................................................................................................... I
Document Content and Organization
......................................................................... I
Conventions
Revision History
Chapter 1. Samsung Multi-ModalSystem Abstract 1-1
1.1 Introduc tion to S mart MBS S ystem ............................................................................ 1-1
1.2
Samsung Multi-Modal System Network A rchitecture ......................................................... 1-4
1.2.1
CDMA System Network Architecture ........................................................... 1-5
1.2.2
LTE System Network Structure .................................................................. 1-6
1.3
Samsung Multi-Modal System Feature ........................................................................ 1-9
1.3.1
CDMA System Feature ........................................................................... 1-9
1.3.2
LTE System Feature ............................................................................. 1-10
Chapter 2. Smart MBS Abstract 2-1
2.1 Sma rt MBS System Desc rip tion ............................................................................... 2-1
2.1.1 Smart MBS CDMA System Feature
2.1.3 Smart MBS LTE System Feature
...................................................................................................... II
.................................................................................................. II
............................................................... 2-3
................................................................... 2-3
2.2
Smart MBS Main Feature ...................................................................................... 2-6
2.2.1 Physical layer Processing Feature
2.2.2 Call Processing Feature
2.2.3 IP Processing Feature
2.2.4 Convenient Operation and Maintenance Feature
2.3
Smart MB S Spe cif ic atio n ......................................................................................2-14
2.4 Backhaul Interface Operatio n
................................................................. 2-6
............................................................................. 2-9
.............................................................................. 2-10
............................................. 2-11
....................................................................................2-17
Chapter 3. Smart M BS’s Hardw are Stru cture 3-1
3.1 Internal Sy stem Architecture ........................................................................................ 3-3
3.1.1
CDMA Internal System Architecture ............................................................ 3-4
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. III

TAB LE OF CON TE N TS
3.1.2 LTE Internal System Structure .................................................................. 3-6
3.2 UADU(Universal Platform Digital Unit ) ............................................................................ 3-8
3.3 RRH (Remote Radio Head)
3.4 Cooling Mechanism
3.4.1
Digital Unit (DU) .................................................................................. 3-15
3.4.2
RRH (Remote Radio Head) .................................................................... 3-16
3.5 Interface structure
Chapter 4. Smart MB S Software A rchitecture 4-1
4.1 Smart MBS SW Architecture ........................................................................................ 4-1
4.1.1 CDMA System Basic SW architecture
4.1.2 LTE System Basic SW Architecture
4.2
Loading Flow .................................................................................................... 4-7
ABBREVIATION I
........................................................................................ 3-14
................................................................................................ 3-15
.................................................................................................. 3-17
............................................................ 4-1
............................................................... 4-4
IV © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

Smart MBS System Description
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1.1 Smart MBS System Schematic ..................................................................... 1-2
Figure 1.2 Samsung Multi-modal Netwo rk A rchitec ture
Figure 1.3 CDMA Network Architecture o f Sam sung Multi-Modal System
Figure 1.4 Samsung Multi-Mode System’s LTE Network Arch itecture
Figure 1.5 CD MA System F u n ctiona l Structu re
Figure 1.6 Function of E -UTRAN and EPC
Figure 3.1 UADU Configuration - CDMA Single mode
Figure 3.2 UADU Configuration - LTE Single mode
Figure 3.3 UADU Configuration - CDMA + LTE dual mode
Figure 3.4 RRH-C 2A (800MHz)
Figure 3.6 Smart MBS CDMA Internal Block Diagram
Figure 3.7 Smart MBS LTE’s Internal Block Diag ram
Figure 3.8 UADU Configuration - CDMA Only
Figure 3.9 UADU Configuration - CDMA Only(Two UADU)
Figure 3.10 UADU Configuration - LTE Only
Figure 3.11 UADU Configuration - CDMA+LTE Dual Mode
Figure 3.12 UADU Configuration - CDMA+LTE Dual Mode(Two UADU)
Figure 3.13 UADU’s FA N Structure
Figure 3.14 UADU’s Cooling Mechanism
...................................................... 1-4
................................. 1-5
....................................... 1-7
............................................................... 1-9
................................................................. 1-10
...................................................... 3-2
.......................................................... 3-2
................................................. 3-2
............................................................................... 3-3
....................................................... 3-4
........................................................ 3-6
............................................................. 3-12
............................................. 3-13
............................................................... 3-13
.............................................. 3-13
.............................. 3-13
......................................................................... 3-16
................................................................... 3-16
Figure 3.15 HW Interface structure of UA D U (CD MA)
Figure 3.16 HW Interface structure of UA D U (LTE)
Figure 3.17 HW Interface structure of RR H -C2A
Figure 4.1 Smart MBS C DMA Softwa re Architec tu re
Figure 4.2 CDMA Common Software A rc h itecture
Figure 4.3 CDMA OA M Sof tware Arc hitecture
Figure 4.4 CDMA Call Proc essing S of tware S truc ture
Figure 4.5 Smart MBS LTE Software A rchitec tu re
Figure 4.6 Smart MBS' Loading Signal Flow
..................................................... 3-17
......................................................... 3-18
........................................................... 3-18
......................................................... 4-1
........................................................... 4-2
............................................................... 4-3
........................................................ 4-3
............................................................ 4-4
.................................................................. 4-8
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. V

TAB LE OF CON TE N TS
This page is intentionally left blank.
VI © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

Smart MBS System Description
Chapter 1. Samsung Multi-Modal
System Abstract
1.1 In trod uction to Smar t M BS S ystem
As mobile telecommunication technology has experienced rapid growth from “Analog Mobile
Telecommunication(1
2000(3rd Generation)”, and into “LTE(4th Gener ation)”, voice service is being expanded into data servi ce.
Especi all y, “wire/ wir eless hybr id ser vice”, “smar tphone ”, and “mobil e term inal” inc rea sed the d emands
for the high speed wireless technology. Along with the enhancement of various mobile
telecommunication networks, it is now becoming common for a single terminal to support different
mobile technolo gies.
“Smart MBS System” is multi-mode base station that will satisfy such needs of mobile
telecommunication market by integrating Voice(1X), Data(EVDO), LTE(4G) into a single base station
equipment.
Smart MBS System mounts common DU(Digital Unit) Platform, and RRH (per each frequency
bandwidth) that operator can decide to configure it with either single or multiple mobile technology.
Smart MBS System provides CDMA(w/ FDD), LTE(w/FDD), and TD-LTE(w/TDD).
Smart MB S System s up po rts the following tele communicatio n technologies.
CDMA2000 1X/1X Advanced
Having C DMA2 00 0 1X a s a reference, int egr a t e the syst em ( w/ EVRC-B, RLIC, QOF, New RC
algorithm) and the terminal(w/ (e)QLIC, MRD, New RC algorithm) to support 1X Advanced. As
a result, voice capacity enhancement will be provided.
CDMA2000 1xEV-DO Rev.A/Rev .B
Smart MBS supports CDMA2000 1xEV-DO Rev.A/ Rev.B s ervice and data servi ce of CDMA
network.
LTE (Lo ng T e rm Ev olu tion)
Samsung LTE System is a wireless network system that supports 3GPP LTE(Long Term
Evolution)(a.k.a. LTE). It improves the existing 3GPP mobile telecommunication system(low
data throughput, but high in cost) to a next generation wireless network system which provi des a
high speed data service with minimal cost. Samsung LTE System supports “Downlink
st
Generation)” to “Digital Mobile Telecommunication(2nd Gener ation)” to “CDMA
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-1
Samsung Multi-ModalSystem Abstract
Samsung Smart
MBS
800MHz
(CDMA/LTE)
800MHz
CDMA/LTE)
OFDMA”(Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) with either FDD(Frequency
Division Duplex) or TDD(Time Division Duplex), “Uplink SC(Single Carrier) FDMA”, and
“Scalable Bandwidth(for various spectrum allocation)” to provide high speed data service. Also,
high-end hardware is implemented to improve system performance and capacity that various high
speed data feature/service can be provided.
Figure 1.1 Smart MBS Sy s tem S chematic
Samsung Multimodal System consists of f ollowing major featur es.
(
Enhance ment of CDMA Service Qualit y
In case “Smart MBS System” is operating CDMA, it provides “EVDO Rev.0/Rev.A and 1X
Advanced” in order to improve the low throughput and limited voice capacity. In addition, “2branch Rx
Diver si t y” and “4br a nch Rx d iver si t y” fea tu r e is pr ovid ed t ha t CDMA networ k co ver a ge i s enh anc ed f or
versatile CDMA service.
(
기존 기지국 시스템
Ease of Expanding 4G Service
Legacy base stations consist of “3G CDMA 1X” for voice calls, “EVDO” for Data, “Battery”, and
“Rectifier”. If 4G service was to be supplied, additional 4G base station equipment had to be installed.
Nevertheless, “Smart MBS Base Station” only requires DU(Digital Unit) cabinet and Battery cabinet to
provide existing service as well as 4G Service with minimal board replacements and software upgrades.
Therefore, Smart MBS Basestations utilizes the cables, rectifiers, and batteries of the existing basestation
system. Its ease of 4G installation will bring about efficient network implementation in the future
commercial 4G service.
Green Solution
Smart MBS Basestation combines “3G BS equipment” and the “next generation 4G BS equipment” into
a single Base Station, and also contains the rectifier within the DU cabinet . Meanwhi le, RR H(Remote
Radi o Head) (TX/RX processing device) is separated apart from BS equipment for natural air cooling
that it ca n minimize f o otprint, power usage, and ca rb on dioxide emissio ns.
Provides Eff i c i en t Backhaul O peration
Smart MBS Basestation provides functionality that can operate multiple telecommunication technologies
into a single physical backhaul network for reducing backhaul expenses. In addition, it supports an
efficient backhaul operation by providing a “per-technology” sectional network operation by logically
separating the bac khaul, minimizi ng tr affic interference between different technologies.
About Smart M BS
Smart MBS is basestation of Samsung Multi-Modal System that will provide BTS,
RAS, and eNB whi ch wil l respectively serve the functionality of CDMA, and LTE.
It is controlled by its respe ctive uppe r NE (BSC for CD M A, EPC for LTE) to
handle CDMA/LTE calls. For detailed description of function and structure of
1-2 © SAMSUNG Electr onics Co., Ltd.

Smart MBS System Description
Smart MBS CDMA/LTE, please refe r to Chapter 2,3,4 of this document. For the
function and struc ture of S m a rt MBS , please refer to the additional document.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-3
Samsung Multi-ModalSystem Abstract
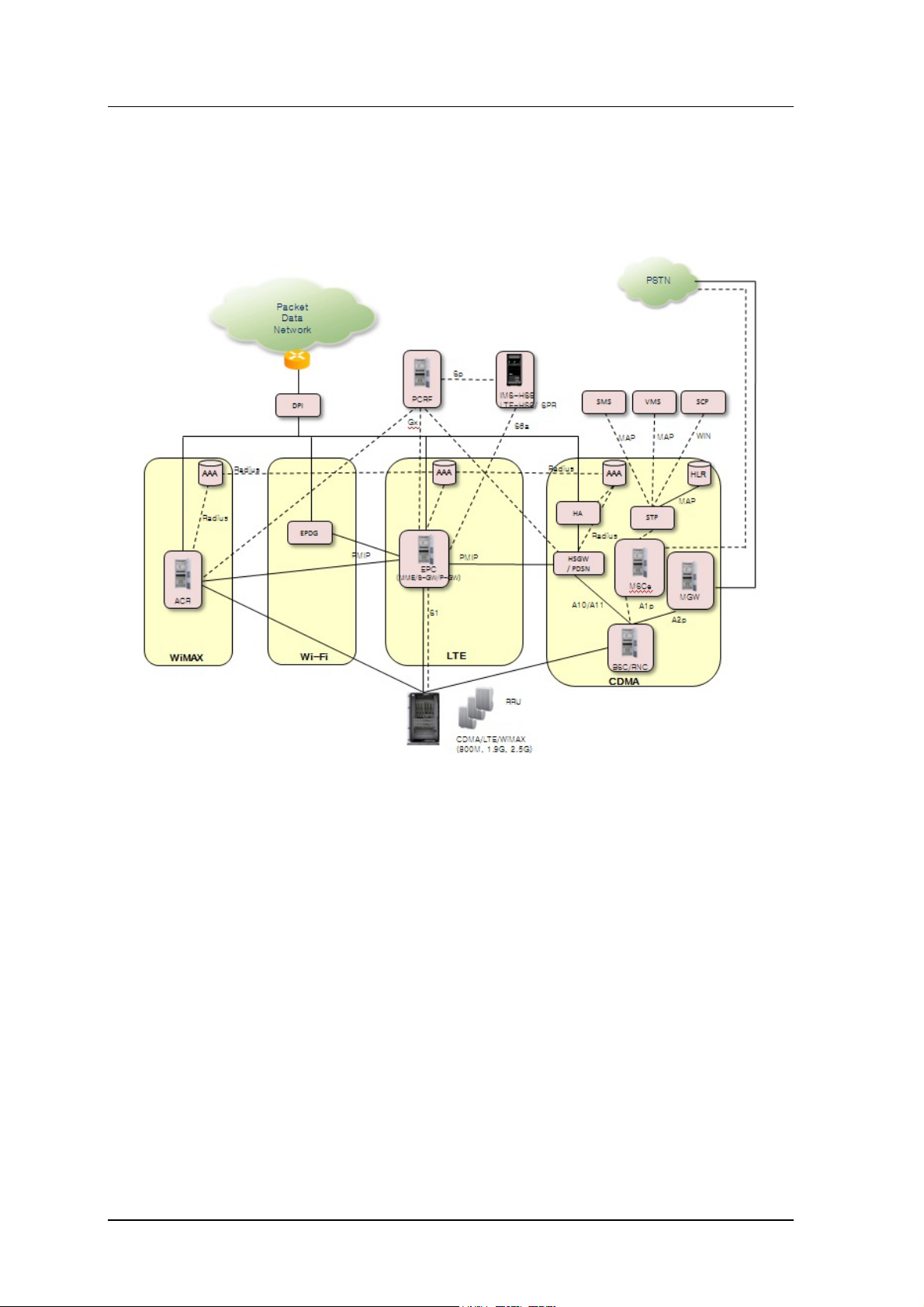
1.2 Sam sung M ulti-Modal System N etwor k A rchi te cture
Samsung Multi-Modal System is configured as shown in following Figure 1.2.
Figure 1.2 Samsung Multi-modal Network Architecture
As shown in Figure 1.2, Smart MBS system pla ys a r ole a s C DMA/ LTE basestati on in a Sa m sung MultiModal System network where CDMA and LTE systems co-exist.
When operat ing as CDMA, Smart MBS communica tes with BSC(CDMA cont r oll er ), and op er at or m ay
use BSM(EMS of CDMA) to contr ol and manage CDMA port ion of Smart MBS.. When operating as
LTE, it c ommunicates with EPC, and o p erator may use LSM -R(EMS or LTE) to co ntrol and manage LTE
portion of Smart MBS.
Follow ing netwo rk structure describes the type of each technology supported by Smart MBS.
1-4 © SAMSUNG Electr onics Co., Ltd.
Smart MBS System Description
Proprietary
Proprietary
1.2.1 CDMA System Network Architecture
CDMA system network of “Samsung Multi-Modal System” consists of AN(Access Networks) for
terminal access, VCN(Voice Core Network) for voice service, and PCN(Packet Core Network) for packet
data service.
AN consists of BTS, BSC( BTS cont roll er ), IP Network, Transport Network, and fina lly BSM to mana ge
these compo nents. AN communica tes with VCN(MGW, MSC/MSCe) and PC N(AN-AAA, PDSN) to
provide voice/data communication service to mobile subscribe rs.
MSCe
ESM
BSM
MGW
A2p
Proprietary
Proprietary
Smart MBS
IS2000,
IS856
UE UE
BSC
A1p
A12
,A10,A11
Smart MBS
AN-AAA
Internet
PDSN
Figure 1.3 CDMA Network Architecture of Samsung Multi-Modal System
CDMA Network Architecture of Samsung Multi-Modal System(where Smart MBS is operated as CDMA
BTS) is shown in Figure 1.3. Follow ing describes the feature per each CDMA network devices.
BTS (Base Transceiver Station)
BTS(CDMA Basestation) is a system that handles wireless interface with mobile terminals in accordance
with CDMA2000 1X and 1xEV-DO standards. It receives data from mobile terminal and forwards it to
Core network through BSC, and receives data from Core via BSC and forwards it to mobile terminal. In
order to play a role as wireless transceiver, BS manages RF resources such as CA(Carrier Allocation),
Walsh. Also, it supports RF(Radio Frequ ency) Scheduling and Pow er Control Functional i ty.
BSC (Base S tation Controll er)
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-5

Samsung Multi-ModalSystem Abstract
Through various backhaul interfaces, BSC coordinates with multiple BTS, and provides resources that
are required for communicating with BTS. BSC communicates with VCN to process “Voice/Circuit Data
Calls”, and coordinates with PCN to process “Packet Data Calls”. Also, it carries out
operation/maintenance function in conjunction with BSM. It executes RLP(Radio Link Protocol) and
SDU(Se lection and Dis tribution Unit) function that Hand-Off will be av ailable for mo bile termi nals.
BSC also has PCF/(SC/MM) feature that “session control and mobility management function” is
executed in 1xEV-DO network.
BSM (BSS System Manager)
BSM provides “operator interface” that operators can control and manage BCS and BTS. For
Operation/Maintenance of BSC and BTS, BSM provides required commands such as
“alarm/status/performance display”, “Configuration Management”, and “Parameter Control” of the
system.
PDSN (Packet Data S erving Node) System
PDSN is a system which connects PCN to CDMA2000 1X (or 1xEV-DO), and it
enables/maintains/disables the PPP to mobile terminal. PDSN particularly carries out functionality as
FA(Fo reig n Age nt) for HA (Ho me Agent) t o provide mobile IP service.
AN-AAA (Acce ss Network-Authori zation, Authentication and Accounting)
AN-AAA is a server that performs authentication for subscribers in CDMA2000 1xEV-DO network. ANAAA executes authentication based on NAI(Network Access Identifier), and manages the “mapping
data” of IMSI and terminal NAI.
MSC (Mobile service Switching Center)/MS Ce (MSC emulator)
MSC(e) is a system component which provides “switching” role in CDMA2000 network. It provides
additional s ervice s by connecting s u bscrib ers to additional equip ments or other netw ork(PSTN )
MGW (Medi a Gateway)
MGW is an equipment that provides “bearer gateway functionality” (Media conversion and handling) in
a CDMA 2000 network. MGW exchanges PCM data(which is based on TDM) with PSTN, and
exchang es voi c e f rame(which i s based on IP) w i t h BS C.
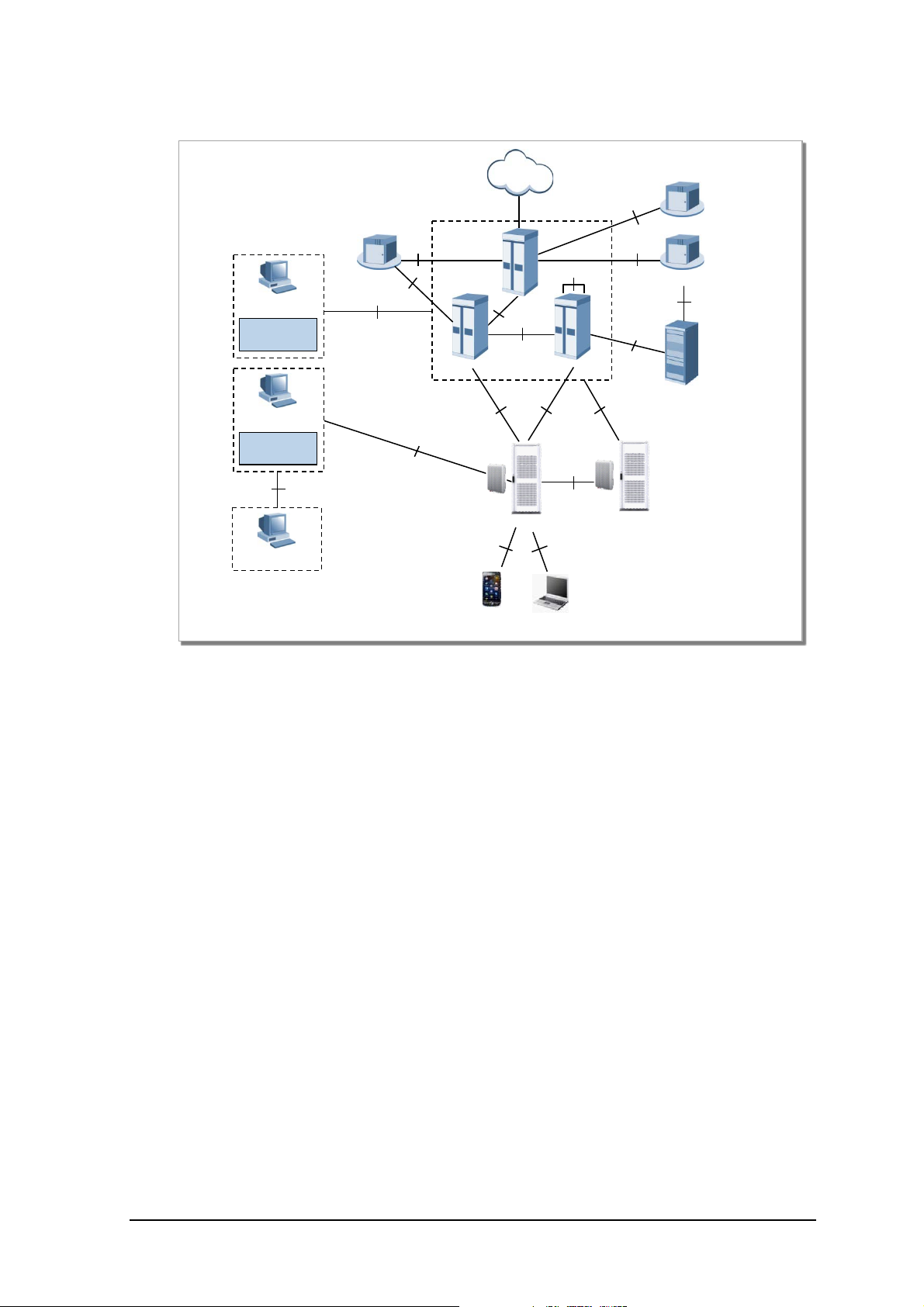
1.2.2 LTE System Network Structu re
LTE network of Samsung Multi-Modal System incorporates Basestation(eNB), packet core(EPC), and
LSM/(MSS). The system consists of multiple basestatio ns(eNB: Evolved UTRAN Node-B) and Gateway
(EPC: Evolved Packet Core, MME, S-GW/P-GW), and provides functionality for UE to connect to
ext e rnal netw o rk .
In addition, LTE system provides LTE System Manager(LSM) and Self-Optimization Server Feature for
Operation/Maintenance of Basestation(eNB).
1-6 © SAMSUNG Electr onics Co., Ltd.
Smart MBS System Description
EMS
LSM-C
EPC
P -GW
O CS
P CRF
CG
P DN
HSS/SPR
MMES -GW
TL1
SN MP/F TP/U DP
X2-C
X2-U
S1
S1MME
S1-U
Gz
Gz
S5/S8
S11
S10
Gy
Gx
Sp
S6a
EMS
LSM-R
MSS
RMI
Smart MBS
Smart MBS
UE
UE
Uu
Figure 1.4 Samsung Multi-Mode System’s LTE Network Architecture
LTE network architecture of Samsung Multi-Modal System, where the Smart MBS is oper at ed as LTE’s
Basestation(eNB), is as shown in the Figure 1.4, and following features are available for each LTE
network equipment.
eNB (Evolved UTRAN Node-B)
LTE Basestation(eNB) is a system located between UE and EPC, and it handles the packet calls by
connecting to UE wirelessly in a ccordance wi th “LTE Air standard ”. eNB execut es vari ous func tions
including Tx/Rx of Wireless signal, Modulation/Demodulation of packet traffic, packet scheduling for
effi ci ent us e of RF res our ce s, HARQ (H ybr id A ut oma ti c Repe a t Reque st) and ARQ (Automati c Repea t
Reque st) p roces s, PDC P(Packe t Data C onvergenc e Pr otoc ol) of c ompr essed p acke t hea der, and wir eles s
resourc e control. Also , it s ynchronizes w ith EPC to e xecute Handov er.
EPC (Evolved Pack et Core)
EPC is a system between Basestation(eNB) and PDN. It incorporates MME(Mobility Management
Entity) , S -GW (Serving Gateway), and PDN Gateway(P-GW).
MME handles control message via basestation(eNB) and NAS signaling protocol, and management of
mobility for terminal, manageme nt of Tracki ng Are a List, bearer and session management.
S-GW pla ys role as “anc hor” on s ubscriber plane bet ween 2G, 3G Access s ystem, and LTE system . It
manages/modifies packet transmit laye r of downlink/uplink data .
P-GW allocat e s I P Address to UE, plays role as “anchor” for mobility between “LTE System” and “non3GPP Access Systems”, manages billing charges for different service levels, and handles
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-7

Samsung Multi-ModalSystem Abstract
management /modific ation of the throughput r ate .
LSM (LTE System Manager)
LSM provides a synchronized interface for operat or that O peration/ Maint enance ca n be perfor med for
Basestaion(eNB) by operator. It also provides Software management, configuration management,
performance management, and alarm management features.
HSS(Home Subscriber Server)
HSS is a database management system that stores the parameter and geographical data of entire
subscribers. HSS manages important data including access availability, basic service, and additional
service of the subscriber. It also performs “Rooting Feature” for subscribers receiving calls.
MSS(Master SON Server)
MSS is a hi gher node of Local SON server. It synchronizes with Local SON Server to optimize the
synchronization in regards to Multi-LSM. MSS is a function that is compatible with the operator OSS,
and the av ailability of this f u nc tion will b e decide d after discus s io n w ith operator.
PCRF(Policy Ch ar ging & Rule Function)
PCRF may generate policy rule in order to apply “QoS/Billing Policies per each Service Flow”
dynamically. Or it may generate Policy rule tha t is applied uniformly to multiple Service Flow.
Since I P ed ge contains PCEF(Policy and Charging Enforcement Function), Policy Rules(received from
PCRF) can be applied per each Service Flow.
OCS (Online Charging System)
If subscribers (with Online Billing information) makes call, subscriber’s billing information is
sent/received.
CG (Chargi ng Gateway)
Sto re s the g enerated billing data, and pro vides b illing data pe r each subs criber.
1-8 © SAMSUNG Electr onics Co., Ltd.
Smart MBS System Description
Abis
BSC
BTS
MAC
PHY
IP Packet Forwarding
Packet Classification
HARQ
L3
Voice Handler
SUA Handler
AN-AAA Client
SC/MM
A11 Handler
A10 Handler
RLP Handler
1XVoice
1xEV-DO
Paging Controller
IP Packet Forwarding
Packet Classification
ARQ
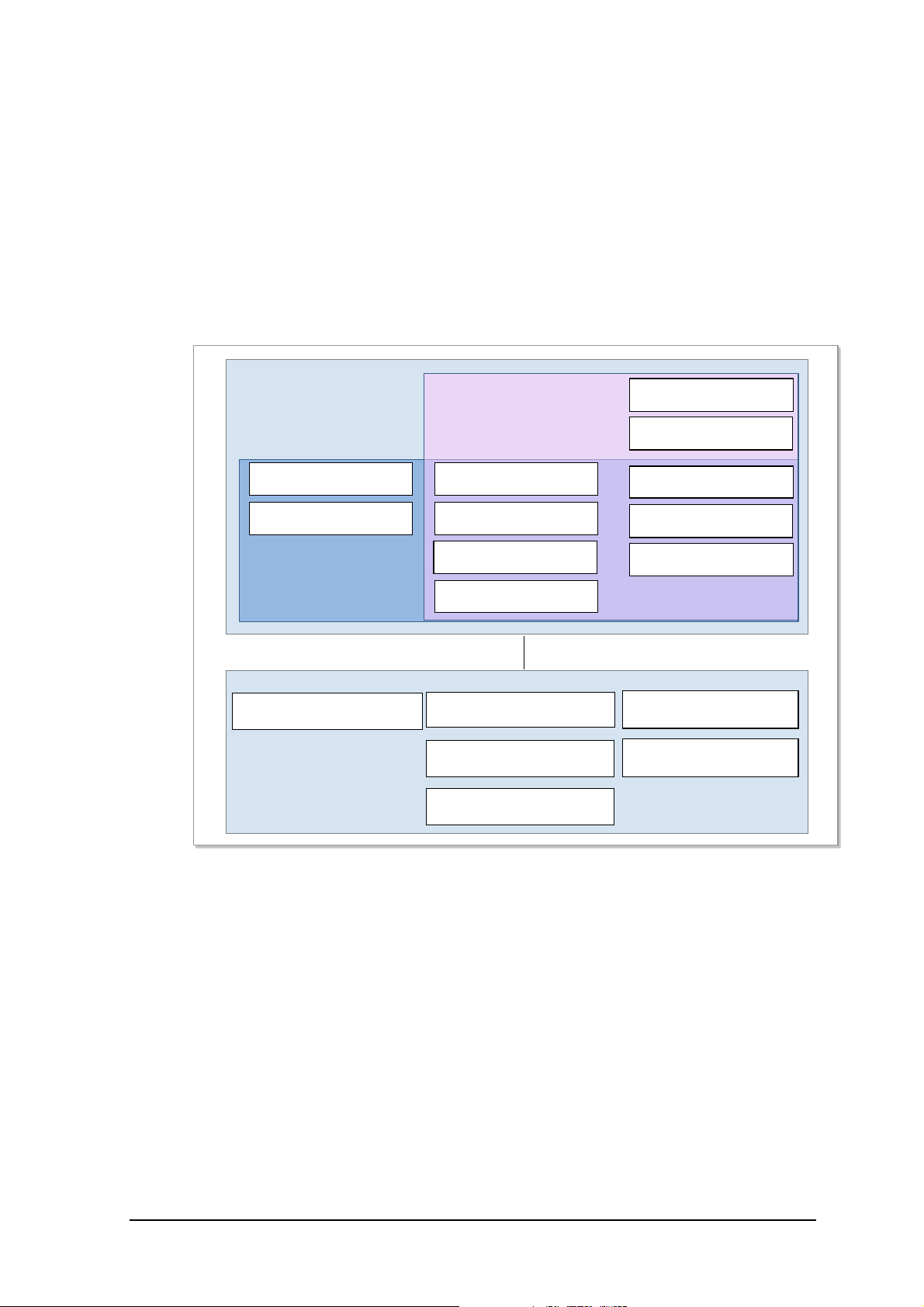
1.3 Samsung Mul ti -Modal System Feature
Following is the feature supported by each mobile tec hnology of Samsung Multi-Modal System.
1.3.1 CDMA System Feature
Following Figure shows CDMA system(BSC, BTS)ba s e d on 1X/1xEV-DO.
Figure 1.5 CDMA System Fu nc tional Struc ture
BSC works with voice cor e equipments (MSCe, MGW) to manage signaling and bearer process for voice
servic e. In BSC, SUA Hand ler is res pons i bl e for Al p si gna ling with MSC e, and Voice Handl er sends the
voice bearer traffic to MGW. In addition, it works with PDSN for 1X data and 1xEV-DO data service.
A10 Hand ler mana ges the bear er tr affi c of such data 1X Da ta and 1xEV-DO Data ser vice. A 11 Handl er
manages signaling for data service. RLP Handler manages ARQ feature for data communication.
For Authentication of 1xEV-DO terminal, AN-AAA client is responsible for synchronization with ANAAA. SC /M M executes s es sion control a nd mob ility management for 1xEV-DO.
BTS is respons i ble for Radi o Re s ource Control and terminal co mmu ni cation. Through CAI( Com m on A ir
Interface), it provides featur es such as high speed data service, mul timedia service, new hand off, in
accordance with standards defined in 3GPP2 C.S0024-0_v4.0, 3GPP2 C.S0024-A_v3.0, and 3GPP2
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-9
C.S0024-B_v3.0, 3GPP2 C.S0063-B_v1.0
Samsung Multi-ModalSystem Abstract
S1
EPC
eNB(E-UTRAN)
RRC
PDCP
RLC
MAC
PHY
MME
NAS Security
Idle State Mobility
Handling
EPS Bearer Control
S-GW
Mobility Anchoring
P-GW
UE IP address
allocation
Packet Filtering
Inter Cell RRM
RB Control
Connection Mobility Control
Radio Admission Control
eNB Measurement Configuration & Provision
Dynamic Resource Allocation (Scheduler)
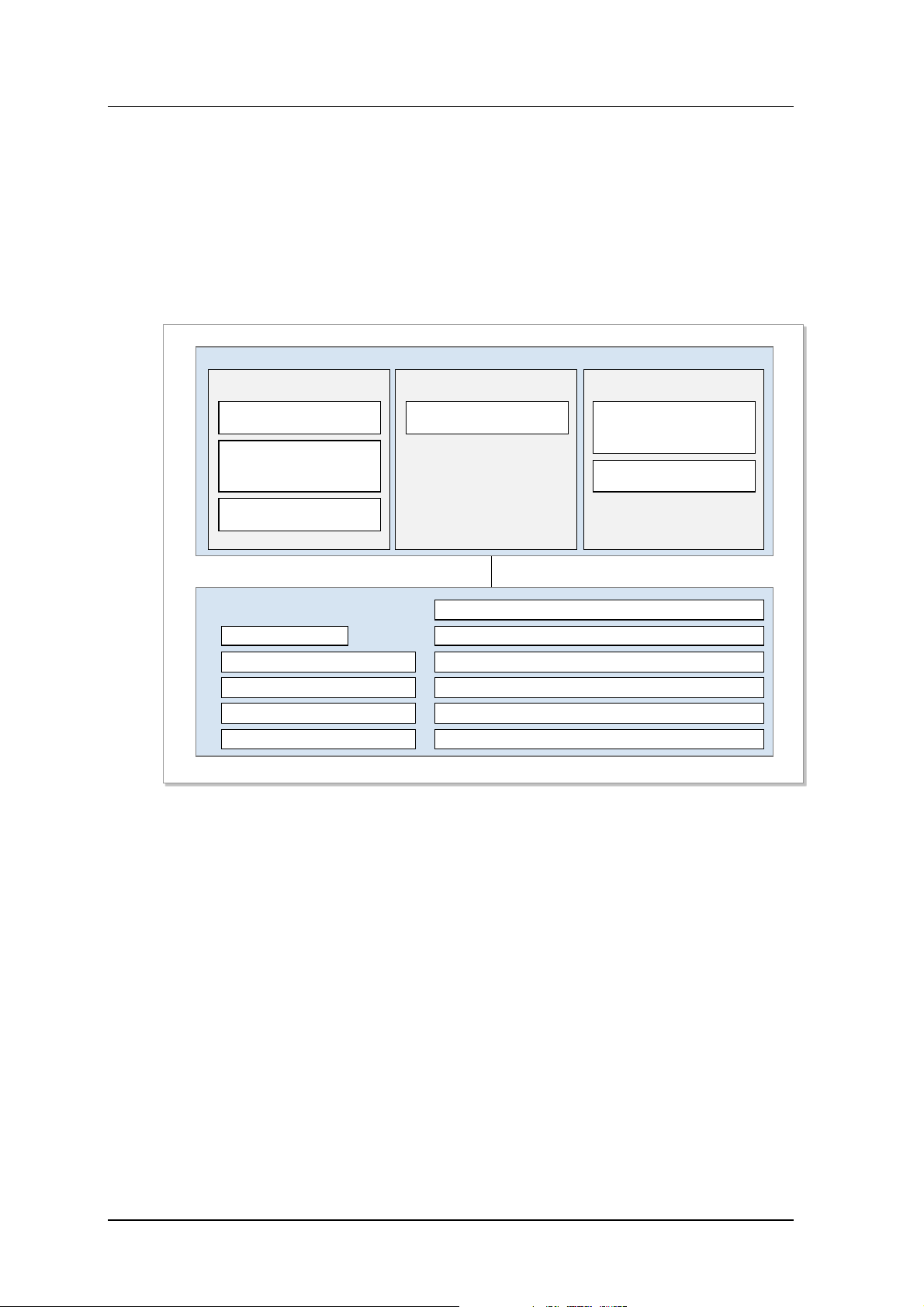
1.3.2
LTE Sys tem Feature
Following Figure shows functional separation between eNB, MME, S-GW, P-GW of E-UTRAN in
accordance with 3GPP standard. Generally, eNB manages “Connected mode” at AS(Access Stratum)
level. MME manages Idle mode terminals in NAS(Non-Access Stratum) level. Both S-GW and P -GW
performs “user data man a gem ent” and provide the “li nk to foreig n network”.
Follow ing dis p lays the functio nality of eNB, MME, S-GW, and P-GW.
1-10 © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.
Figure 1.6 Function of E-UTRAN and EPC
eNB
eNB manages E-UTRAN( Evo lve d U TRAN), the wireless access network of LTE system. Multiple eNB are
connected v ia X2 interface, and these eNB are connected to EPC(Evolved Packet Core) via S1 interface.
Wirele ss protocol la yer of eNB can be di vided int o Layer1 , Layer2, and Layer 3. Layer 3 contains RRC
layer, Layer 2 contains three layers(MAC layer(sublayer), RLC layer, PDCP layer) where each layer
execu tes an inde pendent pr ocess. RRC la yer belong s to layer 3 of the wir eless pr otocol. Gene rally, RRC
Layer is responsible for maintenanc e and control of RB(Radio Bea rer), RRC c onnectivi ty, and Exchange of
System Data. Meanwhi l e, PDCP layer is responsible for head er compressi on of IP packet, security featur es
like “cipherin g/integrity check”, and “selecti ve transmission feature” which can increase the efficiency of
“radio resource”
RLC Layer is resp onsible a ) for segmentation and reassem bly at MAC Layer for data which was received
from PDCP layer; b) of restoring the tx failure(at lower level) via retransmission (ARQ); and c) of
reordering which can be caused because by (HARQ in MAC layer)
For ea ch bearer, MAC Layer distributes RF resour ces according to priorit y, multiplexes the dat a received

Smart MBS System Description
from various “Upper Logical Channels”, and performs HARQ(Hybrid ARQ).
MME(Mobility Management Entity)
MME works in conjunc tion with E-UTRAN( eNB) t o hand le “S1-AP signaling messag e”(of SCTP base;
used to control connecti on between MME and eNB) AND “NAS Signaling message” (of SCTP base; used
to control mobility and connection between terminal and EPC.) In addition, it works in conjunction with
HSS to obtain subscriber information, modification, and authentication. It can work in conjuncti on with SGW, as utilizing GTP-C prot ocol, to all ocate bear er path ( for data routing and forwar ding, rel ease, and
modification)
It can also work in conj unction wit h SGSN(of 2G, 3G) and M SC to provide Mobility, HO, CS fa llback, and
SMS service.
MME can handle mobility, idle mode UE reachability, TA list management, P-GW/S-GW selection,
authentication, and bearer management.
MME supports mobility for handover between eNB, and supports handover between MME. Also, SGSN
selectio n is sup ported when it hands over to 2G, 3G, or 3GPP ne t work.
S-GW(S erv i ng Gat eway)
S-GW plays role as mobilit y anchor when handover is execut ed between eNB, and 3GPP. As a supported
function, packet data is “Routed”, “Forward ed”. Billin g Policy can be configured differently per each of
UE, PDN, and QCN. It can manage and modify the “packet transport layer” of the uplink/datalink data.
In addi tion, S-GW supports GTP and PMIP protocol in conjunction with MME, P-GW, and SGSN.
P-GW(PDN Gateway)
P-GW can execute Billing/Bear er policy in conj unc ti on wit h PCRF, and per it s pol i cy. Billin g, QoS , can be
managed/modified per service level. P-GW provides Packet filtering feature per each subscriber, and
allocates IP address to each UE. P-GW can manage/modify packet transport layer of the downlink Data.
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 1-11
Samsung Multi-ModalSystem Abstract
This page is intentionally left blank.
1-12 © SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd.

Smart MBS System Description
Chapter 2. Smart MBS Abstract
2.1 Smart MBS System Description
Smart M BS is the Bas es ta ti on of Sam sun g Mult i-Modal System. It is managed by packet core (either BSC,
ACR, or EPC), and makes call to terminal to create CDMA /LTE links.
Smart MBS interfaces with UE via either CDMA(3GPP2 CDMA2000 1X Advanced and 1xEV-DO
Rev.0/Rev.A (20110408)), LTE(3GPP LTE Rel.8/9). It provides broadband high speed data service and
multimedia services.
In order to implement this, Smart MBS can perform Modulation/Demodulation (for voice or packet
traffic), assign S cheduling and Wireless Ba ndwidth (for effici ent use of RF r esources a nd to guar antee
QoS), handle ARQ(Automatic Repeat request), perform ranging feature, provide connection control
feature (for sending Smart MBS information and enable/maintain/disable the call), Synchronize
BSC/A CR /EPC, prov ides Power Co ntrol, and e xecutes system ope ratio n manageme nt.
By Fast Ethernet/Gigabit Ethernet backhaul, Smart MBS syn chronize the control station to transceive
reliable control sig nal and traffic signal.
Smart MBS is separated into UADU(Universal Platform Digital Unit, an indoor DU) and the
RRH(Remot e Rad io Hea d, a c ombine d RF uni t). UADU is mounted in the outdoor DU cabinet(along
with the re ctifier) to support outdoor e nv ironment.
UADU is a digital component for 19” shelf. It can be mounted onto either indoor or outdoor 19 inch
commer cial ra ck, and one UAD U can provide the following maximum capacity. Based on operator’s
setup, it can be operated as omni type or sector type.
- CDMA 1X / EVDO : Max 4Carrier/3Sector
- L TE (FDD) : Max 1Carrier/3Sector
RRH is RF component that is built into a single module. It can be mounted o nto Walls, Poles, or Stands
in outdoor environments.
Depending on Frequency bandwidth and duplexing ty pe, RRH can be c lassified into follow ing types.
- RRH-C2A: 800MHz Cellular band, 2Tx/2Rx RF path
© SAMSUNG Electronics Co., Ltd. 2-1

Smart MBS Abstract
Smart MBS has other features provided as below.
Common Pl atform DU/RRH
Digital boards of each wireless technology, to be mounted in Smart MBS, share the common DU
platform. Therefore, different boards(for multiple technology) may be mounted in a single DU, and
operator can mount up to 4 D U in ou td oor DU cabinet to implement va rious configuration.
RRH of Smart MBS can simultaneously support multiple technologies in the same duplexing type with
the same b andwidth.
RRH(Remote Radio Head) separated fr om DU(Dig ital Unit)
In order to provi de ea se of ins ta llati on and vari ous network st ructure, Smar t MBS has separated RRH
from DU. Between RRH and DU, a fiber optic ‘Baseband I/Q and C&M’ interface, based on
CPRI( Comm on Publi c Radi o Inter face ), is used t o send/recei ve “dat a tra ffic signal” an d “OAM data”. DU
and RRH gets -48VDC f rom rectifier inside the outdoo r DU cabinet.
Provide Easy Installation
RRH integrates optic-sync component and RF signal processor, and is a small & light weight single
module. RRH can be mounted onto Walls, Poles, or Stands. In addition, distance between RRH and
Ant enna i s mini m iz ed th at RF si gna l l oss( ca used b y Feeder Line ) i s d ecr eas ed. The r efor e, i t can pr ovid e
improved RF pe rformance whe n compared to Basestation that has Digital Unit and RF Unit alto g ether .
Natural Cooling Mechanism
RRH(Remote Radio Head) may be installed in outdoor environment, and its thermal-dynamic design
efficiently dissipates heat without requirement of additional cooling mechanism. Also, no maintenance cost
is required for RRH cooling.
Feature for Loop-Back Test of the line betw een DU and R RH
In order to check functionality of the “Base-band I/Q and OAM interface” between DU and RRH, Smart
MBS provides Loop-back Test.
Provides Rem ote Fir mware D ownloading
RRH may be rep laced with firmware to enhance service and upgrade new featu res. At this time, Sit e vi sit
is not required as firmware can be downloaded from basestation operation server (such as
BSM/WSM/LSM-R). Ther efore, ope ra tor can m inimiz e the si te visit, redu ce the ma intenanc e cost, and
easily operate the system.
Provides Monit or ing P or t.
Through debug port of RRH, operator c an monitor t he information abo ut the u nit.
Support for Smooth Migration
Smart MB S can provide migration f rom CDMA to 4 G LTE )wireless telecommunication by either adding
2-2 © SAMSUNG Electr onics Co., Ltd.
 Loading...
Loading...