
24-S3-C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249-032004
USER'S MANUAL
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
8-Bit CMOS
Microcontrollers
Revision 4
NOTIFICATION OF REVISIONS
ORIGINATOR: Samsung Electronics, LSI Development Group, Ki-Heung, South Korea
PRODUCT NAME: S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 8-bit CMOS Microcontroller
DOCUMENT NAME: S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 User's Manual, Revision 4
DOCUMENT NUMBER: 24-S3-C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249-032004
EFFECTIVE DATE: March, 2004
SUMMARY: As a result of additional product testing and evaluation, some specifications
published in the S3C8248/C8245/P8245/C8247/C8249/P8249 User's Manual,
Revision 3, have been changed. These changes for S3C8248/C8245/P8245
/C8247/C8249/P8249 microcontroller, which are described in detail in the
Revision Descriptions section below, are related to the
followings:
— S3C8248/C8247 moved.
— Chapter 1. Features
— Chapter 19. Electrical Data
DIRECTIONS: Please note the changes in your copy (copies) of the S3C8248/C8245/P8245/
C8247/C8249/P8249 User's Manual, Revision 3. Or, simply attach the Revision
Descriptions of the next page to S3C8248/C8245/P8245/C8247/C8249 /P8249
User's Manual, Revision 3.
REVISION HISTORY
Revision Date Remark
0 June, 1999 Preliminary Spec for internal release only.
1 September, 1999 First edition.
2 July, 2000 Second edition.
3 March, 2002 Third edition.
4 March, 2004 Fourth edition.
REVISION DESCRIPTIONS
1. DEVICE TYPE
The S3C8247/C8248 device type should be moved. Product name and document name should be changed into
'S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249'.
2. FEATURES
The Operating Temperature Range should be changed '-40°C to 85°C' into '-25°C to 85°C' in the page 1-2, from 19-2
to 19-12, and from 21-4 to 21-7.
3. ELECTRICAL DATA
Table 19-2. D.C. Electrical Characteristics (Concluded) (Page 19-4)
(TA = -25 °C to + 85 °C, VDD = 1.8 V to 5.5 V)
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Supply current
(1)
I
DD5
Main stop mode: sub-osc
stop VDD = 5 V ± 10 %,
TA = 25°C
– 1 3 µA
V
= 3V ± 10%, T
DD
= 25°C
A
0.5 2
Table 19-12. D.C. Electrical Characteristics (Concluded) (Page 19-12)
(TA = -25 °C to + 85 °C, VDD = 2.0 V to 5.5 V)
Oscillator Test Condition Min Typ Max Unit
Crystal VDD = 2.0 V to 5.5 V – – 40 ms
Ceramic Stabilization occurs when VDD is equal to the minimum
– – 4 ms
oscillator voltage range.
External clock XIN input high and low level width (tXH, tXL) 50 – 500 ns
Table 21-4. D.C. Electrical Characteristics (Continued) (Page 19-3, 21-5)
(T
= -25 °C to +85 °C, VDD = 1.8 V to 5.5 V)
A
Parameter Symbol Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Oscillator feed back
resistors
R
osc1
V
= 5.0 V T
DD
X
= V
IN
DD
, X
OUT
= 25 °C
A
= 0 V
300 600 1500 kΩ

S3C8245/P8245
/C8249/P8249
8-BIT CMOS
MICROCONTROLLER S
USER'S MANUAL
Revision 4

Important Notice
The information in this publication has been carefully
checked and is believed to be entirely accurate at the
time of publication. Samsung assumes no
responsibility, however, for possible errors or
omissions, or for any consequences resulting from
the use of the information contained herein.
Samsung reserves the right to make changes in its
products or product specifications with the intent to
improve function or design at any time and without
notice and is not required to update this
documentation to reflect such changes.
This publication does not convey to a purchaser of
semiconductor devices described herein any license
under the patent rights of Samsung or others.
Samsung makes no warranty, representation, or
guarantee regarding the suitability of its products for
any particular purpose, nor does Samsung assume
any liability arising out of the application or use of any
product or circuit and specifically disclaims any and
all liability, including without limitation any
consequential or incidental damages.
"Typical" parameters can and do vary in different
applications. All operating parameters, including
"Typicals" must be validated for each customer
application by the customer's technical experts.
Samsung products are not designed, intended, or
authorized for use as components in systems
intended for surgical implant into the body, for other
applications intended to support or sustain life, or for
any other application in which the failure of the
Samsung product could create a situation where
personal injury or death may occur.
Should the Buyer purchase or use a Samsung
product for any such unintended or unauthorized
application, the Buyer shall indemnify and hold
Samsung and its officers, employees, subsidiaries,
affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims,
costs, damages, expenses, and reasonable attorney
fees arising out of, either directly or indirectly, any
claim of personal injury or death that may be
associated with such unintended or unauthorized use,
even if such claim alleges that Samsung was
negligent regarding the design or manufacture of said
product.
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 8-Bit CMOS Microcontrollers
User's Manual, Revision 4
Publication Number: 24-S3-C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249-032004
© 2004 Samsung Electronics
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any
form or by any means, electric or mechanical, by photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without the prior written
consent of Samsung Electronics.
Samsung Electronics' microcontroller business has been awarded full ISO-14001
certification (BSI Certificate No. FM24653). All semiconductor products are
designed and manufactured in accordance with the highest quality standards and
objectives.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
San #24 Nongseo-Ri, Giheung- Eup
Yongin-City, Gyeonggi-Do, Korea
C.P.O. Box #37, Suwon 449-900
TEL: (82)-(031)-209-1934
FAX: (82)-(331)-209-1889
Home-Page URL: Http://www.samsungsemi.com
Printed in the Republic of Korea

Preface
The S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 Microcontroller User's Manual is designed for application designers and
programmers who are using the S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 microcontroller for application development. It is
organized in two main parts:
Part I Programming Model Part II Hardware Descriptions
Part I contains software-related information to familiarize you with the microcontroller's architecture, programming
model, instruction set, and interrupt structure. It has six chapters:
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Chapter 2 Address Spaces
Chapter 3 Addressing Modes
Chapter 1, "Product Overview," is a high-level introduction to S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 with general product
descriptions, as well as detailed information about individual pin characteristics and pin circuit types.
Chapter 2, "Address Spaces," describes program and data memory spaces, the internal register file, and register
addressing. Chapter 2 also describes working register addressing, as well as system stack and user-defined stack
operations.
Chapter 3, "Addressing Modes," contains detailed descriptions of the addressing modes that are supported by the
S3C8-series CPU.
Chapter 4, "Control Registers," contains overview tables for all mapped system and peripheral control register values,
as well as detailed one-page descriptions in a standardized format. You can use these easy-to-read, alphabetically
organized, register descriptions as a quick-reference source when writing programs.
Chapter 5, "Interrupt Structure," describes the S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 interrupt structure in detail and further
prepares you for additional information presented in the individual hardware module descriptions in Part II.
Chapter 6, "Instruction Set," describes the features and conventions of the instruction set used for all S3C8-series
microcontrollers. Several summary tables are presented for orientation and reference. Detailed descriptions of each
instruction are presented in a standard format. Each instruction description includes one or more practical examples
of how to use the instruction when writing an application program.
A basic familiarity with the information in Part I will help you to understand the hardware module descriptions in Part
II. If you are not yet familiar with the S3C8-series microcontroller family and are reading this manual for the first time,
we recommend that you first read Chapters 1–3 carefully. Then, briefly look over the detailed information in Chapters
4, 5, and 6. Later, you can reference the information in Part I as necessary.
Chapter 4 Control Registers
Chapter 5 Interrupt Structure
Chapter 6 Instruction Set
Part II "hardware Descriptions," has detailed information about specific hardware components of the
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 microcontroller. Also included in Part II are electrical, mechanical, OTP, and
development tools data. It has 16 chapters:
Chapter 7 Clock Circuit
Chapter 8 nRESET and Power-Down
Chapter 9 I/O Ports
Chapter 10 Basic Timer
Chapter 11 8-bit Timer A/B
Chapter 12 16-bit Timer 0/1
Chapter 13 Watch Timer
Chapter 14 LCD Controller/Driver
Two order forms are included at the back of this manual to facilitate customer order for S3C8245/P8245/
C8249/P8249 microcontrollers: the Mask ROM Order Form, and the Mask Option Selection Form. You can
photocopy these forms, fill them out, and then forward them to your local Samsung Sales Representative.
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER iii
Chapter 15 10-bit-to-Digital Converter
Chapter 16 Serial I/O Interface
Chapter 17 Voltage Booster
Chapter 18 Voltage Level Detector
Chapter 19 Electrical Data
Chapter 20 Mechanical Data
Chapter 21 S3P8245/P8249 OTP
Chapter 22 Development Tools


Table of Contents
Part I — Programming Model
Chapter 1 Product Overview
S3C8-Series Microcontrollers ...............................................................................................................1-1
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 Microcontroller .......................................................................................1-1
OTP ...................................................................................................................................................1-1
Features.............................................................................................................................................1-2
Block Diagram ....................................................................................................................................1-3
Pin Assignment ...................................................................................................................................1-4
Pin Descriptions..................................................................................................................................1-6
Pin Circuits .........................................................................................................................................1-7
Chapter 2 Address Spaces
Overview.............................................................................................................................................2-1
Program Memory (ROM)......................................................................................................................2-2
Register Architecture...........................................................................................................................2-3
Register Page Pointer (PP)..........................................................................................................2-5
Register Set 1.............................................................................................................................2-6
Register Set 2.............................................................................................................................2-6
Prime Register Space..................................................................................................................2-7
Working Registers.......................................................................................................................2-8
Using the Register Points.............................................................................................................2-9
Register Addressing ............................................................................................................................2-11
Common Working Register Area (C0H–CFH) .................................................................................2-13
4-bit Working Register Addressing................................................................................................2-14
8-bit Working Register Addressing................................................................................................2-16
System and User Stacks.....................................................................................................................2-18
Chapter 3 Addressing Modes
Overview.............................................................................................................................................3-1
Register Addressing Mode (R)..............................................................................................................3-2
Indirect Register Addressing Mode (IR) ..................................................................................................3-3
Indexed Addressing Mode (X) ...............................................................................................................3-7
Direct Address Mode (DA)....................................................................................................................3-10
Indirect Address Mode (IA) ...................................................................................................................3-12
Relative Address Mode (RA).................................................................................................................3-13
Immediate Mode (IM)...........................................................................................................................3-14
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER v

Table of Contents (Continued)
Chapter 4 Control Registers
Overview.............................................................................................................................................4-1
Chapter 5 Interrupt Structure
Overview.............................................................................................................................................5-1
Interrupt Types ............................................................................................................................5-2
S3C8245/C8249 Interrupt Structure...............................................................................................5-3
Interrupt Vector Addresses...........................................................................................................5-4
Enable/Disable Interrupt Instructions (EI, DI) ..................................................................................5-6
System-Level Interrupt Control Registers .......................................................................................5-6
Interrupt Processing Control Points...............................................................................................5-7
Peripheral Interrupt Control Registers ............................................................................................5-8
System Mode Register (SYM)......................................................................................................5-9
Interrupt Mask Register (IMR).......................................................................................................5-10
Interrupt Priority Register (IPR) .....................................................................................................5-11
Interrupt Request Register (IRQ) ...................................................................................................5-13
Interrupt Pending Function Types..................................................................................................5-14
Interrupt Source Polling Sequence................................................................................................5-15
Interrupt Service Routines .............................................................................................................5-15
Generating Interrupt Vector Addresses ..........................................................................................5-16
Nesting Of Vectored Interrupts ......................................................................................................5-16
Instruction Pointer (IP).................................................................................................................5-16
Fast Interrupt Processing.............................................................................................................5-16
Chapter 6 Instruction Set
Overview.............................................................................................................................................6-1
Data Types .................................................................................................................................6-1
Register Addressing ....................................................................................................................6-1
Addressing Modes .......................................................................................................................6-1
Flags Register (Flags)..................................................................................................................6-6
Flag Descriptions ........................................................................................................................6-7
Instruction Set Notation................................................................................................................6-8
Condition Codes..........................................................................................................................6-12
Instruction Descriptions ................................................................................................................6-13
vi S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER

Table of Contents (Continued)
Part II Hardware Descriptions
Chapter 7 Clock Circuit
Overview.............................................................................................................................................7-1
System Clock Circuit ...................................................................................................................7-1
Clock Status During Power-Down Modes.......................................................................................7-2
System Clock Control Register (CLKCON).....................................................................................7-3
Chapter 8 nRESET and Power-Down
System nRESET.................................................................................................................................8-1
Overview.....................................................................................................................................8-1
Normal Mode Reset Operation ......................................................................................................8-1
Hardware Reset Values ................................................................................................................8-2
Power-Down Modes.............................................................................................................................8-5
Stop Mode ..................................................................................................................................8-5
Idle Mode....................................................................................................................................8-6
Chapter 9 I/O Ports
Overview.............................................................................................................................................9-1
Port Data Registers .....................................................................................................................9-2
Port 0.........................................................................................................................................9-3
Port 1.........................................................................................................................................9-6
Port 2.........................................................................................................................................9-8
Port 3.........................................................................................................................................9-10
Port 4.........................................................................................................................................9-12
Port 5.........................................................................................................................................9-14
Chapter 10 Basic Timer
Overview.............................................................................................................................................10-1
Basic Timer (BT) .............................................................................................................................10-1
Basic Timer Control Register (BTCON)..............................................................................................10-1
Basic Timer Function Description......................................................................................................10-3
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER vii

Table of Contents (Continued)
Chapter 11 8-bit Timer A/B
8-Bit Timer A.......................................................................................................................................11-1
Overview.....................................................................................................................................11-1
Function Description ....................................................................................................................11-2
Timer A Control Register (TACON)................................................................................................11-3
Block Diagram ............................................................................................................................11-4
8-Bit Timer B.......................................................................................................................................11-5
Overview.....................................................................................................................................11-5
Timer B Pulse Width Calculations.................................................................................................11-7
Chapter 12 16-bit Timer 0/1
16-Bit Timer 0.....................................................................................................................................12-1
Overview.....................................................................................................................................12-1
Function Description ....................................................................................................................12-1
Timer 0 Control Register (T0CON).................................................................................................12-2
Block Diagram ............................................................................................................................12-3
16-Bit Timer 1.....................................................................................................................................12-5
Overview.....................................................................................................................................12-5
Function Description ....................................................................................................................12-6
Timer 1 Control Register (T1CON).................................................................................................12-7
Block Diagram ............................................................................................................................12-8
Chapter 13 Watch Timer
Overview.............................................................................................................................................13-1
Watch Timer Control Register (WTCON: R/W)...............................................................................13-2
Watch Timer Circuit Diagram ........................................................................................................13-3
Chapter 14 LCD Controller/Driver
Overview.............................................................................................................................................14-1
LCD Circuit Diagram....................................................................................................................14-2
LCD RAM Address Area ..............................................................................................................14-3
LCD Control Register (LCON), D0H...............................................................................................14-4
LCD Mode Register (LMOD).........................................................................................................14-5
LCD Drive Voltage .......................................................................................................................14-7
LCD SEG/SEG Signals................................................................................................................14-7
LCD Voltage Driving Method.........................................................................................................14-12
viii S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER

Table of Contents (Continued)
Chapter 15 10-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter
Overview.............................................................................................................................................15-1
Function Description ............................................................................................................................15-1
Conversion Timing .......................................................................................................................15-2
A/D Converter Control Register (ADCON) .......................................................................................15-2
Internal Reference Voltage Levels..................................................................................................15-3
Block Diagram ....................................................................................................................................15-4
Chapter 16 Serial I/O Interface
Overview.............................................................................................................................................16-1
Programming Procedure...............................................................................................................16-1
SIO Control Register (SIOCON) ....................................................................................................16-2
SIO Pre-Scaler Register (SIOPS)..................................................................................................16-3
Block Diagram ....................................................................................................................................16-3
Serial I/O Timing Diagram.............................................................................................................16-4
Chapter 17 Voltage Booster
Overview.............................................................................................................................................17-1
Function Description ............................................................................................................................17-1
Block Diagram ....................................................................................................................................17-2
Chapter 18 Voltage Level Detector
Overview.............................................................................................................................................18-1
Voltage Level Detector Control Register (VLDCON).........................................................................18-2
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER ix

Table of Contents (Concluded)
Chapter 19 Electrical Data
Overview.............................................................................................................................................19-1
Chapter 20 Mechanic al Data
Overview.............................................................................................................................................20-1
Chapter 21 S3P8245/P8249 OTP
Overview.............................................................................................................................................21-1
Operating Mode Characteristics ....................................................................................................21-4
Chapter 22 Development Tools
Overview.............................................................................................................................................22-1
SHINE........................................................................................................................................22-1
SAMA Assembler........................................................................................................................22-1
SASM88.....................................................................................................................................22-1
HEX2ROM..................................................................................................................................22-1
Target Boards .............................................................................................................................22-1
TB8245/8249 Target Board...........................................................................................................22-3
SMDS2+ Selection (SAM8) ..........................................................................................................22-5
IDLE LED...................................................................................................................................22-5
STOP LED..................................................................................................................................22-5
x S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER

List of Figures
Figure Title Page
Number Number
1-1 S3C8245/C8249 Block Diagram ............................................................................1-3
1-2 S3C8245/C8249 Pin Assignment (80-QFP-1420C)..................................................1-4
1-3 S3C8245/C8249 Pin Assignment (80-TQFP-1212)..................................................1-5
1-4 Pin Circuit Type B (nRESET)................................................................................1-8
1-5 Pin Circuit Type C...............................................................................................1-8
1-6 Pin Circuit Type D-2 (P3)......................................................................................1-8
1-7 Pin Circuit Type D-4 (P0)......................................................................................1-8
1-8 Pin Circuit Type E-2 (P1)......................................................................................1-9
1-9 Pin Circuit Type F-10 (P2.0–P2.6) .........................................................................1-9
1-10 Pin Circuit Type F-18 (P2.7/VLD
1-11 Pin Circuit Type H (SEG/COM) .............................................................................1-9
1-12 Pin Circuit Type H-4.............................................................................................1-10
1-13 Pin Circuit Type H-14 (P4, P5) ..............................................................................1-10
2-1 Program Memory Address Space.........................................................................2-2
2-2 Internal Register File Organization.........................................................................2-4
2-3 Register Page Pointer (PP)..................................................................................2-5
2-4 Set 1, Set 2, Prime Area Register, and LCD Data Register Map ..............................2-7
2-5 8-Byte Working Register Areas (Slices).................................................................2-8
2-6 Contiguous 16-Byte Working Register Block ..........................................................2-9
2-7 Non-Contiguous 16-Byte Working Register Block...................................................2-10
2-8 16-Bit Register Pair .............................................................................................2-11
2-9 Register File Addressing......................................................................................2-12
2-10 Common Working Register Area ...........................................................................2-13
2-11 4-Bit Working Register Addressing........................................................................2-15
2-12 4-Bit Working Register Addressing Example ..........................................................2-15
2-13 8-Bit Working Register Addressing........................................................................2-16
2-14 8-Bit Working Register Addressing Example ..........................................................2-17
2-15 Stack Operations ................................................................................................2-18
) .....................................................................1-9
REF
3-1 Register Addressing ............................................................................................3-2
3-2 Working Register Addressing ...............................................................................3-2
3-3 Indirect Register Addressing to Register File ..........................................................3-3
3-4 Indirect Register Addressing to Program Memory ...................................................3-4
3-5 Indirect Working Register Addressing to Register File .............................................3-5
3-6 Indirect Working Register Addressing to Program or Data Memory ...........................3-6
3-7 Indexed Addressing to Register File......................................................................3-7
3-8 Indexed Addressing to Program or Data Memory with Short Offset...........................3-8
3-9 Indexed Addressing to Program or Data Memory....................................................3-9
3-10 Direct Addressing for Load Instructions..................................................................3-10
3-11 Direct Addressing for Call and Jump Instructions ....................................................3-11
3-12 Indirect Addressing ..............................................................................................3-12
3-13 Relative Addressing.............................................................................................3-13
3-14 Immediate Addressing .........................................................................................3-14
4-1 Register Description Format .................................................................................4-4
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER xi

List of Figures (Continued)
Figure Title Page
Number Number
5-1 S3C8-Series Interrupt Types.................................................................................5-2
5-2 S3C8245/C8249 Interrupt Structure.......................................................................5-3
5-3 ROM Vector Address Area ...................................................................................5-4
5-4 Interrupt Function Diagram ...................................................................................5-7
5-5 System Mode Register (SYM)..............................................................................5-9
5-6 Interrupt Mask Register (IMR)...............................................................................5-10
5-7 Interrupt Request Priority Groups ..........................................................................5-11
5-8 Interrupt Priority Register (IPR) .............................................................................5-12
5-9 Interrupt Request Register (IRQ) ...........................................................................5-13
6-1 System Flags Register (FLAGS)...........................................................................6-6
7-1 Main Oscillator Circuit (Crystal or Ceramic Oscillator) .............................................7-1
7-2 Main Oscillator Circuit (RC Oscillator) ...................................................................7-1
7-3 System Clock Circuit Diagram ..............................................................................7-2
7-4 System Clock Control Register (CLKCON).............................................................7-3
7-5 Oscillator Control Register (OSCCON)...................................................................7-4
7-6 STOP Control Register (STPCON) ........................................................................7-4
9-1 Port 0 High-Byte Control Register (P0CONH).........................................................9-4
9-2 Port 0 Low-Byte Control Register (P0CONL) ..........................................................9-4
9-3 Port 0 Interrupt Control Register (P0INT) ................................................................9-5
9-4 Port 0 Interrupt Pending Register (P0PND).............................................................9-5
9-5 Port 1 High-Byte Control Register (P1CONH).........................................................9-6
9-6 Port 1 Low-Byte Control Register (P1CONL) ..........................................................9-7
9-7 Port 1 Pull-up Control Register (P1PUP)................................................................9-7
9-8 Port 2 High-Byte Control Register (P2CONH).........................................................9-8
9-9 Port 2 Low-Byte Control Register (P2CONL) ..........................................................9-9
9-10 Port 3 High-Byte Control Register (P3CONH).........................................................9-10
9-11 Port 3 Low-Byte Control Register (P3CONL) ..........................................................9-11
9-12 Port 4 High-Byte Control Register (P4CONH).........................................................9-12
9-13 Port 4 Low-Byte Control Register (P4CONL) ..........................................................9-13
9-14 Port 5 High-Byte Control Register (P5CONH).........................................................9-14
9-15 Port 5 Low-Byte Control Register (P5CONL) ..........................................................9-15
xii S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER

List of Figures (Continued)
Page Title Page
Number Number
10-1 Basic Timer Control Register (BTCON)..................................................................10-2
10-2 Basic Timer Block Diagram..................................................................................10-4
11-1 Timer A Control Register (TACON)........................................................................11-3
11-2 Timer A Functional Block Diagram........................................................................11-4
11-3 Timer B Functional Block Diagram........................................................................11-5
11-4 Timer B Control Register (TBCON)........................................................................11-6
11-5 Timer B Data Register (TBDATAH/L).....................................................................11-6
11-6 Timer B Output Flip-Flop Waveforms in Repeat Mode .............................................11-8
12-1 Timer 0 Control Register (T0CON).........................................................................12-2
12-2 Timer 0 Functional Block Diagram.........................................................................12-3
12-3 Timer 0 Counter Register (T0CNTH/L) ....................................................................12-4
12-4 Timer 0 Data Register (T0DATAH/L)......................................................................12-4
12-5 Timer 1 Control Register (T1CON).........................................................................12-7
12-6 Timer 1 Functional Block Diagram.........................................................................12-8
12-7 Timer 1Counter Register (T1CNTH/L) .....................................................................12-9
12-8 Timer 1 Data Register (T1DATAH/L)......................................................................12-9
13-1 Watch Timer Circuit Diagram ................................................................................13-3
14-1 LCD Function Diagram.........................................................................................14-1
14-2 LCD Circuit Diagram............................................................................................14-2
14-3 LCD Display Data RAM Organization ....................................................................14-3
14-4 Select/No-Select Bias Signals in Static Display Mode............................................14-7
14-5 Select/No-Select Bias Signals in 1/2 Duty, 1/2 Bias Display Mode ..........................14-8
14-6 Select/No-Select Bias Signals in 1/3 Duty, 1/3 Bias Display Mode ..........................14-8
14-7 LCD Signal and Wave Forms Example in 1/2 Duty, 1/2 Bias Display Mode...............14-9
14-8 LCD Signals and Wave Forms Example in 1/3 Duty, 1/3 Bias Display Mode .............14-10
14-9 LCD Signals and Wave Forms Example in 1/4 Duty, 1/3 Bias Display Mode .............14-11
14-10 Voltage Dividing Resistor Circuit Diagram ..............................................................14-12
15-1 A/D Converter Control Register (ADCON) ...............................................................15-2
15-2 A/D Converter Data Register (ADDATAH/L) ............................................................15-3
15-3 A/D Converter Functional Block Diagram ...............................................................15-4
15-4 Recommended A/D Converter Circuit for Highest Absolute Accuracy........................15-5
16-1 Serial I/O Module Control Registers (SIOCON).......................................................16-2
16-2 SIO Pre-scale Registers (SIOPS)..........................................................................16-3
16-3 SIO Functional Block Diagram ..............................................................................16-3
16-4 Serial I/O Timing in Transmit/Receive Mode (Tx at falling, SIOCON. 4 = 0).................16-4
16-5 Serial I/O Timing in Transmit/Receive Mode (Tx at rising, SIOCON.4 = 1) .................16-4
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER xiii

List of Figures (Concluded)
Page Title Page
Number Number
17-1 Voltage Booster Block Diagram............................................................................17-2
17-2 Pin Connection Example ......................................................................................17-2
18-1 Block Diagram for Voltage Level Detect.................................................................18-1
18-2 Voltage Level Detect Circuit and Control Register...................................................18-2
19-1 Input Timing for External Interrupts (Ports 0)...........................................................19-6
19-2 Input Timing for nRESET ......................................................................................19-6
19-3 Stop Mode Release Timing Initiated by nRESET....................................................19-7
19-4 Stop Mode(main) Release Timing Initiated by Interrupts ..........................................19-8
19-5 Stop Mode(sub) Release Timing Initiated by Interrupts............................................19-8
19-6 Serial Data Transfer Timing...................................................................................19-11
19-7 Clock Timing Measurement at XIN.........................................................................19-13
19-8 Operating Voltage Range .....................................................................................19-14
20-1 Package Dimensions(80-QFP-1420C) ...................................................................20-1
20-2 Package Dimensions(80-TQFP-1212) ....................................................................20-2
21-1 S3P8245/P8249 Pin Assignments (80-QFP Package) ............................................21-2
21-2 Operating Voltage Range .....................................................................................21-7
22-1 SMDS Product Configuration (SMDS2+)................................................................22-2
22-2 TB8245/9 Target Board Configuration.....................................................................22-3
22-3 40-Pin Connectors (J101, J102) for TB8245/9 .........................................................22-6
22-4 S3E8240 Cables for 80-QFP Package ...................................................................22-6
xiv S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER

List of Tables
Table Title Page
Number Number
1-1 S3C8245/C8249 Pin Descriptions .........................................................................1-5
2-1 S3C8249/P8249 Register Type Summary ..............................................................2-3
2-2 S3C8245/P8245 Register Type Summary ..............................................................2-3
4-1 Set 1 Registers ...................................................................................................4-1
4-2 Set 1, Bank 0 Registers.......................................................................................4-2
4-3 Set 1, Bank 1 Registers.......................................................................................4-3
5-1 Interrupt Vectors ..................................................................................................5-5
5-2 Interrupt Control Register Overview........................................................................5-6
5-3 Interrupt Source Control and Data Registers ...........................................................5-8
6-1 Instruction Group Summary..................................................................................6-2
6-2 Flag Notation Conventions....................................................................................6-8
6-3 Instruction Set Symbols .......................................................................................6-8
6-4 Instruction Notation Conventions ...........................................................................6-9
6-5 Opcode Quick Reference.....................................................................................6-10
6-6 Condition Codes..................................................................................................6-12
8-1 S3C8245/C8249 Set 1 Register and Values after nRESET......................................8-2
8-2 S3C8245/C8249 Set 1, Bank 0 Register Values after nRESET................................8-3
8-3 S3C8245/C8249 Set 1, Bank 1 Register Values after nRESET................................8-4
9-1 S3C8245/C8249 Port Configuration Overview ..........................................................9-1
9-2 Port Data Register Summary................................................................................9-2
13-1 Watch Timer Control Register (WTCON): Set 1, Bank 1, FAH, R/W .........................13-2
14-1 LCD Control Register (LCON) Organization............................................................14-4
14-2 Relationship of LCON.0 and LMOD.3 Bit Settings ...................................................14-4
14-3 LCD Clock Signal (LCDCK) Frame Frequency ........................................................14-5
14-4 LCD Mode Control Register (LMOD) Organization, D1H ..........................................14-6
14-5 Maximum Number of Display Digits per Duty Cycle................................................14-6
14-6 LCD Drive Voltage Values ....................................................................................14-7
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER xv

List of Tables (Continued)
Table Title Page
Number Number
18-1 VLDCON Value and Detection Level ......................................................................18-2
19-1 Absolute Maximum Ratings ..................................................................................19-2
19-2 D.C. Electrical Characteristics ..............................................................................19-2
19-3 D.C Electrical Characteristics of S3C8245.............................................................19-5
19-4 A.C. Electrical Characteristics ..............................................................................19-6
19-5 Input/Output Capacitance.....................................................................................19-7
19-6 Data Retention Supply Voltage in Stop Mode .........................................................19-7
19-7 A/D Converter Electrical Characteristics ................................................................19-9
19-8 Voltage Booster Electrical Characteristics.............................................................19-10
19-9 Characteristics of Voltage Level Detect Circuit .......................................................19-10
19-10 Synchronous SIO Electrical Characteristics ...........................................................19-11
19-11 Main Oscillator Frequency (f
19-12 Main Oscillator Clock Stabilization Time (t
19-13 Sub Oscillator Frequency (f
19-14 Sub Oscillator(crystal) Stabilization Time (t
).........................................................................19-12
OSC1
).......................................................19-12
ST1
)..........................................................................19-13
OSC2
)......................................................19-14
ST2
21-1 Descriptions of Pins Used to Read/Write the EPROM.............................................21-3
21-2 Comparison of S3P8245/P8249 and S3C8245/C8249 Features................................21-3
21-3 Operating Mode Selection Criteria .........................................................................21-4
21-4 D.C Electrical Characteristics ...............................................................................21-4
21-5 D.C Electrical Characteristics of S3C8245.............................................................21-7
22-1 Power Selection Settings for TB8245/9..................................................................22-4
22-2 Main-clock Selection Settings for TB8245/9 ...........................................................22-4
22-3 Device Selection Settings for TB8245/9.................................................................22-5
22-4 The SMDS2+ Tool Selection Setting .....................................................................22-5
xvi S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER

List of Programming Tips
Description Page
Number
Chapter 2: Address Spaces
Using the Page Pointer for RAM clear (Page 0, Page1) .......................................................................2-5
Setting the Register Pointers............................................................................................................2-9
Using the RPs to Calculate the Sum of a Series of Registers ..............................................................2-10
Addressing the Common Working Register Area................................................................................2-14
Standard Stack Operations Using PUSH and POP .............................................................................2-19
Chapter 11: 8-bit Timer A/B
To Generate 38 kHz, 1/3 duty signal through P3.0..............................................................................11-9
To Generate a one pulse signal through P3.0 .....................................................................................11-10
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER xvii


List of Register Descriptions
Register Full Register Name Page
Identifier Number
ADCON A/D Converter Control Register .............................................................................4-5
BTCON Basic Timer Control Register................................................................................4-6
CLKCON System Clock Control Register .............................................................................4-7
EMT External Memory Timing Register .........................................................................4-8
FLAGS System Flags Register ........................................................................................4-9
IMR Interrupt Mask Register ........................................................................................4-10
INTPND Interrupt Pending Register....................................................................................4-11
IPH Instruction Pointer (High Byte) .............................................................................4-12
IPL Instruction Pointer (Low Byte) ..............................................................................4-12
IPR Interrupt Priority Register......................................................................................4-13
IRQ Interrupt Request Register ....................................................................................4-14
LCON LCD Control Register...........................................................................................4-15
LMOD LCD Mode Control Register..................................................................................4-16
OSCCON Oscillator Control Register....................................................................................4-17
P0CONH Port 0 Control Register (High Byte) .......................................................................4-18
P0CONL Port 0 Control Register (Low Byte)........................................................................4-19
P0INT Port 0 Interrupt Control Register ............................................................................4-20
P0PND Port 0 Interrupt Pending Register ..........................................................................4-22
P1CONH Port 1 Control Register (High Byte) .......................................................................4-22
P1CONL Port 1 Control Register (Low Byte)........................................................................4-23
P1PUR Port 1 Pull-up Control Register..............................................................................4-24
P2CONH Port 2 Control Register (High Byte) .......................................................................4-25
P2CONL Port 2 Control Register (Low Byte)........................................................................4-26
P3CONH Port 3 Control Register (High Byte) .......................................................................4-27
P3CONL Port 3 Control Register (Low Byte)........................................................................4-28
P4CONH Port 4 Control Register (High Byte) .......................................................................4-29
P4CONL Port 4 Control Register (Low Byte)........................................................................4-30
P5CONH Port 5 Control Register (High Byte) .......................................................................4-31
P5CONL Port 5 Control Register (Low Byte)........................................................................4-32
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER xix

List of Register Descriptions (Continued)
Register Full Register Name Page
Identifier Number
PP Register Page Pointer ..........................................................................................4-33
RP0 Register Pointer 0................................................................................................4-34
RP1 Register Pointer 1................................................................................................4-34
SIOCON SIO Control Register ............................................................................................4-35
SPH Stack Pointer (High Byte).....................................................................................4-36
SPL Stack Pointer (Low Byte) .....................................................................................4-36
STPCON Stop Control Register...........................................................................................4-37
SYM System Mode Register ........................................................................................4-38
T0CON Timer 0 Control Register.......................................................................................4-39
T1CON Timer 1 Control Register.......................................................................................4-40
TACON Timer A Control Register......................................................................................4-41
TBCON Timer B Control Register......................................................................................4-42
VLDCON Voltage Level Detector Control Register .................................................................4-43
WTCON Watch Timer Control Register ...............................................................................4-44
xx S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER

List of Instruction Descriptions
Instruction Full Register Name Page
Mnemonic Number
ADC Add with Carry ....................................................................................................6-14
ADD Add....................................................................................................................6-15
AND Logical AND........................................................................................................6-16
BAND Bit AND ..............................................................................................................6-17
BCP Bit Compare........................................................................................................6-18
BITC Bit Complement ..................................................................................................6-19
BITR Bit Reset ............................................................................................................6-20
BITS Bit Set ................................................................................................................6-21
BOR Bit OR ................................................................................................................6-22
BTJRF Bit Test, Jump Relative on False...........................................................................6-23
BTJRT Bit Test, Jump Relative on True.............................................................................6-24
BXOR Bit XOR..............................................................................................................6-25
CALL Call Procedure ....................................................................................................6-26
CCF Complement Carry Flag .......................................................................................6-27
CLR Clear..................................................................................................................6-28
COM Complement .......................................................................................................6-29
CP Compare.............................................................................................................6-30
CPIJE Compare, Increment, and Jump on Equal...............................................................6-31
CPIJNE Compare, Increment, and Jump on Non-Equal ........................................................6-32
DA Decimal Adjust....................................................................................................6-33
DEC Decrement..........................................................................................................6-35
DECW Decrement Word.................................................................................................6-36
DI Disable Interrupts ................................................................................................6-37
DIV Divide (Unsigned).................................................................................................6-38
DJNZ Decrement and Jump if Non-Zero ..........................................................................6-39
EI Enable Interrupts.................................................................................................6-40
ENTER Enter..................................................................................................................6-41
EXIT Exit ....................................................................................................................6-42
IDLE Idle Operation......................................................................................................6-43
INC Increment ...........................................................................................................6-44
INCW Increment Word...................................................................................................6-45
IRET Interrupt Return ...................................................................................................6-46
JP Jump..................................................................................................................6-47
JR Jump Relative ......................................................................................................6-48
LD Load...................................................................................................................6-49
LDB Load Bit..............................................................................................................6-51
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER xxi

xxii S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER

List of Instruction Descriptions (Continued)
Instruction Full Register Name Page
Mnemonic Number
LDC/LDE Load Memory......................................................................................................6-52
LDCD/LDED Load Memory and Decrement...............................................................................6-54
LDCI/LDEI Load Memory and Increment ................................................................................6-55
LDCPD/LDEPD Load Memory with Pre-Decrement ........................................................................6-56
LDCPI/LDEPI Load Memory with Pre-Increment..........................................................................6-57
LDW Load Word ..........................................................................................................6-58
MULT Multiply (Unsigned) ..............................................................................................6-59
NEXT Next...................................................................................................................6-60
NOP No Operation.......................................................................................................6-61
OR Logical OR..........................................................................................................6-62
POP Pop from Stack...................................................................................................6-63
POPUD Pop User Stack (Decrementing)............................................................................6-64
POPUI Pop User Stack (Incrementing).............................................................................6-65
PUSH Push to Stack .....................................................................................................6-66
PUSHUD Push User Stack (Decrementing) ..........................................................................6-67
PUSHUI Push User Stack (Incrementing) ...........................................................................6-68
RCF Reset Carry Flag.................................................................................................6-69
RET Return................................................................................................................6-70
RL Rotate Left..........................................................................................................6-71
RLC Rotate Left through Carry .....................................................................................6-72
RR Rotate Right ........................................................................................................6-73
RRC Rotate Right through Carry ...................................................................................6-74
SB0 Select Bank 0 .....................................................................................................6-75
SB1 Select Bank 1 .....................................................................................................6-76
SBC Subtract with Carry..............................................................................................6-77
SCF Set Carry Flag.....................................................................................................6-78
SRA Shift Right Arithmetic ...........................................................................................6-79
SRP/SRP0/SRP1 Set Register Pointer ............................................................................................6-80
STOP Stop Operation ....................................................................................................6-81
SUB Subtract .............................................................................................................6-82
SWAP Swap Nibbles......................................................................................................6-83
TCM Test Complement under Mask..............................................................................6-84
TM Test under Mask .................................................................................................6-85
WFI Wait for Interrupt ..................................................................................................6-86
XOR Logical Exclusive OR ...........................................................................................6-87
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER xxiii

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
S3C8-SERIES MICROCONTROLLERS
Samsung's S3C8 series of 8-bit single-chip CMOS microcontrollers offers a fast and efficient CPU, a wide range of
integrated peripherals, and various mask-programmable ROM sizes. Among the major CPU features are:
— Efficient register-oriented architecture
— Selectable CPU clock sources
— Idle and Stop power-down mode release by interrupt
— Built-in basic timer with watchdog function
A sophisticated interrupt structure recognizes up to eight interrupt levels. Each level can have one or more interrupt
sources and vectors. Fast interrupt processing (within a minimum of four CPU clocks) can be assigned to specific
interrupt levels.
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 MICROCONTROLLER
The S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 single-chip CMOS
microcontroller are fabricated using the highly
advanced CMOS process, based on Samsung’s
newest CPU architecture.
The S3C8245, S3C8249 are a microcontroller with a
16K-byte, 32K-byte mask-programmable ROM
embedded respectively.
The S3P8245 is a microcontroller with a 16K-byte
one-time-programmable ROM embedded.
The S3P8249 is a microcontroller with a 32K-byte
one-time-programmable ROM embedded.
Using a proven modular design approach, Samsung
engineers have successfully developed the
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 by integrating the
following peripheral modules with the powerful SAM8
core:
— Six programmable I/O ports, including five 8-bit
ports and one 5-bit port, for a total of 45 pins.
— Eight bit-programmable pins for external
interrupts.
— One 8-bit basic timer for oscillation stabilization
and watchdog functions (system reset).
— Two 8-bit timer/counter and two 16-bit
timer/counter with selectable operating modes.
— Watch timer for real time.
— 8-input A/D converter
— Serial I/O interface
The S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 is versatile
microcontroller for camera, LCD and ADC application,
etc. They are currently available in 80-pin TQFP and
80-pin QFP package
OTP
The S3P8245/P8249 are OTP (One Time Programmable) version of the S3C8245/C8249 microcontroller. The
S3P8245 microcontroller has an on-chip 16K-byte one-time-programmable EPROM instead of a masked ROM. The
S3P8249 microcontroller has an on-chip 32K-byte one-time-programmable EPROM instead of a masked ROM. The
S3P8245 is comparable to the S3P8245, both in function and in pin configuration.
The S3P8249 is comparable to the S3P8249, both in function and in pin configuration.
1-1

PRODUCT OVERVIEW S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
FEATURES
Memory
• ROM: 32K-byte (S3C8249/P8249)
• ROM: 16K-byte (S3C8245/P8245)
• RAM: 1056-Byte (S3C8249/P8249)
• RAM: 544-Byte (S3C8245/P8245)
• Data memory mapped I/O
Oscillation Sources
• Crystal, ceramic, RC (main)
• Crystal for subsystem clock
• Main system clock frequency 1-10 MHz
(3 MHz at 1.8 V, 10 MHz at 2.7 V)
• Subsystem clock frequency: 32.768 kHz
• CPU clock divider (1/1, 1/2, 1/8, 1/16)
Two Power-Down Modes
• Idle (only CPU clock stops)
• Stop (System clock stops)
Interrupts
• 6 level 8 vector 8 internal interrupt
• 2 level 8 vector 8 external interrupt
45 I/O Pins
• 45 configurable I/O pins
Basic Timer
• Overflow signal makes a system reset.
• Watchdog function
8-Bit Timer/Counter A
• Programmable 8-bit timer
• Interval, capture, PWM mode
• Match/capture, overflow interrupt
8-Bit Timer/Counter B
• Programmable 8-bit timer
• Carrier frequency generator
16-Bit Timer/Counter 0
• Programmable 16-bit timer
• Match interrupt generates
16-Bit Timer/Counter 1
• Programmable 16-bit timer
• Interval, capture, PWM mode
• Match/capture, overflow interrupt
Watch Timer
• Real-time and interval time measurement
• Clock generation for LCD
• Four frequency outputs for buzzer sound
LCD Controller/Driver
• Maximum 16-digit LCD direct drive capability
• Display modes: static, 1/2 duty (1/2 bias)
• 1/3 duty (1/2 or 1/3 bias), 1/4 duty (1/3 bias)
A/D Converter
• Eight analog input channels
• 50 µs conversion speed at 1 MHz f
ADC
clock
• 10-bit conversion resolution
8-Bit Serial I/O Interface
• 8-bit transmit/receive mode
• 8-bit receive mode
• LSB-first/MSB-first transmission selectable
• Internal/external clock source
Voltage Booster
• LCD display voltage supply
• S/W control en/disable
• 3.0 V drive
Voltage Detector
• Programmable detection voltage
(2.2 V, 2.4 V, 3.0 V, 4.0 V)
• En/Disable S/W selectable
Instruction Execution Times
• 400 ns at 10 MHz (main)
• 122 us at 32.768 kHz (subsystem)
Operating Temperature Range
• -25 °C to 85 °C
Operating Voltage Range
• 1.8 V to 5.5 V
Package Type
• 80-QFP-1420C
• 80-TQFP-1212
1-2
S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
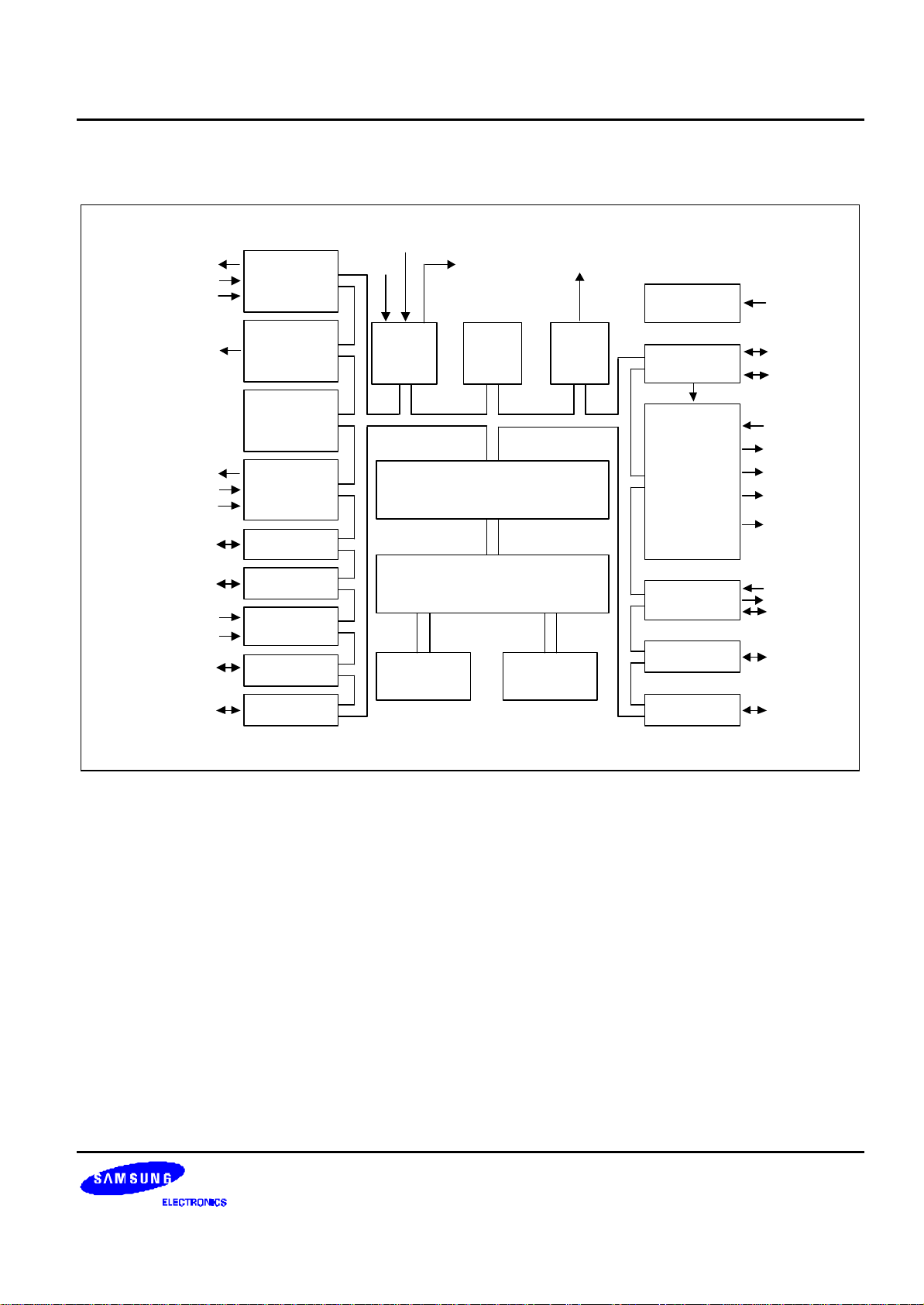
BLOCK DIAGRAM
X
IN
XT
TAOUT/TAPWM/P3.1
TACLK/P3.2
TACAP/P3.3
TBPWM/P3.0
T1CAP/P1.0
T1CLK/P1.1
T1OUT/T1PWM/P1.2
P0.0-P0.7/
INT0-INT7
8-Bit
Timer/
Counter A
8-Bit
Timer/
Counter B
16-Bit
Timer/
Counter 0
16-Bit
Timer/
Counter 1
I/O Port 0
nRESET
nRESET
IN
X
OUT XTOUT
OSC/
Basic
Timer
I/O Port and Interrupt Control
BUZ/P1.4
Watch
Timer
Voltage
Detector
Voltage
Booster
LCD
Driver
V
VLDREF
/
P2.7/ADC7
CB
CA
VLC0-VLC2
COM0-COM3
SEG0-SEG15
SEG16-SEG23/
P4.0-P4.7
SEG24-SEG31/
P5.0-P5.7
P1.0-P1.7
AV
REF
AV
P2.0-P2.7/
ADC0-ADC7
P3.0-P3.4
SS
I/O Port 1
A/D
Converter
I/O Port 2
I/O Port 3
SAM88 RC CPU
544/1056 Byte
Register File
16/32-Kbyte
ROM
Figure 1-1. Block Diagram
Serial I/O
Port
I/O Port 4
I/O Port 5
SI/P1.7
SO/P1.5
SCK/P1.6
P4.0-P4.7/
SEG16-SEG23
P5.0-P5.7/
SEG24-SEG31
1-3
PRODUCT OVERVIEW S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
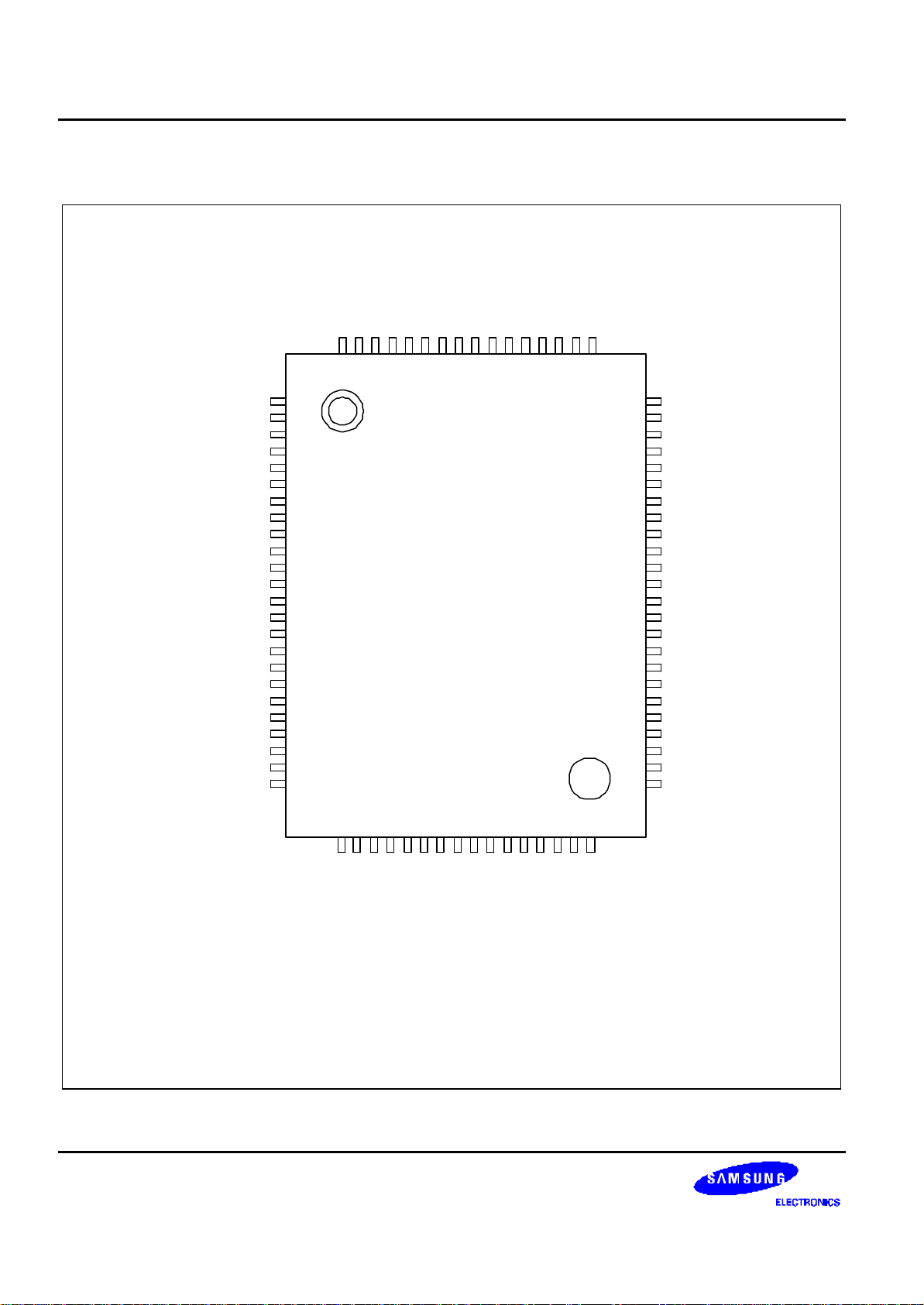
PIN ASSIGNMENT
SEG25/P5.1
SEG24/P5.0
SEG23/P4.7
SEG22/P4.6
SEG21/P4.5
SEG20/P4.4
SEG19/P4.3
SEG18/P4.2
SEG17/P4.1
SEG16/P4.0
SEG15
SEG14
SEG13
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG26/P5.2
SEG27/P5.3
SEG28/P5.4
SEG29/P5.5
SEG30/P5.6
SEG31/P5.7
P3.0/TBPWM
P3.1/TAOUT/TAPWM
P3.2/TACLK
P3.3/TACAP/SDAT
P3.4/SCLK
V
DD
V
SS
X
OUT
X
IN
TEST
XT
IN
XT
OUT
nRESET
P0.0/INT0
P0.1/INT1
P0.2/INT2
P0.3/INT3
P0.4/INT4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
807978777675747372717069686766
S3C8245/C8249
(80-QFP-1420C)
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
SEG0
COM3
COM2
COM1
COM0
V
LC2
V
LC1
V
LC0
CA
CB
AV
SS
AV
REF
P2.7/ADC7/V
P2.6/ADC6
P2.5/ADC5
VLDREF
1-4
NOTE:
252627282930313233343536373839
40
P1.3
P1.7/SI
P1.5/SO
P1.4/BUZ
P0.5/INT5
P0.6/INT6
P0.7/INT7
P1.0/T1CAP
P1.1/T1CLK
P1.6/SCK
P2.0/ADC0
P2.1/ADC1
P2.2/ADC3
P2.3/ADC4
P2.4/ADC4
P1.2/T1OUT/T1PWM
The sequence of pins in TQFP package is identical with that in QFP package.
Figure 1-2. S3C8245/C8249 Pin Assignments (80-QFP-1420C)

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
SEG25/P5.1
SEG24/P5.0
SEG23/P4.7
SEG22/P4.6
SEG21/P4.5
SEG20/P4.4
SEG19/P4.3
SEG18/P4.2
SEG17/P4.1
SEG16/P4.0
SEG15
SEG14
SEG13
SEG12
SEG11
SEG10
SEG9
SEG8
SEG7
SEG6
SEG26/P5.2
SEG27/P5.3
SEG28/P5.4
SEG29/P5.5
SEG30/P5.6
SEG31/P5.7
P3.0/TBPWM
P3.1/TAOUT/TAPWM
P3.2/TACLK
P3.3/TACAP/SDAT
P3.4/SCLK
V
DD
V
SS
X
OUT
X
TEST
XT
XT
OUT
nRESET
P0.0/INT0
80797877767574737271706968676665646362
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
S3C8245/C8249
11
12
(80-TQFP-1212)
13
14
15
IN
16
17
IN
18
19
20
21222324252627282930313233343536373839
61
40
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
SEG5
SEG4
SEG3
SEG2
SEG1
SEG0
COM3
COM2
COM1
COM0
V
LC2
V
LC1
V
LC0
CA
CB
AV
SS
AV
REF
P2.7/ADC7/V
P2.6/ADC6
P2.5/ADC5
LDREF
P1.3
P1.7/SI
P1.5/SO
P1.4/BUZ
P0.1/INT1
P0.2/INT2
P0.3/INT3
P0.4/INT4
P0.5/INT5
P0.6/INT6
P0.7/INT7
P1.1/T1CLK
P1.0/T1CAP
P1.6/SCK
P2.0/ADC0
P2.1/ADC1
P2.2/ADC3
P2.3/ADC4
P2.4/ADC4
P1.2/T1OUT/T1PWM
Figure 1-3. S3C8245/C8249 Pin Assignments (80-TQFP-1212)
1-5

PRODUCT OVERVIEW S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Table 1-1. S3C8245/C8249 Pin Descriptions
Pin
Names
Pin
Type
Pin
Description
P0.0–P0.7 I/O I/O port with bit programmable pins;
Schmitt trigger input or output mode
selected by software; software assignable
pull-up. P0.0–P0.7 can be used as inputs
for external interrupts INT0–INT7
(with noise filter and interrupt control).
P1.0–1.7 I/O I/O port with bit programmable pins; Input
or output mode selected by software;
Open-drain output mode can be selected
by software; software assignable pull-up.
Alternately P1.0–P1.7 can be used as SI,
SO, SCK, BUZ, T1CAP, T1CLK, T1OUT,
T1PWM
P2.0–P2.7 I/O I/O port with bit programmable pins;
normal input and AD input or output mode
selected by software; software assignable
pull-up.
P3.0–P3.4 I/O I/O port with bit programmable pins. Input
or push-pull output with software
assignable pull-up. Alternately P3.0–P3.3
can be used as TACAP, TACLK, TAOUT,
TAPWM, TBPWM
Circuit
Type
Pin
Numbers
(note)
Share
Pins
D–4 20–27 INT0–INT7
E–2 28-35 SI, SO, SCK,
BUZ, T1CAP
T1CLK
T1OUT
T1PWM
F–10
F–18
36–42,
43
ADC0–ADC6
V
VLDREF
(ADC7)
D–2 7–11 TACAP
TACLK
TAOUT
TAPWM
TBPWM
P4.0–P4.7 I/O I/O port with bit programmable pins. Push-
pull or open drain output and input with
software assignable pull-up.
P4.0–P4.7 can alternately be used as
outputs for LCD SEG
P5.0–P5.7 I/O I/O port with bit programmable pins. Push-
pull or open drain output and input with
software assignable pull-up.
P5.0–P5.7 can alternately be used as
outputs for LCD SEG.
1-6
H–14 71–78 SEG16–SEG23
H–14 79–6 SEG24–SEG31

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
Table 1-1. S3C8245/C8249 Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pin
Names
ADC0–ADC6
ADC7
AV
REF
AV
SS
Pin
Type
I A/D converter analog input channels F–10
Pin
Description
Circuit
Type
F–18
Pin
Numbers
36–42
43
(note)
– A/D converter reference voltage – 44 –
– A/D converter ground – 45 –
Share
Pins
P2.0–P2.6
P2.7
INT0–INT7 I External interrupt input pins D–4 20–27 P0.0–P0.7
nRESET I System reset pin
B 19 –
(pull-up resistor: 250 kΩ)
TEST I 0 V: Normal MCU operating
– 16 –
5 V: Test mode
12 V: for OTP writing
SDAT, SCLK O Serial OTP interface pins; serial data
D–2 10, 11 P3.3, P3.4
and clock
V
DD, VSS
– Power input pins for CPU operation
– 12, 13 –
(internal) and Power input for OTP
Writing
X
OUT, XIN
– Main oscillator pins – 14, 15 –
SO, SCK, SI I/O Serial I/O interface clock signal E–2 33–35 P1.5–P1.7
V
VLDREF
I Voltage detector reference voltage input F–18 43 P2.7
TACAP I Timer A Capture input D–2 10 P3.3
TACLK I Timer A External clock input D–2 9 P3.2
TAOUT/TAPWM O Timer A output and PWM output D–2 8 P3.1
TBPWM O Timer B PWM output D–2 7 P3.0
T1CAP I Timer 1 Capture input E–2 28 P1.0
T1CLK I Timer 1 External clock input E–2 29 P1.1
T1OUT/T1PWM O Timer 1 output and PWM output E–2 30 P1.2
COM0–COM3 O LCD common signal output H 51–54 –
SEG0–SEG15 O LCD segment output H 55–70 –
SEG16–SEG23 O LCD segment output H–14 71–78 P4.0–P4.7
SEG24–SEG31 O LCD Segment output H–14 79–6 P5.0–P5.7
V
LC0–VLC2
BUZ O 0.5, 1, 2 or 4 kHz frequency output for
O LCD power supply – 48–50 –
E–2 32 P1.4
buzzer sound with 4.19 MHz main
system clock or 32768 Hz subsystem
clock
CA, CB – Capacitor terminal for voltage booster – 46–47 –
1-7

PRODUCT OVERVIEW S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
PIN CIRCUITS
V
DD
V
DD
Pull-up
Enable
P-Channel
In
Figure 1-4. Pin Circuit Type B (nRESET)
V
DD
Data
Output
Disable
P-Channel
Out
N-Channel
Data
Output
Circuit
Type C
Disable
Figure 1-6. Pin Circuit Type D-2 (P3)
V
V
DD
Data
Output
Pin Circuit
Type C
Disable
Noise
Ext.INT
Filter
I/O
DD
Pull-up
Enable
I/O
1-8
Figure 1-5. Pin Circuit Type C
Input
Normal
Figure 1-7. Pin Circuit Type D-4 (P0)

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
V
DD
V
DD
Open drain
Enable
V
DD
Pull-up
Resistor
Pull-up
Enable
Data
Output
Disable
Schmitt Trigger
Figure 1-8. Pin Circuit Type E-2 (P1)
Pull-up
Enable
P-CH
N-CH
I/O
Data
Output
Disable
Circuit
Type C
I/O
ADC & VLD
Enable
Data
VLD
REF
To ADC
Figure 1-10. Pin Circuit Type F-18 (P2.7/VLD
V
DD
V
LC2
V
LC1
REF
)
Data
Output
Circuit
Type C
Disable
ADCEN
Data
To ADC
Figure 1-9. Pin Circuit Type F-10 (P2.0–P2.6)
I/O
SEG/
COM
V
LC0
Figure 1-11. Pin Circuit Type H (SEG/COM)
Out
1-9

PRODUCT OVERVIEW S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
V
LC2
V
LC1
SEG
Output
Disable
V
LC0
Open Drain EN
Data
LCD Out EN
SEG
Output
Disable
Figure 1-12. Pin Circuit Type H-4
V
DD
V
DD
Circuit
Type H-4
Pull-up
Enable
1-10
Figure 1-13. Pin Circuit Type H-14 (P4, P5)

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESS SPACES
2 ADDRESS SPACES
OVERVIEW
The S3C8245/C8249 microcontroller has two types of address space:
— Internal program memory (ROM)
— Internal register file
A 16-bit address bus supports program memory operations. A separate 8-bit register bus carries addresses and data
between the CPU and the register file.
The S3C8245 has an internal 16-Kbyte mask-programmable ROM. The S3C8249 has an internal 32-Kbyte maskprogrammable ROM.
The 256-byte physical register space is expanded into an addressable area of 320 bytes using addressing modes.
A 16-byte LCD display register file is implemented.
There are 1,109 mapped registers in the internal register file. Of these, 1,040 are for general-purpose.
(This number includes a 16-byte working register common area used as a “scratch area” for data operations, four
192-byte prime register areas, and four 64-byte areas (Set 2)). Thirteen 8-bit registers are used for the CPU and the
system control, and 53 registers are mapped for peripheral controls and data registers. Twelve register locations are
not mapped.
2-1

ADDRESS SPACES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
PROGRAM MEMORY (ROM)
Program memory (ROM) stores program codes or table data. The S3C8249 has 32K bytes internal maskprogrammable program memory, the S3C8245 has 16K bytes.
The first 256 bytes of the ROM (0H–0FFH) are reserved for interrupt vector addresses. Unused locations in this
address range can be used as normal program memory. If you use the vector address area to store a program code,
be careful not to overwrite the vector addresses stored in these locations.
The ROM address at which a program execution starts after a reset is 0100H.
(Decimal)
32,767
16384
16383
255
(HEX)
7FFFH (S3C8249)
32K-byte
4000H
3FFFH (S3C8245)
16K-byte
0FFH
Interrupt
Vector Area
0
0H
2-2
Figure 2-1. Program Memory Address Space

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESS SPACES
REGISTER ARCHITECTURE
In the S3C8245/C8249 implementation, the upper 64-byte area of register files is expanded two 64-byte areas, called
set 1 and set 2. The upper 32-byte area of set 1 is further expanded two 32-byte register banks (bank 0 and bank 1),
and the lower 32-byte area is a single 32-byte common area.
In case of S3C8249/P8249 the total number of addressable 8-bit registers is 1122. Of these 1122 registers, 16 bytes
are for CPU and system control registers, 16 bytes are for LCD data registers, 50 bytes are for peripheral control and
data registers, 16 bytes are used as a shared working registers, and 1024 registers are for general-purpose use,
page 0-page 4 (in case of S3C8245/P8245, page 0-page 2).
You can always address set 1 register locations, regardless of which of the four register pages is currently selected.
Set 1 locations, however, can only be addressed using register addressing modes.
The extension of register space into separately addressable areas (sets, banks, and pages) is supported by various
addressing mode restrictions, the select bank instructions, SB0 and SB1, and the register page pointer (PP).
Specific register types and the area (in bytes) that they occupy in the register file are summarized in Table 2–1.
Table 2-1. S3C8249/P8249 Register Type Summary
Register Type Number of Bytes
General-purpose registers (including the 16-byte common
working register area, four 192-byte prime register area,
and four 64-byte set 2 area)
LCD data registers
CPU and system control registers
Mapped clock, peripheral, I/O control, and data registers
Total Addressable Bytes
Table 2-2. S3C8245/P8245 Register Type Summary
Register Type Number of Bytes
General-purpose registers (including the 16-byte common
working register area, four 192-byte prime register area,
and four 64-byte set 2 area)
LCD data registers
CPU and system control registers
Mapped clock, peripheral, I/O control, and data registers
Total Addressable Bytes
1,040
16
16
50
1,122
528
16
16
50
610
2-3

ADDRESS SPACES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
64
Bytes
32
Bytes
16
Bytes
Set1
FFH
E0H
DFH
D0H
CFH
C0H
0FH
Peripheral Control
(Register Addressing Mode)
System Registers
(Register Addressing Mode)
General Purpose Register
(Register Addressing Mode)
Bank 1
Bank 0
System and
Peripheral Control
System and
Registers
Registers
Page 4
Prime
Data Registers
~ ~
(All addressing modes)
LCD Display Reigster
00H
E0H
Bytes
192
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
General-Purpose
Data Registers
(Indirect Register, Indexed
Mode, and Stack
Operations)
C0H
BFH
~
~ ~
00H
Data Registers
(All Addressing Modes)
Page 1
Page 1
Page 0
Set 2
Page 0
Prime
Page 2
Page3
256
Bytes
~
~
~
~
NOTE:
In case of S3C8245/P8245, there are page 0, page 1, and page 4.
Page 4 is for LCD display register, 16 bytes.
Figure 2-2. Internal Register File Organization
2-4

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESS SPACES
REGISTER PAGE POINTER (PP)
The S3C8-series architecture supports the logical expansion of the physical 256-byte internal register file (using an
8-bit data bus) into as many as 16 separately addressable register pages. Page addressing is controlled by the
register page pointer (PP, DFH). In the S3C8245/C8249 microcontroller, a paged register file expansion is
implemented for LCD data registers, and the register page pointer must be changed to address other pages.
After a reset, the page pointer's source value (lower nibble) and the destination value (upper nibble) are always
"0000", automatically selecting page 0 as the source and destination page for register addressing.
Register Page Pointer (PP)
DFH ,Set 1, R/W
LSBMSB .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
Destination register page selection bits:
0000 Destination: Page 0
NOTE:
A hardware reset operation writes the 4-bit destination and
source values shown above to the register page pointer. These values should
be modified to address other pages.
Source register page selection bits:
0000 Source: Page 0
Figure 2-3. Register Page Pointer (PP)
+ PROGRAMMING TIP — Using the Page Pointer for RAM clear (Page 0, Page 1)
LD PP,#00H ; Destination ← 0, Source ← 0
SRP #0C0H
LD R0,#0FFH ; Page 0 RAM clear starts
RAMCL0 CLR @R0
DJNZ R0,RAMCL0
CLR @R0 ; R0 = 00H
LD PP,#10H ; Destination ← 1, Source ← 0
LD R0,#0FFH ; Page 1 RAM clear starts
RAMCL1 CLR @R0
DJNZ R0,RAMCL1
CLR @R0 ; R0 = 00H
NOTE: You should refer to page 6-39 and use DJNZ instruction properly when DJNZ instruction is used in your program.
2-5

ADDRESS SPACES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
REGISTER SET 1
The term set 1 refers to the upper 64 bytes of the register file, locations C0H–FFH.
The upper 32-byte area of this 64-byte space (E0H–FFH) is expanded two 32-byte register banks, bank 0 and bank
1. The set register bank instructions, SB0 or SB1, are used to address one bank or the other. A hardware reset
operation always selects bank 0 addressing.
The upper two 32-byte areas (bank 0 and bank 1) of set 1 (E0H–FFH) contains 50 mapped system and peripheral
control registers. The lower 32-byte area contains 16 system registers (D0H–DFH) and a 16-byte common working
register area (C0H–CFH). You can use the common working register area as a “scratch” area for data operations
being performed in other areas of the register file.
Registers in set 1 locations are directly accessible at all times using Register addressing mode. The 16-byte
working register area can only be accessed using working register addressing (For more information about working
register addressing, please refer to Chapter 3, “Addressing Modes.”)
REGISTER SET 2
The same 64-byte physical space that is used for set 1 locations C0H–FFH is logically duplicated to add another 64
bytes of register space. This expanded area of the register file is called set 2. For the S3C8249,
the set 2 address range (C0H–FFH) is accessible on pages 0–3.
S3C8245, the set 2 address range (C0H-FFH) is accessible on pages 0-1.
The logical division of set 1 and set 2 is maintained by means of addressing mode restrictions. You can use only
Register addressing mode to access set 1 locations. In order to access registers in set 2, you must use Register
Indirect addressing mode or Indexed addressing mode.
The set 2 register area is commonly used for stack operations.
2-6

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESS SPACES
PRIME REGISTER SPACE
The lower 192 bytes (00H–BFH) of the S3C8245/C8249's four or two 256-byte register pages is called prime register
area. Prime registers can be accessed using any of the seven addressing modes
(see Chapter 3, "Addressing Modes.")
The prime register area on page 0 is immediately addressable following a reset. In order to address prime registers
on pages 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 you must set the register page pointer (PP) to the appropriate source and destination
values.
Bank 0
FFH
FCH
E0H
D0H
C0H
CPU and system control
General-purpose
Peripheral and I/O
LCD data register
Set 1
Bank 1
FFH
C0H
BFH
00H
FFH
FFH
FFH
Page 1
Page 0
Set 2
Page 0
Prime
Space
Page 2
Set 2
Page 3
Set 2
Set 2
Page 4
0FH
LCD Data
Register Area
00H
Figure 2-4. Set 1, Set 2, Prime Area Register, and LCD Data Register Map
2-7

ADDRESS SPACES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
WORKING REGISTERS
Instructions can access specific 8-bit registers or 16-bit register pairs using either 4-bit or 8-bit address fields. When
4-bit working register addressing is used, the 256-byte register file can be seen by the programmer as one that
consists of 32 8-byte register groups or "slices." Each slice comprises of eight 8-bit registers.
Using the two 8-bit register pointers, RP1 and RP0, two working register slices can be selected at any one time to
form a 16-byte working register block. Using the register pointers, you can move this 16-byte register block
anywhere in the addressable register file, except the set 2 area.
The terms slice and block are used in this manual to help you visualize the size and relative locations of selected
working register spaces:
— One working register slice is 8 bytes (eight 8-bit working registers, R0–R7 or R8–R15)
— One working register block is 16 bytes (sixteen 8-bit working registers, R0–R15)
All the registers in an 8-byte working register slice have the same binary value for their five most significant address
bits. This makes it possible for each register pointer to point to one of the 24 slices in the register file. The base
addresses for the two selected 8-byte register slices are contained in register pointers RP0 and RP1.
After a reset, RP0 and RP1 always point to the 16-byte common area in set 1 (C0H–CFH).
1 1 1 1 1 X X X
RP1 (Registers R8-R15)
Each register pointer points to
one 8-byte slice of the register
space, selecting a total 16-byte
working register block.
0 0 0 0 0 X X X
RP0 (Registers R0-R7)
Figure 2-5. 8-Byte Working Register Areas (Slices)
Slice 32
Slice 31
~ ~
Slice 2
Slice 1
FFH
F8H
F7H
F0H
Set 1
Only
CFH
C0H
10H
FH
8H
7H
0H
2-8

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESS SPACES
USING THE REGISTER POINTS
Register pointers RP0 and RP1, mapped to addresses D6H and D7H in set 1, are used to select two movable 8-byte
working register slices in the register file. After a reset, they point to the working register common area: RP0 points
to addresses C0H–C7H, and RP1 points to addresses C8H–CFH.
To change a register pointer value, you load a new value to RP0 and/or RP1 using an SRP or LD instruction.
(see Figures 2-6 and 2-7).
With working register addressing, you can only access those two 8-bit slices of the register file that are currently
pointed to by RP0 and RP1. You cannot, however, use the register pointers to select a working register space in set
2, C0H–FFH, because these locations can be accessed only using the Indirect Register or Indexed addressing
modes.
The selected 16-byte working register block usually consists of two contiguous 8-byte slices. As a general
programming guideline, it is recommended that RP0 point to the "lower" slice and RP1 point to the "upper" slice
(see Figure 2-6). In some cases, it may be necessary to define working register areas in different (non-contiguous)
areas of the register file. In Figure 2-7, RP0 points to the "upper" slice and RP1 to the "lower" slice.
Because a register pointer can point to either of the two 8-byte slices in the working register block, you can flexibly
define the working register area to support program requirements.
+ PROGRAMMING TIP — Setting the Register Pointers
SRP #70H ; RP0 ← 70H, RP1 ← 78H
SRP1 #48H ; RP0 ← no change, RP1 ← 48H,
SRP0 #0A0H ; RP0 ← A0H, RP1 ← no change
CLR RP0 ; RP0 ← 00H, RP1 ← no change
LD RP1,#0F8H ; RP0 ← no change, RP1 ← 0F8H
Register File
Contains 32
8-Byte Slices
0 0 0 0 1 X X X
RP1
0 0 0 0 0 X X X
RP0
8-Byte Slice
8-Byte Slice
FH (R15)
8H
7H
0H (R0)
16-Byte
Contiguous
Working
Register block
Figure 2-6. Contiguous 16-Byte Working Register Block
2-9

ADDRESS SPACES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
F7H (R7)
F0H (R0)
16-Byte
Contiguous
working
Register block
7H (R15)
0H (R0)
1 1 1 1 0 X X X
RP0
0 0 0 0 0 X X X
RP1
8-Byte Slice
Register File
Contains 32
8-Byte Slices
8-Byte Slice
Figure 2-7. Non-Contiguous 16-Byte Working Register Block
+ PROGRAMMING TIP — Using the RPs to Calculate the Sum of a Series of Registers
Calculate the sum of registers 80H–85H using the register pointer. The register addresses from 80H through 85H
contain the values 10H, 11H, 12H, 13H, 14H, and 15 H, respectively:
SRP0 #80H ; RP0 ← 80H
ADD R0,R1 ; R0 ← R0 + R1
ADC R0,R2 ; R0 ← R0 + R2 + C
ADC R0,R3 ; R0 ← R0 + R3 + C
ADC R0,R4 ; R0 ← R0 + R4 + C
ADC R0,R5 ; R0 ← R0 + R5 + C
The sum of these six registers, 6FH, is located in the register R0 (80H). The instruction string used in this example
takes 12 bytes of instruction code and its execution time is 36 cycles. If the register pointer is not used to calculate
the sum of these registers, the following instruction sequence would have to be used:
ADD 80H,81H ; 80H ← (80H) + (81H)
ADC 80H,82H ; 80H ← (80H) + (82H) + C
ADC 80H,83H ; 80H ← (80H) + (83H) + C
ADC 80H,84H ; 80H ← (80H) + (84H) + C
ADC 80H,85H ; 80H ← (80H) + (85H) + C
Now, the sum of the six registers is also located in register 80H. However, this instruction string takes 15 bytes of
instruction code rather than 12 bytes, and its execution time is 50 cycles rather than 36 cycles.
2-10

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESS SPACES
REGISTER ADDRESSING
The S3C8-series register architecture provides an efficient method of working register addressing that takes full
advantage of shorter instruction formats to reduce execution time.
With Register (R) addressing mode, in which the operand value is the content of a specific register or register pair,
you can access any location in the register file except for set 2. With working register addressing, you use a register
pointer to specify an 8-byte working register space in the register file and an 8-bit register within that space.
Registers are addressed either as a single 8-bit register or as a paired 16-bit register space. In a 16-bit register pair,
the address of the first 8-bit register is always an even number and the address of the next register is always an odd
number. The most significant byte of the 16-bit data is always stored in the even-numbered register, and the least
significant byte is always stored in the next (+1) odd-numbered register.
Working register addressing differs from Register addressing as it uses a register pointer to identify a specific 8-byte
working register space in the internal register file and a specific 8-bit register within that space.
MSB
Rn
LSB
Rn+1
Figure 2-8. 16-Bit Register Pair
n = Even address
2-11

ADDRESS SPACES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
Special-Purpose Registers
Bank 1 Bank 1
FFH
Control
Registers
E0H
D0H
C0H
BFH
RP1
RP0
Each register pointer (RP) can independently point
to one of the 24 8-byte "slices" of the register file
(other than set 2). After a reset, RP0 points to
locations C0H-C7H and RP1 to locations C8H-CFH
(that is, to the common working register area).
NOTE:
00H
In the S3C8245/C8249 microcontroller,
pages 0-4 are implemented.
Pages 0-4 contain all of the addressable
registers in the internal register file.
System
Registers
Register
Pointers
General-Purpose Register
FFH
Set 2
CFH
C0H
Prime
Registers
LCD Data
Registers
2-12
Register Addressing Only
Can be Pointed by Register Pointer
Figure 2-9. Register File Addressing
Page 0
All
Addressing
Modes
Page 0
Indirect Register,
Indexed
Addressing
Modes
All
Addressing
Modes
Can be Pointed to
By register Pointer

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESS SPACES
COMMON WORKING REGISTER AREA (C0H–CFH)
After a reset, register pointers RP0 and RP1 automatically select two 8-byte register slices in set 1, locations C0H–
CFH, as the active 16-byte working register block:
RP0 → C0H–C7H
RP1 → C8H–CFH
This 16-byte address range is called common area. That is, locations in this area can be used as working registers
by operations that address any location on any page in the register file. Typically, these working registers serve as
temporary buffers for data operations between different pages.
FFH
FCH
E0H
D0H
C0H
Following a hardware reset, register
pointers RP0 and RP1 point to the
common working register area,
locations C0H-CFH.
RP0 =
RP1 =
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
Set 1
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
C0H
BFH
~ ~
00H
Page 1
Page 0
Set 2
Set 2
Page 0
Prime
Space
Page 3
Page 2
Set 2
Set 2
~
~
~
Page 4
0FH
LCD Data
Registers
00H
Figure 2-10. Common Working Register Area
2-13

ADDRESS SPACES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
+ PROGRAMMING TIP — Addressing the Common Working Register Area
As the following examples show, you should access working registers in the common area, locations C0H–CFH,
using working register addressing mode only.
Examples 1. LD 0C2H,40H ; Invalid addressing mode!
Use working register addressing instead:
SRP #0C0H
LD R2,40H ; R2 (C2H) → the value in location 40H
2. ADD 0C3H,#45H ; Invalid addressing mode!
Use working register addressing instead:
SRP #0C0H
ADD R3,#45H ; R3 (C3H) → R3 + 45H
4-BIT WORKING REGISTER ADDRESSING
Each register pointer defines a movable 8-byte slice of working register space. The address information stored in a
register pointer serves as an addressing "window" that makes it possible for instructions to access working registers
very efficiently using short 4-bit addresses. When an instruction addresses a location in the selected working
register area, the address bits are concatenated in the following way to form a complete 8-bit address:
— The high-order bit of the 4-bit address selects one of the register pointers ("0" selects RP0, "1" selects RP1).
— The five high-order bits in the register pointer select an 8-byte slice of the register space.
— The three low-order bits of the 4-bit address select one of the eight registers in the slice.
As shown in Figure 2-11, the result of this operation is that the five high-order bits from the register pointer are
concatenated with the three low-order bits from the instruction address to form the complete address. As long as the
address stored in the register pointer remains unchanged, the three bits from the address will always point to an
address in the same 8-byte register slice.
Figure 2-12 shows a typical example of 4-bit working register addressing. The high-order bit of the instruction
"INC R6" is "0", which selects RP0. The five high-order bits stored in RP0 (01110B) are concatenated with the three
low-order bits of the instruction's 4-bit address (110B) to produce the register address 76H (01110110B).
2-14

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESS SPACES
RP0
RP1
Selects
RP0 or RP1
Address OPCODE
Register pointer
provides five
high-order bits
Figure 2-11. 4-Bit Working Register Addressing
RP0
0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0
Together they create an
8-bit register address
Selects RP0
Register
address
(76H)
4-bit address
provides three
low-order bits
RP1
0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0
R6
0 1 1 0 1 1 1 0
OPCODE
Instruction
'INC R6'
Figure 2-12. 4-Bit Working Register Addressing Example
2-15

ADDRESS SPACES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
8-BIT WORKING REGISTER ADDRESSING
You can also use 8-bit working register addressing to access registers in a selected working register area. To
initiate 8-bit working register addressing, the upper four bits of the instruction address must contain the value
"1100B." This 4-bit value (1100B) indicates that the remaining four bits have the same effect as 4-bit working register
addressing.
As shown in Figure 2-13, the lower nibble of the 8-bit address is concatenated in much the same way as for 4-bit
addressing: Bit 3 selects either RP0 or RP1, which then supplies the five high-order bits of the final address; the
three low-order bits of the complete address are provided by the original instruction.
Figure 2-14 shows an example of 8-bit working register addressing. The four high-order bits of the instruction address
(1100B) specify 8-bit working register addressing. Bit 4 ("1") selects RP1 and the five high-order bits in RP1
(10101B) become the five high-order bits of the register address. The three low-order bits of the register address
(011) are provided by the three low-order bits of the 8-bit instruction address. The five address bits from RP1 and the
three address bits from the instruction are concatenated to form the complete register address, 0ABH (10101011B).
These address
bits indicate 8-bit
working register
addressing
Selects
RP0 or RP1
1 1 0 0
Register pointer
provides five
high-order bits
RP0
RP1
Address
8-bit logical
address
Three low-order bits
8-bit physical address
2-16
Figure 2-13. 8-Bit Working Register Addressing

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESS SPACES
RP0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1
Specifies working
register addressing
Figure 2-14. 8-Bit Working Register Addressing Example
Selects RP1
R11
8-bit address
form instruction
'LD R11, R2'
RP1
1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1
Register
address
(0ABH)
2-17

ADDRESS SPACES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
SYSTEM AND USER STACK
The S3C8-series microcontrollers use the system stack for data storage, subroutine calls and returns. The PUSH
and POP instructions are used to control system stack operations. The S3C8245/C8249 architecture supports stack
operations in the internal register file.
Stack Operations
Return addresses for procedure calls, interrupts, and data are stored on the stack. The contents of the PC are saved
to stack by a CALL instruction and restored by the RET instruction. When an interrupt occurs, the contents of the
PC and the FLAGS register are pushed to the stack. The IRET instruction then pops these values back to their
original locations. The stack address value is always decreased by one before a push operation and increased by
one after a pop operation. The stack pointer (SP) always points to the stack frame stored on the top of the stack, as
shown in Figure 2-15.
High Address
PCL
PCL
Top of
stack
PCH
Top of
stack
PCH
Flags
Stack contents
after a call
instruction
Low Address
Stack contents
after an
interrupt
Figure 2-15. Stack Operations
User-Defined Stacks
You can freely define stacks in the internal register file as data storage locations. The instructions PUSHUI,
PUSHUD, POPUI, and POPUD support user-defined stack operations.
Stack Pointers (SPL, SPH)
Register locations D8H and D9H contain the 16-bit stack pointer (SP) that is used for system stack operations. The
most significant byte of the SP address, SP15–SP8, is stored in the SPH register (D8H), and the least significant
byte, SP7–SP0, is stored in the SPL register (D9H). After a reset, the SP value is undetermined.
Because only internal memory space is implemented in the S3C8245/C8249, the SPL must be initialized to an 8-bit
value in the range 00H–FFH. The SPH register is not needed and can be used as a general-purpose register, if
necessary.
When the SPL register contains the only stack pointer value (that is, when it points to a system stack in the register
file), you can use the SPH register as a general-purpose data register. However, if an overflow or underflow condition
occurs as a result of increasing or decreasing the stack address value in the SPL register during normal stack
operations, the value in the SPL register will overflow (or underflow) to the SPH register, overwriting any other data
that is currently stored there. To avoid overwriting data in the SPH register, you can initialize the SPL value to "FFH"
instead of "00H".
2-18

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESS SPACES
+ PROGRAMMING TIP — Standard Stack Operations Using PUSH and POP
The following example shows you how to perform stack operations in the internal register file using PUSH and POP
instructions:
LD SPL,#0FFH ; SPL ← FFH
; (Normally, the SPL is set to 0FFH by the initialization
; routine)
•
•
•
PUSH PP ; Stack address 0FEH ← PP
PUSH RP0 ; Stack address 0FDH ← RP0
PUSH RP1 ; Stack address 0FCH ← RP1
PUSH R3 ; Stack address 0FBH ← R3
•
•
•
POP R3 ; R3 ← Stack address 0FBH
POP RP1 ; RP1 ← Stack address 0FCH
POP RP0 ; RP0 ← Stack address 0FDH
POP PP ; PP ← Stack address 0FEH
2-19

ADDRESS SPACES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
NOTES
2-20

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESSING MODES
3 ADDRESSING MODES
OVERVIEW
Instructions that are stored in program memory are fetched for execution using the program counter. Instructions
indicate the operation to be performed and the data to be operated on. Addressing mode is the method used to
determine the location of the data operand. The operands specified in SAM88RC instructions may be condition
codes, immediate data, or a location in the register file, program memory, or data memory.
The S3C8-series instruction set supports seven explicit addressing modes. Not all of these addressing modes are
available for each instruction. The seven addressing modes and their symbols are:
— Register (R)
— Indirect Register (IR)
— Indexed (X)
— Direct Address (DA)
— Indirect Address (IA)
— Relative Address (RA)
— Immediate (IM)
3-1

ADDRESSING MODES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
REGISTER ADDRESSING MODE (R)
In Register addressing mode (R), the operand value is the content of a specified register or register pair
(see Figure 3-1).
Working register addressing differs from Register addressing in that it uses a register pointer to specify an 8-byte
working register space in the register file and an 8-bit register within that space (see Figure 3-2).
Program Memory Register File
8-bit Register
File Address
One-Operand
Instruction
(Example)
Sample Instruction:
dst
OPCODE
Point to One
OPERAND
Register in Register
File
Value used in
Instruction Execution
DEC CNTR ; Where CNTR is the label of an 8-bit register address
4-bit
Working Register
Two-Operand
Instruction
(Example)
Sample Instruction:
Figure 3-1. Register Addressing
Program Memory
dst
OPCODE
src
MSB Point to
RP0 ot RP1
3 LSBs
Point to the
Working Register
(1 of 8)
Register File
RP0 or RP1
Selected
RP points
to start
of working
register
block
OPERAND
3-2
ADD R1, R2 ; Where R1 and R2 are registers in the currently
selected working register area.
Figure 3-2. Working Register Addressing

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESSING MODES
INDIRECT REGISTER ADDRESSING MODE (IR)
In Indirect Register (IR) addressing mode, the content of the specified register or register pair is the address of the
operand. Depending on the instruction used, the actual address may point to a register in the register file, to program
memory (ROM), or to an external memory space (see Figures 3-3 through 3-6).
You can use any 8-bit register to indirectly address another register. Any 16-bit register pair can be used to indirectly
address another memory location. Please note, however, that you cannot access locations C0H–FFH in set 1 using
the Indirect Register addressing mode.
Program Memory Register File
8-bit Register
File Address
One-Operand
Instruction
(Example)
dst
OPCODE
Point to One
ADDRESS
Register in Register
File
Address of Operand
used by Instruction
Value used in
Instruction Execution
Sample Instruction:
RL @SHIFT ; Where SHIFT is the label of an 8-bit register address
OPERAND
Figure 3-3. Indirect Register Addressing to Register File
3-3

ADDRESSING MODES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
INDIRECT REGISTER ADDRESSING MODE (Continued)
Register File
Program Memory
Example
Instruction
References
Program
Memory
Sample Instructions:
CALL @RR2
JP @RR2
REGISTER
dst
OPCODE
Points to
Register Pair
Value used in
Instruction
PAIR
Program Memory
OPERAND
Figure 3-4. Indirect Register Addressing to Program Memory
16-Bit
Address
Points to
Program
Memory
3-4

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESSING MODES
INDIRECT REGISTER ADDRESSING MODE (Continued)
Register File
MSB Points to
4-bit
Working
Register
Address
RP0 or RP1
Program Memory
dst
OPCODE ADDRESS
src
3 LSBs
Point to the
Working Register
(1 of 8)
RP0 or RP1
~ ~
Selected
RP points
to start fo
working register
block
~ ~
Sample Instruction:
OR R3, @R6
Figure 3-5. Indirect Working Register Addressing to Register File
Value used in
Instruction
OPERAND
3-5

ADDRESSING MODES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
INDIRECT REGISTER ADDRESSING MODE (Concluded)
Register File
MSB Points to
4-bit Working
Register Address
Example Instruction
References either
Program Memory or
Data Memory
Program Memory
dst
OPCODE
src
RP0 or RP1
Next 2-bit Point
to Working
Register Pair
(1 of 4)
LSB Selects
Value used in
Instruction
RP0 or RP1
Register
Pair
Program Memory
or
Data Memory
OPERAND
Selected
RP points
to start of
working
register
block
16-Bit
address
points to
program
memory
or data
memory
Sample Instructions:
LCD R5,@RR6 ; Program memory access
LDE R3,@RR14 ; External data memory access
LDE @RR4, R8 ; External data memory access
Figure 3-6. Indirect Working Register Addressing to Program or Data Memory
3-6

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESSING MODES
INDEXED ADDRESSING MODE (X)
Indexed (X) addressing mode adds an offset value to a base address during instruction execution in order to calculate
the effective operand address (see Figure 3-7). You can use Indexed addressing mode to access locations in the
internal register file or in external memory. Please note, however, that you cannot access locations C0H–FFH in
set 1 using Indexed addressing mode.
In short offset Indexed addressing mode, the 8-bit displacement is treated as a signed integer in the range –128 to
+127. This applies to external memory accesses only (see Figure 3-8.)
For register file addressing, an 8-bit base address provided by the instruction is added to an 8-bit offset contained in
a working register. For external memory accesses, the base address is stored in the working register pair
designated in the instruction. The 8-bit or 16-bit offset given in the instruction is then added to that base address (see
Figure 3-9).
The only instruction that supports Indexed addressing mode for the internal register file is the Load instruction (LD).
The LDC and LDE instructions support Indexed addressing mode for internal program memory and for external data
memory, when implemented.
Two-Operand
Instruction
Example
Sample Instruction:
LD R0, #BASE[R1] ; Where BASE is an 8-bit immediate value
Program Memory
Base Address
dst/src
OPCODE
x
Value used in
Instruction
+
3 LSBs
Point to One of the
Woking Register
(1 of 8)
Register File
RP0 or RP1
~ ~
OPERAND
~ ~
INDEX
Selected RP
points to
start of
working
register
block
Figure 3-7. Indexed Addressing to Register File
3-7

ADDRESSING MODES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
INDEXED ADDRESSING MODE (Continued)
Register File
MSB Points to
4-bit Working
Register Address
Program Memory
OFFSET
dst/src
OPCODE
x
RP0 or RP1
NEXT 2 Bits
Point to Working
Register Pair
(1 of 4)
LSB Selects
RP0 or RP1
~ ~
Register
Pair
Program Memory
or
Data Memory
Selected
RP points
to start of
working
register
block
16-Bit
address
added to
offset
+
8-Bits
16-Bits
16-Bits
Sample Instructions:
LDC R4, #04H[RR2] ; The values in the program address (RR2 + 04H)
are loaded into register R4.
LDE R4,#04H[RR2] ; Identical operation to LDC example, except that
external program memory is accessed.
OPERAND
Value used in
Instruction
Figure 3-8. Indexed Addressing to Program or Data Memory with Short Offset
3-8

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESSING MODES
INDEXED ADDRESSING MODE (Concluded)
Register File
MSB Points to
4-bit Working
Register Address
Program Memory
OFFSET
OFFSET
dst/src
OPCODE
src
RP0 or RP1
NEXT 2 Bits
Point to Working
Register Pair
LSB Selects
RP0 or RP1
~ ~
Register
Pair
Program Memory
or
Data Memory
Selected
RP points
to start of
working
register
block
16-Bit
address
added to
offset
+
8-Bits
16-Bits
16-Bits
Sample Instructions:
LDC R4, #1000H[RR2] ; The values in the program address (RR2 + 1000H)
are loaded into register R4.
LDE R4,#1000H[RR2] ; Identical operation to LDC example, except that
external program memory is accessed.
OPERAND
Value used in
Instruction
Figure 3-9. Indexed Addressing to Program or Data Memory
3-9

ADDRESSING MODES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
DIRECT ADDRESS MODE (DA)
In Direct Address (DA) mode, the instruction provides the operand's 16-bit memory address. Jump (JP) and Call
(CALL) instructions use this addressing mode to specify the 16-bit destination address that is loaded into the PC
whenever a JP or CALL instruction is executed.
The LDC and LDE instructions can use Direct Address mode to specify the source or destination address for Load
operations to program memory (LDC) or to external data memory (LDE), if implemented.
Program or
Data Memory
Memory
Program Memory
Upper Address Byte
Lower Address Byte
dst/src
Sample Instructions:
LDC R5,1234H ; The values in the program address (1234H)
LDE R5,1234H ; Identical operation to LDC example, except that
"0" or "1"
OPCODE
are loaded into register R5.
external program memory is accessed.
Address
Used
LSB Selects Program
Memory or Data Memory:
"0" = Program Memory
"1" = Data Memory
Figure 3-10. Direct Addressing for Load Instructions
3-10

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESSING MODES
DIRECT ADDRESS MODE (Continued)
Program Memory
Next OPCODE
Memory
Address
Used
Upper Address Byte
Lower Address Byte
OPCODE
Sample Instructions:
JP C,JOB1 ; Where JOB1 is a 16-bit immediate address
CALL DISPLAY ; Where DISPLAY is a 16-bit immediate address
Figure 3-11. Direct Addressing for Call and Jump Instructions
3-11

ADDRESSING MODES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
INDIRECT ADDRESS MODE (IA)
In Indirect Address (IA) mode, the instruction specifies an address located in the lowest 256 bytes of the program
memory. The selected pair of memory locations contains the actual address of the next instruction to be executed.
Only the CALL instruction can use the Indirect Address mode.
Because the Indirect Address mode assumes that the operand is located in the lowest 256 bytes of program
memory, only an 8-bit address is supplied in the instruction; the upper bytes of the destination address are assumed
to be all zeros.
Program Memory
Next Instruction
LSB Must be Zero
Current
Instruction
Lower Address Byte
Upper Address Byte
Sample Instruction:
CALL #40H ; The 16-bit value in program memory addresses 40H
and 41H is the subroutine start address.
dst
OPCODE
Program Memory
Locations 0-255
Figure 3-12. Indirect Addressing
3-12

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 ADDRESSING MODES
RELATIVE ADDRESS MODE (RA)
In Relative Address (RA) mode, a twos-complement signed displacement between – 128 and + 127 is specified in
the instruction. The displacement value is then added to the current PC value. The result is the address of the next
instruction to be executed. Before this addition occurs, the PC contains the address of the instruction immediately
following the current instruction.
Several program control instructions use the Relative Address mode to perform conditional jumps. The instructions
that support RA addressing are BTJRF, BTJRT, DJNZ, CPIJE, CPIJNE, and JR.
Program Memory
Next OPCODE
Program Memory
Address Used
Current
Displacement
Current Instruction
Sample Instructions:
JR ULT,$+OFFSET ; Where OFFSET is a value in the range +127 to -128
OPCODE
PC Value
Signed
Displacement Value
+
Figure 3-13. Relative Addressing
3-13

ADDRESSING MODES S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
IMMEDIATE MODE (IM)
In Immediate (IM) addressing mode, the operand value used in the instruction is the value supplied in the operand
field itself. The operand may be one byte or one word in length, depending on the instruction used. Immediate
addressing mode is useful for loading constant values into registers.
Program Memory
OPERAND
OPCODE
(The Operand value is in the instruction)
Sample Instruction:
LD R0,#0AAH
Figure 3-14. Immediate Addressing
3-14

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
4 CONTROL REGISTERS
OVERVIEW
In this chapter, detailed descriptions of the S3C8245/C8249 control registers are presented in an easy-to-read
format. You can use this chapter as a quick-reference source when writing application programs. Figure 4-1
illustrates the important features of the standard register description format.
Control register descriptions are arranged in alphabetical order according to register mnemonic. More detailed
information about control registers is presented in the context of the specific peripheral hardware descriptions in Part
II of this manual.
Data and counter registers are not described in detail in this reference chapter. More information about all of the
registers used by a specific peripheral is presented in the corresponding peripheral descriptions in Part II of this
manual.
The locations and read/write characteristics of all mapped registers in the S3C8245/C8249 register file are listed in
Table 4-1. The hardware reset value for each mapped register is described in Chapter 8, "nRESET and Power-Down."
Table 4-1. Set 1 Registers
Register Name Mnemonic Decimal Hex R/W
LCD control register LCON 208 D0H R/W
LCD mode register LMOD 209 D1H R/W
Interrupt pending register INTPND 210 D2H R/W
Basic timer control register BTCON 211 D3H R/W
Clock control register CLKCON 212 D4H R/W
System flags register FLAGS 213 D5H R/W
Register pointer 0 RP0 214 D6H R/W
Register pointer 1 RP1 215 D7H R/W
Stack pointer (high byte) SPH 216 D8H R/W
Stack pointer (low byte) SPL 217 D9H R/W
Instruction pointer (high byte) IPH 218 DAH R/W
Instruction pointer (low byte) IPL 219 DBH R/W
Interrupt request register IRQ 220 DCH R
Interrupt mask register IMR 221 DDH R/W
System mode register SYM 222 DEH R/W
Register page pointer PP 223 DFH R/W
4-1

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
Table 4-2. Set 1, Bank 0 Registers
Register Name Mnemonic Decimal Hex R/W
Port 0 control High register P0CONH 224 E0H R/W
Port 0 control Low register P0CONL 225 E1H R/W
Port 0 interrupt control register P0INT 226 E2H R/W
Port 0 interrupt pending register P0PND 227 E3H R/W
Port 1 control High register P1CONH 228 E4H R/W
Port 1 control Low register P1CONL 229 E5H R/W
Port 2 control High register P2CONH 230 E6H R/W
Port 2 control Low register P2CONL 231 E7H R/W
Port 3 control High register P3CONH 232 E8H R/W
Port 3 control Low register P3CONL 233 E9H R/W
Timer B data register (high byte) TBDATAH 234 EAH R/W
Timer B data register (low byte) TBDATAL 235 EBH R/W
Timer B control register TBCON 236 ECH R/W
Timer A control register TACON 237 EDH R/W
Timer A counter register TACNT 238 EEH R
Timer A data register TADATA 239 EFH R/W
Serial I/O control register SIOCON 240 F0H R/W
Serial I/O data register SIODATA 241 F1H R/W
Serial I/O pre-scale register SIOPS 242 F2H R/W
Oscillator control register OSCCON 243 F3H R/W
STOP control register STPCON 244 F4H R/W
Port 1 pull-up control register P1PUP 245 F5H R/W
Port 0 data register P0 246 F6H R/W
Port 1 data register P1 247 F7H R/W
Port 2 data register P2 248 F8H R/W
Port 3 data register P3 249 F9H R/W
Port 4 data register P4 250 FAH R/W
Port 5 data register P5 251 FBH R/W
Location FCH is factory use only.
Basic timer data register BTCNT 253 FDH R
External memory timing register EMT 254 FEH R/W
Interrupt priority register IPR 255 FFH R/W
4-2

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
Table 4-3. Set 1, Bank 1 Registers
Register Name Mnemonic Decimal Hex R/W
Locations E0H–EBH is not mapped.
Port 4 control High register P4CONH 236 ECH R/W
Port 4 control Low register P4CONL 237 EDH R/W
Port 5 control High register P5CONH 238 EEH R/W
Port 5 control Low register P5CONL 239 EFH R/W
Locations F0H is factory use only.
Timer 0 control register T0CON 241 F1H R/W
Timer 0 counter register (high byte) T0CNTH 242 F2H R
Timer 0 counter register (low byte) T0CNTL 243 F3H R
Timer 0 data register (high byte) T0DATAH 244 F4H R/W
Timer 0 data register (low byte) T0DATAL 245 F5H R/W
Voltage level detector control register VLDCON 246 F6H R/W
A/D converter control register ADCON 247 F7H R/W
A/D converter data register (high byte) ADDATAH 248 F8H R/W
A/D converter data register (low byte) ADDATAL 249 F9H R/W
Watch timer control register WTCON 250 FAH R/W
Timer 1 control register T1CON 251 FBH R/W
Timer 1 counter register (high byte) T1CNTH 252 FCH R
Timer 1 counter register (low byte) T1CNTL 253 FDH R
Timer 1 data register (high byte) T1DATAH 254 FEH R/W
Timer 1 data register (low byte) T1DATAL 255 FFH R/W
4-3

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
Bit number(s) that is/are appended to
the register name for bit addressing
Full Register nameRegister ID
FLAGS - System Flags Register
Bit Identifier
nRESET Value
Read/Write
Bit Addressing
Mode
.7 Carry Flag (C)
.6 Zero Flag (Z)
.5
R/W R/W R/W
Register addressing mode only
0 Operation does not generate a carry or borrow condition
0 Operation generates carry-out or borrow into high-order bit 7
0
0
Sign Flag (S)
0 Operation generates positive number (MSB = "0")
0
Name of individual
bit or related bits
Register address
(hexadecimal)
.7 .6 .5
x x x
Operation result is a non-zero value
Operation result is zero
Operation generates negative number (MSB = "1")
.4 .3 .2 .1 .0
x
R/W
x
R/W
D5H
x
R/W
Register location
in the internal
register file
Set 1
x
R/W
0
R/W
Type of addressing
that must be used to
address the bit
(1-bit, 4-bit, or 8-bit)
4-4
R = Read-only
W = Write-only
R/W = Read/write
'-' = Not used
Description of the
effect of specific
bit settings
Figure 4-1. Register Description Format
Bit number:
MSB = Bit 7
LSB = Bit 0
nRESET value notation:
'-' = Not used
'x' = Undetermined value
'0' = Logic zero
'1' = Logic one

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
ADCON — A/D Converter Control Register F7H Set 1, Bank 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value – 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write – R/W R/W R/W R R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7 Not used for the S3C8245/C8249
.6–.4 A/D Input Pin Selection Bits
0 0 0 ADC0
0 0 1 ADC1
0 1 0 ADC2
0 1 1 ADC3
1 0 0 ADC4
1 0 1 ADC5
1 1 0 ADC6
1 1 1 ADC7
.3 End-of-Conversion bit (read-only)
0 Conversion not complete
1 Conversion complete
.2–.1 Clock Source Selection Bits
0 0 fxx/16
0 1 fxx/8
1 0 fxx/4
1 1 fxx
.0 Start or Enable Bit
0 Disable operation
1 Start operation
4-5

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
BTCON — Basic Timer Control Register D3H Set 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.4 Watchdog Timer Function Disable Code (for System Reset)
1 0 1 0 Disable watchdog timer function
Others Enable watchdog timer function
.3–.2 Basic Timer Input Clock Selection Bits
0 0
fxx/4096
0 1 fxx/1024
1 0 fxx/128
(3)
1 1 fxx/16
.1
Basic Timer Counter Clear Bit
(1)
0 No effect
1 Clear the basic timer counter value
.0
Clock Frequency Divider Clear Bit for Basic Timer and Timer/Counters
(2)
0 No effect
1 Clear both clock frequency dividers
NOTES:
1. When you write a “1” to BTCON.1, the basic timer counter value is cleared to "00H". Immediately following the write
operation, the BTCON.1 value is automatically cleared to “0”.
2. When you write a "1" to BTCON.0, the corresponding frequency divider is cleared to "00H". Immediately following the
write operation, the BTCON.0 value is automatically cleared to "0".
3. The fxx is selected clock for system (main OSC. or sub OSC.).
4-6

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
CLKCON — System Clock Control Register D4H Set 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write – – – R/W R/W – – –
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.5 Not used for the S3C8245/C8249
.4–.3
.2–.0 Not used for the S3C8245/C8249
NOTE : After a reset, the slowest clock (divided by 16) is selected as the system clock. To select faster clock speeds, load
the appropriate v alues to CLKCON.3 and CLKCON.4.
CPU Clock (System Clock) Selection Bits
0 0 fxx/16
0 1 fxx/8
1 0 fxx/2
1 1 fxx
(note)
4-7

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
EMT — External Memory Timing Register FEH Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 – – – – – – –
Read/Write – – – – – – – –
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.0 Not used for the S3C8245/C8249
4-8

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
FLAGS — System Flags Register D5H Set 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value x x x x x x 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7 Carry Flag (C)
0 Operation does not generate a carry or borrow condition
1 Operation generates a carry-out or borrow into high-order bit 7
.6 Zero Flag (Z)
0 Operation result is a non-zero value
1 Operation result is zero
.5 Sign Flag (S)
0 Operation generates a positive number (MSB = "0")
1 Operation generates a negative number (MSB = "1")
.4 Overflow Flag (V)
0 Operation result is ≤ +127 or ≥ –128
1 Operation result is > +127 or < –128
.3 Decimal Adjust Flag (D)
0 Add operation completed
1 Subtraction operation completed
.2 Half-Carry Flag (H)
0 No carry-out of bit 3 or no borrow into bit 3 by addition or subtraction
1 Addition generated carry-out of bit 3 or subtraction generated borrow into bit 3
.1 Fast Interrupt Status Flag (FIS)
0 Interrupt return (IRET) in progress (when read)
1 Fast interrupt service routine in progress (when read)
.0 Bank Address Selection Flag (BA)
0 Bank 0 is selected
1 Bank 1 is selected
4-9

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
IMR — Interrupt Mask Register DDH Set 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value x x x x x x x x
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7 Interrupt Level 7 (IRQ7) Enable Bit; External Interrupts P0.4–0.7
Disable (mask)
0
Enable (unmask)
1
.6 Interrupt Level 6 (IRQ6) Enable Bit; External Interrupts P0.0–0.3
Disable (mask)
0
Enable (unmask)
1
.5 Interrupt Level 5 (IRQ5) Enable Bit; Watch Timer Overflow
0 Disable (mask)
1 Enable (unmask)
.4 Interrupt Level 4 (IRQ4) Enable Bit; SIO Interrupt
0 Disable (mask)
1 Enable (unmask)
.3 Interrupt Level 3 (IRQ3) Enable Bit; Timer 1 Match/Capture or Overflow
0 Disable (mask)
1 Enable (unmask)
.2 Interrupt Level 2 (IRQ2) Enable Bit; Timer 0 Match
0 Disable (mask)
1 Enable (unmask)
.1 Interrupt Level 1 (IRQ1) Enable Bit; Timer B Match
0 Disable (mask)
1 Enable (unmask)
.0 Interrupt Level 0 (IRQ0) Enable Bit; Timer A Match/Capture or Overflow
0 Disable (mask)
1 Enable (unmask)
NOTE: When an interrupt level is masked, any interrupt requests that may be issued are not recognized by the CPU.
4-10

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
INTPND — Interrupt Pending Register D2H Set 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value – – – – – 0 0 0
Read/Write – – – – – R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.3 Not used for the S3C8245/C8249
.2 Timer 1 Overflow Interrupt Pending Bit
Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
0
Interrupt request is pending
1
.1 Timer 1 Match/Capture Interrupt Pending Bit
0 Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
1 Interrupt request is pending
.0 Timer A Overflow Interrupt Pending bit
0 Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
1 Interrupt request is pending
4-11

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
IPH — Instruction Pointer (High Byte) DAH Set 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value x x x x x x x x
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.0 Instruction Pointer Address (High Byte)
The high-byte instruction pointer value is the upper eight bits of the 16-bit instruction
pointer address (IP15–IP8). The lower byte of the IP address is located in the IPL
register (DBH).
IPL — Instruction Pointer (Low Byte) DBH Set 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value x x x x x x x x
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.0 Instruction Pointer Address (Low Byte)
The low-byte instruction pointer value is the lower eight bits of the 16-bit instruction
pointer address (IP7–IP0). The upper byte of the IP address is located in the IPH
register (DAH).
4-12

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
IPR — Interrupt Priority Register FFH Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value x x x x x x x x
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7, .4, and .1 Priority Control Bits for Interrupt Groups A, B, and C
0 0 0 Group priority undefined
0 0 1 B > C > A
0 1 0 A > B > C
0 1 1 B > A > C
1 0 0 C > A > B
1 0 1 C > B > A
1 1 0 A > C > B
1 1 1 Group priority undefined
.6 Interrupt Subgroup C Priority Control Bit
0 IRQ6 > IRQ7
1 IRQ7 > IRQ6
.5 Interrupt Group C Priority Control Bit
0 IRQ5 > (IRQ6, IRQ7)
1 (IRQ6, IRQ7) > IRQ5
.3 Interrupt Subgroup B Priority Control Bit
0 IRQ3 > IRQ4
1 IRQ4 > IRQ3
.2 Interrupt Group B Priority Control Bit
0 IRQ2 > (IRQ3, IRQ4)
1 (IRQ3, IRQ4) > IRQ2
.0 Interrupt Group A Priority Control Bit
0 IRQ0 > IRQ1
1 IRQ1 > IRQ0
4-13

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
IRQ — Interrupt Request Register DCH Set 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R R R R R R R R
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7 Level 7 (IRQ7) Request Pending Bit; External Interrupts P0.4–0.7
0 Not pending
1 Pending
.6 Level 6 (IRQ6) Request Pending Bit; External Interrupts P0.0–0.3
0 Not pending
1 Pending
.5 Level 5 (IRQ5) Request Pending Bit; Watch Timer Overflow
0 Not pending
1 Pending
.4 Level 4 (IRQ4) Request Pending Bit; SIO Interrupt
0 Not pending
1 Pending
.3 Level 3 (IRQ3) Request Pending Bit; Timer 1 Match/Capture or Overflow
0 Not pending
1 Pending
.2 Level 2 (IRQ2) Request Pending Bit; Timer 0 Match
0 Not pending
1 Pending
.1 Level 1 (IRQ1) Request Pending Bit; Timer B Match
0 Not pending
1 Pending
.0 Level 0 (IRQ0) Request Pending Bit; Timer A Match/Capture or Overflow
0 Not pending
1 Pending
4-14

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
LCON — LCD Control Register D0H Set 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W – R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7 LCD Output Segment and Pin Configuration Bits
0 P5.4–P5.7 I/O is selected
1 SEG28–SEG31 is selected, P5.4–P5.7 I/O is disabled
.6 LCD Output Segment and Pin Configuration Bits
0 P5.0–P5.3 I/O is selected
1 SEG24–SEG27 is selected, P5.0–P5.3 I/O is disabled
.5 LCD Output Segment and Pin Configuration Bits
0 P4.4–P4.7 I/O is selected
1 SEG20–EG23 is selected, P4.4–P4.7 I/O is disabled
.4 LCD Output Segment and Pin Configuration Bits
0 P4.0–P4.3 I/O is selected
1 SEG16–SEG19 is selected, P4.0–P4.3 I/O is disabled
.3 Not used for the S3C8245/C8249
.2 LCD Bias Voltage Selection Bit
0 Enable LCD initial circuit (internal bias voltage)
1 Disable LCD initial circuit for external LCD driving resister (external bias voltage)
.1 Voltage Booster Enable/disable Bit
0 Stop voltage booster (Clock stop and cut off current charge path)
1 Run voltage booster (Clock run current and turn on charge path)
.0 LCD Display Control Bit
0 LCD output low; turn display off, COM and SEG output low cut off voltage booster
(Booster clock disable)
4-15

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
1 COM and SEG output is in display mode; turn display on
4-16

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
LMOD — LCD Mode Control Register D1H Set 1
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write – – R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.6 Not used for the S3C8245/C8249
.5–.4 LCD Clock (LCDCK) Frequency Selection Bits
0 0
0 1
1 0
1 1
.3–.0 Duty and Bias Selection for LCD Display
0 x x x LCD display off (COM and SEG output low)
1 0 0 0 1/4 duty, 1/3 bias
1 0 0 1 1/3 duty, 1/3 bias
1 0 1 1 1/3 duty, 1/2 bias
1 0 1 0 1/2 duty, 1/2 bias
1 1 x x Static
32.768 kHz watch timer clock (fw)/29 = 64 Hz
32.768 kHz watch timer clock (fw)/28 = 128 Hz
32.768 kHz watch timer clock (fw)/27 = 256 Hz
32.768 kHz watch timer clock (fw)/26 = 512 Hz
4-17

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
OSCCON — Oscillator Control Register F3H Set 1,Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write – – – R/W R/W R/W – R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.5 Not used for the S3C8245/C8249
.4 Sub-system Oscillator Driving Ability Control Bit
0 Strong driving ability
1 Normal driving ability
.3 Main System Oscillator Control Bit
0 Main System Oscillator RUN
1 Main System Oscillator STOP
.2 Sub System Oscillator Control Bit
0 Sub system oscillator RUN
1 Sub system oscillator STOP
.1 Not used for the S3C8245/C8249
.0 System Clock Selection Bit
0 Main oscillator select
1 Subsystem oscillator select
NOTE: When OSCCON.4 is set to "0", Sub operating current and sub idle current are large.
4-18

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
P0CONH — Port 0 Control Register (High Byte) E0H Set 1,Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.6 P0.7/INT7
0 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; pull-up ; interrupt on falling edge
0 1 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising edge
1 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising or falling edge
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.5–.4 P0.6/INT6
0 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; pull-up ; interrupt on falling edge
0 1 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising edge
1 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising or falling edge
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.3–.2 P0.5/INT5
0 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; pull-up ; interrupt on falling edge
0 1 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising edge
1 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising or falling edge
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.1–.0 P0.4/INT4
0 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; pull-up ; interrupt on falling edge
0 1 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising edge
1 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising or falling edge
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
4-19

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
P0CONL — Port 0 Control Register (Low Byte) E1H Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.6 P0.3/INT3
0 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; pull-up ; interrupt on falling edge
0 1 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising edge
1 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising or falling edge
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.5–.4 P0.2/INT2
0 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; pull-up ; interrupt on falling edge
0 1 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising edge
1 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising or falling edge
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.3–.2 P0.1/INT1
0 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; pull-up ; interrupt on falling edge
0 1 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising edge
1 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising or falling edge
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.1–.0 P0.0/INT0
0 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; pull-up ; interrupt on falling edge
0 1 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising edge
1 0 Schmitt trigger input mode; interrupt on rising or falling edge
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
4-20

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
P0INT — Port 0 Interrupt Control Register E2H Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7 P0.7 External Interrupt (INT7) Enable Bit
0 Disable interrupt
1 Enable interrupt
.6 P0.6 External Interrupt (INT6) Enable Bit
0 Disable interrupt
1 Enable interrupt
.5 P0.5 External Interrupt (INT5) Enable Bit
0 Disable interrupt
1 Enable interrupt
.4 P0.4 External Interrupt (INT4) Enable Bit
0 Disable interrupt
1 Enable interrupt
.3 P0.3 External Interrupt (INT3) Enable Bit
0 Disable interrupt
1 Enable interrupt
.2 P0.2 External Interrupt (INT2) Enable Bit
0 Disable interrupt
1 Enable interrupt
.1 P0.1 External Interrupt (INT1) Enable Bit
0 Disable interrupt
1 Enable interrupt
.0 P0.0 External Interrupt (INT0) Enable Bit
0 Disable interrupt
1 Enable interrupt
4-21

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
P0PND — Port 0 Interrupt Pending Register E3H Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7 P0.7/INT7 Interrupt Pending Bit
0 Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
1 Interrupt request is pending
.6 P0.6/INT6 Interrupt Pending Bit
0 Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
1 Interrupt request is pending
.5 P0.5/INT5 Interrupt Pending Bit
0 Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
1 Interrupt request is pending
.4 P0.4/INT4 Interrupt Pending Bit
0 Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
1 Interrupt request is pending
.3 P0.3/INT3 Interrupt Pending Bit
0 Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
1 Interrupt request is pending
.2 P0.2/INT2 Interrupt Pending Bit
0 Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
1 Interrupt request is pending
.1 P0.1/INT1 Interrupt Pending Bit
0 Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
1 Interrupt request is pending
.0 P0.0/INT0 Interrupt Pending Bit
4-22

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
0 Interrupt request is not pending, pending bit clear when write 0
1 Interrupt request is pending
4-23

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
P1CONH — Port 1 Control Register (High Byte) E4H Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.6 P1.7/SI
0 0 Input mode (SI)
0 1 Output mode, open-drain
1 0 Alternative function (push-pull output)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.5–.4 P1.6/SCK
0 0 Input mode (SCK)
0 1 Output mode, open-drain
1 0 Alternative function (SCK out)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.3–.2 P1.5/SO
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Output mode, open-drain
1 0 Alternative function (SO)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.1–.0 P1.4/BUZ
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Output mode, open-drain
1 0 Alternative function (BUZ)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
4-24

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
P1CONL — Port 1 Control Register (Low Byte) E5H Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.6 P1.3
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Output mode, open-drain
1 0 Alternative function (push-pull output mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.5–.4 P1.2/T1OUT/T1PWM
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Output mode, open-drain
1 0 Alternative function (T1OUT, T1PWM)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.3–.2 P1.1/T1CLK
0 0 Input mode (T1CLK)
0 1 Output mode, open-drain
1 0 Alternative function (push-pull output mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.1–.0 P1.0/T1CAP
0 0 Input mode (T1CAP)
0 1 Output mode, open-drain
1 0 Alternative function (push-pull output mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
4-25

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
P1PUP — Port 1 Pull-up Control Register F5H Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7 P1.7 Pull-up Resistor Enable Bit
0 Pull-up disable
1 Pull-up enable
.6 P1.6 Pull-up Resistor Enable Bit
0 Pull-up disable
1 Pull-up enable
.5 P1.5 Pull-up Resistor Enable Bit
0 Pull-up disable
1 Pull-up enable
.4 P1.4 Pull-up Resistor Enable Bit
0 Pull-up disable
1 Pull-up enable
.3 P1.3 Pull-up Resistor Enable Bit
0 Pull-up disable
1 Pull-up enable
.2 P1.2 Pull-up Resistor Enable Bit
0 Pull-up disable
1 Pull-up enable
.1 P1.1 Pull-up Resistor Enable Bit
0 Pull-up disable
1 Pull-up enable
.0 P1.0 Pull-up Resistor Enable Bit
0 Pull-up disable
1 Pull-up enable
4-26

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
4-27

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
P2CONH — Port 2 Control Register (High Byte) E6H Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.6 P2.7/VLDREF/ADC7
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Input mode, pull-up
1 0 Alternative function (ADC & VLD mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.5-.4 P2.6/ADC6
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Input mode, pull-up
1 0 Alternative function (ADC mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.3–.2 P2.5/ ADC5
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Input mode, pull-up
1 0 Alternative function (ADC mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.1–.0 P2.4/ ADC4
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Input mode, pull-up
1 0 Alternative function (ADC mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
4-28

S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249 CONTROL REGISTER
P2CONL — Port 2 Control Register (Low Byte) E7H Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.6 P2.3/ADC3
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Input mode, pull-up
1 0 Alternative function (ADC mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.5–.4 P2.2/ADC2
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Input mode, pull-up
1 0 Alternative function (ADC mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.3–.2 P2.1/ADC1
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Input mode, pull-up
1 0 Alternative function (ADC mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
.1–.0 P2.0/ADC0
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Input mode, pull-up
1 0 Alternative function (ADC mode)
1 1 Output mode, push-pull
4-29

CONTROL REGISTERS S3C8245/P8245/C8249/P8249
P3CONH — Port 3 Control Register (High Byte) E8H Set 1, Bank 0
Bit Identifier .7 .6 .5 .4 .3 .2 .1 .0
nRESET Value 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Read/Write – – – – – – R/W R/W
Addressing Mode Register addressing mode only
.7–.2 Not used for the S3C8245/C8249
.1–.0 P3.4 Mode Selection Bits
0 0 Input mode
0 1 Input mode, pull-up
1 x Output mode, push-pull
4-30
 Loading...
Loading...