Samsung P10 C XTC 2000, P10 C XTC 2200, P10 C XTC 1900, P10 C XTC 1700, P10 XTC 1600 User Manual
...
Notices
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or
transmitted, in any form or by any means, mechanical photocopying, recording or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of the manufacturer.
The information within this manual is subject to change without notice.
The manufacturer shall not be held liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions
contained in herein; nor for incidental or consequential damages resulting from the
furnishing, performance or use of this material.
Microsoft Windows is a registered trademark of the Microsoft Corporation.
Product names mentioned herein are for identification purposes only, and may be
trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Macrovision Statement
If your computer has a DVD drive and an analog TV Out port, the following
paragraph applies:
This product incorporates copyright protection technology that is protected by method
claims of certain U.S. patents and other intellectual property rights owned by
Macrovision Corporation and other rights owners. Use of this copyright protection
technology must be authorized by Macrovision Corporation, and is intended for home
and other limited viewing uses only unless otherwise authorized by Macrovision
Corporation. Reverse engineering or disassembly is prohibited.
Copyright 2002 All rights are reserved
Notices i

Important Safety Information
Safety Instructions
Your system is designed and tested to meet the latest standards for safety of
information technology equipment. However, to ensure safe use of this product, it is
important that the safety instructions marked on the product and in the documentation
are followed.
Always follow these instructions to help guard against personal injury and
damage to your system.
i
Setting Up your System
• Read and follow all instructions marked on the product and in the
documentation before you operate your system. Retain all safety and operating
instructions for future use.
• Do not use this product near water or a heat source such as a radiator.
• Set up the system on a stable work surface.
• The product should be operated only with the type of power source indicated on
the rating label.
• Ensure that the electrical outlet you are using to power your equipment is easily
accessible in case of fire or short circuit.
• If your computer has a voltage selector switch, make sure that the switch is in
the proper position for your area.
• Openings in the computer case are provided for ventilation. Do not block or
cover these openings. Make sure you provide adequate space, at least 6 inches
(15 cm), around the system for ventilation when you set up your work area.
Never insert objects of any kind into the computer ventilation openings.
• Ensure that the fan vents on the bottom of the casing are clear at all times. Do
not place the computer on a soft surface, doing so will block the bottom vents.
• If you use an extension cord with this system, make sure that the total ampere
rating on the products plugged into the extension cord does not exceed the
extension cord ampere rating.
ii Users Manual
Care During Use
• Do not walk on the power cord or allow anything to rest on it.
• Do not spill anything on the system. The best way to avoid spills is to not eat or
drink near your system.
• Some products have a replaceable CMOS battery on the system board. There is
a danger of explosion if the CMOS battery is replaced incorrectly. Replace the
battery with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer.
Dispose of batteries according to the manufacturer’s instructions. If the CMOS
battery requires replacement insure that a qualified technician performs the task
• When the computer is turned off, a small amount of electrical current still flows
through the computer. To avoid electrical shock, always unplug all power
cables, remove the battery and modem cables from the wall outlets before
cleaning the system.
• Unplug the system from the wall outlet and refer servicing to qualified
personnel if:
– The power cord or plug is damaged.
– Liquid has been spilled into the system.
– The system does not operate properly when the operating instructions are
followed.
– The system was dropped or the casing is damaged.
– The system performance changes.
Replacement Parts and Accessories
Use only replacement parts and accessories recommended by manufacturer.
To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunications
line cord.
Do not use this product in areas classified as hazardous. Such areas include
patient care areas of medical and dental facilities, oxygen rich environments,
or industrial areas.
Battery Disposal
Do not put rechargeable batteries or products powered by non-removable
rechargeable batteries in the garbage.
Contact the Samsung Helpline for information on how to dispose of batteries that you
cannot use or recharge any longer.
Follow all local regulations when disposing of old batteries.
Important Safety Information iii

Laser Safety
All systems equipped with CD or DVD drives comply with the appropriate safety
standards, including IEC 825. The laser devices in these components are classified as
“Class 1 Laser Products” under a US Department of Health and Human Services
(DHHS) Radiation Performance Standard. Should the unit ever need servicing, contact
an authorized service location.
Laser Safety Note:
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those
specified in this manual may result in hazardous radiation exposure. To
prevent exposure to laser beams, do not try to open the enclosure of a CD or
DVD drive.
Power Cord Requirements
The power cord set (wall plug, cable and AC adapter plug) you received with your
computer meets the requirements for use in the country where you purchased your
equipment.
Power cord sets for use in other countries must meet the requirements of the country
where you use the computer. For more information on power cord set requirements,
contact your authorized dealer, reseller, or service provider.
General Requirements
The requirements listed below are applicable to all countries:
• The length of the power cord set must be at least 6.00 feet (1.8m) and a
maximum of 9.75 feet (3.0m).
• All power cord sets must be approved by an acceptable accredited agency
responsible for evaluation in the country where the power cord set will be used.
• The power cord set must have a minimum current capacity of 7 A and a
nominal voltage rating of 125 or 250 volts AC, as required by each country’s
power system.
• The appliance coupler must meet the mechanical configuration of an EN 60
320/IEC 320 Standard Sheet C13 connector, for mating with appliance inlet on
the computer.
iv Users Manual

Regulatory Compliance Statements
Wireless Guidance
Low power, Radio LAN type devices (radio frequency (RF) wireless communication
devices), operating in the 2.4 GHz Band, may be present (embedded) in your notebook
system. The following section is a general overview of considerations while operating
a wireless device.
Additional limitations, cautions, and concerns for specific countries are listed in the
specific country sections (or country group sections). The wireless devices in your
system are only qualified for use in the countries identified by the Radio Approval
Marks on the system rating label. If the country you will be using the wireless device
in, is not listed, please contact your local Radio Approval agency for requirements.
Wireless devices are closely regulated and use may not be allowed.
The power output of the wireless device or devices that may be embedded in your
notebook is well below the RF exposure limits as known at this time. Because the
wireless devices (which may be embedded into your notebook) emit less energy than
is allowed in radio frequency safety standards and recommendations, manufacturer
believes these devices are safe for use. Regardless of the power levels, care should be
taken to minimize human contact during normal operation.
As a general guideline, a separation of 20 cm (8 inches) between the wireless device
and the body, for use of a wireless device near the body (this does not include
extremities) is typical. This device should be used more than 20 cm (8 inches) from the
body when wireless devices are on and transmitting.
This transmitter must not be collocated or operate in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter.
Some circumstances require restrictions on wireless devices. Examples of common
restrictions are listed below:
Radio frequency wireless communication can interfere with equipment on
commercial aircraft. Current aviation regulations require wireless devices to be
turned off while traveling in an airplane. 802.11B (also known as wireless
Ethernet or Wifi) and Bluetooth communication devices are examples of
devices that provide wireless communication.
Regulatory Compliance Statements v

In environments where the risk of interference to other devices or services is
harmful or perceived as harmful, the option to use a wireless device may be
restricted or eliminated. Airports, Hospitals, and Oxygen or flammable gas
laden atmospheres are limited examples where use of wireless devices may
be restricted or eliminated. When in environments where you are uncertain of
the sanction to use wireless devices, ask the applicable authority for
authorization prior to use or turning on the wireless device.
Every country has different restrictions on the use of wireless devices. Since
your system is equipped with a wireless device, when traveling between
countries with your system, check with the local Radio Approval authorities
prior to any move or trip for any restrictions on the use of a wireless device in
the destination country.
If your system came equipped with an internal embedded wireless device, do
not operate the wireless device unless all covers and shields are in place and
the system is fully assembled.
Wireless devices are not user serviceable. Do not modify them in any way.
Modification to a wireless device will void the authorization to use it. Please
contact manufacturer for service.
Only use drivers approved for the country in which the device will be used. See
the manufacturer System Restoration Kit, or contact manufacturer Technical
Support for additional information.
vi Users Manual
European Union
The following information is only applicable to systems labeled with the CE mark .
European Directives
This Information Technology Equipment has been tested and found to comply with the
following European directives:
• EMC Directive 89/336/EEC with amending directives 92/31/EEC & 93/68/
EEC as per
– EN 55022 Class B
– EN 61000-3-2
– EN 61000-3-3
– EN 55024
• Low Voltage Directive (Safety) 73/23/EEC as per EN 60950(A1/A2/A3/A4/
A11)
• Radio and Telecom Terminal Equipment Directive 199/5/EC as per
– CTR21 (if fitted with a modem device)
– ETS 300 328 (if fitted with a 2.4 GHz band embedded wireless device)
– ETS 301 489-1 (if fitted with a 2.4 GHz band embedded wireless device)
– ETS 301 489-17 (if fitted with a 2.4 GHz band embedded wireless device)
European Radio Approval Information (for products fitted with EU-approved radio devices)
This Product is a Notebook computer; low power, Radio LAN type devices (radio
frequency (RF) wireless communication devices), operating in the 2.4 GHz band, may
be present (embedded) in your notebook system which is intended for home or office
use. This section is only applicable if these devices are present. Refer to the system
label to verify the presence of wireless devices.
Wireless devices that may be in your system are only qualified for use in the European
Union or associated areas if a CE mark with a Notified Body Registration Number
and the Alert Symbol is on the system label.
The power output of the wireless device or devices that may be embedded in you
notebook is well below the RF exposure limits as set by the European Commission
through the R&TTE directive.
Regulatory Compliance Statements vii
European States qualified under wireless approvals:
EU
Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France (with frequency
restrictions),
Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, The
Netherlands, Portugal, Spain, Sweden and the United Kingdom.
Accept EU
Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland
European States with restrictions on use:
EU
In France, the frequency range is restricted to 2446.5-2483.5 MHz for
devices above 10 mW transmitting power such as wireless LAN.
Accept EU No limitations at this time.
European Telecommunication Information (for products fitted with EU-approved modems)
Marking by the symbol indicates compliance of this equipment to the Radio and
Telecom Terminal Equipment Directive 1999/5/EC. Such marking is indicative that
this equipment meets or exceeds the following technical standards:
CTR 21 – Attachment requirements for pan-European approval for connection to the
analogue Public Switched Telephone Networks (PSTNs) of TE (excluding TE
supporting voice telephony services) in which network addressing, if provided, is by
means of Dual Tone Multi-Frequency (DTMF) signaling.
Although this equipment can use either loop disconnect (pulse) or DTMF
(tone) signaling, only the performance of the DTMF signaling is subject to
regulatory requirements for correct operation. It is therefore strongly
recommended that the equipment is set to use DTMF signaling for access to
public or private emergency services. DTMF signaling also provides faster call
setup.
This equipment has been approved to Council Decision 98/482/EEC—“CTR 21” for
Pan-European single terminal connection to the Public Switched Telephone Network
(PSTN).
However, due to differences between the individual PSTNs provided in different
countries, the approval does not, of itself, give an unconditional assurance of
successful operation on every PSTN termination point. In the event of problems, you
should contact manufacturer Technical Support.
viii Users Manual

Japan
VCCI Statement
This equipment is in the Class B category (Information Technology Equipment to be
used in a residential area or an adjacent area thereto) and conforms to the standards set
by the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by Information Technology
Equipment aimed at preventing radio interference in such residential areas. When used
near a radio or TV receiver, it may become the cause of radio interference. Read
instructions for correct handling.
Wireless Devices
Low power, Radio LAN type devices (radio frequency (RF) wireless communication
devices), operating in the 2.4 GHz Band, may be present (embedded) in your notebook
system. This section is only applicable if these devices are present. Refer to the system
label to verify the presence of wireless devices.
Wireless devices that may be in your system are only qualified for use in Japan if a
TELEC ID is on the system label.
Operational guidelines for 2.4 GHz band wireless equipment (if equipped)
This equipment uses the 2.4 GHz ISM frequency band. The ISM band is the industrial,
scientific, and medical device band. Devices that might also use this band are
microwave ovens, other LAN devices, amateur radio stations, licensed premises radio
stations, and non-licensed specified low-power radio stations.
Regulatory Compliance Statements ix

Prior to setting up your device:
1. Make sure that there are no other devices in your area using the same frequency
band.
2. Change the channel, location, or discontinue device use if you are interfering with
any other radio station.
3. Contact manufacturer if you have any problems with this device.
x Users Manual
Using Your Documentation
Congratulations on your purchase of a notebook computer with the Windows® XP
operating system. Whether you are new to using a portable computer or are an
experienced user, this user’s manual can help you get the most from your computer.
Manual Documentation Conventions
Information Icons
Three icons and their associated messages appear in this manual. The information
icons are placed before the step/information they apply to:
Warning:
Indicates the possibility of personal injury.
Caution:
Warns you of possible damage to equipment or data.
Note:
Informs you of special circumstances.
Technical Information:
Informs you of special requirements or limitations for use of item(s).
Keyboard Conventions
Keys that you need to press to perform certain functions are displayed in the manual
using a small graphic of the button. For example: <Ctrl>
or <Ctrl> indicates the control key (Ctrl on the keyboard).
If you need to press two keys at the same time, the key names are shown joined by a
plus sign. For example:
+
means that you should press the Fn key and hold it and then press the F8 key.
or <Fn+F8>
Using Your Documentation 1

CD-ROM Device Naming Convention
In many installation programs you will have to get a program from the CD-ROM
device. The program installation sequence assumes that the CD is drive d:\, however
this is not always the case. The name of the CD-ROM drive is the letter following the
letter assigned to your last HDD. For instance, if you have one HDD with two
partitions, the HDD is drives C: and D: and the CD-ROM drive is then drive E.
Touchpad Conventions
You may be asked to click or double-click on items on the display screen. As a general
note the touchpad actions act much in the same way as a wheel mouse, any differences
are explained fully.
The object that needs to be clicked upon will be displayed in Bold text or shown in a
small figure such as the “Start Button” shown on the right =>.
Table 1. Touchpad Click Conventions
Action Process
Click Depress the touchpad left button and release
Double-click Quickly click the left touchpad button two times
Windows Conventions:
Almost all “Windows” programs will display the name/function of a button or
icon if you place the touchpad pointer on the item you want information about.
Software User Documentation
Your computer is shipped from the factory with several software programs installed.
The software may include its own online or printed documentation. Refer to the
documentation or the Help options in the software for more information.
The figures and illustrations in this manual may not be identical to those on
your system.
General Icon Note:
Some of the Icons used in Windows XP may be placed on the taskbar by
selecting (ex: Place the volume icon in the taskbar) in the properties dialog
box.
2 Users Manual

Introducing Your Computer
Your computer is a lightweight portable computer that includes features such as Dolby
Digital & Dolby Home Theater System support, DVD-ROM/floppy drives, Biometric
(fingerprint) security system (factory option), Memory Stick (factory option), wireless
LAN capability (factory option), Bluetooth Wireless (factory option), CD/MP3 player
(factory option) to meet your computing needs at home or on the road.
(Figures may be different depending on options).
Where Everything Is
The next 8 figures will explain the location of all of the buttons, LEDs and equipment
needed to operate your notebook computer.
Front
NOTE:
The protective cover will
replace the Biometric
Security Pad if the option is
Biometric
Security
pad
not ordered.
SENS Keyboard
Buttons
Keyboard
LEDs
Power Button
Protective
Cover
Speaker
Touchpad
LCD Latch
Internal Microphone
Touchpad Buttons
Speaker
Introducing Your Computer 3

Buttons and LEDs
User Programmable Button
E-Mail Button
Internet Button
Power Button
Battery Status LED
Power LED
HDD Access Icon
CD Access Icon
FDD Access Icon
Power, Play/Pause & Track Indicator
Volume Up
Volume Down
MP3/CD Player Option
No MP3/CD Player Option
Scroll Lock Icon
Number Lock Icon
Caps Lock Icon
Power On-Play/Pause
Previous/Fast Search-Reverse
Stop/Eject-Power Off
Next/Fast Search-Forward
4 Users Manual

Right Side
Left Side
Back Side
Modem Port
LAN Port
CD/DVD - ROM
Fan Vent
Memory Stick Slot
* Factory Option
PC Card Slot
PC Card Eject Button
Headphone / S/PDIF Jack
Microphone Jack
PS/2 Port
1394 Port
Parallel
Printer Port
DC-In Port
VHS TV-Out Port
Serial Port
Security Lock Port
Fan Vent
USB Ports
External Monitor Port
Introducing Your Computer 5
FIR
* Factory Option

Bottom
Compartment
Flex-Bay
Battery
Flex-Bay Latch
Fan Vent
Docking
Connector
Battery Latch
Memory
Compartment
6 Users Manual
Using Your Computer for the First Time
This section gives you detailed information on using your computer for the first time.
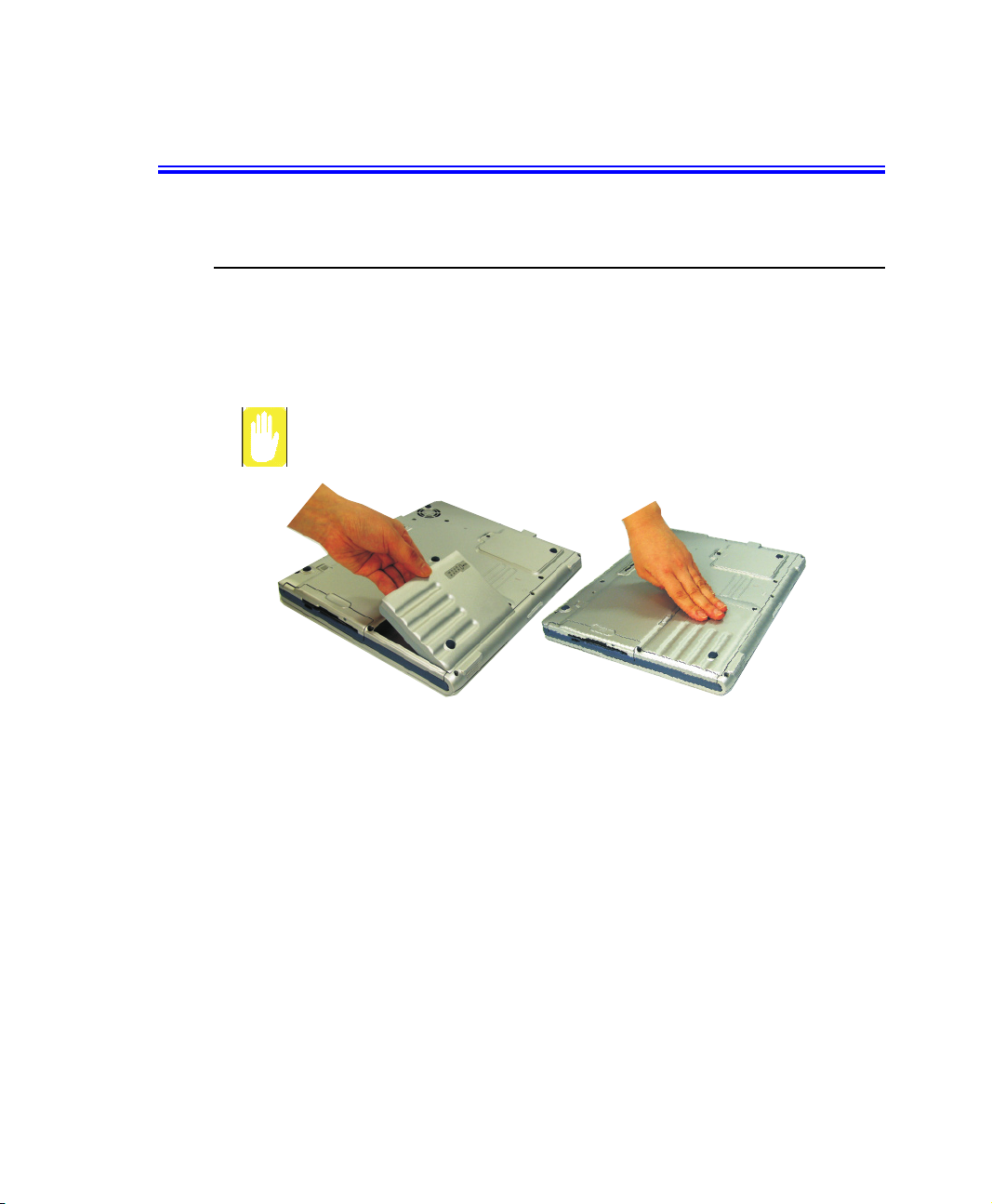
Installing the Battery
To install the battery pack:
1. With the computer’s power off, close the LCD panel and turn the computer over
so the bottom of the unit faces up.
Insert the battery into the battery compartment, ensuring the correct
orientation so that the battery fits in its slot properly.
2. Place the battery inside and against front side of the computer battery compartment
at an angle of approximately 30 degrees.
3. Push the battery down until the latch snaps into place, securing the battery.
Using Your Computer for the First Time 7

Attaching the AC Adapter
Your computer runs on power from the battery in the computer or from an electrical
outlet. The first time that you use your computer, fully charge the battery by attaching
the power cord to the computer and to an electrical outlet.
All batteries lose their charge if they sit unused for an extended time period.
When not used, battery can discharge fully in 2 to 3 months. The battery may
have discharged in the time it took for the computer to go from the factory to
you.
To attach the power cord:
1. Plug the AC adapter into the power connector on the back side of the computer.
2. Connect the power cord to the AC adapter and then to an electrical outlet.
AC Adapter
The battery starts charging as soon as you plug the power cord into an electrical outlet.
The battery charges faster if the computer is turned off during charging.
If the battery is fully depleted and the computer is turned off, the battery charges in
about 3 hours. If the computer is turned on, the battery charges in about 6 hours. When
the battery is charging, the battery charge light is red. When the battery is fully charged,
the light turns green.
See ”Using Power Management Options” on page 57 for more information on using
your computer’s battery.
8 Users Manual
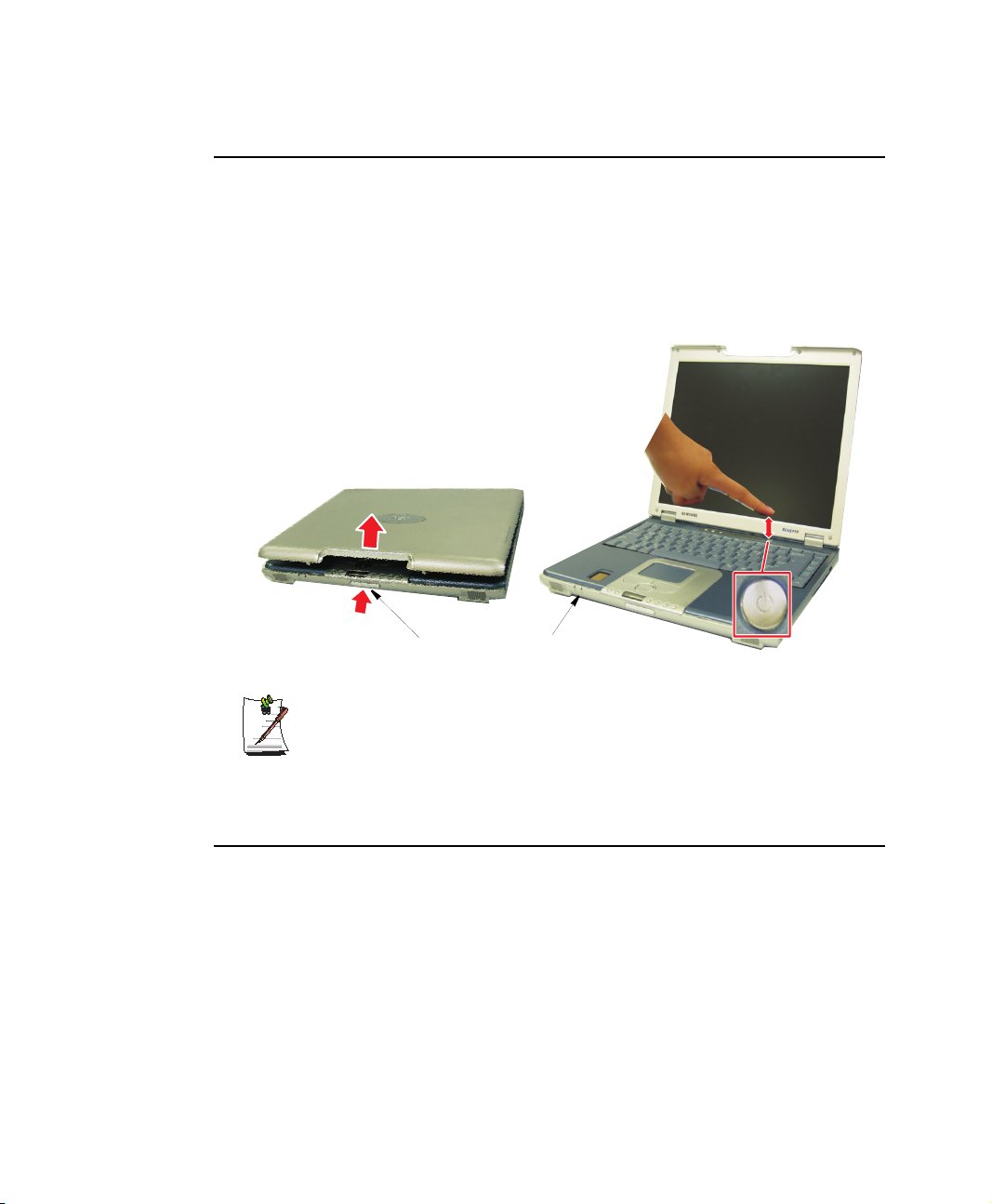
Turning On the Computer
To turn on the computer’s power for the first time:
1. Push the LCD cover button, located on the front of the computer below the MP3/
CD Player.
2. Lift up the cover.
3. Press and then release the power button.
The power light is on when the computer’s power is on.
Cover Latch Button
Initial Computer Startup:
The first time you start your computer you will see the operating system
registration screens. Simply read each screen and follow the simple directions.
You must complete this process in order to use your computer. A tutorial is
provided if you require it.
Power Light
Power Button
Adjusting the LCD Display
You may wish to adjust the LCD (Liquid-Crystal Display) when you begin using your
computer. A TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) LCD does not require adjustment for contrast
because the contrast is set to remain at maximum.
To adjust the LCD:
• Press <Fn+Up Arrow> to increase the display brightness.
• Press <Fn+Down Arrow> to decrease the display brightness.
Using Your Computer for the First Time 9

Turning Off Your Computer
Prior to shutting down your computer ensure all of your data and current work are
saved. The system will ask if you wish to save any unsaved work, saving your work
first will speed the shutdown process.
To turn off the computer, complete the following steps:
1. Click on the taskbar.
If you need to restart your computer after software (re)installation or because it is not
responding select the Restart option in step 3 below.
2. Click Shut Down Computer to display the shutdown popup window shown
below.
3. Click Turn Off to complete the shutdown sequence.
Power Off:
If the system does not power off, then press and hold the power button for over
5 seconds. See ”Using Power Management Options” on page 57.
You can also perform a soft boot by saving your files and pressing
<Ctrl+Alt+Del> to pop-up the “Windows Task Manager” window.
Click Shut Down > Restart.
You can perform a cold boot by pressing the power button for more than 4 seconds to
turn the computer off, waiting more than five seconds, and then pressing the power
button to turn the computer on. The system may perform some extra checks during the
restart.
10 Users Manual
Power Button Functions:
The power button has several functions other than just turning on and off your
computer, see “Using Power Management Options” on page 57.

Tips for Using Your Computer
The following information helps you avoid potential problems as you use your
computer:
Do not try to disassemble your computer. Opening the system chassis voids
your warranty. Only an authorised manufacturer service center can replace or
add any parts inside the chassis.
• Follow all the instructions and cautions in your computer user documentation.
• The LCD has a polarized surface and can be damaged easily. To prevent
damage, avoid touching the screen.
• Use only approved AC adapters, auto adapters, memory modules and other
options.
• Because a notebook computer is small and has restricted air flow around
components, it is more likely to overheat than a desktop computer. A fan inside
your computer runs when needed to help eliminate heat. Make sure the fan vent
on the left side of your computer is not blocked when you use the computer.
Occasionally check the vents and remove any accumulated dust on the outside.
• Avoid using or storing the computer in extremely hot or cold areas, such as a
car on a hot day. Keep the computer away from heaters and out of direct
sunlight. Exposure to excessive heat may damage computer components. If you
have left your computer in a hot place, let it cool down slowly to room
temperature (with the LCD panel open) before using it.
• Do not remove the memory-module compartment door, or try to install a
memory module when the computer is on. (For information on installing
memory modules, see “Installing a Memory Module” on page 70.)
• Set up your computer work area to avoid physical strain. Sit with your back
straight and supported by your chair. Adjust your chair or work table so that
your arms and wrists can remain in a relaxed position, parallel with the floor.
Avoid bending or twisting your wrists as you work. Your hands should “float”
slightly above the keyboard. Refer to a book on office ergonomics for more
information on setting up your work area.
• Take frequent breaks from working at the computer to rest your eyes and
stretch your muscles.
• Remember to save your data files frequently and to make backup copies of your
files.
Using Your Computer for the First Time 11

Travelling with Your Computer
Air Travel
If you are travelling by air, follow these tips:
• Take the computer with you as carry-on luggage. Do not check the computer
with your baggage.
• Allow the computer and disks to go through the X-ray security devices. Do not
hand-carry disks through the walk-through metal detectors, which can cause
loss of data.
• Make sure that the battery is charged or the power cord is easily accessible.
You may be required to turn on the computer for airport security personnel.
• Be prepared to turn off the computer during take off and landing.
Locking your Computer
As a precaution when you are travelling or using your computer in an unsecured area,
you should keep your computer as safe as possible. An option to do this is the Security
Lock System. Follow the Security Lock System manufacturers instructions for specific
installation and use. The following figure shows generally how to use the lock.
12 Users Manual
From Lock
To Lock
Handling Spills
Do not spill anything on your computer. The best way to avoid spills is to avoid eating
and drinking around your computer. If you do spill something on your computer, turn
off your computer, unplug it immediately, and do the following:
• If you spill liquid on the keyboard, drain as much of the liquid from the
keyboard as possible. Be careful not to let the liquid drip onto the LCD panel.
Allow the system to dry for several days before trying to use it.
• If you spill liquid on an external keyboard or keypad, unplug it and drain as
much of the liquid as possible. Allow the keyboard to sit at room temperature
for a full day before trying to use it.
Sweet liquids leave a sticky residue that may jam the keyboard despite your
efforts to dry it.
• If you spill liquid on the LCD panel, clean it immediately with a soft cloth and
denatured alcohol or a proprietary LCD screen cleaner. Do not use water,
window cleaner, acetone, aromatic solvent, or dry, rough towels to clean it.
Some liquids damage the polarized LCD screen. If your screen is damaged,
contact your authorized manufacturer’s service center for a replacement.
Storing the Computer for Long Periods
If possible, leave the power cord connected to the computer and an electrical outlet
when the computer is not in use. This extends the life of the battery and keeps the
battery fully charged.
If you will not be using the computer for a long period of time (a month or more), you
should charge the battery until it is completely full. After you have done so, remove the
battery from the unit.
Using Your Computer for the First Time 13
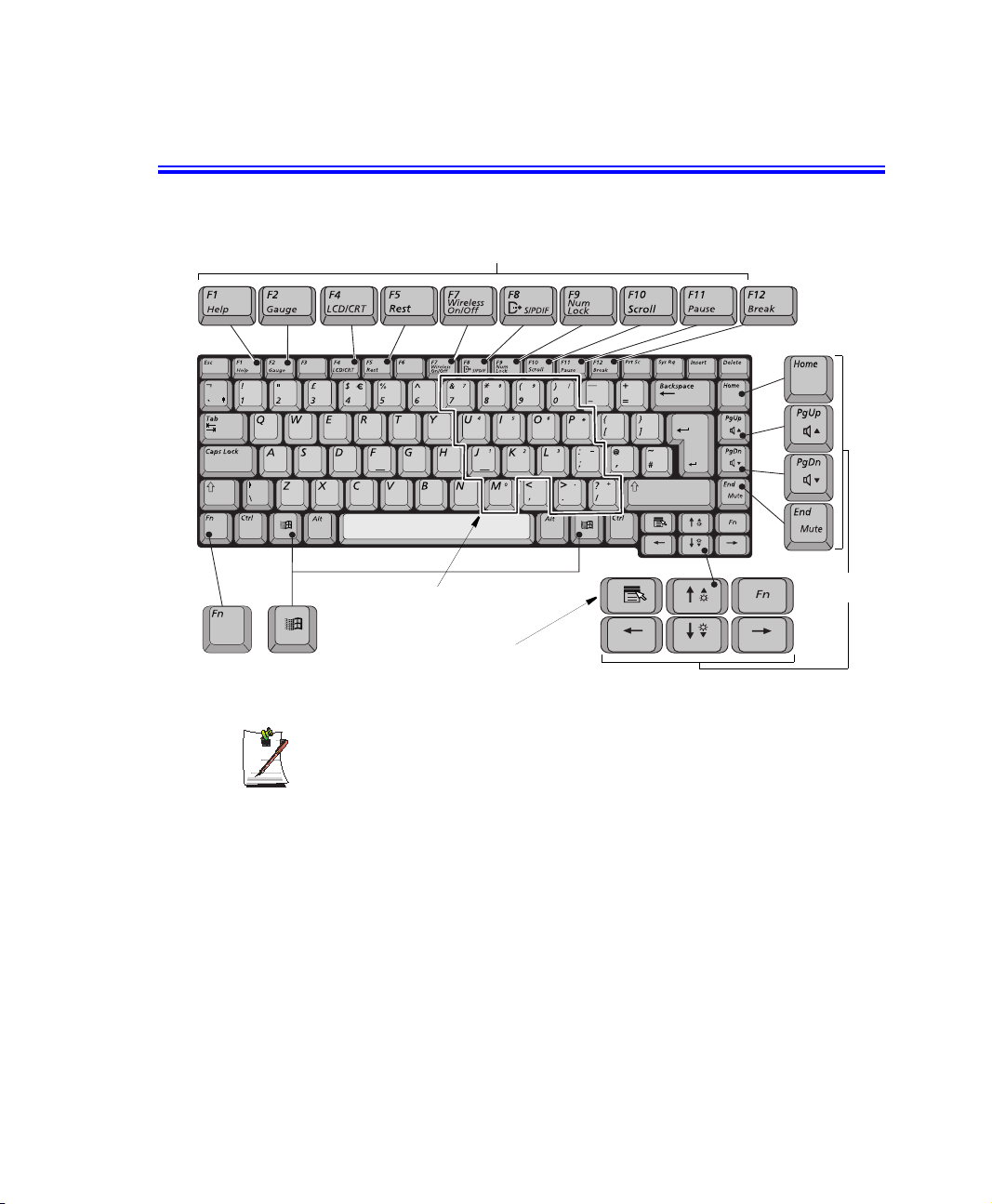
Using the Keyboard
Your computer has an 87/88-key keyboard. By pressing designated key combinations,
you can have access to all the key functions of a full-sized keyboard.
Function & Special Purpose Keys
Embedded Numeric Keypad
Cursor/Screen
Control Keys
Function
Key
The keys on the keyboard can be grouped into the following categories:
14 Users Manual
Windows
Key
Although the layout of the keys on your computer’s keyboard is different from
that on a desktop computer’s keyboard, the keyboard feels like a full-sized
keyboard when you use it.
Application Key
• Full-sized Alphanumeric typewriter keys are arranged like a standard
typewriter keyboard and are used for text entry. The Windows keys on either
side of the spacebar open Windows menus and perform other special functions.
• Function keys, when pressed together with the <Fn> key, enable special
functions.
• Cursor and Screen control keys move the cursor. They may perform other
functions, depending on your software.
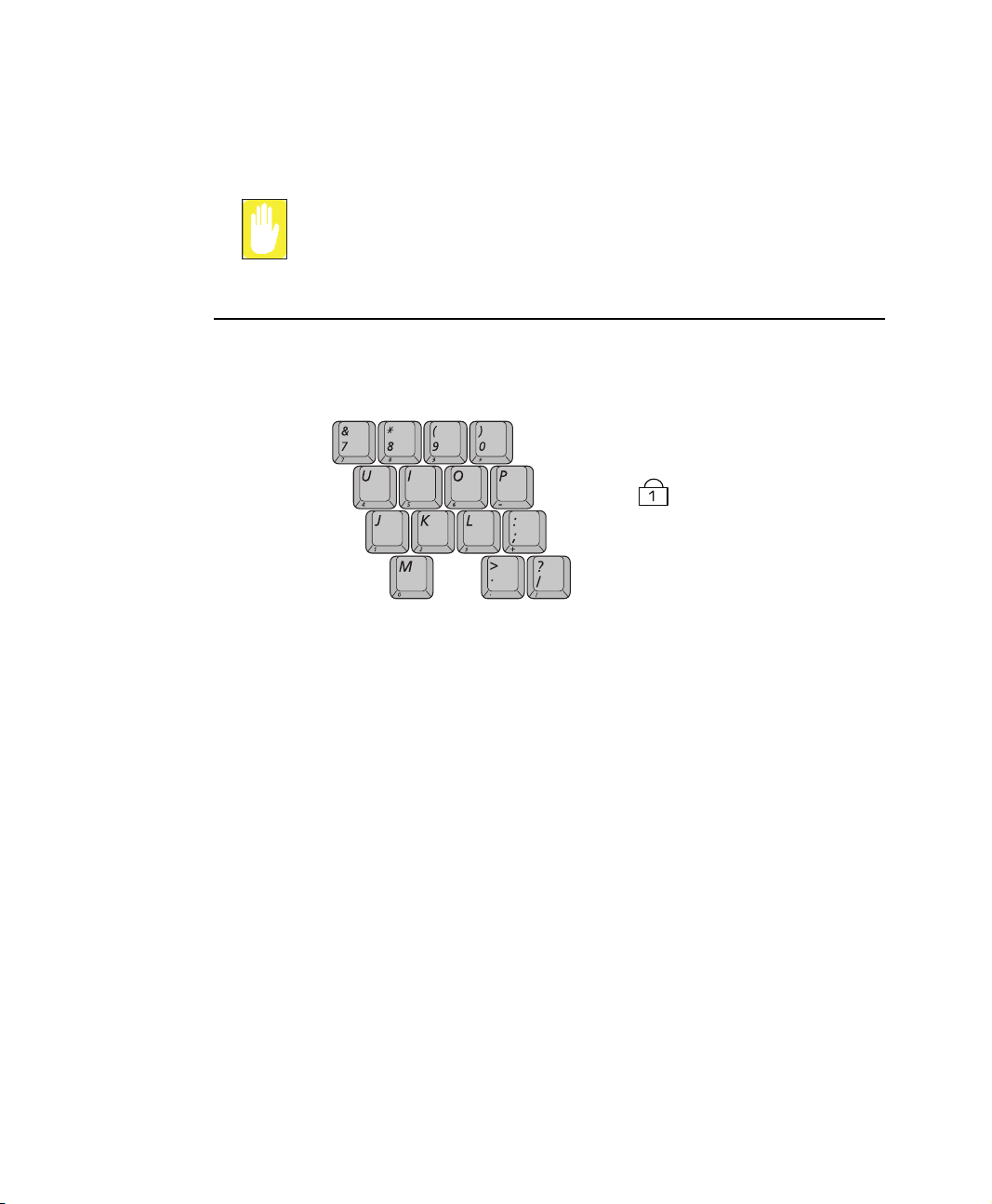
To clean the computer keyboard, use slightly damp cotton swabs. Scrub the keys and
the surface around the keys.
Do not allow liquid to drip into the keyboard or you may damage the keyboard.
Using the Numeric Keypad
Your keyboard includes a numeric keypad, which is a group of keys that you can set to
type numbers and mathematical symbols, such as the plus sign. A number or symbol
on the right corner of each keypad key shows its numeric function.
Num Lock LED
Press <Fn+F9> to turn on the embedded numeric keypad. The numeric functions of
the keypad are enabled and the Num Lock LED turns on. (See ”Reading the System
Status Lights” on page 22 for the location of the Num Lock LED.)
While the numeric functions are enabled, you can temporarily return a key to its normal
function by pressing and the <Fn> key. For example to type the letter m, press
<Fn+M>, this operation displays the letter m.
To turn the numeric keypad off, press <Fn+F9> again. The Num Lock LED turns off.
Using the Keyboard 15

Using Special Function Keys
The function key activates special functions when it is pressed in combination with
another keys. Table 2 shows the special key combinations.
Table 2. Description of Special Function Key Combinations
<Fn> Key
Combinations
<Fn+F2> F2
<Fn+F4> F4
<Fn+F5> F5
<Fn+F7> F7
<Fn+F8> F8
<Fn+F9> F9
<Fn+F10> F10
<Fn+PgUp> PgUp: Volume up: Increases the audio volume.
Key Name Key Function
Gauge
CRT/LCD
Rest:
WLAN
S/PDIF
Numlock
Scroll
Gauge Displays the battery gauge in the upper-right corner
CRT/LCD: Switches the display between the LCD, the external
Rest: Puts the computer into Suspend mode. To resume
WLAN: Toggles the Wireless LAN function On/Off
S/PDIF: Toggles the S/PDIF function On/Off
Numlock: Activates the numeric keypad
Scroll: In some applications, sets the cursor-control keys to
of your screen.
The gauge closes in a few seconds, or you can press
<Esc> to close the gauge. (See ”Monitoring the
Battery Charge” on page 48 for more information on
the battery gauge.)
This function will also display status of Wireless LAN
and
S/PDIF functions.
monitor, and simultaneous display on both the LCD
and the external monitor.
normal operation from rest, press the power button.
(See ”Using Power Management Options” on page
57 for more information about the rest mode.)
scroll the page up or down while the cursor position
does not change. Pressing key combination again
turns off the scrolling function.
<Fn+PgDn> PgDn Volume
<Fn+End> End
<Fn+Up Arrow> Brightness
<Fn+Down Arrow> Brightness
Mute:
When you press a function key combination, the system sound may be
temporarily muted.
16 Users Manual
down:
Mute: Mutes the audio.
Up:
Down:
Decreases the audio volume.
Increases the LCD brightness.
Decreases the LCD brightness.
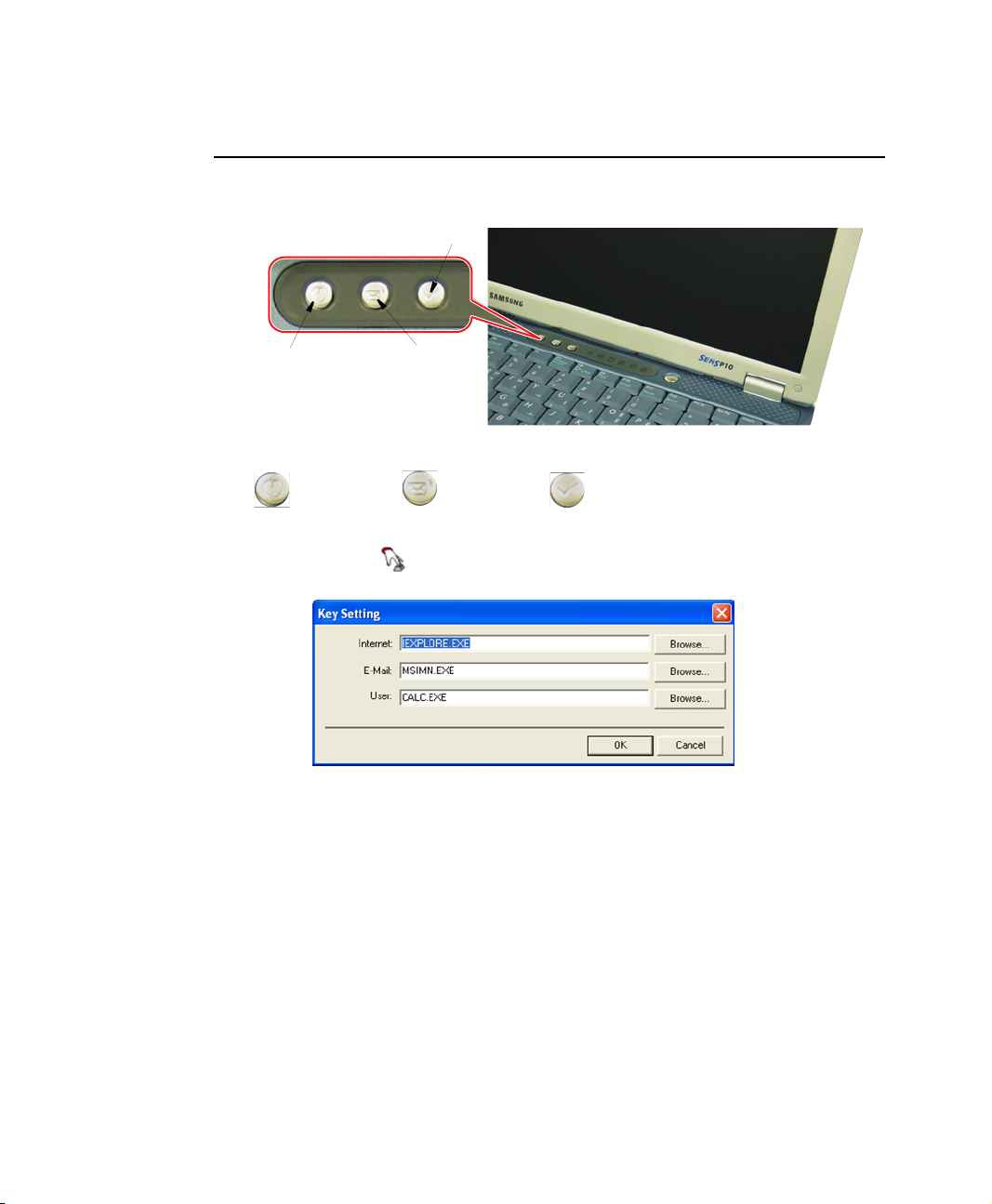
User Defined Buttons (SENS Keyboard)
You may program the three buttons to the left of the power button to start any program
you have installed on your computer.
User defined program
Internet Explorer
Outlook Express
The default settings for these buttons are:
Internet E-Mail - Outlook Windows Calculator
To reprogram the Sens Keyboard, follow the steps below:
1. Double-click icon on the Windows taskbar, the Key Setting window is
displayed.
2. Select Button you wish to reprogram from the drop down menus in the Key
Setting window.
3. Use the Browse button to locate the program you wish to assign to the SENS
Keyboard button selected.
4. Click on your program choice to select it.
5. Click Open.
6. Click OK to close window and complete programming the Sens Keyboard.
Using the Keyboard 17

Using the Touchpad
Your computer is equipped with a touchpad, which is an integrated-pointing device
that is used to perform standard mouse functions. The touchpad is an advanced and
reliable pointing device that works with a touch of your finger.
Touchpad
Mouse Buttons
Scroll Button
Four (4) Direction Scroll Button (Default is a 2 Direction Button)
If you have purchased your computer without the CD/MP3 player option your
computer will have a four (4) direction scroll button. The operation of the scroll
button is explained below.
18 Users Manual
Scroll Button Use
The scroll button driver is not installed as part of the original program/driver
installation. If you wish to use the scroll button you must install the scroll button
driver located on the Software CD that comes with your computer.
Press on the touchpad gently. The touchpad responds to light pressure.

d
Action Process and Comment
Click/Tap
Process
Depress the touchpad left button and release or position the pointer
over the object and Quickly tap the touchpad once with your finger.
This action is called clicking.
Comment
This will cause a process to begin or select an object on the screen.
Double-click/Tap
Click-Hold
Right-click
Process
Quickly click the left touchpad button two times or position the pointer
over the object and Quickly tap the touchpad twice with your finger.
This action is called Double-clicking.
Comment
This will cause a process to begin or open a file folder.
Process
Depress the left touchpad button and do not release.
Comment
This is used to move/drag objects to new locations. See ”Drag (Move)”
on page 21.
Process
Position the pointer over the object. Quickly press and release the right
button once.
This action is called Right-clicking.
Comment
This is usually used to obtain information about an object or
access a short cut menu.
Using the Touchpad 19

Action Process and Comment
Scroll Up
Scroll Down
Process
Place your finger on the top half of the button to scroll up the current
window.
Comment
Moves the current window down.
Process
Place your finger on the bottom half of the button to scroll up the current
window.
Comment
Moves the current window up.
Scroll Left
Scroll Right
Process
Place your finger on the left half of the button to scroll left in the current
window.
Comment
Moves the current window right.
Process
Place your finger on the right half of the button to scroll right in the
current window.
Comment
Moves the current window left.
PS/2 Mouse Menu:
You may change the setup in Setup > Advanced Menu
Disabled : Prevents any installed PS/2 mouse from functioning, but frees
up IRQ12.
Enabled : Forces the PS/2 mouse port to be enabled regardless if there is
a mouse present.
Auto Detect :Enables the PS/2 mouse only if present.
20 Users Manual

Drag (Move)
To move a window on the desktop, complete the following:
1. Click the window title bar or icon in the bottom of the window which you want
to drag using the touchpad.
2. Press the left touchpad button and hold it.
3. Drag the window using the touchpad.
Cursor in Windows
Title Bar
2
1
1 Click the Window
Title Bar and Hold
Area or Multiple item selection:
The drag function may be used to select an area or multiple items in an area
by clicking in one area and then dragging to create a selection window. The
items inside the window will be selected.
2 Drag your finger to
move the window
Using the Touchpad 21

Reading the System Status Lights
System Top
System Status lights show the status of computer functions.
LED Name Function
HDD Access Blinking Green - HDD is being accessed.
CD Access Blinking Green - CD is being accessed.
FDD Access Blinking Green - FDD is being accessed.
System Bottom
LED Name Function
22 Users Manual
Num Lock Changes a portion of the keyboard to a numeric keypad.
Caps Lock Changes all alpha or letter input into capital letters.
Scroll Lock Scroll lock in certain software.
Power Green - System power on.
Battery Status Green - No battery pack installed/battery fully charged.
See ”Using the Numeric Keypad” on page 15.
No changes occur to numeric and special keys.
Blinking - Standby mode.
Amber - Charging.
Blinking - Bad Battery

Connecting to the Internet
This section explains how to connect you to the internet. For details on how to establish
the connection contact the Internet Service Provider [ISP] or system administrator
[SysAdmin].
Using the Modem
Install the Modem cable by simply plugging the cable into the modem slot as shown in
the figure below.
Your Notebook computer will have a Modem/LAN installed.
Modem Cable
(Minimum 26 AWG)
1. Contact your Internet Service Provider to obtain information or CD required to
make the connection in your area.
2. After the cable is connected create a “Dialup” connection by clicking
Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet Connections.
3. Click Set up or change your Internet connection > Setup to start the connection
wizard.
4. Follow the instructions in provided in the Make New Connection wizard.
Connecting to the Internet 23

Precautions Before Use
Country Selection
Country Selection:
Because your computer is very mobile you must ensure you select the
country you are calling from is selected correctly, otherwise you may
experience connection problems.
To change the country selection proceed as follows:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet Connections.
2. Click Phone and Modem Options.
3. Click on the connection you wish to edit in the Locations: box.
4. Click Edit in the Dialing Rules Tab
5. Select the Country/region you are calling from in the General tab.
6. Click OK to close the “Edit Locations” box.
7. Click OK to close “Phone and Modem Options” box.
Digital Phone Lines:
If you connect the modem to a digital phone line (such as a company
4-wire system), the modem may be damaged.
DOS support
• Windows XP: Does not support pure DOS mode and the modem does not
support a DOS box in Windows. So you cannot use a
communication application which runs under DOS.
Using the Modem on a PBX system
If you use a Windows Communication Program:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet Connections.
2. Click Phone and Modem Options.
3. Click Properties in the Modems tab section.
4. Check off “Wait for dial tone before dialing” check box in the Modem tab section.
5. Click OK to close the dialog box.
6. Click OK to close “Modem Properties” dialog box.
24 Users Manual

If you use a simple terminal program (i.e. hyper terminal):
Type the “ATX3&W” or “ATX3” command as an initialization command.
MODEM Notes:
1. In order to use the 56K feature, be sure to check if the standards supported
by the on-line service provider and the modem are identical.
2. If you use a PBX phone system, you can not connect using the 56K mode.
3. Internationally connected calls will be limited to 33.6K (Max.)
Using the LAN
You may connect to the network using either a LAN cable or by establishing a wireless
connection if factory option is installed.
Cable Connection
Install the LAN cable by simply plugging the cable into the slot in the left side of the
computer.
Your computer’s LAN adapter is ready to use for most situations, however if your
system does not have a DHCP server or you wish to personally configure your LAN
connection, proceed as outlined in “Configuring Network Environment” below.
Network Protocols:
You may need to consult your SysAdmin if their network protocols and settings
are required for your LAN environment.
Connecting to the Internet 25

Configuring Network Environment
Configure the Network Adapter as follows:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet Connections
2. Click icon (Network Connections).
3. Right-click the icon (Labeled Local Area Network) then click Properties
button.
4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) in the “This connection uses the following
items:” box.
Intel(R) Pro/100 VE Network Connection
5. Click Properties. The TCP/IP Properties window opens.
6. Click “Use the following IP address” in the General tab
7. In the “Use the following IP address” box, enter your IP address:, subnet mask:
8. In the “Use the following DNS server addresses” box, Enter your Preferred DNS
9. Click OK when you finish the TCP/IP set-up.
26 Users Manual
Step 7
Step 8
and Default Gateway:.
server: and Alternate DNS server:.

Wireless Connection (Factory Option)
Your computer’s wireless LAN adapter is ready to use for most situations, however if
your system does not have a DHCP server or you wish to personally configure your
wireless LAN connection, proceed as outlined in “Configuring Network Environment”
below.
Regulatory Notice for Channel Use in France
The number of channels that can be used for wireless LAN differs from country
to country.
In France however, use only 4 channels (2446.5~2483.5MHz) when using
wireless networks.
• Channel Allocation: Channel 10, 11, 12, 13.
The table below shows the Windows taskbar icons for the wireless LAN.
Icon Name Description
Connection
Established
Connection
Unavailable
Displays if connection is available.
Displays if connection is unavailable.
To display relative Signal Strength:
1. Double-click the icon in the taskbar to display the Wireless Network
Connection Status window. This window also displays connection Status, Speed,
Duration and Activity.
Network Protocols:
You may need to consult your System Administrator if their network protocols
and settings are required for your wireless LAN environment.
Connecting to the Internet 27

Configuring Network Environment
Configure the Wireless Network Adapter as follows:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Network and Internet Connections
2. Click icon (Network Connections)
3. Double-click the Wireless Network Connection icon. The Connect to Wireless
Network window pops up.
General Office Net
Supervisor Office Net
4. Select one of the available networks in the Available networks section, if
displayed.
No networks are displayed
Office - Consult your system administrator.
Home - Verify your access point is working properly.
5. Click the Connect button. The Wireless Network Connection icon in the control
Change Wireless Network Access Point as follows:
1. Right-click the Wireless Network Connection icon.
2. Click View Available Wireless Networks. The Connect to Wireless Network
3. Select the new network from the available networks in the Available networks
4. Click Connect button. The Wireless Network Connection icon in the control panel
28 Users Manual
panel will show your connection is Enabled. You may proceed using the network
as normal wired LAN connections.
window pops up.
section, if displayed.
will show your connection is Enabled. You may proceed using the network as
normal wired LAN connections

Using the Flex-Bay
CD-ROM drive:
Available as an option for your computer.
CD-ROM R/W drive:
Available as an option for your computer.
DVD-ROM drive:
Available as an option for your computer.
DVD/CD-RW Combo drive:
Available as an option for your computer.
Optional secondary hard drive:
Available as an option for your computer.
If your operating system is Windows, you must install the Softex Bay Manager
software on the software CD in order to use the Bay Manager Utility to hotswap the devices.
The Flex-Bay provides an impressive array of
secondary storage devices listed below:
If you do not use Windows, make sure that the computer’s power is off before
you remove or install any devices.
Using the Flex-Bay 29

Swap a Flex-Bay Device - Power On
You can use the Softex Bay Manager utility to hot-swap your devices in the flex-bay.
To start the Softex Bay Manager utility:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Other Control Panel Options > Softex Bay
Manager.
- or -
2. Double-click the SwapBay icon in the Windows taskbar.
Device Swap
To swap a device with the power on proceed as follows:
1. Start the Softex Bay Manager Utility.
You do not have to turn the computer over or tip it on its side to change
devices. Simply tilt the computer up about 10 cm at the back and locate the
Flex-Bay latch. See Figure below for the location of the Flex-Bay latch. The
computer in the figure is turned over for clarity.
Flex-Bay Latch
2. Click Remove / Swap. A Device Change popup window stating, “Please wait until
3. Tilt the computer up & locate the smart bay latch.
4. Slide and hold the device latch toward the rear of the computer.
30 Users Manual
the system processes the device change” appears then another popup window
appears and says, “Please remove or swap your bay device(s) now and press OK.”

5. Slide the device out.
6. Slide the new device in
7. Click OK. The message “Please wait until the system processes the device
change” appears again.
8. Click OK to close the Softex Bay Manager Utility.
Swap a Flex-Bay Device - Power Off
Device Swap
To remove a device with the power off proceed as follows:
1. Turn the computer’s power off.
2. Tilt the computer up & locate the smart bay latch.
3. Slide and hold the device latch toward the rear of the computer.
4. Slide the device out.
5. Carefully slide the new device into the bay.
6. Push the device in until it is flush with the chassis and the Flex-Bay latch snaps
into place. Your computer’s operating system automatically recognizes the device
in the Flex-Bay and configures your computer accordingly when power is restored.
Using the Flex-Bay 31

Using the Disk Drives
To use the Floppy drive or the CD-ROM drive you must verify it is installed in the
flexbay slot. To swap devices see “Using the Flex-Bay” on page 29.
Using the Floppy Disk Drive
Your computer comes with a 1.44 MB, 3.5-inch, floppy drive.
To use a floppy disk in your computer, insert it into the floppy drive.
Floppy Disk Eject Button
To remove a floppy disk, press the floppy disk eject button on the front of the floppy
drive.
To protect the data on your floppy disks, follow the manufacturers guidelines.
Using the CD/DVD-ROM Drive
Compact discs are designed so that you can easily insert one into the computer when
you need it, and then remove it. See ”Using the Flex-Bay” on page 29 for information
on installing the DVD-ROM drive into the computer.
DVD Notes:
A DVD player is a factory option and if you ordered this option you will have to
install the provided DVD software to view the DVD Title.
32 Users Manual

1. Press the button on the CD-ROM or DVD-ROM drive, and the tray slides out.
(Do not lean on the tray; because it will not support much weight.)
CD/DVD Drive Warnings:
Do not place reflective objects other than the CD/DVD disks in the disk slot
because of possible hazardous laser emissions. The laser beam used in this
CD/DVD-ROM drive is harmful to the eyes. Do not attempt to disassemble the
CD/DVD-ROM drive. Refer servicing to your authorized service center.
Do not touch the CD/DVD lens, doing so may damage the device.
CD/DVD Precautions:
The tray may be stuck, in which case straighten out a paper clip, insert
it into the Emergency Eject hole in the front of the CD/DVD-ROM and push it
until the tray ejects.
A LED on the drive tray is on when the computer is reading from a CD. Do not
remove a disc when this LED is on.
To clean a CD/DVD, wipe from the center outwards with clean and dry cloth.
Remove the CD/DVD when the drive activity LED is off.
2. Insert a CD/DVD, label side up (or remove a disc, if you have finished using it).
3. Push the tray in gently to close the drive tray.
CD-ROM Light
Eject Button
Emergency
Eject Button
Install and/or start a CD-based program as you would run a program on a floppy disk.
Using the Disk Drives 33

Using the Memory Stick (Factory Option)
The Memory Stick is a factory option that will increase your computer storage capacity as well
as increase data portability. The Memory Stick may used in many types of equipment such as
digital cameras and PDAs for example.
Memory Stick and are a trademarks of the Sony Corporation.
Memory Stick Support
The Magic Gate model is not currently supported.
Inserting the Memory Stick
To insert the memory stick proceed as follows:
Ensure you Insert the Memory Stick into the slot with the correct orientation
(Name Up) so that the Memory Stick will operate properly and be recognized
by the computer.
1. Slide the Memory stick into the slot until you feel the first latch catch.
2. Then push the Memory stick in until it clicks into place.
34 Users Manual

Using the Memory Stick
The Memory Stick is used the same as the FDD drive on your computer but with much
larger capacity, currently up to 128MB.
Formatting the Memory Stick
The Memory Stick may need to be formatted before use, if so insert it into the
slot and format it the same as the FDD Drive.
Protecting Data on the Memory Stick
To prevent overwriting/deleting your data in the Memory Stick, move the slide
lock to the “Lock” position.
to see the contents of the Memory Stick:
1. Double-click “My Computer” on the desktop, the My Computer window opens.
2. Double-click the icon in the Devices with Removable Storage section of the
window.
Removing the Memory Stick
To use the Memory Stick proceed as follows:
Ensure any operations using the Memory stick have completed before you
remove it. Otherwise you will corrupt your data.
1. Push the Memory Stick in until it clicks and release.
2. The Memory Stick will pop out ~ 1 cm and then you can slide it out.
Using the Disk Drives 35

Working with PC Cards
By installing PC Cards, you can add functions to your notebook computer similar to
those found on add-in boards for desktop computers. Available PC Cards include:
• Input/output, such as modem, network, video capture, and SCSI cards.
• Storage, such as hard drive and flash memory cards.
Your computer includes the following PC Card support:
• One PC-Card slot: You can install Type I or II cards in the slot.
• CardBus hardware and software: CardBus enables the computer to use 32-bit
PCMCIA Cards. Windows supports 32-bit and 16-bit PC Cards.
Maintaining PC Cards
To maintain your PC Cards, follow these guidelines:
• Keep cards away from excessive heat, direct sunlight, and liquids.
• Do not drop, bend, flex, or crush cards when handling.
• Keep dust, magnets, and static electricity away from PC Cards.
• When a card is not in use, carry it in its protective carrying case.
• Some PC Cards include cables that extend from the back of the cards. Be
careful not to bend or put excessive strain on these cables.
36 Users Manual

Using PC Cards
To insert a PC Card into a slot:
1. Push the slot door in with the PC Card.
2. Align the card with a slot and insert the card into the slot until it locks in place.
PCMCIA Card
Eject button
PC Card :
Insert PC card with product
information facing up
Windows automatically assigns computer resources (such as communication ports and
memory addresses) to a PC Card installed in your computer.
To remove a PC Card from your computer:
Use the following procedures to remove PC Cards, or you may lose data that
is being stored to a card.
1. Click icon on the taskbar.
2. Select the card currently in use, and click the Stop button.
The eject button for the card slot operates in two steps, therefore to remove a PC
Card:
PCMCIA Card
Eject button
3. Push the eject button once to pop it outward then push the eject button again to
eject the card.
4. Pull the card out of the PC Card slot.
Working with PC Cards 37

Multi Media Functions/Equipment
Media Player
The Windows Media player is used to play audio files while the computer is on. You
can play audio/video CD files using the Windows Media Player, as well as watching
TV, video and listening to the radio through internet. The instructions to play a video
CD-ROM are the same as the instructions for the audio CD below.
Playing a Audio/Multimedia CD
To play an CD follow the instructions below:
1. Insert a compact disc into your CD-ROM drive.
2. Press the eject button on the CD-ROM drive to open the CD-ROM device.
3. Insert a CD, label side up.
4. Carefully push the tray in to close the drive tray. The Windows Media Player
button appears on the taskbar if not already there, and the music begins to play. If
the disk does not play click Start > All Programs > Accessories >
Entertainment > Windows Media Player.
CD LED On:
A LED on the drive tray is on when the computer is reading from a CD. Do not
remove a disc when this LED is on.
Removing the Audio/Multimedia CD
To remove the CD follow the instructions below:
1. Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Entertainment > Windows Media
2. Click Stop in the Windows Media Player window or simply close the Windows
3. Press the button on your CD-ROM drive. The drive tray opens and you can remove
4. For more information on playing compact discs, see the Help menu in the
38 Users Manual
Player to open the Windows Media Player window, if not already open.
media player.
the CD from the CD-ROM drive.
Windows Media Player window.

MP3/CD Player (Factory Option)
The MP3/CD Player can play music CDs and MP3 files while the computer is off. It
will not, however play video CDs.
Button Operation
The buttons & display for the MP3/CD Player operate as follows:
Button Name Function
Volume Down Decreases speaker volume when MP3/CD Player is on.
Volume Up Increases speaker volume when MP3/CD Player is on.
+
MUTE Press the <Volume Down+Volume Up> buttons simultaneously
Track Display Indicates power on => and total tracks available on CD and
Stop/Eject Stops & Ejects the Audio CD.
MP3/CD Player Power
CD Play/Pause
Previous Track/Song
Fast Search Reverse
Next
Track/Song
Fast Search Forward
Lock Press the <Stop/Eject+Volume Down> buttons simultaneously
+
Unlock Press the <MP3/CD Player Power CD Play/Pause+Volume
+
for ~ 1 sec. to mute the sound.
track playing => .
The blinks when the music file is paused.
Press the button ~ 3 seconds to turn off power.
Starts/Pauses the Audio CD and MP3 Files.
Changes the Audio CD to the previous track/song.
Changes the Audio CD to the next track/song.
for ~ 3 sec. to lock the MP3/CD Player buttons.
Down> buttons simultaneously for ~ 3 sec. to unlock the MP3/CD
Player buttons and energize the MP3/CD Player.
Multi Media Functions/Equipment 39

Using the MP3/CD Player
Play an Audio CD
1. Verify the computer is off and that a CD-ROM device is in the flex-bay.
MP3/CD Player Power Buttons:
If a CD-ROM device is not in the flex-bay, the MP3/CD Player power button
will not energize the MP3/CD Player player.
Computer Button Operation:
All computer and SENS keyboard buttons are non functional while MP3/CD
Player is operating except the Computer Power Button. To use the MP3/CD
Player buttons while the system is on, you must start the Windows media
player.
2. Press the MP3/CD Player power button until the icon is displayed in the track
display window [Labeled: DIGITAL AUDIO].
3. Press the eject button on the CD-ROM drive or the button on the MP3/CD
Player button bar.
4. Insert a Audio CD into your CD-ROM drive label side up.
5. Press the button on the MP3/CD Player.
Pause/Resume an Audio CD
1. Press the CD button to pause the CD.
2. Press the button again to restart the CD.
Stop an Audio CD
1. Press the button to stop and eject the CD.
2. Remove the Audio CD, then close the tray.
3. Press the MP3/CD Player power button for ~ 3 seconds to turn off the MP3/
Fast Search an Audio CD
1. Press the or buttons for ~1 second while the music is playing to start Fast
2. Press the
40 Users Manual
CD Player player.
Search.
button and or buttons to stop the Fast Search.

Dolby Digital & Home Theater System (S/PDIF Port)
This product supports 5.1 channel output, which is a basic function for home theater
systems and DVD drives. It provides 3D surround sound and a vivid screen.
Home theater system usually consists of a TV, DVD, 5.1 channel speakers,
and a digital amplifier to provide a high-resolution vivid (MPEG2) picture and
3D surround sound (Dolby 5.1 or DTS). With a home theater system, you can
enjoy the same vivid picture and sound in your home that you would in a movie
theater.
You will need the following to enjoy a home theater system:
• 5.1 channel speaker system / Digital amplifier (Purchased separately).
• DVD drive and DVD Program (Option).
• S/PDIF cable (Option)
Setting Up Your Home Theater
1. Connect the digital amplifier to the S/PDIF port of your computer.
To Digital Amplifier
S/PDIF Port
Multi Media Functions/Equipment 41

2. Connect the speakers to the digital amplifier.
TV
Digital Amplifier
Front Left Speaker
Surround Left Speaker Surround Right Speaker
If your computer supports a TV-Out port, you can connect and enjoy a large
screen.
After connecting the TV, you will need to select the TV as the display device
using the Windows Display Properties window.
After making all connections, ensure you enable S/PDIF:
1. Enable S/PDIF in Windows.
2. Enable S/PDIF in the DVD program.
When purchasing a 5.1 channel speaker system, make sure it supports a S/
PDIF (coaxial) port.
To use the headphones, change the setting to[ Analog Audio] as
described in the next “Using the S/PDIF Connection” section below.
Computer
Center
Speaker
Sub
Woofer
Front Right Speaker
Using the S/PDIF Connection
1. Use <Fn+F8> keys to set the S/PDIF port to digital.
2. Verify the S/PDIF port is set to digital by pressing the <Fn+F2> keys to see if the
42 Users Manual
[
Digital Audio] is displayed. If not, repeat the <Fn+F2> key combination again.
To use the headphones, change the setting to[ Analog Audio] as
described in the next “Using the S/PDIF Connection” section below.
When purchasing a 5.1 channel speaker system, make sure it supports a S/
PDIF (coaxial) port.
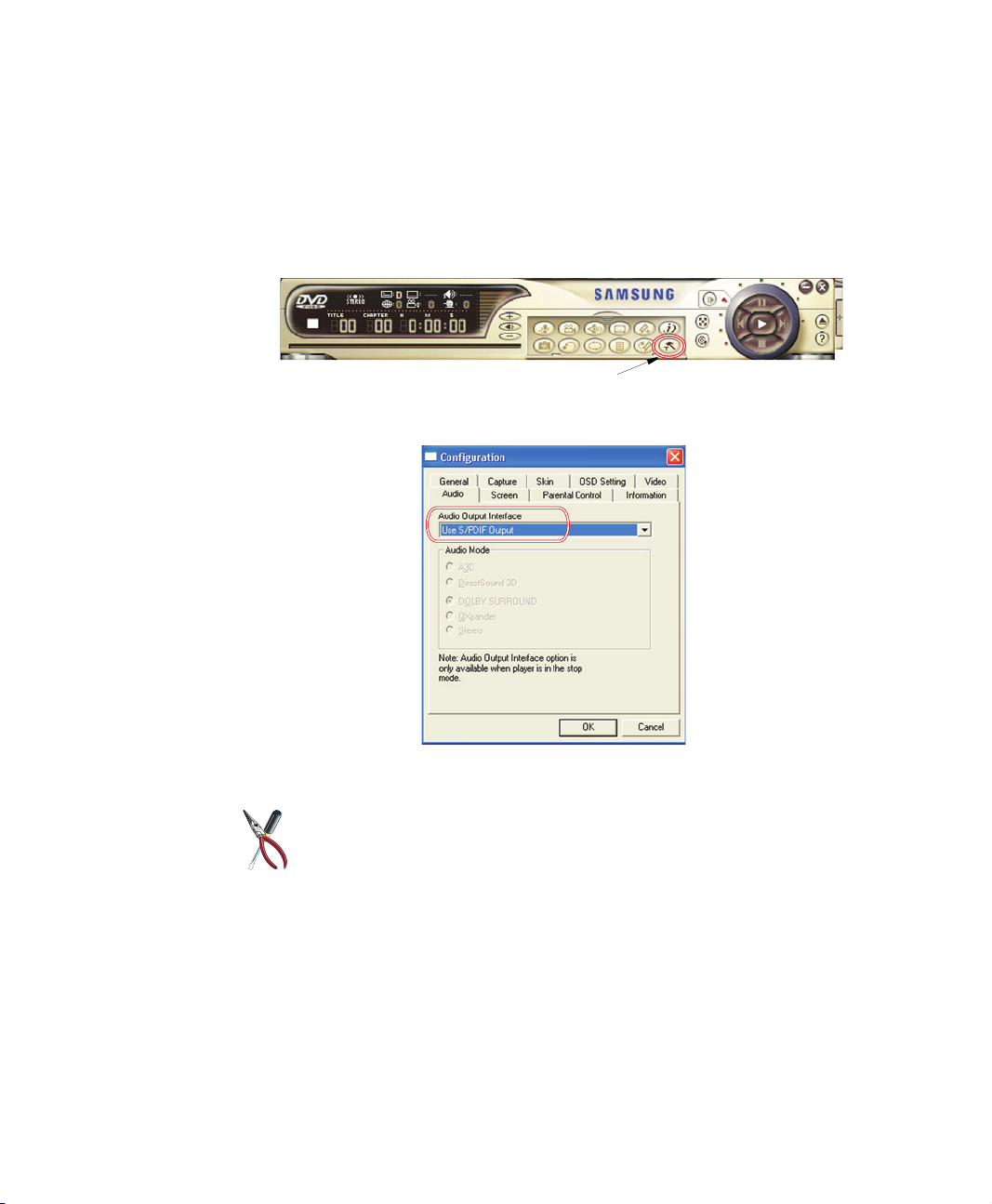
Enabling S/PDIF on the DVD Program
When using 5.1 channel speakers, you will need to install the “Power DVD” program
on the DVD Installation CD (supplied Separately) and then set it up as described
below:
1. Run the “Power DVD” program and click the settings button., the configurations
window pops up.
Settings Button
2. On the “Audio tab”, change the Audio Output Interface setting to “Use S/PDIF
Output”.
Audio Output Interface
3. You are ready to enjoy your home theater system with your own DVD’s.
• If you have enabled S/PDIF in the DVD program, the computer speakers
and headphone are not functional.
• To control the sound volume on your 5.1 channel speaker system, use the
control on the digital amplifier. (Please refer to the speaker manual.)
Multi Media Functions/Equipment 43

Volume Control
The instructions below are for controlling speaker volume when the computer is on. To
control speaker volume when the MP3/CD Player only is on see “MP3/CD Player
(Factory Option)” on page 39.
Using the Keyboard
Changing the volume with your keyboard.
Use <Fn+PgDn> to decrease the volume or <Fn+PgUp> to increase the volume.
Using the Volume Control Icon
Double-click icon in the active program tray. The Volume Control window pops
up. Use this window to adjust the volume. You can pop up a simple volume slider by
a single click icon.
Movie Maker
You can edit audio and video data using this Movie Maker included with Windows XP.
It is also possible to make a slide show with each frame or picture.
To start the program:
Click Start > All Programs > Accessories > Windows Movie Maker.
Please refer to the on-line help manual to operate the Windows Movie Maker.
44 Users Manual

Using the Battery
Your computer uses a smart rechargeable Lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery pack for power
when the AC adapter is not attached to an electrical outlet. The smart battery gives a
accurate measurement of the current battery capacity which helps extend operating
time by enabling effective power management in operating systems that take
advantage of the accurate information supplied by the battery.
Charging the Battery
Your computer’s battery starts charging automatically when you connect the power to
the computer and to an electrical outlet. If the computer is off, the battery charges faster
than if the computer’s power is on.
Approximate charging times for the Li-Ion battery are
• 3 hours with the computer off.
• 6 hours with the computer on.
While the battery is charging normally, the battery charge light on the computer is red.
When the battery is fully charged, the light changes to green.
When you use a new battery pack for the first time or use a battery after a long period
of storage, the initial battery life is shorter than normal. Normal battery life resumes
after a few discharge-recharge cycles.
Follow these rules for charging your battery:
• A battery normally discharges power when not used for long periods of time.
Be sure to recharge the battery every two months when it is not in use.
• Make it a practice to discharge your battery fully before recharging the battery.
This can help extend the life of the battery.
• Do not attempt to charge the battery in temperatures of under 5
o
C or over 45oC
All batteries eventually wear out and lose the ability to hold a charge. You may
need to replace your battery pack after a year of average usage.
Using the Battery 45

Safely Using the Battery
Follow these guidelines to safely use the battery:
• Turn off your computer and unplug it if you accidentally:
– Expose the equipment to liquid.
– Drop, jar, or damage the computer.
• Use only approved battery chargers.
• Do not disassemble the battery, heat it above 100°C, or burn it. The battery
used in this computer may cause a fire or chemical burn if mistreated.
• Your computer's rechargeable battery may be considered hazardous waste. If
you replace your battery with a new one:
– Keep the old battery out of the reach of children.
– Dispose of the old battery promptly.
– Make sure that you follow all local requirements when you dispose of the
old battery.
Removing the Battery
Your computer comes with the battery pack inserted in the computer.
To remove the battery from the computer:
1. Turn the computer’s power off.
2. Close the LCD panel, and turn the computer over so that the bottom of the unit
faces up.
3. Slide the battery compartment latch toward the left side of the computer and hold,
this raises the battery slightly.
4. Slip your fingernail under the edge of the battery and pull it up and then grab the
battery and remove it from the compartment.
46 Users Manual

Installing the Battery
To install the battery pack:
1. With the computer’s power off, close the LCD panel and turn the computer over
so the bottom of the unit faces up.
Insert the battery into the battery compartment, ensuring the correct
orientation so that the battery fits in its slot properly.
2. Place the battery inside and against right side of the computer battery compartment
at an angle of approximately 30 degrees.
3. Push the battery down until the latch snaps into place, securing the battery.
Using the Battery 47

Monitoring the Battery Charge
Battery life is affected by factors such as the power-management settings in System
Setup, the applications you use, and the brightness settings of the LCD. Under normal
usage, the battery charge lasts approximately 2.5 hours.
Battery life estimates are subject to variation. The actual life of your battery
may be less than the estimates given in the manual.
You can monitor the charge of the battery pack installed in your computer by using the
Power Meter or Battery Gauge.
Power Meter
The Power Meter displays the charge of the batteries and the current source of
computer power, AC or batteries. You may monitor the battery charge or usage by
using the “Power Meter”. To access the power meter click icon on the task bar or
click Start > Control Panel > Performance and Maintenance > Power Options >
Power Meter Tab.
The Power Status icons shown below are displayed
during Battery Charging Operations
At ~15% and 10% remaining battery power the
current power source and the battery Icons
respectively change to the icon shown below and
you should follow the instructions in “Battery
Warnings” section below
You may also check battery charge by moving the cursor to the icon, a small dialog
box will display the % of charge.
48 Users Manual

Battery Gauge
You may display the battery gauge while you are in any program by pressing
<Fn+F2>. While the battery gauge is being displayed, all keys except <Esc> are
disabled. The battery gauge is only displayed for a few seconds.
Power Source: (Top Right)
Indicates that the computer is
powered by the AC adapter.
Battery Level: (Lower Right)
Indicates the approximate amount of
the primary battery charge remaining.
Radio Frequency: (Top Left)
Wireless LAN On Wireless LAN Off
Digital/Analog Audio: (Lower Left)
Digital Audio On: Indicates the S/PDIF
/ Headphone jack is set for digital
output.
Indicates that the computer is
powered by the battery.
Indicates the computer is on AC
power only.
(No Battery Present).
Digital Audio Off: Indicates the S/PDIF
/ Headphone jack is set for analog
output.
You may also determine the charge of your battery by simply pushing the symbol
below the word PUSH located on the bottom of the battery. The green LEDs
will illuminate to show you the percentage of charge remaining in the battery.
Using the Battery 49

Battery Warnings
If the battery charge is low (about 10%) you have ~ 5–10 minutes of battery life left.
You should:
• Save your work and,
• Connect the power cord to the computer or turn off the computer and install a
fully charged battery.
You can adjust the battery alarm features by using the operating systems power
management program (Start > Control Panel > Power Options in Windows).
If you cannot run your computer from the battery and the battery will not charge when
you attach the power cord, the problem may be that:
• The battery temperature is below 0°C or over 45°C. If you think the battery
temperature is too hot or too cold, turn off the computer, remove the battery,
and let the battery reach room temperature. Then try charging the battery again.
• The battery is defective. Replace the battery with a new battery.
Battery Calibration
Calibrating your battery once a month is one of the recommended methods of
increasing your computer’s battery life. To calibrate the battery complete the following
steps:
Calibration Notes:
You should start the battery calibration process with a fully charged battery,
battery status LED is green. The power meter may not show 100%.
Before you commence the battery calibration process you should fully charge,
then fully discharge and finally fully recharge the battery again.
1. Disconnect the AC power adapter after turning off the system.
2. Restart your computer and press <F2> to enter BIOS setup.
3. Using the arrow keys, highlight Smart Battery Calibration in the Power menu.
4. Press <Enter> to start calibration process. The calibration usually takes 2 to 3
hours depending on the current battery charge.
5. When the calibration process is complete, recharge the battery fully.
50 Users Manual

Using System Setup
The System Setup (BIOS) program enables you to configure your computer hardware
and set security and power-savings options. The settings you choose are stored in
battery-maintained CMOS memory that saves the information even when the
computer’s power is turned off. When your computer is turned back on, it is configured
with the values found in this memory.
Run System Setup if you get a message prompting you to run the program. You may
also want to run System Setup, particularly the first time you use your computer, to set
the time and date, use security or power-management features, or alter the settings of
other features.
BIOS Caution:
If you are not familiar with BIOS setup and what the parameters mean, seek
help from a person who is knowledgeable. Incorrect settings may cause your
system to “Crash”.
Your computer’s version of System Setup may not include all the fields listed
here or may include additional fields. Field names and order of appearance
can vary according to the version of the BIOS (basic input/output system) on
your computer.
Starting System Setup
To start System Setup, turn on your computer and then press <F2> and hold until the
System Setup screen appears.
Table 3. System Setup Menus
Menu Function
Main Changes the basic system.
Advanced Configures advanced features on your computer.
Security Enables security features, including passwords and backup
Power Configures power-management features.
Boot Specifies the order of boot devices and configures boot
Exit Specifies how to exit System Setup.
and virus-check reminders.
features.
To open the menu you need to use, use the left or right arrow keys to select the menu
name.
Using System Setup 51

Table 4. System Setup Navigation Keys
Navigation Key Function
<F1> Displays the General Help window.
<Esc> Exits the current menu.
<Up Arrow> or
<Down Arrow>
<Left Arrow> or
<Right Arrow>
<Plus> Scrolls backwards through the options for the highlighted field.
<Minus> Scrolls forward through the options for the highlighted field.
<F9> Sets the parameters for the current menu to their default values.
<F10> Sets the parameters for the current menu to their previous
<Enter> Executes commands or opens a submenu.
Moves the cursor up and down between fields.
Selects different menus. Pressing the ESC key at the Main menu
brings you to the Exit menu.
values.
52 Users Manual

Changing Booting Priority
The Boot menu in System Setup enables you to select the booting device and to set
booting options.
Boot Device Priority field enables:
You to select the order in which the computer attempts to boot from different devices.
The field has four (4) options: CD-ROM Drive, Removable Devices, Hard Drive
and Network Boot.
To change the booting device priority, choose the device positions by completing
the following:
1. At startup, press <F2> to open System Setup.
2. Use <Right Arrow> to select the Advanced CMOS Setup menu.
3. Highlight the 1
4. Press <Shift+Plus> keys until the option moves up in the list to the desired
position or press <Minus> key until the option moves down in the list to the
desired position.
5. Press <Esc> to return to the Exit menu.
6. Press <Enter> or <F10> to exit and save your changes.
7. Press <Enter> again to restart the computer.
If you want to start the system using a bootable CD, change the CD-ROM
Drive to be the 1st Boot Device.
st Boot Device option with <Up Arrow> or <Down Arrow> keys.
Changing Booting Priority 53

Using System Security
This section describes your computer security programs. The first is the standard BIOS
security which is standard on almost all computers. The second is a advanced factory
option Biometric security system that uses your fingerprint(s) to control access to your
computer and individual files if necessary. You no longer have to worry about
passwords being lost, stolen or forgotten.
BIOS Security
The BIOS security operations are explained below:
System Passwords
The computer provides (4) levels of password security: administrative-level
(supervisor), user-level (user), HDD access and Password on Boot. These passwords
prevent unauthorized access to the computer. The supervisor password enables full
access to all System Setup fields. The user password enables full access to only the Set
User Password and Password on boot security fields and read access to all other
System Setup fields. The HDD Password controls access to the hard drive.
If you enter your HDD password wrong two times, the correct password will
not be recognized on the third attempt. Restart your computer and enter the
correct password.
You may also enable the biometric security at boot.
The (3) security boot time options are:
If multiple users have access to the computer (such as in a network environment), a
supervisor password can prevent unauthorized access to certain security options.
Choose the type of password security that is appropriate for your work.
54 Users Manual
The Biometric Security software MUST be installed prior to setting the security
options to any of the fingerprint options.
• Disabled
• Text password
• Finger Print

If You Forget Your Password
It is very important that you do not forget your password. If you do, you cannot access
your system. Write your password down and keep it in a safe place. If you do forget
and cannot find the written note, please contact the Samsung Helpline. Please have
your receipts available to verify the type and model of your computer. You may be
charged for password removal.
Creating a Password
To create a password follow the instructions below:
1. At startup, press <F2> to open System Setup.
2. Use <Right Arrow> to select the Security menu.
Precautions for Password Entry:
You can enter letters or numbers, but you cannot use the function keys, such
as the Shift key. Your computer does not distinguish between capitalized and
lowercase letters in your password. As you type the password, the cursor
moves but your password does not appear on the screen. Choose the type of
password security that is appropriate for your work. If you want to set a user
password, you must set a supervisor password first.
3. Use <Down Arrow> to select Set Supervisor Password or Set User Password.
4. Press <Enter>. The Set Password dialog box appears.
5. Press <Enter> after you have typed your password. The computer prompts you to
reenter your password for verification.
6. Type your password again and press <Enter>. A message appears telling you that
the changes have been saved.
The “Password on boot” password MUST also be set in order for your machine
to boot properly.
7. Use <Down Arrow> to select Password on boot.
8. Press <Enter>. The Set Password dialog box appears.
9. Select the “Text Password” option.
10. Press <Enter> again to return to the Security menu.
11. Press <Esc> to go to the Exit menu.
12. Press <Enter> or <F10> to exit and save your changes.
13. Press <Enter> again to restart the computer.
Using System Security 55

If password use is not desired:
Follow the creating a password procedure above except leave the password field empty in
step 5.
Biometric Security (Factory Option)
The factory optional fingerprint sensor provides unique
security access to your computer. You will no longer have to
worry about losing or forgetting your password. Since every
person has a unique set of fingerprints, only a biometrically
enrolled person may have access to your computer.
Advantages of Biometric Security are:
• Very high level of security
• No password to remember, lose or have stolen.
• Streamlined logon process.
• Single fingerprint will access many programs, eliminating passwords.
If you purchased the Biometric Security option, please refer to the manual provided for
installation and use.
56 Users Manual

Using Power Management Options
Your computer includes Power Management options that can help the battery charge
last longer and extend the life of the battery. Power-management options will slow
down or shut off system components when the components are not being used.
Power management may slow down system performance. Your computer runs fastest
with the power cord attached, when power management is disabled.
In the next sections, basic and advanced methods of power management will be
discussed.
Basic Power Management Schemes
This section discusses the basic schemes of power management when the computer is
operating on battery power or using AC power.
Standby vs. Hibernation
Standby unlike hibernation mode does not store unsaved information on your
hard disk; it's stored only in the computer memory. If there is an interruption in
power, the information is lost. So before putting your computer on standby,
you should save your files.
Changing Devices:
Do not change PC Cards while in standby or hibernate modes.
To enter the power management window complete the following:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Performance and Maintenance.
2. Click icon to display the Power Options Properties window.
Using Power Management Options 57

3. Click the Power Schemes tab to display the basic power management options.
Power Schemes Tab
4. Select the time that you wish each of the following actions to occur in Battery and
AC power mode.
• Turn off monitor:
• Turn off hard disks:
• System standby:
• System hibernates:
Turning off the monitor and HDDs will save a substantial battery power, therefore
when in battery only mode select the shortest time practical.
a Hibernate Mode (Power Management or Manual Method)
When hibernation is used, your computer turns off and when you power up again,
everything is restored exactly as you left it—including programs and documents
you may not have saved or closed. Everything in memory gets saved to the HDD,
and the monitor and hard disk get turned off.
58 Users Manual

If You Reinstall Windows:
You should re-establish hibernate in power options by opening
Power
Options Properties window and click on the Hibernate tab then click
“Enable Hibernation”.
Hibernate Tab
Frequent Interruptions:
If you experience frequent interruptions, you might also consider putting your
computer into automatic hibernation after a specified number of minutes using
the power management options.
a Standby Mode (Power Management or Manual Method)
Standby is used mainly for conserving battery power in your notebook computer. It
also gives you the benefit of getting right back to your work without waiting for the
computer to restart. Standby turns off your monitor and hard disks, placing your entire
system in a low-power state. When you return to your computer, restores your desktop
exactly as you left it. It is recommended that you do not enter standby mode with less
than 20% battery power.
5. Click OK to set your power management options and close the window.
Rest Key:
The manual <Fn+F5> key combination will not activate Standby or Hibernate
modes whilst you are playing a multimedia program or have an active USB
device connected.
Using Power Management Options 59

Advanced Power Management Schemes
This section discusses the advanced power management schemes. There are two
buttons that you can use to manually conserve power.
To enter the power management window complete the following:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Performance and Maintenance.
2. Click icon to display the Power Options Properties window.
3. Click the Advanced tab to display the advanced power management options.
Advanced Tab
Power & Sleep Button
Programming Windows
4. Select the mode (Do nothing/Ask me what to do/Standby/Hibernate/Shut
5. Click OK to set your power management options and close the window.
You can return to normal operation after you have used one of the “Power
Management” buttons by quickly pushing and releasing the Power button.
60 Users Manual
down) assigned to the Power button and/or Rest <F5> key. Also select the action
(Do nothing/Standby/Hibernate) associated with closing the computer lid.
The “Rest” key is assigned to the <Fn+F5> key combination. See ”Basic
Power Management Schemes” on page 57 for a better understanding of
Standby and Hibernate modes.

Using the Hard Drive
Your computer includes a removable IDE (integrated drive electronics) hard drive. The
IDE hard drive can store the data and programs your computer uses. The drive plugs
into a connector on the system board.
The hard drive that comes with your computer has already been formatted. Do
not format the hard drive. Doing so destroys all data contained on the drive. If
you need to format a new drive, or want to erase all data on your existing hard
drive, refer to the manual for your operating system.
Installing/Reinstalling a HDD
To install a new HDD you must contact your local service representative. He will do
the physical change of the drive. You should complete the instructions below before
you go to the service center.
See the information below before you install your HDD:
• Back up data files of your old hard drive.
• For system boot with CD-ROM, under the Boot menu in System setup, set
Bootable CD Check to Enabled and set Boot Device Priority is ordered starting
from the [DVD/CD-ROM].
When you are ready to install the new HDD use the Recovery CD-ROM to install the
device driver.
(Re)Installing Windows and Device Drivers
Use System Recovery CD to (re)install OS and System Software CD to (re)install
device' drivers.
The System Recovery CD is used to (re)install the OS and System Software
to a new HDD or recover from a system crash.
Notebook computers that ship from the factory include System Recover CDROM and System Software CD-ROM, which contains a copy of the
applications and drivers needed for computer's operating system.
In the unlikely event that programs on the computer hard drive become
corrupted or are erased, you can use the System Recovery CD-ROM to
reinstall your operating system and then System Software CD-ROM to
reinstall your original applications and drivers.
Using the Hard Drive 61

Video Features and Configuration
All these video modes can be displayed on an external monitor. However, if you
disconnect an external monitor that was attached to your computer and then start the
computer, the LCD may revert to a different resolution than the one you chose for the
external monitor.
Resolution and Colour Depth
The resolution of the LCD is the sharpness of the image it can display. Resolution is
measured by the number of pixels (individual dots) displayed on the entire screen. In
general, the more pixels the LCD can display, the better the image.
The number of colours the LCD can display is measured by how many bits the LCD
uses to represent each pixel:
• 16-bit colour can support 64 K (65,536) colours.
• 32-bit colour can support 16 M (16.8 million) colours.
All these video modes can be displayed on an external monitor. However, if you
disconnect an external monitor that was attached to your computer and then start the
computer, the LCD may revert to a different resolution than the one you chose for the
external monitor.
Adjusting the LCD Display
You may wish to adjust the LCD (Liquid-Crystal Display) when you begin using your
computer. A TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) LCD does not require adjustment for contrast
because the contrast is set to remain at maximum.
To adjust the LCD:
62 Users Manual
• Press <Fn+Up Arrow> to increase the display brightness.
• Press <Fn+Down Arrow> to decrease the display brightness.

Configuring Display Features
The following sections describe how to configure the display settings on your
computer.
Display Resolution Notes:
When Windows XP is initially installed it will automatically adjust the resolution
to maximum available.
Changing Colour Depth and Resolution
To change the colour depth and resolution of your LCD:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Appearance and Themes.
2. Click icon. The Display Properties window appears.
3. Click the Settings tab. The Settings screen appears.
4. To change the colour depth, click the arrow next to the Colour quality palette and
select the available colour depth you want.
5. To change the resolution, click and drag the slider under the Screen resolution
until you select the available resolution you want.
6. Click OK.
7. Follow the prompts that appear on the screen.
Video Features and Configuration 63

Using Dual View Mode
Single View mode is the basic display mode which displays same view on all the
display devices connected to a system.
Dual View mode is the “Extended screen mode” supported in Windows, which
displays separate views on each display devices connected to a system.
<Fn+F4 LCD/CRT> Key Combination
The <Fn+F4> Key Combination will not operate while you are playing a MPEG
file or a Video CD.
Occasionally the video output in dual view mode becomes erratic.
The default setting on your system is Single View mode.
Setting Dual View Mode
To set Dual View mode on your system:
1. Connect peripheral display device such as monitor or television to your system and
start the system.
2. Select Start > Control Panel > Appearance and Themes.
3. Click icon. The Display Properties window appears.
4. Click the Settings tab. The Settings window appears.
5. Check Extend my Windows desktop onto this monitor.
6. You can drag the second monitor image to position where you want your extended
screen space with respect to the primary monitor (usually the LCD).
To confirm whether the system is set properly with Dual View mode:
1. Open Display properties and click Settings tab.
2. Place the cursor on the first monitor picture and click and hold over a second, a
number 1
the second monitor picture and click and hold over a second, then digit number 2
will be shown on the second actual monitor screen.
will be shown on the first actual monitor screen. And place the cursor on
64 Users Manual

3. The monitor displays digit number 1 is the primary monitor and number 2 is the
secondary monitor.
In Windows explorer, the program is displayed on the primary monitor, if you can
drag it to the secondary monitor, then Duo View mode is now working properly.
The secondary monitor has a display of 256 colours (colour depth) and 640x480 pixels
(resolution) at first. The colour depth and resolution of primary/secondary monitors are
separately changeable.
Changing Colour Depth and Resolution of 2nd Monitor
To change the colour depth and resolution of 2nd Monitor or TV:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Appearance and Themes.
2. Click icon. The Display Properties window appears.
3. Click the Settings tab. The Settings screen appears.
4. Click on the display number of the monitor you wish to change.
TV Display Resolution Limitations
ou can change the Colour Depth and Resolution within the limitations
Y
of the TV. Adjust as necessary to get a good display.
5. To change the colour depth, click the arrow next to the Colour quality palette and
select the available colour depth you want.
6. To change the resolution, click and drag the slider under the Screen resolution
until you select the available resolution you want.
7. Click OK.
8. Follow the prompts that appear on the screen.
Using Dual View Mode 65

To reset the system to Single View mode:
1. Start Display properties.
2. Click Settings tab.
3. Click the second monitor among two monitor pictures.
4. Uncheck Extend my Windows desktop onto this monitor.
5. Click OK.
Using Multimonitor Mode
You may duplicate your LCD screen on an external monitor, television or digital flat
panel.
TV Connection Restrictions:
You should only connect/disconnect cables and wires to your computer and
TV when the power is off.
TV Support Limitations:
The computer will only support televisions with S-VHS input capability. The
standard composite video in port is not supported.
You can not use TV-out port to connect to your television in DOS mode.
When TV-Out is activated, your computer screen will not be active.
To start using multimonitor mode proceed as follows:
1. Connect the external monitor to the connection on the back of your computer.
2. Press the <Fn+F4> key combination, the LCD will be duplicated on the monitor,
television or digital flat panel.
66 Users Manual
<Fn+F4> key combinations
Each time you use the <Fn+F4> key combination the LCD/Monitor
combination changes as follows:
• Both displays are displaying the computer output (LCD & Monitor).
• Monitor, television or digital flat panel only is displayed the computer
output.
• LCD only is displaying the computer output.

To stop using multimonitor mode proceed as follows:
1. Press the <Fn+F4> key combination until only the LCD is displaying the
computer output.
2. Disconnect the external monitor or television from the connection on the back of
your computer.
Using Powerplay
The Powerplay technology supplied with your graphics adapter to extend battery life.
POWERPLAY Use Limitations
Activating POWERPLAY will reduce your graphic card performance.
To activate POWERPLAY proceed as follows:
1. Click Start > Control Panel > Appearance and Themes.
2. Click icon. The Display Properties window appears.
3. Click the Settings tab. The Settings screen appears.
4. Click the Advanced button. The (Multiple Monitors) and M7 Properties
window appears.
5. Click the POWERPLAY tab
6. Click the POWERPLAY button in the POWERPLAY Settings section. The
button will change to a button and activate the other options available.
Using Dual View Mode 67

Using Options
You can order the following options for your Notebook computer from your authorised
reseller:
• An extra AC adapter.
• An auto adapter that enables you to charge the computer’s battery and operate
the computer while in an automobile.
• An extra battery pack.
• 128, 256 and 512 MB DDR SDRAM memory modules that enable you to
upgrade your computer’s memory to a maximum of 1 GB.
• A CD-ROM drive module (CD Only or CD R/W).
• DVD/CD-RW Combo drive:
• A DVD-ROM drive module.
• MP3/CD Player
• Bluetooth/Wireless
• FIR (Fast Infrared) Connection
• 2nd HDD
• Port Replicator
• Biometric Security
• Memory Stick
The options that are available may change periodically. Contact your reseller for
updated information on current and new options.
68 Users Manual

Memory Modules
You can increase system memory by installing optional memory modules. You can
install a 128, 256 or 512 MB modules.
To avoid possible system problems, use only approved memory modules in
your computer.
Before You Install Memory
To prevent personal injury and damage to the equipment, follow the
precautions listed here before installing a memory module.
Take the following precautions when installing a memory module:
• Before you remove the memory module compartment door, turn off the
computer, unplug the power cord, and remove the battery. Also, disconnect any
peripheral devices.
• Before handling a memory module, discharge any static electricity by touching
a grounded surface or using a grounding wrist strap.
• Do not insert objects with conductive material, such as metal screwdrivers or
graphite pencils, into the memory-module compartment.
• Be careful in handling the metal plate of the memory door.
Using Options 69

Installing a Memory Module
Handle a memory module carefully. Hold them only by the edges.
To install a memory module:
1. Turn the computer over so that the bottom faces up.
2. Using a screwdriver, remove the screw that holds the memory-module
compartment door in place.
3. Grasp the edge of the door and pull the door off the chassis.
Memory Module Precautions:
When removing the module, pull on the plastic portion of the connector slots
tabs only. Do not pull on the metal part of the tabs, this may damage the tabs.
4. Remove the installed module if necessary.
70 Users Manual
a. Pull the tabs on the connector slot outward slightly, until the edge of the
memory module pops up.
b. Hold the memory module by the edges and pull it forward out of the
compartment.

5. Align the connector on the memory module with the connector of the slot.
6. Push the memory module into the slot at a slight angle (~45
o
) until the connectors
are fully engaged.
o
45
7. Push down on the edge of the memory module until the module snaps into place.
8. Align the memory module compartment door with the compartment and push the
door down until it snaps into place.
9. Reinstall the screw you removed in step 2.
10. Turn on the computer and perform a complete POST to check the memory
integrity.
Bluetooth/Wireless
Bluetooth/Wireless technology allows wireless communication between bluetooth
communication devices, such as cellular phones, desktop and other notebook
computers.
To setup and use the Wireless LAN, Please refer to the user manual provided with the
option at the time of purchase.
Wireless LAN
The wireless LAN option allows easy connection to large or small office networks
while also providing freedom from the constraints of cables and sockets.
Port Replicator
Contact your reseller for a list of port replicator options available for your Notebook
computer. User’s manuals are included with the port replicator options.
Using Options 71

FIR (Fast Infrared) Connection
FIR Technology Limitation
The transmitter and the receiver should be no more than 50cm apart.
BIOS Setup
The BIOS setup must be completed first in order for the option to operate
properly.
1. At startup, press <F2> to open System Setup.
2. Use <Right Arrow> to select the Advanced CMOS Setup menu.
3. Highlight the I/O Device Configuration option with <Up Arrow> or <Down
Arrow> keys and press <Enter>.
4. Highlight the FIR port with the <Up Arrow> or <Down Arrow> keys.
5. Press <Shift+Plus> keys until the option changes to Enabled.
6. Press <Esc> to return to the Exit menu.
7. Press <Enter> or <F10> to exit and save your changes.
Windows Setup
1. Right-click My Computer.
2. Click Properties, the System properties window pops up.
3. Click the hardware tab then click the device manager button in the device manager
section.
4. Double-click the Infrared devices
5. Double-click the IrDA Fast Infrared Port, the IrDA Fast Infrared Port properties
window pops up.
6. Click on the Advanced tab and set the device as follows.
• Select the “Infrared Transceiver A” in the properties section.
• Select the “Vishay TFDS-6500” in the value section.
7. Click OK
72 Users Manual

Troubleshooting
Complete the following in the order presented until your system is functioning
properly. If all of the steps below fail then contact your local reseller for assistance.
Questions and Answers
Please see “Questions and Answers” on page 74 for assistance in correcting any
computer operational problems.
Check the Connections
Verify all of the power and peripheral cables are securely plugged into their sockets
and that your system and power supply is on.
Norton AntiVirus
Run Norton AntiVirus to insure a virus is not affecting your computer.
To run Norton AntiVirus proceed as follows:
Click Start > Programs > Norton AntiVirus > Norton AntiVirus 2002
Windows Help and Support
Run Windows Help and Support to find problem that may be affecting your
computer.
To run Windows Help and Support proceed as follows:
Click Start > Help
Reinstalling Software
If for some reason your system crashes you may corrupt your HDD, Windows
Operating system and/or some of your device drivers. If this is the case, use System
Recovery CD to reinstall OS and System Software CD to reinstall the corrupt device
drivers.
System Recovery Precaution:
Before you start restoring your windows operating system insure you backup
all data on your hard drive.
Samsung is NOT responsible for any data loss.
Troubleshooting 73

Questions and Answers
Operating System Problems
Problem Action
The computer does nothing
when you turn it on.
Some of the letter keys type
numbers instead of the
indicated letters.
Battery power seems to run
out faster than expected.
Certain software programs
“hang” during operations
when there is no interaction
with the keyboard or
peripheral devices.
PC Card does not work
correctly.
Your ATA or Compact
Flashcard do not work.
The System Setup settings
are not retained when you
turn off the computer.
Has the battery run down? Connect the power cord
to the computer and recharge the battery. Try turning
on the computer again.
Is the Num Lock light on? If so, the numeric keypad
on the keyboard is active. To return the keypad keys
to typing letters, press <Num Lock>.
If you are running the computer from the battery
rather than the power cord, make sure that you set
the Idle Mode field in System Setup to On. This
setting enables the microprocessor and the hard
drive to slow down when the computer is not busy.
Your computer may be in Suspend or Rest mode.
Tap the touchpad to resume from Suspend or press
the power button to resume from rest.
Make sure that the PC Card is inserted left side up in
the PC Card slot. Check that the card is inserted fully
into the slot. If you are using a PC Card modem,
check the modem cable connections.
A patch is provided for these cards on the Recovery
CD
The CMOS battery inside the computer may need to
be replaced. The CMOS battery provides power to
save the system BIOS information when the
computer is turned off. Normally, the CMOS battery
lasts for several years. Do not attempt to open the
chassis and replace this battery yourself or your
warranty is void. Have an authorized the
manufacturer’s service center replace the CMOS
battery.
74 Users Manual

Problem Action
No sound.
System/BIOS behaves
erratically
Video Problems
Problem Action
Nothing appears on the LCD
panel when you turn on the
computer.
Error Message when
entering Power Management
while in Multimonitor mode.
Nothing appears on the
external monitor when you
switch the display to it.
Only the LCD Display works
when system returns from
Power management mode
while in Multimonitor mode.
The external monitor
displays flashes or waves.
Cannot toggle between CRT
and LCD while playing the
3D game.
Verify if the mute check box is checked or the
volume is not turned down in the pop up menu by
clicking the speaker icon of the task bar.
If you caused an abnormal power interruption (i.e..
removing battery while on battery power), you may
cause BIOS data corruption.
Adjust the brightness on a TFT LCD. Are you using
an external monitor? If so, press <Fn+F4> to return
to the LCD panel.
If the secondary monitor is set to 256 colours, this
error message could appear. Change the colour of
the secondary monitor to ‘high colour (16 bit)’.
Is the monitor properly connected to the computer?
Is the monitor’s power cord connected to an AC wall
outlet? Check the brightness and contrast controls on
the monitor. Does the program appear on the LCD
panel instead of the external monitor? If so, press
<Fn+F4> to switch to the monitor. Try turning the
monitor off and on again.
The system resets to the original BIOS setup when
the system returns from the power management
mode. If the Display mode, in the Advanced menu of
BIOS setup is set to LCD, then only the LCD will be
turned on when the system wakes up. Set the Display
mode in the BIOS to Both to turn on the LCD &
CRT on wakeup.
Check the cables between the monitor and the
computer. Are they properly installed?
If you are using the Multimonitor mode, you can not
use the <Fn+F4> key combination and also you
cannot use this function in 3D games using
Direct-X.
Troubleshooting 75

Problem Action
There is LCD or CRT has
noise (speckles, lines or
raged edges) on the
picture when playing a
MPEG file with the Media
player/ DVD software or
using the USB camera.
In DOS mode the CRT/LCD
button does not work.
If the connected CRT
monitor display is not steady.
Modem Problems
Adjust the resolution and the colour to 1400 x 1050
and 32 bit to display clearly, or avoid playing two
programs at the same time.
The LCD only mode is not supported using this Key
combination.
If the refresh rate is not optimal for the connected
CRT, then this problem may occur.
To correct this problem do the following:
1.Click Start > Settings > Control Panel.
2.Double-click the Display icon to open the Display
properties.
3.Select Settings
4.Click the Advanced button.
5.Click the Adapter tab
6.Adjust the Refresh rate to optimal or other selections
until you see the CRT clearly.
Problem Action
76 Users Manual
My modem doesn't connect
to services or disconnects
during communication
If your modem has difficulty in connecting to online services and sustaining communications, first
check if other devices are connected and remove
them. Also remove any extension leads. Interference
from certain devices or poor line power conditions
may degrade the quality of your connection. Under
these conditions gradually reduce the
communication speed of your modem until a reliable
connection is achieved.
Check with your on-line service provider.

Problem Action
When using a PBX phone
system I can't dial on my
modem.
Screen displays random or
garbage characters during
communications.
Reports error message that
insufficient Hard Disk space
is available.
If you use a PBX phone system you may need to
press a number i.e. '9' to connect to an external line,
you should enter the following command before
trying the connection and check modem
initialization. (ATX3&W)
And add “9,” as the external line prefix (example) of
the phone number when using the dial command
“ATDT9, 123-4567”.
After your modem has connected to the on-line
service, your screen may display garbage characters
or after-images in screen transitions. This problem is
caused by a mismatch of the terminal modes
between communications service and
communications programs. You need to match the
terminal modes to each other. Refer to the user's
guide of the communications program you're using.
Delete the unnecessary messages or data you
received by Modem or Fax every one to three
months as required.
If you're using the internet, many picture and data
files can get downloaded to your HARD DISK every
time you visit a home page, which will consume a lot
of your HARD DISK space. For more detailed
information about the method of deleting, refer to
the help of the Web browser you've been using or
your user's guide.
FAX Problems:
Depending on telephone line status, or types of Fax machines/programs that
send/receive the Fax, Fax transmission/reception may not work correctly. In
that case, please try other Fax programs. (e.g. Win Fax)
Troubleshooting 77

Reinstalling Software
Windows Application/Driver (Re)Installation
If you wish to reinstall drivers or applications, please use the Software CD.
If you wish to reinstall the Windows operating system, please use the Recovery CD.
Application/Driver (Re)Installation
Simply install the driver(s) according to the instructions below:
1. Insert the System Software CD-ROM.
2. Follow the directions provided in the opening window.
Windows (Re)Installation
To reinstall the your Microsoft Windows XP Operating System:
1. Start your computer.
2. Open the CD Drawer and insert the Recovery CD. Close the drawer.
3. When the Recovery Menu appears, select the option as required to restore your
system. You have two options for system recovery. The Standard Installation and
the User Installation.
• The Standard Installation Option will SAVE all user data files on your hard
disk and restore your operating system to normal.
• The User Installation Option will DESTROY all data on your hard disk. If
you have any data files or other software you do not wish to lose, make a
backup of these files to a diskette or other medium using a backup utility
before proceeding.
Samsung is NOT responsible for any data loss.
78 Users Manual
You MUST, however reinstall all of your applications and drivers using the
Software CD and other application software as required.
If the Recovery Menu does not appear, proceed as follows:
1. Restart your computer
2. Open the CD Drawer and insert the Recovery CD. Close the drawer.
3. You will see a message “Press any key to boot from the CD”, press any
key.
4. You will be presented with the User Installation Option.
If your computer cannot boot from the CD, change the boot priority to the
CD-ROM device as described in this manual.

Specifications
Dimension
LCD viewing area (14.1” TFT) 285.6 x 214.3 mm
Width 32.0 cm
Depth 26.5 cm
Height 2.95 cm
Weight (CD Drive, Li-Ion battery & 14.1” TFT LCD) 2400 g
Environment
Ambient temperature, operating 5o–35oC
Ambient temperature, storage -32o–60o C
Relative humidity (noncondensing), operating 30–80%
Relative humidity (noncondensing), storage 95%
Altitude, operating 0 to 4,572 m
Altitude, storage 0 to 13,716 m
Shock, operating 122 G for 2 ms half sine
Shock, nonoperating 163 G for 2 ms half sine
Lithium-Ion Smart Battery
Normal Weight 435g
Nominal open circuit voltage 14.8 VDC
Capacity, typical 4400 mAhr, 65.0whr
Charging time, approximate, with computer turned off, typical 3.0 hr
Charging time, approximate, with computer turned on , typical 6.0 hr
External AC Adapter
Operating voltage 100-240 VAC
Line frequency 50-60 Hz
Input current 1.5 A 100 V ~ 0.8 A 240 V
Output current 4.2 A
Output voltage 19.0 VDC
Specifications 79

Abbreviations
A . . . . . . . . . Amperes
AC . . . . . . . . Alternating current
ACPI . . . . . . Advanced Configuration and Power management Interface
APM . . . . . . Advanced Power Management
ATA. . . . . . . AT attachment (refers to the hard-drive interface in an AT-
ATAPI. . . . . AT attachment packet interface
BBS . . . . . . . Bulletin board system
BIOS . . . . . . Basic input/output system
C . . . . . . . . . Centigrade
CD . . . . . . . . Compact disc
CD-ROM . . Compact disc read-only memory
cm . . . . . . . . Centimeters
COM . . . . . . Communication (as in communication port)
CMOS . . . . . Complementary metal-oxide semiconductor
DC . . . . . . . . Direct current
DMA . . . . . . Direct memory access
DPMS . . . . . Display power-management signaling
DRAM. . . . . Dynamic random access memory
DSTN . . . . . Double layer super twist nematic
ECP . . . . . . . Extended capabilities port
EPP . . . . . . . Enhanced parallel port
g . . . . . . . . . . gram
G . . . . . . . . . Gravity
GB . . . . . . . . Gigabytes
hr . . . . . . . . . hour
Hz . . . . . . . . Hertz
IDE . . . . . . . Integrated drive electronics
I/O . . . . . . . . Input/output
IRQ . . . . . . . Interrupt request line
compatible computer)
80 Users Manual

ISA . . . . . . . Industry Standard Architecture
KB . . . . . . . . Kilobytes
kg . . . . . . . . . Kilograms
LAN. . . . . . . Local-area network
lb.. . . . . . . . . Pounds
LBA . . . . . . . Logical block addressing
LCD. . . . . . . Liquid-crystal display
m . . . . . . . . . Meters
mA. . . . . . . . Milliampere
mAhr. . . . . . Milliampere hour
MB. . . . . . . . Megabyte
mm . . . . . . . millimeter
MPEG . . . . . Motion Picture Experts Group
MPU . . . . . . Microprocessor unit
ms . . . . . . . . Millisecond
PDF . . . . . . . Portable document format
PC . . . . . . . . Personal computer
PCI . . . . . . . Peripheral component interconnect
PCMCIA. . . Personal Computer Memory Card International Association
POST. . . . . . Power-on self-test
PNP . . . . . . . Plug and play
PS/2 . . . . . . . Personal System/2
RAM . . . . . . Random-access memory
ROM . . . . . . Read-only memory
SVGA . . . . . Super video graphics array
TFT . . . . . . . Thin-film transistor
USB . . . . . . . Universal serial bus
V . . . . . . . . . Volt
VAC . . . . . . Voltage alternating current
VCC . . . . . . Voltage collector current
VDC . . . . . . Voltage direct current
whr . . . . . . . Watt hour
Abbreviations 81

Glossary
AC adapter
The AC (or alternating current) adapter regulates current coming into your
computer from the wall outlet. The current at the wall outlet is alternating current
and needs to be changed by the adapter to DC (direct current) before your
computer can use it for power.
ACPI
ACPI (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface)- a method for describing
hardware interfaces in terms abstract enough to allow flexible and innovative
hardware implementations and concrete enough to allow shrink-wrap OS code to
use such hardware interfaces.
BIOS
BIOS stands for basic input/output system. The BIOS is software (often called
firmware) that is independent of any operating system. It enables the computer to
communicate with the screen, keyboard, and other peripheral devices without
using programs on the hard disk.
The BIOS on your computer is flash BIOS, which means that it has been recorded
on a flash memory chip that can be updated if needed.
Boot
To start your computer. A cold boot resets the entire computer and runs through
all computer self-tests. A warm boot clears out computer memory only.
Boot disk
A disk containing operating system programs required to start your computer. A
boot disk can be a floppy disk, hard drive, or compact disc.
Byte
The basic unit of measure for computer memory. A character—such as a letter of
the alphabet—uses one byte of memory. Computer memory is often measured in
kilobytes (1,024 bytes) or megabytes (1,048,576 bytes).
Each byte is made up of eight bits. For more information on bytes and bits, see an
introductory book on computers.
Cache memory
Cache is very fast, zero-wait-state memory located between the microprocessor
and main memory. Cache reduces the average time required by the
microprocessor to get the data it needs from the main memory by storing recently
accessed data in the cache.
82 Users Manual

CardBus
CardBus technology enables the computer to use 32-bit PC Cards. Hardware in
the computer and the Windows operating system provide support for the 32-bit
cards. The voltage of 32-bit cards (3.3 volts) is lower than that of 16-bit cards (5
volts). The 32-bit cards can transmit more data at a time than the 16-bit cards, thus
increasing their speed.
CMOS memory
CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) memory is powered by the
CMOS battery. The System Setup settings and other parameters are maintained in
CMOS memory. Even when you turn your computer off, the information in
CMOS memory is saved.
COM port
COM stands for communication. COM ports are the serial ports in your computer.
Compact Disc
A compact disc (CD).
Conventional memory
The first 640 KB of system memory. Operating systems and application programs
can directly access this memory without using memory-management software.
Disk
The device used by the computer to store and retrieve information. Disk can refer
to a floppy disk, hard disk, or RAM disk.
Disk cache
A software device that accumulates copies of recently used disk sectors in RAM.
The application program can then read these copies without accessing the disk.
This, in turn, speeds up the performance of the application.
A cache is a buffer for transferring disk sectors in and out of RAM. Data stored in
a disk cache is a copy of data already stored on the physical disk.
DMA (direct memory access)
A method of transferring data from a device to memory without having the data
pass through the microprocessor. Using DMA can speed up system performance.
DPMS
Display Power Management Signalling. Displays or monitors that comply with
this can be managed by the Power Management features found in the system
setup.
Floppy disk
A removable disk, also called floppy or diskette.
Glossary 83

Hard drive
Also called fixed disk. A hard drive is connected to the computer and can be
installed or removed. Data written to a hard drive remains until it is overwritten
or corrupted.
The 2.5-inch hard drive in your computer was designed for use in a notebook
computer. Because hard drives in notebook computers are smaller than those in
desktop computers, their maximum storage capacity may be less than that of
desktop hard drives. However, because of their smaller size, the drives handle
shock and vibration better than larger drives, which is important for a notebook
computer.
I/O
Input/output. Refers to peripheral devices, such as printers, that are addressed
through an I/O address.
I/O address
I/O stands for input/output. Peripheral devices, such as printers, are addressed
through the I/O port address.
IRQ (interrupt request line)
The IRQ is a hardware line that a device uses to signal the microprocessor when
the device needs the microprocessor’s services. The number of IRQs is limited by
industry standards.
LCD (liquid-crystal display)
The LCD screen on your computer differs from the display screen of a desktop
monitor. Most desktop monitors use CRT (cathode-ray tube) displays, which
work by moving an electron beam across phosphor dots on the back of the screen.
The phosphor dots light up to show the image. LCDs use a liquid-crystal solution
between two sheets of polarizing material. Electric current passing through the
liquid aligns the crystals so that light can or cannot pass through them, creating an
image.
MB (megabyte)
1,024 kilobytes.
Megabit
1,048,576 bits or about 128 kilobytes.
Operating system
A program that supervises the computer's operation, including handling I/O.
Application programs and users can request operating-system services. A user
might request operation-system services to copy files or format a disk. An
application program might use the operating system to obtain keyboard input,
write data to a file, or write data to a screen.
84 Users Manual

PC Card
PC Card stands for personal computer card. The Personal Computer Memory
Card International Association (PCMCIA) defines the standards used to develop
all PC Cards. PC Card types include: modems, Ethernet adapters, SCSI adapters,
ATA cards, and memory cards.
PC slot
The PC slot is the hardware slot in the computer where the PC Card is placed.
Pixel
A pixel is an individual dot in a graphic displayed on your computer. The pixels
are so close together that they look as though they are connected. An LCD screen
displays thousands or millions of pixels.
Plug and Play
A plug and play operating system automatically configures computer components
to work with your system. With this type of operating system, you normally do
not need to set jumpers on devices or set memory addresses or IRQs.
RAM (random access memory)
The computer's system memory, including conventional and extended memory.
You can write to and read from RAM. Information stored in RAM is temporary,
and is erased when the system is turned off.
Refresh rate
The refresh rate is the rate at which the image on the LCD screen is rewritten to
the screen. A fast refresh rate helps keep the image from flickering.
Resolution
The resolution is the sharpness or clarity of the image on your LCD screen.
Resolution is measured by the number of pixels the computer’s screen can
display. For example, a resolution of 800 x 600 means that the screen can display
800 pixels in row and can display 600 rows. The more pixels displayed, the higher
the resolution and the better the image.
ROM (read-only memory)
Permanent computer memory dedicated to a particular function. For example, the
instructions for starting the computer when you first turn on power are contained
in ROM. You cannot write to ROM. (ROM is not the same as RAM).
Sector
Also known as disk sector. The portion of a track that is numbered and can hold
a specified number of characters (usually 512 KB).
Glossary 85

Shadow RAM
A write-protected area of RAM that contains a copy of the BIOS. As the computer
boots, the BIOS is copied from its permanent location in ROM to RAM. The
BIOS can be executed much faster in RAM than in ROM. The BIOS remains in
shadow RAM until you turn off the computer.
TFT (thin film transistor) LCD
A TFT LCD uses a separate transistor circuit to control each pixel. This
technology provides the best resolution for an LCD screen. A TFT LCD is also
sometimes called an active matrix LCD.
Zoomed video
Zoomed video technology enables zoom video PC Card to transfer data directly
from the card to video and audio systems without going through the
microprocessor. This process improves video performance. Video conferencing
and real-time multimedia devices, such as video cameras, are supported by zoom
video.
86 Users Manual
 Loading...
Loading...