Page 1

- TFT-LCD
(Thin film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display)
ADC(Analog to Digital Converter)
This is a circuit that converts from analog signal
to digital signals.
- PLL(Phase Locked Loop)
During progressing ADC, Device makes clock
synchronizing HSYNC with Video clock
- Inverter
Device that supply Power to LCD panel lamp.
this device gernerate about 1,500~2,000V.
- AC Adapter
Device that converts AC(90V~240V) to DC(+12V
or 14V)
- SMPS(Switching Mode Power Supply)
Switching Mode Power supply. This design technology is used to step up/down the input power
by switching on/off
- FRC(Frame Rate Controller)
Technology that change image frame quantity
displayed on screen for one second.
Actually TFT-LCD panel require 60 pcs of frame
for one second.
so,this technology is needed to convert input
image to 60 pcs regardless input frame quantity.
- Image Scaler
Technology that convert various input resolution
to other resolution.(ex. 640* 480 to 1024*768)
- Auto Configuration(Auto adjustment)
This is an algorithm to adjust monitor to optimum
condition by pushing one key.
- OSD(On Screen Display)
On screen display. customer can control the
screen easily with this.
- Image Lock
This means "Fineness adjustment" in LCD
Monitor, the features are "Fine" and "Coarse"
- FINE
"Fine" adjustment is used to adjust visibility by
control phase difference.
- COARSE
This is a adjustment by tuning with Video colck
and PLL clock.
- L.V.D.S.(Low Voltage Differential Signaling)
a kind of transmission method for Digital.It can
be used from Main PBA to Panel.
- DVI (Digital Visual Interface)
This provides a high speed digital connection for
visual data types that is display technology independent. this interface is primarily forcused at
providing a connection between a computer and
its display device.
- T.M.D.S
(Transition minimized Differential Signaling)
a kind of transmission method for Digital.
It can be used from Video card to Main PBA.
14 Reference Infomation
14-1
14 Reference Infomation
14-1 Technical Terms
Page 2

14 Reference Infomation
14-2
- DDC(Display data channel)
It is a communication method between Host
Computer and related equipment.
It can make it Plug and Play between PC and
Monitor.
- EDID
Extended Display Identification Data PC can recognize the monitor information as Product data,
Product name,Display mode,Serial number and
Signal source,etc through DDC Line communicating with PC and Monitor.
- Dot Pitch
The image on a monitor is composed of red,
green and blue dots. The closer the dots, the
higher the resolution. The distance between two
dots of the same color is called the 'Dot Pitch'.
Unit: mm
- Vertical Frequency
The screen must be redrawn several times per
second in order to create and display an image
for the user. The frequency of this repetition per
second is called Vertical Frequency or Refresh
Rate. Unit: Hz
Example: If the same light repeats itself 60
times per second, this is regarded as 60 Hz.
- Horizontal Frequency
The time to scan one line connecting the right
edge to the left edge of the screen horizontally is
called Horizontal Cycle. The inverse number of
the Horizontal Cycle is called Horizontal
Frequency. Unit: kHz
- Interlace and Non-Interlace Methods
Showing the horizontal lines of the screen from
the top to the bottom in order is called the NonInterlace method while showing odd lines and
then even lines in turn is called the Interlace
method. The Non-Interlace method is used for
the majority of monitors to ensure a clear image.
The Interlace method is the same as that used in
TVs.
- Plug & Play
This is a function that provides the best quality
screen for the user by allowing the computer and
the monitor to exchange information automatically. This monitor follows the international standard
VESA DDC for the Plug & Play function.
- Resolution
The number of horizontal and vertical dots used
to compose the screen image is called 'resolution'. This number shows the accuracy of the display. High resolution is good for performing multiple tasks as more image information can be
shown on the screen.
Example: If the resolution is 1280 x 1024 , this
means the screen is composed of 1280 horizontal dots (horizontal resolution) and 1024 vertical
lines (vertical resolution).
- BTSC
Broadcast Television System Committee
The stereo broadcasting system that is used in
most of the countries that have adopted the
NTSC system, including the United States,
Canada, Chile, Venezuela and Taiwan. It also
refers to the organization that has been organized to promote its development and management.
- EIAJ
Electronic Industries Association of Japan.
Page 3

- RF Cable
A round signal cable generally used for TV
antennas.
- Satellite Broadcasting
Broadcasting service provided via satellite.
Enables high picture quality and clear sound
throughout the country regardless of the location
of the viewer.
- Sound Balance
Balances the levels of the sound coming from
each speaker in televisions with two speakers.
- Cable TV
Whereas the terrestrial broadcasting is delivered
via frequency signals through the air, cable
broadcasting is transmitted via a cable network.
In order to view cable TV, one must purchase a
cable receiver and hook it up to the cable network.
- CATV
"CATV" refers to the broadcasting service
offered at hotels, schools and other buildings
through their own broadcasting system, apart
from VHF or UHF broadcasting by terrestrial
broadcasters. The CATV programs may include
movies, entertainment and educational programs. (Different from cable TV.)
CATV can be viewed only within the area in
which the CATV service is offered.
- S-Video
Short for "Super Video." S-Video allows up to
800 lines of horizontal resolution, enabling highquality video.
- VHF/UHF
VHF indicates TV channels 2 to 13, and UHF
indicates channels 14 through 69.
- Channel Fine Tuning
This feature allows the viewer to fine-tune the TV
channel to obtain the best viewing conditions.
The Samsung LCD TV has both automatic and
manual channel fine-tuning features to enable
the viewer to adjust their desired settings.
- External Device Input
External device input refers to video input from
such external video devices as VCRs, camcorders and DVD players, separate from a TV
broadcast.
14 Reference Infomation
14-3
Page 4
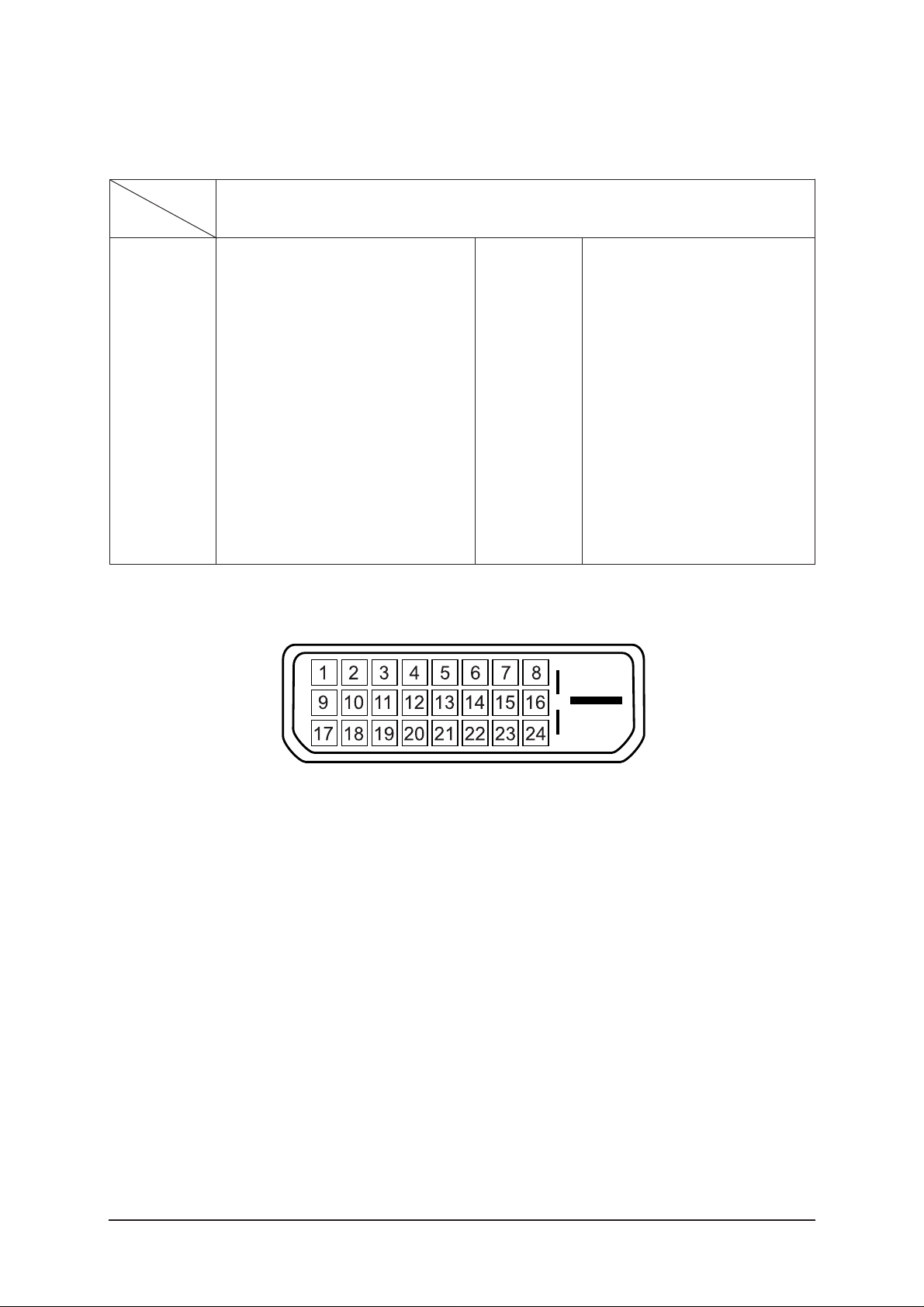
14 Reference Infomation
14-4
14-2-1 DVI-D
14-2 Pin Assignments
NC
DDC Input power (+5V)
IDENT-DVI
Output Signal (HDCP Control)
Rx0-
Rx0+
GND
NC
NC
GND
RxC+
RxC-
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Rx2-
Rx2+
GND
NC
NC
DDC - SCL
DDC - SDA
NC
Rx1-
Rx1+
GND
NC
Sync
Type
Pin No.
24P DVI-D
Figure 1.
Page 5
14 Reference Infomation
14-5
Both screen position and size will vary depending on the type of PC monitor and its resolution.
The resolutions in the table are recommended. (All resolutions between the supported limits are supported)
- The interlace mode is not supported.
- The set might operate abnormally if a non-standard video format is selected.
- DVI dose not support PC function.
Pin
Separate
1
2
3
4
5
GND
Y
C
GND
GND
RCA Green
RCA Blue
RCA Red
RCA White
RCA Red
Y
GND
Pb (Cb)
GND
Pr (Cr)
GND
Audio L
GND
Audio R
GND
14-2-3 S-Video
Pin
Separate
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Red
Green
Blue
GND
GND
GND Red
GND Green
GND Blue
DDC Input power(+5V)
IDENT PC
GND
DDC Data(SDA)
H SYNC
V SYNC
DDC Clock(SCL)
14-2-5 D-SUB
14-2-2 Component
RCA White
RCA Red
CVBS
Audio L
GND
Audio R
GND
14-2-4 A/V
RCA Yellow
14-2-6 PC Display mode
Mode
IBM
VESA
Resolution
640 x 480
720 x 400
640 x 480
640 x 480
800 x 600
800 x 600
800 x 600
1024 x 768
1024 x 768
1024 x 768
1360 x 768
Horizontal
Frequency (kHz)
31.469
31.469
37.861
37.500
37.879
48.077
46.875
48.364
56.476
60.023
47.712
Vertical
Frequency (Hz)
59.940
70.087
72.809
75.000
60.317
72.188
75.000
60.000
70.069
75.029
60.015
Pixel Clock
Frequency (MHz)
25.175
28.322
31.500
31.500
40.000
50.000
49.500
65.000
75.000
78.750
85.800
Sync Polarity
(H/V)
- / -
- / +
- / -
- / + /+
+ /+
+ /+
- / -
- / + /+
+ /+
Page 6

14 Reference Infomation
14-6
14-2-7 Scart 1
14-2-8 Scart 2
Pin Signal
1 Audio output R
2 Audio input R
3 Audio output L
4 Audio common GND
5 Video GND (RGB blue)
6 Audio input L
7 RGB blue input
8 Switching voltage
9 Video GND (RGB green)
10 NC
11 RGB green input
Pin Signal
12 NC
13 Video GND (RGB red)
14 GND
15 RGB red input
16 Fast Blanking signal
(RGB switching)
17 Video output GND
18 Video input GND
19 Video output (CVBS out)
20 Video input (CVBS in)
21 Common GND
Pin Signal
1 Audio output R
2 Audio input R
3 Audio output L
4 Audio common GND
5 Video GND (RGB blue)
6 Audio input L
7 RGB blue input
8 Switching voltage
9 Video GND (RGB green)
10 NC
11 RGB green input
Pin Signal
12 NC
13 Video GND (RGB red)
14 GND
15 RGB red input
16 NC
17 Video output GND
18 Video input GND
19 Video output (CVBS out)
20 Video input (CVBS in)
21 Common GND
Page 7

14 Reference Infomation
14-7
14-3 Timing Chart
This section of the service manual describes the timing that the computer industry recognizes as standard for
computer-generated video signals.
14-3-1 LCD Panel Mode1 mode
Page 8

14 Reference Infomation
14-8
14-3-2 Supported Modes (1)
Page 9

14 Reference Infomation
14-9
14-3-3 Supported Modes (2)
Page 10

14 Reference Infomation
14-10
14-3-4 Supported Modes (3)
Page 11

14-4 Panel Description
14 Reference Infomation
14-11
SEC LT140X1-002 BN07-00004A SA BN68-00239H SEC LT150XS-L01 BN07-00009A SB SEC LT150XS-L01-B BN07-00022A SC SEC LTM150XS-L02 BN07-00005A SD SEC LT181E2-132 BN07-00001A SE SEC LT150XS-T01 BN07-00010A SF SEC LTM181E3-132 BN07-00019A SG SEC LT170E2-131 BN07-10001D SH SEC LT181E2-131 BN07-10001E SJ SEC LTM170E4-L01 BN07-00018A SK SEC LTM240W1-L01 BN07-00015A SL SEC LTM213U3-L01 BN07-00016A SM SEC LTM150XH-L01 BN07-00026A SN SEC LTM150XH-L03 BN07-00027A SP SEC LTM150XS-L01 BN07-00032A SQ DELL(ZPD)
SEC LTM181E4-L01 BN07-00034A SR PVA
SEC LTM170EH-L01 BN07-00036A SS TN
SEC LTM170E5-L01 BN07-00037A SU PVA
SEC LTM150XH-L11 BN07-00041A SV SEC LTM213U4-L01 BN07-00039A SW PVA
SEC LTM150XH-L01(ZPD) BN07-00045A SX ZPD
SEC LTM150XH-L04 BN07-00046A SY New panel with high brightness
SEC LTM170W1-L01 BN07-00047A SZ Panel for TV
SEC LTM150XH-L06 BN07-00053A EA Panel for TV/ High luminance for 450cd _ SONY&EOS Team Panel for
TV
SEC LTM153W1-L01 BN07-00054A EB Use NIKE MODEL
SEC LTM170EH-L05 BN07-00055A EC Panel EOS proj. for high brightness of 17" EH-L05
SEC LTM170E5-L03 BN07-00056A ED Dell 1702FP pro. E4. EH mechanicalCompatible
SEC LTM190E1-L01 BN07-00057A EE DELL 1900 FP
SEC LTM181E5-L01 BN07-00061A EF 18" narrow bezel GH18PS
SEC LTM150XP-L01 BN07-00065A EG AMLCD PVA PANEL
SEC LTM240W1-L02 BN07-00062A EH Panel for 15" Wide TV
SEC LTM170EU-L01 BN07-00071A EJ Slim design, TN
SEC LTM170E5-L04 BN07-00072A EK E5-L04 6 bits FRC... for IBM
SEC LTA220W1-L01 BN07-00074A EL Panel for 22" TV
SEC LTM170E6-L02 BN07-00075A EM AMLCD Narrow & slim design 17" PVAmode
SEC LTM170W1-L01 BN07-00082A EN LTM170W1-L01 ZPD panel
SEC LTM170EH-L01 BN07-00080A EP LTM170EH-L01 ZPD panel
SEC LTM170E5-L01 BN07-00081A EQ LTM170E5-L01 ZPD panel
SEC LTM170EH-L05 BN07-00083A ER LTM170EH-L05 ZPD panel
SEC LTM170E5-L03 BN07-00084A ES LTM170E5-L03 ZPD panel
SEC LTM170EU-L01 BN07-00085A ET LTM170EU-L01 ZPD panel
SEC LTM170E5-L04 BN07-00086A EU LTM170E5-L04 ZPD panel
SEC LTM170E6-L02 BN07-00087A EV LTM170E6-L02 ZPD panel
SEC LTM150XH-L06 BN07-00091A EW Color coordinates change for LCD TV
SEC LTM153W1-L01 BN07-00092A EX AMLCD WIDE 15",9/10
SEC LTM170W1-L01 BN07-00100A EY Color Coordinates change code management
SEC LTM170EH-L05 BN07-00097A EZ LTM170E5-L05 Color Coordinates Change Panel Code
SEC LTA400W1-L01 BN07-00109A S1 PANEL of AMLCD 40" TV
SEC LTM153W1-L01 BN07-00110A S2 Color coordinates change 0.280/0.290, 10000k & ZPD Panel
SEC LTM150XH-L06 BN07-00111A S3 Color coordinates change 0.280/0.290, 10000k & ZPD Panel
SEC LTM170W1-L01 BN07-00112A S4 Color coordinates change 0.280/0.290, 10000k & ZPD Panel
SEC LTM170EH-L05 BN07-00113A S5 Color coordinates change 0.280/0.290, 10000k & ZPD Panel
SEC LTM220W1-L01 BN07-00114A S6 ZPD Panel for AMLCD 22" TV
SEC LTM150XH-L06 BN07-00117A S7 ZPD Panel code
SEC LTM153W1-L01 BN07-00118A S8 ZPD Panel code
SEC LTM170WP-L01 BN07-00119A S9 PVA Panel for NIKE
SEC LTM213U4-L01 BN07-00039A E1 21.3" NARROW
SEC LTA260W1-L01 BN07-00121A E2 VENUS
SEC LTA220W1-L01 BN07-00074B E3 Panel B-level panel code for 22" TV Panel
SEC LTA320W1-L01 BN07-00108A E4 Panel for AMLCD 32" TV
SEC LTM213U4-L01 BN07-00124A E5 NARROW BEZEL 21 " PANEL
SEC LTM170E6-L04 BN07-00129A E6 HIGHLAND 17" LOW PANEL (Panel only for TCO03)
SEC LTM190E1-L01 BN07-00088A E7 LTM190E1-L01 ZPD panel
SEC M150X4-L06 BN07-00137A E8 15" Narrow & Slim panel
Maker VENDOR P/N PANEL_CODE PANEL_ABB STICKER_CODE Remarks
Page 12

14 Reference Infomation
14-12
SEC LTA170V1 BN07-00139A E9 17" Panel for Muse 4:3 VGA TV
SEC LTM190E1-L02 BN07-00128A E10 New Panel from AMLCDl, Specification : 6bit Driver IC
SEC LTM170EX-L01 BN07-00143A E11 Development new Panel from AMLCD
SEC LTM170E8-L01 BN07-00144A E12 Development new Panel from AMLCD
SEC LTM170E6-L04 BN07-00129B E13 ZPD panel for AMLCD (Panel only for TCO03)
SEC LTA320W1-L02 BN07-00108B E14 Creat B-level Panel code for AMLCD 32" TV
SEC LTM190E1-L03 BN07-00151A E15 Development new 19" Panel form AMLCD (Panel only for TCO03)
SEC LTM240W1-L03 BN07-00134A E16 AMLCD 24" panel development
SEC LTM190E1-L02 BN07-00128B E17 New Panel from AMLCD, Specification : 6bit Driver IC(ZPD)
SEC LTM190E4-L01 BN07-00145A E18 AMLCD 24" new panel development
SEC LTM170E8-L01 BN07-00158A E19 ZPD code derivation
SEC LTM170EX-L01 BN07-00159A E20 ZPD code derivation
SEC LTM190E1-L03 BN07-00151B E21 Creat new panel code for AMLCD 19" (Panel only for TCO03)
SEC LTA460H1-L01 BN07-00157A E22 creat panel code for AMLCD 46" TV
SEC LTM170EU-L11 BN07-00160A E23 creat new panel code for AMLCD 17" (Panel only for TCO03)
SEC LTM240W1-L03 BN07-00134B E24 24" panel ZPD code derivation
SEC LTM190E4-L01 BN07-00145B E25 AMLCD 19" ZPD Panel code derivation
SEC LTM240W1-L03 BN07-00134B E26 24" panel ZPD code derivation
SEC LTM150XO-L01 BN07-00164A E27 AMLCD 15" XO-L01 new panel development
SEC LTM150XO-L01 BN07-00164B E28 AMLCD 15" XO-L01 ZPD code derivation
SEC LTM170EU-L11 BN07-00160B E29 AMLCD 17" NEW panel code derivation
SEC LTA320W2-L01 BN07-00172A SPZ AMLCD 32" NEW panel
SEC LTM213U4-L01 BN07-00124B SPZ 21.3" Narrow PANEL ZPD Panel derivation
SEC LTM170EU-L11 BN07-00189A STH AMLCD EU-L11 Pb free panel code derivtion
SEC LTM170EU-L11 BN07-00189B STZ AMLCD EU-L11 Pb free panel ZPD code derivation
SEC LTM240W1-L04 BN07-00188A SPH 24" A-DCC NEW panel
SEC LTM240W1-L04 BN07-00188B SPZ 24" A-DCC panel ZPD code derivation
SEC LTM190EX-L01 BN07-00191A STH AMLCD 19" TN NEW Panel
SEC LTM190EX-L02 BN07-00191B STZ AMLCD 19" TN NEW Panel ZPD
SEC LTA230W1-L02 BN07-00184A SPZ AMLCD 23" 16:9 NEW Panel
SEC LTA260W2-L01 BN07-00185A SPZ AMLCD 26" 16:9 NEW Panel
SEC LTA400W2-L01 BN07-00186A SPZ AMLCD 40" 16:9 NEW Panel
SEC LTM240M1-L01 BN07-00195A SPH 24" high brightness panel
SEC LTM150XO-L01 BN07-00197A STH AMLCD 15" XO-L01 Pb free panel code
SEC LTM150XO-L01 BN07-00197B STZ AMLCD 15" XO-L01 Pb free panel ZPD code
SEC LTM170EU-L21 BN07-00202A STZ AMLCD EU-L21 ZPD NEW code derivation
SEC LTA460W2-L03 BN07-00187A SPZ BEETOVEN 46"ZPD NEW Panel
SEC LTM240M1-L01 BN07-00195B SPZ 24" high brightness panel ZPD code derivation
SEC M170EX-L21 BN07-00206A STZ AMLCD LTM170EX-L21 ZPD NEW code derivation
SEC LTA460H3-L01 BN07-00200A SPZ AMLCD 46" LED BLU panel
SEC LTM170EU-L15 BN07-00214A STZ High brightness For AMLCD EU-L15 TV ZPD NEW code derivation
SEC LTM170E8-L21 BN07-00218A SPZ AMLCD LTM170E8-L21 PVA ZPD NEW code derivation
SEC LTM190EX-L21 BN07-00222A STZ DISPLAY LCD
SEC LTM201U1-L01 BN07-00190B SPZ AMLCD 20.1" Normal panel ZPD code derivation
SEC LTM190E4-L21 BN07-00223A SPZ HAYDN 17" PZD code PANELderivation
SEC LTA570H1-L01 BN07-00196A SPZ AMLCD 57" NEW Panel
SEC LTM150XO-L21 BN07-00229A STZ AMLCD 15" XO-L21 8ms panel code
SEC LTA260W2-L11 BN07-00239A SPZ AMLCD 26" 16:9 7Line NEW Panel
SEC LTA400WS-LH1 BN07-00245A SPZ AMLCD 40" 16:9 SPVA 90% NEW Panel
SEC LTM213U6-L01 BN07-00231A SPZ AMLCD 21.3" PVA NEW Panel Code
SEC LTM213U6-L01 BN07-00231B SPH AMLCD 21.3" PVA Panel HPD Code
SEC LTA320WS-LH2 BN07-00244A SPZ AMLCD 32" 16:9 SPVA 90% NEW Panel
SEC LTA400WS-LH1 BN07-00245A SPZ AMLCD 40" 16:9 SPVA 90% NEW Panel
SEC LTM190M2-L01 BN07-00227A STZ AMLCD 19" TN Wide NEW Panel Code
SEC LTM201UX-L01 BN07-00249A STZ AMLCD 20.1" TN NEW Panel Code
SEC LTM240M1-L02-A05 BN07-00250A SPZ 24" High brightness Slim panel ZPD code derivation
SEC LTA320W3-L02 BN07-00219A SPZ AMLCD 32" NEW FFL Panel
SEC LTA320W2-L11 BN07-00259A SPZ IP Board for AMLCD 32" 16:9 NEW Panel
SEC LTA460WS-L02 BN07-00252A SPZ AMLCD 46" 16:9 SPVA 72% NEW Panel
SEC LTA400WT-L01 BN07-00264A SPZ SEC LTM240M2-L02 BN07-00267A SPZ All LCD Monitor 24" wide SPVA ZPD NEW code derivation
SEC LTM210M2-L02 BN07-00230A SPZ SEC LTA320WT-L11 BN07-00257A SPZ SEC LTM190EX-L21-G BN07-00274A STZ AMLCD 19" TN Glare NEW Panel Code
SEC LTA320WT-L14 BN07-00247A SPZ -
Maker VENDOR P/N PANEL_CODE PANEL_ABB STICKER_CODE Remarks
Page 13

14 Reference Infomation
14-13
SEC LTM190M2-L01-D016 BN07-00280A STZ AMLCD 19" TN Wide change Gamma Panel Code
SEC LTM190EX-L31 BN07-00279A STZ AMLCD 19" TN NEW Panel Code
SEC LTM190M2-L02 BN07-00287A STZ AMLCD 19" TN Wide High brightness NEW Panel Code
SEC LTA400WS-L01 BN07-00246A SPZ Display-LCD (Div) 07AH
SEC LTA460WS-L01 BN07-00311A SPZ SEC LTM190E4-L31 BN07-00316A SPZ SEC LTM170EX-L31 BN07-00278A STZ AMLCD LTM170EX-L31 ZPD
SEC LTA460HS-LH1 BN07-00291A SPZ AMLCD 46" 16:9 FHD / 60Hz / 8bit / SPVA 92%
SEC LTA320WT-LF1 BN07-00323A SPZ SEC LTA460WT-L02 BN07-00284A SPZ AMLCD 46" 16:9 HD / 60Hz / 8bit / SPVA 72% /
SEC LTA400WH-LH1 BN07-00271A SPZ AMLCD 40" 16:9 SPVA 92% 10bit 120Hz
SEC LTM240M1-L02-D015 BN07-00331A SPZ SEC LTM300M1-P01 BN07-00326A SPZ
CPT CLAA150XG09 BN07-00141A PA CPT 15" Monitor new panel development
CPT CLAA170EA02 BN07-00148A PB 17" CPT NEW development panel
CPT CLAA170EA02 BN07-00148B PC 17" CPT ZPD panel code derivation
CPT CLAA150XG09 BN07-00141B PTZ CPT 15" panel ZPD code derivation (GOYA-PJT)
CPT CLAA150XP01 BN07-00173A PTH CPT 15" PSWG code derivation
CPT CLAA150XP01 BN07-00173B PTZ CPT 15" PSWG panel ZPD code derivation
CPT CLAA170EA07 BN07-00174A PTH CPT 17" PSWG code derivation
CPT CLAA170EA07 BN07-00174B PTZ CPT 17" PSWG type New Panel code
CPT CLAA170EA07Q BN07-00220A PTZ CPT 17" PSWG R/T 8msec code derivation
CPT CLAA170EA07Q BN07-00220B PTH CPT 17" PSWG R/T 8msec HPD code derivation
CPT CLAA150XP01F BN07-00236A PTZ CPT 15" PSWG panel ZPD & Lead free code derivation
CPT CLAA201WA03Q BN07-00269A PTZ CPT 20.1" wide TN ZPD New code derivation
CPT CLAA320WA01 BN07-00276A PMZ CPT 32" 16:9 MVA 8bit 60Hz / Panel brown
CPT CLAA170ES01 BN07-00261A PTZ CPT 17" Slim TN ZPD Type New code derivation
CPT CLAA070VA02 BN07-00265A PTZ CPT Panel code derivation for Digital Album
TOSHIBA LTM15C419(A) BN07-00002A TA TOSHIBA LTM15C423(B) BN07-00006A TB TOSHIBA LTM18C161 BN07-00008A TC TOSHIBA LTM15C443 BN07-00031A TD TOSHIBA LTM15C458 BN07-00043A TE TOSHIBA LTM15C458S BN07-00077A TF TSB 15" high brightness Panel
TOSHIBA LTM15C458 BN07-00078A TG Toshiba ZPD panel
TOSHIBA LTM15C458S BN07-00099A TH TSB LTM15C458S ( ZPD )
HANNSTAR HSD150MX41A(A) BN07-00020A NA TTL type
HANNSTAR HSD150MX12 BN07-00030A NB TTL type
HANNSTAR HSD170ME13 BN07-00180A NTH Hannstar 17" TN new panel development
HANNSTAR HSD170ME13 BN07-00180B NTZ Hannstar 17" TN new panel development ZPD code derivation
HANNSTAR HSD190ME12 BN07-00210A NTZ Hannstar 19" TN new panel development
HANNSTAR HSD150MX17-A BN07-00226A NTZ Hannstar 15" slim panel ZPD code derivation
HANNSTAR HSD190ME12-A10 BN07-00256A NTZ Hannstar 19" TN PSWG 8ms new panel development
HANNSTAR HSD190ME13-D11 BN07-00270A NTZ Hannstar 19" TN Slim 5ms new panel development
HANNSTAR HSD190ME13-A13 BN07-00317A NTZ
TORISAN TM150XG-22L03(A) BN07-00021A RA TORISAN TM150XG-26L06 BN07-00042A RB TORISAN TM181SX-76N01 BN07-00048A RC TORISAN TM150XG-26L06 BN07-00059A RD 15" XGA TN MODE(ZPD)
TORISAN TM290WX-71N31 BN07-00063A RE RS24NS (TORISAN 29" NEW PANEL)
TORISAN TM396WX-71N31 BN07-00064A RF RS24NS (TORISAN 40" NEW PANEL)
TORISAN TM150XG-26L09 BN07-00073A RG Panel for 15" TV
TORISAN TM150XG-26L10 BN07-00089A RH L10(change except D/IC) ZPD
TORISAN TM150XG-26L10 BN07-00090A RJ L10 NORMAL
TORISAN TM190SX-70N01 BN07-00098A RK Torisan 19" Panel
TORISAN TM181SX-76N01 BN07-00106A RL ZPD Panel code
TORISAN TM190SX-70N01 BN07-00107A RM ZPD Panel code
TORISAN TM290WX-71N31 BN07-00115A RN Color Coordinates change panel for TORISAN 29" TV
TORISAN TM396WX-71N31 BN07-00116A RP,Q Color Coordinates change panel for TORISAN 40" TV
TORISAN TM22OWX-71N31 BN07-00125A RR Development TORISAN 22" TV PANEL (ZPD)
TORISAN TM22OWX-71N31 BN07-00127A RS Development TORISAN 22" TV PANEL (HPD)
Maker VENDOR P/N PANEL_CODE PANEL_ABB STICKER_CODE Remarks
Page 14

14 Reference Infomation
14-14
TORISAN TM396WX-71N32A BN07-00150A RT 120V inverter Exclusive panel
TORISAN TM190SX-70N02 BN07-00154A RMH Torisan 6bit panel code Derivation
TORISAN TM190SX-70N02 BN07-00154B RMZ Torisan 6bit panel code Derivation
TORISAN TM150XG-A01 BN07-00162A RTH Torisan 15" Narrow & Slim panel development
TORISAN TM150XG-A01 BN07-00162B RTZ Torisan 15" N&S panel ZPD code derivation
SHARP LQ181E1DG11(A) BN07-10001C PA SHARP LQ150X1LW71 BN07-00067A PB SHARP 15" PVA PANEL
SHARP LQ370T3LZ41 BN07-00216A FAZ Rome2
HITACHI TX38D12VC0CAA(A) BN07-00003A HA HITACHI TX43DVCOCAB BN07-00060A HB 17" SXGA PVA MODE
HITACHI TX43D15VC0CAB BN07-00101A HC ZPD Panel
HITACHI TX51D11VC0CAB BN07-00122A HD 20.1" NARROW
HITACHI TX54D11VC0CAB BN07-00123A HE 21.3" NARROW
HITACHI TX80D12VC0CAB BN07-00169A HIZ Development new panel for Hitachi 32" TV (ZPD)
HITACHI TX54D11VC0CAB BN07-00123B HIZ Hitachi 21.3"ZPD panel
IBM ITSX94S BN07-00017A IA -
UNIPAC UM170E0 BN07-00028A UA Loaded by cisdba
HYUNDAI HT15X13 BN07-00035A DA HYUNDAI HT17E11-200 BN07-00049A DB TN MODE
HYUNDAI HT17E11-300 BN07-00093A DC HT17E11-300 ZPD panel
HYUNDAI HT17E11-400 BN07-00094A DD HT17E11-400 normal panel
HYUNDAI HT17E11-400 BN07-00095A DE HT17E11-400 ZPD panel code
HYUNDAI HT17E12 BN07-00096A DF HT17E12 ( Narow & slim Design )
HYUNDAI HT17E12 BN07-00105A DG ZPD Panel code
HYUNDAI HT15X15-D00 BN07-00146A DH Development for Ares 15" Hydis TV
HYUNDAI HT15X15-D01 BN07-00146B DJ Derivation panel HPD for Ares 15" Hydis TV
HYUNDAI HT17E13-100 BN07-00167A DTH PINEHURST-2(IBM) PJT 17" HYDIS PANEL Derivation
HYUNDAI HT17E13-100 BN07-00167B DTZ PINEHURST-2(IBM) Hydis 17" ZPD code Derivation
HYUNDAI HT170EX1-100 BN07-00240A DTZ 17" EX compatible Hydis Slim panel development
HYUNDAI HT201V01-100 BN07-00263A DTZ Hydis 20.1" 4:3 VGA Mode TN NEW Panel
HYUNDAI HT170EX1-101 BN07-00266A DTZ 17" EX compatible Hydis Slim panel multi channel IC NEW Derivation
ACER L170E3 BN07-00044A AA TN(ADT)
ACER M170EN05 BN07-00076A AB AU 17" Panel ( Narrow & slim design )
ACER M170EN05 BN07-00102A AC ZPD Panel code
ACER M190EN02 BN07-00170A AMH AU Monitor 19" new panel development (P19-1S)
ACER M190EN02 BN07-00170B AMZ AU 19" ZPD code derivation (ZPD)
ACER M170EN06 BN07-00171A ATH AU Monitor 17" New panel development
ACER T260XW01 BN07-00163A AMZ AU 26" new panel development (NF26EO)
ACER A201SN01 BN07-00177A ATZ AU TV panel 20.1" TN SVGA new panel development
ACER M170EN06 BN07-00171B ATZ AU Monitor 17" ZPD code Derivation
ACER T315XW01 BN07-00194A AMZ New AU 32"
ACER M170EG01 BN07-00192A ATH AU TN PSWG type New Panel code
ACER M170EG01 BN07-00192B ATZ AU TN PSWG type New Panel ZPD Derivation code
ACER M190EN04 BN07-00203A ATH AU Monitor 19" ZPD New code Derivation
ACER T260XW02 BN07-00208A AMZ AUO 26"
ACER M170EG01 V8 BN07-00221A ATZ AU TN PSWG type New Panel (8msec) ZPD Derivation code
ACER T260XW02 BN07-00233A AMZ AUO 26" New Panel (Cosmetic spec down grade)
ACER T315XW01 BN07-00234A AMZ AUO 32" New Grade (Cosmetic spec down grade)]
ACER M190EN03 BN07-00224A AMZ AU Monitor 19" MVA New code Derivation
ACER T315XW01 BN07-00237A AMZ New LCD TV VE project : delete DBEF sheet * Panel, model division ve
ACER T315XW01 BN07-00238A AMZ
New LCD TV VE project : delete DBEF sheet + 'A-' grade * Panel
ACER M201UN02 V3 BN07-00168A AMZ ACER M201UN02 V3 BN07-00168B AMH ACER M190EN04 V7 BN07-00248A ATZ AU Monitor 19" TN Glare ZPD New code Derivation
ACER A070VW01 BN07-00235A ATZ New Panel code Derivation for Digital Album
ACER T315XW01 BN07-00253A AMZ
LCD TV VE item model * Panel, Model division add version: T315XW01
ACER T260XW02 BN07-00254A AMZ AUO 26" VE item apply model
ACER M170EU01 BN07-00260A ATZ AUO 17" Slim TN ZPD Type New code Derivation
ACER T370XW01 BN07-00255A AMZ for ROME 37" model development
Maker VENDOR P/N PANEL_CODE PANEL_ABB STICKER_CODE Remarks
Page 15

14 Reference Infomation
14-15
ACER T315XW02(V3), BN07-00324A AMZ ACER A201SN02 V5 BN07-00314A ATZ
CHIMEI M170E3-LO1 BN07-00050A CA TN PANEL
CHIMEI M150X3-L01 BN07-00051A CB COMPATIBLE
CHIMEI M170E4-L01 BN07-00052A CC MVA PANEL
CHIMEI M150X2-L01 BN07-00066A CD CHIME 15"I PVA PANEL
CHIMEI M150X3-L01 BN07-00079A CE Chimei ZPD panel
CHIMEI M170E3-L01 BN07-00103A CF ZPD Panel code
CHIMEI M170E4-L01 BN07-00104A CG ZPD Panel code
CHIMEI V296W1-L01 BN07-00120A CH MVA
CHIMEI M170E6-L02 BN07-00126A CJ HIGHLAND 17" LOW PANEL
CHIMEI M190E2-L01 BN07-00131A CK GH19AS,BS CHIMEI PANEL
CHIMEI M150X4-L06 BN07-00137A CL 15" Narrow & Slim panel
CHIMEI M170E6-L01 BN07-00133A CM 2003-03-11 vendor change
CHIMEI M170E6-L01 BN07-00133B CN ZPD derivation panel
CHIMEI V201V1-T01 BN07-00135A CP CHIMEI 20.1" panel development
CHIMEI M170E6-L02 BN07-00126B CQ HIGHLAND 17" LOW PANEL ZPD derivation panel
CHIMEI M170E6-L05 BN07-00152A CR CMO 17" new panel development code
CHIMEI M170E6-L05 BN07-00152B CS CMO 17" ZPD panel code derivation
CHIMEI M150X4-L06 BN07-00137B CT Chimei 15" Narrow & Slim panel ZPD derivation
CHIMEI M170E5-L05 BN07-00165A CTH CMO 17" new panel development code (GOYA2-PJT)
CHIMEI M170E5-L05 BN07-00165B CTZ CMO 17" ZPD panel(GOYA2-PJT)
CHIMEI V230W1-L02 BN07-00209A CMZ CMO 23" new development
CHIMEI V320B1-L01 BN07-00207A CMZ CMO 32" new development
CHIMEI V270W1-L01 BN07-00136A CMZ CHI MEI 27" panel development
CHIMEI M190E5-L0A BN07-00213A CTZ CHIMEI M190E3-L0A BN07-00212A CMZ CMO M190E3-L0A MVA Type New code derivation
CHIMEI M170E7-L01 BN07-00232A CTZ CMO 17" Slim TN ZPD Type New code derivation
CHIMEI M190A1-L01 BN07-00228A CTZ CMO 19" Wide TN ZPD Type New code derivation
CHIMEI V201V1-T03 BN07-00275A CTZ CMO 20.1" (V201V1-T01) VE model
CHIMEI M201P1-L01 BN07-00268A CTZ CMO 20.1" TN ZPD derivation
CHIMEI M220Z1-L01 BN07-00321A CTZ
CHIMEI M190E5-L0G BN07-00337A CTZ
NEC SVA150XG04TB BN07-00225A BTZ SVA NEC 15" panel ZPD code
NEC SVA170SX01TB BN07-00272A BTZ SVA NEC 17" panel ZPD code Brown
Maker VENDOR P/N PANEL_CODE PANEL_ABB STICKER_CODE Remarks
Page 16

Memo
14 Reference Infomation
14-16
Page 17

14 Reference Infomation
14-17
Page 18

14 Reference Infomation
14-18
 Loading...
Loading...