Samsung DVD-P355 Block Diagram
Samsung Electronics 13-1
13. Circuit Operating Descriptions
13-1 Power
13-1-1 Comparsion between Linear Power Supply and S.M.P.S.
13-1-1 (a) Linear
Vreg
Vin
+
–
+
+
–
Vs
(Ns)
Vp
(Np)
REGULATOR
Common power
(Ex.120V 60Hz)
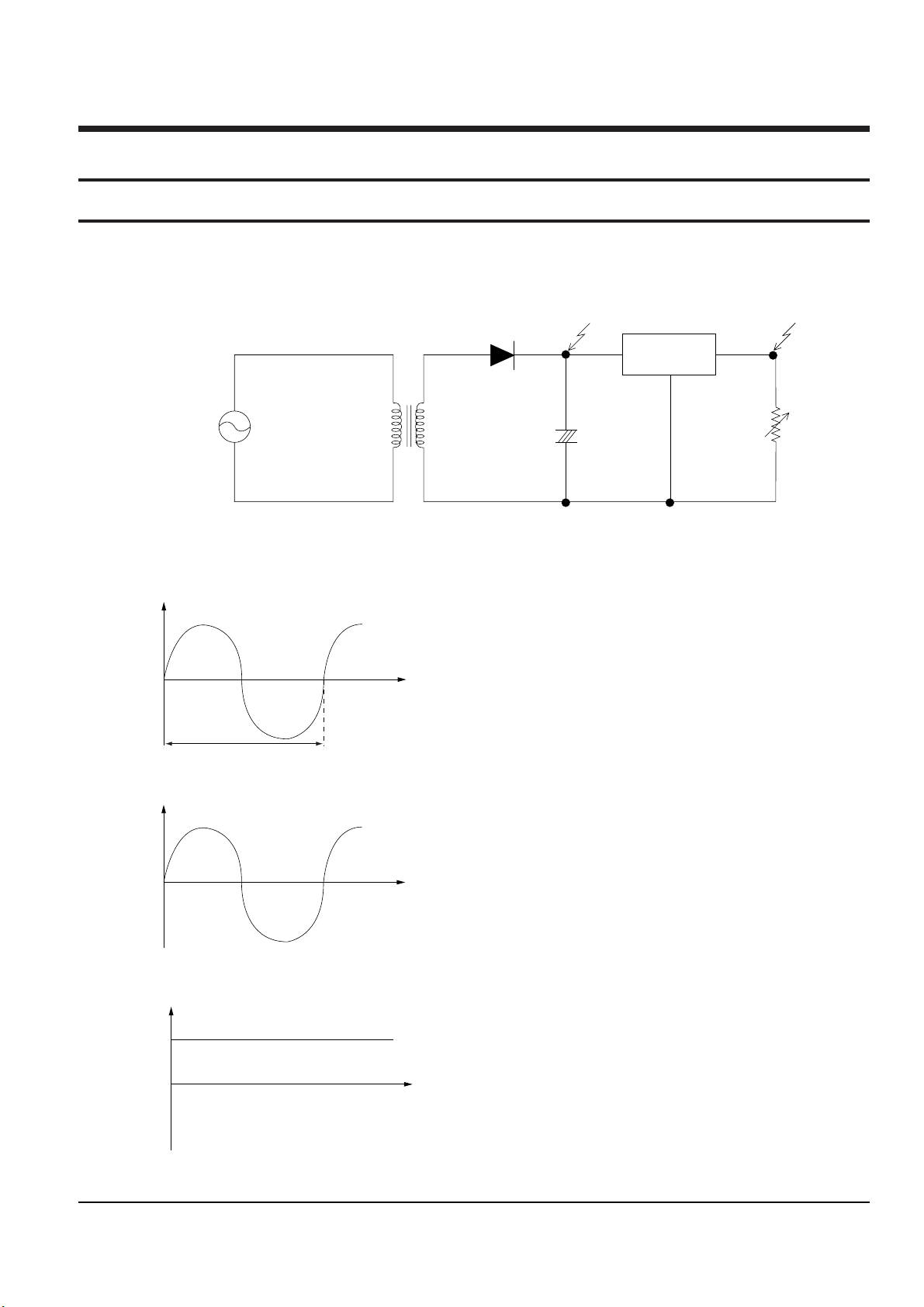
Fig.13-1 Linear Power Supply
◆ Waveform/Description
Vp
t
0
Fig. 13-2
Vs
t
0
Fig. 13-3
Vout
t
0
Fig. 13-4
Input : Common power to transformer (Vp).
The output Vs of transformer is determined by the ratio
of 1st Np and 2nd Ns.
Vs = (Ns/Np) x Vp
Vout is output (DC) by diode and condensor.
Circuit Operating Descriptions
13-2 Samsung Electronics
◆ Advantages and disadvantages of linear power supply
1) Advantages : Little noise because the output waveform
of transformer is sine wave.
2) Disadvantages :
ΠAdditional margin is required because Vs is chan-
ged (depending on power source). (The regulator
loss is caused by margin design).
´ Greater core size and condensor capacity are ne-
eded, because the transformer works on a single
power frequency.
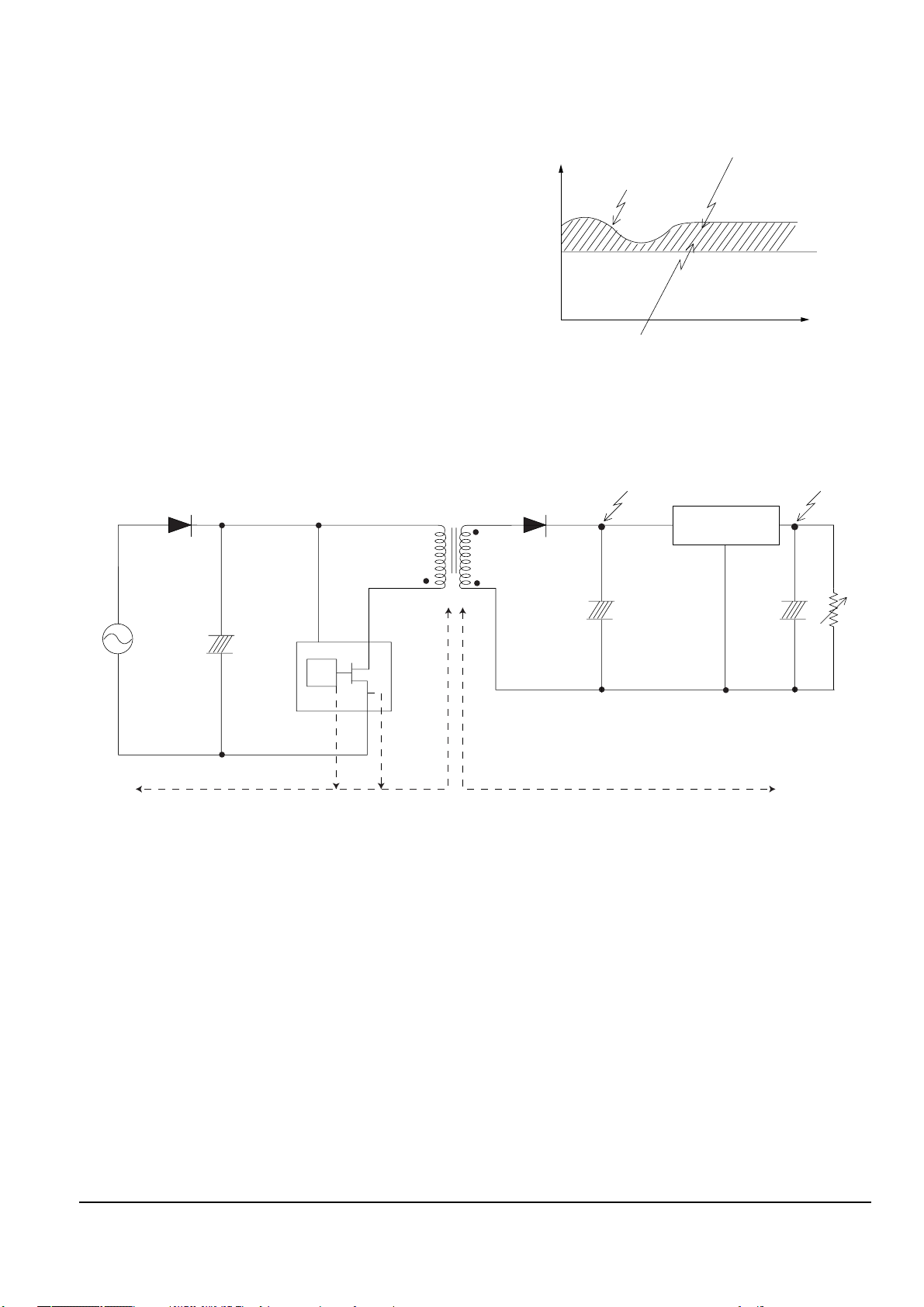
13-1-1 (b) S.M.P.S. (Pulse Width Modulation)
v
Vreg
Vout
0
t
Change by common power
Regulator loss
Fig. 13-5
◆ Terms
1) 1st : Common power input to 1st winding.
2) 2nd : Circuit followings output winding of transformer.
3) f (Frequency) : Switching frequency (T : Switching cycle)
4) Duty : (Ton/T) x 100
Transformer
Vin
(Np)
(Vp)
PICF1
CTL IC
Vin
PWM CTL + MOS Fet
+
—
+
—
—
+
+
(Vs)
(Ns)
REGULATOR
Vout
+
Fig. 13-6
Circuit Operating Descriptions
Samsung Electronics 13-3
13-1-2 Circuit description [FLY-Back PWM(Pulse Width Modulation)] Control
13-1-2 (a) AC Power Rectification/Smoothing Terminal
1) PDS01, PDS02, PDS03, PDS04 : Convert AC power to DC(Full wave rectification).
2) PER10 : Smooth the voltage converted to DC.
3) PCD01, PCD02, PBS01 : Noise removal at power input/output.
4) PVA1 : SMPS protection at power surge input.
13-1-2 (b) SNUBBER Circuit : PDS11, PCD12, PRS13, PCD11, PPS12
0
Vswitch
dt
Toff
t
Inverted power
by leakage
inductance
Fig. 13-7
1) Prevent residual high voltage at the terminals of
switch during switch off/Suppress noise.
High inverted power occurs at switch (PQR11) off,
because of the 1st winding of transformer :
(V=-L1 xdi/dt. L1 : Leakage Induction)
A very high residual voltage exist on both terminals
of PIC1 4, 5~8pin because dt is a very short.
2) SNUBBER circuit protects PQR11 from damage
through leakage voltage suppression by RC,
(Charges the leakage voltage to PDS11, PER13,
PCD12 and discharges to PRS11, PRS12).
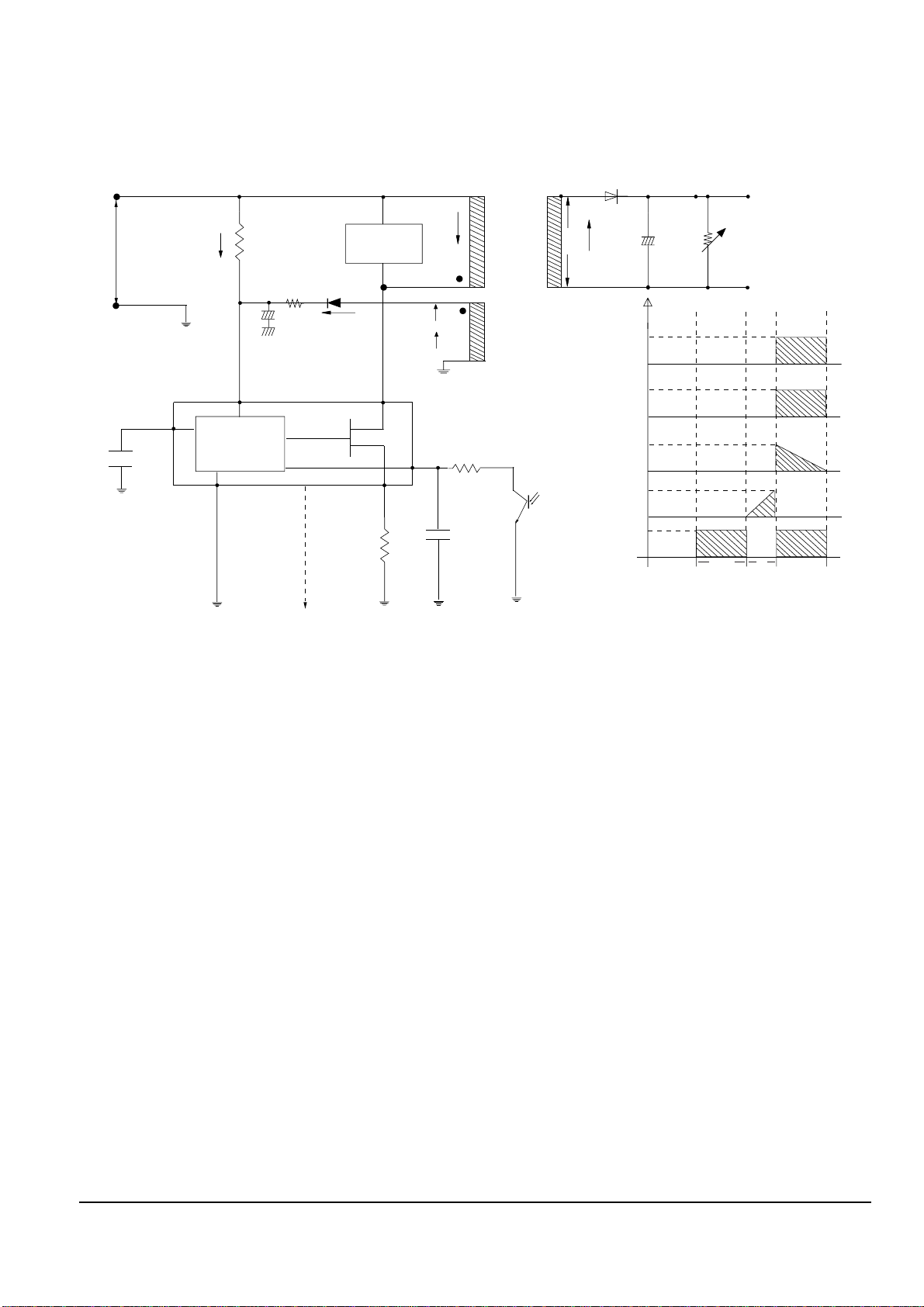
13-1-2 (c) Driving circuit
When Vin supplied, driving current Ig occurs throuhg the PICF1. By this I1(=Hfe x Ig) occurs throug the PIC1
and the Vb is inducted to base winding coil NB. By inducted Vb, Ib start flow and the VCCvoltage of PQR11 is
sustained stable. Ib is constant and I1increases in Proportion to time. After constant time passed Ib become to
shortage and PIC1 is cut OFF (S/W OFF).
Circuit Operating Descriptions
13-4 Samsung Electronics
GND
PICF1
Icease
R
C
R
FB
C
Softs
POWER-CTL
Mos-Fet
Drain
VCC
Ib
R
D
C
Ig
R
Vin
Snubber
NP
Ig
VB
VB
PTDI
Ns
Vs
I2
PDS34
PES34
+
Vout
GND
Ib
Vb
I2
I1
VD-G
0
<<
< <
Off
ON
+
Fig. 13-8 Driving Circuit
Circuit Operating Descriptions
Samsung Electronics 13-5
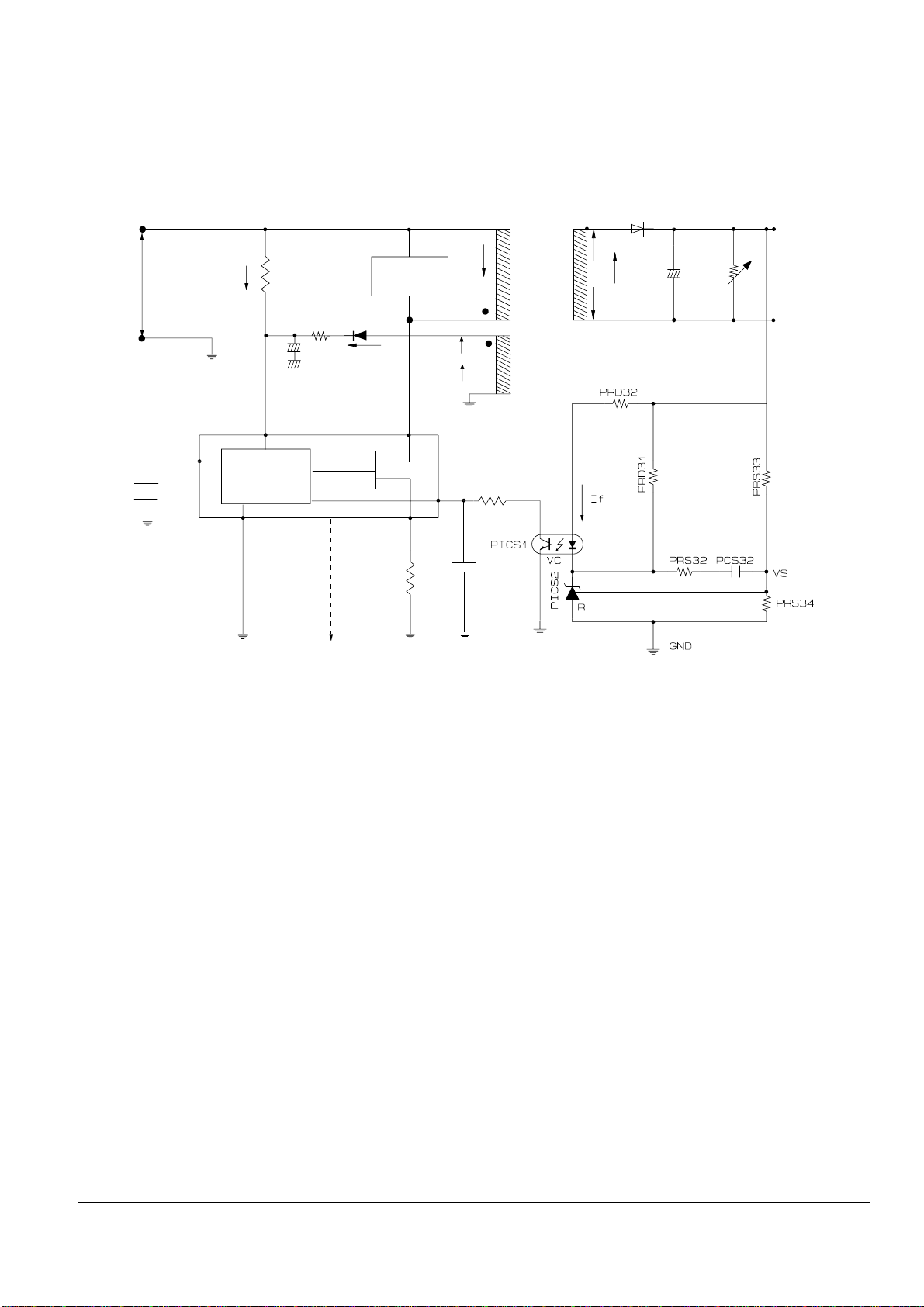
◆ Operation descriptions
1) Internal OP-Amp ‘+’ base potential of PICS2 is 2.5V and external “-” input potential is connected with PRS33
and PRS34 to maintain Vout of 4.4V.
2) If load of 4.4V terminal increase (or AC inout voltage decrease) and Vout decrease over 4.4V,
Then : PICS2 “R” potential decrease over 2.5V --> PICS2 A-K BASE Current decrease --> PICS2 A-K Current
decrease --> PICS1 DIODE Current decrease --> PICS1 C-E Current decrease --> PICS1 C-E Voltage increase -->
PICS1 F-B Voltage increase --> OUT DUTY increase TRANS Primary Cuttent Increase --> TRANS Primary
Power increase --> Vout increase --> Vout maintain 4.4V
- PRD31, PRD32 : Reduce 4.4V overshoot.
- PRS32, PCS32 : Prevent PICS2 oscillation (for phase correction).
13-1-2 (d) Feedback Control Circuit
GND
PICF1
Icease
R
C
R
FB
C
Softs
POWER-CTL
Mos-Fet
Drain
VCC
Ib
R
D
C
Ig
R
Vin
Snubber
NP
Ig
VB
VB
PTDI
Ns
Vs
I2
PDS34
PES34
+
Vout
GND
+
A
K
Fig.13-9
