SAMSUNG CGP1607TXX Service Manual

COLOR MONITOR
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
Manual
SERVICE
COLOR MONITOR CONTENTS
1. Precautions
2. Reference Information
3. Product Specifications
4. Operating Instructions
5. Disassembly & Reassembly
6. Alignment & Adjustments
7. Troubleshooting
8. Exploded View & Parts List
9. Electrical Parts List
10. Block Diagram
11. PCB Diagrams
12. Wiring Diagram
13. Schematic Diagrams

Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. June 1998
Printed in Korea
Code No.: BH68-61087A

WARNINGS
1. For continued safety, do not attempt to modify the
circuit board.
2. Disconnect the AC power before servicing.
3. When the chassis is operating, semiconductor
heatsinks are potential shock hazards.
1-1-1 Servicing the High Voltage VR
and CRT :
WARNING: A high voltage VR replaced in the wrong
direction may cause excessive X-ray
emissions.
Caution:
When replacing the high voltage
adjustment VR, it must be fixed by a
soldering iron after it is properly set.
1. When servicing the high voltage system, remove
the static charge by connecting a 10 kohm resistor
in series with an insulated wire (such as a test
probe) between the chassis and the anode lead.
2. If the HV VR requires adjustment, (a) Replace the
VR and adjust the high voltage to the specification.
(b) Use a soldering iron to melt the adjustment cap
on the HV VR to prevent any movement.
3. When troubleshooting a monitor with excessively
HV, avoid being unnecessarily close to the monitor.
Do not operate the monitor for longer than is
necessary to locate the cause of excessive voltage.
4. High voltage should always be kept at the rated
value, no higher. Only when high voltage is
excessive are X-rays capable of penetrating the shell
of the CRT, including the lead in glass material.
Operation at high voltages may also cause failure of
the CRT or high voltage circuitry.
5. When the HV regulator is operating properly, there
is no possibility of an X-ray problem. Make sure the
HV does not exceed its specified value and that it is
regulating correctly.
6. The CRT is especially designed to prohibit
X-ray emissions. To ensure continued X-ray
protection, replace the CRT only with one that is
the same or equivalent type as the original.
7. Handle the CRT only when wearing shatterproof
goggles and after completely discharging the high
voltage anode.
8. Do not lift the CRT by the neck.
1-1-2 Fire and Shock Hazard :
Before returning the monitor to the user, perform the
following safety checks:
1. Inspect each lead dress to make certain that the
leads are not pinched or that hardware is not
lodged between the chassis and other metal parts in
the monitor.
2. Inspect all protective devices such as nonmetallic
control knobs, insulating materials, cabinet backs,
adjustment and compartment covers or shields,
isolation resistor-capacitor networks, mechanical
insulators, etc.
3. Leakage Current Hot Check (Figure 1-1):
WARNING: Do not use an isolation transformer during
this test.
Use a leakage current tester or a metering system
that complies with American National Standards
Institute (
ANSI C101.1, Leakage Current for
Appliances), and Underwriters Laboratories (UL
Publication UL1410, 59.7).
4. With the unit completely reassembled, plug the AC
line cord directly into a 120V AC outlet. With the
unit’s AC switch first in the ON position and then
OFF, measure the current between a known earth
ground (metal water pipe, conduit, etc.) and all
exposed metal parts, including: metal cabinets,
screwheads and control shafts. The current
measured should not exceed 0.5 milliamp. Reverse
the power-plug prongs in the AC outlet and repeat
the test.
Figure 1-1. Leakage Current Test Circuit
1-1-4 Product Safety Notices
Some electrical and mechanical parts have special
safety-related characteristics which are often not
evident from visual inspection. The protection they give
may not be obtained by replacing them with
components rated for higher voltage, wattage, etc. Parts
that have special safety characteristics are identified by
on schematics and parts lists. A substitute
replacement that does not have the same safety
characteristics as the recommended replacement part
might create shock, fire and / or other hazards. Product
safety is under review continuously and new
instructions are issued whenever appropriate.
Components identified by on schematics and parts
lists must be sealed by a soldering iron after
replacement and adjustment.
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 1-1
1 Precautions
1-1 Safety Precautions
!
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
TEST ALL
EXPOSED METAL
SURFACES
(READING SHOULD
NOT BE ABOVE 0.5mA)
LEAKAGE
CURRENT
TESTER
2-WIRE CORD
ALSO TEST WITH
PLUG REVERSED
(USING AC ADAPTER
PLUG AS REQUIRED)
EARTH
GROUND

1. Servicing precautions are printed on the cabinet,
and should be followed closely.
2. Always unplug the unit’s AC power cord from the
AC power source before attempting to: (a) remove
or reinstall any component or assembly, (b)
disconnect PCB plugs or connectors, (c) connect all
test components in parallel with an electrolytic
capacitor.
3. Some components are raised above the printed
circuit board for safety. An insulation tube or tape
is sometimes used. The internal wiring is
sometimes clamped to prevent contact with
thermally hot components. Reinstall all such
elements to their original position.
4. After servicing, always check that the screws,
components and wiring have been correctly
reinstalled. Make sure that the area around the
serviced part has not been damaged.
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor
components or assemblies, drain the electrostatic
charge from your body by touching a known earth
ground. Alternatively, wear a discharging wriststrap device. To avoid a shock hazard, be sure to
remove the wrist strap before applying power to
the monitor.
2. After removing an ESD-equipped assembly, place it
on a conductive surface such as aluminum foil to
prevent accumulation of an electrostatic charge.
3. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can
generate electrical charges sufficient to damage
ESDs.
4. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or
desolder ESDs.
5. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some
solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static”
can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage
ESDs.
5. Check the insulation between the blades of the AC
plug and accessible conductive parts (examples:
metal panels, input terminals and earphone jacks).
6. Insulation Checking Procedure: Disconnect the
power cord from the AC source and turn the power
switch ON. Connect an insulation resistance meter
(500 V) to the blades of the AC plug.
The insulation resistance between each blade of the
AC plug and accessible conductive parts (see
above) should be greater than 1 megohm.
7. Never defeat any of the +B voltage interlocks. Do
not apply AC power to the unit (or any of its
assemblies) unless all solid-state heat sinks are
correctly installed.
8. Always connect a test instrument’s ground lead to
the instrument chassis ground before connecting the
positive lead; always remove the instrument’s
ground lead last.
6. Do not remove a replacement ESD from its
protective package until you are ready to install it.
Most replacement ESDs are packaged with leads
that are electrically shorted together by conductive
foam, aluminum foil or other conductive materials.
7. Immediately before removing the protective
material from the leads of a replacement ESD,
touch the protective material to the chassis or
circuit assembly into which the device will be
installed.
Caution: Be sure no power is applied to the
chassis or circuit and observe all
other safety precautions.
8. Minimize body motions when handling
unpackaged replacement ESDs. Motions such as
brushing clothes together, or lifting your foot from
a carpeted floor can generate enough static
electricity to damage an ESD.
9. Indicates ESDs on the Schematic Diagram in
this manual.
1 Precautions
1-2 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
1-3 Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESD) Precautions
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be easily damaged by static electricity. Such components are commonly
called Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESD). Examples of typical ESD devices are integrated circuits and some fieldeffect transistors. The following techniques will reduce the incidence of component damage caused by static electricity.
1-2 Servicing Precautions
WARNING1: First read the “Safety Precautions” section of this manual. If unforeseen circumstances
create conflict between the servicing precautions and safety precautions, always
follow the safety precautions.
WARNING2: A high voltage VR replaced in the wrong direction may cause excessive X-ray
emissions.
WARNING3: An electrolytic capacitor installed with the wrong polarity might explode.
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 2-1
2 Reference Information
2-1 List of Abbreviations, Symbols and Acronyms
2-1-1 Abbreviations
Abbreviation Definition Abbreviation Definition
ASS’Y Assembly
B Blue
B+ ADJ B+ Adjustment
B-CUT Blue-Cutoff
B-GAIN Blue Gain
BRIGHT Brightness
C R-Composition
C-MIC Condenser Microphone
CLK Clock
CM R-Cement
CN Connector
CONT Contrast
D-SUB D-Subminiature
EEP-CLK Electrically Erasable and
Programmable Clock
EXT External
EXT-MIC External Microphone
Freq. Frequency
FU Fusible
G Green
G-CUT Green-Cutoff
G-GAIN Green Gain
GND Ground
H Horizontal
H Heater
H-DRV Horizontal Drive
H-DY Horizontal Deflection Yoke
H-FLB Horizontal Flyback
H-FV Horizontal-Feedback Voltage
H-LIN Horizontal Linearity
H-POSI Horizontal Position
H-SIZE Horizontal Size
H/PHONE Headphone
Hz Hertz
I-SENSE Current-Sense
lb Pound
MAX Maximum
MIC Microphone
MIN Minimum
MP C-Metalized Polyester
MPP Metal Polypropylene
MO R-Metal Oxide
OSC Oscillator
P C-Polyester
PARA Parabola
PARALL Parallelogram
PIN-BAL Pincushion Balance
PRE-AMP Pre-Amplifier
PS1 Power Saving1 (suspend)
PS2 Power Saving2 (off)
PWR Power
R Red
R-CUT Red-Cutoff
R-GAIN Red Gain
RST Reset
S-PIN Side Pincushion
S-RASTER Self Raster
S/W Switch
SCAP S Correction Capacitor
SPK Speaker
SYNC Synchronization
T C-Tantalum
TR Transistor
TRAP Trapezoid
U-COM Microprocessor
V Vertical
V-DY Vertical Deflection Yoke
V-FLB Vertical Flyback
V-LIN Vertical Linearity
V-MUTE Video Mute
V-OUT Vertical Output
V-PARA Vertical Parabola
V-POL V-Polarity
V-POSI Vertical Position
V-SENSE Voltage-Sense
V-SIZE Vertical Size
WW R-Wire Wound
X-TAL Crystal
Ω ohm
KΩ 1000 ohm
MΩ 1000 KΩ
uF microfarad (10-6F)
nF nanofarad (10-9F)
pF picofarad (10
-12
F)
2 Reference Information
2-2 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
Acronym Definition Acronym Definition
ABL Automatic Brightness Limits
AC Alternating Current
ACL Automatic Contrast Limit
AFC Automatic Frequency Control
ANSI American National Standards Institute
CMOS Complementary Metal Oxide
Semiconductor
CRT Cathode Ray Tube
DC Direct Current
DDC Data Display Channel
DF Dynamic Focus
DMM Digital Multimeter
DPMS Display Power Management Signaling
DVM Digital Voltmeter
DY Deflection Yoke
EEPROM Electrically Erasable and
Programmable Read only Memory
ESD Electrostatically Sensitive Device
ESF Electronic Static Field
FBT Flyback Transformer
FET Field Effect Transistor
FH Horizontal Frequency
FS Fail Safe
FV Vertical Frequency
GD Geometric Distortion
H/V Horizontal/Vertical
HV High Voltage
I/O Input/Output
IC Integrated Circuit
LED Light Emitting Diode
MAC Macintosh
MOFA Mask Outside Frame Assembly
OCP Over Current Protection
OP AMP Operational Amplifier
OSD On Screen Display
P-P Peak to Peak
PCB Printed Circuit Board
PLL Phase Locked Loop
PWM Pulse Width Modulation
SMPS Switch Mode Power Supply
SVGA Super Video Graphics Array
SWEDAC
TP Test Point
UL Underwriters Laboratories
USB Universal Serial Bus
VESA Video Electronics Standard
Association
VGA Video Graphics Array
VR Variable Registor
W/B White Balance
2-1-2 Acronyms
2-1-2 Symbols
Can emit X-radiation
Hot Ground
Cold Ground
Electrostatically Sensitive Device (ESD)
Provides special safety considerations
!

SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 3-1
3 Product Specifications
3-1 Specifications
Picture Tube: 21-Inch (53 cm): 19.7-inch (50 cm) viewable, Full-square flat-face tube, 90˚ Deflection,
0.28 mm Dot pitch, Dark-tint, Non-glare, Anti-reflection and Anti-static charge coating
Scanning Frequency Horizontal : 30 kHz to 96 kHz (Automatic)
Vertical : 50 Hz to 160 Hz (Automatic)
Display Colors Unlimited colors
Maximum Resolution Horizontal : 1600 Dots
Vertical : 1200 Lines
Input Video Signal Analog, 0.714 Vp-p positive at 75 Ω, internally terminated
Input Sync Signal Separate Sync : TTL level positive/negative
Sync-on-green : Composite Sync 0.286 Vp-p ± 5%/ negative (video on Vp-p positive)
Composite Sync : TTL level positive/negative
Maximum Pixel Clock rate 205 MHz
Active Display Horizontal : 390 mm ± 3 mm (4:3 ratio)/366 mm ± 3 mm (5:4 ratio)
Vertical : 292.5 mm ± 3 mm
Input Voltage AC 90-132 / 198-264 Volts, 60/ 50 Hz ± 3 Hz
Power Consumption 150 Watt (max)
Dimensions
Unit (W x D x H) 19.3 x 19.9 x 20.1 Inches (490 x 505 x 510 mm)
Carton (W x D x H) 24.1 x 25.0 x 25.3 Inches (612 x 633 x 642 mm)
Weight Net/Gross : 70.6 lbs (32 kg) / 79.4 lbs (36 kg)
Environmental Considerations Operating Temperature : 32°F to 104°F (0°C to 40°C)
Humidity : 10 % to 80 %
Storage Temperature : -4°F to 113°F (-20°C to 45°C)
Humidity : 5 % to 95 %
• The SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) complies with SWEDAC (MPR II) recommendations for reduced electromagnetic fields.
• Designs and specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
Item Description

3 Product Specifications
3-2 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
3-2 Pin Assignments
5
15
Figure 3-1. Male Type Figure 3-2. Male Type
Sync
Type
Pin No.
15-Pin Signal Cable Connector (Figure 3-1)
Cable Adapter (Figure 3-2)
Macintosh
Separate Composite Sync-On Green
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Red
Green
Blue
GND
DDC Return
GND-R
GND-G
GND-B
Reserved
GND-Sync/Self-raster
GND
DDC Data
H-Sync
V-Sync
DDC Clock
Red
Green
Blue
GND
DDC Return
GND-R
GND-G
GND-B
Reserved
GND-Sync/Self-raster
GND
DDC Data
H/V-Sync
Not Used
DDC Clock
Red
Green + H/V Sync
Blue
GND
DDC Return
GND-R
GND-G
GND-B
Reserved
GND-Sync/Self-raster
GND
DDC Data
Not Used
Not Used
DDC Clock
GND-R
Red
H/V Sync
Sense 0
Green
GND-G
Sense 1
Reserved
Blue
Sense 2
GND
V-Sync
GND-B
GND
H-Sync
BNC Connectors
BNC connectors are used with coaxial cable for
improved signal transmission. Better signal
transmission becomes critical at high frequencies,
such as those required for 1280 x 1024 resolution.
Most video boards that operate at 1280 x 1024
resolution recommend using coaxial cable with
BNC connectors. The 5 BNC connectors on the
rear of the monitor can accept Red, Green and
Blue video. Composite sync can be applied
separately, or combined with the Green video
signal (commonly referred to as “composite
sync-on green”). If composite sync-on green is
used, then only 3 of the 5 BNC connectors are
used. The connectors are labeled accordingly.
Pin
Assignment
Signals
Sync-on-Green Composite Sync Separate Sync
Red
Green + Sync
Blue
NC
NC
1
2
3
4
5
Red
Green
Blue
H/V Comp. Sync
NC
Red
Green
Blue
H-Sync
V-Sync
Figure 3-3. BNC Signal Input Type
1
R G B
2 3
4
H/V V
5

3 Product Specifications
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 3-3
QRS
P
O
Video
Sync
Sync
Horizontal
Vertical
CDE
P
O
B
A
Video
Sync
Sync
Separate Sync
Table 3-1. Timing Chart
3-3 Timing Chart
This section of the service manual describes the timing that the computer industry recognizes as standard
for computer-generated video signals.
C D
A
O
E
B
P
Video
Sync
Sync
Video
Q R S
A : Line time total B : Horizontal sync width O : Frame time total P : Vertical sync width
C : Back porch D : Active time Q : Back porch R : Active time
E : Front porch S : Front porch
VIDEO
A
B
O
P
Q
R
S
Horizontal
Vertical
H/V Composite Sync
B
Green
Vertical
P
Q
R
S
O
Horizontal
Sync-on-Green
800/85 Hz
800 x 600
1600/75 Hz
1600 x 1200
640/85 Hz
640 x 480
VGA3/60Hz
640 x 480
VGA2/70Hz
720 x 400
fH (kHz)
A µsec
B µsec
C µsec
D µsec
E µsec
fV (Hz)
O msec
P msec
Q msec
R msec
S msec
Clock
Freq.
(MHz)
Polarity
H.Sync
V.Sync
Remark
31.469
31.777
3.813
1.589
25.422
0.318
70.087
14.268
0.064
0.858
12.711
0.191
28.322
Negative
Positive
Separate
31.469
31.778
3.813
1.589
25.422
0.318
59.940
16.683
0.064
0.794
15.253
0.064
25.175
Negative
Negative
Separate
43.269
23.111
1.556
2.222
17.778
1.556
85.008
11.764
0.069
0.578
11.093
0.023
36.000
Negative
Negative
Separate
53.674
18.631
1.138
2.702
14.222
0.569
85.061
11.756
0.056
0.503
11.179
0.019
56.250
Positive
Positive
Separate
93.750
10.667
0.948
1.501
7.901
0.316
75.000
13.333
0.032
0.491
12.800
0.011
202.500
Positive
Positive
Separate
Mode
IBM VESA MAC.
Timing
68.677
14.561
1.016
2.201
10.836
0.508
84.997
11.765
0.044
0.524
11.183
0.015
94.500
Positive
Positive
Separate
81.400
12.285
0.988
1.624
9.037
0.635
100.000
10.000
0.037
0.516
9.435
0.012
113.309
Negative
Positive
Separate
68.681
14.560
1.280
1.440
11.520
0.320
75.062
13.322
0.044
0.568
12.667
0.044
100.000
Negative
Negative
SOG
91.146
10.971
1.016
1.422
8.127
0.406
85.024
11.761
0.033
0.483
11.235
0.011
157.50
Positive
Positive
Separate
79.976
12.504
1.067
1.837
9.481
0.119
75.025
13.329
0.038
0.475
12.804
0.013
135.000
Positive
Positive
Separate
1024/85 Hz
1024 x 768
1024/100 Hz
1024 x 768
1152/75 Hz
1152 x 870
1280/75 Hz
1280 x 1024
1280/85 Hz
1280 x 1024

Memo
3 Product Specifications
3-4 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)

4-1 Controls and Connectors
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 4-1
4 Opearating Instructions
1
3
5
6
7
8
4
2
Figure 4-1. Front View and Controls
1 Power Button
Power Indicator LED (Dual Color)
Up Button
Left Button
Right Button
Down Button
Menu (
↵) Button
Exit Button
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
Location Symbol Description
Table 3-1. Front Panel Controls

This monitor has a built-in power management
system called PowerSaver. This system saves
energy by switching your monitor into a lowpower mode when it has not been used for a
certain amount of time. The available modes are
“On,” “Standby,” “Suspend,” and “Off.”
This system operates with a VESA DPMS
compliant video card installed in your computer.
You use a software utility installed on your
computer to set up this feature. See the table
below for details.
Note 1:This monitor automatically returns to
normal operation when horizontal and
vertical sync return. This occurs when you
move the computer's mouse or press a key
on the keyboard.
Note 2:This monitor is EPA Energy Star
compliant and NUTEK compliant when
used with a computer equipped with
VESA DPMS functionality. If your
computer system cannot support a display
power management function, you can
purchase an optional DPMS software
program to enable the power saving
function. Please contact Samsung or your
dealer for more information.
Note 3:For energy conservation, turn your
monitor OFF when it is not needed, or
when leaving it unattended for long
periods.
4 Operating Instructions
4-2 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
4-2 Power Management System
State
Items
Normal
Operation
Horizontal Sync
Vertical Sync
Video
Power
Indicator
Power
Consumption
Active
Active
Active
Green Orange
Orange/Green
Blinking
Orange
Blinking
150 W (max.)
130 W (nominal)
Less than
15 W
130 W (max)
110 W
(nominal)
Less than
5 W
Inactive
Active
Blanked
Active
Inactive
Blanked
Power Saving Function EPA/NUTEK
Standby Mode
Suspend Mode/
Position A1
Power-off Mode/
Position A2
Inactive
Inactive
Blanked
Table 4-2. Display Power Management Signaling (DPMS)

5-1-1 Disassembling the Cabinet
1. To uncover the 2 uppermost screws, press in
the end of each Screw Cap and pull it away
from the cabinet.
2. Remove the 4 screws on the Rear Cover and
pull it backward to remove it.
3. Remove the 6 screws on the Top Shield Cover
and remove it.
4. Remove the 6 screws and Chassis ground wire
on the side of both the Left and Right Shield
and remove the Shields.
5. Remove both side screws on the lower edge of
the Stand Assembly and pull the assembly
towards you to remove it.
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 5-1
5 Disassembly and Reassembly
This section of the service manual describes the disassembly and reassembly procedures for the
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) monitor.
WARNING: This monitor contains electrostatically sensitive devices. Use caution when handling
these components.
5-1 Disassembly
Cautions:1. Disconnect the monitor from the power source before disassembly.
2. Follow these directions carefully; never use metal instruments to pry apart the cabinet.
Figure 5-1
Figure 5-3
Figure 5-2
Figure 5-4

5-1-2 Removing the Entire PCB Assembly
1. Complete all previous steps.
2. Using pinch-nosed pliers or long-nosed pliers,
carefully disconnect the Anode Cap from the
CRT.
3. Disconnect connector GTP901 on the CRT
Socket PCB.
4. Disconnect the CRT Socket PCB Assembly.
5. Disconnect connectors CN401_1~CN401_4,
C301_1~CN301_3, CN403, CN404 and CN405
on the Main PCB and CN605, CN606 on the
Power PCB.
6. Remove the 3 screws on the Main PCB Chassis
Bracket.
7. Lift off the entire PCB Assembly and place it
on a flat, level surface that is protected from
Static electricity.
5-1-3 Removing the CRT Socket PCB
1. Complete all previous steps.
2. Disconnect connectors CN104B, CN104RG and
G2 (GTP902) on the CRT Socket PCB.
3. Hold the CRT Socket PCB Assembly while
you lift the Cap on the CRT Socket and
desolder the two focus wires.
5-1-4 Removing the Video PCB
1. Complete all previous steps.
2. Disconnect connector CN801 on the Video
PCB.
3. Remove both side screws on the Video PCB
Assembly Rear Shield.
4. Lift off the Video PCB Assembly.
5. Remove all screws on the Video PCB
Assembly and remove the Video Shield.
6. Remove the 3 screws on the Video PCB.
7. Lift out the Video PCB and place it on a flat,
level surface that is protected from static
electricity.
5 Disassembly and Reassembly
5-2 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
Figure 5-5
Figure 5-6
Figure 5-7
Figure 5-8

5-1-5 Removing the Power PCB
1. Complete all previous steps.
2. Disconnect CN603 on the Power PCB.
3. Remove the screw on the lower side of the
SMPS Bracket.
4. Lift off the Power PCB Assembly.
5. Remove the Shield Cover and disconnect
CN601 on the Power PCB.
6. Remove the 4 screws on the Power PCB.
7. Lift out the Power PCB and place it on a flat,
level surface that is protected from static
electricity.
5-1-6 Removing the Main PCB
1. Complete all previous steps.
2. Remove the 7 screws on the Main PCB.
3. Carefully lift out the Main PCB and place it on
a flat, level surface that is protected from static
electricity.
5-1-7 Disassembling the CRT Assembly
1. Complete all previous steps.
2. Remove the 1 screw on the CRT frame.
3. Remove the 2 screws on the Bottom frame.
4. Remove the other 10 screws and lift off the
CRT frame.
5. Straighten the Degaussing Coil Assembly
coated metal ties and lift the Coil from the
CRT.
6. Lift the CRT up and away from the Front
Cover Assembly and place it on a padded
surface.
Do not lift the CRT by the neck.
5 Disassembly and Reassembly
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 5-3
Figure 5-10
Figure 5-11
Figure 5-9
Figure 5-12
!

5 Disassembly and Reassembly
5-4 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
5-2 Reassembly
Reassembly procedures are in the reverse order of Disassembly procedures.

6-1-1 Before Making Adjustments
6-1-1 (a) ORIENTATION
When servicing, always face the monitor to the
east.
6-1-1 (b) MAGNETIC FIELDS
Whenever possible, use magnetic field isolation
equipment such as a Helmholtz field to surround
the monitor. If a Helmholtz field is not available,
frequently degauss the unit under test.
Caution: Other electrical equipment may cause
external magnetic fields which may
interfere with monitor performance.
Use an external degaussing coil to limit magnetic
build up on the monitor. If an external degaussing
coil is not available, use the internal degaussing
circuit. However, do not use the internal
degaussing circuit more than once per 30 minutes.
6-1-1 (c) WARM-UP TIME
The monitor must be on for 30 minutes before
starting alignment. Warm-up time is especially
critical in color temperature and white balance
adjustments.
6-1-1 (d) SIGNAL
Analog, 0.714 Vp-p positive at 75 ohm, internal
termination
Sync: Separate/Composite
(TTL level negative/positive)
Sync-on-Green:
Composite sync 0.286 Vp-p negative
(Video 0.714 Vp-p positive)
6-1-1 (e) SCANNING FREQUENCY
Horizontal: 30 kHz to 96 kHz
Vertical: 50 Hz to 160 Hz
All modes must be individually adjusted and
adjustments saved. This monitor does not
automatically adjust each mode.
Refer to Table 3-1 on page 3-3.
6-1-1 (f) HIGH VOLTAGE AND +B 195V LINE ADJUSTMENT
Signal: 1024 x 768 mode
(68 kHz/85 Hz)
Display image:Full white
Contrast: Maximum
Brightness: Maximum
Limit: 27.5 kV ± 0.5 kV
Measure the high voltage level at the anode cap.
High voltage should be within the limit as above.
If the high voltage needs adjustment use the
following procedure:
PROCEDURE
1. Adjust VR501 on the Main PCB so that the
high voltage measures 27.5 kV ± 0.5 kV.
2. Using a soldering iron, melt the adjustment
cap on VR501 to prevent any movement.
6-1-1 (g) G2 (SCREEN) VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT
Signal: 1024 x 768 mode
(68 kHz/85 Hz)
Display image:Crosshatch pattern
Contrast: Maximum
Brightness: Maximum
Adjust the Screen VR of the FBT so that the G2
(Screen) Voltage for Hitachi is 530 V ± 10 V.
6-1-1 (h) CENTER RASTER
Signal: 1024 x 768 mode (68 kHz/85 Hz)
Display image:Crosshatch pattern
Contrast: Maximum
Brightness: Maximum
Adjust VR401 so that the back raster comes to the
center.
6-1-1 (i) BRIGHTNESS AND CONTRAST
Unless otherwise specified, adjust control buttons:
Brightness: Maximum
Contrast: Maximum
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 6-1
6 Alignment and Adjustments
This section of the service manual explains how to make permanent adjustments to the monitor. Direction
is given for adjustment using the RS232C Serial Communications Adapter and software.
6-1 Adjustment Conditions
Caution: Changes made without the SoftJig are saved only to the user mode settings. As such, the
settings are not permanently stored and may be inadvertently deleted by the user.

6-1-2 Required Equipment
The following equipment may be necessary for
adjustment procedures:
6-1-2 (a) DISPLAY CONTROL ADJUSTMENT
1. Non-metallic (–) screwdriver: 1.5 mm
Non-metallic (–) screwdriver: 3 mm
2. Philips (+) screwdriver: 1.5 mm
3. Non-metallic hexkey: 2.5 mm
4. Digital Multimeter (DMM), or
Digital Voltmeter (DVM)
5. Signal generator, or
Computer with a video board that uses the
ET-4000 chipset (strongly recommended if
using Samsung DM 200 software) and that
displays: 1280 x 1024 @ 85 Hz, or 1600 x 1200
@ 85 Hz (maximum).
6. Personal computer
7. Required software: Softjig.exe from Samsung
which includes the cg17p.c data file
Samsung DM200, or DisplayMate for
Windows from Sonera Technologies
8. Interface Board Ver. 2.0 Code No.
BH81-90001K
9. Parallel communications cable (25-pin to
25-pin); Code No. BH81-90001H
10. Signal cable (15-pin to 15-pin cable with
additional 3-pin connector); Code No.
BH81-90001J
11. 5 V DC adapter, not supplied
Note: SoftJig Ass’y (includes items 8, 9 and 10)
Code No. BH81-90001L
6-1-2 (b) COLOR ADJUSTMENTS
1. All equipment listed in 6-1-2 (a), above
2. Color analyzer, or any luminance
measurement equipment
6-1-3 Connecting the SoftJig
Connect the monitor to the signal generator and/
or PC as illustrated in Figures 6-1 and 6-2.
Note: The signal cable connector which includes
the 3-wire cable must connect to the
monitor. If you use Setup 2 (PC only, no
signal generator) you can only make
adjustments to the signal timing available
on that computer system. To make
corrections to all factory timings requires
the use of an additional signal generator.
6-1-4 After Making Adjustments
After finishing all adjustments, test the monitor in
all directions. If, for example, the monitor does not
meet adjustment specifications when facing north,
reposition the monitor to face east and readjust.
This time, try for an adjustment closer to the ideal
setting within the tolerance range. Test the unit
again in all directions. If the monitor again fails to
meet specifications in every direction, contact
your Regional After Service Center for possible
CRT replacement.
6 Alignment and Adjustments
6-2 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
MONITOR
RS232C
PORT
PC
SIGNAL
GENERATOR
3-WIRE
CABLE
SIGNAL CABLE
(COM1 OR COM2)
Figure 6-1. Setup 1, With Signal Generator
MONITOR
RS232C
PORT
PC
3-WIRE CABLE
SIGNAL CABLE
D-SUB
CONNECTOR
(COM1 OR COM2)
RS-232 SERIAL PORT CONNECTION
PC RS-232 9 PIN (25 PIN) STEREO PHONE JACK
2 (2) 3
3 (3) 1
5 (7) 2
PC RS-232 PORT (COM1 OR COM2 PORT)
STEREO PHONE JACK (2.5 MM)
1 2 3 4 5
9 8 7 6
1 2 3
Figure 6-2. Setup 2, Without Signal Generator
Figure 6-3. 3 Wire Cable

6-2-1 Centering
Centering means to position the center point of
the display in the middle of the display area.
Horizontal size and position and vertical size and
position control the centering of the display.
For each mode, adjust the horizontal size and
vertical size to their optimal settings:
390 mm (H) x 292.5 mm (V).
Adjust the horizontal position and vertical
position to ≤ 5.0 mm of the center point of the
screen.
|A-B| ≤ 5.0 mm. |C-D| ≤ 5.0 mm.
Figure 6-4. Centering
6-2-1 (a) HORIZONTAL SIZE ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: Adjust for each mode listed
in Table 3-1.
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Adjust the H SIZE setting of the display pattern to
390 mm. (Tolerance: ± 3 mm.)
6-2-1 (b) VERTICAL SIZE ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: Adjust for each mode listed
in Table 3-1.
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Adjust the V SIZE setting of the display pattern to
292.5 mm. (Tolerance: ± 3 mm.)
6-2-1 (c) HORIZONTAL POSITION ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: Adjust for each mode listed
in Table 3-1.
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Adjust the H POSI setting to center the horizontal
image on the raster.
6-2-1 (d) VERTICAL POSITION ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: Adjust for each mode listed
in Table 3-1.
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Adjust the V POSI setting to center the vertical
image on the raster.
6-2-2 Trapezoid Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: Adjust for each mode listed
in Table 3-1.
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Adjust the TRAP setting to make the image area
rectangular.
Figure 6-5. Trapezoid
6-2-3 Pinbalance Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: Adjust for each mode listed
in Table 3-1.
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Adjust the PINBAL setting to optimize the image.
6 Alignment and Adjustments
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 6-3
6-2 Display Control Adjustments
C
A
DISPLAY AREA
EDGE OF BEZEL
B
D
| A - B | < 2.5 mm
A
B
| D1 |, | D2 | ≤ 1.0 mm
Figure 6-6. Pinbalance
D1 D2 D1
A
B

6-2-4 Parallelogram Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning Frequency: Adjust for each mode listed
in Table 3-1.
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Adjust the PARA setting to make the image area
rectangular.
Figure 6-7. Parallelogram
6-2-5 Side Pincushion Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: Adjust for each mode listed
in Table 3-1.
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
Adjust the PIN setting to straighten the sides of
the image area.
6-2-6 Tilt Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning Frequency: Adjust for each mode listed
in Table 3-1.
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
Adjust the TILT setting to correct the tilt of the
display.
6-2-7 Degauss
No adjustments are available for the degaussing
circuit. The degaussing circuit can effectively
function only once per 30 minutes.
6-2-8 Horizontal Linearity
CONDITIONS
Scanning Frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Adjust the H_Lin setting to correct the Linearity of
the display.
Linearity formula
6-2-9 Vertical Linearity
Refer to 6-2-8 Horizontal Linearity adjust the
V_Lin balance setting to correct the linearity of the
display.
6-2-10 Save the Data and Delete the User
Mode Data
After adjustment, press Factory Save and Delete
the User Mode.
6 Alignment and Adjustments
6-4 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
2.5 mm
| C1 |, | C2 | ≤ 2.0 mm, | D1 |, | D2 | ≤ 2.0 mm.
Figure 6-8. Pincushion
C2
C1
D1 D2
MAX – MIN
MAX + MIN
X 100 = %
Mode Entire Adjustment
Preset Mode 10 % 4 %
Other Mode 14 % 5 %
Table 6-1. Linearity Spec.

6-3-1 Color Coordinates (Temperature)
Color temperature is a measurement of the
radiant energy transmitted by a color. For
computer monitors, the color temperature refers
to the radiant energy transmitted by white. Color
coordinates are the X and Y coordinates on the
chromaticity diagram of wavelengths for the
visible spectrum.
CONDITIONS
Measurement instrument: Color analyzer
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display Size : 390 (H) x 292.5 (V)
Display image: White flat field at
center of display area
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
PROCEDURE
Use the directions in sections 6-3-2 through 6-3-4
to adjust the color coordinates for:
9300K to x = 0.283 ± 0.02, y = 0.298 ± 0.02
6500K to x = 0.313 ± 0.02, y = 0.329 ± 0.02
5000K to x = 0.346 ± 0.02, y = 0.359 ± 0.02
6-3-2 Color Adjustments for 9300K
6-3-2 (a) BACK RASTER COLOR ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Back raster pattern
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
1. Select COLOR CHANNEL 1 to control the
color for 9300K.
2. Adjust the luminance of the back raster to
between 0.3 to 1ft-L using the G_CUT
controls.
3. Click on the << or >> box next to B_CUT to
set the “y” coordinate to 0.298 ± 0.02.
4. Click on the << or >> box next to R_CUT to
set the “x” coordinate to 0.283 ± 0.02.
Note: If the above adjustments cannot be
done to each coordinate, click on the
<< or >> box next to G_CUT to decrease
or increase the green cutoff (bias) and
repeat procedures 2 and 3.
6-3-2 (b) G-GAIN ADJUSTMENT
Figure 6-9. Green Box Pattern
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Green box pattern
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
1. Click on the << or >> box next to G_GAIN to
adjust the brightness of the Green Gain to
25 ± 1 ft-L.
Note: If you can’t increase the Green Gain to
the appropriate value, click on the >>
box next to increase the ABL point.
6-3-2 (c) WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Full white pattern
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
Figure 6-10. Full White Pattern
1. Click on the << or >> boxes next to R_GAIN
and B_GAIN to make the video white.
(For 9300K color adjustment:
x = 0.283 ± 0.02, y = 0.298 ± 0.02.)
Note: Do not touch the G_GAIN controls.
2. Check the ABL. If it is not within the
specifications (30 ± 1 ft-L), use the ABL
controls to adjust it.
3. Select COLOR FACTORY SAVE to save the
data.
6 Alignment and Adjustments
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 6-5
6-3 Color Adjustments
1/3H-1/2H
1/3V-1/2V
FRONT BEZEL OPENING
BACK RASTER
GREEN WINDOW
FRONT BEZEL OPENING
BACK RASTER
WHITE WINDOW

6-3-2 (d) WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT VERIFICATION
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Back raster pattern
X-Y Coordinates: x = 0.283 ± 0.02,
y = 0.298 ± 0.02
Raster Luminance 0.3 ~ 1ft-L
ABL Luminance 30 ±1 ft-L
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
1. Check whether the color coordinates of the
back raster satisfy the above spec.
If they do not, return to 6-3-2 (a) and readjust
all settings.
2. Display a full white pattern.
Note: Do not touch the G_GAIN controls.
3. Adjust the Contrast Control on the monitor so
that the luminance of the video is about 5 ft-L.
4. Check whether the white coordinates of the
video meet the above coordinates spec.
5. Adjust the Contrast Control again so that the
luminance of the video is about 20 ft-L.
6. Check whether the white coordinates of the
video satisfies the above spec.
If they do not, return to 6-3-2 (a) and readjust
all settings.
6-3-3 Color Adjustments for 6500K
6-3-3 (a) BACK RASTER COLOR ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Back raster pattern
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
1. Select COLOR CHANNEL 2 to control the
color for 6500K.
2. Adjust the luminance of the back raster to
between 0.3 to 1.0 ft-L using the G_CUT
controls.
3. Click on the << or >> boxes next to R_CUT
and B_CUT to adjust the R-Bias to x = 0.313 ±
0.02 and the B-Bias to y = 0.329 ± 0.02.
6-3-3 (b) G-GAIN ADJUSTMENT
This procedure is the same as that for 9300K, refer
to the procedure on page 6-5.
6-3-3 (c) WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Full white pattern
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
1. Click on the << or >> boxes next to R_GAIN
and B_GAIN to make the video white.
(For 6500K color adjustment:
x = 0.313 ± 0.02, y = 0.329 ± 0.02.)
2. Refer to the procedure for 9300K, section
6-3-2 (c) steps 2 and 3.
6-3-3 (d) WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT VERIFICATION
Refer to the procedure for 9300K, section 6-3-2 (d).
6-3-4 Color Adjustments for 5000K
6-3-4 (a) BACK RASTER COLOR ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Back raster pattern
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
1. Select COLOR CHANNEL 3 to control the
color for 5000K.
2. Adjust the luminance of the back raster to
between 0.3 to 1.0 ft-L using the G_CUT
controls.
3. Click on the << or >> boxes next to R_CUT
and B_CUT to adjust the R-Bias to x = 0.346 ±
0.02 and the B-Bias to y = 0.359 ± 0.02.
6-3-4 (b) G-GAIN ADJUSTMENT
This procedure is the same as that for 9300K, refer
to the procedure on page 6-5.
Adjust the brightness of the G_GAIN less 5 ft-L
than brightness of procedure for 9300K.
6-3-4 (c) WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: Full white pattern
Brightness: Cut-off
Contrast: Maximum
1. Click on the << or >> boxes next to R_GAIN
and B_GAIN to make the video white.
(For 5000K color adjustment:
x = 0.346 ± 0.02, y = 0.359 ± 0.02.)
2. Refer to the procedure for 9300K, section
6-3-2 (c) steps 2 and 3.
6 Alignment and Adjustments
6-6 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)

6-3-4 (d) WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT VERIFICATION
Refer to the procedure for 9300K, section 6-3-2 (d).
6-3-5 Luminance Uniformity Check
Luminance is considered uniform only if the ratio
of lowest to highest brightness areas on the screen
is not less than 7.5:10.
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
(1024 x 768)
Display image: White flat field
Display size 390 (H) x 292.5 (V)
Brightness: Cut off point
Contrast: Maximum
PROCEDURE
Measure luminance at nine points on the display
screen (see figure below).
6-3-6 Focus Adjustment
CONDITIONS
Scanning frequency: 68 kHz/85 Hz
Display image: “H” character pattern
Brightness: Cut off point
Contrast: Maximum
PROCEDURE
1. Adjust the Focus VR on the FBT to display the
sharpest image possible.
2. Use Locktite to seal the Focus VR in position.
6-3-7 Color Purity Adjustment
Color purity is the absence of undesired color.
Conspicuous mislanding (unexpected color in a
uniform field) within the display area shall not be
visible at a distance of 50 cm from the CRT
surface.
CONDITIONS
Orientation: Monitor facing east
Scanning frequency: Adjust for each mode
listed in Table 3-1.
Display image: White flat field
Luminance: Cutoff point at the center
of the display area
Note: Color purity adjustments should only be
attempted by qualified personnel.
PROCEDURE
For trained and experienced service technicians
only.
Use the following procedure to correct minor
color purity problems:
1. Make sure the display is not affected by
external magnetic fields.
2. Very carefully break the glue seal between the
2-pole purity convergence magnets (PCM), the
band and the spacer (see Figure 6-13).
3. Make sure the spacing between the PCM
assembly and the CRT stem is 29 mm ± 1 mm.
4. Display a green pattern over the entire display
area.
5. Adjust the purity magnet rings on the PCM
assembly to display a pure green pattern.
(Optimum setting: x = 0.295 ± 0.015,
y = 0.594 ± 0.015)
6. Repeat steps 4 and 5 using a red pattern and
then again using a blue pattern.
Table 6-2. Color Purity Tolerances
(For 9300K color adjustment: x = 0.283 ± 0.02, y = 0.298 ± 0.02)
7. When you have the PCMs properly adjusted,
carefully glue them together to prevent their
movement during shipping.
6 Alignment and Adjustments
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 6-7
Red: x = 0.640 ± 0.015 y = 0.323 ± 0.015
Green: x = 0.295 ± 0.015 y = 0.594 ± 0.015
Blue: x = 0.142 ± 0.015 y = 0.066 ± 0.015
Figure 6-11. Luminance Uniformity Check Locations

Table 6-3. Misconvergence Tolerances
Figure 6-12. Convergence Measurement Areas
Figure 6-13. Hitachi Magnet Configuration
6-4-1 Static (Center) Convergence
Static convergence involves alignment of the red,
blue and green lines in the center area of the
display. See “Dynamic Convergence” for
alignment of the color fields around the edges of
the display.
CONDITIONS
Orientation: Monitor facing east
Warm-up: 30 minutes
Display image: Crosshatch pattern
Tolerances: See Table 6-3
PROCEDURE
As shown in Figure 6-12, the CRT used in these
monitors has the same magnet configuration as
shown in Table 6-3 below.
Table 6-4. Magnet Order
Use the following steps to correct any static
misconvergence:
1. Make sure the display is not affected by
external magnetic fields.
2. Locate the pair of 4-pole magnet rings.
3. Unlock the rings and rotate the individual
rings (change the spacing between tabs) to
converge the vertical red and blue lines.
4. Rotate the pair of rings (maintaining the
spacing between tabs) to converge the
horizontal red and blue lines.
6 Alignment and Adjustments
6-8 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
6-4 Convergence Adjustments
Misconvergence occurs when one or more of the electron beams in a multibeam CRT fail to meet the
other beams at a specified point.
CRT
FRONT
1
2
3
4
8
5
9
6
7
10
11
Hitachi CRT
1 Setup Bolt 2 Bow Magnet 3 Band 4 2-Pole Magnet
5 Spacer 6 4-Pole Magnet 7 Spacer 8 6-Pole Magnet
9 Holder 10 Band 11 Tabs
A
B
286 MM
381 MM
CRT Manufacturer Magnet Order from Front of CRT
Hitachi Convergence bow, 2-pole,
4-pole, 6-pole
Position Error in mm CRT Dot Pitch REMARK
Center (A) 0.3 0.28 All Mode
Edge (B) 0.4 0.28 < 1024 x 768
0.45 0.28 ≥ 800 x 600

5. After completing the red and blue center
convergence adjustment, locate the pair of
6-pole magnet rings.
6. Rotate the individual rings (change the
spacing between tabs) to converge the vertical
red and blue (magenta) and green lines.
7. Rotate the pair of rings (maintaining the
spacing between tabs) to converge the
horizontal red and blue (magenta) and green
lines. Don’t rotate the 2-pole magnets as they
adjust for color purity.
8. Mark the correct position for the magnets and
apply a small line of glue to hold the magnets
in place. Lock the rings in place.
6-4-2 Dynamic (Edge) Convergence
Use the following procedure to correct minor
dynamic (edge) misconvergence. If, after using
this procedure, dynamic misconvergence around
the periphery of the display area is still greater
than the tolerance, contact the Regional After
Service Center for possible CRT replacement.
1. Make sure the display is not affected by
external magnetic fields.
2. Make sure the static convergence is properly
adjusted.
3. Strategically place small rubber magnets on
the back of the CRT to correct the
misconvergence. Be careful not to remove the
paper protecting the adhesive on the magnets
until you are satisfied with their placement
and the dynamic convergence.
4. When you are satisfied with the convergence
around the edge of the CRT, permanently glue
the magnets to the back of the CRT.
WARNING: Do not remove or change the
position of the factory installed
wedges. These wedges were
installed by the CRT manufacturer
and are properly placed for this
CRT; their removal may result in
damage to the CRT.
6 Alignment and Adjustments
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 6-9
!
Red and Blue Alignment
(4-pole magnet movement)
Red, Blue and Green Alignment
(6-pole magnet movement)
R
B
B
R
O-Magnetic
Field
Motion (1)
Motion (2)
(1) SPREAD
TAB
MAGNET
VERTICAL
MISALIGNMENT
HORIZONTAL
MISALIGNMENT
SHIFT DIRECTION OF
CROSSHATCH PATTERN
SHIFT DIRECTION OF
CROSSHATCH PATTERN
OR
MOVE
TOGETHER
Figure 6-14. Magnet Movements
B
R
B
R
B
R
B
R
M
G
G
R
G
M
G
R
B
G
M
G
M
B

6-4-3 Bow Convergence Adjustments
CONDITIONS
Orientation: Monitor facing east.
Display Image: Crosshatch pattern with mixed
RGB colors.
Required tools: Flathead (–) screwdriver, 1.5 mm
Philips (+) screwdriver, 1.5 mm
Hexkey, 2.5 mm
PROCEDURE
Bow convergence adjustments are not available
for the CRTs used in the SyncMaster 1000s
(CGP1607L) monitor. While all CRTs have bow
convergence magnets, they are sealed in the CRT
factory and are not user or service technician
adjustable. Do not touch these magnets (see
Figure 6-12). If bow convergence adjustment is out
of alignment, replace the CRT.
Bow misconvergence should not exceed the values
listed in Table 6-3: Misconvergence Tolerances.
6-4-4 Balance Convergence Adjustments
Balance Convergence involves alignment of red
and blue lines when they are misaligned at one
end more so than at the other end. The Deflection
Yoke holds the balance coils which can correct
balance misconvergences.
6 Alignment and Adjustments
6-10 SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L)
V
CR
Y
HC
Y
H
Y
V
Y
VS
G
R,B
G
R,B
VCR
B
R
B
R
YH (bow)
R
B
B
R
YHC (cross)
R
B
B
R
YV (balance)
B
R
B
R
YVS (amp)
SyncMaster 1000s (CGP1607L) 7-1
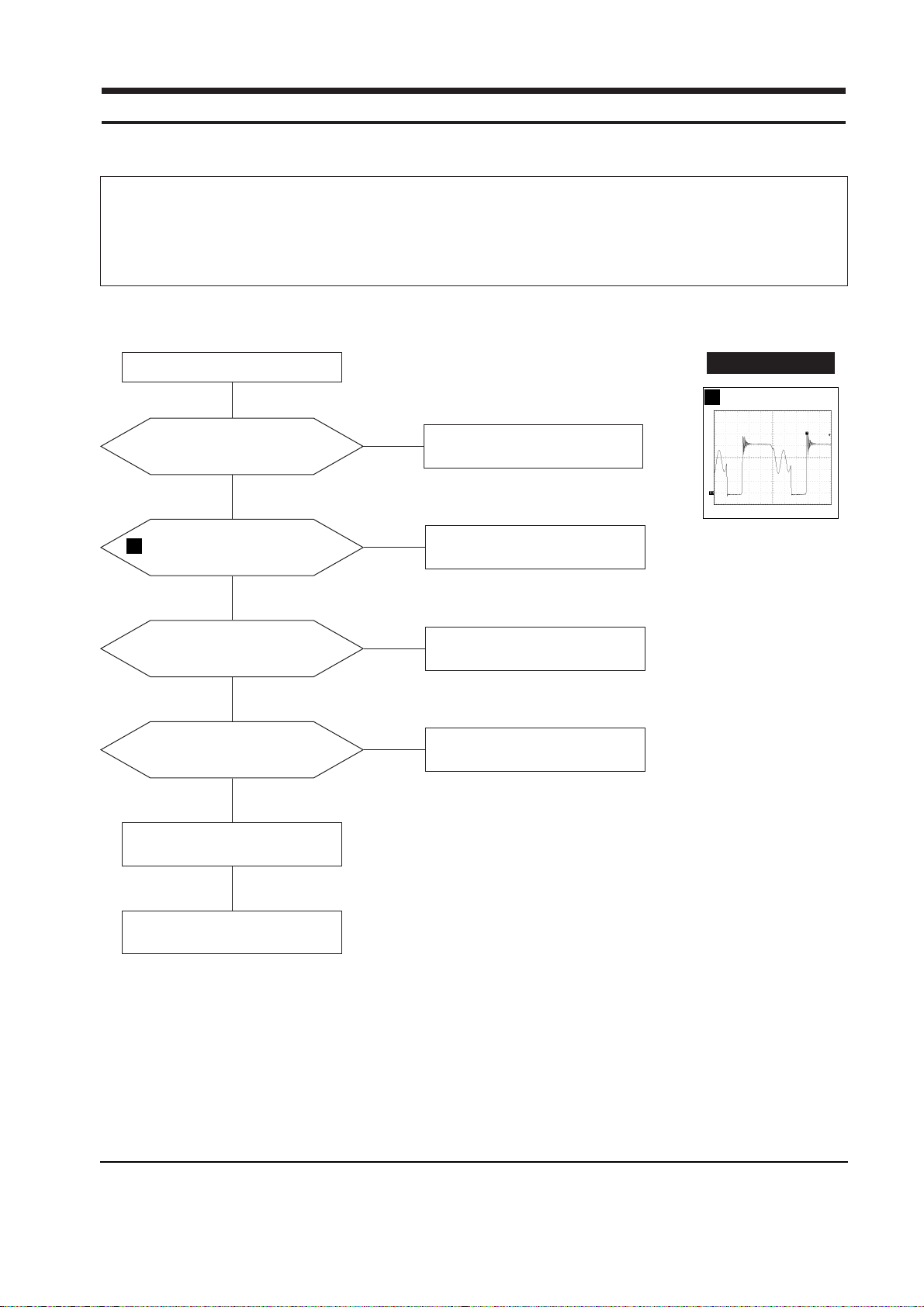
7 Troubleshooting
7-1 Parts Level Board Repair Section
Notes: 1. If a picture does not appear, fully rotate the brightness and contrast controls clockwise and reinspect.
2. Check the following circuits.
• No raster appears: Power circuit, Horizontal output circuit, H/V control circuit, and H/V output circuit.
• High voltage develops but no raster appears: Video output circuits.
• High voltage does not develop: Horizontal output circuits.
7-1-1 No Power Supply
Does power supply make chirping
noise?
Check and replace Q604, Q607, T601
and D634.
Check and replace FH601, D601.
Verify voltages.
Done.
No
Yes
Does the IC601 Pin 1
waveform correct?
Check and replace IC601, OP602,
IC604 and D606.
Yes
No
Do OP602, IC604 and
D606 work normally?
Relace parts and verify voltages.
Yes
No
Is the power board work well?
Replace power board.
Yes
No
WAVEFORMS
2
552 V (IC601, #1))
CH1 P-P = 552 V CH1 RMS = 323 V
2
 Loading...
Loading...