SAMES SA589 Datasheet
FEATURES
ROW6
COL1
MFOUT
MUTE
COL7
ROW1
COL2
ROW2
COL3
ROW7
COL4
COL5
ROW4
ROW3
sames
WITH DEDICATED KEYS FOR 20 MEMORIES
SA589
LD/DTMF SWITCHABLE DIALLERS
n Selectable Loop-Disconnect or DTMF
Modes
n Keypad Switchable LD to DTMF
n 20 x 24-Digit Memories, (each with
Dedicated Key)
n 24 Digit Last Number Redial
n Selectable Make/Break Ratios 2:1 and 3:2
DESCRIPTION
The SA589 family are keypad switchable LD/
DTMF dialler devices with a last number
redial facility and twenty 24-digit memories
each with its own dedicated dialling key.
Three operating modes are available: LD
only mode, DTMF only mode and LD mode
with the ability to switch temporarily to DTMF
mode from the keypad during a call. This last
mode enables subscribers to access such
services as home banking. Mixed LD and
DTMF numbers can also be stored in memory.
The SA589 devices are pin compatible with
the SAMES switchable dialler families SA541,
SA545, SA585, SA587 and SA588 - providing
a complete range of telephone features within
a single PCB and circuit design. Metal mask
and pin selectable options are available to
service specific requirements of particular
countries and customers.
n Uses Inexpensive 560kHz Ceramic
Resonator
n Batteryless operation - Low Power CMOS
n Mask Programmable Options to suit
application
n Timed Break Recall (Flash) and Earth
Recall
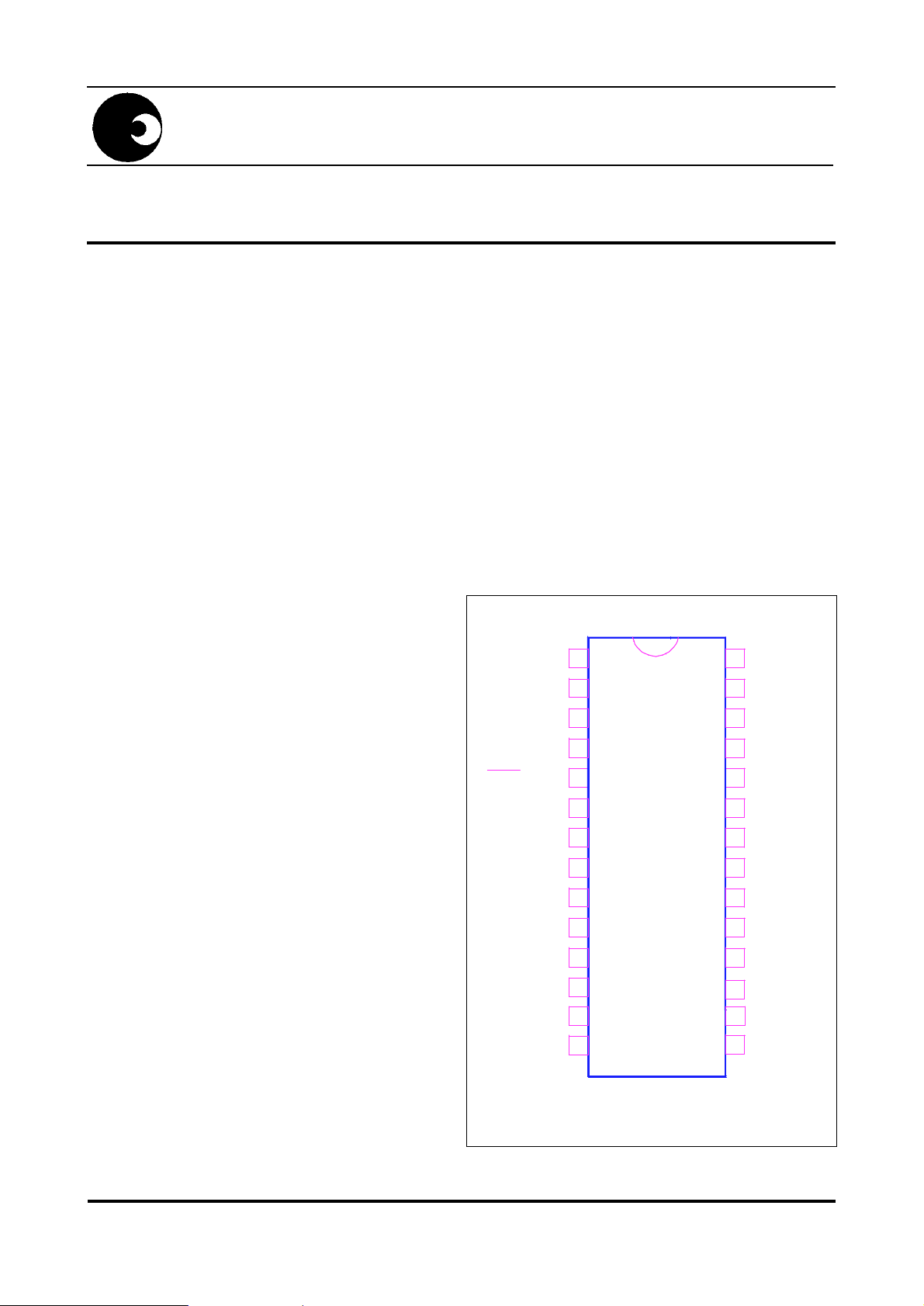
FIG. 1 PIN CONNECTIONS
SA589
NC
COL6
IMP
SELECT
MASK
OSC OUT
OSC IN
FILT IN
FILT OUT
HSW
V
SS
V
DD
PAUSE OUT
ROW5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
DR-00684
Package: DIP28
1/14
4120 PDS039-SA589-001 REV. C 09-03-1995
SA589 FAMILY
TABLE 1: PIN FUNCTIONS
Pin Pin
number name
Function
1 NC Not connected
3 IMP 'Loop disconnect' dialling output
4 SELECT LD/DTMF selection, IDP and B/M ratio programming
5 MASK Output to disable speech circuit during pulse dialling and recall
(see note 1)
6 OSC OUT Connections for 560kHz ceramic resonator
7 OSC IN
8 FILT IN Unity gain amplifier input and output for DTMF tone filtering
9 FILT OUT
10 HSW Hookswitch input - a logic 1 at this pin is used to indicate 'Off-
Hook'
11 V
12 V
SS
DD
Negative supply
Positive supply
13 PAUSE OUT Active high indicating a pause when dialling from memory
17 MF OUT Unfiltered DTMF output
18 MUTE Output active during keying and tone transmission (see note 2)
19 COL1
20 COL2
21 COL3
26 COL4
27 COL5
2 COL6
16 COL7
22 ROW1 Connections for 38 key single contact keypad
23 ROW2
24 ROW3
25 ROW4
14 ROW 5
15 ROW 6
28 ROW 7
1. MASK may be used to disconnect the whole speech circuit in order to maintain the break
condition whilst on-hook and during a TBR (Timed Flash) operation.
2. MUTE is provided to disable the microphone while maintaining the loop during DTMF
transmission.
OPERATION
Power-on
When power is applied to the chip, a power-on reset circuit operates and ensures that the
Memories are cleared and all logic is reset. The power-on reset circuit is designed such that
if the chip supply voltage drops to a level at which the memories may be corrupted, it will
always, under all conditions, clear the memory, so that corrupt data is not retained.
2/14
sames

SA589 FAMILY
Hookswitch Operation
The HSW input is used to inform the SA589 of whether the telephone is on or off hook. Logic
'0' is recognised as on-hook. Logic '1' is recognised as off-hook. When the HSW input rises
from '0' to '1' the off-hook state is recognised immediately and keypad inputs are accepted.
However, when the HSW input falls from '1' to '0' the on-hook state is not recognised for 200
- 300ms. This is so that short line breaks of less than 200ms, such as the line reversals applied
by the exchange, are ignored. In this case the IMP and MASK outputs will go low immediately
the HSW input goes low in order to preserve current, but will resume normal operation
immediately HSW goes high.
On-hook state
In the on-hook state all chip outputs are set low, the oscillator circuit is inhibited and no key
inputs are accepted. This conserves supply current so that the MEMORY contents may be
retained.
Off-hook state
When the HSW input goes high, the MASK output immediately goes to the logic '1' level and
remains there until going on-hook or signalling a TBR, (see timing diagram). COLUMN
outputs also go high until a key is pressed and are normally off whenever timing functions are
not required.
Keypad Operation
A Single Contact, Normally Open keypad is required. When off-hook the COLUMN outputs
are normally held high and the ROW inputs are low. When a key is pressed this connects a
COLUMN output to a ROW input and the ROW input is pulled high.
This action initiates keyboard scanning. During keyboard scanning, the COLUMN outputs
are normally low but generate scanning pulses at 7ms intervals on each output in sequence.
A key is accepted as valid when two successive scanning pulses from the same COLUMN are
seen on a ROW input. Hence, the minimum bounce-free key closure period which is
necessary to guarantee detection is about 14ms (plus the oscillator start-up time if it was not
already running).
Simultaneous key depressions
If two keys are pressed simultaneously (i.e. a second key is pressed before the first has been
verified) neither key will be accepted until both keys are released and the correct key is pressed
again.
Dialling Mode Selection
The dialling mode may be selected via the SELECT pin (Pin 4) as detailed in Table 2. Four
'Loop-Disconnect' + DTMF options, two 'Loop-disconnect only' options and three DTMF
modes are available. Each mode offers a different combination of LD and/or MF timing. If
one of the 'LD only' or DTMF only modes is selected then dialling will remain fixed in LD mode
or DTMF mode respectively.
sames
3/14
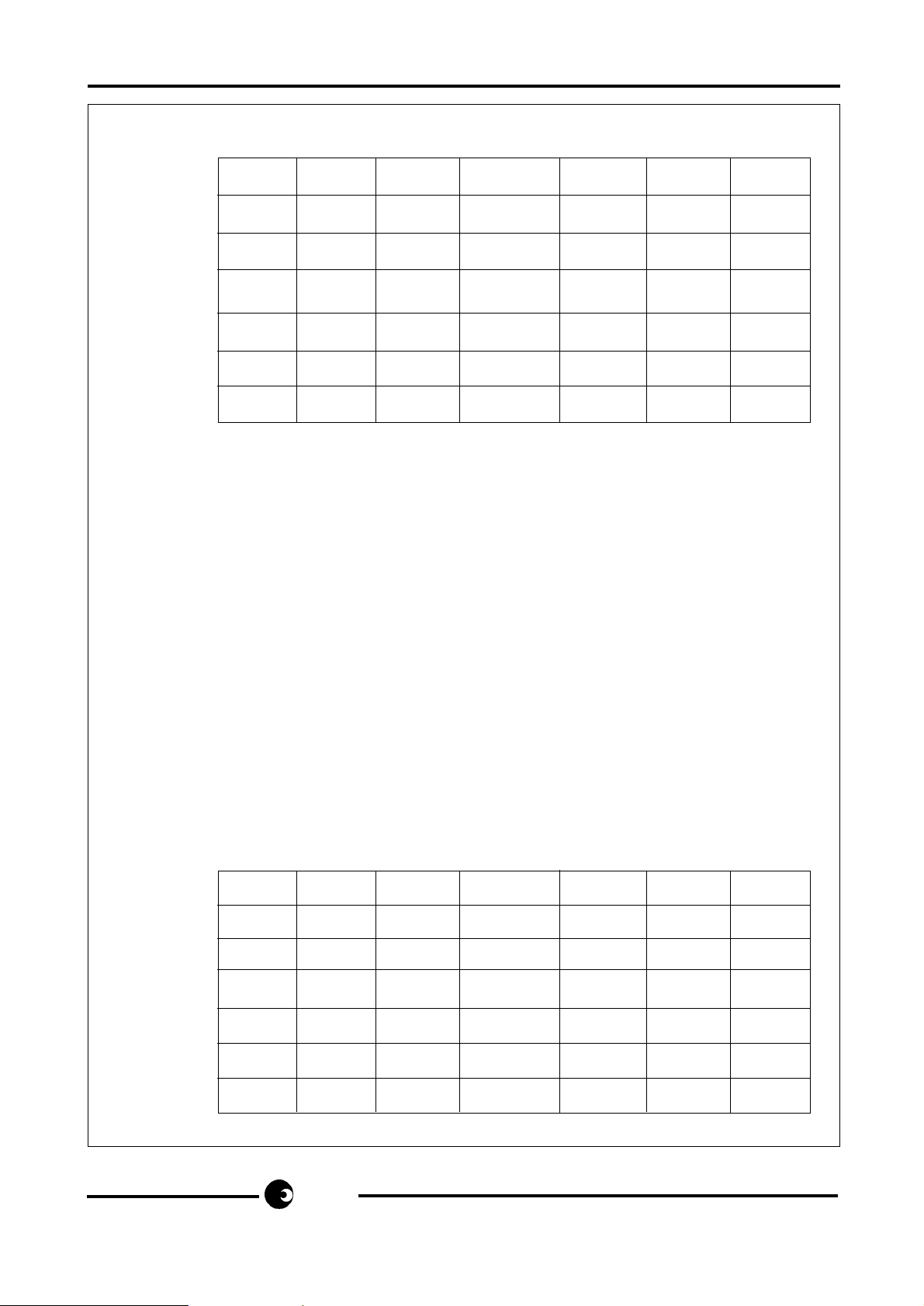
SA589 FAMILY
COL COL COL COL COL COL COL
123 4 5 67
ROW 1 1 2 3 TBR S01 S02 S03
ROW2 4 5 6 REDIAL S04 S05 S06
ROW3 7 8 9 STORE S07 S08 S09
ROW4 * 0 # SHIFT S00 LNR
PAUSE/
CONT
ROW5 S11 S12 S13
ROW6 S10 S14 S15 S16
ROW7 S17 S18 S19
Fig. 2a Versions without TONE key
* or */# are used to change from LD to DTMF dialling and are available as digits when in DTMF
mode.
TBR: Timed Break Recall (Flash).
STORE: Memory Programming key. Use in conjunction with dedicated memory keys or a
two-digit code representing the number of the memory to be programmed
S00-S19: 'Single touch' dedicated memory dialling keys
LNR: Last Number Redial
REDIAL and SHIFT: These keys are clearly unnecessary where keypad positions are
provided for all the dedicated memory keys but may be useful to access memories in
applications where the telephone provides insufficient keys for all these functions. For a
description of the function of the REDIALand SHIFT keys, see the SA585 and SA587 data
sheets, respectively. Do not fir keys in these positions if not required.
PAUSE/CONT: Insert pause in memory/continue dialling
TONE: Change dialling mode from LD to DTMF
COL COL COL COL COL COL COL
123 4 5 67
ROW 1 1 2 3 TBR S01 S02 S03
ROW2 4 5 6 REDIAL S04 S05 S06
ROW3 7 8 9 STORE S07 S08 S09
ROW4 * 0 # TONE SHIFT S00 LNR
ROW5 S11 S12 S13
ROW6 S10 S14 S15 S16
ROW7 S17 S18 S19
Fig. 2b Versions with TONE key
Fig. 2 Keypad layout and connections
4/14
sames
SA589 FAMILY
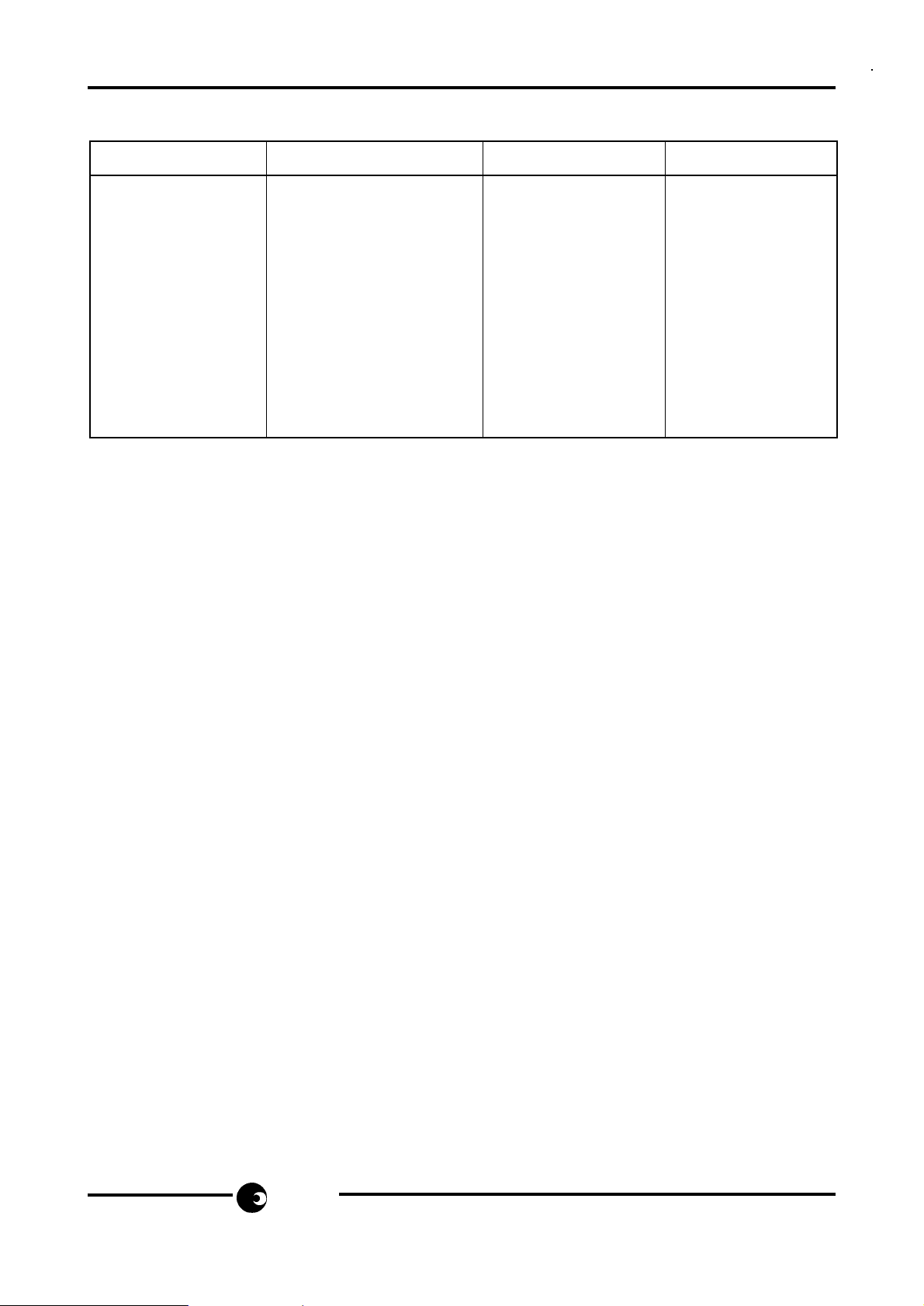
TABLE 2: Dialling mode selection
Select Pin to Dialling Mode B:M Ratio TBR (msec)
V
SS
LD + DTMF 2:1 100
COL1 LD + DTMF 2:1 270
COL2 LD + DTMF 3:2 270
COL3 LD + DTMF 3:2 100
COL4 LD only 2:1 COL5 DTMF only - 270
COL6 DTMF only - 270
COL7 LD only 3:2 -
V
DD
DTMF only - 100
However, if one of the 'LD + DTMF' modes is selected the chip will be in LD mode initially in
the off-hook condition but may be switched to DTMF by pressing either *, */# or TONE key
(depending on the mask variant - see Fig. 2 and page 11), provided that dialling is not in
progress. If any of these keys are pressed during LD dialling, they will be ignored.
Only if * or # are pressed subsequent to switching to DTMF, will * or # be dialled. Only digits
entered prior to a switch to DTMF will subsequently be available for redialling (see Last
Number Redial operation), unless specified otherwise.
Once switched to DTMF, dialling will remain in this mode until either a Recall (Flash) operation
or until the chip returns to the on-hook state.
Last Number Redial (LNR)
The function of the on-chip LNR store is to retain automatically a manually dialled number for
redialling later. The capacity of the memory is 24 digits. If a number is dialled which is longer
than this, dialling will continue, but redialling will not be allowed with this number. To redial
a number in the LNR store, the LNR key may be pressed once, or the Redial key can be
pressed twice.
The last number redial store has several features designed to assist the user:
Moving cursor facility
This facility is provided to aid use in PABX applications, where the user must first dial an
access digit, or digits, and then wait for a second dial tone before continuing dialling.
This allows a user to enter the first digit or digits of the number in the last number redial store
manually before pressing the LNR key; the remainder of the number will be dialled when
the LNR key is pressed.
If the digit(s) dialled manually do not match those in the LNR memory, then redialling will
be inhibited for the remainder of the call, and the numbers entered will be saved in the LNR
memory for redialling in a subsequent call.
If the user manually dials the first digit(s) in the LNR memory, and then goes on-hook, the
whole contents of the memory will be retained.
sames
5/14
 Loading...
Loading...