Sailor 500 FleetBroadband, Sailor 250 FleetBroadband, 250 FleetBroadband Installation Manual
Page 1

Page 2

INSTALLATION MANUAL
SAILOR
500/250 FleetBroadband
Page 3

Thrane & Thrane A/S
SAILOR
®
500 FleetBroadband
SAILOR
®
250 FleetBroadband
Installation manual
Document number: TT98-125646-C
Release date: December 13, 2007
Page 4

Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent
a commitment on the part of Thrane & Thrane A/S. We recommend downloading the
latest version of the manual from the Thrane & Thrane Extranet.
Copyright © 2007 Thrane & Thrane A/S. All rights reserved.
Trademark acknowledgements
• Thrane & Thrane is a registered trademark of Thrane & Thrane A/S in the European
Union and the United States.
• SAILOR is a registered trademark of Thrane & Thrane A/S in the European Union, the
United States and other countries.
• Windows and Outlook are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the
United States and other countries.
• Inmarsat is a registered trademark of International Maritime Satellite Organisation
(IMSO) and is licensed by IMSO to Inmarsat Limited and Inmarsat Ventures plc.
• Inmarsat’s product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of Inmarsat.
• Other product and company names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or
trade names of their respective owners.
Company addresses
www.thrane.com
Denmark
Denmark
Company headquarters
Norway
Thrane & Thrane Aalborg A/S
Porsvej 2
DK-9200 Aalborg SV
Denmark
Thrane & Thrane A/S
Lundtoftegårdsvej 93 D
DK-2800 Kgs. Lyngby
Denmark
Thrane & Thrane Norway
Bergerveien 12
PO Box 91
1375 Billingstad,
Norway
USA China
Thrane & Thrane, Inc.
509 Viking Drive, Suites
K, L and M
Virginia Beach, VA 23452
USA
Thrane & Thrane Shanghai
Unit 602 - Building 4,
289 Bisheng Rd.
Zhangjiang High-tech Park,
Pudong
201204 Shanghai
P. R. China
Page 5
iii
Safety summary 1
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all
phases of operation, service and repair of this equipment. Failure to comply
with these precautions or with specific warnings elsewhere in this manual
violates safety standards of design, manufacture and intended use of the
equipment. Thrane & Thrane A/S assumes no liability for the customer's
failure to comply with these requirements.
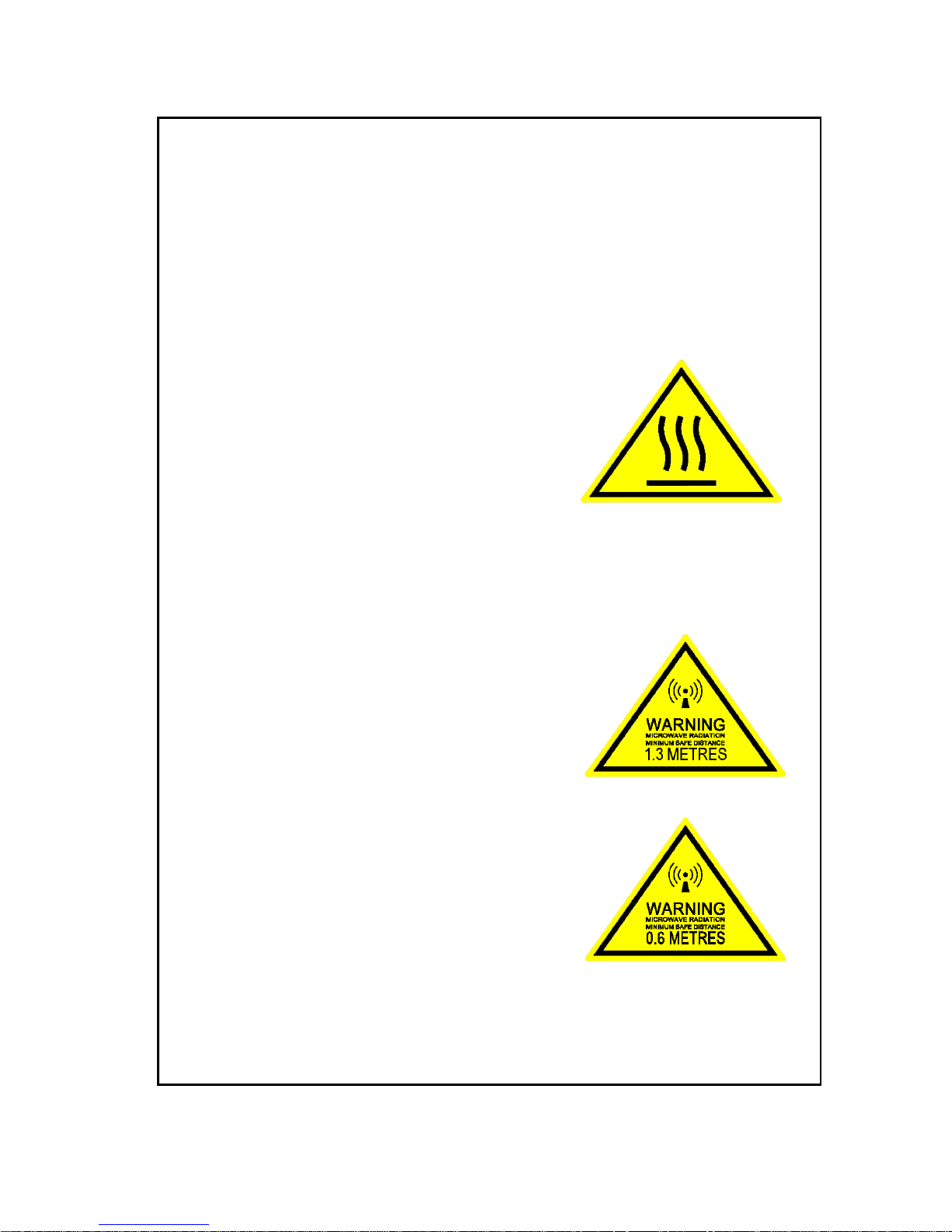
Observe marked areas
Under extreme heat conditions do not touch
areas of the terminal or antenna that are
marked with this symbol, as it may result in
injury.
Microwave radiation hazards
During transmission the antenna in this system radiates microwave power.
This radiation may be hazardous to humans close to the antenna. During
transmission, make sure that nobody gets closer than the recommended
minimum safety distance.
On the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband, the
minimum safety distance on the focal line to
the antenna panel is 1.3 m, based on a
radiation level of 10 W/m
2
. The radiation level is
100 W/m
2
at a distance of 0.4 m from the
antenna panel. Refer to the drawing on the
next page.
On the SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband, the
minimum safety distance on the focal line to the
antenna panel is 0.6 m, based on a radiation
level of 10 W/m
2
. The radiation level is 100
W/m
2
at a distance of 0.2 m from the antenna
panel. Refer to the drawing on the next page.
Page 6
iv
Distance to other equipment
Do not move the antenna closer to radars than the minimum safe distance
specified in Radar distance on page 12 - it may cause damage to the
antenna. The equipment must be installed with the following minimum safe
distances to magnetic steering compass:
SAILOR FleetBroadband terminal: min. 0.3 m.
SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna: min. 1.0 m
SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband antenna: min. 1.1 m
Service
User access to the interior of the terminal is prohibited. Only a technician
authorized by Thrane & Thrane A/S may perform service - failure to comply
with this rule will void the warranty. Access to the interior of the antenna is
allowed, but only for replacement of certain modules - as described in this
manual. General service may only be performed by a technician authorized
by Thrane & Thrane A/S.
Do not service or adjust alone
Do not attempt internal service or adjustments unless another person,
capable of rendering first aid resuscitation, is present.
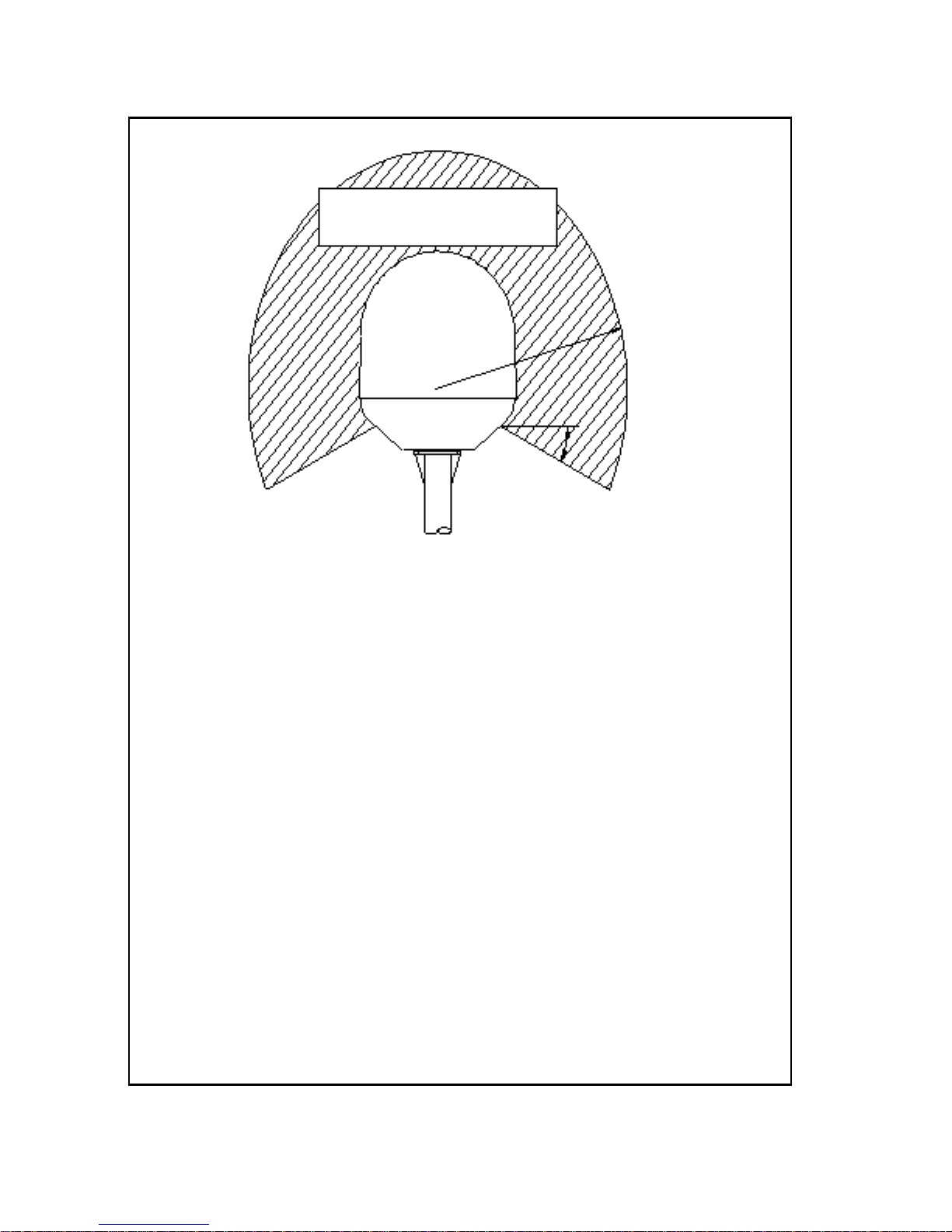
SAILOR 500:
MICROWAVE RADIATION
No personnel within safety distance
25° for SAILOR 500
60° for SAILOR 250
Safety distance:
(0.4 m, 100 W/m
2
)
1.3 m, 10 W/m
2
SAILOR 250:
(0.2 m, 100 W/m
2
)
0.6 m, 10 W/m
2
Page 7
v
Grounding, cables and connections
To minimize shock hazard, the equipment chassis and cabinet must be
connected to an electrical ground. The terminal must be grounded to the
ship. For further grounding information refer to Grounding and RF
protection on page 109.
Do not extend the cables beyond the lengths specified for the equipment.
The cable between the terminal and antenna can be extended if it complies
with the specified data concerning cable losses etc.
All cables for your SAILOR FleetBroadband system are shielded and should
not be affected by magnetic fields. However, try to avoid running cables
parallel to AC wiring as it might cause malfunction of the equipment.
Power supply
The voltage range is 10.5 - 32 V DC; 14 A - 5.5 A. It is recommended that the
voltage is provided by the 24 V DC power bus on the ship. Be aware of high
start-up peak current: 20 A at 24 V, 5 ms.
If a 24 V DC power bus is not available, an external 115/230 VAC to 24 V DC
power supply can be used.
Equipment ventilation
To ensure adequate cooling of the terminal, 5 cm of unobstructed space
must be maintained around all sides of the unit (except the bottom side).
The ambient temperature range of the terminal is: -25° to +55°C.
Do not operate in an explosive atmosphere
Do not operate the equipment in the presence of flammable gases or fumes.
Operation of any electrical equipment in such an environment constitutes a
definite safety hazard.
Keep away from live circuits
Operating personnel must not remove equipment covers. Component
replacement and internal adjustment must be made by qualified
maintenance personnel. Do not replace components with the power cable
connected. Under certain conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even
with the power cable removed. To avoid injuries, always disconnect power
and discharge circuits before touching them.
Failure to comply with the rules above will void the warranty!
Page 8

vi
Mandatory safety instructions to installers &
users of SAILOR
®
250 FleetBroadband 2
Use only manufacturer or dealer supplied antenna.
Antenna minimum safe distance: 0.415 m.
Antenna gain 12.2 dBi referenced to isotropic.
The Federal Communications Commission has adopted a safety
standard for human exposure to RF (Radio Frequency) energy,
which is below the OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Act)
limits.
Antenna mounting
The antenna supplied by the manufacturer or radio dealer must
not be mounted at a location such that during radio transmission,
any person or persons can come closer than the above indicated
minimum safe distance to the antenna i.e. 0.415 m.
To comply with current FCC RF Exposure limits, the antenna must
be installed at or exceeding the minimum safe distance shown
above, and in accordance with the requirements of the antenna
manufacturer or supplier.
Base Station Installation: The antenna should be fixed-mounted
on an outdoor permanent structure. RF Exposure compliance must
be addressed at the time of installation.
Antenna substitution
Do not substitute any antenna for the one supplied or
recommended by the manufacturer or radio dealer. You may be
exposing person or persons to excess radio frequency radiation.
You may contact your radio dealer or the manufacturer for further
instructions.
Page 9
vii
Warning
Maintain a separation distance from the antenna to a person(s) of
at least 0.415 m.
You, as the qualified end-user of this radio device must control the
exposure conditions of bystanders to ensure the minimum
separation distance (above) is maintained between the antenna
and nearby persons for satisfying RF Exposure compliance. The
operation of this transmitter must satisfy the requirements of
Occupational/Controlled Exposure Environment, for work-related
use. Transmit only when person(s) are at least the minimum
distance from the properly installed, externally mounted antenna.
Note
Thrane & Thrane recommends a minimum safety
distance of 0.6 m to the SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband
antenna.
Page 10

viii
About the manual 3
Intended readers
This is an installation manual for the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband
and the SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband systems. The readers of the
manual include installers of the system and service personnel.
Personnel installing or servicing the system must be properly
trained and authorized by Thrane & Thrane. It is important that
you observe all safety requirements listed in the beginning of this
manual, and install the system according to the guidelines in this
manual.
Manual overview
Note that this manual does not cover general use of the system nor
does it cover how to use the IP handset that comes with the
system. For this information, refer to the user manual for this
system and the user manual for the IP handset, both listed in the
next section.
This manual has the following chapters:
• System units contains a short description of each main unit in
the system.
• Installing the system describes where to place the system units,
how to mount them, special considerations for grounding,
distance to other equipment etc.
• Connecting power explains how to connect the terminal to
power and gives recommendations for cables.
• Hardware interfaces describes each interface on the terminal
and shows pin-out for the connectors.
• Starting up the system explains how to insert the SIM card,
power up the system and enter the PIN. It also gives a short
overview of how to use the system.
• Service and repair describes how to replace modules for
service.
Page 11
ix
• Troublesho otin g describes the function of the Reset button and
the light indicators on the terminal. It also describes event
messages that may appear in the web interface.
This manual may not always reflect the latest software
functionality of your transceiver. To obtain the latest version of the
manual, please enter the Thrane & Thrane Extranet and download
the latest version, or acquire it from your distributor.
Related documents
The below list shows the documents related to this manual and to
the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband and SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband
systems.
Title and description
Document
number
SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband
SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband
User Manual
Explains how to set up and use the
SAILOR FleetBroadband systems.
TT 98-125645
SAILOR 500/250 FleetBroadband, Quick Guide
A short guide to the most important functions
of the SAILOR FleetBroadband systems.
TT98-125647
Thrane & Thrane IP Handset, User Manual
Explains the features and functions of the
Thrane & Thrane IP handset. The IP handset
works as a standard IP handset, but also
serves as a user interface for the
SAILOR FleetBroadband systems.
TT98-126059
Page 12

x
Typography
In this manual, typography is used as indicated below:
Bold is used for the following purposes:
• To emphasize words.
Example: “Do not touch the antenna”.
• To indicate what the user should select in the user interface.
Example: “Select Settings > LAN”.
Italic is used to emphasize the paragraph title in cross-
references.
Example: “For further information, see Connecting Cables on
page...”.
COURIER is used to indicate low level commands such as AT
commands.
Example: “In your terminal program, type ATD”.
Page 13

xi
Table of contents
Chapter 1 System units
1.1 Introduction ............................................................... 1
1.2 Terminal .................................................................... 1
1.3 SAILOR
®
500 FleetBroadband antenna .......................2
1.4 SAILOR
®
250 FleetBroadband antenna .......................3
1.5 IP handset and cradle ................................................4
Chapter 2 Installing the system
2.1 Unpacking .................................................................7
2.2 Placing the antenna ...................................................8
2.3 Installing the antenna ...............................................21
2.4 Placing the terminal ................................................27
2.5 Installing the terminal .............................................28
Chapter 3 Connecting power
3.1 Power source ...........................................................37
3.2 Power cable selection ..............................................38
3.3 To connect power ....................................................42
3.4 Remote on/off ..........................................................43
Chapter 4 Hardware interfaces
4.1 The connector panel ................................................45
4.2 Antenna interface on terminal .................................46
4.3 DC power input ........................................................47
4.4 Ground stud .............................................................49
Page 14

Table of contents
xii
4.5 Analog Phone/Fax interface .................................... 50
4.6 ISDN interface .......................................................... 51
4.7 LAN interface ...........................................................53
4.8 Discrete I/O interface ...............................................55
4.9 L-Band interface ..................................................... 58
Chapter 5 Starting up the system
5.1 Using the SIM card ...................................................59
5.2 Powering the system ................................................ 61
5.3 Entering the SIM PIN for the terminal ......................62
5.4 Operating the system ...............................................64
Chapter 6 Service and repair
6.1 Introduction .............................................................65
6.2 Replacing modules .................................................65
Chapter 7 Troubleshooting
7.1 Reset button ............................................................75
7.2 Status signaling .......................................................78
7.2.3 Logging of events .....................................................83
App. A Part numbers
A.1 System units ........................................................... 85
A.2 Spare parts, SAILOR
®
500 FleetBroadband .............. 86
A.3 Spare parts, SAILOR
®
250 FleetBroadband ...............87
A.4 Accessories ............................................................. 88
Page 15

Table of contents
xiii
App. B Technical specifications
B.1 Overview ..................................................................89
B.2 SAILOR
®
500 FleetBroadband antenna .....................89
B.3 SAILOR
®
250 FleetBroadband antenna .....................95
B.4 Minimum distance to transmitters. ......................... 100
B.5 SAILOR FleetBroadband terminal ............................ 101
App. C Grounding and RF protection
C.1 Why is grounding required? ....................................109
C.2 General about marine DC systems .......................... 110
C.3 General about marine grounding ............................ 112
C.4 Grounding Recommendations ................................. 114
C.5 Alternative grounding for steel hulls ....................... 116
C.6 Alternative grounding for aluminum hulls .............. 118
C.7 Alternative grounding for fiberglass hulls ...............120
C.8 Alternative grounding for timber hulls ....................122
C.9 Separate ground cable ............................................124
C.10 RF interference .......................................................128
C.11 Electrostatic Discharge ............................................129
Glossary ........................................................................................ 131
Index ........................................................................................135
Page 16

Table of contents
xiv
Page 17

1
Chapter 1
1111
System units
System units 1
1.1 Introduction
The basic system consists of three units: The terminal, the antenna and the IP
handset with cradle.
There are two different types of antennas, depending on whether you have a
SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband system or a SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband system.
1.2 Terminal
The terminal – which contains the primary electronic parts – is designed for
wall or desktop installation.
The terminal supplies 18-29 V DC to the antenna through a single coaxial
cable.
The DC input for the terminal is designed for both 24 V DC and 12 V DC power
supply.
Page 18

Chapter 1: System units
2SAILOR
®
500 FleetBroadband antenna
1.3 SAILOR®500 FleetBroadband antenna
The SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna is a BGAN Class 8 mechanical
tracking antenna, consisting of a stabilized antenna with RF-unit, antenna
control unit and GPS antenna. All communication between the antenna and
terminal passes through a single coaxial cable. The antenna unit is protected
by a fibre glass radome.
Page 19

Chapter 1: System units
SAILOR®250 FleetBroadband antenna 3
1111
System units
1.4 SAILOR®250 FleetBroadband antenna
The SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband antenna is a BGAN Class 9 mechanical
tracking antenna. All communication between the antenna and terminal
passes through a single coaxial cable. The antenna unit is protected by a
thermo-plastic radome.
Page 20

Chapter 1: System units
4 IP handset and cradle
1.5 IP handset and cradle
1.5.1 Thrane & Thrane IP handset
Besides the normal functions of an IP handset, the Thrane & Thrane IP
handset also provides a user interface for the SAILOR FleetBroadband system.
The IP handset connects to the LAN interface of the terminal, and is power
supplied with Power over Ethernet (PoE) through the LAN interface.
For further information on the IP handset, refer to the user manual for the
Thrane & Thrane IP handset.
Page 21

Chapter 1: System units
IP handset and cradle 5
1111
System units
1.5.2 Thrane & Thrane IP cradle
The IP cradle serves as a holder for the IP handset. It is power supplied from
the terminal using Power over Ethernet (PoE). The cradle is connected to the
handset with a coil cord and to the terminal with a standard LAN cable.
Page 22

Chapter 1: System units
6 IP handset and cradle
Page 23
7
Chapter 2
2222
Installing the system
Installing the system 2
2.1 Unpacking
Unpack your SAILOR FleetBroadband system and check that the following
items are present:
• TT-3738A SAILOR FleetBroadband terminal
• TT-3052A SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna or
TT-3050A SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband antenna
• TT-3670A IP handset and cradle
• Basic cable support kit
•Power cable
• Antenna cable
•LAN cable
• I/O connector
•User manual
• Installation manual (this manual)
•Quick guide
Inspect all units and parts for possible transport damage.
Note
For information on how to install the IP handset and cradle, refer to
the user manual for the handset.
Page 24
Chapter 2: Installing the system
8 Placing the antenna
2.2 Placing the antenna
2.2.1 Obstructions
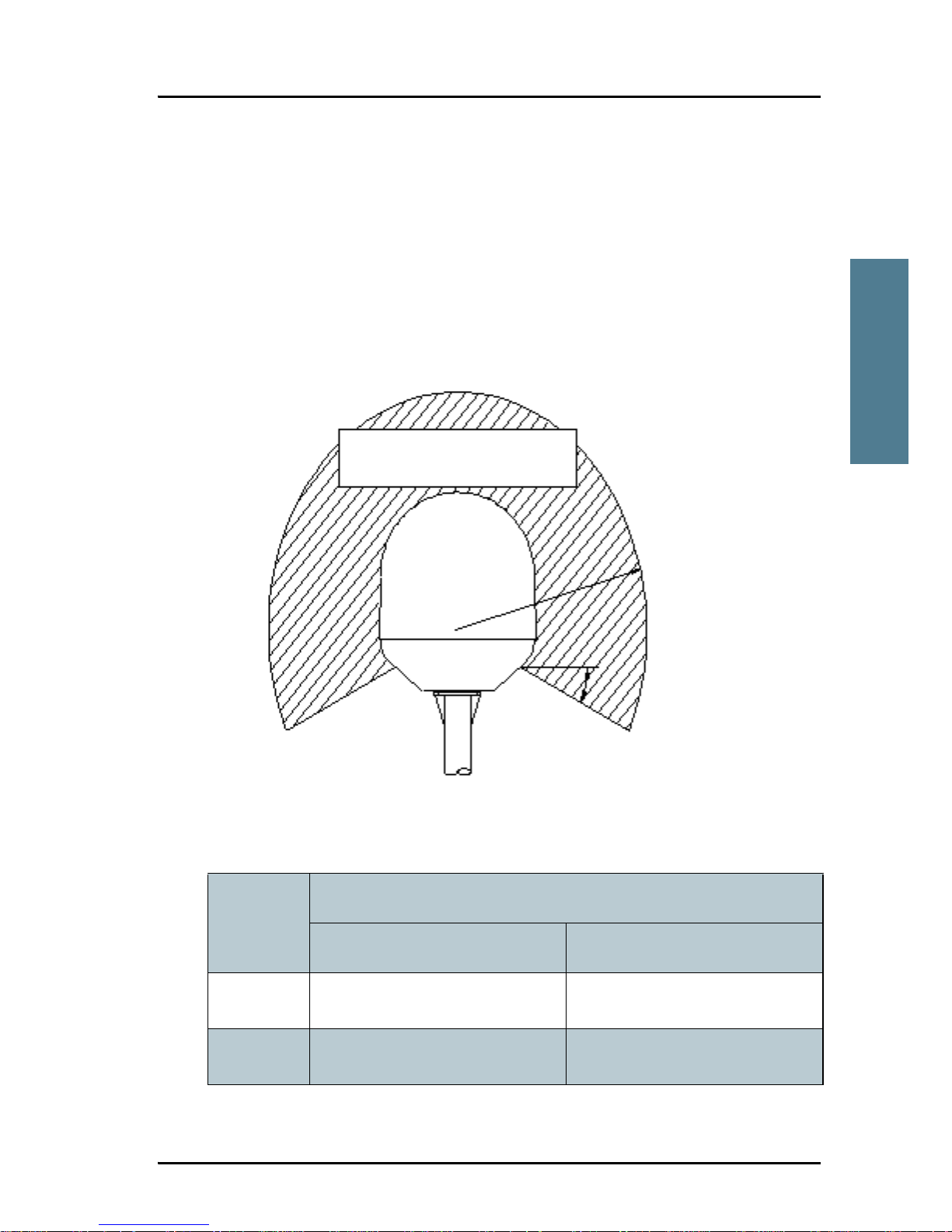
The antenna rotates 360° and down to –25° for the
SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband and -60° for the SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband in
pitch and roll, to allow for continuous pointing even in heavy sea conditions.
Any obstructions within this volume can cause signal degradation.
The amount of degradation depends on the size of the obstruction and the
distance from the antenna. As a rule of thumb any obstruction that subtends
an angle of less than 3° at the antenna has limited effect. The table below
gives a guideline for obstruction sizes, which will cause limited degradation.
Distance of
Obstruction
Size of Obstruction
3m 16cm
5m 26 cm
10 m 52 cm
20 m 104 cm
Page 25
Chapter 2: Installing the system
Placing the antenna 9
2222
Installing the system
2.2.2 Radiation hazard
The SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna radiates 22 dBW EIRP. This
translates to a minimum safety distance of 1.3 m from the antenna while it is
transmitting, based on a radiation level of 10 mW/cm
2
.
The SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband antenna radiates 16.1 dBW EIRP. This
translates to a minimum safety distance of 0.6 m from the antenna while it is
transmitting, based on a radiation level of 10 mW/cm
2
.
For higher radiation levels, see the table below.
Radiation
level
Distance
SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband
100 W/m
2
0.4 m 0.2 m
10 W/m
2
1.3 m 0.6 m
MICROWAVE RADIATION
NO PERSONNEL
based on 10 W/m
2
SAILOR 500:
Safety distance:
1.3 m, 10 W/m
2
SAILOR 250:
0.6 m, 10 W/m
2
25° for SAILOR 500
60° for SAILOR 250
Page 26

Chapter 2: Installing the system
10 Placing the antenna
2.2.3 Interference
Overview
The antenna must be mounted as far away as possible from the ship’s radar
and high power radio transmitters (including other Inmarsat based systems),
because they may compromise the antenna performance. RF emission from
radars might actually damage the antenna.
The SAILOR FleetBroadband antenna itself may also interfere with other radio
systems. Especially other Inmarsat systems and GPS receivers with poor
frequency discrimination are vulnerable to the radiation generated by the
SAILOR FleetBroadband antennas.
Page 27
Chapter 2: Installing the system
Placing the antenna 11
2222
Installing the system
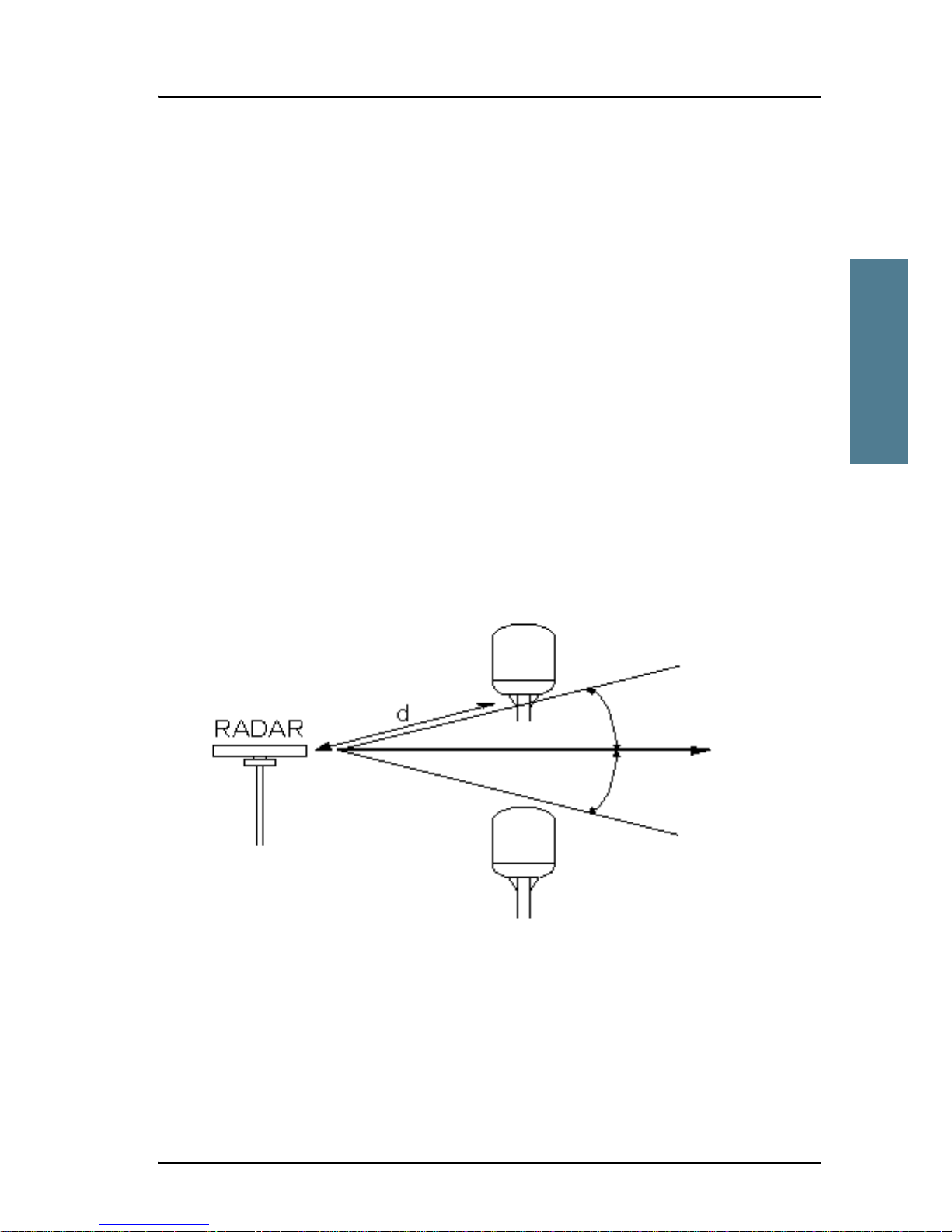
Radar
It is difficult to give exact guidelines for the minimum distance between a
radar and the antenna because radar power, radiation pattern, frequency and
pulse length/shape vary from radar to radar. Further, the antenna is typically
placed in the near field of the radar antenna and reflections from masts, decks
and other items in the vicinity of the radar are different from ship to ship.
However, it is possible to give a few guidelines:
Since a radar radiates a fan beam with a horizontal beam width of a few
degrees and a vertical beam width of up to +/- 15°, the worst interference can
be avoided by mounting the antenna at a different level – meaning that the
antenna is installed minimum 15° above or below the radar antenna. Due to
near field effects the benefit of this vertical separation could be reduced at
short distances (below approximately 10 m) between radar antenna and the
SAILOR FleetBroadband antenna. Therefore it is recommended to ensure as
much vertical separation as possible when the SAILOR FleetBroadband
antenna has to be placed close to a radar antenna.
Min. 15°
Min. 15°
Page 28
Chapter 2: Installing the system
12 Placing the antenna
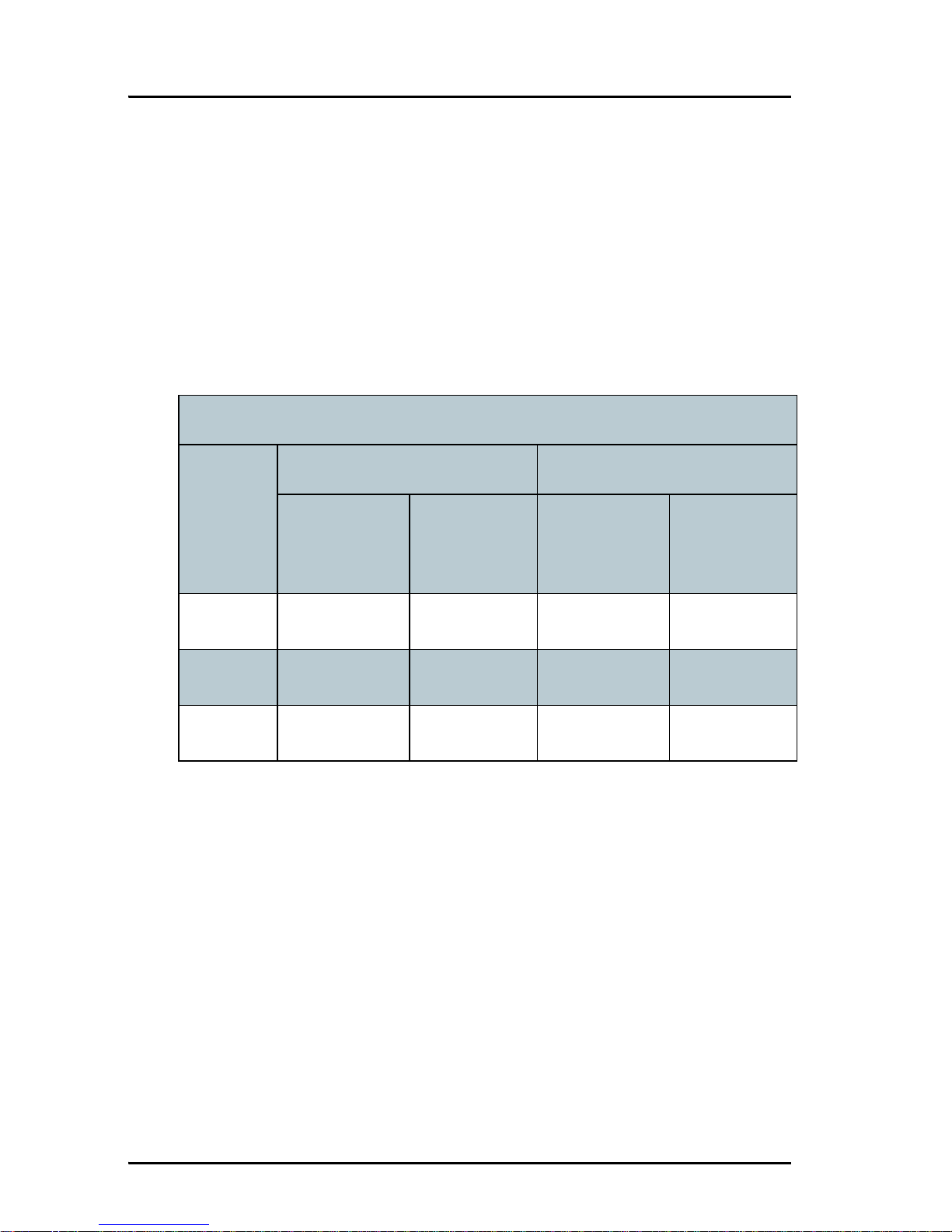
Radar distance
The minimum acceptable separation (d min.) between a radar and the
antenna is determined by the radar wavelength/frequency and the power
emitted by the radar. The tables below show some “rule of thumb” minimum
separation distances as a function of radar power at X and S band. If the d
min. separation listed below is applied, antenna damage is normally avoided.
“d min.” is defined as the shortest distance between the radar antenna (in any
position) and the surface of the SAILOR FleetBroadband antenna.
X-band (~ 3 cm / 10 GHz) damage distance
Radar
power
SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband
d min. at 15°
vertical
separation
d min. at 60°
vertical
separation
d min. at 15°
vertical
separation
d min. at 60°
vertical
separation
0 – 10 kW 0.8 m 0.4 m 0.8 m 0.4 m
30 kW 2.4 m 1.2 m 2.4 m 1.2 m
50 kW 4.0 m 2.0 m 4.0 m 2.0 m
Page 29
Chapter 2: Installing the system
Placing the antenna 13
2222
Installing the system
The separation distance for C-band (4-8 GHz) radars should generally be the
same as for X-band radars.
Interference
Even at distances greater than “d min.” in the previous section the radar
might still be able to degrade the performance of the SAILOR FleetBroadband
system.
The presence of one or more X-band radars within a radius up to 100 m could
cause a minor degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio during high speed and
data calls. The degradation will be most significant at high radar pulse
repetition rates.
As long as receiving conditions are favorable, this limited degradation is
without importance. However, if receiving conditions are poor – e.g. due to
objects blocking the signal path, heavy rainfall or icing, low satellite elevation
and violent ship movements – the small extra degradation due to the radar(s)
could cause poor call quality. A voice call might become noisy and perhaps fail
while a data connection might decrease in speed and performance.
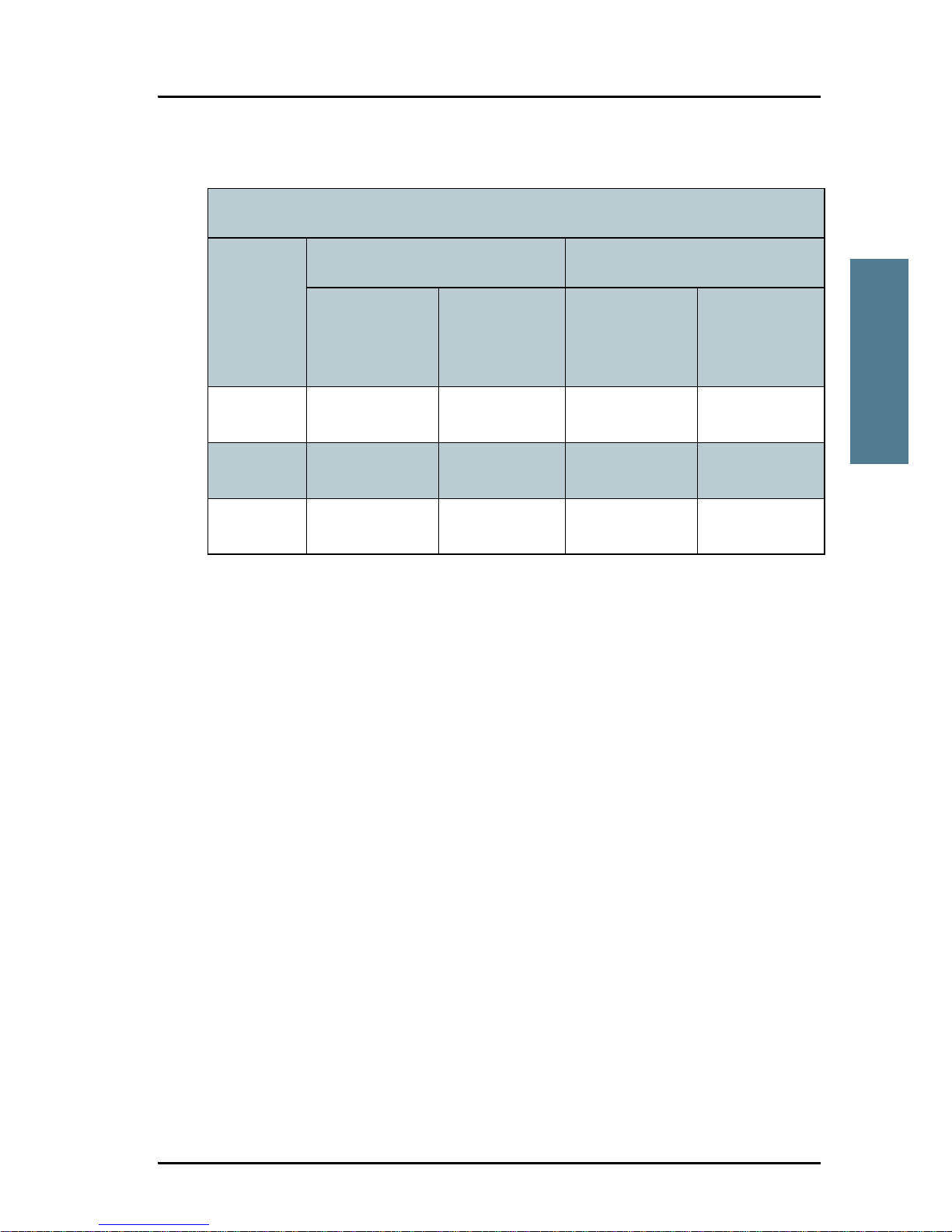
S-band (~ 10 cm / 3 GHz) damage distance
Radar
power
SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband
d min. at 15°
vertical
separation
d min. at 60°
vertical
separation
d min. at 30°
vertical
separation
d min. at 75°
vertical
separation
0 – 10 kW 0.4 m 0.2 m 0.4 m 0.2 m
30 kW 1.0 m 0.5 m 1.0 m 0.5 m
50 kW 2.0 m 1.0 m 2.0 m 1.0 m
Page 30

Chapter 2: Installing the system
14 Placing the antenna
The presences of S-band radar(s) are unlikely to cause any performance
degradation – as long as the minimum distances (d min.) listed in the previous
section are applied.
It is strongly recommended that interference free operation is verified
experimentally before the installation is finalized.
Other Inmarsat systems
Recommended minimum safe distance to other Inmarsat antennas is 10 m.
GPS receivers
Good quality GPS receivers will work properly very close to the antenna typically down to one meter outside the main beam, and down to a few meters
inside the main beam. However, simple GPS receivers with poor frequency
discrimination could be affected at longer range (typically 10 m). It is always
recommended to test the GPS performance before the installation is finalized.
Other transmitters
See Minimum distance to transmitters. on page 100 in Appendix B for
minimum recommended distance to transmitters in the frequency range below
1000 MHz.
Other precautions
Do not place the antenna close to a funnel, as smoke deposits are corrosive.
Furthermore, deposits on the radome can degrade performance.
Caution! The antenna must never be installed closer to a radar
than “d min.” - even if experiments show that
interference free operation can be obtained at shorter
distances than “d min.” in the previous section.
Page 31

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Placing the antenna 15
2222
Installing the system
2.2.4 Antenna mast design
Overview
The antenna mast must be designed to carry the weight of the antenna unit,
which is approximately
• 16 kg (+ the weight of the mast flange) for the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband
antenna and
• 3.9 kg (+ 1.1 kg for the mast mount kit) for the SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband
antenna.
The mast must also be able to withstand onboard vibrations and wind forces
up to 108 knots on the radome, even in icing conditions.
The SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband and SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband antennas
use different methods for mast mounting. The following sections describe the
the two methods separately.
SAILOR®500 FleetBroadband antenna mast flange
The top of the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna mast should be fitted with
a flange with holes matching the bushes in the radome.
The flange thickness must be at least 10 mm. The antenna is to be mounted on
the flange by means of 4 M10 bolts. The length of the bolts must be such that
they engage into the bushes of the radome with minimum 6 mm and
maximum 12 mm. Drill a hole in the centre of the flange for the antenna cable
and for drainage from the radome. For recommended dimensions of the
flange, see Outline dimensions, SAILOR 500 flange on page 94 in Appendix B.
Important
Avoid sharp edges where the flange is in direct contact with the
radome. Round all edges as much as possible to avoid
damaging the surface of the radome.
Page 32

Chapter 2: Installing the system
16 Placing the antenna
SAILOR®250 FleetBroadband antenna mast mounting
Mast mount kit:
The top of the SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband antenna mast should be fitted with
the dedicated mounting kit, see SAILOR
®
250 FleetBroadband mast mount kit
on page 88.
Assemble the mast mount kit according to the assembly instruction included
with the kit.
The mast mount kit interfaces to a 1½” pipe (OD 48.3 mm). If the supplied
plastic sleeve is omitted, a maximum diameter OD of 52 mm can be used.
Custom mast mounting:
For a custom mast mounting, use 4 M6 bolts (A4) in the threaded bushes on
the 175.4 mm diameter circle in the bottom of the antenna (see outline
drawing SAILOR
®
250 FleetBroadband antenna on page 99). The length of the
bolts must be such that they engage into the bushes of the radome with min.
6 mm and max. 12 mm. No drainage hole is necessary. Drill a hole for the
cable or use an angled connector.
Page 33

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Placing the antenna 17
2222
Installing the system
Mast length and diameter
The placement of the antenna must ensure a rigid structural connection to the
hull or structure of the ship. Parts of the ship with heavy resonant vibrations
are not suitable places for the antenna.
A small platform or short mast shall provide rigid support for the antenna
fastening bolts and a rigid interface to the ship.
If it is necessary to use a tall mast, use the tables on page 19 and page 20 to
obtain the maximum free length of the mast. Note that these values depend on
rigid antenna-ship interfaces. The cross-sectional properties and the
corresponding maximum free length give a natural frequency above 30 Hz.
It is recommended to shorten the mast length as much as possible to obtain
higher frequencies. Alternatively, mount stays or wires to stabilize the mast
further.
Note
The hole in the lower part of the mast is necessary for drainage and
ventilation for the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna. Please refer
to Condensation, SAILOR
®
500 FleetBroadband on page 24.
Free mast length (m)
OD (mm)
Page 34

Chapter 2: Installing the system
18 Placing the antenna
The tables in the next sections give some suggested design values for the free
part of the mast (shown on the previous page).
High masts or installations on ships with high vibration levels should be
further stabilized by stays or wires from the mast flange. Also mount vibration
isolators between the flange and the radome, as described in Vibration,
SAILOR
®
500 FleetBroadband on page 25. For SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband,
the vibration isolators are included in the Mast mount kit.
Note
The tables list the values for steel masts.
For aluminium masts, the free mast length is reduced to 75% of the
values for steel.
Note
Stays and rigid masts can still not prevent vertical vibration if the
mast is attached to a deck plate that is not rigid. Make every effort to
mount the mast on a surface that is well supported by ribs. If this is
not possible, provide extra deck plate propping.
Page 35

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Placing the antenna 19
2222
Installing the system
SAILOR®500 FleetBroadband antenna mast length
The below table shows the values for a SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna
mast without stays or wires. Note that these values are only guidelines always consider the environment and characteristics of the ship before
deciding on the mast dimensions.
OD
(mm)
Wall
Thickness
(mm)
Weight
(kg/m)
Inertia
(X10
6
mm4)
Max. free mast length
(steel), m
88.9 4.05 8.47 0.974 < 0.9
88.9 4.85 10.1 1.14
100 5 11.7 1.69 < 1.0
101.6 5 11.9 1.77
114.3 4.5 12.1 2.34 < 1.2
114.3 5.4 14.4 2.75
139.7 4.85 16.1 4.68 < 1.4
139.7 5.4 17.9 5.14
165.1 4.85 19.2 7.85 < 1.6
165.1 5.4 21.3 8.65
200
a
a. The diameter of the circle where the bolts are to be mounted on the antenna is
Ø183.8. Since the mast diameter is larger, you must use a tapered end on the
mast, or find other means of accessing the mounting bushes.
52414.6 < 2.0
200
a
10 46.9 27
300
a
7.5 5 4.1 73.75 < 2 .7
300
a
15 105.4 136.7
Page 36

Chapter 2: Installing the system
20 Placing the antenna
SAILOR®250 FleetBroadband antenna mast length
The below table shows the values for a SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband antenna
mast without stays or wires. Note that these values are only guidelines always consider the environment and characteristics of the ship before
deciding on the mast dimensions.
The mast mount kit interfaces to a 1½” tube (OD 48.3 mm - absolute maximum
OD 52 mm). Masts with larger diameters must be tapered and the upper part
of the tube (approximately 50 mm) must have a diameter of 1½”.
OD
(mm)
Wall
Thickness
(mm)
Weight
(kg/m)
Inertia
(X10
6
mm4)
Max. free mast length
(steel), m
48.3 3.25 3.61 0.117 < 0.6
48.3 4.05 4.43 0.139
50 3.00 3.48 0.123
60.3 3.65 5.10 0.262 <0.8
60.3 4.50 6.17 0.309
76.1 3.65 6.80 0.547 < 1.0
76.1 4.50 7.90 0.651
88.9 4.05 8.47 0.974 < 1.1
88.9 4.85 10.10 1.140
Page 37

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the antenna 21
2222
Installing the system
2.3 Installing the antenna
2.3.1 Antenna grounding
You may ground the antenna using the mounting bolts.
If the antenna cannot or should not be electrically connected directly to the
mounting surface, you can use a separate grounding cable to make the
connection between the antenna and the common ground to which the
terminal is also connected. For example, you can connect a separate
grounding cable when vibration isolators are used at the mounting bolts.
To obtain a good ground connection, the metal underneath the head of at
least one bolt must be clean of insulating protective coating and a serrated
washer should be used. After tightening the bolts we recommend that you seal
the area suitably in order to avoid corrosion of the grounding point.
Use stainless steel bolts and washers.
For further grounding information read Appendix C Grounding and RF
protection on page 109.
2.3.2 Antenna cables
Guidelines
A coaxial cable for connection between the antenna and terminal is delivered
with the system. If you need a different cable, make sure that the cable meets
the requirements. Preferably choose one of the cable types in Recommended
antenna cables on page 22.
Select a suitable area for installation of the terminal, antenna and cradle.
Where the cables are exposed to mechanical wear - on deck, through
bulkheads, etc. - protect the cables with steel pipes. Otherwise, follow
standard procedures for cabling in ship installations.
The maximum allowed RF-loss in the antenna cable is 20 dB at 1660 MHz. This
is to ensure the performance of the system.
Page 38

Chapter 2: Installing the system
22 Installing the antenna
Recommended antenna cables
The table below shows recommended cable types and maximum cable lengths
for both SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband and SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband.
Check in the data sheet from the cable supplier that both the RF- attenuation
and the DC-resistance are kept within the maximum specified values:
• Antenna cable RF-attenuation max: 20 dB incl. connector at L-band.
• Antenna cable modem-attenuation max: 4 dB at 54 MHz, 3 dB at 36 MHz.
• Antenna cable loop DC-resistance max: 1 Ω.
Also ensure that the specified minimum bending radius is respected. If this is
not the case, the loss in the cable will increase. Check the instruction from the
cable supplier.
Cable Type Absolute maximum length
G02232-D 6 m
RG223-D 25 m
RG214/U 50 m
S 07272B-05 95 m
Page 39

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the antenna 23
2222
Installing the system
2.3.3 Important mounting notes
Line of sight
Place the antenna with free line of sight in all directions to ensure proper
reception of the satellite signal. Do not place the antenna close to large
objects that may block the signal.
Water intrusion
After having connected the antenna cable to the antenna - ensure that the
connector assembly is properly protected against seawater and corrosion. As a
minimum, use self-amalgamating rubber.
If possible, install the radome such that direct spray of sea water is avoided.
It is recommended not to use pneumatic tools for cleaning the radome,
specially at a short distance and directly at the split between top and bottom.
Make sure the requirements to drainage are met. See Condensation,
SAILOR
®
500 FleetBroadband on page 24.
Page 40

Chapter 2: Installing the system
24 Installing the antenna
Condensation, SAILOR®500 FleetBroadband
In some cases there will be condensation inside the radome. The gasket in the
bottom center of the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna is designed to lead
any water away from the radome.
Make sure this draining gasket is not blocked. If the antenna is mounted on a
pole, make sure the pole is hollow inside and open at the bottom, allowing
water from the gasket to escape and providing ventilation for the antenna.
If the antenna is mounted on a flat surface, use 10 mm spacers (washers) at
each bolt so that the gasket in the center of the antenna bottom is free and
water can escape.
Gasket with drainage
10 mm spacer
Antenna bottom
Page 41

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the antenna 25
2222
Installing the system
Vibration, SAILOR®500 FleetBroadband
Install the antenna where vibrations are limited to a minimum. If you cannot
avoid heavy vibrations, we recommend using vibration isolators between the
hull/mast and the radome. E.g. use Paulstra isolators (530903 11) together
with Paulstra washers. Mount the isolators as shown in the drawings below.
Always use all 4 screws when installing. It is recommended to use screws of
A4 quality / stainless steel.
Note
The mounting bolts alone cannot be used for grounding the antenna
when the isolators are mounted. If the antenna should be grounded,
you can use a separate grounding cable. For further information, see
Grounding and RF protection on page 109.
Page 42

Chapter 2: Installing the system
26 Installing the antenna
2.3.4 Mounting the antenna
Overview
The radome can now be installed on the ship with 4 stainless steel bolts
fastened to the hull or to a mast.
For information on mast mounting, see Antenna mast design on page 15.
Mounting the SAILOR®500 FleetBroadband antenna onto the hull
Make sure the antenna has line of sight to the satellites. When the antenna is
mounted directly on the hull, it may be difficult to obtain line of sight,
especially down to -25°, which is the maximum rotation angle (pitch and roll)
for the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna.
Use M10 bolts for mounting the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna.
The bolt thread must not penetrate more than 12 mm (or 8 turns of the bolt) and not less than 6 mm (or 4 turns of the bolt)- into the threaded part of the
bushes in the radome. Fasten the bolts with 25 ±5 Nm torque.
The only electrical connector is a single N-connector in the center bottom of
the radome.
Mounting the SAILOR®250 FleetBroadband antenna onto the hull
Make sure the antenna has line of sight to the satellites. When the antenna is
mounted directly on the hull, it may be difficult to obtain line of sight,
especially down to -60°, which is the maximum rotation angle (pitch and roll)
for the SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband antenna.
Use M6 bolts for mounting the SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband antenna.
The bolt thread must not penetrate more than 12 mm (or 8 turns of the bolt) and not less than 6 mm (or 4 turns of the bolt)- into the threaded part of the
bushes in the radome. Fasten the bolts with 7-8 Nm torque.
The only electrical connector is a single TNC-connector in the bottom of the
radome.
Page 43

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Placing the terminal 27
2222
Installing the system
2.4 Placing the terminal
2.4.1 Where to place the terminal
Temperature conditions
The terminal must be placed in a ventilated area with free space around all
sides of the unit, except the bottom side.
Ambient temperature range is –25° to +55°C.
If the terminal is installed in a location where the ambient temperature may
exceed 50°C, we recommend placing the terminal where unintentional contact
is avoided. If the maximum ambient temperature does not exceed 50°C, the
terminal can be placed in a public area.
Grounding access
The terminal is designed with a cabinet for bulkhead or desktop installation.
The cabinet is equipped with mounting brackets, making it possible to secure
the unit on a bulkhead.
See Outline dimensions, terminal on page 104 in Appendix B.
Important
The terminal must be placed in an area where access to the
hull or equivalent grounding can be reached within 0.5 m.
Page 44

Chapter 2: Installing the system
28 Installing the terminal
2.5 Installing the terminal
2.5.1 Grounding the terminal
Antenna cable
The antenna is connected to the terminal by means of a coax cable.
For the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna the coax cable is connected with
a TNC connector at the terminal end and an N connector at the antenna end.
For the SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband antenna the coax cable is connected with
a TNC connector at both ends.
For information on antenna grounding, see Antenna grounding on page 21.
At the terminal end, it is strongly recommended to ground the antenna cable.
• If you are using the Extended cable support for the terminal the TNC
connector is grounded through the cable support, which must be
connected to the hull or other common ground. For further information on
the Extended cable support, see Mounting the Extended cable support on
page 33.
• If you are not using the Extended cable support, it is still strongly
recommended to connect the antenna cable to common ground at the
terminal end. Use a short coax cable from the terminal to the grounding
point, where the short cable is connected to the antenna cable.
Page 45

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the terminal 29
2222
Installing the system
Ground stud
To ensure that the terminal is grounded – also if the cable is disconnected
from the terminal, connect an extra ground wire to the ground stud on the
terminal. This ground wire must be a heavy wire or braid cable with a larger
diameter than the coax cable. The ground stud is located next to the power
switch.
Extending the ground plane
In some cases it is not possible to access the hull and at the same time place
the terminal in a suitable place.
A way to insure good grounding and at the same time make it possible to
ground the coax cable - is to extend the ship ground plane by means of copper
foil. The maximum length of the foil is determined by the width of the foil.
Copper foil 5 cm wide: Max 50 cm
Copper foil 10 cm wide: Max 100 cm
Copper foil 20 cm wide: Max 200 cm
Ground stud
Note
The foil must be at least 0.1 mm thick.
Page 46

Chapter 2: Installing the system
30 Installing the terminal
Connect the foil to the hull by plenty of screws or hard–soldering. Run the foil
past the place where the short antenna cable is to be grounded and mount the
grounding kit on top of the foil.
For further grounding information read Appendix C Grounding and RF
protection on page 109.
2.5.2 Cable support systems
Thrane & Thrane offers two cable support systems.
•The Basic cable support comes with the terminal as part of the delivery. It
is a simple system to which you can secure your cables using cable strips.
For information on how to mount the Basic cable support, see the next
section Mounting the Basic cable support.
•The Extended Cable support is longer than the Basic cable support, and
has connectors for the cables, providing a better ground connection. For
information on how to mount the Extended cable support, see Mounting
the Extended cable support on page 33.
Page 47

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the terminal 31
2222
Installing the system
2.5.3 Mounting the Basic cable support
The Basic cable support comes with the terminal as part of the delivery.
When mounted on the terminal the Basic cable support offers a number of
holders to which you can secure the cables from the terminal, using cable
strips.
To mount the Basic cable support, do as follows:
1. Remove the two rubber feet from the bottom of the terminal at the
connector panel end. The mounting bushes are underneath the rubber
feet.
Page 48

Chapter 2: Installing the system
32 Installing the terminal
2. Fasten the Basic cable support to the two mounting bushes close to the
connector panel on the terminal, using two M4 x 6 mm countersunk
screws.
3. Install the terminal as described in Installing the terminal on a bulkhead
on page 34 or Installing the terminal on a desktop on page 36.
Page 49

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the terminal 33
2222
Installing the system
2.5.4 Mounting the Extended cable support
The Extended cable support is available
from Thrane & Thrane. For part number,
see Cable support on page 88.
The Extended cable support offers
connectors and grounding for the
antenna cable, as well as a number of
holders to which you can secure the
cables from the terminal, using cable
strips.
To mount the Extended cable support, do
as follows:
1. Fasten the cable support to the terminal from the bottom, using the screws
in the Extended cable support kit.
2. Install the terminal with the cable support as described in the following
sections.
Page 50

Chapter 2: Installing the system
34 Installing the terminal
2.5.5 Installing the terminal on a bulkhead
Terminal with no cable support
Do as follows to mount the terminal on a bulkhead:
1. Insert four screws through the holes in the mounting bracket and into the
mounting surface. If the mounting surface is used for grounding, make
sure that you have a good electrical connection to the surface.
2. Connect all cables.
Make sure that the grounding requirements are met. See Grounding and
RF protection on page 109.
Page 51

Chapter 2: Installing the system
Installing the terminal 35
2222
Installing the system
Terminal with Basic cable support
First mount the Basic cable support on the terminal as described in Mounting
the Basic cable support on page 31.
1. Mount the terminal with the Basic cable support on the bulkhead by
inserting four screws through the holes in the mounting bracket and into
the mounting surface.
2. Connect all cables.
Make sure that the grounding requirements are met. See Grounding and
RF protection on page 109.
3. Secure the cables to the cable support using cable strips.
Terminal with Extended cable support
First mount the Extended cable support on the terminal as described in
Mounting the Extended cable support on page 33.
1. Mount the Extended cable support with the terminal on the bulkhead by
inserting six screws through the holes in the Extended cable support and
into the mounting surface.
2. Connect the short cables between the terminal and the cable support.
3. Connect all other cables.
Make sure that the grounding requirements are met. See Grounding and
RF protection on page 109.
4. Secure the cables to the cable support using cable strips.
Page 52

Chapter 2: Installing the system
36 Installing the terminal
2.5.6 Installing the terminal on a desktop
Four rubber feet make the terminal well suited for desktop installation. Simply
place the terminal on a desktop and connect all cables. Make sure the
grounding requirements are met. See Grounding and RF protection on
page 109.
If required, fasten the terminal to the desktop with four screws, as described in
the previous section Installing the terminal on a bulkhead.
Page 53

37
Chapter 3
3333
Connecting power
Connecting power 3
3.1 Power source
There are different options for the power supply:
• The 24 V DC ship supply provides power for the terminal.
• A 12 V DC supply provides power for the terminal. Be aware that the
maximum allowed source impedance is much lower for a 12 V DC supply
than for a 24 V DC supply.
• A 230 V AC supply provides power through an AC/DC power supply.
Be aware of high start-up peak current: 20 A at 24 V, 5 ms.
The terminal is equipped with an internal 20 A Fuse, so no external fuse is
necessary in order to protect the terminal. However, in order to avoid short
circuit in the power cable/connector, the ships DC outlet should be protected
by a 30 A fuse or circuit breaker.
Page 54

Chapter 3: Connecting power
38 Power cable selection
3.2 Power cable selection
3.2.1 Source impedance
The length of the terminal power cable depends on the type of cable used and
the source impedance of the ship’s DC power installation.
The maximum allowed source impedance depends on the utilization of the
power range of the terminal DC input (10.5 - 32 V DC; 14 - 5.5 A).
Select a power outlet from the ship’s DC system, and measure the source
impedance of the ship installation as described in Measuring the ship source
impedance on page 107 in Appendix B.
For further recommendations on power cable selection, see the next section.
Note
If the total source impedance is higher than the limits stated in this
section, the terminal may start to on/off oscillate.
Page 55

Chapter 3: Connecting power
Power cable selection 39
3333
Connecting power
3.2.2 Power cable recommendations
Overview
The terminal is delivered with a power cable, which can be extended
according to the recommendations below:
When extending the power cable, positive and negative supply wires must be installed
closely together side by side to keep cable inductance low.
Ensure that cable inductance for the selected cable at the desired length is below the
50 μH requirement.
If you are going to use the Remote on/off function, also extend the two wires (green
and orange) used for this function. For further information, see Remote on/off on
page 43.
Red: +
Black: -
Page 56

Chapter 3: Connecting power
40 Power cable selection
Calculating the maximum power cable extension
For 24 V DC operation, the total impedance must be max. 500 mΩ, including
the ship’s source impedance.
For 12 V DC operation, the total impedance must be max. 85 mΩ, including
the ship’s source impedance.
The total impedance is made up of the following:
• the ship’s source impedance
• the cable impedance of the supplied power cable, including the
impedance in the joint of the two cables. In the following example, the
impedance of the cable and joint is set to 10 mΩ (1 m power cable). Note
that if the cable length or type is changed, the impedance will change
accordingly.
• the extension cable impedance.
To calculate the maximum cable extension, do as follows:
1. First measure the ship’s source impedance as shown in Measuring the
ship source impedance on page 107.
2. Then find the resistance per meter for the cable type you are going to use.
For 4 mm
2
/AWG 11, the value is 4 mΩ/m at 20°C
For 1.5 mm
2
/AWG 15, the value is 10 mΩ/m at 20°C
For other cable types, refer to the data sheet for the cable.
3. Calculate the maximum allowed impedance in the extension cable as
follows:
Max. allowed impedance in extension cable = max. total impedance (measured source impedance + impedance of the supplied cable).
4. Then calculate the max. extension cable length as follows:
Max. impedance in extension cable (from
step 3)
Max. length = 0.5 x impedance/meter (from step 2)
The length is multiplied by 0.5 above because there are two conductors in
the cable. If you need more length, you can double the maximum allowed
Page 57

Chapter 3: Connecting power
Power cable selection 41
3333
Connecting power
length by connecting two cables in stead of one, or you can use a cable
with a larger diameter.
Example:
Ship supply voltage: 12 V DC
Ship source impedance (measured): 50 mΩ
Extension cable type: 4 mm
2
(AWG 11)
85 m
Ω - (50 mΩ + 10 mΩ)
Max. cable extension = 0.5 x 4 mΩ/m = 3.12 m
Page 58

Chapter 3: Connecting power
42 To connect power
3.3 To connect power
Do as follows:
1. Connect the power cable to the ship’s 24 V DC supply according to the
recommendations in the previous section.
2. Connect the D-sub connector on the power cable to the DC input connector
on the terminal.
For information on pin-out, see DC power input on page 47.
For specifications of the DC input on the terminal, see SAILOR FleetBroadband
terminal on page 101.
Note
If you need a remote on/off function, connect the wires from pin
2 (green wire) and 5 (orange wire) in the power connector to a
switch or similar which can connect/disconnect these two pins.
See the next section for details.
Page 59

Chapter 3: Connecting power
Remote on/off 43
3333
Connecting power
3.4 Remote on/off
The terminal has a remote on/off function. When the terminal power switch is
in the “on” position you can remote control the power function.
By installing a switch that can short-circuit the “Remote on/off” pins (2 and 5)
in the power connector you can power the terminal on or off with this “remote
switch”.
When pins 2 and 5 are not short-circuited and valid input power is present the
terminal is powered on, provided the Power switch is in the “on” position.
For pin-out for the power connector and a description of the wire colors in the
power cable, see Pin-out on page 48.
Page 60

Chapter 3: Connecting power
44 Remote on/off
Page 61

45
Chapter 4
4444
Hardware interfaces
Hardware interfaces 4
4.1 The connector panel
The connector panel is placed at one end of the terminal and has the following
connectors:
• 1 L-Band connector for reception of maritime data
• 1 Antenna connector (TNC)
• 2 Phone/Fax connectors
• 1 ISDN connector
• 4 LAN connectors with Power over Ethernet (PoE)
• 1 DC power input connector for connection to 10.5-32 V DC, with remote
on/off
• 1 Input/Output connector with 5 inputs/outputs for external control or
signaling
• 1 ground stud with wing nut
For information on how to connect to a specific interface, see the next
sections.
Page 62

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
46 Antenna interface on terminal
4.2 Antenna interface on terminal
4.2.1 Overview
The antenna interface on the terminal connects to the TT-3052A antenna in
the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband system or to the TT-3050A antenna in the
SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband system.
The antenna connector on the terminal is a TNC female connector placed in
the connector panel.
For information on cables and how to install and connect the antenna, see
Installing the antenna on page 21.
4.2.2 Pin-out
The below drawing shows the TNC female connector in the terminal.
Signal
GND
Page 63

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
DC power input 47
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.3 DC power input
4.3.1 Overview
The DC power input for the terminal is a 10.5 - 32 V DC; 14 - 5.5 A input with a
remote on/off function. The input is protected against reverse polarity. For
information on power recommendations and how to connect, see Connecting
power on page 37. The power connector is a D-sub connector placed in the
connector panel.
Page 64

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
48 DC power input
4.3.2 Pin-out
The power connector is a Mixed D-Sub connector 7W2, control pin male /
power pin male. The below table shows the pin-out for the connector and the
colors of the corresponding wires.
Pin
number
Pin function
Color of wire in
power cable
A1 Vin+ Red
A2 Vin- Black
1 not connected (Black)
2 Remote on/off Green
3 not connected (Brown)
4 not connected (Red)
5 Remote on/off Orange
2 1
5 4 3
A2 A1
Mixed D-Sub connector,
7W2, male
Page 65

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
Ground stud 49
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.4 Ground stud
The terminal has a ground stud with a wing nut. The ground stud is located in
the connector panel and is used for grounding the terminal.
For information on how to ensure proper grounding of the terminal, see
Grounding the terminal on page 28 and Grounding and RF protection on
page 109.
Page 66

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
50 Analog Phone/Fax interface
4.5 Analog Phone/Fax interface
4.5.1 Overview
The terminal has two RJ-11 ports, which can be used for connection of analog
phones, fax machines or analog modems.
4.5.2 Pin-out
The Phone/Fax connectors are RJ-11, 6/4 female connectors. The table and
figure below show the pin-out for the connectors.
Phone/Fax 2
Phone/Fax 1
Pin number Pin function
1-
2 not connected
3Tip
4 Ring
5 not connected
6 -
123456
RJ-11 female connector
Page 67

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
ISDN interface 51
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.6 ISDN interface
4.6.1 Overview
The terminal has one ISDN connector for connecting an ISDN phone or an
ISDN modem. The ISDN interface supports 56/64 kbps data rate. It is
configured as the network side, i.e. Rx is an input and Tx is an output.
Page 68

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
52 ISDN interface
4.6.2 Pin-out
The figure and table below show the connector outline and pin assignments.
Pin number Pin function
1 not connected
2 not connected
3 Rx+ (c) input
4 Tx+ (d) output
5 Tx- (e) output
6 Rx- (f) input
7 not connected
8 not connected
RJ-45 female connector
Page 69

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
LAN interface 53
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.7 LAN interface
4.7.1 Overview
The terminal has four Ethernet LAN ports with Power over Ethernet (PoE). The
Ethernet ports are standard IEEE 802.3 af ports using RJ-45 connectors.
4.7.2 Power over Ethernet (PoE)
One power supply powers all four interfaces with a floating 48 V DC supply
(44 - 57 V DC). Therefore, the interfaces are not galvanically separated from
each other. All Tx signals are DC connected to the Positive PoE Voltage and all
Rx signals to the Negative PoE Voltage.
The total output power from all 4 interfaces is set to 61.2 Watt, so all interfaces
can support devices of power class 1, 2 and 3 (4, 7 and 15.4 Watt).
In case of power hold-up (failure on input power), PoE will be turned off.
Page 70

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
54 LAN interface
4.7.3 Pin-out
The figure and table below show the connector outline and pin assignments.
4.7.4 Connecting an IP handset
To connect the Thrane & Thrane IP handset to the terminal, do as follows:
Connect the cable from the IP cradle to one of the LAN connectors on the
terminal. For information on how to install the IP handset, refer to the user
manual for the handset.
The cable between IP cradle and terminal must be maximum 80 m.
Pin number Pin function
1TxD+ input
(positive PoE)
2 TxD-input
(positive PoE)
3RxD+ output
(negative PoE)
4 not connected
5 not connected
6 RxD- output
(negative PoE)
7 not connected
8 not connected
RJ-45 female connector
Note
If you insert a switch or similar between the cradle and the terminal,
make sure that it conforms to the industry standard IEEE 802.3 af
(using data pairs).
Page 71

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
Discrete I/O interface 55
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.8 Discrete I/O interface
4.8.1 Overview
The terminal has an I/O connector with 5 configurable inputs/outputs.
The connector is a WieCon Type 8513S connector.
A mating I/O connector is included in the delivery.
Page 72

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
56 Discrete I/O interface
4.8.2 Pin-out
The figure and table below show the connector outline and pin assignments.
Pin number Connection Default configuration
a
a. The default functions of the I/O pins are described in the next section.
1 GPIO 1 Radio silence acknowledge
output, active high
2 GPIO 2 Mute input, active high
3 GPIO 3 Radio silence input, active
high
4 GPIO 4 Ringer output, active high
5 GPIO 5 Ignition input
6 Chassis GND
7 DC out 9-15 V DC, 50 mA
8 DC in (ignition input)
12345678
WieCon Type 8513S connector
Page 73

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
Discrete I/O interface 57
4444
Hardware interfaces
4.8.3 Default configuration of I/O pins
The built-in web interface of the terminal offers a page for configuring the I/O
pins.
The default configuration of the I/O pins is as follows:
• Pin 1: Radio silence acknowledge output.
This pin changes state from low to high as soon as deregistration
completes and transmission has stopped as a result of activating pin 3.
• Pin 2: Mute input.
When high (active) the terminal is muted so that the Phone/Fax interface,
the ISDN interface and the IP handsets do not ring, and the Ringer output
on pin 4 is silenced as well. The IP handset is allowed to indicate ringing
in the display. When the pin is low, the terminal is in normal operation.
• Pin 3: Radio silence input.
When high (active) the terminal observes Radio Silence. The terminal
gracefully closes all open connections, and deregisters from the BGAN
network. No transmission is allowed until the pin is deactivated.
• Pin 4: Ringer output.
This pin changes state from low to high when the terminal is notified of an
incoming call from the satellite interface. When the call is answered, or
the caller gives up and releases the call, the pin changes back to low.
• Pin 5: Ignition input.
Normally not used in maritime installations. Use Remote on/off in the
power connector instead.
Pin 7 (non-configurable): Apart from the 5 configurable inputs/outputs, the DC
connector has an additional output pin, pin 7 DC output, which can be
connected to a ringer, relay or similar. The output voltage is 9-15 V, 50 mA.
For information on how to configure the I/O pins, see the user manual for the
SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband and SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband systems.
Page 74

Chapter 4: Hardware interfaces
58 L-Band interface
4.9 L-Band interface
4.9.1 Overview
The terminal has an L-Band output for automatic delivery of maritime
broadcast data. Use a coax cable with an SMA connector to connect a
broadcast receiver for maritime data to the L-band output.
4.9.2 Pin-out
The figure below shows the pin-out for the SMA female connector.
Signal
GND
Page 75

59
Chapter 5
5555
Starting up the system
Starting up the system 5
5.1 Using the SIM card
5.1.1 Inserting the SIM card
The SIM card is provided by your Airtime Provider. Insert the SIM card as
follows:
1. Open the SIM cover in the left
side of the connector panel.
2. Insert the SIM card into the SIM
slot.
Place the card with the gold-
plated side facing up as shown.
3. Press gently until it clicks.
4. Slide the lock in front of the
SIM card.
5. Close the cover for the SIM slot.
Page 76

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
60 Using the SIM card
Removing the SIM card
Remove the SIM card as follows:
1. Open the SIM cover in the left
side of the connector panel.
2. Slide the lock aside.
3. Gently push the SIM card and
let it pop out.
4. Remove the SIM card and
close the cover for the SIM
slot.
Note
When the SIM card is removed, you cannot use the BGAN menu of
the IP handset nor make calls or start data sessions.
Only emergency calls are allowed, and only if permitted by the
network.
However, if you have an administrator user name and password, you
can upload software using the web interface without having a SIM
card. For further information, see the user manual.
Page 77

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
Powering the system 61
5555
Starting up the system
5.2 Powering the system
5.2.1 Switching the terminal on
To switch on the terminal, use
the Power switch in the
connector panel It normally
takes one or two seconds for the
terminal to switch on.
5.2.2 Switching the terminal off
To switch off the terminal, change the position of the Power switch again.
5.2.3 Remote on/off
Alternatively, you may use the Remote on/off function. In this case, leave the
power switch in the On position and switch off the terminal remotely using a
switch or similar connected to the Remote on/off pins in the DC power
interface. For further information, see Remote on/off on page 43.
Caution! When the system is powered on, stay clear of the
antenna! The antenna emits radio frequency energy, not
only when the system is used. Always keep a minimum
distance of 1.3 m from the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband
antenna and 0.6 m from the SAILOR 250 FleetBroadband
antenna.
Note
Wait at least 5 seconds after power off, before trying to power on the
system again.
Page 78

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
62 Entering the SIM PIN for the terminal
5.3 Entering the SIM PIN for the terminal
5.3.1 Overview
You normally have to enter a PIN to use the system. You can enter the PIN
using a standard or ISDN phone, the IP handset or the web interface.
For information on how to connect the handset or computer you are going to
use, refer to the user manual.
5.3.2 Entering the PIN using a phone or IP handset
If you have a phone connected to the terminal, you can use it to enter the PIN
at start up.
Do as follows:
Dial the PIN the same way you would dial a phone number:
• For an analog or ISDN phone:
Pick up the phone. When the terminal is waiting for a PIN, you will hear 2
beeps - pause - 2 beeps - etc.
Dial <PIN> followed by #.
When you hear a “busy” tone or a dialing tone, the PIN has been accepted
and you can hang up or dial a number.
• For an IP handset:
Select the BGAN menu, enter the user name and password for the
terminal. Then enter the PIN for the terminal.
Wrong PIN
Analog phone or ISDN phone: If, instead of the busy tone or dialing tone, you
continue to hear 2 beeps - pause - 2 beeps - etc., it means the PIN was not
accepted. Check that you have the correct PIN and try again.
If a wrong PIN has been entered three times, you will hear 3 beeps - pause - 3
beeps - etc. This means you have to enter the PUK (PIN Unblocking Key)
provided with your SIM card.
Page 79

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
Entering the SIM PIN for the terminal 63
5555
Starting up the system
After entering the PUK, you must enter a new PIN of your own choice (4 to 8
digits long).
Dial the following:
<PUK> * <New PIN> * <New PIN> followed by # or off-hook key.
Example: If the PUK is 87654321 and the new PIN is 1234, dial
87654321 * 1234 * 1234 followed by # or off-hook key.
If you enter 10 wrong PUKs, the SIM card will no longer be functional. Contact
your Airtime Provider for a new SIM card.
IP handset: After having entered the user name and password for the terminal
You have 3 attempts to enter the terminal PIN, before you are asked to enter
the PUK (Pin Unblocking Key). The PUK is supplied with your terminal SIM
card.
Enter the PUK followed by a new PIN of your own choice. The PIN must be
from 4 to 8 digits long.
If you enter a wrong PUK 10 times, the SIM card will no longer be functional,
and you have to contact your BGAN Airtime Provider for a new SIM card.
Entering the PIN using the web interface
If the PIN has not yet been entered when you start up the web interface, the
start-up page will be the PIN page. Enter the PIN and click OK.
For further information on how to enter the PIN using the web interface, see
the user manual.
Page 80

Chapter 5: Starting up the system
64 Operating the system
5.4 Operating the system
5.4.1 General use
The user manual for the SAILOR FleetBroadband systems describes general
use of the system and goes through all the functions of the web interface. It
also contains a brief description of how to use the Thrane & Thrane IP handset
with the terminal.
5.4.2 User interfaces
Overview
The main user interfaces for operation of the system are
• the built-in web interface
• the Thrane & Thrane IP handset
Built-in web interface
The built-in web interface is used for easy configuration and daily use. You
access the web interface from a computer connected to the terminal, using an
Internet browser. No installation of software is needed.
An Administrator password is required to access advanced configuration of
the system.
For further information on the web interface, refer to the user manual for the
SAILOR FleetBroadband systems.
IP handset
Apart from the standard functions of an IP handset, the Thrane & Thrane IP
handset contains a display menu for setting up and using the
SAILOR FleetBroadband system. For further information on the Thrane &
Thrane IP handset, refer to the user manual for the IP handset.
Page 81

65
Chapter 6
6666
Service and repair
Service and repair 6
6.1 Introduction
The Thrane & Thrane SAILOR FleetBroadband systems are designed to operate
without preventive routine maintenance.
Although the system is designed and built very service friendly, we strongly
recommend that any acting service technician is trained specifically on the
product. Repair or repair attempts performed by unqualified personnel may
limit the warranty. The warranty on the system is defined and outlined by the
distributor that supplied the system.
For further information on warranty and service, you may also use the Thrane
& Thrane home page at http://www.thrane.com.
6.2 Replacing modules
6.2.1 Overview
We do not recommend repairing the terminal on board the ship. Replace the
defective unit and have it repaired at a qualified workshop on shore.
Some of the modules in the SAILOR 500 FleetBroadband antenna can be
replaced. See the next sections for details.
Page 82

Chapter 6: Service and repair
66 Replacing modules
6.2.2 Modules in the SAILOR®500 FleetBroadband antenna
Remove the top of the radome to access the antenna modules.
The electronic part of the antenna consists of a number of modules.
The following modules are available as spare parts. See Appendix A.
• HPA Module (High Power Amplifier)
• ATB/LNA Module (Antenna Tracking Board/Low Noise Amplifier)
• GPS module (Global Positioning System)
HPA module
GPS module
ATB/LNA module
Page 83

Chapter 6: Service and repair
Replacing modules 67
6666
Service and repair
6.2.3 High Power Amplifier (HPA)
Removing the HPA module
To remove the HPA from the antenna, do as follows:
1. Disconnect the six plugs indicated in the drawing below. Remember to
release connector latches on the connectors. Do not pull the wires - pull
the plugs.
2. Gently lift the cable holders and release the cables.
Page 84

Chapter 6: Service and repair
68 Replacing modules
3. Unscrew the four finger screws on the back of the HPA and gently remove
the HPA.
Page 85

Chapter 6: Service and repair
Replacing modules 69
6666
Service and repair
Mounting the HPA module
To mount the new HPA, repeat the above procedure in reverse:
1. Fit the threaded studs on the back of the HPA into the holes in the
mounting bracket on the antenna. Apply a small amount of Loctite 243
onto each of the four threaded studs before mounting the finger screws on
the threaded studs. Fasten the screws with 1.2 Nm torque.
2. Reconnect the plugs. Make sure the plugs are fitted properly. You should
hear a click when the plug is fully inserted.
3. Gently lift the cable holders and fit the cables in the holders.
Page 86

Chapter 6: Service and repair
70 Replacing modules
6.2.4 Antenna Tracking Board/Low Noise Amplifier
(ATB/LNA)
Removing the ATB/LNA module
To remove the ATB/LNA module from the antenna, do as follows:
1. Disconnect the six plugs indicated in the drawing below.
Important notes:
• Remember the exact position of each plug, so you do not connect to
the wrong connector when installing the new module.
• Remember to release connector latches on the plugs before pulling
them out.
•Do not pull the wires - pull the plugs.
Page 87

Chapter 6: Service and repair
Replacing modules 71
6666
Service and repair
2. Gently lift the cable holder and release the cables.
3. Unscrew the two finger screws and gently remove the ATB/LNA module.
Page 88

Chapter 6: Service and repair
72 Replacing modules
Mounting the ATB/LNA module
To mount the new ATB/LNA module, repeat the above procedure in reverse:
1. Fit the threaded studs on the antenna into the holes in the sides of the
ATB/LNA module, and fasten the finger screws with torque 1.2 Nm.
2. Reconnect the plugs. Make sure the plugs are connected to the right
connectors on the antenna, and that they are fitted properly. You should
hear a click when the plug is fully inserted.
The cable from the right part of the antenna panel goes to the connector
marked A and the cable from the left part of the antenna panel goes to the
connector marked B in the below drawing. When those two plugs are
inserted, it is easier to see where the remaining plugs belong.
3. Gently lift the cable holder and fit the cables in the holder.
A
B
Page 89

Chapter 6: Service and repair
Replacing modules 73
6666
Service and repair
6.2.5 GPS module
Removing the GPS module
To remove the GPS module from the antenna, do as follows:
1. Disconnect the plug from the GPS module. Remember to release the
connector latch on the connector. Do not pull the wires - pull the plug.
2. Unscrew the four screws on the GPS module with a torx screwdriver and
remove the module.
Page 90

Chapter 6: Service and repair
74 Replacing modules
Mounting the GPS module
To mount the new GPS module, repeat the above procedure in reverse:
1. Fit the GPS module over the dedicated four threaded bushes on the
mounting plate above the HPA module.
2. Mount the four screws through the holes in the corners of the GPS module
and into the threaded bushes on the antenna. Fasten the screws with
torque 1.0 Nm using a torx screwdriver.
3. Reinsert the plug. Make sure the plug is fitted properly.
Page 91

75
Chapter 7
7777
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting 7
7.1 Reset button
7.1.1 How to access the Reset button
The terminal has a Reset button placed next to the SIM slot behind the SIM
cover. The functions of this button is described in the next section.
To press the Reset button, use a pointed device.
Page 92

Chapter 7: Troubleshooting
76 Reset button
7.1.2 Function of the Reset button
The Reset button on the terminal has the following functions:
Action Function
With the terminal
running, press the
Reset button
normally.
The terminal IP address and IP netmask are
temporarily set to the default value (default IP
address: 192.168.0.1).
With this function, even if the IP address has been
changed and you do not remember the new IP
address, you can still access the web interface and
see your current configuration. The default value is
not saved in the configuration, but is only valid until
next reboot.
With the terminal
running, press
and hold the Reset
button for 30
seconds, until the
Power indicator
on the terminal is
flashing orange.
The terminal restores factory settings and reboots the
system.
Page 93
Chapter 7: Troubleshooting
Reset button 77
7777
Troubleshooting
While the terminal
is booting, press
and hold the Reset
button.
For service use only!
The bootloader initiates software upload. This
firmware upload procedure is only supposed to be
used if the other procedures fail due to missing or
corrupted firmware.
This setup uploads SW to the terminal from a TFTP
server via the LAN connection. The procedure is as
follows:
1. Activate or install a TFTP server on a PC.
2. Locate the correct SW image (xxx.dl) for the
terminal and place it in the TFTP server directory.
3. Rename the image to ttexp.dl.
4. Reconfigure the PC LAN interface to use the static
address 192.168.0.2/255.255.255.0.
5. Power off the terminal.
6. Connect the PC LAN Interface to the terminal.
7. Press and hold down the Reset button.
8. Keep the Reset button pressed while powering on
the terminal, and through the next step.
9. Monitor the TFTP server window. When the
upload starts you can release the Reset button.
10. When the TFTP upload finishes the terminal boots
up using the new image.
Action Function
Page 94

Chapter 7: Troubleshooting
78 Status signaling
7.2 Status signaling
7. 2. 1 O v er v ie w
The SAILOR FleetBroadband system uses event messages and light indicators
to display the status of the system.
7.2.2 Light indicators
Overview
The terminal has a number of light indicators, placed in the panel at the top of
the terminal:
• a green/orange Power indicator,
• a green/red/ orange Terminal indicator,
• a green/red/orange Antenna indicator,
• a green Message indicator and
• 3 LAN indicators for each LAN interface, showing Activity (Green),
Link/Speed (Green/Yellow) and PoE (Green/Red).
Page 95

Chapter 7: Troubleshooting
Status signaling 79
7777
Troubleshooting
General status indicator functions
Power indicator
Terminal indicator
Behavior Meaning
Steady green Power OK.
Flashing green The terminal is powering up.
Flashing orange The terminal is closing down.
Off No power.
Behavior Meaning
Steady green Ready. BGAN registration completed.
Flashing green Please wait - process in progress.
BGAN registration ongoing.
Orange Warning - temporary malfunction. User action is
required.
Red Alarm - return the unit for repair.
Page 96

Chapter 7: Troubleshooting
80 Status signaling
Antenna indicator
Message indicator
Behavior Meaning
Steady green Tracking. The antenna is ready for use.
Flashing green Please wait - process in progress.
Slow flashing: The antenna is starting up
Rapid flashing: Sky scan
Orange Warning - temporary malfunction. User action is
required.
Red Alarm - critical error.
Check the event log. If the problem is in the
SAILOR FleetBroadband system and you cannot
solve it, return the unit for repair.
Behavior Meaning
Flashing green A new SMS message has arrived.
Off No new messages, or the unit is off.
Page 97

Chapter 7: Troubleshooting
Status signaling 81
7777
Troubleshooting
LAN indicator functions
Activity indicator
Link/Speed indicator
PoE indicator
Behavior Meaning
Flashing green The LAN port is active.
Behavior Meaning
Green Link speed is 100 Mbps.
Yellow Link speed is 10 Mbps.
Off The link is down.
Behavior Meaning
Green The terminal is supplying power to the LAN port.
Red The connected device requires more power than
the terminal can supply to the LAN port.
Off The terminal is not supplying power to the port.
Page 98

Chapter 7: Troubleshooting
82 Status signaling
7.2.3 Event messages
Display of event messages
The terminal can detect events during POST (Power On Self Test), PAST
(Person Activated Self Test) or CM (Continuous Monitoring). When the
terminal detects an event that requires your action, it issues an event
message.
When your terminal issues an
event message, the Terminal
indicator or the Antenna
indicator in the LED panel on
top of the terminal signals the
event, according to the tables
Terminal indicator and Antenna
indicator in the previous
section.
You can see the active event messages in the web interface by clicking the
warning symbol in the icon bar at the top in the web interface.
All events are logged in the event log. For information on the event log, see
the user manual.
Page 99

Chapter 7: Troubleshooting
Logging of events 83
7777
Troubleshooting
Logging of events
Diagnostic report
When contacting Thrane & Thrane for support, please include a diagnostic
report.
The diagnostic report contains information relevant for the service personnel
during troubleshooting.
To generate the diagnostic report, access the web interface and select Help
Desk. Then click Generate report.
Event log
The event log holds information of all registered events in the terminal or
antenna that are also shown in the terminal LED panel in the Antenna and
Terminal LEDs.
The log includes the time of the occurrence, a short description, location of the
error etc. This information can help troubleshooting errors in the system. You
can see the event log in the web interface. For further information in the web
interface, see the user manual.
Page 100

Chapter 7: Troubleshooting
84 Logging of events
 Loading...
Loading...