Page 1

FP5/GP5
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
TECHNICAL MANUAL
Page 2

efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Page 3

PREFACE
•
•
•
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Saftronics’ FP5/GP5 is the world’s first optimized Inverter specifically designed for general-purpose applications. This manual describes
installation, maintenance and inspection, troubleshooting, and specifications of the FP5/GP5. Read this manual thoroughly before operation.
General Precautions
Some drawings in this manual are shown with the protective cover or shields removed, in
order to describe detail with more clarity. Make sure all covers and shields are replaced
before operating this product.
This manual may be modified when necessary because of improvement of the product,
modification, or changes in specifications. Such modifications are denoted by a revision
number.
• To order a copy of this manual, contact your Saftronics representative.
Saftronics is not responsible for any modification of the product made by the user, since that
will void your warranty.
Page 4
PREFACE
•
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Notes for Safe Operation
Read this manual thoroughly before installation, operation, maintenance or inspection of the FP5/GP5. In this manual, notes for safe
operation are classified as followed:
WARNING
CAUTION
Even items described in CAUTION may result in a fatal accident in some situations. In either case, follow these important notes.
Take the following steps to ensure proper operation.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury
to personnel.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury
to personnel and damage to equipment. It may also be used to alert against unsafe practices.
§ Receiving
CAUTION
Do not install or operate any Inverter that is damaged or has missing parts. Failure to observe this may
result in personal injury or equipment damage.
§ Installation
CAUTION
• When moving the unit, lift the cabinet by the base, never lift by the front cover. Otherwise, the main unit
may be dropped causing damage to the unit.
• Mount the Inverter on nonflammable material (i.e., metal). Failure to observe this can result in a fire.
• When mounting units in an enclosure, install a fan or other cooling device to keep the intake air
temperature below 45°C. Overheating may cause a fire or damage the unit.
Page
2
Page
6
6
6
§ Wiring
WARNING
• Only commence wiring after verifying that the power supply is turned OFF. Failure to observe this
warning can result in an electrical shock or fire.
• Wiring should be performed only by qualified personnel. Failure to observe this warning can result in an
electrical shock or fire.
• When wiring the emergency stop circuit, check the wiring thoroughly before operation. Failure to
observe this warning can result in personal injury.
• Make sure to ground the ground terminal ( ). (Ground resistance 200V class: 100Ω or less, 400V
class: 10Ω or less.) Failure to observe this warning can result in an electrical shock or fire.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) ii © Saftronics, Inc.
Page
10
10
10
11
Page 5

PREFACE
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
CAUTION
• Verify that the Inverter rated voltage coincides with the AC power supply voltage. Failure to observe this
can result in personal injury or fire.
• Do not perform a withstand voltage test on the Inverter. It may cause semi-conductor elements to be
damaged.
• To connect a Braking Resistor, Braking Resistor Unit or Braking Unit, follow the procedures described in
Chapter 11. Improper connection may cause a fire.
• Tighten terminal screws to the specified tightening torque. Failure to observe this can result in a fire.
• Never connect the AC main circuit power supply to output Terminals T1, T2, and T3 (U, V, and W). The
Inverter will be damaged and invalidate the warranty.
§ Operation
WARNING
• Only turn ON the input power supply after replacing the front cover. Do not remove the cover while
current is flowing. Failure to observe this can result in an electrical shock.
• When the retry function (n057) is selected, do not approach the Inverter or the load, since it may restart
suddenly after being stopped. (Construct machine system, so as to assure safety for personnel, even if
the Inverter should restart.) Failure to observe this can result in personal injury.
• Since the stop button can be disabled by a function setting, install a separate emergency stop switch.
Failure to observe this can result in personal injury.
Page
10
10
10
10
11
Page
24
24
24
CAUTION
• Never touch the heatsink or discharging resistor since the temperature is very high. Failure to observe
this can result in harmful burns to the body.
• Since it is easy to change operation speed from low to high speed, verify the safe working range of the
motor and machine before operation. Failure to observe this can result in personal injury and machine
damage.
• Install a holding brake separately, if necessary. Failure to observe this can result in personal injury.
• Do not change signals during operation. The machine or the Inverter may be damaged.
• All the constants of the Inverter have been preset at the factory. Do not change the settings
unnecessarily. The Inverter may be damaged. For supply voltage, follow Paragraph 4.3 of Chapter 4.
Page
24
24
24
24
24
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) iii © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 6
PREFACE
•
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
§ Maintenance and Inspection
WARNING
• Never touch high-voltage terminals in the Inverter. Failure to observe this can result in an electrical
shock.
• Replace all protective covers before powering up the Inverter. To remove the cover, make sure to shut
OFF the Molded Case Circuit Breaker. Failure to observe this can result in an electrical shock.
• Perform maintenance or inspection only after verifying that the CHARGE LED goes OFF, after main
circuit power supply is turned OFF. The capacitors are still charged and can be dangerous.
• Only authorized personnel should be permitted to perform maintenance, inspections or parts
replacement. (Remove all metal objects (watches, bracelets, etc.) before operation. Use tools that are
insulated against electrical shock.) Failure to observe this can result in an electrical shock.
CAUTION
• The control PC board employs CMOS ICs. Do not touch the CMOS elements. They are easily damaged
by static electricity.
• Do not connect or disconnect wires or connectors while power is applied to the circuit. Failure to observe
this can result in personal injury.
Page
64
64
64
64
Page
64
64
§ Others
WARNING
Never modify the product. Failure to observe this can result in an electrical shock or personal injury and
will invalidate the warranty.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) iv © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 7

Table of Contents
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
1 Receiving .............................................................................................. 1
1.1 Inspection Checkpoints.................................................................................. 2
1.2 Identifying the Parts....................................................................................... 2
2 Installation ............................................................................................ 5
2.1 Removing and Replacing the Digital Operator................................................ 6
2.2 Removing and Replacing the Front Cover...................................................... 7
2.3 Choosing a Location to Mount the Inverter..................................................... 7
2.4 Clearances .................................................................................................... 8
3 Wiring .................................................................................................... 9
3.1 Connection Diagram...................................................................................... 10
1.1.1 Receiving Checkpoints........................................................................................................ 2
1.1.2 Checking the Nameplate Data............................................................................................ 2
2.1.1 Removing the Digital Operator .......................................................................................... 6
2.1.2 Replacing the Digital Operator............................................................................................ 6
3.2 Wiring the Main Circuit................................................................................... 11
3.2.1 Wiring Precautions for Main Circuit Point ........................................................................... 11
3.2.2 Wiring Precautions for Main Circuit Output........................................................................ 12
3.2.3 Grounding............................................................................................................................ 12
3.2.4 Functions of Main Circuit Terminals................................................................................... 13
3.2.5 Main Circuit Configuration................................................................................................... 15
3.2.6 Parts Required for Wiring.................................................................................................... 17
3.3 Wiring the Control Circuit............................................................................... 21
3.3.1 Functions of Control Circuit Terminals ............................................................................... 21
3.3.2 Wiring the Control Circuit Terminals................................................................................... 22
3.3.3 Precautions on Control Circuit Wiring................................................................................. 22
3.4 Wiring Inspection........................................................................................... 22
4 Operation .......................................................................................... 23
4.1 Operation Mode Selection.............................................................................. 25
4.2 Test Run Checkpoints.................................................................................... 26
4.3 Setting the Line Voltage Using Jumper (For 400V Class 18.5kW and Above). 26
4.4 Test Run........................................................................................................ 27
4.4.1 Digital Operator Display at Power-Up................................................................................. 27
4.4.2 Operation Check Points...................................................................................................... 28
4.4.3 Example of Basic Operation ............................................................................................... 28
5 Simple Data Setting.............................................................................. 31
5.1 Digital Operator Key Description.................................................................... 32
5.2 LED Description............................................................................................. 32
6 Programming Features ........................................................................ 35
6.1 Constant Set-Up and Initialization.................................................................. 36
6.1.1 Constant Selection/Initialization (n001).............................................................................. 36
6.2 V/f Pattern Setting.......................................................................................... 36
6.2.1 Preset V/f Pattern................................................................................................................ 37
6.2.2 Custom V/f Pattern.............................................................................................................. 38
6.3 Setting Operation Conditions ......................................................................... 38
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) v © Saftronics, Inc.
6.3.1 Reverse Run Prohibit (n006) .............................................................................................. 38
6.3.2 Multi-Step Speed Selection................................................................................................. 38
6.3.3 Operation at Low Speed ..................................................................................................... 39
6.3.4 Adjusting Frequency Setting Signal.................................................................................... 40
6.3.5 Adjusting Frequency Upper and Lower Limits ................................................................... 41
Page 8

6.3.6 Using Two Accel/Decel Times............................................................................................ 41
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.3.7 Automatic Restart after Momentary Power Loss (n051) ................................................... 42
6.3.8 Soft-Start Characteristics (n023)........................................................................................ 42
6.3.9 Torque Detection................................................................................................................. 43
6.3.10 Frequency Detection (n073)............................................................................................... 44
6.3.11 Jump Frequencies (n058 to n060) ..................................................................................... 44
6.3.12 Continuing Operation by Automatic Fault Reset (n056).................................................... 45
6.3.13 Operating Coasting Motor without Trip .............................................................................. 45
6.3.14 Using Frequency Meter of Ammeter (n048)....................................................................... 46
6.3.15 Calibrating Frequency Meter of Ammeter (n049) .............................................................. 46
6.3.16 Reducing Motor Noise or Leakage Current (n050)............................................................ 47
6.4 Selecting Stopping Method ............................................................................. 48
6.4.1 Selecting Stopping Method (n004)..................................................................................... 48
6.4.2 Coast to Stop with Timer 1 (n004=2) ................................................................................. 49
6.4.3 Applying DC Injection Braking Current (n064)................................................................... 49
6.5 Building Interface Circuits with External Devices............................................. 50
6.5.1 Using Sequence Input Signals (n035 to n039).................................................................. 50
6.5.2 Using Analog Input Signals (n042 to n045) ....................................................................... 53
6.5.3 Using Output Signals (n040, n041).................................................................................... 55
6.6 Setting Operation Conditions.......................................................................... 56
6.6.1 Torque Compensation Gain (n067).................................................................................... 56
6.7 Motor Protection ............................................................................................. 57
6.7.1 Motor Overload Detection................................................................................................... 57
6.8 PID Control .................................................................................................... 58
6.8.1 Intended Value Setting........................................................................................................ 58
6.8.2 Detected Value Setting....................................................................................................... 58
6.9 Energy Saving Control ................................................................................... 59
6.9.1 Energy Saving Gain K2 (n096)........................................................................................... 59
6.9.2 Energy Saving Tuning......................................................................................................... 59
6.10 MEMOBUS Control........................................................................................ 60
6.10.1 Communication Specifications ........................................................................................... 60
6.10.2 Data to be Sent/Received by Communication................................................................... 60
7 Maintenance and Inspection................................................................ 63
7.1 Periodic Inspector .......................................................................................... 64
7.2 Parts Replacement Schedule (Guidelines)...................................................... 64
8 Troubleshooting.................................................................................... 65
8.1 Fault Diagnosis and Corrective Actions .......................................................... 66
8.2 Alarm Display and Explanation....................................................................... 69
8.3 Motor Faults and Corrective Actions............................................................... 70
9 Specifications........................................................................................ 71
9.1 Standard Specifications .................................................................................. 72
10 Dimensions............................................................................................ 75
10.1 Dimensions .................................................................................................... 76
11 Typical Connection Diagram................................................................ 79
11.1 Braking Resistor Unit...................................................................................... 80
11.2 Braking Unit and Braking Resistor Unit........................................................... 81
12 Constant List .........................................................................................83
12.1 Constant List.................................................................................................. 84
13 Digital Operator Monitor Display ......................................................... 91
13.1 Digital Operator Monitor Display..................................................................... 92
INDEX................................................................................................................ 95
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) vi © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 9

1
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Receiving
This chapter describes how to inspect the inverter after delivery to the user.
1.1 Inspection Checkpoints.................................................. 2
1.1.1 Receiving Checkpoints....................................................................................... 2
1.1.2 Checking the Nameplate Data ........................................................................... 2
1.2 Identifying the Parts........................................................ 2
Page 10

Chapter 1: Receiving
•
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
CAUTION
Do not install or operate any Inverter which is damaged or has missing parts. Failure to observe this may result in personal injury or
equipment damage.
1.1 Inspections Checkpoints
1.1.1 Receiving Checkpoints
Table 1 Checkpoints
Does the Inverter model number correspond with the purchase
order?
Are any parts damaged?
Is hardware properly seated and securely tightened?
Was an instruction manual received? FP5/GP5 Instruction Manual
If any of the above checkpoints are not satisfactory, contact your Saftronics representative.
1.1.2 Checking the Nameplate Data
§ Nameplate Data
Checkpoints Description
Check the model number on the nameplate on the side of the
FP5/GP5. (See below.)
Visually check the exterior and verify that there was no
damage during transport.
Remove Inverter front cover. Check all visible hardware with
appropriate tools.
§ Model Designation
Figure 1 Nameplate Data
Figure 2 Model Designation
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 2 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 11

§ Specification Designation
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
∗ For special specifications, a spec sheet number appears on the nameplate.
1.2 Identifying the Parts
Chapter 1: Receiving
Figure 3 Specification Designation
Figure 4 Configuration of FP5/GP5
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 3 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 12

Chapter 1: Receiving
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
NOTES:
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 4 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 13

2
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Installation
This chapter describes configuration, location and clearances when mounting the FP5/GP5.
2.1 Removing and Replacing the Digital Operator............. 6
2.1.1 Removing the Digital Operator........................................................................... 6
2.1.2 Replacing the Digital Operator........................................................................... 6
2.2 Removing and Replacing the Front Cover.................... 7
2.3 Choosing a Location to Mount the Inverter.................. 7
2.4 Clearances....................................................................... 8
Page 14

Chapter 2: Installation
•
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
CAUTION
When moving the unit, lift the cabinet by the base, never lift by the front cover. Otherwise, the main unit may be dropped causing
damage to the unit.
• Mount the Inverter on nonflammable material, (i.e., metal). Failure to observe this can result in a fire.
• When mounting units in an enclosure, install a fan or other cooling device to keep the intake air temperature below 45°C. Overheating
may cause a fire or damage to the unit.
2.1 Removing and Replacing the Digital Operator
Remove and replace the Digital Operator as follows:
2.1.1 Removing the Digital Operator
To remove the Digital Operator from the front cover,
push the Digital Operator lever in the direction
shown by arrow 1 and lift the Digital Operator in the
direction shown by arrow 2.
Figure 5 Removing the Digital Operator
2.1.2 Replacing the Digital Operator
Engage the Digital Operator on claws A in the
direction shown by arrow 1 and then on claws B in
the direction shown by arrow 2 to lock the Digital
Operator.
Figure 6 Replacing the Digital Operator
NOTE: Never fit the Digital Operator in any other direction or by any other method. The Digital Operator will not be connected to the
Inverter.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 6 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 15

2.2 Removing and Replacing the Front Cover
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
To remove the front cover, first move the Digital Operator in the direction shown by arrow 1. (Figure 5). Then squeeze the cover in
the direction shown by arrows 2 on both sides and lift in the direction shown by arrow 3.
Figure 7 Removing and Replacing the Front Cover
Chapter 2: Installation
NOTE: Do not replace the front cover with the Digital Operator connected. The Digital Operator will not be connected to the Inverter.
Replace the front cover first and then install the Digital Operator on the cover. See Figure 6 for replacing the Digital Operator.
2.3 Choosing a Location to Mount the Inverter
To ensure proper performance and long operating life, follow the recommendations below when choosing a location for installing the
FP5/GP5. Make sure the Inverter is protected from the following conditions:
o Extreme cold and heat. Use only within ambient temperature range: −10°C to + 40°C.
o Rain, moisture. (For enclosed wall-mounted type.)
o Oil sprays, splashes.
o Salt spray.
o Direct sunlight. (Avoid using outdoors.)
o Corrosive gases or liquids.
o Dust or metallic particles in the air. (For enclosed wall-mounted type.)
o Physical shock, vibration.
o Magnetic noise. (Example: welding machines, power devices, etc.)
o High humidity.
o Radioactive materials.
o Combustibles: thinners, solvents, etc.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 7 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 16
Chapter 2: Installation
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
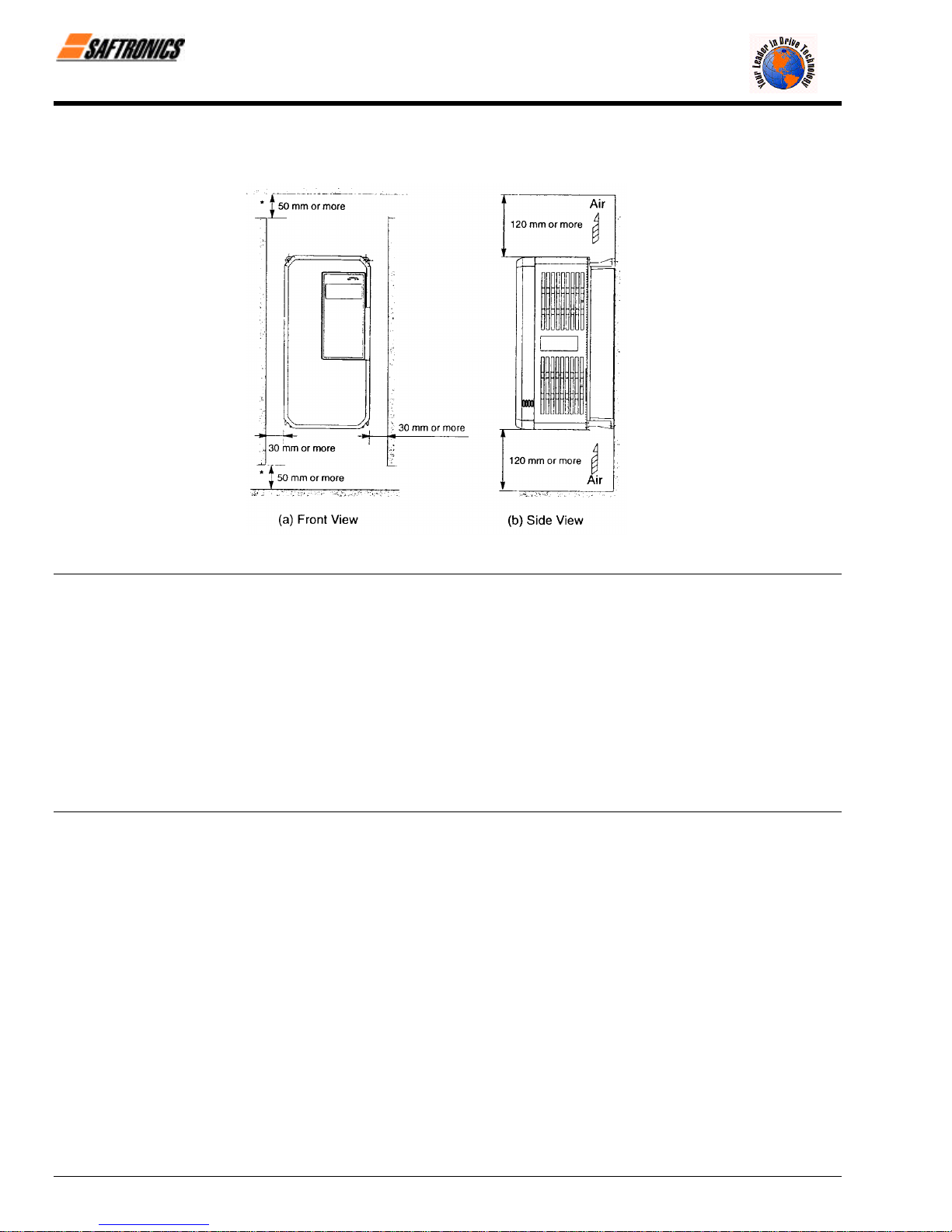
2.4 Clearances
Install the FP5/GP5 vertically and allow sufficient clearances for effective cooling as shown below.
Figure 8 Clearances
NOTE: 1. The clearances required at the top and bottom and both sides are common in open chassis type (IP00) and enclosed
wall-mounted type (NEMA1/IP20).
2. Remove the top and bottom covers to use the open chassis type of 200V/400V 15kW or less.
3. When installing the models of 200V/400V 30kW or more equipped with eyebolts, extra spacing will be required on either
side. For detailed dimensions, contact your Saftronics representative.
4. For the external dimensions and mounting dimensions, refer to Chapter 10 Dimensions.
5. Allowable intake air temperature to the Inverter:
• Open chassis type (IP00) : - 10°C to 45°C
• Enclosed wall-mounted type : - 10°C to 40°C (NEMA 1/IP20)
6. Ensure sufficient space for the sections at the upper and lower parts marked with [ in order to permit the flow of
intake/exhaust air to/from the Inverter.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 8 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 17

3
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Wiring
This chapter describes the main circuit wiring and the control circuit wiring of the FP5/GP5.
3.1 Connection Diagram....................................................... 10
3.2 Wiring the Main Circuit................................................... 11
3.2.1 Wiring Precautions for Main Circuit Input .......................................................... 11
3.2.2 Wiring Precautions for Main Circuit Output........................................................ 12
3.2.3 Grounding ........................................................................................................... 12
3.2.4 Functions of Main Circuit Terminals................................................................... 13
3.2.5 Main Circuit Configuration.................................................................................. 15
3.2.6 Parts Required for Wiring................................................................................... 17
3.3 Wiring the Control Circuit .............................................. 21
3.3.1 Functions of Control Circuit Terminals............................................................... 21
3.3.2 Wiring the Control Circuit Terminals.................................................................. 22
3.3.3 Precautions on Control Circuit Wiring................................................................ 22
3.4 Wiring Inspection............................................................ 22
Page 18

Chapter 3: Wiring
•
•
•
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
WARNING
Only commence wiring after verifying that the power supply is turned OFF. Failure to observe this can result in an electrical shock or
fire.
• Wiring should be performed only by qualified personnel. Failure to observe this can result in an electrical shock or fire.
When wiring the emergency stop circuit, check the wiring thoroughly before operation. Failure to observe this can result in personal
injury.
CAUTION
• Verify that the Inverter rated voltage coincides with the AC power supply voltage. Failure to observe this can result in personal injury
or fire.
• Do not perform a withstand voltage test of the Inverter. It may cause semi-conductor elements to be damaged.
To connect a Braking Resistor, Braking Resistor Unit or Braking Unit, follow the procedures described in Chapter 11. Improper
connection may cause fire.
• Tighten terminal screws to the specified tightening torque. Failure to observe this can result in a fire.
3.1 Connection Diagram
Below is a connection diagram of the main circuit and control circuit. Using the Digital Operator, the motor can be operated by
wiring the main circuit only.
Figure 9 FP5/GP5 Connection Diagram
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 10 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 19

Chapter 3: Wiring
•
•
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
NOTE:
1.
2. Voltage or current input for the master frequency reference can be selected by constant n042. Voltage reference input is
preset at the factory (FV).
3. Control circuit Terminal FS of + 15V has a maximum output current capacity of 20 mA.
4. Multi-function analog output should be used for monitoring meters (e.g., output frequency meter) and should not be used
for feedback control system.
3.2 Wiring the Main Circuit
Make sure to ground the ground terminal ( ). (Ground resistance 200V class: 100Ω or less, 400V class: 10× or less.)
Failure to observe this can result in an electrical shock or a fire.
Never connect the AC main circuit power supply to output Terminals T1, T2, and T3 (U, V and W). The Inverter will be
damaged and invalidate the warranty.
3.2.1 Wiring Precautions for Main Circuit Input
§ Installation of Molded Case Circuit Breaker (MCCB)
Make sure to connect Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB) or fuses between AC main circuit power supply and
FP5/GP5 input Terminals L1, L2 and L3 (R, S, and T) to protect wiring.
P
indicates twisted-pair shielded wires.indicates shielded wires and
WARNING
CAUTION
§ Installation of Ground Fault Interrupter
When connecting a ground fault interrupter to input Terminals L1, L2 and L3 (R, S, and T), select one that is not
affected by high frequency.
Examples: NV series by Mitsubishi Electric Co., Ltd. (manufactured in or after 1988), EG, SG series by Fuji Electric
Co., Ltd. (manufactured in or after 1984).
§ Installation of Magnetic Contactor
Inverters can be used without a Magnetic Contactor (MC) installed at the power supply side. When the main circuit
power supply is shut OFF in the sequence, a MC can be used instead of a MCCB. However, when a MC is switched
OFF at the primary side, regenerative braking does not function and the motor coasts to a stop.
• The load can be operated/stopped by opening/closing the MC at the primary side. However, frequent switching
may cause the Inverter to malfunction.
• When using a Braking Resistor Unit, use a sequencer to break power supply side on overload relay trip contact.
If the Inverter malfunctions, the Braking Resistor Unit may be damaged.
§ Terminal Block Connection Sequence
Input power supply phases can be connected to any terminal regardless of the order of L1, L2 and L3 (R, S, and T)
on the terminal block.
§ Installation of AC Reactor
When connecting an Inverter (200V/400V 15kW or less) to a large capacity power supply transformer (600k VA or
more), or when switching a phase advancing capacitor, excessive peak current flows in the input power supply
circuit, which may damage the converter section. In such cases, install a DC Reactor (optional) between Inverter ¾
1 and ¾ 2 terminals or an AC Reactor (optional) on the input side. Installation of a reactor is effective for
improvement of power factor on the power supply side.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 11 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 20

Chapter 3: Wiring
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
§ Installation of Surge Suppressor
§ Prohibition of Installation of Phase Advancing Capacitor
3.2.2 Wiring Precautions for Main Circuit Output
§ Connection of Terminal Block and Load
§ Strict Prohibition of Connection of Input Power Supply to Output Terminals
§ Strict Prohibition of Short Circuiting or Grounding of Output Circuit
For inductive loads (magnetic contactors, magnetic relays, magnetic valves, solenoids, magnetic brakes, etc.)
connected near the Inverter, use a surge suppressor simultaneously.
If a Phase Advancing Capacitor or Surge Suppressor is connected in order to improve the power factor, it may
become overheated and damaged by Inverter high harmonic components. Also, the Inverter may malfunction
because of overcurrent.
Connect output Terminals T1, T2, and T3 (U, V, and W) to motor lead wires T1, T2, and T3 (U, V, and W). Verify
that the motor rotates in the forward direction (CCW: counterclockwise when viewed from the motor load side) with
the forward RUN command. If the motor rotation is incorrect, exchange any two of output Terminals T1, T2, and T3
(U, V, and W).
Never connect the input power supply to output Terminals T1, T2, and T3 (U, V, and W).
Never touch the output circuit directly or put the output line in contact with the Inverter case. Otherwise, it may cause
an electrical shock or grounding. In addition, never short-circuit the output line.
§ Prohibition of Connection of Phase Advancing Capacitor or LC/RC Noise Filter
Never connect a Phase Advancing Capacitor or LC/RC noise filter to the output circuit.
§ Avoidance of Installation of Magnetic Starter
Do not connect a Magnetic Starter or MC to the output circuit. If the load is connected while the Inverter is running,
the Inverter overcurrent protective circuit operates because of inrush current.
§ Installation of Thermal Overload Relay
An electronic overload protective function is incorporated into the Inverter. However, connect a Thermal Overload
Relay when driving several motors with one Inverter or when using a multi-pole motor. When using a Thermal
Overload Relay, set Inverter constant n033 to 0 (motor overload protection selection: no protection). Additionally, for
Thermal Overload Relay at 50Hz, set the same rated current value as that described on the motor nameplate, or at
60Hz 1.1 times larger than the rated current value described on the motor nameplate.
§ Wiring Distance between Inverter and Motor
If the total wiring distance between Inverter and motor is excessively long and the Inverter carrier frequency (main
transistor switching frequency) is high, harmonic leakage current from the cable will adversely affect the Inverter and
peripheral devices.
If the wiring distance between Inverter and motor is long, reduce the Inverter carrier frequency as described below.
Carrier frequency can be set by constant n050.
Table 2 Wiring Distance between Inverter and Motor
Wiring Distance between Inverter and Motor
Carrier Frequency
(Set value of constant n050)
Up to 164ft
(50m)
15kHz or less
(6)
Up to 328ft
(100m)
10kHz or less
(4)
More than 328ft
(100m)
5kHz or less
(2)
3.2.3 Grounding
• Ground resistance
• 200 V class: 100 Ω or less, 400 V class: 10 Ω or less
• Never ground the Inverter in common with welding machines, motors, or other large-current electrical equipment.
Run all the ground wires in a conduit separate from wires for large-current electrical equipment.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 12 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 21
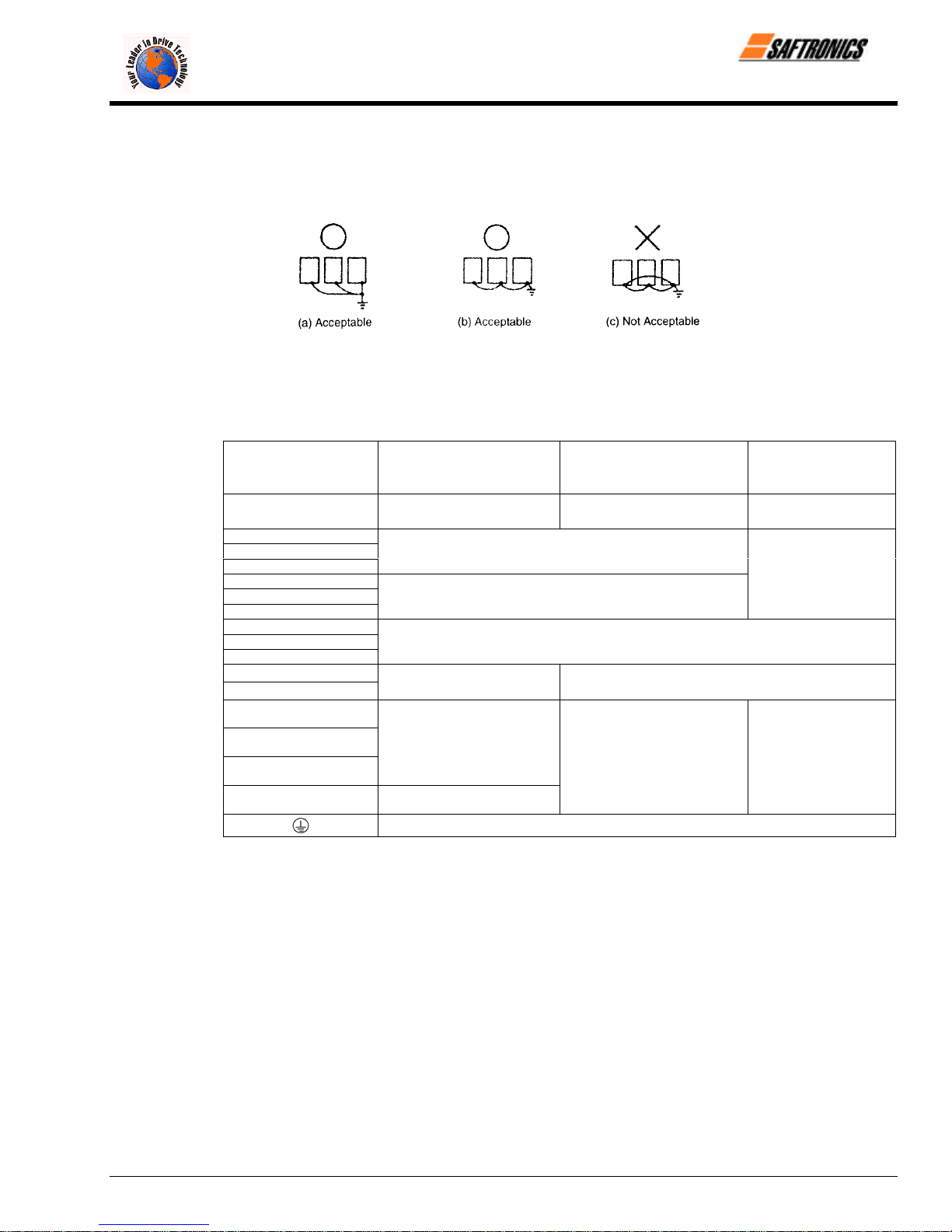
• Use the ground wires described in Tables 5 or 6 and keep the length as short as possible.
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
• When using several Inverter units side by side, ground the units as shown in Figure 10, (a) or (b). Do not loop the
ground wires as shown in (c).
Figure 10 Grounding of Three Inverter Units
3.2.4 Functions of Main Circuit Terminals
The following table outlines the functions of the main circuit terminals. Wire according to each terminal function.
Table 3 200 V Class Terminal Functions
Chapter 3: Wiring
Models
FP5/GP5
Max Applicable Motor
Output
L1 (R)
L2 (S)
L3 (T)
L11 (R1)
L21 (S1)
L31 (T1)
T1 (U)
T2 (V)
T3 (W)
B1
B2
Ö
¾ 1
¾ 2
¾ 3
23P7 to 27P5 2011 to 2015 2018 to 2075
3.7 to 7.5 kW 11 to 15 kW 18.5 to 75 kW
Main circuit input power supply
Inverter output
Braking Resistor Unit
• DC Reactor (¾1 − ¾2)
• DC bus terminals (¾1 − ¾2
Ground terminal (Ground resistance: 100 Ω or less)
• DC Reactor (¾1 − ¾2)
• DC bus terminals (¾1 − ¾2
• Braking Unit (¾3 − Ö)
Main circuit input
power supply
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 13 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 22

Chapter 3: Wiring
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Table 4 400 V Class Terminal Functions
Models
FP5/GP5
Max Applicable Motor
Output
L1 (R)
L2 (S)
L3 (T)
L11 (R1)
L21 (S1)
L31 (T1)
T1 (U)
T2 (V)
T3 (W)
B1
B2
Ö
¾ 1
¾ 2
¾ 3
r (l 1)
s 200 (l 2 200)
s 400 (l 2 400)
40P4 to 4015 4018 to 4045 4055 to 4160 4185 to 4300
0.4 to 15 kW 18.5 to 45 kW 55 to 160 kW 185 to 300 kW
Main circuit input
power supply
Braking Resistor Unit
• DC Reactor
(¾1 − ¾2
• DC bus terminals
(¾1 − Ö)
Main circuit input power supply
Inverter output
Ground terminal (Ground resistance: 10Ω or less)
• Braking Unit (¾ 3 − Ö)
• Braking Unit (¾ 3 − Ö)
Cooling fan power supply
(Control power supply
r (l 1) − s 200 (l 2 200):
200 to 230 VAC input
r (l 1) − s 400 (l 2 400):
380 to 460 VAC input
Main circuit input
power supply
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 14 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 23

3.2.5 Main Circuit Configuration
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
200V Class
FP5/GP523P7 to FP5/GP527P5 FP5/GP52011 to FP5/GP52015
FP5/GP52018 to FP5/GP52022 FP5/GP52030 to FP5/GP52075
Chapter 3: Wiring
= The wiring has been completed at the factory prior to shipping.
‡ When installing a DC Reactor (option) on models of 15kW or below, remove the short-circuit bar between
¾ 1 and ¾2 terminals and connect a DC Reactor with the terminals.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 15 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 24

Chapter 3: Wiring
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
400V Class
FP5/GP540P4 to FP5/GP541P5 FP5/GP542P2 to FP5/GP54015
FP5/GP54018 to FP5/GP54045 FP5/GP54055 to FP5/GP54160
FP5/GP54185 to FP5/GP54300
= The wiring has been completed at the factory prior to shipping.
‡ When installing a DC Reactor (option) on models of 15kW or below, remove the short-circuit bar between
¾ 1 and ¾ 2 terminals and connect a DC Reactor with the terminals.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 16 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 25

3.2.6 Parts Required for Wiring
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Select wires or Closed-Loop Connectors to be used for wiring from Tables 5, 6 and 7.
Circuit
Model
FP5/GP5
Table 5 200 V Class Wire Size
Terminal Symbol
Terminal
Screw
Wire Size
=
AWG mm
Chapter 3: Wiring
2
Wire Type
Main
Control
23P7 M4 10 5.5
25P5 M5
(U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3, (R, S, T) Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
(U, V, W)
8 8
10-8 5.5 − 8
L1, L2, L3, (R, S, T) Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
27P5 M5
(U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3, (R, S, T) Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
8 8
10-8
2011 M6
V, W)
L1, L2, L3, (R, S, T) Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, ¾ 3, T1, T2, T3 (U,
4 22
8 8
2015
L1, L2, L3, (R, S, T) Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, ¾ 3, T1, T2, T3 (U,
V, W)
M8 3 30
M6 8 8
L1,L2, L3, (R, S, T) L11, L21, L31, (R1, S1, T1), T1,
2018 M8
T2, (U, V, W)
3 30
6 14
L1,L2, L3, (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31, (R1, S1, T1), T1,
2022 M8
T2, T3 (U, V, W)
2 38
6 14
2030
L1,L2, L3, (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31, T1, T2, T3, (U, V,
W)
M10 4/0 100
M8 4 22
2037
L1,L2, L3, (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31, T1, T2, T3, (U, V,
W)
M10 1/0 x 2P 60 5 2P
M8 4 22
2045
L1,L2, L3, (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31, T1, T2, T3, (U, V,
W)
M10 1/0 x 2P 60 5 2P
M8 4 22
2055
L1,L2, L3, (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31, T1, T2, T3, (U, V,
W)
M10 1/0 x 2P 60 5 2P
M8 3 30
2075
L1,L2, L3, (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31, T1, T2, T3, (U, V,
W)
M12 4/0 x 2P 100 5 2P
M8 1 50
S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, SC,
Common to
all models
FV, FI, FS, FC,
AM, AC, M1, M2, MA, MB, MC
20-16
G M3.5 20-14
5.5 − 8
Stranded
0.5 − 1.25
Solid
0.5 − 1.25
0.5 − 2
Power cable:
600V vinyl
sheathed wire
or equivalent
Twisted
shielded wire
= Where size is determined using 75°C temperature-rated copper wire.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 17 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 26

Chapter 3: Wiring
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Circuit
Model
FP5/GP5
Table 6 400 V Class Wire Size
Terminal Symbol
Terminal
Screw
Wire Size
=
AWG mm
2
Wire Type
Main
40P4 M4 2 − 5.5
(U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
L1, L2, L3, (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
40P7 M4
(U, V, W)
2 − 5.5
L1, L2, L3, (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
41P5 M4
(U, V, W)
2 − 5.5
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
42P2 M4
(U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
43P7 M4
(U, V, W)
14-10
12-10
2 − 5.5
2 − 5.5
3.5 − 5.5
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
44P0 M4
(U, V, W)
2 − 5.5
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
45P5 M4 12-10 3.5 − 5.5
(U, V, W)
Power cable:
600V vinyl
sheathed wire
or equivalent
47P5 M5 8-6 5.5
4011
(U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3, (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
(U, V, W)
M5 8-6
M6 8 8
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
4015
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 2, B1, B2, T1, T2, T3
(U, V, W)
M5 8-6
M6 8 8
4018
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31 (R1, S1, T11), T1,
T2, T3 (U, V, W)
M6 6 14
M8 8 8
4022
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31 (R1, S1, T11), T1,
T2, T3 (U, V, W)
M6 4 22
M8 8 8
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31 (R1, S1, T11), T1,
4030 M8
T2, T3 (U, V, W)
= Where size is determined using 75°C temperature-rated copper wire.
8 − 14
8 − 14
4 22
8 8
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 18 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 27

Table 6 400 V Class Wire Size (Continued)
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Circuit
Model
FP5/GP5
Terminal Symbol
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31 (R1, S1, T11), T1,
4037 M8
T2, T3 (U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31 (R1, S1, T11), T1,
4045 M8
T2, T3 (U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31 (R1, S1, T11), T1,
4055
T2, T3 (U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31 (R1, S1, T11), T1,
4075
T2, T3 (U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31 (R1, S1, T11), T1,
4110
Main
4160
T2, T3 (U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), L11, L21, L31 (R1, S1, T11), T1,
T2, T3 (U, V, W)
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 3, T1, T2, T3 (U, V, W)
4185
r (l1), s 200 (l2 200), s 400 (l
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 3, T1, T2, T3 (U, V, W)
400)
2
4220
r (l1), s 200 (l2 200), s 400 (l
L1, L2, L3 (R, S, T), Ö, ¾ 1, ¾ 3, T1, T2, T3 (U, V, W)
400)
2
4300
Control
Common to
all models
r (l1), s 200 (l2 200), s 400 (l
S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6, SC,
FV, FI, FS, FC,
AM, AC, M1, M2, MA, MB, MC
G M3.5 20-14
400)
2
= Where size is determined using 75°C temperature-rated copper wire.
Terminal
Screw
Wire Size
AWG mm
3 30
6 14
1 50
6 14
M10 4/0 100
M8 4 22
M10 1/0 x 2P 60 x 2P
M8 4 22
M10 1/0 x 2P 60 x 2P
M8 3 30
M12 4/0 x 2P 100 x 2P
M8 1 50
M16
M8 1 50
M4 20-10
M16
M8 1/0 60
M4 20-10
M16
M8 1/0 60
M4 20-10
650MCM
x 2P
650MCM
x 2P
650MCM
x 2P
20-16
325 x 2P
0.5 − 5.5
325 x 2P
0.5 − 5.5
325 x 2P
0.5 − 5.5
Stranded
0.5 − 1.25
0.5 − 1.25
0.5 − 2
Chapter 3: Wiring
=
2
Solid
Wire Type
Power cable:
600V vinyl
sheathed wire
or equivalent
Twisted
shielded wire
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 19 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 28

Chapter 3: Wiring
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Table 7 Closed-Loop Connectors
AWG Size Wire Size mm
2
20 0.5
18 0.75
16 1.25
14 2
12-10 3.5 / 5.5
8 8
6 14
4 22
3-2 30 / 38 M8
1-1/0 50 / 60
3/0 80
4/0 100
4/0 100
300MCM 150
400MCM 200
650MCM 325
Terminal Screw Closed-Loop Connectors
M3.5
M4
M3.5
M4
M3.5
M4
M3.5
M4
M5
M6
M8
M4
M5
M6
M8
M5
M6
M8
M6
M8
1.25 − 3.5
1.25 − 4
1.25 − 3.5
1.25 − 4
1.25 − 3.5
1.25 − 4
2 − 3.5
2 − 4
2 − 5
2 − 6
2 − 8
5.5 − 4
5.5 − 5
5.5 − 6
5.5 − 8
8 − 5
8 − 6
8 − 8
14 − 6
14 − 8
M6 14 - 6
M8 14 - 8
38 − 8
M8
M10
M10
60 − 8
60 − 10
80 − 10
100 − 10
100 − 12
M12
150 − 12
200 − 12
M12 x 2
M16
325 − 12
325 − 16
NOTE: When determining wire size, consider voltage drop. Select a wire size so that voltage drop will be less than 2% of the normal
rated voltage. Voltage drop is calculated by the following equation:
Phase-to-phase voltage drop (V) = /3 5 wire resistance (Ω/km) 5 wiring distance (m) 5 current (A) 5 10
−3
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 20 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 29

3.3 Wiring the Control Circuit
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
The following table outlines the functions of the control circuit terminals. Wire according to each terminal function.
3.3.1 Functions of Control Circuit Terminals
Classification
Terminal Signal Function Description Signal Level
S1 Forward run/stop Forward run when closed, stop when open
Chapter 3: Wiring
Table 8 Control Circuit Terminals
S2 Reverse run/stop
S3 External fault input
S4 Fault reset input Reset when closed
S5 Multi-step speed reference 1 Effective when closed
Sequence Input Signal
Analog Input Signal
S6 Multi-step speed reference 2 Effective when closed
SC
FS
FV
FI
FC
G
M1
M2
Sequence control input
common terminal
+ 15 V
Power supply output
Frequency reference input
(voltage)
Frequency reference input
(current)
Common terminal for control
circuit
Connection to shield sheath
of signal lead
During running (NO contact) Closed when running
Reverse run when closed,
stop when open
Fault when closed,
normal state when open
Multi-function contact
inputs (n035 to n039)
For analog command + 15 V power supply
0 to + 10 V/100% 0 to + 10 V (20 kΩ)
4 to 20 mA/100%
0 V
n042 = 0 : FV
effective
n042 = 1 : FI
effective
Multi-function
contact output
(n041)
Photo-coupler insulation
Input: + 24 VDC 8 mA
+ 15 V
(Allowable current 20 mA
maximum)
4 to 20mA (250Ω)
Dry contact
Contact capacity:
250 VAC 1 A or less
30 VDC 1 A or less
MA
MB
Sequence Output Signal
Analog Output
G
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 21 © Saftronics, Inc.
MC
AM Frequency meter output
Signal
AC Common
S1 S2 S3 SC SC S4 S5 S6 FV FI FS FC AM AC M1 M2 MA MB MC
Fault contact output (NO/NC
contact)
Figure 11 Control Circuit Terminal Arrangement
Fault when closed between
Terminals MA and MC.
Fault when open between
Terminals MB and MC.
0 to + 10 V/100% frequency
Multi-function
contact output
(n040)
Multi-function
analog monitor 1
(n048)
Dry contact
Contact capacity:
250 VAC 1 A or less
30 VDC 1 A or less
0 to + 10 V 2 mA or less
Page 30

Chapter 3: Wiring
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
3.3.2 Wiring the Control Circuit Terminals
Insert the wire into the lower part of the terminal block and connect it tightly with a screwdriver. Wire sheath strip length
must be 7 mm (approximately ¼ inch).
3.3.3 Precautions on Control Circuit Wiring
• Separate control circuit wires from main circuit wires and other power cables to prevent erroneous operation caused
by noise interference.
• Use twisted shielded or twisted-pair shielded wire for the control circuit line and connect the shielded sheath to the
Inverter Terminal G. See Figure 12.
3.4 Wiring Inspection
After completing installation and wiring, check for the following items. Never use control circuit megger check.
o Wiring is proper.
o Wire clippings or screws are not left in the unit.
o Screws are securely tightened.
o Bare wire in the terminal does not contact other terminals.
Figure 12 Shielded Wire Termination
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 22 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 31

4
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Operation
This chapter describes the basic operation procedures of the FP5/GP5.
4.1 Operation Mode Selection......................................... 25
4.2 Test Run Checkpoints............................................... 26
4.3 Setting the Line Voltage Using Jumper
(For 400V Class 18.5kW and Above) ........................ 26
4.4 Test Run...................................................................... 27
4.4.1 Digital Operator Display at Power-Up....................................................... 27
4.4.2 Operation Check Points............................................................................. 2/
4.4.3 Example of Basic Operation...................................................................... 28
Page 32

Chapter 4: Operation
•
•
•
•
•
•
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
WARNING
Only turn ON the input power supply after replacing the front cover. Do not remove the cover while current is flowing. Failure to
observe this can result in an electrical shock.
When the retry function (n057) is selected, do not approach the Inverter or the load, since it may restart suddenly after being
stopped. (Construct machine system, so as to assure safety for personnel, even if the Inverter should restart.) Failure to observe
this can result in personal injury.
Since the stop button can be disabled by a function setting, install a separate emergency stop switch. Failure to observe this can
result in personal injury.
CAUTION
Never touch the heatsink or discharging resistor since the temperature is very high. Failure to observe this can result in harmful
burns to the body.
Since it is easy to change operation speed from low to high speed, verify the safe working range of the motor and machine before
operation. Failure to observe this can result in personal injury and machine damage.
• Install a holding brake separately if necessary. Failure to observe this caution can result in personal injury.
• Do not change signals during operation. The machine or the Inverter may be damaged.
All the constants of the Inverter have been preset at the factory. Do not change the settings unnecessarily. The Inverter may be
damaged. For supply voltage, follow Paragraph 4.3 of Chapter 4.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 24 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 33

4.1 Operation Mode Selection
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
The FP5/GP5 has two operation modes, LOCAL and REMOTE, as described in Table 9. These two modes can be selected by
the Digital Operator LOCAL/REMOTE key only while the operation is stopped. The selected Operation mode can be verified by
observing the Digital Operator SEQ and REF LED’s as shown below. The Operation mode is set to REMOTE (run by control
circuit Terminals FV and FI frequency reference and RUN command from a control circuit terminal) prior to shipment. Multifunction contact inputs from control circuit Terminals S3 to S6 are enabled in both Operation modes LOCAL/REMOTE.
• LOCAL : Both frequency reference and RUN command are set by the Digital Operator. SEQ and REF LED’s go OFF.
• REMOTE : Master frequency reference and RUN command can be selected as described in Table 9.
Table 9 Reference Selection in REMOTE Mode (n002: Operation Method Selection)
Chapter 4: Operation
Setting Operation Method Selection
0 Operation by RUN command from Digital Operator OFF Master frequency reference from Digital Operator OFF
Operation by RUN command from control circuit
1
terminal
2 Operation by RUN command from Digital Operator OFF
Operation by RUN command from control circuit
3
terminal
4 Operation by RUN command from Digital Operator OFF
Operation by RUN command from control circuit
5
terminal
Operation by RUN command from serial
6
communication
Operation by RUN command from serial
7
communication
Operation by RUN command from serial
8
communication
SEQ
LED
ON Master frequency reference from Digital Operator OFF
Master frequency reference from control circuit
Terminals FV and FI
Master frequency reference from control circuit
ON
Terminals FV and FI
Master frequency reference set by serial
communication
Master frequency reference set by serial
ON
communication
Master frequency reference set by serial
ON
communication
ON Master frequency reference from Digital Operator OFF
Master frequency reference from control circuit
ON
Terminals FV and FI
Reference Selection
REF
LED
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 25 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 34

Chapter 4: Operation
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
4.2 Test Run Checkpoints
To assure safety, prior to initial operation, disconnect the machine coupling so that the motor is isolated from the machine. If
initial operation must be performed while the motor is still coupled to the machine, use great care to avoid potentially hazardous
conditions. Check the following items before a test run.
o Wiring and terminal connections are correct.
o No short-circuit caused by wire clippings.
o Screw-type terminals are securely tightened.
o Motor is securely mounted
o All items are correctly earthed (grounded).
4.3 Setting the Line Voltage Using Jumper (For 400V Class 18.5kW and Above)
Set the line voltage jumper according to the main circuit power supply. (See Figure 13.) Insert the jumper at the appropriate
location corresponding to the input line voltage. It has been preset at the factory to 440V.
Figure 13 Line Voltage Jumper (For 400V Class 18.5kW to 45kW)
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 26 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 35

4.4 Test Run
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
4.4.1 Digital Operator Display at Power-up
When the system is ready for operation, turn ON the power supply. Verify that the Inverter powers up properly. If any
problems are found, turn OFF the power supply immediately. The Digital Operator display illuminates as shown below
when turning the power supply ON.
Chapter 4: Operation
Figure 14 Digital Operator Display at Power-Up
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 27 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 36

Chapter 4: Operation
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
4.4.2 Operation Check Points
Check the following items during operation.
o Motor rotates smoothly.
o Motor rotates in the correct direction.
o Motor does not have abnormal vibration or noise.
o Acceleration and deceleration are smooth.
o Current matches the load flow.
o Status indicator LED’s and Digital Operator display are correct.
4.4.3 Example of Basic Operation.
§ Operation by Digital Operator
The diagram below shows a typical operation pattern using the Digital Operator.
Figure 15 Operation Sequence by Digital Operator
Table 10 Typical Operation by Digital Operator
Description Key Sequence Digital Operator Display LED Display
¬ Power ON
• Display frequency reference value. 0.0
Operation Condition Setting REMOTE LED (SEQ. REF) OFF
Frequency Setting Change the value
-
• Select LOCAL mode.
• Change reference value.
• Write-in set value.
by pressing
\ /
15.0
/ \
15.0
• Select output frequency monitor display.
0.0
® Forward Run
• Forward run (15 Hz) 15.0
RUN LED ON
Fref
Fref
Fref
Fout
Fout
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 28 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 37

¯ Frequency Reference Value Change
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
(15 Hz to 60 Hz)
• Select frequency reference value
display.
Table 10 Typical Operation by Digital Operator (continued)
Press 7 times
15.0
Chapter 4: Operation
Fref
Reverse Run
°
• Change set value.
• Write-in set value.
• Select output frequency monitor display.
• Select reverse run.
• Write-in set value.
Change the value
by pressing
Press 3 times
Switch to “rev”
by pressing
\ /
60.0
/ \
60.0
60.0
fo
\ /
eu
/ \
eu
Fref
Fref
Fref
F/R
F/R
F/R
• Select output frequency monitor display.
Press 5 times
60.0
Stop
±
• Decelerates to a stop.
RUN LED OFF STOP LED ON
0.0
Fout
Fout
§ Operation by Control Circuit Terminal Signal
The diagram below shows a typical operation pattern using the control circuit terminal signals.
Figure 16 Operation Sequence by Control Circuit Terminal Signal
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 29 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 38

Chapter 4: Operation
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Description Key Sequence Digital Operator Display LED Display
Power ON
¬
Frequency Setting
-
Output Frequency Display
Forward Run
®
Stop
¯
• Display frequency reference value. 0.0
REMOTE mode is preset at the factory REMOTE LED (SEQ, REF) ON
• Input frequency reference voltage 60.0
(current) by control circuit Terminal FV For reference voltage 10V
or FI and verify the input value by the
Digital Operator.
• Select output frequency monitor display.
• Close between control circuit Terminals 60.0
SI and SC to perform forward run. RUN LED ON
• Open between control circuit Terminals
SI and SC to stop operation.
Table 11 Typical Operation by Control Circuit Terminal Signal
STOP LED ON
(RUN LED blinking
during deceleration)
0.0
0.0
Fref
Fref
Fout
Fout
Fout
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 30 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 39

5
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Simple Data Setting
This chapter describes simple data setting.
5.1 Digital Operator Key Description................................... 32
5.2 LED Description.............................................................. 32
Page 40

Chapter 5: Simple Data Setting
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
5.1 Digital Operator Key Description
Mode Indicator LED’s (Remote Mode)
Lights when selecting Input mode from the control circuit terminal or
serial communication.
SEQ: Lights when selecting RUN command from control circuit
terminal or serial communication.
REF: Lights when selecting frequency reference from control
circuit Terminals FV and FI or serial communication.
Display
Displays set values of each function or monitoring values such as
frequency and output current. (4 Digits)
Quick-Start LED’s
LED Description
Fref Frequency reference setting/monitoring Enable
Fout Output frequency monitor Enable
Iout Output current monitor Enable
kWout Output power monitor Enable
F/R FWD/REV RUN command selection Enable
Montr Monitor selection Enable
Accel Acceleration time Enable
Decel Deceleration time Enable
Vmtr Motor rated voltage Disable
V/F V/f pattern selection Disable
Fgain Frequency reference gain Disable
Fbias Frequency reference bias Disable
FLA Motor rated current Disable
PID PID selection Disable
kWsav Energy Saving selection Disable
PRGM Constant number/data Disable
Set/Read
During
Run
5.2 LED Description
By using the Quick-Start LED’s on the Digital Operator, simple operation of the Inverter is possible. Each Quick-Start LED is
selected each time DSPL key is pressed. Following is a table describing Quick-Start LED selection.
(Example of model FP5/GP5)
Enter Key
Displays each constant set value. By pressing this key again, the
set value is written in.
Number Change Keys
Changes set values or constant numbers.
∧ : Increment key
∨ : Decrement key
Operation Command Keys
Operation command keys operate the Inverter.
*STOP/RESET : Red LED lights by pressing STOP.
(Resets operation at faults. Reset is disabled
while a RUN command is ON.)
RUN : Red LED lights by pressing RUN.
Operation Mode Selection Key
The Operation mode is alternated between REMOTE and LOCAL
(Digital Operator).
Display Selection Key
Selects the contents of Quick-Start LED’s. (See Page 33)
Figure 17 Digital Operator Key Description
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 32 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 41

LED
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Display
Chapter 5: Simple Data Setting
Table 12 LED Description
Description Key Sequence Digital Operator Display Remarks
Power ON
Fref Frequency reference setting/monitoring
Fout Output frequency monitor
Iout Output current monitor
kWout Output power monitor
F/R FWD/REV RUN command selection
Montr Monitor selection
Accel Acceleration time
Decel Deceleration time
(During run)
Vmtr Motor rated voltage
0.0
0.0
0.0
0.0
Press ENTER key to
display the monitor value.
Fo
U – 01
10.0
10.0
200.0
V/F V/f pattern selection
Fgain Frequency reference gain
Fbias Frequency reference bias
FLA Motor rated current
PID PID selection
kWsav Energy saving selection
PRGM Constant number/data
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 33 © Saftronics, Inc.
1
100
0
14.0
0
0
002
Set/read is enabled only
during stop.
Press ENTER key to
display the data.
Page 42

Chapter 5: Simple Data Setting
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
NOTES:
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 34 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 43

6
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Programming Features
This chapter describes programming features.
6.1 Constant Set-Up and Initialization................................. 36
6.1.1 Constant Selection/Initialization (n001) ............................................................. 36
6.2 V/f Pattern Setting........................................................... 36
6.2.1 Preset V/f Pattern ............................................................................................... 37
6.2.2 Custom V/f Pattern ............................................................................................. 38
6.3 Setting Operation Conditions ........................................ 38
6.3.1 Reverse Run Prohibit (n006).............................................................................. 38
6.3.2 Multi-Step Speed Selection................................................................................ 38
6.3.3 Operation at Low Speed..................................................................................... 39
6.3.4 Adjusting Frequency Setting Signal................................................................... 40
6.3.5 Adjusting Frequency Upper and Lower Limits................................................... 41
6.3.6 Using Two Accel/Decel Times ........................................................................... 41
6.3.7 Automatic Restart after Momentary Power Loss (n051)................................... 42
6.3.8 Soft-Start Characteristics (n023)........................................................................ 42
6.3.9 Torque Detection................................................................................................ 43
6.3.10 Frequency Detection (n073)............................................................................... 44
6.3.11 Jump Frequencies (n058 to n060)..................................................................... 44
6.3.12 Continuing Operation by Automatic Fault Reset (n056).................................... 45
6.3.13 Operating Coasting Motor without Trip.............................................................. 45
6.3.14 Using Frequency Meter of Ammeter (n048) ...................................................... 46
6.3.15 Calibrating Frequency Meter of Ammeter (n049).............................................. 46
6.3.16 Reducing Motor Noise or Leakage Current (n050) ........................................... 47
6.4 Selecting Stopping Method............................................ 48
6.4.1 Selecting Stopping Method (n004)..................................................................... 48
6.4.2 Coast to Stop with Timer 1 (n004=2)................................................................. 49
6.4.3 Applying DC Injection Braking Current (n064)................................................... 49
6.5 Building Interface Circuits with External Devices........ 50
6.5.1 Using Sequence Input Signals (n035 to n039) .................................................. 50
6.5.2 Using Analog Input Signals (n042 to n045)....................................................... 53
6.5.3 Using Output Signals (n040, n041).................................................................... 55
6.6 Setting Operation Conditions ........................................ 56
6.6.1 Torque Compensation Gain (n067) ................................................................... 56
6.7 Motor Protection ............................................................. 57
6.7.1 Motor Overload Detection .................................................................................. 57
6.8 PID Control ...................................................................... 58
6.8.1 Intended Value Setting....................................................................................... 58
6.8.2 Detected Value Setting....................................................................................... 58
6.9 Energy Saving Control ................................................... 59
6.9.1 Energy Saving Gain K2 (n096) .......................................................................... 59
6.9.2 Energy Saving Tuning........................................................................................ 59
6.10 MEMOBUS Control.......................................................... 60
6.10.1 Communication Specifications........................................................................... 60
6.10.2 Data to be Sent/Received by Communication................................................... 60
Page 44

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.1 Constant Set-up and Initialization
6.1.1. Constant Selection/Initialization (n001)
The following table describes the data which can be set or read when n001 is selected.
Setting Constant that can be set Constant that can be read
0
(Constant write disable)
1
(Factory setting)
2 n001 to n049 n001 to n108
3 n001 to n108 n001 to n108
4, 5 Not used (disabled)
8 Initialize: 2-wire sequence
9 Initialize: 3-wire sequence
[ Refer to Page 50.
6.2 V/f Pattern Setting
V/f pattern can be set by constant n010.
Set value 0 to E: Preset V/f pattern can be selected.
F : Custom V/f pattern can be set.
n001 n001 to n108
n001 to n034 n001 to n108
[
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 36 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 45

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.2.1. Preset V/f Pattern
The following shows the preset V/f patterns. (The voltages are for 200V class. For 400V class, the value is twice that of
200V class.)
Table 13 Preset V/f Pattern (n010 = 0 to E)
Specifications n010 V/f Pattern *1 Specifications n010 V/f Patterns *1
Low
Starting
Torque
50 Hz 0 50 Hz
High
Starting
Torque
8
9
60 Hz
Saturation
60 Hz
General-Purpose
50 Hz
60 Hz
Variable Torque Characteristics
50 Hz
Saturation
72 Hz 3 90 Hz C
Variable
Torque 1
Variable
Torque 2
Variable
Torque 3
Variable
Torque 4
1
F
2
4
5
6
7
High Starting Torque *2
60 Hz
High Speed Operation
Low
Starting
Torque
High
Starting
Torque
120 Hz D
180 Hz E
A
B
∗ 1 Consider the following items as the conditions for selecting a V/f pattern. They must be suitable for:
• The voltage and frequency characteristics of motor.
• The maximum rotation speed of motor.
∗ 2 Select high starting torque only in the following conditions. Normally, this selection is not required.
• The wiring distance is long (150 meters (492 feet) and above).
• Voltage drop at startup is large.
• AC Reactor is inserted in the input or output of the Inverter.
• A motor smaller than the nominal output of the Inverter is used.
∗ 3 Voltages when the models of 200V, 55kW or above, or 400V, 55kW or above are selected.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 37 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 46

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.2.2. Custom V/f Pattern
Set each pattern when using a special motor (high-speed motor, etc.) or when requiring special torque adjustment of
machine.
Make sure to satisfy the following
conditions for setting of constants
n012 to n018.
n017 < n015 < n014 < n012
Constant No. Name Unit Setting Range Factory Setting
n012 Maximum output frequency 0.1 Hz
n013 Maximum voltage 0.1 V
n014
n015 Middle output frequency 0.1 Hz
n016
n017 Minimum output frequency 0.1 Hz
n018
Maximum voltage output
frequency (base frequency)
Middle output frequency
voltage
Minimum output frequency
voltage
Figure 18 Custom V/f Pattern Setting
50.0 − 400.0 Hz
0.1 − 255.0 V
0.1 Hz 0.2 − 400.0 Hz 60.0 Hz
0.1 −399.9 Hz
0.1 V 0.1 − 255.0 V
0.1 − 10.0 Hz
0.1 V 0.1 − 50.0 V
[
[
[
60.0 Hz
200.0 V
15.0 V
10.0 V
[
3.0 Hz
[
1.5 Hz
[
∗ For 400 V class, the value is twice that of 200 V class.
Increasing the voltage of the V/f pattern increases motor torque, but an excessive increase may cause the following:
• Inverter malfunction because of motor overexcitation.
• Motor overheat or excessive vibration.
Increase voltage gradually while verifying the motor current.
6.3 Setting Operation Conditions
6.3.1. Reverse Run Prohibit (n006)
“Reverse run disabled” setting does not accept a reverse RUN command from the control circuit terminal or Digital
Operator. This setting is used for applications where a reverse RUN command can cause problems.
Setting Description
0 Reverse run enabled
1 Reverse run disabled
6.3.2. Multi-Step Selection
By combining frequency reference and input terminal function selections, up to four steps of speed can be set.
Four step speed change
n002 = 1 (Operation mode selection)
n025 = 30.0 Hz
n026 = 40.0 Hz
n027 = 50.0 Hz
n028 = 60.0 Hz
n038 = 9 (Multi-function contact input Terminal S5)
n039 = 10 (Multi-function contact input Terminal S6)
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 38 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 47

Figure 19 Multi-Speed Selection – Control Circuit Terminals
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Chapter 6: Programming Features
Figure 20 Multi-Step Speed Operation Timing Diagram
6.3.3. Operating at Low Speed
Set jog frequency reference selection in multi-function contact input terminals (S2 to S6). Then input a FWD or REV RUN
command. Operation is enabled at the jog frequency set in n029. When multi-step speed references 1 or 2 are input
simultaneously with the jog frequency reference, the jog frequency reference has priority.
Name Constant No. Setting
Jog frequency reference n029 (Factory setting: 6.0 Hz)
Multi-function contact input
selection (S2 to S6)
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 39 © Saftronics, Inc.
n035, n036, n037, n038, n039
Set to “11” (jog frequency selection)
for any constant.
Page 48

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.3.4. Adjusting Frequency Setting Signal
When the frequency reference is output by an analog input of control circuit Terminals FV and FI, the relationship between
the analog input (voltage/current) and the frequency reference can be set.
§ Frequency Reference Gain (n046)
The frequency reference at the analog input value of 10V (20mA) can be set in units of 1%. (n012 Maximum output
frequency: 100%) Factory setting: 100%
§ Frequency Reference Bias (n047)
The frequency reference at the analog input value of 0 V (4 mA) can be set in units of 1%. (n012 Maximum output
frequency: 100%) Factory setting: 0%
Typical setting
Figure 21 Frequency Signal Adjustment
• To operate the Inverter with frequency reference of 0% to 100% at 0 to 5V input.
Gain: Constant n046 = 200
Bias: Constant n047 = 0
Figure 22 Frequency Signal Adjustment Example
(0 to 5V Input)
• To operate the Inverter with frequency reference of 50% to 100% at 0 to 10V input.
Gain: Constant n046 = 100
Bias: Constant n047 = 50
Figure 23 Frequency Signal Adjustment Example
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 40 © Saftronics, Inc.
(0 to 10V Input)
Page 49

6.3.5. Adjusting Frequency Upper and Lower Limits
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Figure 24 Setting Frequency Upper and Lower Limits
§ Frequency Reference Upper Limit (n030)
Sets the upper limit of the frequency reference in units of 1%. (n012 Maximum output frequency: 100%) Factory
setting: 100%
§ Frequency Reference Lower Limit (n031)
Sets the lower limit of the frequency reference in units of 1%. (n012 Maximum output frequency: 100%)
When operating at a frequency reference of 0, operation is continued at the frequency reference lower limit.
However, when the frequency lower limit is set to less than the minimum output frequency (n017), operation is not
performed. Factory setting: 0%
6.3.6 Using Two Accel/Decel Times
Chapter 6: Programming Features
* When deceleration to stop is selected (n004 = 0)
Figure 25 Timing Diagram of Accel/Decel Time Adjustment
By setting multi-function contact input selection (n035, n036, n037, n038 or n039) to “12 (accel/decel time
selection)”, accel/decel time is selected by turning ON/OFF the accel/decel time selection (Terminal S2, S3, S4, S5
or S6).
At OFF : n019 (accel time 1), n020 (decel time 1)
At ON : n021 (accel time 2), n022 (decel time 2)
Constant No. Name Unit Setting Range Factory Setting
n019 Accel time 1 0.1 s (1 s for 1000 s and above) 0.0 to 3600 s 10.0 s
n020 Decel time 1 0.1 s (1 s for 1000 s and above) 0.0 to 3600 s 10.0 s
n021 Accel time 2 0.1 s (1 s for 1000 s and above) 0.0 to 3600 s 10.0 s
n022 Decel time 2 0.1 s (1 s for 1000 s and above) 0.0 to 3600 s 10.0 s
• Accel time: Set the time needed for output frequency to reach 100% from 0%.
• Decel time: Set the time needed for output frequency to reach 0% from 100%.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 41 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 50

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.3.7 Automatic Restart after Momentary Power Loss (n051)
When momentary power loss occurs, operation restarts automatically.
Setting Description
0 Not provided (Factory setting)
[
1
=
2
∗ Hold the Operation command to continue operation after recovery from a momentary power loss.
= When 2 is selected, operation restarts if power supply voltage reaches its normal level. No fault signal is output.
6.3.8. Soft-Start Characteristics (n023)
To prevent shock during machine starting and/or stopping, accel/decel can be performed in S-curve pattern.
Setting S-curve Characteristic Time
0 S-curve not provided
1 0.2 s (Factory setting)
2 0.5 s
3 1.0 s
Note: S-curve characteristic time is the time from accel/decel rate 0 to a regular accel/decel rate determined by the set
accel/decel time.
Continuous operation after power recovery within 2 seconds
Continuous operation after power recovery within control logic time
(No fault output. Restarts only while control power supply is ON.)
Figure 26 S-Curve Characteristic Timing
The following time chart shows switching from FWD/REV at deceleration to stop.
Figure 27 S-Curve Characteristic FWD/REV Operation
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 42 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 51

6.3.9 Torque Detection
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
If an excessive load is applied to the machine, output current increase can be detected by output alarm signals at multifunction contact output Terminals MA, MB and M1.
To output an overtorque detection signal, set multi-function contact output selection n040 or n041 to “overtorque
detection” [Setting: 6 (NO contact) or 7 (NC contact)].
∗ Release width (hysteresis) during overtorque detection is 5% of the level of Inverter current.
§ Overtorque Detection Function Selection (n074)
Chapter 6: Programming Features
Figure 28 Torque Characteristics
Setting Description
0 Detection disabled (Factory setting).
1 Detected during constant-speed running, and operation continues after detection.
2 Detected during running, and operation continues after operation.
3
4 Detected during running, and Inverter output is shut OFF during detection.
1. To detect overtorque during acceleration or deceleration, set to 2 or 4.
2. To continue the operation after overtorque detection, set to 1 or 2. During detection, the Digital Operator
displays “OL3” alarm (blinking).
3. To halt the Inverter by a fault at overtorque detection, set to 3 or 4. At detection, the Digital Operator displays
“OL3” fault (ON).
Detected during constant-speed running, and Inverter output is shut OFF during
detection.
§ Overtorque Detection Level (n075)
Sets the overtorque detection current level in units of 1%. (Inverter rated current: 100%) Factory setting: 160%
§ Overtorque DetectionTime (n076)
If the time when motor current exceeds the overtorque detection level (n075) is longer than overtorque detection time
(n076), the overtorque detection function operates. Factory setting: 0.1 seconds
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 43 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 52

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.3.10 Frequency Detection (n073)
Effective when multi-function contact output selections n040 or n041 are set to frequency detection (Setting: 4 or 5).
Frequency detection turns ON when output frequency is higher or lower than the frequency detection level (n073).
§ Frequency Detection (Output Frequency << Frequency Detection Level)
(Set n040 or n041 to 4.)
§ Frequency Detection (Output Frequency >> Frequency Detection Level)
(Set n040 or n041 to 5.)
Figure 29 Frequency Detection Example
(Fout ≤ Freq Detection Level)
Figure 30 Frequency Detection Example
(Fout ≥ Freq Detection Level)
6.3.11 Jump Frequencies (n058 to n060)
This function allows the prohibition or “jumping” of critical frequencies so that the motor can operate without resonance
caused by machine systems. This function is also used for dead band control. Setting the value to 0.0Hz disables this
function.
Set jump frequency 1 or 2 as follows:
n058 < n059 − n060
If this condition is not satisfied, the Inverter displays constant setting error OPE6.
Figure 31 Jump Frequencies
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 44 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 53

6.3.12 Continuing Operation by Automatic Fault Reset (n056)
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Sets the Inverter to restart and reset fault detection after a fault occurs. The number of self-diagnosis and retry attempts
can be set in n056 up to 10. The Inverter will automatically restart after the following faults occur:
• OC (overcurrent)
• OV (overvoltage)
• UV1 (undervoltage PUV) (when n051 = 1 is selected)
• GF (ground fault)
• rr (regenerative transistor fault)
The number of retry attempts are cleared to 0 in the following cases:
• If no other fault occurs within 10 minutes after retry.
• When the fault reset signal is ON after the fault is detected.
• Power supply is turned OFF.
6.3.13 Operating Coasting Motor without Trip
To operate coasting motor without trip, use the Speed Search command or DC Injection Braking at start.
§ Speed Search Command
Restarts a coasting motor without stopping it. This function enables smooth switching between motor commercial
power supply operation and Inverter operation.
Set multi-function contact input selection (constants n035 to n039) to 15 (Search command from maximum output
frequency) or 16 (Search command from set frequency).
Build a sequence so that FWD or REV RUN command is input at the same time or after the Search command. If the
RUN command is input before the Search command, the Search command becomes disabled.
Following is a time chart at Search command input.
Chapter 6: Programming Features
Figure 32 Search Command Input Timing Diagram
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 45 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 54

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
§ DC Injection Braking at Start (n064, n066)
Restarts a coasting motor after stopping it. Set the DC Injection Braking time at start in constant n066 in units of 0.1
second. When constant n066 is set to 0, DC Injection Braking is not performed and acceleration starts from the
minimum output frequency.
Set DC Injection Braking current in constant n064 in units of 1%. The Inverter rated current is 100%.
6.3.14 Using Frequency Meter of Ammeter (n048)
Selects to output either output frequency or output current to analog output Terminals AM-AC for monitoring.
Setting Analog Monitor Output Item
0 Output frequency (10 V/maximum frequency)
1 Output current (10 V/Inverter rated current)
2 Output power (10 V/Inverter rated voltage)
3
Figure 33 DC Injection Braking at Starting
DC bus voltage [10 V/400 V (200 V class), 10 V/800 V (400 V class)]
6.3.15 Calibrating Frequency Meter of Ammeter (n049)
Used to adjust analog output again.
Set the analog output voltage at 100% of output frequency.
Figure 34 Frequency Meter/Ammeter Calibration
Frequency meter displays 0 to 60Hz at 0 to 3V.
10 V X
n049 Setting
0.30
= 3 V
.
.
.
Output frequency becomes 100% at this value.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 46 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 55

6.3.16 Reducing Motor Noise or Leakage Current (n050)
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Sets Inverter output transistor switching frequency (carrier frequency).
Chapter 6: Programming Features
Setting Carrier Frequency (kHz)
1 2.5 Higher Smaller
2 5.0
3 8.0
4 10.0
5 12.5
6 15.0 Not audible Larger
Metallic Noise from
Motor
Noise and Current
Leakage
Figure 35 Custom Setting of Carrier Frequency Patterns
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 47 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 56

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.4 Selecting Stopping Method
6.4.1. Selecting Stopping Method (n004)
Selects the stopping method suitable for the application.
Setting Description
0 Deceleration to stop (Factory setting)
1 Coast to stop
2 Coast to stop with timer 1
3 Coast to stop with timer 2
§ Deceleration to Stop (n004 = 0)
Figure 36 Stopping Method
(Deceleration to Stop)
Upon removal of the FWD or REV RUN command, the motor decelerates at the deceleration rate determined by the
time set to decel time 1 (n020), and DC Injection Braking is applied immediately before stop. If the decel time is
short or the load inertia is large, an overvoltage (OV) fault may occur at deceleration. In this case, increase the decel
time or install an optional Braking Resistor (can be equipped with GP5).
Braking torque : Without Braking Resistor : Approximately 20% torque of motor rating
With Braking Resistor : Approximately 150% torque of motor rating
§ Coast to Stop (n004 = 1)
Figure 37 Stopping Method
(Coast to Stop)
Upon removal of the FWD or REV RUN command, the motor starts coasting.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 48 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 57

6.4.2. Coast to Stop with Timer
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
§ Coast to Stop with Timer 1 (n004 = 2)
Example of accel/decel time 1 selection
A RUN command is not accepted while the motor decelerates after a STOP command is given. However, if the time
required for the motor to decelerate to a stop is shorter than the time set in constant n053 (minimum baseblock time),
a RUN command is not accepted during the baseblock time.
Chapter 6: Programming Features
Figure 38 Example of Stopping Method
(Coast to Stop with Timer)
§ Coast to Stop with Timer 2 (n004 = 3)
Example of accel/decel time 1 selection
Figure 39 Example of Stopping Method
(Coast to Stop w/ Timer 2)
Operation is disabled while the motor decelerates after a STOP command is given. A RUN command is accepted,
but operation does not start until the motor stops. However, if the deceleration time is shorter than the time set in
n053 (minimum baseblock time), the Inverter does not operate during the baseblock time.
6.4.3. Applying DC Injection Braking
§ DC Injection Braking Current (N064)
Sets the DC Injection Braking current in units of 1%. (Inverter rated current: 100%)
§ DC Injection Braking Time at Stop (n065)
Sets the DC Injection Braking time at stopping in units of 0.1 second. When the setting is 0, DC Injection Braking is
not performed, but Inverter output is shut OFF when DC Injection Braking starts.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 49 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 58

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Figure 40 DC Injection Braking
When coast to stop is specified in stopping method selection (n004), DC Injection Braking at stop does not operate.
6.5 Building Interface Circuits with External Devices
6.5.1. Using Sequence Input Signals (n035 to n039)
Multi-function contact input Terminal S2 to S6 functions can be changed when necessary by setting constants n035 to
n039, respectively. Neither of these parameters can receive a setting common with the other.
• Terminal S2 function: Set to n035
• Terminal S3 function: Set to n036
• Terminal S4 function: Set to n037
• Terminal S5 function: Set to n038
• Terminal S6 function: Set to n039
Setting Name Description Page
0 REV RUN command (2-wire sequence) Only constant n035 can be set. 51
FWD/REV RUN command
1
(3-wire sequence)
2 External fault (NO constant input)
3 External fault (NC contact input)
4 Fault reset Resets fault. Fault reset is disabled during RUN command input.
5 LOCAL/REMOTE selection
Serial communication/control circuit
6
terminal selection
7 Fast stop Decelerates to stop by decel time 2 (n022) when fast stop is input.
Master frequency reference input level
8
selection
9 Multi-step speed reference 1
10 Multi-step speed reference 2
11 Jog frequency selection
12 Accel/decel time selection
13 External baseblock (NO contact input)
14 External baseblock (NC contact input)
Search command from maximum
15
frequency
16 Search command from set frequency
17 Constant setting enable/disable
18 PID integral value reset
19 PID Control disable
20 Timer function
21 OH3 (Inverter overheat alarm)
22 Analog reference sample/hold Analog frequency reference is sampled at closed and held at open. 52
25 UP/DOWN command Only constant n039 can be set. 53
26 Loop test Only constant n039 can be set. 53
∗2 to 6 are displayed in o corresponding to Terminals S2 to S6.
Factory settings: n035=0, n036=2, n037=4, n038=9, n039=10
Table 14 Multi-Function Input Variables
Only constant n035 can be set. 51
Inverter stops at fault when external fault signal is input.
Digital Operator displays EFo∗.
Master frequency reference input level (voltage input at open, current
input at closed) can be selected.
Coasting signal. Motor starts coasting when the signal is input. Digital
Operator displays bb (blinking).
Speed Search command signals. 45
Permission or prohibition of constant setting from the Digital Operator or
serial communication (setting disabled at closed, enabled at open) can be
selected.
When this signal is input, the Digital Operator displays OH3 (blinking).
Inverter continues operation.
51
52
38
39
41
58
52
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 50 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 59

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
§ Terminal Function at 2-Wire Sequence Selection (Setting: 0)
Figure 41 Terminal Function at 2-Wire Sequence Selection
§ Terminal Function at 3-Wire Sequence Selection (Setting: 1)
Figure 42 Terminal Function at 2-Wire Sequence Selection
§ LOCAL/REMOTE Selection (Setting: 5)
Selects operation reference by the Digital Operator or by the control circuit terminal. LOCAL/REMOTE selection is
available only during stop.
Open : Run according to the setting of Operation mode selection (n022).
Closed : Run by frequency reference and RUN command from the Digital Operator.
(Example) Set n002 to 3.
Open : Run by frequency reference from control circuit Terminals FV, FI and RUN command from control
Closed : Run by frequency reference and RUN command from the Digital Operator.
circuit Terminals S1, S2.
§ Serial Communication/Control Circuit Terminal Selection (Setting: 6)
Selects operation reference by serial communication or by the control circuit terminal. This selection is available only
during stop.
Open : Run according to the setting of Operation mode selection (n022).
Closed : Run by frequency reference and RUN command from serial communication.
(Example) Set n002 to 3.
Open : Run by frequency reference from control circuit Terminals FV, FI and RUN command from control
Closed : Run by frequency reference and RUN command from serial communication.
circuit Terminals S1, S2.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 51 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 60

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
§ Timer Function (Setting: 20)
When the timer function input is longer than ON-delay timer (n077), the timer function output closes.
When the timer input is open for longer than OFF-delay timer (n078), the timer function output opens.
§ Analog Reference Sample/Hold Selection (Setting: 22)
If input terminal is closed for 100ms or more, the analog frequency reference is sampled; when it opens, the analog
frequency reference is held.
Figure 43 Timing Diagram of Timer Function
Note: t1, t3 : Reference is held at 100ms or more.
t2 : Reference is not held at less than 100ms.
Figure 44 Sample of Hold Selection (Analog Reference)
§ UP/DOWN Command (Setting: n039 = 25)
With the FWD or REV RUN command entered, accel/decel is enabled by inputting the UP or DOWN signals to
control circuit Terminals S5 and S6 without changing the frequency reference, so that operation can be performed at
the desired speed.
When UP/DOWN commands are specified by n039, any function set to n038 becomes disabled; Terminal S5
becomes an input terminal for the UP command and Terminal S6 for the DOWN command.
Table 15 Timing Diagram of UP/DOWN Command Input
Control Circuit Terminal S5 (UP command) Closed Open Open Closed
Control Circuit Terminal S6 (DOWN command) Open Closed Open Closed
Operation Status Accel Decel Hold Hold
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 52 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 61

The following shows the time chart at UP/DOWN command input.
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Figure 45 Timing Diagram of VP/Down Command Input
U = UP (accelerating) status
D = DOWN (decelerating) status
H = HOLD (constant Speed) status
U1 = UP status, clamping at upper limit speed
D1 = DOWN status, clamping at lower limit speed
Chapter 6: Programming Features
NOTE: 1. When UP/DOWN command is selected, the upper limit speed is set regardless of frequency reference.
Upper limit speed = Maximum output frequency (n012) 5 Frequency reference upper limit (n030)/100
2. Lower limit value is either frequency by Analog command from control circuit Terminals, FV, FI or frequency reference lower
limit (n031) (whichever is larger).
3. When the FWD or REV RUN command is input, operation starts at the lower limit speed without an UP/DOWN command.
4. If the jog frequency selection command is input while running by the UP/DOWN command, the jog command has priority.
§ Loop Test (Setting: 26)
Checks operation in the serial I/F circuit. If a fault occurs, the Digital Operator displays CE.
Procedure
1. Set the multi-function contact input selection (n039) after turning ON the Inverter power supply, and then turn
OFF the Inverter power supply.
2. Short-circuit Terminals S6 and SC, connector 2CN pins 1 and 2. (Do not short-circuit when connecting
communication interface card SI-K2/P.)
3. Loop test is started by turning ON the Inverter power supply.
The Digital Operator displays the frequency reference after the loop test is completed satisfactorily.
6.5.2. Using Analog Input Signals (n042 to n045)
§ Master Analog Input Selection (n042)
To input the master frequency reference from the control circuit terminal, select voltage reference Terminal FV or
current reference Terminal FI by setting constant n042.
Setting
0 FV 0 to 10 V input
1 FI 4 to 20 mA input
Master Frequency
Reference Terminal
Input Level
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 53 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 62

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
§ Auxiliary Analog Input Selection (n043)
To change the control circuit Terminal FI input level, set constant n043.
Setting FI Terminal Input Level
0 0 to 10 V input
1 4 to 20 mA input
NOTE: To set constant n043 to 0, cut jumper J1 on the Inverter control PC board.
§ Frequency Reference Retention (n044)
Effective when UP/DOWN or Sample/Hold commands are selected for multi-function contact inputs. To retain the
held frequency reference at power OFF, set constant n044 to 0.
Setting Description
0 Hold reference retained in frequency reference 1 (constant n025)
1 Not retained
§ Operation Method for Frequency Reference Loss Detection (no45)
Select operation in case the frequency reference from control circuit terminal decreases rapidly.
Setting Description
0 No detection
1 Continue to run at 80% of Fmax.
(Operation when 1 is selected)
If frequency reference decreases by 90% within 400ms, operation is performed at 80% of the reference reached
before decreasing.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 54 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 63

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.5.3. Using Output Signals (n040, n041)
Multi-function contact output Terminals MA, MB and M1 functions can be changed when necessary by setting constants
n040 and n041.
• Terminal MA and MB functions: Set to n040.
• Terminal M1 function: Set to n041.
Table 16 Multi-Function Output Variables
Setting Name Description Page
0 Fault Closed when Inverter fault occurs.
1 During running
2 Frequency agree
Desired frequency
3
agree
4 Frequency detection 1
5 Frequency detection 2
Overtorque detection
6
(NO contact)
Overtorque detection
7
(NC contact)
8 During baseblock Closed when Inverter output shuts OFF.
9 Operation mode Closed when RUN command or frequency reference from Digital Operator is selected.
Inverter operation
10
ready
11 Timer function
12 Automatic restart Closed during fault retry operation.
13 OL pre-alarm
Frequency reference
14
loss
Output from serial
15
communication
16 PID feedback loss
17 OH1 alarm Closed during heatsink overtemperature (Digital Operator displays OH1” blinking).
Closed when either FWD or REV RUN command is input or when the Inverter outputs
voltage.
Closed when no Inverter fault does not occur and the Inverter can be operated.
Outputs an alarm before Inverter and motor overload protection are enabled. Pre-alarm level
is 150% for 48 seconds for the Inverter and more than 80% of the overload protection time for
the motor.
Outputs a contact when detecting a rapid decrease in the frequency reference. A rapid
decrease in the frequency reference means that the reference value is reduced more than
90% within 400ms when the reference is input to control circuit terminal.
Activates contact output independently from Inverter operation by a command from serial
communications (MEMOBUS).
Detects a rapid decrease in feedback and outputs a contact when the PID Control mode is
set. Detects when the feedback value decreases less than the detection level (n093) for
longer than the feedback loss detection delay time (n094); the Inverter continues operation.
56
56
44
44
43
43
52
Factory settings: n040=0, n041=1
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 55 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 64

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
§ Setting Example of Frequency Agree Signal (Setting: 2)
§ Setting Example of Desired Frequency Agree Signal (Setting: 3)
Figure 46 Example of Frequency Agree Signal
Figure 47 Example of Desired Frequency Agree Signal
6.6 Adjusting Motor Torque
6.6.1. Torque Compensation Gain (n067)
Motor torque requirement changes according to load conditions. Full-range automatic torque boost adjusts voltage of V/f
pattern according to the requirement. The FP5/GP5 automatically adjusts the voltage during constant-speed operation as
well as during acceleration. The required torque is calculated by the Inverter.
Output voltage ∝ Torque compensation gain (n067) 5 Required torque
• Operation
Normally, no adjustment is necessary for torque compensation gain (n067 factory setting: 1.0). When the wiring distance
between the Inverter and the motor is long, or when the motor generates vibration, change the torque compensation gain.
Increasing torque compensation gain increases motor torque, but an excessive increase may cause the following:
• Inverter malfunctions because of motor overexcitation.
• Motor overheat or excessive vibration.
Increase torque compensation gain gradually while verifying the motor current.
Figure 48 Torque Characteristics
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 56 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 65

6.7 Motor Protection
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.7.1. Motor Overload Detection
The Inverter protects against motor overload with a built-in electronic Thermal Overload Relay.
§ Motor Rated Current (n032)
Set to the rated current value shown on the motor nameplate.
§ Motor Overload Protection Selection (n033)
Setting Electronic Thermal Characteristics
0 No protection
1 Standard motor (time constant 8 minutes) (Factory setting)
2 Standard motor (time constant 5 minutes)
3 Inverter motor (time constant 8 minutes)
4 Inverter motor (time constant 5 minutes)
The electronic Thermal Overload Relay function monitors motor temperature, based on Inverter output current and
time, to protect the motor from overheating. When electronic Thermal Overload Relay is enabled, an OL1 error
occurs, shutting OFF the Inverter output and preventing excessive overheating in the motor.
When operating with one Inverter connected to one motor, an external Thermal Overload Relay is not needed.
When operating several motors with one Inverter, install a Thermal Overload Relay on each motor. In this case, set
constant n033 to 0.
§ Standard Motor and Inverter Motor
Induction motors are classified as standard motors or Inverter motors, based on their cooling capabilities. Therefore,
the motor overload function operates differently between these two motor types.
Table 17 Overload Curves
Cooling Effect Torque Characteristics
Chapter 6: Programming Features
Electronic Thermal
Overload
Effective when operated
at 50/60 Hz from
commercial power supply.
Standard Motor
Effective even when
operated at low speed
(approximately 6 Hz).
Inverter Motor
OL1 error (motor overload
protection) occurs when
continuously operated at
50/60 Hz or less at 100%
load.
Operation Frequency (Hz)
Base Frequency 60 Hz
(V/f for 60 Hz, 220 V Input Voltage)
For low speed operation, torque must be
limited in order to stop motor temperature rise.
Electronic Thermal
Overload Relay protection
not enabled even when
continuously operated at
50/60 Hz or less at 100%
load.
Operation Frequency (Hz)
Base Frequency 60 Hz
(V/f for 60 Hz, 220 V Input Voltage)
Use an inverter motor for continuous
operation at low speed.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 57 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 66

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
6.8 PID Control
To enable PID Control, set PID selection (n084) from 1 to 3.
Setting Description
0 PID disabled
1 PID enabled (Deviation I D-controlled.)
2 PID with feed forward (Feedback value is D-controlled.)
3 PID with feed forward (Feedback is reversed characteristics.)
Then select the PID Control intended value or detected value settings as follows.
6.8.1. Intended Value Setting
For setting the intended value, control circuit Terminal FV voltage signal (0 to 10 V) or multi-step speed constants n025 to
n029 can be used.
Control circuit Terminal FV voltage signal: Set Operation mode selection (n002) to 2 or 3.
Multi-step speed constants (n025 to n029): Set Operation mode selection (n002) to 0 or 1. (Combination of multi-step
speed reference and jog frequency reference.)
6.8.2. Detected Value Setting
For setting the detected value, control circuit Terminal FI current signal (4 to 20mA) or voltage signal (0 to 10 V) can be
used.
Control circuit Terminal FI current signal: Set auxiliary analog input selection (n043) to 1.
Control circuit Terminal FI voltage signal: Set auxiliary analog input selection (n043) to 0. (Cut jumper J1 on the control
PC board.)
The following shows the block diagram of PID Control.
Figure 49 PID Control Block Diagram
NOTE: 1. Value I is reset to 0 in the following cases:
• When operation stops.
• When the integral value reset signal is input by multi-function contact input selection. (Any of constants n035 to n039 are
set to 18.
2. The upper limit of value I can be set by constant n090. Increase the value of constant n090 to upgrade control capability by
integration. If the control system vibrates and it cannot be stopped by adjusting the integral time or output lag filter time,
etc., decrease the setting of constant n090.
3. PID Control can be canceled by a multi-function contact input signal. By setting any of constants n035 to n039 to 19, and by
closing the contact during running, PID Control is disabled and the intended value signal itself is used as a frequency
reference signal.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 58 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 67

6.9 Energy Saving Control
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
To enable Energy Saving Control, set energy saving selection (n095) to 1.
Setting Description
0 Energy saving is disabled
1 Energy saving is enabled
Since the constants used in the Energy Saving Control mode have been preset at the factory to the optimum values prior to
shipment, it is not necessary to adjust them under normal operation. If your motor characteristics differ greatly from those of
Saftronics standard motors, refer to the following description to change the constants.
6.9.1. Energy Saving Control Mode
§ Energy Saving Gain K2 (n096)
Use this energy saving gain when running in the Energy Saving Control mode to calculate the voltage at which motor
efficiency will be greatest, and set it as the output voltage reference. This value is preset at the factory to the
Saftronics standard motor value prior to shipment. As the energy saving gain increases, output voltage increases
also.
§ Energy Saving Voltage Lower Limit (n097, n098)
Sets the output voltage lower limit. If the voltage reference value calculated in the Energy Saving Control mode is
smaller than the specified lower limit, this lower limit value is output as the voltage reference value. The lower limit
value is set in order to prevent stalling at light loads. Set voltage limits at 6Hz and 60Hz; a value obtained by linear
interpolation should be set to any limit values other than at 6Hz or 60Hz. Setting is made as a percentage of motor
rated voltage.
Chapter 6: Programming Features
∗ For 400 V class, the value is twice that of 200 V class.
Figure 50 Energy Saving Voltage Lower Limit
6.9.2. Energy Saving Tuning
In the Energy Saving Control mode, the optimum voltage is calculated according to load power, and the voltage is
supplied to the load. However, the set constant may vary due to temperature variations or using other manufacturers’
motors, therefore, the optimum voltage may not be supplied in some cases. Automatic tuning controls voltage so that
highly efficient operation is maintained.
§ Voltage Limit of Tuning (n100)
Limits the range to control voltage by tuning. Setting is made in a percentage of motor rated voltage. By setting this
value to 0, turning is disabled.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 59 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 68

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
§ Step Voltage of Tuning (n100, n101)
Sets voltage variation width of one tuning cycle. Setting is made in a percentage of motor rated voltage. By
increasing this value, the rotating speed variation becomes larger. This voltage variation width is set when starting
tuning voltage is 100% and motor rated voltage is 5%. Values obtained by linear interpolation are set to any voltage
values other than these values.
Figure 51 Energy Saving Voltage Variation Width
6.10 MEMOBUS Control
FP5/GP5 can perform serial transmission by using a Programmable Controller (PLC) and MEMOBUS communication. MEMOBUS
is composed of one master PLC and 1 to 31 (maximum) slave units (FP5/GP5). In signal transmission (serial transmission)
between the master and slaves, the master always starts transmission and the slaves respond to it.
The master performs signal transmission with one slave at a time. Therefore, address numbers are assigned to each slave in
advance and the master specifies a number to perform signal transmission. The slave which receives the command from the
master executes the function and returns the response to the master.
6.10.1. Communication Specifications
• Interface
• Synchronization
• Transmission parameter
• Protocol
• Maximum number of units
to be connected
6.10.2. Data to be Sent/Received by Communication
Data to be sent/received by communication are RUN commands, frequency reference, fault contents, Inverter status and
constant setting/reading.
§ Operation Mode Selection (n002)
Select the RUN command and frequency reference input method in constant n002. To provide a RUN command
and frequency reference by communication, set this constant to settings 4 to 8. Also, without regard to this selection,
monitoring of running status, constant setting/reading, fault reset and multi-function input command from the PLC are
enabled. The multi-function input command becomes OR with the command input from control circuit Terminals S2
to S6.
: RS-485 (Communication interface card SI-K2/P must be mounted.)
: Asynchronous
:
• Baud rate
• Data length
• Parity
• Stop bit
: In accordance with MEMOBUS
: 31 units (when RS-485 is used)
: Selectable from 2400, 4800, 9600 BPS (Constant n107)
: Fixed to 8 bits
: Parity / no-parity, even / odd selectable (Constant n108)
: Fixed to 1 bit
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 60 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 69

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
§ MEMOBUS Frequency Reference Unit (n105)
The frequency reference units from the PLC and in the frequency reference and output frequency monitors (by
communication) are selected. The output frequency resolution of the FP5/GP5 is 0.1 Hz. Even if the frequency
reference unit is changed to 0.01 Hz in constant n105, the value in the hundredth digit of 0.01 Hz of the received
frequency reference is rounded off internally. When 30000/100% in units of 0.1% is selected, the value is rounded
off in the same way.
§ MEMOBUS Slave Address (n106)
The slave address number is set. It is necessary to set the address number so that it will not overlap with the
address number of another slave connected on the same transmission line.
NOTE: To change the values set in constants n106 to n108 and enable new settings, it is necessary to turn OFF the power supply, and
then turn it ON again.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 61 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 70

Chapter 6: Programming Features
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
NOTES:
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 62 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 71

7
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Maintenance and Inspection
This chapter describes basic maintenance and inspection procedures for the FP5/GP5.
7.1 Periodic Inspector........................................................... 64
7.2 Parts Replacement Schedule (Guidelines)................... 64
Page 72

Chapter 7: Maintenance and Inspection
•
•
•
•
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
WARNING
• Never touch high-voltage terminals in the Inverter. Failure to observe this can result in an electrical shock.
Replace all protective covers before powering up the Inverter. To remove the cover, make sure to shut OFF the Molded Case Circuit
Breaker. Failure to observe this can result in an electrical shock.
Perform maintenance or inspection only after verifying that the CHARGE LED goes OFF, after the main circuit power supply is turned
OFF. The capacitors are still charged and can be dangerous.
Only authorized personnel should be permitted to perform maintenance, inspections or parts replacements. (Remove all metal
objects (watches, bracelets, etc.) before operation. Use tools which are insulated against electrical shock.) Failure to observe this
can result in an electrical shock.
CAUTION
• The control PC board employs CMOS ICs. Do not touch the CMOS elements. They are easily damaged by static electricity.
Do not connect or disconnect wires or connectors while power is applied to the circuit. Failure to observe this can result in personal
injury.
7.1 Periodic Inspection
The FP5/GP5 will function longer if it is kept clean, cool and dry, while observing the precautions listed in 2.3 Choosing a Location to
Mount the Inverter. Check for tightness of electrical connections, discoloration or other signs of overheating or aging. Use Table 18
as your inspection guide. Before servicing, turn OFF AC main circuit power and be sure that the CHARGE LED is OFF.
Table 18 Periodic Inspection
Component Check Corrective Action
External Terminals,
Unit Mounting Bolts,
Connectors, etc.
Heatsink Build-up of dust and dirt.
Printed Circuit Board
Cooling Fan
Power Elements Accumulation of dust and dirt.
Smoothing Capacitor Discoloration or odor. Replace the capacitor or Inverter unit.
Loose screws. Tighten.
Loose connectors. Tighten.
Accumulation of conductive dust or
oil.
For abnormal noise and vibration.
Whether the cumulative operation
time exceeds 20,000 hours or not.
7.2 Parts Replacement Schedule (Guidelines)
Replace the following parts periodically, for a long, safe, trouble free working life of FP5/GP5.
Table 19 Parts Replacement Schedule
Parts Interval (Approximately) Remarks
Cooling Fan 2 to 3 years Replace with new one.
Smoothing Capacitor 5 years Replace with new one. (Decided after inspection.)
Breakers or Relays Decided after inspection.
Fuse 10 years Replace with new one.
Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor on PC Board 5 years Replace with new one. (Decided after inspection.)
Blow with dry compressed air of 39.2 5 104 to 58.8 5 104 Pa (4
to 6kg⋅cm2) pressure.
Blow with dry compressed air of 39.2 5 104 to 58.8 5 104 Pa (4
to 6kg⋅cm2) pressure. If dust and oil cannot be removed,
replace the board.
Replace the cooling fan.
Blow with dry compressed air of 39.2 5 104 to 58.8 5 104 Pa (4
to 6kg⋅cm2) pressure.
NOTE: Operating conditions are as follows:
Ambient temperature : 30°C yearly average
Load factor : 80% or below
Operation rate : 12 hours or below/day
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 64 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 73

8
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Troubleshooting
This chapter describes the Inverter fault display and the fault contents caused by motor/machine
malfunctions and the corrective actions to be taken.
8.1 Fault Diagnosis and Corrective Actions....................... 66
8.2 Alarm Display and Explanation ..................................... 69
8.3 Motor Faults and Corrective Actions ............................ 70
Page 74

Chapter 8: Troubleshooting
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
8.1 Fault Diagnosis and Corrective Actions
§ When the FP5/GP5 detects a fault, the fault is displayed on the Digital Operator and activates the fault contact output and the
motor coasts to a stop. Check the cause in the table below and take the corrective actions.
§ If the inspections or corrective actions described cannot solve the problem, contact your Saftronics representative immediately.
§ To restart, turn ON the reset input signal or press the RESET key or shut OFF the main circuit power supply once, to reset the
stop status.
§ To change the setting of a constant during fault display, first press the DSPL key to call up the monitor display. Then press
DSPL and ENTER keys simultaneously to enter PRGM mode.
NOTE: When a FWD or REV RUN command is input, the Inverter does not receive a fault reset signal. Make sure to reset after turning
OFF the FWD or REV RUN command.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 66 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 75

Table 20 Fault Diagnosis and Corrective Actions
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Chapter 8: Troubleshooting
Fault
Display
U 1
U 2
U 3
O c
O
G F
P U F
∗ O H 1
O H 2
O L 1
O L 2
Description Details Corrective Action
Undervoltage in the DC main circuit during
Main circuit
undervoltage (PUV)
Control circuit
undervoltage (CUV)
MC fault
Overcurrent (OC)
Overvoltage (OV)
Grounding (GF)
Earth fault)
Main circuit fault (PUF)
Heatsink overheat
(OH1)
Heatsink overheat
(OH2)
Motor overload (OL1)
Inverter overload (OL2)
running.
Detection level:
200 V class: Approximately 190 V or less.
400 V class: Approximately 380 V or less.
Undervoltage in the control circuit during
running.
The pre-charge contactor opened during
running.
The Inverter output current exceeded the OC
level.
The main circuit DC voltage exceeded the OV
level.
Detection level:
200 V class: Approximately 400 V
400 V class: Approximately 800 V
Inverter output grounding current exceeded
50% of Inverter rated current.
• The direct current circuit fuse is blown.
• The output transistors were damaged.
The transistor heatsink temperature exceeded
the allowable value.
(Fin temperature > n130: OH1 detection level)
(approximately 95°C)
The transistor heatsink temperature exceeded
the allowable value.
(Fin temperature > n134: OH2 detection level)
(approximately 105°C)
Inverter output exceeded the motor overload
level.
Inverter output exceeded the Inverter overload
level.
• Check the power supply wiring.
• Correct the line voltage.
• Check the motor coil resistance.
• Extend the accel/decel time.
• Check the motor insulation.
• Multi-meter check.
Extend the deceleration time, add braking
circuit.
• Check that motor insulation has not
deteriorated.
• Check that connection between Inverter and
motor is not damaged.
Check for damaged transistor, load side short
circuit, grounding, etc.
Check the fan and ambient temperature.
Check the fan and ambient temperature.
Reduce the load.
Reduce the load, extend the acceleration
time.
∗ O L 3
5 C
E F O
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 67 © Saftronics, Inc.
Overtorque detection
(OL3)
Load short-circuit (SC) Inverter output (load) is short-circuited.
External fault from serial
communication
∗ Stopping method selection is available.
Inverter output current exceeded the
overtorque detection level (n075).
Fault occurred in the external control circuit. Check the external control circuit.
Reduce the load, extend the acceleration
time.
• Check the motor coil resistance.
• Check the motor insulation.
Page 76

Chapter 8: Troubleshooting
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Table 20 Fault Diagnosis and Corrective Actions (Continued)
Fault
Display
E F 2
E F 3
E F 4
E F 5
E F 6
S P I
S P O
∗ C E
H
C P F O
C P F 1
C P F 4
C P F 5
∗Stopping method selection is available.
Description Details Corrective Action
External fault at
Terminal S2
External fault at
Terminal S3
External fault at
Terminal S4
External fault at
Terminal S5
External fault at
Terminal S6
Excessive ripple
in bus bar
Output openphase
MEMOBUS
transmission
fault
Braking
transistor failure
Braking Resistor
Unit overheat
Control circuit
fault 1
(CPF0)
(Digital Operator
transmission
fault)
Control circuit
fault 2
(CPF1)
(Digital Operator
transmission
fault)
EEPROM fault
(CPF4)
CPU A/D
converter fault
(CPF5)
Fault occurred in the external control circuit.
• Inverter input power supply has open-phase.
• Large unbalance in input voltage.
Inverter output has open-phase.
Control data cannot be received normally.
The braking transistor has failed. Replace the Inverter.
The Braking Resistor Unit temperature has
exceeded the allowable value. (Protects only
Inverter built-in type.)
• Transmission between the Inverter and Digital
Operator cannot be established 5 seconds after
supplying power.
• MPU peripheral element check fault (initial).
• Transmission between the Inverter and Digital
Operator is established once after supplying
power, but later transmission fault continues for
more than 2 seconds.
• MPU peripheral element check fault (initial).
Inverter control unit fault. Replace the control card.
Check the condition of the input terminal.
If the LED lights when terminal is not
connected, replace the Inverter.
• Check the line voltage.
• Re-tighten the input terminal screws.
• Check the output wiring.
• Check the motor impedance.
• Retighten the output terminal screws.
• Check the transmission devices or signals.
• Verify the setting of the constant. Refer to
8.1 Fault Diagnosis and Corrective Actions
for verification/change of the constant.
Reduce the regenerative load.
• Insert the Digital Operator connector again.
• Check the control circuit wiring.
• Replace the control card.
• Insert the Digital Operator connector again.
• Check the control circuit wiring.
• Replace the control card.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 68 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 77

8.2 Alarm Display and Explanation
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Alarms do not activate fault contact outputs and the Inverter returns to its former operation status automatically when the cause is
removed. The following table explains the different types of alarms.
Table 21 Alarm Display and Explanation
Alarm Display Contents Explanation
Chapter 8: Troubleshooting
U
Blinking
O
Blinking
O H 1
Blinking
O L 3
Blinking
Blinking
E F
Blinking
C A L L
Blinking
O H 3
Blinking
C E
Blinking
Undervoltage detection Undervoltage has been detected.
OV during stop
Heatsink overheating
Overtorque detection
External baseblock External baseblock command is input from control circuit terminal.
Simultaneous FWD/REV
RUN commands
MEMOBUS transmission
waiting
Inverter overheat pre-alarm Inverter overheat pre-alarm signal is input from control circuit terminal.
MEMOBUS transmission
error
Main circuit DC voltage exceeds the overvoltage detection level while the Inverter
output is OFF.
Under condition of heatsink temperature > [OH1 detection level (approximately 95°C)],
continuous operation at OH1 detection is selected.
Under condition of Inverter output current > n075 (overtorque detection level),
continuous operation at overtorque detection is selected.
Both FWD and REV RUN commands are input simultaneously for over 500 ms.
Under condition of n002 (operation method selection) > 4, the Inverter has not received
the normal data from serial communication after power ON. Refer to 8.1 Fault
Diagnosis and Corrective Actions for verification/change of the constant.
Continuous operation is selected at MEMOBUS transmission error. Refer to 8.1 Fault
Diagnosis and Corrective Actions for verification of the constant.
O P E 1
O P E 3
O P E 5
O P E 6
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 69 © Saftronics, Inc.
Inverter kVA setting fault Inverter kVA setting error.
One of the following setting errors occurred in the multi-function contact input selection
Multi-function contact input
setting error
V/f data setting error Setting error of n012 to n018 (V/f data).
Constant setting error
(n035 to n039):
• Two or more of the same values are set.
• Both 15 and 16 are set at the same time.
• Both 22 and 25 are set at the same time.
One of the following setting errors occurred:
• Inverter rated current 5 0.1 > n032 (motor rated current), or n032 > Inverter rated
current 5 2.
• n058 (jump frequency 1) > n059 (jump frequency 2) − n60 (jump frequency range).
• n030 (output frequency upper limit) < n031 (output frequency lower limit).
Page 78

Chapter 8: Troubleshooting
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
8.3 Motor Faults and Corrective Actions
§ If any of the following faults occurs in the motor, check the cause and provide the relevant corrective action.
§ If these inspections and corrective actions cannot solve the problem, contact your Saftronics representative immediately.
Table 22 Motor Faults and Corrective Actions
Fault Check Point Corrective Action
Power supply voltage applied to power
supply Terminals L1, L2, and L3 (R, S, and
T)? Is CHARGED LED ON?
Use rectifier type voltmeter to test. Is
voltage output to output Terminals T1, T2
Motor does not rotate.
Motor rotation reverses.
Motor rotates, but variable
speed not available.
Motor RPM too high or too low.
Motor RPM not stable during
operation.
and T3 (U, V, and W) correct?
Motor locks due to excessive load? Reduce the load and release the lock.
Fault displayed in Digital Operator display? Check troubleshooting table.
FWD or REV RUN command entered? Check the wiring.
Frequency setting voltage entered?
Operation mode setting (n002) correct? Input the correct the set value.
Wiring of Terminals T1, T2, and T3 (U, V,
and W) correct?
FWD and REV wiring run signals entered? Correct the wiring.
Wiring of frequency setting circuit correct? Correct the wiring.
Operation mode setting (n002) correct?
Load excessively large? Reduce the load.
Motor ratings (number of poles, voltage)
correct?
Accel/decel speed change ratio for gears,
etc. correct?
Maximum frequency set value correct? Check the maximum frequency set value.
Use rectifier voltmeter. Voltage between
motor terminals not excessively reduced?
Load excessively large? Reduce the load.
Load variation excessively large?
3-phase or single-phase power supply
used? For 3-phase power supply, open
phase?
• Turn ON power supply.
• Turn OFF power supply, and then ON
again.
• Check power supply voltage.
• Make sure terminal screws are tight.
Turn OFF power supply, then turn ON again.
• Correct the wiring.
• Check frequency setting voltage.
Match wiring to the phase order of the motor
leads T1, T2, and T3 (U, V, and W).
With the Digital Operator, check the operation
mode selection.
Check motor nameplate specifications.
Check speed changer (gears, etc.).
Check V/f characteristics values.
• Reduce the load variation.
• Increase Inverter motor capacity.
For 3-phase power supply, check the wiring if
power supply is open phase.
For single-phase power supply connect AC
reactor to the power supply.
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 70 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 79

9
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Specifications
This chapter describes the specifications of the FP5/GP5 Inverter.
9.1 Standard Specifications................................................. 72
Page 80

Chapter 9: Specifications
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
9.1 Standard Specifications
Series FP5/GP5
Table 23 200 V Class Specifications
Models
FP5/GP5
Maximum Applicable Motor
Output *(kW)
Inverter Capacity (kVA) 6.7 9.5 13 19 24 30 37 50 61 70 85 110
Rated Output Current (A) 17.5 25 33 49 64 80 96 130 160 183 224 300
Output
Maximum Output Voltage 3-Phase, 200/208/220/230 V (Proportional to input voltage)
Characteristics
Rated Output Frequency Up to 400 Hz available by programming
Rated Input Voltage and
Frequency
Allowable Voltage
Fluctuation
Power
Supply
Allowable Frequency
Fluctuation
Control Method Sine wave PWM
Frequency Control Range 0.1 to 400 Hz
Frequency Accuracy
Frequency Resolution
Output Frequency
Resolution
Overload Capacity 150% of rated output current for 1 minute 120% of rated output current for 1 minute
Frequency Setting Signal
Control Characteristics
Accel/Decel Time 0.0 to 3600 sec (Accel/decel time setting independently)
Braking Torque
Number of V/f Patterns 15 preset V/f patterns, 1 custom V/f with voltage limit, 1 custom without voltage limit
Motor Overload
Protection
Instantaneous
Overcurrent
Overload
Overvoltage Motor coasts to a stop if converter output voltage exceeds 410 V.
Undervoltage Motor coasts to a stop if converter output voltage drops to 190 V or below.
Momentary Power Loss
Heatsink Overheat Protected by thermistor.
Protective Functions
Stall Prevention Stall Prevention during accel/decel and constant speed operation.
Ground Fault Protected by electronic circuit.
Power Charge Indication CHARGE LED stays ON until bus voltage drops below 50 V.
Ambient Temperature
Humidity 90% RH or less
Storage Temperature −20°C to + 60°C
Locatioan Indoor (protected from corrosive gases and dust)
Environment
Elevation 1000 meters or less
Vibration 9.81m/s2 (1G) at 10 to less than 20 Hz, up to 1.96m/s2 (0.2G) at 20 to 50 Hz.
∗Based on a Saftronics standard 4-pole motor for maximum applicable motor output.
23P7 25P5 27P5 2011 2015 2018 2022 2030 2037 2045 2055 2075
3.7 5.5 7.5 11 15 18.5 22 30 37 45 55 75
3-Phase 200/208/220 V 50 Hz
200/208/220/230 V 60 Hz
+ 10%, − 15%
± 5%
Digital Command: 0.01% (− 10°C to + 40°C)
Analog Command: 0.1% (25°C ± 10°C)
Digital Operator reference: 0.1 Hz
Analog reference: 0.1 Hz
0.1 Hz
0 to + 10 V (20kΩ), 4 to 20 mA (250Ω)
(Approximately 125% with Braking Resistor)
Approximately 20%
Protected by electronic Thermal Overload Relay
Motor coasts to a stop at approximately 200% of
Inverter rated current.
Motor coasts to a stop after 1 minute at 150% of
rated output current.
Immediately stop by 15 ms and above momentary power loss. (Factory setting)
Continuous operation during power loss less than 2 seconds is equipped as standard.
− 10°C to + 40°C (Enclosed wall-mounted type)
− 10°C to + 45°C (Open chassis type)
(Braking Resistor cannot be mounted)
Motor coasts to a stop at approximately 180% of
Inverter rated current.
Motor coasts to a stop after 1 minute at 120% of
rated output current.
Approximately 20%
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 72 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 81

Table 24 400 V Class Specifications (FP5/GP5)
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Chapter 9: Specifications
Models
FP5/GP5
Maximum Applicable Motor
Output *(kW)
Inverter Capacity (kVA) 1.4 2.6 3.7 4.7 6.1 8.4 11 14 21 26
Rated Output Current (A) 1.8 3.4 4.8 6.2 8 11 14 18 27 34
Maximum Output Voltage 3-Phase 380/400/415/440/460 V (Proportional to input voltage)
Output
Characteristics
Rated Output Frequency Up to 400 Hz available by programming
Rated Input Voltage and
Frequency
Allowable Voltage
Fluctuation
Power
Supply
Allowable Frequency
Fluctuation
Control Method Sine wave PWM
Frequency Control Range 0.1 to 400 Hz
Frequency Accuracy
Frequency Resolution
Output Frequency
Resolution
Overload Capacity 150% of rated output current for 1 minute
Frequency Setting Signal
Control Characteristics
Accel/Decel Time 0.0 to 3600 seconds (Accel/decel time setting independently)
Braking Torque Approximately 20% (Approximately 125% with Braking Resistor)
Number of V/f Patterns 15 preset V/f patterns, 1 custom V/f with voltage limit, 1 custom without voltage limit
Motor Overload
Protection
Instantaneous
Overcurrent
Overload Motor coasts to a stop after 1 minute at 150% of rated output current.
Overvoltage Motor coasts to a stop if converter output voltage exceeds 820 V.
Undervoltage Motor coasts to a stop if converter output voltage drops to 380 V or below.
Momentary Power Loss
Heatsink Overheat Protected by thermistor.
Protective Functions
Stall Prevention Stall Prevention during accel/decel and constant speed operation.
Ground Fault Protected by electronic circuit.
Power Charge Indication Charge LED stays ON until bus voltage drops below 50 V.
Ambient Temperature
Humidity 90% RH or less
Storage Temperature −20°C to + 60°C
Locatioan Indoor (protected from corrosive gases and dust)
Environment
Elevation 1000 meters or less
Vibration 9.81m/s2 (1G) at 10 to less than 20 Hz, up to 1.96m/s2 (0.2G) at 20 to 50 Hz.
∗Based on a Saftronics standard 4-pole motor for maximum applicable motor output.
40P4 40P7 41P5 42P2 43P7 44P0 45P5 47P5 4011 4015
0.55 1.1 1.5 2.2 3.7 4.0 5.5 7.5 11 15
3-Phase 380/400/415/440/460 V 50/60 Hz
+ 10%, − 15%
± 5%
Digital Command: ± 0.01% (− 10°C to + 40°C)
Analog Command: ± 0.1% (25°C ± 10°C)
Digital Operator reference: 0.1 Hz
Analog reference: 0.1 Hz
0.1 Hz
0 to + 10 V (20kΩ), 4 to 20 mA (250Ω)
Protected by electronic Thermal Overload Relay
Motor coasts to a stop at approximately 200% of Inverter rated current.
Immediately stop by 15 ms and above momentary power loss. (Factory setting)
Continuous operation during power loss less than 2 seconds is equipped as standard.
− 10°C to + 40°C (Enclosed wall-mounted type)
− 10°C to + 45°C (Open chassis type)
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 73 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 82

Chapter 9: Specifications
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Table 25 400 V Class Specifications (FP5/GP5)
Models
FP5/GP5
Maximum Applicable Motor
Output * (kW)
Inverter Capacity (kVA) 31 40 50 61 73 98 130 170 230 260 340 460
Rated Output Current (A) 41 52 65 80 96 128 165 224 302 340 450 605
Output
Maximum Output Voltage 3-Phase, 380/400/415/440/460 V (Proportional to input voltage)
Characteristics
Rated Output Frequency Up to 400 Hz available by programming
Rated Input Voltage and
Frequency
Allowable Voltage
Fluctuation
Power
Supply
Allowable Frequency
Fluctuation
Control Method Sine wave PWM
Frequency Control Range 0.1 to 400 Hz
Frequency Accuracy
Frequency Resolution
Output Frequency
Resolution
Overload Capacity 120% of rated output current for 1 minute.
Frequency Setting Signal 0 to + 10 V (20kΩ), 4 to 20 mA (250Ω)
Accel/Decel Time 0.0 to 3600 seconds (Accel/decel time setting independently)
Control Characteristics
Braking Torque
Number of V/f Patterns 15 preset V/f patterns, 1 custom V/f with voltage limit, 1 custom without voltage limit
Motor Overload
Protection
Instantaneous
Overcurrent
Overload Motor coasts to a stop after 1 minute at 120% of rated output current.
Overvoltage Motor coasts to a stop if converter output voltage exceeds 820 V.
Undervoltage Motor coasts to a stop if converter output voltage drops to 380 V or below.
Momentary Power Loss
Heatsink Overheat Protected by thermistor.
Protective Functions
Stall Prevention Stall Prevention during accel/decel and constant speed operation.
Ground Fault Protected by electronic circuit.
Power Charge Indication CHARGE LED stays ON until bus voltage drops below 50 V.
Ambient Temperature
Humidity 90% RH or less
Storage Temperature −20°C to + 60°C
Locatioan Indoor (protected from corrosive gases and dust)
Environment
Elevation 1000 meters or less
Vibration 9.81m/s2 (1G) at 10 to less than 20 Hz, up to 1.96m/s2 (0.2G) at 20 to 50 Hz.
∗Based on a Saftronics standard 4-pole motor for maximum applicable motor output.
4018 4022 4030 4037 4045 4055 4075 4110 4160 4185 4220 4300
18.5 22 30 37 45 55 75 110 160 185 220 300
3-Phase 380/400/415/440/460 V 50/60 Hz
+ 10%, − 15%
± 5%
Digital Command: ± 00.1% (− 10°C + 40°C)
Analog command: ± 0.1% (25°C ± 10°C)
Digital Operator reference: 0.1 Hz
Analog reference: 0.1 Hz
0.1 Hz
(Braking Resistor cannot be mounted)
Approximately 20%
Protected by electronic Thermal Overload Relay
Motor coasts to a stop at approximately 180% of Inverter rated current.
Immediately stop by 15 ms and above momentary power loss. (Factory setting)
Continuous operation during power loss less than 2 seconds is equipped as standard.
− 10°C to + 40°C (Enclosed wall-mounted type)
− 10°C to + 45°C (Open chassis type)
(Approximately 100% with Braking Unit and
Approximately 20%
Braking Resistor)
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 74 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 83

10
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Dimensions
The following chapter describes the dimensions of the FP5/GP5.
10.1 Dimensions...................................................................... 76
Page 84

Chapter 10: Dimensions
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
10.1 Dimensions
The figures below show a 200V 3.7kW model. Use open chassis type 200V/400V 15kW or less with the top and bottom covers
removed.
The following figure shows the mounting dimensions of 400V 185 to 300kW.
Figure 52 Dimensions of FP5/GP5
Maximum Applicable
Motor Output (kW)
185, 220 750 440 310 850 285 565
300 750 440 310 873 298 575
Figure 53 Mounting Dimensions of 400V 185 to 300kW
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 76 © Saftronics, Inc.
W1 W2 W3 W4 W5 W6
Page 85

Table 26 FP5/GP5 Dimensions (mm) and Approximate Mass (kg)
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Chapter 10: Dimensions
Voltage
Motor
Capacity
(kW)
W H D W1 H1 H2
Open Chassis Type (IP00) Enclosed Wall-mounted type (NEMA1/IP20)
Mass
(kg)
W H H W1 H1 H2
3.7 140 280 180 126 266 7.0 4.5 140 280 180 126 266 7.0 4.5 M5
200V
Class
5.5 5.5 5.5
7.5
11 380 7.5
15
18.5 610 87.5
22
30 61 67
37
45
55
200 300 205 186 285 8.0
200 300 205 186 285 8.0
6
250 380 225 236 365 7.5 11 250
325 450 285 275 435 7.5 28 330
425 675 350 320 650 12.5
430 985 350 320 650 212.5
62
475 800 350 370 775 12.5 80 480 1110 350 370 775 212.5 87 M10
75 575 925 400 445 895 15.0 135 580 1290 400 445 895 270 145 M12
0.55
1.1
140 280 160 126 266 7.0 3 140 280 160 126 266 7.0 3 M5
1.5 4 4
2.2
3.7
140 280 180 126 266 7.0
140 280 180 126 266 7.0
4.5
4.0
400V
Class
5.5
7.5
11
15
18.5 29 32
22
200 300 205 186 285 8.0 6 200
250 380 225 236 365 7.5 11 250 380 225 236 365 7.5 11 M6
325 450 285 275 435 7.5
330 610 285 275 435 87.5
31
30
37
325 625 285 275 610 7.5 44 330
45
55 81 87
75
110 375 135 375 145
160
185
220
455 820 350 350 795 12.5
575 925
445 895 15.0
400
82
145
950 1450 435 *2 1400 25 360
460 1130 350 350 795 212.5
580 1290
300 960 1600 455 *2 1550 25 420
1
∗
Mounting holes are the same for the open chassis type and the enclosed wall-mounted type.
2
∗
Refer to the mounting dimensions on Page 76.
225 236 365
400
285 275 435
675
280
205 186 285 8.0 6 M6
300
785 87.5
285 275 610
850
445 895 270.0
400
27.5
152.5
152.5
M12
Mass
(kg)
6
11 M6
32 M6
68
4.5
34
48 M6
88
155
d *
M6
M10
M5
M6
M10
M12
1
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 77 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 86

Chapter 10: Dimensions
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
NOTES:
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 78 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 87

11
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Typical Connection Diagram
This chapter describes the connection diagrams for the GP5.
11.1 Braking Resistor Unit ..................................................... 80
11.2 Braking Unit and Braking Resistor Unit........................ 81
Page 88

Chapter 11: Typical Connection Diagram
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
11.1 Braking Resistor Unit
For Models GP5 23P7 to − GP5 27P5 (200 V Class 3.7 to 7.5 kW).
Models GP5 40P4 TP − GP5 4015 (400 V Class 0.4 to 15 kW).
GP5
= The transformer is not necessary for 200V class.
‡ When installing a DC Reactor (option), remove the common bar between ¾1 and ¾2 terminals (provided as
standard) and connect a DC Reactor with the terminals.
# When using the Thermal Overload Relay, set constant n070 to 0. (Stall Prevention selection during decel is
disabled.) If it is not changed, the Inverter may not stop within set decel time.
Figure 54 Connection Diagram for Braking Resistor
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 80 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 89

11.2 Braking Unit and Braking Resistor Unit
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
For models GP5 2011, − GP5 2015 (200 V Class 11, 15 kW).
GP5
Chapter 11: Typical Connection Diagram
= When installing a DC Reactor (option), remove the common bar between ¾1 and ¾2 terminals (provided as standard) and
connect a DC Reactor with the terminals.
‡ When using the Thermal Overload Relay, set constant n070 to 0. (Stall Prevention selection during decel is disabled.) If it is not
changed, the Inverter may not stop within set decel time.
NOTE: Braking Unit or Thermal Overload Relay cannot be connected to Inverters of 200V class 18.5 to 75kW or 400V class 18.5
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 81 © Saftronics, Inc.
to 160 kW.
Figure 55 Connection Diagram for Braking Unit and Braking Resistor
Page 90

Chapter 11: Typical Connection Diagram
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
NOTES:
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 82 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 91

12
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Constant List
This chapter lists the constants for the FP5/GP5.
12.1 Constant List................................................................... 84
Page 92

Chapter 12: Constant List
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
12.1 Constant List
Table 27 Constant List
Constant Function Name Description
0 : n001 read and set, n002 to n108 read only
1 : n001 to n034 read and set, n035 to n108 read only
2 : n001 to n049 read and set, n050 to n108 read only
3 : n001 to n108 read and set
4 : Not used
n001 Password
n002 Operation mode selection
n003 Input voltage
n004 Stopping method selection
n005 Power rotation
n006 Reverse run prohibit
n007 LOCAL/REMOTE key function
n008 Stop key function
n009
n010
n011
n012 Maximum output frequency
n013 Maximum voltage
n014 Maximum voltage output frequency
n015 Middle output frequency
n016 Middle frequency voltage
n017 Minimum output frequency
n018 Minimum output frequency voltage
n019
n020
n021 Acceleration time 2
Frequency reference setting method
from Digital Operator
V/f pattern selection (same as V/f
LED)
Motor rated voltage
(same as Vmtr LED)
Acceleration time 1
(same as Accel LED)
Deceleration time 1
(same as Decel LED)
5 : Not used
6 : 2-wire initialization − reset (Japanese standard)
7 : 3-wire initialization − reset (Japanese standard)
8 : 2-wire initialization − reset (U.S. specifications)
9 : 3-wire initialization − reset (U.S. specifications)
10 : 2-wire initialization – reset (European specifications)
11 : 3-wire initialization – reset (European specifications)
(Setting) (Operation) (Reference)
0 : Operator Operator
1 : Terminal Operator
2 : Operator Terminal
3 : Terminal Terminal
4 : Operator Serial com
5 : Terminal Serial com
6 : Serial com Serial com
7 : Serial com Operator
8 : Serial com Terminal
Unit : 0.1V
Setting range : 150.0 to 255.0V (510V for 400V units)
0 : Deceleration to stop
1 : Coast to stop
2 : Coast to stop with timer 1
3 : Coast to stop with timer 2
0 : CCW
1 : CW
0 : Reverse run enabled
1 : Reverse run disabled
0 : Disabled
1 : Enabled
0 : STOP key is effective when operated from Digital Operator
1 : STOP key is always effective
0 : ENTER key not used
1 : ENTER key used
0 to E : 15 preset V/f patterns
F : Custom V/f pattern with voltage limit
FF : Custom V/f pattern without voltage limit
Unit : 0.1V
Setting range: 150.0 to 255.0V (510 V for 400V units)
Unit : 0.1Hz
Setting range: 50.0 to 400.0Hz
Unit : 0.1V
Setting range: 0.1 to 255.0V (510 V for 400V units)
Unit : 0.1HZ
Setting range: 0.2 to 400.0V
Unit : 0.1Hz
Setting range: 0.1 to 399.9Hz
Unit : 0.1V
Setting range: 0.1 to 255.0V (510V for 400V units)
Unit : 0.1Hz
Setting range: 0.1 to 10.0Hz
Unit : 0.1V
Setting range 0.1 to 50.0V
Unit : 0.1 seconds (1 seconds for 1000 seconds and above)
Setting range: 0.0 to 3600 seconds
Unit : 0.1 sec (1 seconds for 1000 seconds and above)
Setting range: 0.0 to 3600 seconds
Unit : 0.1 seconds (1 seconds for 1000 seconds and above)
Setting range: 0.0 to 3600 seconds
Factory
Setting
1
3
200.0V
(400.0V)
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
200.0V
60.0 Hz
200.0V
60.0Hz
3.0Hz
15.0V
1.5Hz
10.0V
10.0
seconds
10.0
seconds
10.0
seconds
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 84 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 93

Table 27 Constant List (Continued)
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Constant Function Name Description
n022 Deceleration time 2
n023
n024 Display mode
n025
n026 Frequency reference 2
n027 Frequency reference 3
n028 Frequency reference 4
n029 Jog frequency
n030 Frequency reference upper limit
n031 Frequency reference lower limit
n032
n033
n034 Stopping method selection (OH1)
n035
n036
n037
S−curve selection
Frequency reference 1
(same as Fref LED)
Motor rated current
(same as FLA LED)
Motor overload protection selection
(OL1)
Multi-function contact input selection
(Terminal S2)
Multi-function contact input selection
(Terminal S3)
Multi-function contact input selection
(Terminal S4)
Unit : 0.1 seconds (1 seconds for 1000 seconds and
above)
Setting range: 0.0 to 3600 seconds
(Setting) (S−curve time)
0 : S−curve not provided
1 : 0.2 seconds
2 : 0.5 seconds
3 : 1.0 seconds
(Setting) (Unit)
0 : 0.1 Hz
2 to 39 : RPM (input # of motor poles)
40 to 3999 : custom
Setting depends on n024 setting
Range : 0 to 9999
Setting depends on n024 setting
Range : 0 to 9999
Setting depends on n024 setting
Range : 0 to 9999
Setting depends on n024 setting
Range : 0 to 9999
Setting depends on n024 setting
Range : 0 to 9999
Unit : 1%
Setting range : 0 to 100%
Unit : 1%
Setting range : 0 to 100%
Unit: 0.1A Range: 10 to 200% INV rated
Unit is 1A, when setting is more than 1000A
(Setting) (Characteristics)
0 : No protection
1 : Standard motor (time constant 8 minutes)
2 : Standard motor (time constant 5 minutes)
3 : Inverter motor (time constant 8 minutes)
4 : Inverter motor (time constant 5 minutes)
(Setting) (Stop Method)
0 : Ramp to stop − Decel 1 (fault)
1 : Coast to stop (fault)
2 : Ramp to stop − Decel 2 (fault)
3 : Inverter motor (time constant 8 minutes)
0 : REV RUN command (2-wire sequence)
1 : FWD/REV RUN command (3-wire sequence)
2 : External fault (NO contact input)
3 : External fault (NC contact input)
4 : Fault reset
5 : LOCAL/REMOTE selection
6 : Serial communication/control circuit terminal selection
7 : Fast stop
8 : Master frequency reference input level selection
9 : Multi-step speed reference
10 : Multi-step speed reference
11 : Jog frequency selection
12 : Accel/decel time selection
13 : External baseblock (NO contact input)
14 : External baseblock (NC contact input)
15 : Search command from maximum frequency
16 : Search command from set frequency
17 : Constant setting enable/disable
18 : PID integral value reset
19 : PID Control disable
20 : Timer function
21 : OH3 (Inverter overheat alarm)
22 : Analog reference sample/hold
Set items are same as n035 2
Set items are same as n035 4
Chapter 12: Constant List
Factory
Setting
10.0 seconds
1
0
0.0Hz
0.0Hz
0.0Hz
0.0Hz
6.0Hz
100%
0%
kVA
dependent
1
3
0
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 85 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 94

Chapter 12: Constant List
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Table 27 Constant List (Continued)
Constant Function Name Description
n038
n039
N040
n041
n042
n043
n044 Frequency reference retention
n045
n046
n047
n048
n049 Analog monitor gain
n050 Carrier frequency
n051
n052
n053 Minimum baseblock time
n054
n055 Power loss ridethru time
Multi-function contact input selection
(Terminal S5)
Multi-function contact input selection
(Terminal S6)
Multi-function contact output selection
(Terminal MA−MB−MC)
Multi-function contact output selection
(Terminal M1−M2)
Master analog input selection
(FV or FI Terminal)
Auxiliary analog input selection (FI
Terminal)
Operation method for freq. ref. loss
detection
Frequency reference gain
(same as Fgain LED)
Frequency reference bias
(same as Fbias LED)
Multi-function analog output (AM−AC)
Momentary power loss ridethrough
method
Speed search level
(decel time is 2 seconds except 4
seconds for 200V/400V, 55kW or
above)
V/f reduction level during speed
search
Set items are same as n035 9
Set items are same as n035
25 : UP/DOWN command
26 : Loop test (MEMOBUS)
0 : Fault
1 : During running
2 : Frequency agree
3 : Desired frequency agree
4 : Frequency detection 1
5 : Frequency detection 2
6 : Overtorque detection (NO contact)
7 : Overtorque detection (NC contact)
8 : During baseblock
9 : Operation mode
10 : Inverter operation ready
11 : Timer function
12 : Automatic restart
13 : OL pre-alarm
14 : Frequency reference loss
15 : Output from serial communication (DO function)
16 : PID feedback loss
17 : OH1 alarm
Set items are as same as n040 1
0 : 0 to 10V input (FV)
1 : 4 to 20mA input (FI)
0 : 0 to 10V input (Jumper must be cut)
1 : 4 to 20mA input
0 : Held reference retained in frequency reference 1 (constant
n025)
1 : Not retained
0 : No detection
1 : Continue to run at 80% previous ref.
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 200%
Unit : 1%
Setting range: − 100 to 100%
(Setting) (Monitor)
0 : Output frequency
1 : Output current
2 : Output power
3 : DC bus voltage
Unit : 0.01
Setting range: 0.01 to 2.00
1, 2, 4, 5, 6 : Set value 5 2.5kHz
3 : 8.0kHz
7, 8, 9 : Proportional to output frequency of 2.5kHz maximum
(Setting) (Method)
0 : Not provided
1 : Continuous operation after power recovery within
the time set in n055
2 : Continuous operation after power recovery within
control logic time (no fault output)
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 200%
100% = INV rated current
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: 0.5 to 5.0 seconds
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 100%
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: 0.0 to 2.0 seconds
Factory
Setting
10
0
0
1
0
0
100%
0%
0
1
kVA
dependent
0
110%
kVA
dependent
kVA
dependent
kVA
dependent
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 86 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 95

Table 27 Constant List (Continued)
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Constant Function Name Description
n056 Automatic retry attempts
n057
n058 Jump frequency 1
n059 Jump frequency 2
n060 Jump frequency range
n061 Elapsed timer selection
n062 Elapsed timer 1
n063 Elapsed timer 2
n064 DC Injection Braking current
n065 DC Injection Braking time at stop
n066 DC Injection Braking time at start
n067 Torque compensation gain
n068 Motor line to line resistance
n069 Iron loss
n070 Stall Prevention during deceleration
n071
n072 Stall Prevention level during running
n073
n074
n075 Overtorque detection level (OL3)
n076 Overtorque detection time (OL3)
n077 ON-delay timer
n078 OFF-delay timer
n079 dB resistor overheat function (rH)
n080 Input phase loss detection level (SPI)
n081
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 87 © Saftronics, Inc.
Fault contact selection during
automatic retry
Stall Prevention level during
acceleration
Frequency detection
(multi-function contact output)
Overtorque detection function
selection
(OL3)
Input phase loss detection delay time
(SPI)
Unit : 1 time
Setting range: 0 to 10
0 : Closed during fault retry
1 : Open during fault retry
Unit : 0.1Hz
Setting range: 0.0 to 400.0Hz
Unit : 0.1Hz
Setting range: 0.0 to 400.0Hz
Unit : 0.1Hz
Setting range: 0.0 to 400.0Hz
0 : Accumulated time during power on
1 : Accumulated time during running
Unit : 1 hour
Range : 0 to 9999
Unit : 10,000 hours
Range : 0 to 27
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 100%
100% = INV rated current
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Range : 0.0 to 10.0 seconds
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Range : 0.0 to 10.0 seconds
Unit : 0.1
Range : 0.0 to 3.0
Unit : 0.001 Ω (0.01 Ω for
10.00 Ω or above)
Setting range: 0.000 to 65.53
Unit : 0W
Setting range: 0 to 9999W
0 : Disabled
1 : Enabled
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 30 to 200%
When level is set to 200%, Stall Prevention during acceleration is
disabled.
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 30 to 200%
When level is set to 200%, Stall Prevention running is disabled.
Unit : 0.1Hz
Setting range: 0.0 to 400Hz
(Setting) (Function)
0 : Detection disabled
1 : Detected during constant-speed running, and
operation continues after detection.
2 : Detected during running, and operation continues
after operation
3 : Detected during constant-speed running, and
Inverter output is shut OFF during detection.
4 : Detected during running, and Inverter output is
shut OFF during detection.
Unit : 1%
Setting range: − 30 to 200%
100% = INV rated current
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: 0.0 to 10.0 seconds
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: 0.0 to 25.5seconds
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: − 0.0 to 25.5 seconds
0 : No dB protection calculated or provided
1 : Protection provided for installed Saftronics resistor only
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 1 to 100%
When setting is 100%, this function is disabled
Unit : 1 (1.28 seconds)
Setting range: 2 to 255 (2.56 to 326.4 seconds)
Normally, no adjustment
is necessary.
Chapter 12: Constant List
Factory
Setting
0
0
0.0Hz
0.0Hz
1.0Hz
1
0
0
50%
0.5 seconds
0.0 seconds
1.0
kVA
dependent
kVA
dependent
1
kVA
dependent
kVA
dependent
0.0Hz
0
160%
0.1 seconds
0.0 seconds
0.0 seconds
0
7%
(10.24
seconds)
Page 96

Chapter 12: Constant List
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Table 27 Constant List (Continued)
Constant Function Name Description
n082
n083
n084 PID selection (same as PID LED)
n085 Feedback calibration gain (PID)
n086 Proportional gain (PID)
n087 Integral time (PID)
n088 Derivative time (PID)
n089 Offset (PID)
n090 Limit of integral value (PID)
n091 Output lag filter time (PID)
n092 Feedback loss detection (PID)
n093 Feedback loss detection level(PID)
n094
n095
n096 Energy Saving gain K2
n097
n098
n099 Time of average k W (Energy Saving)
n100 Voltage limit of tuning (Energy Saving)
n101
n102
n103 MEMOBUS time over detection
n104
n105 MEMOBUS frequency reference unit
n106 MEMOBUS slave address
n107 MEMOBUS BPS selection
n108 MEMOBUS parity selection
Output phase loss detection level
(SPO)
Output phase loss detection delay time
(SPO)
Feedback loss detection delay time
(PID)
Energy Saving selection
(same as kWsav LED
Energy Saving voltage lower limit at
60Hz
Energy Saving voltage lower limit at
6Hz
Step voltage of tuning at 100% output
voltage (Energy Saving)
Step voltage of tuning at 5% output
voltage (Energy Saving)
MEMOBUS stop method at
communication error (CE)
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 100%
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: 0.0 to 2.0 seconds
0 : PID disabled
1 : PID enabled (Deviation is D-controlled)
2 : PID with feed forward (Feedback value is D-controlled)
3 : PID with feed forward (Feedback is reversed characteristics)
Unit : 0.01
Setting range: 0.00 to 10.00
Unit: : 0.1
Setting range: 0.0 to 10.0
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: 0.0 to 100.0 seconds
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: 0.0 to 100.0 seconds
Unit : 1%
Setting range: − 109 to 109%
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 109%
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: 0.0 to 2.5 seconds
0 : Detection is disabled
1 : Detection is enabled
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 100%
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: 0.0 to 25.5 seconds
0 : Energy Saving is disabled
1 : Energy Saving is enabled
Unit : 0.01 (0.1 for 100.0 or above)
Setting range: 0.00 to 655.0
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 120%
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 25%
Unit : 1 = 25ms
Setting range: 1 to 200
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 100%
Unit : 0.1%
Setting range: 0.1 to 10.0%
Unit : 0.1%
Setting range: 0.1 to 10.0%
0 : Time over detection is disabled
1 : Time over detection is enabled
(Setting) (Stop Method)
0 : Ramp to stop − Decel 1 (fault)
1 : Coast to stop (fault)
2 : Ramp to stop − Decel 2 (fault)
3 : Continue operation (alarm)
(Setting) (Frequency Unit)
0 : 0.1Hz / 1
1 : 0.01Hz / 1
2 : 100% / 30000
3 : 0.1% / 1
Unit : 1
Setting range: 0 to 31
(Setting) (BPS Rate)
0 : 2400 BPS
1 : 4800 BPS
2 : 9600 BPS
(Setting) (BPS Rate)
0 : No parity
1 : Even parity
2 : Odd parity
Factory
Setting
0%
0.2 seconds
0
1.00
1.0
10.0
seconds
0.00
seconds
0%
100%
0.0 seconds
0
0%
1.0 seconds
0
kVA
dependent
50%
12%
1
0%
0.5%
0.2%
1
1
0
0
2
1
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 88 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 97

Table 27 Constant List (Continued)
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Constant Function Name Description
n109∗
n110∗
n111∗
n112∗
n113∗
n114∗
n115∗
n116 CT/VT Selection
n117 Low Frequency OL Starting Point
n118 0Hz Continuous Operation level
Slip compensation gain
Motor no-load current
Primary delay time constant
Digital Operator connection fault
detection
Frequency agree detection width
selection
Function selection at LOCAL/REMOTE
switching
kVA selection
Unit: : 0.1%
Setting range: 0.0 to 9.9%
Unit: : 1%
Setting range: 0 to 99%
Unit : 0.1 seconds
Setting range: 0.0 to 25.5 seconds
0 : Connection fault detection is disabled
1 : Connection fault detection is enabled
Unit : 0.1Hz
Setting range: 0.0 to 25.5Hz
0 : At LOCAL/REMOTE switching, restart is enabled after stop
command is input.
1 : At LOCAL/REMOTE switching, restart is enabled at once.
Unit : 1
Setting range:
GP5 (VSP2010): 0 to 8, 20 to 29
FP5 (VSP3010): 9 to F, 2A to 35
0 : Constant Torque
1 : VariableTorque
Unit : 0.1Hz
Setting range: 0.0 to 10.0Hz
Unit : 1%
Setting range: 25 to 100%
Chapter 12: Constant List
Factory
Setting
0.0%
30%
2.0 seconds
0
2.0Hz
0
6.0Hz
50%
∗ These constants are disabled for former softwares VSP1010 to VSP1015.
Enabled for the following software number (or after).
GP5 : VSP2010
FP5 : VSP3010
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 89 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 98

Chapter 12: Constant List
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
NOTES:
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 90 © Saftronics, Inc.
Page 99

13
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
Digital Operator Monitor Display
This chapter describes the monitor displays of the Digital Operator of the FP5/GP5.
13.1 Digital Operator Monitor Display................................... 92
Page 100

Chapter 13: Digital Operator Monitor Display
efesotomasyon.com - Control Techniques,emerson,saftronics -ac drive-servo motor
13.1 Digital Operator Monitor Display
The following table shows the contents of the Digital Operator monitor display.
Table 28 Digital Operator Monitor Display
LED Name Description
Fref Frequency reference
Fout Output frequency
Iout Output current Output current can be monitored in units of 0.1 A (1 A for 1000 A and above).
kWout Output voltage Output voltage can be monitored in units of 0.1 kW (1 kW for 1000 k and above).
F/R
FWD/REV RUN
command
• Frequency reference can be monitored/set.
• Setting/display unit depends on display mode (n024).
• Output frequency can be monitored.
• Display unit depends on display mode (n024).
• FWD/REV RUN command can be set/monitored.
• Setting enabled during RUN command from Digital Operator.
• FWD run displays For, REV run displays rev.
The following contents can be monitored.
No. Contents
U−01
U−02
U−03
U−04
U−05
U−06
Frequency reference (same as Fref)
Output frequency (same as Fout)
Output current (same as Iout)
Output voltage reference can be monitored in units of 1 V
DC voltage can be monitored in units of 1 V
Output power (same as kWout)
Input terminal status can be monitored (Terminals S1 to S6)
U−07
Montr Monitor
Inverter status can be monitored
U−08
Firmware – S2011 and S3012
Revision: 1 (9/98) 92 © Saftronics, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...