Page 1
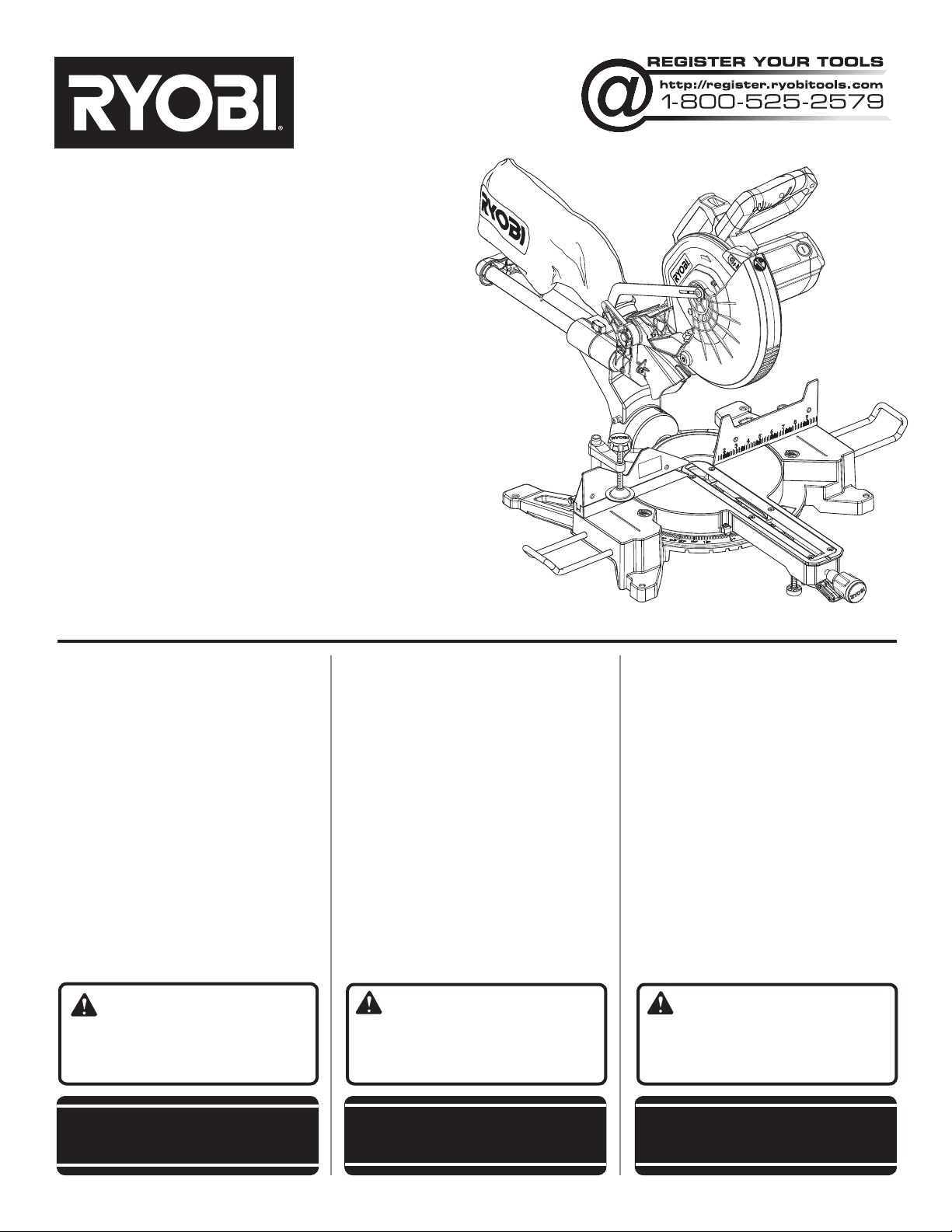
OPERATOR’S MANUAL
MANUEL D’UTILISATION
MANUAL DEL OPERADOR
12 in. SLIDING COMPOUND
MITER SAW WITH LASER
DE 305 mm (12 po) SCIE À ONGLETS
COMBINÉS COULISSANTE AVEC
LASER
SIERRA INGLETEADORA
COMPUESTA DESLIZANTE DE
305 mm (12 pulg.) CON GUÍA LÁSER
TSS120L
TABLE OF CONTENTS
****************
General Safety Rules .......................2-3
Specific Safety Rules ......................3-4
Symbols ..............................................5
Electrical ............................................. 6
Glossary of Terms ............................... 7
Features .........................................8-11
Tools Needed ................................... 12
Loose Parts List ................................12
Assembly .....................................13-22
Operation .....................................23-32
Adjustments ................................33-34
Maintenance ..................................... 35
Parts Ordering / Service ..... Back Page
WARNING: To reduce the
risk of injury, the user must read and
understand the operator’s manual
before using this product.
TABLE DES MATIÈRES
****************
Règles de sécurité générales ..........2-3
Règles de sécurité particulières ......3-4
Symboles ............................................ 5
Caractéristiques électriques ............... 6
Glossaire .............................................7
Caractéristiques ............................8-11
Outils nécessaires ............................12
Liste des pièces détachées .............. 12
Assemblage .................................13-22
Utilisation .....................................23-32
Réglages ......................................33-34
Entretien ...........................................35
Commande de pièces /
réparation ..........................Page arrière
AVERTISSEMENT :
réduire les risques de blessures,
l’utilisateur doit lire et veiller à bien
comprendre le manuel d’utilisation avant
d’employer ce produit.
Pour
ÍNDICE DE CONTENIDO
****************
Reglas de seguridad generales .......2-3
Reglas de seguridad específicas ....3-4
Símbolos ............................................5
Aspectos eléctricos ............................ 6
Glosario de términos .......................... 7
Características ..............................8-11
Herramientas necesarias .................. 12
Lista de piezas sueltas ..................... 12
Armado ........................................13-22
Funcionamiento ...........................23-32
Ajustes .........................................33-34
Mantenimiento .................................. 35
Pedidos de piezas /
servicio .......................... Pág. posterior
ADVERTENCIA: Para reducir
el riesgo de lesiones, el usuario debe leer
y comprender el manual del operador
antes de usar este producto.
SAVE THIS MANUAL FOR
FUTURE REFERENCE
CONSERVER CE MANUEL
POUR FUTURE RÉFÉRENCE
GUARDE ESTE MANUAL
PARA FUTURAS CONSULTAS
Page 2

GENERAL SAFETY RULES
WARNING:
Read all safety warnings and all instructions. Failure to
follow the warnings and instructions may result in electric
shock, fire and/or serious injury.
READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS
KNOW YOUR POWER TOOL. Read the operator’s
manual carefully. Learn the applications and limitations
as well as the specific potential hazards related to this
tool.
GUARD AGAINST ELECTRICAL SHOCK BY
PREVENTING BODY CONTACT WITH GROUNDED
SURFACES. For example: pipes, radiators, ranges,
refrigerator enclosures.
KEEP GUARDS IN PLACE and in good working order.
REMOVE ADJUSTING KEYS AND WRENCHES. Form
habit of checking to see that keys and adjusting wrenches
are removed from tool before turning it on.
KEEP WORK AREA CLEAN. Cluttered areas and
benches invite accidents. DO NOT leave tools or pieces
of wood on the tool while it is in operation.
DO NOT USE IN DANGEROUS ENVIRONMENTS. Do
not use power tools in damp or wet locations or expose
to rain. Keep the work area well lit.
KEEP CHILDREN AND VISITORS AWAY. All visitors
should wear safety glasses and be kept a safe distance
from work area. Do not let visitors contact tool or
extension cord while operating.
MAKE WORKSHOP CHILDPROOF with padlocks,
master switches, or by removing starter keys.
DON’T FORCE THE TOOL. It will do the job better and
safer at the feed rate for which it was designed.
USE THE RIGHT TOOL. Do not force the tool or
attachment to do a job for which it was not designed.
USE THE PROPER EXTENSION CORD. Make sure
your extension cord is in good condition. Use only a
cord heavy enough to carry the current your product
will draw. An undersized cord will cause a drop in line
voltage resulting in loss of power and overheating. A wire
gauge size (A.W.G.) of at least 14 is recommended for an
extension cord 25 feet or less in length. If in doubt, use
the next heavier gauge. The smaller the gauge number,
the heavier the cord.
DRESS PROPERLY. Do not wear loose clothing,
neckties, or jewelry that can get caught and draw you
into moving parts. Rubber gloves and nonskid footwear
are recommended when working outdoors. Also wear
protective hair covering to contain long hair.
ALWAYS WEAR SAFETY GLASSES WITH SIDE
SHIELDS. Everyday eyeglasses have only impact-
resistant lenses, they are NOT safety glasses.
SECURE WORK. Use clamps or a vise to hold work when
practical, it is safer than using your hand and frees both
hands to operate the tool.
DO NOT OVERREACH. Keep proper footing and balance
at all times.
MAINTAIN TOOLS WITH CARE. Keep tools sharp
and clean for better and safer performance. Follow
instructions for lubricating and changing accessories.
DISCONNECT TOOLS. When not in use, before servicing,
or when changing attachments, blades, bits, cutters, etc.,
all tools should be disconnected from power source.
AVOID ACCIDENTAL STARTING. Be sure switch is off
when plugging in any tool.
USE RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES. Consult the
operator’s manual for recommended accessories. The
use of improper accessories may result in injury.
NEVER STAND ON TOOL. Serious injury could occur if
the tool is tipped or if the cutting tool is unintentionally
contacted.
CHECK DAMAGED PARTS. Before further use of the
tool, a guard or other part that is damaged should be
carefully checked to determine that it will operate properly
and perform its intended function. Check for alignment
of moving parts, binding of moving parts, breakage of
parts, mounting and any other conditions that may affect
its operation. A guard or other part that is damaged must
be properly repaired or replaced by an authorized service
center to avoid risk of personal injury.
USE THE RIGHT DIRECTION OF FEED. Feed work into
a blade, cutter, or sanding spindle against the direction
or rotation of the blade, cutter, or sanding spindle only.
NEVER LEAVE TOOL RUNNING UNATTENDED. TURN
THE POWER OFF. Don’t leave tool until it comes to a
complete stop.
PROTECT YOUR LUNGS. Wear a face or dust mask if
the cutting operation is dusty.
PROTECT YOUR HEARING. Wear hearing protection
during extended periods of operation.
DO NOT ABUSE CORD. Never carry tool by the cord or
yank it to disconnect from receptacle. Keep cord from
heat, oil, and sharp edges.
USE OUTDOOR EXTENSION CORDS. When tool is
used outdoors, use only extension cords with approved
ground connection that are intended for use outdoors
and so marked.
KEEP BLADES CLEAN, SHARP, AND WITH SUFFICIENT
SET. Sharp blades minimize stalling and kickback.
BLADE COASTS AFTER BEING TURNED OFF.
NEVER USE IN AN EXPLOSIVE ATMOSPHERE. Normal
sparking of the motor could ignite fumes.
2 − English
Page 3

GENERAL SAFETY RULES
INSPECT TOOL CORDS PERIODICALLY. If damaged,
have repaired by a qualified service technician at an
authorized service facility. The conductor with insulation
having an outer surface that is green with or without
yellow stripes is the equipment-grounding conductor.
If repair or replacement of the electric cord or plug is
necessary, do not connect the equipment-grounding
conductor to a live terminal. Repair or replace a damaged
or worn cord immediately. Stay constantly aware of cord
location and keep it well away from the rotating blade.
INSPECT EXTENSION CORDS PERIODICALLY and
replace if damaged.
POLARIZED PLUGS. To reduce the risk of electric shock,
this tool has a polarized plug (one blade is wider than
the other). This plug will fit in a polarized outlet only one
way. If the plug does not fit fully in the outlet, reverse the
plug. If it still does not fit, contact a qualified electrician
to install the proper outlet. Do not change the plug in any
way.
KEEP TOOL DRY, CLEAN, AND FREE FROM OIL AND
GREASE. Always use a clean cloth when cleaning. Never
use brake fluids, gasoline, petroleum-based products, or
any solvents to clean tool.
STAY ALERT AND EXERCISE CONTROL. Watch what
you are doing and use common sense. Do not operate
tool when you are tired. Do not rush.
DO NOT USE TOOL IF SWITCH DOES NOT TURN IT
ON AND OFF. Have defective switches replaced by an
authorized service center.
USE ONLY CORRECT BLADES. Do not use blades with
incorrect size holes. Never use blade washers or blade
bolts that are defective or incorrect. The maximum blade
capacity of your saw is 12 in.
BEFORE MAKING A CUT, BE SURE ALL ADJUSTMENTS
ARE SECURE.
BE SURE BLADE PATH IS FREE OF NAILS. Inspect for
and remove all nails from lumber before cutting.
NEVER TOUCH BLADE or other moving parts during
use.
NEVER START A TOOL WHEN ANY ROTATING
COMPONENT IS IN CONTACT WITH THE WORKPIECE.
DO NOT OPERATE A TOOL WHILE UNDER THE
INFLUENCE OF DRUGS, ALCOHOL, OR ANY
MEDICATION.
WHEN SERVICING use only identical replacement parts.
Use of any other parts may create a hazard or cause
product damage.
USE ONLY RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES listed
in this manual or addendums. Use of accessories that
are not listed may cause the risk of personal injury.
Instructions for safe use of accessories are included with
the accessory.
DOUBLE CHECK ALL SETUPS. Make sure blade is tight
and not making contact with saw or workpiece before
connecting to power supply.
SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES
FIRMLY CLAMP OR BOLT the tool to a workbench or
table at approximately hip height.
KEEP HANDS AWAY FROM CUTTING AREA. Do not
reach underneath work or in blade cutting path with hands
and fingers for any reason. Always turn the power off.
ALWAYS SUPPORT LONG WORKPIECES while cutting
to minimize risk of blade pinching and kickback. Saw may
slip, walk or slide while cutting long or heavy boards.
ALWAYS USE A CLAMP to secure the workpiece when
possible.
BE SURE THE BLADE CLEARS THE WORKPIECE.
Never start the saw with the blade touching the workpiece.
Allow motor to come up to full speed before starting cut.
MAKE SURE THE MITER TABLE AND SAW ARM (BEVEL
FUNCTION) ARE LOCKED IN POSITION BEFORE
OPERATING YOUR SAW. Lock the miter table by securely
tightening the miter lock handle. Lock the saw arm (bevel
function) by securely tightening the bevel lock knob.
3 − English
NEVER USE A LENGTH STOP ON THE FREE SCRAP
END OF A CLAMPED WORKPIECE. NEVER hold onto or
bind the free scrap end of the workpiece in any operation.
If a work clamp and length stop are used together, they
must both be installed on the same side of the saw table to
prevent the saw from catching the loose end and kicking
up.
NEVER cut more than one piece at a time. DO NOT
STACK more than one workpiece on the saw table at a
time.
NEVER PERFORM ANY OPERATION FREEHAND.
Always place the workpiece to be cut on the miter table
and position it firmly against the fence as a backstop.
Always use the fence.
NEVER hand hold a workpiece that is too small to be
clamped. Keep hands clear of the cutting area.
NEVER reach behind, under, or within three inches of the
blade and its cutting path with hands and fingers for any
reason.
Page 4

SPECIFIC SAFETY RULES
NEVER reach to pick up a workpiece, a piece of scrap,
or anything else that is in or near the cutting path of the
blade.
NEVER move the workpiece or make adjustment to any
cutting angle while the saw is running and the blade is
rotating. Any slip can result in contact with the blade
causing serious personal injury.
AVOID AWKWARD OPERATIONS AND HAND
POSITIONS where a sudden slip could cause your hand
to move into the blade. ALWAYS make sure you have
good balance. NEVER operate the miter saw on the floor
or in a crouched position.
NEVER stand or have any part of the body in line with
the path of the saw blade.
ALWAYS release the power switch and allow the saw blade
to stop rotating before raising it out of the workpiece.
DO NOT TURN THE MOTOR SWITCH ON AND OFF
RAPIDLY. This could cause the saw blade to loosen and
could create a hazard. Should this ever occur, stand clear
and allow the saw blade to come to a complete stop.
Disconnect your saw from the power supply and securely
retighten the blade bolt.
IF ANY PART OF THIS MITER SAW IS MISSING or
should break, bend, or fail in any way, or should any
electrical component fail to perform properly, shut off
the power switch, remove the miter saw plug from the
power source and have damaged, missing, or failed parts
replaced before resuming operation.
ALWAYS STAY ALERT! Do not allow familiarity (gained
from frequent use of the saw) to cause a careless mistake.
ALWAYS REMEMBER that a careless fraction of a second
is sufficient to inflict severe injury.
IF THE POWER SUPPLY CORD IS DAMAGED, it must
be replaced only by the manufacturer or by an authorized
service center to avoid risk.
MAKE SURE WORK AREA HAS AMPLE LIGHTING to
see the work and that no obstructions will interfere with
safe operation BEFORE performing any work using the
saw.
ALWAYS TURN OFF THE SAW before disconnecting it
to avoid accidental starting when reconnecting to power
supply. NEVER leave the saw unattended while connected
to a power source.
RELEASE THE SWITCH TRIGGER and allow the saw
blade to stop rotating before raising the blade out of
workpiece.
THIS TOOL should have the following markings:
a) Wear eye protection.
b) Keep hands out of path of saw blade.
c) Do not operate saw without guards in place.
d) Do not perform any operation freehand.
e) Never reach around saw blade.
f) Turn off tool and wait for saw blade to stop before
moving workpiece or changing settings.
g) Disconnect power (or unplug tool as applicable) before
changing blade or servicing.
h) No load speed.
ALWAYS MAKE SURE THE SAW BLADE HAS
CLEARANCE OF ALL OBSTRUCTIONS BEFORE
TURNING THE SAW ON.
MAKE SLIDING CUTS by pushing the saw blade down
on top of the workpiece then sliding it back toward the
rear of the saw. DO NOT pull the saw toward you while
making a cut.
ALWAYS carry the tool only by the carrying handle.
AVOID direct eye exposure when using the laser guide.
THIS SAW CAN TIP OVER if the saw head is released
suddenly and the saw is not secured to a work surface.
ALWAYS secure this saw to a stable work surface before
any use to avoid serious personal injury.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS. Refer to them frequently
and use to instruct other users. If you loan someone this
tool, loan them these instructions also.
4 − English
Page 5
SYMBOLS
The following signal words and meanings are intended to explain the levels of risk associated with this product.
SYMBOL SIGNAL MEANING
DANGER:
WARNING:
CAUTION:
NOTICE:
Some of the following symbols may be used on this tool. Please study them and learn their meaning. Proper interpretation
of these symbols will allow you to operate the tool better and safer.
SYMBOL NAME
Safety Alert Indicates a potential personal injury hazard.
Read Operator’s Manual
Eye Protection
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, will result
in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, could result
in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which, if not avoided, may result in
minor or moderate injury.
(Without Safety Alert Symbol) Indicates important information not related to an
injury hazard, such as a situation that may result in property damage.
DESIGNATION/EXPLANATION
To reduce the risk of injury, user must read and understand
operator’s manual before using this product.
Always wear eye protection with side shields marked to comply
with ANSI Z87.1.
No Hands Symbol
Wet Conditions Alert Do not expose to rain or use in damp locations.
V Volts Voltage
A Amperes Current
Hz Hertz Frequency (cycles per second)
min Minutes Time
Alternating Current Type of current
n
o
.../min Per Minute Revolutions, strokes, surface speed, orbits, etc., per minute
No Load Speed Rotational speed, at no load
Class II Construction Double-insulated construction
Failure to keep your hands away from the blade will result in
serious personal injury.
5 − English
Page 6
ELECTRICAL
DOUBLE INSULATION
Double insulation is a concept in safety in electric power tools,
which eliminates the need for the usual three-wire grounded
power cord. All exposed metal parts are isolated from the
internal metal motor components with protecting insulation.
Double insulated tools do not need to be grounded.
WARNING:
The double insulated system is intended to protect the
user from shock resulting from a break in the tool’s internal
wiring. Observe all normal safety precautions to avoid
electrical shock.
NOTE: Servicing of a product with double insulation requires
extreme care and knowledge of the system and should
be performed only by a qualified service technician. For
service, we suggest you return the tool to your nearest
authorized service center for repair. Always use original
factory replacement parts when servicing.
ELECTRICAL CONNECTION
This tool has a precision-built electric motor. It should be
connected to a power supply that is 120 V, AC only (normal
household current), 60 Hz. Do not operate this tool on
direct current (DC). A substantial voltage drop will cause a
loss of power and the motor will overheat. If the tool does
not operate when plugged into an outlet, double check the
power supply.
EXTENSION CORDS
When using a power tool at a considerable distance from
a power source, be sure to use an extension cord that has
the capacity to handle the current the product will draw. An
undersized cord will cause a drop in line voltage, resulting in
overheating and loss of power. Use the chart to determine
the minimum wire size required in an extension cord. Only
round jacketed cords listed by Underwriter’s Laboratories
(UL) should be used.
When working outdoors with a product, use an extension
cord that is designed for outside use. This type of cord is
designated with “WA” or “W” on the cord’s jacket.
Before using any extension cord, inspect it for loose or
exposed wires and cut or worn insulation.
**Ampere rating (on product data plate)
0-2.0 2.1-3.4 3.5-5.0 5.1-7.0 7.1-12.0 12.1-16.0
Cord Length Wire Size (A.W.G.)
25' 16 16 16 16 14 14
50' 16 16 16 14 14 12
100' 16 16 14 12 10 —
**Used on 12 gauge - 20 amp circuit.
NOTE: AWG = American Wire Gauge
WARNING:
Keep the extension cord clear of the working area.
Position the cord so that it will not get caught on lumber,
tools, or other obstructions while you are working with a
power tool. Failure to do so can result in serious personal
injury.
WARNING:
Check extension cords before each use. If damaged
replace immediately. Never use tool with a damaged cord
since touching the damaged area could cause electrical
shock resulting in serious injury.
CALIFORNIA PROPOSITION 65
WARNING:
This product and some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities may
contain chemicals, including lead, known to the State of California to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive
harm. Wash hands after handling.
Some examples of these chemicals are:
• lead from lead-based paints,
• crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry products and,
• arsenic and chromium from chemically treated lumber.
Your risk from exposure to these chemicals varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your
exposure, work in a well-ventilated area and with approved safety equipment, such as dust masks that are specially
designed to filter out microscopic particles.
6 − English
Page 7

GLOSSARY OF TERMS
Anti-Kickback Pawls (radial arm and table saws)
A device which, when properly installed and maintained,
is designed to stop the workpiece from being kicked back
toward the front of the saw during a ripping operation.
Arbor
The shaft on which a blade or cutting tool is mounted.
Bevel Cut
A cutting operation made with the blade at any angle other
than 90° to the table surface.
Compound Cut
A cross cut made with both a miter and a bevel angle.
Cross Cut
A cutting or shaping operation made across the grain or the
width of the workpiece.
Cutterhead (planers and jointer planers)
A rotating cutterhead with adjustable blades or knives. The
blades or knives remove material from the workpiece.
Dado Cut
A non-through cut which produces a square-sided notch or
trough in the workpiece (requires a special blade).
Featherboard
A device used to help control the workpiece by holding
it securely against the table or fence during any ripping
operation.
FPM or SPM
Feet per minute (or strokes per minute), used in reference
to blade movement.
Freehand
Performing a cut without the workpiece being guided by a
fence, miter gauge, or other aids.
Gum
A sticky, sap-based residue from wood products.
Heel
Alignment of the blade to the fence.
Kerf
The material removed by the blade in a through cut or the
slot produced by the blade in a non-through or partial cut.
Kickback
A hazard that can occur when the blade binds or stalls,
throwing the workpiece back toward operator.
Miter Cut
A cutting operation made with the workpiece at any angle
to the blade other than 90°.
Non-Through Cuts
Any cutting operation where the blade does not extend
completely through the thickness of the workpiece.
Pilot Hole (drill presses)
A small hole drilled in a workpiece that serves as a guide for
drilling large holes accurately.
Push Blocks (for jointer planers)
Device used to feed the workpiece over the jointer planer
cutterhead during any operation. This aid helps keep the
operator’s hands well away from the cutterhead.
Push Blocks (for table saws)
Device used to hold the workpiece during cutting operations.
This aid helps keep the operator’s hands well away from
the blade.
Push Sticks (for table saws)
Device used to push the workpiece during cutting operations.
A push stick should be used for narrow ripping operations.
The aid helps keep the operator’s hands well away from
the blade.
Resaw
A cutting operation to reduce the thickness of the workpiece
to make thinner pieces.
Resin
A sticky, sap-based substance that has hardened.
Revolutions Per Minute (RPM)
The number of turns completed by a spinning object in one
minute.
Ripping or Rip Cut
A cutting operation along the length of the workpiece.
Riving Knife/Spreader/Splitter (table saws)
A metal piece, slightly thinner than the blade, which helps
keep the kerf open and also helps to prevent kickback.
Saw Blade Path
The area over, under, behind, or in front of the blade. As it
applies to the workpiece, that area which will be or has been
cut by the blade.
Set
The distance that the tip of the saw blade tooth is bent (or
set) outward from the face of the blade.
Snipe (planers)
Depression made at either end of a workpiece by cutter
blades when the workpiece is not properly supported.
Taper Cut
A cut where the material being cut has a different width at
the beginning of the cut from the the end.
Through Sawing
Any cutting operation where the blade extends completely
through the thickness of the workpiece.
Throw-Back
The throwing back of a workpiece usually caused by the
workpiece being dropped into the blade or being placed
inadvertently in contact with the blade.
Workpiece or Material
The item on which the operation is being done.
Worktable
Surface where the workpiece rests while performing a cutting,
drilling, planing, or sanding operation.
7 − English
Page 8
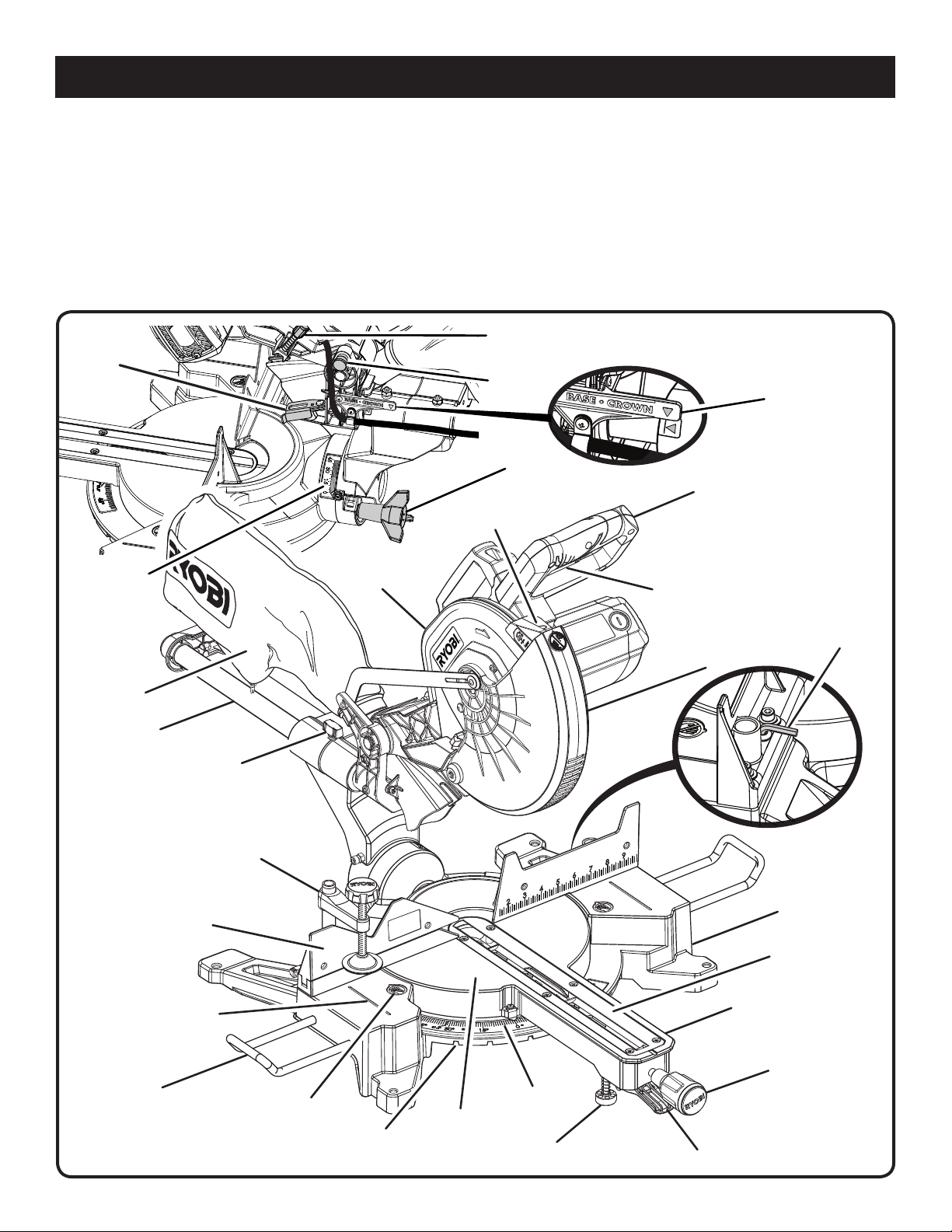
FEATURES
PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS
Arbor Hole ..........................................................................1 in.
Blade Diameter .................................................................12 in.
No Load Speed .......................................... 4,000 r/min. (RPM)
Input ..............................................120 V, AC only, 60 Hz, 15 A
Cutting Capacity with Miter at 0°/Bevel 0°:
Maximum nominal lumber sizes .............. 2 x 14 in., 4 x 6 in.
Cutting Capacity with Miter at 45°/Bevel 0°:
Maximum nominal lumber size ............................... 2 x 10 in.
DEPTH
STOP
Cutting Capacity with Miter at 0°/Bevel 45°:
Maximum nominal lumber size ............................... 2 x 14 in.
Cutting Capacity with Miter at 45°/Bevel 45°:
Maximum nominal lumber size ............................... 2 x 10 in.
Cutting Capacity for Crown Molding (Nested):
Maximum lumber size .............................................. 5-1/4 in.
Cutting Capacity for Baseboards Against the Fence:
Maximum height ............................................. 5-1/2 x 3/4 in.
DEPTH
CONTROL KNOB
LOCK PIN
BEVEL
LOCK KNOB
LASER
GUIDE
“D”
HANDLE
BASE/CROWN
INDICATOR
BEVEL
SCALE
DUST
BAG
SLIDE BAR
SLIDE
LOCK KNOB
SLIDING
MITER FENCE
“NO HANDS ZONE”
BOUNDARY LINE
WORK
CLAMP
UPPER BLADE
GUARD
SWITCH
TRIGGER
LOWER BLADE
GUARD
CONTROL
LOCK HANDLE
BLADE
WRENCH
BASE
THROAT
PLATE
ARM
MITER
TABLE
EXTENSION
“NO HANDS
ZONE” LABEL
POSITIVE
STOP(S)
MITER
TABLE
8 − English
MITER
SCALE
SUPPORT FOOT
DETENT RELEASE LEVER
Fig. 1
Page 9
FEATURES
KNOW YOUR COMPOUND MITER SAW
See Figure 1.
The safe use of this product requires an understanding of
the information on the tool and in this operator’s manual as
well as a knowledge of the project you are attempting. Before
use of this product, familiarize yourself with all operating
features and safety rules.
12 in. BLADE
A 12 in. blade is included with the compound miter saw.
It will cut materials up to 3-1/2 in. thick or 13-1/2 in. wide,
depending upon the angle at which the cut is being made.
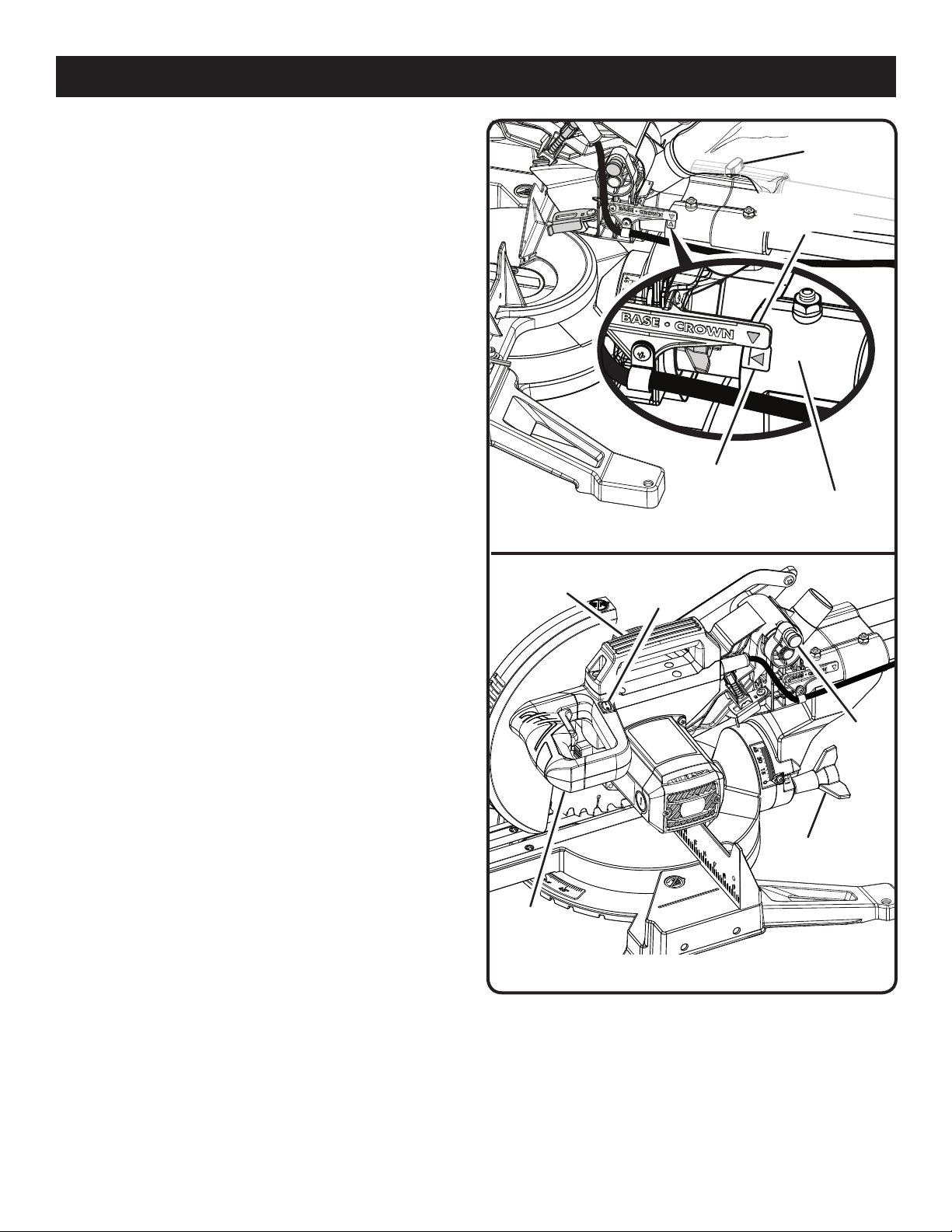
BASE/CROWN INDICATOR
See Figure 2.
To cut base or crown molding in the upright position, align
the arrow on the base/crown indicator with the arrow on
the pivot assembly and tighten the slide lock knob securely.
BEVEL LOCK KNOB
See Figure 3.
The bevel lock knob securely locks your compound miter
saw at desired bevel angles. A positive stop adjustment
screw has been provided on each side of the saw arm.
These adjustment screws are for making fine adjustments
at 0° and 45°.
CARRYING
HANDLE
ARROWS
LASER GUIDE
SWITCH
SLIDE
LOCK KNOB
BASE/CROWN
INDICATOR
ALIGN
PIVOT
ASSEMBLY
Fig. 2
CARRYING HANDLE
See Figure 3.
For convenience when carrying or transporting the miter
saw from one place to another, a carrying handle has been
provided on top of the saw arm. To transport, turn off and
unplug the saw, then lower the saw arm and lock it in the
down position by depressing the lock pin towards the saw
housing.
NOTE: DO NOT perform any cutting operation with the saw
in the locked position.
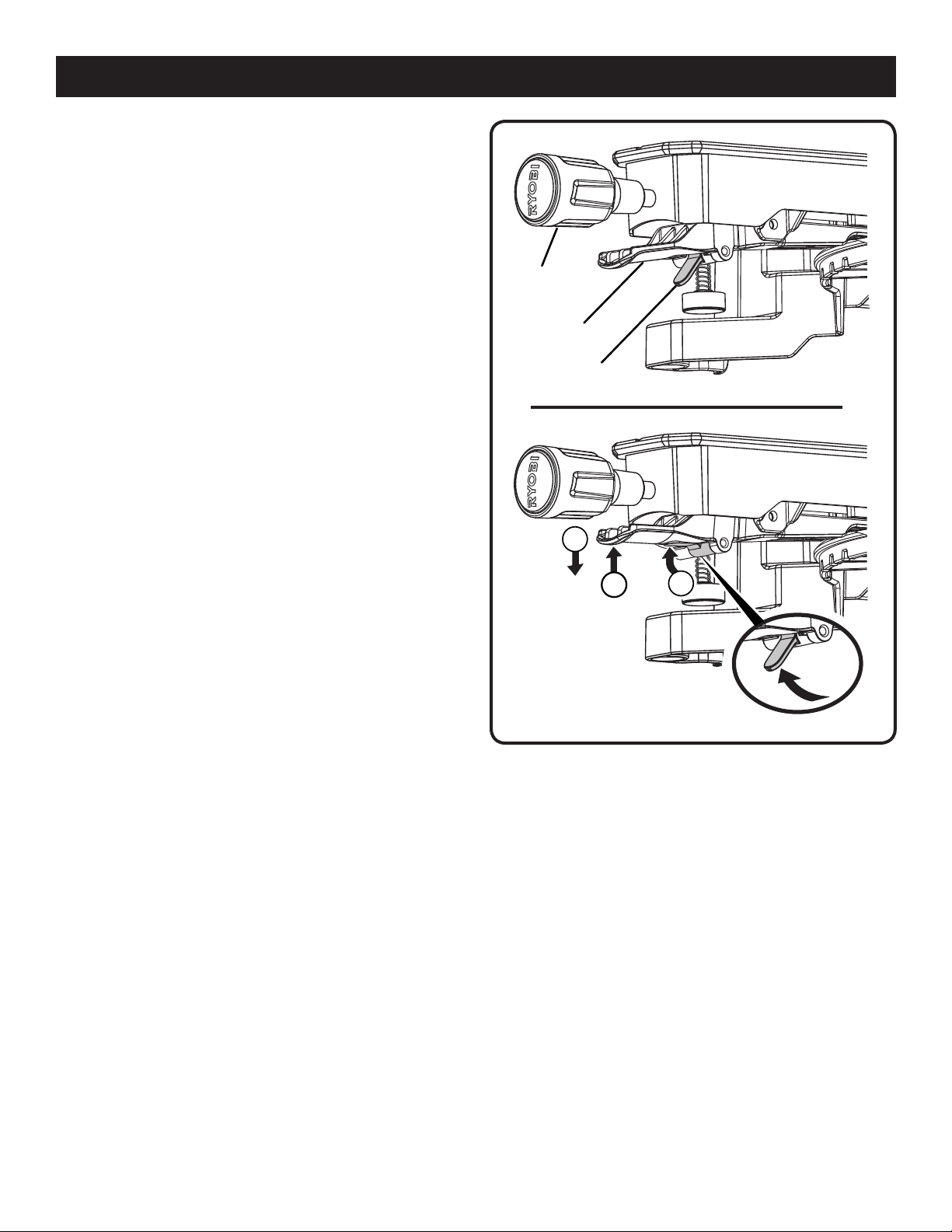
DETENT OVERRIDE
See Figure 4.
The detent override allows the miter table to move freely to
any desired angle. With the miter lock handle loosened and
the detent release lever squeezed (1), pull the detent override up (2) and release the detent release lever (3) to bypass
the positive stops on the miter scale. To release the detent
override and allow the miter table to engage the positive
stops, squeeze and release the detent release lever.
ELECTRIC BRAKE
An electric brake has been provided to quickly stop blade
rotation after the switch is released.
LOCK
PIN
BEVEL
LOCK KNOB
“D”
HANDLE
SAW ARM LOCKED IN DOWN POSITION
Fig. 3
LASER GUIDE SWITCH
See Figure 3.
Use the laser guide switch to turn the laser guide on and off.
LASER GUIDE
For more accurate cuts, a laser guide is included with the
miter saw. When used properly, the laser guide makes
accurate, precision cutting simple and easy.
9 − English
Page 10
FEATURES
MITER LOCK HANDLE
See Figure 4.
The miter lock handle securely locks the saw at desired
miter angles. Tighten the handle to lock the saw in place. To
release the saw, loosen the handle and squeeze the detent
release lever.
MITER SCALE
The miter scale has index points provided at 0°, 15°, 22.5°,
30, 31.6°, and 45°.
POSITIVE STOPS ON MITER TABLE
Positive stops have been provided at 0°, 15°, 22.5°, 31.6°,
and 45° on both the left and right side of the miter table.
NOTE: To bypass the positive stops, squeeze the detent
release lever and lift the detent override. To release the
override, squeeze the detent release lever.
SELF-RETRACTING LOWER BLADE GUARD
The lower blade guard is made of shock-resistant, seethrough plastic that provides protection from each side of
the blade. It retracts over the upper blade guard as the saw
is lowered into the workpiece.
SLIDE BARS
When unlocked, the saw arm will glide forward and backward
the length of the slide bars for cutting various workpiece
widths.
SLIDE LOCK KNOB
The slide lock knob locks and unlocks the sliding feature
of this tool.
SLIDING MITER FENCE
The sliding miter fence on your compound miter saw has
been provided to help secure the workpiece when making
cuts; the portion of the miter fence located farthest from the
blade is larger to provide additional vertical support.
The sliding feature makes it easy to remove or adjust the
position of the fence and allows for clearance of the saw arm
when making bevel or compound cuts. Loosen the fence
screw before attempting to slide the miter fence. Once the
desired position of the miter fence is determined, tighten the
fence screw to secure the sliding fence.
MITER
LOCK HANDLE
DETENT
RELEASE LEVER
DETENT
OVERRIDE
3
1
2
Fig. 4
10 − English
Page 11
FEATURES
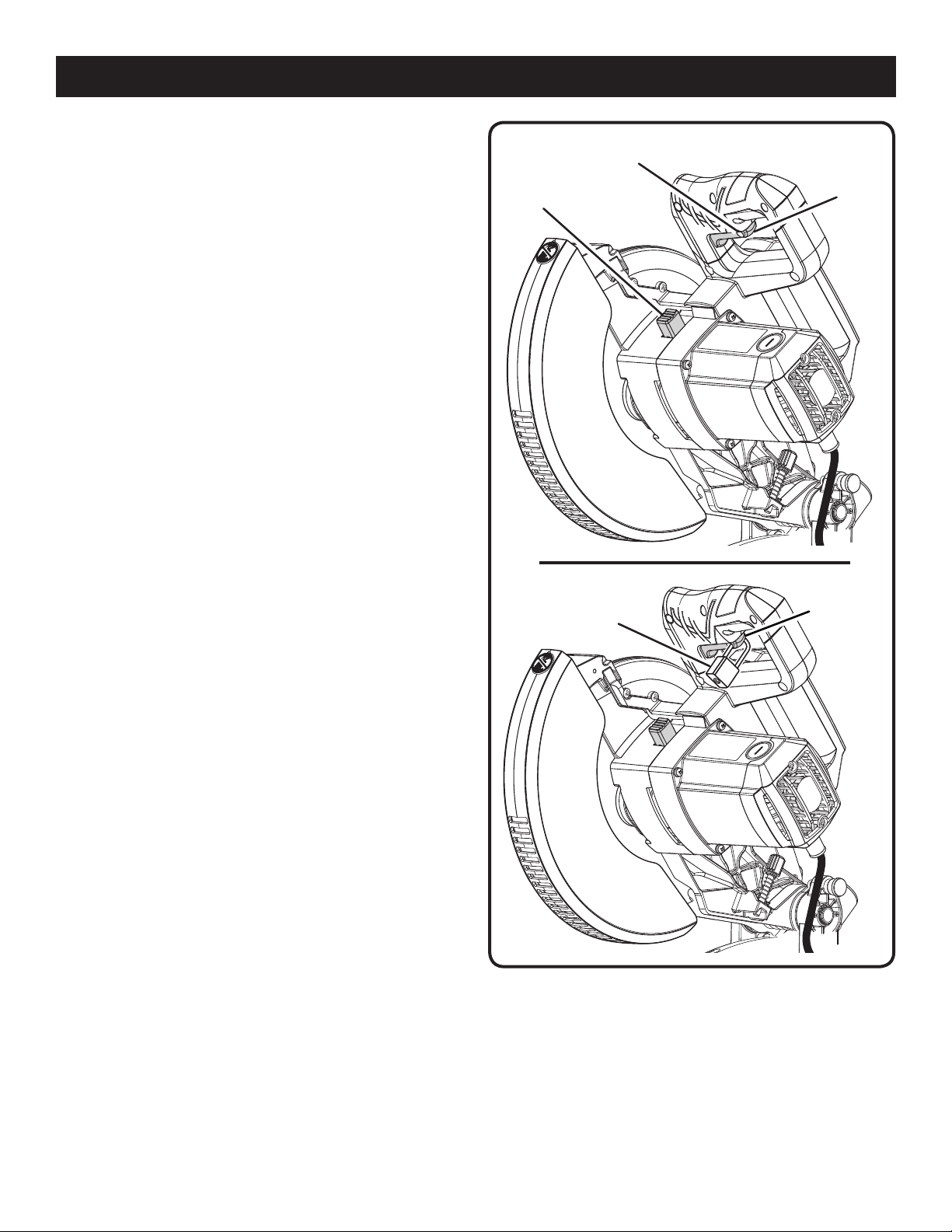
SPINDLE LOCK BUTTON
See Figure 5.
The spindle lock button locks the spindle and stops the
blade from rotating. Depress and hold the lock button while
installing, changing, or removing blade.
SWITCH TRIGGER
See Figure 5.
To prevent unauthorized use of the compound miter saw,
disconnect it from the power supply and lock the switch in the
off position. To lock the switch, install a padlock (not included)
through the hole in the switch trigger and make certain the
switch is inoperable. If the switch is still operable with the
padlock installed, a padlock with a larger shackle diameter
must be used. Store the padlock key in another location.
SPINDLE
LOCK BUTTON
PADLOCK
HOLE
SWITCH
TRIGGER
PADLOCK
SWITCH
TRIGGER
Fig. 5
11 − English
Page 12
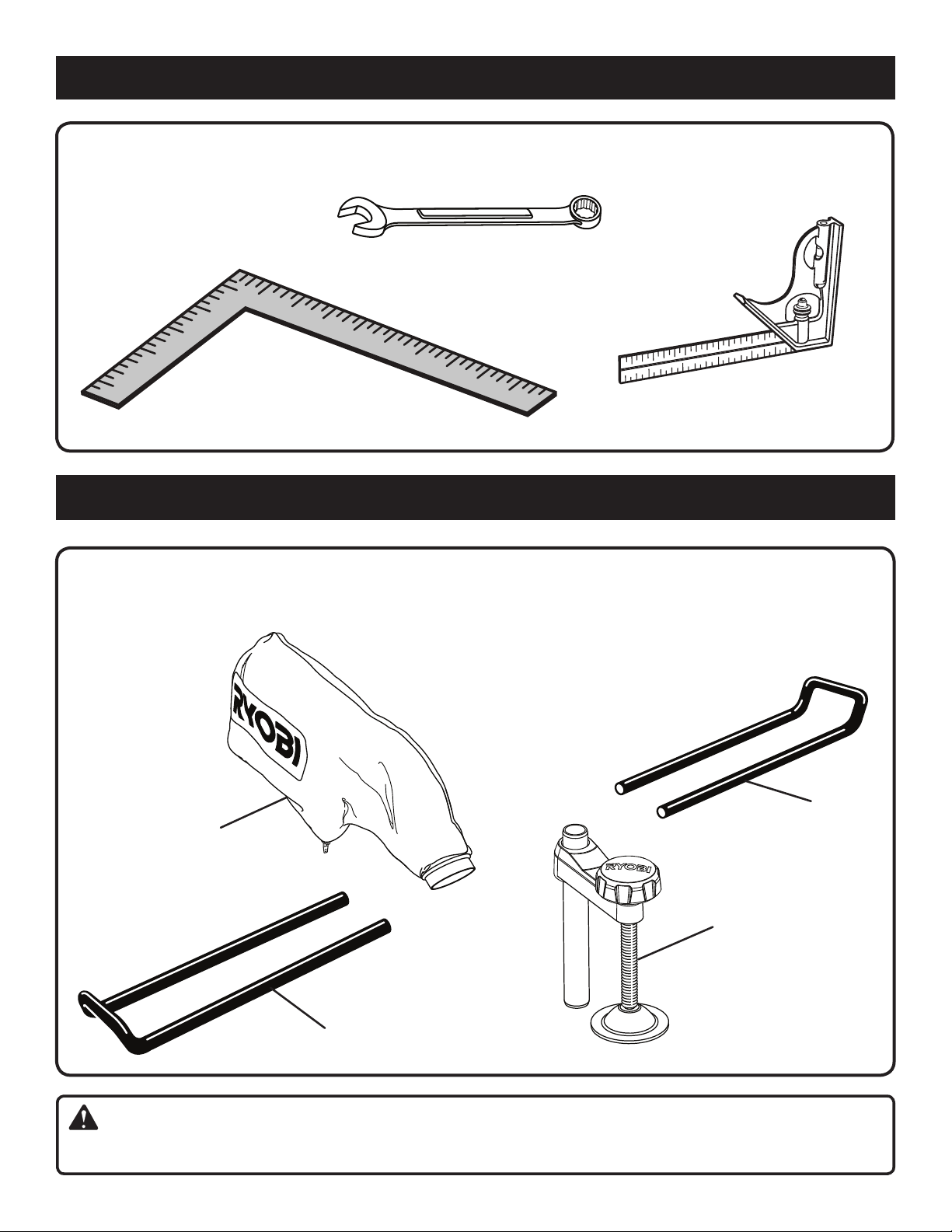
TOOLS NEEDED
The following tools (not included) are needed for making adjustments or installing the blade:
COMBINATION WRENCHES (2)
(10 mm, 12 mm)
COMBINATION
SQUARE
LOOSE PARTS LIST
SQUARE
Fig. 6
The following items are included with the tool:
Dust Bag
Table Extensions (2)
DUST
BAG
Work Clamp
Operator’s Manual
TABLE
EXTENSION
WORK
CLAMP
TABLE
EXTENSION
WARNING:
The use of attachments or accessories not listed might be hazardous and could cause serious personal injury.
12 − English
Fig. 7
Page 13
ASSEMBLY
UNPACKING
This product requires assembly.
Carefully lift saw from the carton by the carrying handle
and the saw base, and place it on a level work surface.
WARNING:
Do not use this product if any parts on the Loose Parts List
are already assembled to your product when you unpack
it. Parts on this list are not assembled to the product by
the manufacturer and require customer installation. Use
of a product that may have been improperly assembled
could result in serious personal injury.
This saw has been shipped with the saw arm secured in
the down position. To release the saw arm, push down
on the “D” handle, cut the tie-wrap, and pull out on the
lock pin.
Lift the saw arm by the handle. Hand pressure should
remain on the “D” handle to prevent sudden rise upon
release of the tie wrap.
Inspect the tool carefully to make sure no breakage or
damage occurred during shipping.
D o not discard the packing mate rial until you have carefully
inspected and satisfactorily operated the product.
The saw is factory set for accurate cutting. After
assembling it, check for accuracy. If shipping has
influenced the settings, refer to specific procedures
explained in this manual.
If any parts are damaged or missing, please call
1-800-525-2579 for assistance.
WARNING:
If any parts are damaged or missing do not operate this
product until the parts are replaced. Use of this product
with damaged or missing parts could result in serious
personal injury.
WARNING:
Do not attempt to modify this product or create
accessories not recommended for use with this tool.
Any such alteration or modification is misuse and could
result in a hazardous condition leading to possible serious
personal injury.
WARNING:
Do not connect to power supply until assembly is
complete. Failure to comply could result in accidental
starting and possible serious personal injury.
WARNING:
Do not start the compound miter saw without checking
for interference between the blade and the miter fence.
Serious personal injury or damage to the blade could result
if it strikes the miter fence during operation of the saw.
WARNING:
This saw can tip over if the saw head is released suddenly
and the saw is not secured to a work surface. ALWAYS
secure this saw to a stable work surface before any use
to avoid serious personal injury.
TRACE HOLES
AT THESE LOCATIONS
FOR HOLE PATTERN
SAW BASE
TRACE HOLES
AT THESE LOCATIONS
FOR HOLE PATTERN
MOUNTING
SURFACE
Fig. 8
13 − English
Page 14

ASSEMBLY
MOUNTING HOLES
See Figure 8.
WARNING:
Before starting any cutting operation, clamp or bolt your
miter saw to a workbench or an approved miter saw stand.
If a miter saw stand is used, read operator’s manual and
follow the instructions for the miter saw stand. Never
operate your miter saw on the floor or in a crouched
position. Failure to heed this warning can result in serious
personal injury.
The compound miter saw should be mounted to a firm
supporting surface such as a workbench. Four bolt holes
have been provided in the saw base for this purpose. Each
of the four mounting holes should be bolted securely using
5/16 in. machine bolts, lock washers, and hex nuts (not
included). Bolts should be of sufficient length to accommodate
the saw base, lock washers, hex nuts, and the thickness of
the workbench. Tighten all four bolts securely.
The hole pattern for mounting to a workbench is shown in
figure 8. Carefully check the workbench after mounting to
make sure that no movement can occur during use. If any
tipping, sliding, or walking is noted, secure the workbench
to the floor before operating.
To unlock and raise the saw arm:
Firmly grasp the “D” handle and apply downward pressure
while at the same time pulling the lock pin out and away
from the saw housing.
Release the lock pin and slowly raise the saw arm.
To lock the saw arm:
Firmly grasp the “D” handle and apply downward pressure
while at the same time pushing the lock pin in and toward
the saw housing.
Release the lock pin allowing it to lock the saw into place.
DEPTH
CONTROL KNOB
USING THE DEPTH STOP
See Figure 9.
When used, the depth stop limits the downward travel of
the blade when cutting dadoes and other non-through cuts.
To use the depth stop:
Unplug the saw.
If the saw is in storage or transport position, unlock the
saw arm.
Rotate the depth stop away from the motor housing.
With the end of the depth control knob touching the depth
stop, adjust the depth control knob by turning the knob
until the desired depth of cut is attained.
A wooden spacer of at least 2 1/4 inches must be placed
between the workpiece and the fence for a consistent
depth of cut in the workpiece. Use the work clamp to
clamp the spacer and another suitable clamp to clamp
the workpiece. Make the slide cut at the desired depth.
See Figures 36 and 37.
Rotate the depth stop back towards the motor housing
for normal through cuts.
NOTE: The depth stop must be moved toward the motor
housing before locking / unlocking the saw arm.
DEPTH STOP
Fig. 9
“D”
HANDLE
LOCK
PIN
LOCKING / UNLOCKING THE SAW ARM
See Figure 10.
When locking and unlocking the saw arm, it is not necessary
to loosen the depth control knob.
14 − English
Fig. 10
Page 15
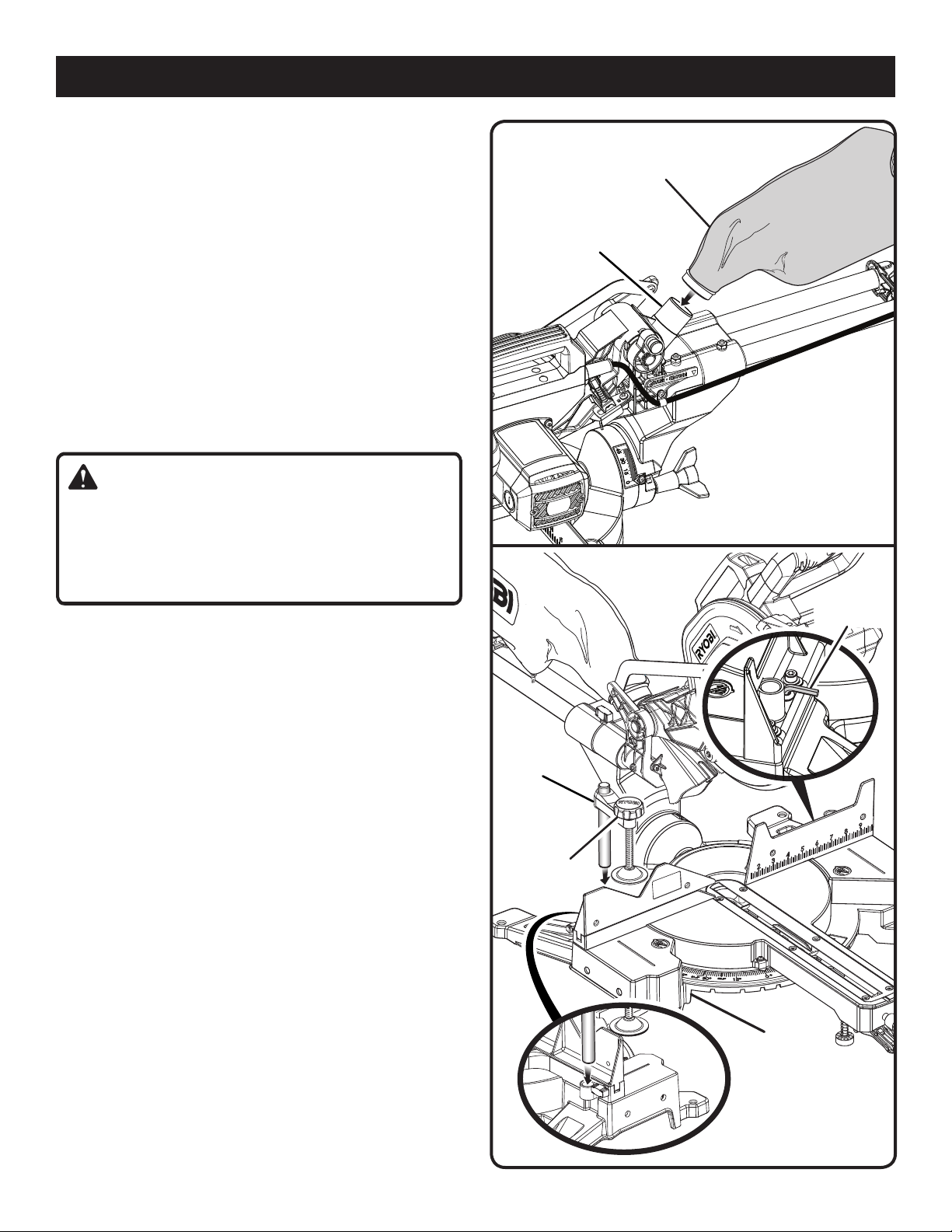
ASSEMBLY
DUST BAG
See Figure 11.
A dust bag is provided for use on this miter saw. It fits over
the exhaust port on the back of the saw.
NOTE: The exhaust port also accepts 1-1/4 in. vacuum hose.
BLADE WRENCH
See Figure 12.
A blade wrench is included with this saw. One end of the
wrench is a phillips screwdriver and the other end is a hex
key. Use the hex key end when installing or removing blade
and the phillips end when removing or loosening screws. A
storage area for the blade wrench is located on the back of
the miter fence.
WORK CLAMP
See Figure 12.
WARNING:
In some operations, the work clamp assembly may
interfere with the operation of the blade guard assembly.
Always make sure there is no interference with the blade
guard prior to beginning any cutting operation to reduce
the risk of serious personal injury.
The work clamp provides greater control by clamping the
workpiece to the fence or the saw table. It also prevents
the workpiece from creeping toward the saw blade. This is
very helpful when cutting compound miters. Depending on
the cutting operation and the size of the workpiece, it may
be necessary to use a C-clamp or other suitable clamp
instead of the work clamp to secure the workpiece prior to
making the cut.
To install the work clamp:
Place the work clamp shaft in one of the holes located
behind the miter fence.
Rotate the work clamp knob to move it up or down as
needed to secure the workpiece.
DUST
BAG
EXHAUST
PORT
Fig. 11
BLADE
WRENCH
WORK
CLAMP
WORK
CLAMP KNOB
15 − English
BASE
Fig. 12
Page 16
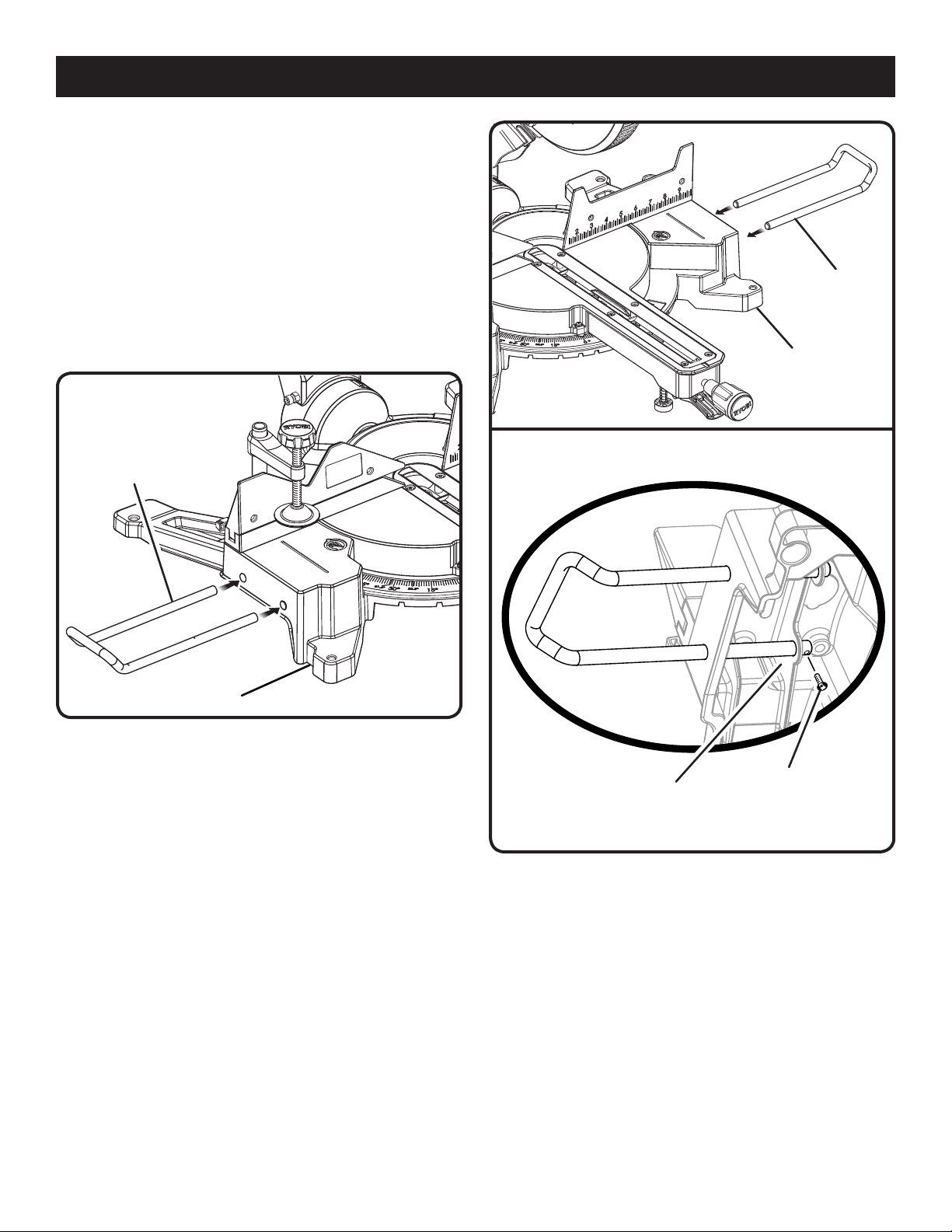
ASSEMBLY
TABLE EXTENSIONS
See Figures 13 - 15.
Table extensions have been provided for both the left and
the right side of the saw.
To install table extensions:
Remove the screw from the end of the table extension.
Insert the ends of extension into the holes in the sides of
the base.
Replace screw and tighten to secure the extension in
place.
Repeat for other extension.
TABLE
EXTENSION
BASE
Fig. 14
TABLE
EXTENSION
BASE
Fig. 13
SAW VIEWED FROM BOTTOM
TABLE
BASE
EXTENSION
SCREW
Fig. 15
16 − English
Page 17
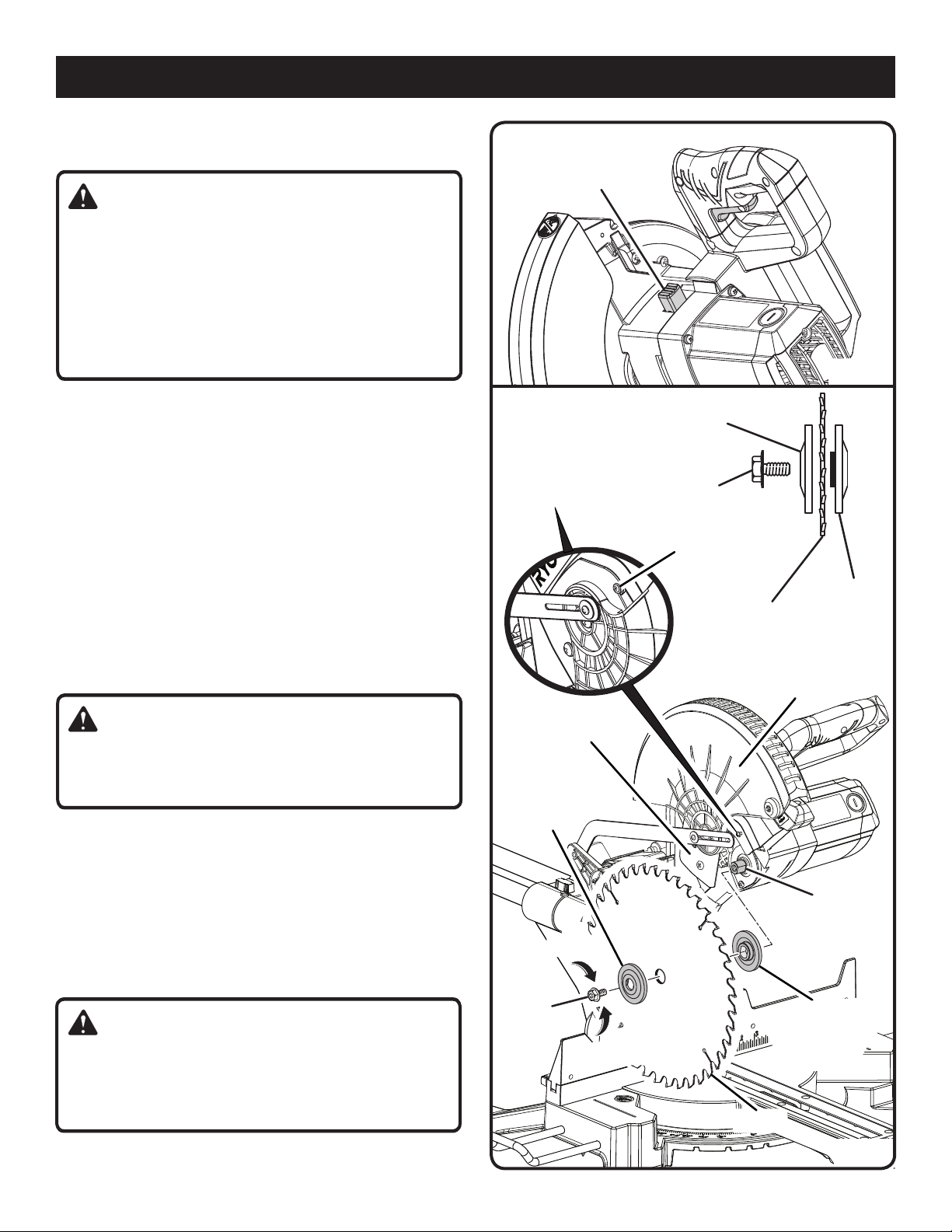
ASSEMBLY
TO INSTALL / REPLACE THE BLADE
See Figures 16 - 17.
WARNING:
A 12 in. blade is the maximum blade capacity of the saw.
Never use a blade that is too thick to allow outer blade
washer to engage with the flats on the spindle. Larger
blades will come in contact with the blade guards, while
thicker blades will prevent the blade bolt from securing
the blade on the spindle. Either of these situations
could result in a serious accident and can cause serious
personal injury.
SPINDLE
LOCK BUTTON
Fig. 16
Unplug the saw.
Loosen blade bolt cover screw. Rotate lower blade guard
and blade bolt cover up and back to expose the blade
bolt.
Depress the spindle lock button and rotate the blade bolt
until the spindle locks.
Using the blade wrench provided, loosen and remove the
blade bolt.
NOTE: The blade bolt has left hand threads. Turn blade
bolt clockwise to loosen.
Remove the outer blade washer. Do not remove the inner
blade washer.
Wipe a drop of oil onto inner blade washer and outer
blade washer where they contact the blade.
WARNING:
If inner blade washer has been removed, replace it before
placing blade on spindle. Failure to do so could cause an
accident since blade will not tighten properly.
Fit saw blade inside lower blade guard and onto shoulder
of inner washer. The blade teeth point downward at the
front of saw as shown in figure 17.
Replace the outer blade washer. Double “D” flats on blade
washers align with flats on spindle.
Depress spindle lock button and replace blade bolt.
NOTE: The blade bolt has left hand threads. Turn blade bolt
counterclockwise to tighten.
CAUTION:
Always install the blade with the blade teeth and the arrow
printed on the side of the blade pointing down at the front
of the saw. The direction of blade rotation is also stamped
with an arrow on the upper blade guard.
NOTE: BEFORE USE,
REPLACE SCREWS AND
TIGHTEN SECURELY
TO PREVENT GUARD
MOVEMENT
BLADE
BOLT COVER
OUTER BLADE
WASHER
WITH DOUBLE
“D” FLATS
TO
LOOSEN
BLADE
BOLT
TO
TIGHTEN
OUTER
BLADE
WASHER
BLADE
BOLT
BLADE
BOLT COVER
SCREW
BLADE
LOWER BLADE
GUARD
FLAT(S)
ON SPINDLE
INNER BLADE
WASHER WITH
DOUBLE “D”
FLATS
BLADE
INNER
BLADE
WASHER
17 − English
Fig. 17
Page 18
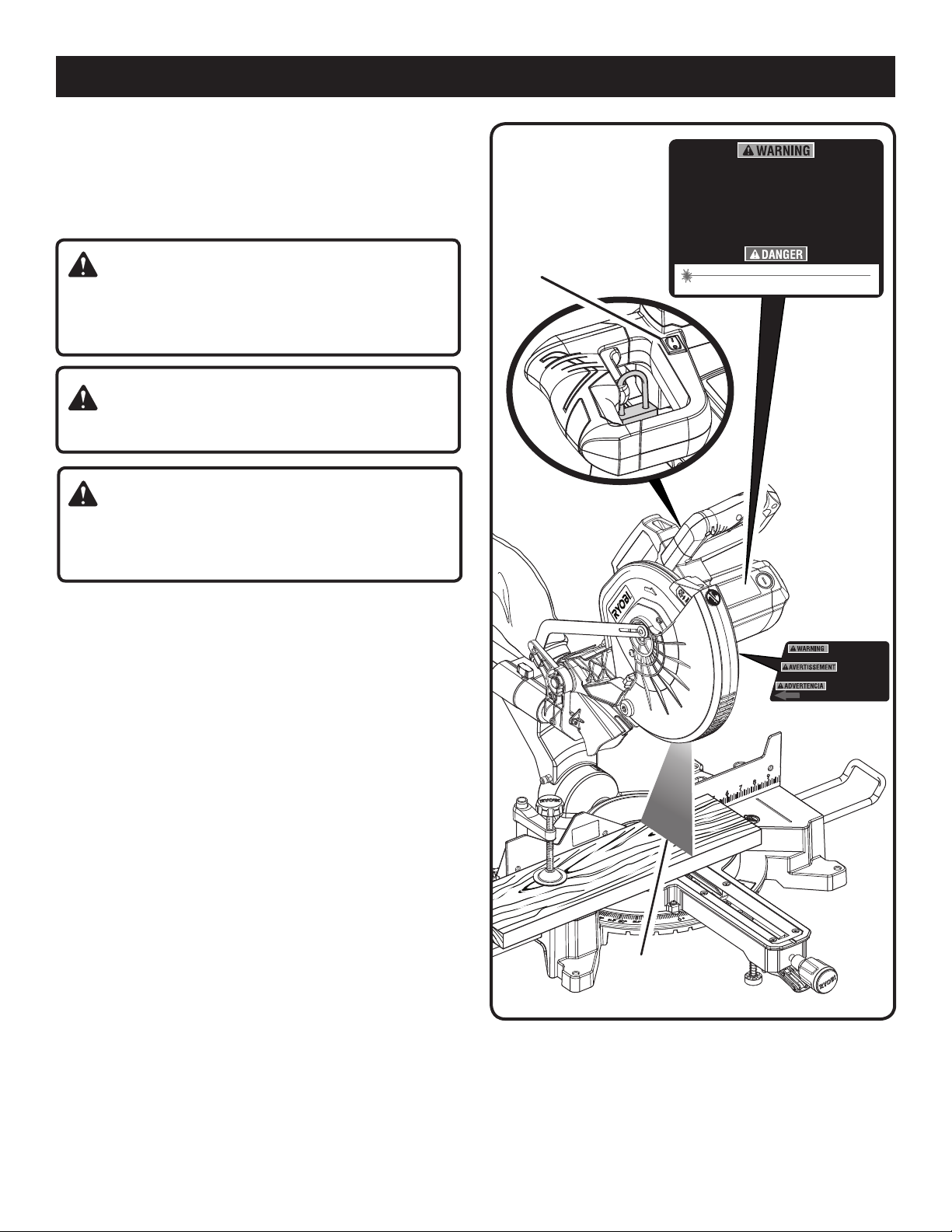
ASSEMBLY
LASER RADIATION AVOID DIRECT EYE EXPOSURE
CLASS IIIa LASER PRODUCT
MAXIMUM OUTPUT: <5mW WAVELENGTH: 635-660nm
• To reduce the risk of injury, user must read and understand the
operator’s manual before using the miter saw.
• Wear eye protection.
• Keep hands out of path of saw blade.
• Do not operate saw without guards in place.
• Do not perform any operation freehand.
• Never reach around the saw blade.
• Turn off tool and wait for saw blade to stop before raising saw
arm, moving workpiece, or changing settings.
• Disconnect the saw from the power source before changing blade
or servicing.
Complies with 21 CFR
Parts 1040.10 & 1040.11
RYLD
Fixer gâchette avant
làser est réglagé. EVITER
L’EXPOSITION: Rayonnement laser émise de cet orifice.
Asegure gatillo antes de ajuste
de laser. EVITE LA EXPOSICIÔN:
Radiación laser se emite por esta abertura.
Lock trigger prior to adjusting
laser. AVOID EXPOSURE:
Laser radiation is emitted from this aperture.
Tighten blade bolt securely.
Replace the lower blade guard and blade bolt cover.
Securely tighten the blade bolt cover screw.
Raise and lower the saw head and ensure that the lower
blade guard operates properly.
WARNING:
Make sure the spindle lock button is not engaged before
reconnecting saw into power source. Never engage
spindle lock button when blade is rotating.
DANGER:
Laser radiation. Avoid direct eye contact with light source.
WARNING:
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified herein may result
in hazardous radiation exposure.
LASER
GUIDE
SWITCH
ALIGNING THE LASER GUIDE LINE
See Figure 18.
Lock the switch by installing a padlock (not included) through
the hole in the switch trigger and closing the shackle.
Draw a line on the workpiece. When the laser guide switch
is turned on it will generate a red line on the work surface.
This line will let you see your mark and the laser guide line
at the same time, and will assist you in lining up the mark
for more accurate cutting of the workpiece.
Align the laser line and the mark with the blade at the
uppermost position. Once both lines are in alignment, do
not move the workpiece.
Remove the padlock then plug the saw into the power
source. Make several practice cuts on different styles and
thickness of material. Repeat the steps above as necessary.
Removing Your Mark:
Position the laser line near the left edge of your mark on the
work surface in order to remove the mark.
To Cut Your Mark:
Position the laser line near or over your mark on the work
surface in order to cut the mark.
To Leave Your Mark:
Position the laser line near the right edge of your mark on
the work surface in order to leave the mark.
After you have become familiar with using the laser guide,
you will be able to remove, cut, or leave your mark on the
work surface. Practice will teach you the correct position for
aligning the laser line with your mark.
RED
LINE
Fig. 18
18 − English
Page 19
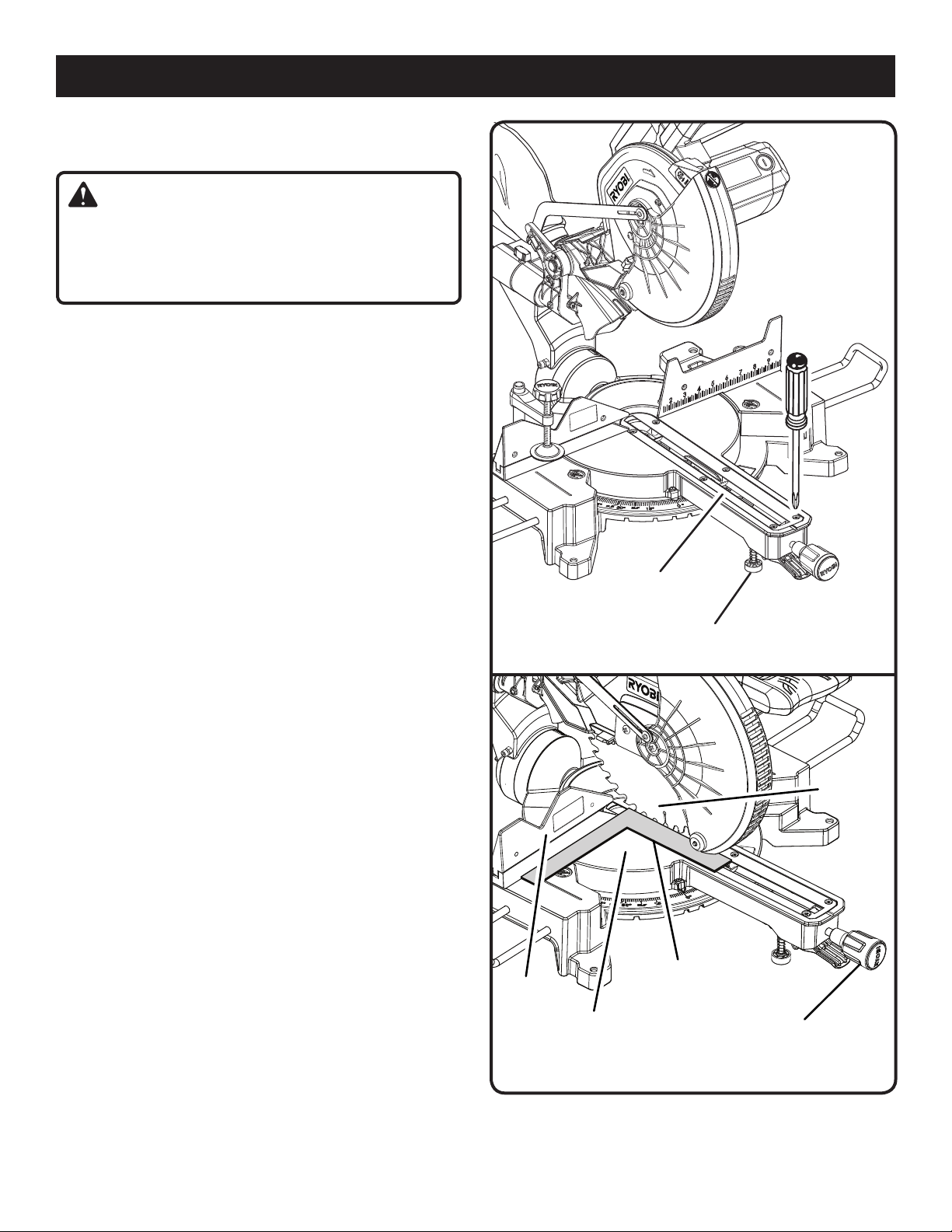
ASSEMBLY
REMOVING / REPLACING THE THROAT PLATE
See Figure 19.
WARNING:
The throat plate must be below the miter table. If the throat
plate is too high or too low, the workpiece can catch on
the uneven edges resulting in binding which could result
in serious personal injury.
Never operate the saw without a throat plate installed.
To remove / replace:
Unplug the saw.
Remove the screws securing the throat plate.
Lift the throat plate from the saw.
To reinstall the throat plate, align the holes in the throat
plate with the holes in the saw base.
Retighten the screws, being careful not to overtighten
which can cause the throat plate to bow or bend.
ADJUSTING SUPPORT FOOT
See Figure 19.
Turn the support foot clockwise or counterclockwise
depending on the amount of support needed for making
sliding cuts.
NOTE: Many of the illustrations in this manual show only
portions of the compound miter saw. This is intentional so that
we can clearly show points being made in the illustrations.
Never operate the saw without all guards securely in
place and in good operating condition.
SQUARING THE BLADE TO THE FENCE
See Figures 20 - 26.
Unplug the saw.
Pull the saw arm all the way down and engage the lock
pin to hold the saw arm in transport position.
Loosen the miter lock handle approximately one-half turn
and squeeze the detent release lever.
Rotate the miter table until the scale indicator is positioned
at 0°.
Release the detent release lever, and ensure the control
arm is seated in the positive notch.
Tighten the miter lock knob to secure the miter table.
Loosen bevel lock knob and set saw arm at 0° bevel
(blade set 90° to miter table). Tighten bevel lock knob.
Lay a square flat on the miter table. Place one leg of the
square against the fence. Slide the other leg of the square
against the flat part of saw blade.
NOTE: Make sure that the square contacts the flat part
of the saw blade, not the blade teeth.
The edge of the square and the saw blade should be
parallel as shown in figure 20.
19 − English
SLIDING
MITER
FENCE
THROAT
PLATE
SUPPORT
FOOT
SQUARE
MITER
TABLE
VIEW OF BLADE SQUARE WITH FENCE
MITER
LOCK HANDLE
Fig. 19
BLADE
Fig. 20
Page 20
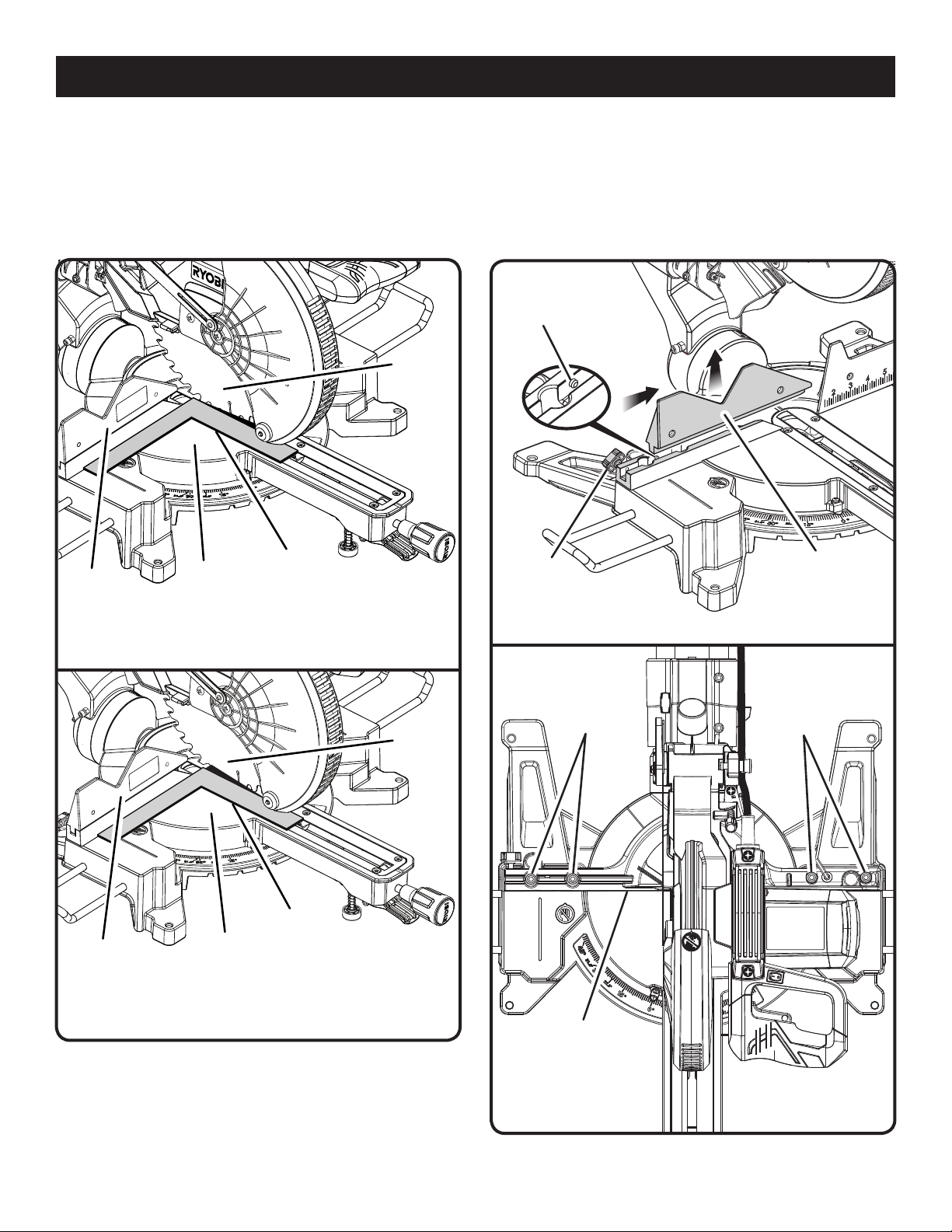
ASSEMBLY
If the front or back edge of the saw blade angles away
from the square as shown in figures 21 - 22, adjustments
are needed.
Loosen the fence adjusting screw, push the sliding fence
approx. 1 in. to the right to get past the set screw, then
lift to remove the sliding fence from the miter fence.
BLADE
SQUARE
Fig. 21
SLIDING
MITER
FENCE
MITER
TABLE
VIEW OF BLADE NOT SQUARE WITH
FENCE, ADJUSTMENTS ARE REQUIRED
Using the blade wrench provided, loosen the socket head
screws that secure the miter fence to the miter table.
Rotate the miter fence left or right until the saw blade is
parallel with the square.
Retighten the screws securely and recheck the blade-to-
fence alignment.
SET SCREW
FENCE
ADJUSTING
SCREW
SLIDING
MITER FENCE
Fig. 23
SLIDING
MITER
FENCE
SQUARE
MITER
TABLE
VIEW OF BLADE NOT SQUARE WITH
FENCE, ADJUSTMENTS ARE REQUIRED
BLADE
Fig. 22
SOCKET HEAD
SCREW(S)
SLIDING
MITER
FENCE
SOCKET HEAD
SCREW(S)
Fig. 24
20 − English
Page 21
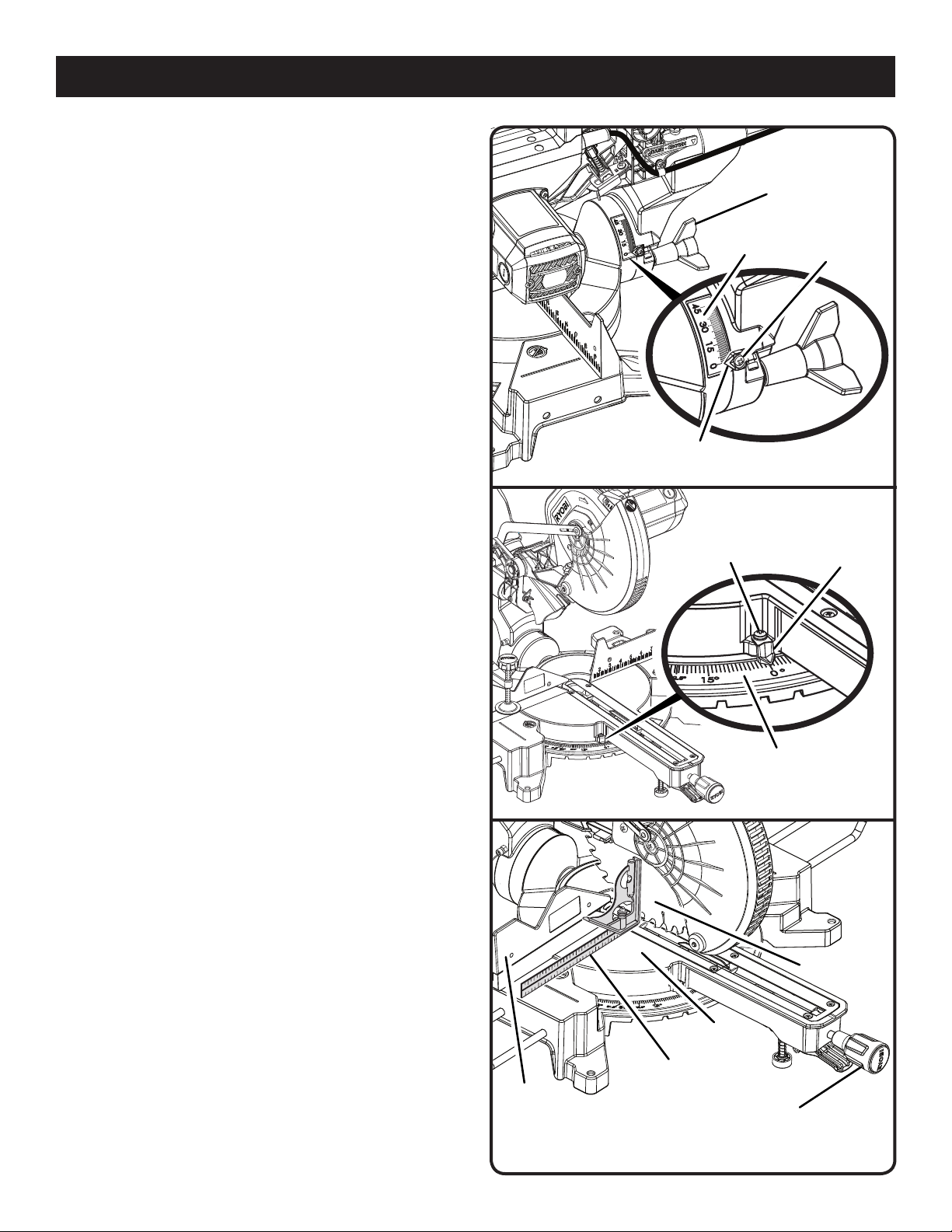
ASSEMBLY
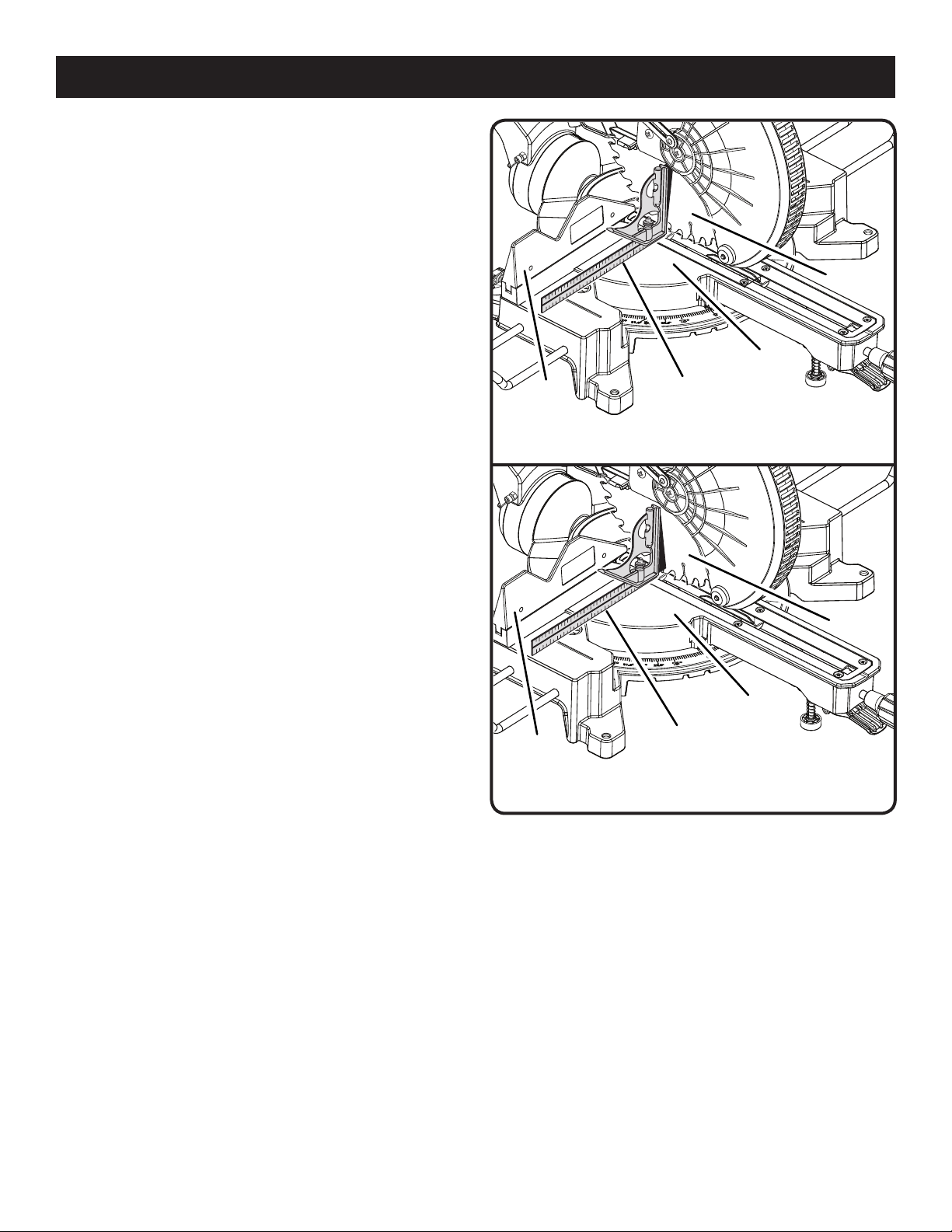
Your saw has several scale indicators. After squaring
adjustments have been made, it may be necessary to loosen
the indicator screws and reset them to zero. See Figures
25 - 26.
BEVEL
LOCK KNOB
SQUARING THE BLADE TO THE MITER TABLE
See Figures 27 - 29.
Unplug the saw.
Pull the saw arm all the way down and engage the lock
pin to hold the saw arm in transport position.
Loosen the miter lock handle approximately one-half turn
and squeeze the detent release lever.
Rotate the miter table until the scale indicator on the
control arm is positioned at 0°.
Release the detent release lever, then tighten the miter
lock knob to secure the miter table.
Loosen the bevel lock knob and set saw arm at 0° bevel
(blade set 90° to miter table). Tighten bevel lock knob.
Place a combination square against the miter table and
the flat part of saw blade.
NOTE: Make sure that the square contacts the flat part
of the saw blade, not the blade teeth.
Rotate the blade by hand and check the blade-to-table
alignment at several points.
The edge of the square and the saw blade should be
parallel as shown in figure 27.
SCALE
INDICATOR
INDICATOR
SCREW
BEVEL
SCALE
INDICATOR
SCREW
Fig. 25
SCALE
INDICATOR
SLIDING
MITER
FENCE
21 − English
MITER
SCALE
MITER
TABLE
COMBINATION
SQUARE
MITER
LOCK HANDLE
CORRECT VIEW OF BLADE
SQUARE WITH MITER TABLE
Fig. 26
BLADE
Fig. 27
Page 22
ASSEMBLY
If the top or bottom of the saw blade angles away from
the square as shown in figures 28 and 29, adjustments
are needed.
Loosen bevel lock knob.
Adjust positive stop adjustment screw to bring saw
blade into alignment with the square. See Positive Stop
Adjustment in the Adjustment section.
Tighten bevel lock knob. Recheck blade-to-table
alignment.
NOTE: The above procedure can be used to check blade
squareness of the saw blade to the miter table at both 0°
and 45° angles.
Your saw has several scale indicators. After squaring
adjustments have been made, it may be necessary to loosen
the indicator screws and reset them to zero. See Figures
25 - 26.
MITER
SLIDING
MITER FENCE
VIEW OF BLADE NOT SQUARE WITH MITER TABLE,
COMBINATION
SQUARE
ADJUSTMENTS ARE REQUIRED
TABLE
BLADE
Fig. 28
MITER
TABLE
SLIDING
MITER FENCE
VIEW OF BLADE NOT SQUARE WITH MITER TABLE,
COMBINATION
SQUARE
ADJUSTMENTS ARE REQUIRED
BLADE
Fig. 29
22 − English
Page 23
OPERATION
WARNING:
Do not allow familiarity with tools to make you careless.
Remember that a careless fraction of a second is sufficient
to inflict serious injury.
WARNING:
Always wear eye protection with side shields marked to
comply with ANSI Z87.1. Failure to do so could result in
objects being thrown into your eyes, resulting in possible
serious injury.
WARNING:
Do not use any attachments or accessories not
recommended by the manufacturer of this tool. The use
of attachments or accessories not recommended can
result in serious personal injury.
APPLICATIONS
This product has been designed only for the purposes listed
below:
Cross cutting wood and plastic (do not cut metals,
ceramics or masonry products.)
Cross cutting miters, joints, etc., for picture frames,
moldings, door casings, and fine joinery
Bevel and compound cutting
Cross cutting wide workpieces
NOTE: The blade provided is fine for most wood cutting
operations, but for fine joinery cuts or cutting plastic, use
one of the accessory blades available from the Ryobi dealer.
WARNING:
To avoid serious personal injury, keep hands outside the
no hands zone, at least 3 in. from the blade. Never perform
any cutting operation freehand (without holding workpiece
against the fence). The blade could grab the workpiece
if it slips or twists.
NOTICE:
Do not start the compound miter saw without checking
for interference between the blade and the miter fence.
Damage could result to the blade if it strikes the miter
fence during operation of the saw.
CUTTING WITH YOUR COMPOUND MITER SAW
WARNING:
When using a work clamp, C-clamp,
clamp
to secure your workpiece, clamp workpiece on one
side of the blade only. The workpiece must remain free on
one side of the blade to prevent the blade from binding
in workpiece. The workpiece binding the blade will cause
motor stalling and kickback. This situation could cause
an accident resulting in possible serious personal injury.
or other suitable
WARNING:
NEVER move the workpiece or make adjustment to any
cutting angle while the saw is running and the blade is
rotating. Any slip can result in contact with the blade
causing serious personal injury.
WARNING:
Before starting any cutting operation, clamp or bolt the
compound miter saw to a workbench. Never operate the
miter saw on the floor or in a crouched position. Failure
to heed this warning can result in serious personal injury.
WARNING:
To avoid serious personal injury, always tighten the miter
lock handle and bevel lock handle securely before making
a cut. Failure to do so could result in movement of the
miter table or saw head while making a cut.
23 − English
WARNING:
Do not try to cut narrow pieces using the sliding feature.
Failure to heed this warning could result in serious
personal injury.
Page 24
OPERATION
TO MAKE NON-SLIDING CUTS
WARNING:
Securely tighten the slide lock knob when making any
non-sliding cuts. Failure to tighten the knob could result
in the saw head moving during the cutting operation.
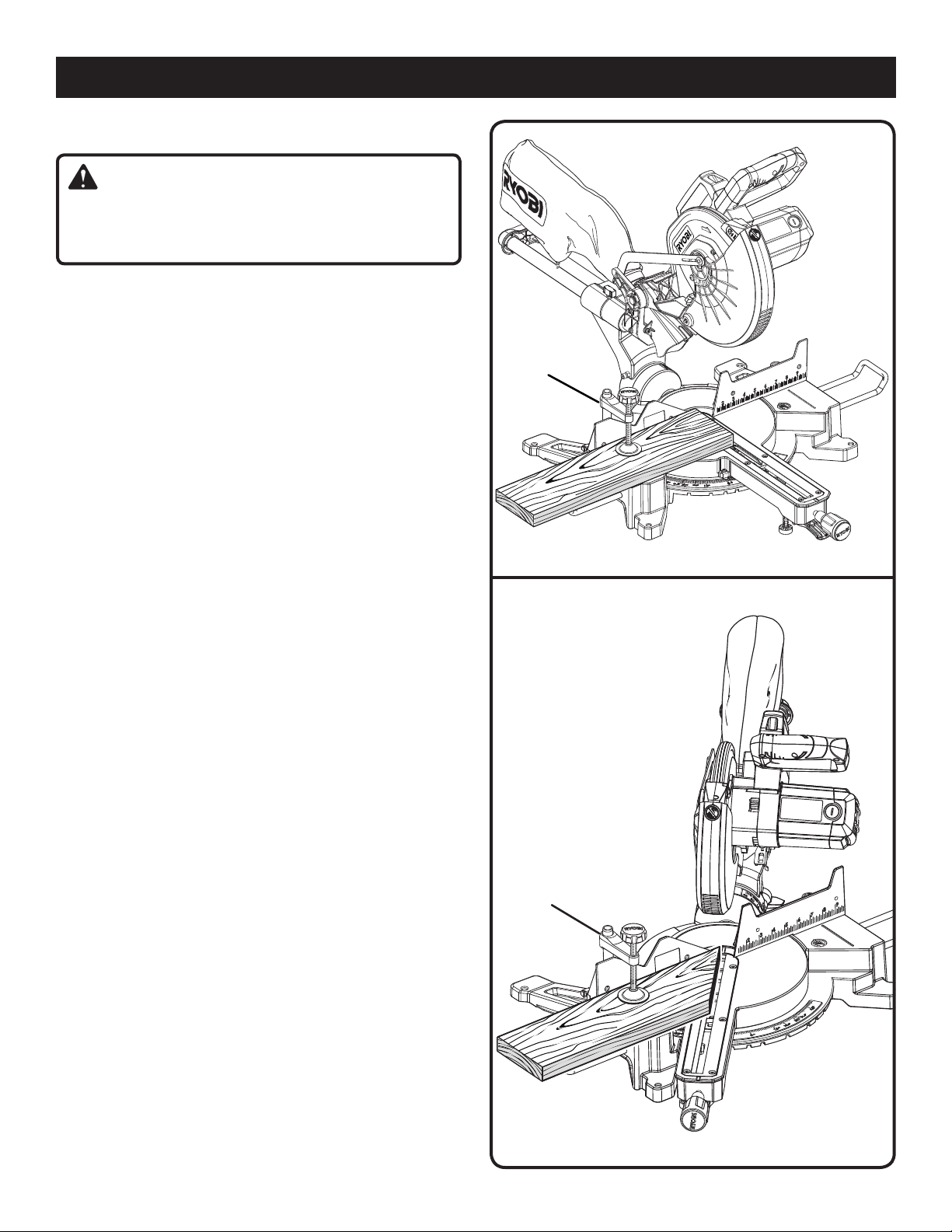
TO MITER CUT / CROSS CUT
See Figures 30 - 31.
A cross cut is made by cutting across the grain of the
workpiece. A straight cross cut is made with the miter table
set at the 0° position. Miter cross cuts are made with the
miter table set at some angle other than 0°.
Raise saw arm to its full height.
Loosen the miter lock handle approximately one-half turn
and squeeze the detent release lever.
Rotate the control arm until the pointer aligns with the
desired angle on the miter scale.
Release the detent release lever, then tighten the miter
lock knob to secure the miter table.
NOTE: You can quickly locate 0°, 15°, 22-1/2°, 31.6°,
and 45° left or right by releasing the detent release lever
as you rotate the control arm. The control arm will seat
itself in one of the positive stop notches, located in the
miter table base.
Place the workpiece flat on the miter table with one edge
securely against the fence. If the board is warped, place
the convex side against the fence. If the concave edge
of a board is placed against the fence, the board could
collapse on the blade at the end of the cut, jamming the
blade. See Figures 42 - 43.
When cutting long pieces of lumber or molding, support
the opposite end of the stock with a roller stand or with
a work surface level with the saw table. See Figure 35.
Slide the saw head to its most rearward position and
tighten the slide lock knob securely.
Align cutting line on the workpiece with the edge of saw
blade or laser line.
Grasp the stock firmly with one hand and secure it against
the fence. Use the work clamp, C-clamp, or other suitable
clamp to secure the workpiece when possible.
Before turning on the saw, perform a dry run of the cutting
operation to make sure that no problems will occur when
the cut is made.
CROSS CUT
WORK
CLAMP
Fig. 30
MITER CUT
WORK
CLAMP
24 − English
Fig. 31
Page 25
OPERATION
Grasp the saw handle firmly. Squeeze the switch trigger.
Allow several seconds for the blade to reach maximum
speed.
Slowly lower the blade into and through the workpiece.
Release the switch trigger and allow the saw blade to
stop rotating before raising the blade out of workpiece
and removing the workpiece from the miter table.
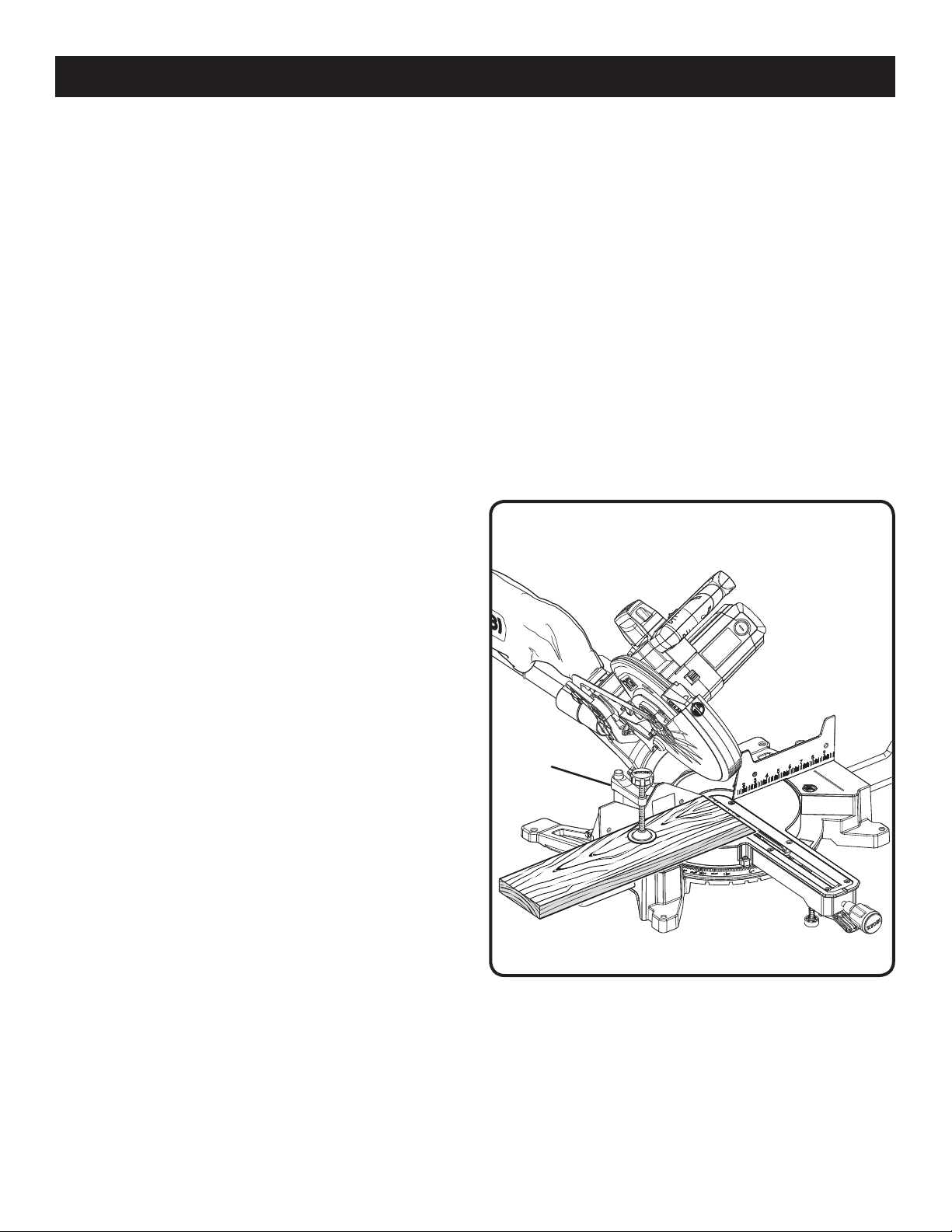
TO BEVEL CUT
See Figure 32.
A bevel cut is made by cutting across the grain of the
workpiece with the blade angled to the workpiece. A straight
bevel cut is made with the miter table set at the zero degree
position and the blade set at an angle between 0° and 45°.
NOTE: It may be necessary to adjust or remove the sliding
miter fence to insure proper clearance prior to making the cut.
Pull out the lock pin and lift saw arm to its full height.
Loosen the miter lock handle approximately one-half turn
and squeeze the detent release lever.
Rotate the control arm until the pointer aligns with the
desired angle on the miter scale.
Release the detent release lever, then tighten the miter
lock knob to secure the miter table.
NOTE: You can quickly locate 0°, 15°, 22-1/2°, 31.6°,
and 45° left or right by releasing the detent release lever
as you rotate the control arm. The control arm will seat
itself in one of the positive stop notches, located in the
miter table base.
Loosen the bevel lock knob and move the saw arm to
the desired bevel angle.
Bevel angles can be set from 0° to 45°.
Align the indicator point for the desired angle.
Once the saw arm has been set at the desired angle,
securely tighten the bevel lock knob.
Place the workpiece flat on the miter table with one edge
securely against the fence. If the board is warped, place
the convex side against the fence. If the concave edge
of a board is placed against the fence, the board could
collapse on the blade at the end of the cut, jamming the
blade. See Figures 42 - 43.
When cutting long pieces of lumber or molding, support
the opposite end of the stock with a roller stand or with
a work surface level with the saw table. See Figure 35.
Slide the saw head to its most rearward position and
tighten the slide lock knob securely.
Align the cutting line on the workpiece with the edge of
saw blade or laser line.
Grasp the stock firmly with one hand and secure it against
the fence. Use the work clamp, C-clamp, or other suitable
clamp to secure the workpiece when possible.
Before turning on the saw, perform a dry run of the cutting
operation just to make sure that no problems will occur
when the cut is made.
Grasp the saw handle firmly then squeeze the switch
trigger. Allow several seconds for the blade to reach
maximum speed.
Slowly lower the blade into and through the workpiece.
Release the switch trigger and allow the saw blade to stop
rotating before raising the blade out of workpiece. Wait
until the electric brake stops blade from turning before
removing the workpiece from miter table.
BEVEL CUT
WORK
CLAMP
Fig. 32
25 − English
Page 26
OPERATION
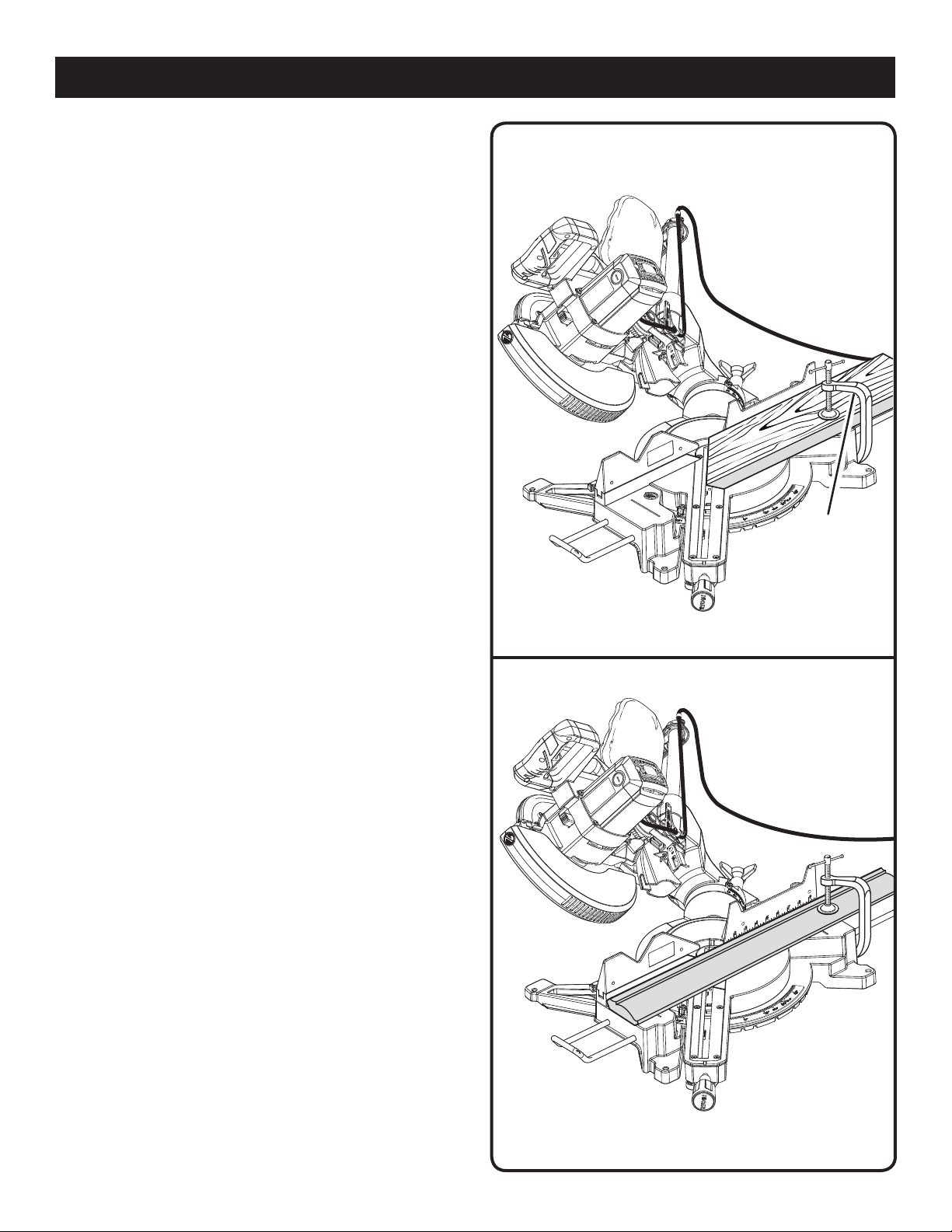
TO COMPOUND MITER CUT
See Figures 33 - 34.
A compound miter cut is a cut made using a miter angle and
a bevel angle at the same time. This type of cut is used to
make picture frames, cut molding, make boxes with sloping
sides, and for certain roof framing cuts.
To make this type of cut the control arm on the miter table
must be rotated to the correct angle and the saw arm must
be tilted to the correct bevel angle. Care should always
be taken when making compound miter setups due to the
interaction of the two angle settings.
Adjustments of miter and bevel settings are interdependent
with one another. Each time you adjust the miter setting you
change the effect of the bevel setting. Also, each time you
adjust the bevel setting you change the effect of the miter
setting.
It may take several settings to obtain the desired cut. The
first angle setting should be checked after setting the second
angle, since adjusting the second angle affects the first.
Once the two correct settings for a particular cut have been
obtained, always make a test cut in scrap material before
making a finish cut in good material.
NOTE: It may be necessary to adjust or remove the sliding
miter fence to insure proper clearance prior to making the cut.
Pull out the lock pin and lift saw arm to its full height.
Loosen the miter lock handle approximately one-half turn
and squeeze the detent release lever.
Rotate the control arm until the pointer aligns with the
desired angle on the miter scale.
Release the detent release lever, then tighten the miter
lock knob to secure the miter table.
Loosen the bevel lock knob and move the saw arm to
the left to the desired bevel angle.
Bevel angles can be set from 0° to 45°.
Once the saw arm has been set at the desired angle,
securely tighten the bevel lock knob.
Recheck miter angle setting. Make a test cut in scrap
material.
Place the workpiece flat on the miter table with one edge
securely against the fence. If the board is warped, place
the convex side against the fence. If the concave edge
of a board could collapse on the blade at the end of the
cut, jamming the blade. See Figures 42 - 43.
When cutting long pieces of lumber or molding, support
the opposite end of the stock with a roller stand or with
a work surface level with the saw table. See Figure 35.
Slide the saw head to its most rearward position and
tighten the slide lock knob securely.
Align the cutting line on the workpiece with the edge of
saw blade or laser line.
COMPOUND MITER CUT
45° X 45° COMPOUND MITER CUT
C-CLAMP
Fig. 33
Fig. 34
26 − English
Page 27
OPERATION
Grasp the stock firmly with one hand and secure it against
the fence. Use the work clamp, C-clamp, or other suitable
clamp to secure the workpiece when possible.
Before turning on the saw, perform a dry run of the cutting
operation just to make sure that no problems will occur
when the cut is made.
Grasp the saw handle firmly then squeeze the switch
trigger. Allow several seconds for the blade to reach
maximum speed.
Slowly lower the blade into and through the workpiece.
Release the switch trigger and allow the saw blade to stop
rotating before raising the blade out of workpiece. Wait
until the electric brake stops blade from turning before
removing the workpiece from miter table.
TO SUPPORT LONG WORKPIECES
See Figure 35.
Long workpieces need extra supports. Supports, roller stand,
or work surface level with the saw table should be placed
along the workpiece so it does not sag. The support should
let the workpiece lay flat on the base of the saw and work
table during the cutting operation. Use the work clamp,
C-clamp, or other suitable clamp to secure the workpiece
when possible.
LONG
WORKPIECE
WARNING:
Never make a cut by pulling the saw toward you as the
blade can climb on top of the workpiece and come toward
you. Failure to heed this warning could result in serious
personal injury.
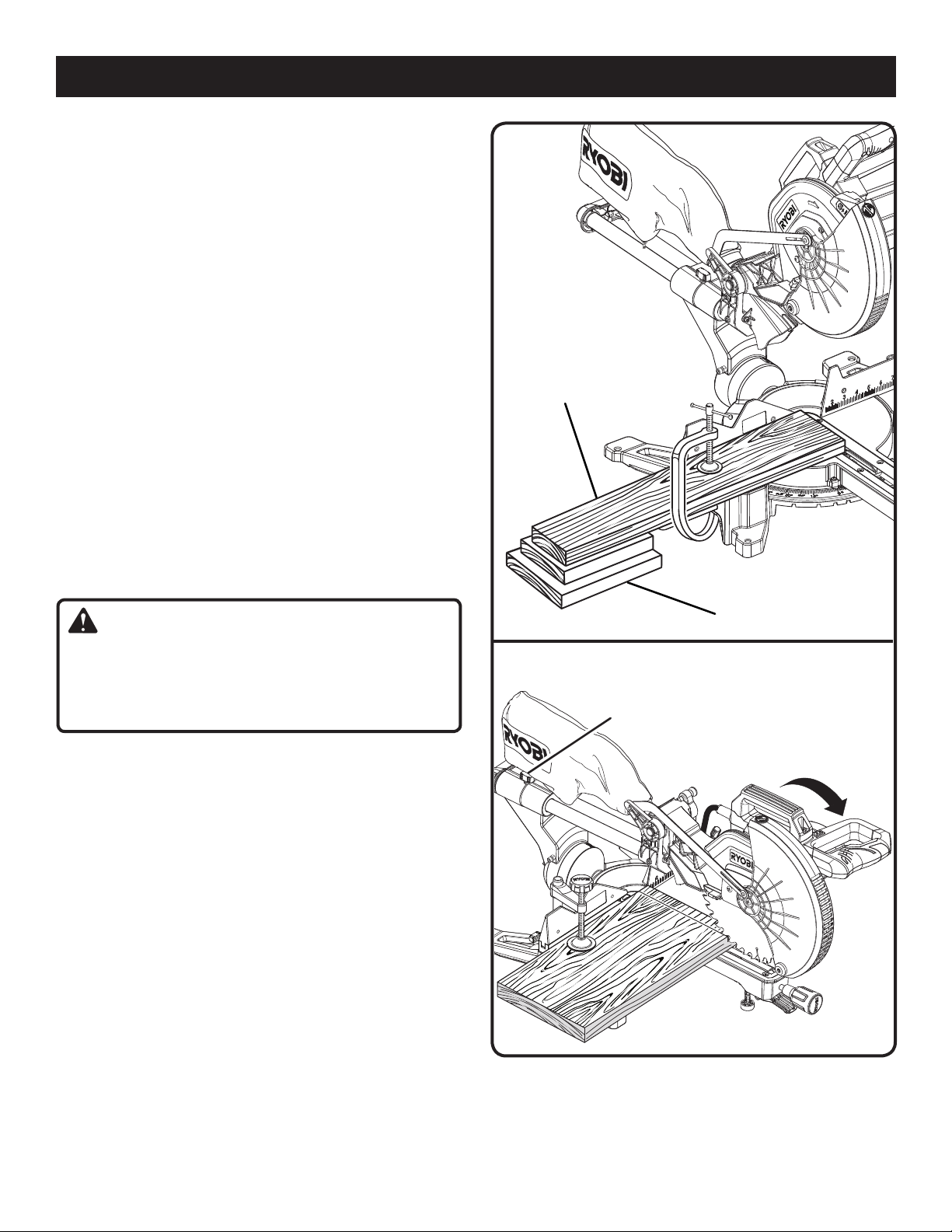
TO SLIDE CUT
See Figures 36 - 37.
The sliding feature will cut workpieces 13-1/2 in. wide by
1-1/2 in. thick or 5-1/2 in. wide by 3-1/2 in. thick. With the
saw off, pull the saw arm forward. Turn the saw on (let blade
reach maximum speed), push the blade down cutting into the
workpiece then back toward the rear of the saw to make a
cut. Cuts are made by pushing the saw blade away from you
and toward the bevel scale at the back of the saw stopping
when the full rear position has been reached after each cut.
When the saw is running (turned on), NEVER pull the saw
blade toward you or toward the front of the saw.
Raise saw arm to its full height.
Place the workpiece flat on the miter table with one edge
securely against the fence. If the board is warped, place
the convex side against the fence. If the concave edge
of a board is placed against the fence, the board could
collapse on the blade at the end of the cut, jamming the
blade. See Figures 42 - 43.
SLIDE LOCK
KNOB
WORKPIECE SUPPORTS
SLIDE CUT
SLIDE SAW ARM
FORWARD THEN
PUSH DOWN
Fig. 35
Fig. 36
27 − English
Page 28
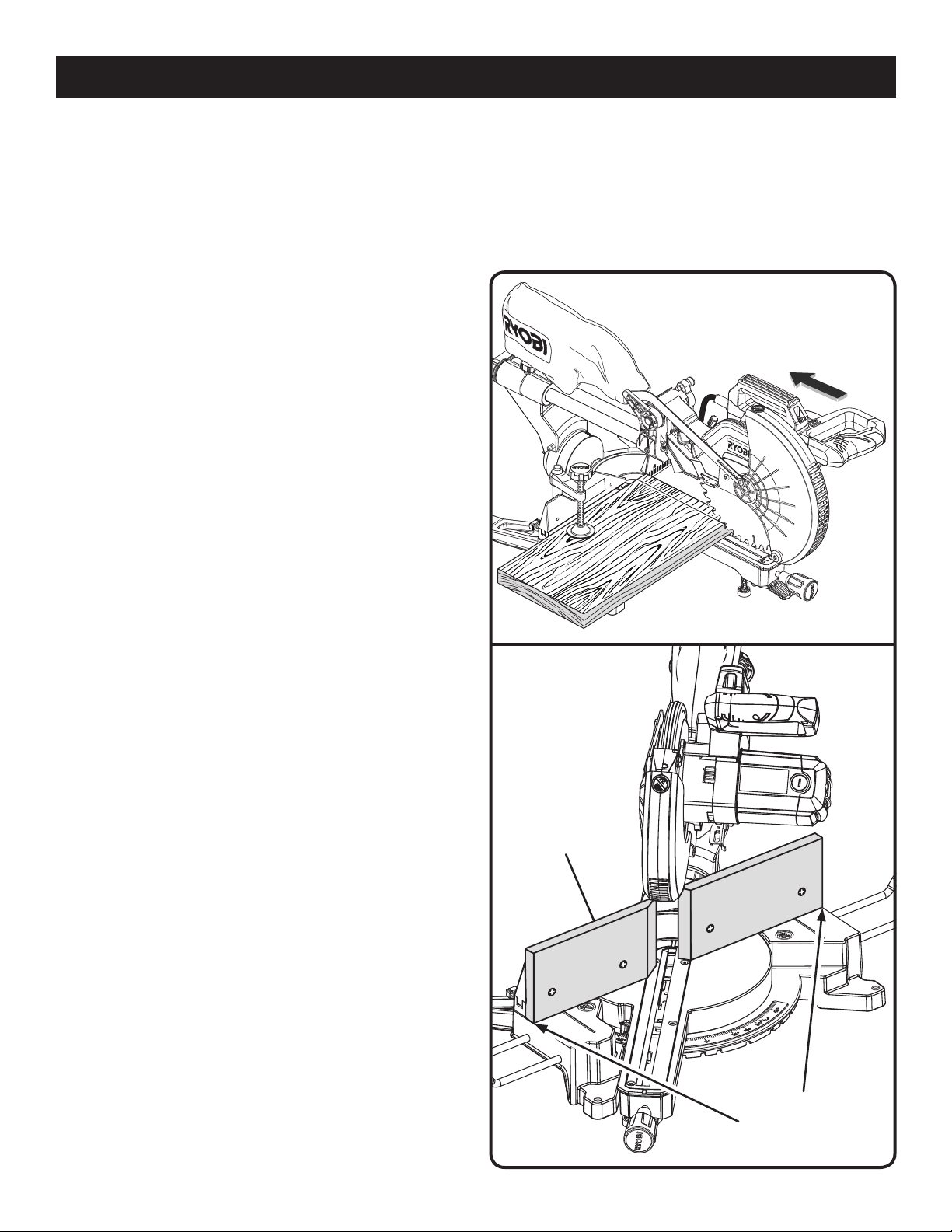
OPERATION
When cutting long pieces of lumber or molding, support
the opposite end of the stock with a roller stand or with
a work surface level with the saw table. See Figure 35.
Align the cutting line on the workpiece with the edge of
saw blade or laser line.
Loosen the slide lock knob by turning the knob
counterclockwise.
Grasp the stock firmly with one hand and secure it against
the fence. Use the work clamp or a C-clamp to secure
the workpiece when possible.
Before turning on the saw, perform a dry run of the cutting
operation to make sure that no problems will occur when
the cut is made.
With the saw off, grasp the saw handle firmly then pull
the saw forward until the blade arbor (center of the saw
blade) is over the front of the workpiece or until the saw
is fully extended.
Squeeze the switch trigger. Allow several seconds for the
blade to reach maximum speed.
Slowly lower the blade into and through the front edge
of the workpiece.
Push the saw handle away from you and toward the bevel
scale at the back of the saw.
Release the switch trigger and allow the saw blade to
stop rotating before raising the blade out of workpiece
and removing the workpiece from miter table.
NOTE: A cross cut is made by cutting across the grain of
the workpiece. A straight cross cut is made with the miter
table set at the 0° position. Miter cross cuts are made with
the miter table set at some angle other than 0°.
NOTE: Check for interference between the auxiliary fence
and the lower blade guard. Correct any interference
before proceeding.
Repeat steps with second board by aligning with right
side of miter table.
SLIDE CUT
PUSH
BACK
Fig. 37
MAKING AN AUXILIARY FENCE
See Figure 38.
Certain unusual cuts may benefit from a thicker miter fence
(auxiliary fence) due to the size and position of the workpiece.
The holes provided in the miter fence are there for just this
purpose. The miter fence holes are used to secure the auxiliary fence which requires two pieces of wood 1/2 in. thick,
3-1/2 in. high, and 10 in. long to make.
NOTE: The auxiliary fence can only be used when the bevel
is set at 0°. When making a bevel cut, the auxiliary fence
MUST be removed.
To attach the auxiliary fence to the saw:
Place one piece of wood against the miter fence and
aligned with the left edge of the miter table and mark the
hole location from behind the fence using a pencil.
Drill holes through the wood then countersink the holes
on the front of the wood.
Secure the wood to the miter fence using flat head
screws.
Make a full 45° left miter cut through the left side auxiliary
fence.
28 − English
AUXILIARY
FENCE
ALIGN BOARD
WITH EDGE OF
MITER TABLE
Fig. 38
Page 29
OPERATION
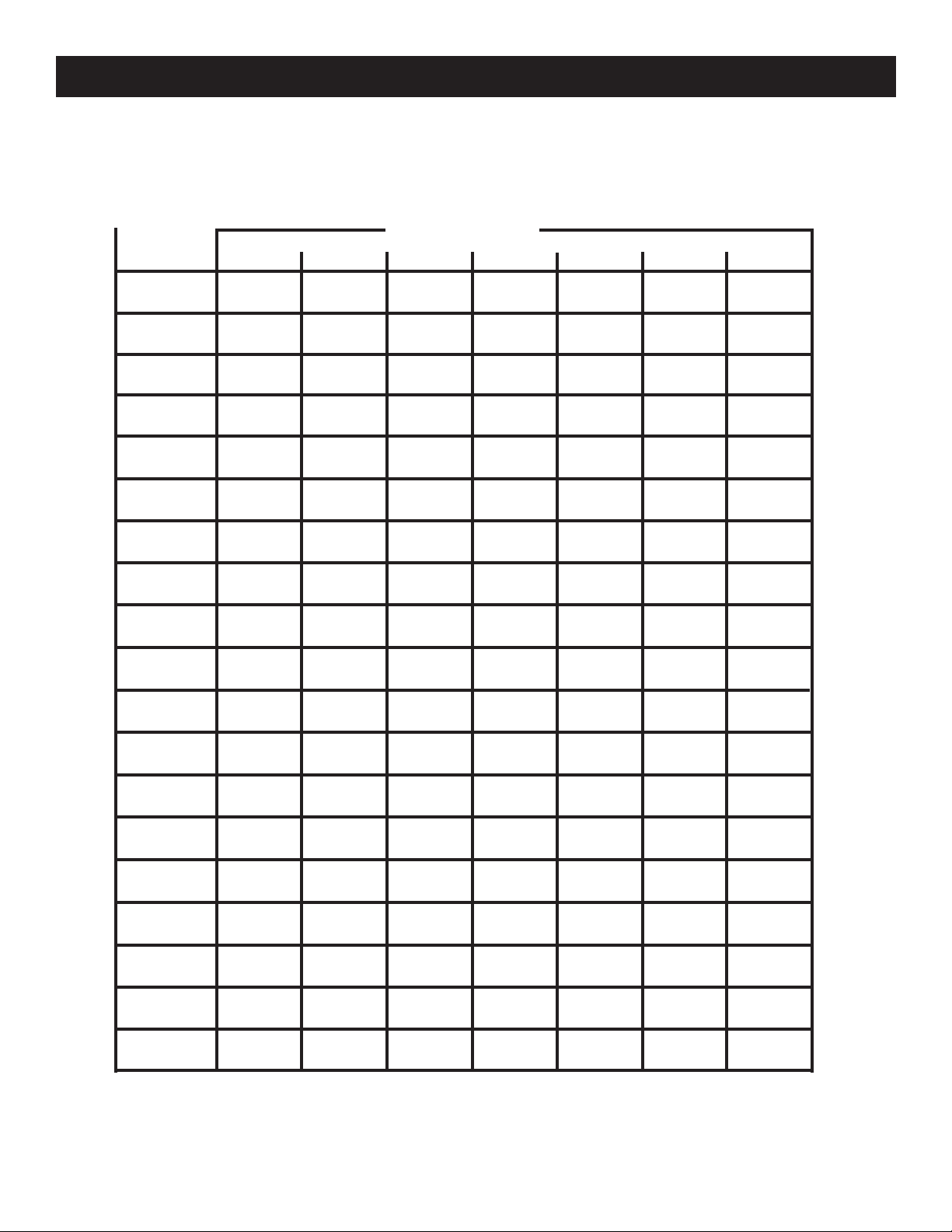
CUTTING COMPOUND MITERS
To aid in making the correct settings, the compound angle setting chart below has been provided. Since compound cuts
are the most difficult to accurately obtain, trial cuts should be made in scrap material, and much thought and planning
made, prior to making the required cut.
PITCH
OF SIDE
0°
5°
10°
15°
20°
25°
30°
35°
40°
45°
50°
55°
60°
65°
70°
75°
80°
85°
90°
4
M- 45.00°
B- 0.00°
M- 44.89°
B- 3.53°
M- 44.56°
B- 7.05°
M- 44.01°
B- 10.55°
M- 43.22°
B- 14.00°
M- 42.19°
B- 17.39°
M- 40.89°
B- 20.70°
M- 39.32°
B- 23.93°
M- 37.45°
B- 27.03°
M- 35.26°
B- 30.00°
M- 32.73°
B- 32.80°
M- 29.84°
B- 35.40°
M- 26.57°
B- 37.76°
M- 22.91°
B- 39.86°
M- 18.88°
B- 41.64°
M- 14.51°
B- 43.08°
M- 9.85°
B- 44.14°
M- 4.98°
B- 44.78°
M- 0.00°
B- 45.00°
5
M- 36.00°
B- 0.00°
M- 35.90°
B- 2.94°
M- 35.58°
B- 5.86°
M- 35.06°
B- 8.75°
M- 34.32°
B- 11.60°
M- 33.36°
B- 14.38°
M- 32.18°
B- 17.09°
M- 30.76°
B- 19.70°
M- 29.10°
B- 22.20°
M- 27.19°
B- 24.56°
M- 25.03°
B- 26.76°
M- 22.62°
B- 28.78°
M- 19.96°
B- 30.60°
M- 17.07°
B- 32.19°
M- 13.95°
B- 33.53°
M- 10.65°
B- 34.59°
M- 7.19°
B- 35.37°
M- 3.62°
B- 35.84°
M- 0.00°
B- 36.00°
NUMBER OF SIDES
6
M- 30.00°
B- 0.00°
M- 29.91°
B- 2.50°
M- 29.62°
B- 4.98°
M- 29.15°
B- 7.44°
M- 28.48°
B- 9.85°
M- 27.62°
B- 12.20°
M- 26.57°
B- 14.48°
M- 25.31°
B- 16.67°
M- 23.86°
B- 18.75°
M- 22.21°
B- 20.70°
M- 20.36°
B- 22.52°
M- 18.32°
B- 24.18°
M- 16.10°
B- 25.66°
M- 13.71°
B- 26.95°
M- 11.17°
B- 28.02°
M- 8.50°
B- 28.88°
M- 5.73°
B- 29.50°
M- 2.88°
B- 29.87°
M- 0.00°
B- 30.00°
7
M- 25.71°
B- 0.00°
M- 25.63°
B- 2.17°
M- 25.37°
B- 4.32°
M- 24.95°
B- 6.45°
M- 24.35°
B- 8.53°
M- 23.56°
B- 10.57°
M- 22.64°
B- 12.53°
M- 21.53°
B- 14.41°
M- 20.25°
B- 16.19°
M- 18.80°
B- 17.87°
M- 17.20°
B- 19.41°
M- 15.44°
B- 20.82°
M- 13.54°
B- 22.07°
M- 11.50°
B- 23.16°
M- 9.35°
B- 24.06°
M- 7.10°
B- 24.78°
M- 4.78°
B- 25.30°
M- 2.40°
B- 25.61°
M- 0.00°
B- 25.71°
8 9
M- 22.50°
B- 0.00°
M- 22.42°
B- 1.91°
M- 22.19°
B- 3.81°
M- 21.81°
B- 5.68°
M- 21.27°
B- 7.52°
M- 20.58°
B- 9.31°
M- 19.73°
B- 11.03°
M- 18.74°
B- 12.68°
M- 17.60°
B- 14.24°
M- 16.32°
B- 15.70°
M- 14.91°
B- 17.05°
M- 13.36°
B- 18.27°
M- 11.70°
B- 19.35°
M- 9.93°
B- 20.29°
M- 8.06°
B- 21.08°
M- 6.12°
B- 21.69°
M- 4.11°
B- 22.14°
M- 2.07°
B- 22.41°
M- 0.00°
B- 22.50°
M- 20.00°
B- 0.00°
M- 19.93°
B- 1.71°
M- 19.72°
B- 3.40°
M- 19.37°
B- 5.08°
M- 18.88°
B- 6.72°
M- 18.26°
B- 8.31°
M- 17.50°
B- 9.85°
M- 16.60°
B- 11.31°
M- 15.58°
B- 12.70°
M- 14.43°
B- 14.00°
M- 13.17°
B- 15.19°
M- 11.79°
B- 16.27°
M- 10.31°
B- 17.23°
M- 8.74°
B- 18.06°
M- 7.10°
B- 18.75°
M- 5.38°
B- 19.29°
M- 3.62°
B- 19.68°
M- 1.82°
B- 19.92°
M- 0.00°
B- 20.00°
10
M- 18.00°
B- 0.00°
M- 17.94°
B- 1.54°
M- 17.74°
B- 3.08°
M- 17.42°
B- 4.59°
M- 16.98°
B- 6.07°
M- 16.41°
B- 7.50°
M- 15.72°
B- 8.89°
M- 14.90°
B- 10.21°
M- 13.98°
B- 11.46°
M- 12.94°
B- 12.62°
M- 11.80°
B- 13.69°
M- 10.56°
B- 14.66°
M- 9.23°
B- 15.52°
M- 7.82°
B -16.26°
M- 6.34°
B- 16.88°
M- 4.81°
B- 17.37°
M- 3.23°
B- 17.72°
M- 1.62°
B- 17.93°
M- 0.00°
B- 18.00°
Each B (Bevel) and M (Miter) Setting is Given to the Closest 0.005°.
COMPOUND-ANGLE SETTINGS FOR POPULAR STRUCTURES
29 − English
Page 30
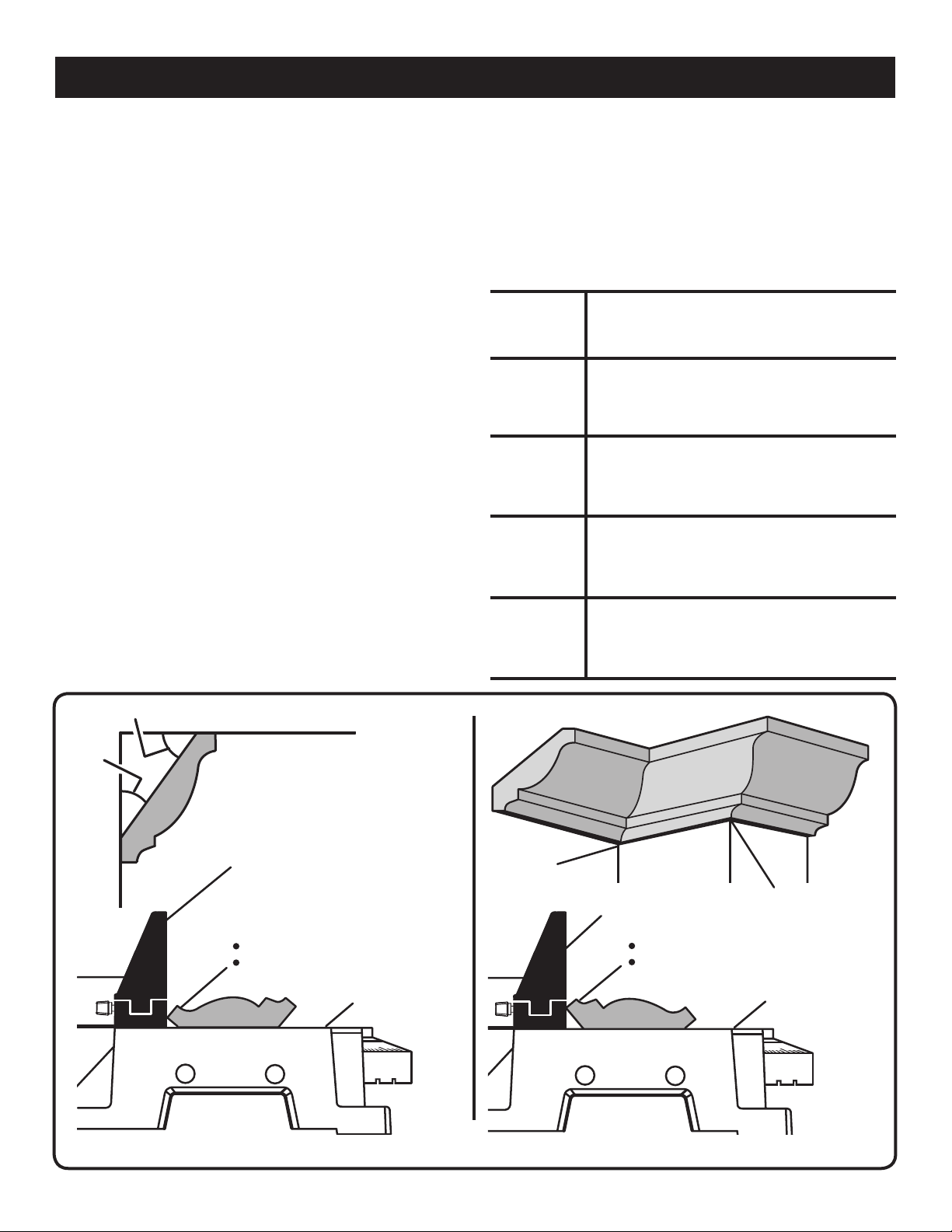
OPERATION
CUTTING CROWN MOLDING
The compound miter saw does an excellent job of cutting crown
molding. In general, compound miter saws do a better job of
cutting crown molding than any other tool made.
In order to fit properly, crown molding must be compound
mitered with extreme accuracy.
The two contact surfaces on a piece of crown molding that fit
flat against the ceiling and the wall of a room are at angles that,
when added together, equal exactly 90°. Most crown molding
has a top rear angle (the section that fits flat against the ceiling)
of 52° and a bottom rear angle (the section that fits flat against
the wall) of 38°.
LAYING MOLDING FLAT ON THE MITER
TABLE
See Figure 39.
To use this method for accurately cutting crown molding for a
90° inside or outside corner, lay the molding with its broad back
surface flat on the miter table and against the fence.
When setting the bevel and miter angles for compound
miters, remember that the settings are interdependent; changing
one angle changes the other angle as well.
Keep in mind that the angles for crown molding are very precise
and difficult to set. Since it is very easy for these angles to shift,
all settings should first be tested on scrap molding. Also most
walls do not have angles of exactly 90°; therefore, you will need
to fine tune your settings.
When cutting crown molding by this method, the bevel angle
should be set at 33.85°. The miter angle should be set at
31.6° either right or left, depending on the desired cut for the
application. See the chart below for correct angle settings and
correct positioning of crown molding on miter table.
The settings in the chart below can be used for cutting All
Standard (U.S.) crown molding with 52° and 38° angles. The
crown molding is placed flat on the miter table using the
compound features of your miter saw.
Bevel
Angle Type of Cut
Setting
Left side, inside corner
33.85°
33.85°
33.85°
33.85°
1. Top edge of molding against fence
2. Miter table set right 31.62°
3. Save left end of cut
Right side, inside corner
1. Bottom edge of molding against fence
2. Miter table set left 31.62°
3. Save left end of cut
Left side, outside corner
1. Bottom edge of molding against fence
2. Miter table set left 31.62°
3. Save right end of cut
Right side, outside corner
1. Top edge of molding against fence
2. Miter table set right 31.62°
3. Save right end of cut
38
W
°
52
°
CEILING
A
L
L
SLIDING
MITER
FENCE
INSIDE
CORNER
SLIDING MITER
OUTSIDE CORNER
FENCE
TOP EDGE AGAINST FENCE =
LEFT SIDE, INSIDE CORNER
RIGHT SIDE, OUTSIDE CORNER
MITER TABLE
CROWN MOLDING FLAT ON MITER TABLE
BOTTOM EDGE AGAINST FENCE =
RIGHT SIDE, INSIDE CORNER
LEFT SIDE, OUTSIDE CORNER
MITER TABLE
Fig. 39
30 − English
Page 31

OPERATION
NESTING CROWN MOLDING AGAINST THE
MITER FENCE
See Figures 40 - 41.
NOTE: This method of cut is for crown molding between
4-5/8 in. and 5-1/4 in. tall. Do not attempt to cut molding
that is larger than 5-1/4 in. tall.
Tighten the fence screws to secure the fences in place.
Set the bevel angle at 0° and the miter angle at 45° to
either the left or the right. (For making 90° corners.)
Nest and secure the crown molding against miter fence
using a spring clamp and hold crown molding securely.
Before turning on the saw, perform a dry run of the cut-
ting operation to make sure that no problems will occur
when the cut is made.
Grasp the saw handle firmly. Squeeze the switch trigger.
Allow several seconds for the blade to reach maximum
speed.
Slowly lower the blade into and through the crown
molding.
SLIDING
MITER FENCE
SPRING
CLAMP
BOTTOM EDGE
AGAINST FENCE
SPRING
CLAMP
Fig. 40
CROWN
MOLDING
Fig. 41
31 − English
Page 32

OPERATION
RIGHT
Fig. 42
CUTTING WARPED MATERIAL
See Figures 42 - 43.
When cutting warped material, always make sure it is
positioned on the miter table with the convex side against
the fence as shown in figure 42.
If the warped material is positioned the wrong way as shown
in figure 43, it will pinch the blade near the completion of
the cut.
WARNING:
To avoid a kickback and to avoid serious personal injury,
never position the concave edge of bowed or warped
material against the fence.
CLAMPING WIDE WORKPIECES
See Figure 44.
When cutting wide workpieces, such as 2 in. x 6 in., boards
should be clamped with a work clamp as shown in figure 44.
WRONG
Fig. 43
WIDE
BOARD
32 − English
Fig. 44
Page 33

ADJUSTMENTS
WARNING:
Before performing any adjustment, make sure the tool
is unplugged from the power supply. Failure to heed this
warning could result in serious personal injury.
The compound miter saw has been adjusted at the factory
for making accurate cuts. However, some of the components
might have been jarred out of alignment during shipping. Also,
over a period of time, readjustment will probably become
necessary due to wear. After unpacking the saw, check the
following adjustments before you begin using saw. Make any
readjustments that are necessary and periodically check the
parts alignment to make sure that the saw is cutting accurately.
PIVOT ADJUSTMENTS
NOTE: These adjustments were made at the factory and
normally do not require readjustment.
TRAVEL PIVOT ADJUSTMENT
The saw arm should rise completely to the up position
by itself.
If the saw arm does not raise by itself or if there is play
in the pivot joints, have saw repaired at your nearest
AUTHORIZED SERVICE CENTER.
POSITIVE STOP ADJUSTMENTS
See Figure 45.
NOTE: These adjustments were made at the factory and
normally do not require readjustment.
To adjust:
Unplug the saw.
Loosen the bevel lock knob by turning the knob
counterclockwise.
Square the blade to the miter table as described in the
Assembly section of this manual.
If the blade is out of square, secure the lock nut in place
and loosen or tighten the positive stop adjustment screw
using a 5 mm hex wrench (not supplied).
Retighten bevel lock knob. Recheck blade-to-table
alignment.
NOTE: The above procedure can be used to check blade
squareness of the saw blade to the miter table at both 0°
and 45° angles.
Your saw has several scale indicators. After squaring
adjustments have been made, it may be necessary to loosen
the indicator screws and reset them to zero. See Figures
25 - 26.
TO ADJUST THE BEVEL PIVOT
The compound miter saw should bevel easily by
loosening the bevel lock knob and tilting the saw.
If movement is tight or if there is play in the pivot, have
saw repaired at your nearest AUTHORIZED SERVICE
CENTER.
POSITIVE STOP
ADJUSTMENT
SCREW FOR
0° ANGLES
LOCK NUT
LOCK NUT
POSITIVE STOP
ADJUSTMENT
SCREW FOR
45° ANGLES
Fig. 45
33 − English
Page 34

ADJUSTMENTS
DANGER:
Laser radiation. Avoid direct eye contact with light source.
WARNING:
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of
procedures other than those specified herein can result
in hazardous radiation exposure.
LASER
ADJUSTMENT
SCREW
TO ADJUST THE LASER GUIDE
See Figure 46.
Set miter and bevel angles to 0º and lock in place.
Use the work clamp, C-clamp, or other suitable clamp
to secure a piece of scrap wood.
Plug the saw into the power source and make a slight
cut to score the wood.
Release the switch trigger and allow the saw blade to
stop rotating before raising the blade.
Using a padlock, lock the switch trigger to make the saw
inoperable.
Turn on the laser guide.
To adjust the position of the laser, rotate the laser
adjustment screw. Turn the screw clockwise to move the
laser to the right and counterclockwise to move the laser
to the left.
NOTE: When properly aligned, the laser should be on
the left edge of the kerf. If laser does not align correctly,
return to your nearest AUTHORIZED SERVICE CENTER
for repair.
LASER
GUIDE
34 − English
Fig. 46
Page 35

MAINTENANCE
WARNING:
When servicing, use only identical replacement parts. Use
of any other part can create a hazard or cause product
damage.
WARNING:
Always wear eye protection with side shields marked
to comply with ANSI Z87.1 during product operation. If
operation is dusty, also wear a dust mask.
WARNING:
Before performing any adjustment, make sure the tool
is unplugged from the power supply. Failure to heed this
warning could result in serious personal injury.
GENERAL MAINTENANCE
Avoid using solvents when cleaning plastic parts. Most
plastics are susceptible to damage from various types of
commercial solvents and may be damaged by their use. Use
clean cloths to remove dirt, carbon dust, etc.
LUBRICATION
All of the bearings in this tool are lubricated with a sufficient
amount of high grade lubricant for the life of the unit under
normal operating conditions. Therefore, no further lubrication
is required.
BRUSH REPLACEMENT
See Figure 47.
The saw has externally accessible brush assemblies that
should be periodically checked for wear.
Proceed as follows when replacement is required:
Unplug the saw.
Remove brush cap with a screwdriver. Brush assembly is
spring loaded and will pop out when you remove brush
cap.
Remove brush assembly.
Check for wear. Replace both brushes when either has
less than 1/4 in. length of carbon remaining. Do not
replace one side without replacing the other.
Reassemble using new brush assemblies. Make sure
curvature of brush matches curvature of motor and that
brush moves freely in brush tube.
Make sure brush cap is oriented correctly (straight) and
replace.
Tighten brush cap securely. Do not overtighten.
WARNING:
Do not at any time let brake fluids, gasoline, petroleumbased products, penetrating oils, etc., come in contact
with plastic parts. They contain chemicals that can
damage, weaken, or destroy plastic.
Electric tools used on fiberglass material, wallboard, spackling
compounds, or plaster are subject to accelerated wear and
possible premature failure because the fiberglass chips
and grindings are highly abrasive to bearings, brushes,
commutators, etc. Consequently, we do not recommend
using this tool for extended work on these types of materials.
However, if you do work with any of these materials, it is
extremely important to clean the tool using compressed air.
BRUSH
CAP
BRUSH
CAP
BRUSH
ASSEMBLY
BRUSH
ASSEMBLY
Fig. 47
This product has a Three-year Limited Warranty.
For Warranty details go to www.ryobitools.com
35 − English
Page 36

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ GÉNÉRALES
AVERTISSEMENT :
Lire attentivement toutes les instructions. Le non respect
de toutes les instructions ci-dessous peut entraîner un choc
électrique, un incendie et / ou des blessures graves.
LIRE TOUTES LES INSTRUCTIONS
VEILLER À BIEN CONNAÎTRE L’OUTIL. Lire
attentivement le manuel d’utilisation. Apprendre les
applications et les limites de l’outil, ainsi que les risques
spécifiques relatifs à son utilisation.
SE PROTÉGER DES CHOCS ÉLECTRIQUES EN
ÉVITANT TOUT CONTACT DU CORPS AVEC DES
SURFACES MISES À LA TERRE. Par exemple : tuyaux,
radiateurs, cuisinières, réfrigérateurs.
MAINTENIR TOUS LES DISPOSITIFS DE PROTECTION
EN PLACE et en bon état de fonctionnement.
RETIRER LES CLÉS ET OUTILS DE RÉGLAGE. Prendre
l’habitude de vérifier que tous les outils et clés de réglage
en ont été retirés de l’outil avant de le mettre en marche.
GARDER LE LIEU DE TRAVAIL PROPRE. Les établis
encombrés et les endroits sombres sont propices aux
accidents. NE PAS laisser d’outils ou de pièces de bois
sur la machine en fonctionnement.
NE PAS UTILISER DANS UN ENVIRONNEMENT
DANGEREUX. Ne pas utiliser les outils électriques dans
des endroits mouillés ou humides, ne pas les exposer à
la pluie. Garder le lieu de travail bien éclairé.
GARDER LES ENFANTS ET VISITEURS À L’ÉCART. Tous
les visiteurs doivent porter des lunettes de sécurité et se
tenir à bonne distance de la zone de travail. Ne pas laisser
les visiteurs toucher l’outil ou son cordon d’alimentation
pendant le fonctionnement.
ASSURER LA SÉCURITÉ DES ENFANTS dans l’atelier en
installant des cadenas et des disjoncteurs ou en retirant
les clés de contact.
NE PAS FORCER L’OUTIL. Il exécutera le travail mieux
et de façon moins dangereuse s’il fonctionne dans les
limites prévues.
UTILISER L’OUTIL APPROPRIÉ. Ne pas utiliser l’outil
ou un accessoire pour effectuer un travail pour lequel il
n’est pas conçu.
UTILISER UN CORDON PROLONGATEUR ADÉQUAT.
S’assurer que le cordon prolongateur est en bon état.
Utiliser exclusivement un cordon d’une capacité suffisante
pour supporter le courant de fonctionnement de l’outil. Un
cordon de capacité insuffisante causerait une baisse de
la tension de ligne, entraînant une perte de puissance et
une surchauffe. Un calibre de fil (A.W.G.) d’au minimum
14 est recommandé pour un cordon prolongateur de 7,6
mètres (25 pieds) ou moins. En cas de doute, utiliser un
cordon du calibre immédiatement supérieur. Moins le
numéro de calibre est élevé, plus la capacité du fil est
grande.
PORTER UNE TENUE APPROPRIÉE. Ne pas porter de
vêtements amples, cravates, ou bijoux susceptibles de se
prendre et vous entraîner dans les pièces mobiles. Des
gants en caoutchouc et des chaussures antidérapantes
sont recommandées pour le travail à l’extérieur. Les
cheveux longs doivent être ramassés sous un couvrechef.
TOUJOURS PORTER DES LUNETTES DE SÉCURITÉ
À COQUES LATÉRALES. Les lunettes de vue ordinaires
sont munies seulement de verres résistants aux impacts ;
ce ne sont PAS des lunettes de sécurité.
ASSUJETTIR LES PIÈCES. Dans la mesure du possible,
utiliser des serre-joint ou un étau, ce qui réduit les risques
et laisse les deux mains libres pour contrôler l’outil.
NE PAS TRAVAILLER HORS DE PORTÉE. Toujours se
tenir bien campé et en équilibre.
ENTRETENIR SOIGNEUSEMENT LES OUTILS. Garder
les outils bien affûtés et propres pour accroître la sécurité
et les performances. Suivre les instructions de lubrification
et de changement d’accessoires.
DÉBRANCHER TOUS LES OUTILS. Tous les outils
doivent être débranchés lorsqu’ils ne sont pas en usage
et avant toute opération d’entretien ou de changement
d’accessoire, lame, forer, fers, etc.
ÉVITER LES DÉMARRAGES ACCIDENTELS. S’assurer
que le commutateur est en position d’arrêt avant de
brancher un outil.
UTILISER LES ACCESSOIRES RECOMMANDÉS. Voir
les accessoires recommandés dans le manuel d’utilisation.
L’usage de tout accessoire incorrect peut être dangereux.
NE JAMAIS MONTER SUR L’OUTIL. Un basculement
pourrait entraîner des blessures graves ou si l’on touche
involontairementla partie tranchante.
VÉRIFIER L’ÉTAT DES PIÈCES. Avant d’utiliser l’outil
de nouveau examiner soigneusement les pièces et
dispositifs de protection qui semblent endommagés afin
de déterminer s’ils fonctionnent correctement et s’ils
remplissent les fonctions prévues. Vérifier l’alignement
des pièces mobiles, s’assurer qu’aucune pièce n’est
bloquée ou cassée, vérifier la fixation de chaque pièce et
s’assurer qu’aucun autre problème ne risque d’affecter le
bon fonctionnement de l’outil. Pour éviter les risques de
blessures, toute protection ou pièce endommagée doit
être correctement réparée ou remplacée dans un centre
de réparations agréé.
ENGAGER LES PIÈCES DANS LE SENS CORRECT. La
pièce ne doit être engagée que contre le sens de rotation
de la lame, de l’accessoire ou de la toupie de ponçage.
NE JAMAIS LAISSER L’OUTIL EN FONCTIONNEMENT
SANS SURVEILLANCE. COUPER L’ALIMENTATION
ÉLECTRIQUE. Ne pas s’éloigner de l’outil avant qu’il
soit parvenu à un arrêt complet.
PORTER UNE PROTECTION RESPIRATOIRE. Porter
un masque facial ou respiratoire si le travail produit de la
poussière.
2 − Français
Page 37

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ GÉNÉRALES
PORTER UNE PROTECTION AUDITIVE. Porter une
protection auditive durant les périodes d’utilisation prolongée.
NE PAS MALTRAITER LE CORDON D’ALIMENTATION.
Ne jamais utiliser le cordon d’alimentation pour transporter
l’outil et ne jamais débrancher ce dernier en tirant sur le
cordon. Garder le cordon à l’écart de la chaleur, de l’huile
et des objets tranchants.
N’UTILISER QUE DES CORDONS PROLONGATEURS
POUR EXTÉRIEUR. Pour les travaux à l’extérieur, utiliser
exclusivement des cordons spécialement conçus à cet
effet, marqués en conséquence, et dotés d’une prise de
terre agréé.
GARDER LES LAMES PROPRES, BIEN AFFÛTÉES ET
SUFFISAMMENT AVOYÉES. Des lames affûtées réduisent
les risques de blocage et de rebond.
LES LAMES CONTINUENT DE TOURNER EN ROUE
LIBRE UNE FOIS LA SCIE MISE HORS TENSION.
NE JAMAIS UTILISER CET OUTIL DANS UNE
ATMOSPHÈRE EXPLOSIVE. Les étincelles normalement
produites par le moteur pourraient enflammer les vapeurs.
INSPECTER RÉGULIÈREMENT LES CORDONS DE
L’OUTIL. Faire remplacer tout commutateur défectueux par
un technicien qualifié ou un centre de réparations agréé. Le fil
à gaine verte, avec ou sans traceur jaune est le fil de terre. Si
le cordon doit être réparé ou remplacé, ne pas connecter le
fil de terre de l’outil sur une borne sous tension. Tout cordon
endommagé doit être réparé ou remplacé immédiatement.
Toujours rester conscient de l’emplacement du cordon et veiller
à le tenir à l’écart de la lame en rotation.
INSPECTER RÉGULIÈREMENT LES CORDONS
PROLONGATEURS et les remplacer s’ils sont endommagés.
FICHES POLARISÉES. Pour réduire les risques de choc
électrique, cet outil est équipé d’une fiche polarisée (une
broche est plus large que l’autre). Cette fiche ne peut être
branchée sur une prise polarisée que dans un sens. Si la
fiche ne peut pas être insérée dans la prise, l’inverser. Si
elle ne peut toujours pas être insérée, faire installer une
prise adéquate par un électricien qualifié. Ne pas modifier
la fiche, de quelque façon que ce soit.
GARDER L’OUTIL SEC, PROPRE ET EXEMPT D’HUILE
OU DE GRAISSE. Toujours utiliser un chiffon propre pour le
nettoyage. Ne jamais utiliser de liquide de freins, d’essence
ou de produits à base de pétrole pour nettoyer l’outil.
RESTER VIGILANT ET GARDER LE CONTRÔLE. Se
montrer attentif et faire preuve de bon sens. Ne pas utiliser
l’outil en état de fatigue. Ne pas se presser.
NE PAS UTILISER L’OUTIL SI LE COMMUTATEUR NE
PERMET PAS DE LE METTRE EN MARCHE OU DE
L’ARRÊTER. Faire remplacer les commutateurs défectueux
dans un centre de réparations agréé.
N’UTILISER QUE LES LAMES APPROPRIÉES. Ne pas
utiliser de lames dont le trou n’est pas de la taille correcte. Ne
jamais utiliser de rondelles ou boulons de lame défectueux
ou de type incorrect. La taille maximum de lame pouvant
être utilisée sur cet outil est de 305 mm (12 po).
S’ASSURER QUE TOUS LES DISPOSITIFS DE
PROTECTION FONCTIONNENT CORRECTEMENT
AVANT D’EFFECTUER UNE COUPE.
S’ASSURER QU’AUCUN CLOU NE SE TROUVE SUR LA
TRAJECTOIRE DE LA LAME. Inspecter la pièce et retirer
les clous éventuels avant de la couper.
NE JAMAIS TOUCHER LA LAME ou les pièces en
mouvement pendant le fonctionnement.
NE JAMAIS METTRE UN OUTIL EN MARCHE
LORSQU’UNE PIÈCE EN ROTATION QUELCONQUE
EST EN CONTACT AVEC LA PIÈCE À COUPER.
NE PAS UTILISER CET OUTIL SOUS L’INFLUENCE DE
L’ALCOOL, DE DROGUES OU DE MÉDICAMENTS.
Utiliser exclusivement des pièces identiques à celles
d’origine POUR LES RÉPARATIONS. L’usage de toute
autre pièce pourrait créer une situation dangereuse ou
endommager l’outil.
UTILISER EXCLUSIVEMENT LES ACCESSOIRES
RECOMMANDÉS dans ce manuel ou ses addendas.
L’emploi de tout accessoire non recommandé peut
présenter un risque de blessure. Les instructions de
sécurité d’utilisation sont fournies avec les accessoires.
VÉRIFIER DEUX FOIS TOUS LES RÉGLAGES. S’assurer
que la lame est bien serrée et ne touche ni la scie, ni la
pièce à couper avant de brancher la scie sur le secteur.
RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ PARTICULIÈRES
ASSUJETTIR OU BOULONNER SOLIDEMENT la machine
sur un établi ou autre plan de travail, approximativement
à la hauteur des hanches.
GARDER LES MAINS À L’ÉCART DE LA ZONE DE
COUPE. Ne placer en aucun cas la main ou les doigts
au-dessous de la pièce à couper ou sur la trajectoire de
la lame. Toujours éteindre la scie.
TOUJOURS SOUTENIR LES PIÈCES LONGUES pendant
le travail, afin d’éviter les risques de pincement de la lame
et de rebond. La scie peut riper, se déplacer ou glisser lors
de la coupe de planches longues ou lourdes.
3 − Français
Dans la mesure du possible, TOUJOURS UTILISER UN
SERRE-JOINT pour maintenir la pièce.
S’ASSURER QUE LA LAME NE TOUCHE PAS LA PIÈCE.
Ne jamais mettre la scie en marche si la lame touche la
pièce à couper. Toujours laisser le moteur atteindre sa
pleine vitesse de rotation avant de commencer la coupe.
S’ASSURER QUE LA TABLE À ONGLETS ET LE BRAS DE
LA SCIE ( FONCTION DE BISEAU) SONT VERROUILLÉS
EN PLACE AVANT DE METTRE LA SCIE EN MARCHE.
Bloquer la table à onglets en serrant fermement la poignée
de verrouillage d’onglet. Verrouiller le bras de la scie
Page 38

RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ PARTICULIÈRES
(fonction de biseau) en serrant fermement le bouton de
verrouillage de biseau.
NE JAMAIS UTILISER DE BUTÉE RÉGLABLE SUR
L’EXTRÉMITÉ CHUTE D’UNE PIÈCE À COUPER. NE
JAMAIS tenir ou attacher l’extrémité chute d’une pièce,
quelle que soit l’opération de coupe. Si un serre-joint
et une butée réglable sont utilisés ensemble, ces deux
articles doivent être installés du même côté de la table de
scie pour empêcher que la lame ne morde dans le côté
libre et projette la pièces vers le haut.
NE JAMAIS couper plus d’une pièce à la fois. NE JAMAIS
empiler de pièces sur la table de la scie.
NE JAMAIS TRAVAILLER À MAIN LEVÉE. Toujours
placer la pièce à couper sur la table à onglets et la pousser
fermement contre le guide pour la bloquer. Toujours utiliser
le guide.
NE JAMAIS tenir à la main une pièce trop petite pour être
maintenue par un serre-joint. Garder les mains à l’écart
de la zone de coupe.
NE JAMAIS placer la main ou les doigts derrière, au-
dessous ou à moins de 76 mm (3 po) de la lame ou de
sa trajectoire, pour quelque raison que ce soit.
NE JAMAIS essayer de saisir une pièce, une chute ou
quoi que ce soit se trouvant dans ou à proximité de la
trajectoire de la lame.
NE JAMAIS s e dé pl ac e r l ’aj us te me nt d e p iè c e o u m a r q u e
à n’i mp or te q u e l an gl e d e c o up e pe nd an t q u e l a sc ie c o u r t
et la lame tourne. N’importe quelle erreur peut avoir pour
résultat le contact avec la lame causant des blessures
graves.
ÉVITER LES OPÉRATIONS ET POSITIONS
INCOMMODES posant un risque de glissement soudain
de la main vers la lame. TOUJOURS se tenir bien en
équilibre. NE JAMAIS utiliser la scie à onglets sur le sol
ou en se tenant accroupi.
NE JAMAIS se tenir ou laisser une partie du corps se
trouver dans la trajectoire de la lame.
TOUJOURS éteindre la scie et attendre l’arrêt complet
de la lame avant de la relever de la pièce.
NE JAMAIS FAIRE PASSER LE COMMUTATEUR
DE LA POSITION MARCHE À LA POSITION ARRÊT
RAPIDEMENT. Ceci pourrait causer le desserrage de la
lame, créant une situation dangereuse. Si cela se produit,
s’éloigner de la scie et attendre l’arrêt complet de la
lame. Débrancher la scie de la prise secteur et resserrer
le boulon de lame.
SI UNE PIÈCE QUELCONQUE DE LA SCIE MANQUE, est
brisée, déformée ou présente quelque défaut que ce soit,
ou si un composant électrique quel qu’il soit ne fonctionne
pas correctement, éteindre la scie, la débrancher de la prise
secteur et faire réparer ou remplacer la pièce manquante,
endommagée ou défaillante avant de remettre la scie en
service.
TOUJOURS ÊTRE ATTENTIF ! N e p a s l ai s s e r l a f a m i l i a r it é
avec l’outil (acquise par une utilisation fréquente) causer
une erreur stupide. TOUJOURS ÊTRE CONSCIENT
qu’une fraction de seconde d’inattention peut entraîner
des blessures graves.
SI LE CORDON D’ALIMENTATION EST ENDOMMAGÉ,
il doit être remplacé uniquement pas le fabricant ou par
un centre de réparation agréé pour éviter tout risque.
S’ASSURER QUE LA ZONE DE TRAVAIL EST
SUFFISAMMENT ÉCLAIRÉE pour voir ce que l’on fait et
qu’aucun obstacle ne peut nuire à la sécurité d’utilisation
AVANT d’effectuer quelque coupe que ce soit.
TOUJOURS ÉTEINDRE LA SCIE avant de la débrancher
pour éviter un démarrage accidentel lors du branchement
pour l’utilisation suivante. NE JAMAIS laisser la scie
branchée sans surveillance.
METTRE L’OUTIL HORS TENSION et attendre l’arrêt
complet de la lame avant de déplacer la pièce ou de
modifier les réglages.
Les avertissements ci-dessous doivent être apposés sur
CET OUTIL :
a) Porter une protection oculaire.
b) Garder les mains hors du passage de la lame.
c) Ne pas utiliser la scie sans que tous les dispositifs
de protection soient en place.
d) Ne jamais travailler à main levée.
e) Ne jamais passer la main ou le bras autour de la lame.
f) Éteindre l’outil et attendre l’arrêt de la lame pour
déplacer la pièce ou modifier les réglages.
g) Couper l’alimentation (ou débrancher l’outil, selon
le cas) avant de changer la lame ou d’effectuer un
entretien.
h) Vitesse à vide.
TOUJOURS S’ASSURER QUE L’A VU QUE LA LAME
A LE DEGAGEMENT DE TOUTES OBSTRUCTIONS
AVANT DE TOURNER L’A VU SUR.
EFFECTUER DES COUPESCOULISSANTES en
poussant la lame de la scie contre le haut de la pièce à
travailler puis en la faisant coulisser vers l’arrière de la
scie. NE PAS tirer la scie vers soi lors de la coupe.
TOUJOURS transporter l’outil par la poignée prévue à
cet effet.
ÉVITER le contact oculaire direct avec le guide laser.
CETTE SCIE PEUT BASCULER SI SA TÊTE e st r e l â c h é e
brusquement et assujettie à un plan de travail. Pour éviter
des blessures graves, TOUJOURS assujettir la scie à un
plan de travail stable.
CONSERVER CES INSTRUCTIONS. Les consulter
fréquemment et les utiliser pour instruire les autres
utilisateurs. Si cet outil est prêté, il doit être accompagné
de ces instructions.
4 − Français
Page 39

SYMBOLES
Les termes de mise en garde suivants et leur signification ont pour but d’expliquer le degré de risques associé à
l’utilisation de ce produit.
SYMBOLE SIGNAL SIGNIFICATION
DANGER :
AVERTISSEMENT :
ATTENTION :
AVIS :
Certains des symboles ci-dessous peuvent être utilisés sur l’outil. Veiller à les étudier et à apprendre leur signification.
Une interprétation correcte de ces symboles permettra d’utiliser l’outil plus efficacement et de réduire les risques.
SYMBOLE NOM
Symbole d’alerte de sécurité Indique un risque de blessure potentiel.
Lire le manuel d’utilisation
Protection oculaire
Indique une situation extrêmement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée,
aura pour conséquences des blessures graves ou mortelles.
Indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas
évitée, pourrait entraîner des blessures graves ou mortelles.
Indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas
évitée, pourraît entraîner des blessures légères ou de gravité modérée.
(Sans symbole d’alerte de sécurité) Indique une information importante
ne concernant pas un risque de blessure comme une situation pouvant
occasionner des dommages matériels.
DÉSIGNATION / EXPLICATION
Pour réduire les risques de blessures, l’utilisateur doit lire et veiller à
bien comprendre le manuel d’utilisation avant d’utiliser ce produit.
Toujours porter une protection oculaire avec écrans latéraux
certifiée conforme à la norme ANSI Z87.1.
Symbole Mains à l’écart
Avertissement concernant
l’humidité
V Volts Tension
A Ampères Intensité
Hz Hertz Fréquence (cycles par seconde)
min Minutes Temps
Courant alternatif Type de courant
n
o
.../min Par minute Tours, coups, vitesse périphérique, orbites, etc., par minute
Vitesse à vide Vitesse de rotation à vide
Construction de classe II Construction à double isolation
Le non-respect de cette mise en garde peut entraîner des blessures
graves.
Ne pas exposer à la pluie ou l’humidité.
5 − Français
Page 40

CARACTÉRISTIQUES ÉLECTRIQUES
DOUBLE ISOLATION
La double isolation est un dispositif de sécurité utilisé sur les
outils à moteur électriques, éliminant le besoin de cordon
d’alimentation habituel à trois fils avec terre. Toutes les pièces
métalliques exposées sont isolées des composants internes
du moteur par l’isolation protectrice. Les outils à double
isolation ne nécessitent pas de mise à la terre.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Le système à double isolation est conçu pour protéger
l’utilisateur contre les chocs électriques causés par une
rupture du câblage interne de l’outil. Prendre toutes les
précautions de sécurité normales pour éviter les chocs
électriques.
NOTE : La réparation d’un outil à double isolation exigeant
des précautions extrêmes ainsi que la connaissance du
système, elle ne doit être confiée qu’à un réparateur qualifié.
En ce qui concerne les réparations, nous recommandons de
confier l’outil au centre de réparation le plus proche. Utiliser
exclusivement des pièces d’origine pour les réparations.
CONNEXIONS ÉLECTRIQUES
Cet outil est équipé d’un moteur électrique de précision.
Ildoit être branché uniquement sur une alimentation 120 V,
c.a. (courant résidentiel standard), 60 Hz. Ne pas utiliser
cet outil sur une source de courant continu (c.c.). Une chute
de tension importante causerait une perte de puissance et
une surchauffe du moteur. Si l’outil ne fonctionne pas une
fois branché, vérifier l’alimentation électrique.
CORDONS PROLONGATEURS
Lors de l’utilisation d’un outil électrique à grande distance
d’une prise secteur, veiller à utiliser un cordon prolongateur
d’une capacité suffisante pour supporter l’appel de courant de
l’outil. Un cordon de capacité insuffisante causerait une baisse
de la tension de ligne, entraînant une perte de puissance
et une surchauffe. Se reporter au tableau ci-dessous pour
déterminer le calibre minimum de fil requis pour un cordon
donné. Utiliser exclusivement des cordons à gaine cylindrique
homologués par Underwriter’s Laboratories (UL).
Pour le travail à l’extérieur, utiliser un cordon prolongateur
spécialement conçu à cet effet. Ce type de cordon porte
l’inscription « WA » ou « W » sur sa gaine.
Avant d’utiliser un cordon prolongateur, vérifier que ses fils
ne sont ni détachés ni exposés et que son isolation n’est ni
coupée, ni usée.
**Intensité nominale (sur la plaquette signalétique de l’outil)
0-2,0 2,1-3,4 3,5-5,0 5,1-7,0 7,1-12,0 12,1-16,0
Longueur Calibre de fil
du cordon (A.W.G.)
25' 16 16 16 16 14 14
50' 16 16 16 14 14 12
100' 16 16 14 12 10 —
**Utilisé sur circuit de calibre 12 – 20 A
NOTE : AWG = American Wire Gauge
AVERTISSEMENT :
Maintenir le cordon prolongateur à l’écart de la zone de
travail. Lors du travail avec un cordon électrique, placer le
cordon de manière à ce qu’il ne risque pas de se prendre
dans les pièces de bois, outils et autres obstacles. Ne
pas prendre cette précaution peut entraîner des blessures
graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Vérifier l’état des cordons prolongateurs avant chaque
utilisation. Remplacer immédiatement tout cordon
endommagé. Ne jamais utiliser un outil dont le cordon
d’alimentation est endommagé, car tout contact avec la
partie endommagée pourrait causer un choc électrique
et des blessures graves.
PROPOSITION 65 DE L’ÉTAT DE CALIFORNIE
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ce produit et la poussière dégagée lors du ponçage, sciage, meulage, perçage de certains matériaux et lors d’autres
opérations de construction peuvent contenir des produits chimiques, notamment du plomb qui, selon l’État de la
Californie, peuvent causer le cancer, des anomalies congénitales et d’autres dommages au système reproducteur.
Bien se laver les mains après toute manipulation.
Voici certains exemples de ces produits chimiques :
• le plomb contenu dans la peinture au plomb,
• la silice cristalline contenue dans les briques, le béton et d’autres produits de maçonnerie, ainsi que
• l’arsenic et le chrome contenus dans le bois de construction traité par produits chimiques.
Le risque présenté par l’exposition à ces produits varie en fonction de la fréquence de ce type de travail. Pour réduire
l’exposition, travailler dans un endroit bien aéré et utiliser des équipements de sécurité approuvés tels que masques
antipoussières spécialement conçus pour filtrer les particules microscopiques.
6 − Français
Page 41

GLOSSAIRE
Griffes antirebond (scies à table et radiales)
Dispositifs qui, s’ils sont correctement installés et entretenus,
sont conçus pour empêcher que la pièce coupée soit
propulsée en direction de l’opérateur durant la refente.
Axe
Pièce sur laquelle une lame ou un outil de coupe est monté.
Coupe en biseau
Coupe effectuée avec la lame sur toute position autre que
perpendiculaire (90°) à la table.
Coupe composée
Coupe transversale présentant un angle d’onglet et un angle
de biseau.
Coupe transversale
Coupe ou profilage effectué en travers du grain de la pièce.
Tête de coupe (raboteuses et raboteuses/dégauchisseuses)
Pièce rotative munie de lames réglables. La tête de coupe
enlève du matériau de la pièce.
Rainage
Coupe non traversante produisant une encoche ou gorge de
forme rectangulaire dans la pièce (exige une lame spéciale).
Cale-guide
Dispositif utilisé pour faciliter le contrôle de la pièce à couper
en la guidant contre la table ou le guide lors des coupes
longitudinales.
pi/min ou coups/min
Nombre de pieds par minute (ou coups par minute). Terme
utilisé en référence au mouvement de la lame.
Main levée
Exécution d’une coupe sans que la pièce soit soutenue par
un gide longitudinal, un guide d’onglet ou autre dispositif.
Gomme
Résidu collant formé par la sève du bois.
Talon
Alignement de la lame par rapport au guide.
Trait de scie
Quantité de matériau éliminé par la lame lors de coupes
traversantes ou l’entaille produite lors de coupes non
traversantes ou partielles.
Rebond
Réaction dangereuse se produisant lorsque la lame est
pincée ou bloquée et projetant la pièce en train d’être coupée
en direction de l’opérateur.
Coupe d’onglet
Coupe effectuée avec la lame sur toute position autre que
perpendiculaire (90°) à la table.
Coupes non traversantes
Toute coupe avec laquelle la lame ne traverse pas
complètement la pièce.
Trou pilote (perceuses à colonne)
Petit trou pratiqué dans une pièce servant de guide pour
assurer la précision d’un trou de plus grand diamètre.
Blocs poussoirs (pour dégauchisseuses/raboteuses)
Dispositif utilisés pour pousser le matériau contre la tête de
coupe lors de toute opération. Ce dispositif aide à tenir la
main de l’opérateur bien à l’écart de la lame.
Blocs poussoirs (pour scies à table)
Dispositifs utilisés pour pousser le matériau contre la scie
lors de la coupe. Un bâton poussoir doit être utilisé pour la
refente de pièces étroires. Ce dispositif aide à tenir la main
de l’opérateur bien à l’écart de la lame.
Bâtons poussoirs (pour scies à table)
Dispositifs utilisés pour pousser le matériau contre la lame lors
de la coupe. Ce dispositif aide à tenir la main de l’opérateur
bien à l’écart de la lame.
Refente
Opération de coupe destinée à réduire l’épaisseur d’une
pièce pour en produire plusieurs, plus minces.
Résine
Résidu collant formé par la sève du bois durcie.
Tours minute (r/min)
Nombre de rotations effectuées par un objet en une minute.
Coupe longitudinale ou refente
Opération de coupe dans le sens de la longueur de la pièce.
Couteau diviseur/écarteur (scies à table)
Pièce de métal légèrement plus mince que la trait de scie,
gardant le trait de scie ouvert pour empêcher le rebond.
Trajectoire de la lame de scie
Zone au-dessus, au-dessous, en avant ou en arrière de la
lame. En ce qui concerne la pièce, la partie qui sera ou a
été coupée par la lame.
Voie
Déport de la pointe des dents de la lame par rapport à sa face.
Sifflet (raboteuses)
Enfoncement à l’extrémité d’une pièce causé par les lames
de la tête de coupe lorsque la pièce n’est pas correctement
soutenue.
Effiler la coupe
Une coupe où le matériel est coupe a une ancho différente
au début de la coupe de la la fin.
Coupe traversante
Toute opération de coupe avec laquelle la lame traverse
toute l’épaisseur de la pièce.
Ricochet
Le ricochet est habituellement causé par une pièce
lâchée contre la lame ou mise en contact avec la lame
accidentellement.
Pièce ou matériau
L’article sur lequel le travail est effectué.
Table
Surface sur laquelle la pièce repose lors des opérations de
coupe, de perçage, de rabotage ou de ponçage.
7 − Français
Page 42

CARACTÉRISTIQUES
FICHE TECHNIQUE
Trou d’axe .................................................................... 25,4 mm (1 po)
Diamètre de la lame.................................................... 305 mm (12 po)
Vitesse à vide ..........................................................4 000 r/min (RPM)
Alimentation..................................120 V, C.A. seulement, 60 Hz, 15 A
Capacité de coupe avec onglet 0° / biseau 0° :
Dimensions nominales maximum
de planches de bois ............ 51 mm x 356 mm, 102 mm x 152 mm
Capacité de coupe avec onglet 45° / biseau 0° :
Dimensions nominales maximum
de planches de bois ...........................51 mm x 254 mm (2 x 10 po)
BUTÉE DE
PROFONDEUR
ÉCHELLE
DE BISEAU
(2 x 14, 4 x 6 po)
PROTECTION DE
LAME SUPÉRIEURE
Capacité de coupe avec onglet 0° / biseau 45° :
Dimensions nominales maximum
de planches de bois ...........................51 mm x 356 mm (2 x 14 po)
Capacité de coupe avec onglet 45° / biseau 45° :
Dimensions nominales maximum
de planches de bois ..........................51 mm x 254 mm (2 x 10 po)
Capacité de coupe avec moulures couronnées (imbriquée) :
Dimensions maximum de planches
de bois ............................................................... 133 mm (5-1/4 po)
Capacité de coupe avec plinthe contre la guide :
Hauteur max ............................. 140 mm x 19 mm (5-1/2 po x 3/4 po)
BOUTON DE COMMANDE
DE PROFONDEUR
GOUPILLE DE
VERROUILLAGE
INDICATEUR POUR
PLINTHE/MOULURE
COURONNÉE
BOUTON DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE BISEAU
GUIDE
LASER
POIGNÉE
EN « D »
GÂCHETTE
SAC À
POUSSIÈRE
BARRA
COULISSANTE
BOUTON DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE COULISSE
SERRAGE DE
GUIDE D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
LIGNE DE LIMITE
« MAINS À L’ÉCART »
RALLONGE
DE TABLE
« MAINS À L’ÉCART »
BRIDE DE
PIÈCE
AUTOCOLLANT
BUTÉE(S)
POSITIVE(S)
RAPPORTEUR
D’ANGLE
TABLE À
ONGLETS
8 − Français
PIED DE
SUPPORT
GARDE DE LAME
INFÉRIEURE
BASE
PLAQUE À
BRAS DE
COMMANDE
VERROUILLAGE
LEVIER DE VERROUILLAGE
À ENCLIQUETAGE
CLÉ DE
LAME
GORGE
POIGNÉE DE
D’ONGLET
Fig. 1
Page 43

CARACTÉRISTIQUES
APPRENDRE À CONNAÎTRE LA SCIE À
ONGLETS COMPOSÉS
Voir la figure 1.
L’utilisation sûre de ce produit exige une compréhension
des renseignements figurant sur l’outil et contenus dans le
manuel d’utilisation, ainsi qu’une bonne connaissance du
projet entrepris. Avant d’utiliser ce produit, se familiariser
avec toutes ses fonctions et règles de sécurité.
305 mm (12 po) LAME
Une lame de 305 mm (12 po) est fournie avec la scie à
onglets composés. Cette lame permet de couper des pièces
de 88,9 mm (3-1/2 po) maximum d’épaisseur ou 342,9 mm
(13-1/2 po) de large, selon l’angle de la coupe.
INDICATEUR POUR PLINTHE/MOULURE
COURONNÉE
Voir la figure 2.
Pour couper une plinthe ou une moulure couronnée en position verticale, aligner la flèche de l’indicateur pour plinthe/
moulure couronnée située sur l’assemblage de pivot et serrer
fermement le bouton de verrouillage du coulissement.
BOUTON DE VERROUILLAGE DE BISEAU
Ce bouton permet de verrouiller solidement la scie sur l’angle
de biseau désiré. Des vis de réglage de butées positives se
trouvent de chaque côté du bras de la scie. Ces vis permettent
d’effectuer le réglage fin aux positions 0° et 45°.
POIGNÉE DE
TRANSPORT
ALIGNER
LES FLÈCHES
COMMUTATEUR
GUIDE LASER
BOUTON DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE COULISSE
INDICATEUR POUR
PLINTHE/MOULURE
COURONNÉE
ENSEMBLE
DE PIVOT
Fig. 2
POIGNÉE DE TRANSPORT
Voir la figure 3.
La scie à onglets est équipée d’une poignée pratique
montée sur le dessus du bras de la scie pour faciliter son
transport d’un endroit à un autre. Pour transporter, éteindre
et débrancher la scie puis abaisser le bras de la scie et le
verrouiller en position fermée en poussant la goupille de
verrouillage vers le logement de la scie.
NOTE : NE PAS faire de coupe pendant que la scie est
fermée et verrouillée.
MANETTE D’ENJAMBEMENT
Voir la figure 4.
La manette d’enjambement permet de faire bouger librement
la table à onglets vers tous les angles désirés. Lorsque
la poignée de verrouillage d’onglet est relâchée et que le
levier de verrouillage à encliquetage (1) est pressé, tirer la
manette d’enjambement (2) vers le haut et relâcher le levier
de verrouillage à encliquetage (3) pour outrepasser les butées
positives de l’échelle d’onglets. Pour relâcher la manette
d’enjambement et permettre l’enclenchement des butées
positives de la table d’onglets, presser et relâcher le levier
de verrouillage à encliquetage.
FREIN ÉLECTRIQUE
La scie est équipée d’un frein électrique pour arrêter
rapidement la rotation de la lame une fois que la gâchette
est relâchée.
9 − Français
AXE DE
BLOCAGE
BOUTON DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE BISEAU
POIGNÉE
EN « D »
BRAS BLOQUÉ EN POSITION ABAISSÉE
Fig. 3
GUIDE LASER
Pour des coupes plus précises, un guide laser est inclus
avec la scie à onglets combinés. Utilisé correctement, le
guide laser permet d’effectuer facilement et simplement
des coupes précises.
COMMUTATEUR GUIDE LASER
Voir la figure 3.
Utiliser le commutateur guide laser pour allumer ou éteindre
le laser.
Page 44

CARACTÉRISTIQUES
POIGNÉE DE VERROUILLAGE D’ONGLET
Voir la figure 4.
Cette poignée permet de verrouiller solidement la scie sur
l’angle de coupe désiré. Serrer la poignée pour bloquer la
scie en place. Pour dégager la scie, desserrer la poignée et
presser le levier de verrouillage à encliquetage.
RAPPORTEUR D’ONGLET
Le rapporteur d’onglet est référencé à 0°, 15°, 22,5°, 30,
31,6°, et 45°.
BUTÉES POSITIVES DE LA TABLE À ONGLETS
Des butées positives sont installées aux positions 0°, 15°,
22,5°, 31,6°, et 45° se trouvent de chaque côté de la table
à onglets.
NOTE : Pour outrepasser les butées positives, presser le
levier de verrouillage à encliquetage et soulever la manette
d’enjambement. Pour relâcher l’enjambement, presser le
levier de verrouillage à encliquetage.
PROTECTION RÉTRACTABLE DE LAME
INFÉRIEURE
La protection de lame inférieure est construite dans un
plastique transparent et résistant aux chocs qui couvre les
deux côtés de la lame. Elle se rétracte sur la protection de
lame supérieure lorsque la lame est abaissée sur la pièce
à couper.
BARRES COULISSANTE
Lorsqu’il est déverrouillé, le bras de la scie glisse vers l’avant
et vers l’arrière sur la longueur de la barres coulissante pour
la coupe de diverses largeurs de pièces de travail.
POIGNÉE DE
VERROUILLAGE
D’ONGLET
LEVIER DE
VERROUILLAGE
À ENCLIQUETAGE
D’ENJAMBEMENT
3
MANETTE
1
2
Fig. 4
BOUTON DE VERROUILLAGE DU
COULISSEMENT
Le bouton de verrouillage du coulissement verrouille et
déverrouille la fonction de coulissement de l’outil.
GUIDE D’ONGLETS COULISSANT
La scie à onglets composés est équipée d’un guide d’onglets
coulissant pour maintenir la pièce à couper en place pendant
la coupe. La partie du guide d’onglet la plus éloignée de la
lame est plus large pour offrir un soutien vertical accru.
La caractéristique à coulisse facilite le retrait et l’ajustement
de la position de guide et un espace pour le bras de la scie
pendant les coupes de biseaux ou composés. Desserrer la
vis du guide avant d’essayer de le faire coulisser. Une fois le
guide sur la position voulue, resserrer la vis pour l’assujettir
en place.
10 − Français
Page 45

CARACTÉRISTIQUES
BOUTON DE VERROUILLAGE DE BROCHE
Voir la figure 5.
Le bouton de verrouillage de broche verrouille la broche en
empéchant la lame de tourner. Maintenir le bouton enfoncé
pour l’installation, le changement ou la dépose de la lame.
GÂCHETTE
Voir la figure 5.
Pour empêcher toute utilisation non autorisée de la scie, la
débrancher de l’alimentation et verrouiller son commutateur
en position d’arrêt. Pour verrouiller le commutateur, installer un
cadenas (non inclus) dans le trou de la gâchette et s’assurer
que l’interrupteur ne peut pas être enfoncé. Si l’interrupteur
peut être enfoncé même si le cadenas est installé, un cadenas
équipé d’une anse de diamètre plus grand doit être utilisé.
Conserver le cadenas dans un autre endroit.
BOUTON DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE BROCHE
TROU DE
CADENAS
GÂCHETTE
CADENAS
GÂCHETTE
Fig. 5
11 − Français
Page 46

OUTILS NÉCESSAIRES
Les outils suivants (non compris) sont nécessaires pour vérifier les réglages de votre scie ou pour installer la lame :
CLÉ MIXTE (2)
(10 mm, 12 mm)
ÉQUERRE
ÉQUERRE À
COMBINAISONS
Fig. 6
LISTE DES PIÈCES DÉTACHÉES
Les articles suivant doivent être inclus avec l’outil:
Sac à pouissière
Rallonges de table (2)
SAC À
POUSSIÈRE
Bride de serrage de pièce
Manuel d’utilisation
RALLONGE
DE TABLE
BRIDE DE
SERRAGE DE
PIÈCE
RALLONGE
DE TABLE
AVERTISSEMENT :
L’utilisation de pièces et accessoires non listés peut être dangereux et entraîner des blessures graves.
12 − Français
Fig. 7
Page 47

ASSEMBLAGE
DÉBALLAGE
This product requires assembly.
Sortir soigneusement la scie du carton en la tenant par la
poignée de transport et la base de la scie, et la poser sur
un plan de travail horizontal.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas utiliser le produit si, en le déballant, vous constatez
que des éléments figurant dans la liste des pièces détachées
sont déjà assemblés. Certaines pièces figurant sur cette liste
n’ont pas été assemblées par le fabricant et exigent une
installation. Le fait d’utiliser un produit qui a été assemblé
de façon inadéquate peut entraîner des blessures.
La machine a été expédié avec le bras en position abaissée.
Pour le libérer, appuyer sur le poignée en « D », couper
l’attache et tirer la goupille de verrouillage.
R ele v e r l e b r a s d e l a s ci e e n le ti ra nt pa r s a p o i g né e. C o nt i nue r
de maintenir le poignée en « D » d’une main, pour empêcher
q u ’i l n e s e re l ève br us qu e me n t l or s qu e l ’a t t ac he e s t co u pée .
Examiner soigneusement l’outil pour s’assurer que rien n’a
été brisé ou endommagé en cours de transport.
Ne pas jeter les matériaux d’emballage avant d’avoir
soigneusement examiné ce produit et avoir vérifié qu’il
fonctionne correctement.
L a s ci e e st r égl ée e n u s i ne p o u r e f fe c tue r u n e c o upe p r é c i s e.
A p r è s l’a v oi r a s s e m bl é e , v ér if ie r s a p ré ci s ion . S i le s r égl ag e s
ont été modifiés en cours d’expédition, voir les procédures
spécifiques présentées dans ce manuel.
Si des pièces sont manquantes ou endommagées, appeler
le 1-800-525-2579.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Si des pièces manquent ou sont endommagées, ne pas
utiliser ce produit avant qu’elles aient été remplacées.
Le fait d’utiliser ce produit même s’il contient des pièces
endommagées ou s’il lui manque des pièces peut entraîner
des blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas essayer de modifier cet outil ou de créer des
accessoires non recommandés pour cet outil. De telles
altérations ou modifications sont considérées comme un
usage abusif et peuvent créer des conditions dangereuses,
risquant d’entraîner des blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas brancher sur le secteur avant d’avoir terminé
l’assemblage. Le non respect de cet avertissement peut
causer un démarrage accidentel, entraînant des blessures
graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas mettre la scie en marche sans s’être assuré de
l’absence d’interférence entre la lame et le guide d’onglets.
La lame pourrait être endommagée si elle entrait en contact
avec le guide d’onglets pendant le fonctionnement.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Cette scie peut basculer si sa tête est relâchée brusquement
et assujettie à un plan de travail. Pour éviter des blessures
graves, TOUJOURS assujettir la scie à un plan de travail
stable.
TRACER DES TROUS À
CES EMPLACEMENTS
SELON LE GABARIT
DE TROUS
BASE DE LA
SCIE
TRACER DES TROUS À
CES EMPLACEMENTS
SELON LE GABARIT
DE TROUS
SURFACE DE
FIXATION
Fig. 8
13 − Français
Page 48

ASSEMBLAGE
TROUS DE FIXATION
Voir la figure 8.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Avant d’entreprendre toute opération de coupe, assujettir
ou boulonner la scie à onglets sur le plan de travail ou
un stand approuvé pour scie à onglets. Si on utilise un
support de scie à onglet, lire le manuel d’utilisation et
suivre les instructions pour le support de scie à onglet. Ne
jamais utiliser la scie à onglets sur le sol ou en se tenant
accroupi. Le non respect de cette mise en garde peut
entraîner des blessures graves.
La scie à onglets composés doit être montée solidement sur un
plan de travail ferme, tel qu’un établi. Pour ce faire, la base
de la scie comporte quatre trous. Ces quatre trous doivent
être utilisés pour fixer la scie sur le plan de travail au moyen
de quatre boulons de 7,9 mm (5/16 po), rondelles et écrous
à six pans (non inclus). Les boulons doivent être assez longs
pour traverser la base de la scie, les rondelles frein, les écrous
et l’établi. Serrer les quatre boulons fermement.
La figure 8 illustre la configuration des trous pour l’installation
sur un établi. Une fois la scie installée, vérifier soigneusement
l’établi pour s’assurer qu’aucun mouvement ne peut se
produire pendant l’utilisation. Si l’établi bascule, glisse ou
se déplace, l’assujettir sur le sol avant d’utiliser la scie.
VERROUILLAGE/DÉVERROUILLAGE DU BRAS
DE LA SCIE
Voir la figure 10.
Il n’est pas nécessaire de relâcher le bouton de commande de
profondeur pour verrouiller ou déverrouiller le bras de la scie.
Pour déverrouiller et relever le bras de la scie :
Saisir fermement la poignée en « D » et appliquer une
pression vers le bas tout en tirant en même temps le
guide de profondeur à l’écart du logement de la scie.
Relâcher le guide et relever lentement le bras de la scie.
BOUTON DE COMMANDE
DE PROFONDEUR
UTILISATION DU GUIDE DE PROFONDEUR
Voir la figure 9.
Lorsqu’il est utilisé, le guide de profondeur limite la course
vers le bas de la lame lors de la coupe de rainures et d’autres
coupes non traversantes.
Pour utiliser le guide de profondeur :
Débrancher la scie
Si la scie est en position de remisage ou de transport,
déverrouiller le bras de la scie.
Tourner le butée de profondeur vers la boîtier du moteur.
Avec l’extrémité du bouton de commande de profondeur
touchant l’arrêt butée de profondeur, ajuster le bouton
de commande profondeur en tournant le bouton jusqu’à
ce que la profondeur désirée de coupure est atteinte.
Une entretoise en bois d’au moins 57,15 mm
(2-1/4 pulg.) doit être placé entre la pièce et le guide
pour une profondeur de coupe uniforme dans la pièce.
Utilisation de la prensa de trabajo pour serrer le entretoise
et une autre pince appropriée pour serrer la pièce.
effectuer la coupe à coulissement à la profondeur désirée.
Voir les figures 36 et 37.
Tourner la butée de profondeur vers le logement du
moteur pour effectuer des coupes complètes.
NOTE : La butée de profondeur doit être poussée vers le
logement du moteur avant de verrouiller ou déverrouiller
le bras de la scie.
BUTÉE DE
PROFONDEUR
Fig. 9
POIGNÉE
EN « D »
GOUPILLE DE
VERROUILLAGE
Fig. 10
14 − Français
Page 49

ASSEMBLAGE
Pour reverrouiller le bras de la scie :
Tenir fermement la poignée en D et appuyer vers le bas
en poussant simultanément la goupille de verrouillage à
l’intérieur et vers le logement de la scie.
Relâcher la goupille de verrouillage et lui permettre de
verrouiller la scie en place.
SAC À POUSSIÈRE
Voir la figure 11.
Un sac à poussières est fourni avec cette scie à onglets.
Il s’adapte sur l’orifice de sortie situé à l’arrière de la scie.
NOTE : Le orifice d’évacuation accepte aussi 1-1/4 dans.
le tuyau d’aspirateur.
CLÉ DE LAME
Voir la figure 12.
La scie est fournie avec une clé de lame. Une extrémité
de la clé est un tournevis cruciforme et l’autre est une clé
hexagonale. Utiliser l’extrémité à clé hexagonale pour installer
et déposer la lame et l’extrémité à tournevis cruciforme pour
retirer ou desserrer des vis. Un espace de rangement pour
la clé de lame se trouve à l’arrière du guide d’onglets.
SAC À
POUSSIÈRE
ORIFICE
D’ÉVACUATION
Fig. 11
BRIDE DE SERRAGE DE PIÈCE
Voir la figure 12.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Dans certaines conditions, la bride de serrage de pièce
peut perturber le fonctionnement de la protection de
lame. Toujours s’assurer du libre fonctionnement de la
protection de lame avant de commencer la coupe, afin
de réduire le risque de blessure grave.
La bride de serrage de pièce permet un contrôle accru en
bridant la pièce sur le guide ou la table de la scie. Elle évite
aussi le déplacement de la pièce vers la lame. C’est très utile
lors de la coupe d’onglets composés. Selon l’opération de
coupe et les dimensions de la pièce, il peut être nécessaire
d’utiliser un serre-joint ou autre pince adaptée au lieu de
la bride de serrage de pièce pour bloquer la pièce avant
d’effectuer la coupe.
Installation de la bride de serrage de pièce :
Placer l’axe de la bride de serrage dans l’un des trous
situé derrière le guide d’onglet.
Tourner le bouton de bride de serrage de pièce pour
le déplacer vers le haut ou le bas afin de maintenir
fermement la pièce à couper en place.
CLÉ DE
LAME
BRIDE DE
SERRAGE
DE PIÈCE
TRAVAIL LE
BOUTON
D’ARBRE
BASE
15 − Français
Fig. 12
Page 50

ASSEMBLAGE
RALLONGES DE TABLE
Voir les figures 13 à 15.
Des rallonges de table sont fournies pour les côtés gauche
et droit de la scie.
Pour l’installer les rallonges de table :
Retirer la vis située sur l’extrémité de la rallonge de table.
Insérer les extrémités des rallonges dans les trous situés
sur les côtés de la base.
Réinstaller la vis et serrer afin de bloquer la rallonge en
place.
Répéter l’opération pour l’autre rallonge de table.
RALLONGE DE
TABLE
BASE
Fig. 14
RALLONGE DE
TABLE
BASE
Fig. 13
SCIE VUE D’EN DESSOUS
VIS DE RALLONGE
BASE
DE TABLE
Fig. 15
16 − Français
Page 51

ASSEMBLAGE
INSTALLATION / REMPLACEMENT DE LA
LAME
Voir les figures 16 et 17.
AVERTISSEMENT :
La taille maximum de lame pouvant être utilisée sur cette
scie est de 305 mm (12 po). Ne jamais utiliser une lame trop
épaisse pour permettre à la rondelle extérieure de la lame de
s’engager sur les méplats de la broche. Des lames de plus
grandes dimensions toucheraient les protections de lame et
des lames plus épaisses empêcheraient le boulon de lame de
maintenir la lame sur la broche. Ces deux situations peuvent
causer un accident et des blessures graves.
BOUTON DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE BROCHE
Fig. 16
Débrancher la scie.
Desserrer le vis du couvercle de boulon de la lame. Faire
tourner la garde inférieure et faire tourner le couvercle de
boulon de lame vers le haut et vers l’arrière pour exposer le
boulon de lame.
Appuyer sur bouton de verrouillage de la broche et tourner
le boulon de lame jusqu’à ce que la broche se verrouille.
À l’aide de la clé de lame fournie, desserrer et retirer le boulon
de lame.
NOTE : Le boulon de lame est fileté à gauche. Il doit donc
être tourné vers la droite pour être desserré.
Retirer la rondelle de lame extérieure. Ne pas retirer la
rondelle intérieure de la lame.
Appliquer une goutte d’huile sur la surface de contact des
rondelles intérieure et extérieure.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Si la rondelle intérieure de la lame a été retirée, la remettre
en place avant d’installer la lame sur la broche. L’absence
de cette pièce pourrait causer un accident, car la lame ne
serait pas correctement serrée.
Engager la lame dans la garde inférieure et sur l’épaule de
rondelle intérieure. Les dents doivent être orientées vers le
bas à l’avant de la lame, comme le montre la figure 17.
Remettre en place la rondelle de lame extérieure. Les deux
méplats en « D » des rondelles de lame s’alignent sur les
méplats de la broche.
Appuyer sur le bouton de verrouillage de la broche et
réinstaller le boulon de lame.
NOTE : Le boulon de lame est fileté à gauche. Il doit donc être
tourné vers la gauche pour être serré.
ATTENTION :
Toujours installer la lame avec les dents et la flèche imprimée
sur son côté, orientées vers le bas à l’avant de la scie. Le
sens de rotation de la lame est également représenté par une
flèche estampée sur la protection supérieure.
NOTE : AVANT D’UTILISER,
REMETTRE LES VIS EN
PLACE ET LA SERRE
FERMEMENT POUR
EMPÊCHER LE
MOUVEMENT DE GARDE
COUVERCLE DU
BOULON DE LAME
RONDELLE
EXTÉRIEURE
DE LAME AVEC
DOUBLES
MÉPLATS EN « D »
POUR
DESSERRER
BOULON
DE LAME
POUR
SERRER
RONDELLE
DE LAME
EXTÉRIEURE
BOULON DE
LA LAME
VIS DU COUVERCLE
DE BOULON DE LA
LAME
LAME
RONDELLE DE
LAME INTÉRIEURE
GARDE DE LAME
INFÉRIEURE
MÉPLAT(S)
DE LA BROCHE
RONDELLE
INTÉRIEURE DE
LAME AVEC
DOUBLES
MÉPLATS
EN « D »
LAME
Fig. 17
17 − Français
Page 52

ASSEMBLAGE
LASER RADIATION AVOID DIRECT EYE EXPOSURE
CLASS IIIa LASER PRODUCT
MAXIMUM OUTPUT: <5mW WAVELENGTH: 635-660nm
• To reduce the risk of injury, user must read and understand the
operator’s manual before using the miter saw.
• Wear eye protection.
• Keep hands out of path of saw blade.
• Do not operate saw without guards in place.
• Do not perform any operation freehand.
• Never reach around the saw blade.
• Turn off tool and wait for saw blade to stop before raising saw
arm, moving workpiece, or changing settings.
• Disconnect the saw from the power source before changing blade
or servicing.
Complies with 21 CFR
Parts 1040.10 & 1040.11
RYLD
Fixer gâchette avant
làser est réglagé. EVITER
L’EXPOSITION: Rayonnement laser émise de cet orifice.
Asegure gatillo antes de ajuste
de laser. EVITE LA EXPOSICIÔN:
Radiación laser se emite por esta abertura.
Lock trigger prior to adjusting
laser. AVOID EXPOSURE:
Laser radiation is emitted from this aperture.
Serrer le boulon fermement.
Remettre la garde de lame inférieure et le couvercle du
boulon en place.
Serrer solidement le vis du couvercle de boulon de la
lame.
Soulever et abaisser la tête de la scie et s’assurer que le
protège-lame inférieur fonctionne correctement.
AVERTISSEMENT :
S’assurer que le bouton de verrouillage de la broche
n’est pas engagé avant de brancher la scie sur la
source d’alimentation. Ne jamais engager le bouton de
verrouillage de la broche lorsque la lame est en rotation.
DANGER :
Rayonnement laser. Éviter tout contact oculaire direct
avec la source du rayon.
INTERRUPTOR
DE GUÍA DE
LÁSER
AVERTISSEMENT :
L’usage de contrôles, de réglages ou de procédures ne
figurant pas dans ce manuel peut entraîner l’exposition
à des rayonnements dangereux.
ALIGNEMENT DU TRAIT LASER
Voir la figure 18.
Pour verrouiller le commutateur, installer un cadenas (non
inclus) dans le trou de la gâchette et la fermeture de la
arceau.
Dessiner une ligne sur la pièce. Cuándo el interruptor de guía
de láser lo es prendido, le laser projette un trait lumineux
rouge sur la pièce. Le pointillé permet de voir la marque
tracée sur la pièce en même temps que le trait laser ce qui
permet d’aligner les deux lignes afin d’obtenir une coupe
plus précise.
Aligner le trait laser sur le tracé de coupe de la pièce, la lame
étant relevée au maximum. Une fois que les deux lignes se
chevauchent, ne plus bouger la pièce.
Retirer le cadenas et brancher la scie. Effectuer plusieurs
coupes d’essais sur des chutes de différents type de
matériau et de différentes épaisseurs. Répéter les étapes
ci-dessus comme nécessaire.
Effacement du tracé de coupe :
Positionner le trait laser près du bord gauche du tracé de
coupe de la pièce, pour l’effacer.
Coupe sur le tracé :
Positionner le trait laser près du tracé ou sur celui-ci pour
effectuer la coupe sur la marque.
Pour laisser le tracé de coupe :
Positionner le trait laser près du bord droit du tracé de coupe
de la pièce, pour le laisser en place.
Une fois familiarisé avec l’usage du laser, l’opérateur pourra
effacer le tracé, le laisser ou effectuer la coupe sur celui-ci.
La pratique permettra de découvrir la position adéquate du
trait laser par rapport au tracé.
18 − Français
LIGNE
POINTILLÉE
ROUGE
Fig. 18
Page 53

ASSEMBLAGE
RETRAIT / REMPLACEMENT DE LA PLAQUE
À GORGE
Voir la figure 19.
AVERTISSEMENT :
La plaque à gorge doit être au dessous de la table à
onglets. Si la plaque à gorge est trop haute ou trop basse,
la pièce de bois peut accrocher les bords inégaux et
causer un blocage entraînant des blessures graves.
Ne jamais utiliser la scie à moins que la plaque à gorge ne
soit installée.
Retrait / remplacement :
Débrancher la scie.
Retirer les vis fixant la plaque à gorge.
Retirer la plaque à gorge de la scie.
Pour réinstaller la plaque à gorge, aligner ses trous sur
ceux de la base de la scie.
Remettre les vis en place en veillant à ne pas trop les
serrer ce qui pourrait causer le voilage ou la déformation
de la plaque.
RÉGLAGE DU PIED DE SUPPORT
Voir la figure 19.
Tourner le pied de support vers la droite ou la gauche selon
l’intensité de soutien nécessaire pour réaliser des coupes
coulissantes.
PLAQUE À
GORGE
PIED DE
SUPPORT
Fig. 19
NOTE : De nombreuses illustrations de ce manuel ne
montrent que des parties de la scie à onglets composés.
Cette présentation a été choisie pour montrer clairement
les différents aspects de la scie. Ne jamais utiliser la scie
sans avoir vérifié que tous les dispositifs de protection
sont en place et en bon état.
ÉQUERRAGE DE LA LAME PAR RAPPORT AU
GUIDE
Voir les figures 20 à 26.
Débrancher la scie.
Abaisser complètement le bras de la scie et engager
l’axe de verrouillage pour maintenir le bras en position
de transport.
Desserrer la poignée de verrouillage d’angle d’environ
un demi-tour et presser le levier de verrouillage à
encliquetage.
Tourner la table à onglet jusqu’à ce que l’indicateur
d’échelle soit en position 0°.
Relâcher le levier de verrouillage à encliquetage et
s’assurer que le bras de commande est enclenché dans
une encoche positive.
Serrer le bouton de verrouillage d’onglet pour immobiliser
la table à onglets.
GUIDE
D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
VUE DE LA LAME D’ÉQUERRE AVEC LE GUIDE
TABLE À
ONGLETS
ÉQUERRE
POIGNÉE DE
VERROUILLAGE
D’ONGLET
BLADE
Fig. 20
19 − Français
Page 54

ASSEMBLAGE
Desserrer le bouton de verrouillage d’angle de biseau et
régler le bras de la scie pour un biseau de 0° (lame à 90°
de la table). Serrer le bouton de verrouillage de biseau.
Poser une équerre à plat sur la table à onglets. Placer
une branche de l’équerre contre le guide. Glisser l’autre
branche de l’équerre contre le plat de la lame.
NOTE : Vérifier que l’équerre est en contact avec le plat
de la lame, pas les dents.
Le bord de l’équerre et la lame doivent être parallèles,
comme le montre la figure 20.
Si l’avant ou l’arrière de la lame s’écarte de l’équerre, des
réglages, illustrés aux figures 21 et 22, sont nécessaires.
LAME
Desserrer la vis de réglage du guide, pousser le guide
coulissant sur environ 25,4 mm (1 po) vers la droite de
manière à outrepasser la vis de réglage puis soulever pour
retirer le guide coulissant du guide d’onglets coulissant.
À l’aide de la clé de lame fournie, desserrer les vis à tête
creuse fixant le guide d’onglet à la table à onglets.
Tourner le guide d’onglet vers la gauche ou la droite, afin
de mettre la lame de scie parallèle à l’équerre.
Resserrer fermement les vis et vérifier de nouveau
l’alignement du guide et de la lame.
VIS D’ARRÊT
GUIDE
D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
VUE DE LA LAME PAS D’ÉQUERRE AVEC LE GUIDE,
GUIDE
D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
VUE DE LA LAME PAS D’ÉQUERRE AVEC LE GUIDE,
TABLE À
ONGLETS
DES RÉGLAGES SONT NÉCESSAIRES
TABLE À
ONGLETS
DES RÉGLAGES SONT NÉCESSAIRES
ÉQUERRE
ÉQUERRE
Fig. 21
LAME
Fig. 22
VIS DE
RÉGLAGE
D’ONGLET
VIS À TÊTE
CREUSE
GUIDE
D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
GUIDE
D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
Fig. 23
VIS À TÊTE
CREUSE
Fig. 24
20 − Français
Page 55

ASSEMBLAGE
La scie présente plusieurs indicateur d’échelle. Une fois les
réglages d’alignement effectués, il peut être nécessaire de
desserrer les vis indicateur pour les régler à zéro. Voir les
figures 25 et 26.
ÉQUERRAGE DE LA LAME PAR RAPPORT À
LA TABLE À ONGLETS
Voir les figures 27 à 29.
Débrancher la scie.
Abaisser complètement le bras de la scie et engager
l’axe de verrouillage pour maintenir le bras en position
de transport.
Desserrer la poignée de verrouillage d’angle d’environ
un demi-tour et presser le levier de verrouillage à
encliquetage.
Tourner le table à onglets à aligner le indicateur d’échelle
sur la graduation zéro du rapporteur d’onglet.
Relâcher le levier de verrouillage à encliquetage puis
serrer le bouton de verrouillage d’onglet pour immobiliser
la table à onglets.
Desserrer le bouton de verrouillage d’angle de biseau et
régler le bras de la scie jusqu’à ce que soit assis dans la
butée de biseau positive de 0° (lame à 90° de la table).
Serrer le bouton de verrouillage de biseau.
Placer une équerre combinée contre la table à onglets et
le plat de la lame.
NOTE : Vérifier que l’équerre est en contact avec le plat
de la lame, pas les dents.
Faire tourner la lame à la main et vérifier son alignement
sur la table en plusieurs points.
Le bord de l’équerre et la lame doivent être parallèles,
comme le montre la figure 27.
RAPPORTEUR
D’ANGLE
INDICATEUR
D’ÉCHELLE
VIS
D’INDICATEUR
BOUTON DE
VERROUILLAGE
DE BISEAU
VIS
D’INDICATEUR
Fig. 25
INDICATEUR
D’ÉCHELLE
RAPPORTEUR
D’ANGLE
D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
21 − Français
GUIDE
TABLE À
ONGLETS
ÉQUERRE
COMBINÉE
POIGNÉE DE
VERROUILLAGE D’ONGLET
VUE DE LA LAME D’ÉQUERRE
AVEC LA TABLE À ONGLETS
Fig. 26
LAME
Fig. 27
Page 56

ASSEMBLAGE
Si le haut ou le bas de la lame s’écarte de l’équerre, des
réglages, figures 28 et 29, sont nécessaires.
Dévisser le bouton de verrouillage de biseau.
Régler la vis de butée de biseau à 0° pour aligner la lame
de la scie avec le tracé perpendiculaire. Voir le Réglage
de butée positive dans la section Réglages.
Resserrer le bouton de verrouillage de biseau. Vérifier à
nouveau l’alignement de la lame sur la table.
NOTE: La procédure ci-dessus peut être utilisée pour
vérifier l’alignement de la lame sur la table à 0° et 45°.
La scie présente plusieurs indicateur d’échelle. Une fois les
réglages d’alignement effectués, il peut être nécessaire de
desserrer les vis indicateur pour les régler à zéro. Voir les
figures 25 et 26.
TABLE À
GUIDE
D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
VUE DE LA LAME PAS D’ÉQUERRE AVEC LA TABLE,
DES RÉGLAGES SONT NÉCESSAIRES
ÉQUERRE
COMBINÉE
ONGLETS
LAME
Fig. 28
LAME
TABLE À
GUIDE
D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
VUE DE LA LAME PAS D’ÉQUERRE AVEC TABLE À ONGLETS,
DES RÉGLAGES SONT NÉCESSAIRES
ÉQUERRE
COMBINÉE
ONGLETS
Fig. 29
22 − Français
Page 57

UTILISATION
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas laisser la familiarité avec l’outil faire oublier la
prudence. Ne pas oublier qu’une fraction de seconde
d’inattention peut entraîner des blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Toujours porter une protection oculaire certifiée conforme
à la norme ANSI Z87.1. Si cette précaution n’est pas prise,
des objets peuvent être projetés dans les yeux et causer
des lésions graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas utiliser d’outils ou accessoires non recommandés
pour cet outil. L’utilisation de pièces et accessoires non
recommandés peut entraîner des blessures graves.
APPLICATIONS
Ce produit est conçu uniquement pour les applications
suivantes :
Coupe transversale de pièces de bois et de plastique
(ne pas couper de métaux, céramiques ou produits de
maçonnerie.)
Coupe d’onglets, joints, etc., pour cadres, moulures,
encadrements de portes et menuiserie fine
Coupe en biseau et coupe composée
Coupe transversale de larges pièces
NOTE : La lame fournie convient à la plupart des opérations
de coupe de bois, toutefois, pour les travaux de menuiserie
fine et la coupe de matières plastiques, utiliser l’une des
lames accessoires en vente dans les magasins Ryobi.
AVERTISSEMENT :
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour éviter des blessures graves, toujours garder les
mains hors de la zone dangereuse, c’est-à-dire à au moins
76 mm (3 po) de la lame. Ne jamais effectuer de coupes
à main levée (c.-à-d. sans maintenir la pièce contre le
guide). La lame pourrait se coincer dans la pièce si celleci glisse ou tourne.
AVIS:
Ne pas mettre la scie en marche sans s’être assuré
de l’absence d’interférence entre la lame et le guide
d’onglets. La lame pourrait être endommagée si elle
entrait en contact avec le guide d’onglets pendant le
fonctionnement.
TRAVAUX DE COUPE AVEC LA SCIE À ONGLETS
COMPOSÉS
AVERTISSEMENT :
Si un serre-joint, une bride de serrage
adaptée
doit être placé que d’un côté de la lame. La pièce doit être
libre d’un côté de la lame afin qu’elle ne risque pas de la
bloquer. Un pincement de la lame dans la pièce causerait
le calage du moteur et un rebond. Le blocage de la lame
peut entraîner des blessures graves.
de pièce est utilisé pour maintenir la pièce, il ne
ou ou autre pince
AVERTISSEMENT :
NE JAMAIS se déplacer l’ajustement de pièce ou marque
à n’importe quel angle de coupe pendant que la scie court
et la lame tourne. N’importe quelle erreur peut avoir pour
résultat le contact avec la lame causant des blessures
graves.
Avant d’entreprendre toute opération de coupe, assujettir
ou boulonner la scie à onglets composés sur un établi. Ne
jamais utiliser la scie à onglets sur le sol ou en se tenant
accroupi. Le non respect de cette mise en garde peut
entraîner des blessures graves.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour éviter des blessures, toujours serrer fermement la
poignée de verrouillage d’angle et levier de verrouillage de
biseau avant d’effectuer une coupe. Si cette précaution
n’est pas prise, la table o tête de la scie risquent de se
déplacer pendant la coupe.
23 − Français
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne pas couper de pièces étroites au moyen du dispositif
de coulissement. Le non-respect de cet avertissement
pourrait entraîner des blessures graves.
Page 58

UTILISATION
POUR RÉALISER DES COUPES NON
COULISSANTES
AVERTISSEMENT :
Bien serrer le bouton de verrouillage du coulissement lors
de coupes non coulissantes. Si le bouton est mal serré,
la tête de la scie peut bouger durant la coupe.
POUR COUPES D’ONGLETS/
TRANS-VERSALES
Voir les figures 30 et 31.
La coupe est effectuée en travers du grain de la pièce de
bois. Pour effectuer une coupe transversale droite, la table
à onglet doit être réglée sur 0°. Les coupes d’onglets sont
réalisées en réglant la table sur tout angle autre que 0°.
Relever complètement le bras de la scie.
Desserrer la poignée de verrouillage d’angle d’environ
un demi-tour et presser le levier de verrouillage à
encliquetage.
Tourner le bras de commande de manière à aligner le
pointeur sur la graduation correspondant à l’angle désiré.
Relâcher le levier de verrouillage à encliquetage puis
serrer le bouton de verrouillage d’onglet pour immobiliser
la table à onglets.
NOTE : Repérer rapidement sur 0°, 15°, 22,5°, 31,6°
ou 45° à gauche ou à droite en relâchant le bouton
de dégagement à encliquetage tout en tournant le
bras de commande. Le bras de commande reposera
automatiquement dans l’un des crans d’arrêt situé sur
la base de la table à onglets.
Placer la pièce à couper à plat sur la table à onglet, l’un
de ses bords solidement appuyé contre le guide. Si la
planche est voilée, placer le côté convexe contre le guide.
Si le bord concave d’une pièce est placé contre le guide,
la pièce peut se refermer sur la lame en fin de coupe et
la bloquer. Voir les figures 42 et 43.
Lors de la coupe de planches ou de moulures longues,
soutenir l’extrémité libre de la pièce avec un chevalet à
rouleau ou un plan de travail se trouvant au même niveau
que la scie. Voir la figure 35.
Glisser la tête de la scie complètement vers l’arrière
et serrer fermement le bouton de verrouillage de
coulissement.
Aligner la ligne de coupe de la pièce sur le bord de la
lame ou ligne laser.
Saisir fermement la pièce d’une main et la caler contre
le guide. Dans la mesure du possible, utiliser la bride de
serrage de pièce, un serre-joint ou ou autre pince adaptée
pour maintenir la pièce.
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, effectuer un essai
à vide, afin de s’assurer qu’aucun problème ne se
présentera lorsque la coupe est effectuée.
COUPE TRANSVERSALE
BRIDE DE
SERRAGE
DE PIÈCE
Fig. 30
COUPE D’ONGLET
BRIDE DE
SERRAGE
DE PIÈCE
Fig. 31
24 − Français
Page 59

UTILISATION
Saisir fermement le manche de la scie. Enfoncer le
dispositif de verrouillage avec le po puis serrer la
gâchette. Attendre quelques secondes que la lame
atteigne sa vitesse de rotation maximale.
Abaisser lentement la lame sur la pièce.
Relâcher la gâchette et attendre l’arrêt complet de la lame
avant de la relever de la pièce et de retirer la pièce de la
table à onglet.
COUPE EN BISEAU
Voir le figure 32.
Une coupe en biseau est réalisée en travers du grain de la
pièce, avec la lame en biais. Pour effectuer une coupe en
biseau droite, la table à onglets doit être réglée sur 0° et la
lame entre 0° et 45°.
NOTE : Il peut être nécessaire d’ajuster ou de retirer le guide
coulissant et/ou déplace le bride de serrage de pièce au trou
dans rallonge de table pour assurer un dégagement suffisant
avant d’effectuer la coupe.
Tirer l’axe de verrouillage du bras et relever ce dernier
complètement.
Desserrer la poignée de verrouillage d’angle d’environ
un demi-tour et presser le levier de verrouillage à
encliquetage.
Tourner le bras de commande de manière à aligner le
pointeur sur la graduation correspondant à l’angle désiré.
Relâcher le levier de verrouillage à encliquetage puis
serrer le bouton de verrouillage d’onglet pour immobiliser
la table à onglets.
NOTE : La scie peut être réglée rapidement sur 0, 15,
22,5, 31,6 ou 45° à gauche ou à droite en relâchant le
levier de verrouillage à encliquetage tout en tournant le
bras de commande. Le bras de commande s’insérera
automatiquement dans l’une des encoches de butée
positive de la base de la table à onglets.
Desserrer le bouton de verrouillage d’angle de biseau et
régler le bras de la scie sur l’angle désiré.
L’angle de biseau est réglable de 0° à 45°.
Aligner le point de repère sur la graduation correspondant
à l’angle désiré.
Une fois le bras réglé sur l’angle désiré, serrer fermement
le bouton de verrouillage de biseau.
Placer la pièce à couper à plat sur la table à onglets, l’un
de ses bords solidement appuyé contre le guide. Si la
planche est voilée, placer le côté convexe contre le guide.
Si le bord concave d’une pièce est placé contre le guide,
la pièce peut se refermer sur la lame en fin de coupe et
la bloquer. Voir les figures 42 et 43.
Lors de la coupe de planches ou de moulures longues,
soutenir l’extrémité libre de la pièce avec un chevalet à
rouleau ou un plan de travail se trouvant au même niveau
que la scie. Voir la figure 35.
COUPE EN BISEAU
BRIDE DE
SERRAGE
DE PIÈCE
Fig. 32
Glisser la tête de la scie complètement vers l’arrière
et serrer fermement le bouton de verrouillage de
coulissement.
Aligner la ligne de couoe de la pièce sur le bord de la
lame ou ligne laser.
Saisir fermement la pièce d’une main et la caler contre
le guide. Dans la mesure du possible, utiliser la bride de
serrage, un serre-joint ou ou autre pince adaptée pour
maintenir la pièce.
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, effectuer un essai à
vide, afin de s’assurer qu’aucun problème ne se présentera
lorsque la coupe est effectuée.
Saisir la poignée de la scie fermement et appuyer sur
la gâchette. Attendre quelques secondes que la lame
parvienne à sa vitesse de rotation maximum.
Abaisser lentement la lame sur la pièce.
Relâcher la gâchette et attendre l’arrêt complet de la
lame avant de la relever de la pièce. Attendre que le
frein électrique ait complètement stoppé la lame avant
de retirer la pièce de la table.
COUPE D’ONGLET COMPOSÉ
Voir les figures 33 et 34.
Une coupe d’onglet composé consiste à utiliser un angle
d’onglet et un angle de biseau simultanément. Ce type de
coupe est utilisé pour la réalisation de cadres, de boîtes à
pans inclinés et certains travaux de charpente.
25 − Français
Page 60

UTILISATION
Pour effectuer ce type de coupe, le bras de commande de
la table doit être réglé sur l’angle d’onglet désiré et la scie
doit être inclinée sur l’angle de biseau correct. Le plus grand
soin doit être apporté aux réglages pour onglets composés,
du fait de l’interaction des deux réglages d’angle.
Les réglages d’angles d’onglet et de biseau sont relationnels.
Tout changement de l’angle d’onglet affecte le réglage de
l’angle de biseau. De même, tout changement de l’angle de
biseau affecte le réglage de l’angle d’onglet.
Plusieurs réglages peuvent s’avérer nécessaires pour obtenir
la coupe désirée. Le premier réglage d’angle doit être vérifié
après avoir effectué le second, étant donné que ce second
réglage affecte le premier.
Une fois les réglages correct pour une coupe désirée obtenus,
toujours effectuer une coupe d’essai sur une chute avant de
couper la pièce définitive.
NOTE : Il peut être nécessaire d’ajuster ou de retirer le guide
coulissant et/ou déplace le bride de serrage de pièce au trou
dans rallonge de table pour assurer un dégagement suffisant
avant d’effectuer la coupe.
Tirer l’axe de verrouillage du bras et relever ce dernier
complètement.
Desserrer la poignée de verrouillage d’angle d’environ
un demi-tour et presser le levier de verrouillage à
encliquetage.
Tourner le bras de commande de manière à aligner le
pointeur sur la graduation correspondant à l’angle désiré.
Relâcher le levier de verrouillage à encliquetage puis
serrer le bouton de verrouillage d’onglet pour immobiliser
la table à onglets.
Desserrer le bouton de verrouillage d’angle de biseau et
régler le bras de la scie sur l’angle désiré.
L’angle de biseau est réglable de 0° à 45°.
Une fois le bras de scie réglé à l’angle désiré, serrer
fermement le bouton de verrouillage de biseau.
Vérifiez à nouveau l’angle de coupe d’onglet. Faites une
coupe d’essai dans une chute.
Placez la pièce à plat sur la table d’onglet, l’un des bords
bien placé contre le guide. Si la pièce est gauchie, placez
le côté convexe contre le guide. Si le bord concave
de la pièce se trouve contre le guide, la pièce pourrait
s’affaisser à la fin de la coupe et coincer la lame. Voir les
figures 42 et 43.
Lors de la coupe de longues pièces ou moulures, retenez
l’extrémité opposée de la pièce avec un support à rouleau
ou une surface de travail de niveau avec la table de la
scie. Voir la figure 35.
Glisser la tête de la scie complètement vers l’arrière
et serrer fermement le bouton de verrouillage de
coulissement.
Alignez la ligne de coupe de la pièce avec le bord de la
lame de la scie ou ligne laser.
Saisir fermement la pièce d’une main et la caler contre
le guide. Dans la mesure du possible, utiliser la bride de
serrage de pièce, un serre-joint ou ou autre pince adaptée
pour maintenir la pièce.
26 − Français
COUPE D’ONGLET COMPOSÉ
SERRE-JOINT
COUPE D’ONGLET COMPOSÉ 45° X 45°
Fig. 33
Fig. 34
Page 61

UTILISATION
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, effectuer un essai
à vide, afin de s’assurer qu’aucun problème ne se
présentera lorsque la coupe est effectuée.
Saisir fermement le manche de la scie. Enfoncer le
dispositif de verrouillage avec le pouce puis serrer la
gâchette. Attendre quelques secondes que la lame
atteigne sa vitesse de rotation maximale.
Abaissez lentement la lame dans la pièce pour la couper.
Relâcher la gâchette et attendre l’arrêt complet de la lame
avant de la relever de la pièce et de retirer la pièce de la
table à onglet.
SUPPORT DE PIÈCES LONGUES
Voir la figure 35.
Les pièces longues nécessitent un support additionnel. Les
supports, un support à rouleau, ou une surface de travail de
niveau avec la table de la scie doivent être placés sous la
pièce, de manière à ce qu’elle ne fléchisse pas. Les supports
doivent permettre à la pièce de reposer à plat sur la base
de la scie et la table pendant la coupe. Dans la mesure du
possible, utiliser bride de serrage de pièce, serre-joint ou ou
autre pince adaptée pour maintenir la pièce.
PIÈCE
LONGUE
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne jamais couper en tirant la scie vers soi car la lame
pourrait grimper sur le haut de la pièce et se déplacer vers
l’opérateur. Le non-respect de cet avertissement pourrait
entraîner des blessures graves.
COUPE À COULISSEMENT
Voir les figures 36 et 37.
La fonction de coulissement coupe des pièces de 342,9 mm
(13-1/2 po) de large par 38,1 mm (1-1/2 po) d’épaisseur ou
139,7 mm (5-1/2 po) de large par 89 mm (3-1/2 po). Avec
la scie à l’arrêt, tirer le bras de la scie vers l’avant. Mettre la
scie en marche (laisser la lame atteindre la vitesse maximum)
puis pousser la lame vers le bas sur la pièce à travailler
puis vers l’arrière de la scie pour faire la coupe. Les coupes
peuvent être réalisées en poussant la lame de la scie à
l’écart de soi et vers le rapporteur de biseau à l’arrière de
la scie et en s’arrêtant lorsque la position arrière complète
a été atteinte après chaque coupe. Lorsque la scie est en
marche, NE JAMAIS tirer la lame de la scie vers soi ou vers
l’avant de la scie.
Relever complètement le bras de la scie.
Placer la pièce à couper à plat sur la table à onglet, l’un
de ses bords solidement appuyé contre le guide. Si la
planche est voilée, placer le côté convexe contre le guide.
Si le bord concave d’une pièce est placé contre le guide,
la pièce peut se refermer sur la lame en fin de coupe et
la bloquer. Voir les figures 42 et 43.
Lors de la coupe de planches ou de moulures longues,
soutenir l’extrémité libre de la pièce avec un chevalet à
rouleau ou un plan de travail se trouvant au même niveau
que la scie. Voir la figure 35.
27 − Français
SUPPORTS DE LA PIÈCE
COUPE À COULISSEMENT
BOUTON DE
VERROUILLAGE DU
COULISSEMENT
VERS L’AVANT PUIS VERS LE BAS
Fig. 35
GLISSER LE BRAS DE LA SCIE
Fig. 36
Page 62

UTILISATION
Aligner la ligne de coupe de la pièce sur le bord de la
lame ou ligne laser.
Desserrer le bouton de verrouillage de coulissement en le
tournant dans le sens inverse des aiguilles d’une montre.
Saisir fermement la pièce d’une main et la caler contre
le guide. Dans la mesure du possible, utiliser la bride de
serrage de pièce, un serre-joint ou autre pince adaptée
pour maintenir la pièce.
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, effectuer un essai
à vide, afin de s’assurer qu’aucun problème ne se
présentera lorsque la coupe est effectuée.
Avec la scie à l’arrêt, saisir fermement la poignée de la
scie et tirer la scie vers l’avant jusqu’à ce que l’arbre
de la lame (centre de la lame de la scie) soit au-delà de
l’avant de la pièce à travailler ou jusqu’à ce que la scie
soit complètement déployée.
Serrer la gâchette. Attendre quelques secondes que la
lame atteigne sa vitesse de rotation maximale.
Abaisser lentement la lame sur et au travers du bord avant
de la pièce.
Pousser la poignée de la scie à l’écart de soi et vers le
rapporteur de biseau à l’arrière de la scie.
Relâcher la gâchette et attendre l’arrêt complet de la lame
avant de la relever de la pièce et de retirer la pièce de la
table à onglet.
NOTE : La coupe est effectuée en travers du grain de la
pièce de bois. Pour effectuer une coupe transversale droite,
la table à onglet doit être réglée sur 0°. Les coupes d’onglets
sont réalisées en réglant la table sur tout angle autre que 0°.
Faire une coupe d’onglet de 45° gauche complète en
passant par le côté gauche du guide auxiliaire.
NOTE : Vérifier qu’il n’y a pas d’interférence entre le guide
auxiliaire et la protection de lame inférieure. Corriger toute
interférence avant de continuer.
Répéter les étapes avec une deuxième plinthe en
l’alignant avec le côté droit de la table d’onglets.
COUPE À COULISSEMENT
POUSSER
VERS
L’ARRIÈRE
Fig. 37
COMMENT FABRIQUER UNE GUIDE
AUXILIAIRE
Voir la figure 38.
Certaines coupes inhabituelles peuvent être facilitées par un
guide d’onglet plus épais (guide auxiliaire) en raison de la
taille et de la position de la pièce. Les trous fournis dans le
guide d’onglets sont destinés à cet usage. Les trous du guide
d’onglet sont utilisés pour fixer le guide auxiliaire qui exige
deux morceaux de bois de 13 mm (1/2 po) de profondeur,
89 mm (3-1/2 po) de hauteur et 254 mm (10 po) de long
pour être fabriqué.
NOTE : Le guide auxiliaire ne peut être utilisé que lorsque
le biseau est réglé à 0°. Lorsqu’une coupe biseautée est
effectuée, le guide auxiliaire DOIT être retiré.
Pour fixer le guide auxiliaire à la scie :
Placer un morceau de bois contre le guide d’onglets en
l’alignant avec le bord gauche de la table d’onglets et
tracer l’emplacement du trou derrière le guide à l’aide
d’un crayon.
Percer les trous à travers le bois puis fraiser les trous à
l’avant de la pièce de bois.
Bloquer le bois sur le guide d’onglet avec des vis à tête
plate.
28 − Français
GUIDE
AUXILIAIRE
ALIGNER LA
PLINTHE AVEC LE
BORD DE LA TABLE
D’ONGLETS
Fig. 38
Page 63

UTILISATION
COUPE D’ONGLETS COMPOSÉS
Le tableau des réglages d’angles ci-dessous est conçu pour faciliter les réglages. Les coupes composées étant les plus
difficiles à réaliser, des essais doivent être effectués sur des chutes et la coupe définitive ne doit être effectuée qu’après
mûre réflexion et planification.
ANGLE
DE CÔTÉ
0°
5°
10°
15°
20°
25°
30°
35°
40°
45°
50°
55°
60°
65°
70°
75°
80°
85°
90°
4
M- 45,00°
B- 0,00°
M- 44,89°
B- 3,53°
M- 44,56°
B- 7,05°
M- 44,01°
B- 10,55°
M- 43,22°
B- 14,00°
M- 42,19°
B- 17,39°
M- 40,89°
B- 20,70°
M- 39,32°
B- 23,93°
M- 37,45°
B- 27,03°
M- 35,26°
B- 30,00°
M- 32,73°
B- 32,80°
M- 29,84°
B- 35,40°
M- 26,57°
B- 37,76°
M- 22,91°
B- 39,86°
M- 18,88°
B- 41,64°
M- 14,51°
B- 43,08°
M- 9,85°
B- 44,14°
M- 4,98°
B- 44,78°
M- 0,00°
B- 45,00°
5
M- 36,00°
B- 0,00°
M- 35,90°
B- 2,94°
M- 35,58°
B- 5,86°
M- 35,06°
B- 8,75°
M- 34,32°
B- 11,60°
M- 33,36°
B- 14,38°
M- 32,18°
B- 17,09°
M- 30,76°
B- 19,70°
M- 29,10°
B- 22,20°
M- 27,19°
B- 24,56°
M- 25,03°
B- 26,76°
M- 22,62°
B- 28,78°
M- 19,96°
B- 30,60°
M- 17,07°
B- 32,19°
M- 13,95°
B- 33,53°
M- 10,65°
B- 34,59°
M- 7,19°
B- 35,37°
M- 3,62°
B- 35,84°
M- 0,00°
B- 36,00°
NOMBRE DE CÔTÉS
6
M- 30,00°
B- 0,00°
M- 29,91°
B- 2,50°
M- 29,62°
B- 4,98°
M- 29,15°
B- 7,44°
M- 28,48°
B- 9,85°
M- 27,62°
B- 12,20°
M- 26,57°
B- 14,48°
M- 25,31°
B- 16,67°
M- 23,86°
B- 18,75°
M- 22,21°
B- 20,70°
M- 20,36°
B- 22,52°
M- 18,32°
B- 24,18°
M- 16,10°
B- 25,66°
M- 13,71°
B- 26,95°
M- 11,17°
B- 28,02°
M- 8,50°
B- 28,88°
M- 5,73°
B- 29,50°
M- 2,88°
B- 29,87°
M- 0,00°
B- 30,00°
7
M- 25,71°
B- 0,00°
M- 25,63°
B- 2,17°
M- 25,37°
B- 4,32°
M- 24,95°
B- 6,45°
M- 24,35°
B- 8,53°
M- 23,56°
B- 10,57°
M- 22,64°
B- 12,53°
M- 21,53°
B- 14,41°
M- 20,25°
B- 16,19°
M- 18,80°
B- 17,87°
M- 17,20°
B- 19,41°
M- 15,44°
B- 20,82°
M- 13,54°
B- 22,07°
M- 11,50°
B- 23,16°
M- 9,35°
B- 24,06°
M- 7,10°
B- 24,78°
M- 4,78°
B- 25,30°
M- 2,40°
B- 25,61°
M- 0,00°
B- 25,71°
8 9
M- 22,50°
B- 0,00°
M- 22,42°
B- 1,91°
M- 22,19°
B- 3,81°
M- 21,81°
B- 5,68°
M- 21,27°
B- 7,52°
M- 20,58°
B- 9,31°
M- 19,73°
B- 11,03°
M- 18,74°
B- 12,68°
M- 17,60°
B- 14,24°
M- 16,32°
B- 15,70°
M- 14,91°
B- 17,05°
M- 13,36°
B- 18,27°
M- 11,70°
B- 19,35°
M- 9,93°
B- 20,29°
M- 8,06°
B- 21,08°
M- 6,12°
B- 21,69°
M- 4,11°
B- 22,14°
M- 2,07°
B- 22,41°
M- 0,00°
B- 22,50°
M- 20,00°
B- 0,00°
M- 19,93°
B- 1,71°
M- 19,72°
B- 3,40°
M- 19,37°
B- 5,08°
M- 18,88°
B- 6,72°
M- 18,26°
B- 8,31°
M- 17,50°
B- 9,85°
M- 16,60°
B- 11,31°
M- 15,58°
B- 12,70°
M- 14,43°
B- 14,00°
M- 13,17°
B- 15,19°
M- 11,79°
B- 16,27°
M- 10,31°
B- 17,23°
M- 8,74°
B- 18,06°
M- 7,10°
B- 18,75°
M- 5,38°
B- 19,29°
M- 3,62°
B- 19,68°
M- 1,82°
B- 19,92°
M- 0,00°
B- 20,00°
10
M- 18,00°
B- 0,00°
M- 17,94°
B- 1,54°
M- 17,74°
B- 3,08°
M- 17,42°
B- 4,59°
M- 16,98°
B- 6,07°
M- 16,41°
B- 7,50°
M- 15,72°
B- 8,89°
M- 14,90°
B- 10,21°
M- 13,98°
B- 11,46°
M- 12,94°
B- 12,62°
M- 11,80°
B- 13,69°
M- 10,56°
B- 14,66°
M- 9,23°
B- 15,52°
M- 7,82°
B -16,26°
M- 6,34°
B- 16,88°
M- 4,81°
B- 17,37°
M- 3,23°
B- 17,72°
M- 1,62°
B- 17,93°
M- 0,00°
B- 18,00°
Chaque angle B (biseau) et M (onglet) est indiquée au 0,005 ème de degré le plus proche.
RÉGLAGES D’ANGLES COMPOSÉS POUR LES CONSTRUCTIONS COURANTES
29 − Français
Page 64

UTILISATION
COUPE DE MOULURE COURONNÉE
Cette scie à onglets est idéale pour la coupe de moulures
couronnées. En général, les scies à onglets sont préférables à
tout autre outil pour la coupe de moulures couronnées.
Pour un ajustage adéquat, les moulures couronnées doivent
être coupées avec une précision extrême.
Les deux surfaces de contact d’une section de moulure
couronnée se fixant à plat sur le plafond et le mur d’une pièce, à
des angles qui, lorsqu’ils sont additionnés, totalisent exactement
90°. La plupart des moulures couronnées présentent un angle
supérieur arrière (partie reposant à plat contre le plafond) de
52° et un angle inférieur arrière (partie reposant à plat sur le
mur) de 38°.
POSE DE LA MOULURE À PLAT SUR LA TABLE
À ONGLETS
Voir la figure 39.
Pour effectuer une coupe à 90° intérieure ou extérieure précise
selon cette méthode, poser la moulure avec sa face arrière large
à plat sur la table, contre le guide.
Lors du réglage des angles d’onglets et de biseaux pour les
onglets combinés, se rappeler que les réglages sont interdépendants : la modification d’un angle modifie également
l’autre angle.
Se rappeler également que les angles de moulures couronnées
doivent être extrêmement précis et qu’ils sont difficiles à obtenir.
Étant donné que ces angles peuvent très facilement être
faussés, tous les réglages doivent être vérifiés en effectuant une
coupe d’essai sur une chute. En outre, la plupart des murs ne
présentant pas des angles d’exactement 90°, il est nécessaire
d’ajuster les réglages en conséquence.
Lors de la coupe d’une moulure couronnée à l’aide de cette
méthode, l’angle de biseau doit être réglé à 33,85°. L’angle
d’onglet doit être réglé à 31,6° à droite ou à gauche, suivant
le sens de coupe nécessaire pour l’application. Consulter le
tableau ci-dessous pour les réglages d’angle et le positionnement
corrects de la moulure sur la table.
Les réglages indiqués au tableau ci-dessous peuvent être utilisés
pour la coupe de toutes les moulures américaines standard à
angles de 52° et 38°. La moulure couronnée est placée à plat sur
la table pour utiliser les fonctions de coupe composée de la scie.
Biseau
Angle
Réglage
33,85°
33,85°
33,85°
33,85°
Coin intérieur, côté gauche
1. Bord supérieur de la moulure contre le guide
2. Angle d’onglet réglé à droite sur 31,62°
3. Conserver la section gauche de la pièce coupée
Coin intérieur, côté droit
1. Bord inférieur de la moulure contre le guide
2. Angle d’onglet réglé à gauche sur 31,62°
3. Conserver la section gauche de la pièce coupée
Coin extérieur, côté gauche
1. Bord inférieur de la moulure contre le guide
2. Angle d’onglet réglé à gauche sur 31,62°
3. Conserver la section droite de la pièce coupée
Côté droit, coin extérieur
1. Bord supérieur de la moulure contre le guide
2. Angle d’onglet réglé à droite sur 31,62°
3. Conserver la section droite de la pièce coupée
Type de coupe
38°
52°
PLAFOND
M
U
R
GUIDE D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
COIN
INTÉRIEUR
GUIDE D’ONGLETS
COIN EXTÉRIEUR
COULISSANT
BORD SUPÉRIEUR CONTRE LE GUIDE =
COIN INTÉRIEUR GAUCHE
COIN EXTÉRIEUR DROIT
TABLE À ONGLETS
MOULURE COURONNÉE À PLAT SUR LA TABLE À ONGLET
BORD INFÉRIEUR CONTRE LE GUIDE =
COIN INTÉRIEUR DROIT
COIN EXTÉRIEUR GAUCHE
TABLE À ONGLETS
Fig. 39
30 − Français
Page 65

UTILISATION
MOULURE COURONNÉE EMBOÎTÉE CONTRE
LE GUIDE D’ONGLET
Voir les figures 40 et 41.
NOTE : Cette méthode de coupe est pour les moulures
couronnées mesurant entre 117,5 et 133,3 mm (4-5/8 et
5-1/4 po) de hauteur. Ne pas tenter de couper une moulure
de plus de 133,3 mm (5-1/4 po) de hauteur.
Serrer les vis du guide longitudinal pour le fixer fermement
en place.
Régler l’angle de biseau à 0° et l’angle d’onglet à 45°
vers la droite ou la gauche (pour faire des coins à 90°).
Embriquer et immobiliser fermement la moulure
couronnée contre le guide longitudinal en utilisant
une pince à ressort et maintenir fermement la moulure
couronnée.
Avant de mettre la scie en marche, effectuer un exercice
général pour s’assurer qu’aucun problème ne se produira
lors de la coupe.
Saisir fermement la poignée de la scie. Appuyer sur
l’interrupteur à gâchette. Attendre plusieurs secondes
afin que la lame atteigne sa vitesse maximale.
Abaisser lentement la lame sur la moulure couronnée et
traverser celle-ci.
GUIDE
D’ONGLETS
COULISSANT
PINCE À
RESSORT
BORD INFÉRIEURCONTRE
LE GUIDE
PINCE À
RESSORT
Fig. 40
MOULURE
COURONNÉE
Fig. 41
31 − Français
Page 66

UTILISATION
CORRECT
Fig. 42
COUPE DE PIÈCES VOILÉES
Voir les figures 42 et 43.
Lors de la coupe d’une pièce voilée, toujours s’assurer
que son bord convexe est placé contre le guide, comme le
montre la figure 42.
Si une pièce voilée est placée dans le mauvais sens, comme
illustré à la figure 43, elle pincera la lame vers la fin de la coupe.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Pour éviter les risques de rebond et de blessures graves,
ne jamais placer le bord concave d’une pièce voilée ou
déformée contre le guide.
FIXATION DE PIÈCES LARGES
Voir la figure 44.
Les pièces larges, de dimensions telles que 51 x 152 mm
(2 x 6 po) doivent être assujetties avec baride de serrage de
pièce comme illustré à la figure 44.
INCORRECT
Fig. 43
PLANCHE
LARGE
32 − Français
Fig. 44
Page 67

RÉGLAGES
AVERTISSEMENT :
Avant d’effectuer tout réglage, s’assurer que l’outil est
débranché. Le non respect de cet avertissement pourrait
entraîner des blessures graves.
La scie à onglets composés a été réglée en usine pour
effectuer des coupes très précises. Toutefois, certains
composants peuvent avoir été désalignés pendant le
transport. En outre, après un certain temps des réglages
s’avéreront probablement nécessaires, du fait de l’usure. Une
fois la scie déballée, vérifier les réglages indiqués ci-dessous
avant de l’utiliser. Effectuer tous les réglages nécessaires et
vérifier périodiquement l’alignement des pièces pour s’assurer
que la scie effectue des coupes précises.
RÉGLAGES DES PIVOTS
NOTE : Ces réglages ont été effectués en usine et n’ont
normalement pas besoin d’être refaits.
RÉGLAGE DU PIVOT DE BRAS
Le bras de la scie doit se relever complètement de lui-
même.
Si le bras de la scie ne se relève pas de lui-même ou si
les articulations présentent du jeu, faire réparer la scie
par le CENTRE DE RÉPARATIONS le plus proche.
RÉGLAGES DE BUTÉE POSITIVE
Voir la figure 45.
NOTE : Ces réglages ont été effectués en usine et n’ont
normalement pas besoin d’être refaits.
Réglage :
Débrancher la scie.
Desserrer le bouton de verrouillage d’angle de biseau
en le tournant dans le sens inverse des aiguilles d’une
montre.
Mettre la lame perpendiculaire à la table à onglets, comme
décrit au chapitre Assemblage de ce manuel.
Si la lame n’est pas à angle droit, serrer fermement l’écrou
de blocage et serrer ou desserrer la vis de réglage de
butée positive avec une clé hexagonale de 5 mm (non
incluse).
Resserrer le bouton de verrouillage de biseau. Vérifier de
nouveau l’alignement de la lame sur la table.
NOTE : La procédure ci-dessus peut être utilisée pour
vérifier l’alignement de la lame sur la table à 0° et 45°.
La scie présente plusieurs indicateur d’échelle. Une fois les
réglages d’alignement effectués, il peut être nécessaire de
desserrer les vis indicateur pour les régler à zéro. Voir les
figures 25 et 26.
RÉGLAGE DU PIVOT DE BISEAU
La scie à onglets composés doit biseauter facilement en
dévissant le bouton de verrouillage de biseau.
Si le mouvement est restreint ou si les articulations
présentent du jeu, faire réparer la scie par le CENTRE
DE RÉPARATIONS le plus proche.
VIS DE RÉGLAGE
DE BUTÉE
POSITIVE POUR
ONGLETS À 0°
ÉCROU
DE BLOCAGE
ÉCROU
DE BLOCAGE
VIS DE RÉGLAGE DE
BUTÉE POSITIVE POUR
ONGLETS À 45°
Fig. 45
33 − Français
Page 68

RÉGLAGES
DANGER :
Rayonnement laser. Éviter tout contact oculaire direct
avec la source du rayon.
AVERTISSEMENT :
L’usage de contrôles, de réglages ou de procédures ne
figurant pas dans ce manuel peut entraîner l’exposition
à des rayonnements dangereux.
RÉGLAGE DU LASER
Voir la figure 46.
Régler le guide d’onglet et bisel des angles à 0º.
Utiliser le serre-joint de travail facultatif, serre-joint ou
autre pince adaptée pour obtenir un morceau de bois de
fragment.
Brancher la scie et faire une coupe insignifiante pour
marquer le bois.
Relâcher la gâchette et attendre l’arrêt complet de la
lame.
Utiliser un cadenas, verrouiller la verrouiller le commutateur
pour faire la scie être actionné.
Allumer le guide laser.
Tourner la vis de réglage du laser pour ajuster sa position.
Tourner la vis vers la droite pour déplacer le laser vers la
droite ou tourner la vis vers la gauche pour déplacer le
laser vers la gauche.
NOTE : Correctement entretenue aligné, la laser doit être
sur le bord gauche du trait de scie. Si le laser n’aligne pas
correctement, le retour au CENTRE DE RÉPARATIONS
pour la réparation.
VIS DE
RÉGLAGE DE
LASER
GUIDE
LASER
34 − Français
Fig. 46
Page 69

ENTRETIEN
AVERTISSEMENT :
Utiliser exclusivement des pièces d’origine pour les
réparations. L’usage de toute autre pièce pourrait créer
une situation dangereuse ou endommager le produit.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Toujours porter une protection oculaire certifiée conforme
à la norme ANSI Z87.1 lors de l’utilisation de produit. Si
une opération dégage de la poussière, porter également
un masque anti-poussière.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Avant d’effectuer tout réglage, s’assurer que l’outil est
débranché. Le non respect de cet avertissement pourrait
entraîner des blessures graves.
ENTRETIEN GÉNÉRAL
Éviter d’utiliser des solvants pour le nettoyage des pièces en
plastique. La plupart des matières plastiques peuvent être
endommagées par divers types de solvants du commerce.
Utiliser un chiffon propre pour éliminer la saleté, la poussière,
l’huile, la graisse, etc.
LUBRIFICATION
Tous les roulements de cet outil sont garnis d’une quantité
de graisse de haute qualité, suffisante pour la durée de vie
de l’outil, dans des conditions d’utilisation normales. Aucune
autre lubrification n’est donc nécessaire.
REMPLACEMENT DES BALAIS
Voir la figure 47.
Le moteur de la scie est équipé de balais accessibles de
l’extérieur, dont l’usure doit être vérifiée périodiquement.
Lorsque le remplacement des balais s’avère nécessaire,
procéder comme suit :
Débrancher la scie.
Retirer le couvercle des balais à l’aide d’un tournevis. Les
balais sont montés sur ressort et sont éjectés lorsque le
couvercle est retiré.
Retirer les balais.
Regarder s’ils sont usés. Remplacer les deux balais
lorsque la longueur du carbone est de 6 mm (1/4 po) ou
moins. Ne pas remplacer un balai sans remplacer l’autre.
Installer les nouveaux balais. S’assurer que la courbure
des balais correspond à celle du moteur et que les balais
tournent librement dans leurs tubes.
S’assurer que le couvercle est correctement aligné (droit)
et l’assujettir.
Serrer le couvercle solidement. Ne pas trop serrer.
AVERTISSEMENT :
Ne jamais laisse de liquides tels que le fluide de freins,
l’essence, les produits à base de pétrole, les huiles
pénétrantes, etc., entrer en contact avec les pièces en
plastique. Les produits chimiques peuvent endommager,
affaiblir ou détruire le plastique, ce qui peut entraîner des
blessures graves.
Les outils électriques utilisés sur la fibre de verre, le
placoplâtre, les mastics de bouchage ou le plâtre s’usent
plus vite et sont susceptibles de défaillance prématurée car
les particules et les éclats de fibre de verre sont fortement
abrasifs pour les roulements, balais, commutateurs, etc. Il
est donc déconseillé d’utiliser cet outil de façon prolongée
sur ces types de matériaux. Toutefois, si l’outil a été utilisé
sur l’un de ces matériaux, il est extrêmement important de
le nettoyer à l’air comprimé.
COUVERCLE
DE BALAI
ENSEMBLE
DE BALAI
ENSEMBLE
DE BALAI
Ce produit est couvert par une garantie limitée de trois (3) ans. Veuillez visiter notre site
internet au www.ryobitools.com pour obtenir tous les détails de la garantie.
COUVERCLE
DE BALAI
Fig. 47
35 − Français
Page 70

REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD GENERALES
ADVERTENCIA:
Lea y comprenda todas las instrucciones. El incumplimiento
de las instrucciones señaladas abajo puede causar
descargas eléctricas, incendios y lesiones serias.
LEA TODAS LAS INSTRUCCIONES
FAMILIARÍCESE CON SU HERRAMIENTA ELÉCTRICA.
Lea cuidadosamente el manual del operador. Aprenda los
usos, limitaciones y posibles peligros relacionados con
esta herramienta.
PROTÉJASE CONTRA DESCARGAS ELÉCTRICAS
EVITANDO TOCAR CON EL CUERPO SUPERFICIES
CONECTADAS A TIE RRA. Por ejemplo: tubos, radiadores,
estufas y cajas de refrigeradores.
MANTENGA LAS PROTECCIONES EN SU LUGAR y en
buenas condiciones de trabajo.
RETIRE TODA LLAVE Y HERRAMIENTA DE AJUSTE.
Adquiera el hábito de verificar que se haya retirado de la
herramienta eléctrica toda llave y herramienta de ajuste
antes de encenderla.
MANTENGA LIMPIA EL ÁREA DE TRABAJO. Una mesa
o área de trabajo mal despejada es causas común de
accidentes. NO deje herramientas o piezas de madera en
la herramienta mientras esté funcionando.
NO UTILICE LA HERRAMIENTA EN ENTORNOS
PELIGROSOS. No utilice las herramientas eléctricas en
lugares húmedos o mojados ni las exponga a la lluvia.
Mantenga bien iluminada el área de trabajo.
MANTENGA ALEJADOS A LOS NIÑOS Y DEMÁS
CIRCUNSTANTES. Todos los presentes deben llevar
p u e s to s a nt e ojo s d e s eg u ri da d y p e rm a n e c e r a u na d i s t an ci a
segura del área de trabajo. No permita que ninguno de
los presentes toque la herramient eléctrica o el cordón de
extensión mientras esté funcionando la unidad.
HAGA SU TALLER A PRUEBA DE NIÑOS con candados,
interruptores maestros y retirando las llaves de arranque.
NO FUERCE LA HERRAMIENTA. Efectúa el trabajo mejor
y de manera más segura, si se utiliza a la velocidad de
avance para la que está diseñada.
USE LA HERRAMIENTA ADECUADA PARA LA TAREA.
No fuerce la herramienta ni ningún accesorio a efectuar
tareas para las que no están hechos.
USE UN CORDÓN DE EXTENSIÓN ADECUADO.
Asegúrese de que esté en buen estado el cordón de
ex te n sió n. A l u ti l i z a r un c o r d ón d e e x ten si ó n s ó lo u til ic e u no
d e l c ali br e s uf i c ie nt e p ara s o p o r ta r l a co r ri e nt e q ue c o ns um e
el producto. Un cordón de un grueso insuficiente causa una
caída en el voltaje de línea, y produce recalentamiento y
pérdida de potencia. Se recomienda que los conductores
sean de calibre 14 (A . W.G .) po r l o men o s , p ar a un c ord ó n d e
extensión de 7,6 metros (25 pies) de largo o menos. Si tiene
dudas, utilice un cordón del calibre más grueso siguiente.
Cuanto menor es el número de calibre, mayor es el grueso
del cordón.
VÍSTASE ADECUADAMENTE. Evite ponerse ropas
holgadas, corbatas ni joyas que puedan engancharse y tirar
de usted hacia las piezas en movimiento. Se recomiendan
2 − Español
guantes y calzado antiderrapantes al trabajar al aire libre.
Si tiene el pelo largo cúbraselo de alguna manera para
contenerlo.
SIEMPRE PÓNGASE ANTEOJOS DE SEGURIDAD CON
PROTECCIÓ N LATERAL. Los anteojos de uso diario tienen
lentes resistentes a golpes únicamente; NO son anteojos
de seguridad.
ASEGURE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO. Utilice prensas de
mano o de banco para sujetar la pieza de trabajo cuando
resulte práctico hacerlo; es más seguro que utilizar la mano
y qued a n a mbas man o s libre s pa ra mane j a r la herr a mient a .
NO ESTIRE EL CUERPO PARA ALCANZAR MAYOR
DISTANCIA. Mant e n g a un a po s t u r a fi r m e y bu e n equ i l i b r i o
en todo momento.
DÉ MANTENIMIENTO CON CUIDADO A LAS
HERRAMIENTAS. Mantenga afiladas y limpias las
herramientas para obtener de las mismas un desempeño
mejor y más seguro. Siga las instrucciones correspondientes
al cambio y lubricación de accesorios.
DESCONECTE LAS HERRAMIENTAS. Todas las
herramientas deben desconectarse del suministro de
corriente cuando no estén usándose, o al cambiarles
aditamentos, hojas de corte, brocas, fresas, etc.
EVITE UN ARRANQUE ACCIDENTAL DE LA UNIDAD.
Asegúrese de que el interruptor esté en la posición
de apagado antes de conectar la clavija de cualquier
herramienta.
USE ACCESSORIOS RECOMENDADOS. Consulte este
manual del operador, donde aparecen los accesorios
recomendados. El empleo de accesorios inadecuados
puede causar lesiones.
NO SE PARE NUNCA EN LA HERRAMIENTA. Pueden
producirse lesiones serias si se vuelca la herramienta o si
accidentalmente se toca la hoja.
INSPECCIONE LAS PIEZAS DAÑADAS. Antes de seguir
utilizando la herramienta, es necesario inspeccionar
cuidadosamente toda protección o pieza dañada para
determinar si funcionará correctamente y desempeñará
la función a la que está destinada. Verifique la alineación
de las partes móviles, que no haya atoramiento de partes
móviles, que no haya piezas rotas, el montaje de las
piezas y cualquier otra condición que pudiera afectar su
funcionamiento. Toda protección o pieza que esté dañada
debe repararse apropiadamente o reemplazarse en un
centro de servicio autorizado.
AVANCE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO EN LA DIRECCIÓN
CORRECTA. Solamente empuje la pieza de trabajo hacia la
hoja, fresa o tambor de lijado, contra el sentido de rotación
de éstos.
NUNCA DEJE FUNCIONANDO DESATENDIDA LA
HERR AMIENTA. APAGUE LA C ORRIENTE . No abandone
la herramienta hasta verla completamente detenida.
PROTÉJAS E LOS PULMONES . Us e u n a c a r e t a o ma sc ar il l a
c o nt ra e l p ol vo si l a o p e r a ci ón d e c or te g e n er a mu c h o p ol v o.
PROTÉJASE EL OÍDO. Durante períodos prolongados de
util i zación de la unidad pó n gase protección pa r a los oídos.
NO MALTRATE EL CORDÓN ELÉCTRICO. Nunca porte
la herramienta sujetándola por el cordón eléctrico, ni tire
Page 71

REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD GENERALES
del mismo para desconectarla de la toma de corriente.
Mantenga el cordón eléctrico alejado del calor, del aceite
y de los bordes afilados.
UTILICE CORDONES DE EXTENSIÓN PARA USO EN
EL EXTERIOR. Al utilizar la herramienta en el exterior,
sólo utilice cordones de extensión con conexión a tierra
aprobada apropiados para uso al aire libre y marcados
para tal tipo de uso.
MANTENGA LAS HOJAS DE CORTE LIMPIAS Y
AFILADAS. Las hojas de corte afiladas reducen al mínimo
los paros y los contragolpes.
L A HOJA DE CORT E CONTINÚA GIR ANDO POR IN ERCIA
DESPUÉS DE APAGARSE LA UNIDAD.
NUNCA UTILICE LA UNIDAD EN UNA ATMÓSFERA
EXPLOSIVA. El chispeo normal del motor podría encender
los gases presentes.
INSPECCIONE PERIÓDICAMENTE LOS CORDONES
ELÉCTR ICOS DE LA S HERRAM IENTAS. Si están dañados,
llévelos a un establecimiento de servicio autorizado para
q u e l os re v i s e u n t é c n i c o d e s e rv i cio c a l i f i c a do . E l c ond u cto r
con aislamiento que tiene una superficie exterior verde con
o sin tiras amarillas es el conductor de conexión a tierra
del equipo. Si es necesaria la reparación o reemplazo del
cordón eléctrico o de la clavija, no conecte el conductor
de conexión a tierra a una terminal portadora de corriente.
Repare o reemplace de inmediato todo cordón dañado
o gastado. Siempre esté consciente de la ubicación del
cordón y manténgalo bien alejado de la hoja en movimiento
de giro.
INSPECCIONE PERIÓDICAMENTE LOS CORDONES DE
EXTENSIÓN y reemplácelos si están dañados.
CLAVIJAS POLARIZADAS. Las herramientas con
aislamiento doble están equipadas de una clavija polarizada
(una patilla es más ancha que la otra). Esta clavija encaja
de una sola forma en una toma de corriente polarizada. Si
la clavija no encaja completamente en la toma de corriente,
invierta la clavija. Si aún así no encaja, comuníquese con un
electricista calificado para que instale una toma de corriente
adecuada. No modifique la clavija de ninguna manera.
MANTENGA LA HERRAMIENTA SECA, LIMPIA Y LIBRE
DE ACEITE Y GRASA. Siempre utilice un paño limpio para
la limpieza de la unidad. Nunca utilice fluidos para frenos,
gasolina, productos a base de petróleo ni solventes para
limpiar la herramienta.
PERM ANEZCA ALERTA Y EN CONTRO L. Preste atención
a lo que esté haciendo y aplique el sentido común. No utilice
la herramienta cuando esté cansado. No se apresure.
NO UTILICE LA HERRAMIENTA SI EL INTERRUPTOR
NO ENCIENDE O NO APAGA. Lleve todo interruptor
defectuoso a un centro de servicio autorizado para que lo
reparen.
SÓLO UTILICE HOJAS DE CORTE ADECUADAS. No
use hojas con orificio de un tamaño incorrecto. Nunca
utilice arandelas ni pernos de la hoja de corte dañados o
inadecuados. La sierra tiene capacidad para hojas hasta
de un diámetro de 305 mm (12 pulg.).
ANTES DE EFECTUAR UN CORTE VERIFIQUE QUE
ESTÉN BIEN ASEGURADOS TODOS LOS DISPOSITIVOS
DE AJUSTE.
ASEGÚRESE DE QUE NO HAYA CLAVOS EN LA
TRAYECTORIA DE LA HOJA. Inspeccione la madera y
elimine todos los clavos presentes en la misma antes de
empezar a cortar.
NUNCA TOQUE LA HOJA ni ninguna otra pieza en
movimiento durante el funcionamiento de la unidad.
NUNCA ARRANQUE LA HERRAMIENTA CUANDO LA
PIEZA GIRATORIA CORRESPONDIENTE ESTÉ
TOCANDO LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO.
NO UTILICE NINGUNA HERRAMIENTA SI SE
ENCUENTRA BAJO LOS EFECTOS DE DROGAS,
ALCOHOL O MEDICAMENTOS.
AL DAR SERVICIO a la unidad, sólo utilice piezas de
repuesto idénticas. El empleo de piezas diferentes puede
causar un peligro o dañar el producto.
SOLAMENTE UTILICE ACCESORIOS señalados en
este manual o en los apéndices. El uso de accesorios
no señalados en este manual puede presentar riesgos
de lesiones corporales. Con los accesorios se incluyen
instrucciones para el uso seguro de los mismos.
REVISE DOS VECES TODA CONFIGURACIÓN DE LA
HERRAMIENTA. Asegúrese de que la hoja esté apretada
y de que no toque la sierra o la pieza de trabajo antes de
conectar la unidad al suministro de corriente.
REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD ESPECÍFICAS
SUJETE FIRMEMENTE CON PRENSAS DE MANO O
PERNOS la herramienta en una mesa o banco de trabajo
aproximadamente a la altura de la cadera.
MANTENGA LAS MANOS ALEJADAS DEL ÁREA DE
CORTE. No trate de alcanzar bajo la pieza de trabajo o en
la trayectoria de corte de la hoja con las manos y dedos por
ninguna razón. Siempre apague la corriente.
SIEMPRE APOYE LAS PIEZAS DE TRABAJO LARGAS
mientras corta para reducir al mínimo el riesgo de un
pellizcamiento de la hoja de corte y de un contragolpe.
3 − Español
La sierra puede resbalarse, caminar o deslizarse al cortar
tablas largas o pesadas.
SIEMPRE UTILICE LA PRENSA para asegurar la pieza de
trabajo cuando sea posible.
ASEGÚRESE DE QUE LA HOJA TRASPASE LA PIEZA DE
TRABAJO. Nunca arranque la sierra con la hoja tocando
la pieza de trabajo. Permita que el motor se detenga
completamente antes de iniciar el corte.
ASEGÚRESE DE QUE LA MESA DE INGLETES Y EL BRAZO
DE LA SIERRA (FUNCIÓN DE BISEL) ESTÉN EN POSICIÓN
Page 72

REGLAS DE SEGURIDAD ESPECÍFICAS
ASEGURADA ANTES DE PONER EN FUNCIONAMIENTO
SU SIERRA. Fije la mesa de ingletes ajustando en forma
segura el mango de fijación de ingletes. Asegure el brazo
de la sierra (función de bisel) ajustando en forma segura la
perilla de bloqueo de bisel.
NUNCA UTILICE UN TOPE DE LONGITUD EN EL
EXTREMO DE DESPERDICIOS SUELTOS DE UNA PIEZA
DE TRABAJO SUJETA CON PRENSA. NUNCA sujete o
doble el extremo de desperdicio de una pieza de trabajo en
cualquier operación. Si se utilizan juntos una prensa para
pieza de trabajo y un tope de longitud, ambos deben estar
instalados en el mismo lado de la mesa de la sierra para
evitar que la sierra coja el extremo suelto y dé un contragolpe
hacia arriba.
NUNCA corte más de una pieza a la vez. NO APILE más
de una pieza de trabajo sobre la mesa de la sierra a la vez.
NUNCA EFECTÚE A PULSO NINGUNA OPERACIÓN.
Siempre coloque la pieza de trabajo por cortar en la mesa
de ingletes y acomódela firmemente contra la guía como
tope trasero. Siempre use la guía.
NUNCA sujete con la mano una pieza de trabajo que sea
demasiado pequeña para ser sujetada con prensa. Mantenga
las manos alejadas del área del corte.
NUNCA alcance por detrás, por abajo o a menos de 76
mm (3 pulg.) de la hoja y de su trayectoria de corte con las
manos o con los dedos, por ninguna razón.
NUNCA trate de estirarse para levantar una pieza trabajo, un
trozo de desecho o cualquier cosa que esté en el trayecto
de corte de la hoja, o cerca del mismo.
NUNCA mueva el ajuste de la pieza de trabajo ni marca a
algún ángulo cortante mientras el vio corre y la hoja gira.
Cualquier tropiezo puede tener como resultado el contacto
con la hoja que causa lesiones serias.
EVITE OPERACIONES Y POSICIONES EXTRAÑAS DE
LAS MANOS en las cuales un deslizamiento rápido pudiera
causar que la mano tocara la hoja. SIEMPRE asegúrese de
estar en una postura equilibrada. NUNCA utilice la sierra
ingleteadora en el piso o estando en cuclillas.
NUNCA se pare ni tenga ninguna parte del cuerpo en línea
con la trayectoria de la hoja de la sierra.
SIEMPRE suelte el interruptor de corriente y permita que
se cese de girar la hoja de la sierra antes de levantarla de
la pieza de trabajo.
NO ENCIENDA Y APAGUE CON RAPIDEZ EL
INTERRUPTOR. Esto podría causar el aflojamiento de la
hoja de la sierra y el consiguiente peligro. Si esto llegara a
ocurrir, aléjese y permita que se detenga completamente
la hoja de la sierra. Desconecte la sierra del suministro de
corriente y vuelva a apretar firmemente el perno de la hoja.
SI CUALQUIER PIEZA DE ESTA SIERRA INGLETEADORA
ESTÁ FALTANTE, rota, doblada o funciona mal de cualquier
forma, o si cualquier componente eléctrico de la misma no
funciona debidamente, apague el interruptor de corriente,
retire la clavija del suministro de corriente y llame a un
técnico para que reemplace toda pieza dañada, faltante o
defectuosa antes de reanudar el trabajo.
¡SIEMPRE PERMANEZCA ALERTA! No permita que su
familiaridad con la máquina (proveniente del uso frecuente
de la sierra) sea causa de un error de descuido. SIEMPRE
TENGA PRESENTE que un descuido de un instante
essuficiente para causar una lesión grave.
SI ESTÁ DAÑADO EL CORDÓN DE CORRIENTE, debe ser
reemplazado únicamente por el fabricante o en un centro
de servicio autorizado para evitar riesgos.
ASEGÚRESE DE QUE EL ÁREA DE TRABAJO CUENTE
CON SUFICIENTE ILUMINACIÓN para ver la pieza de
trabajo y de que ninguna obstrucción interfiera en la seguridad
de la operación ANTES de efectuar cualquier trabajo en la
sierra.
SIEMPRE APAGUE LA SIERRA antes de desconectarla
para evitar un arranque accidental de la misma al volver
a conectarla al suministro de corriente. NUNCA deje
desatendida la sierra mientras esté conectada a un suministro
de corriente.
APAGUE LA HERRAMIENTA y espere a que se detenga
completamente la hoja de corte antes de proceder a mover
la pieza de trabajo o de efectuar ajustes.
ESTA HERRAMIENTA tendrá los siguientes avisos:
a) Póngase protección ocular.
b) Mantenga las manos fuera de la trayectoria de la hoja de
corte.
c) No utilice la sierra sin las protecciones montadas en su
lugar.
d) No efectúe a pulso ninguna operación.
e) Nunca intente alcanzar nada alrededor de la hoja de corte.
f) Apague la herramienta y espere a que se detenga la hoja
de corte de la sierra antes de mover la pieza de trabajo
o de cambiar los ajustes.
g) Desconecte la corriente (o desenchufe la herramienta,
según corresponda) antes de cambiar la hoja de corte o
de dar servicio a la unidad.
h) Velocidad en vacío.
S IEMPRE CE RCIORES E EL VIO HO JA TIENE EL E SPACIO
LIBRE DE TODAS OBSTRUCCIONES ANTES GIRAR EL
VIO EN.
EFECTÚE CORTES DESLIZANTES presionando la hoja
de la sierra hacia abajo sobre el material de trabajo, y
seguidamente deslizándola hacia la parte trasera de la
sierra. NO tire de la sierra hacia usted mientras realiza el
corte.
SIEMPRE porte la herramienta por el mango de acarreo.
EVITE toda exposición directa de los ojos al utilizar la guía
láser.
E STA SIER RA PUEDE VOLCAR SE s i s e s u e lt a s úbi ta me n te
la cabeza de la misma y la sierra no está asegurada a una
superficie de trabajo. SIEMPRE asegure esta sierra a una
superficie de trabajo estable antes de usarla para evitar
lesiones serias.
GUARDE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES. Consúltelas con
frecuencia y empléelas para instruir a otros usuarios. Si
presta a alguien esta herramienta, facilítele también las
instrucciones.
4 − Español
Page 73

SÍMBOLOS
Las siguientes palabras de señalización y sus significados tienen el objeto de explicar los niveles de riesgo relacionados con este producto.
SÍMBOLO SEÑAL SIGNIFICADO
PELIGRO:
ADVERTENCIA:
PRECAUCIÓN:
AVISO:
Es posible que se empleen en esta herramienta algunos de los siguientes símbolos. Le suplicamos estudiarlos y
aprender su significado. Una correcta interpretación de estos símbolos le permitirá utilizar mejor y de manera más
segura la herramienta.
SÍMBOLO NOMBRE
Alerta de seguridad Indica un peligro posible de lesiones personales.
Lea el manual del operador
Protección ocular
Indica una situación peligrosa inminente, la cual, si no se evita, causará la
muerte o lesiones serias.
Indica una situación peligrosa posible, la cual, si no se evita, podría causar la
muerte o lesiones serias.
Indica una situación peligrosa posible, la cual, si no se evita, podría causar
lesiones menores o leves.
(Sin el símbolo de alerta de seguridad) Indica información importante no
relacionada con ningún peligro de lesiones, como una situación que puede
ocasionar daños físicos.
DENOMINACIÓN/EXPLICACIÓN
Para reducir el riesgo de lesiones, el usuario debe leer y comprender
el manual del operador antes de usar este producto.
Siempre póngase protección ocular con protección lateral con la
marca de cumplimiento de la norma ANSI Z87.1.
Símbolo de no acercar las
manos
Alerta de condiciones húmedas No exponga la unidad a la lluvia ni la use en lugares húmedos.
V Volts Voltaje
A Amperes Corriente
Hz Hertz Frecuencia (ciclos por segundo)
min Minutos Tiempo
Corriente alterna Tipo de corriente
n
o
.../min Por minuto
Velocidad en vacío Velocidad de rotación, en vacío
Fabricación Clase II Fabricación con doble aislamiento
Si no mantiene las manos alejadas de la hoja de corte, se causará
serias lesiones corporales.
Revoluciones, carreras, velocidad superficial, órbitas, etc., por
minuto
5 − Español
Page 74

ASPECTOS ELÉCTRICOS
DOBLE AISLAMIENTO
El doble aislamiento es una característica de seguridad de las
herramientas eléctricas, la cual elimina la necesidad de usar
el típico cordón eléctrico de tres conductores con conexión
a tierra. Todas las partes metálicas expuestas están aisladas
de los componentes metálicos internos del motor por medio
de aislamiento de protección. No es necesario conectar a
tierra las herramientas con doble aislamiento.
ADVERTENCIA:
El sistema de doble aislamiento está destinado para
proteger al usuario contra las descargas eléctricas
resultantes de la ruptura del cableado interno de
la herramienta. Observe todas las precauciones de
seguridad para evitar descargas eléctricas.
NOTA: El mantenimiento de una herramienta con doble
aislamiento requiere sumo cuidado y conocimiento del
sistema, y únicamente deben realizarlo técnicos de servicio
calificados. Para el servicio de la herramienta, le sugerimos
llevarla al centro de servicio autorizado más cercano para
toda reparación. Siempre utilice piezas de repuesto de la
fábrica original al dar servicio a la unidad.
CONEXIÓN ELÉCTRICA
Esta herramienta dispone de un motor eléctrico fabricado
con precisión. Debe conectarse únicamente a un suministro
de voltaje de 120 V, corriente alterna solamente
(corriente normal para uso doméstico), 60 Hz. No utilice
esta herramienta con corriente continua (c.c.). Una caída
considerable de voltaje causa una pérdida de potencia y
el recalentamiento del motor. Si la herramienta no funciona
al conectarla en una toma de corriente, vuelva a verificar el
suministro de voltaje.
CORDONES DE EXTENSIÓN
Al utilizar una herramienta eléctrica a una distancia
considerable de la fuente de voltaje, asegúrese de utilizar
un cordón de extensión con la suficiente capacidad para
soportar la corriente de consumo de la herramienta. Un cordón
de un calibre insuficiente causa una caída en el voltaje de
línea, la cual a su vez produce recalentamiento y pérdida de
potencia. Básese en la tabla suministrada para determinar el
grueso mínimo requerido del cordón de extensión. Solamente
deben utilizarse cordones con forro redondo registrados en
Underwriter’s Laboratories (UL).
Al trabajar a la intemperie con una herramienta, utilice un
cordón de extensión fabricado para uso en el exterior. Este
tipo de cordón lleva las letras “WA” o “W” en el forro.
Antes de utilizar un cordón de extensión, inspecciónelo para
ver si tiene conductores flojos o expuestos y aislamiento
cortado o gastado.
**Amperaje (aparece en la placa de datos de la herramienta)
0-2,0 2,1-3,4 3,5-5,0 5,1-7,0 7,1-12,0 12,1-16,0
Longitud Calibre conductores
del cordón (A.W.G.)
25' 16 16 16 16 14 14
50' 16 16 16 14 14 12
100' 16 16 14 12 10 —
**Used on 12 gauge - 20 amp circuit.
NOTE: AWG = American Wire Gauge
ADVERTENCIA:
Mantenga el cordón de extensión fuera del área de
trabajo. Al trabajar con una herramienta eléctrica, coloque
el cordón de tal manera que no pueda enredarse en
la madera, herramientas ni en otras obstrucciones. La
inobservancia de esta advertencia puede causar lesiones
serias.
ADVERTENCIA:
Inspeccione los cordones de extensión cada vez antes
de usarlos. Si están dañados reemplácelos de inmediato.
Nunca utilice la herramienta con un cordón dañado,
ya que si toca la parte dañada puede producirse una
descarga eléctrica, y las consecuentes lesiones serias.
CALIFORNIA - PROPUESTA DE LEY NÚM. 65
ADVERTENCIA:
Este producto y algunos polvos generados al efectuarse operaciones de lijado, aserrado, esmerilado, taladrado y
otras actividades de la construcción, contienen sustancias químicas reconocidas por el estado de California como
causantes de cáncer, defectos congénitos y otras afecciones del aparato reproductor. Lávese las manos después
de utilizar el aparato.
Algunos ejemplos de estas sustancias químicas son:
• plomo de las pinturas a base de plomo,
• sílice cristalino de los ladrillos, del cemento y de otros productos de albañilería, y
• arsénico y cromo de la madera químicamente tratada.
El riesgo de la exposición a estos compuestos varía, según la frecuencia con que se realice este tipo de trabajo. Para
reducir la exposición personal, trabaje en áreas bien ventiladas, y con equipo de seguridad aprobado, tal como las
caretas para el polvo especialmente diseñadas para filtrar partículas microscópicas.
6 − Español
Page 75

GLOSARIO DE TÉRMINOS
Trinquetes anticontragolpe (sierras radiales y de mesa)
Es un dispositivo, el cual, cuando se instala y da mantenimiento
correctamente, sirve para detener la pieza de trabajo para no
ser lanzada hacia atrás, hacia la parte frontal la sierra durante
una operación de corte al hilo.
Árbol
Es el eje donde se monta una hoja o herramienta de corte.
Corte en bisel
Es una operación de corte efectuada con la hoja a un ángulo
diferente de 90° con respecto a la superficie de la mesa.
Corte combinado
Es un corte transversal efectuado a inglete y a bisel.
Corte transversal
Es una operación de corte o fresado efectuada a través de la
fibra o ancho de la pieza de trabajo.
Cabeza de corte (cepillos normales y de juntas)
Es una cabeza de corte giratoria con hojas o cuchillas ajustables.
Las hojas o cuchillas eliminan material de la pieza de trabajo.
Corte de ranura
Es un corte parcial sin traspaso que produce una muesca, o
un canal de lado a lado, de lados a escuadra, en la pieza de
trabajo (se requiere una hoja especial).
Peine de sujeción
Es un dispositivo empleado como ayuda para controlar la pieza
de trabajo guiándola con seguridad contra la mesa o la guía
durante las operaciones de corte al hilo.
PPM o CPM
Pies por minuto (o carreras por minuto), se emplea refiriéndose
al movimiento de la hoja.
A pulso
Es efectuar un corte sin guiar la pieza de trabajo con ninguna
guía, guía de ingletes ni ningún otro medio.
Goma
Es el residuo pegajoso de savia presente en la madera.
Talón
Es la alineación de la hoja con respecto a la guía de corte al hilo.
Corte
Es la cantidad de material eliminado por la hoja en un corte
completo con traspaso, o en una ranura producida por la hoja
en un corte sin traspaso o parcial.
Contragolpe
Es un peligro que puede ocurrir cuando la hoja se atora o se
atasca, y lanza la pieza de trabajo hacia atrás, en dirección del
operador.
Corte a inglete
Es una operación de corte efectuada con la pieza de trabajo a
un ángulo diferente de 90° con respecto a la hoja.
Cortes sin traspaso
Es cualquier operación de corte en la cual la hoja de corte no
traspasa completamente el espesor de la pieza de trabajo.
Agujero guía (taladradoras de columna)
Es un agujero pequeño taladrado en una pieza de trabajo, el
cual sirve como guía para taladrar con precisión agujeros más
grandes.
Bloques empujadores (para cepillos de juntas)
Son dispositivos empleados para avanzar la pieza de trabajo por
el cepillo de juntas durante cualquier operación. Este medio ayuda
al operador a mantener las manos alejadas de la cabeza de corte.
Bloques empujadores (para sierras de mesa)
Son dispositivos empleados para empuje la pieza de trabajo a
través de la sierra durante operaciones de corte. Estos medios
ayudan al operador a mantener las anos alejadas de la hoja
de corte.
Palos empujadores (para sierras de mesa)
Son dispositivos empleados para empuje la pieza de trabajo a
través de la sierra durante operaciones de corte. Estos medios
ayudan al operador a mantener las manos alejadas de la hoja
de corte.
Reaserrado
Es una operación de corte efectuada para reducir el espesor de
la pieza de trabajo para hacer piezas más delgadas.
Resina
Es la sustancia pegajosa a base de savia que se endurece.
Revoluciones por minuto (RPM)
Es el número de vueltas realizadas por un objeto en movimiento
de giro en un minuto.
Corte longitudinal o al hilo
Es una operación de corte paralela al largo de la pieza de trabajo.
Cuchilla separadora/abridor/separador (sierras de mesa)
Es una pieza metálica, levemente más delgada que la hoja, la
cual se emplea para mantener abierto el corte y también ayuda
a evitar un contragolpe.
Trayectoria de la hoja de la sierra
Es el área encima, abajo, detrás o delante de la hoja. En relación con
la pieza de trabajo, es el área que será o ha sido cortada por la hoja.
Triscado
Es la distancia que se ha doblado hacia afuera (que se ha
triscado) la punta de los dientes de la hoja de la sierra, a partir
de la cara de la hoja.
Redondeo de aristas (cepillos)
Es una depresión hecha en cualquiera de los dos extremos de
una pieza de trabajo por las cuchillas de corte cuando no se
proporciona un apoyo adecuado a la pieza de trabajo.
Cónico Corte
Un corte donde el material para ser corte tiene una anchura
diferente al principio del corte del el fin.
Aserrado con traspaso
Es cualquier operación de corte en la cual la hoja de corte
traspasa completamente el espesor de la pieza de trabajo.
Lanzamiento
Es el lanzamiento hacia atrás de una pieza de trabajo, y
normalmente es causado al dejar caer dicha pieza en la hoja o
al hacerla tocar accidentalmente ésta.
Pieza de trabajo o material
Es la pieza a la que se efectúa la operación.
Mesa
Es la superficie sobre la cual descansa la pieza de trabajo
mientras se le efectúa una operación de corte, taladrado,
cepillado o lijado.
7 − Español
Page 76

CARACTERÍSTICAS
ESPECIFICACIONES DEL PRODUCTO
Orificio del eje ........................................................... 25,4 mm (1 pulg.)
Diámetro de la hoja .................................................305 mm (12 pulg.)
Velocidad en vacío ..................................................4 000 r/min (RPM)
Corriente de entrada .......................120 V, sólo corr. alt., 60 Hz, 15 A
Capacidad de corte con inglete a 0°/bisel a 0°:
Tamaños nominales máximos de la
madera................ 51 x 356 mm, 102 x 152 mm (2 x 14, 4 x 6 pulg.)
Capacidad de corte con inglete a 45°/bisel a 0°:
Tamaños nominales máximos
de la madera .......................................... 51 x 254 mm (2 x 10 pulg.)
TOPE DE
PROFUNDIDAD
PROTECCIÓN
ESCALA DE
BISELES
SUPERIOR DE
LA HOJA
Capacidad de corte con inglete a 0°/bisel a 45°:
Tamaños nominales máximos
de la madera ................................... 51 mm x 356 mm (2 x 14 pulg.)
Capacidad de corte con inglete a 45°/bisel a 45°:
Tamaños nominales máximos
de la madera ................................... 51 mm x 254 mm (2 x 10 pulg.)
Capacidad de corte para molduras de corona (angulado):
Tamaños máximos de la madera .................. 133 mm (5-1/4 pulg.)
Capacidad de corte para rodapié contra la guía:
Alt. máximos ........................... 140 mm x 19 mm (5-1/2 x 3/4 pulg.)
PERILLA DE CONTROL
DE PROFUNDIDAD
PASADOR
DE FIJACIÓN
INDICADOR DE MOLDURA
BASE/CORONA
PERILLA DE
FIJACIÓN DEL
BISEL
MANGO EN “D”
GUÍA LÁSER
GATILLO DEL
INTERRUPTOR
PROTECCIÓN
INFERIOR DE LA HOJA
LLAVE
DE HOJA
SACO
CAPTAPOLVO
GUÍA
TELESCÓPICA
PERILLA DE FIJACIÓN DE
LA CORREDERA
PRENSA DE
GUÍA DE INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
LÍNEA DIVISORIA
DE LA “ZONA DE NO
ACERCAR LAS MANOS”
EXTENSION
DE LA MESA
ETIQUETA “ZONA DE NO
ACERCAR LAS MANOS”
TRABAJO
TOPE(S)
POSITIVO(S)
MESA DE
INGLETES
ESCALA DE
INGLETES
PIE DE SOPORTE
BASE
BRAZO DE
CONTROL
PALANCA DE
DETENCIÓN DE AFLOJE
PLACA DE
GARGANTA
MANIJA DE
FIJACIÓN DE
INGLETE
Fig. 1
8 − Español
Page 77

CARACTERÍSTICAS
FAMILIARÍCESE CON LA SIERRA
INGLETEADORA COMPUESTA
Vea la figura 1.
El uso seguro que este producto requiere la comprensión de
la información impresa en la herramienta y en el manual del
operador así como ciertos conocimientos sobre el proyecto
a realizar. Antes de usar este producto, familiarícese con
todas las características de funcionamiento y normas de
seguridad.
HOJA DE 305 mm (12 pulg.)
Con la sierra ingleteadora combinada se incluye una hoja de
corte de 305 mm (12 pulg.). Corta materiales hasta de 88,9 mm
(3-1/2 pulg.) de espesor ó 342,9 mm (13-1/2 pulg.) de ancho,
según el ángulo al que se efectúe el corte.
INDICADOR DE MOLDURA BASE/CORONA
Vea la figura 2.
Para cortar la moldura base o corona en posición vertical,
alinee la flecha del indicador de moldura base/corona con
la flecha en el ensamblaje pivote y apriete la perilla de cierre
firmemente.
PERILLA DE FIJACIÓN DE BISEL
La perilla de seguridad del bisel asegura su sierra ingleteadora
combinada en los ángulos de bisel deseados. Hay un tornillo
de ajuste de tope en cada lado del brazo de la sierra. Estos
tornillos de ajuste son para efectuar ajustes finos a 0° y a 45°.
MANGO DE
ACARREO
LAS FLECHAS
INTERRUPTOR
EL LÁSER
PERILLA DE
FIJACIÓN DE
LA CORREDERA
INDICADOR DE MOLDURA
BASE/CORONA
ALINEAR
CONJUNTO
PIVOTANTE
Fig. 2
MANGO DE ACARREO
Vea la figura 3.
Para facilitar el transporte de la sierra ingleteadora desde
un lugar a otro, se proporciona un mango de transporte en
la parte superior del brazo de la sierra. Para transportarla,
apague y desconecte la sierra, luego baje el brazo de la
sierra y fíjelo en la posición inferior presionando el pasador
de seguro hacia el alojamiento de la sierra.
NOTA: NO realice ninguna operación de corte con la sierra
en la posición de fijación.
CONTROL MANUAL DE RETENCIÓN
Vea la figura 3.
El control manual de retención permite que la mesa de ingletes
se mueva libremente hacia cualquier ángulo deseado. Con
el mango de fijación de ingletes aflojado y la palanca de
detención de afloje apretada (1), tire del control manual de
retención hacia arriba (2) y suelte la palanca de detención
de afloje (3) para atravesar los topes firmes de la escala de
ingletes. Para liberar el control manual de retención y permitir
que la mesa de ingletes se enganche en los topes firmes,
apriete y suelte la palanca de detención de afloje.
FRENO ELÉCTRICO
Hay un freno eléctrico para detener rápidamente el giro de
la hoja después de soltarse el gatillo del interruptor.
9 − Español
PASADOR DE
FIJACIÓN
PERILLA DE
FIJACIÓN DEL
BISEL
MANGO
EN “D”
BRAZO DE LA SIERRA ASEGURADO EN
LA POSICIÓN INFERIOR
Fig. 3
GUÍA LÁSER
Para cortes más precisos, se incluye una guía láser con la
sierra ingleteadora. Cuando se usa correctamente la guía
láser, sirve para efectuar cortes de precisión con mayor
facilidad.
INTERRUPTOR EL LÁSER
Vea la figura 3.
Utilice el interruptor el láser para encender y apagar el láser.
Page 78

CARACTERÍSTICAS
MANIJA DE FIJACIÓN DE INGLETE
Vea la figura 4.
La manija de fijación de inglete asegura firmemente la sierra
en los ángulos de inglete deseados. Ajuste el mango para
fijar la sierra en su lugar. Para liberar la sierra, afloje el mango
y apriete la palanca de detención de afloje.
ESCALA DE INGLETES
La escala de ingletes dispone de puntos de fijación en
ángulos de 0°, 15°, 22,5°, 30, 31,6°, y 45°.
TOPES DE LA MESA DE INGLETES
Hay topes a 0°, 15°, 22,5°, 31,6°, y 45° a ambos lados,
izquierdo y derecho, de la mesa de ingletes.
NOTA: Para atravesar los topes firmes, apriete la palanca de
detención de afloje y levante el control manual de retención.
Para liberar el control manual, apriete la palanca de detención
de afloje.
PROTECCIÓN INFERIOR RETRÁCTIL DE LA
HOJA
La protección inferior de la hoja está hecha de plastico
transparente resistente a impactos que proporciona
protección a cada lado de la hoja. Se retrae por encima de
la protección superior a medida que se baja la hoja hacia
la pieza de trabajo.
GUÍAS TELESCÓPICA
Cuando está destrabado, el brazo de la sierra se desliza
hacia delante y hacia atrás a lo largo de la guías telescópica
para hacer cortes de diferente ancho.
PERILLA DE FIJACIÓN DE LA CORREDERA
La perilla de fijación de la corredera traba y destraba la
función de deslizamiento de esta herramienta.
MANIJA DE
FIJACIÓN DE
INGLETE
PALANCA DE
DETENCIÓN DE
AFLOJE
CONTROL MANUAL
DE RETENCIÓN
3
1
2
Fig. 4
GUÍA DE INGLETES DESLIZABLE
La guía de ingletes deslizables de su sierra ingleteadora
combinada ha sido provistos para ayudarle a asegurar la
pieza de trabajo cuando se efectúen cortes; la porción de
la guía de inglete situada más lejos de la hoja es más larga
para proveer un apoyo vertical adicional.
La característica de deslizamiento hace que sea fácil quitar o
ajustar la posición de la guía, y permite la distancia del brazo
de la sierra cuando se hacen cortes en bisel o combinados.
Afloje el tornillo de la guía antes de intentar deslizar la guía
de ingletes. Una vez determinada la posición de la guía de
ingletes, apriete el tornillo de la guía para asegurar la guía
deslizable.
10 − Español
Page 79

CARACTERÍSTICAS
BOTÓN DEL SEGURO DEL HUSILLO
Vea la figura 5.
El botón del seguro del husillo sirve para asegurar el husillo
y impedir el giro de la hoja. Oprima y no suelte el botón del
seguro del husillo mientras instala, cambia o desmonta la hoja.
GATILLO DEL INTERRUPTOR
Vea la figura 5.
Para evitar el uso no autorizado de la sierra ingleteadora
combinada, desconéctela del suministro de corriente y
asegurar el interruptor en la posición de apagado. Para
asegurar el interruptor, coloque un candado (no viene incluido)
a través del agujero del gatillo del interruptor y asegúrese de
que el interruptor no pueda ser accionado. Si el interruptor
puede ser accionado aun habiendo instalado el candado,
se debe usar un candado con un diámetro de grillete mayor.
Guarde la llave del candado en otro lugar.
ORIFICIO PARA
EL CANDADO
BOTÓN DEL SEGURO
DEL HUSILLO
GATILLO DEL
INTERRUPTOR
CANDADO
GATILLO DEL
INTERRUPTOR
Fig. 5
11 − Español
Page 80

HERRAMIENTAS NECESARIAS
Se necesitan las siguientes herramientas (no vienen incluidas) para efectuar ajustes o instalar la hoja:
LLAVES DE COMBINACIÓN (2)
(10 mm, 12 mm)
ESCUADRA
ESCUADRA DE COMBINACIÓN
LISTA DE PIEZAS SUELTAS
Fig. 6
Vienen incluidos los siguientes artículos con la herramienta:
Saco captapolvo
Extensiones de la mesa (2)
SACO
CAPTAPOLVO
Prensa de trabajo
Manual del operador
EXTENSION DE
LA MESA
PRENSA DE
TRABAJO
EXTENSION DE
LA MESA
ADVERTENCIA:
El empleo de aditamentos o accesorios no enumerados arriba podría ser peligros y causar lesiones serias.
12 − Español
Fig. 7
Page 81

ARMADO
DESEMPAQUETADO
Este producto requiere armarse.
Levante cuidadosamente de la caja la sierra sujetándola
del mango de acarreo y de la base, y colóquela sobre una
superficie de trabajo a nivel.
ADVERTENCIA:
No utilice este producto si alguna pieza incluida en la lista
de piezas sueltas ya está ensamblada al producto cuando
lo desempaqueta. El fabricante no ensambla las piezas de
esta lista en el producto. Éstas deben ser instaladas por
el usuario. El uso de un producto que puede haber sido
ensamblado de forma inadecuada podría causar lesiones
personales graves.
E mba rc a mos l a s i e r r a co mp l et a me nt e a r m ad a, c o n e l b r a zo
de la misma asegurado en la posición inferior. Para liberar
el brazo de la sierra, empújelo hacia abajo por la manga en
“D”, corte la amarra y extraiga el pasador de seguridad.
Levante la sierra sujetándola del mango. La presión de la
mano debe permanecer en la manga en “D” para evitar un
levantamiento súbito del mismo al soltarse la amarra.
Inspeccione cuidadosamente la herramienta para
asegurarse de que no haya sufrido ninguna rotura o daño
durante el transporte.
No deseche el material de empaquetado sin haber
inspeccionado cuidadosamente este producto y haberla
utilizado satisfactoriamente.
La sierra viene ajustada desde la fábrica para realizar cortes
exactos. Después de armarla verifique la exactitud de la
misma. Si en el envío resultaron afectados los ajustes,
consulte los procedimientos específicos explicados en este
manual.
Si hay piezas dañadas o faltantes, le suplicamos llamar al
1-800-525-2579 for assistance.
ADVERTENCIA:
Si hay piezas dañadas o faltantes, no utilice esta producto
sin haber reemplazado todas las piezas. Usar este producto
con partes dañadas o faltantes puede causar lesiones serias
al operador.
ADVERTENCIA:
No intente modificar esta producto ni hacer accesorios
no recomendados para la misma. Cualquier alteración o
modificación constituye maltrato el cual puede causar una
condición peligrosa, y como consecuencia posibles lesiones
corporales serias.
ADVERTENCIA:
No conecte la unidad al suministro de corriente antes de
terminar de armarla. De lo contrario la unidad puede ponerse
en marcha accidentalmente, con el consiguiente riesgo de
lesiones serias.
ADVERTENCIA:
No encienda la sierra ingleteadora combinada sin revisar
para ver si hay interferencia entre la hoja y la guía de ingletes.
evitar lesiones serias o puede dañarse la hoja si toca la guía
de ingletes durante el funcionamiento de la sierra.
ADVERTENCIA:
Esta sierra puede volcarse si se suelta súbitamente la cabeza
de la misma y la sierra no está asegurada a una superficie
de trabajo. SIEMPRE asegure esta sierra a una superficie de
trabajo estable antes de usarla para evitar lesiones serias.
SEÑALE EL CENTRO
DE LOS AGUJEROS EN
ESTOS LUGARES
BASE
DE LA
SIERRA
SEÑALE EL CENTRO
DE LOS AGUJEROS EN
ESTOS LUGARES
SUPERFICIE
DE MONTAJE
Fig. 8
13 − Español
Page 82

ARMADO
AGUJEROS DE MONTAJE
Vea la figura 8.
ADVERTENCIA:
Antes de iniciar cualquier operación de corte, sujete con
prensa(s) o atornille la sierra ingleteadora al banco de
trabajo o pedestal para sierra ingleteadora aprobado. Si se
utiliza un pedestal para sierra ingleteadora, lea el manual
del operador y siga las instrucciones del pedestal. NUNCA
utilice la sierra ingleteadora en el piso o estando en cuclillas.
La inobservancia de esta advertencia puede causar lesiones
corporales serias.
La sierra ingleteadora combinada debe montarse en una
superficie de soporte firme, como un banco de trabajo. Hay
cuatro agujeros para perno en la base de la sierra para este
fin. Cada uno de los cuatro agujeros de montaje deben estar
atornillados firmemente con pernos de máquina de 7,9 mm
(5/16 pulg.), arandelas de seguridad y tuercas hexagonales (no
vienen incluidos). Los pernos deben ser la suficiente longitud
para dar acomodo a la base de la sierra, las arandelas de
seguridad, las tuercas hexagonales y el espesor del banco de
trabajo. Apriete firmemente los cuatro pernos.
En la figura 8 aparecen los agujeros para el montaje en un banco
de trabajo. Revise cuidadosamente el banco de trabajo después
de montar la unidad para asegurarse de que no ocurra ningún
durante el uso de la misma. Si el banco de trabajo se inclina,
desliza o camina, asegúrelo al piso antes de utilizar la unidad.
PROCEDIMIENTO DE TRABA Y DESTRABA EL
BRAZO DE LA SIERRA
Vea la figura 10.
Cuando bloquee y desbloquee el brazo de la sierra, no es
necesario aflojar la perilla de control de profundidad.
Para destrabar y levantar el brazo de la sierra:
Sujete firmemente el mango en “D” y presione hacia abajo
mientras tira de la pasador de seguridad hacia afuera,
separándola de la carcasa de la sierra.
Suelte la pasador de seguridad y levante lentamente el brazo
de la sierra.
PERILLA DE
CONTROL DE
PROFUNDIDAD
USO EL TOPE DE PROFUNDIDAD
Vea la figura 9.
Su uso limita el descenso de la hoja durante cortes de ranura
y demás tipos de corte no pasante.
Para usar el tope de profundidad:
Desconecte la sierra
Si la sierra está en posición de almacenamiento o transporte,
destrabe el brazo de la sierra.
Gire el tope de profundidad hacia la alojamiento del motor.
Con el extremo de la perilla de control de profundidad que
tocas el tope de profundidad, adjuste el perilla de control
de profundidad girando el tope de profundidad hasta que
la profundidad deseada del corte se alcance.
Un espaciador de madera de por lo menos 57,15 mm
(2-1/4 pulg.) debe ser colocado entre la pieza y la guía para
una profundidad constante de corte en la pieza de trabajo.
Use la prensa de trabajo para sujetar el espaciador y otra
prensa adecuada para sujetar la pieza de trabajo. Vea las
figuras 36 y 37.
Gire el tope de profundidad hacia el alojamiento del motor
para cortes normales no pasantes.
NOTA: El tope de profundidad debe empujarse hacia el
alojamiento del motor antes de bloquear/desbloquear el
brazo de la sierra.
TOPE DE
PROFUNDIDAD
Fig. 9
MANGO
EN “D”
PASADOR DE
SEGURIDAD
Fig. 10
14 − Español
Page 83

ARMADO
Para volver a trabar el brazo de la sierra:
Agarre firmemente el mango “D” y aplique presión hacia
abajo mientras, al mismo tiempo, empuja el pasador de
seguro hacia el alojamiento de la sierra.
Libere el pasador de seguro permitiendo que fije a la sierra
en su lugar.
SACO CAPTAPOLVO
Vea la figura 11.
Se suministra un saco captapolvo para utilizarse con la sierra
ingleteadora. Se acopla en la abertura de salida del aserrín,
en la parte posterior de la sierra.
NOTA: El orificio de escape acepta también 1-1/4 en. saco
captapolvo.
LLAVE DE LA HOJA
Vea la figura 12.
Esta sierra incluye una llave para la hoja. Un extremo de la
llave es un destornillador Phillips y el otro una llave hexagonal.
La llave hexagonal sirve para montar o desmontar la hoja
de corte y el extremo de destornillador Phillips sirve para
retirar o aflojar tornillos. En la parte posterior de la guía de
inglete, está ubicada el área de almacenamiento de la llave
de la hoja.
SACO
CAPTAPOLVO
ORIFICIO DE
ESCAPE
Fig. 11
PRENSA DE TRABAJO
Vea la figura 12.
ADVERTENCIA:
En algunas operaciones el conjunto de la prensa de
trabajo puede interferir en el movimiento del conjunto de
protección de la hoja. Siempre asegúrese de que no haya
interferencia en el movimiento de la protección de la hoja
antes de comenzar cualquier operación de corte, para
reducir el riesgo de lesiones corporales serias.
La prensa de trabajo ofrece mayor control al prensar la
pieza de trabajo contra la guía o contra la mesa de la sierra.
También evita que la pieza de trabajo avance hacia la hoja
de la sierra. Esto es muy útil al efectuar cortes a inglete
combinados. Según sea la operación de corte y el tamaño
de la pieza de trabajo, puede ser necesario usar una prensa
de mano (en forma de “C”) u otra abrazadera adecuada en
lugar de la prensa de trabajo para asegurar la pieza antes
de efectuar el corte.
Para instalar la prensa de trabajo:
Sitúe el eje de la prensa de trabajo en uno de los orificios
situados detrás de la guía de ingletes.
Gire la perilla de la prensa de trabajo para moverla hacia
arriba o abajo según sea necesario para asegurar la pieza
de trabajo.
LLAVE
DE HOJA
PRENSA DE
TRABAJO
PERILLA DE EJE
DE TRABAJO
BASE
15 − Español
Fig. 12
Page 84

ARMADO
EXTENSIONES DE LA MESA
Vea las figuras 13 a 15.
Se proporcionan extensiones de la mesa para los lados
izquierdo y derecho de la sierra.
Para asegurar las extensiones de la mesa:
Retire el tornillo del extremo de la extensión de la mesa.
Inserte los extremos de la extensión dentro de los orificios
de los costados de la base.
Vuelva a colocar el tornillo y ajuste para asegurar la
extensión en su lugar.
Repita para la otra extensión.
EXTENSIÓN
DE LA MESA
BASE
Fig. 14
EXTENSIÓN
DE LA MESA
BASE
Fig. 13
VISTA INFERIOR DE LA SIERRA
BASE
TORNILLO DE
EXTENSIÓN DE
LA MESA
Fig. 15
16 − Español
Page 85

ARMADO
PARA INSTALAR O REEMPLAZAR LA HOJA
Vea las figuras 16 y 17.
ADVERTENCIA:
La sierra tiene capacidad para hojas hasta de un diámetro de
305 mm (12 pulg.). Nunca utilice una hoja tan gruesa
que la arandela exterior de la hoja no se enganche en las
partes planas del husillo. Las hojas más grandes tocan
las protecciones de la hoja, y las más gruesas impiden
asegurarlas con el perno correspondiente en el husillo.
Cualquiera de estas dos situaciones puede producir un
accidente serio, con las consiguientes lesiones corporales
serias.
Desconecte la sierra.
Destornille el tornillo de la cubierta de la hoja. Levante la
protección inferior de la hoja y suba la tapa del perno de la
hoja y deje expuesto éste.
Oprima el botón del seguro del husillo y gire el perno de la
hoja hasta inmovilizar el husillo.
Con la llave de hoja suministrada de la hoja afloje el perno
de la misma y retírelo.
NOTA: El perno tiene rosca izquierda. Gire hacia la derecha
el perno de la hoja para aflojarlo.
Retire la arandela exterior de la hoja. No retire la arandela
interior de la hoja.
Unte una gota de aceite en la arandela interior y en la
arandela exterior de la hoja, donde tocan ésta.
ADVERTENCIA:
Si la arandela interior de la hoja ha sido retirada, vuelva a
colocarla antes de instalar la hoja en el husillo. Si no lo hace
podría producirse un accidente ya que la hoja no se apretaría
correctamente.
Acomode la hoja de la sierra dentro de la protección inferior,
y móntela en el hombro de la arandela interior. Los dientes
de la sierra apuntan hacia abajo en la parte delantera de la
sierra, como se muestra en la figura 17.
Retire la arandela exterior de la hoja. Las dos partes planas
en “D” de la hoja se alinean con las partes planas del husillo.
Oprima el botón del seguro del husillo y vuelva a colocar el
perno de la hoja.
NOTA: El perno tiene rosca izquierda. Gire hacia la izquierda
el perno de la hoja para apretarlo.
PRECAUCIÓN:
Siempre instale la hoja con los dientes de la misma y la flecha
impresa en el costado de la hoja apuntando hacia abajo
en la parte frontal de la sierra. El sentido de giro de la hoja
también está impreso en forma de flecha en la protección
superior de la hoja.
BOTÓN DEL SEGURO
DEL HUSILLO
NOTA: ANTES DE USO,
VUELVA A COLOCAR LOS
TORNILLO Y APRIÉTELO
FIRMEMENTE PARA
PREVENIR EL MOVIMIENTO
DE PROTECCIÓN
TORNILLO DE LA
CUBIERTA DE LA
TAPA DEL PERNO
DE LA HOJA
ARANDELA
EXTERIOR
DE LA HOJA CON
DOS PARTES
PLANAS EN “D”
PARA
AFLOJAR
PERNO DE
LA HOJA
PARA
APRETAR
ARANDELA EXTERIOR
DE LA HOJA CON DOS
PARTES PLANAS EN
“D”
PERNO DE
LA HOJA
HOJA
HOJA
ARANDELA INTERIOR DE LA
HOJA CON DOS PARTES
PLANAS EN “D”
PROTECCIÓN
INFERIOR DE LA
HOJA
PLANA(S) DEL
LA HOJA CON
PLANAS EN “D”
HOJA
Fig. 16
PARTE(S)
HUSILLO
ARANDELA
INTERIOR DE
DOS PARTES
Fig. 17
17 − Español
Page 86

ARMADO
LASER RADIATION AVOID DIRECT EYE EXPOSURE
CLASS IIIa LASER PRODUCT
MAXIMUM OUTPUT: <5mW WAVELENGTH: 635-660nm
• To reduce the risk of injury, user must read and understand the
operator’s manual before using the miter saw.
• Wear eye protection.
• Keep hands out of path of saw blade.
• Do not operate saw without guards in place.
• Do not perform any operation freehand.
• Never reach around the saw blade.
• Turn off tool and wait for saw blade to stop before raising saw
arm, moving workpiece, or changing settings.
• Disconnect the saw from the power source before changing blade
or servicing.
Complies with 21 CFR
Parts 1040.10 & 1040.11
RYLD
Fixer gâchette avant
làser est réglagé. EVITER
L’EXPOSITION: Rayonnement laser émise de cet orifice.
Asegure gatillo antes de ajuste
de laser. EVITE LA EXPOSICIÔN:
Radiación laser se emite por esta abertura.
Lock trigger prior to adjusting
laser. AVOID EXPOSURE:
Laser radiation is emitted from this aperture.
Apriete firmemente el perno de la hoja.
Vuelva a colocar la protección inferior y la tapa del perno
de la hoja.
Aprieta firmemente el tornillo de la cubierta de la hoja.
Levante y baje el cabezal de la sierra y asegúrese de que el
protector de la hoja inferior funcione correctamente.
ADVERTENCIA:
Asegúrese de que el botón del seguro del husillo no esté
oprimido antes de volver a conectar la sierra al suministro
de corriente. Nunca oprima el botón del seguro del husillo
cuando esté girando la hoja.
PELIGRO:
Radiación láser. Evite todo contacto directo de los ojos con
la fuente de luz.
INTERRUPTOR
DE GUÍA DE
LÁSER
ADVERTENCIA:
Todo control, ajuste o procedimiento diferente de los
especificados aquí, puede causar una exposición peligrosa
a la radiación.
ALINEACIÓN DE LA LÍNEA DE LA GUÍA LÁSER
Vea la figura 18.
Para asegurar el interruptor, coloque un candado (no viene
incluido) a través del agujero del gatillo del interruptor y en fin
el grillete.
Trace una línea en la pieza de trabajo. Cuándo el interruptor
de guía de láser lo es prendido, la guía láser genera una línea
roja en la superficie de trabajo. La línea le permite ver la marca
que usted puso y la propia línea al mismo tiempo, lo cual le
ayuda a alinear la marca para lograr un corte más preciso en
la pieza de trabajo.
Alinee la línea láser y la marca con la hoja estando en la posición
superior. Una vez que estén alineadas ambas líneas, no mueva
la pieza de trabajo.
Desmontaje el candado y conecte la sierra en el suministro
de corriente. Realice varios cortes de prueba en materiales
de diferentes tipos y espesores. Repita el encima de pasos
necesitó.
Remoción de la marca puesta por usted:
Acomode la línea láser cerca del borde izquierdo de la marca de
usted sobre la superficie de trabajo con el fin de retirar la marca.
Para cortar la marca:
Acomode la línea láser cerca o sobre la marca de usted en la
superficie de trabajo con el fin de cortar la marca.
Para dejar la marca:
Acomode la línea láser cerca del borde derecho de la marca de
usted sobre la superficie de trabajo con el fin de dejar la marca.
LÍNEA ROJA
SEGMENTADA
Fig. 18
Después de familiarizarse con el uso de la guía láser, podrá
retirar, cortar o dejar la marca de usted en la superficie de
trabajo. Con la práctica aprenderá la posición correcta para
alinear la línea láser con la marca de usted.
18 − Español
Page 87

ARMADO
EXTRACCIÓN / REEMPLAZO DE LA PLACA DE
GARGANTA
Vea la figura 19.
ADVERTENCIA:
La placa de la garganta debe estar a debajo de la mesa de
ingletes. Si la placa de la garganta está demasiado alta o
demasiado baja, la pieza de trabajo puede engancharse
en los bordes desiguales y resultar en atoramientos, lo
cual podría causar lesiones corporales serias.
Nunca utilice la sierra sin la placa de garganta instalada.
Extracción / reemplazo:
Desconecte la sierra.
Retirer los tornillos que sujetan la placa de la garganta.
Levante de la placa de garganta para de la sierra.
Para volver a instalar la placa de la garganta, alinee los
orificios de la misma con los de la base de la sierra.
Vuelva a apretar los tornillos, teniendo cuidado de no
hacerlo excesivamente, lo cual podría combar o doblar
la placa de garganta.
PARA AJUSTAR PIED DE SUPPORT
Vea la figura 19.
Gire el pie de soporte hacia la derecha o izquierda, según
la cantidad de soporte que necesite para realizar cortes
deslizantes.
NOTA: En muchas de las ilustraciones de este manual se
muestran sólo porciones de la sierra ingleteadora compuesta.
Se hace así deliberadamente para mostrar con claridad lo que
intentamos comunicar en las ilustraciones. Nunca utilice la
sierra sin todas las protecciones montadas en su lugar
y en buen estado de funcionamiento.
ESCUADRADO DE LA HOJA CON LA MESA DE
INGLETES
Vea las figuras 20 a 26.
Desconecte la sierra.
Tire del brazo de la sierra completamente hacia abajo y
enganche el pasador de seguridad para asegurar el brazo
en la posición de traslado.
Afloje la perilla de fijación de inglete aproximadamente
media vuelta y apriete la palanca de detención de afloje.
Gire la mesa de ingletes hasta que el puntero del brazo
de control quede colocado en la marca de 0°.
Suelte la palanca de detención de afloje y asegúrese
de que el brazo de control esté asentado en la muesca
positiva.
Ajuste la perilla de fijación de inglete para fijar la mesa
de ingletes.
GUÍA DE
INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
PLACA DE LA
GARGANTA
PIED DE
SUPPORT
ESCUADRA
MESA DE
INGLETES
VIEW OF BLADE SQUARE WITH FENCE
MANIJA DE FIJACIÓN
DE INGLETE
Fig. 19
HOJA
Fig. 20
19 − Español
Page 88

ARMADO
Afloje la perilla de fijación de bisel a 0° (la hoja puesta a
90° con la mesa de ingletes). Apriete la perilla de fijación
de bisel.
Coloque horizontalmente una escuadra sobre la mesa
de ingletes. Coloque una pata de la escuadra contra la
guía. Deslice la otra pata de la escuadra para colocarla
contra la parte plana de la hoja de la sierra.
NOTA: Asegúrese de que la escuadra toque la parte plana
de la hoja de la sierra, no los dientes.
El borde de la escuadra y la hoja de la sierra deben estar
paralelas, como se muestra en la figure 20.
HOJA
Si el borde delantero o trasero de la hoja de la sierra forma
un ángulo con respecto a la escuadra, como se muestra
en las figuras 21 y 22, se requieren ajustes.
Afloje el tornillo de ajuste de la guía, empuje la guía
deslizante aproximadamente 25,4 mm (1 pulg.) hacia la
derecha para pasar el tornillo puesto, luego remueva la
guía deslizante de las esquinas unidas de la guía.
Utilizando la llave de hoja suministrada, afloje los tornillos
de cabeza hueca que aseguran la guía de ingletes a la
mesa de ingletes.
TORNILLO
DE FIJACIÓN
GUÍA DE
INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
VISTA DE LA HOJA FUERA DE ESCUADRA
GUÍA DE
INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
MESA DE
INGLETES
CON LA GUÍA; SE REQUIEREN AJUSTES
MESA DE
INGLETES
ESCUADRA
ESCUADRA
Fig. 21
HOJA
TORNILLO DE
AJUSTE DE LA
GUÍA
TORNILLO(S) DE
CABEZA HUECA
GUÍA DE
INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
Fig. 23
TORNILLO(S) DE
CABEZA HUECA
VISTA DE LA HOJA FUERA DE ESCUADRA CON LA GUÍA;
SE REQUIEREN AJUSTES
Fig. 22
GUÍA DE
INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
Fig. 24
20 − Español
Page 89

ARMADO
Gire la guía hacia la izquierda o hacia la derecha hasta
que la hoja esté en forma paralela a la escuadra.
Vuelva a apretar los tornillos firmemente y revise de nuevo
la alineación de la hoja con la guía.
La sierra ofrece varios indicadores de escala. Después de
efectuar los ajustes de escuadrado, puede ser necesario
aflojar los tornillos de los indicadores y reajustarlos a cero.
Vea las figuras 25 et 26.
ESCUADRADO DE LA HOJA CON LA MESA DE
INGLETES
Vea las figuras 27 a 29.
Desconecte la sierra.
Tire del brazo de la sierra completamente hacia abajo y
enganche el pasador de seguridad para asegurar el brazo
en la posición de traslado.
Afloje la perilla de fijación de inglete aproximadamente
media vuelta y apriete la palanca de detención de afloje.
Gire la mesa de ingletes hasta que el indicador quede en
la marca de 0°
Suelte la palanca de detención de afloje, y luego ajuste la
perilla de fijación de inglete para fijar la mesa de ingletes.
Afloje la perilla de fijación de bisel a 0° (la hoja puesta a
90° con la mesa de ingletes). Apriete la perilla de fijación
de bisel.
Coloque una escuadra de combinación contra la mesa
de ingletes y parte plana de la hoja de la sierra.
NOTA: Asegúrese de que la escuadra toque la parte plana
de la hoja de la sierra, no los dientes.
Gire la hoja con la mano y revise la alineación de la hoja
con la mesa en varios puntos.
El borde de la escuadra y la hoja de la sierra deben estar
paralelas, como se muestra en la figura 27.
ESCALA DE
BISELES
INDICADOR
DE LA ESCALA
TORNILLO DEL
INDICADOR
PERILLA DE
FIJACIÓN DEL
BISEL
TORNILLO DEL
INDICADOR
Fig. 25
INDICADOR
DE LA ESCALA
ESCALA DE
INGLETES
Fig. 26
INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
21 − Español
GUÍA DE
HOJA
MESA DE
INGLETES
ESCUADRA DE
COMBINACIÓN
MANIJA DE
FIJACIÓN DE INGLETE
VISTA CORRECTA DE LA HOJA
A ESCUADRA CON LA MESA DE INGLETES
Fig. 27
Page 90

ARMADO
Si la parte superior o inferior de la hoja de la sierra forma
un ángulo con respecto a la escuadra, como se muestra
en las figuras 28 y 29, se requieren ajustes.
Afloje la perilla de seguridad de bisel.
Ajuste el tornillo de ajuste del tope para alinear la hoja
con la escuadra. Vea el apartado Ajuste de los topes
en la sección Ajuste.
Reajuste la perilla de seguridad de bisel. Vuelva a
comprobar la alineación de la hoja a la mesa.
NOTA: El procedimiento descrito arriba puede aplicarse
para revisar el escuadrado de la hoja con la mesa de
ingletes a 0° y a 45°.
La sierra ofrece varios indicadores de escala. Después de
efectuar los ajustes de escuadrado, puede ser necesario
aflojar los tornillos de los indicadores y reajustarlos a cero.
Vea las figuras 25 y 26.
HOJA
MESA DE
GUÍA DE
INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
VISTA DE LA HOJA FUERA DE ESCUADRA CON LA MESA DE
INGLETES; SE REQUIEREN AJUSTES
ESCUADRA DE
COMBINACIÓN
INGLETES
Fig. 28
HOJA
MESA DE
GUÍA DE
INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
VISTA DE LA HOJA FUERA DE ESCUADRA CON LA MESA DE
INGLETES; SE REQUIEREN AJUSTES
ESCUADRA DE
COMBINACIÓN
INGLETES
Fig. 29
22 − Español
Page 91

FUNCIONAMIENTO
ADVERTENCIA:
No permita que su familarización con las herramientas lo
vuelva descuidado. Tenga presente que un descuido de
un instante es suficiente para causar una lesión grave.
ADVERTENCIA:
Siempre póngase protección ocular con la marca de
cumplimiento de la norma ANSI Z87.1. Si no cumple esta
advertencia, los objetos que salen despedidos pueden
producirle lesiones serias en los ojos.
ADVERTENCIA:
No utilice ningún aditamento o accesorio no recomendado
por el fabricante de esta herramienta. El empleo de
aditamentos o accesorios no recomendandos podría
causar lesiones serias.
APPLICATIONS
Esta herramienta puede emplearse para los fines siguientes:
Cortes transversales en madera y plástico (no corte
artículos de metal, cerámica o mampostería.)
Cortes transversales a inglete, de uniones, etc., para
marcos de cuadros, molduras, marcos de puertas y
ensambladuras finas
Cortes a bisel y cortes compuestos
Cortes transversales de piezas anchas de trabajo
NOTA: La hoja suministrada es adecuada para la mayoría de
las operaciones de corte, pero para cortes de ensambladuras
finas y en plástico, utilice una de las hojas de accesorio a
la venta en la tienda de venta de productos Ryobi de su
preferencia.
ADVERTENCIA:
ADVERTENCIA:
Para evitar lesiones corporales serias, siempre apriete
la manija de fijación de inglete y perilla de fijación del
bisel antes de efectuar un corte. De lo contrario podría
producirse un movimiento de la mesa de ingletes o
cabezal de la sierra mientras se efectúa el corte.
ADVERTENCIA:
Para evitar lesiones corporales serias, mantenga las
manos fuera de la zona de no acercar las manos; por
lo menos a 76 mm (3 pulg.) de la hoja. Nunca efectúe a
pulso ninguna operación de corte (sin asegurar la pieza
de trabajo contra la guía). La hoja podría coger la pieza
de trabajo si se resbala o tuerce.
AVISO:
No encienda la sierra ingleteadora compuesta sin
comprobar que no haya interferencia entre la hoja y la
guía de ingletes. La hoja puede dañarse si toca la guía de
ingletes durante el funcionamiento de la sierra.
PROCEDIMIENTO DE CORTE CON LA SIERRA
INGLETEADORA COMPUESTA
ADVERTENCIA:
Al usar la prensa de trabajo, prensa en c, u otra prensa
adecuada para asegurar la pieza, sujete ésta sólo en un
lado de la hoja. La pieza de trabajo debe quedar libre
en un lado de la hoja para evitar que ésta se atore en la
pieza de trabajo. El atoramiento de la hoja en la pieza de
trabajo causa un agarrotamiento y un contragolpe del
motor. Esta situación podría causar un accidente, y como
consecuencia posibles lesiones serias.
Antes de iniciar cualquier operación de corte, sujete
con prensa(s) o atornille en el banco de trabajo la
sierra ingleteadora combinada. Nunca utilice la sierra
ingleteadora en el piso o estando en cuclillas. La
inobservancia de esta advertencia puede causar lesiones
serias.
23 − Español
ADVERTENCIA:
NUNCA mueva el ajuste de la pieza de trabajo ni marca
a algún ángulo cortante mientras el vio corre y la hoja
gira. Cualquier tropiezo puede tener como resultado el
contacto con la hoja que causa lesiones serias.
ADVERTENCIA:
No intente cortar piezas estrechas usando la función
de deslizamiento. La inobservancia de esta advertencia
podría causar lesiones graves.
Page 92

FUNCIONAMIENTO
PARA REALIZAR CORTES NO DESLIZANTES
ADVERTENCIA:
Apriete firmemente la perilla de fijación de la guía telescópica
para realizar cortes no deslizantes. Si no se aprieta esta perilla,
podría moverse el cabezal de la sierra durante la tarea de corte.
PARA REALIZAR CORTES DE INGLETE /
TRANSVERSALES
Vea las figuras 30 y 31.
Los cortes transversales se efectúan cortando a través de la veta
de la pieza de trabajo. Un corte transversal recto se efectúa con
la mesa de ingletes ajustada en la posición de 0°. Los cortes de
inglete se efectúan con la mesa de ingletes puesta en un ángulo
diferente de 0°.
Suba el brazo de la sierra hasta su altura máxima.
Afloje la perilla de fijación de inglete aproximadamente media
vuelta y apriete la palanca de detención de afloje.
Gire el brazo de control hasta no alinear el indicador con el
ángulo deseado de la escala de ingletes.
Suelte la palanca de detención de afloje, y luego ajuste la perilla
de fijación de inglete para fijar la mesa de ingletes.
NOTA: Puede ubicar rápidamente 0°, 15°, 22-1/2°, 31,6°, y 45°
a la izquierda o a la derecha soltando el botón de detención de
afloje a medida que rota el brazo de control. El brazo de control
se asentará en una de las muescas de los topes, ubicados en
la base de la mesa de ingletes.
Coloque la pieza de trabajo plana en la mesa de inglete con un
borde firmemente contra la guía. Si la madera está combada,
coloque el lado convexo contra la guía. Si se coloca el borde
cóncavo de una madera contra la guía, la madera puede
romperse en la hoja al final de un corte, dejando atascada la
hoja. Vea las figuras 42 y 43.
Cuando corte pedazos largos de madera o moldura, apoye
el extremo opuesto del material con un pedestal con rodillos
o con una superficie de trabajo que esté al mismo nivel de la
mesa de la sierra. Vea la figura 35.
Deslice el cabezal de la sierra hacia su posición más trasera y
ajuste la perilla de fijación de la corredera en forma segura.
Alinee la línea de corte de la pieza de trabajo con el borde de
la hoja de la sierra o línea de láser.
Sujete firmemente la pieza con una mano y colóquela contra
la guía. Cuando sea posible, use el sujetamadera o la prensa
en C para asegurar la pieza de trabajo.
Antes de encender la sierra, efectúe una simulación de la
tarea de corte, sólo para asegurarse de que no suceda ningún
problema durante la tarea de corte real.
Sujete firmemente el mango de la sierra. Oprima el gatillo.
Deje transcurrir varios segundos para que la hoja alcance su
velocidad máxima.
Baje lentamente la hoja de la sierra haciendo que se introduzca
y traspase la pieza de trabajo. Use la prensa de trabajo, prensa
en c, u otra prensa adecuada para asegurar la pieza cuando
sea posible.
Suelte el gatillo del interruptor y espere a que la hoja de la sierra
deje de girar antes de levantarla de la pieza de trabajo y retirar
la pieza de trabajo de la mesa de ingletes.
CORTE TRANSVERSAL
PRENSA DE
TRABAJO
Fig. 30
COUPE D’ONGLET
PRENSA DE
TRABAJO
Fig. 31
24 − Español
Page 93

FUNCIONAMIENTO
PARA CORTAR A BISEL
Vea la figura 32.
Un corte en bisel se efectúa cortando a través de la fibra de
la pieza de trabajo con la hoja en ángulo con dicha pieza. Un
corte en bisel recto se efectúa con la mesa de ingletes en la
posición de cero grados y la hoja a un ángulo entre 0° y 45°.
NOTA: Puede ser necesario ajustar o extraer la guía de ingletes
deslizante.
Extraiga el pasador de seguridad y levante el brazo de la
sierra a su máxima altura.
Afloje la perilla de fijación de inglete aproximadamente media
vuelta y apriete la palanca de detención de afloje.
Gire el brazo de control hasta no alinear el indicador con el
ángulo deseado de la escala de ingletes.
Suelte la palanca de detención de afloje, y luego ajuste la
perilla de fijación de inglete para fijar la mesa de ingletes.
NOTA: Puede ubicar rápidamente 0°, 15°, 22-1/2°, 31,6°,
y 45° a la izquierda o a la derecha soltando la palanca de
detención de afloje a medida que rota el brazo de control.
El brazo de control se asentará en una de las muescas de
los topes, ubicados en la base de la mesa de ingletes.
Afloje la perilla de fijación de bisel y mueva el brazo de la
sierra hacia la izquierda al ángulo de bisel deseado.
Los ángulos de bisel pueden fijarse de 0° a 45°.
Alinee el indicador con el ángulo deseado.
Una vez puesto el brazo de la sierra en el ángulo deseado,
apriete firmemente la perilla de fijación de bisel.
Coloque la pieza de trabajo horizontal en la mesa de ingletes,
con un borde firme contra la guía. Si está distorsionada la
tabla, coloque el lado convexo contra la guía. Si se coloca
el canto cóncavo de la tabla contra la guía, la tabla podría
venirse sobre la hoja al final del corte, y la frenaría. Vea las
figuras 42 y 43.
Al cortar tablas o molduras largas, apoye el extremo opuesto
del material sobre un soporte de rodillo o con una superficie
de trabajo a nivel con la mesa de la sierra. Vea la figura 35.
Deslice el cabezal de la sierra hacia su posición más trasera
y ajuste la perilla de fijación de la corredera en forma segura.
Alinee la línea de corte de la pieza de trabajo con el borde
de la hoja de la sierra o línea de láser.
Sujete firmemente la pieza con una mano y asegúrela contra
la guía. Use la prensa de trabajo, prensa en c, u otra prensa
adecuada para asegurar la pieza cuando sea posible.
Antes de encender la sierra, efectúe una simulación de la
operación de corte, sólo para asegurarse de que no suceda
ningún problema durante la operación de corte real.
Sujete firmemente el mango de la sierra y oprima el gatillo
del interruptor. Permita transcurrir varios segundos para que
la hoja alcance su velocidad máxima.
Baje lentamente la hoja de la sierra hacia la pieza de trabajo
y corte ésta.
Suelte el gatillo del interruptor y permita que se cese de
girar la hoja de la sierra antes de levantarla de la pieza de
trabajo. Espere hasta que el freno eléctrico detenga la hoja
antes de retirar la pieza de trabajo de la sierra ingleteadora.
CORTE EN BISEL
PRENSA DE
TRABAJO
Fig. 32
PARA EFECTUAR UN CORTE A INGLETE
COMBINADO
Vea las figuras 33 y 34.
Un corte en bisel combinado es un corte efectuado a un ángulo
de inglete y a un ángulo de bisel al mismo tiempo. Este tipo de
corte se usa para elaborar marcos de cuadros, cortar molduras,
elaborar cajas con lados inclinados y para ciertos cortes para
entramado de techos.
Para efectuar este tipo de corte, el brazo de control de la
mesa de ingletes debe girarse al ángulo correcto y el brazo de
la sierra debe inclinarse al ángulo de bisel correcto. Siempre
debe tenerse cuidado al preparar la unidad para cortes a inglete
combinados debido a la interacción existente entre los ajustes
de los dos ángulos.
El ajuste de los ángulos de inglete y de bisel son interdependientes
entre sí. Cada vez que se ajusta el ángulo de inglete se cambia
el efecto en el ángulo de bisel. También, cada vez que se ajusta
el ángulo de bisel se cambia el efecto en el ángulo de inglete.
Puede tomarse varios ajustes obtener el corte deseado. El
ajuste del primer ángulo debe revisarse después de ajustarse
el segundo, puesto que el ajuste del segundo afecta el primero.
Una vez obtenidos los dos ajustes correctos para un corte en
particular, siempre efectúe un corte de prueba en material de
desecho antes de efectuar un corte final en material bueno.
NOTA: Puede ser necesario ajustar o extraer la guía de ingletes
deslizante.
Extraiga el pasador de seguridad y levante el brazo de la
sierra a su máxima altura.
Afloje la perilla de fijación de inglete aproximadamente media
vuelta y apriete la palanca de detención de afloje.
25 − Español
Page 94

FUNCIONAMIENTO
Gire el brazo de control hasta no alinear el indicador con el
ángulo deseado de la escala de ingletes.
Suelte la palanca de detención de afloje, y luego ajuste la
perilla de fijación de inglete para fijar la mesa de ingletes.
Afloje la perilla de fijación de bisel y mueva el brazo de la
sierra hacia la izquierda al ángulo de bisel deseado.
Los ángulos de bisel pueden fijarse de 0° a 45°.
Una vez puesto el brazo de la sierra en el ángulo deseado,
apriete firmemente la perilla de fijación de bisel.
Vuelva a revisar el ajuste del ángulo de inglete. Efectúe un
corte de prueba en material de desecho.
Coloque la pieza de trabajo horizontal en la mesa de ingletes,
con un borde firme contra la guía. Si está distorsionada la
tabla, coloque el lado convexo contra la guía. Si se el canto
cóncavo de la tabla se viniera sobre la hoja al final del corte,
la atoraría. Vea las figuras 42 y 43.
Al cortar tablas o molduras largas, apoye el extremo opuesto
del material sobre un soporte de rodillo o con una superficie
de trabajo a nivel con la mesa de la sierra. Vea la figura 35.
Deslice el cabezal de la sierra hacia su posición más trasera
y ajuste la perilla de fijación de la corredera en forma segura.
Alinee la línea de corte de la pieza de trabajo con el borde
de la hoja de la sierra o línea de láser.
Sujete firmemente la pieza con una mano y asegúrela contra
la guía. Use la prensa de trabajo, prensa en C, u otra prensa
adecuada para asegurar la pieza cuando sea posible.
Antes de encender la sierra, efectúe una simulación de la
operación de corte, sólo para asegurarse de que no suceda
ningún problema durante la operación de corte real.
Sujete firmemente el mango de la sierra y oprima el gatillo
del interruptor. Permita transcurrir varios segundos para que
la hoja alcance su velocidad máxima.
Baje lentamente la hoja de la sierra hacia la pieza de trabajo
y corte ésta.
Suelte el gatillo del interruptor y permita que se cese de
girar la hoja de la sierra antes de levantarla de la pieza de
trabajo. Espere hasta que el freno eléctrico detenga la hoja
antes de retirar la pieza de trabajo de la sierra ingleteadora.
CORTE EN BISEL COMBINADO
PRENSA EN C
Fig. 33
26 − Español
CORTE A INGLETE COMBINADO DE 45° X 45°
Fig. 34
Page 95

FUNCIONAMIENTO
PARA APOYAR LAS PIEZAS DE TRABAJO
LARGAS
Vea la figura 35.
Las piezas de trabajo largas necesitan soportes extra. Los
soportes base con ruedas, o superficie de trabajo nivelada
con la sierra de mesa deben colocarse a lo largo de la pieza
de trabajo de manera que no se pandee. El soporte debe
permitir que la pieza permanezca horizontal en la base de la
sierra y la mesa de trabajo durante el corte. Use la prensa de
trabajo, prensa en C, u otra prensa adecuada para asegurar
la pieza cuando sea posible.
ADVERTENCIA:
Nunca realice cortes tirando de la sierra hacia usted, ya
que esto podría hacer que la hoja se montara sobre la
pieza de trabajo, viniéndose hacia usted. La inobservancia
de esta advertencia podría causar lesiones graves.
PARA HACER CORTES POR DESLIZAMIENTO
Vea las figuras 36 y 37.
La función de deslizamiento le permite cortar piezas de
trabajo de 342,9 mm (13-1/2 pulg.) de ancho por 38,1 mm
(1-1/2 pulg.) de grosor o 139,7 mm (5-1/2 pulg.) de ancho
por 89 mm (3-1/2 pulg.) de grosor. Con la sierra apagada, tire
del brazo de la sierra hacia adelante. Encienda la sierra (deje
que la hoja alcance la velocidad máxima) y a continuación
presione la hoja hacia abajo y sobre la pieza de trabajo, y
seguidamente presiónela hacia la parte trasera de la sierra
para realizar el corte. Los cortes se realizan: presionando
la hoja de la sierra en dirección opuesta a la de su cuerpo
y hacia la escala de biseles situada en la parte trasera de la
sierra, parando al alcanzar plenamente la posición posterior
después de cada cada corte. Cuando la sierra este en marcha
(encendida) NUNCA tire de la hoja de la sierra hacia usted
ni hacia la parte delantera de la sierra.
Suba el brazo de la sierra hasta su altura máxima.
Coloque la pieza de trabajo horizontal en la mesa de
ingletes, con un canto firmemente apoyado contra la
guía. Si la tabla está doblada, coloque el canto convexo
contra la guía. Si se coloca el canto cóncavo de la tabla
contra la guía, la tabla podría venirse sobre la hoja al final
del corte, atascándola. Vea las figuras 42 y 43.
Al cortar tablas o molduras largas, apoye el extremo
opuesto del material sobre un soporte de rodillo o sobre
una superficie de trabajo a nivel con la mesa de la sierra.
Vea la figura 35.
Alinee la línea de corte de la pieza de trabajo con el borde
de la hoja de la sierra o línea de láser.
Afloje la perilla de fijación de la corredera girándola en
sentido antihorario.
Sujete firmemente la pieza con una mano y asegúrela
contra la guía. Use la prensa de trabajo, prensa en C, u
otra prensa adecuada para asegurar la pieza cuando sea
posible.
PIEZA DE
TRABAJO
LARGA
SOPORTES DE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO
CORTE POR DESLIZAMIENTO
PERILLA DE FIJACIÓN
DE LA CORREDERA
DESLIZAR EL BRAZO DE LA SIERRA
HACIA DELANTE Y, SEGUIDAMENTE,
PRESIONAR HACIA ABAJO
Fig. 35
Fig. 36
27 − Español
Page 96

FUNCIONAMIENTO
Antes de encender la sierra, efectúe una simulación de la
tarea de corte, sólo para asegurarse de que no suceda
ningún problema durante la tarea de corte real.
Con la sierra apagada, sujete firmemente el mango de
la sierra y tire de ella hacia delante hasta que el eje de
la hoja (centro de la hoja de la sierra) haya sobrepasado
la parte delantera de la pieza de trabajo o hasta que la
sierra esté completamente extendida.
Oprima el gatillo. Deje transcurrir varios segundos para
que la hoja alcance su velocidad máxima.
Baje lentamente la hoja de la sierra para que se introduzca
y atraviese el canto delantero de la pieza del trabajo.
Presione el mango de la sierra en dirección contraria a
la de su cuerpo, y hacia la escala de biseles situada en
la parte trasera de la sierra.
Suelte el gatillo del interruptor y espere a que la hoja de
la sierra deje de girar antes de levantarla de la pieza de
trabajo y retirar la pieza de trabajo de la mesa de ingletes.
NOTA: Los cortes transversales se efectúan cortando a través
de la veta de la pieza de trabajo. Un corte transversal recto
se efectúa con la mesa de ingletes ajustada en la posición
de 0°. Los cortes de inglete se efectúan con la mesa de
ingletes puesta en un ángulo diferente de 0°.
CORTE POR DESLIZAMIENTO
PRESIONE HACIA
ATRÁS
Fig. 37
FORMA DE HACER UNA GUÍA AUXILIAR
Vea la figura 38.
Puede ser útil el uso de una guía de ingletes de mayor grosor
(guía auxiliar) para ciertos cortes inusuales, debido al tamaño
y la posición de la pieza de trabajo. Los orificios que trae la
guía de ingletes son exclusivamente para este propósito.
Los orificios de la guía de ingletes se utilizan para sujetar la
guía auxiliar, la cual se elabora con dos piezas de madera
de 13 mm (1/2 pulg.) de grosor por 89 mm (3-1/2 pulg.) de
alto y 254 mm (10 pulg.) de largo.
NOTA: La guía auxiliar sólo se puede utilizar cuando el ángulo
del bisel está ajustado a 0°. Al realizar un corte en bisel, la
guía auxiliar DEBE extraerse.
Para conectar la guía auxiliar a la sierra:
Coloque un pedazo de madera contra las esquinas unidas
de la guía y alinee con el borde izquierdo de las esquinas
unidas de la mesa y marque la posición de los orificio
desde detrás de la guía, utilizando un lápiz.
Haga orificios a través de la madera y avellánelos en la
parte delantera de la pieza de madera.
Asegure la madera a la guía de ingletes con tornillos de
cabeza plana.
Haga un corte completo de 45° de las esquina izquierda
a través del lado izquierdo de la guía auxiliar.
NOTA: Compruebe que la guía a auxiliar no interfiera
con el protector inferior de la hoja. Corrija cualquier
interferencia antes de proceder.
Repita estos pasos con la segunda tabla alineándola con
el lado derecho de las esquinas unidas de la mesa.
GUÍA
AUXILIAR
ALINEE LA TABLA CON
EL BORDE DE LAS
ESQUINAS UNIDAS DE
LA MESA
Fig. 38
28 − Español
Page 97

FUNCIONAMIENTO
CÓMO EFECTUAR CORTES A INGLETE COMBINADOS
Como ayuda para realizar los ajustes correctos, se suministra la siguiente tabla de ángulos combinados. Puesto que los cortes combinados
son los más difíciles de obtener, deben efectuarse cortes de prueba en material de desecho, así como una gran cantidad de reflexión y
planeación, antes de efectuar el corte final.
INCLINACIÓN
DEL LADO
0°
5°
10°
15°
20°
25°
30°
35°
40°
45°
50°
55°
60°
65°
70°
75°
80°
85°
90°
4
M- 45,00°
B- 0,00°
M- 44,89°
B- 3,53°
M- 44,56°
B- 7,05°
M- 44,01°
B- 10,55°
M- 43,22°
B- 14,00°
M- 42,19°
B- 17,39°
M- 40,89°
B- 20,70°
M- 39,32°
B- 23,93°
M- 37,45°
B- 27,03°
M- 35,26°
B- 30,00°
M- 32,73°
B- 32,80°
M- 29,84°
B- 35,40°
M- 26,57°
B- 37,76°
M- 22,91°
B- 39,86°
M- 18,88°
B- 41,64°
M- 14,51°
B- 43,08°
M- 9,85°
B- 44,14°
M- 4,98°
B- 44,78°
M- 0,00°
B- 45,00°
5
M- 36,00°
B- 0,00°
M- 35,90°
B- 2,94°
M- 35,58°
B- 5,86°
M- 35,06°
B- 8,75°
M- 34,32°
B- 11,60°
M- 33,36°
B- 14,38°
M- 32,18°
B- 17,09°
M- 30,76°
B- 19,70°
M- 29,10°
B- 22,20°
M- 27,19°
B- 24,56°
M- 25,03°
B- 26,76°
M- 22,62°
B- 28,78°
M- 19,96°
B- 30,60°
M- 17,07°
B- 32,19°
M- 13,95°
B- 33,53°
M- 10,65°
B- 34,59°
M- 7,19°
B- 35,37°
M- 3,62°
B- 35,84°
M- 0,00°
B- 36,00°
NÚMERO DE LADOS
6
M- 30,00°
B- 0,00°
M- 29,91°
B- 2,50°
M- 29,62°
B- 4,98°
M- 29,15°
B- 7,44°
M- 28,48°
B- 9,85°
M- 27,62°
B- 12,20°
M- 26,57°
B- 14,48°
M- 25,31°
B- 16,67°
M- 23,86°
B- 18,75°
M- 22,21°
B- 20,70°
M- 20,36°
B- 22,52°
M- 18,32°
B- 24,18°
M- 16,10°
B- 25,66°
M- 13,71°
B- 26,95°
M- 11,17°
B- 28,02°
M- 8,50°
B- 28,88°
M- 5,73°
B- 29,50°
M- 2,88°
B- 29,87°
M- 0,00°
B- 30,00°
7
M- 25,71°
B- 0,00°
M- 25,63°
B- 2,17°
M- 25,37°
B- 4,32°
M- 24,95°
B- 6,45°
M- 24,35°
B- 8,53°
M- 23,56°
B- 10,57°
M- 22,64°
B- 12,53°
M- 21,53°
B- 14,41°
M- 20,25°
B- 16,19°
M- 18,80°
B- 17,87°
M- 17,20°
B- 19,41°
M- 15,44°
B- 20,82°
M- 13,54°
B- 22,07°
M- 11,50°
B- 23,16°
M- 9,35°
B- 24,06°
M- 7,10°
B- 24,78°
M- 4,78°
B- 25,30°
M- 2,40°
B- 25,61°
M- 0,00°
B- 25,71°
8 9
M- 22,50°
B- 0,00°
M- 22,42°
B- 1,91°
M- 22,19°
B- 3,81°
M- 21,81°
B- 5,68°
M- 21,27°
B- 7,52°
M- 20,58°
B- 9,31°
M- 19,73°
B- 11,03°
M- 18,74°
B- 12,68°
M- 17,60°
B- 14,24°
M- 16,32°
B- 15,70°
M- 14,91°
B- 17,05°
M- 13,36°
B- 18,27°
M- 11,70°
B- 19,35°
M- 9,93°
B- 20,29°
M- 8,06°
B- 21,08°
M- 6,12°
B- 21,69°
M- 4,11°
B- 22,14°
M- 2,07°
B- 22,41°
M- 0,00°
B- 22,50°
M- 20,00°
B- 0,00°
M- 19,93°
B- 1,71°
M- 19,72°
B- 3,40°
M- 19,37°
B- 5,08°
M- 18,88°
B- 6,72°
M- 18,26°
B- 8,31°
M- 17,50°
B- 9,85°
M- 16,60°
B- 11,31°
M- 15,58°
B- 12,70°
M- 14,43°
B- 14,00°
M- 13,17°
B- 15,19°
M- 11,79°
B- 16,27°
M- 10,31°
B- 17,23°
M- 8,74°
B- 18,06°
M- 7,10°
B- 18,75°
M- 5,38°
B- 19,29°
M- 3,62°
B- 19,68°
M- 1,82°
B- 19,92°
M- 0,00°
B- 20,00°
10
M- 18,00°
B- 0,00°
M- 17,94°
B- 1,54°
M- 17,74°
B- 3,08°
M- 17,42°
B- 4,59°
M- 16,98°
B- 6,07°
M- 16,41°
B- 7,50°
M- 15,72°
B- 8,89°
M- 14,90°
B- 10,21°
M- 13,98°
B- 11,46°
M- 12,94°
B- 12,62°
M- 11,80°
B- 13,69°
M- 10,56°
B- 14,66°
M- 9,23°
B- 15,52°
M- 7,82°
B- 16,26°
M- 6,34°
B- 16,88°
M- 4,81°
B- 17,37°
M- 3,23°
B- 17,72°
M- 1,62°
B- 17,93°
M- 0,00°
B- 18,00°
Cada cantidad, B (bisel) y M (inglete), se da con una tolerancia de 0,005°.
AJUSTES DE ÁNGULOS COMBINADOS PARA ESTRUCTURAS COMUNES
29 − Español
Page 98

FUNCIONAMIENTO
CÓMO CORTAR MOLDURAS DE CORONA
La sierra ingleteadora compuesta realiza una labor excelente para
cortes de molduras de corona. En general, las sierras para cortar
ingletes compuestos realizan una labor mejor en el corte de molduras de corona que ninguna otra herramienta.
Con el fin de lograr un ajuste correcto, las molduras de corona
deben cortarse a inglete compuesto con una precisión extrema.
Las dos superficies de contacto de una moldura de corona que
queda horizontal contra el techo y la pared de un cuarto están en
ángulos que, añadidos, equivalen a 90°. La mayoría de molduras
de corona tienen un ángulo posterior superior (es la sección que
queda horizontal contra el techo) de 52° y un ángulo posterior
inferior (la sección que queda contra la pared) de 38°.
MOLDURA DE CORONA EN POSICIÓN
HORIZONTAL EN LA MESA DE INGLETES
Vea la figura 37.
Para usar este método a fin de cortar con precisión molduras
de corona para una esquina interior o exterior de 90°, coloque la
moldura con su superficie posterior ancha horizontalmente sobre
la mesa de ingletes y contra la guía.
Al ajustar los ángulos de bisel e inglete de sierras para cortar
ingletes compuestos, recuerde que los ajustes son interdependientes; el cambio de un ángulo afecta al otro. Tenga presente que
los ángulos de las molduras de corona son muy precisos y difíciles
de ajustar. Puesto que es muy fácil que estos ángulos cambien,
todos los ajustes deben probarse primero en molduras de desecho.
Asimismo, la mayoría de las paredes no tienen ángulos exactos de
90°, por lo tanto usted debe efectuar ajustes finos a los ángulos.
Al cortar molduras de corona con este método, el ángulo de
bisel debe fijarse a 33,85°. El ángulo de inglete debe fijarse a
31,6°, a la derecha o izquierda, según el corte deseado para
cada aplicación en particular. En la tabla mostrada a continuación encontrará los ajustes correctos de los ángulos y la colocación correcta de la moldura de corona en la mesa de ingletes.
Los ajustes mostrados en la tabla siguiente pueden utilizarse para
cortar molduras de corona 100% estándar (“All Standard” en
EE.UU.) con ángulos de 52° y 38° . La moldura de corona se coloca
horizontal sobre la mesa de ingletes usando las características de
corte compuesto de su sierra ingleteadora compuesta.
Bisel
Ángulo Tipo de corte
Ajuste
Lado izquierdo, esquina interior
33,85°
33,85°
33,85°
33,85°
1. Canto superior de la moldura contra la guía
2. Mesa de ingletes a 31,62° a la derecha.
3. Guarde extremo izquierdo del corte
Lado derecho, esquina interior
1. Canto inferior de la moldura contra la guía
2. Mesa de ingletes a 31,62° a la izquierda.
3. Guarde extremo izquierdo del corte
Lado izquierdo, esquina exterior
1. Canto inferior de la moldura contra la guía
2. Mesa de ingletes a 31,62° a la izquierda.
3. Guarde extremo derecho del corte
Lado derecho, esquina exterior
1. Canto superior de la moldura contra la guía
2. Mesa de ingletes a 31,62° a la derecha.
3. Guarde extremo derecho del corte
38°
52°
TECHO
P
A
R
E
D
GUÍA DE INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
CANTO SUPERIOR CONTRA LA GUÍA =
ESQUINA INTERIOR DEL LADO IZQUIERDO
ESQUINA EXTERIOR DEL LADO DERECHO
MESA DE INGLETES
MOLDURA DE CORONA EN POSICIÓN HORIZONTAL EN LA MESA DE INGLETES
ESQUINA
INTERIOR
GUÍA DE INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
ESQUINA EXTERIOR
CANTO INFERIOR CONTRA LA GUÍA =
ESQUINA INTERIOR DEL LADO DERECHO
ESQUINA EXTERIOR DEL LADO IZQUIERDO
MESA DE INGLETES
Fig. 39
30 − Español
Page 99

FUNCIONAMIENTO
ENCAJE DE MOLDURA EN CORONA CONTRA
LA GUÍA DE INGLETE
Vea las figuras 40 y 41.
NOTA: Este método de corte es para las molduras de corona
de entre 117,5 mm (4-5/8 pulg.) y 133,3 mm (5-1/4 pulg.) de
altura. No intente cortar una moldura de más de 133,3 mm
(5-1/4 pulg.) de alto.
Ajuste los tornillos de la guía para asegurar las guías en
su lugar.
Configure el ángulo del bisel en 0° y el ángulo del inglete
en 45° hacia la izquierda o hacia la derecha. (Para realizar
esquinas de 90°).
Encaje y asegure moldura de la corona contra la guía de
ingletes use la prensa de resorte y asegure la moldura
corona.
Antes de encender la sierra, efectúe una simulación de
la operación de corte, sólo para asegurarse de que no
suceda ningún problema durante la operación de corte
real.
Sujete firmemente el mango de la sierra. Presione el ga-
tillo del interruptor. Permita transcurrir varios segundos
para que la hoja alcance su velocidad máxima.
Baje lentamente la hoja de a través de la moldura de la
corona.
PRENSA DE
RESORTE
CANTO INFERIOR
CONTRA LA GUÍA
GUÍA DE
INGLETES
DESLIZABLE
PRENSA DE
RESORTE
Fig. 40
MOLDURA
EN CORONA
Fig. 41
31 − Español
Page 100

FUNCIONAMIENTO
FORMA CORRECTA
Fig. 42
CÓMO CORTAR MATERIAL DISTORSIONADO
Vea las figuras 42 y 43.
Al cortar material distorsionado, siempre asegúrese de que
esté colocado en la mesa de ingletes con el lado convexo
contra la guía, como se muestra en la figura 42.
Si se coloca de una forma equivocada el material
distorsionado, como se muestra en la figura 43, pellizcará
la hoja al llegar al final del corte.
ADVERTENCIA:
Para evitar un contragolpe y posibles lesiones graves,
nunca coloque el canto cóncavo de un material arqueado
o distorsionado contra la guía.
SUJECIÓN DE PIEZAS ANCHAS
Vea la figura 44.
Al cortar piezas anchas, como las de 51 x 152 mm (2 x 6
pulg.), deben sujetarse con prensas de trabajo, como se
muestra en la figura 44.
FORMA INCORRECTA
Fig. 43
TABLA
ANCHA
32 − Español
Fig. 44
 Loading...
Loading...