Page 1

RVON Resource Guide
RVON-8
RVON-1
RVON-I/O
Page 2

Page 3

CHAPTER 1
Basic Network Configuration
Basic Network Configuration
This section covers basic network configuration set-up and testing. Also covered are basic concepts and operations, including
the difference between LAN and WAN networks and how IP Addressing is used.
In a networked environment, such as a company, typically there are many computers connected together using a router or a
switch. In larger companies, there may be several different routers distributed in buildings and plant locations. A router allows
any LAN-side computer to communicate with other computers and devices outside the LAN (local area network). Routers
send data packets from one place to another place on a network. routers use network addresses to route packets to the correct
destination. For example, in a TCP/IP network, the IP (internet protocol) address of the network interface is used to direct
router destinations.
Because routers help computers inside the LAN “talk” with computers outside of the LAN, the security of a company’s LAN
may be compromised by gaps of open ports in the router. Security measures may have been instituted to compensate for these
vulnerabilities. Consult you network administrator to learn about the security measures taken to protect your network. VPN, or
virtual private network, is one such security measure to protect the intelligence of the LAN. A computer outside the LAN must
have an address or key known by the VPN to allow access to the LAN. Many companies use a VPN to connect two different
LANs, thus allowing the transfer of data between two networks.
LAN (local area network) vs. WAN (wide area network)
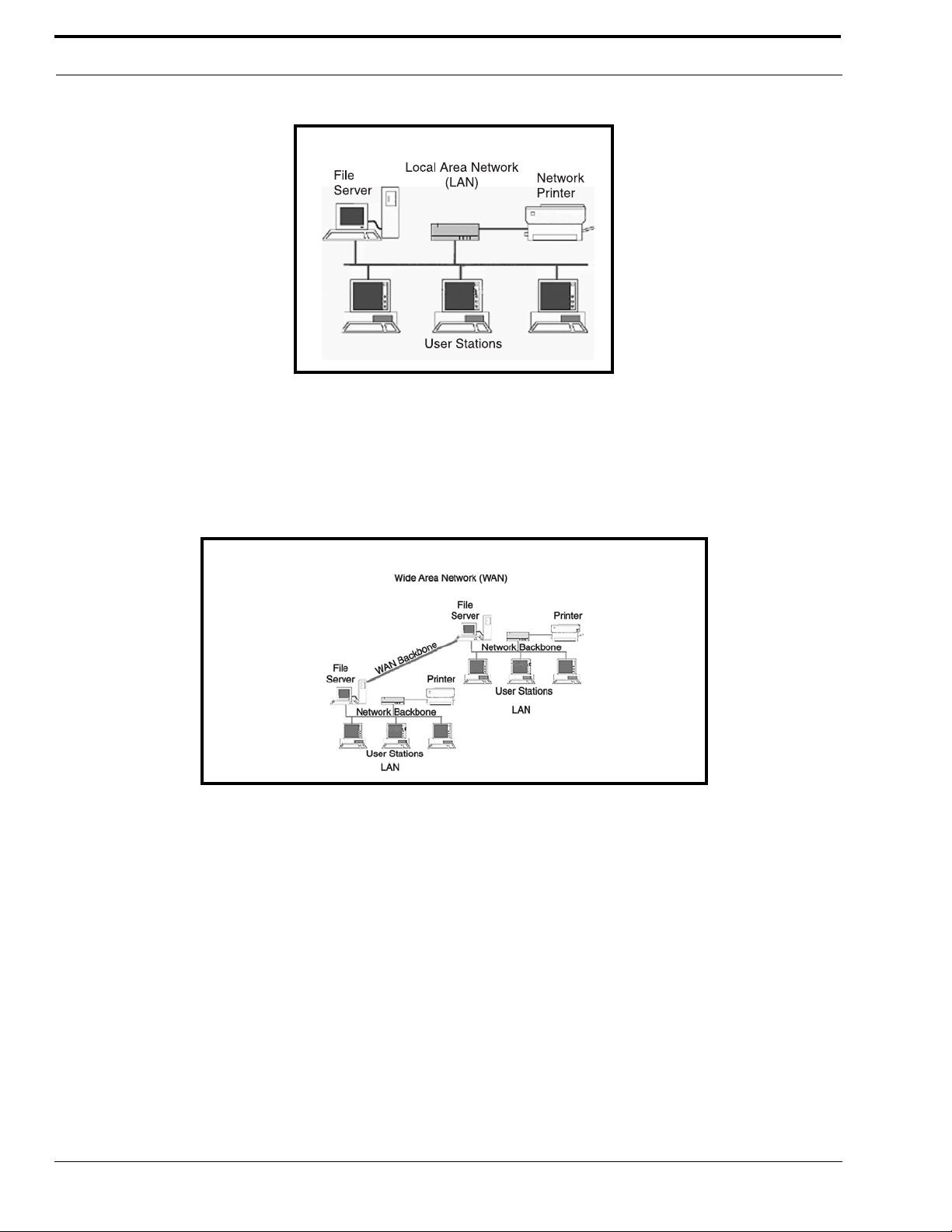
LOCAL AREA NETWORK
Simply put, a LAN is a computer network that connects a relatively small area (a single building or group of buildings). Most
LANs connect workstations and computers to each other. Each computer (also known as a “node”), has its own processing unit
and executes its own programs; however, it can also access data and devices anywhere on the LAN. This means many users
can access and share the same information and devices. A good example of a LAN device is a network printer. Most
companies cannot afford the budgetary or hardware expense of providing printers for each of its users; therefore, one printer
(or device) is placed on the LAN where every user can access the same printer.
The LAN uses IP Addresses to route data to different destinations on the network. An IP Address is a 32-bit numeric address
consisting of four numbers separated by periods (for example, 1.160.10.240).
NOTE: For more information on IP Addresses, see you local network administrator.
3
Page 4
Basic Network Configuration
Figure 1. Local Area Network Diagram
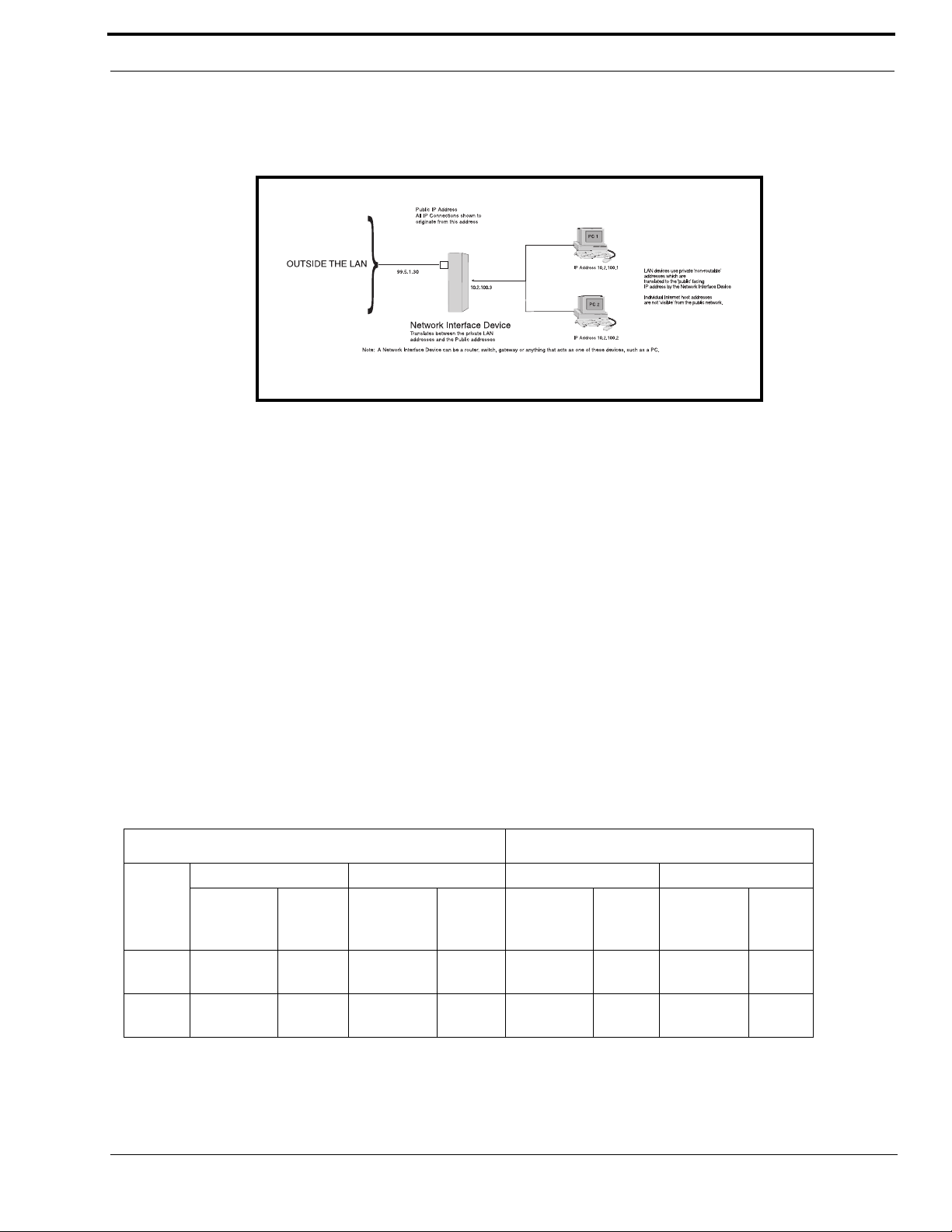
WIDE AREA NETWORK
A wide area network (WAN) connects two or more LANs and can span a relatively large geographical area. For example,
Telex Headquarters in Burnsville, MN is connected to several branch offices in Nebraska and Arkansas over a WAN. The
largest WAN in existence is the Internet.
Figure 2. Wide Area Network Diagram
4
Page 5
Basic Network Configuration
ACCESSING THE WIDE AREA NETWORK (WAN)
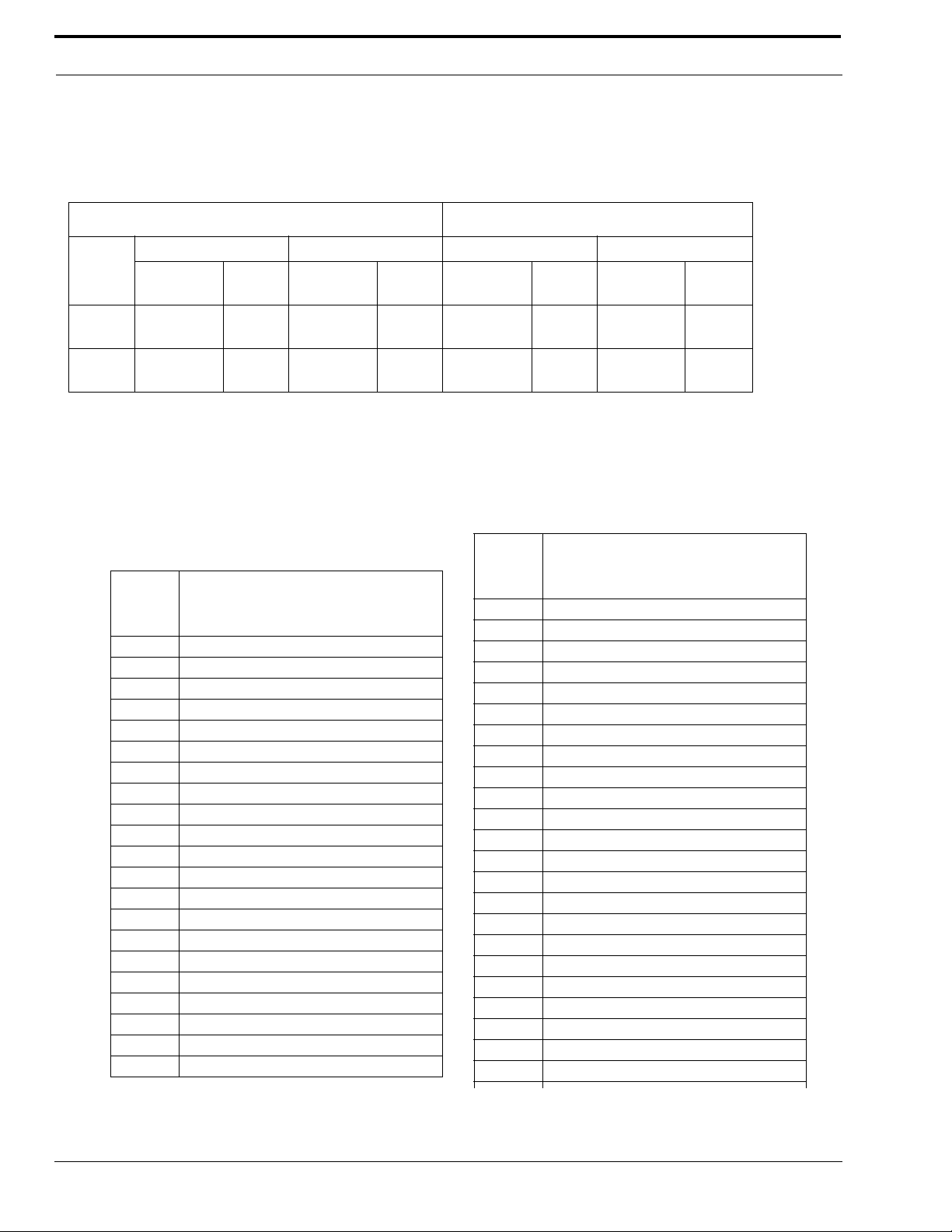
Figure 3 shows LAN IP Addresses using a common IP Address, 10.2.100.X (192.168.X.X is another common address). Most
devices are shipped with these addresses as its default. It is recommended to use these addresses for LANs.
Figure 3. Network Address Translation
NETWORK ADDRESS TRANSLATION (NAT)
Using the initial IP Address, then converting it to a valid WAN IP Address is how the network address translation works, in
theory . Once the IP address is changed, it is up to the network interface device (such as a router, gateway, switch, etc.) to keep
track of which computers are talking on which ports. For example, if two local devices (PC1 and PC2 in Figure 3) both wanted
to talk via port 1031, then the network interface device would have to change one of the port requests to the next available port,
1032.
PORTS
In general, a network port is an endpoint to a logical connection. The port number identifies what type of port it is. For
example, port 80 is used for HTTP traffic. When you type an address into the address bar of a web browser, your computer
goes to find an IP Address for the url you are requesting (http://www.telex.com). To obtain this address, the computer contacts
a DNS server (Domain Name Server). Once the IP Address is found, it tries to connect to the http port of the network device
(port 80). See Table 1 for a list of the more well-known port numbers.
Each network device can be set-up to respond or not respond to the various ports. The function of responding or “hosting a
service” is called “serving”.
TABLE 1. Packet Translation
Packet before Translation Packet after Translation
Source Destination Source Destination
Port
Numbe
r
To
Internet
From
Internet
IP Address
10.2.100.2 1031 192.156.136.22 80 99.5.1.30 1031 192.156.136.22 80
192.156.136.22 80 99.5.1.30 1031 192.156.136.22 80 10.2.100.2 1031
Port
Number
IP Address
Port
Number
IP Address
Port
Number
IP Address
If a second workstation on the LAN wants to communicate to the same server, and happens to use the same source port
number, then the LAN Modem will translate the source port number as well as the source IP address. In Table, 2, a second
5
Page 6
Basic Network Configuration
TABLE 3. Well-Known TCP Port Numbers
Port
Numbe
r
Description
1 TCP Port Service Multiplexer (TCPMUX)
5 Remote Job Entry (RJE)
7ECHO
18 Message Send Protocol (MSP)
20 FTP-Data
21 FTP- Control
23 Telnet
25 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
29 MSG ICP
37 Time
42 Host Name Server (Nameserv)
43 Whols
49 Login Host Protocol (Login)
53 Domain Name Server (DNS)
69 Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP)
70 Gopher Service
79 Finger
80 HTTP
103 X.400 Standard
108 SNA Gateway Access Server
109 POP2
110 POP3
115 Simple File Transfer Protocol
118 SQL Services
119 Newsgroup (NNTP)
137 NetBIOS Name Service
139 NetBIOS Datagram Service
143 Interim Mail Access Protocol (IMAP)
150 NetBIOS Session Service
156 SQL Server
161 SNMP
179 Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)
190 Gateway Access Control Protocol (GACP)
194 Internet Relay Chat (IRC)
197 Directory Location Services (DLS)
389 Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDA P)
396 Novell Netware over IP
443 HTTPS
444 Simple Network Paging Protocol (SNPP)
445 Microsoft-DS
458 Apple Quick Time
546 DHCP Client
547 DHCP Server
563 SNEWS
TABLE 3. Well-Known TCP Port Numbers
Port
Numbe
r
Description
LAN computer wants to access a web page. The NAT device now uses port 1032 for this connection where it used port 1031
in Table 1.
TABLE 2. Packet Translation
Packet before Translation Packet After Translation
Source Destination Source Destination
To
Internet
From
Internet
IP Address
10.2.100.1 1031 192.156.136.22 80 99.5.1.30 1032 192.156.136.22 80
192.156.136.22 80 99.5.1.30 1032 192.156.136.22 80 10.2.100.1 1031
Port
Number
IP Address
Port
Number
IP Address
Port
Number
IP Address
Port
Number
Amazingly , all the address translation that occurs takes place automatically in order to make web browsing and other functions
easier. This is also a way for large web hosting services to speed up the network by having different devices perform different
functions.
6
Page 7
Basic Network Configuration
IP ADDRESSES
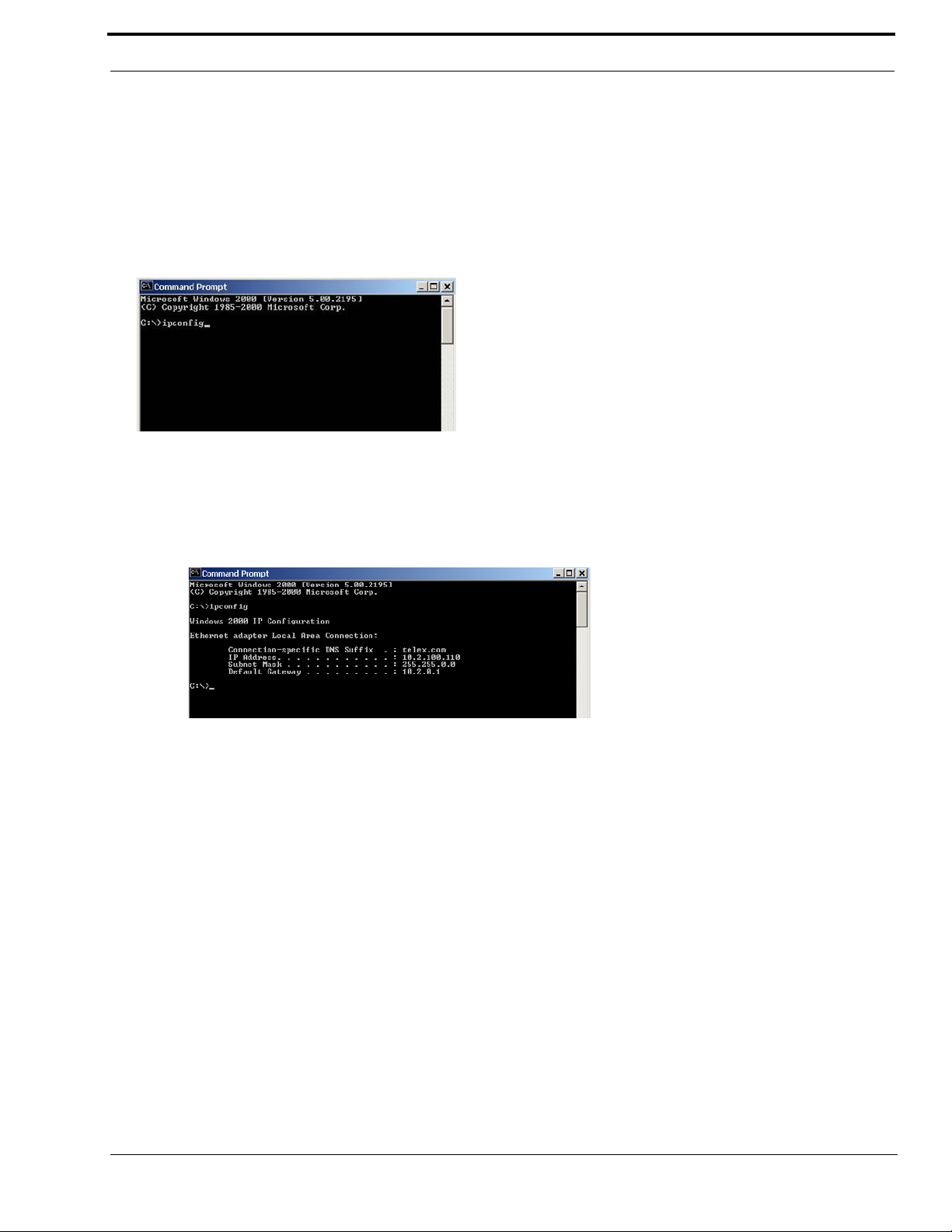
If you do not know your IP Address, you can open a DOS screen in a Windows®- based environment and bring up the ipconfig
screen.
To find your IP Address using ipconfig, do the following:
1. From the Start Menu, open a Command Prompt screen.
2. At the prompt, type ipconfig, then press Enter.
The IP configurations appear for your machine, such as the DNS suffix, IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Default
Gateway.
3. At the prompt, type Exit to close the screen.
NOTE: If you want more detailed parameters for your machine, type ipconfig/All. This screen shows the computers network
configuration settings.
7
Page 8
Basic Network Configuration
Ping a Computer
Pinging a computer on the network makes sure it is able to be “seen” and receive messages on the network.
NOTE: You can also ping your RVON-8 card to verify that it is responding over the network by putting the cards IP Address
in place of the computer IP Address.
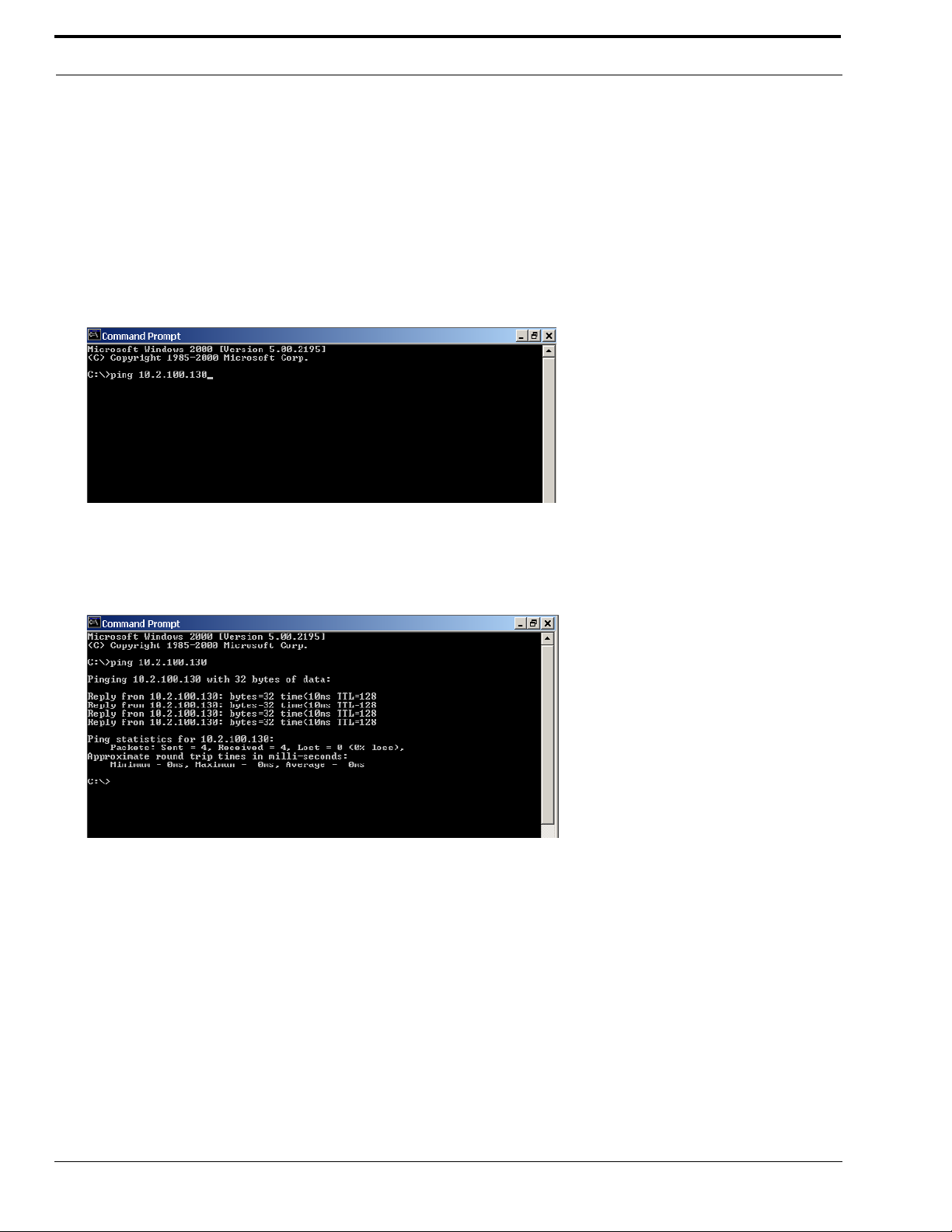
To Ping a computer on the network, do the following:
1. From the S t art menu, select Run... .
2. At the Run command, type CMD to open a Command Prompt screen.
3. At the prompt, type the IP Address of the computer you wish to ping (for example, 10.2.100.130).
4. Press Enter.
NOTE: If the computer you are pinging is not responding to the ping, you will receive a time-out message in the command
prompt screen.
POSSIBLE PITFALL WITH ROUTERS, GATEWAYS, AND SWITCHES
Anytime computers communicate through routers, gateways, and switches, they may be allowed or denied the connection.
Network interface devices can be configured to block specific outgoing requests, as well as incoming requests, based on the IP
Address and/or port. This is one of the security mechanisms of a router. This also happens when broadcast messages are sent
and received.
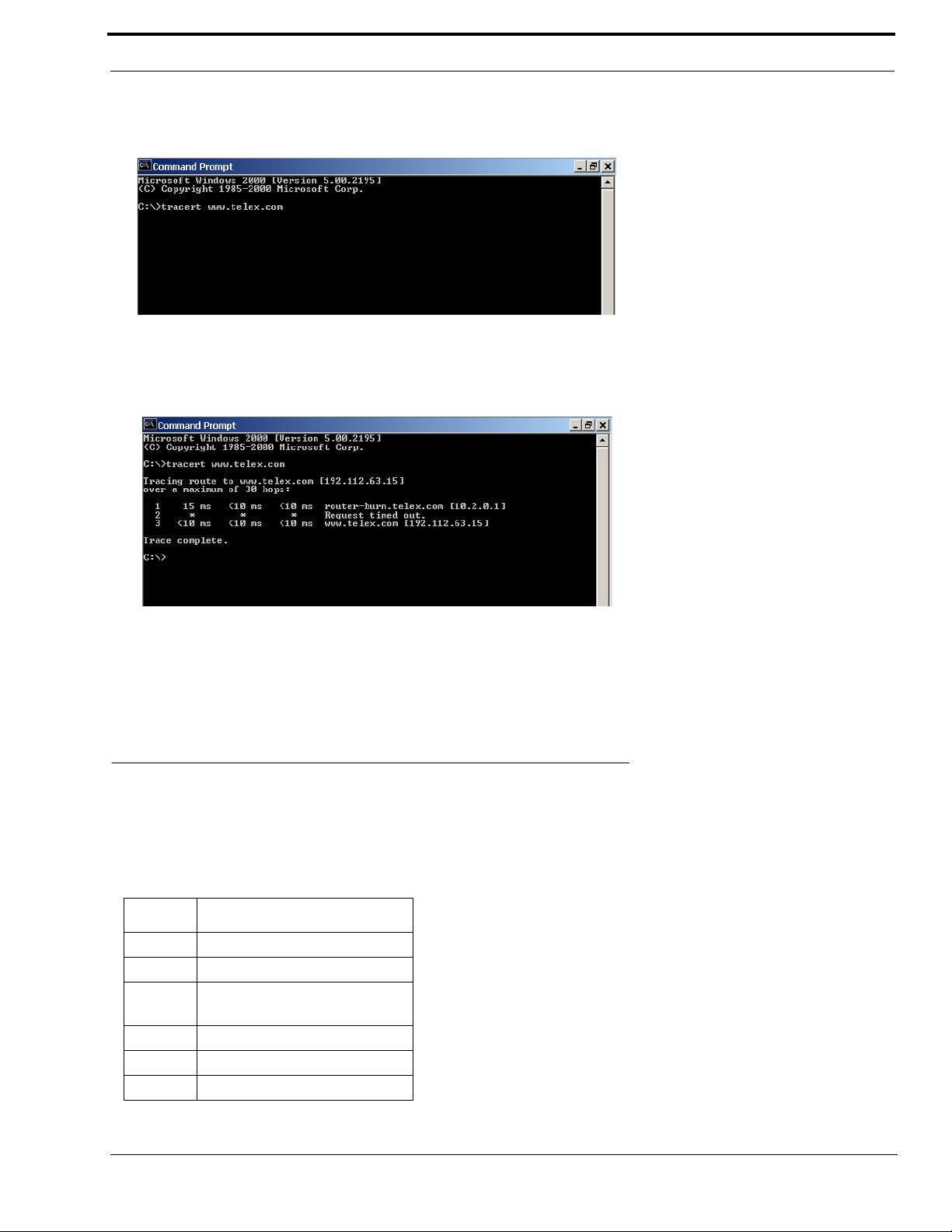
To view the path an IP Address takes to retrieve information, you can execute a tracert from the Command Prompt Screen.
1. From the Start Menu, open a Command Prompt screen.
8
Page 9
RVON Configuration
2. At the prompt, type tracert and type the url or IP Address you want to trace.
3. Press Enter.
The details of the tracer route are displayed.
NOTE: You will the message “request timed ou t” if the IP Address/ port IN or OUT is denied to the incoming or outgoing
message.
4. When you are finished, type exit to close the Command Prompt screen.
RVON Configuration
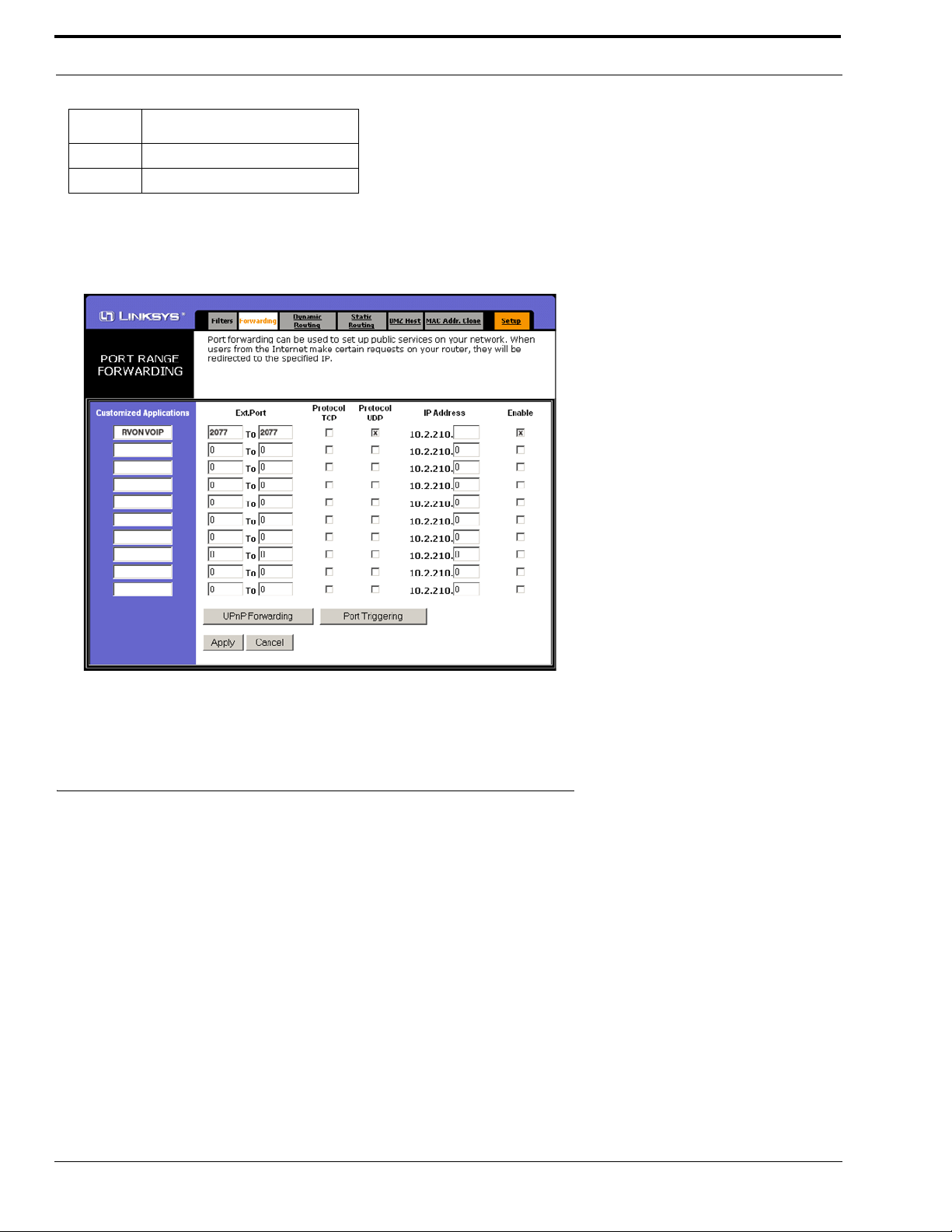
RVON cards use ports for communication of audio and control packets. Because routers can be configured to block certain
incoming and outgoing requests, you will need to open the following ports in your network to allow WAN connections to and
from a Network Interface Device. See Table X for the ports that need to be opened for the RVON cards to operate properly.
TABLE 4. Ports necessary for RVON card functionality.
Port Port Description
2076 UDP Call Control Signalling
2077 UDP Audio Packets
2079
2080 TCP T e lex Keypanel Protocol
2081 UDP Pass Through Serial
2082 TCP Firmware Download
UDP Telex Proprietary
Signalling
9
Page 10
Basic Network Configuration
TABLE 4. Ports necessary for RVON card functionality.
Port Port Description
2100 Remote Administration
2102 Authentication Server
Below, is an example of a router configuration screen. Not all routers are configured the same way and may not look exactly
like this screen.
NOTE: Linksys™ supports up to 253 nodes on a router. This is why it is called a Router/Switch because there are WAN
functions like a router as well as having a 4-port LAN sw itch. It also does not support simultaneous forward and DHCP.
Network Terminology
Bridges
A bridge is a device that connects two LANs, or two segments of the same LAN that use the same protocol.
Sometimes called “transparent bridges, they work at the OSI model Layer 2. Simply put, they are not
concerned with protocols. Their main job is to pass data to a destination address that is predetermined in the
data packet.
With a bridge, all of your computers are on the same network subnet (see Subnet). This means your
computers can communicate with each other and have their own Internet connection. If you assign your own
IP Addresses be sure to use the same first 3 “octets” of the IP Address (for example, 192.168.0.X).
Domain Name Server (DNS)
A DNS Server is an Internet service that translates domain names (for example, in the URL http://
www.telex.com, the domain name is the telex.com) into IP Addresses. The Internet is based on IP Addresses
10
Page 11

Network Terminology
which are numeric and since domain names are alphabetic, they are easier to remember. Every time a
domain name is used it must go through the DNS server to be translated into an IP Address.
Gateway
A gateway is a node on a network that serves as an entrance to another network. The gateway routes traffic
from a computer to an outside network that is serving the web pages. For example, the gateway for a home
computer is the ISP provider that connects the user to the Internet.
In a corporate environment, the gateway often acts as a proxy server and a firewall. Gateways are similar to
routers and switches in that they forward data to the destination and provide the path for which the data will
travel to the destination.
Hub
A hub is a common connection point for devices in a network. A hub has multiple ports. When a data packet
arrives at a hub, it is copied and distributed to all of its ports so that all nodes on the LAN can see the packets.
There are three types of hubs:
passive hub
- this hub serves as a conduit for the data, enabling it to go from one device to another.
intelligent hub (also known as manageable hubs) - this hub includes addition features that enable administrators
to monitor traffic through the hub.
switching hub - this hub reads the destination address of each packet and then forwards the data pack to the
appropriate port.
IP Address (Internet Protocol Address)
An IP Address is an identifier or numerical name for a computer or device on a network. Data between
computers are routed over the network using these addresses to identify the computer the message is being
sent to and the computer the message is being sent from.
The format of an IP Address is a 32-bit numeric address written as four numbers separated by periods. For
example, an IP Address looks like 10.100.1.1.
IMPORTANT: When working within an isolated network (meaning there is no Internet access), IP
Addresses can be assigned at random just as long as they are unique to each computer and device. When the
isolated network is connected to the Internet, registered Internet Addresses must be obtained. This is to
prevent duplication of addresses.
The four numbers in and IP Address are used in different was to identify a particular network and host on
that network. There are three classes of Internet Addresses.
CLASS A - supports 16 million hosts on each of 127 networks.
CLASS B - supports 65,000 hosts on each of 16,000 networks.
CLASS C - supports 254 hosts on each of 2 million networks.
LAN
A LAN is a computer network that connects a relatively small area (a single building or group of buildings).
Most LANs connect work stations and computers to each other. Each computer (also known as a “node”),
has its own processing unit and executes its own processing unit and executes its own programs; however it
can also access data and devices anywhere on the LAN. This means that many users can access and share the
same information and devices. A good example of a LAN device is a network printer. Most companies
cannot afford the budgetary or hardware expense of providing printers for each of its users; therefore, one
printer (i.e., device) is placed on the LAN where every user can access the same printer.
11
Page 12

Basic Network Configuration
The LAN uses IP Addresses to route data to different destinations on the network. An IP Address is a 32-bit
numeric address written as four numbers separated by periods (for example 1.160.10.240).
Port
A port, when referring to TCP and UDP networks, is an endpoint in a logical connection. The port number
identifies the type of port it is. For example, port 80 is used for HTTP traffic.
Routers
A router is a device that forwards data packets over networks. Most commonly, a router is connected to at
least two networks (normally LANs or WANs). Routers are located at gateways, the place where two
networks are connected. Routers do little data filtering, they mainly deliver the data.
Subnet
A subnet is a portio n of a network that shares a common address component. On a TCP/IP network, a subnet
is described as all computers or devices whose IP Address have the same prefix.
Subnetting a network is useful because it provides security for the network as well as increases performance
of the network. IP networks are divided using subnet masks.
Switches
WAN
A switch is a device that filters and forwards data packets between networks. Switches operate at the data
layer, and sometimes at the network layer.
A wide area network connects two or more LANs and can span a relatively large geographical area. For
example, T elex Headquarters in Burnsville, MN is connected to several of its branch of fices in Nebraska and
Arkansas over the wide area network. The largest WAN is the Internet.
12
Page 13

CHAPTER 2
Serial Port Pr ogramming
RVON Serial And Telnet Commands
RV ON card programming can be done via direct serial or telnet connection. There are several physical connections to an
RV ON board.
• Direct serial through custom debug cable (J20 6-pin botton front)
• Backcard DB-9 J2 - The backcardDB-9 must be disabled/enabled via a DIP Switch because it can also be used
for serial port pass-through. The backcard DB-9 can be used for a debug terminal when DIP swith 6 is switched
to the ON position.
• Backcard RJ-45 J1 (Telnet Only)
Setup
Serial Port 38,400 baud, no-flow control
Telnet IP Address, port 23
TABLE 5. RVON Supplemental Coding Table
Coding Codec Codec Rate Size VAD
1 711u 64k 10 Y
2 711u 64k 20 Y
3 711u 64k 30 Y
4 711u 64k 10 N
5 711u 64k 20 N
6 711u 64k 30 N
7 711A 64k 10 Y
8 711A 64k 20 Y
9 711A 64k 30 Y
10 711A 64k 10 N
11 711A 64k 20 N
12 711A 64k 30 N
13 729AB 8k 10 Y
13
Page 14

Serial Port Programming
TABLE 5. RVON Supplemental Coding Table
Coding Codec Codec Rate Size VAD
14 729AB 8k 20 Y
15 729AB 8k 40 Y
16 729AB 8k 60 Y
17 729AB 8k 10 N
18 729AB 8k 20 N
19 729AB 8k 40 N
20 729AB 8k 60 N
21 723 5.3k 30 Y
22 723 5.3k 60 Y
23 723 5.3k 30 N
24 723 5.3k 60 N
25 723 6.3k 30 Y
26 723 6.3k 60 Y
27 723 6.3k 30 N
28 723 6.3k 60 N
TABLE 6. Codec Specifications
Codec
Coding Profile
Codec Rate
Audio (ms) / Packet
Packets / Second
Encoded Audio (bytes)
IP Overhead (bytes)
Total Package Size (bytes)
Bandwidth (Bytes/sec)
Bandwidth (kbps/side)
Bandwidth (kbps/channel)
0,3,6,9 G.711 64k 10 100.00 80 60 140 14000 112 224
1,4,7,10 G.711 64k 20 50.00 160 60 220 11000 88 176
2,5,8,11 G.711 64k 30 33.33 240 60 300 10000 80 160
12,16 G.729 8k 10 100.00 10 60 70 7000 56 112
13,17 G.729 8k 20 50.00 20 60 80 4000 32 64
14,18 G.729 8k 40 25.00 40 60 100 2500 20 40
15,19 G.729 8k 60 16.67 60 60 120 2000 16 32
20,22 G.723 5.3k 30 33.33 24 60 84 2800 22.4 44.8
24,26 G.723 6.3k 30 33.33 24 60 84 2800 22.4 44.8
21,23 G.723 5.3k 60 16.67 48 60 108 1800 14.4 28.8
25,27 G.723 6.3k 60 16.67 48 60 108 1800 14.4 28.8
NOTE: A channel consists of a transmitting and a receiving side, so the bandwidth is double for a bi-directional audio
stream.
NOTE: Bandwidth values are approximate maximums, actual bandwidth could be considerable lower with VAD
enabled.
14
Page 15

RVON Serial And Telnet Commands
Codec Determines how the audio is compressed/decompressed and the name given to the defined
algorithm.
Codec Rate Actual bits per second of the audio in compressed form. This is sent over the network
through various data packets. Network efficiency can be calculated with an IP header for
each packet of X ms of audio.
Size Amount of audio in each IP packet, milliseconds (ms)
VAD Voice Activity Detection, when enabled and only when audio is above a certain threshold,
will send packets. Otherwise, a silence packet is sent once, and not again until audio is
above the threshold. Enabling this will result in a more efficient network. If there is ever a
need to have all audioo paths open and active, a network designer must account for this
scenario.
*****************************************************
RVON−8 Revision 1.00.00
(C) Copyright 2003 Telex, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Flash File System initialized.
DIP Switch settings:........X
Configuration via AZedit disabled (via DIP Switch 1 ON)
Back Card UART enabled for pass−through serial (via DIP Switch 6 OFF)
Boot Downloader disabled (via DIP Switch 7 OFF)
Autoload enabled (via DIP Switch 8 OFF)
Monitor Revision 1.00.00
Monitor Compilation time Sept 4 2003, 15.52.31
Board type / revision 0 (RVON−8) / 1
RTL ID / revision 9 (RVON−8) / 0.16
Processor ID / Revision 0x80 (4Kc) / 0x50
Avalanche Device Type Avalanche−I, Revision 1.3
Memroy Controller Revision 1.204
Endianness Big
External Memory rate Full
CPU Frequency 125 MHz
Flash memory size 8 MBytes
RAM size 64 MBytes
First free RAM address 0x9401fla8
PLL Mode Operating 2.50X
Press any key to abort OS load, or wait 5 seconds for OS to boot....
**Defragmenting File System flash area(s)**
Reading flash file system... No deleted flash file entries found.
Loading file/ bin/telex1 from EFS
PC: 94020000
FTP done!, PC: 94020000
Target Name: vxTarget
Attached TCP/IP interface to emac unit 0
Attaching network interface 1o0,,, done
NFS client support not included.
Adding 5270 symbols for standalone.
appCreate: autoBootLevel=2
MXP environment is created.
Creating RVON−8 application...
15
Page 16

Serial Port Programming
−> Bringing DSP subsystem out of reset...
DSP Daughtercard type is set to NONE − No DSP Daughtercard Found
0000002223 − ROOT: FPGA Version = ff24
0x97e796f0 (tNetTask): Link is up on EMAC A: 100 MBps and HALF duplex.
About to create Idle Task
About to create Measurement Task
Idle Measurement Tasks created
0000002536 − SERV: initializing connection server
0000002536 − DNLD: initializing download server
0000002535 − NMM: ATPM Update Database Granted
0000002735 − NMM: ATPM Configured for RVON operation
0000002735 − NMM: ATPM Update database done
0000002735 − NMM: 0, states: oper=NORMAL, admin=NORMAL, call=IDLE
0000002741 − NMM: 1, states: oper=NORMAL, admin=NORMAL, call=IDLE
0000002742 − NMM: 2, states: oper=NORMAL, admin=NORMAL, call=IDLE
0000002743 − NMM: 3, states: oper=NORMAL, admin=NORMAL, call=IDLE
0000002744 − NMM: 4, states: oper=NORMAL, admin=NORMAL, call=IDLE
0000002744 − NMM: 5, states: oper=NORMAL, admin=NORMAL, call=IDLE
0000002745 − NMM: 6, states: oper=NORMAL, admin=NORMAL, call=IDLE
0000002746 − NMM: 7, states: oper=NORMAL, admin=NORMAL, call=IDLE
0000002746 − RVON: port 0, now idle
0000002746 − RVON: port 1, now idle
0000002746 − RVON: port 2, now idle
0000002746 − RVON: port 3, now idle
0000002746 − RVON: port 4, now idle
0000002746 − RVON: port 5, now idle
0000002746 − RVON: port 6, now idle
0000002746 − RVON: port 7, now idle
0000003037 − CBTX: MC/DBX is talking
0000003041 − FNRX: control bus FIFO now enabled
0000003093 − FNRX: new card configuration received
Following the power-ON messages, press Return.
The -> appears. This is the operating system prompt.
There are many different serial port commands support from here, but is NOT recommended that any be used EXCEPT:
dbgcmd
Type “dbgcmd”, then press Return.
This places the serial port into the MXP> (MXP command mode)
The MXP Command Mode is the only mode that will be used. Table 1 is a list of commands support from the MXP Shell
Prompt.
16
Page 17

RVON-8 Command Table
RVON-8 Command Table
TABLE 7. RVON-8 Command Table
Command Variable 1 Variable 2 Description
set rvon
set rvon ip_addr X.X.X.X Set the IP Address for the RVON-8 Card.
set rvon netmask X.X.X.X Set network mask for the RVON-8 Card.
set rvon gateway X.X.X.X
set rvon user abcdefg
set rvon password abcdefg
set rvon vad_threshold [adaptive ⎢#]
Help screen which lists all “set rvon”
commands.
Set the gateway IP Address for the RVON-8
card.
Set the RVON-8 user name for telnet access.
Default “telex”
Set the RVON-8 password for telnet access (840 characters).
Default “password”
Set the VAD threshold (silence detection)
Adaptive refers to auto-select. The # can be -20
to +10dBm.
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set emac auto*
set emac 10 half
set emac 10 full
set emac 100
half
set emac 100
full
Help screen which lists all “set tcid” commands
(TCID 0-7).
dest_ip X.X.X.X
dest_type X
chan_codec X
onhook Force the channel to disconnect the port.
offhook Force the channel to connect the port.
Set the destination IP Address for this particular
RVON_Channel (same as tcid).
dest_type X = 0 (rvon-8), 1 (rvon-1), 2 (rvon-I/
O).
Set the profile to use which includes the
compression codec see below (0-27).
Enables auto-negotiation of the Ethernet
interface configuration.
Configures the Ethernet interface for 10Mbps
half duplex.
Configures the Ethernet interface for 10Mbps
full duplex.
Confgures the Ethernet interface for 100 Mbps
half duplex.
Configures the Ethernet interface for 100 Mbps
full duplex.
set serial ip_addr X.X.X.X
Set the destination IP Address for this serial
pass-through port.
17
Page 18

TABLE 7. RVON-8 Command Table
Command Variable 1 Variable 2 Description
set serial baud X Set the baud rate to use: 50 through 115000.
activate
show rvon Display current settings
show channel
[chan]
show emac Display current settings
Must do an activate command to cause changes
to take effect.
Display current settings
18
Page 19

RVON-1 Command Table
RVON-1 Command Table
TABLE 8. RVON-1 Command Table
Command Variable 1 Variable 2 Description
set rvon
set rvon ip_addr X.X.X.X Set the IP Address for the RVON-1 Card.
set rvon netmask X.X.X.X Set network mask for the RVON-1 Card.
set rvon gateway X.X.X.X
set rvon user abcdefg
set rvon password abcdefg
set rvon vad_threshold [adaptive ⎢#]
Help screen which lists all “set rvon”
commands.
Set the gateway IP Address for the RVON-1
card.
Set the RVON-1 user name for telnet access.
Default “telex”
Set the RVON-1 password for telnet access (840 characters).
Default “password”
Set the VAD threshold (silence detection)
Adaptive refers to auto-select. The # can be -20
to +10dBm.
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
activate
show rvon Display current settings.
show channel
[chan]
dest_ip X.X.X.X
dest_type X
dest_chan X
chan_codec X
onhook Force the channel to disconnect the port.
offhook Force the channel to connect the port.
Help screen which lists all “set chan” commands
(CHAN 0-7).
Set the destination IP Address for this particular
RV ON channel.
dest_type X = 0 (rvon-8), 1 (rvon-1), 2 (rvon-I/
O).
Set the destination channel - the port at the far
end of the connection (0-7).
Set the profile to use, which includes the
compression codec see below (0-27).
Must do an activate command to cause changes
to take effect.
Display current settings
19
Page 20

20
Page 21

RVON-I/O Command Table
RVON-I/O Command Table
TABLE 9. RVON-I/O Command Table
Command Parameter 1 Parameter 2 Description
show rvon
show channel
show serial Shows serial port setting.
show gpio Shows gpio settings.
show panel
show emac Shows Ethernet settings.
Shows RVON-I/O IP Address and other
general information.
Shows destination address and connection
information.
Shwos the channel control settings (poll id
and baud rate).
set rvon
set rvon ip_addr X.X.X.X Set the IP Address for the RVO N-I/O.
set rvon netmask X.X.X.X Set the Network Mask for the RVON-I/O.
set rvon gateway X.X.X.X
set rvon user username
set rvon password password
set rvon vad_threshold adaptive (#)
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
dest_ip X.X.X.X
dest_type X X = 0 (rvon-8), 1 (rvon-1, 2 (rvon-I/O
dest_chan X
chan_codec X
input_gain X
output_gain X
Help screen which lists all “set rvon”
commands.
Set the Gateway IP Address for the RVON-I/
O.
Set the RVON-I/O user name for Telnet
access.
Default = telex
Set the RVON-I/O password for Telnet
access (8-40 characters).
Default = password
Set the VAD threshold (silence detection).
Adaptvie refers to autoselect. The # can be 20 to +10 dBm.
Help screen, which lists all “set chan”
commands (0-7). This refers to VOIP
channel setting.
Set the destination IP Address for this
particular RVON channel.
Set the destination channel - the port on the
far end (0-7).
Set the profile to use which includes the
compression codec (see page X) (0-27).
Set the input gain for the specified channel 14 to +14dB
Set the output gain for the specified channel 14 to +14 dB.
21
Page 22

TABLE 9. RVON-I/O Command Table
Command Parameter 1 Parameter 2 Description
set channel
[chan]
set channel
[chan]
onhook force the channel to disconnect.
offhook force the channel to connect.
set serial
set serial mode X
set serial ip_addr X.X.X.X
set serial ip_addr_2 X.X.X.X Not Available
set serial baud X
set gpio
set gpio mode X
set gpio ip_addr X.X.X.X
set gpio panel X
Help screen, which lists all “set serial”
commands.
Set the serial mode.
0 = Pass Through mode
Set the destination IP Address for this serial
pass-through port.
Set the baud rate to use:
50 through 115000.
Help screen, which lists all “set gpio”
commands.
Set the gpio mode.
0 = Pass Through
1 = 1 Keypanel
2 = All Keypanels
Set the destination IP Address for passthrough mode.
Set the IO port the gpio are associated with
on the RVON-I/O.
set panel
set panel
[pnl]
set panel
[pnl]
22
poll_id X
baud X
Help screen, which lists all “set panel”
commands.
Make sure the panel poll_id corresponds to
the source of the audio it is connected to.
0-10
0= do not respond to polls
Set the baud rate for the panel.
9600 or 76800
Page 23

Default RVON-8 Setup
Default RVON-8 Setup
Every attempt is made to ensure the board is shipped from the factory containing the following:
All are “set rvon” commands
TABLE 1. Default Set RVON-8 Commands
Variable Environment Name
ip_addr EMACA_IPADDR 192.168.1.1 IP Address for the RVON-8 card.
netmask EMACA_NETMASK 255.255.255.0 Network mask for the RVON-8 card.
gateway EMACA_GW none Gateway IP Address for the RVON-8 card.
serial_ip RVON_SERIAL_IP none
serial_baud RVON_SERIAL_BAUD 9600
user RVON_USER telex RVON-8 user name for Telnet access
password RVON_PASSWORD password
vad_thresholdRVON_THRESHOLD_V
AD
There are more parameters that the software will auto-configure if they have not been previously setup. The user can also set these
parameters, in which case the software would not modify, but take them as they are.
All are “set chan #” commands because they are for each audio channel.
TABLE 2. Set Chan # Setup Commands
Default
Value
Pass-thru serial port IP Address for the
RVON-8
Set the pass-thru serial port baud rate for the
RVON-8 card
RVON-8 password for Telnet access (8-40
characters)
adaptive VAD Threshold
Description
Variable Environment Name Value Description
dest_ip RVON_DEST_IP_# X.X.X.X
dest_type RVON_DEST_TYPE_# X
dest_chan RVON_DEST_CHAN_# X
chan_codec
Typing “printenv”, then pressing Return from RVON-8 boot code or “sys_printenv” from the “MXP” debug system prompt
may show these commands. The Environment name is listed because this is the label used by the software.
IMPORTANT: If the user is attempting to do a “setenv” to change a parameter from the RVON-8 boot code, the Environment
Name must be used, NOT the “set rvon” Variable name.
RV ON_CHAN_CODEC_
#
X Profile to use (see coding table)
Destination IP Address for this particular
RVON_CH
Destination Type - Y = 0 (rvon-8), 1 (rvon-
1),
2 (rvon-I/O).
Destination Channel - What port of far-end
(0-7).
23
Page 24

Default RVON-1 Setup Commands
Every attempt is made to ensure the board is shipped from the factory containing the following:
All are “set rvon” commands
TABLE 1. Default RVON-1 Setup Commands
Command Environment Name
ip_addr EMACA_IPADDR 10.2.210.170 IP Address for the RVON-1 card.
netmask EMACA_NETMASK 255.255.255.0 Network mask for the RVON-1 card.
gateway EMACA_GW none Gateway IP Address for the RVON-1 card.
user RVON_USER telex RVON-1 user name for Telnet access.
password RVON_PASSWORD password
vad_threshol
d
There are more parameters the software will auto-configure if they have not been previously setup.
All are “set channel #” commands because they are for each audio channel.
TABLE 2. Set Channel # Setup Commands
Command
dest_ip RVON_DEST_IP_# (0,1) X.X.X.X
dest_type
dest_chan
chan_codec
RVON_THRESHOLD adaptive VAD Threshold
Environmental Variable
Name
RVON_DEST_TYPE_#
(0,1)
RVON_DEST_CHAN_#
(0,1)
RVON_CHAN_CODEC_
# (0,1)
Default
Value
RVON-1 password for Telnet access (8-40
characters).
Value Description
Destination IP Address for this particular
channel.
X
X
X Profile to use (see coding table).
Destination Type: X = 0 (rvon-8), 1 (rvon-1),
2 (rvon-I/O).
Destination Channel - what port of far-end
(0-7).
Description
Typing “sys_printenv” from the “MXP” Debug system prompt these settings.
24
Page 25

Default RVON-I/O Setup
Default RVON-I/O Setup
Every attempt is made to ensure the board is shipped from the factory containing the following settings.
All are “set rvon” commands
COMMAN
D
ip_addr 192.168.0.1 IP address for the RVON-I/O
netmask 255.255.0.0 Network mask for the RVON-I/O
gateway none Gateway IP address for the RVON-I/O
user telex RVON-I/O username for Telnet access.
password password RVON-I/O password for Telnet access (8-40 characters).
vad_threshold adaptive VAD Threshold
Table 1.
Set rvon default values. For more information shee table on page X.
DEFAULT VALUE DESCRIPTION
There are more parameters the software will auto-configure if they have not been previously setup.
All are “set channel #” commands because they are for each audio channel.
COMMAN
D
dest_ip X.X.X.X Destination IP Address for this particular channel.
dest_type X Destination type X = 0 (rvon-8), 1 (rvon-1), 2 (rvon-I/O)
dest_chan X Destination channel - the port on the far end (0-7)
chan_codec X Profile to use (previous coding table).
Table 2.
Set Channel # commands
DEFAULT
VALUE
DESCRIPTION
25
Page 26

26
Page 27

CHAPTER 3
Pr oduct Specific Descriptions
27
Page 28

Product Specific Descriptions
RVON-1 Jumpers and Connections
A selectable RS232/485 serial port is a connector J1. Jumper connections on J10, J11, and J12 select the signal mode on J1.
• When J10, J11, and J12 are jumped from pins 1 to 2 - J1 is configured for RS485.
• When J10, J11, and J12 are jumped from pins 2 to 3 - J1 is configured for RS232.
J21 must be jumped from pins 1 to 2 to select UART B for RS485 RVON-1 keypanel operation.
J2 Connector
The RVON-1 card is designed to be used with either a keypanel or an RVON-I/O card. The J2 connector mounts the RVON1 card onto a keypanel.
RS232 debug serial port via Connector J3. J3 is a 6-pin heater that connects to RS-232 compatible serial ports of the
TNETV2020.
Figure 1. Front and back of the RVON-1 board
How to Configure the RVON-1 using Telnet
Without access to the physical KP-32 with RVON-1 installed on it, you can still configure the card through the use of Telnet.
The following instructions will show you how to access the Telnet screen and show you some of the information you can see
and edit.
NOTE: These instructions are to help you get to the Telnet screens and give you an overview of what can be done. This is
NOT an all inclusive document. Not every action that can be performed are contained within the document.
28
Page 29

Product Specific Descriptions
To Display the settings for the RVON-1 Card, do the following:
1. Open a command prompt.
2. At the prompt, type Telnet <IP ADDRESS> (The IP Address is the IP Address assigned to the RVON-1 card).
3. Press Enter.
The RVON logon screen appears.
4. In the logon field, type the RVON logon (default = telex).
5. Press Enter.
6. In the password field, type the RVON password (default = password).
7. Press Enter.
A prompt appears.
29
Page 30

Product Specific Descriptions
8. Type dbgcmd to access the debug command screens.
9. Press Enter.
An MXP prompt appears.
10. At the prompt, type Show.
11. Press Enter.
The show commands screen and MXP prompt appears.
12. At the MXP prompt, type the show command you want to see (for example, “show rvon”).
13. Press Enter.
The values for the RVON-1 card appear.
T o edit the RVON-1 configuration, do the following:
1. Repeat steps 1 through 9 from above.
2. At the MXP prompt, type either set RVON or set EMAC (see screen descriptions below).
3. Press Enter.
30
Page 31

Product Specific Descriptions
set rvon ip_addr Allows you to edit the IP Address
set rvon netmask Allows you to edit the netmask
set rvon gateway Allows you to edit the gateway
set rvon serial_ip Allows you to edit the serial IP Address
set rvon serial_baud Allows you to set the baud rate (50-38400)
set rvon user
set rvon password
set rvon vad_threshold
Allows you to set the username for the RVON-1
card. By default the user name is “telex”
Allows you to set the password for the RVON-1
card. By default, the password is “password”
Lets you set the vad threshold.
NOTE: In AZedit, you can enable and disable
VAD, however, through Telnet you able to set the
amount. You will able to set the VAD threshold in
later versions of AZedit.
Note: This Telnet screen is almost duplicate to the right side of the Configuration screen for the RVON in AZedit.
31
Page 32

Product Specific Descriptions
set channel dest_ip
set channel dest_type
set channel dest_channel
set channel channel_codec
set channel input_gain
set channel output_gain
set the channel onhook
set channel offhook
Allows you edit the destination IP Address the
RVON-1 card will communicate with
Allows you to edit the destination type for the device
the RVON-1 card will talk with
Allows you to edit the destination channel of the
device the RVON-1 will talk with
Allows you to edit the CODEC to be used for
transferring the data between the two devices
Allows you to edit the input gain for the RVON-1
card
Allows you to edit the output gain for the RVON-1
card.
onhook = hang up
If the channel was already connected, going offhook
will have no effect (it is already offhook if
connected). Going onhook will hang up the call, and
it should then try to reconnect.
If the channel was not already connected, going
offhook will cause it to try and establish a
connection. Going onhook in this state will have no
effect (it is already onhook if idle.
offhook = connected
If the channel was already connected, going offhook
iwll have no effect (it is already offhook if
connected). Goign onhook will hang up the call, and
it should then try to reconnect.
If the channel was not already connected, going
offhook will cause it to try and establish a
connection . Going onhook in this state will have no
effect (it is already onhook).
NOTE: This Telnet screen is almost duplicate to the left side of the Configuration screen for the RVON in AZedit. One item
to note is the ONHOOK and OFFHOOK.....this is a setting regarding the connection of the card to the Matrix.
set emac Allows you to edit the Ethernet Speed settings
Auto (automatically negotiates the Ethernet settings)
10 half duplex
10 full duplex
100 half duplex
100 full duplex
32
Page 33

Appendix A
RV ON-I/O Quick S tart
Setting Channel Information of an RVON-I/O for a Local Keypanel
NOTE: In this example, the RVON-I/O is directly connected to the ADAM Intercom System with an RVON-8 installed.
This example installs a keypanel on the first port of an RVON-I/O that connects back to the first channel of the RVON-8.
RVON-I/O Unit Settings
• All four DIP switches need to be in the OPEN position (Up).
• RVON-I/O IP Address should be set to 192.168.0.1
• Running version 1.0.0 firmware or higher
RVON-8 Unit settings (done in AZedit)
• RVON-8 IP Address should be set to 192.168.0.10
• Running version 1.2.0 firmware or higher
To set the channel information, do the following:
1. Connect a keypanel to the J1 I/O 1 (Ethernet) connector on the RVON-I/O.
Addressing the keypanel is not needed.
2. Open a Telnet session.
3. At the prompt, type telnet 192.168.0.1 (default RVON-I/O IP Address).
The RVON login screen appears.
4. In the logon field, type telex (default user logon for the unit).
5. Press Enter.
6. In the password field, enter password (default password for the unit).
7. Press Enter.
8. At the prompt, type dbgcmd and press Enter to access the MXP programming shell.
9. At the prompt, type set channel.
10. Press Enter.
The Set Channel menu list appears.
33
Page 34

11. At the prompt, type set channel 0 dest_ip 192.168.0.10 (the address of the RVON-8 you want to connect with).
12. Press Enter.
13. At the prompt, type set channel 0 dest_type 0 (this tells the RVON-I/O it is connecting to an RVON-8).
14. Press Enter.
15. At the prompt, type set channel 0 dest_chan 0 (this tells the RVON-I/O it is connecting to channel 0 of the RVON-
8).
16. Press Enter.
17. At the prompt, type set channel 0 chan_codec 2.
This tells the RVON-I/O to use Codec G.711u, 64k 30ms packtes, VAD ON connecting back to the RVON-8. To use a
different codec, see Table 11, “Supplemental Coding Table,” on pag e 27.
18. Once finished, type activate.
19. Press Enter.
20. Configure the RVON-8 via AZedit to connect to the RVON-I/O.
The panel connected should be passing data and audio within a few moments.
The front panel Green LED for the first channel should be flashing, instead of solid, from the data.
Setting Channel Information of an RVON-I/O for a Remote Keypanel
NOTE: In this example, the first port of Zeus (J1) is connected to the I/O connector of the RVON-I/O, then connected via
Ethernet back to the first channel of an RVON-1 card installed in a KP-32.
RVON-I/O Unit Settings
• DIP switches two through four need to be in the OPEN position (Up).
• DIP Switch 1 should be in the “Down” position (Remote)
• RVON-I/O IP Address should be set to 192.168.0.1
• Running version 1.0.0 firmware or higher
KP-32 Unit settings
• The KP-32 with RVON-1 IP Address should be set to 192.168.0.10
• Running version 1.1.0 firmware or higher on the RVON-1 card
To find the RVON-1 version of the KP-32, do the following:
1. Open a Telnet Session.
2. Type telnet 192.168.0.10 (default).
3. Press Enter.
RVON login appears.
4. Type telex, and press Enter.
RVON pa ssword appears.
5. Type password, and press Enter.
6. At the prompt, type dbgcmd and press Enter.
You have entered MXP programming shell.
7. At the MXP prompt, type show rvon and press Enter.
A list of settings will appear which contains the RVON-1 version.
NOTE: If the RVON-1 is not at Version 1.1.0 or higher, contact your RTS service engineer.
34
Page 35

Setting Channel Information of an RVON-I/O for a Remote Keypanel
To set the channel information, do the following:
1. Connect the RVON-I/O Ethernet to the LAN.
2. Open a Telnet session.
3. At the prompt, type telnet 192.168.0.1 (default RVON-I/O IP Address).
The RVON login screen appears.
4. In the logon field, type telex (default user logon for the unit).
5. Press Enter.
6. In the password field, enter password (default password for the unit).
7. Press Enter.
8. At the prompt, type dbgcmd and press Enter to access the MXP programming shell.
9. At the prompt, type set channel.
10. Press Enter.
The Set Channel menu list appears.
11. At the prompt, type set channel 0 dest_ip 192.168.0.10 (the address of the RVON-1 you want to connect with).
12. Press Enter.
13. At the prompt, type set channel 0 dest_type 1 (this tells the RVON-I/O it is connecting to an RVON-1).
14. Press Enter.
15. At the prompt, type set channel 0 dest_chan 0 (this tells the RVON-I/O it is connecting to channel 0 of the RVON -
1).
16. Press Enter.
17. At the prompt, type set channel 0 chan_codec 3.
This tells the RVON-I/O to use Codec G.711u, 64k 30ms packtes, VAD ON connecting back to the RVON-1 channel.
To use a different codec, see X.
18. Type the set panel 0 poll_id 1 and press Enter.
This tells the RVON-I/O channel that is connection back to a matrix port with a poll id address of 1, por 1,9,17,25,
etc.).
19. Type set panel 0 baud 9600 and press Enter.
This tells the RVON-I/O that the data baud rate is 9600 bps for this channel.
20. Once finished, type activate.
21. Press Enter.
22. Configure the RVON-1 tp accept the RVON-I/O connection.
The panel connected should be passing data and audio within a few moments. The front panel gr een LED for the first
channel of the RVON-I/O should be flashing from the data instead of just solid when the keypanel is connected.
35
Page 36

 Loading...
Loading...