Page 1

RSA RADIUS Server 6.1
Administrator’s Guide
Powered by Steel-Belted Radius
®
Page 2

Contact Information
See our web site for regional Customer Support telephone and fax numbers.
RSA Security Inc. RSA Security Ireland Limited
www.rsasecurity.com
www.rsasecurity.ie
Copyright
Copyright © 2005 RSA Security, Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, modified,
distributed, sold, leased, transferred, or transmitted, in any form or by any means, without the written permission of
RSA Security, Inc. Information in this document is subject to change without notice.
Portions of this software copyright © 1995–2005 Funk Software, Inc. All rights reserved.
Portions of this software copyright © 1989, 1991, 1992 by Carnegie Mellon University Derivative Work - 1996, 19982000 Copyright 1996, 1998-2000 The Regents of the University of California All Rights Reserved Permission to use,
copy, modify and distribute this software and its documentation for any purpose and without fee is hereby granted,
provided that the above copyright notice appears in all copies and that both that copyright notice and this permission
notice appear in supporting documentation, and that the name of CMU and The Regents of the University of California
not be used in advertising or publicity pertaining to distribution of the software without specific written permission.
CMU AND THE REGENTS OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES WITH
REGARD TO THIS SOFTWARE, INCLUDING ALL IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND
FITNESS. IN NO EVENT SHALL CMU OR THE REGENTS OF THE UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA BE LIABLE
FOR ANY SPECIAL, INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES OR ANY DAMAGES WHATSOEVER
RESULTING FROM THE LOSS OF USE, DATA OR PROFITS, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT,
NEGLIGENCE OR OTHER TORTIOUS ACTION, ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE USE OR
PERFORMANCE OF THIS SOFTWARE.
Portions of this software copyright © 2001-2002, Networks Associates Technology, Inc All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the
following conditions are met:
• Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
disclaimer.
• Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
• Neither the name of the Networks Associates Technology, Inc nor the names of its contributors may be used to
endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS ``AS IS'' AND ANY
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES
OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT
SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED
TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR
BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY
WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
Portions of this software are copyright © 2001-2002, Cambridge Broadband Ltd. All rights reserved. Redistribution and
use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are
met:
• Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
disclaimer.
Page 3

• Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
• The name of Cambridge Broadband Ltd. may not be used to endorse or promote products derived from this
software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY
AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
HOLDER BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE
GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
(INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS
SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
Portions of this software copyright © 1995-2002 Jean-loup Gailly and Mark Adler This software is provided 'as-is',
without any express or implied warranty. In no event will the authors be held liable for any damages arising from the use
of this software. Permission is granted to anyone to use this software for any purpose, including commercial
applications, and to alter it and redistribute it freely, subject to the following restrictions:
• The origin of this software must not be misrepresented; you must not claim that you wrote the original software. If
you use this software in a product, an acknowledgment in the product documentation would be appreciated but is
not required.
• Altered source versions must be plainly marked as such, and must not be misrepresented as being the original
software.
• This notice may not be removed or altered from any source distribution.
HTTPClient package copyright © 1996-2001 Ronald Tschalär (ronald@innovation.ch).
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied
warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public
License for more details. For a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307, USA.
StrutLayout Java AWT layout manager copyright © 1998 Matthew Phillips (mpp@ozemail.com.au).
This library is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU Library General Public
License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied
warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Library General Public
License for more details. For a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc.,
59 Temple Place, Suite 330, Boston, MA 02111-1307, USA.
Trademarks
ACE/Agent, ACE/Server, Because Knowledge is Security, BSAFE, ClearTrust, Confidence Inspired, e-Titlement,
IntelliAccess, Keon, RC2, RC4, RC5, RSA, the RSA logo, RSA Secured, the RSA Secured logo, RSA Security,
SecurCare, SecurID, SecurWorld, Smart Rules, The Most Trusted Name in e-Security, Transaction Authority, and
Virtual Business Units are either registered trademarks or trademarks of RSA Security Inc. in the United States and/or
other countries. All other goods and/or services mentioned are trademarks of their respective companies.
Microsoft, Windows, Windows 2000, Internet Explorer, and other Microsoft products referenced herein are either
trademarks or registered trademarks of the Microsoft Corporation in the United States and other countries. Solaris is a
registered trademark in the U.S. and other countries, licensed exclusively through X/Open Company Limited. Sun,
Page 4

Sun Microsystems, Solaris, and all Sun-based trademarks and logos, Java, HotJava, JavaScript, the Java Coffee Cup
Logo, and all Java-based trademarks and logos are trademarks or registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the
United States and other countries. Raima, Raima Database Manager and Raima Object Manager are trademarks of
Birdstep Technology.
License agreement
This software and the associated documentation are proprietary and confidential to RSA Security, are furnished under
license, and may be used and copied only in accordance with the terms of such license and with the inclusion of the
copyright below. This software and any copies thereof may not be provided or otherwise made available to any other
person.
Neither this software nor any copies thereof may be provided to or otherwise made available to any third party. No title
to or ownership of the software or any intellectual property rights thereto is hereby transferred. Any unauthorized use or
reproduction of this software may be subject to civil and/or criminal liability.
This software is subject to change without notice and should not be construed as a commitment by RSA Security.
Note on encryption technologies
This product may contain encryption technology. Many countries prohibit or restrict the use, import, or export of
encryption technologies, and current use, import, and export regulations should be followed when exporting this
product.
Distribution
Limit distribution of this document to trusted personnel.
RSA notice
The RC5™ Block Encryption Algorithm With Data-Dependent Rotations is protected by U.S. Patent #5,724,428 and
#5,835,600.
First Printing: September 2005
Part Number: M05917ADM
Page 5

About This Guide
Audience .......................................................................................................................... ix
What’s In This Manual...................................................................................................ix
Related Documentation.................................................................................................xi
Chapter 1 About RSA RADIUS Server
RSA RADIUS Server Features...................................................................................... 1
RSA RADIUS Server Overview.................................................................................... 2
RADIUS Packets...................................................................................................... 4
RADIUS Configuration .......................................................................................... 5
Shared Secrets........................................................................................................... 6
RADIUS Ports.......................................................................................................... 8
Authentication..................................................................................................................8
Accounting........................................................................................................................9
Accounting Sequence ............................................................................................10
Attributes ........................................................................................................................12
Dictionaries .............................................................................................................12
Attribute Lists ......................................................................................................... 13
Attribute Values......................................................................................................14
Default Values ........................................................................................................15
Centralized Configuration Management .................................................................... 16
Replacing a Replica RADIUS Server ..................................................................17
Designating a New Primary RADIUS Server.................................................... 17
Recovering a Replica After a Failed Download ................................................18
Changing the Name or IP Address of a Server................................................. 18
Contents
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Contents v
Page 6

Chapter 2 Installing the RSA RADIUS Server
Before You Begin.......................................................................................................... 19
Required Files......................................................................................................... 19
Data Migration/Registration................................................................................ 19
Installing on Windows.................................................................................................. 20
System Requirements ............................................................................................ 20
Installing the RSA RADIUS Server.................................................................... 21
Uninstalling the RSA RADIUS Server Software .............................................. 22
Installing on Solaris....................................................................................................... 23
System Requirements ............................................................................................ 23
Installer Syntax....................................................................................................... 23
Installing the RSA RADIUS Server Software ................................................... 25
Stopping and Starting the RADIUS Daemon................................................... 27
Uninstalling the RSA RADIUS Server Software .............................................. 27
Migration Log File................................................................................................. 28
Installing on Linux ........................................................................................................ 29
System Requirements ............................................................................................ 29
Installer Syntax....................................................................................................... 29
Installing the RSA RADIUS Server Software ................................................... 31
Stopping and Starting the RADIUS Daemon................................................... 33
Uninstalling the RSA RADIUS Server Software .............................................. 34
Chapter 3 Using RSA RADIUS Administrator
Running RSA RADIUS Administrator...................................................................... 35
Navigating in RSA RADIUS Administrator............................................................. 36
RSA RADIUS Administrator Menus ................................................................. 36
RSA RADIUS Administrator Toolbar............................................................... 38
RSA RADIUS Administrator Windows ............................................................ 39
Using Context Menus ........................................................................................... 42
Accessing Online Help................................................................................................. 43
Displaying Version Information................................................................................. 43
Adding a License Key................................................................................................... 43
Exiting the RSA RADIUS Administrator ................................................................. 44
Chapter 4 Administering RADIUS Clients
RADIUS Clients Panel................................................................................................. 45
Adding a RADIUS Client ............................................................................................ 46
Verifying a Shared Secret ............................................................................................. 48
Deleting a RADIUS Client .......................................................................................... 49
vi Contents September 2005
Page 7

Chapter 5 Administering Profiles
About Profiles ................................................................................................................51
Adding a Checklist or Return List Attribute for a Profile ............................... 51
Resolving Profile and User Attributes ................................................................ 52
Default Profile ........................................................................................................52
Setting Up Profiles.........................................................................................................53
Adding a Profile......................................................................................................53
Removing a Profile ................................................................................................55
Chapter 6 Displaying Statistics
Displaying Server Authentication Statistics...............................................................57
Displaying Server Accounting Statistics..................................................................... 60
Resetting Server Statistics.............................................................................................62
Displaying RADIUS Client Statistics.......................................................................... 62
Chapter 7 Administering RADIUS Servers
Replication Panel ...........................................................................................................66
Adding a RADIUS Server Manually........................................................................... 66
Enabling a RADIUS Server .........................................................................................68
Deleting a RADIUS Server .......................................................................................... 68
Publishing Server Configuration Information ..........................................................69
Notifying Replica RADIUS Servers ...........................................................................69
Designating a New Primary RADIUS Server ...........................................................70
Recovering a Replica After a Failed Download........................................................ 70
Changing the Name or IP Address of a Server ........................................................71
Regenerating a Node Secret.........................................................................................72
Resetting the RADIUS Database................................................................................73
Chapter 8 Logging
Logging Files ..................................................................................................................75
Using the RADIUS System Log..................................................................................75
Level of Logging Detail.........................................................................................76
Controlling Log File Size ......................................................................................76
Using the Accounting Log ...........................................................................................77
Accounting Log File Format................................................................................77
First Line Headings................................................................................................ 78
Comma Placeholders.............................................................................................78
Standard RADIUS Accounting Attributes.........................................................79
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Contents vii
Page 8

Appendix A Using the LDAP Configuration Interface
LDAP Configuration Interface File ........................................................................... 81
About the LDAP Configuration Interface................................................................ 82
LDAP Utilities........................................................................................................ 82
LDAP Requests ..................................................................................................... 83
Downloading the LDAP Utilities........................................................................ 83
LDAP Version Compliance................................................................................. 84
Configuring the LDAP TCP Port....................................................................... 84
LDAP Virtual Schema.................................................................................................. 85
LDAP Command Examples ....................................................................................... 90
Searching for Records........................................................................................... 90
Modifying Records ................................................................................................ 91
Adding Records ..................................................................................................... 93
Deleting Records ................................................................................................... 94
Statistics Variables......................................................................................................... 95
Counter Statistics ................................................................................................... 95
Rate Statistics.......................................................................................................... 97
Glossary
Index
viii Contents September 2005
Page 9

Audience
About This Guide
The RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide describes how to install,
configure, and administer the RSA RADIUS Server software on a server running
the Solaris operating system, the Linux operating system, or the Windows 2000 or
Windows Server 2003 operating systems.
This manual is intended for network administrators responsible for implementing
and maintaining authentication, authorization, and accounting services. This
manual assumes that you are familiar with general RADIUS and networking
concepts and the specific environment in which you are installing
RSA RADIUS Server.
What’s In This Manual
This manual contains the following chapters and appendix:
X Chapter 1, “About RSA RADIUS Server,” presents an overview of
RSA RADIUS Server and summarizes important concepts relating to the
operation of RSA RADIUS Server.
X Chapter 2, “Installing the RSA RADIUS Server,” describes how to install and
uninstall the RSA RADIUS Server software on a Solaris, Linux, or Windows
computer.
X Chapter 3, “Using RSA RADIUS Administrator,” describes how to use the
RSA RADIUS Server Administrator to configure RSA RADIUS Server.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About This Guide ix
Page 10

X Chapter 4, “Administering RADIUS Clients,” describes how to set up remote
access server (RAS) devices as RSA RADIUS Server clients.
X Chapter 5, “Administering Profiles,” describes how to set up user profiles to
simplify user administration.
X Chapter 7, “Administering RADIUS Servers,” describes how to manage
RADIUS server replication.
X Chapter 6, “Displaying Statistics,” describes how to use the monitoring
capabilities in RSA RADIUS Server.
X Chapter 8, “Logging,” describes how to set up and use logging functions in
RSA RADIUS Server.
X Appendix A, “Using the LDAP Configuration Interface,” describes how to
use the optional LDAP Configuration Interface (LCI) add-on to
RSA RADIUS Server.
X The Glossary provides brief explanations for RADIUS terminology used in
this and other RSA RADIUS Server manuals.
Syntax Conventions
This manual uses the following conventions to present file and command line
syntax.
X radiusdir represents the directory into which RSA RADIUS Server has
been installed. By default, this is
RSA RADIUS
for Windows systems and /opt/rsa/radius on Linux and
C:\Program Files\RSA Security\
Solaris systems.
X Brackets [ ] enclose optional items in format and syntax descriptions. In the
following example, the first
include an optional second
Attribute argument is required; you can
Attribute argument by entering a comma and
the second argument (but not the square brackets) on the same line.
<add | replace> = Attribute [,Attribute]
In configuration files, brackets identify section headers:
the [Configuration] section of
radius.ini
In screen prompts, brackets indicate the default value. For example, if you
press E
uses the indicated default value (
x About This Guide September 2005
NTER without entering anything at the following prompt, the system
/opt).
Enter install path [/opt]:
Page 11

X Angle brackets < > enclose a list from which you must choose an item in
format and syntax descriptions.
X A vertical bar ( | ) separates items in a list of choices. In the following
example, you must specify
[AttributeName]
<add | replace> = Attribute [,Attribute]
add or replace (but not both):
Related Documentation
The following documents supplement the information in this manual.
RSA RADIUS Server Documentation
The RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Reference Guide describes configuration options for
the RSA RADIUS Server software.
Vendor Information
You can consult the online Vendor Information file for information about using
RSA RADIUS Server with different remote access servers and firewalls. To
access this file:
1 Start the RSA RADIUS Administrator application.
2 Choose
You can access the same information by clicking the
Web > NAS Vendor Information.
Web Info button on the
Add RADIUS Client or Edit RADIUS Client window.
Requests for Comments (RFCs)
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) maintains an online repository of
Request for Comments (RFC)s online at
X RFC 2865, Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS). C. Rigney, S.
Willens, A. Rubens, W. Simpson. June 2000.
X RFC 2866, RADIUS Accounting. C. Rigney. June 2000.
X RFC 2869, RADIUS Extensions. C. Rigney, W. Willats, P. Calhoun. June 2000.
X RFC 2882, Network Access Servers Requirements: Extended RADIUS Practices. D.
Mitton. July 2000.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About This Guide xi
http://www.ietf.org/rfc.html.
Page 12

X Internet-Draft, “The Protected One-Time Password Protocol
(EAP-POTP)”, M. Nystrom, June 2005.
ftp://ftp.rsasecurity.com/pub/otps/eap/
draft-nystrom-eap-potp-02.html
Third-Party Products
For more information about configuring your access servers and firewalls, consult
the manufacturer’s documentation provided with each device.
Getting Support and Service
RSA SecurCare Online https://knowledge.rsasecurity.com
Customer Support Information www.rsasecurity.com/support
Before You Call for Customer Support
Make sure you have direct access to the computer running the
RSA Authentication Manager software. Have the following information available
when you call:
X Your RSA Security Customer/License ID. You can find this number on the
license distribution medium or by running the Configuration Management
application on Windows servers, or by issuing an
sdinfo command on
Linux or Solaris servers.
X RSA Authentication Manager software version number.
X The make and model of the machine on which the problem occurs.
X The name and version of the operating system under which the problem
occurs.
xii About This Guide September 2005
Page 13

Chapter 1
About RSA RADIUS Server
RSA RADIUS Server is a complete implementation of the industry-standard
RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) protocols.
RSA RADIUS Server is designed to meet the access control and policy
management requirements of enterprises. It interfaces with a wide variety of
network access servers—including virtual private networks (VPNs), dial-in
servers, and wireless LAN (WLAN) access points (APs)—and authenticates
remote and WLAN users against your existing security infrastructure. This lets
you control who can access your network and what resources are available to
them, and requires little administration beyond your current management of LAN
users. RSA RADIUS Server then logs all access usage, so you can track and
document usage statistics.
RSA RADIUS Server Features
X Centralized management of user access control and security.
X Support for a wide variety of 802.1X-compliant access points and other
network access servers ensures compatibility in your network environment.
X Support for a variety of authentication methods, including Tunneled
Transport Layer Security (TTLS), Protected Extensible Authentication
Protocol (PEAP), Generic Token Card, RSA Security EAP (EAP-15), and
Protected One-Time Password (EAP-32).
X Use of encryption keys eliminates the possibility of spoofing or masquerading
as an “imposter agent.”
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About RSA RADIUS Server 1
Page 14

X Centralized configuration management (CCM) provides simplified
configuration management and automatic data distribution for multi-server
environments.
X Authentication logs provide a complete audit trail of user authentication
activity and administrative transactions.
X Encryption of communication between the RSA RADIUS Server and the
RSA Authentication Manager prevents electronic eavesdropping.
RSA RADIUS Server Overview
RADIUS is an industry-standard protocol for providing authentication,
authorization, and accounting services.
X Authentication is the process of verifying a user’s identity and determining
whether the user is allowed on the network.
X Authorization is the process of controlling the network resources that the
user can access on the protected network, such as privileges and time limits.
X Accounting is the process of generating log files that record statistics
describing each connection session, used for billing, system diagnosis, and
usage planning.
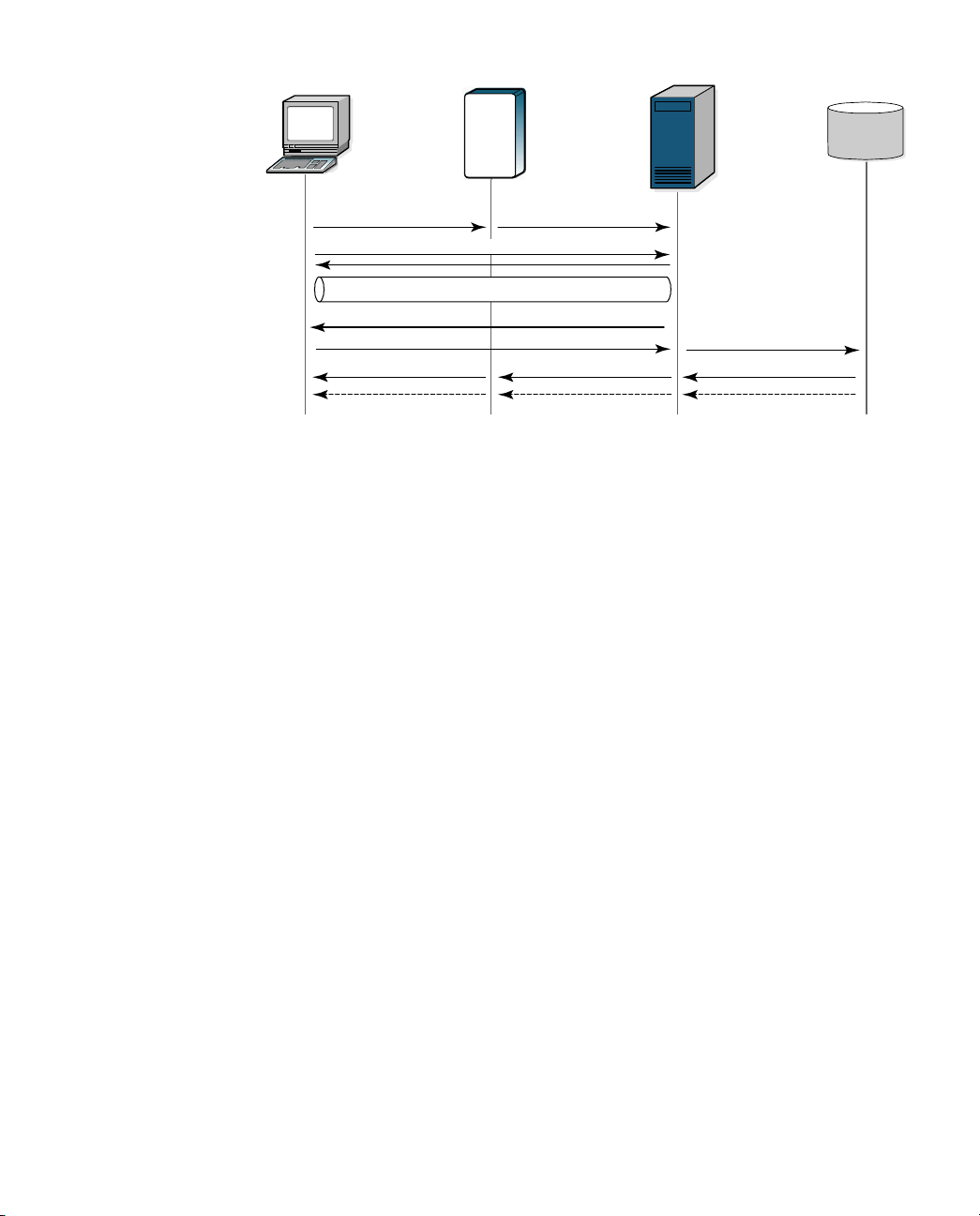
Figure 1 illustrates a simple RSA RADIUS authentication and authorization
sequence using a TTLS/PAP tunnel to facilitate communication between the
access client and the RSA RADIUS server.
Note that some access clients may be configured to use RSA Security EAP or
Protected One-Time Password (POTP) instead of a TTLS/PAP tunnel. In such
cases, the sequence of transactions is similar, though the communication
mechanics are different.
Note also that the RSA RADIUS server and the RSA Authentication Manager
can reside on the same network host or on different network hosts.
2 About RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 15
Access
Client
Remote
Access
Server
RSA
RADIUS
Server
RSA
Authentication
Manager
1. Connection Request
2. TTLS/PAP Tunnel Negotiation
TTLS/PAP Tunnel
4. User ID/Passcode
8a. Connection Accepted
8b. Connection Refused
Connection Notification
3. User ID/Passcode?
7a. Access-Accept (Attributes)
7b. Access-Reject
5. User ID/Passcode
6a. Passcode Accepted (Profile Name)
6b. Passcode Rejected
Figure 1 RSA RADIUS Authentication
1A RADIUS access client, who could be a dial-in user, a mobile user with
wireless network access, or someone working at a remote office, sends an
authentication request to a remote access server (RAS), which might be a wireless
Access Point, an ISDN bridge, or a modem pool.
NOTE: The terms “remote access server” (RAS) and “network access server”
(NAS) are interchangeable. This manual uses RAS, though some attribute
names and parameters retain the older ‘NAS’ in their names.
2 When the RAS receives a user’s connection request, it performs an initial
access negotiation with the user to establish connection information. It
forwards this information to the RSA RADIUS server, which uses the
information to create a tunnel between itself and the access client.
3 The RSA RADIUS server sends a request for the user’s credentials through
the TTLS tunnel.
4 The access client sends a user ID and passcode (tokencode and personal
identification number) to the RSA RADIUS server.
5 The RSA RADIUS server forwards the user’s user ID and passcode to the
RSA Authentication Manager, which verifies that the user ID exists and that
the passcode is correct for that user at that specific time.
6 If the user’s information is accepted, the RSA Authentication Manager
returns a message indicating that the passcode is accepted (6a). The
RSA Authentication Manager may also return the name of the profile
associated with this user in the Access-Accept message.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About RSA RADIUS Server 3
Page 16

If the user ID is not found or if the passcode is not appropriate for the
specified user, the RSA Authentication Manager returns a message indicating
the passcode is not accepted (6b).
7 If the RSA RADIUS server receives a message indicating the passcode is
accepted, it forwards a RADIUS Access-Accept message to the RAS (7a).
Z If the RSA Authentication Manager specified a profile name with the
accept message, the RSA RADIUS server sends the return list attributes
associated with that profile to the RAS.
Z If the RSA Authentication Manager did not specify a profile name with
the accept message, the RSA RADIUS server sends the return list
attributes associated with the default profile to the RAS.
For example, the Access-Accept message might specify that the access client
must use a specific IP address or be connected to a specific VLAN on the
network.
If the RSA RADIUS server receives a message indicating the passcode is
rejected, it forwards a RADIUS Access-Reject message to the RAS (7b).
NOTE: If the user requesting the network connection is in New Pin mode
or New Token mode (not shown), the RSA Authentication Manager sends
a message asking for more information, which the RSA RADIUS server
forwards to the user. When the user responds with values the
RSA RADIUS server can accept, the authentication sequence continues.
8 Depending on what information the RAS receives from the RSA RADIUS
server, the RAS accepts and configures the user connection or rejects the
user connection.
9 Based on the information it receives from the RSA RADIUS server, the RAS
grants or denies the connection request.
After the user is authenticated and the connection established, the RAS might
forward accounting data to the RSA RADIUS server to document the
transaction; the RSA RADIUS server can store or forward this data to support
billing for services provided during the network connection.
RADIUS Packets
A RADIUS client and a RADIUS server communicate by means of RADIUS
packets. RADIUS packets carry messages between the RADIUS client and
RADIUS server in a series of request and response transactions: the client sends a
request and expects a response from the server. If the response does not arrive,
the client can retry the request periodically.
4 About RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 17

Each RADIUS packet supports a specific purpose: authentication or accounting.
A packet can contain values called attributes. The attributes found in each packet
depend upon the type of packet (authentication or accounting) and the device
that sent it (for example, the specific make and model of the RAS device acting as
a RADIUS client).
For information on RADIUS authentication packet structures and attributes, see
RFC 2865, Remote Authentication Dial In User Service (RADIUS). For information
on RADIUS accounting packet structures and attributes, see RFC 2866, RADIUS
Accounting.
RADIUS Configuration
You must configure a RADIUS client and a RADIUS server before they can
communicate. If the client and server are on the same network, one administrator
might be able to configure both sides of the RADIUS communication. If the
client and server are on different networks, you might have to coordinate
RADIUS configuration details with the administrators of other networks.
RADIUS Server Configuration
You must configure how a RADIUS server responds to each of its clients. To
configure the RSA RADIUS Server, run the RSA RADIUS Administrator,
(described in “Running RSA RADIUS Administrator” on page 35), open the
RADIUS Clients panel (described in “RADIUS Clients Panel” on page 45), and
enter the following information for each RADIUS client:
X The IP address of the client device.
X The authentication shared secret used by RSA RADIUS Server and the client
device. For information on RADIUS shared secrets, see “Shared Secrets” on
page 6.
X The make and model of the client device, selected from a list of devices that
RSA RADIUS Server supports. If a specific make and model is not listed,
choose
- Standard Radius -.
RADIUS Client Configuration
You must configure each RADIUS client to contact its RADIUS server. To
configure a client to work with an RSA RADIUS Server, log on to the client
device, run its administration program, and enter the following information:
X The IP address of the RSA RADIUS Server.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About RSA RADIUS Server 5
Page 18
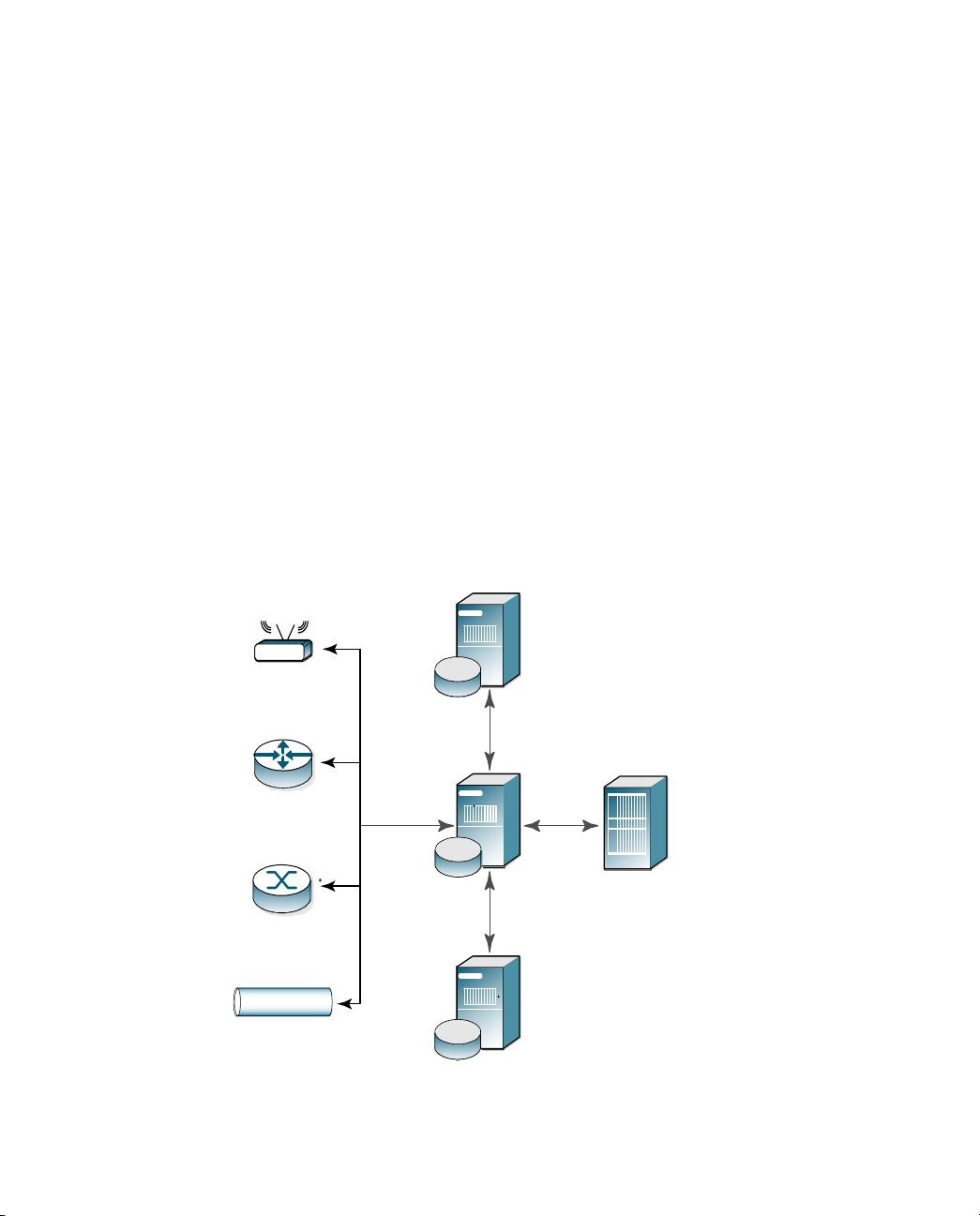
X The RADIUS shared secret to be used by the RSA RADIUS Server and the
X The UDP ports on which to send and receive RADIUS authentication and
Shared Secrets
A shared secret is a text string that serves as a password between hosts.
RSA RADIUS Server uses three types of shared secrets:
X RADIUS secret – Used to authenticate communication between a RADIUS
X Replication secret – Used to authenticate communication between a primary
X Node secret – Used to authenticate communication between a RADIUS
client device. For information on RADIUS shared secrets, see “Shared
Secrets” on page 6.
accounting packets. RSA RADIUS Server uses UDP ports 1645 and 1812 for
authentication and UDP ports 1646 and 1813 for accounting. For more
information, see “RADIUS Ports” on page 8.
server and a RADIUS client
RADIUS server and a replica RADIUS server
server and an RSA Authentication Manager server.
Replica
RADIUS
Access
Point
Server
Replication
Secret
Remote Access
Server (RAS)
802.1X-Compatible
Switch
Virtual Private
Network
RADIUS
Secret
Replication
Secret
Node
Secret
Primary
RADIUS
Server
Replica
RADIUS
Server
RSA
Authentication
Manager Server
Figure 2 Shared Secrets
6 About RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 19

RADIUS Secret
A RADIUS shared secret is a case-sensitive password used to validate
communications between a RADIUS server, such as RSA RADIUS Server, and a
RADIUS client, such as an Access Point (AP) or Remote Access Server (RAS).
RSA RADIUS Server supports shared secrets of up to 127 alphanumeric
characters, including spaces and the following special characters:
~!@#$%^&*()_+|\=-‘{}[]:”’;<>?/.,
Identical shared secrets must be configured on both sides of the RADIUS
communication link.
NOTE: Not all RAS devices support shared secrets of up to 127
alphanumeric/special characters. You should select shared secrets that are
fully supported by RADIUS devices in your network.
Most RADIUS clients allow you to configure different secrets for authentication
and accounting. On the server side, the configuration interface allows you to
create a list of known RADIUS clients (RAS devices). You should be able to
identify the authentication shared secret and accounting shared secret that a
server uses to communicate with each of the clients on this list.
During an authentication transaction, password information must be transmitted
securely between the RADIUS client (RAS or AP) and the RSA RADIUS Server.
RSA RADIUS Server uses the authentication shared secret to encrypt and
decrypt password information.
No encryption is involved in transmitting accounting data between a RADIUS
client and RADIUS server. However, the accounting shared secret is used by each
device to verify that it can “trust” any RADIUS communications it receives from
the other device.
Replication Secret
A replication secret is a text string used to authenticate communications between
a Primary RADIUS Server and a Replica RADIUS Server. You do not need to
configure the replication secret for a realm: the Primary RADIUS Server
generates it automatically, and each Replica RADIUS Server in a realm receives
the replication secret as part of its configuration package.
Node Secret
A node secret is a pseudorandom string known only to the RSA RADIUS Server
and RSA Authentication Manager. Before the RSA RADIUS Server sends an
authentication request to the RSA Authentication Manager, it encrypts the data
using a symmetric node secret key.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About RSA RADIUS Server 7
Page 20

RADIUS Ports
The RSA Authentication Manager software views the RSA RADIUS Server
service as a host agent. Communication between RSA RADIUS Server and
RSA Authentication Manager uses specific UDP ports, which are configured
during installation. To prevent “masquerading” by unauthorized hosts, you
configure RSA Authentication Manager with the IP addresses of each
RSA RADIUS Server host. Before RSA Authentication Manager accepts an
authentication request, it verifies that the source address contained in the request
matches an authorized host agent.
The RADIUS standard initially used UDP ports 1645 and 1646 for RADIUS
authentication and accounting packets. The RADIUS standards group later
changed the port assignments to 1812 and 1813, but many organizations continue
using the old 1645 and 1646 port numbers for RADIUS.
Any two devices that exchange RADIUS packets must use compatible UDP port
numbers. If you are configuring a RAS to exchange authentication packets with a
RADIUS server, you must find out which port the server uses to receive
authentication packets from its clients (1812, for example). You must then
configure the RAS to send authentication packets on the same port (1812). The
same is true for RADIUS accounting.
RSA RADIUS Server can listen on multiple ports. For compatibility, the server
listens to the old and new default RADIUS ports: ports 1645 and 1812 for
authentication, and ports 1646 and 1813 for accounting.
Authentication
Table 1 describes the conditions under which each type of RADIUS
authentication message is issued, and the purpose of any RADIUS attributes the
message contains.
Table 1. RADIUS Authentication Messages and Attributes
Message Conditions Purpose of Message Attributes
When a RAS receives a connection
request from a user, the RAS
authenticates the request by sending an
Access-Request to its RADIUS server.
8 About RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Identify the user.
Describe the type of connection the user is
trying to establish.
Page 21

Table 1. RADIUS Authentication Messages and Attributes (Continued)
Message Conditions Purpose of Message Attributes
When a RADIUS server authenticates a
connection request, it returns a RADIUS
Access-Accept to the RAS.
When a RADIUS server is unable to
authenticate a connection request, it
returns an Access-Reject to the RAS.
If initial authentication conditions are
met, but additional input is needed from
the user, the RADIUS server returns an
Access-Challenge to the RAS.
Accounting
To understand the RSA RADIUS Server accounting sequence, you need an
overview of RADIUS accounting messages. Table 2 describes the conditions
under which each type of message is issued, and the purpose of any RADIUS
attributes that a message contains.
Allow the RAS to complete access
negotiations.
Configure connection details such as
providing the RAS with an IP address it
can assign to the user.
Enforce time limits and other “class of
service” restrictions on the connection.
Terminate access negotiations.
Identify the reason for the authorization
failure.
Enable the RAS to prompt the user for
more authentication data.
Complete the current Access-Request, so
the RAS can issue a new one.
Table 2. Message Conditions and Attributes
Message Conditions Purpose of Message Attributes
Accounting data is sent from client to
server using an Accounting-Request
message. The client manufacturer
decides which types of accounting
requests are sent, and under which
conditions. This table describes the
most typical conditions.
The client ensures that the server
receives accounting requests. Most
clients retry periodically until the server
responds.
Depending on the value of the
Acct-Status-Type attribute, the message
type is considered to be Start, Stop,
Interim-Acct, Accounting-On, or
Accounting-Off.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About RSA RADIUS Server 9
Page 22

Table 2. Message Conditions and Attributes (Continued)
Message Conditions Purpose of Message Attributes
After receiving an Access-Accept from
the server, the RAS completes its
access negotiation with the user. The
RAS then sends a Start message to the
server.
After a connection is terminated, the
RAS sends a Stop message to the
server.
At intervals of approximately every six
minutes, the RAS sends an Interim-Acct
message to the server.
Every time a client device comes online,
whether after a failure or after an orderly
shutdown, it sends an Accounting-On
message to the server.
Every time a client device experiences
an orderly shutdown, before completing
its shutdown sequence it sends an
Accounting-Off message to the server.
Upon receipt of an Accounting-Request
message, the server sends an
Accounting-Response.
Record connection data such as user ID,
RAS identifier, RAS port identifier, port
type, and connection start time.
Record statistics regarding the connection.
One message contains the final value of
every statistic that this RAS is capable of
recording about this type of connection.
Record a “snapshot” of statistics regarding
the connection. One message contains the
current value of every statistic that this
RAS is capable of recording about this
type of connection.
Identify the device that is going online and
clear all session information.
Identify the device that is going offline and
clear all session information.
Complete the request/response cycle.
Accounting Sequence
A RAS can issue an Accounting-Request whenever it chooses, for example upon
establishing a successful connection. Each time an Accounting-Request message
arrives at the RSA RADIUS Server, an accounting transaction begins. During this
transaction, the server handles the message by examining the Acct-Status-Type
and other attributes within the message, and taking the appropriate action.
Comma-Delimited Log Files
When the RSA RADIUS Server accounting log is enabled, all of the RADIUS
accounting attributes that the server receives are reformatted and logged to a
Comma Separated Value (CSV) text file, which is easily imported into
spreadsheets and database programs for report generation and billing.
10 About RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 23

Tunneled Accounting
During authentication, a user is typically identified by attributes such as
User-Name (in the authentication request) and Class (in the authentication accept
response). Standard RADIUS accounting requests typically include these
attributes in messages flagging Start, Interim, and Stop events so that the user’s
identity can be recorded for accounting and auditing purposes.
When an organization uses a tunneled authentication protocol such as
EAP/TTLS or EAP/PEAP, the identity of a user requesting authentication might
be concealed from the RAS; the User-Name attribute carried by the outer
authentication protocol is typically a nonunique value such as anonymous. As a
result, the outer User-Name value included in accounting requests might not be
sufficient to determine a user’s identity. Class attributes provided by an
authentication server cannot be included in cleartext in an outer Access-Accept
message because they might contain clues about the user’s identity, thereby
defeating the identity-hiding feature of the tunneled protocol.
Tunneled accounting enables RSA RADIUS Server to pass user identity
information to accounting processes without exposing user identities to a RAS or
AP that should not see them. When tunneled accounting is enabled, RADIUS
attributes are encrypted and encapsulated in a Class attribute. If the information
for a Class attribute exceeds the attribute payload size (253 octets),
RSA RADIUS Server returns more than one Class attribute for a user.
Tunneled accounting works as follows:
1 The RSA RADIUS Server acting as the tunnel endpoint for EAP/TTLS or
EAP/PEAP encrypts a user’s inner User-Name and Class attributes when it
authenticates the user.
2 The server returns the encrypted information to the RAS or AP encapsulated
in a Class attribute in the outer Access-Accept message. The RAS or AP
associates this encapsulated identity attribute with the user, and echoes the
encapsulated identity attribute whenever it generates an accounting request
for the user.
3 When the RSA RADIUS Server receives an accounting request from a RAS
or Access Point, the server scans the request for an encapsulated identity
attribute.
4 If the server finds an encapsulated identity attribute, it decapsulates and
decrypts the attributes to reconstitute the original inner User-Name and Class
attributes.
5 The server substitutes the decrypted attributes for the ones returned from
the RAS or AP.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About RSA RADIUS Server 11
Page 24

6 The server processes the accounting request locally.
Attributes
Dictionaries
To implement tunneled accounting, you must configure the
to specify how attributes should be presented, and you must configure the
spi.ini file to specify the keys that are used to encrypt and decrypt users’
identity information.
You work with RADIUS attributes while setting up users, profiles, and RADIUS
clients on the RSA RADIUS Server. The RSA RADIUS Server Administrator
program allows you to choose RADIUS attributes by name from a predefined list.
For each attribute, the RSA RADIUS Administrator prompts you to enter values
using familiar data types such as string, integer, telephone number, or network
address.
RSA RADIUS Server uses dictionary files to store lists of RADIUS attributes.
RSA RADIUS Server uses these dictionaries to parse authentication and
accounting requests and generate responses.
The main RSA RADIUS Server dictionary file (
defined by the RADIUS standard. The
directory as the RSA RADIUS Server service (usually
\RSA Security\RSA RADIUS\Service
/opt/rsa/radius on Solaris and Linux computers).
radius.dct file resides in the same
radius.dct) lists attributes
on Windows computers and
classmap.ini file
C:\Program Files
Vendor-Specific Attributes
In addition to the standard attributes, many RAS devices use vendor-specific
attributes (VSAs) to complete a connection. RSA RADIUS Server supports a
large number of specific RAS devices by providing vendor-specific, proprietary
dictionary files. These files also reside in the server directory and use the filename
extension
.dct.
Make/Model Field
During RSA RADIUS Server configuration, when you make a selection in the
RADIUS client
contains the VSAs for this client device. Thereafter, whenever the server receives
a RADIUS packet from this client device, it can consult this dictionary file for any
12 About RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Make/model field, you are telling the server which dictionary file
Page 25

nonstandard attributes that it encounters in the packet. Standard RADIUS
attributes are always defined by the
make/model for a RADIUS client, choose the default option:
Radius -
.
radius.dct file. If you do not know the
- Standard
Attribute Lists
For the most part, the selections currently available in the
Make/model field are
devices whose vendors have provided up-to-date attribute dictionaries.
Documentation for these vendors and their products is available online by
clicking the
Web info button on the RADIUS Clients panel (described on
page 45).
Updating Attribute Information
If your RAS vendor announces a new product, a new attribute, or a new value for
an attribute, you can add this information to your RSA RADIUS Server
configuration. You can edit the dictionary file for that vendor to add new
attributes or attribute values, or you can create a new vendor-specific dictionary
file that contains new attributes and values.
For information on modifying vendor dictionary files, refer to the
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Reference Guide.
You can use profiles to control authentication at finer levels of detail than simple
user ID and password checking allow. Checklists and return lists provide powerful
tools for the authentication and authorization of users.
Checklist Attributes
A checklist is a list of attributes that must accompany the request for connection
before the connection request can be authenticated. The RAS must send
attributes that match the checklist associated with a user entry; otherwise,
RSA RADIUS Server rejects the user even if the user’s name and password are
valid.
By including appropriate attributes in the checklist, a variety of rules can be
enforced. For example, only specific users might be permitted to use ISDN or
dial-in connections to a particular RAS, or Caller ID might be used to validate a
user against a list of acceptable originating telephone numbers.
A checklist is created by choosing attributes from a list of all RADIUS attributes
known to the RSA RADIUS Server. This list can include a variety of
vendor-specific attributes.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About RSA RADIUS Server 13
Page 26

During authentication, RSA RADIUS Server filters the checklist based on the
dictionary for the RADIUS client that sent the authentication request. The server
ignores any checklist attribute that is not valid for this device.
Return List Attributes
A return list is a list of attributes that RSA RADIUS Server must return to the RAS
after authentication succeeds. The return list usually provides additional
parameters that the RAS needs to complete the connection, typically as part of
PPP negotiations. Return list attributes can be “authorization configuration
parameters.”
By including appropriate attributes in the return list, you can create a variety of
connection policies. Specific users can be assigned particular IP addresses or IPX
network numbers; IP header compression can be turned on or off; or a time limit
can be assigned to the connection.
You create a return list by choosing attributes from a list of all RADIUS attributes
known to the RSA RADIUS Server. This list can include a variety of
vendor-specific attributes.
During authentication, RSA RADIUS Server filters the return list based on the
dictionary for the specific RADIUS client that sent the authentication request.
The server omits any return list attribute that is not valid for this device.
Attribute Values
The value of each RADIUS attribute has a well-defined data type: numeric, string,
IP or IPX address, time, or hexadecimal. For example,
string and contains a telephone number. RAS-Port-Type is an item
type
from a list, and can be
Sync, Async, and so forth.
Multi-Valued Attributes
Attributes can be single- or multi-valued. Single-valued attributes appear at most
once in the checklist or return list; multi-valued attributes might appear several
times.
If an attribute appears more than once in the checklist, this means that any one of
the values is valid. For example, you can set up a checklist to include both
and
Async values for attribute RAS-Port-Type. This means that the user can
dial into a Sync port or an Async port, but not one of the ISDN ports.
If an attribute appears more than once in the return list, each value of the
attribute is sent as part of the response packet. For example, to enable both IP
and IPX header compression for a user, you would configure the
14 About RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Callback-Number is of
Sync
Page 27

Framed-Compression
VJ-TCP-IP-header-compression and once with the value
value
IPX-header-compression.
attribute to appear twice in the return list: once with the
Orderable Attributes
Certain multi-valued return list attributes are also orderable; that is, the attribute
can appear more than once in a RADIUS response, and the order in which the
attributes appear is important.
For example, the
to the user for display. A multi-line message is sent by including this attribute
multiple times in the return list, with each line of the message in its proper
sequence.
Reply-Message attribute allows text messages to be sent back
System Assigned Values
Some attributes do not allow the administrator to set a value.
RSA RADIUS Server retrieves the appropriate values for these attributes when
they are needed.
Echo Property
Using the echo property, you can force an attribute from the RADIUS request to
be echoed in the RADIUS response. For example, you might add
Callback-Number to the return list and click the echo checkbox.
RSA RADIUS Server takes the value of the Callback-Number it receives in the
RADIUS request and echoes it back to the client in the RADIUS response; if it
receives no Callback-Number, it echoes nothing.
You enter
indicates that one of the callback numbers you supplied must be present in the
RADIUS request, and that number should be echoed in the RADIUS response.
Callback-Number one or more times into the checklist. This
Default Values
Choosing default for a checklist attribute specifies that, if the RADIUS request
does not include this attribute, the request should not be rejected. Instead, the
value supplied as the default should be used as if it were received as part of the
request. One use for default values is to require that an attribute in a RADIUS
request must have one of several values, or must not be present at all. Another use
is to provide a default value for an attribute in conjunction with the echo property
in the return list.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About RSA RADIUS Server 15
Page 28

If an attribute appears once in the checklist marked as default, and the same
attribute appears in the return list marked as
echo, the server echoes the actual
value of the attribute in the RADIUS response if the attribute appears in the
RADIUS request. If the attribute does not appear in the RADIUS request, the
server echoes the default value (from the checklist) in the response.
If you add multiple values of the same attribute to the checklist, only one of them
can be marked as default.
For example, an administrator adds several Callback-Number values to the
checklist and marks one of them as default. The administrator adds
Callback-Number to the return list and specifies it as echo.
X If a Callback-Number value is present in the RADIUS request, it must match
one of the checklist values or the user is rejected.
X If it does match, the user is accepted and the value supplied is echoed in the
RADIUS response.
X If no Callback-Number is supplied in the request, the user is accepted and
the default value is echoed in the response.
Other checklist attributes provide configuration for the user, such as time-of-day
and concurrent-login-limit information.
Centralized Configuration Management
The RSA RADIUS Server supports the replication of RADIUS configuration
data from a Primary RADIUS Server to a maximum of 10 Replica RADIUS Servers
within a realm on a customer network. Replica servers help balance the load of
authentication requests coming in from RADIUS clients, and ensure that
authentication services are not interrupted if the Primary or other Replica
RADIUS servers stops working.
All the servers within a realm reflect the current configuration specified by the
network administrator: the network administrator modifies the configuration on
the Primary RADIUS Server, and the Primary RADIUS Server propagates the
new configuration to its Replica RADIUS Servers. For example, after a network
administrator configures a new RADIUS client or profile on the Primary
RADIUS Server, the network administrator tells the Primary RADIUS Server to
publish a configuration package file (
updated configuration information. After publication, the Primary RADIUS
Server notifies each Replica RADIUS Server that a new configuration package is
ready. Each Replica then downloads and installs the configuration package to
update its settings.
16 About RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
replica.ccmpkg) that contains the
Page 29
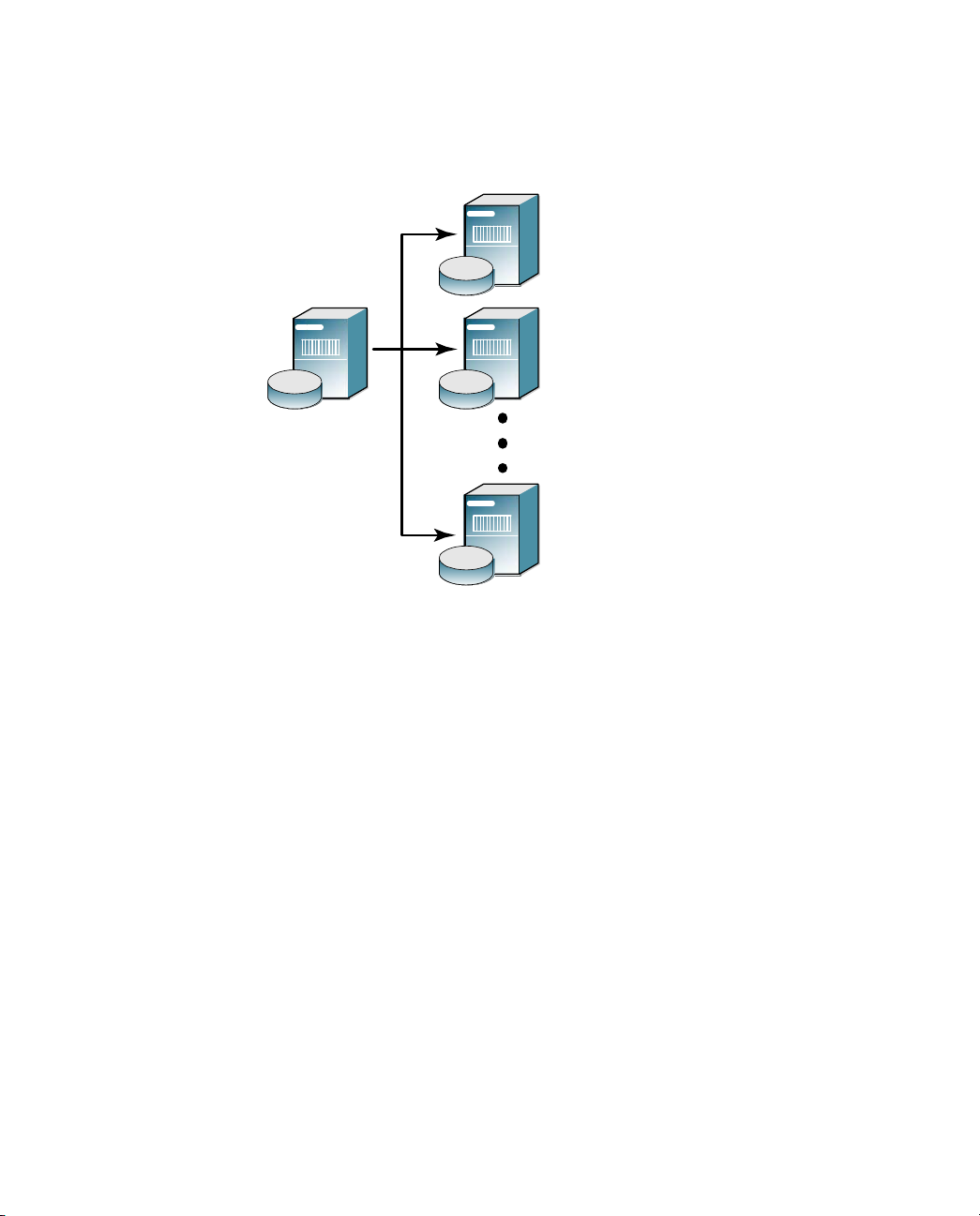
The Primary RADIUS Server maintains a list of the Replica RADIUS Servers
that have registered with it. The Primary RADIUS Server uses this list to track
which servers to notify after it publishes an updated configuration package to
resynchronize the configuration of Replica RADIUS Servers.
RADIUS
Replica 1
RADIUS
Replica 2
Primary
RADIUS
Server
RADIUS
Replica 10
Figure 3 Primary and Replica RADIUS Servers
Replacing a Replica RADIUS Server
To replace a failed Replica RADIUS Server, a network administrator shuts down
the failed server, installs the RSA RADIUS Server software on a replacement
server, and enables the Replica RADIUS Server. The Replica RADIUS Server
then downloads and installs its configuration package from the Primary RADIUS
Server.
Designating a New Primary RADIUS Server
You can change which server within a realm is designated as the Primary
RADIUS Server for that realm. For more information, see “Designating a New
Primary RADIUS Server” on page 70.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide About RSA RADIUS Server 17
Page 30

Recovering a Replica After a Failed Download
If a Replica RADIUS Server fails during the download of a configuration
package, its configuration may be corrupted or it may have a stale secret. For
information on how to recover a Replica after a failed download, refer to
“Recovering a Replica After a Failed Download” on page 70.
Changing the Name or IP Address of a Server
To change the DNS name or IP address of a Primary or Replica RADIUS Server,
you run the
(Solaris/Linux) utility. For more information, refer to “Changing the Name or IP
Address of a Server” on page 71.
rsainstalltool (Windows) or the rsaconfiguretool
18 About RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 31

Chapter 2
Installing the RSA RADIUS Server
The RSA RADIUS Server software package includes the server software and
various dictionary and configuration files to support authentication and
accounting. This chapter describes how to install the RSA RADIUS Server
software on a Windows, Solaris, or Linux host.
Before You Begin
Required Files
The RSA RADIUS Server software requires the path to four files (sdconf.rec,
radius.cer, radius.key, and server.cer) to communicate with
RSA Authentication Manager.
If you install the RSA RADIUS Server software on the host running
RSA Authentication Manager (local installation), the installer obtains the path to
these files automatically. If you install the RSA RADIUS Server software on a
different host (remote installation), the installer asks you for the path to these
files.
Data Migration/Registration
When you install a Primary RADIUS Server on a host that previously ran an older
version of RSA Authentication Manager configured to use RSA RADIUS Server,
the installer provides an option to migrate your RADIUS data to the new
RSA RADIUS Server. Information transferred during data migration includes
RADIUS client names, IP addresses, and shared secrets; profile names, checklist
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Installing the RSA RADIUS Server 19
Page 32

attributes, and return list attributes; and RSA SecurID prompts used to format
messages to users.
Data migration also registers the RSA RADIUS Server as an agent host with
RSA Authentication Manager. Registration information includes the server type
(Primary or Replica), fully qualified name, administrative port number, and IP
address.
NOTE: If aliases are required to support network address translation (NAT),
they must be configured manually on the RSA Authentication Manager host.
Data migration is not available for new RSA Authentication Manager
installations.
Installing on Windows
This section describes how to install the RSA RADIUS Server software on a
Windows server.
System Requirements
Table 3 lists the hardware and software requirements of the RSA RADIUS Server
software.
Table 3. Windows Server – System Requirements
Operating system • Windows 2000 with Service Pack 4
• Windows Server 2003 (STD edition) with Service Pack 1.
Networking TCP/IP must be configured on the Windows host for the
RSA RADIUS Server to function properly.
Memory The RSA RADIUS Server software requires a host with at least
256 megabytes of working memory (512 megabytes for servers
with more than 10,000 RADIUS users.)
Disk space Installing the RSA RADIUS Server software requires 26
megabytes of space on the hard disk; hard disk requirements
for running RSA RADIUS Server depend on your system's
product configuration.
20 Installing the RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 33

Installing the RSA RADIUS Server
To install the RSA RADIUS Server software on a Windows host:
1 Log on to the Windows server.
2 Run the RSA RADIUS Server software installation from a CD or from a
network server.
Z Using the CD-ROM installer – If you want to install the
RSA RADIUS Server software from a CD, insert the
RSA RADIUS Server installation CD-ROM, choose
enter the drive letter and
D:\setup
Z Using the .msi file – Run the RSA RADIUS Server.msi file from
the network server or CD-ROM, or copy the file to your computer and
run it locally.
Start > Run, and
setup command:
3 When the installer wizard window opens, click
4 When the Welcome window opens, click
Next to continue.
Next to continue.
5 When the Place of Purchase window opens, click the appropriate radio
button and click
6 When the License Agreement window opens, click the
the license agreement
7 When the Setup Type window opens, click the
want to install the RSA RADIUS Server files in the
RSA Security\RSA RADIUS
Next to continue.
I accept the terms in
radio button. Click Next to continue.
Complete radio button if you
C:\Program Files\
directory.
If you want to install RSA RADIUS Server software in a directory other than
the default
directory, click the
C:\Program Files\RSA Security\RSA RADIUS
Custom radio button, then click the Change button. Select
the directory in which you want to install the RSA RADIUS Server software.
Click
OK.
Click
Next to continue.
8 If you are installing a Primary RADIUS Server, click the
RSA RADIUS Server button.
If you are installing a Replica RSA RADIUS Server, click the
Replica RSA RADIUS Server
button. If the RSA Authentication Manager
Install as Primary
Install as
application is not running on the server, you are prompted to specify the
location of the Primary RSA RADIUS Server. You can specify the name, IP
address(es), and replication secret of the Primary RADIUS Server, or you can
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Installing the RSA RADIUS Server 21
Page 34

click the Browse button to locate the directory containing the sdconf.rec,
radius.cer, server.cer, and radius.key files on your network.
9 When the Primary RSA RADIUS Server window opens, specify the
replication secret used to authenticate communications between the Primary
RADIUS Server and Replica RADIUS Servers in the Primary Shared Secret
field.
If you are upgrading from a previous release of the
RSA Authentication Manager software and you want to import your profile
information into RSA RADIUS Server, click the
database
checkbox.
Migrate RSA RADIUS
10 When the Start Service window opens, click the
service checkbox if you want your computer to run the RADIUS service at
the end of the installation sequence.
Click
Next to continue.
11 When the Ready to Install the Program window opens, click
the installation of the RSA RADIUS Server software.
12 When installation is completed, the InstallShield Wizard Completed window
opens. Click
Finish.
After you finish installing the RSA RADIUS Server software, run the
RSA Authentication Manager application and launch the
RSA RADIUS Administrator application to verify that it can communicate with
the RADIUS server.
NOTE: After you install the RSA RADIUS Server software, you may need to
modify the server configuration files. For more information, refer to the
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Reference Guide.
Uninstalling the RSA RADIUS Server Software
To uninstall the RSA RADIUS Server software from a Windows host, run the
Add or Remove Programs Control Panel, choose
Remove.
RSA RADIUS Server, and click
Yes, start the RSA RADIUS
Install to begin
22 Installing the RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 35

Installing on Solaris
This section describes how to install and uninstall the RSA RADIUS Server on a
Solaris server.
System Requirements
The RSA RADIUS Server software package includes the server daemon and
various dictionary and database files to support user authentication.
Table 4. Solaris Server – System Requirements
Hardware Sun UltraSPARC workstation
Operating system Solaris 9
Memory At least 256 megabytes of working memory.
Disk space Installing the RSA RADIUS Server software requires at least
Networking TCP/IP must be configured on the Solaris host for the
Installer Syntax
234 megabytes of space on the hard disk; hard disk
requirements for running RSA RADIUS Server depend on
your system's product configuration.
RSA RADIUS Server to function properly.
To run the Solaris version of the RSA RADIUS Server installer, you execute the
following command:
install_rsa.sh [-dir directory] [-identity {PRIMARY |
REPLICA}] [-port port-num}] [-path path]
[-reppkg path] [-primary hostname] [-primary_ips ips]
[-primary_secret secret] [-overwrite] [-migrate}
[-silent] [-start_sbr] [-usage|-help|-h]
Table 5 explains the function of each command option.
Table 5. Command Options for the install_rsa.sh Command
Option Function
-dir
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Installing the RSA RADIUS Server 23
Specifies the top-level directory for installation of the
RSA RADIUS Server files.
Default value is
/opt.
Page 36

Table 5. Command Options for the install_rsa.sh Command (Continued)
Option Function
-identity
-migrate
Specifies whether you are installing a Primary or Replica
RADIUS Server.
Valid values are
Default value is
Indicates you want to run the RSA RADIUS Server
migration utility (rsainstalltool), which transfers
RADIUS settings from an older version of
RSA Authentication Manager and registers the
RSA RADIUS Server as a host agent.
For information on the migration utility, refer to “Data
Migration/Registration” on page 19.
PRIMARY and REPLICA.
PRIMARY.
-overwrite Specifies that the tprsMigReg.log installation log
file from a previous installation of RSA RADIUS Server
can be overwritten.
-path
Specifies the path to the radius.cer, server.cer,
radius.key, and sdconf.rec files.
/opt.
-primary option if you are specifying the
-port
-primary
Default value is
Specifies the TCP port used for administration of the
RSA RADIUS Server.
Default value is 1813.
Specifies the name of the Primary RADIUS Server.
Use only when installing a Replica RADIUS Server. Do
not use the
-reppkg option.
-primary_ips
-primary_secret
Specifies the IPv4 address or addresses of the Primary
RADIUS Server. If your Primary RADIUS Server has
more than one network interface, you can enter as many
as four IP addresses separated by commas.
Use only when installing a Replica RADIUS Server. Do
not use the -primary_ips option if you are specifying
the
-reppkg option.
Specifies the CCM shared secret used to authenticate
communications between the Primary RADIUS Server
and Replica RADIUS Servers.
Do not use the
specifying the
-primary_secret option if you are
-reppkg option.
24 Installing the RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 37

Table 5. Command Options for the install_rsa.sh Command (Continued)
Option Function
-reppkg Specifies the path to the replica.ccmpkg
configuration file.
Use only when installing a Replica RADIUS Server. Do
not use the
-reppkg option if you are specifying the
-primary, -primary_ips, and
-primary_secret options.
/opt.
-silent option and a required setting is
-silent option, the installer
-silent
-start_sbr
Default value is
Specifies that, if all required information is supplied
through command options, the installer does not display
user prompts.
If you use the
missing, the installer prompts you for the missing setting.
If you specify other command options and values and
you do not specify the
uses the values you specified as defaults and prompts
you to confirm or override them.
Specifies that the installer should start the RADIUS
daemon at the conclusion of the installation process.
-usage|-help|-h Displays help for the install_rsa.sh command.
Installing the RSA RADIUS Server Software
The following procedure describes how to install the RSA RADIUS Server
software on a Solaris server. Some of the steps in the procedure are omitted if you
specify the
1 Log into the Solaris server as
2 Copy the RSA RADIUS Server installation files (
install_rsa.sh) to the Solaris server.
The
directory on the server.
3 Change your current working directory to the location of the installation files
you copied in Step 2.
4 Execute the following command to run the installation script.
# ./install_rsa.sh [options]
See Table 5 on page 23 for an explanation of the install_rsa.sh
command options.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Installing the RSA RADIUS Server 25
-silent option for the install_rsa.sh command.
root.
RSARadius.pkg and
RSARadius.pkg and install_rsa.sh files must reside in the same
Page 38

5 Specify the directory where you want to install the RSA RADIUS Server files.
By default, the installation script puts the
the
/opt directory (that is, /opt/rsa/radius).
Enter install path [/opt]:
/rsa/radius directory files in
6 If you are installing the RSA RADIUS Server software on a host that is not
running the RSA Authentication Manager software (remote installation),
specify the location of the
sdconf.rec files.
Enter path to RSA files [/export/home/opt/rsa]:
radius.cer, server.cer, radius.key, and
If you are installing the RSA RADIUS Server software on a host that is
running the RSA Authentication Manager software (local installation), the
installer copies the
sdconf.rec files automatically.
radius.cer, server.cer, radius.key, and
7 Specify the number of the TCP port used to administer
RSA RADIUS Server.
The default port number is 1813.
Enter RSA administration port [1813]:
8 Specify whether you are installing a Primary or Replica RADIUS Server.
Enter RADIUS identity (REPLICA or PRIMARY) [PRIMARY]:
9 If you are installing a Replica RADIUS Server, specify whether a
configuration package generated by the Primary RADIUS Server is available.
Is replica.ccmpkg file present (y/n) [n]?
If you enter y, you are prompted to specify the path to the replica.ccmpkg file.
Enter path to replica.ccmpkg [/opt/rsa]:
10 If you are installing a Replica RADIUS Server and a configuration package is
not available, specify the name of the Primary RADIUS Server.
Enter primary host name:
11 If you are installing a Replica RADIUS Server and a configuration package is
not available, specify the IP address or addresses of the Primary RADIUS
Server. If the Primary RADIUS Server has more than one network interface
(multi-homed), you can enter as many as four IP addresses, separating
addresses with commas.
Enter primary host IP address list (max 4, comma
separated):
12 Specify the host secret used to authenticate communication between the
Primary RADIUS Server and Replica RADIUS Servers.
26 Installing the RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 39

Enter primary host secret:
13 If you are installing a Primary RADIUS Server on a host running an earlier
version of the RSA Authentication Manager software, specify whether you
want to migrate data to the current installation.
Do you want to migrate data from RSA Server (y/n) [n]?
If the installation succeeds, the installer displays the following message.
Configuring for use with generic database
RSA RADIUS installation succeeded.
If the installation fails, the installer displays the following message and asks you
whether you want to roll back the files that were installed.
Installation failed. Please see
/opt/rsa/radius/tprsMigReg.log for details.
Configuration of RSA Radius failed.
The installation has failed, would you like it cleaned
up (y/n) [y]? y
Cleaning up installation....
Removing /etc/rc2.d/S90radius script.
Removing /etc/rc2.d/K90radius script.
Stopping and Starting the RADIUS Daemon
After the RADIUS daemon is installed on the server, it stops and starts
automatically each time you shut down or restart the server. You can stop the
RADIUS daemon at any time by issuing the following command:
/etc/rc2.d/S90radius stop
Use the following command to start the RADIUS daemon:
/etc/rc2.d/S90radius start
Uninstalling the RSA RADIUS Server Software
To uninstall the RSA RADIUS Server software:
1 Stop the RADIUS daemon currently running on your server.
2 Back up your RSA RADIUS Server directory.
3 Log into the Solaris server as
4 Type the following command to uninstall the RSA RADIUS Server software:
# ./opt/rsa/radius/install/uninstall_rsa.sh
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Installing the RSA RADIUS Server 27
root.
Page 40

5 Type y when you are asked to confirm that you want to uninstall the
RSA RADIUS Server software.
Confirm removal of sbr-rsa_1.0-1 (y/n) [y]? y
Removing /etc/rc2.d/S90radius script.
Removing /etc/rc2.d/K90radius script.
Removal of <RSARadius> was successful.
RSARadius removed.
Migration Log File
If the RSA RADIUS Server migration utility (rsainstalltool) encounters a
problem while it is running, it records the problem in the
which is stored in the RSA RADIUS Server directory (
default).
Log for RSA to SBR Install Utility.
Install Date:07/15/2005 Install Time:12:52:55
INFO: SBR Radius services directory is /opt/rsa/radius/
INFO: Host Name phobos != DNS Name phobos.mars.com,
Replacing Host Name
INFO: SBR Radius server name is phobos.mars.com
INFO: SBR Radius server IP Address is 192.168.21.137
INFO: SBR Radius server port is 1813
INFO: Attempting to Locate RSA Server
INFO: RSA Server is Remote. Attempting to Locate Key
and Certificate Files.
INFO: Copying RSA files from /export/home/ecarter/RSA/
to /opt/rsa/radius/
ERROR: server.cer not found
tprsMigReg.log file,
/opt/rsa/radius by
28 Installing the RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 41

Installing on Linux
This section describes how to install and uninstall the RSA RADIUS Server
software on a Linux server.
System Requirements
The RSA RADIUS Server software package includes the server daemon and
various dictionary and database files to support authentication.
Table 6. Linux Server – System Requirements
Hardware X86 workstation
Operating system RedHat Enterprise 3.0
Memory At least 256 megabytes of working memory
Disk space Installing the RSA RADIUS Server software requires at
Networking TCP/IP must be configured on the Linux host for the
(512 megabytes for servers with more than 10,000
RADIUS users.)
least 234 megabytes of space on the hard disk; hard disk
requirements for running RSA RADIUS Server depend on
your system's product configuration.
RSA RADIUS Server to function properly.
Installer Syntax
To run the Linux version of the RSA RADIUS Server installer, you execute the
following command:
install_rsa.sh [-dir directory] [-identity {PRIMARY |
REPLICA}] [-port port-num}] [-path path] [-reppkg path]
[-primary hostname] [-primary_ips ips] [-primary_secret
secret] [-overwrite] [-migrate} [-silent] [-start_sbr]
[-usage|-help|-h]
Table 7 explains the function of each command option.
Table 7. Command Options for the install_rsa.sh Command
Option Function
-dir
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Installing the RSA RADIUS Server 29
Specifies the top-level directory for installation of the
RSA RADIUS Server files.
Default value is
/opt.
Page 42

Table 7. Command Options for the install_rsa.sh Command (Continued)
Option Function
-identity
-migrate
Specifies whether you are installing a Primary or Replica
RADIUS Server.
Valid values are
Default value is
Indicates you want to run the RSA RADIUS Server
migration utility (rsainstalltool), which transfers
RADIUS settings from an older version of
RSA Authentication Manager and registers the
RSA RADIUS Server as a host agent.
For information on the migration utility, refer to “Data
Migration/Registration” on page 19.
PRIMARY and REPLICA.
PRIMARY.
-overwrite Specifies that the tprsMigReg.log installation log
file from a previous installation of RSA RADIUS Server
should be overwritten.
-path
Specifies the path to the radius.cer, server.cer,
radius.key, and sdconf.rec files.
/opt.
-primary option if you are specifying the
-port
-primary
Default value is
Specifies the TCP port used for administration of the
RSA RADIUS Server.
Default value is 1813.
Specifies the name of the Primary RADIUS Server.
Use only when installing a Replica RADIUS Server. Do
not use the
-reppkg option.
-primary_ips
-primary_secret
Specifies the IPv4 address or addresses of the Primary
RADIUS Server. If your Primary RADIUS Server has
more than one network interface, you can enter as many
as four IP addresses separated by commas.
Use only when installing a Replica RADIUS Server. Do
not use the -primary_ips option if you are specifying
the
-reppkg option.
Specifies the CCM shared secret used to authenticate
communications between the Primary RADIUS Server
and Replica RADIUS Servers.
Do not use the
specifying the
-primary_secret option if you are
-reppkg option.
30 Installing the RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 43

Table 7. Command Options for the install_rsa.sh Command (Continued)
Option Function
-reppkg Specifies the path to the replica.ccmpkg
configuration file.
Use only when installing a Replica RADIUS Server. Do
not use the
-primary, -primary_ips, and
-primary_secret options.
Default value is
-silent
-start_sbr
-usage|-help|-h Displays help for the install_rsa.sh command.
Specifies that, if all required information is supplied
through command options, the installer does not display
user prompts.
If you use the
missing, the installer prompts you for the missing setting.
If you specify other command options and values and
you do not specify the
uses the values you specified as defaults and prompts
you to confirm or override them.
Specifies that the installer should start the RADIUS
daemon at the conclusion of the installation process.
-reppkg option if you are specifying the
/opt.
-silent option and a required setting is
-silent option, the installer
Installing the RSA RADIUS Server Software
The following procedure describes how to install the RSA RADIUS Server
software on a Linux server. Some of the steps in the procedure are omitted if you
specify the
1 Log into the Linux server as
2 Copy the RSA RADIUS Server installation files
(
The
in the same directory on the server.
3 Change your current working directory to the location of the installation files
you copied in Step 2.
4 Execute the following command to run the installation script.
# ./install_rsa.sh [options]
See Table 7 on page 29 for an explanation of the install_rsa.sh
command options.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Installing the RSA RADIUS Server 31
-silent option for the install_rsa.sh command.
root.
sbr-rsa-1.0-1.i386.rpm and install_rsa.sh) to the Linux server.
sbr-rsa-1.0-1.i386.rpm and install_rsa.sh files must reside
Page 44

5 Specify the directory where you want to install the RSA RADIUS Server files.
By default, the installation script puts the
the
/opt directory (that is, /opt/rsa/radius).
Enter install path [/opt]:
/rsa/radius directory files in
6 If you are installing the RSA RADIUS Server software on a host that is not
running the RSA Authentication Manager software (remote installation),
specify the location of the
sdconf.rec files.
Enter path to RSA files [/export/home/opt/rsa]:
radius.cer, server.cer, radius.key, and
If you are installing the RSA RADIUS Server software on a host that is
running the RSA Authentication Manager software (local installation), the
installer copies the
sdconf.rec files automatically.
radius.cer, server.cer, radius.key, and
7 Specify number of the TCP port used to administer RSA RADIUS Server.
The default port number is 1813.
Enter RSA administration port [1813]:
8 Specify whether you are installing a Primary or Replica RADIUS Server.
Enter RADIUS identity (REPLICA or PRIMARY) [PRIMARY]:
9 If you are installing a Replica RADIUS Server, specify whether a
configuration package generated by the Primary RADIUS Server is available.
Is replica.ccmpkg file present (y/n) [n]?
If you enter y, you are prompted to specify the path to the replica.ccmpkg file.
Enter path to replica.ccmpkg [/opt/rsa]:
10 If you are installing a Replica RADIUS Server and a configuration package is
not available, specify the name of the Primary RADIUS Server.
Enter primary host name:
11 If you are installing a Replica RADIUS Server and a configuration package is
not available, specify the IP address or addresses of the Primary RADIUS
Server. If the Primary RADIUS Server has more than one network interface
(multi-homed), you can enter as many as four IP addresses, separating
addresses with commas.
Enter primary host IP address list (max 4, comma
separated):
32 Installing the RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 45

12 Specify the host secret used to authenticate communication between the
Primary RADIUS Server and Replica RADIUS Servers.
Enter primary host secret:
13 If you are installing a Primary RADIUS Server on a host running an earlier
version of the RSA Authentication Manager software, specify whether you
want to migrate data to the current installation.
Do you want to migrate data from RSA Server (y/n) [n]?
If the installation succeeds, the installer displays the following message.
Configuring for use with generic database
RSA RADIUS installation succeeded.
If the installation fails, the installer displays the following message and asks you
whether you want to roll back the installation.
Installation failed. Please see
/opt/rsa/radius/tprsMigReg.log for details.
Configuration of RSA Radius failed.
The installation has failed, would you like it cleaned
up (y/n) [y]? y
Cleaning up installation....
Removing /etc/init.d/sbrd script.
Stopping and Starting the RADIUS Daemon
After the RADIUS daemon is installed on the server, it stops and starts
automatically each time you shut down or restart the server. You can stop the
RADIUS daemon on a Linux server at any time by issuing the following
command:
/etc/init.d/sbrd stop
When you execute the sbrd stop command, RSA RADIUS Server allows its
subsystems to complete outstanding work, release resources, and then stops the
mkded (btrieve) daemon and the radius service gracefully.
If the RADIUS daemon fails to stop after you issue an
you can use the optional
force argument to terminate all subsystems
immediately.
/etc/init.d/sbrd stop force
Use the following command to start the RADIUS daemon:
/etc/init.d/sbrd start
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Installing the RSA RADIUS Server 33
sbrd stop command,
Page 46

Uninstalling the RSA RADIUS Server Software
To uninstall the RSA RADIUS Server software:
1 Stop the RADIUS daemon currently running on your server.
2 Back up your RSA RADIUS Server directory.
3 Log into the Linux server as
root.
4 Type the following command to uninstall the RSA RADIUS Server software:
# ./uninstall_rsa.sh
5 Type y when you are asked to confirm that you want to uninstall the
RSA RADIUS Server software.
Confirm deletion of RSA RADIUS Server (y/n) [y]?
The uninstall script displays a confirmation message (RSA RADIUS Server
removed
NOTE: If you delete the RSA RADIUS Server directory before you execute the
uninstall_rsa.sh command, the uninstall script cannot find the files it is
supposed to delete, causing it to fail. If this occurs, execute the following
command to clear the package database:
) when it finishes running.
rpm -e --noscripts sbr-rsa-1.0-1.i386.rpm
34 Installing the RSA RADIUS Server September 2005
Page 47

Chapter 3
Using RSA RADIUS Administrator
The RSA RADIUS Administrator is a Java-based application that enables you to
configure settings for the RSA RADIUS Server. This chapter presents an
overview of how to use the RSA RADIUS Administrator.
Running RSA RADIUS Administrator
NOTE: The RSA RADIUS Administrator will not start unless the
“Administrator” user in the RSA Authentication Manager application has been
configured with a token or password. For information on how to configure the
Administrator user with a token or password, refer to the RSA Authentication
Manager 6.1 Administrator’s Guide.
To run the RSA RADIUS Administrator:
1 Choose
Host Mode
2 When the RSA Authentication Manager 6.1 Administration window opens,
choose
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Using RSA RADIUS Administrator 35
Start > All Programs > RSA Security > RSA Authentication Manager
.
RADIUS > Manage RADIUS Server.
Page 48

Navigating in RSA RADIUS Administrator
Figure 4 illustrates the RSA RADIUS Administrator user interface. This section
describes how to use the RSA RADIUS Administrator menus and toolbar.
Menu Bar
Toolbar
Navigation Frame
Content Frame
Figure 4 RSA RADIUS Administrator User Interface
RSA RADIUS Administrator Menus
The main RSA RADIUS Administrator window has four menus: File, Panel,
Web, a nd He l p.
File Menu
Table 8 describes the functions of each entry in the File menu in the
RSA RADIUS Administrator.
Table 8. File Menu Options
Menu Entry Function
License Opens the Add a License for Server window, which lets you
add a license string for your RSA RADIUS Server software.
For more information, see “Adding a License Key” on page 43.
Page Setup Opens the Page Setup window, which lets you configure your
printer settings.
36 Using RSA RADIUS Administrator September 2005
Page 49

Table 8. File Menu Options (Continued)
Menu Entry Function
Print Prints the information in the active window. When you print the
information in a panel, RSA RADIUS Administrator preserves
the column spacing used on screen. If a table is wider than the
printed page, pages are printed in a matrix, with pages
numbered to indicate columns and rows (1-1, 1-2, 2-1, 2-2) in
the matrix.
Exit Exits the RSA RADIUS Server application.
Panel Menu
Table 9 describes the functions of each entry in the Panel menu in the
RSA RADIUS Administrator.
Table 9. Panel Menu Options
Menu Entry Function
RADIUS Clients Displays the RADIUS Clients panel in the
RSA RADIUS Administrator window. For more information,
see Chapter 4, “Administering RADIUS Clients” on
page 45.
Profiles Displays the Profiles panel in the
RSA RADIUS Administrator window. For more information,
see Chapter 5, “Administering Profiles” on page 51.
Replication Displays the Replication panel in the
RSA RADIUS Administrator window. For more information,
see Chapter 7, “Administering RADIUS Servers” on
page 65.
Statistics Displays the Statistics panel in the
RSA RADIUS Administrator window. For more information,
see Chapter 6, “Displaying Statistics” on page 57.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Using RSA RADIUS Administrator 37
Page 50

Web Menu
Table 10 describes the functions of each entry in the Web menu in the
RSA RADIUS Administrator.
Table 10. Web Menu Options
Menu Entry Function
More about RSA
RADIUS Server
NAS Vendor Information Opens the Funk RADIUS/AAA Compatibility Guide
Opens the Funk Software webpage.
webpage, which lets you review information about remote
access devices and wireless LAN devices made by
third-party vendors.
Help Menu
Table 11 describes the functions of each entry in the Help menu in the
RSA RADIUS Administrator.
Table 11. Help Menu Options
Menu Entry Function
Contents Opens the online help for the RSA RADIUS Administrator
application.
Manuals Displays the RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s
Guide or RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Reference Guide (in
PDF format).
About Displays the About RSA RADIUS Administrator window,
which lists version information for the
RSA RADIUS Administrator. For more information, see
“Displaying Version Information” on page 43.
RSA RADIUS Administrator Toolbar
After you log on to the RSA RADIUS Server, you can use the toolbar (Figure 5)
to manipulate RSA RADIUS Administrator objects. The buttons on the
RSA RADIUS Administrator toolbar change when you change panels to provide
buttons appropriate for the current context.
38 Using RSA RADIUS Administrator September 2005
Page 51

Figure 5 RSA RADIUS Administrator Toolbar
Table 12. RSA RADIUS Administrator Toolbar
Toolbar Button Function
Refresh Refreshes the displayed list of items in the
RSA RADIUS Administrator window.
Print Prints the contents of the active panel.
Add Adds an object to the RSA RADIUS Server database.
Edit Edits an existing object in the RSA RADIUS Server database.
Active only when an object is selected in the active panel.
Cut Deletes an existing object from the RSA RADIUS Server
database and copies its information to the Clipboard. Active
only when an object is selected in the active panel.
Copy Copies settings for the selected object from the
RSA RADIUS Server database to the Clipboard. Active only
when an object is selected in the active panel.
Paste Pastes an object from the Clipboard to the
RSA RADIUS Server database. Active only after a Cut or
Copy command has been used.
Delete Deletes an existing object from the RSA RADIUS Server
database.
Publish (Replication
panel only)
Notify (Replication
panel only)
Reset (Statistics
panel only)
Initiates creation of replication package on the Primary
RADIUS Server.
Initiates download of replication package by Replica RADIUS
Servers.
In the Statistics panel, resets statistics to zero.
RSA RADIUS Administrator Windows
This section summarizes how to use RSA RADIUS Administrator windows and
controls.
Adding an Entry
To add an entry to the RSA RADIUS Server database, open the appropriate panel
and click the
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Using RSA RADIUS Administrator 39
Add button on the RSA RADIUS Administrator toolbar. The
Page 52

RSA RADIUS Administrator displays an Add window. A sample Add window
appears in Figure 6.
Figure 6 Sample Add Window
Every object of the same type must have a unique name. If the name you assign
to an item is already being used by another item of the same type, the
RSA RADIUS Administrator displays a warning.
Editing an Entry
To edit an existing entry to the RSA RADIUS Server database, open the
appropriate panel and double-click the item you want to change (or choose the
item and click the
RSA RADIUS Administrator displays the settings for the item you selected in an
Edit window. A sample Edit window appears in Figure 7. The
disabled until the contents of a field in the Edit window changes.
NOTE: You cannot change the name associated with an item in the Edit
window. To change an item’s name, you must cut and paste the item and
assign the cut/copied item its new name.
40 Using RSA RADIUS Administrator September 2005
Edit button on the RSA RADIUS Administrator toolbar). The
Save button is
Page 53

Figure 7 Sample Edit Window
Cutting/Copying/Pasting Records
Panels displaying tables of items have Cut, Copy, and Paste buttons in the toolbar.
You can choose an item from the display and cut or copy it to the Clipboard, and
then add a new record to the display by pasting it from the Clipboard.
The Clipboard can contain one item of each type, such as one RADIUS client or
one user. If you copy an item to the Clipboard and then copy another item of the
same type, the information for the second item overwrites the information for the
first item. Clipboard contents are preserved until you exit the
RSA RADIUS Administrator.
When you paste an item, the RSA RADIUS Administrator displays a window
similar to the Add window with the pasted record’s contents. The
cleared; you must enter a unique name to save the pasted information as a new
record. Canceling from a Paste operation does not change the contents of the
Clipboard.
Name field is
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Using RSA RADIUS Administrator 41
Page 54

Figure 8 Sample Paste Window
Resizing Columns
You can resize columns in an RSA RADIUS Administrator table by dragging the
column header boundary to the left or right.
Changing Column Sequence
You can change the sequence of columns in an RSA RADIUS Administrator
table by dragging the column headers left or right.
Sorting Information
By default, items in RSA RADIUS Administrator tables are sorted by name. You
can sort items in any order by clicking a column header.
Previously sorted tables retain their order when the table is sorted on another
column. If you want to sort a table by more than one column, click the less
significant column, and then click the more significant column.
Using Context Menus
You can right-click an object in RSA RADIUS Administrator windows to display
a context menu for that object. The contents of the context menu depends on the
type of item; for example, if you right-click a RADIUS client entry, the context
menu provides options for copying, cutting, pasting, and deleting items.
42 Using RSA RADIUS Administrator September 2005
Page 55
If you right-click a blank area in an RSA RADIUS Administrator window, the
context menu displays a different set of options. For example, if you right-click a
blank space in the RADIUS Client panel, the context menu provides options for
refreshing the display and for adding, pasting, or printing information.
Accessing Online Help
To access help with the RSA RADIUS Server Administrator, click the ? (Help)
button on an RSA RADIUS Administrator window, press
Contents
.
F1, or choose Help >
To view the PDF version of the RSA RADIUS Server manuals, choose
Manuals and choose the manual you want to open.
Displaying Version Information
To identify the current version of the RSA RADIUS Administrator, choose Help
> About
Figure 9 About RSA RADIUS Server Window
to open the About RSA RADIUS Server window (Figure 9).
Adding a License Key
Help >
You must add a license key if you want to use the LDAP Configuration Interface
(LCI), which is described in Appendix A, “Using the LDAP Configuration
Interface.”
To add a license key to an RSA RADIUS Server installation:
1 Start the RSA RADIUS Administrator application.
2 Choose
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Using RSA RADIUS Administrator 43
File > License.
Page 56

3 When the Add a License for Server window (Figure 10) opens, enter the
license key and click
OK.
When the server displays a confirmation message, click
Figure 10 Add a License for Server Window
4 Restart your RSA RADIUS Server.
Exiting the RSA RADIUS Administrator
To close the RSA RADIUS Administrator, choose File > Exit.
Closing the RSA RADIUS Administrator has no impact on the
RSA RADIUS Server service or daemon.
OK.
44 Using RSA RADIUS Administrator September 2005
Page 57

Administering RADIUS Clients
A RADIUS client is a network device or software application that interfaces with
the RSA RADIUS Server when it needs to authenticate a user or to record
accounting information about a network connection.
This chapter describes how to set up RADIUS clients.
RADIUS Clients Panel
The RADIUS Clients panel (Figure 11) lets you identify the devices that you want
to define as clients of the RSA RADIUS Server.
Chapter 4
Figure 11 RADIUS Clients Panel
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering RADIUS Clients 45
Page 58
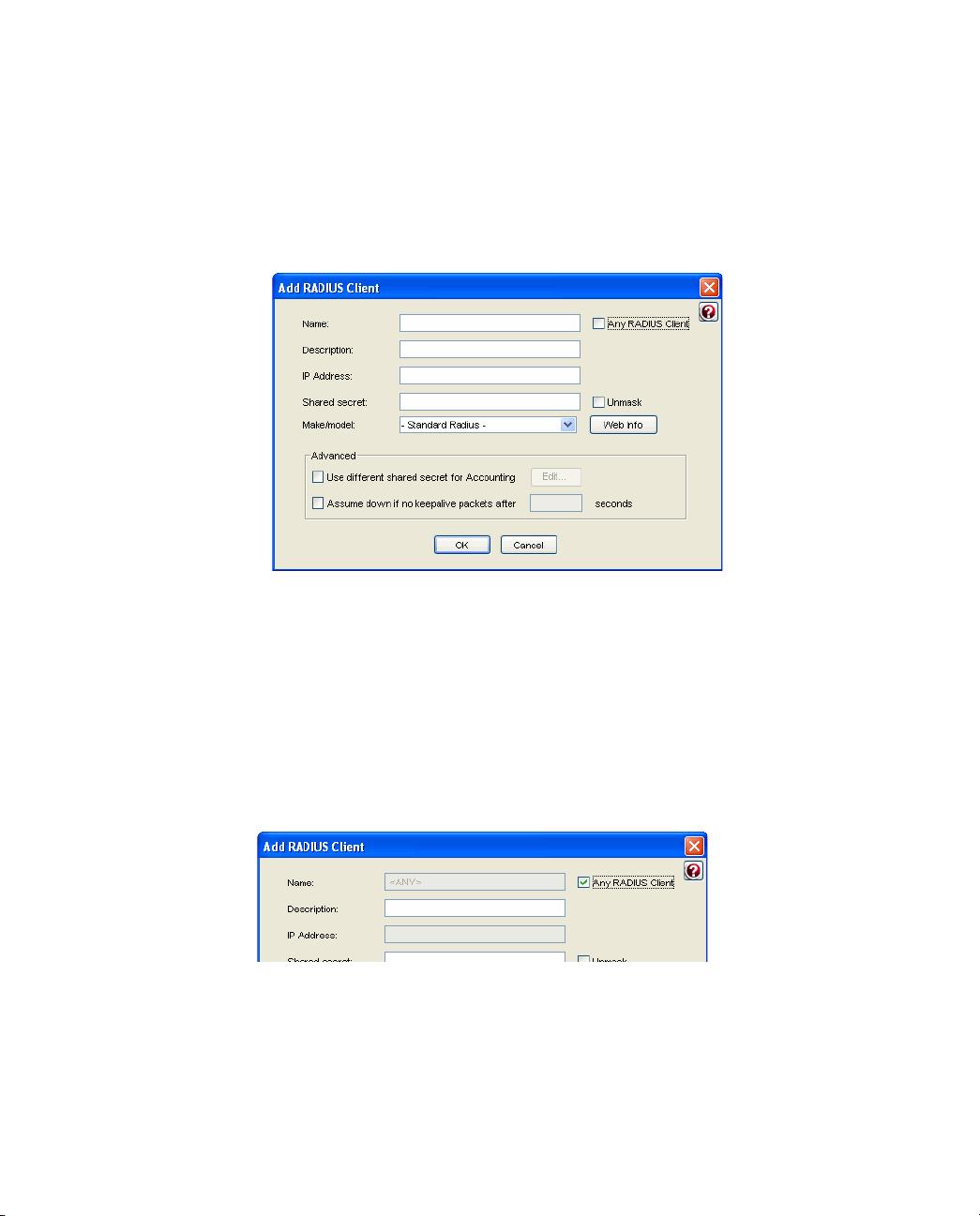
Adding a RADIUS Client
To add a RADIUS client:
1 Open the RADIUS Clients panel.
2 Click the
Add button.
The Add RADIUS Client window (Figure 12) opens.
Figure 12 Add RADIUS Client Window
3 Enter the name of the RADIUS client in the Name field.
Although you can assign any name to a RADIUS client entry, you should use
the device's hostname to avoid confusion.
You can create a special RADIUS client entry called
Any RADIUS Client checkbox (Figure 13). The <ANY> RADIUS client
<ANY> by clicking the
enables RSA RADIUS Server to accept requests from any RAS, as long as
the shared secret is correct.
Figure 13 Creating an <ANY> RADIUS Client
Note that the IP Address field for an <ANY> RADIUS client cannot be
edited.
<ANY> implies that the server accepts requests from any IP address,
provided that the shared secret is correct.
46 Administering RADIUS Clients September 2005
Page 59
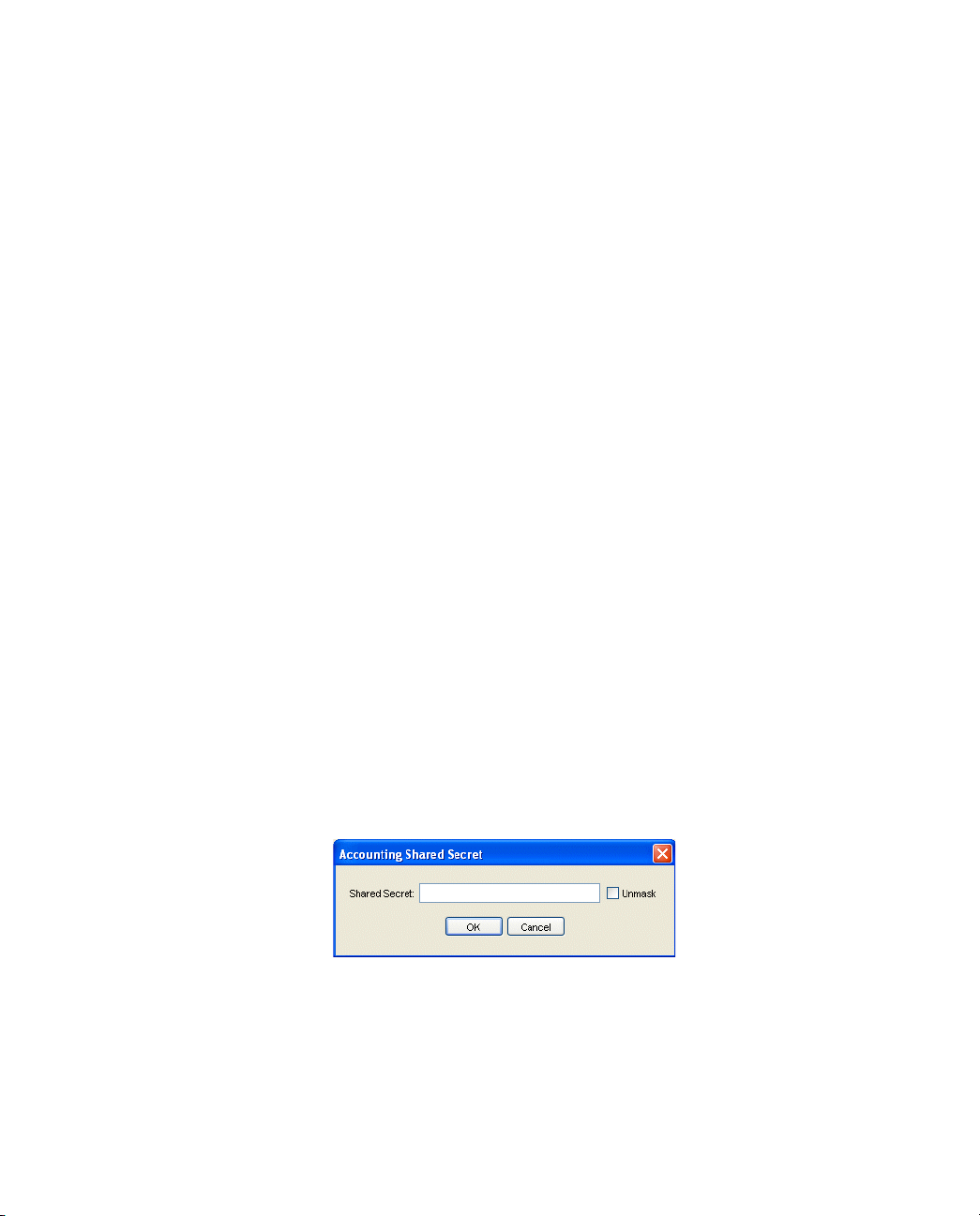
See “Shared
Secrets” on
page 6.
4 Enter the IP address or DNS name of the RADIUS client in the IP Address
field.
If you enter a DNS name, the RSA RADIUS Administrator resolves the
name you enter to its corresponding IP address and displays the result in the
IP Address field.
5 Enter the RADIUS authentication shared secret for the RADIUS client in
the
Shared secret field.
For privacy, asterisks are echoed as you type. You can choose
to display the characters in the shared secret.
secret
Unmask shared
After you complete configuration of the RADIUS authentication secret on
the server side, you must enter the same RADIUS authentication secret when
you configure the RADIUS client.
6 Use the
Make/model list to choose the make and model of your RADIUS
client device.
The
Make/model selection tells RSA RADIUS Server which dictionary of
RADIUS attributes to use when communicating with this client. If you are
not sure which make and model you are using or if your device is not in the
list, choose
NOTE: For information about the various brands of RAS device supported by
RSA RADIUS Server, click the
- Standard Radius -.
Web Info button.
7 If you want the RADIUS client to use different RADIUS secrets for
authentication and accounting:
a Click the
b Click the
Use different shared secret for accounting checkbox.
Edit button.
c When the Accounting Shared Secret window (Figure 14) opens, enter the
RADIUS secret you want the RADIUS client to use for accounting.
Figure 14 Accounting Shared Secret Window
For privacy, asterisks are echoed as you type. You can click the Unmask
checkbox to display the characters in the shared secret.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering RADIUS Clients 47
Page 60

d Click OK.
You must enter the same accounting shared secret when you configure
the RADIUS client.
8 Optionally, indicate whether you want to enable keepalive processing and
specify how long the server waits for RADIUS packets from the client before
assuming connectivity has been lost.
If you click the
enter a value in the
Assume down if no keepalive packets after checkbox, you can
(seconds) field. If the server does not receive any
RADIUS packets from this client after the specified number of seconds, the
server assumes that the connection to the client is lost or that the client
device has failed. When this happens, RSA RADIUS Server gracefully closes
any user it has authenticated for the client. RSA RADIUS Server adjusts the
counts of concurrent user connections appropriately.
NOTE: If the value you enter in the (seconds) field is too low, valid user or
tunnel connections can be lost. For example, during low usage periods, a RAS
device might not send any RADIUS packets to the RSA RADIUS Server, even
though the device is still functioning.
Verifying a Shared Secret
To verify a shared secret on the RSA RADIUS Server:
1 Open the RADIUS Clients panel.
2 Select the RADIUS client whose shared secret you want to verify and click
the
Edit button (or double-click the RADIUS client entry).
The Edit RADIUS Client window opens.
3 Enter the shared secret you think is assigned to the RADIUS client in the
Shared secret field.
4 Click the
Val ida te button.
If you entered the correct shared secret, the Validation Successful window opens.
Click
OK.
Deleting a RADIUS Client
To delete a RADIUS client:
1 Open the RADIUS Clients panel.
48 Administering RADIUS Clients September 2005
Page 61

2 Select the RADIUS client entry you want to delete.
3 Click the
Delete button on the RSA RADIUS Administrator toolbar.
4 When you are prompted to confirm the deletion request, click
Yes.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering RADIUS Clients 49
Page 62

50 Administering RADIUS Clients September 2005
Page 63

This chapter describes how to set up and administer user profiles.
About Profiles
RSA RADIUS Server lets you define default templates of checklist and return list
attributes called profiles. A profile provides specific attributes for one or both lists.
You can define as many profiles as you require. Profiles provide a powerful means
of managing and configuring accounts. To change attributes settings across many
users immediately, edit the profile that you have assigned to these users.
Chapter 5
Administering Profiles
Adding a Checklist or Return List Attribute for a Profile
A checklist attribute is an item of information that must accompany a RADIUS
Access-Request for a connection before the connection can be authenticated.
A return list attribute is an item of information that the RSA RADIUS Server
includes in the RADIUS Access-Accept message when a user is authenticated and
a connection request is approved.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering Profiles 51
Page 64

Resolving Profile and User Attributes
If user-specific attributes are stored in the RSA Authentication Manager database,
RSA RADIUS Server determines the final set of attributes for a user by merging
the attributes stored in the user’s profile with user-specific attributes from the
RSA Authentication Manager database. This calculation is performed as follows:
1 The attributes from the profile assigned to the user are retrieved.
2 These attributes are then merged with the user-specific attributes in the
following manner:
Z If an attribute is multi-valued, then the user-specific attribute is added to
the overall list of attributes.
Z If an attribute is single-valued, then the user-specific attribute replaces
the attribute of the same name that was provided by the profile.
Z If the attribute is orderable, then the user-specific attribute replaces the
attribute of the same name that was provided by the profile.
Default Profile
After RSA Authentication Manager authenticates a user, it can return the profile
name associated with that user to RSA RADIUS Server. The profile name
specified by RSA Authentication Manager identifies a profile configured on
RSA RADIUS Server; that profile specifies the return list attributes to send back
to the RADIUS client as part of the Access-Accept message for that user.
If RSA Authentication Manager does not return a profile name for a user,
RSA RADIUS Server returns the attributes specified in the Default profile. You
can use the Default profile to create a default set of return list attributes for users.
52 Administering Profiles September 2005
Page 65

Setting Up Profiles
The Profiles panel (Figure 15) lets you define standard sets of checklist and return
list attributes. You can then associate these profiles with users in the
RSA Authentication Manager to simplify user administration.
Figure 15 Profiles Panel
Adding a Profile
To add a profile:
1 Open the Profiles panel.
2 Click the
The Add Profile window (Figure 16) opens.
Figure 16 Add Profile Window
3 Enter a name for the new profile in the Name field.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering Profiles 53
Add button on the RSA RADIUS Administrator toolbar.
Page 66

4 Optionally, enter a description for the profile in the Description field.
5 Add checklist and return list attributes to the profile.
a Click the
b Click
Checklist tab or the Return list tab.
Add. The Add Checklist Attribute window or the Add Return List
Attribute window (Figure 17) opens.
Figure 17 Add Checklist Attribute and Add Return List Attribute Windows
c Select the attribute you want to add from the Attributes list.
d Select or enter a value for the attribute.
The window changes according to the attribute you choose. Some
attributes require that you enter a value, string, or IP address. Other
attributes require that you choose from a predefined list of values.
If the
Multivalued indicator is dimmed, an attribute can have only one
value. If the
Multivalued attribute is not dimmed, you can add multiple
values for the attribute.
(Checklist attributes only) To set this value to the default value for the
attribute (which is useful in situations where the attribute is not included
in the RADIUS request), click the
Default value checkbox.
(Return list single-valued attributes only) If you do not want to
specify a particular value, but want to make sure that whatever value of
the attribute appears in the RADIUS request is echoed to the client in the
RADIUS response, click the
e Click
54 Administering Profiles September 2005
Add to add this attribute/value pair to the list.
Echo checkbox.
Page 67

f When you are finished adding attribute/value pairs, click Close to return
to the Add Profile window.
6 Click
Removing a Profile
To remove a profile:
1 Open the Profiles panel.
2 Select the entry for the profile you want to remove.
3 Click the
right-click the profile entry and choose
4 When you are prompted to confirm the deletion, click
OK to save the profile.
Delete button on the RSA RADIUS Administrator toolbar (or
Delete from the context menu).
Yes.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering Profiles 55
Page 68

56 Administering Profiles September 2005
Page 69

Chapter 6
Displaying Statistics
The Statistics panel lets you display statistics for authentication and accounting
transactions by a RADIUS server or RADIUS client. You can also use the
Statistics panel to see how long RSA RADIUS Server has been running.
Displaying Server Authentication Statistics
Authentication statistics (Figure 18) summarize the number of authentication
acceptances and rejections, with summary totals for each type of rejection or
retry.
To display authentication statistics for the RSA RADIUS server:
1 Open the Statistics panel.
2 Select the server for which you want to display statistics in the
3 Click the
4 Click the
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Displaying Statistics 57
System tab.
View list and choose Authentication.
Server list.
Page 70

Figure 18 Statistics Panel: System Authentication Statistics
Table 13 explains the fields on the Authentication tab and describes possible
causes for authentication rejections.
Table 13. Authentication Statistics
Authentication
Statistic Meaning
Transactions
Accepts The current, average, and peak number of RADIUS
transactions that resulted in an Access-Accept response
since the last time authentication statistics were reset.
Rejects The current, average, and peak number of RADIUS
transactions that resulted in an Access-Reject response
since the last time authentication statistics were reset.
These are detailed in the Reject Details fields.
58 Displaying Statistics September 2005
Page 71

Table 13. Authentication Statistics (Continued)
Authentication
Statistic Meaning
Silent Discards The number of requests in which the client could not be
identified since the last time authentication statistics were
reset. This might occur if a RADIUS client entry cannot be
found for a device with the name and/or IP address of a
device requesting authentication services.
Total Transactions The sum of the accept, reject, and silent discard totals
since the last time authentication statistics were reset.
Reject Details
Dropped Packet The number of RADIUS authentication packets dropped by
RSA RADIUS Server because the server was flooded with
more packets than it could handle.
Invalid Request The number of invalid RADIUS requests made.
A RADIUS client is sending incorrectly formed packets to
RSA RADIUS Server. Either the RADIUS client is
misconfigured, or the RADIUS client does not conform to
the RADIUS standard.
Failed Authentication The number of failed authentication requests, where the
failure is due to invalid user ID or password.
If all transactions are failing authentication, the shared
secret configured on the RSA RADIUS Server does not
match the shared secret configured on the RADIUS client.
Failed on Checklist The number of requests that were authenticated but failed
to meet the checklist requirements.
Insufficient Resources The number of rejects due to a server resource problem.
Retries Received
Transactions Retried The number of requests for which one or more duplicates
was received.
Total Retry Packets The number of duplicate packets received.
Challenges The number of challenges received.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Displaying Statistics 59
Page 72

Displaying Server Accounting Statistics
Accounting statistics provide information such as the number of transaction
starts and stops and the reasons for rejecting attempted transactions. The
transaction start and stop numbers rarely match, as many transactions can be in
progress at any given time.
To display accounting statistics for the RSA RADIUS server:
1 Open the Statistics panel.
2 Select the server for which you want to display statistics in the
3 Click the
4 Click the
System tab.
View list and choose Accounting.
Server list.
Figure 19 Statistics Panel: System Accounting Statistics
60 Displaying Statistics September 2005
Page 73

Table 14 describes the accounting statistics and suggested actions in italics (if
appropriate).
Table 14. Accounting Statistics
Accounting Statistic Meaning
Transactions
Starts The current, average, and peak number of transactions in
which a connection was started following a successful
authentication since the last time accounting statistics were
reset.
Stops The current, average, and peak number of transactions in
which a connection was terminated since the last time
authentication statistics were reset.
Ons The number of Accounting-On messages received,
indicating that a RADIUS client has started since the last
time authentication statistics were reset.
Offs The number of Accounting-Off messages received,
indicating that a RADIUS client has shut down gracefully
since the last time authentication statistics were reset.
Total The sum of the start, stop, on and off totals since the last
time authentication statistics were reset.
Failure Details
Dropped Packet The number of RADIUS accounting packets dropped by
RSA RADIUS Server because the server was flooded with
more packets than it could handle.
Invalid Request The number of invalid RADIUS requests received by the
RSA RADIUS Server.
A device is sending incorrectly formed packets to
RSA RADIUS Server; either there is a configuration error,
or the device does not conform to the RADIUS standard.
Failed Accounting The number of RADIUS accounting requests that
RSA RADIUS Server was unable to process.
Insufficient Resources The number of rejects due to a server resource problem.
Retries Received
Transactions Retried The number of requests for which one or more duplicates
was received.
Total Retry Packets The number of duplicate packets received.
Interim Requests The number of interim accounting packets received.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Displaying Statistics 61
Page 74

Resetting Server Statistics
To reset authentication and accounting statistics for an RSA RADIUS server to
zero:
1 Open the Statistics panel.
2 Select the server for which you want to reset statistics in the
3 Click the
4 Click the
5 Click the
System tab.
View list and choose Accounting or Authentication.
Reset button in the toolbar.
Displaying RADIUS Client Statistics
RADIUS client statistics (Figure 20) provide information about the number of
authentication and accounting requests by client.
To display RADIUS client statistics for the RSA RADIUS server:
1 Open the Statistics panel.
2 Select the server for which you want to display statistics in the
3 Click the
4 Click the
Z Accounting Request Diagnostics – Displays the number of duplicate
System tab.
View list and choose the type of statistics you want to display.
messages, messages with invalid secrets, malformed messages, messages
with incorrect types, ignored messages, and dropped requests for each
RADIUS client.
Server list.
Server list.
Z Accounting Request Types – Displays the number of accounting start
messages, accounting stop messages, interim messages, Accounting-On
messages, Accounting-Off messages, and acknowledgement messages
sent for each RADIUS client.
Z Authentication Request Details – Displays the number of duplicate
messages, challenges, messages containing invalid authentication
information, bad authentication requests, bad types, and dropped
requests for each RADIUS client.
Z Summary – Displays the number of authentication requests, accepts, and
reject messages and the total number of accounting requests, starts, and
stops for each RADIUS client.
62 Displaying Statistics September 2005
Page 75
5 Optionally, sort the messages by clicking a column header.
NOTE: The RADIUS client statistics are not displayed dynamically. To see the
most recent statistics for a RADIUS client, click the
toolbar.
Figure 20 Statistics Panel: RADIUS Client Statistics
Refresh button in the
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Displaying Statistics 63
Page 76

64 Displaying Statistics September 2005
Page 77

Chapter 7
Administering RADIUS Servers
RSA RADIUS Server supports the replication of RADIUS configuration data
from a Primary RADIUS Server to a maximum of 10 Replica RADIUS Servers
within a realm on a customer network. All the servers within a realm reflect the
current configuration specified by the network administrator: the network
administrator modifies the configuration on the Primary RADIUS Server, and the
Primary RADIUS Server propagates the new configuration to its Replica
RADIUS Servers.
This chapter describes how to manage your Primary and Replica RADIUS
servers.
NOTE: Settings in RSA RADIUS Server configuration (*.ini) files are not
copied as part of the replication process. If you change a setting in an
RSA RADIUS Server configuration file, you must copy the file manually to
each server (Primary and Replica) in a realm to keep them synchronized.
Refer to the RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Reference Guide for information on the
configuration files.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering RADIUS Servers 65
Page 78
Replication Panel
The Replication panel (Figure 21) lists your Primary and Replica RADIUS
Servers and indicates whether the configuration of each server is current.
Figure 21 Replication Panel
Adding a RADIUS Server Manually
Under most circumstances, Replica RADIUS Servers register themselves
automatically after you install the RSA RADIUS Server software and
configuration package file (
each Replica RADIUS Server automatically connects to its Primary RADIUS
Server once an hour to check whether an updated configuration package is
available.
replica.ccmpkg) and restart the server. Thereafter,
In some circumstances, however, you may want to add a Replica RADIUS Server
to the server list so that it shows up immediately. To add a RADIUS server
manually:
1 Open the Replication panel.
2 Click the
The Add Server window (Figure 22) opens.
66 Administering RADIUS Servers September 2005
Add button.
Page 79
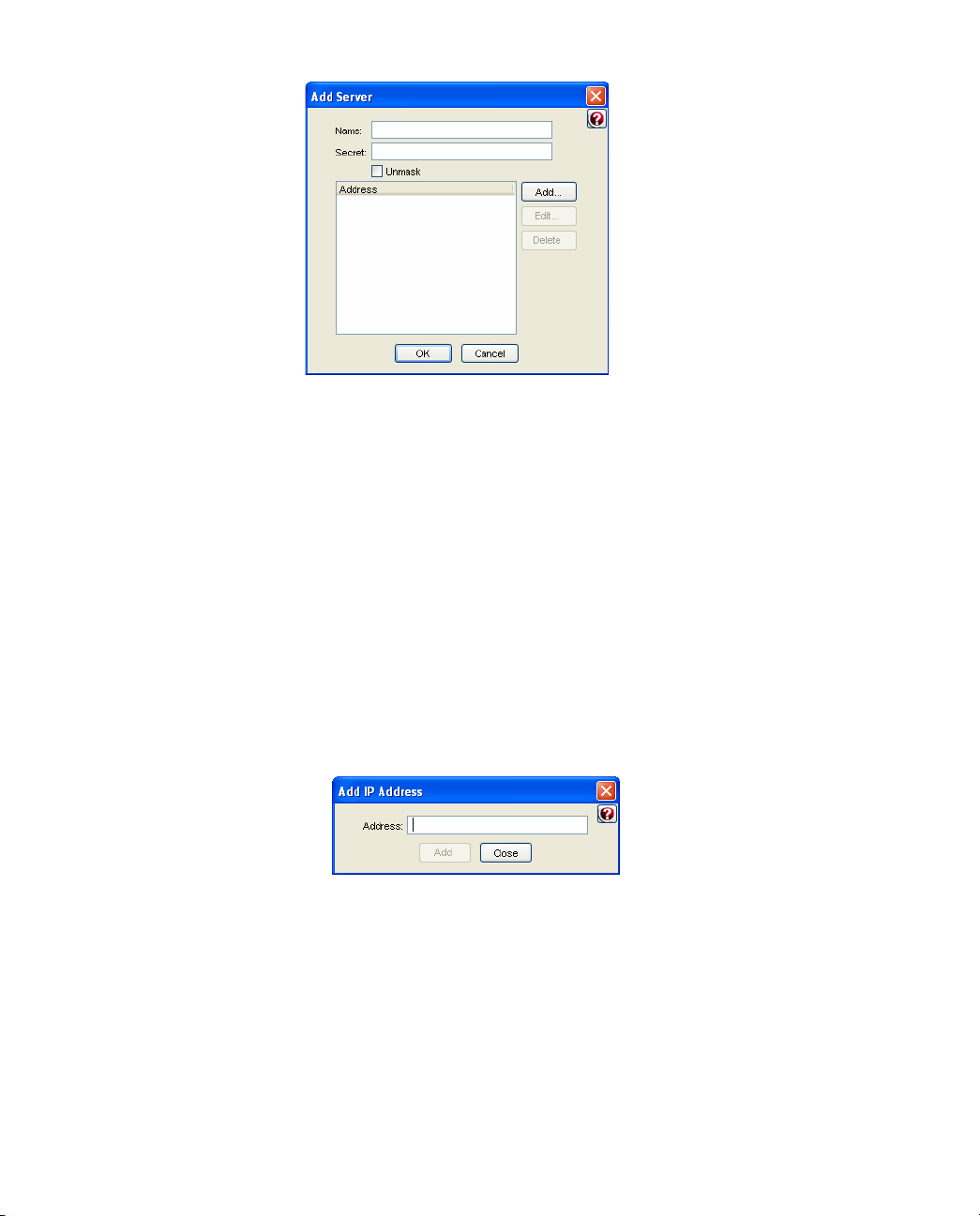
Figure 22 Add Server Window
3 Enter the name of the RADIUS server in the Name field.
Although you can assign any name to a RADIUS server, you should use the
device's hostname to avoid confusion.
4 Enter the replication secret for the RADIUS server in the
For privacy, asterisks are echoed as you type. You can click the
Secret field.
Unmask
checkbox to display the characters in the shared secret.
5 Enter one or more IP addresses for your server.
a Click the
Add button.
b When the Add IP Address window (Figure 23) opens, enter an IP
address you want to associate with the server in the
Add.
click
Figure 23 Add IP Address Window
Address field and
cRepeat Step 5b until you have finished adding IP addresses for the server.
d Click
6 Click
Close.
OK.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering RADIUS Servers 67
Page 80

Enabling a RADIUS Server
To enable a RADIUS server:
1 Open the Replication panel.
2 Select the RADIUS server you want to enable and click the
double-click the RADIUS server entry).
The Edit Server window (Figure 24) opens.
Figure 24 Edit Server Window
3 Click the Enabled checkbox.
Edit button (or
4 Click the
Save button.
Deleting a RADIUS Server
To delete a RADIUS server:
1 Open the Replication panel.
2 Select the RADIUS server entry you want to delete.
3 Click the
4 When you are prompted to confirm the deletion request, click
68 Administering RADIUS Servers September 2005
Delete button on the RSA RADIUS Administrator toolbar.
Yes.
Page 81

Publishing Server Configuration Information
If you change the configuration of your Primary RADIUS Server, you must
publish the modified configuration so that your Replica RADIUS Servers can
download the modified settings.
To publish server configuration information:
1 Open the Replication panel.
2 Click the
This creates a file called
../rsa radius/packages/timestamp_RSA.ccmpkg (Solaris/Linux)
or
(Windows), where
created.
Publish button on the toolbar.
..\RSA Radius\Service\packages\timestamp_RSA.ccmpkg
timestamp reflects the date and time the package was
Notifying Replica RADIUS Servers
A network administrator can manually notify a Replica RADIUS Server to
download and install the current configuration package from the Primary
RADIUS Server. Manual notification is useful when network issues prevent the
automatic download and installation of a configuration package when it is first
published, and the configuration on the Replica no longer matches the
configuration on the Primary RADIUS Server.
To notify Replica RADIUS Servers that new configuration information has been
published:
1 Open the Replication panel.
2 Select the Replica RADIUS Server you want to notify.
3 Click the
The Replica RADIUS Server downloads and installs its configuration
package from the Primary RADIUS Server. After the package is installed, the
Replica RADIUS Server is resynchronized with the Primary RADIUS Server.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering RADIUS Servers 69
Notify button on the toolbar.
Page 82

Designating a New Primary RADIUS Server
You can change which server within a realm is designated as the Primary
RADIUS Server for that realm.
To designate a new Primary RADIUS Server:
1 Stop the RADIUS service/daemon on the Replica RADIUS Server.
2 Log into the Replica RADIUS Server as
root (Solaris/Linux) or
administrator (Windows).
3 Navigate to the
/opt/rsa/radius (Solaris/Linux) directory.
4 Run the
rsainstalltool (Windows) or rsaconfiguretool
(Solaris/Linux) utility with the
# ./rsaconfiguretool -promote
..RSA Radius\Service (Windows) or
promote option.
The utility creates a configuration package to change this server to the
Primary server.
5 Restart the updated Replica RADIUS Server to make it the new Primary
RADIUS Server.
6 Publish a new configuration package administratively to configure all Replica
RADIUS Servers to use the new Primary RADIUS Server.
After you designate a new Primary RADIUS Server for a realm, you can
configure the old Primary RADIUS Server as a Replica RADIUS Server by
downloading a configuration package published by the new Primary RADIUS
Server.
NOTE: If your old Primary RADIUS Server used aliases to handle
authentication requests, you must configure aliases on the new Primary
RADIUS Server after you promote it, and you must define an alias on the
corresponding Agent Host record in the RSA Authentication Manager (
Host > Edit Agent Host > RADIUS Configuration
).
Agent
Recovering a Replica After a Failed Download
If a Replica RADIUS Server fails during the download of a configuration
package, its configuration may be corrupted or it may have a stale secret.
To recover after a failed download:
1 Stop the RSA RADIUS service/daemon on the Replica RADIUS Server.
70 Administering RADIUS Servers September 2005
Page 83

2 Log into the Replica RADIUS Server as root (Solaris/Linux) or
administrator (Windows).
3 Navigate to the
/opt/rsa/radius (Solaris/Linux) directory.
4 Run the
rsainstalltool (Windows) or rsaconfiguretool
(Solaris/Linux) utility with the
..RSA Radius\Service (Windows) or
identity option and information on where
to download configuration information.
To obtain configuration from a configuration package, issue the following
command:
# ./rsaconfiguretool -identity REPLICA -reppkg pathname
where pathname specifies the path to a replica.ccmpkg package.
To obtain configuration from the Primary RADIUS Server for the realm,
issue the following command:
# ./rsaconfiguretool -identity REPLICA -primary name
address secret
where name specifies the DNS name of the Primary RADIUS Server,
address specifies the IP address of the Primary RADIUS Server, and
secret specifies the shared secret used to authenticate configuration
downloads.
5 Restart the updated Replica RADIUS Server so that it can load its new
configuration.
After the Replica RADIUS Server is restarted, it will be re-synchronized with the
current Primary RADIUS Server.
Changing the Name or IP Address of a Server
You may need to change the DNS name or IP address assigned to a Primary or
backup RADIUS server if your network changes.
To change the DNS name or IP address of a Primary or Replica RADIUS Server:
1 Stop the RSA RADIUS service/daemon on the RADIUS server you want to
change.
2 Log into the RADIUS server as
(Windows).
3 Navigate to the
/opt/rsa/radius (Solaris/Linux) directory.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering RADIUS Servers 71
..RSA Radius\Service (Windows) or
root (Solaris/Linux) or administrator
Page 84

4 Run the rsainstalltool (Windows) or rsaconfiguretool
(Solaris/Linux) utility with the
identity option.
To rename a Primary RADIUS Server, enter the following command:
# ./rsaconfiguretool -identity PRIMARY
To rename a Replica RADIUS Server, enter the following command:
# ./rsaconfiguretool -identity REPLICA
5 Restart the updated server so that it can load its new configuration.
6 Run the RSA RADIUS Administrator and modify the DNS name or IP
address for the server you want to rename. Verify that the secret on the
renamed server is correct.
You may need to use the Replication panel to delete the old server name from
the list of servers in the realm.
NOTE: After you change the name or IP address of a Primary or Replica
RADIUS Server, use RSA Authentication Manager to change the Agent Host
record in the Authentication Manager database.
7 Publish the modified configuration to propagate the name change to the
Replica RADIUS Servers.
Regenerating a Node Secret
You can regenerate the node secret used to authenticate communication between
the RSA Authentication Manager and RSA RADIUS Server at any time.
To regenerate a node secret:
1 Stop the RSA RADIUS service/daemon on the RADIUS server.
2 Log into the RADIUS server as
(Windows).
3 Navigate to the
/opt/rsa/radius (Solaris/Linux) directory.
4 Run the
rsainstalltool (Windows) or rsaconfiguretool
..RSA Radius\Service (Windows) or
(Solaris/Linux) utility with the
To regenerate the node secret for a Primary RADIUS Server, enter the
following command:
# ./rsaconfiguretool -identity PRIMARY
72 Administering RADIUS Servers September 2005
root (Solaris/Linux) or administrator
identity option.
Page 85

To regenerate the node secret for a a Replica RADIUS Server, enter the
following command:
# ./rsaconfiguretool -identity REPLICA
5 Restart the RSA RADIUS service.
Resetting the RADIUS Database
If the RSA RADIUS Server fails, the RADIUS database may remain running. If
this happens, the RSA RADIUS Server may refuse to run. To resolve this
problem, execute the following command to stop the
/etc/init.d/sbrd stop force
After the mkded (btrieve) daemon is stopped, you can start the RADIUS service
and the database by executing the following command:
/etc/init.d/sbrd start
mkded (btrieve) daemon.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Administering RADIUS Servers 73
Page 86

74 Administering RADIUS Servers September 2005
Page 87

This chapter describes how to set up and use logging functions in
RSA RADIUS Server.
Logging Files
The following files establish settings for logging and reporting.
Table 15. Logging and Reporting Files
File Name Function
radius.ini
Chapter 8
Logging
Controls the types of messages RSA RADIUS Server
records in the RADIUS system log file and the location of
the log directory.
Using the RADIUS System Log
The RADIUS system log records RADIUS events, such as server startup or
shutdown or user authentication or rejection, as a series of messages in an ASCII
text file. Each line of the system log file identifies the date and time of the
RADIUS event, followed by event details. You can open the current RADIUS
system log file while RSA RADIUS Server is running.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Logging 75
Page 88

Level of Logging Detail
You can control the level of detail recorded in the system log files with
LogLevel, LogAccept, and LogReject settings.
X The LogLevel setting determines the level of detail given in the RADIUS
system log file. The
of information, 1 is intermediate, and 2 is the most verbose. It is specified in
the [Configuration] section of
X The LogAccept and LogReject flags allow you to turn on or off the
logging of Access-Accept and Access-Reject messages in the log file. These
flags are set in the [Configuration] section of
default) causes these messages to be logged, and a value of 0 causes the
messages to be omitted. An Accept or Reject is logged only if LogAccept or
LogReject, respectively, is enabled and the LogLevel is “verbose” enough for
the message to be recorded.
The
TraceLevel setting specifies whether packets should be logged when they
are received and being processed, and what level of detail should be recorded in
the log.
Controlling Log File Size
LogLevel can be 0, 1, or 2, where 0 is the least amount
radius.ini file.
radius.ini: a value of 1 (the
Optionally, you can specify a maximum size for a RADIUS system log file by
entering a non-zero value for the
[Configuration] section of the
X If a maximum file size is set, the name of the RADIUS system log file
identifies the date and time it was opened (
LogfileMaxMBytes setting in the
radius.ini file.
YYYYMMDD_HHMM.log). When the
current RADIUS system log file approaches the specified number of
megabytes (1024 x 1024 bytes), the current log file is closed and a new one is
opened. The closed file will be slightly smaller than the specified maximum
file size.
X If the maximum file size is set to 0 (or if the LogfileMaxMBytes setting is
absent), the RADIUS system log file size is ignored and log file names are
datestamped to identify when they were opened (
NOTE: If LogFileMaxMBytes is configured for a small non-zero number, the
log file may exceed the specified maximum file size in less than a minute. To
avoid file name collisions (two log files created during the same minute
interval), the log info does not roll over more than once per minute. Instead, the
log file size is ignored until the minute precision clock changes to ensure that
log files have unique file names. No log data is lost.
76 Logging September 2005
YYYYMMDD.log).
Page 89

By default, RADIUS system log files are located in the RADIUS database
directory. You can specify an alternate destination directory in the [Configuration]
section of the
radius.ini file.
Using the Accounting Log
RADIUS accounting events are recorded in the accounting log file. Accounting
events include START messages, which indicate the beginning of a connection;
STOP messages, which indicate the termination of a connection; and INTERIM
messages, which indicate a connection is ongoing.
Accounting log files use comma-delimited, ASCII format, and are intended for
import into a spreadsheet or database program. Accounting log files are located
in the RADIUS database directory area by default, although you can specify an
alternate destination directory in the [Configuration] section of the
account.ini file. Accounting log files are named yyyymmdd.act, where yyyy
is the four-digit year,
created.
The current log file can be opened while RSA RADIUS Server is running.
mm is the month, and dd is the day on which the log file was
Accounting Log File Format
The first six fields in every accounting log entry are provided by
RSA RADIUS Server for your convenience in reading and sorting the file:
X Date - the date when the event occurred
X Time - the time when the event occurred
X RAS-Client - the name or IP address of the RADIUS client sending the
accounting record
X Record-Type - START, STOP, INTERIM, ON, or OFF, the standard
RADIUS accounting packet types
X Full-Name - the fully distinguished name of the user, based on the
authentication performed by the RADIUS server
X Auth-Type - a number that indicates the class of authentication performed:
By default, the standard RADIUS attributes follow the
See “Standard RADIUS Accounting Attributes” on page 79.
You can include vendor-specific attributes if the device sending the accounting
packet supports them. For more information on using vendor-specific attributes,
refer to the RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Reference Guide.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Logging 77
Auth-Type identifier.
Page 90

You can edit the account.ini initialization file to add, remove or reorder the
standard RADIUS or vendor-specific attributes that are logged. For more
information on the account.ini file, refer to the RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Reference
Guide.
First Line Headings
The first line of the accounting log file is a file header that lists the attributes that
have been enabled for logging in the order in which they are logged. The
following example of a first line shows required headings in bold italic, standard
RADIUS headings in bold, and vendor-specific headings in regular text:
"Date","Time", "RAS-Client", "Record-Type", "Full-Name",
"Auth-Type", "User-Name", "NAS-Port", "Acct-Status-Type",
"Acct-Delay-Time", "Acct-Input-Octets",
"Acct-Output-Octets", "Acct-Session-Id",
"Acct-Authentic","Acct-Session-Time",
"Acct-Input-Packets", "Acct-Output-Packets",
"Acct-Termination-Cause", "Acct-Multi-Session-Id",
"Acct-Link-Count","Acc-Err-Message",
"Nautica-Acct-SessionId","Nautica-Acct-Direction",
"Nautica-Acct-CauseProtocol","Nautica-Acct-CauseSource",
"Telebit-Accounting-Info","Last-Number-Dialed-Out",
"Last-Number-Dialed-In-DNIS","Last-Callers-Number-ANI",
"Channel","Event-Id","Event-Date-Time",
"Call-Start-Date-Time","Call-End-Date-Time",
"Default-DTE-Data-Rate","Initial-Rx-Link-Data-Rate",
"Final-Rx-Link-Data-Rate","Initial-Tx-Link-Data-Rate",
"Final-Tx-Link-Data-Rate","Sync-Async-Mode",
"Originate-Answer-Mode","Modulation-Type",
"Equalization-Type","Fallback-Enabled","Characters-Sent",
"Characters-Received","Blocks-Sent","Blocks-Received",
"Blocks-Resent","Retrains-Requested","Retrains-Granted",
"Line-Reversals","Number-Of-Characters-Lost",
"Number-of-Blers","Number-of-Link-Timeouts",
"Number-of-Fallbacks","Number-of-Upshifts",
"Number-of-Link-NAKs","Back-Channel-Data-Rate",
"Simplified-MNP-Levels","Simplified-V42bis-Usage",
"PW_VPN_ID"
Comma Placeholders
RSA RADIUS Server writes accounting events to the accounting log file. If an
event recorded in the accounting log file does not have data for every attribute, a
comma “placeholder” marks the empty entry, so that all entries remain correctly
78 Logging September 2005
Page 91

aligned with their headings. For example, based on the “first line” of headings
described above, the following is a valid accounting log entry, in which the value
of the Acct
"12/23/1997","12:11:55","RRAS","Accounting-On",
,,,,7,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
-Status-Type attribute is 7:
Standard RADIUS Accounting Attributes
Table 16 lists the standard RADIUS accounting attributes defined in RFC 2866,
“RADIUS Accounting.”
Table 16. Standard RADIUS Accounting Attributes
User-Name
NAS-Port
Acct-Status-Type
Acct-Delay-Time
Acct-Input-Octets
Acct-Output-Octets
Acct-Session-Id
Acct-Authentic
Acct-Session-Time
The name of the user as received by the client.
The port number on the client device.
A number that indicates the beginning or
ending of the user service:
1 - Start
2 - Stop
3 - Interim-Acct
7 - Accounting-On
8 - Accounting-Off
Indicates how many seconds the client has
been trying to send this record, which can be
subtracted from the time of arrival on the server
to find the approximate time of the event
generating this request.
Number of octets (bytes) received by the port
over the connection; present only in STOP
records.
Number of octets (bytes) sent by the port over
the connection; present only in STOP records.
Identifier used to match START and STOP
records in a log file.
indicates how the user was authenticated by
RADIUS, the RAS itself, or another remote
authentication protocol:
1 - RADIUS
2 - Local
3 - Remote
Elapsed time of connection in seconds; present
only in STOP records.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Logging 79
Page 92

Table 16. Standard RADIUS Accounting Attributes (Continued)
Acct-Input-Packets
Acct-Output-Packets
Acct-Termination-Cause
Acct-Multi-Session-Id
Acct-Link-Count
Number of packets received by the port over
the connection; present only in STOP records.
Number of packets sent by the port over the
connection; present only in STOP records.
Number that indicates how the session was
terminated; present only in STOP records:
1 - User Request
2 - Lost Carrier
3 - Lost Service
4 - Idle Timeout
5 - Session Timeout
6 - Admin Reset
7 - Admin Reboot
8 - Port Error
9 - NAS Error
10 - NAS Request
11 - NAS Reboot
12 - Port Unneeded
13 - Port Preempted
14 - Port Suspended
15 - Service Unavailable
16 - Callback
17 - User Error
18 - Host Request
Unique accounting identifier to make it easy to
link together multiple related sessions in a log
file.
The count of links that are known to have been
in a given multi-link session at the time the
accounting record is generated.
80 Logging September 2005
Page 93

Appendix A
Using the LDAP Configuration
Interface
The LDAP Configuration Interface (LCI) is an optional add-on to
RSA RADIUS Server. You must enter a separate license number and restart
RSA RADIUS Server to activate LCI functions. After the license key is registered,
you can edit the settings in the configuration files. For information on adding
license numbers, see “Adding a License Key” on page 43.
This appendix provides:
X The file used to enable and configure the LDAP configuration interface
(LCI)
X An overview of the LCI and LDAP utilities
X A description of the LDAP virtual schema
X Information about how to use LDAP utilities to configure the
RSA RADIUS Server database
X Sample LDIF files that control the execution of LDAP utilities
X Information about how to view rate statistics variables with LCI utilities
LDAP Configuration Interface File
The radius.ini file specifies (among other things) the interfaces on which
RSA RADIUS Server listens for LCI requests. If a specification is not present,
RSA RADIUS Server listens for LCI requests on all bound IP ports.
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Using the LDAP Configuration Interface 81
Page 94
About the LDAP Configuration Interface
The LDAP Configuration Interface (LCI) consists of an LDAP interface in the
RSA RADIUS Server and an LDAP virtual schema. The LDAP virtual schema
enables the LDAP interface to translate LDAP requests into a format that can be
understood by the RSA RADIUS Server database.
Figures 25 illustrates the relationship between LDAP components.
Core RADIUS Modules
LDAP Utilities
LDAP Command
Line Utility
Java
Administration
Program
Figure 25 LDAP Components
LDAP
Interface
Virtual
Schema
Proprietary
HTTPS
Embedded
RADIUS
Database
Freeware LDAP utilities, such as ldapsearch, ldapmodify, and
ldapdelete, act as clients of the LDAP interface. LDAP utilities let you read
and modify an LDAP database.
X ldapsearch – The ldapsearch utility locates and retrieves LDAP
directory entries. The
ldapsearch utility opens a connection to an LDAP
interface using the specified distinguished name and password, binds, and
locates entries based on the specified search filter. A search can return a
single entry, an entry's immediate subentries, or an entire tree or subtree.
Search results are returned in LDIF format.
X ldapmodify – The ldapmodify utility adds or modifies entries in an
existing LDAP directory.
ldapmodify opens a connection to an LDAP
interface using the distinguished name and password you supply, binds, and
adds or modifies the entries based on the LDIF update statements contained
82 Using the LDAP Configuration Interface September 2005
Page 95

in a specified file. Because ldapmodify uses LDIF update statements,
ldapmodify can do everything ldapdelete can do.
X ldapdelete – The ldapdelete utility deletes entries from an existing
LDAP directory.
ldapdelete opens a connection to the specified server
using the distinguished name and password you provide, binds, and deletes
the entry or entries.
LDAP Requests
LDAP requests are submitted in two ways:
X By specifying options on the LDAP command line.
X By placing instructions and data into an LDAP Data Interchange Format
LDIF) file, which you then invoke on the command line by using the -f
(
option.
Because communication between the LDAP client and server must occur in the
clear (unencrypted), run the LDAP utilities on the same computer as
RSA RADIUS Server.
Downloading the LDAP Utilities
To use the LCI, you need the freeware ldapsearch, ldapmodify, and
ldapdelete utilities. You can download the free LDAP utilities as follows:
1 Use a browser to navigate to
http://www.sun.com/download/products.xml?id=/3ec28dbd.
2 When the Sun ONE Directory SDK (software development kit) download
page appears, click the
Download link at the bottom of the page.
3 If you are prompted to register yourself, complete the registration form.
4 When you are prompted to accept the license agreement, click the
button and then click
Continue.
Accept
5 Download the SDK by clicking the link for the version of the SDK that is
appropriate for your computer.
Versions of the SDK are available for Solaris, Linux, and Windows.
6 When the download is completed, extract the following files from the
compressed image to a directory on your computer:
Z ldapsearch.exe
Z ldapmodify.exe
Z ldapdelete.exe
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Using the LDAP Configuration Interface 83
Page 96

Z nsldapssl32v30.dll (if you are on a Windows host)
Z libldap30.so (if you are on a Solaris host)
To run the LDAP utilities, execute them from this directory. If you set the path
environment variable to point to this directory, you can run them any location on
the system.
NOTE: The examples that follow assume you are using the LDAP utilities
provided as part of the Sun ONE Directory SDK. If you are using LDAP utilities
from another source, the command options you use may be different. Consult
the documentation for your LDAP utilities for more information.
LDAP Version Compliance
The LDAP server software that has been incorporated into RSA RADIUS Server
is compliant with version 2 of the LDAP specification. Therefore, we suggest
using the
-V 2 command line option to direct the utilities to use version 2
features. For example:
ldapmodify -c -V 2 -p 354 -D "cn=admin,o=radius"
-w radius -f filename
Configuring the LDAP TCP Port
To avoid conflicts with LDAP services that may already be installed, the default
TCP port number for communication between RSA RADIUS Server and the
LDAP client is 667. If you are certain that there will not be any conflicts, you can
change this port number to 389, the standard LDAP TCP port.
You can configure RSA RADIUS Server to use a different TCP port to
communicate with the LDAP client. In the following example, port 354 is
assigned.
1In the
radius.ini configuration file, create an [LDAP] section if one does
not exist, and set the
TCPPort field to the port number you want to use. For
example:
[LDAP]
Enable = 1
TCPPort = 354
2 If you want to specify the interfaces on which you want RSA RADIUS Server
to listen for LCI requests, add a [LDAPAddresses] section to the
radius.ini file. This section should contain a list of IP addresses, one per
line:
[LDAPAddresses]
84 Using the LDAP Configuration Interface September 2005
Page 97

199.198.197.196
196.197.198.199
If the [LDAPAddresses] section is omitted or empty, RSA RADIUS Server
listens for LCI requests on all bound IP interfaces.
3 Specify the same port number using the
line. For example:
ldapsearch -V 2 -p 354 -D "cn=admin,o=radius" -w radius
-s sub -T -b "radiusclass=Client,o=radius" radiusname=*
LDAP Virtual Schema
The LDAP server uses the virtual schema (illustrated in Figures 26–29) to format
configuration data so that this data can be understood by the
RSA RADIUS Server database.
NOTE: radiusstatus items can be read, but they cannot be modified.
radiusclass=
securid-user
1...n
radiusclass=
profile
1...n
radiusclass=
client
1...n
-p option on the LDAP command
radiusclass=
server
radiusclass=
rsa_cached_passwords
(read-only)
radiusname=
MYPROFILE
Available Attributes:
Login-Limit <number>
Profile <string>
Available Child Objects:
radiuslist=reply
radiuslist=check
Available Reply
Attributes:
All reply list attributes
from dictionaries
radiusname=
MYPROFILE
Available Attributes:
Shared-Secret <string>
Acct-Shared-Secret <string>
IP-Address nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
Product <string>
Inactivity-Timeout <seconds>
Available Check
Attributes:
All check list attributes
from dictionaries
radiusname=
MYRASCLIENT
Available Attributes:
Server-Password <string>
Server-Password-Enabled 0|1
Default-Reject-Msg <string>
Unknown-User-Msg <string>
Lists-Mismatch-Msg <string>
Invalid-Lists-Msg <string>
Auth-Methods <meth1>; <meth2>; ...
Log-Max-Days <number>
Available Attribute:
cached-password
Figure 26 LDAP Schema (Slide 1 of 4)
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Using the LDAP Configuration Interface 85
Page 98

Root
o=radius
cn=admin
radiusstatus=
sessions_by_calling_station
calling-station-id=
<dialing number>
Figure 27 LDAP Schema (Slide 2 of 4)
radiusstatus=
sessions_by_called_station
called-station-id=
<dialed number>
Available Attributes:
client <string>
acct-session-id <number>
nas-ip-address <string>
nas-port <string>
nas-port-type <string>
acct-multi-session-id <number>
framed-ip-address <string>
session-start-time <time>
fullname <string>
username <string>
called-station-id <string>
calling-station-id <string>
elapsed <number>
radiusstatus=
sessions_by_user
username=
<user name>
client=
NASCLIENT
acct-session-id=
<sessionid>
radiusstatus=
sessions
radiusstatus=
sessions_by_ipaddress
framed-ip-address=
<aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd>
86 Using the LDAP Configuration Interface September 2005
Page 99

Available Attributes:
accept <number>
reject <number>
silent-discard <number>
total-transactions <number>
invalid-request <number>
failed-authentication <number>
failed-on-check-list <number>
insufficient-resources <number>
transactions-retried <number>
total-retry-packets <number>
stattype=
authentication
Available Attributes:
start <number>
stop <number>
interim <number>
on <number>
off <number>
total-transactions <number>
invalid-request <number>
invalid-client <number>
invalid-shared-secret <number>
insufficient-resources <number>
transactions-retried <number>
total-retry-packets <number>
stattype=
accounting
stattype=server
Available Attributes:
start-time <yyyy/mm/dd hh:mm:ss>
up-time <seconds>
ip-address <aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd>
version <major minor rev>
authentication-threads <number>
accounting-threads <number>
total-threads <number>
max-acct-threads <number>
max-auth-threads <number>
max-total-threads <number>
high-acct-threads <number>
high-auth-threads <number>
high-total-threads <number>
high-acct-threads-since-reset <number>
high-auth-threads-since-reset <number>
high-total-threads-since-reset <number>
radiusstatus=
statistics
stattype=rate
Available Attributes:
rate-statistics-seconds-per-interval <number>
auth-request-current-rate <number>
auth-request-average-rate <number>
auth-request-peak-rate <number>
auth-accept-current-rate <number>
auth-accept-average-rate <number>
auth-accept-peak-rate <number>
auth-reject-current-rate <number>
auth-reject-average-rate <number>
auth-reject-peak-rate <number>
acct-start-current-rate <number>
acct-start-average-rate <number>
acct-start-peak-rate <number>
acct-stop-current-rate <number>
acct-stop-average-rate <number>
acct-stop-peak-rate <number>
Figure 28 LDAP Schema (Slide 3 of 4)
RSA RADIUS Server 6.1 Administrator’s Guide Using the LDAP Configuration Interface 87
Page 100

radiusstatus=
acct_stats_by_nas
radiusstatus=
acct_stats_by_nasipaddr
cn=<monitor>
nasname=
<nas-name>
Available Attributes:
nasname <name>
nasipaddr <name
start <number>
stop <number>
interim <number>
on <number>
off <number>
invalid-shared-secret <number>
nasipaddr=
<nas-ip-addr>
Available Attributes:
dn <string>
version <string>
threads <number>
connection <string>
currentconnections <number>
totalconnections <number>
dtablesize <number>
writewaiters <number>
readwaiters <number>
opsinitiated <number>
opscompleted <number>
entriessent <number>
bytessent <number>
currenttime <time>
starttime <time>
nbackends <number>
Figure 29 LDAP Schema (Slide 4 of 4)
While the LDAP virtual schema diagram shows as much of the detail of the
LDAP virtual schema as possible, the following rules and limitations should be
considered.
X Bind request – All attempts to perform operations on the virtual schema
must be preceded by an LDAP Bind request that authenticates the
administrator to the RSA RADIUS Server. The Bind request must reference
an RSA RADIUS Server administrative account and must provide the
password that authenticates that account. This translates into the following
command line options for each invocation of the LDAP utilities:
-D "cn=username,o=radius" -w { passcode | cachedPW }
where username is the user account name, passcode is the RSA passcode
associated with the user, and
X Uppercase and lowercase – The uppercase/lowercase rules for object
cachedPW is the user’s cached password.
names are the same as in the RSA RADIUS Administrator application;
almost all object names are stored in the database in uppercase format.
X Attributes – The LDAP virtual schema diagram does not explicitly list all the
dictionary attributes that are available in the latest version of
RSA RADIUS Server. The rules for entering dictionary attributes are that the
attribute name must match the name found in the dictionary and the syntax
type determines what is allowed for the attribute's value.
88 Using the LDAP Configuration Interface September 2005
 Loading...
Loading...