Page 1

Operational Manual
RGM-3000/REB-3000
Operational Manual
Version 1.3
2002/5/29
This document contains information highly confidential to RoyalTek Company LTD (RoyalTek). It
is provided for the sole purpose of the business discussions between supplier and RoyalTek and
is covered under the terms of the applicable Non-Disclosure Agreements. Disclosure of this
information to other parties is prohibited without the written consent of RoyalTek.
Prepared by
RoyalTek Company LTD.
A Company of Royal Group
1071, Chung Cheng Rd., Suite 9F-1
Tao Yuan City, Taiwan, R.O.C.
TEL: 886-3-3569666
FAX: 886-3-3560900
E-Mail: sales@royaltek.com
http://www.royaltek.com
Page 2

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
RoyalTek GPS Module: RGM-3000/REB-3000101 Operational Manual
NTRODUCTION
I
RODUCT FEATURES
P
RODUCT APPLICATIONS
P
ECHNIQUE DESCRIPTION
T
ICTURE
P
RGM-3000E.......................................................................................................................................2
RGM-3000L.......................................................................................................................................2
RGM-3000M ......................................................................................................................................2
REB-3000..........................................................................................................................................3
.........................................................................................................................................1
................................................................................................................................1
...........................................................................................................................1
..........................................................................................................................1
..................................................................................................................................................2
RGM-3000/REB-3000 S
ECHNIQUE SPECIFICATIONS
T
ERIES SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM
..........................................................................3
......................................................................................................................5
RGM-3000/REB-3000 Mechanical Layout.........................................................................................6
ARDWARE INTERFACE
H
BSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
A
RITICAL DESIGN GUIDE AND DIAGRAM
C
ESIGN LAYOUT DIAGRAM
D
NMEA V2.2 P
ROTOCOL
.............................................................................................................................9
..................................................................................................................10
......................................................................................................10
...................................................................................................................... 11
.........................................................................................................................12
GGA-Global Positioning System Fixed Data....................................................................................13
GLL-Geographic Position – Latitude/Longitude ...............................................................................13
GSA-GNSS DOP and Active Satellites............................................................................................13
GSV-GNSS Satellites in View..........................................................................................................14
RMC-Recommended Minimum Specific GNSS Data.......................................................................14
VTG-Course Over Ground and Ground Speed................................................................................15
SIRF P
ROPRIETARY
NMEA I
NPUT MESSAGES
..........................................................................................15
SIRF NMEA Input Messages...........................................................................................................16
Set Serial Port..................................................................................................................................16
Set DGPS Port.................................................................................................................................17
Query/Rate Control..........................................................................................................................17
LLA Navigation Initialization.............................................................................................................18
Development Data On/Off................................................................................................................19
Calculating Checksums for NMEA Input..........................................................................................19
INARY PROTOCOL
SIRF B
........................................................................................................................19
Initialize Data Source-Message I.D. 128..........................................................................................21
Switch To NMEA Protocol – Message I.D. 129................................................................................22
Set Almanac- Message I.D. 130 ......................................................................................................22
DGPS Source – Message I.D. 133 ..................................................................................................23
1
Page 3

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Set Main Serial Port-Message I.D. 134 ............................................................................................24
Mode control – Message I.D .136....................................................................................................24
DOP Mask Control – Message I.D. 137...........................................................................................25
DGPS Control – Message I.D.138...................................................................................................25
Elevation Mask – Message I.D.139..................................................................................................26
Power Mask – Message I.D.140......................................................................................................26
Editing Residual – Message I.D.141................................................................................................27
Steady State Detection – Message I.D.142.....................................................................................27
Static Navigation – Message I.D.144...............................................................................................27
Almanac – Message I.D.146............................................................................................................27
Ephemeris Message I.D.147............................................................................................................28
Switch To SiRF Protocol ..................................................................................................................28
Switch Operating Modes - Message I.D. 150...................................................................................28
Set Trickle Power Parameters - Message I.D. 151 ..........................................................................28
Computation of Duty Cycle and On Time.........................................................................................29
Push-to-Fix ......................................................................................................................................30
Poll Navigation Parameters - Message I.D. 152 ..............................................................................30
Set UART Configuration - Message I.D. 165...................................................................................30
Set Message Rate - Message I.D. 166............................................................................................31
Low Power Acquisition Parameters - Message I.D. 167..................................................................32
UTPUT MESSAGES FOR SI
O
Measured Tracker Data Out – Message I.D.4..................................................................................34
Raw Tracker Data Out – Message I.D.5..........................................................................................35
Calculation of Pseudo-Range Measurements..................................................................................37
Response :Software Version String – Message I.D.6....................................................................37
Response :Clock Status Data – Message I.D.7 ............................................................................38
50BPS Data – Message I.D.8..........................................................................................................38
CPU Throughput – Message I.D.9...................................................................................................39
Command Acknowledgment – Message I.D.11 ...............................................................................39
Command N Acknowledgment – Message I.D. 12...........................................................................39
Visible List – Message I.D.13...........................................................................................................40
Almanac Data – Message I.D.14 .....................................................................................................40
INARY PROTOCOL
RF B
...................................................................................32
OkToSend - Message I.D. 18...........................................................................................................40
Navigation Parameters (Response to Poll) – Message I.D. 19........................................................41
Navigation Library Measurement Data - Message I.D. 28 ...............................................................42
Navigation Library DGPS Data - Message I.D. 29...........................................................................42
Navigation Library SV State Data - Message I.D. 30.......................................................................43
Navigation Library Initialization Data - Message I.D. 31...................................................................43
2
Page 4

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
RoyalTek Navigation Data – Message I.D.100.................................................................................44
Set Ephemeris – Message I.D.254 ..................................................................................................45
Development Data – Message I.D.255............................................................................................45
GPS Receiver User’s Tip.................................................................................................................46
3
Page 5

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
RoyualTek GPS Module:
RGM-3000/REB-3000
Operational Manual
WAAS demodulator
Excellent sensitive for urban canyon and
foliage environments.
Single satellite positioning.
Dual multi path rejection.
Data-log capability – At least 1 Mega-bits
memory space will be implement in the
Introduction
RGM-3000/REB-3000 is the third generation of
RoyalTek GPS Receiver. RGM-3000(E,M)
consists of active antenna and GPS receiver.
REB-3000(or RGM-3000L) consists of GPS
receiver without active antenna. The GPS
receiver is powered by SiRF Star II technology
and RoyalTek proprietary navigation algorithm
that providing you more stable navigation data.
The miniature design is the best choice to be
embedded in a portable device like PDA,
mobile phone, person locator and vehicle
locator. It supports TricklePower function which
can be enabled by external command for
power saving. The excellent sensitivity of
RGM-3000 gets the great performance when
going though the urban canyon and foliage.
product
Product applications
RGM-3000/REB-3000
Portable IA device for personal navigation/
position commerce (P-Commerce)
Automotive applications
Personal positioning and navigation
Marine navigation
Timing application
Extendable I/O capability –
provide programming I/O function and
development tool kit for customer
Technique description
RGM-3000M, RGM-3000E
General information. The RGM-3000 is a
stamp size GPS receiver with an active
antenna. It provides the antenna power
Product Features
RGM-3000/REB-3000
OEM product development is fully
supported through applications
engineering and WEB technique
forum.
Small form factor.
12 parallel channels
0.1 second re-acquisition time.
Enhanced algorithm for navigation stability.
NMEA-0183 compliant protocol/custom
protocol.
through RF cable. The default DC input of
active antenna is 2.8 ~3.3V. Since it needs 3
satellites or more to do the first position fix.
The suitable view angle of the active antenna
is necessary. It will determine the first time
position update after getting good satellites
geometry. If the satellites are blocked, it may
take time to determine the position. Caution:
Please do not put any metal stuff on the
antenna. It results in GPS receiver getting
nothing. In urban canyon, the fast 0.1 second
re-acquisition capability can make it determine
the position right away through the
1
Page 6
RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
cross-intersection.
REB-3000,RGM-3000L
General Information. This is a stamp size GPS
receiver without active antenna. It provides the
external antenna power (2.8DCV ± 5%)
through RF cable. There are 2 models for
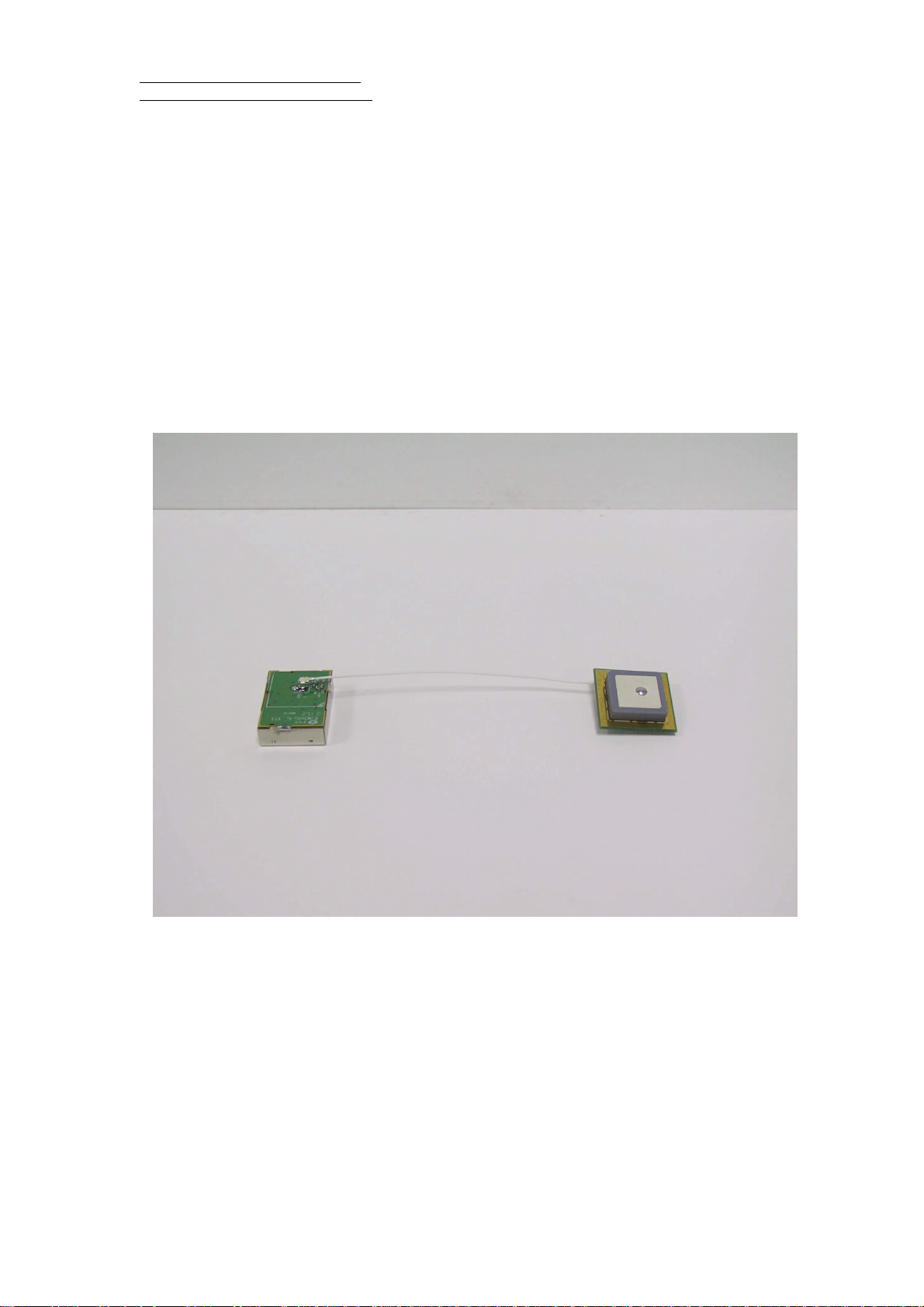
Picture
RGM-3000E
versatile antenna connectors:
1) RGM-3000L: with SMA RF cable.
3) REB-3000: with HRS type of antenna
connector (male) which you can connect to
versatile types of antenna.
2
Page 7
RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
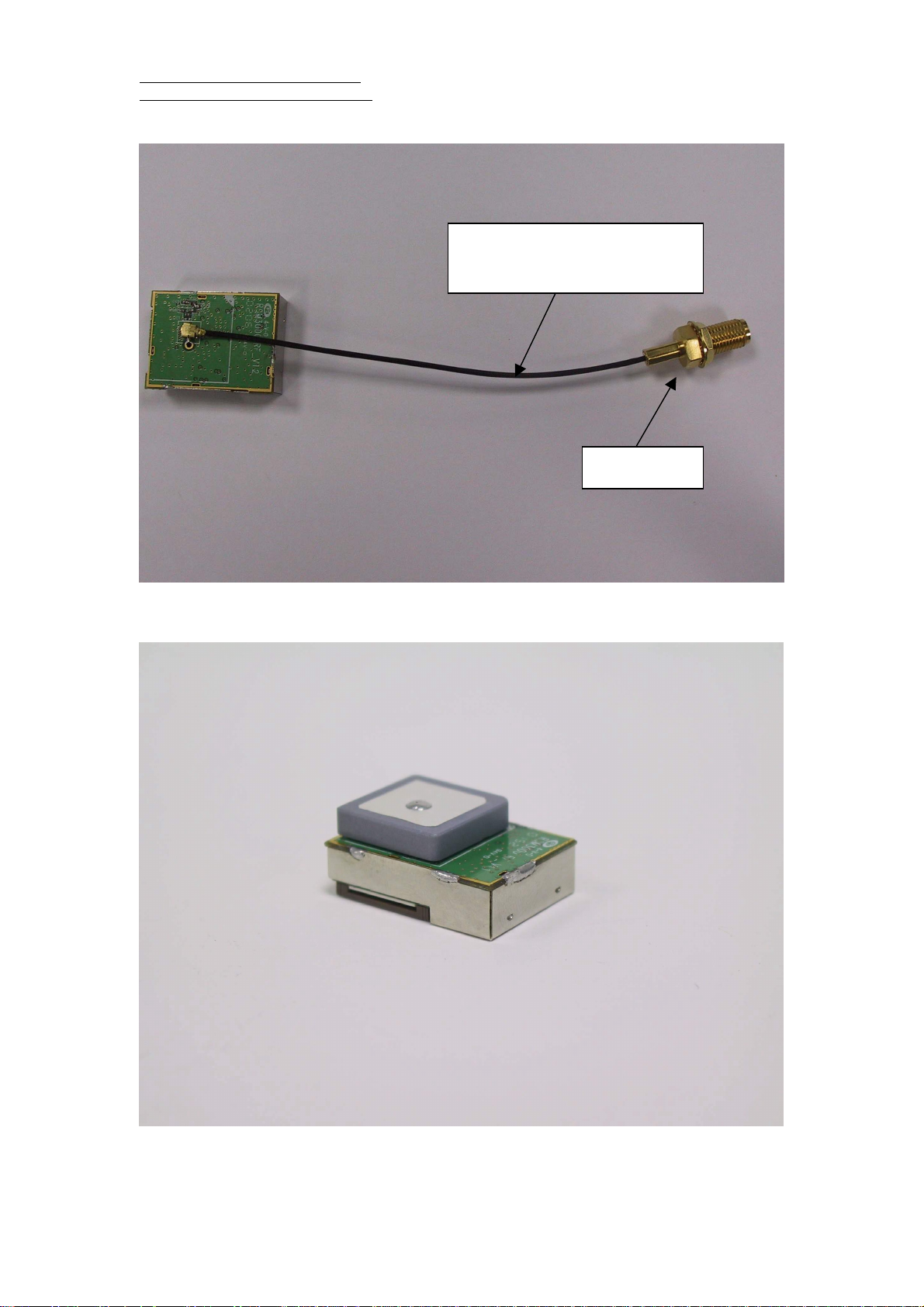
RGM-3000L
The cable length can be adjusted by
customer’s requirement (standard:10cm)
SMA connector
RGM-3000M
2
Page 8
RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
REB-3000
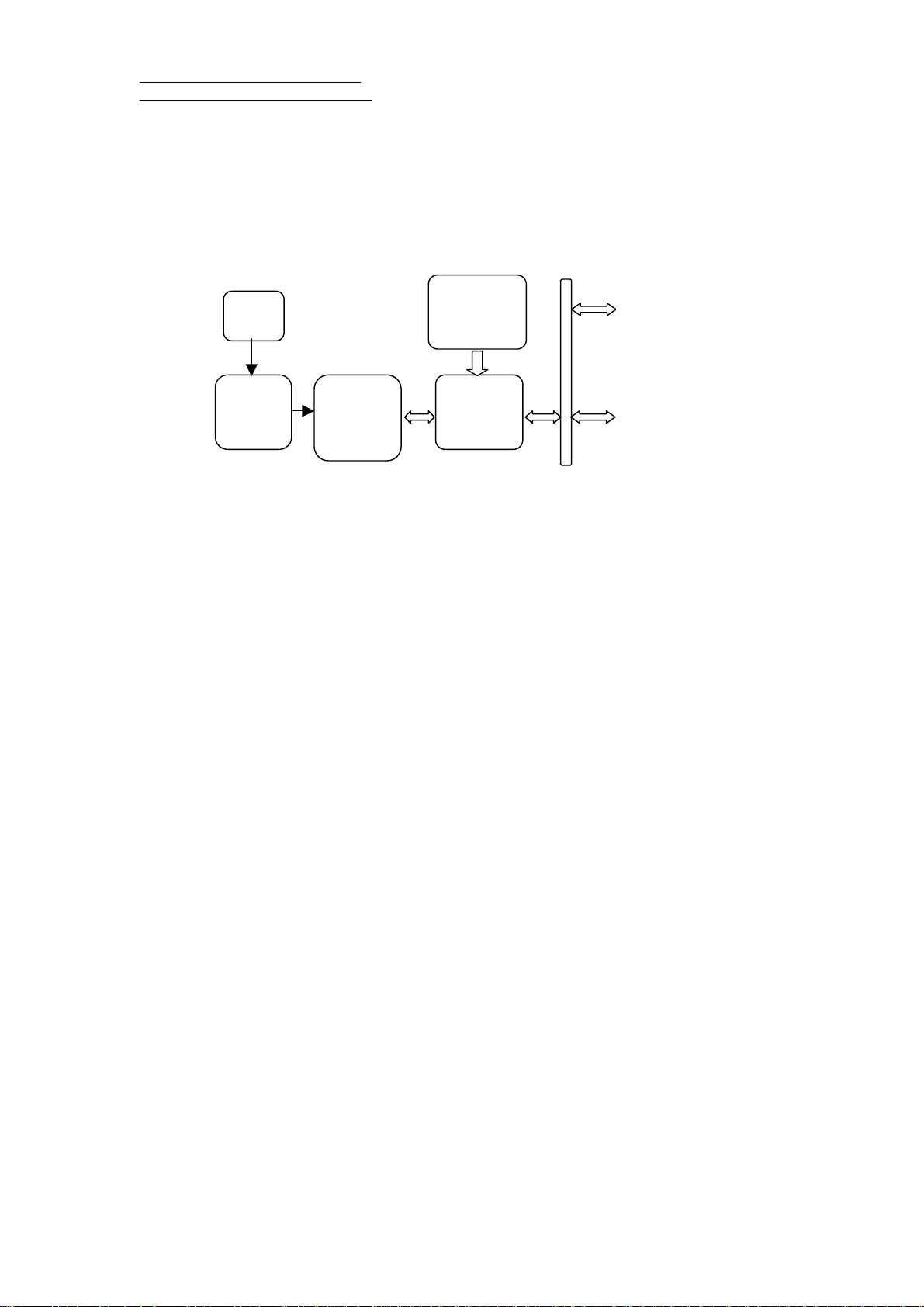
RGM-3000/REB-3000 Series System Block Diagram
The RGM-3000/REB-3000 series consists of SiRF star II chipsets technology, RoyalTek LNA and
proprietary software. The system is described as follows.
RGM-3000M/RGM-3000E
Patch ANT
Flash
LNA
Memory
RS232 port (TTL) x 2
SAW
Filter
SIRF
GRF2I
SiRF
GSP2e
3
Programming I/O port x 7
Control line x 4
Page 9
RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
RGM-3000L/REB-3000
LNA
SAW
Filter
GPS.receiver w/o patch
ANT.
Flash
Memory
SIRF
GRF2I
SiRF
GSP2e
RS232 port (TTL) x 2
Programming I/O port x 7
Control line x 4
4
Page 10

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
supplied by RGM-3000/REB-3000 series.
Technique specifications
RGM-3000/REB-3000 series.
Operational Characteristics.
12 Channels
L1, 1575.42MHz.
C / A code, 1.023MHz chip rate.
Snap start: 3 seconds, typical
Hot start: 8 seconds, typical
Warm start: 40 seconds, typical
Cold start: 48 seconds, typical
Reacquisition:0.1 second, typical
Navigation update rate: Once per second.
Datum: WGS-84.
(The above specification is for standard
version software . The specification for ES
version of software may vary.)
Accuracy.
Position accuracy: 25m CEP without SA
Velocity accuracy:0.1 meters/second
without SA
DGPS Accuracy.
Position:1 to 5 m, typical
Velocity: 0.05 meters/second, typical
Dynamics.
Altitude: 18000 meters (60000 feet) Max.
Velocity: 515 meters / second Max.
Acceleration: 4 g. , Max.
Power Requirements.
The input voltage is 3.3V±10%, ripple ≦
The full run (without trickle power)
maximum current is less than 180mA.
Weight. 30g(RGM-3000),15g(REB-3000)
Environment.
Temperature.
Operating temperature -40 ~ +85 Degree
(Celsius).
Storage temperature: -40 ~ +85 Degree
(Celsius).
Humidity ≦95% noncondensing.
GPS Antenna Specification(RGM-3000E,
RGM-3000M)
Center Frequency: 1575.42±1.023MHz
Bandwidth (-10dB return loss):9MHz min
Gain at Zenith: 3.0dBi Typ
Gain at 10° elevation :-1.0 dBi Typ
Polarization :R.H.C.P
Axial Ratio : 2.0dB max
LNA Specification:(External ANT for
RGM-3000E )
Center Frequency: 1575.42±1.023MHz
Gain : 12dB Typ
Noise Figure : 1.8dB Typ
Out Band Attenuation : 7dB min for ±20MHz
20dB min for ±50MHz
30dB min for ±100MHz
Output V.S.W.R 2.0dB max
Voltage DC 2.8.0±0.5V
Current 12mA max
200mV. The power of active antenna is
5
Page 11
RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
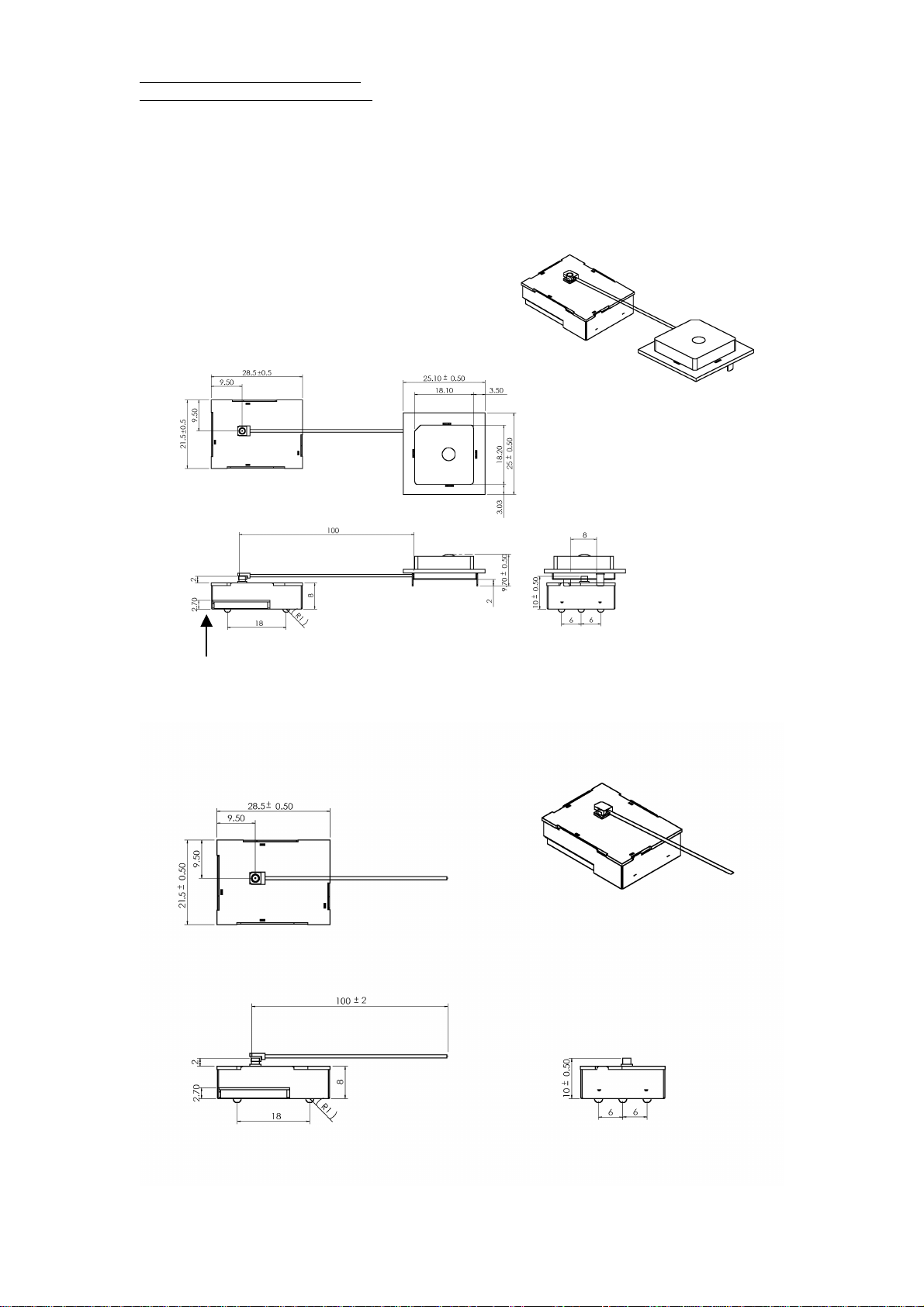
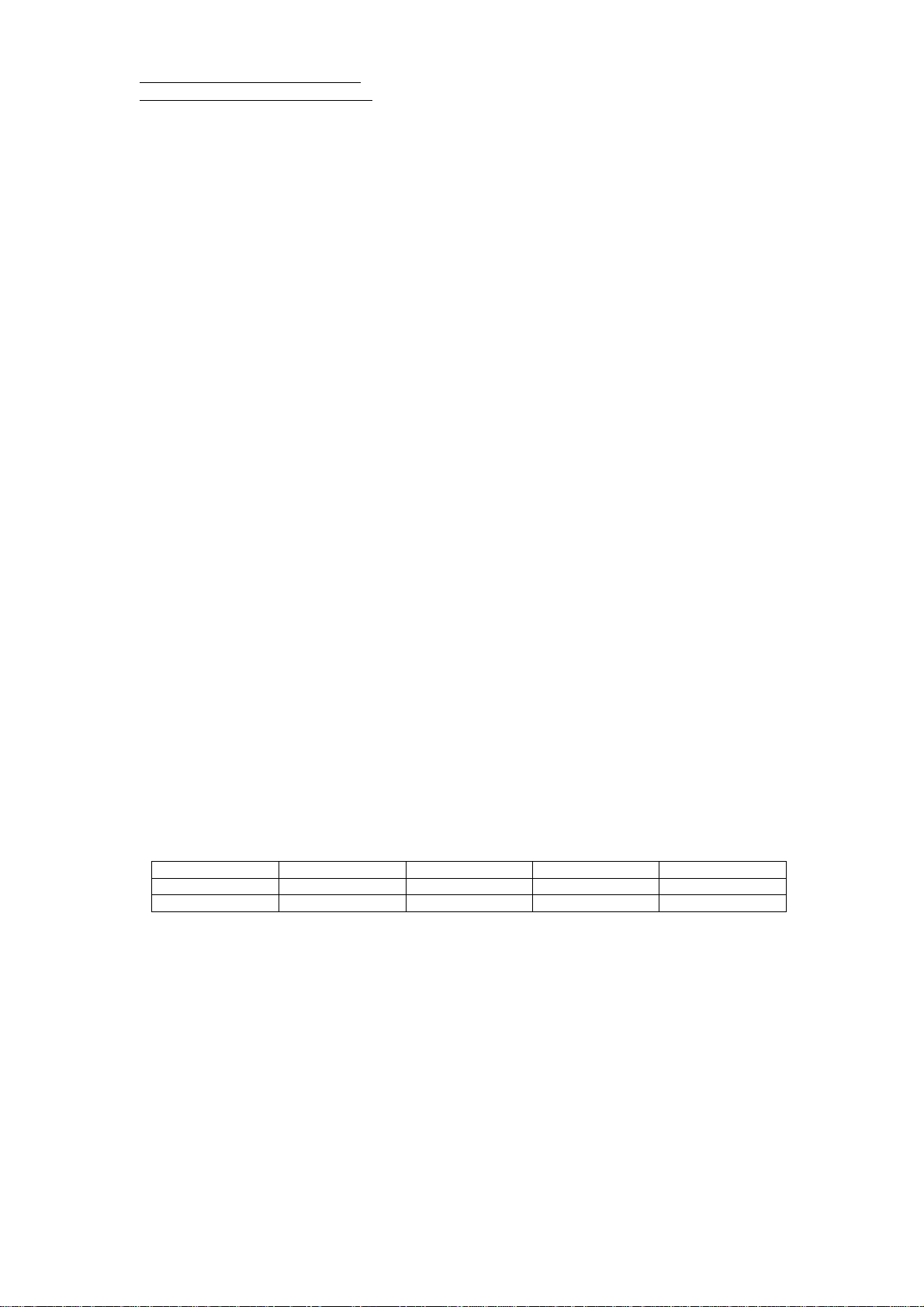
Mechanical Layout
RGM-3000/REB-3000 Mechanical Layout
RGM-3000E
Pin 1
RGM-3000L
6
Page 12
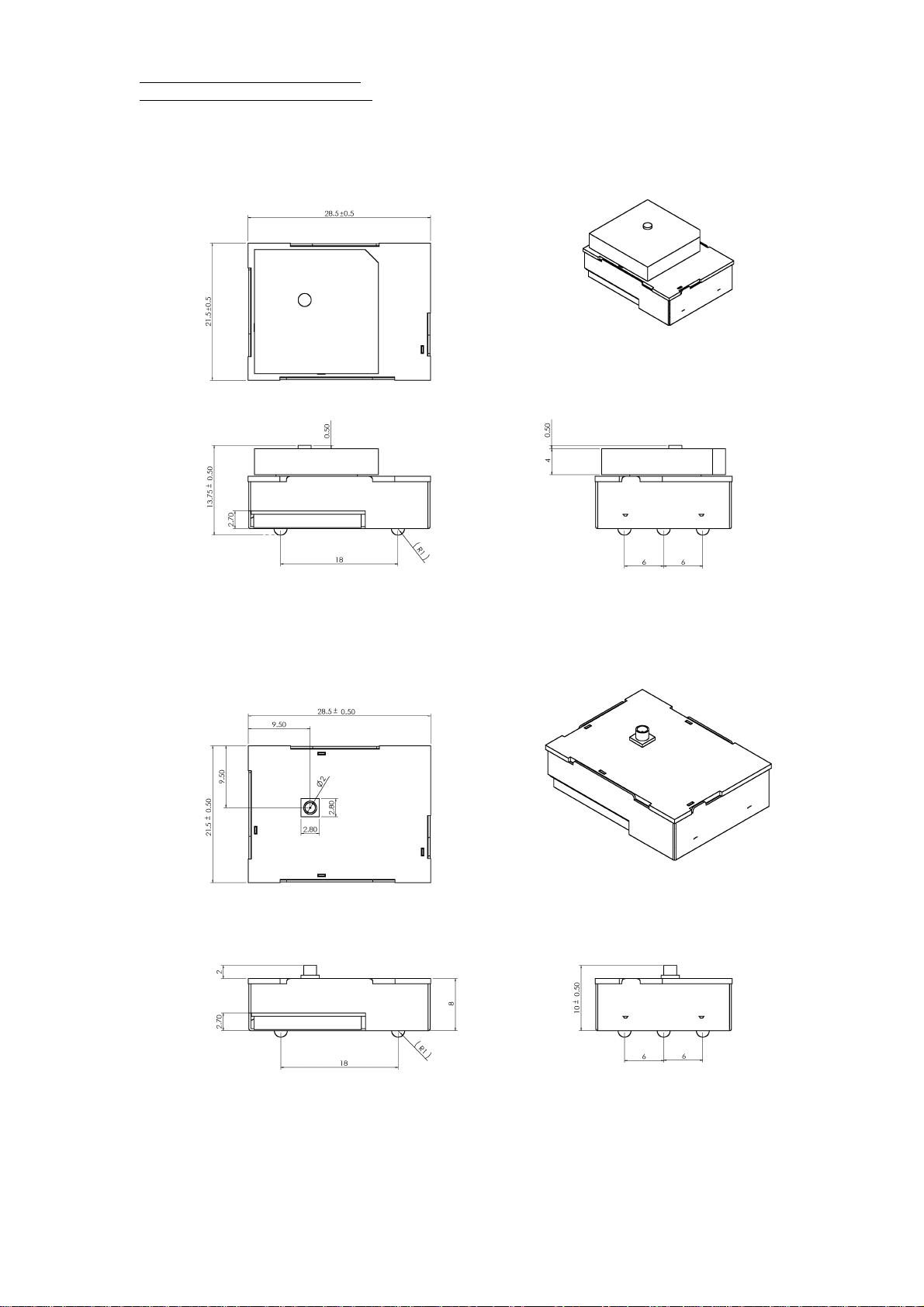
RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
RGM-3000M
REB-3000
7
Page 13
RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
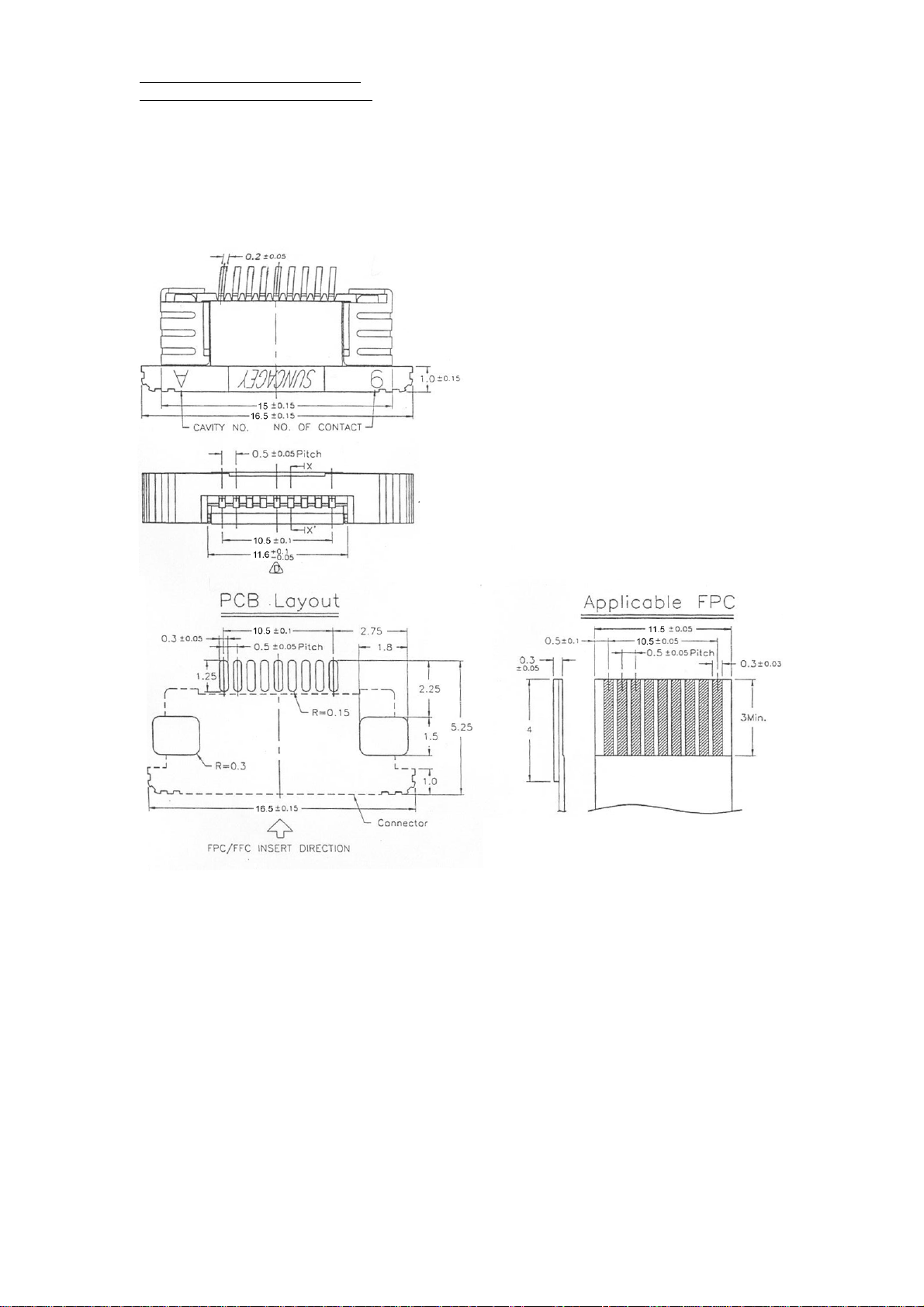
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Flexible Flat Circuit & Connectot
8
Page 14
RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
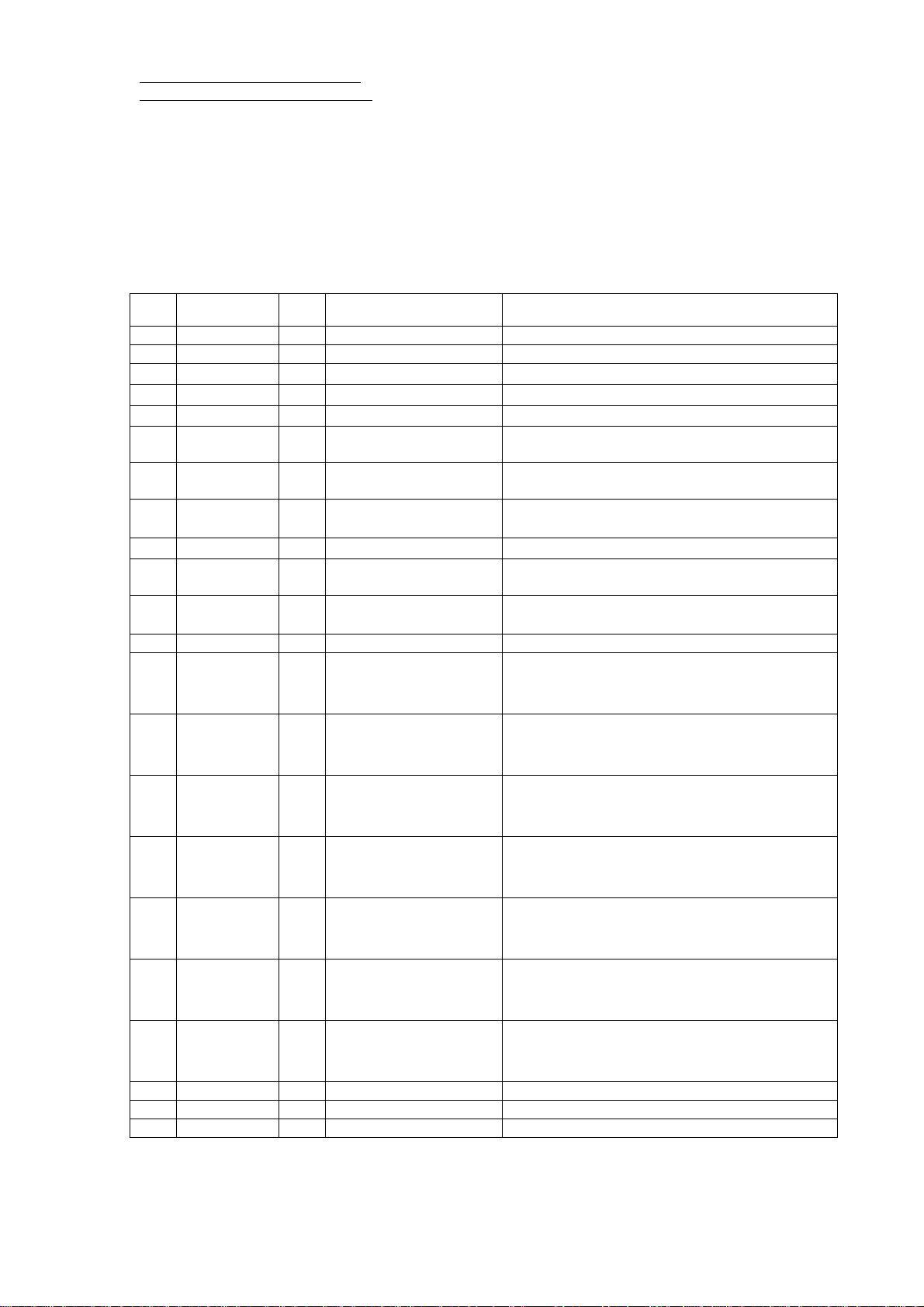
Hardware interface
RGM-3000/REB-3000.
Pin
NO
1 VCC System Power DC 3.3V ± 10%
2 VCC System Power DC 3.3V ± 10%
3 TXA O Navigation Data Output
4 RXA I Serial Data Input
5 TXB O Reserved
6 RXB I RTCM 104 Differential
7 TIMEMARK O 1 Pulse per second time
8 RESET I
9 BOOTSEL I
10 WAKEUP I Active low wakeup from
11 VBAT External Backup Power
12 RESERVED
13 GPIO3 I/O General Purpose I/O Pin
14 GPIO5 I/O General Purpose I/O Pin
15 GPIO6 I/O General Purpose I/O Pin
16 GPIO7 I/O General Purpose I/O Pin
17 GPIO10 I/O General Purpose I/O Pin
18 GPIO13 I/O General Purpose I/O Pin
19 GPIO15 I/O General Purpose I/O Pin
20 GND System GND
21 GND System GND
22 GND System GND
Name I/O Description Characteristic
TTL Level;Voh≧2.4V,Vol≦0.4V;Ioh=Iol=2mA
TTL Level;Vih≧0.7*VCC;Vil≦0.3*VCC
TTL Level;Voh≧2.4V,Vol≦0.4V;Ioh=Iol=2mA
TTL Level;Vih≧0.7*VCC;Vil≦0.3*VCC
GPS Input
Vil≦0.2V,Pulse Width≧10ms
mark Output
System Reset , Active
Vil≦0.2V,Pulse Width≧1ms
Low
Internal boot,Active High TTL Level;Vih≧0.7*VCC;Vil≦0.3*VCC
TTL Level;Voh≧2.4V,Vol≦0.4V;Ioh=Iol=2mA
the RTC
2.1V≦ Vbat ≦3.6V
Input
TTL Level;
Output:Voh≧2.4V,Vol≦0.4V;Ioh=Iol=2mA
Input:Vih≧0.7*VCC;Vil≦0.3*VCC
TTL Level;
Output:Voh≧2.4V,Vol≦0.4V;Ioh=Iol=2mA
Input:Vih≧0.7*VCC;Vil≦0.3*VCC
TTL Level;
Output:Voh≧2.4V,Vol≦0.4V;Ioh=Iol=2mA
Input:Vih≧0.7*VCC;Vil≦0.3*VCC
TTL Level;
Output:Voh≧2.4V,Vol≦0.4V;Ioh=Iol=2mA
Input:Vih≧0.7*VCC;Vil≦0.3*VCC
TTL Level;
Output:Voh≧2.4V,Vol≦0.4V;Ioh=Iol=2mA
Input:Vih≧0.7*VCC;Vil≦0.3*VCC
TTL Level;
Output:Voh≧2.4V,Vol≦0.4V;Ioh=Iol=2mA
Input:Vih≧0.7*VCC;Vil≦0.3*VCC
TTL Level;
Output:Voh≧2.4V,Vol≦0.4V;Ioh=Iol=2mA
Input:Vih≧0.7*VCC;Vil≦0.3*VCC
9
Page 15
RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
VCC DC Power Input
This is the main power supply for the Engine
board. The power range is from 3.3V±10%,
ripple ≤ 200mV. The maximum current of
RGM-3000 is ≤ 200mA.
GND
GND provides the ground for the Engine
board. Connect all grounds.
VBAT
This is the battery backup supply that
powers the SRAM and RTC when main
power is removed. The input voltage level is
from 2.1V~3.6V. Max current draw is 10 uA
at 3.3volt. Without an external backup
battery or on board battery, engine board will
execute a cold start after every turn on. To
achieve the faster start-up offered by a hot
or warm start, either a backup battery must
setup is NMEA Output, 4800bps, 8 data bits,
no parity, 1 stop bit. The default sentences
are GPGGA, GPGSA, GPRMC once per
second and GPGSV once per 5 seconds.
Please refer to “software interface” for the
detail protocol.
RXA
This is the main receiving channel and is
used to receive software commands to the
Engine board from user written software.
Please refer to “software interface” for the
detail protocol.
RXB
This is used for DGPS differential input .
BOOTSEL
Pull Bootsel pin high & reset , then it will get
to boot mode.
GPIO
be connected or battery installed on board.
TXA
This is the main transmit channel and is
used to output navigation and measurement
data to user written software. The default
This pin can be programmed to input or
output. For more application, please contact
Royaltek’s sales.
Absolute maximum ratings
Parameter Symbol Unit Min. Value Max. Value
Supply voltage VCC V 2.97 3.63
Output current mA 200
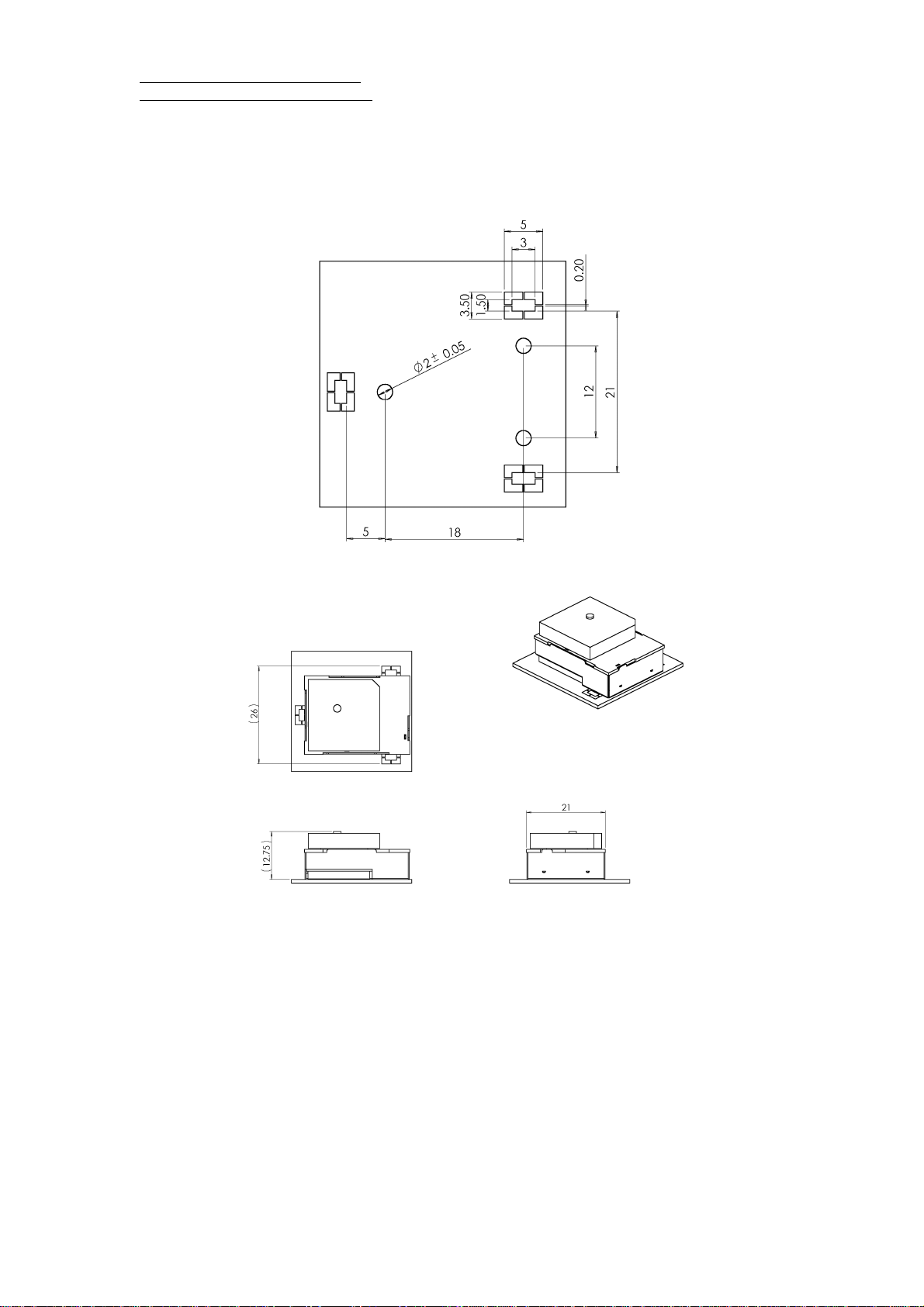
Critical design guide and diagram
1. It is recommanded to attach GNDu plate (30*30MM) below RGM3000M module or the antenna
module of RGM-3000E to increase the intensity of reception . Please refers to “Design Layout
Diagram “ .
2. During design of integrated layout, please isolate high frequency noise source (power Switch,data
or address signal lines ) from GPS antenna.
3. Please don’t place metal object above patch antenna.
10
Page 16
RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Design Layout Diagram
Recommanded Ground plate for RGM-3000M
RGM-3000M with ground plate
11
Page 17

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Recommanded RGM-3000-A Antenna Ground Plate
Connector tool (Option, not included in standard kit)
It is used to remove or install FPC on connector.
Software interface
NMEA V2.2 Protocol
It is the RS-232 interface:9600 bps, 8 bit
data, 1 stop bit and no parity. It supports the
following NMEA-0183 messages:GGA, GLL,
Table 1 NMEA-0183 Output Messages
NMEA Record Description
GGA Global positioning system fixed data
GLL Geographic position – latitude / longitude
GSA GNSS DOP and active satellites
GSV GNSS satellites in view
RMC Recommended minimum specific GNSS data
VTG Course over ground and ground speed
GSA, GSV, RMC and VTG.
NMEA Output Messages
The Engine board outputs the following
messages as shown in Table 1:
12
Page 18

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
3723.2475, N, 12158.3416, W, 1,
GGA-Global Positioning System
07, 1.0, 9.0, M, , , ,0000*18
Fixed Data
Table 2 contains the values of the following
example: $GPGGA, 161229.487,
Table 2 GGA Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $GPGGA GGA protocol header
UTC Position 161229.487 hhmmss.sss
Latitude 3723.2475 ddmm.mmmm
N/S Indicator N N=north or S=south
Longitude 12158.3416 dddmm.mmmm
E/W Indicator W E=east or W=west
Position Fix Indicator 1 See Table 2-1
Satellites Used 07 Range 0 to 12
HDOP 1.0 Horizontal Dilution of Precision
MSL Altitude 9.0 meters
Units M meters
Geoid Separation meters
Units M meters
Age of Diff. Corr. second Null fields when DGPS is not used
Diff. Ref. Station ID 0000
Checksum *18
<CR><LF>
End of message termination
Table 2-1 Position Fix Indicator
Value Description
0 Fix not available or invalid
1 GPS SPS Mode, fix valid
2 Differential GPS, SPS Mode, fix valid
3 GPS PPS Mode, fix valid
example:$GPGLL, 3723.2475, N,
GLL-Geographic Position –
12158.3416, W, 161229.487, A*2C
Latitude/Longitude
Table 3 contains the values of the following
Table 3 GLL Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $GPGLL GLL protocol header
Latitude 3723.2475 ddmm.mmmm
N/S Indicator N N=north or S=south
Longitude 12158.3416 Dddmm.mmmm
E/W Indicator W E=east or W=west
UTC Position 161229.487 hhmmss.ss
Status A A=data valid or V=data not valid
Checksum *2C
<CR><LF> End of message termination
GSA-GNSS DOP and Active Satellites
Table 4 contains the values of the following
13
example:$GPGSA, A, 3, 07, 02, 26,
27, 09, 04, 15, , , , , , 1.8,1.0,1.5*33
Page 19

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Table 4 GSA Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $GPGSA GSA protocol header
Mode 1 A See Table 4-2
Mode 2 3 See Table 4-1
Satellite Used 07 Sv on Channel 1
Satellite Used 02 Sv on Channel 2
…. ….
Satellite Used Sv on Channel 12
PDOP 1.8 Position Dilution of Precision
HDOP 1.0 Horizontal Dilution of Precision
VDOP 1.5 Vertical Dilution of Precision
Checksum *33
<CR><LF> End of message termination
Table 4-1 Mode 1
Value Description
1 Fix not available
2 2D
3 3D
Table 4-2 Mode 2
Value Description
M Manual-forced to operate in 2D or 3D mode
A Automatic-allowed to automatically switch 2D/3D
256, 42, 27, 27, 138,
GSV-GNSS Satellites in View
Table 5 contains the values of the following
example: $GPGSV, 2, 1, 07, 07, 79,
048, 42, 02, 51, 062, 43, 26, 36,
Table 5 GSV Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $GPGSV GSV protocol header
Number of Messages1 2 Range 1 to 3
Messages Number1 1 Range 1 to 3
Satellites in View 07
Satellite ID 07 Channel 1(Range 1 to 32)
Elevation 79 degrees Channel 1(Maximum 90)
Azimuth 048 degrees Channel 1(True, Range 0 to 359)
SNR (C/No) 42 dBHz Range 0 to 99, null when not tracking
…. ….
Satellite ID 27 Channel 4(Range 1 to 32)
Elevation 27 degrees Channel 4(Maximum 90)
Azimuth 138 degrees Channel 4(True, Range 0 to 359)
SNR (C/No) 42 dBHz Range 0 to 99, null when not tracking
Checksum *71
<CR><LF>
1
Depending on the number of satellites
End of message termination
Specific GNSS Data
42*71$GPGSV, 2, 2, 07, 09, 23,
313, 42, 04, 19, 159, 41, 15, 12,
041, 42*41
tracked multiple messages of GSV data may
be required.
RMC-Recommended Minimum
14
Table 6 contains the values of the following
example: $GPRMC, 161229.487, A,
3723.2475, N, 12158.3416, W, 0.13,
309.62, 120598, ,*10
Page 20

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Table 6 RMC Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $GPRMC RMC protocol header
UTC Position 161229.487 hhmmss.sss
Status A A=data valid or V=data not valid
Latitude 3723.2475 ddmm.mmmm
N/S Indicator N N=north or S=south
Longitude 12158.3416 dddmm.mmmm
E/W Indicator W E=east or W=west
Speed Over Ground 0.13 knots
Course Over Ground 309.62 degrees True
Date 120598 ddmmyy
Magnetic Variation degrees E=east or W=west
Checksum *10
<CR><LF>
VTG-Course Over Ground and
End of message termination
example:$GPVTG, 309.62, T, , M, 0.13, N,
0.2, K*6E
Ground Speed
Table 7 contains the values of the following
Table 7 VTG Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $GPVTG VTG protocol header
Course 309.62 degrees Measured heading
Reference T True
Course degrees Measured heading
Reference M Magnetic
Speed 0.13 knots Measured horizontal speed
Units N Knots
Speed 0.2 km/hr Measured horizontal speed
Units K Kilometer per hour
Checksum *6E
<CR><LF>
End of message termination
Message I.D.129 ” on page 17 using a user
SiRF Proprietary NMEA Input
Messages
NMEA input messages allow you to control
the Evaluation Unit in NMEA protocol mode.
The Evaluation Unit may be put into NMEA
mode by sending the SiRF Binary protocol
message “ Switch To NMEA Protocol –
Transport Message
Start Sequence Payload Checksum End Sequence
$PSRF<MID>1 Data2 *CKSUM3 <CR><LF>4
1
Message Identifier consists of three
numeric characters . Input messages begin
program or using SiRFdemo.exe and
selecting Switch to NMEA Protocol from the
Action manual. If the receiver is in SiRF
Binary mode, all the NMEA input messages
are ignored. Once the receiver is put into
NMEA mode, the following messages may
be used to command the module.
at MID 100.
2
Message specific data. Refer to a specific
15
Page 21

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
message section for <data>…<data>
definition
3
CKSUM is a two-hex character checksum
as defined in the NMEA specification . Use
of checksums is required on all input
messages.
4
Each message is terminated by using
Carriage Return (CR) Line Feed (LF) which
not printable ASCII characters , they are
omitted from the example strings, but must
be sent to terminate the message and cause
the receiver to process that input message.
Note – All fields in all proprietary NMEA
messages are required, none are exceptional.
All NMEA messages are comma delimited
is \r\n which is hex 0D 0A. Because \r\n are
SIRF NMEA Input Messages
Message
Set Serial Port 100 Set PORT A Parameters and protocol
Navigation Initialization 101 Parameters required for start using X/Y/Z
Set DGPS Port 102 Set PORT B parameters for DGPS input
Query / Rate Control 103 Query standard NMEA message and/or set output rate
LLA Navigation
Initialization
Development Data On/Off 105 Development Data messages On/Off
Input coordinates must be WGS84.
Message
Identifier
Description
(MID)
104 Parameters required for start using Lat/Lon/Alt1
extensive command message set is
available. When a valid message is received,
Set Serial Port
This command message is used to set the
protocol (SiRF Binary or NMEA) and/or the
communication parameters (baud , data bits,
stop bits, parity). Generally, this command is
used to switch the module back to SiRF
Binary protocol mode where a more
the parameters are stored in battery-backed
SRAM and then the Evaluation Unit restarts
using the saved parameters.
Table 8 contains the input values for the
following example:Switch to SIRF Binary
protocol at 9600,8,N,1
$PSRF100,0,9600,8,1,0*0C
Table 8 Set Serial Port Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $PSRF100 PSRF100 protocol header
Protocol 0 0=SiRF Binary, 1=NMEA
Baud 9600 4800,9600,19200,38400
Data Bits 8
8,71
Stop Bits 1 0,1
Parity 0 0=None ,1=Odd,2=Even
Checksum *0C
<CR><LF> End of message termination
1
SiRF protocol is only valid for 8data bits, 1 stop bit,
and no parity.
LLA Navigation Initialization
This command is used to initialize the
16
module for a warm start, which provide
current position (in X, Y, Z coordinates),
Page 22

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
clock offset , and time .This enables the
Evaluation Unit to search for the correct
satellite signals at the correct signal
parameters . Correct initialization
parameters enable the Evaluation Unit to
acquire signals quickly.
Table 9 Navigation Initialization Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $PSRF101 PSRF101 protocol header
ECEF X -2686700 Meters X coordinate position
ECEF Y -4304200 Meters Y coordinate position
ECEF Z 3851624 Meters Z coordinate position
CLK Offset 95000 Hz
Time Of Week 497260 seconds GPS Time OF Week
Week No 921 GPS Week Number
Channel Count 12 Range 1 to 12
Reset Cfh 3 See Table 10
Checksum *22
<CR><LF> End of message termination
Use 0 for last saved value if available . If this is unavailable, a default value of 96,000 will be used…
Table 10 Reset Configuration
Hex Description
0x01 Data Valid – Warm /Hot Starts=1
0x02 Clear Ephemeris – Warm Start=1
0x04 Clear Memory – Cold Start =1
Set DGPS Port
This command is used to control Serial Port
B which is an input – only serial port used to
receive RTCM differential corrections.
Differential receivers may output corrections
using different communication parameters.
The default communication parameters for
Table 9 contains the input values for the
following example:Switch to SiRF Binary
protocol at 9600,8,N,1
$PSRF101,-2686700,-4304200, 3851624,
95000, 497260, 921, 12, 3*22
Clock Offset of the Evaluation Unit1
PORT B are 9600 baud, 8 data bits, stop bit,
and no parity. If a DGPS received , the
parameters are stored in battery – backed
SRAM and then the receiver restarts using
the saved parameters.
Table 11 contains the input values for the
following example:Set DGPS Port to be
9600,8,N,1. $PSRF102,9600,8,1,0*3C
Table 11 Set DGPS Port Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $PSRF102 PSRF102 protocol header
Baud 9600 4800,9600,19200,38400
Data Bits 8 8,7
Stop Bits 1 0,1
Parity 0 0==None, 1=Odd, 2=Even
Checksum *3C
<CR><LF> End of message termination
be polled once, or setup for periodic output.
Query/Rate Control
This command is used to control the output
of standard NMEA messages GGA, GLL,
GSA, RMC, and VTG. Using this command
message, standard NMEA messages may
17
Checksums may also be enabled or disabled
depending on the needs of the receiving
program. NMEA message settings are saved
in battery-backed memory for each entry
when the message is accepted.
Page 23

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Table 12 Query/Rate Control Data
Format(See example 1.)
1.Quety the GGA message with checksum
enabled: $PSRF103,00,01,00,01*25
2.Enable VTG message for a 1 Hz
constant output with checksum enabled:
Table 12 Query/Rate Control Data Format(See example 1.)
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $PSRF103 PSRF102 protocol header
Message 00 See Table 13
Mode 01 0=Set Rate, 1=Query
Rate 00 seconds Output – off=0,max=255
Cksum Enable 01 0=Disable Checksum, 1=Enable Checksum
Checksum *25
<CR><LF> End of message termination
Table 13 Messages
Value Description
0 GGA
1 GLL
2 GSA
3 GSV
4 RMC
5 VTG
LLA Navigation Initialization
This command is used to initialize the
module for a warm start , by providing
current position(in latitude, longitude, and
altitude coordinates), clock offset, and time.
This enables the receiver to search for the
correct satellite signals at the correct signal
$PSRF103,05,00,01,01*20
3.Disable VTG message
$PSRF103,05,00,00,01*21
parameters . Correct initialization
parameters enable the receiver to acquire
signals quickly.
Table 14 contains the input values for the
following example: Start using known
position and time $PSRF104, 37.3875111,
-121.97232, 0, 95000, 237759, 922, 12,
3*3A
Table 14 LLA Navigation Initialization Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $PSRF104 PSRF104 protocol header
Lat 37.3875111 Degrees Latitude position (Range 90 to –90)
Lon -121.97232 Degrees Longitude position (Range 180 to –180)
Alt 0 Meters Altitude position
CLK Offset 95000 Hz
Time Of Week 237759 Seconds GPS Time Of Week
Week No 922 GPS Week Number
Channel Count 12 Range 1 to 12
Reset Cfg 3 See Table 15
Checksum *3A
<CR><LF> End of message termination
Use 0 for last saved value if available. If this is unavailable, a default value of 96,000 will be used.
Table 15 Reset Configuration
Hex Description
0x01 Data Valid – Warm /Hot Starts=1
0x02 Clear Ephemeris – Warm Start=1
Clock Offset of the Evaluation Unit1
18
Page 24

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
0x04 Clear Memory – Cold Start =1
checksum of parameter out of specified
Development Data On/Off
Use this command to enable development
data information if you can not get the
commands accepted. Invalid commands
generate debug information that enables the
user to determine the source of the
command rejection. Common reasons for
input command rejection are invalid
Table 16 Development Data On/Off Data Format
Name Example Units Description
Message ID $PSRF105 PSRF105 protocol header
Debug 1 0=Off , 1= On
Checksum *3E
<CR><LF> End of message termination
range.
Table 16 contains the input values for the
following examples:
1. Debug On $PSRF105,1*3E
2. Debug Off $PSRF 105,0*3F
Calculating Checksums for NMEA
Input
The Checksum is the 8-bit exclusive OR of all
the characters after $ and before *. (Not
including $ and *)
SiRF Binary Protocol
The serial communication protocol is designed
Start
Sequence
0xA01,
0xA2
0xYY denotes a hexadecimal byte value. 0xA0 equals 160.
Transport
The transport layer of the protocol
Payload
Length
Two-bytes
(15-bits)
Payload
Up to 2
(<1023 )
10-1
to include:
● Reliable transport of messages
● Ease of implementation
● Efficient implementation
● Independence from payload
Protocol Layers Transport Message
Message
Checksum
Two-bytes
(15-bits)
two-byte (15- bit)message length and a
two-byte(15-bit) choice of a 15-bit values for
EndSequence
0xB0,
0xB3
encapsulates a GPS message in two start
characters and two stop characters. The
values are chosen to be easily identifiable
and such that they are unlikely to occur
frequently in the data. In addition, the
transport layer prefixes the message with a
length and check sum are designed such
that both message length and check sum
can not alias with either the stop of start
code.
Message Validation
The validation layer is of part of the transport,
19
Page 25

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
but operates independently. The byte count
refers to the payload byte length. Likewise,
the check sum is a sum on the payload.
Message Length
The message length is transmitted high
order byte first followed by the low byte.
High Byte Low Byte
<0x7F> Any value
Even though the protocol has a maximum
length of (2
considerations require the SiRF GPS
module implementation to limit this value to
a smaller number. Likewise, the SiRF
receiving programs (e.g., SiRF demo) may
limit the actual size to something less than
15
-1) bytes practical
data neither the alignment nor the byte order
are defined as part of the transport although
SiRF payloads will use the big-endian order.
Checksum
The check sum is transmitted high order
byte first followed byte the low byte. This is
the so-called big- endian order
High Byte Low Byte
<0x7F Any value
The check sum is 15-bit checksum of the
bytes in the payload data .The following
pseudo code defines the algorithm used. Let
message to be the array of bytes to be sent
by the transport. Let msgLen be the number
of bytes in the message array to be
transmitted .
Index = first
this maximum..
Payload Data
The payload data follows the message
length. It contains the number of bytes
specified by the message length. The
payload data may contain any 8-bit value.
Where multi-byte values are in the payload
Input Messages for SiRF Binary Protocol
Note – All input messages are sent in BINARY
format
Table 19 SiRF Messages – Input Message List
Hex ASCII Name
0 x 80 128 Initialize Data Source
0 x 81 129 Switch to NMEA Protocol
0 x 82 130 Set Almanac
0 x 84 132 Software Version
0x 85 133 DGPS Source Control
0x 86 134 Set Main Serial Port
0 x 88 136 Mode Control
0 x 89 137 DOP Mask Control
0 x 8A 138 DGPS Mode
0 x 8B 139 Elevation Mask
0 x 8C 140 Power Mask
0 x 8D 141 Editing Residual
0 x 8E 142 Steady-State Detection
0 x 8F 143 Static Navigation
0 x 90 144 Clock Status
0 x 91 145 Set DGPS Serial Port
checkSum = 0
while index < msgLen
checkSum = checkSum +message[index]
checkSum = checkSum AND(215-1)
20
Page 26

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
0 x 92 146 Almanac
0 x 93 147 Ephemeris
0 x 95 149 Set Ephemeris
0 x 96 150 Switch Operating Mode
0 x 97 151 Set Trickle Power Parameters
0 x 98 152 Navigation Parameters (Poll)
0x A5 165 Change UART Configuration
0x A6 166 Set Message Rate
0x A7 167 Low Power Acquisition Parameters
Initialize Data Source-Message I.D.
128
Table 18 contains the input values for the
following example:Warm start the receiver
with the following initialization data:ECEF
WYZ (-2686727 m,-4304282 m,3851642
m),Clock Offset (75,000 Hz),Time of
Week(86,400 s),Week Number(924),Week
Number(924),and Channels(12). Raw
track data Debug data enabled.
Example:
A0A20019-Start Sequence and Payload
Length
80FFD700F9FFBE5266003AC57A000124
F80083S600039C0C33- Payload
0A91B0B3-Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Table 20 Initialize Data Source
Name
Message ID 1 80 ASCII 128
ECEF X 4 FFD700F9 meters
ECEF Y 4 FFBE5266 meters
ECEF Z 4 003AC57A meters
Clock Offset 4 000124F8 Hz
Time of Week 4 *100 0083D600 seconds
Week Number 2 039C
Channels 1 0C Range 1-12
Reset Config. 1 33 See Table 19
Payload Length: 25 bytes
Table 21 Initialize Data Source
Bit Description
0 Data valid flag-set warm/hot start
1 Clear ephemeris-set warm start
2 Clear memory-set cold start
3 Factory Reset
4 Enable Nav Lib data (YES=1,NO=0)
5 Enable debug data for SiRF binary protocol(YES=1,NO=0)
6 Enable debug data for NMEA protocol(YES=1,NO=0)
7 Reserved (must be 0)
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
NL Initialize Data (MID 31). All messages are
Units
Description
Note - If Nav Lib data is ENABLED then the
resulting messages are enabled. Clock
Status (MID 7), 50 BPS (MID 8), Raw DGPS
(17), NL Measurement Data (MID 28), GPS
Data (MID 29), SV State Data (MID 30), and
21
sent at 1 Hz and the baud rate will be
automatically set to 57600.
Page 27

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Switch To NMEA – Message I.D. 129
Table 20 contains the input values for the
following example:
Request the following NMEA data at 9600
baud:
GGA – ON at 1 sec , GLL – 0sec , GSA – ON
at 5 sec GSV – ON at 5 sec , RMC – 0 sec ,
VTG – 0 sec
Table 22 Switch To NMEA Protocol
Name
Message ID 1 81 ASCII 129
Mode 1 02
GGA Message1 1 01 1/s
Checksum2 1 01
GLL Message 1 00 1/s
Checksum 1 01
GSA Message 1 05 1/s
Checksum 1 01
GSV Message 1 05 1/s
Checksum 1 01
RMC Message 1 00 1/s
Checksum 1 01
VTG Message 1 00 1/s
Checksum 1 01
MSS Message 1 00 Recommended value
Checksum 1 01 Recommended value
Unused Field 1 00 Recommended value
Unused Field 1 01 Recommended value
Unused Field 1 00 Recommended value
Unused Field 1 01 Recommended value
Unused Field 1 00 Recommended value
Unused Field 1 01 Recommended value
Baud Rate 1 12C0 38400,19200,9600,4800,2400
Payload Length: 24bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Example:
A0A20018 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
8102010100010501050100010001000100010
001000112C0 – Payload
016AB0B3 – Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
Description
(1) A value of 0x00 implies NOT to send
message, otherwise data is sent at 1
message every X seconds requested
(i.e., to request a message to be sent
every 5 seconds, request the message
using a value of 0x05.)Maximum rate is
1/255s.
(2) A value of 0x00 implies the checksum
is NOT calculated OR transmitted with
the message (not recommended ) .A
value of 0x01 will have a checksum
calculated and transmitted as part of the
message (recommended).
Set Almanac- Message I.D. 130
This command enables the user to upload
an almanac to the Evaluation Unit
Note – This feature is not documented in
this manual. For information on
implementation contact SiRF Technology
Inc.
Software Version – Message I.D. 132
Table 21 contains the input values for the
following example:Poll the software
version
22
Page 28

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Example:
A0A20002 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
Table 23 Software Version
Name
Message ID 1 84 ASCII 132
TBD 1 00
Payload Length: 2 bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
8400 – Payload
0084B0B3 – Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
Description
Example 1: Set the DGPS source to External
DGPS Source – Message I.D. 133
This command allows the user to select the
source for DGPS corrections. Options available
are:
RTCM Data
A0A20007—Start Sequence and Payload Length
85020000000000—Payload
0087B0B3—Checksum and End Sequence
External RTCM Data (any serial port)
WAAS (subject to WAAS satellite availability)
Internal DGPS beacon receiver
Table B-6 DGPS Source Selection (Example 1)
Name
Message ID 1 85 Message identifier
DGPS Source 1 00 See Table B-8. DGPS Source Selections
Internal Beacon 4 00000000 Hz See Table B-9. Internal Beacon Search
Internal Beacon
Bit Rate
Payload: 7Bytes.
Bytes
1 0 BPS See Table B-9. Internal Beacon Search
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Units
Description
setting.
setting.
Example2: Set the DGPS source to Internal
DGPS Beacon Receiver
Search Frequency 310000, Bit Rate 200
Table B-7 DGPS Source Selection (Example 2)
Name
Message ID 1 85 Message identifier
DGPS Source 1 03 See Table B-8. DGPS Source Selections
Internal Beacon 4
Internal Beacon
Bit Rate
Payload: 7Bytes.
Table B- 8 DGPS Source Selections
DGPS Source Hex Decim
None 00 0
Bytes
1 C8 BPS See Table B-9. Internal Beacon Search
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
0004BAF0
al
A0A20007—Start Sequence and Payload Length
85030004BAF0C802—Payload
02FEB0B3—Checksum and End Sequence
Units
Hz See Table B-9. Internal Beacon Search
setting.
setting.
Description
DGPS corrections will not be used (even if available).
Description
23
Page 29

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
WAAS
External RTCM Data 02 2
Internal DGPS
Beacon Receiver
Table B- 9 Internal Beacon Search Settings
Search Type Frequen
Auto Scan
Full Frequency Scan 0 Non zero
Full Bit Rate Scan
Specific Search
01 1
03 3
Bit Rate Description
cy
0 0
Non
Zero
Non
Zero
0
Non Zero
Set Main Serial Port-Message I.D. 134
Table B-10 contains the input values for the
following example:
Set Main Serial port to 9600,n,8,1.
Uses WAAS Satellite (subject to availability).
External RTCM input source (i.e., Coast Guard Beacon).
Internal DGPS beacon receiver.
Auto scanning of all frequencies and bit rates are
performed.
Auto scanning of all frequencies and specified bit rate
are performed.
Auto scanning of all bit rates and specified frequency
are performed.
Only the specified frequency and bit rate search are
performed.
Length
860000258008010000—Payload
0134B0B3—Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Example:
A0A20009—Start Sequence and Payload
Table B- 10 Set Main Serial Port
Name
Message ID 1 86 Message identifier
Baud 4 00002580
Data Bits 1 08 8,7
Stop Bit 1 01 0,1
Parity 1 00 None=0, Odd=1, Even=2
Pad 1 00 Reserved
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Units
Description
38400,19200,9600,4800,2400,1200
Payload Length: 9 bytes
Example:
Mode control – Message I.D .136
Table 24 contains the input values for the
following example: 3D Mode = Always , Alt
Constraining = Yes , Degraded Mode –
clock then direction , TBD = 1 , DR Mode
= Yes , Altitude = 0, Alt Hold Mode = Auto,
Alt Source = Last Computed , Coast Time
A0A2000W – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
88010101010100000002140501 –
Payload
00A9B0B3 – Message Checksum and
End Sequence
Out = 20, Degraded Time Out = 5, DR
Time Out = 2, Track Smoothing = Yes
Table 24 Mode Control
24
Page 30

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Name
Message ID 1 88 ASCII 136
3D Mode 1 01 1 (always true=1)
Alt Constraint 1 01 YES = 1,NO = 0
Degraded Mode 1 01 See Table C-7
TBD 1 01 Reserved
DR Mode 1 01 YES = 1,NO = 0
Altitude 2 0000 Meters Range –1,000 to 10,000
Alt Hold Mode 1 00 Auto = 0,Always=1,Disable=2
Alt Source 1 02 Last Computed=0,Fixed to=1
Coast Time Out 1 14 Seconds 0 to 120
Degraded Time
Out
Dr Time Out 1 01 Seconds 0 to 120
Track Smoothing 1 01 YES = 1,NO = 0
Payload Length:14 bytes
Table 25 Degraded Mode Byte Value
Byte Value Description
0 Use Direction then Clock Hold
1 Use Clock then Direction Hold
2 Direction(Curb)Hold Only
3 Clock(Time)Hold Only
4 Disable Degraded Modes
Bytes
1 05 Seconds 0 to 120
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Units
Description
Example:
DOP Mask Control – Message I.D. 137
Table 26 contains the input values for the
following example:
Auto Pdop/Hdop, Gdop =
8(default),Pdop=8,Hdop=8
Table 26 DOP Mask Control
Name
Message ID 1 88 ASCII 137
DOP Selection 1 00 See Table 25
GDOP Value 1 08 Range 1 to 50
PDOP Value 1 08 Range 1 to 50
HDOP Value 1 08 Range 1 to 50
Payload Length: 5 bytes
Table 27 DOP Selection
Byte Value Description
0 Auto PDOP/HDOP
1 PDOP
2 HDOP
3 GDOP
4 Do Not Use
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
A0A20005 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
8900080808 – Payload
00A1B0B3 – Message Checksum and
End Sequence
Units
Description
DGPS Control – Message I.D.138
Table 28 contains the input values for the
following example:
25
Set DGPS to exclusive with a time out of
30 seconds.
Example:
Page 31

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
A0A20003 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
8A011E – Payload
00A9B0B3 – Message Checksum and
Table 28 DGPS Control
Name
Message ID 1 8A ASCII 138
DGPS Selection 1 01 See Table 27
DGPS Time Out 1 1E Seconds Range 1 to 120
Payload Length:3 bytes
Table 29 DGPS Selection
Byte Value Description
0 Auto
1 Exclusive
2 Never
3 Mixed (not recommended)
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Elevation Mask – Message I.D.139
Table 30 contains the input values for the
following example:
Set Navigation Mask to 15.5 degrees
(Tracking Mask is defaulted to 5 degrees).
End Sequence
Units
Example:
A0A20005 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
8B0032009B – Payload
0269B0B3 – Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Description
Table 30 Elevation Mask
Name
Message ID 1 8B ASCII 139
Tracking Mask 2 *10 0032 degrees Not currently used
Navigation Mask 2 *10 009B degrees Range –20.0 to 90.0
Payload Length:5 bytes
Power Mask – Message I.D.140
Table 31 contains the input values for the
following example: Navigation mask to
33dBHz (tracking default value of 28)
Example:
A0A20003 – Start Sequence and Payload
Table 31 Power Mask
Name
Message ID 1 8C ASCII 140
Tracking Mask 1 1C dBHz Not currently implemented
Navigation Mask 1 21 dBHz Range –28 to 50
Payload Length:3 bytes
Bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Units
Length
8C1C21 – Payload
00C9B0B3 – Message Checksum and
End Sequence
Units
Description
Description
26
Page 32

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Editing Residual – Message I.D.141
Note – Not implemented currently
Example:
Steady State Detection – Message
I.D.142
Table 32 contains the input values for the
following example: Set Stead State
Threshold to 1.5 m/sec2
Table 32 Steady Detection
Name
Message ID 1 8E ASCII 142
Threshold 1 0F M /sec2 Range 0 to 20
Payload: 2 bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
A0A20002 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
8E0F – Payload
009DB0B3 – Message Checksum and
End Sequence
Units
Description
Static Navigation – Message I.D.144
Table 33 Steady State Detection
Name
Message ID 1 90 ASCII 144
TBD 1 00 Reserved
Payload Length:2 bytes
Set DGPS Serial Port – Message I.D 145
Table 34 contains the input values for the
following example:Set DGPS Serial port to
9600.n,8,1.
Example:
Table 34 Set DGPS Serial Port
Name
Message ID 1 91 ASCII 145
Baud 4 00002580 38400,19200,9600,4800,2400,
Data Bits 1 08 8,7
Stop Bit 1 01 0,1
Parity 1 00 None=0,Odd=1,Even=2
Pad 1 00 Reserved
Payload Length: 9 bytes
Bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Units
A0A20009-Start Sequence and Payload
Length
910000258008010000 – Payload
013FB0B3 – Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
1200
Description
Description
Almanac – Message I.D.146
Table 35 contains the input values for the
following example:Poll for the Almanac.
Example:
Table 35 Almanac
27
A0A20002 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
9200 – Payload
0092B0B3 – Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Page 33

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Name
Message ID 1 92 ASCII 146
TBD 1 00 Reserved
Payload Length: 2 bytes
Bytes
Ephemeris Message I.D.147
Table 36 contains the input values for the
following example:Poll for Ephemeris Data
for all satellites.
Example:
A0A20003 – Start Sequence and Payload
Table 36 Almanac
Name
Message ID 1 93 ASCII 147
Sv I.D.1 1 00 Range 0 to 32
TBD 1 00 Reserved
Payload Length:3 bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Units
Length
930000 – Payload
0092B0B3 – Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
Description
Description
A value of 0 requests all available
ephemeris records, otherwise the
ephemeris of the Sv I.D. is requested.
Switch To SiRF Protocol
Note – To switch to SiRF protocol you
must send a SiRF NMEA message to
revert to SiRF binary mode. (See page 9, ”
NMEA Input Messages “ for more
information)
Table 37 Switch Operating Mode I.D. 150
Name
Message ID 1 96 ASCII 150
Mode 2 1E51 1E51=test, 0=nomal
SvID 2 0006 Satellite to Track
Period 2 001E seconds Duration of Track
Payload length: 7 bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Switch Operating Modes - Message
I.D. 150
Table 37 contains the input values for the
following example:
Sets the receiver to track a single satellite
on all channels.
Example:
A0A20007—Start Sequence and Payload
Length
961E510006001E—Payload
0129B0B3—Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
Description
Set Trickle Power Parameters -
Message I.D. 151
Table 38 contains the input values for the
28
Page 34

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
following example: Sets the receiver into
low power Modes. Example: Set receiver
into Trickle Power at 1 hz update and 200
ms On Time.
A0A20009—Start Sequence and Payload
Table 38 Set Trickle Power Parameters I.D. 151
Name
Message ID 1 97 ASCII 151
Push To FixMode 2 0000 ON=1, OFF=0
Duty Cycle 2 *10 00C8 % % Time on
Milli Seconds On
Time
Payload Length: 9bytes.
Bytes
4 000000C8 ms Range 200 ~ 500 ms
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Computation of Duty Cycle and On
Time.
The Duty Cycle is the desired time to be
spent tracking.The On Time is the duration
of each tracking period (range is 200 - 900
ms). To calculate the TricklePower update
rate as a function of Duty cycle and On
Length
97000000C8000000C8—Payload
0227B0B3—Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
Time, use the following formula:
Off Time = (On Time - (Duty Cycle * On
Time)) / Duty Cycle
Update rate = Off Time + On Time
Note – On Time inputs of > 900 ms will
default to 1000 ms
Following are some examples of
selections:
Description
Table 39 Example of selections for Trickle Power Mode of Operation
Mode On Time (ms) Duty Cycle (%) Update rate (1/Hz)
Continuous 1000 100 1
Trickle Power 200 20 1
Trickle Power 200 10 2
Trickle Power 300 10 3
Trickle power 500 5 10
See Table 40 for supported/unsupported settings.
Table 40 Trickle Power Mode Settings
On
Time
(ms)
200 Y Y N N N N N N
300 Y Y Y Y Y Y N N
400 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
500 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
600 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
700 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
800 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
900 Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Y = Yes (Mode supported)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Update Rate (second)
N = No (Mode NOT supported)
29
Page 35

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Push-to-Fix
In this mode the receiver will turn on every
30 minutes to perform a system update
consisting of a RTC calibration and
satellite ephemeris data collection if
required (i.e., a new satellite has become
visible) as well as all software tasks to
support SnapStart in the event of an NMI.
approximately On Period/1800, or about
1%. Push-to-Fix keeps the ephemeris for
all visible satellites up to date so
position/velocity fixes can generally be
computed within SnapStart times (when
requested by the user) on the order of 3
seconds.
Ephemeris collection time in general this
takes 18 to 30 seconds. If ephemeris data
is not required then the system will
re-calibrate and shut down. In either case,
the amount of time the receiver remains
off will be in proportion to how long it
stayed on:
Off period = (On Period*(1-Duty Cycle) /
Duty Cycle)
Off Period is limited to 30 minutes. The
duty cycle will not be less than
Table C-20 Poll Receiver for Navigation Parameters
Name
Message ID 1 98 ASCII 152
Reserved 1 00
Payload length: 2 bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Poll Navigation Parameters Message I.D. 152
Table C-20 contains the input values for
the following example:
Example: Poll receiver for current
navigation parameters.
A0A20002—Start Sequence and Payload
Length
9800—Payload
0098B0B3—Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
Description
Set UART Configuration - Message
I.D. 165
Table B-28 contains the input values for the
following example:
Example: Set port 0 to NMEA with 9600 baud,
8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity. Set
port 1 to SiRF binary with 57600 baud, 8
data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity. Do not
configure ports 2 and 3.
Example:
30
A0A20031—Start Sequence and Payload
Length
A5000101000025800801000000010000000
0E1000801000000FF050500000000000
0000000FF0505000000000000000000—Pa
yload
0452B0B3—Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Page 36

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Table B- 28 Set UART Configuration
Name
Bytes
Message ID 1 A5 Decimal 165
Port 1 00 For UART 0
In Protocol1 1 01 For UART 0
Out Protocol 1 01 For UART 0 (Set to In protocol)
Baud Rate2 4 00002580 For UART 0
Data bits3 1 08 For UART 0
Stop bits4 1 01 For UART 0
Parity5 1 00 For UART 0
Reserved 1 00 For UART 0
Reserved 1 00 For UART 0
Port 1 00 For UART 1
In Protocol 1 01 For UART 1
Out Protocol 1 01 For UART 1
Baud Rate 4 0000E100 For UART 1
Data bits 1 08 For UART 1
Stop bits 1 01 For UART 1
Parity 1 00 For UART 1
Reserved 1 00 For UART 1
Reserved 1 00 For UART 1
Port 1 00 For UART 1
In Protocol 1 01 For UART 2
Out Protocol 1 01 For UART 2
Baud Rate 4 00000000 For UART 2
Data bits 1 08 For UART 2
Stop bits 1 01 For UART 2
Parity 1 00 For UART 2
Reserved 1 00 For UART 2
Reserved 1 00 For UART 2
Port 1 00 For UART 3
In Protocol 1 01 For UART 3
Out Protocol 1 01 For UART 3
Baud Rate 4 00000000 For UART 3
Data bits 1 08 For UART 3
Stop bits 1 01 For UART 3
Parity 1 00 For UART 3
Reserved 1 00 For UART 3
Reserved 1 00 For UART 3
Payload Length: 49 bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Units
Description
1. 0 = SiRF Binary, 1 = NMEA, 2 = ASCII, 3 = RTCM, 4 = User1, 5 = No Protocol.
2. Valid values are 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200, 38400, and 57600.
3. Valid values are 7 and 8.
4. Valid values are 1 and 2.
5. 0 = None, 1 = Odd, 2 = Even.
Set Message Rate - Message I.D. 166
Table B-29 contains the input values for the following example:
Set message ID 2 to output every 5 seconds starting immediately.
Example:
A0A20008—Start Sequence and Payload Length
A601020500000000—Payload
31
Page 37

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
00AEB0B3—Message Checksum and End Sequence
Table B- 29 Set Message Rate
Name
Message ID 1 A6 Decimal 166
Send Now1 1 01 Poll message
MID to set 1 02
Update Rate 1 05 sec Range= 1 - 30
TBD 1 00 Reserved
TBD 1 00 Reserved
TBD 1 00 Reserved
TBD 1 00 Reserved
Payload Length: 8 bytes
1. 0 = No, 1 = Yes, if no update rate the message will be polled.
Bytes
Low Power Acquisition Parameters Message I.D. 167
Table B-30 contains the input values for the
following example:
Set maximum off and search times for
re-acquisition while receiver is in low power.
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Units
Example:
A0A20019—Start Sequence and Payload
Length
A7000075300001D4C000000000000000000
000000000000000—Payload
02E1B0B3—Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Description
Table B- 30 Set Low Power Acquisition Parameters
Name
Message ID 1 A7 Decimal 167
Max Off Time 4 00007530 ms
Max Search Time 4 0001D4C0 ms
TBD 4 00000000 Reserved
TBD 4 00000000 Reserved
TBD 4 00000000 Reserved
TBD 4 00000000 Reserved
Payload Length: 25 bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex)
Scale Example
Units
Description
Maximum time for sleep mode
Max. satellite search time
Output Messages for SiRF Binary Protocol
Note – All output messages are received in BINARY format. SiRF demo interprets the binary data
and saves if to the log file in ASCII format.
Table 42 lists the message list for the SiRF output messages
Hex ASCII Name Description
0x02 2 Measured Navigation Data Position, velocity, and time
0x04 4 Measured Tracking Data Signal to noise information
0x05 5 Raw Track Data Measurement information
0x06 6 SW version Receiver software
0x07 7 Clock Status
0x08 8 50 BPS Subframe Date Standard ICD format
32
Page 38

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
0x09 9 Throughput CPU load
0x0B 11 Command Acknowledgment Successful request
0x0C 12 Command N Acknowledgment Unsuccessful request
0X0D 13 Visible List Auto Output
0x0E 14 Almanac Data
0x0F 15 Ephemeris Data
0x11 17 Differential Corrections
0x12 18 OkToSend
0x13 19 Navigation Parameters
0x1C 28
0x1D 29
0x1E 30
0x1F 31
0x64 100 RoyalTek Navigation Data UTC , lat , lon, validate output
0xFF 255 Development Data Various data messages
Nav. Lib. Measurement Data Measurement Data
Nav. Lib. DGPS Data Differential GPS Data
Nav. Lib. SV State Data Satellite State Data
Nav. Lib. Initialization Data Initialization Data
Received from DGPS broadcast
CPU ON / OFF (Trickle Power)
Response to Poll
Measure Navigation Data Out –
Message I.D.2
Output Rate: 1 Hz
Table 43 lists the binary and ASCII
message data format for the measured
navigation data
Example:
A0A20029 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
Table 43 Measured Navigation Data Out – Binary & ASCII Message Data Format
Name
Message ID 1 02 2
X – position 4 FFD6F78C M -2689140
Y – position 4 FFBE536E M -4304018
Z – position 4 003AC004 M 3850244
X – velocity 2 *8 00 M/s Vx/8 0
Y – velocity 2 *8 03 M/s Vy/8 0.375
Z – velocity 2 *8 01 M/s /8 0.125
Mode1 1 04 Bitmap1 4
DOP2 1 *5 A /5 2.0
Mode3 1 00 Bitmap3 0
GPS Week 2 036B 875
GPS TOW 4 *100 039780E3 seconds /100 602605.79
SVs in Fix 1 06 6
CH 1 1 12 18
CH 2 1 19 25
CH 3 1 0E 14
CH 4 1 16 22
CH 5 1 0F 15
CH 6 1 04 4
CH 7 1 00 0
CH 8 1 00 0
CH 9 1 00 0
CH 10 1 00 0
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
02FFD6F78CFFBE869E003AC004000301
04A00036B039780E3
0612190E160F04000000000000 –
Payload
09BBB0B3 – Message Checksum, and
End Sequence
Units
Scale Example
33
Page 39

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
CH 11 1 00 0
CH 12 1 00 0
Payload Length :41 bytes
1
For further information , go to Table 42
2
Dilution of precision (DOP) field contains
3
For further information , go to Table 43
Note – Binary units scaled to integer
values need to be divided by the scale
value of PDOP when Position is obtained
using 3D solution and HDOP in all other
cases.
Table 44 Mode 1
Mode 1
Hex ASCII
0x00 0 No Navigation Solution
0x01 1 1 Satellite Solution
0x02 2 2 Satellite Solution
0x03 3 3 Satellite Solution (2D)
0x04 4 >=4 Satellite Solution (3D)
0x05 5 2D Point Solution(Krause)
0x06 6 3D Point Solution(Krause)
0x07 7 Dead Reckoning (Time Out)
Table 45 Mode 2
Mode 2
Hex ASCII
0x00 0 DR Sensor Data
0x01 1 Validated / Unvalidated
0x02 2 Dead Reckoning (Time Out)
0x03 3 Output Edited by UI
0x04 4 Reserved
0x05 5 Reserved
0x06 6 Reserved
0x07 7 Reserved
value to receive true decimal value (i.e.,
decimal Xvel = binary Xvel /8).
Description
Description
04036C0000937F0C0EAB46003F
Measured Tracker Data Out –
Message I.D.4
Output Rate: 1 Hz
Table 46 lists the binary and ASCII
message data format for the measured
1A1E1D1D191D1A1A1D1F1D594
23
F1A1A…. – Payload ****B0B3 –
Message Checksum and End
Sequence
tracker data.
Example:A0A200BC – Start Sequence
and Payload Length
Table 46 Measured Tracker Data Out
Name
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Units
Scale Example
Message ID 1 04 None 4
GPS Week 2 036C 876
GPS TOW 4 S*100 0000937F S S/100 37759
34
Page 40

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Channels 1 0C 12
1st Sv ID 1 0E 14
Azimuth 1 Az*[2/3] AB Degree /[2/3] 256.5
Elev. 1 EI*2 46 Degree /2 35
State 2 003F Bitmap1 63
C/NO 1 1 1A 26
C/NO 2 1 1E 30
C/NO 3 1 1D 29
C/NO 4 1 1D 29
C/NO 5 1 19 25
C/NO 6 1 1D 29
C/NO 7 1 1A 26
C/NO 8 1 1A 26
C/NO 9 1 1D 29
C/NO 10 1 1F 31
2nd Sv ID 1 1D 29
Azimuth 1 Az*[2/3] 59 Degree /[2/3] 89
Elev. 1 EI*2 42 Degree /2 66
State 2 3F Bitmap1 63
C/NO 1 1 1A 26
C/NO 2 1 1A 63
…..
Payload Length: 188 bytes
bytes with non tracking channels reporting
For further information, go to Table 45.
Note – Message length is fixed to 188
Table 47 Trk. to NAV Struct. Trk._status Field Definition
Field Definition Hex Value Description
ACQ_SUCCESS 0x0001 Set if acq/reacq if done successfully
DELTA_CARPHASE_VALID 0x0002 Integrated carrier phase is valid
BIT_SYNC_DONE 0x0004 Bit sync completed flag
SUBFRAME_SYNC_DONE 0x0008 Subframe sync has been done
CARRIER_PULLIN_DONE 0x0010 Carrier pull in done
CODE_LOCKED 0x0020 Code locked
ACQ_FAILED 0x0040 Failed to acquire S/V
GOT_EPHEMERIS 0x0080 Ephemeris data available
Note – When a channel is fully locked and all data is valid , the status shown is 0xBF
Raw Tracker Data Out – Message
I.D.5
Output Rate:1 Hz
Table 48 lists the binary and ASCII
message data format for the raw tracker
data .
Example:
zero values
A0A20033 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
05000000070013003F00EA1BD4000D03
9200009783000DF45E000105B5FF90F5
C20000242827272327242427290500000
0070013003F – Payload
0B2DB0B3 – Message Checksum and
End Sequence
Table 48 Raw Tracker Data Out
Name
Message ID 1 05 5
Channel 4 00000007 7
SVID 2 0013 19
State 2 003F Bitmap1 63
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
35
Units
Scale Example
Page 41

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Bits 4 00EA1BD4 Bit 15342548
Ms 2 000D Ms 13
Chips 2 0392 Chip 914
Code Phase 4
Carrier Doppler 4
Time Tag 4 000105B5 Ms 66997
Delta Carrier2 4 2-10
Search Count 2 0000 0
C/NO 1 1 24 dBHz 36
C/NO 2 1 28 dBHz 40
C/NO 3 1 27 dBHz 39
C/NO 4 1 27 dBHz 39
C/NO 5 1 23 dBHz 35
C/NO 6 1 27 dBHz 39
C/NO 7 1 24 dBHz 36
C/NO 8 1 24 dBHz 36
C/NO 9 1 27 dBHz 39
C/NO 10 1 29 dBHz 41
Power Loss
1 05 5
Count
Phase Loss
1 00000007 7
Count
Integration
2 0013 Ms 19
Interval
Track Loop
2 003F 63
Iteration
Payload Length:51 bytes per satellite tracked (up to 12)
-16
2
-10
2
00009783 Chip
000DF45E Rad/2ms
FF90F5C2 Cycles
-16
/2
-10
/2
-10
/2
38787
914526
-7277118
1.For further information,go to Table 45
2.Multiply by (1000÷4π)÷2
16
to convert to Hz.
The meaning of I.D.5 is described as following table
Message ID: Each SiRF binary message is defined based on the ID.
Channel: Receiver channel where data was measured (range 1-12).
SVID: PRN number of the satellite on current channel.
State: Current channel tracking state (see Table 45)
Bit Number: Number of GPS bits transmitted since Sat-Sun midnight (in Greenwich)
at a 50 bps rate.
Millisecond
Number:
Number of milliseconds of elapsed time since the last received bit(20
ms between bits)
Chip Number: Current C/A code symbol being transmitted (range 0 to 1023
chips;1023 chips=1 ms).
Code Phase: Fractional chip of the C/A code symbol at the time of sampling(scaled
by 2
-16
,=1/65536)
Carrier Doppler: The current value of the carrier frequency as maintained by the
tracking loops.
Receiver Time
Tag:
This is the count of the millisecond interrupts from the start of the
receiver (power on) until the measurement sample is taken. The ms
interrupts are generated by the receiver clock.
Delta Carrier
Phase:
The difference between the carrier phase(current) and the carrier
phase(previous). Units are in carrier cycles with the LSB= 0.00185 carrier
cycles. The delta time for the accumulation must be known.
Note –Carrier phase measurements are not necessarily in sync with
code phase measurement for each measurement epoch.
Search Count: This is the number of times the tracking software has completed full
satellite signal searche.s
C/No: Ten measurements of carrier to noise ratio(C/No) values in dBHZ at
input to the receiver.Each value represents 100 ms of tracker data and
its sampling time is not necessarily in sync with the code phase
measurement.
Power Loss
Count:
The number of times the power detectors fell below the threshold between the
present code phase sample and the previous code phase sample. This task is
performed every 20 ms (max count is 50).
36
Page 42

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Phase Loss
Count:
Integration
Interval:
Track Loop
Iteration:
The number of time the phase lock fell below the threshold between the
present code phase sample and the previous code phase sample. This task is
performed every 20 ms (max count is 50).
The time in ms for carrier phase accumulation . This is the time difference (as
calculated by the user clock) between the Carrier Phase(current) and the
Carrier Phase(previous).
The tracking Loops are run at 2 ms and 10 ms intervals. Extrapolation values
for each interval is 1 ms and 5 ms for range computations.
Calculation of Pseudo-Range
Measurements
The pseudo-range measurement in meters
can be determined from the raw track data
by solving the following equation:
Pseudo-range (PR) = {Received Tine
(RT) – Transmit Time (TT)} * C
where C = speed of light
The following variables from the raw track
data are required for each satellite:
Bit Number (BN) – 50 bits per second
Millisecond Number (MSN)
Chip Number (CN)
Code Phase (CP)
Receiver Time Tag (RTTag)
Delta Carrier Phase (DCP)
The following steps are taken to get the psr
data and carrier data for each measurement
epoch.
1. Computation of initial Receiver
channel measurements are NOT
taken at the same time. Therefore, all
ranges must be extrapolated to a
common measurement epoch. For
simplicity, the first channel of each
measurement set is used as the
reference to which all other
measurements are extrapolated.
4. Extrapolate the pseudo-range based
on the correlation interval to improve
precision.
5. Compute the delta range.
If the accumulation time of the Dalta Carrier
Phase is 1000 ms then the measurement is
valid and can be added to the previous Delta
Carrier Phase to get Accumulated Carrier
Phase data. If the accumulation time of the
Delta Carrier Phase is not equal to 1000 ms
then the measurement is not valid and the
accumulation time must be restarted to get
Accumulated Carrier Phase data.
Time(RT) in seconds. Note-Where the
initial arbitrary value chosen at start
up to make the PR reasonable
(i.e.,set equal to TT+70ms) and then
incriminated by one second for each
measurement epoch.
2. Computation of Transmit Time (TT) in
seconds.
3. Calculate Pseudo-range at a common
receiver time of the first channel of
the measurement data set. Note-All
Response :Software Version
String – Message I.D.6
Output Rate:Response to polling message
Example:
A0A20015 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
0606312E322E30444B495431313920534
D0000000000-Payload
0382B0B3 – Message Checksum and End
Sequence
37
Page 43

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Table 49 Software Tracker Data Out
Name
Message ID 1 06 6
Character 20 1 2
Payload Length: 21 bytes
Note – Convert to symbol to assemble message (i.e., 0x4E is ’N’). These are low priority task and
are not necessarily output at constant intervals.
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Units
Scale Example
Response :Clock Status Data – Message I.D.7
Output Rate:1Hz or response to polling message
Example:
A0A20014 – Start Sequence and Payload Length
0703BD021549240822317923DAEF – Payload
0598B0B3 – Message Checksum and End Sequence
Table 50 Clock Status Data Message
Name
Message ID 1 07 7
GPS Week 2 03BD 957
GPS TOW 4 *100 02154924 S /100 349494.12
Svs 1 08 8
Clock Drift 4 2231 Hz 74289
Clock Bias 4 7923 ns 128743715
Estimated GPS
Time
Payload Length:20 bytes
50BPS Data – Message I.D.8
Output Rate:As available (12.5 minute
download time)
Example:A0A2002B – Start Sequence and
Payload Length
Bytes
4 DAEF ms 349493999
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Units
08******** - Payload
****B0B3 – Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Scale Example
Table 51 Clock Status Data Message
Name
Message ID 1 08 8
Channel 1
Sv ID 1
Word [10] 40
Payload Length:43 bytes per subframe
(6subframes per page, 25 pages
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
38
Units
Almanac)
Note – Data is logged in ICD format
Scale Example
Page 44

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
(available from www.navcen.uscg.mail)
CPU Throughput – Message I.D.9
Output Rate:1 Hz
Table 52 CPU Throughput
Name
Message ID 1 09 9
SegStatMax 2 *186 003B ms /186 .3172
SegStatLat 2 *186 0011 ms /186 .0914
AveTrkTime 2 *186 0016 ms /186 .1183
Last MS 2 01E5 ms 485
Payload Length: 9 bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Command Acknowledgment –
Message I.D.11
Output Rate: Response to successful
input message
This is successful almanac (message ID
Example:A0A20009 – Start Sequence and
Payload Length
09003B0011001601E5 – Payload
0151B0B3 – Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
0x92)request example:
Scale Example
A0A20002 – Start Sequence and
Payload Length
0B92 – Payload
009DB0B3 – Message Checksum and
End Sequence
Table 53 Command Acknowledgment
Name
Message ID 1 0B 11
Ack.I.D. 1 92 146
Payload Length: 2 bytes
Command N Acknowledgment –
Message I.D. 12
Output Rate: Response to rejected Input
message
This is unsuccessful almanac (message
Table 54 Command N Acknowledgment
Name Bytes
Message ID 1 0C 12
N Ack. I.D 1 92 146
Payload Length:2 bytes
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Units
ID 0x92) request example:
A0A20002 – Start Sequence and Payload
Length
0C92 – Payload
009EB0B3 – Message Checksum and
End Sequence
Units
Scale Example
Scale Example
39
Page 45

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Payload Length
Visible List – Message I.D.13
Output Rate:Updated approximately every
2minutes. Note – This is a variable length
message. Only the number of visible
satellites are reported(as define by visible
Svs in Table 55), Maximum is 12 satellites
Example:A0A2002A – Start Sequence and
Table 55 Visible List
Name
Message ID 1 0D 13
Visible Svs 1 08 8
CH 1 –Sv I.D 1 07 7
CH 1 –Sv Azimuth 2 0029 Degrees 41
CH 1 –Sv Elevation 2 0038 Degrees 56
CH 2 –Sv I.D 1 09 9
CH 2 –Sv Azimuth 2 0133 Degrees 307
CH 2 –Sv Elevation 2 002C Degrees 44
……
Payload Length:62 bytes(maximum)
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
0D080700290038090133002C*************
****** - Payload
****B0B3 – Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
Scale Example
and Payload Length
Almanac Data – Message I.D.14
Output Rate:Response to poll
Example :A0A203A1 – Start Sequence
Table 56 Visible List
Name
Message ID 1 0E 14
Sv I.D.(1) 1 01 1
Almanac Data[14][2] 28
….
Sv I.D.(32) 1 20 32
Almanac Data[14][2] 28
Payload Length: 929 bytes(maximum)
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Units
0E01************* - Payload
****B0B3 – Message
checksum and End Sequence
Scale Example
OkToSend - Message I.D. 18
Output Rate: Trickle Power CPU on/off indicator
Example:
A0A20002—Start Sequence and Payload Length
1200—Payload
0012B0B3—Message Checksum and End Sequence
Table B- 52 Almanac Data
40
Page 46

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Name
Message ID 1 12 18
Send indicator1 1 00 00
Payload Length: 2 bytes
1.
0 implies that CPU is about to go OFF, OkToSend==NO, 1 implies CPU has just come ON, OkToSend==YES
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Units
Scale Example
Navigation Parameters (Response to Poll) – Message I.D. 19
Output Rate:1 Response to Poll
Example:
A0A20018—Start Sequence and Payload Length
130100000000011E3C0104001E004B1E00000500016400C8—Payload
022DB0B3—Message Checksum and End Sequence
Table B- 53 Navigation Parameters
Name
Message ID 1 13 19
Reserved 4 00000000
Altitude Hold Mode 1 00 0
Altitude Hold Source 1 00 0
Altitude Input Source 2 0000 meters 0
Degraded Mode1 1 01 1
Degraded Timeout 1 1E seconds 30
DR Timeout 1 3C seconds 60
Track Smooth Mode 1 01 1
Static Navigation 1
3SV Least Squares 1
Reserved 4
DOP MASK Mode
Navigation Elevation
Mask
Navigation Power Mask 1
Reserved 4
DGPS Source 1
DGPS Mode3 1 00 0
DGPS Timeout 1 1E seconds 30
Reserved 4
LP Push-to-Fix 1
LP On-Time 4
LP Interval 4
LP User Tasks Enabled 1
LP User Task Interval 4
LP Power Cycling
Enabled
LP Max. Acq. Search
Time
LP Max. Off Time 4
Reserved 4
Reserved 4
Payload Length: 65 bytes
2
Bytes
1 04 4
2
1
4
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Units
Scale Example
1. See Table 22.
2. See Table 24.
3. See Table 26.
41
Page 47

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Length
Navigation Library Measurement
Data - Message I.D. 28
Output Rate: Every measurement cycle (full
power / continuous : 1Hz)
Example:
A0A20038—Start Sequence and Payload
Table B- 54 Measurement Data
Name
Message ID 1 1C 28
Channel 1 00
Time Tag 4 000660D0 ms
Satellite ID 1 15
GPS Software Time 8
Pseudo Range 8
Carrier Frequency
Carrier Phase
Time in Track
Sync Flags
C/No1 1 34
C/No2 1
C/No3 1
C/No4 1
C/No5 1
C/No6 1
C/No7 1
C/No8 1
C/No9 1
C/No10 1
Delta Range Interval
Mean Delta Range Time
Extrapolation Time
Phase Error Count
Low Power Count
Payload Length: 56 bytes
Bytes
4
8
2 7530 ms
1 17
2
2 01F4 ms
2 0000 ms
1 00
1 00
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
F143F62C
4113F42F
F3FBE95E
417B235C
468C6964
B8FBC582
415CF1C3
03E801F4
1C00000660D015F143F62C4113F42FF3FB
E95E417B235C468C6964B8FBC5824
15CF1C375301734.....03E801F400000000
—Payload
1533B0B3—Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
ms
m
m
Scale Example
A0A2001A—Start Sequence and Payload
Navigation Library DGPS Data Message I.D. 29
Output Rate: Every measurement cycle (full
power / continuous : 1Hz)
Example:
Table B- 55 Measurement Data
Name
Message ID 1 1D 29
Satellite ID
IOD
1
Source
Bytes
2
2 00B5 181
1 01 1
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
42
Length
1D000F00B501BFC97C673CAAAAAB3FBF
FE1240A0000040A00000—Payload
0956B0B3—Message Checksum and End
Sequence
000F
Units
15
Scale Example
Page 48

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Pseudo-range Correction
Pseudo-range Rate
Correction
Correction Age
Reserved 4
Reserved 4
Payload Length: 26 bytes
1. 0 = Use no corrections, 1 = Use WAAS channel, 2 = Use external source, 3 = Use Internal
Beacon, 4 = Set DGPS Corrections
4
4 3CAAAAAB m/s
4
Navigation Library SV State Data Message I.D. 30
Output Rate: Every measurement cycle (full
power / continuous : 1Hz)
Example:
Table B- 56 SV State Data
Name
Message ID 1 1E 30
Satellite ID
GPS Time 8 s
Position X 8 m
Position Y 8 m
Position Z 8 m
Velocity X 8 m/s
Velocity Y 8 m/s
Velocity Z 8 m/s
Clock Bias 8 s
Clock Drift 4
Ephemeris Flag
Reserved
Ionospheric Delay
Payload Length: 83 bytes
1
Bytes
1 15 21
1
8
4
Scale Example
BFC97C67
3FBFFE12
m
s
A0A20053—Start Sequence and Payload
Length
3217652839
1017817771
1069547026
1E15....2C64E99D01....408906C8—Paylo
ad
2360B0B3—Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
2C64E99D
01
408906C8
Units
s
m
Scale Example
744810909
1
1082721992
1. 0 = no valid SV state, 1 = SV state calculated from ephemeris, 2 = Satellite state calculated from almanac
1F....00000000000001001E000F....00....000
Navigation Library Initialization Data Message I.D. 31
Output Rate: Every measurement cycle (full
power / continuous : 1Hz)
Example:
A0A20054—Start Sequence and Payload
Length
Table B- 57 Measurement Data
Name
Message ID 1 1F 31
Reserved 1
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
43
000000F....00....02....043402....
....02—Payload
0E27B0B3—Message Checksum and End
Sequence
Units
Scale Example
Page 49

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
Altitude Mode
Altitude Source 1 00 0
Altitude 4 00000000 0
Degraded Mode
Degraded Timeout 2 001E 30
Dead-Reckoning Timeout 2 000F 15
Reserved 2
Track Smoothing Mode
Reserved 1
Reserved 2
Reserved 2
Reserved 2
DGPS Selection
DGPS Timeout
Elevation Nav. Mask
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Static Nav. Mode
Reserved
Position X
Position Y
Position Z
Position Init. Source
GPS Time
GPS Week
Time Init. Source 7
Drift
Drift Init. Source 8
Payload Length: 84 bytes
1
2
1 00 0
1 01 1
3
1 00 0
4
1
2
2
2
1
2
1
5
2
1
2
8
8
6
8
1
8
2
1
8
1
00
0000
000F
00
02
0434
02
02
0
0
15
0
2
1076
2
2
1. 0 = Use last know altitude 1 = Use user
input altitude 2 = Use dynamic input from
external source
2. 0 = Use direction hold and then time hold
1 = Use time hold and then direction hold
2 = Only use direction hold
3 = Only use time hold
4 = Degraded mode is disabled
3. 0 = True and 1 = False
4. 0 = Use DGPS if available
1 = Only navigate if DGPS corrections are
available
2 = Never use DGPS corrections
5. 0 = True 1 = False
RoyalTek Navigation Data – Message I.D.100
6. 0 = ROM position
1 = User position
2 = SRAM position
3 = Network assisted position
7. 0 = ROM time
1 = User time
2 = SRAM time
3 = RTC time
4 = Network assisted time
8. 0 = ROM clock
1 = User clock
2 = SRAM clock
3 = Calibration clock
4 = Network assisted clock
Output Rate: 1Hz
Example :A0A2001A – Start Sequence
44
and Payload Length
6407D1*********** - Payload
Page 50

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
****B0B3 – Message checksum and End Sequence
Table 57 Royaltek Navigation Data
Name
Message ID 1 64 100
Year 2 07D1 2001
Month 2 000C 12
Day 2 0005 5
Hours 2 0011 17
Minutes 2 001E 30
Seconds 4 *1000 5202 Sec.
Degree of Latitude 2 19 degree 25
Minutes of Latitude 4 *10000 0001818C Min.
Degree of Longitude 2 79 degree 121
Minute of Longitude 4 *10000 0002BA64 Min.
Altitude 4 000000FA meter 250
Validity 1 01 1
Speed 2 *10 0064 Km/h
Course over ground 2 0080 Degree 128
PDOP 2 *10 012C
HDOP 2 *10 012C
VDOP 2 *10 012C
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Units
Scale Example
÷1000
÷10000
÷10000
÷10
÷10
÷10
÷10
20.994
9.8700
17.8788
10.0
30.0
30.0
30.0
Payload Length: 42 bytes. This protocol is provided from RoyalTek firmware Ver. 1.7. release
* *hh<CR><LF> Check Sum and sentence termination delimiter
Set Ephemeris – Message I.D.254
This command enables the user to upload an ephemeris to the Evaluation unit.
Note – This feature is not documented in this manual . For information on implementation contact
SiRF Technology Inc.
Development Data – Message I.D.255
Output Rate: Receiver generated
Example :A0A2**** - Start Sequence and Payload Length
FF************* - Payload
****B0B3 – Message Checksum and End Sequence
Table 58 Development Data
Name
Message ID 1 FF 255
Payload Length:Variable
Bytes
Binary(Hex) ASCII(Decimal)
Scale Example
Units
Scale Example
Note – Messages are output to give the
user information of receiver activity.
Convert to symbol to assemble message
45
(i.e., 0x4E is ‘N’) these are low priority task
and are not necessarily output at constant
intervals.
Page 51

RoyalTek RGM-3000/REB-3000
GPS Module Operational Manual)
GPS Receiver User’s Tip
1. GPS signal will be affected by weather and environment conditions, thus suggest to use the GPS
receiver under less shielding environments to ensure GPS receiver has better receiving performance.
2. When GPS receiver is moving, it will prolong the time to fix the position, so suggest to wait for the
satellite signals to be locked at a fixed point when first power-on the GPS receiver to ensure to lock
the GPS signal at the shortest time.
3. The following situation will affect the GPS receiving performance:
a. Solar control filmed windows.
b. Metal shielded, such as umbrella, or in vehicle.
c. Among high buildings.
d. Under bridges or tunnels.
e. Under high voltage cables or near by radio wave sources, such as mobile phone base
stations.
f. Bad or heavy cloudy weather.
4. If the satellite signals can not be locked or encounter receiving problem (while in the urban area), the
following steps are suggested:
a. Please plug the external active antenna into GPS receiver and put the antenna on outdoor or the
roof of the vehicle for better receiving performance.
b. Move to another open space or reposition GPS receiver toward the direction with less blockage.
c. Move the GPS receiver away from the interferences resources.
d. Wait until the weather condition is improved.
5. While a GPS with a backup battery, the GPS receiver can fix a position immediately at next power-on
if the build-in backup battery is full-recharged.
Contact Information Section
Contact : sales@royaltek.com
HEADQUARTER :
Add : 1071 Chung Cheng Rd., Suite 9F-1
Tao Yuan City , Taiwan , R.O.C.
Tel :886 – 3 - 3569666
Fax :886 – 3 - 3560900
Web Site : www.royaltek.com
Customer Service mail : sales@royaltek.com
46
 Loading...
Loading...