Page 1

USO RESTRITO
NK Series
Compact Routers
User Guide
Page 2

NK Series · User Guide
®
USO RESTRITO
• Ross Part Number: 9807DR-0100-1.0
• Release Date: March 18, 2011. Printed in Canada.
The information contained in this Guide is subject to change without notice or obligation.
Copyright
© 2011 Ross Video Limited. All rights reserved.
Contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any form without the written permission of Ross Video
Limited. Reproduction or reverse engineering of copyrighted software is prohibited.
Patents
This product is protected by the following US Patents: 4,205,346; 5,115,314; 5,280,346; 5,561,404; 7,034,886;
7,508,455; 7,602,446; 7,834,886. This product is protected by the following Canadian Patents: 2039277; 1237518;
1127289. Other patents pending.
Notice
The material in this manual is furnished for informational use only. It is subject to change without notice and should
not be construed as commitment by Ross Video Limited. Ross Video Limited assumes no responsibility or liability
for errors or inaccuracies that may appear in this manual.
Trademarks
• is a registered trademark of Ross Video Limited.
• Ross, ROSS, and ROSS
• Microsoft, Encarta, MSN, and Windows are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation
in the United States and/or other countries.
• All other product names and any registered and unregistered trademarks mentioned in this guide are used for
identification purposes only and remain the exclusive property of their respective owners.
®
, are registered trademarks of Ross Video Limited.
Page 3

Important Regulatory and Safety Notices to Service Personnel
USO RESTRITO
Before using this product and any associated equipment, read all the Important Safety Instructions listed below so
as to avoid personal injury and to prevent product damage.
Symbol Meanings
Protective Earth — This symbol identifies a Protective Earth (PE) terminal, which is provided for
connection of the supply system’s protective earth (green or green/yellow) conductor.
This symbol on the equipment refers you to important operating and maintenance (servicing) instructions
within the Product Manual Documentation. Failure to heed this information may present a major risk of
damage or injury to persons or equipment.
Warning — The symbol with the word “Warning” within the equipment manual indicates a potentially
hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
Caution — The symbol with the word “Caution” within the equipment manual indicates a potentially
hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury. It may also be used to
alert against unsafe practices.
Warning Hazardous Voltages — This symbol is intended to alert the user to the presence of
uninsulated “dangerous voltage” within the product enclosure that may be of sufficient magnitude to
constitute a risk of shock to persons.
ESD Susceptibility — This symbol is used to alert the user that an electrical or electronic device or
assembly is susceptible to damage from an ESD event.
Important Safety Instructions
Read these instructions and heed all warnings.
Warning
Warning
The safe operation of this product requires that a protective earth connection be provided.
A grounding conductor in the equipment's supply cord provides this protective earth. To
reduce the risk of electrical shock to the operator and service personnel, this ground
conductor must be connected to an earthed ground.
Use only power cords specified for this product and certified for the country of use. Refer
to the Product Power Cord Requirement Section that follows.
Do not defeat safety purpose of the grounding-type plug. A grounding type plug has two
blades and a third grounding prong. The third prong is prong is provided for your safety. If
the provided plug does not fit in to your outlet, consult an electrician for replacement of
the obsolete outlet.
Protect the power cord from being walked on or pinching particularly at plugs,
convenience receptacles, and point where they exit from the apparatus.
Indoor Use: “WARNING – TO REDUCE THE RISK OF FIRE OR ELECTRIC SHOCK,
DO NOT EXPOSE THIS APPARATUS TO RAIN OR MOISTURE”
Do not block any ventilation openings. Install in accordance with manufacturer’s
instructions.
Only use attachments/accessories specified by the manufacturer.
Page 4

Warning
USO RESTRITO
Refer all servicing to qualified personnel. Servicing is required when the apparatus has
been damaged in any way, such as power-supply cord or plug damage, liquid has been
spilled or objects have fallen into the apparatus, the apparatus has been exposed to rain or
moisture, does not operate normally, or has been dropped.
Caution
Warning
Product Power Cord Requirements
To reduce the risk of fire, replacement fuses must be the same type and rating.
This product contains safety critical parts, which if incorrectly replaced may present a risk
of fire or electrical shock. Components contained within the product’s power supplies and
power supply area, are not intended to be customer serviced and should be returned to the
factory for repair
Warning North American Line Voltages 100 - 120 Volt
This product is supplied with certified 10A/125V SVT type supply cords.
Conductors are color coded white (neutral), black (line) and green or green/yellow
(ground).
Operation of this equipment at line voltages exceeding 130V requires that alternative
supply cords with appropriate voltage and current ratings be used.
Warning International Line Voltages 200 - 240 Volt
This product has been designed for use with certified IEC 320- C13 10A/250V - H03
VV-F3G 1.00mm2 type line cord.
International product orders are supplied with a certified 10A/250V line cords, utilizing a
molded 3-pin IEC 320-C13 type connector at one end and stripped conductors on the
other. One line cord is provided. Conductors are CEE color coded; blue (neutral), brown
(line), and green/yellow (ground).
Installation by a qualified Electrician, of an appropriately approved A/C wall plug
certified for the country of use, is required.
Alternatively, other IEC 320 C-13 type power cords may be used, provided that they meet
the necessary safety certification requirements for the country in which they are to be
used. Refer to the correctly specified line cord above.
EMC Notices
US FCC Part 15
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class A Digital device, pursuant to part 15
of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a Commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful
interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
Notice — Changes or modifications to this equipment not expressly approved by Ross Video Ltd. could
void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
CANADA
This Class “A” digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numerique de la classe “A” est conforme a la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Page 5

EUROPE
USO RESTRITO
This equipment is in compliance with the essential requirements and other relevant provisions of CE Directive
93/68/EEC.
INTERNATIONAL
This equipment has been tested to CISPR 22:1997 along with amendments A1:2000 and A2:2002 and found to
comply with the limits for a Class A Digital device.
Notice — This is a Class A product. In domestic environments, this product may cause radio
interference, in which case the user may have to take adequate measures.
CE/C-tick approval
The equipment meets the requirements of the Australian Communications and Media Authority (Limits & Methods
Of Measurement Of Radio Interference Characteristics Of Information Technology Equipment (EN55022/CISPR
22)).
Warranty and Repair Policy
The product is backed by a comprehensive one-year warranty on all components.
Notice — Changes or modifications to this equipment not expressly approved by Ross Video Limited
could void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
If an item becomes defective within the warranty period Ross will repair or replace the defective item, as
determined solely by Ross.
Warranty repairs will be conducted at Ross, with all shipping FOB Ross dock. If repairs are conducted at the
customer site, reasonable out-of-pocket charges will apply. At the discretion of Ross, and on a temporary loan basis,
plug in circuit boards or other replacement parts may be supplied free of charge while defective items undergo
repair. Return packing, shipping, and special handling costs are the responsibility of the customer.
This warranty is void if products are subjected to misuse, neglect, accident, improper installation or application, or
unauthorized modification.
In no event shall Ross Video Limited be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages
(including loss of profit). Implied warranties, including that of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose,
are expressly limited to the duration of this warranty.
This warranty is TRANSFERABLE to subsequent owners, subject to Ross’ notification of change of ownership.
Extended Warranty
For customers that require a longer warranty period, Ross offers an extended warranty plan to extend the standard
warranty period by one year increments. For more information, contact your regional sales manager.
Page 6

Environmental Information
USO RESTRITO
The equipment that you purchased required the extraction and use of natural resources for its production. It may
contain hazardous substances that could impact health and the environment.
To avoid the potential release of those substances into the environment and to diminish the need for the extraction
of natural resources, Ross Video encourages you to use the appropriate take-back systems. These systems will reuse
or recycle most of the materials from your end-of-life equipment in an environmentally friendly and health
conscious manner.
The crossed-out wheeled bin symbol invites you to use these systems.
If you need more information on the collection, reuse, and recycling systems, please contact your local or regional
waste administration.
You can also contact Ross Video for more information on the environmental performances of our products.
Page 7

Company Address
®
USO RESTRITO
Ross Video Limited
8 John Street
Iroquois, Ontario
Canada, K0E 1K0
Ross Video Incorporated
P.O. Box 880
Ogdensburg, New York
USA 13669-0880
General Business Office:
Technical Support: (+1) 613 • 652 • 4886
After Hours Emergency: (+1) 613 • 349 • 0006
E-mail for Technical Support: techsupport@rossvideo.com
E-mail for General Information: solutions@rossvideo.com
Website: http://www.rossvideo.com
(+1) 613 • 652 • 4886
(+1) 613 • 652 • 4425
Fax:
Ross Video Australia
Unit 3, 49 London Drive
Bayswater VIC 3153
Australia
Page 8

USO RESTRITO
Page 9

Contents
USO RESTRITO
Introduction 1
Overview of this Guide..........................................................................................................................................1-1
Overview 2
Features ..................................................................................................................................................................2-1
Installation 3
NK-16, NK-32 and NK-34 Routers .......................................................................................................................3-1
SDI Video Level ................................................................................................................................................3-1
Multi-Definition Video Level ............................................................................................................................3-1
AES/EBU Digital Audio Level ..........................................................................................................................3-2
Analog Video Level ...........................................................................................................................................3-4
Stereo Analog Audio Level ................................................................................................................................3-6
Machine Control / Data Level ............................................................................................................................3-8
NK-64 and NK-72 Router Formats........................................................................................................................3-9
SDI Video Level ................................................................................................................................................3-9
Multi-Definition Video Level ............................................................................................................................3-9
3G/HD/SD SDI Level ........................................................................................................................................3-9
AES/EBU Digital Audio Level ........................................................................................................................3-10
Stereo Analog Audio Level ..............................................................................................................................3-12
Control Panels......................................................................................................................................................3-13
RCP-NK1 .........................................................................................................................................................3-13
RCP-NKM .......................................................................................................................................................3-14
RCP-NKQ ........................................................................................................................................................3-14
NK-VCP ...........................................................................................................................................................3-15
NK-VRC ..........................................................................................................................................................3-16
Interface and Connectivity ...................................................................................................................................3-16
The NK-IPS ......................................................................................................................................................3-16
The NK Hub .....................................................................................................................................................3-17
The NK-3RD ....................................................................................................................................................3-18
The NK-SCP ....................................................................................................................................................3-19
The NK-GPI .....................................................................................................................................................3-19
The T-Bus Control System ..............................................................................................................................3-20
The Heartbeat ...................................................................................................................................................3-20
NK Series Router Power Supplies ...................................................................................................................3-20
Connecting NK Components ...............................................................................................................................3-21
Unpacking and Pre-Installation ........................................................................................................................3-21
Connection Overview .......................................................................................................................................3-21
Connecting the NK-SCP ..................................................................................................................................3-23
Connecting the NK-GPI ...................................................................................................................................3-25
Customizing RCP-NK1 Control Panels...............................................................................................................3-27
Overview ..........................................................................................................................................................3-27
Localizing the Panel .........................................................................................................................................3-27
Configuration 4
Default Configuration ............................................................................................................................................4-1
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................4-1
RCP-NK1 Control Panel Default Configuration ...............................................................................................4-1
RCP-NKM/Q Control Panel Default Configuration ..........................................................................................4-3
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Contents • i
Page 10

Configuring Routers.............................................................................................................................................. 4-4
USO RESTRITO
Overview ........................................................................................................................................................... 4-4
Configuration Options — NK-IPS .................................................................................................................... 4-4
Configuration Options — Phoenix .................................................................................................................... 4-9
Configuring the RCP-NK1 Panel........................................................................................................................ 4-13
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 4-13
RCP-NK1 Configuration ................................................................................................................................. 4-14
Configuring the NK-SCP .................................................................................................................................... 4-21
NK-SCP/A Configuration ............................................................................................................................... 4-21
NK-SCP/K2 Configuration ............................................................................................................................. 4-24
Configuring the GPI ............................................................................................................................................ 4-27
Configuration Options ..................................................................................................................................... 4-27
Operation 5
NK Series Operation ............................................................................................................................................. 5-1
Start-up Process ................................................................................................................................................. 5-1
Router Start-up .................................................................................................................................................. 5-1
Control Panel Start-up ....................................................................................................................................... 5-1
Single Panel RCP-NK1 Operation ........................................................................................................................ 5-1
Overview ........................................................................................................................................................... 5-1
Operation Basics ................................................................................................................................................ 5-2
Linked RCP-NK1 Panel Operation ..................................................................................................................... 5-10
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 5-10
NK-A64 Control Layer ....................................................................................................................................... 5-10
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 5-10
Control Layer Operation via NK Control Panels ............................................................................................ 5-11
NK-SCP Operation.............................................................................................................................................. 5-13
NK-SCP/A Operation Overview ..................................................................................................................... 5-13
Using the ASCII Protocol ................................................................................................................................ 5-13
NK-SCP/K2 Operation .................................................................................................................................... 5-15
Video Referencing............................................................................................................................................... 5-15
Overview ......................................................................................................................................................... 5-15
Connecting a Video Reference to NK Routers ............................................................................................... 5-15
Appendix A: Connectors and Pinouts 6
DB-25 Pinouts for Analog and Digital Audio Routers ......................................................................................... 6-1
16x16 Routers .................................................................................................................................................... 6-1
32x32 Routers .................................................................................................................................................... 6-2
64x64 Routers .................................................................................................................................................... 6-3
Power Connector - DB-9 (All NK-16 and NK-32 Routers).................................................................................. 6-5
Machine Control DB-9 Pinouts (NK-M16 and NK-M32) .................................................................................... 6-5
GPI Alarm (NK-64 & NK-72 Models only) ......................................................................................................... 6-6
T-Bus RJ-45 Connector......................................................................................................................................... 6-6
SCP/A DB-9 Pinouts............................................................................................................................................. 6-7
SCP/K2 DB-9 Pinouts........................................................................................................................................... 6-7
Appendix B: Analog Audio Router I/O Levels 7
Overview ............................................................................................................................................................... 7-1
NK-A16 and NK-A32 Routers (Input).................................................................................................................. 7-1
NK-A16 and NK-A32 Routers (Output)............................................................................................................... 7-2
NK-A64 Router (Input)......................................................................................................................................... 7-2
NK-A64 Router (Output) ...................................................................................................................................... 7-3
ii • Contents NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 11

Appendix C: Multi-Definition Router Format Selection 8
USO RESTRITO
Output Rise Time DIP Switches ............................................................................................................................8-1
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Contents • iii
Page 12

iv • Contents NK Series User Guide (1.0)
USO RESTRITO
Page 13

Introduction
USO RESTRITO
Thank you for purchasing the Ross Video NK Series Routing System. With Ross Video’s reputation for delivering
leading-edge routing switcher equipment and our unsurpassed level of customer service and support, you can look
forward to many years of reliable broadcasting. Please read this guide thoroughly and retain it for future reference.
Overview of this Guide
This guide is for system administrators, installers and operators of the Ross Video NK Series Routing System. It
provides instructions on how to connect and configure the routing switcher system. It assumes that you are
experienced with general broadcast concepts, and that you are familiar with the planning requirements for a routing
switcher system.
A separate user manual is available for the following products:
• NK-3G320 Routing Switcher
• NK-3G144 Routing Switcher
• NK-IPS Internet Protocol Server
• NK-VRC Virtual Routing Core
• NK-3RD Third Party Interface
• RCP-NKM Remote Control Panel
• RCP-NKQ Remote Control Panel
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Introduction • 1–1
Page 14

1–2 • Introduction NK Series User Guide (1.0)
USO RESTRITO
Page 15

Overview
USO RESTRITO
Ross Video's NK Series Routing Systems are a comprehensive family of routing solutions with a wide variety of
matrix sizes and types to choose from, several flexible control panels, and a powerful control system tying it all
together.
Features
The NK Series of routers are available in a variety of sizes and signal types.
Figure 2.1 16x4 Utility Switchers and 16x16 Routers (1RU)
Figure 2.2 32x32 Routers (2RU)
Figure 2.3 64x64 and 72x72 Routers (3RU)
Matrix Sizes Signal Types
• Fixed size 16x4 and 16x16 in 1RU • 3G/HD/SD Multi-Definition SDI
• Fixed size 32x32 and 34x34 in 2RU • HD/SD Multi-Definition SDI
• Expandable up to 64x64 and 72x72 in 3RU • SD SDI
• Expandable up to 144x144 in 10RU • 75 Ohm and 110 Ohm AES/EBU Digital Audio
• Expandable up to 320x320 in 19RU • Analog Video
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Overview • 2–1
• Stereo Analog Audio
• Machine / Data Control (RS422)
Page 16

Control of the routers can be done using a variety of methods, including:
USO RESTRITO
• 40 Button Remote Control Panel (RCP-NK1)
• 40 Button & LCD Display Remote Control Panel (RCP-NKM)
• 17 LCD Button Remote Control Panel (RCP-NKQ)
• Phoenix Control Surface software for setup and control
• 10/100 Ethernet Interface
• Virtual routing
• Third Party RS422 serial control
• RS232 and GPI/Tally Interface
Figure 2.4 RCP-NKQ Control Panel
Figure 2.5 RCP-NKM Control Panel
Figure 2.6 RCP-NK1 Control Panel
2–2 • Overview NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 17

Installation
USO RESTRITO
NK-16, NK-32 and NK-34 Routers
SDI Video Level
The SDI level of the NK-16 and NK-34 range conforms to SMPTE standard 259M and is available in 16x4
(NK-S164), 16x16 (NK-S16), and 34x34 (NK-S34) sizes.
Multi-Definition Video Level
The Multi-Definition (MD) level of the NK-16 and NK-34 range conforms to SMPTE standards 259M, 292M and
344M, 16x4 (NK-MD164), 16x16 (NK-MD16), and 34x34 (NK-MD34) sizes.
All NK Multi-Definition level routers have a selectable output rise and fall times, via on-board DIP switches; please
refer to “Appendix C: Multi-Definition Router Format Selection” on page 8–1.
Video Reference Loop
T-Bus Connections
Power
Video Reference Loop
T-Bus Connections
Power
Video Reference Loop
Inputs
Figure 3.1 NK-S164 & NK-MD164 – 16x4 Rear IO
Inputs
Figure 3.2 NK-S16 & NK-MD16 – 16x16 Rear IO
Inputs
Outputs
Outputs
Outputs
T-Bus Connections
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–1
Power
Figure 3.3 NK-S34 & NK-MD34 – 34x34 Rear IO
Page 18

Specifications
USO RESTRITO
Table 3.1 Inputs
SDI Video Level Multi-Definition Video Level
Connection 75 Ω BNC 75 Ω BNC
Return Loss > 22 dB > 17 dB
Cable EQ Up to 350 m Belden 8281 Up to 100 m Belden 8281
Table 3.2 Outputs
SDI Video Level Multi-Definition Video Level
Connection 75 Ω BNC 75 Ω BNC
Clocking Non-reclocking Non-reclocking
Return Loss > 22 dB 15 dB
Level 800 mV p-p 800 mV p-p
Table 3.3 Performance
SDI Video Level Multi-Definition Video Level
Jitter < 370 ps (.09 UI) < 0.2 UI
Data Rates 143 Mb/s to 540 Mb/s 143 Mb/s to 1.485 Gb/s
Overshoot < 10 % < 10 %
Rise/Fall Time 700 ps (typical) 700 ps (typical SD)
120 ps (typical HD)
Table 3.4 General
SDI Video Level Multi-Definition Video Level
Partitioning Up to 8 partitions with independent
level assignment
Configuration Phoenix or web browser via NK-IPS Phoenix or web browser via NK-IPS
Dimensions 1 RU x 64 mm deep (NK-S16 and
NK-S164)
2 RU x 64 mm deep (NK-S34)
Power Consumption 10.5 W (NK-S16 and NK-S164) 30
W (NK-S34)
Power Supply +15 V DC +15 V DC
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
Up to 8 partitions with independent
level assignment
1 RU x 64 mm deep (NK-MD16 and
NK-MD164)
2 RU x 64 mm deep (NK-MD34)
10.5 W (NK-MD16 and NK-MD164)
30 W (NK-MD34)
AES/EBU Digital Audio Level
The AES/EBU level of the NK-16 and NK-32 range conforms to AES/EBU standards for digital audio. It is
available in 16x4 (NK-D164), 16x16 (NK-D16), and 32x32 (NK-D32) sizes.
NK-D16, NK-D164 and NK-D32 models are available in 75 Ω BNC models or 110 Ω DB-25 models.
3–2 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 19

Video Reference Loop
USO RESTRITO
T-Bus Connections
Power
Video Reference Loop
T-Bus Connections
Power
Video Reference Loop
T-Bus Connections
Inputs
Outputs
Figure 3.4 NK-D164/75 – 75 Ω, 16x4 Rear IO
Inputs
Outputs
Figure 3.5 NK-D164 /110 – 110 Ω, 16x4 Rear IO
Inputs
Outputs
Power
Video Reference Loop
T-Bus Connections
Power
Video Reference Loop
T-Bus Connections
Figure 3.6 NK-D16/75 – 75 Ω, 16x16 Rear IO
Inputs
Figure 3.7 NK-D16/110 – 110 Ω, 16x16 Rear IO
Inputs
Power
Figure 3.8 NK-D32/75 – 75 Ω, 32x32 Rear IO
Outputs
Outputs
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–3
Page 20

Video Reference Loop
USO RESTRITO
Inputs
Outputs
T-Bus Connections
Specifications
Connection 75 Ω BNC (D16/75 and D32/75)
Level 1 V p-p (75 Ω)
Cable EQ Up to 300 m RG59/U
Connection 75 Ω BNC (D16/75 and D32/75)
Clocking Non-reclocking
Level 1 V p-p (75 Ω)
Power
Figure 3.9 NK-D32/110 – 110 Ω, 32x32 Rear IO
Table 3.5 Inputs
110 Ω DB-25 connectors (D16/110 and D32/110)
2-7 V p-p (110 Ω)
Table 3.6 Outputs
110 Ω DB-25 connectors (D16/110 and D32/110)
3-4 V p-p (110 Ω)
Table 3.7 Performance
Jitter < 2 ns (.013 UI)
Data Rates 32 kHz to 192 kHz
Table 3.8 General
Partitioning Up to 8 partitions with independent level assignment
Configuration Phoenix or web browser via NK-IPS
Dimensions 1 RU x 64 mm deep (NK-D16 and NK-D164)
2 RU x 64 mm deep (NK-D32)
Power Consumption 7.5 W (NK-D16 and NK-D164) 10.5 W (NK-D32)
Power Supply +15 V DC
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
Analog Video Level
The Analog Video level of the NK-16 and NK-32 range is a wide bandwidth, high performance router available in
16x4 (NK-V164-HQ), 16x16 (NK-V16-HQ), and 32x32 (NK-V32-HQ) sizes.
3–4 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 21
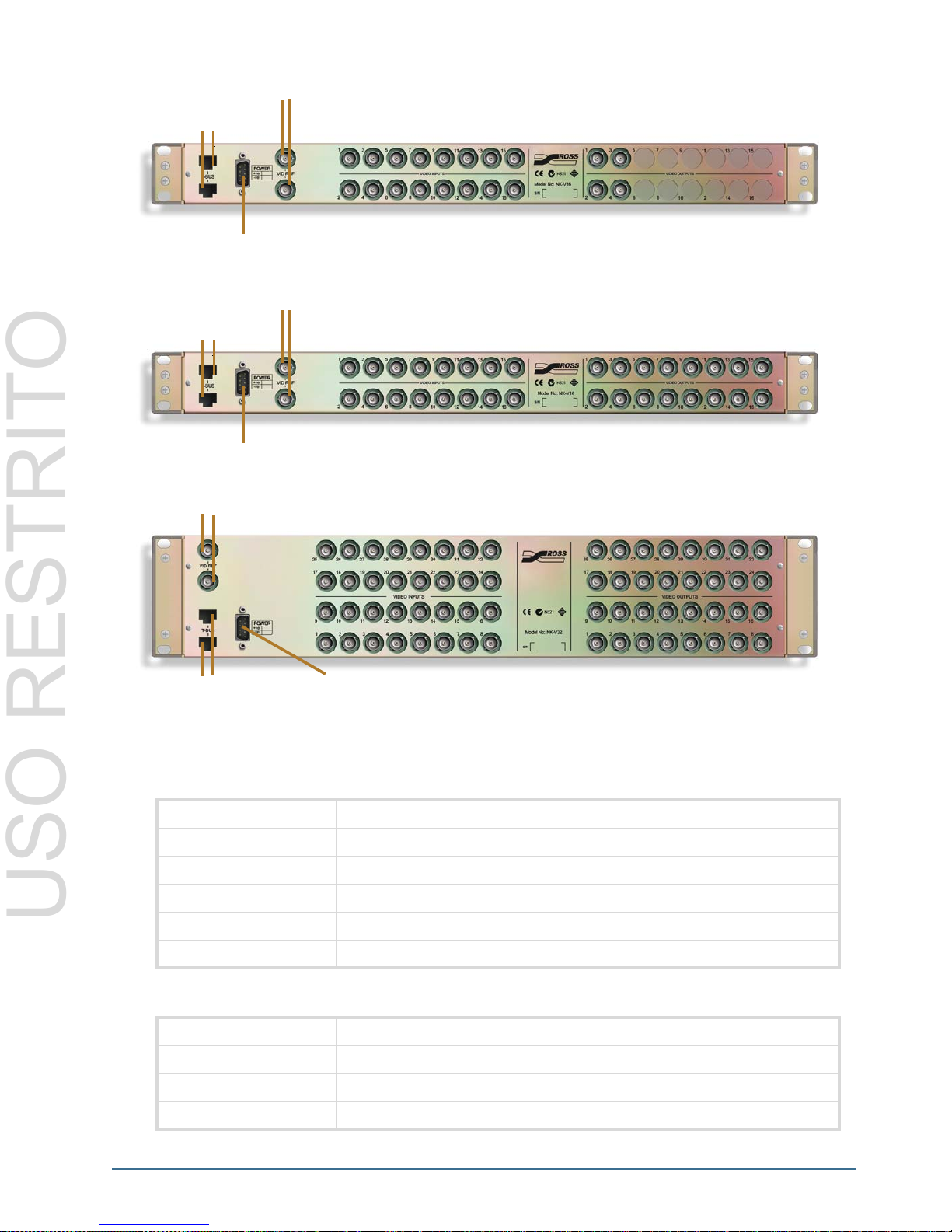
Video Reference Loop
USO RESTRITO
T-Bus Connections
Power
Video Reference Loop
T-Bus Connections
Power
Video Reference Loop
Inputs
Figure 3.10 NK-V164-HQ – 16x4 Rear IO
Inputs
Figure 3.11 NK-V16-HQ – 16x16 Rear IO
Inputs
Outputs
Outputs
Outputs
T-Bus Connections
Specifications
Power
Figure 3.12 NK-V32-HQ – 32x32 Rear IO
Table 3.9 Inputs
Connection 75 Ω BNC
Nominal Input Level 1 V p-p
Maximum Input Level 2 V p-p
Clamping Method AC coupled with sync tip Clamping
Clamping DC Adjustment Between blanking = 0 V and sync tip = 0 V
Return Loss 44 dB
Table 3.10 Outputs
Connection 75 Ω BNC
Level 1 V p-p
Coupling DC coupled
Return Loss 30 dB
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–5
Page 22

Table 3.11 Performance
USO RESTRITO
Differential Gain 0.05 deg
Differential Phase 0.05 deg
Frequency Response 30 MHz, ±0.1 dB
60 Mhz, ±1 dB
230 Mhz, -3 dB
Noise -76 dB peak
Crosstalk -60 dB, 5 MHz
Propagation Delay 2 ns
Timing Scatter 0.5 deg fsc
Table 3.12 General
Partitioning Up to 8 partitions with independent level assignment
Configuration Phoenix or web browser via NK-IPS
Dimensions 1 RU x 64 mm deep (NK-V16-HQ and NK-V164-HQ)
2 RU x 64 mm deep (NK-V32-HQ)
Power Consumption 8 W (NK-V16-HQ and NK-V164-HQ)
20 W (NK-V32-HQ)
Power Supply +/-15 V DC
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
Stereo Analog Audio Level
The Stereo Analog Audio level of the NK-16 and NK-32 range is a wide bandwidth, high performance router,
available in 16x4 (NK-A164-HQ), 16x16 (NK-A16-HQ), and 32x32 (NK-A32-HQ) sizes.
All Analog Audio level routers have selectable +4 / -10 dBu input and output levels, via on-board solder links,
please refer to “Appendix B: Analog Audio Router I/O Levels” on page 7–1.
Video Reference Loop
T-Bus Connections
Power
Video Reference Loop
T-Bus Connections
Inputs Outputs
Figure 3.13 NK-A164-HQ – 16x4 Rear IO
Inputs Outputs
LEFT RIGHT
Outputs Inputs
LEFT RIGHT
Outputs Inputs
Power
3–6 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Figure 3.14 NK-V16-HQ – 16x16 Rear IO
Page 23

Video Reference Loop
USO RESTRITO
Inputs Outputs
LEFT RIGHT
Outputs Inputs
T-Bus Connections
Specifications
Connection DB-25 Female on chassis (8 audio channels)
Connection Type Balanced active differential
Input Z 24 K Ω
Nominal Input Level +4 dBu or -10 dBu (selectable via solder links)
Maximum Input Level +24 dBu
CMRR 60 dB
Connection DB-25 Female on chassis (8 audio channels)
Connection Type Balanced active differential
Output Z 50 Ω differential
Nominal Output Level +4 dBu or -10 dBu (selectable via solder links)
Power
Figure 3.15 NK-A32-HQ – 32x32 Rear IO
Table 3.13 Inputs
Table 3.14 Outputs
Maximum Output Level +24 dBu
Table 3.15 Performance
Frequency Response ±0.1 dB, 20 Hz to 20 kHz
-3 dB, 100 kHz
Distortion .005 %
Noise -90 dB below +4 dBu
Crosstalk -86 dB below +4 dBu Below noise
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–7
Page 24

Table 3.16 General
USO RESTRITO
Partitioning Up to 8 partitions with independent level assignment
Configuration Phoenix or web browser via NK-IPS
Dimensions 1 RU x 64 mm deep (NK-A16-HQ and NK-A164-HQ)
2 RU x 64 mm deep (NK-A32-HQ)
Power Consumption 13.5 W (NK-A16-HQ and NK-A164-HQ)
33 W (NK-A32-HQ)
Power Supply ±15 V DC
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
Machine Control / Data Level
The Machine Control level of the NK-16 and NK-32 range is capable of routing RS-422 signals for reciprocal
switches. It is available both 16x16 (NK-M16), and 32x32 (NK-M32) models.
T-Bus Connections
T-Bus Connections
Specifications
Bi-directional RS-422 Ports
Power
Figure 3.16 NK-M16 – 16x16 Rear IO
Bi-directional RS-422 Ports
Power
Figure 3.17 NK-M32 – 32x32 Rear IO
Connection DB-9 Female on chassis
Electrical Standard RS-422
Direction Auto port direction switching
Data Rates Up to 115.2 kBd
3–8 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Table 3.17 Inputs
Table 3.18 Performance
Page 25

Table 3.19 General
USO RESTRITO
Configuration Phoenix or web browser via NK-IPS
Dimensions 1RU x 64 mm deep (NK-M16)
2RU x 64 mm deep (NK-M32)
Power Consumption 10.5 W (NK-M16)
18 W (NK-M32)
Power Supply +15 V DC
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
NK-64 and NK-72 Router Formats
SDI Video Level
The SDI level conforms to SMPTE standard 259M.
Multi-Definition Video Level
The Multi-Definition (MD) level conforms to SMPTE standards 259M, 292M and 344M.
All NK MD level routers have a selectable output rise and fall times, via on-board DIP switches.
3G/HD/SD SDI Level
The NK-3G72 supports SMPTE standards 424M, 344M, 259M, and 292M with output reclocking. The input EQ
and reclocker are bypassable through the control system. The output slew rates are automatically set.
Inputs Outputs
Inputs Outputs
Figure 3.18 NK-S72, NK-MD72 & NK-3G72 – 72x72 Rear IO
Specifications
Connection 75 Ω BNC 75 Ω BNC 75 Ω BNC
Return Loss >22 dB > 17 dB > 17 dB
T-Bus Connections Video Reference Loop
GPI AlarmsPower
Table 3.20 Inputs
SD SDI
NK-72
Multi-Definition SDI
NK-MD72
3G/HD/SD SDI
NK-3G72
Cable EQ Up to 350 m Belden
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–9
8281
Up to 100 m Belden
8281
Up to 100 m Belden
8281
Page 26

Table 3.21 Outputs
USO RESTRITO
SDI Video
Level
Connection 75 Ω BNC 75 Ω BNC 75 Ω BNC
Clocking Non-relocking Non-reclocking Reclocking
Return Loss >22 dB 15 dB 15 dB
Level 800 mV p-p 800 mV p-p 800 mV p-p
Table 3.22 Performance
SDI Video
Level
Jitter < 370 ps (.09 UI) < 0.2 UI < 0.2 UI
Data Rates 143 Mb/s to 540 Mb/s 143 Mb/s to 1.485 Gb/s 143 Mb/s to 3 Gb/s
Overshoot < 10% < 10 % < 10 %
Rise Time
Partitioning Up to 8 partitions with
–
Table 3.23 General
SDI Video
Level
independent level
assignment
Multi-Definition Video
Level
Multi-Definition Video
Level
Selectable SD/HD rise
time via on-board DIP
switches
Multi-Definition Video
Level
Up to 8 partitions with
independent level
assignment
NK-3G72
NK-3G72
Auto SD/HD
NK-3G72
Up to 8 partitions with
independent level
assignment
Configuration Phoenix or web browser
via NK-IPS
Dimensions 3 RU x 120 mm deep 3 RU x 120 mm deep 3 RU x 120 mm deep
Power Supply +15 V DC +15 V DC +15 V DC
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
AES/EBU Digital Audio Level
The AES/EBU level conforms to AES/EBU standards in digital audio streaming.
The NK-D64 is available in 75 Ω BNC models or optional 110 Ω DB-25 models.
Phoenix or web browser
via NK-IPS
Phoenix or web browser
via NK-IPS
3–10 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 27

Inputs Outputs
USO RESTRITO
T-Bus Connections Video Reference Loop
Inputs Outputs
Figure 3.19 NK-D64/75 – 75 Ω, 64x64 Rear IO
T-Bus Connections Video Reference Loop
Inputs Outputs
Inputs Outputs
Figure 3.20 NK-D64/110 – 110 Ω, 64x64 Rear IO
Specifications
Table 3.24 Inputs
Connection 75 Ω BNC (D64/75) 110 Ω DB-25 connectors (D64/110)
GPI AlarmsPower
GPI AlarmsPower
Level 1 V p-p (75 Ω)
Cable EQ Up to 300 m RG59/U
Connection 75 Ω BNC (D64/75) 110 Ω DB-25 connectors (D64/110)
Clocking Non-reclocking
Level 1 V p-p (75 Ω)
Jitter < 2 ns (0.13 UI)
Data Rates 32 kHz to 192 kHz
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–11
2-7 V p-p (110 Ω)
Table 3.25 Outputs
3-4 V p-p (110 Ω)
Table 3.26 Performance
Page 28
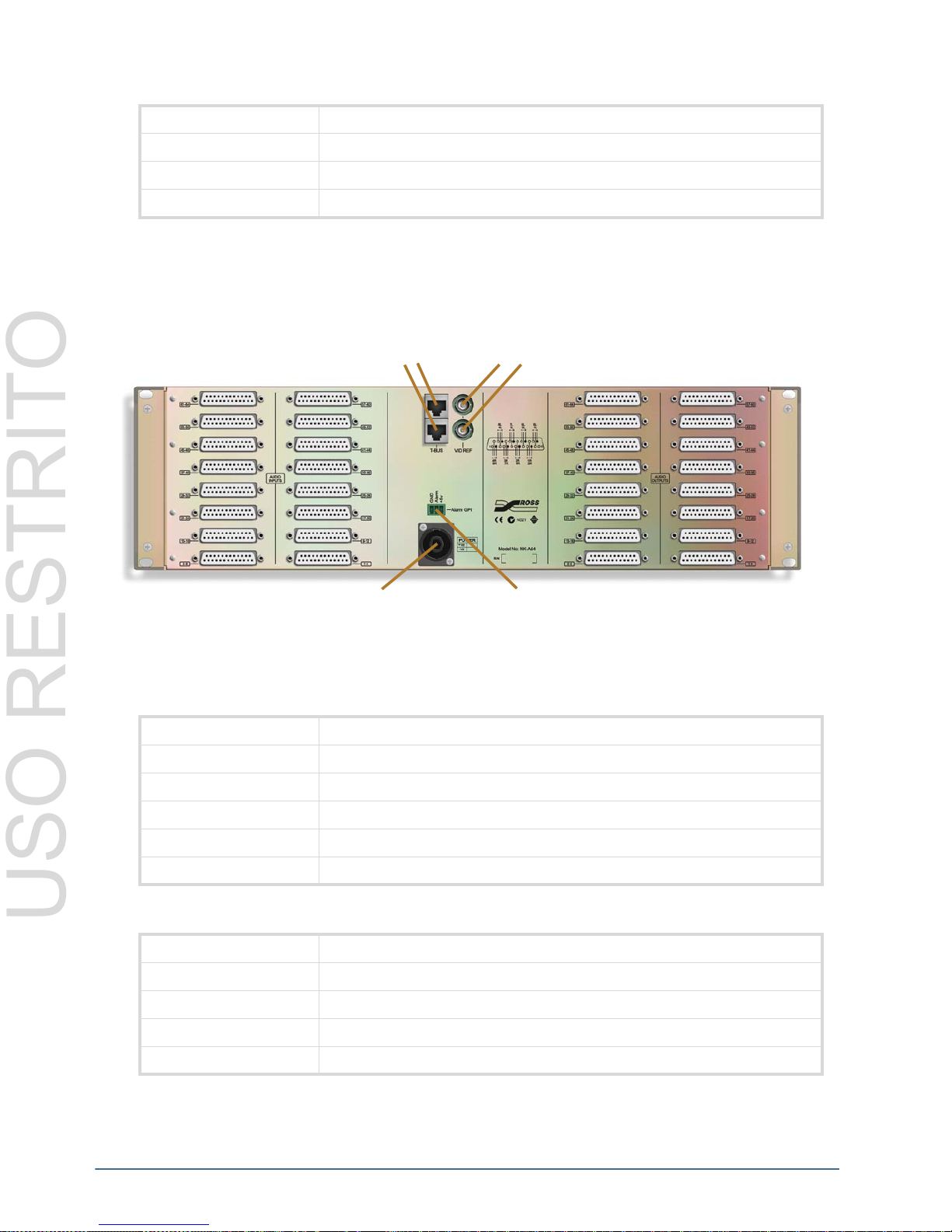
Table 3.27 General
USO RESTRITO
Partitioning Up to 8 partitions with independent level assignment
Configuration Phoenix or web browser via NK-IPS
Dimensions 3 RU x 120 mm deep
Power Supply +15 V DC
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
Stereo Analog Audio Level
All Analog Audio level routers have selectable +4 / -10 dBu input and output levels, via on-board solder links,
please refer to “Appendix B: Analog Audio Router I/O Levels” on page 7–1.
Inputs Outputs
Inputs Outputs
Specifications
Connection DB-25 Female on chassis (8 audio channels)
Connection Type Balanced active differential
Input Z 24 K Ω
T-Bus Connections Video Reference Loop
GPI AlarmsPower
Figure 3.21 NK-A64 – 64x64 Rear IO
Table 3.28 Inputs
Nominal Input Level +4 dBu or -10 dBu (selectable via solder links)
Maximum Input Level +25 dBu
CMRR 60 dB
Connection DB-25 Female on chassis (8 audio channels)
Connection Type Balanced active differential
Output Z 50 Ω
Nominal Input Level +4 dBu or -10 dBu (selectable via solder links)
Maximum Input Level +24 dBu
3–12 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Table 3.29 Outputs
Page 29
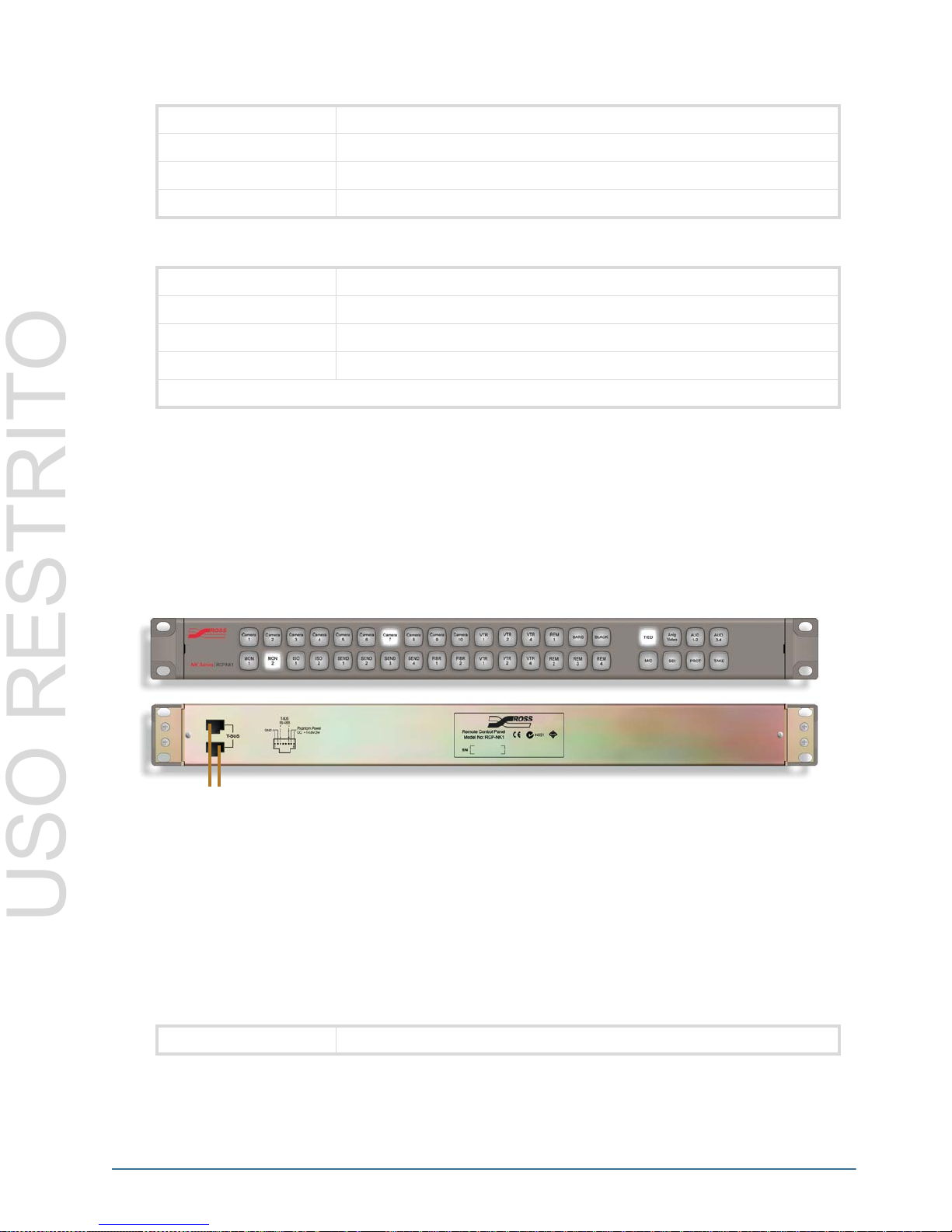
Table 3.30 Performance
USO RESTRITO
THD (Typical) 0.0025 % @ 1 kHz, +4 dB
THD + Noise (Typical) 0.0094 % @ 1 kHz, +4 dB
Level Deviation ±0.02 dB
Channel Separation -80 dB maximum
Table 3.31 General
Partitioning Up to 8 partitions with independent level assignment
Configuration Phoenix or web browser via NK-IPS
Dimensions 3 RU x 120 mm deep
Power Supply ±15 V DC
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
Control Panels
RCP-NK1
The RCP-NK1 40 button panel controls NK Series Routers, it switches and protects outputs, it can also display
router status. It has 40 soft, programmable backlit keys, arranged in a 32 + 8 configuration for convenient function
key layout.
T-Bus Connections
Connected via the T-Bus Control System, with CAT5 cables, the RCP-NK1 is phantom powered by the router it is
connected to. Multiple control panels can be linked together and powered from the one router.
Panel layout has been designed with 2 rows of 16 keys on the left-hand side, and 2 rows of 4 keys on the right-hand
side for users who wish to keep function keys separate from their source, destination and breakaway keys. The LED
brightness can be set through the NK-IPS for both on and off states.
Specifications
Number 40 backlit keys
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–13
Figure 3.22 Front and Rear of RCP-NK1
Table 3.32 Keys
Page 30

Table 3.33 General
USO RESTRITO
Configuration Phoenix or web browser via NK-IPS
Dimensions 1 RU x 25 mm deep
Power Consumption 1.5 watts
Power Supply +15 V DC phantom power
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
RCP-NKM
The RCP-NKM 40 button panel controls NK Series Routers, has a variety of assignable functions, and it can also be
used for virtual routing. It has 40 programmable backlit keys, a 16 character by 2 line backlit LCD screen, and can
control up to 32 router levels.
T-Bus Connections
Figure 3.23 Front and Rear of RCP-NKM
See the RCP-NKM Remote Control Panel User Guide for more information.
RCP-NKQ
The RCP-NKQ control panel has a variety of assignable functions and it can also be used for virtual routing. It has
17 programmable backlit keys, panel linking with other remote control panels, and can control up to 32 router
levels.
T-Bus Connections
Figure 3.24 Front and Rear of RCP-NKQ
See the RCP-NKQ Remote Control Panel User Guide for more information.
3–14 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 31

NK-VCP
USO RESTRITO
Figure 3.25 NK-VCP
The NK Virtual Control Panel (NK-VCP), accessible only through the NK-IPS, enables users to remotely control an
entire NK system. If required, it is also possible to control multiple systems, alternating between each as needed.
The VCP can be purchased as an addition to an existing NK system or can be purchased as part of a new system.
The NK-VCP is built with Java technology, enabling flexibility and cross-platform control. Users are advised to
have installed the latest version of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) before using the VCP. For further
information on the VCP and the Java Runtime Environment, please refer to the NK-IPS Internet Protocol Server
User Guide.
As the VCP works in conjunction with the NK-IPS, VCP control can be password protected to allow only
authorised users to perform router functions. One VCP license is provided with the purchase of an NK-IPS. If
further licenses are required, an upgrade file can be purchased and installed.
Please note that as VCP licenses and usage are inherently linked to and modified by the NK-IPS, all configuration
and functionality details are outlined in the NK-IPS Internet Protocol Server User Guide.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–15
Page 32

NK-VRC
USO RESTRITO
Figure 3.26 NK-VRC Editor in the Phoenix Control Surface
The NK Virtual Routing Core (NK-VRC) provides virtual routing for complex NK Series routing switcher systems.
The NK-VRC, accessible using the Phoenix Control Surface via the NK-IPS, enables users to map inputs and
outputs from routing switchers through to the NK-VRC for control via any remote control panel. These parameters
can be saved in a configuration document and sent to an NK-VRC at any time using Phoenix. Therefore, if an
NK-VRC is used in a number of different operating scenarios, the configuration can be changed easily and quickly.
See the NK-VRC Virtual Routing Core User Guide for all configuration and functionality details for the NK-VRC.
Interface and Connectivity
The NK-IPS
T-Bus Connections
Ethernet Port
Power RS-232 Port
The NK-IPS (Internet Protocol Server) is the device used for configuration of NK Series devices including routers,
control panels and control interface devices. Connection of the NK-IPS to either a single computer or a network
allows configuration of the NK routers and panels using Phoenix or a web browser, further enhancing the capability
3–16 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Figure 3.27 Front and Rear of NK-IPS
Page 33

of any installation of NK Series products by providing access to the entire range of functions. The NK-IPS also
USO RESTRITO
enables users to configure T-Bus enabled Ross Video devices.
Computer
Configuration
VCP Control
NK Hub Control
Internet Protocol Server
NK Series Control Panels
NK Series Router Levels
Legend
T-Bus
Ethernet
Figure 3.28 NK-IPS Connection Example
The NK-IPS is also required for use of the NK Hub, for information and usage of this software component, please
refer to the NK-IPS Internet Protocol Server User Guide.
The NK-IPS does not require Internet access for operation, only Phoenix or an Internet browser is required for
operation and configuration. For further information, please refer to the NK-IPS Internet Protocol Server User
Guide.
The NK Hub
The NK Hub, accessible only through the NK-IPS, is a software component used to connect two or more NK-IPS
devices, enabling NK Series protocol and switch communication between NK Series components connected to each
NK-IPS. Internet Protocol Servers can be locally or remotely connected allowing NK Series components to respond
to status requests, switch requests and protect requests.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–17
Figure 3.29 NK Hub
Page 34

NK Series Control Panel
T-Bus Connections
USO RESTRITO
Internet Protocol Server
Internet Protocol Server
Internet / LAN / VPN
Computer
Configuration
NK Hub Control
Figure 3.30 NK Hub Example
NK Series Control Panel
NK Series Router Levels
Legend
T-Bus
Ethernet
A local connection enables two NK-IPS devices within the same network to communicate with NK Series
components connected to each. A remote connection, via an Internet connection or Virtual Private Network (VPN),
allows two or more Internet Protocol Servers to communicate over longer distances.
The NK Hub is built with Java technology, enabling flexibility and cross-platform control. Users are advised to
have installed the latest version of the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) before using the NK Hub. For further
information on the NK Hub and the Java Runtime Environment, please refer to the NK-IPS Internet Protocol
Server User Guide.
Please note that as NK Hub connection and usage requires the NK-IPS, all configuration and functionality details
are outlined in the NK-IPS Internet Protocol Server User Guide.
The NK-3RD
The NK-3RD Third-Party Interface enables a third-party control system to control an NK Series routing switcher
system using the SW-P-08 protocol.
The NK-3RD works with any NK Series router and supports crosspoint switch commands and crosspoint status
requests. Up to 1024 inputs and 1024 outputs can be controlled and it supports up to 16 levels.
Figure 3.31 Front and Rear of NK-3RD
See the NK-3RD Third-Party Control Interface User Guide for more information.
3–18 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 35

The NK-SCP
USO RESTRITO
The NK-SCP Serial Control Port allows an NK Series routers to be controlled via the Kondor 2 or an external
RS-232 device. It is available in RS-232 (NK-SCP/A) and RS-485 (NK-SCP/K2) models. Configuration of either
the NK-SCP/A or the NK-SCP/K2, as well as router configuration and partitioning, requires the NK-IPS.
Figure 3.32 NK-SCP/A RS-232 and NK-SCP/K2 RS-485
The NK-SCP/A – RS-232 Control
The NK-SCP/A model allows an RS-232 device, such as an automation system or computer terminal, to control NK
routers using the Ross Video EOS ASCII protocol. Any combination of NK routers can be controlled with a
maximum size of 255 inputs and 255 outputs with up to 8 levels. The bidirectional protocol incorporates both
crosspoint status monitoring and crosspoint switching. Crosspoint switching can be performed using individual
levels or through user-defined breakaway mapping.
The NK-SCP/K2 – RS-485 Control
The NK-SCP/K2 allows Kondor 2 routers to be extended by utilizing NK routers as additional levels. Any
combination of NK routers can be added to a Kondor 2 system with a maximum size of 255 inputs and 255 outputs
with up to 8 levels. Kondor 2 router inputs, outputs and levels are directly mapped to NK Series router inputs,
outputs and levels, requiring no user mapping.
The NK-GPI
The NK-GPI is a universal GPI interface for the NK family of routers. Providing both GPI inputs and outputs, the
NK-GPI allows flexible GPI control, configured from the NK-IPS Device Properties pages. The NK-GPI also
supports both GPI input return and latch modes.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–19
Figure 3.33 NK-GPI
Page 36

16 GPI Inputs
USO RESTRITO
16 GPI Outputs
NK-GPI
.....
CCUs 1-16
NK-GPI configuration, via the NK-IPS and a PC connected to a network, allows users to customize GPI inputs and
outputs, as well as the input mode (Latch or Return), and a Panel Link Address, configuring the NK-GPI to be
controlled from a connected NK Control Panel.
The T-Bus Control System
NK routers and panels are linked via the T-Bus Control System, a multi-drop RJ-45 control system supporting
collision detection and half-duplex communication. The T-Bus Control System minimizes cable connections
between devices, acting as both a reliable means to phantom power selected devices and as the communications
line.
The T-Bus Control System’s collision detection support ensures that if two devices transmit messages at the same
time they will not send incorrect data to other devices on the line. All components that utilise the T-Bus Control
System are able to monitor communication on the line to ensure that no two devices are transmitting at the same
time.
.....
1
GPI Tallies
18
Figure 3.34 NK-GPI Connection Example
T-Bus
RS-485
Internet Protocol Server
NK Series Router Level
NK Series Control Panel
The Heartbeat
Figure 3.35 Heartbeat Display
NK Series routers indicate their status by a pulsating LED, called a heartbeat. The heartbeat flickers when a switch
message is handled by the router. It dims slightly to indicate a handled message that did not result in a switch.
The heartbeat is also connected to the alarm status. It monitors the status of the power supply and signifies a
problem by pulsating at a noticeably faster rate.
NK Series Router Power Supplies
Each NK router, control panel and control device comes standard with a single external AC/DC power supply. The
exceptions to this are devices that are powered from the T-Bus, such as the RCP-NK1, NK-SCP/A and NK-GPI.
Redundant external power supplies are available. Please contact Ross Video.
Optionally, a 100W rack mount redundant power supply, NK-RP1/P, is available to power up to 4 devices. Refer to
the NK-RP1/P User Guide for additional information.
Figure 3.36 NK-RP1/P and NK-RP1/PN Rear Connectors
3–20 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 37

Figure 3.37 Example of NK-RP1/P Power Connections
Address
21
13
NK Series Control Panel
NK Series Router Level
RS-485
T-Bus
USO RESTRITO
Connecting NK Components
Unpacking and Pre-Installation
After unpacking NK components, please inspect all NK Series components for any signs of damage that may have
occurred during transportation. In the event of such damage, please notify a Ross Video representative immediately.
NK Series components should be installed in an adequately ventilated rack frame, ideally in an appropriate
environment for audio visual equipment. Relative humidity should be no more than 70% (non-condensing) and
temperatures should not exceed 30°C or 86°F.
If the above conditions are not attainable for operation, it is advised that NK Series routers be installed with 1 RU
space between them before use.
Connection Overview
NK Series components are connected via the T-Bus multi-drop control system by a single CAT5 Ethernet cable.
Routers are supplied with their own power supply, the NK1 panels are phantom powered by the routers they are
connected to via the CAT5 cable. Each control panel has two RJ-45 ports for phantom power and communications.
When connecting devices, either port may be used to connect panels or routers to each other.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–21
Figure 3.38 Single Panel Connection Example
Page 38

Panels can be linked together to expand the number of available buttons. Panels are linked if they have the same
Address
21
13
NK Series Control Panels
NK Series Router Levels
RS-485
T-Bus
d
21
14
15
Panel Link
Address
3
4
USO RESTRITO
address and a different device link address that is not 0 (zero). Linked panels behave exactly as if they were one
larger panel except that macros can not be appended or added across panels.
The NK-IPS is required to configure linked panels and also for changing individual component addresses.
A
Figure 3.39 Linked Panel Connection Example
Power may also be distributed evenly throughout an NK system by way of direct connections between phantom
powered connections (control panels, NK-SCP and NK-GPI) from a common power source (NK Series routers or
the NK-IPS), or by daisy chaining components. Daisy chaining components allows several phantom powered
components to be connected to the one router.
3–22 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 39

Figure 3.40 Daisy-Chain Connection Example
RS-485
T-Bus
NK Series Router Level
NK Series Control Panels
Power
NK Series Router Panels
Internet Protocol Server
NK Series Control Panels
Power
Power
Power Power
Power
USO RESTRITO
A maximum of four RCP-NK1 control panels may be connected (daisy-chain) to an individual router at any one
time; and a maximum of seven RCP-NK1 control panels to one NK-IPS. Adding other power sources to the same
system will contribute further power to the T-Bus connection if required.
Connecting the NK-SCP
Connecting the NK-SCP/A
The NK-SCP/A is connected to a computer or RS-232 device with a straight through RS-232 cable.
The NK-SCP is phantom powered by the T-Bus, allowing the heartbeat to show communication activity when
messages and switches are operated from the RS-232 device.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–23
Figure 3.41 T-Bus Distributed Power Example
Page 40

Bidirectional communications
USO RESTRITO
Internet Protocol Server
NK Series Router Levels
NK Series Control Panel
RS-232 Device
(eg. computer or
automation system)
Legend
T-Bus
Serial
NK-SCP / A
T-Bus to RS-232
T-Bus
RS-485
Figure 3.42 SCP/A Connection Example
Connecting the NK-SCP/K2
The NK-SCP/K2 is connected to the Geneos CPU with the parallel to serial converter cable supplied (Part number
9801 2001). If the NK-SCP/K2 and NK routers have been purchased as an addition to a preexisting Kondor 2 and
Geneos CPU system, this cable would have been supplied with the initial Kondor 2 / Geneos shipment.
The NK-SCP is phantom powered by the T-Bus, allowing the heartbeat to show communication activity when
messages are sent from the Geneos CPU.
Unidirectional communications
Geneos Control Panels
Computer
Geneos Routing
Control
Geneos CPU
Kondor 2
NK-SCP / K2
Serial Matrix Control
to T-Bus
T-Bus
RS-485
Internet Protocol Server
NK Series Router Levels
Legend
T-Bus
Serial
Figure 3.43 SCP/K2 Connection Example
Parallel to Serial Converter
The Parallel to Serial converter is housed inside the DB-37 connector shell which plugs into the Parallel Output
Control connector located at the bottom left side at the rear of the Geneos CPU frame. Power to the converter is
supplied via the DB-25 connector (wired to the DB-37). The DB-25 connector plugs into the AUX connector
located at the bottom left side at the rear of CPU frame. The Serial output from the converter is available from the
DB-9 plug (wired to the DB-37), this DB-9 plugs into the top RS-485 DB-9 on the Rear left of the Kondor 2 frame.
The PC communications cable is wired to the DB-25, the PC end has both a DB-25 and a DB-9 for connection to an
RS-232 communications connector on a PC running Geneos.
3–24 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 41

Figure 3.44 Parallel to Serial Converter
DB-37 Male
Parallel to Serial Converter
to the Router Control Port on CPU
DB-9 Male
RS-485 Serial Control
to the Kondor 2
Power Cable
for Parallel to Serial Converter
DB-25 & DB-9 Female
to the PC Communications Port
DB-25
to AUX connector on CPU
(Power & PC Communications)
USO RESTRITO
To connect the NK-SCP/K2 to the Geneos CPU:
1. Connect the DB-37 connector of the Parallel to Serial Converter to the Router Control Port on the rear of the
Geneos CPU.
2. Connect to DB-25 connector of the Parallel to Serial Converter to the Auxiliary Port on the rear of the Geneos
CPU.
3. Connect the single DB-9 connector of the Parallel to Serial Converter to the DB-9 connector of the
NK-SCP/K2. Alternatively, this connector can be connected to the Kondor 2 frame itself, and the NK-SCP/K2
connected to the frame via a serial cable.
4. Connect either the linked DB-25 or the DB-9 to a PC for Geneos software configuration and control.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–25
The NK-SCP/K2 can be connected to the Geneos CPU at any time, but to ensure status updates are
completed, it is recommended that it be connected after configuration details have been entered on both
the Device Properties page via the NK-IPS, and the Geneos Software.
Connecting the NK-SCP to the T-Bus Control System
To connect the NK-SCP/K2 or NK-SCP/A to the T-Bus Control System follow the steps below:
1. Connect one end of a straight through CAT5 cable to the RJ-45 connector on the SCP.
2. Connect the other end of the CAT5 cable to any available T-Bus port on the NK-IPS, or any other T-Bus
compatible device connected to the NK-IPS.
Connecting the NK-GPI
The NK-GPI connects to the T-Bus control system using the RJ-45 connectors on the box edge. The loop through
connector allows the NK-GPI to reside at any point on the control bus. The NK-GPI connects to general purpose
interface inputs and outputs via a DB-37 port.
Page 42

NK-GPI Pinouts
USO RESTRITO
Figure 3.45 NK-GPI Pinouts
Connecting GPI Inputs
Use Figure 3.46 to wire NK-GPI inputs; refer to Figure 3.45 for input pin numbers.
GND
Pin 19 or Pin 29
Contact Closure / Switch
To Input pin
Figure 3.46 GPI Input Connection
Connecting GPI Outputs
Use Figure 3.47 to wire NK-GPI output; refer to Figure 3.45 for output pin numbers.
The example diagram uses a LED to indicate status. The LED can be replaced with another indicator, load or a GPI
input from another device.
3–26 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 43

+5v
USO RESTRITO
Pin 1 or Pin 28
To Output pin
Figure 3.47 GPI Output Connection
When connecting GPI outputs to the NK-GPI, users must remember there is a 10 mA current limit on
each output, and a resistor must be connected to the GPI output to maintain peak operation. Figure 3.47
depicts how to wire outputs correctly.
10mA current limit
on outputs
470R
LED
Customizing RCP-NK1 Control Panels
Overview
One of the flexible features of the NK Series of routers and panels is the ability to install RCP-NK1 control panels
either locally or remotely to NK-16 routers. Localizing panels ensures that rack space is maximized and cable
connections are minimized. Remotely installing panels means that panels do not necessarily have to be installed in
the immediate vicinity of the routers, and can be connected and installed in other rooms if required.
Localizing the Panel
If users are localizing control panels, a short (between 12.5 and 20cm or 5 and 8”) standard (not crossover) CAT5
cable is required to connect the panel to the router internally.
Ensure that the router and the panel you wish to localise are not connected to any other devices before proceeding.
Also ensure that both the router and the control panel are disconnected from the power source.
To fit the control panel locally to the front of the router:
1. Remove the front button panel from the case it was originally shipped in.
2. Remove the front panel of the router.
3. Disconnect the wire that connects the heartbeat to the circuit board.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–27
Page 44

4. Connect one end of the CAT5 cable to either of the control panel’s RJ-45 ports.
USO RESTRITO
5. Connect the other end of the CAT5 cable to the internal RJ-45 of the router.
6. Ensure the excess cable is packed in the empty space of the casing before attaching the panel face.
7. Slowly clip the button panel into the router casing, on both the left and the right sides.
8. When the face is firmly in place on the router casing, it can be installed as any normal router, saving rack space.
Customizing RCP-NK1 Button Labels
The button labels of the RCP-NK1 may be customized to suit the needs of any application. Button labels may be
customized in any word processing, spreadsheet or design software providing that the label size is set to exactly 9.5
x 9.5 mm (3/8” x 3/8”).
3–28 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 45

It is recommended that labels be printed on overhead transparency rather than paper so that LED illumination is not
USO RESTRITO
obscured.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Installation • 3–29
Page 46

3–30 • Installation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
USO RESTRITO
Page 47

Configuration
USO RESTRITO
Default Configuration
Overview
When NK Series components are shipped, the default configuration is set to allow both NK routers and control
panels to be used straight out of the box.
No matter how large or small the system, each is individually configured and tested by Ross Video engineers.
RCP-NK1 Control Panel Default Configuration
Key Assignment Default
The RCP-NK1 control panel is factory configured with the key assignments as depicted in Figure 4.1.
Source Shift
Breakaway 1
(Tied)
Level 2
Inputs
1
2
445
3
2
1
5
3
889910101111121213131414151516
6
7
6
7
16
(SDI)
Level 5
(An. Vid.)
Outputs
SHIFT Inputs
SHIFT Outputs
17
18
19
18
17
19
202021
22
2424252526262727282829293030313132
23
21
22
23
Destination Shift
Macro 1
Level 6
(An. Aud. Right)
Level 7
(An. Aud. Left)
32
Shift keys lit to indicate that
Shift Mode is on.
Figure 4.1 RCP-NK1 Control Panel Default Configuration
Further configuration and key panel settings, as well as router configuration, can be accessed using the NK-IPS and
Phoenix or a web browser.
When purchasing a complete NK system, the RCP-NK1 will be custom programed so that it can be used straight
out of the box without further configuration via the NK-IPS. Further documentation depicting key panel layout will
be provided with systems that do not adhere to the factory default.
The key functions listed below are assigned to buttons in the factory default configuration of the RCP-NK1.
DESTINATION Changes the destination the panel is controlling.
The bottom, left hand row of 16 keys selects destinations 1-16 on the default page/set.
When the DESTINATION SHIFT key has been pressed, the second page of
destinations (17-32) is accessible.
SOURCE Switches using the current destination and level pattern.
The top left hand row of 16 keys selects the sources 1-16 on the default page/set.
When the SOURCE SHIFT key has been pressed, the second page of sources (17-32) is
accessible.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–1
Page 48

DESTINATION SHIFT Changes the destination page of the panel
USO RESTRITO
SOURCE SHIFT Changes the source page of the panel.
LEVEL Toggles the specified level number from the current level pattern.
Four Level keys are available on the factory default configuration: Level 2 - SDI Video
Level 5 - Analog Video Level 6 - Analog Audio (Left channel) Level 7 - Analog Audio
(Right channel)
MACRO Records key press events that can be replayed later.
BREAKAWAY Selects a preconfigured breakaway level pattern.
Keys that are not available on the factory default configuration of the RCP-NK1, but may be assigned and
configured via the NK-IPS, are listed below.
CROSSPOINT Switches the input, output and level/breakaway associated with this key.
BREAKAWAY STEP Steps through breakaways.
PROTECT Protects the currently selected output/level pair. The PROTECT key also activates the
panel lock function.
TAKE Confirms input key events. After a switch is set up, press the TAKE key to activates the
switch.
CHOP Alternates between the last two selected inputs.
DEASSIGN Allows users to reset a destination assignment.
Default
Level 1
Level 2
Level 3
Level 4
Level 5
Level 6
Level 7
Level 8
MACHINE CONTROL
KEY
PANEL LOCK Activates the panel lock function, for environments where a PROTECT KEY is not
UNASSIGNED Key is not assigned any function or value.
NK Series Router Levels Default
The factory default configuration breakaway and levels for the NK routers is as depicted in Table 4.1.
Table 4.1 Configuration Breakaway and Levels for the NK Routers
3G/HD/SD
Video
SD Video
Toggles on/off RS-422 Machine Control reciprocal switching.
required.
AES/EBU
Audio (1)
AES/EBU
Audio (2)
Analog
Video
Analog
Audio (Left)
Analog
Audio
(Right)
99999999
9
9
9
9
9
9
9
Machine
Control
9
4–2 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 49

RCP-NKM/Q Control Panel Default Configuration
USO RESTRITO
The RCP-NKM and RCP-NKQ default configuration is viewed by opening the editor for the device in the Phoenix
Control Surface.
See the RCP-NKM Remote Control Panel User Guide for more information about the RCP-NKM default
configuration.
See the RCP-NKQ Remote Control Panel User Guide for more information about the RCP-NKQ default
configuration.
Key Assignments Default
By default, the 20 keys in the top row on the RCP-NKM are assigned as sources and the 20 keys in the bottom row
are assigned as destinations.
Figure 4.2 RCP-NKM Control Panel Default Configuration
By default, the RCP-NKQ has these key assignments:
• keys 1 to 6: destinations (outputs 1 to 6 respectively)
• keys 7 to 13: sources (inputs 1 to 7 respectively)
• key 14: Level 1 (MD)
• key 15: Macro 1
• key 16: Menu 1
• key 17: Menu 2
Figure 4.3 RCP-NKQ Control Panel Default Configuration
Breakaways Default
The default breakaway is tied, that is, the first eight router levels are switched together when requested from the
RCP-NKM or RCP-NKQ.
Router Levels Default
The RCP-NKM and RCP-NKQ send switch requests to the routing switcher. Each routing switcher is assigned a
level, or number of levels if it has been partitioned.
Table 4.2 RCP-NKM/Q Default Router Levels
Router Level Name
1 Multi-definition video
2 Serial digital interface video
3 AES/EBU digital audio 1
4 AES/EBU digital audio 2
5 Analog video
6 Analog audio (left)
7 Analog audio (right)
8 Machine control
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–3
Page 50

Configuring Routers
USO RESTRITO
Overview
If a simple, standard setup is all that is required, NK Series routers can be used straight out of the box. After
unpacking the NK Series router and connecting the inputs and outputs, the system is ready to go. Where an
alternative configuration is required, the NK-IPS allows unparalleled configuration using the web interface on the
NK-IPS or with Phoenix.
The NK Series routers have an input and output range of 1 to 65535 that can be set on up to 32 levels. Routers may
be configured identically using the web interface on the NK-IPS or with Phoenix, in which case they will switch at
the same time. Routers maintain status for their output range and also retain that status between power down cycles.
Routers also maintain protect information for their output range. A control panel can protect a specified output, if
another device attempts to switch that output, it will be denied.
Routers may be configured to have internal partitions. These are always a factor of the maximum size; for example,
a 32x32 router can be two 16x16 routers, three 10x10 routers, four 8x8 routers, five 6x6 routers, seven 4x4 routers
or eight 4x4 routers. Where there are unused crosspoints due to partitioning, they will be the last inputs and outputs.
Configuration Options — NK-IPS
The router Device Properties page, accessible through the NK-IPS, allows users to configure interface and usability
options for all NK Series routers and also displays the alarm status of the router, as well as having the unique ability
to assign names and brief descriptions for the devices themselves.
For details on how to query devices and use of the NK-IPS, refer to the NK-IPS Internet Protocol Server User
Guide.
4–4 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Figure 4.4 Router Device Properties Page
Page 51

Device Properties Fields
USO RESTRITO
Family
The Family name is set in the factory before shipping and displays the family that the device belongs to. This
parameter is read-only.
Device
The Device name is set in the factory before shipping and displays the name assigned to the device. This parameter
is read-only.
Serial Number
The Serial Number is set in the factory before shipping and is unique to each device. This parameter is read-only.
Name
The Name field can be assigned by the user to uniquely name a device. This field has a maximum of 16 characters
and is used for description and identification only.
Details
The Details field can be assigned by the user to give a device specific details. For example, a physical location or a
brief description of its use. This field has a maximum of 16 characters and is used for description and identification
only.
Group
The Group number can be assigned by the user to organize devices into groups. For example, users can assign
separate Group numbers for devices in different physical areas. This field has a maximum of 10 characters and is
used for description and identification only.
Configuration Fields
Address
The Address is used within the overall control system to identify devices. Each device must be given a unique
Address to avoid hardware and communication conflicts. The valid value range for assigning an individual device
Address is 2-255.
Ignore Out Of Range Inputs
The Ignore Out of Range Inputs option will ignore switches on an offset router that has been configured to the same
level as another connected router. By default, the Ignore Out of Range Inputs option is not active (the check box is
cleared).
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–5
Page 52

The Ignore Out of Range Inputs option is only available on the NK-64 and NK-72 routers and is only used for
USO RESTRITO
specific installations.
Switching Point
The Switching Point option is only available on the NK-64 and NK-72 routers.
Custom Switching Line (NK-64 Routers only)
The Custom Switching Line option is only available on the NK-64 and NK-72 routers.
Custom Switching Position (NK-64 Routers only)
The Custom Switching Position option is only available on the NK-64 and NK-72 routers.
Number of Partitions
The Num Partitions (Number of Partitions) indicates how you wish the router to be partitioned. The default value of
the partitions is 1 (no partitions.), the maximum value is 8.
Table 4.3 shows the relative input and output sizes to the number of partitions configured for 16x16, 32x32, 64x64
and 72x72 routers.
Table 4.3 Relative input and output size s to the number of configured partitions
16x16 Router 32x32 Router 64x64 Router 72x72 Router
Partitions I/O Size Partitions I/O Size Partitions I/O Size Partitions I/O Size
1 16x16
28x8
3* 5x5
44x4
5* 3x3
6* 2x2
7* 2x2
8* 2x2
* Denotes that partition leaves unusable inputs/outputs as ‘remainders’.
When partitioning routers, some configurations will leave ‘remaindered’ inputs and outputs. Any division of the
router that leaves a remainder will not use the remaining inputs and outputs. For example, a 32x32 partitioned into
3, will be equivalent to three 10x10 routers (30 inputs and 30 outputs in total). The last two inputs and the last two
outputs will remain unused and inaccessible for router functions.
1 32x32 1 64x64 1 72x72
2 16x16 2 32x32 2 36x36
3* 10x10 3* 21x21 3 24x24
48x8 4 16x16 4 18x18
5* 6x6 5* 12x12 5* 14x14
6* 5x5 6* 10x10 6 12x12
7* 4x4 7* 9x9 7* 10x10
84x4 88x8 89x9
Partition Levels
The Partition Levels table allows users to configure levels to each partition. Selecting a level, by selecting a check
box in the Levels column, assigns that level to a partition number from the Part. Num. column.
4–6 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 53

Levels can be assigned more than once to different or distinct partitions, but only one level can be selected for each
USO RESTRITO
partition.
Figure 4.5 Partition Levels
Control Layer Partitions (NK-A64 only)
The NK-A64 Analog Audio Level Router has a control layer in addition to the first and second levels (left and right
channels respectively). The control layer is used for lossless signal mixing, for more information, refer to “NK-A64
Control Layer” on page 5–10.
The Control Layer Partition table allows users to configure levels to each partition. Selecting a level, by selecting a
check-box in the Levels column, assigns that level to a partition number from the Part. Num. (Partition Number)
column.
Levels can be assigned more than once to different or distinct partitions, but only one level can be selected for each
partition.
Figure 4.6 Control Layer Partitions
First Input
The First Input defines the first source used (from the range of 1-255) by the router. The valid range for the First
Input is 1-65535, the default is 1.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–7
Page 54

First Output
USO RESTRITO
The First Output defines the first destination used (from the range of 1-255) by this router. The valid range for the
First Output is 1-65535, the default is 1.
Machine Control Destination (NK-M Routers only)
The Machine Control Destination radio buttons specify whether the destinations are used as the Slave or as the
Master.
The Machine Control Destination option is only available on the Machine Control router’s Device Properties
page. It is not applicable to other NK router models.
Status Field s
Reference Signal Type
The Reference Signal Type automatically detects if a video reference is being looped through the router. It will
show the signal type if there is a reference present, either PAL or NTSC, or, if no reference is detected, it will
display Local.
The Local signal is the internal random switching pulse that is generated by the router to ensure successful switch
timing. For more information on video referencing, please refer to “Video Referencing” on page 5–15.
Alarms
The Alarms status section of the Device Properties page is divided into three headings: Reference, Matrix Power
and RCP Power. The NK-64 routers also have an additional alarm warning for I/O Power.
There are four degrees of alarm urgency: Green (Normal operation), Yellow (Warning), Orange (Error) and Red
(Critical Error). The possible Reference, Matrix Power, and RCP Power statuses are displayed in Table 4.4.
Table 4.4 Alarms
Heading Possible Status Alarm Urgency Status Color
Reference No Reference Detected Warning Yellow
Reference Present None (Safe) Green
Matrix Power Matrix Power Error Critical Error Red
Matrix Power OK None (Safe) Green
RCP Power RCP Power Error Critical Error Red
RCP Power OK None (Safe) Green
I/O Power (NK-64 only) I/O Power OK None (Safe) Green
I/O Power Error Critical Error Red
Reference
The Reference status alarm indicates if there if a video reference connected to the router. It will also display the
format of the reference, either PAL or NTSC. If a video reference is connected, the router will attempt to perform all
switches during the vertical interval of the reference. If there is no reference connected, the router will still function,
4–8 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 55

but the switches may be activated by the router at any time. For more information on the NK video/switching
USO RESTRITO
reference feature, please refer to “Video Referencing” on page 5–15.
Matrix Power
The Matrix Power status alarm indicates the power status of the router. A router that displays any alarm status other
than Green (safe) should be switched off and unplugged. Another power pack can be used to test the router frame
again, but if the status alarm remains on the Device Properties page, a Ross Video representative should be
contacted.
RCP Power
The RCP Power status alarm indicates the power status that the router distributes to the control panels connected to
it. For any alarm status other than Green (safe), panels should be disconnected one by one, and the alarm status
checked. In some instances there may be too many devices connected to the router to ensure regulated power
consumption by each device. If all devices have been disconnected from the router and the alarm status remains
activated, the router should be switched off and unplugged. Another power pack can be used to test the router frame
again, but if the alarm status remains higher than Green on the Device Properties page, a Ross Video representative
should be contacted.
I/O Power (NK-64 Routers only)
The I/O Power status alarm indicates the I/O card status for the router. As NK-64 routers are comprised of 8
separate I/O cards, each card has its own alarm. If any card has a fault or fails during operation, the I/O Power status
alarm will be triggered. If the alarm has been triggered, each input and output card should be checked individually
before using the router for further operations.
Submit and Upgrade Fields
Submit Settings
The Submit Settings button will upload the settings to the device.
If users wish to cancel or ignore the settings they have made, click the Online tab to return to the Online Devices
page, or click the Refresh button of your browser to revert to the original settings displayed.
Upgrade Firmware
The Upgrade Firmware button is used to upload to the device the latest firmware, contained in a binary file.
Upgrading firmware allows new features, enhancements and improvements of the NK router to be installed.
Configuration Options — Phoenix
Any device that can be configured from a web browser via the IPS may also be configured by the Phoenix Control
Surface with the default interface.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–9
Page 56

Figure 4.7 Phoenix Router Configuration Window
USO RESTRITO
Device configuration is implemented by the use of text fields, check-boxes, radio buttons and other user-entered or
user-modifiable fields. Configuration fields may differ, depending on the functionality of the device. For full
configuration field details, please consult the user guide of the device.
Device Details Fields
Name
The Name field can be assigned by the user to uniquely name a device.
Group
The Group number can be assigned by the user to organize devices into groups. For example, users can assign
separate Group numbers for devices in different physical areas.
Details
The Details field can be assigned by the user to give a device specific details. For example, a physical location or a
brief description of its use.
Address
The Address is used within the overall control system to identify devices. Each device must be given a unique
Address to avoid hardware and communication conflicts.
4–10 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 57

Configuration Fields
USO RESTRITO
First Input
The First Input defines the first source used (from the range of 1-255) by the router. The valid range for the First
Input is 1-65535, the default is 1.
First Output
The First Output defines the first destination used (from the range of 1-255) by this router. The valid range for the
First Output is 1-65535, the default is 1.
Number of Partitions
The Num Partitions (Number of Partitions) indicates how you wish the router to be partitioned. The default value of
the partitions is 1 (no partitions.), The maximum value is 8.
Partition Levels
The Partition Levels table allows users to configure levels to
each partition. Selecting a level, by clicking on a radio button
in the Level Mask column, assigns that level to a partition
number from the Part. Num. column.
Levels can be assigned more than once to different or distinct
partitions, but only one level can be selected for each partition.
Machine Control Destination (NK-M Routers only)
The Machine Control Destination radio buttons specify whether the destinations are used as the Slave or as the
Master.
The Machine Control Destination option is only available on the Machine Control router’s Device Properties
page. It is not applicable to other NK router models.
Other Fields
Ignore Out Of Range Inputs
The Ignore Out of Range Inputs option will ignore switches on an offset router that has been configured to the same
level as another connected router. By default, the Ignore Out of Range Inputs option is not active (the check box is
not checked).
The Ignore Out of Range Inputs option is only available on the NK-64 and NK-72 routers and is only used for
specific installations.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–11
Page 58

Reference Fields
USO RESTRITO
Switching Point
The Switching Point option is only available on the NK-64 and NK-72 routers.
Custom Switching Line (NK-64 Routers only)
The Custom Switching Line option is only available on the NK-64 and NK-72 routers.
Custom Switching Position (NK-64 Routers only)
The Custom Switching Position option is only available on the NK-64 and NK-72 routers.
Status Field s
Reference Signal Type
The Reference Signal Type automatically detects if a video reference is being looped through the router. It will
show the signal type if there is a reference present, either PAL or NTSC, or, if no reference is detected, it will
display Local.
Alarms Fields
The Alarms section divided into three headings: Reference, Matrix Power and RCP Power. The NK-64 routers also
have an additional alarm warning for I/O Power.
There are four degrees of alarm urgency: Green (Normal operation), Yellow (Warning), Orange (Error) and Red
(Critical Error). The possible Reference, Matrix Power and RCP Power statuses are displayed in Table 4.5.
Table 4.5 Alarms
Heading Possible Status Alarm Urgency Status Color
Reference No Reference Detected Warning Yellow
Reference Present None (Safe) Green
Matrix Power Matrix Power Error Critical Error Red
Matrix Power OK None (Safe) Green
RCP Power RCP Power Error Critical Error Red
RCP Power OK None (Safe) Green
I/O Power (NK-64 only) I/O Power OK None (Safe) Green
I/O Power Error Critical Error Red
Reference
The Reference status alarm indicates if there if a video reference connected to the router. It will also display the
format of the reference, either PAL or NTSC. If a video reference is connected, the router will attempt to perform all
switches during the vertical interval of the reference. If there is no reference connected, the router will still function,
4–12 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 59

but the switches may be activated by the router at any time. For more information on the NK video/switching
USO RESTRITO
reference feature, please refer to “Video Referencing” on page 5–15.
Matrix Power
The Matrix Power status alarm indicates the power status of the router. A router that displays any alarm status other
than Green (safe) should be switched off and unplugged. Another power pack can be used to test the router frame
again, but if the status alarm remains on the Device Properties page, contact Ross Technical Support.
RCP Power
The RCP Power status alarm indicates the power status that the router distributes to the control panels connected to
it. For any alarm status other than Green (safe), panels should be disconnected one by one, and the alarm status
checked. In some instances there may be too many devices connected to the router to ensure regulated power
consumption by each device. If all devices have been disconnected from the router and the alarm status remains
activated, the router should be switched off and unplugged. Another power pack can be used to test the router frame
again, but if the alarm status remains higher than Green on the Device Properties page, contact Ross Technical
Support.
I/O Power (NK-64 Routers only)
The I/O Power status alarm indicates the I/O card status for the router. As NK-64 routers are comprised of 8
separate I/O cards, each card has its own alarm. If any card has a fault or fails during operation, the I/O Power status
alarm will be triggered. If the alarm has been triggered, each input and output card should be checked individually
before using the router for further operations.
Device Properties Fields
Figure 4.8 Device Properties Fields
Configuring the RCP-NK1 Panel
Overview
All NK Series components are preconfigured and can be used with the factory default setup immediately after being
installed, without the need for additional configuration. Where an alternative configuration is required, the NK-IPS
allows unparalleled configuration using little more than a PC and Phoenix or a web browser.
The RCP-NK1 40 button panel controls NK Series routers, displaying router status, switching and protecting
crosspoints. It has 40 soft, programmable backlit keys, with 8 being physically separate for convenient function key
layout. The LED brightness can be set through the NK-IPS for both on and off brightness.
Each panel is capable of controlling the whole address space for the NK system (1-65535 inputs and outputs on 32
levels). Panels operate in XY mode by default, but can easily be configured to work in dual cutbus mode using the
NK-IPS.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–13
Page 60

Control Panels can be linked together if they have the same address and a different panel link address (that is not 0).
USO RESTRITO
Linked panels behave exactly as if they were one larger panel with the exception that macros can not be appended
or added across panels. The panels communicate using the T-Bus protocol with support for collision detection.
Each key can be assigned a function, with up to 3 parameters (Default, Shift1 and Shift2). This function will be
called when that switch is pressed. The key functions are:
DESTINATION Changes the destination that the panel is controlling. If the DESTINATION KEY is not
active, the default value is selected. When the DESTINATION KEY has been selected
first, the relative destination is selected.
SOURCE Switches the input using the current destination and level pattern. If the SOURCE KEY
is not active, the default value is switched. When the SOURCE KEY has been selected
first, the relative source is switched.
CROSSPOINT Switches the input, output and level/breakaway associated with this key.
LEVEL Toggles this level number from the current level pattern.
BREAKAWAY Selects a preconfigured breakaway level pattern.
BREAKAWAY STEP Steps through breakaways.
MACRO Records key events that can be replayed later.
PROTECT The PROTECT key attempts to protect the currently selected output/level pair.
TAKE The TAKE key confirms input key events. The user sets up a switch, and presses the
TAKE key to activate the switch.
CHOP Alternates between the last two selected inputs.
SHIFT Changes the source or destination page of the panel.
DEASSIGN Allows users to reset a destination assignment.
MACHINE CONTROL Toggles on/off RS-422 Machine Control for reciprocal switching.
PANEL LOCK Locks the panel from all switches or function key operation.
UNASSIGNED Key is not assigned any function or value.
RCP-NK1 Configuration
The Device Properties page, accessible through the NK-IPS, allows users to configure interface and key
assignments for RCP-NK1 control panels, as well as having the unique ability to assign names and brief
descriptions for the devices themselves.
For More Information on...
• how to query devices, and use of the NK-IPS, refer to the NK-IPS Internet Protocol Server User Guide.
• how to configure RCP-NK1 via Phoenix, refer to the Phoenix Online Help Guide.
4–14 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 61

Figure 4.9 RCP-NK1 Device Properties Page
USO RESTRITO
Device Properties Fields
Family
The Family name is set in the factory before shipping and displays the family that the device belongs to. This
parameter is read-only.
Device
The Device name is set in the factory before shipping and displays the name assigned to the device. This parameter
is read-only.
Serial Number
The Serial Number is set in the factory before shipping and is unique to each device. This parameter is read-only.
Name
The Name field can be assigned by the user to uniquely name a device. This field has a maximum of 16 characters
and is used for description and identification only.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–15
Page 62

Details
USO RESTRITO
The Details field can be assigned by the user to give a device specific details. For example, a physical location or a
brief description of its use. This field has a maximum of 16 characters and is used for description and identification
only.
Group
The Group number can be assigned by the user to organize devices into groups. For example, users can assign
separate Group numbers for devices in different physical areas. This field has a maximum of 10 characters and is
used for description and identification only.
Configuration Fields
Address
The Address is used within the overall control system to identify devices. Each device must be given an unique
Address to avoid hardware and communication conflicts. The valid value range for assigning an individual device
Address is 2-255.
When linking multiple control panels, each device must be given the same address to communicate to other devices
as one panel, but a different Panel Link Address must be given to prevent internal control system conflicts.
4–16 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 63

Breakaways
USO RESTRITO
The Breakaways table is used to assign levels to breakaways.
Users can customize their breakaways to include any levels
desired. Levels can be utilized in as many breakaways as is
needed.
Checking the boxes representing levels 1-8 next to the
breakaways (1-16) will include that level in that breakaway,
when the BREAKAWAY or BREAKAWAY STEP keys are
pressed.
Different breakaways can be defined for each panel. This is
configured in each panel’s Device Properties page via the
NK-IPS.
Key Definitions
The Key Definitions table is where the buttons of the
RCP-NK1 are assigned. Any function can be assigned to
any key. The keys are represented in the first column by
their respective number (1-40). Keys 1-20 represent the
first row of keys on the RCP-NK1 and keys 21-40
represent the second row of keys on the panel.
The desired key function is selected from the drop down
box in the second column (Function column). Any function
can be assigned to any key on the panel and keys can be
assigned multiple times.
Details of parameters used in the Key Definition table are explained in detail in Table 4.6. For brief descriptions of
the keys, please refer to “Overview” on page 4–13; for key operation and usage, refer to “Operation” on page 5–1.
The Shift1 and Shift2 values only apply to SOURCE, DESTINATION and CROSSPOINT keys, all other keys only
require the Default value to be defined, and some keys require no user defined values for operation. All Shift1 and
Shift2 values are ignored when not assigned to SOURCE, DESTINATION or CROSSPOINT keys.
Cutbus Destination 1
Configures the Cutbus destination of the top row of keys when no DESTINATION or CROSSPOINT keys have
been assigned. The valid range for the Cutbus Destination 1 is 1-255.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–17
Page 64

Cutbus Destination 2
USO RESTRITO
Configures the Cutbus destination of the bottom row of keys when no DESTINATION or CROSSPOINT keys have
been assigned. The valid range for the Cutbus Destination 2 is 1-255.
Breakaway Reset
When enabled the Breakaway Reset option resets to the first breakaway (Default Breakaway) after a crosspoint
switch. By default, the Breakaway Reset is off (check box is cleared).
Breakaway Warning Mode
The Breakaway Warning Mode determines which breakaway the current switch status is compared with to check if
a Breakaway Warning condition has occurred. Two modes are available, Current (Current Breakaway) and Default
(First Breakaway).
On Brightness
The On Brightness sets the LED brightness for the RCP-NK1 control panel buttons when the button is ‘on’; that is
when it has been pressed, is already active, or when indicating an error by several quick flashes. The default value
is 200. The valid input value range is 1-250.
The On Brightness does not necessarily have to be a higher value than that of the Off Brightness, although it is
generally advised to avoid confusion.
Table 4.6 Configuration Values
Key Default Value Shift Value Shift2 Value Value Range
Dest (Output) # (DESTINATION SHIFT 1)
Output #
The value range for DESTINATION keys is 1-255, representing any valid output value. There may be three pages/sets of
DESTINATION keys on any one panel (the default page, first DESTINATION SHIFT page and one second
DESTINATION SHIFT page).
Source (Input) # (SOURCE SHIFT 1)
Input #
The value range for SOURCE keys is 1-255, representing any valid input value. There may be three pages/sets of SOURCE
keys on any one panel (the default page, first SOURCE SHIFT page and one second SOURCE SHIFT page).
Xpoint (Destination) # (Source) # (Breakaway/Level) # Source/Destination = 1-255
The CROSSPOINT key requires a destination value, a source value, and a breakaway or level value to be correctly defined.
Level (Level) # — — Level = 1-32
For details on levels and formats, please refer to “Default Configuration” on page 4–1.
Breakaway (Breakaway) # — — Breakaway = 1-16
(DESTINATION SHIFT 2)
Output #
(SOURCE SHIFT 2)
Input #
Output = 1-65535
Input = 1-65535
Breakaway = 1-16
Level = 17-24 (Level # +16)
For details on assigning breakaways, please refer to “Breakaways” on page 4–17.
Brk Step————
4–18 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 65

Table 4.6 Configuration Values
USO RESTRITO
Key Default Value Shift Value Shift2 Value Value Range
The BREAKAWAY STEP key is a function key that, once assigned, does not require any user defined values to operate.
Macro (Macro) # — — Macro = 1-40
The valid range for the MACRO key is 1-40. (Up to 40 MACRO keys can be assigned to one panel.)
Protect — — — —
The PROTECT key is a function key that, once assigned, does not require any user defined values to operate.
Take————
The TAKE key is a function key that, once assigned, does not require any user defined values to operate.
Chop — — — —
The CHOP key is a function key that, once assigned, does not require any user defined values to operate.
Shift (Shift) # — — Shift = 1-4
1 = DESTINATION
SHIFT 1
2 = DESTINATION
SHIFT 2
3 = SOURCE SHIFT 1
4 = SOURCE SHIFT 2
Defines the value of the SHIFT key, can be assigned as either a DESTINATION SHIFT or a SOURCE SHIFT.
Deassign — — — —
The DEASSIGN key is a function key that, once assigned, does not require any user defined values to operate.
MC Key————
The MACHINE CONTROL key is a function key that, once assigned, does not require any user defined values to operate.
Panel Lock————
The PANEL LOCK key is a function key that, once assigned, does not require any user defined values to operate.
*Unassigned* — — — —
*UNASSIGNED* means that the key has no function or value assigned.
*A dash (—) indicates that user defined values are not required and that any value entered here will be ignored.
Off Brightness
The Off Brightness sets the LED brightness for the RCP-NK1 control panel buttons when the button is ‘off’; that is
when it has not been pressed and is not already active. The default value is 50. The valid input value range is 1-250.
The Off Brightness does not necessarily have to be a lower value than that of the On Brightness, although it is
generally advised to avoid confusion.
Panel Locked
The Panel Locked check box indicates when the panel has been locked to not respond to key presses. By default,
this feature is off.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–19
Page 66

Panels can be locked by clicking on the Panel Locked check box, by pressing the PANEL LOCK key once or by
USO RESTRITO
holding down the PROTECT key (if one has been assigned) for about 3 seconds.
Machine Control Enabled
The Machine Control Enabled option allows reciprocal switching when the check box is checked. By default,
Machine Control Enabled is turned off (the check box is not checked).
If the Machine Control Enabled option is checked on the control panel’s Device Properties page, all switches
activated from the panel will be reciprocal regardless of whether or not there is an MC KEY assigned to the
panel.
Machine Control Level
The Machine Control Level configures the level that the machine control (if connected) switches reciprocally when
switches are performed. The valid range for this field is 1-32 (representing levels).
If an invalid level (above 32) is entered for the Machine Control Level then the level will default to 32 when the
settings are updated to the panel, regardless of whether the Machine Control Enabled option has been set or not.
Panel Link Address
The Panel Link Address is required when users wish to use multiple control panels as one linked panel. When
linking panels, the Address field must be the same for each panel, whereas the Panel Link Address must be different
for each individual panel. By default, the Panel Link Address is set to 0. The valid value range for linking panels is
1-254.
Clear Protect
The Clear Protect check box will clear any protects on the panel when the Submit Settings button has been clicked.
Comms Retry Delay
The Comms Retry Delay configures the delay (in milliseconds) by which the panel resends data in instances where
an error has occurred. Errors may be encountered when the NK system is operating over a large network or when
remote panels are being used over long distances. By default, the Comms Retry Delay value is set at 5
(milliseconds) and the valid range is 1 to 65,536 (milliseconds).
Typically, larger systems or systems operated across multiple networks or VPNs will require larger values.
Nominally, the following values are recommended for specific standard configurations:
• Single network system: 5 ms
• Single network system (via NK Hub): 250 to 500 ms
• VPN or Internet system (via NK Hub): 500 to 750 ms
4–20 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 67

Alarms
USO RESTRITO
Protect Alarm
The Protect Alarm indicates whether an output has been protected from the control panel. The Protect Alarm status
is also displayed on the NK-IPS Online Devices page and in Phoenix.
Submit and Upgrade Fields
Submit Settings
The Submit Settings button will upload the settings to the device.
If users wish to cancel or ignore the settings they have made, click the Online tab to return to the Online Devices
page, or click the Refresh button of your browser to revert to the original settings displayed.
Upgrade Firmware
The Upgrade Firmware button is used to upload to the device the latest firmware, contained in a binary file.
Upgrading firmware allows new features, enhancements and improvements of the RCP-NK1 to be installed.
Configuring the NK-SCP
NK-SCP/A Configuration
The NK-SCP/A requires breakaway and baud rate configuration only via the NK-IPS for use. When connected to
the T-Bus Control System it will be displayed on the NK-IPS Online Devices pages. The NK routers to be
interfaced by the NK-SCP/A can be configured individually on the Device Properties page, accessed via the
NK-IPS, of each router.
For details on how to configure NK-SCP/A via Phoenix, refer to the Phoenix Online Help Guide.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–21
Page 68

Figure 4.10 NK-SCP/A Device Properties Page
USO RESTRITO
Device Properties Fields
Family
The Family name is set in the factory before shipping and displays the family that the device belongs to. This
parameter is read-only.
Device
The Device name is set in the factory before shipping and displays the name assigned to the device. This parameter
is read-only.
Serial Number
The Serial Number is set in the factory before shipping and is unique to each device. This parameter is read-only.
Name
The Name field can be assigned by the user to uniquely name a device. This field has a maximum of 16 characters
and is used for description and identification only.
4–22 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 69

Details
USO RESTRITO
The Details field can be assigned by the user to give a device specific details. For example, a physical location or a
brief description of its use. This field has a maximum of 16 characters and is used for description and identification
only.
Group
The Group number can be assigned by the user to organize devices into groups. For example, users can assign
separate Group numbers for devices in different physical areas. This field has a maximum of 10 characters and is
used for description and identification only.
Configuration Fields
Address
The Address is used within the overall control system to identify devices. Each device must be given a unique
Address to avoid hardware and communication conflicts. The valid value range for assigning an individual device
Address is 2-255.
ASCII Port Baud Rate
The ASCII Port Baud Rate configures the baud speed of the NK-SCP/A. The available options from the drop down
box are 9600, 14.4k, 28.8k, 38.4k, 57.6k and 115.2k. By default, the baud rate is set to 9600.
Breakaway Level Map
The Breakaway Level Map is used to configure the router levels
to defined breakaways used when switching with the SCP via
the ASCII protocol. For ASCII protocol terms and parameters,
please refer to “NK-SCP Operation” on page 5–13.
Submit and Upgrade Fields
Submit Settings
The Submit Settings button will upload the settings to the device.
If users wish to cancel or ignore the settings they have made, click the Online tab to return to the Online Devices
page, or click the Refresh button of your browser to revert to the original settings displayed.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–23
Page 70

Upgrade Firmware
USO RESTRITO
The Upgrade Firmware button is used to upload to the device the latest firmware, contained in a binary file.
Upgrading firmware allows new features, enhancements and improvements of the NK-SCP/A to be installed.
NK-SCP/K2 Configuration
The NK-SCP/K2 itself does not need to be configured via the NK-IPS for use, but when connected to the T-Bus
Control System it will be displayed on the NK-IPS Online Devices page. The NK routers to be interfaced by the
Geneos CPU need to be configured identically in both the router’s Device Properties page accessed via the NK-IPS
and the Physical Map and Virtual Labels pages in Geneos.
For details on how to configure NK-SCP/K2 via Phoenix, please refer to the Phoenix Online Help Guide.
Configuring the Router via the NK-IPS
Each router that is to be accessed by the Geneos CPU, needs to be configured via the NK-IPS. Details on
configuring routers can be found in “Configuring Routers” on page 4–4.
Configure the router’s level, first input and first output on the router’s Device Properties page. The values entered
here are exactly what are used and stored by the Geneos CPU for control system operation. If multiple routers are
being used, each router will have to be configured independently.
It is recommended that if multiple routers are to be used for switching, that they be configured to have only one
level per format.
For details on how to configure NK-SCP/K2 via Phoenix, please refer to the Phoenix Online Help Guide.
Figure 4.11 NK-SCP/K2 Device Properties Page
4–24 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 71

Device Properties Fields
USO RESTRITO
Family
The Family name is set in the factory before shipping and displays the family that the device belongs to. This
parameter is read-only.
Device
The Device name is set in the factory before shipping and displays the name assigned to the device. This parameter
is read-only.
Serial Number
The Serial Number is set in the factory before shipping and is unique to each device. This parameter is read-only.
Name
The Name field can be assigned by the user to uniquely name a device. This field has a maximum of 16 characters
and is used for description and identification only.
Details
The Details field can be assigned by the user to give a device specific details. For example, a physical location or a
brief description of its use. This field has a maximum of 16 characters and is used for description and identification
only.
Group
The Group number can be assigned by the user to organize devices into groups. For example, users can assign
separate Group numbers for devices in different physical areas. This field has a maximum of 10 characters and is
used for description and identification only.
Configuration Fields
Address
The Address is used within the overall control system to identify devices. Each device must be given a unique
Address to avoid hardware and communication conflicts. The valid value range for assigning an individual device
Address is 2-255.
Machine Control Enabled
Machine Control Enabled allows reciprocal switching when the check box is checked. By default, Machine Control
Enabled is turned off.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–25
Page 72

Machine Control Level
USO RESTRITO
The Machine Control Level configures the level that the machine control (if connected) switches reciprocally when
switches are performed. The valid range for this field is 1-8 (representing levels).
If an invalid level (above 8) is entered for the Machine Control Level then the level will default to 8 when the
settings are updated to the SCP, regardless of whether the Machine Control Enabled option has been set or not.
First Input/Output
These options allow the Geneos input and output range to be located anywhere within the 16 bit NK Series
input/output range. The NK input and output will be offset to start at these values.
Level Position
The level position option allows the user to place the eight Geneos levels within four defined ranges in the 32-level
NK Series system. Users can select between:
•1 -> 8
•9 -> 16
• 17 -> 24
• 25 ->32
The NK level will be offset to use this range.
Startup Delay
The startup delay allows the user to configure a time (in seconds) for the NK-SCP/K2 to wait until the Geneos
system is ready before requesting all status.
Manual Filter
By default, the NK-SCP/K2 will automatically detect NK-Series routers connected to the T-Bus on startup. With
larger routers systems, it is better to manually specify which router output ranges are present.
T o use the manual filter:
1. Select the Manual Filter Enabled check box
2. For each router Level, specify:
• The First Output
• The number of outputs (Num. Outputs)
3. Select the Enable check box for each router level in the system.
4–26 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 73

Submit and Upgrade Fields
USO RESTRITO
Submit Settings
The Submit Settings button will upload the settings to the device.
If users wish to cancel or ignore the settings they have made, click the Online tab to return to the Online Devices
page, or click the Refresh button of your browser to revert to the original settings displayed.
Upgrade Firmware
The Upgrade Firmware button is used to upload to the device the latest firmware, contained in a binary file.
Upgrading firmware allows new features, enhancements and improvements of the NK-SCP/K2 to be installed.
Configuring the Router in Geneos
When each router has been configured from the NK-IPS, the levels, first input and first output must be entered into
the Physical Map and Virtual Labels pages in Geneos exactly as they were configured in the router’s Device
Properties page via the NK-IPS. Configuration of the Virtual Labels page requires that mnemonics be entered from
the Mnemonics page.
For more information on configuring levels, inputs and outputs as well as entering mnemonics, refer to the Geneos
User Guide.
Configuring the GPI
Configuration Options
The NK-GPI Device Properties page, accessible through the NK-IPS, allows users to configure the GPI input and
output range, as well as the input and output modes.
For details on how to configure the GPI via Phoenix, please refer to the Phoenix Online Help Guide.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–27
Page 74

Figure 4.12 NK-GPI Device Properties Page
USO RESTRITO
Device Properties Fields
Family
The Family name is set in the factory before shipping and displays the family that the device belongs to. This
parameter is read-only.
Device
The Device name is set in the factory before shipping and displays the name assigned to the device. This parameter
is read-only.
Serial Number
The Serial Number is set in the factory before shipping and is unique to each device. This parameter is read-only.
Name
The Name field can be assigned by the user to uniquely name a device. This field has a maximum of 16 characters
and is used for description and identification only.
4–28 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 75

Details
USO RESTRITO
The Details field can be assigned by the user to give a device specific details. For example, a physical location or a
brief description of its use. This field has a maximum of 16 characters and is used for description and identification
only.
Group
The Group number can be assigned by the user to organize devices into groups. For example, users can assign
separate Group numbers for devices in different physical areas. This field has a maximum of 10 characters and is
used for description and identification only.
Configuration Fields
Address
The Address is used within the overall control system to identify devices. Each device must be given a unique
Address to avoid hardware and communication conflicts. The valid value range for assigning an individual device
Address is 2-255.
GPI Input Table
The GPI Input Table (GPI Ins) configures the GPI and
crosspoint behavior. When the GPI input is triggered, the
specified cross-point is switched.
GPI In Mode
The GPI In Mode configures the GPI input for either Return or Latch mode. Return mode will hold the switch only
while the GPI input trigger is held. Latch will switch and hold the crosspoint until another switch is activated.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–29
Page 76

GPI Output Table
USO RESTRITO
The GPI Output Table (GPI Outs) configures the GPI
output that is triggered when a specified crosspoint is
selected.
GPI Out Mode
The GPI Out Mode configures the GPI outputs to either Follow GPI Ins, as configured in the GPI Input Table, or to
Use GPI Out Table for crosspoint configuration.
Debounce Delay
The Debounce Delay field configures the time (in milliseconds) that the NK-GPI will allow before sending a trigger
event.
The NK-GPI does not require a Debounce Delay to be configured when used with other NK Series devices. The
field only requires user input if using third party devices.
Panel Link Address
The Panel Link Address is required when users wish to use a panel to select the GPI outputs. When switches are
activated by the control panel, the NK-GPI will follow the destinations as chosen by the panel.
When linking the NK-GPI to a control panel, the Address field must be the same for both devices, whereas the
Panel Link Address must be different for each device. By default, the Panel Link Address is set to 0. The valid
value range for linking panels is 1-254.
Defining an NK-GPI Panel Link Address to follow crosspoint and switch events as selected by an NK control
panel will use the panel’s destination instead of the destination defined by the GPI Out Mode selection (either in
the GPI Input Table or GPI Output Table, depending on the mode selected).
Submit and Upgrade Fields
Submit Settings
The Submit Settings button will upload the settings to the device.
If users wish to cancel or ignore the settings they have made, click the Online tab to return to the Online Devices
page, or click the Refresh button of your browser to revert to the original settings displayed.
4–30 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 77

Upgrade Firmware
USO RESTRITO
The Upgrade Firmware button is used to upload to the device the latest firmware, contained in a binary file.
Upgrading firmware allows new features, enhancements and improvements of the NK-GPI to be installed.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Configuration • 4–31
Page 78

4–32 • Configuration NK Series User Guide (1.0)
USO RESTRITO
Page 79

Operation
In4
Out27
(11)
USO RESTRITO
NK Series Operation
Start-up Process
After power has been supplied to the NK Series components, the routers broadcast their status to each other. Panels
also listen to these broadcasts and are able to download the matrix status within this time. Linked panels broadcast
their internal state (shift, destination, levels, take, chop and machine control). Panels will attempt to retrieve the
status for their current output/level pair. Finally panels will request for any protects they may be holding. Any
routers (possibly multiple routers) with a protect held by this address will respond.
Router Start-up
On start-up, the newly connected router will attempt to download status from an operating router with the same
output range and level. It will then switch all crosspoints and broadcast its status. Routers respond to data messages
from other routers to allow this synchronization.
Control Panel Start-up
When a control panel is powered up, the LEDs will light 2 at a time from left to right. It will then fade to a Ross
logo, fade that logo out and fade in the current status. This is to allow time for all connected NK devices to
synchronize on start up.
Panels remember the last selected output and breakaway/level. These will be restored on power up unless
overridden by a linked panel with different values.
Single Panel RCP-NK1 Operation
Overview
The control panel functions detailed below can be programed with the NK-IPS for full functionality. The examples
herein are described using the factory default configuration, loaded with every NK router. For details on the factory
configuration, as well as use and features of the NK-IPS, refer to “Configuration” on page 4–1.
Key Press/Event Instructions
Please note the following when following the examples in the this section.
A single, thick black border signifying the key indicates a simple key
In5
Macro1
Out1
S SHIFT
press to execute the action.
Two thin, black lines signifying the key indicates that the key should
be held down for approximately 3 seconds and then released to
execute to action.
Source and destination keys are labelled as Input and Output keys, in
this instance ‘Out11’ signifies Output 11 and ‘In4’ signifies Input 4.
In the example that use the SHIFT key, S SHIFT signifies SOURCE
SHIFT and D SHIFT signifies DESTINATION SHIFT. The Input or
Output then shown is the desired Input or Output and in brackets
underneath the actual key number pressed, as it would be on the
default page.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Operation • 5–1
Page 80

Operation Basics
Tak e
USO RESTRITO
Destination Keys
Selecting a destination changes the virtual destination the panel controls or switches the next time a SOURCE key
is pressed. Destinations can be selected by pressing a preset DESTINATION key
When a preset DESTINATION key is pressed, that key and its source status key (if a preset key exists) will be
illuminated. If a breakaway warning occurs, the BREAKAWAY key will flash.
The default configuration for the RCP-NK1 is shown in “Configuration” on page 4–1. The bottom, left hand row
of 16 keys is set to destination keys 1-16, pressing the DESTINATION SHIFT key will change the bottom row to
destination keys 17-32.
Example
Selects preset destination ‘Out11’ as the panel’s controlled
Out11
Source Keys
Source switching is performed by pressing a preset SOURCE key. Selecting a source (when a TAKE function key is
not assigned) results in the controller requesting the selected source to be switched by the router to the panel’s
current destination.
If the switch request was successful the preset SOURCE key is illuminated. If the switch was not successful or
generated errors the key will flash several times quickly to indicate that an error has occurred. If a TAKE function
key is assigned, the TAKE key will be illuminated and the preset SOURCE key will flash once quickly (this
indicates that TAKE is armed). To perform the switch press the TAKE key or press any other key to cancel.
destination.
The default configuration for the RCP-NK1 is shown at the start of “Configuration” on page 4–1. The top, left
hand row of keys is set to source keys 1-16, pressing the SOURCE SHIFT key will change the top row to source
keys 17-32.
Example
Switches preset source ‘In5’ to the current destination (if TAKE is not
In5
In3
Shift Keys
SHIFT keys allow the different pages or sets available to preset SOURCE and DESTINATION keys to be accessed.
Up to three different sets of SOURCE and/or DESTINATION keys may be accessed from the panel. The SOURCE
SHIFT keys change the current set of SOURCE keys available on the panel and the DESTINATION SHIFT keys
change the current set of DESTINATION keys available. All other keys are not affected by SHIFT keys.
When no SHIFT keys are selected, the keys are on the first or default page/set. By pressing a specific SOURCE
SHIFT or DESTINATION SHIFT key, the panel immediately changes its relevant sources or destinations to the
specified set. The SHIFT key is active when illuminated. Pressing the SHIFT key again, toggles it to the default key
set. As the sets change if a SOURCE or DESTINATION key matches the currently controlled destination or the
source status that key will be illuminated.
assigned).
Switches preset source ‘In3’ to the current destination (if TAKE is
assigned).
The default configuration for the RCP-NK1 is shown at the start of “Configuration” on page 4–1. The top, left
hand row of keys is set to source keys 1-16, the bottom, left hand row of keys is set to destination keys 1-16.
5–2 • Operation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 81

Pressing the respective SHIFT key (SOURCE SHIFT or DESTINATION SHIFT) will change the top row to source
In21
(5)
Tak e
USO RESTRITO
keys 17-32, and the bottom row to destination keys 17-32.
Example
When selecting a source on the current page (when the SOURCE SHIFT key is not illuminated):
Switches preset source ‘In5’ to the current destination (if TAKE is not
In5
When selecting a source on the second page/set:
S Shift
Crosspoint Keys
CROSSPOINT keys perform a preset crosspoint switch in a single key press, and the key will illuminate to indicate
the state of that crosspoint. When a crosspoint switch is performed the panel’s current destination, source and
breakaway (optional) changes to those specified in the CROSSPOINT key assignment. If a breakaway is not
specified, the currently selected breakaway on the panel is used for the switch.
If a CROSSPOINT key’s preset destination and source status matches that destination’s source status in the router
on all levels on the current breakaway (or set breakaway) the key will be illuminated. If a TAKE function key is
assigned, the TAKE key is illuminated and the preset CROSSPOINT key flashes (this indicates that TAKE is
armed).
assigned).
Switches preset source ‘In21’ to the current destination (if TAKE is
not assigned).
Example
Switches user defined Xpoint2 (source to destination on
Xpoint2
Xpoint5
A CROSSPOINT key is not available on the factory default configuration. For configuration and functionality of
the CROSSPOINT key, the NK-IPS is required.
Level Keys
LEVEL keys select the router levels. In the factory default configuration, there are four LEVEL keys assigned to
the RCP-NK1. Levels and keys are described below.
breakaway/level), if TAKE is not assigned.
Switches user defined Xpoint5 (source to destination on
breakaway/level), if TAKE is assigned.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Operation • 5–3
Page 82

Example
USO RESTRITO
Pressing the ‘Level2’ key will select the SDI level of the router.
Level2
Pressing the ‘Level5’ key will select the Analog Video level of the
Level5
Level6
Level7
Breakaway Keys
BREAKAWAY keys select preset groups of levels to be controlled. Breakaways can be customized from the control
panel’s Device Properties page via the NK-IPS. If BREAKAWAY and LEVEL keys are assigned, then the LEVEL
keys will reflect the breakaway pattern. When the current breakaway is the first breakaway, the LEVEL keys will
not be illuminated. The source status displayed is only for the first level of any given breakaway or level selection.
router.
Pressing the ‘Level6’ key will select the Left Channel of the Analog
Audio level of the router.
Pressing the ‘Level7’ key will select the Right Channel of the Analog
Audio level of the router.
Example
Pressing the ‘Brkway1’ key will select the default breakaway as
Brkway1
Brkway2
In the factory default configuration of the RCP-NK1, all levels are set to the default breakaway, which is the only
defined breakaway.
Breakaway Step Key
When breakaways have been configured from the NK-IPS, a BREAKAWAY STEP key may be used to cycle
through the configured breakaways. Pressing this key will change the breakaway to the next breakaway with any
levels. The BREAKAWAY STEP key will be illuminated if the current breakaway is not the first breakaway.
Holding down the BREAKAWAY STEP key displays the levels enabled in the (current) breakaway pattern.
A BREAKAWAY STEP key is not available on the factory default configuration. For configuration and
functionality of the BREAKAWAY STEP key, the NK-IPS is required.
defined in the control panel’s Device Properties page via the NK-IPS.
Pressing the ‘Brkway2’ key will select the custom breakaway as
defined in the control panel’s Device Properties page via the NK-IPS.
5–4 • Operation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 83

Example
USO RESTRITO
Pressing the ‘BrkStep’ key will cycle through the breakaways as
BrkStep
Macro Keys
Macros can be used to initiate multiple switches in one quick key press. Several MACRO keys can be assigned to
one panel and then different macros recorded to each key. When users are required to regularly switch between two
or more static switch assignments, macros can be used to switch these in one easy key press.
A macro is an event playback feature similar to a salvo. A salvo will only trigger a series of switches, whereas a
macro will record a series of events for express playback at a later time. When the macro is played back, it will
activate a sequence of switches to configure the router. Macros can be extremely valuable in minimizing repetitive
key presses by configuring multiple switch events (source, destination and crosspoint) to one key.
A macro event comprises a source, destination, crosspoint, macro or protect key press. When appending one macro
to another, this is counted as 1 event. This is covered in more detail later under the heading Appending Macros.
A MACRO key can store a maximum of 84 events and users can assign up to 40 MACRO keys on the RCP-NK1
panel. It is recommended that users with only a single, unlinked panel only assign two or three keys as MACRO
keys. Users who have several linked panels may find it convenient to have one panel set aside solely for the purpose
of macros and assign as many MACRO keys as is required.
Pressing a SHIFT key when recording a macro does not count as an event, as the macro recorder simply recognizes
that the key that is actually pressed is the relevant source or destination.
defined in the control panel’s Device Properties page of the NK-IPS.
Recording Macros
To record a macro, you first need to start ‘macro recording mode’.
1. Hold down the MACRO key for about three seconds. The MACRO key will flash quickly to indicate that the
panel has entered macro recording mode.
2. Release the MACRO key. The MACRO key will flash slowly to indicate that the panel is in macro recording
mode.
3. Enter the events you wish to record, as you would if you were to activate a switch. Key presses will be
acknowledged by a quick flash on the key you have entered into the macro.
4. When you have finished entering switch events, press the MACRO key to exit macro recording mode.
The MACRO key will stop flashing to indicate the panel has exited macro recording mode.
Example 1
To create a macro (Macro1) that sends Input 1 to Outputs 1, 2 and 3, and also sends Input 2 to Outputs 7, 8 and 9
you would follow this sequence of key presses:
Key press 1 Key press 2 Key press 3 Key press 4 Key press 5 Key press 6 Key press 7
Macro1
Key press 8 Key press 9 Key press 10 Key press 11 Key press 12 Key press 13 Key press 14
Out1 In1 Out2 In1 Out3 In1
Out7 In2 Out8 In2 Out9 In2 Macro1
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Operation • 5–5
Page 84

Only one MACRO key is available on the factory default configuration. For implementation of additional MACRO
USO RESTRITO
keys, the NK-IPS is required.
Example 2
To create a macro (Macro2) that sends Input 1 to Outputs 4, 5, 6 and 7 and also sends Input 2 to Outputs 8 and 9 you
would follow this sequence of key presses:
Key press 1 Key press 2 Key press 3 Key press 4 Key press 5 Key press 6 Key press 7
Macro2
Key press 8 Key press 9 Key press 10 Key press 11 Key press 12 Key press 13 Key press 14
Out7 In1 Out8 In2 Out9 In2 Macro2
Example 3
To create a macro (Macro3) that sends Input 1 to all Outputs on a 16x16 router, you would follow this sequence:
Key press 1 Key press 2 Key press 3 Key press 4 Key press 5 Key press 6 Key press 7
Macro3
Follow in this pattern, pressing the next sequential ‘Out’ number and then ‘In1’ until you reach the last
output desired. In this example, the last desired output is ‘Out16’.
Key press 28 Key press 29 Key press 30 Key press 31 Key press 32 Key press 33 Key press 34
Out14 In1 Out15 In1 Out16 In3 Macro3
Out4 In1 Out5 In1 Out6 In1
Out1 In1 Out2 In1 Out3 In1
Appending Macros
Appending macros is a feature that allows the addition of more events (or another macro) to an already existing
macro.
To append a macro, you first need to enter macro recording mode, and then enter macro recording mode again to
append the macro.
1. Hold down the MACRO key for about three seconds. The MACRO key will flash quickly to indicate that the
panel has entered macro recording mode.
2. Release the MACRO key. The MACRO key will flash slowly to indicate that the panel is in macro recording
mode.
3. Hold down the MACRO key again (this will play back the macro internally so that it may be appended). The
MACRO key will flash quickly.
4. Release the MACRO key. The MACRO key will again flash slowly to indicate that the panel is in macro
recording mode.
5. Enter the events you wish to record as you would if you were to activate a switch. Key presses will be
acknowledged by a quick flash on the key you have entered into the macro.
6. When you have finished entering switch events, press the MACRO key to exit macro recording mode.
5–6 • Operation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 85

The MACRO key will stop flashing to indicate the panel has exited macro recording mode.
USO RESTRITO
When appending macros or adding one macro to another, if you use a single input or output in more than one
macro, it will override the previous status of that key.
Example
If you wish to add the output status Input 9 to Output 10 to an already existing macro (Macro1 from Example 1 in
the previous heading, Recording Macros) you would follow this sequence of key presses:
Key press 1 Key press 2 Key press 3 Key press 4 Key press 5
Macro1 Macro1
Adding one Macro to another Macro
Adding one macro to another can be useful when you have more than one macro that shares the same output status
(the same source to destination switch assignments) but where one macro also has output status that the other macro
has not assigned.
As the macro function is only an event recorder, other macros are stored as one single event, not the sum of the
events in that macro. Similarly, if a macro that has already been added to another macro is changed, the appended
macro when played back will reflect that change.
Example
If you wish to append Macro1, adding Macro2 to it (from Examples 1 and 2 in the previous heading, Recording
Macros) follow this sequence of key presses:
Key press 1 Key press 2 Key press 3 Key press 4
Macro1 Macro1
In the example above, the Macros are as follows:
Out10 In9 Macro1
Macro2 Macro1
• Macro1 = Input 1 to Outputs 1, 2 and 3, and also sends input 2 to outputs 7, 8 and 9.
• Macro2 = Input 1 to Outputs 4, 5, 6 and 7, and also sends Input 2 to Outputs 8 and 9.
In this example, because Output 7 is used twice, the last status added will be the one used when the macro is played
back. The final status of Macro1 when it is played back will be as such will be:
• Input 1 to Outputs 1,2,3,4,5,6 and 7.
• Input 2 to Outputs 8 and 9.
To cancel recording or appending a Macro
To cancel recording or appending a macro, press the macro key after entering macro record mode.
Macros can not be cancelled after entering events in macro recording mode. If a mistake has been made, you will
have to exit macro recording mode and enter it again to re-enter events you wish to be played back.
Protect Key
The PROTECT key is used to lock current destination from use by other sources, as well as from other linked
panels. The PROTECT key is especially useful in instances where destination must be held after a switch has been
made.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Operation • 5–7
Page 86

Panel Lock
Tak e
Tak e
Tak e
USO RESTRITO
A panel may be locked to prevent unwanted key presses (particularly accidental switches). The Panel Lock is
reflected on the control panel’s Device Properties page of the NK-IPS, and can be locked or unlocked as required
both from the NK-IPS configuration page or from the panel.
To activate the panel lock from the RCP-NK1, follow these steps:
1. Hold down the PROTECT key for about three seconds. The PROTECT key will flash quickly to indicate that
the panel lock has been activated.
2. Release the PROTECT key. The PROTECT key will flash slowly to indicate that the panel is locked.
Example
Pressing the PROTECT key will protect the current destination.
Protect
Holding the PROTECT key for about 3 seconds will lock the panel.
Protect
The PROTECT key’s panel lock function and the PANEL LOCK key are interchangeable. If both function keys are
configured on the one panel, a panel lock can be activated from one key, and deactivated from the other.
A PROTECT key is not available on the factory default configuration. For configuration and functionality of the
PROTECT key, the NK-IPS is required. A PROTECT key can also be configured on the NK1 panel via Function
Key Program Mode.
Holding the key again will unlock the panel.
Take Key
A TAKE function key is used to activate the selected switch. First the required destination is entered, then the
required source; the SOURCE key on the panel flashes and the TAKE key illuminates. The switch is activated once
the TAKE key is pressed. The entered crosspoint change will be completed immediately after the TAKE key has
been pressed. This enables the user to preset a crosspoint change before the switch is required. The pending switch
can be aborted by pressing any key other that the TAKE key.
Example
Switches preset source ‘In9’ to the current destination when TAKE is
In9
Xpoint7
Macro1
A TAKE key is not available on the factory default configuration. For configuration and functionality of the TAKE
key, the NK-IPS is required. A TAKE key can also be configured on the NK1 panel via Function Key Program
Mode.
assigned.
Switches user defined ‘Xpoint7’ (source to destination on
breakaway/level) when TAKE is assigned.
Pressing a MACRO key and then TAKE will activate the Macro
when TAKE is assigned.
Chop Key
The CHOP function key enables the user to alternate between two sources. Pressing CHOP will alternate the two
previously selected sources for a given destination. Pressing CHOP once will start a slow chop. Pressing CHOP
5–8 • Operation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 87

again will increase the speed of the chop to a fast chop and pressing again will discontinue the chop mode. When
In2
Out1
USO RESTRITO
CHOP is enabled all other keys are disabled.
Example
This sequence of key presses will alternate
Out1 In1
A CHOP key is not available on the factory default configuration. For configuration and functionality of the CHOP
key, the NK-IPS is required. A CHOP key can also be configured on the NK1 panel via Function Key Program
Mode.
Deassign Key
The DEASSIGN key parks the current output. It is only available when the Machine Control Enabled option is
checked on the router’s Device Properties page.
Example
MC Key In2
Chop
Deass..
between sources ‘In1’ and ‘In2’ on destination
‘Out1’.
This will turn Machine Control on, switch
‘In2’ to ‘Out1’ and reciprocally switch ‘In1’
to ‘Out2’. When the DEASSIGN key is
pressed, this switches ‘In1 to ‘Out1, parking
the output and ‘In2’ to ‘Out2’, parking the
output.
A DEASSIGN key is not available on the factory default configuration. For configuration and functionality of the
DEASSIGN key, the NK-IPS is required. A DEASSIGN key can also be configured on the NK1 panel via Function
Key Program Mode.
Machine Control Key
The panel may be configured to operate a machine control (RS-422) level. The machine control level will
automatically be switched reciprocally for the source (master) and destination (slave) selected. To execute a
machine control reciprocal switch, press the MC KEY to enable machine control operation (key will be
illuminated) and then press the required destination and source.
Machine control operation is dependent on three settings:
1. Machine Control mode and level options are configured on the control panel’s Device Properties page.
2. Machine Control is enabled (using the MC KEY function key).
3. Current breakaway includes the Machine Control level.
An MC KEY does not necessarily have to be assigned to the control panel to enable reciprocal switching. If the
Machine Control Enabled option is checked on the control panel’s Device Properties page, all switches activated
from the panel will be reciprocal.
An MC Key is required to disable machine control reciprocal switching in multiple slave scenarios.
An MC KEY key is not available on the factory default configuration. For configuration and functionality of the
MC KEY key, the NK-IPS is required. An MC KEY key can also be configured on the NK1 panel via Function Key
Program Mode.
Panel Lock Key
The PANEL LOCK key will lock the panel to prevent unwanted key presses (particularly accidental switches). The
PANEL LOCK key can be implemented in environments that do not require a PROTECT key, but do require the
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Operation • 5–9
Page 88

ability to lock the panel. The panel lock function is reflected in the control panel’s Device Properties page of the
USO RESTRITO
NK-IPS, and can be locked or unlocked as required both from the NK-IPS or from the panel itself.
Pressing the PANEL LOCK key will lock the panel. Pressing the key
Pan Lock
The PANEL LOCK key and the PROTECT key’s panel lock function are interchangeable. If both function keys are
configured on the one panel, a panel lock can be activated from one key, and deactivated from the other.
A PANEL LOCK key is not available on the factory default configuration. For configuration and functionality of
the PANEL LOCK key, the NK-IPS is required. A PANEL LOCK key can also be configured on the NK1 panel via
Function Key Program Mode.
again will unlock the panel.
Linked RCP-NK1 Panel Operation
Overview
When panels are linked together, key behavior remains as above (with single panel system), although the following
details must be noted when linking panels:
• Pressing CHOP will alternate between two sources, including cases when the sources are on different physical
panels.
• Pressing TAKE will activate a take, including cases when the SOURCE key is on a different panel to the TAKE
key.
• If any linked panel has a TAKE key, the linked device enters take mode when a source or crosspoint key is
pressed.
• Locking one physical panel from the control panel’s Device Properties page will also lock all linked panels. The
NK-IPS can be used to unlock panels if required.
• Entering macro record mode causes all linked panels to be in macro record mode, switch events and protects can
be added from different physical panels.
• Macros cannot be appended or added across panels.
• Page SHIFT keys control source and destination pages for the whole linked panel.
• DESTINATION keys control the destination for the whole panel.
• LEVEL and BREAKAWAY keys control the level mask for the whole panel. Breakaway preview is not available
across linked panels.
• If a panel is added to an operating linked panel, the linked panel changes its states in regards to TAKE, PANEL
LOCK and cutbus accordingly.
• If a linked panel is added to an operating linked device that is in TAKE, CHOP, PANEL LOCK, or macro
recording mode, it starts in that mode.
• Menus do not work across linked panels.
NK-A64 Control Layer
Overview
The Analog Audio level of NK-64 routers offers unparalleled configuration and audio processing, allowing users to
mix left and right audio channels to suit their broadcast requirements. Channels may be swapped, phase inverted or
converted to mono (both channels left, both channels right, both channels average, sum and difference).
5–10 • Operation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 89

Figure 5.1 NK-A64 Control Layer Block Diagram
Right Channel
Output
Left Channel Input
Router Matrix
(Right)
Router Matrix
(Left)
Control Layer
Right Channel Input
Left Channel
Output
USO RESTRITO
Signal processing is conducted by way of a Control Layer. The Control Layer is an additional level within the router
matrix that may be mapped to control panel keys to allow users to mix audio channels on the fly. The Control Layer
uses SOURCE keys as the triggers to mix the output audio signal. The Control Layer may be used after a source has
been switched to a selected destination. Table 5.1 shows the audio mixing options available for the Control Layer.
Table 5.1 Audio Mixing Options
Signal Processing
Input Control
Input 1 L R Both channels normal (Default)
Input 2 R L Channels swapped
Input 3 L L Both channels Left
Input 4 R R Both channels Right
DescriptionLeft Channel Right Channel
Input 5 L R Left channel normal, Right channel inverted
Input 6 L R Left channel inverted, Right channel normal
Input 7 L+R L+R Left channel sum (mono), Right channel sum
Input 8 L+R L–R Left channel sum (mono), Right channel
Control Layer Operation via NK Control Panels
The Analog Audio Control Layer can easily be accessed from NK Series control panels. Factory configured
systems will allow the NK-A64 Control Layer to operate out of the box. Further configuration of the NK-A64
Control Layer and control panel options requires the NK-IPS.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Operation • 5–11
(mono)
difference
Page 90

Note when assigning breakaways for NK Series control panels, the Control Layer should not be assigned to a
Control
Layer
Control
Layer
Control
Layer
Control
Layer
Control
Layer
Control
Layer
Control
Layer
Control
Layer
USO RESTRITO
breakaway that contains other levels. If users require a breakaway for the NK-A64 Control Layer, it is vital that it
is the only level active for that breakaway.
Mixing the Output Audio Signal
When using the Control Layer, users must remember that only the output audio stream is processed within the
router matrix, not the input signal. When mixing audio channels, the control layer is selected after the switch has
been made, or if the output that requires mixing is already active. Users may record macros to make mixing and
switches easier, or if regular audio mixing is required.
Selecting the ‘Control Layer’ key and then selecting ‘In1’ will enable
In1
In2
In3
In4
the output audio channels to be normal.
Selecting the ‘Control Layer’ key and then selecting ‘In2’ will enable
the output audio channels to be swapped.
Selecting the ‘Control Layer’ key and then selecting ‘In3’ will enable
both output audio channels to be the left channel of the source.
Selecting the ‘Control Layer’ key and then selecting ‘In4’ will enable
both output audio channels to be the right channel of the source.
Selecting the ‘Control Layer’ key and then selecting ‘In5’ will enable
In5
the left output audio channel to be normal and the right audio channel
to be inverted.
Selecting the ‘Control Layer’ key and then selecting ‘In6’ will enable
In6
the left output audio channel to be inverted and the right audio
channel to be normal.
Selecting the ‘Control Layer’ key and then selecting ‘In7’ will enable
In7
the both output audio channels to be summed.
Selecting the ‘Control Layer’ key and then selecting ‘In’ will enable
In8
the left output audio channel to be summed and the right audio
channel to be differenced.
Example 1
To swap the channels of the output audio signal for ‘Out4’, first activate a switch by selecting the destination
followed by the source and then select the Control Layer, or the breakaway that the Control Layer is on, and lastly
select the designated mixing mode.
Key press 1 Key press 2 Key press 3 Key press 4
5–12 • Operation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Out4
In1
Control
Layer
In2
Page 91

Example 2
USO RESTRITO
To invert the left channel of the output audio signal for ‘Out6’, first activate a switch by selecting the destination
followed by the source and then select the Control Layer, or the breakaway that the Control Layer is on, and lastly
select the designated mixing mode.
Key press 1 Key press 2 Key press 3 Key press 4
Out6
In1
Control
Layer
In6
The Control Layer configuration is retained by the destination until the Control Layer is changed. For example, if
Input 1 is switched to Output 3 and the left and right channels are swapped (by pressing the Control Layer key
and then selecting Input 2) the next Input selected to be switched to Output 3 will also have the left and right
channels swapped.
NK-SCP Operation
NK-SCP/A Operation Overview
The NK-SCP/A can be used for control of an entire NK routing system. Switches activated from an external
RS-232 device are monitored by all devices on the T-Bus line
The protocol used is a simple ASCII protocol designed to give users a means for simple control of the router via
custom PC software or by connecting a terminal to the AUX port and sending ASCII characters.
Using the ASCII Protocol
The protocol used is a simple ASCII protocol designed to give users a means for simple control of the router via
custom PC software or by connecting a terminal to the AUX port and sending ASCII characters.
Fixed Parameters
The parameters in Table 5.2 are fixed.
Table 5.2 COMM Port Fixed Parameters
Parameter Setting
Parity None
Stop Bits 1
Data Bits 8
Characters ASCII
Commands
Table 5.3 describes the protocol commands.
Table 5.3 ASCII Protocol Commands
Command Description
<X> Switch an input to an output using a breakaway
<Z> Switch multiple inputs (one per level) to an output
<R> Read the current status of an output
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Operation • 5–13
Page 92

Table 5.4 describes the command parameters.
USO RESTRITO
Table 5.4 ASCII Protocol Command Parameters
Command Description Value Note
<ddd> Destination - output number (000 to 254) 1
<sss> Source - input number (000 to 254) 1
<b> Breakaway number (1 to 8) 2
<---> Blank entry (in place of actual output socket number)
<CR> Carriage return character
<LF> Line feed character
<SP> Space character
An offset of -1 is required so that the lowest value of 000 points to the router input or output number 1. In this way,
inputs and outputs from 1 to 255 can be addressed with dialogue values from 000 to 254.
Switch an input to an output using a defined breakawa y
Start the sequence (11 bytes) with an upper case <X> followed by the destination, source, breakaway and carriage
return as detailed below. Do not include the parentheses.
<X> <ddd> <,> <sss> <,> <b> <CR>
Response from SCP
• If the data sting is valid, the SCP returns response (B).
• If the data string is invalid, the SCP returns response (A).
• If the data string is valid but the source number is unavailable or any of the parameters are incorrectly specified,
i.e. greater than 254 (255 to 999) for destination and source and greater than 1 to 8 (0 or 9) for breakaway, the
SCP returns response (A) then response (B).
Response (A)
Response (B) <CR> <LF> <OK> <SP> <CR> <LF>
Switch multiple inputs (one per level) to a output
Start the sequence (37 bytes) with an upper case <Z> followed by the destination, then a source (or <---> to not
switch a level) for each of 8 levels and carriage return as detailed below. Do not include the parentheses.
Send <---> in place of <sss> to not switch that level.
Response from SCP
• If the data sting is valid, the SCP returns response (B).
• If the data string is invalid, the SCP returns response (A).
• If the data string is valid but the source number is unavailable or any of the parameters are incorrectly specified,
i.e. greater than 254 (254 to 999) for destination and source and greater than 1 to 8 (0 or 9) for breakaway, the
SCP returns response (A) then response (B).
<CR> <LF> <ERROR> <CR> <LF>
L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7 L8
<Z> <ddd> <,> <sss, sss, sss, sss, sss, sss, sss, sss <CR>
Response (A)
Response (B) <CR> <LF> <OK> <SP> <CR> <LF>
5–14 • Operation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
<CR> <LF> <ERROR> <CR> <LF>
Page 93

Read the current status of a output
USO RESTRITO
Start the sequence (5 bytes) with an upper case <R> followed by the destination and carriage return as detailed
below. Do not include the parentheses.
<R> <ddd> <CR>
Response from SCP
• If the data sting is valid, the SCP returns response (C) then (B).
• If the data string is invalid, the SCP returns response (A).
• If the data string is valid but the destination is incorrectly specified, i.e. greater than 254 (255 to 999), the SCP
returns response (A) then response (B).
Response (A) <CR> <LF> <ERROR> <CR> <LF>
Response (B) <CR> <LF> <OK> <SP> <CR> <LF>
L1 L2 L3 L4 L5 L6 L7 L8
Response (C) <CR> <LF> <sss, sss, sss, sss, sss, sss, sss, sss> <CR> <LF>
NK-SCP/K2 Operation
Implementation of the NK-SCP/K2 means that NK routers can be controlled exactly as if they were a matrix
module housed within the Kondor 2 frame. Switches can be activated by Geneos control panels as well as from a
Virtual Control Panel (VCP) from the Panelworks page in the Geneos software.
When switches are activated from a control panel or VCP connected to the Geneos CPU, the SCP/K2 monitors
commands and converts them to the T-Bus protocol. If the command sent corresponds with a level that an NK
router is occupying, then that level will be switched. If there are no NK routers occupying that level, then the switch
will be performed where that level is occupied, most likely within the Kondor 2.
Switches can be activated from the NK control panel (RCP-NK1) but are not advised as they will not be reflected
within the Geneos CPU status table. If an RCP-NK1 is connected to the router (or T-Bus), any switches activated by
the panel will override the status and commands from the Geneos panels or Geneostat virtual control panels.
Video Referencing
Overview
All NK Video and Audio routers are fitted with a video switching reference input to ensure that switching occurs in
the vertical interval across all levels. Normally, the reference input signal is a color black (Black burst) composite
signal, however it may be any normal composite signal. The NK router will automatically detect the signal as being
either 625/50 (PAL) or 525/60 (NTSC) and automatically adjust the switching pulse to comply with RP 168, line 6
for PAL and line 10 for NTSC.
The NK router switches on frame boundaries. There are two 75 Ω BNC reference input BNCs on each NK router
arranged as a passive loop-through pair. Normally, a single Black Burst signal is looped through each of the routers
which are located together and a 75 Ω terminator is connected to the last BNC socket. An individual Black Burst
signal should be wired to routers which are more than a few meters apart.
If the reference signal is absent, the NK router will generate a free-running switching pulse over 40ms. The status of
the switching reference may be monitored on the router’s Device Properties page via the NK-IPS, one of three
conditions may be reported via the NK-IPS: Local, PAL reference present or NTSC reference present.
Connecting a Video Reference to NK Routers
When using a video reference with any of the NK router components, users must remember to terminate the last
video reference that is not looped with a 75 Ω BNC terminator.
When only video referencing one router, the other BNC connector of the video reference loop needs to be
terminated, as in Figure 5.2.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Operation • 5–15
Page 94

To Video
USO RESTRITO
Reference
SDI Video
NK-S16
X
Terminated End
(BNC 75ohm Terminator)
Figure 5.2 Referencing a Single Router
When referencing more than one router, the last reference connector needs to be terminated, as in Figure 5.3.
To Video
Reference
Analogue Video
NK-V16
SDI Video
Analogue Audio
X
Terminated End
(BNC 75ohm Terminator)
Figure 5.3 Referencing Multiple Routers
NK-S16
NK-A16
5–16 • Operation NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 95

Appendix A: Connectors and
13
1
G
-+
G
-+++
++++
GG
GGGG
--
----
2
10
4
12
6
14
8
16
1
9
3
11
5
13
7
15
13
1
G
-+
G
-+++
++++
GG
GGGG
--
----
2
10
4
12
6
14
8
16
1
9
3
11
5
13
7
15
USO RESTRITO
Pinouts
DB-25 Pinouts for Analog and Digital Audio Routers
The following pinouts are applicable only for current NK-A16, NK-A32, NK-D16/110 and NK-D32/110
routers. These routers can be distinguished by the silk screen of the pinouts on the rear of the router.
Previous routers, without pinouts silk screened on the rear, require an alternate wiring. These are
detailed in the NK Series User Guide v1.0 and v1.1 or in the NK Series DB-25 Pinouts Application
Note.
The reason for the altered pinouts is that cables can be purchased off the shelf from most audiovisual,
broadcast or music retailers.
16x16 Routers
NK-A16 and NK-D32/110
Figure 6.1 shows the pinouts for inputs and outputs on the NK-A16 and NK-D16/110.
The pinouts detailed in Figure 6.1 are applicable for both left and right channels (NK-A16 only).
Figure 6.1 Pinouts for Inputs and Outputs on the NK-A16 and NK-D16/110
NK-A16 Model Unbalanced Wiring
Input
Figure 6.2 shows pinouts and wiring details for unbalanced input connections (left and right channels) for the
NK-A16 model.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Appendix A: Connectors and Pinouts • 6–1
Figure 6.2 Input Pinouts
Page 96

Output
13
1
G
-+
G
-+++
++++
GG
GGGG
--
----
2
10
4
12
6
14
8
16
1
9
3
11
5
13
7
15
13
1
G
-+
G
-+++
++++
GG
GGGG
--
----
2
10
4
12
6
14
8
16
1
9
3
11
5
13
7
15
18
26
20
28
22
30
24
32
17
25
19 21 23
27 29 31
USO RESTRITO
Figure 6.3 shows pinouts and wiring details for unbalanced output connections (left and right channels) for the
NK-A16 model.
Figure 6.3 Output Pinouts
32x32 Routers
NK-A32 and NK-D32/110
Figure 6.4 shows the pinouts for both inputs and outputs 17-32 on the NK-A32 and NK-D32/110. Pinouts for
inputs and outputs 1-16 are as depicted previously.
The pinouts detailed in Figure 6.4 are applicable for both left and right channels (NK-A32 only).
Figure 6.4 Pinouts for Inputs and Outputs 17-32 on the NK-A32 and NK-D32/110
NK-A32 Model Unbalanced Wiring
Input
Figure 6.5 shows pinouts and wiring details for unbalanced input connections (left and right channels) for the
NK-A32 model.
6–2 • Appendix A: Connectors and Pinouts NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 97

Figure 6.5 Pinouts for Unbalanced Input Connections for the NK-A32 Model
13
1
G
-+
G
-+++
++++
GG
GGGG
--
----
2
10
4
12
6
14
8
16
1
9
3
11
5
13
7
15
18
26
20
28
22
30
24
32
17
25
19 21 23
27 29 31
13
1
G
-+
G
-+++
++++
GG
GGGG
--
----
2
10
4
12
6
14
8
16
1
9
3
11
5
13
7
15
18
26
20
28
22
30
24
32
17
25
19 21 23
27 29 31
13
1
G
-+
G
-+ + +
++++
GG
GGGG
--
----
4L
8L
3L
7L
2L
6L
1L
5L
4R 3R 2R 1R
8R 7R 6R 5R
USO RESTRITO
Output
Figure 6.6 shows pinouts and wiring details for unbalanced output connections (left and right channels) for the
NK-A32 model.
Figure 6.6 Pinouts for Unbalanced Output Connections for the NK-A32 Model
64x64 Routers
NK-A64
Figure 6.7 shows the pinouts for both inputs and outputs on the NK-A64. Each connector allows balanced audio of
four audio channels, please refer to Table 7.1 for relative I/O numbers.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Appendix A: Connectors and Pinouts • 6–3
Figure 6.7 Pinouts for Inputs and Outputs on the NK-A64
Page 98

NK-A64 Unbalanced Wiring
13
1
G
-+
G
-+ + +
++++
GG
GGGG
--
----
4L
8L
3L
7L
2L
6L
1L
5L
4R 3R 2R 1R
8R 7R 6R 5R
13
1
G
-+
G
-+ + +
++++
GG
GGGG
--
----
4L
8L
3L
7L
2L
6L
1L
5L
4R 3R 2R 1R
8R 7R 6R 5R
USO RESTRITO
Input
Figure 6.8 shows pinouts and wiring details for unbalanced input connections for the NK-A64.
Figure 6.8 Pinouts for Unbalanced Input Connections for the NK-A64
Output
Figure 6.9 shows pinouts and wiring details for unbalanced output connections for the NK-A64.
Figure 6.9 Pinouts for Unbalanced Output Connections for the NK-A64
NK-D64/110
Figure 6.10 shows the pinouts for both inputs and outputs on the NK-D64/110. Pinouts for inputs and outputs 1-32
are as depicted previously.
6–4 • Appendix A: Connectors and Pinouts NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Page 99

Figure 6.10 Pinouts for Inputs and Outputs on the NK-D64/110
13
1
G
-+
G
-+++
++++
GG
GGGG
--
----
2
10
4
12
6
14
8
16
1
9
3
11
5
13
7
15
18
26
20
28
22
30
24
32
17
25
19 21 23
27 29 31
34 36 38 40
42 44
46
48
50
52
54 56
58 60 62 64
33 35 37 39
41 43 45 47
49 51 53 55
57 59 61 63
USO RESTRITO
Power Connector - DB-9 (All NK-16 and NK-32 Routers)
Figure 6.11 shows the DB-9 connector port on the rear of the routers and can be used to connect GPI alarms.
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
DB-9 Male
(External View)
RCP Power Fail
Matrix Power Fail
GND
GND
1
6
+15V
2
7
+15V
3
8
-15V
4
9
-15V
5
Figure 6.11 DB-9 Connector Port for GPI Alarms
Machine Control DB-9 Pinouts (NK-M16 and NK-M32)
Figure 6.12 shows the pinouts for DB-9 connections on the NK-M16 and NK-M32 Machine Control routers.
The Machine Control DB-9 pinouts are dependent on which mode (Master or Slave) is being used.
NK Series User Guide (1.0) Appendix A: Connectors and Pinouts • 6–5
Page 100

Figure 6.12 Pinouts for DB-9 Connections on the NK-M16 and NK-M32 Machine Control Routers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
PIN MASTER SLAVE
1
2
6
7
3
8
4
9
5
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
GND
Tx-
Tx-
Tx+
Tx+
Rx-
Rx+
Rx-
Rx+
DB-9 Male
(External View)
r
USO RESTRITO
GPI Alarm (NK-64 & NK-72 Models only)
Figure 6.13 shows the 3-way Phoenix connector on the rear of the NK-64 and NK-72 routers which is used to
connect GPI alarms.
Figure 6.13 3-way Phoenix Connector for GPI Alarms
T-Bus RJ-45 Connector
Figure 6.14 shows the RJ-45 connector port for the T-Bus control system.
6–6 • Appendix A: Connectors and Pinouts NK Series User Guide (1.0)
Figure 6.14 RJ-45 Connector port for the T-Bus Control System
Current limited to 15mA
+5V
Alarm / GPI
+ RS-485 - RS-485
GND
123 45678
RJ-45 Female
(External View)
GND
Tx/RxTx/Rx
+14.4V RCP
Phantom Powe
 Loading...
Loading...