Page 1

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System
RSV-S4-X
User Manual
Page 2

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
2
Page 3
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
Content
1 WELCOME....................................................................................................................6
1.1 PRECAUTION ................................................................................................................................................6
1.2 FEATURES .....................................................................................................................................................7
1.2.1 DATA SECURITY............................................................................................................................................................................7
1.2.2 DATA PERFORMANCE .................................................................................................................................................................7
1.2.3 DATA VERSATILITY.......................................................................................................................................................................7
1.3 EASE OF USE.................................................................................................................................................7
1.4 SPECIFICATIONS.........................................................................................................................................8
1.5 SUPPORTED OPERATING SYSTEMS .....................................................................................................8
1.6 PRODUCT CONTENTS................................................................................................................................9
2 INTRODUCTION TO RAID......................................................................................10
2.1 RAID VOLUMES ..........................................................................................................................................10
2.2 SEGMENTING DISKS ................................................................................................................................10
2.3 RAID LEVELS...............................................................................................................................................11
2.3.1 DISK STRIPING (RAID 0).............................................................................................................................................................11
2.3.2 DISK MIRRORING (RAID 1) ........................................................................................................................................................12
2.3.3 DISK MIRRORING AND STRIPING (RAID 10) ..........................................................................................................................12
2.3.4 PARITY RAID (RAID 5) .................................................................................................................................................................13
2.3.5 CONCATENATION ......................................................................................................................................................................13
2.3.6 SINGLE DRIVE / SEGMENT........................................................................................................................................................14
RAID VOLUME STATUS ............................................................................................................................14
2.4
3 INSTALLATION..........................................................................................................15
3.1 COMPONENTS............................................................................................................................................15
3.2 INSTALLING HARDWARE ........................................................................................................................15
3.3 INSTALLING ON WINDOWS 2000...........................................................................................................15
3.3.1 INSTALLING SATA RAID HOST BUS ADAPTER .....................................................................................................................15
3
Page 4

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
3.3.2
INSTALLING SATARAID5 UTILITY ............................................................................................................................................21
3.3.3 DISK DRIVE MODE SETUP.........................................................................................................................................................25
3.3.4 ALLOCATING PARTITION ..........................................................................................................................................................25
3.4 INSTALLING ON WINDOWS XP (32/64-BIT).........................................................................................32
3.4.1 INSTALLING SATA RAID HOST BUS ADAPTER .....................................................................................................................32
3.4.2 INSTALLING SATARAID5 UTILITY ............................................................................................................................................35
3.4.3 DISK DRIVE MODE SETUP.........................................................................................................................................................39
3.4.4 ALLOCATING PARTITIONS ON WINDOWS XP 32-BIT..........................................................................................................39
3.4.5 ALLOCATING PARTITIONS ON WINDOWS XP 64-BIT..........................................................................................................46
3.5 INSTALLING ON WINDOWS SERVER 2003 (32/64-BIT) ....................................................................55
3.5.1 INSTALLING SATA RAID HOST BUS ADAPTER .....................................................................................................................55
3.5.2 INSTALLING SATARAID5 UTILITY ............................................................................................................................................58
3.5.3 DISK DRIVE MODE SETUP.........................................................................................................................................................62
3.5.4 ALLOCATING PARTITIONS........................................................................................................................................................62
3.6 INSTALLING ON WINDOWS VISTA (32/64-BIT)...................................................................................71
3.6.1 INSTALLING SATA RAID HOST BUS ADAPTER .....................................................................................................................71
3.6.2 INSTALLING SATARAID5 UTILITY ............................................................................................................................................73
3.6.3 DISK DRIVE MODE SETUP.........................................................................................................................................................77
3.6.4 ALLOCATING PARTITIONS........................................................................................................................................................77
4 SATA RAID5 ARRAY MANAGER ..........................................................................84
4.1 OVERVIEW ...................................................................................................................................................84
4.2 CREATING RAID GROUPS.......................................................................................................................85
4.2.1 CONTIGUOUS RAID GROUPS ..................................................................................................................................................85
4.2.2 CONCATENATED RAID GROUPS............................................................................................................................................. 86
4.2.3 STRIPED RAID GROUPS ............................................................................................................................................................86
4.2.4 MIRRORED RAID GROUPS .......................................................................................................................................................87
4.2.5 MIRRORED STRIPED RAID GROUPS ......................................................................................................................................87
4.2.6 PARITY RAID GROUPS...............................................................................................................................................................88
4.2.7 RAID GROUPS OVERVIEW ........................................................................................................................................................89
4.3 ADDITIONAL MENU COMMANDS .........................................................................................................91
4.3.1 CONFIGURATION........................................................................................................................................................................92
4.3.2 EXIT................................................................................................................................................................................................97
4.3.3 CREATE SPARE ...........................................................................................................................................................................98
4.3.4 DELETE SPARE............................................................................................................................................................................98
4.3.5 DELETE MEMBER .......................................................................................................................................................................99
4.3.6 DELETE ORPHAN........................................................................................................................................................................99
4
Page 5

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
4.3.7
MAKE PASS-THRU ...................................................................................................................................................................100
4.3.8 DEVICE SUMMARY...................................................................................................................................................................100
4.3.9 CREATE RAID GROUP..............................................................................................................................................................101
4.3.10 REBUILD RAID GROUP .........................................................................................................................................................102
4.3.11 DELETE RAID GROUP............................................................................................................................................................103
4.3.12 BRING RAID GROUP ONLINE............................................................................................................................................... 103
4.3.13 RAID GROUP SUMMARY ......................................................................................................................................................103
4.3.14 TASK MANAGER.....................................................................................................................................................................105
4.3.15 EVENT LOG..............................................................................................................................................................................108
4.3.16 RESOURCES ...........................................................................................................................................................................109
4.3.17 CREATE LEGACY RAID GROUP...........................................................................................................................................110
4.3.18 HELP TOPICS..........................................................................................................................................................................110
4.3.19 ABOUT......................................................................................................................................................................................110
5
Page 6

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
1 WELCOME
RSV-S4-X enhances your data storage by combining advanced RAID1 features typically seen
on high-end data systems with low cost/high capacity Serial ATA drives. By using industry
standard SATA drives and Silicon Image Host Bus Adapters, you can achieve extraordinarily
low costs while remaining assured that your data is protected against hardware failure.
1.1 PRECAUTION
Please read the safe precautions carefully before you using RSV-S4-X storage appliance.
Ensure that you use the product correctly according to the procedure described in this guide.
The following safety precautions are intended to remind you to operate the product safely and
correctly. Please read and ensure that you understand them before you proceed to the other
sections of this guide.
z Do not attempt to disassemble or alter any part of the product that is not describe in this
guide.
z Do not allow the product to come into contact with water or other liquids. In the event
that water or other liquids enter the interior, immediately unplug the product from the
computer. Continued use of the product may result in fire or electrical shock. Please
consult your product distributor or the closest support center.
z Do not handle the product near a heat source or expose them to direct flame or heat.
z Never place the product in close to equipment generating storage electromagnetic fields.
Exposure to strong magnetic fields may cause malfunctions or corrupt data.
z Can’t operate properly under Windows 3.x/ 95 / 98SE/ ME/ NT.
z Hard disk drive is not including.
1
RedundantArrayofIndependentDevices,amethodofcombiningdrivestoprovidebetterprotectionand/orperformance.
6
Page 7

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
1.2 FEATURES
1.2.1 DATA SECURITY
The RSV-S4-X software driver includes support for monitoring to predict suspect drives.
RSV-S4-X provides our highest commitment to data security through the use of RAID
architecture to back up and protect data. RAID levels 1, 10, and 5 provide data security. RSV-
S4-X supports sophisticated sparing support so that hardware failure risk can be minimized
by automatically regenerating the failed disk’s data on a backup disk. The RSV-S4-X software
2
driver includes support for Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology (S.M.A.R.T.
to predict disk failures. Drives can be moved between controllers without losing data.
1.2.2 DATA PERFORMANCE
)
The RSV-S4-X can also increase storage throughput by combining the throughput of multiple
drives into a single volume. RAID levels 1, 10, and 5 support this ability. Furthermore, each
volume can be tailored to provide the best performance for the data contained on that disk.
1.2.3 DATA VERSATILITY
The RSV-S4-X software driver also supports Contiguous and Concatenated drives for
applications which do not require increased security or performance.
1.3 EASE OF USE
The RSV-S4-X utility offers an easy to use utility for creating and managing your storage. It
also supports the latest SATA enhancements including SATA-II Port Multiplier support, and
up to 3Gbit/sec transfer rates on controllers that support that speed. Creating and deleting
volumes is also possible without requiring a restart of the operating system and rebuilds never
require the data to be taken off-line.
Drives can also be moved between controllers without losing the data.
2
SelfMonitoring,AnalysisandReportingTesting.
7
Page 8

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
1.4 SPECIFICATIONS
z A single eSATA host port to 4 SATA 3.5-inch hard disks, with tool-less screws & door
cover.
z Power and host status LED, and devices status and activity LED.
z Metal chassis (SECC) and plastic panel frame (ABS) design.
z 135 (W) x 180 (H) x 255 (D) mm, NW: 2.7 Kgs, GW: 3.1Kgs.
z Design based on the Silicon Image SiI3726 Port-Multiplier with SiI3132R5 PCI-Express
1X HBA.
z Support Striped (RAID 0), Mirrored (RAID 1), Mirrored Striped (RAID 10), Parity RAID
(RAID 5) modes, and hot spare on Mirrored (RAID 1) and Parity RAID (RAID 5) modes.
z Support Contiguous (Single Drive) & Concatenation (Combined Drives) modes.
z 150 watts, 100 & 240 Vac / 50~60Hz with FCC, CE requirement.
z Single packing (color box with handle) and 4 in 1 outer box.
1.5 SUPPORTED OPERATING SYSTEMS
The following operating systems are supported by the RSV-S4-X software driver.
z Windows 2000
z Windows XP, 32/64-bit
z Windows Server 2003, 32/64-bit
z Windows Vista, 32/64-bit
z Windows Server 2008, 32/64-bit
z Windows 7, 32/64-bit
8
Page 9

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
1.6 PRODUCT CONTENTS
The following parts are content.
z RSV-S4-X Port-Multiplier Box
z SiI3132R5 PCI-Express 1X HBA
z eSATA Cable
z AC Cable
z Tool-less Screw x 8
z Setup and Installation Driver Repository CD
9
Page 10
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
2 INTRODUCTION TO RAID
2.1 RAID VOLUMES
RAID technology allows one or more disks to be combined into a logical volume which
provides greater performance and/or protection than standard disk drives. These volumes,
also known as RAID Groups, appear like regular disk drives to the operating system and can
be partitioned, formatted and used just like any other normal disk. The complexity of the RAID
is hidden within the driver.
There are several different methods of combining disks, each with its own advantages and
disadvantages. Each method is referred to as a RAID “level” such as RAID 1, or RAID 5. The
details of each level are summarized below and detailed in the following sections.
RAID LEVEL CONFIGURED
AS
0 Striped Excellent performance, low cost No data protection
1 Mirrored Excellent data protection High cost
10 Mirrored Striped
5 Parity RAID
Combination Concatenated
Single Drive /
Segment
Contiguous Same as single disk Same as single disk
ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES
High performance, excellent
data protection.
Good data protection, good
value
Good performance, low cost,
large Volume size
High cost.
Some performance
degradation for writes.
No data protection
2.2 SEGMENTING DISKS
For increased versatility, the SATARAID5 software allows individual disks to be divided into
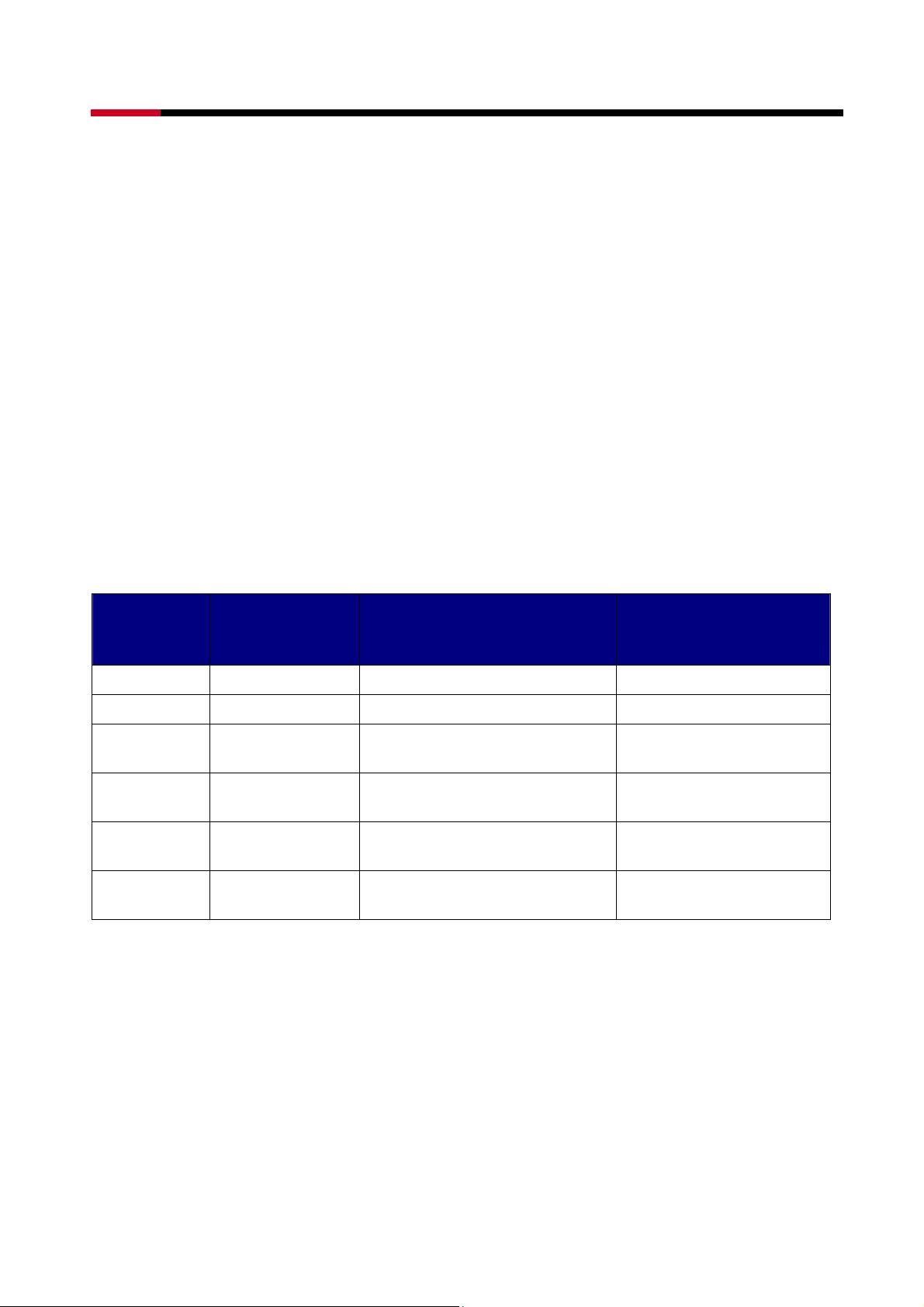
smaller segments which can then be combined into different volumes. As an example, if a
user has one set of data that must be protected at all costs, another set of data which should
be protected at reasonable cost and another set that doesn’t need any protection at all; the
user can divide three disks into sections as shown in Figure 1. The yellow regions define the
10
Page 11
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
high security volume, the greem section is the middle security volume and the light blue
shows the unprotected area.
Figure 1: Dividing Disks into Members
2.3 RAID LEVELS
2.3.1 DISK STRIPING (RAID 0)
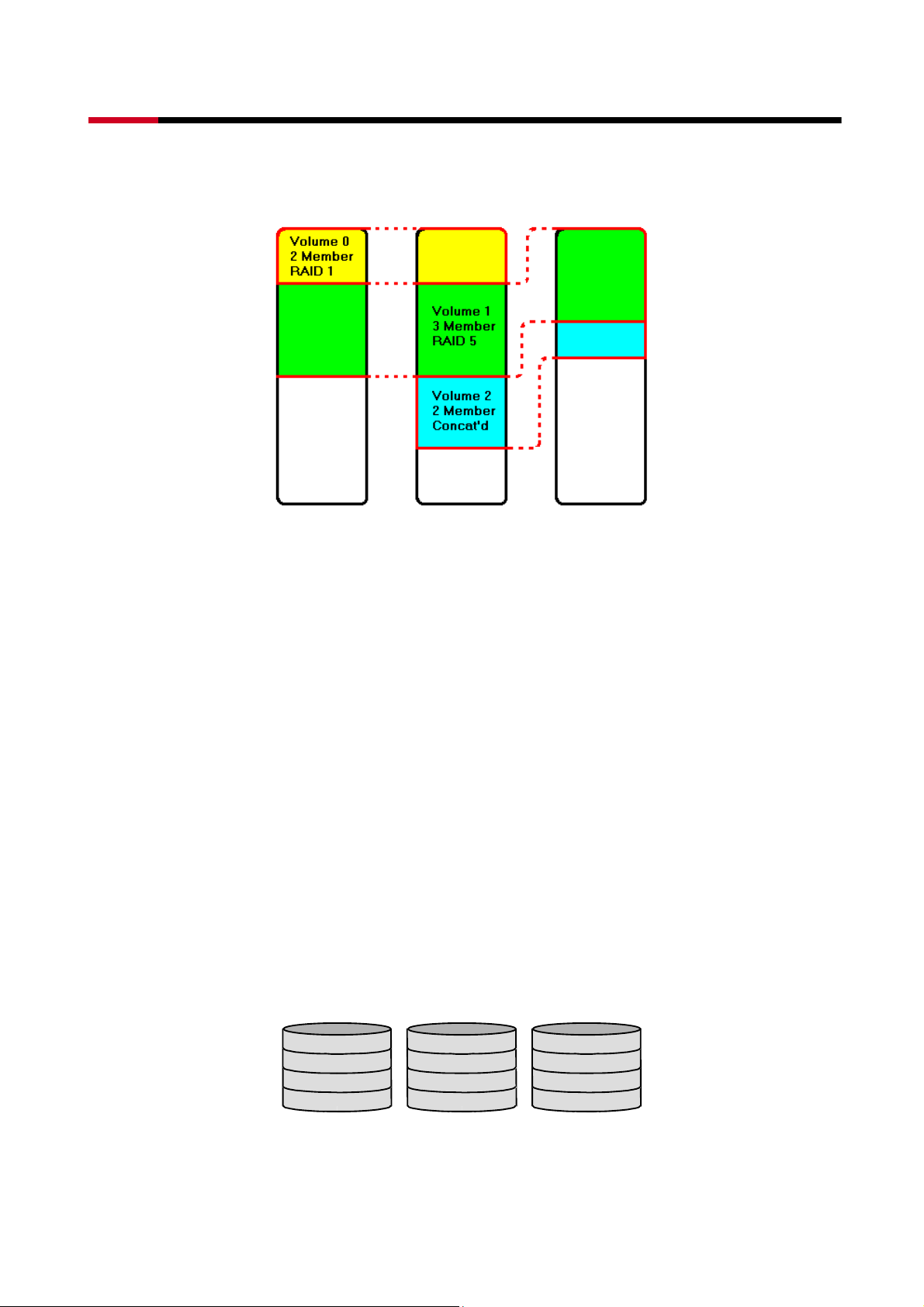
Striping is a performance-oriented, non-redundant data mapping technique. While Striping is
discussed as a RAID Group type, it is does not provide any fault tolerance. With modern
SATA and ATA bus mastering technology, multiple I/O operations can be performed in
parallel, enhancing data throughput. Striping arrays use multiple disks to form a larger virtual
disk. The figure below illustrates a three-disk stripe set. Stripe one is written to disk one,
stripe two to disk two, and so forth. RAID 0 sets can be comprised of two, three, or four
drives. If the sizes of the disk segments are different, the smallest disk segment will limit the
overall size of the RAID Group.
Stripe0
Stripe3
Stripe6
Stripe9
Stripe1
Stripe4
Stripe7
Stripe10
Stripe2
Stripe5
Stripe8
Stripe11
11
Page 12
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
0
oc
ock 3
0
oc
ock 3
2.3.2 DISK MIRRORING (RAID 1)
Disk mirroring creates an identical twin for a selected disk by having the data simultaneously
written to two disks. This redundancy provides instantaneous protection from a single disk
failure. If a read failure occurs on one drive, the system reads the data from the other drive.
RAID 1 sets are comprised of two drives, and a third drive can be allocated as a spare in case
one of the drives in the set fails. If the sizes of the disk segments are different, the smallest
disk segment will limit the overall size of the RAID Group.
Block
Block 1
k 2
Block
Block 1
k 2
Bl
Bl
Bl
Bl
2.3.3 DISK MIRRORING AND STRIPING (RAID 10)
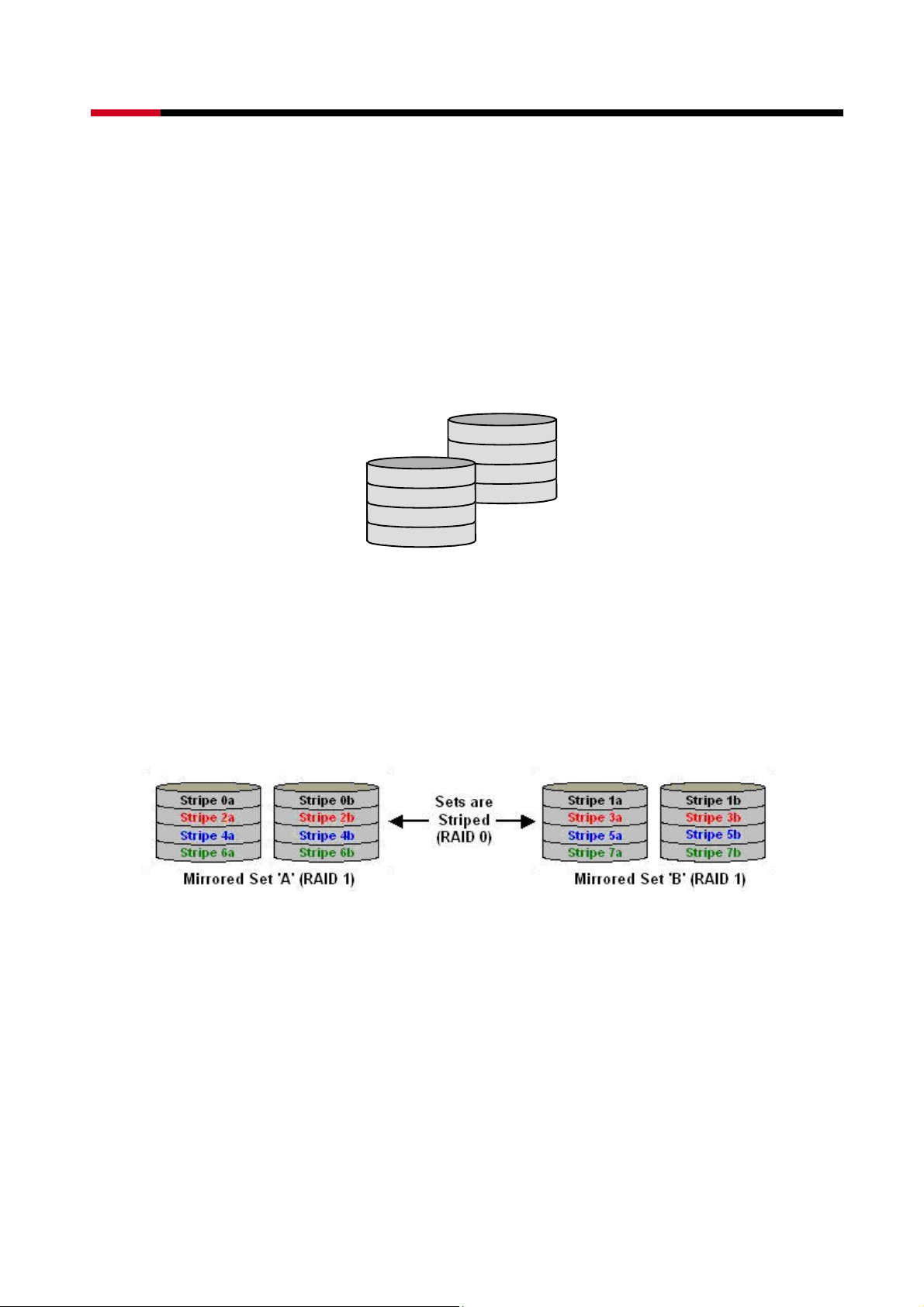
RAID 10 combines the features of both RAID 0 and RAID 1. Performance is provided through
the use of Striping (RAID 0), while adding the fault tolerance of Mirroring (RAID 1). The
implementation of RAID 10 requires four drives. The drives are assigned as two sets of striped
pairs.
The data is written to RAID Group A, which is mirrored (RAID 1) and provides data
redundancy. Alternating blocks of data are then striped across another RAID 1 mirrored set,
shown as Set B in the figure above. This provides improved speed.
Under certain circumstances, a RAID 10 set can sustain multiple simultaneous drive failures.
12
Page 13
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
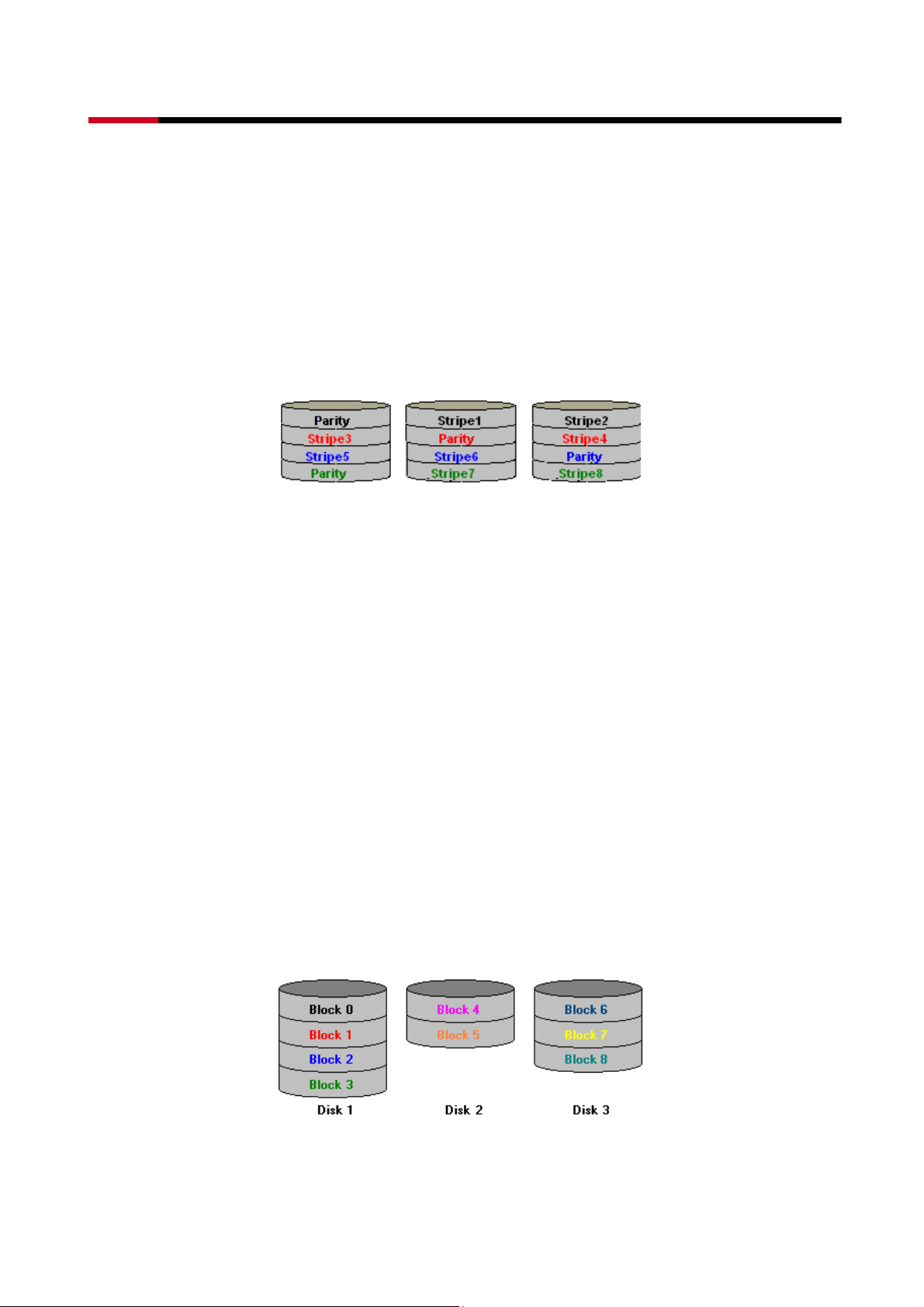
2.3.4 PARITY RAID (RAID 5)
Parity or RAID 5 adds fault tolerance to Disk Striping by including parity information with the
data. Parity RAID dedicates the equivalent of one disk for storing parity stripes. The data and
parity information is arranged on the disk array so that parity is written to different disks.
There are at least 3 members to a Parity RAID set. The following example illustrates how the
parity is rotated from disk to disk. The following example illustrates how the parity is rotated
from disk to disk.
Parity RAID uses less capacity for protection and is the preferred method to reduce the cost
per megabyte for larger installations. Mirroring requires 100% increase in capacity to protect
the data whereas the above example using three hard drives only requires a 50% increase.
The additional required capacity decreases as the number of disks in the group increases (i.e.,
33% for four drives or 25% for five drives).
In exchange for low overhead necessary to implement protection, Parity RAID degrades
performance for all write operations. The parity calculations for Parity RAID may result in write
performance that is somewhat slower than the write performance to a single disk.
2.3.5 CONCATENATION
The Concatenated mode combines multiple disks or segments of disks into a single large
volume. It does not provide any data protection or performance improvement but can be
useful for utilizing leftover space on disks. Concatenation allows the segments that make up
the volume to be of different sizes.
13
Page 14
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
2.3.6 SINGLE DRIVE / SEGMENT
The single drive is a virtual disk that can either be an entire disk drive or a segment of a single
disk drive. Single drive is the “Contiguous” configuration option when creating RAID Groups
(or sets) in the SATARAID5 software.
2.4 RAID VOLUME STATUS
A RAID volume can be in any one of the following statuses.
STATUS MEANING
Good All disks are currently functioning as normal.
For RAID levels that provide data protection, one or more disks have
Reduced
Rebuilding
Resynchronizing
Failed
failed but the data is still available via the RAID algorithms. The failed
disk should be replaced as soon as possible to avoid loss of data.
A failed disk drive has been replaced and the data is being regenerated
on the replacement disk. When complete, the RAID Group will return to
Good status.
An error has occurred and RAID algorithms be regenerated on this
RAID Group. When complete, the RAID Group will return to Good
status.
One or more disks have failed and RAID algorithms can no longer
regenerate the data. The minimum number of failures required to reach
this state depends on the RAID level:
z RAID 0, Concatenated, Contiguous: Single disk failure.
z RAID 1, 10, and 5: Two disk failure.
14
Page 15

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
3 INSTALLATION
3.1 COMPONENTS
There are three separate steps that must be install or setup for RSV-S4-X to function. These
components are the HARDWARE, SATA RAID5 HBA DRIVER, and SATARAID5 Utility. The
steps on how to setup these packages is described in the following sections.
3.2 INSTALLING HARDWARE
Follow the descriptions below, and step by step to complete the installation.
z Turn off your host computer.
z Install the SiI3132 PCI-Express 1X SATA RAID5 HBA into a PCI-Express slot (1X ~ 16X),
than connect one end of the eSATA cable to the eSATA connector on the Sil3132 PCI-
Express 1X SATA RAID5 HBA.
z Connect the other end to the eSATA connecter on RSV-S4-X.
z If hard disk drives are not installed in RSV-S4-X, insert the drives most of the way into
bay 1 to 4 in order (from the bottom to top); gently insert the drive until the drive is fully
inserted, and twist the tool-less screw shut to seat the drive securely.
z Switch the VAC to the correct position (For example, 115 for Japan, and 230 for UK)
attach one end of the AC power cord to RSV-S4-X and the other end to the proper AC
receptacle.
z Turn on RSV-S4-X, than turn on the host computer.
3.3 INSTALLING ON WINDOWS 2000
3.3.1 INSTALLING SATA RAID HOST BUS ADAPTER
Follow the descriptions below, and step by step to complete the setup.
15
Page 16
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
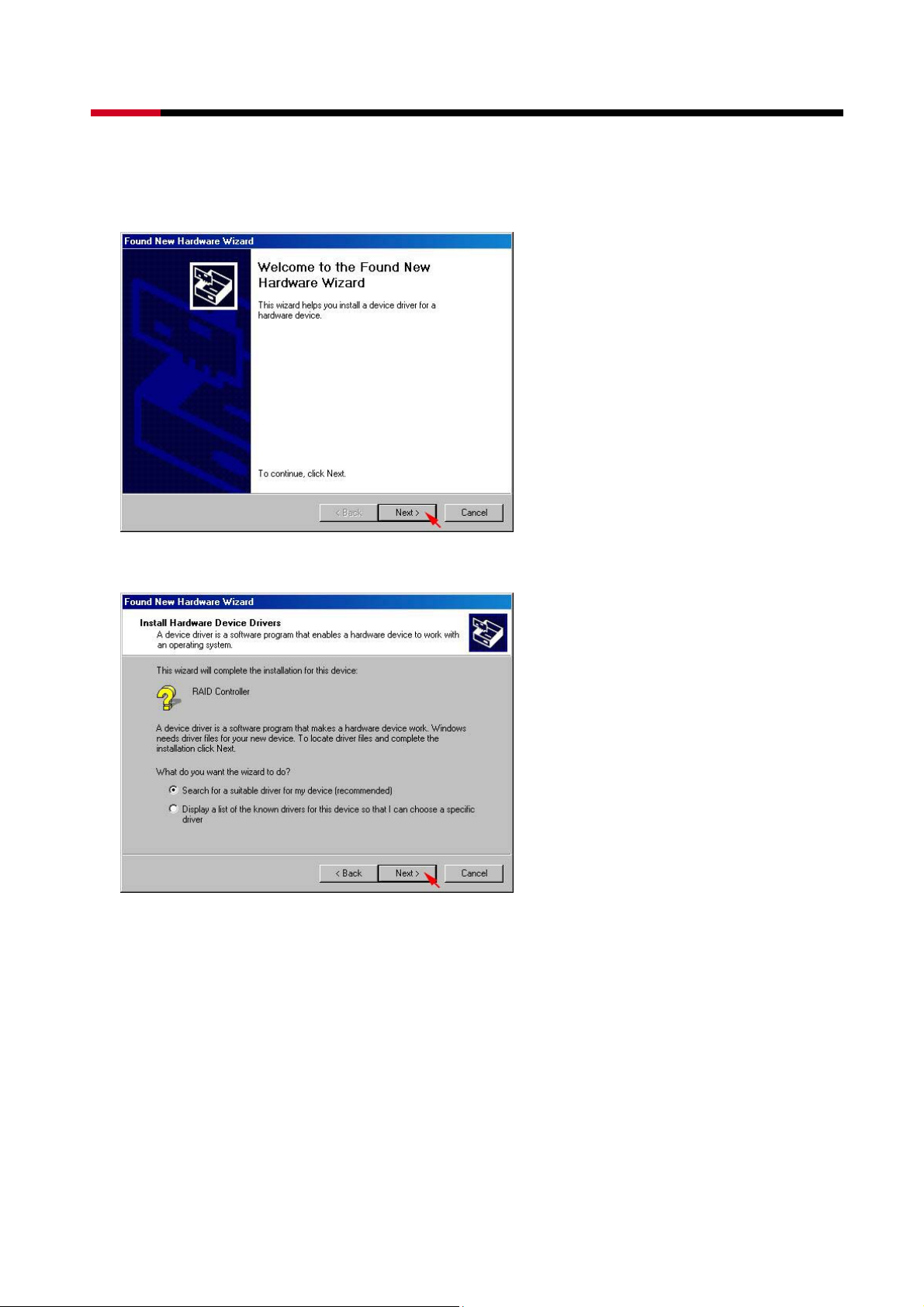
z Insert the Setup and Installation Repository CD in the CD-ROM drive.
z When start the Windows O/S, new hardware will be found, click Next>.
z Select Search for a suitable driver for my device (recommended), than click Next>.
z Select Specify a location, than click Next>.
16
Page 17
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
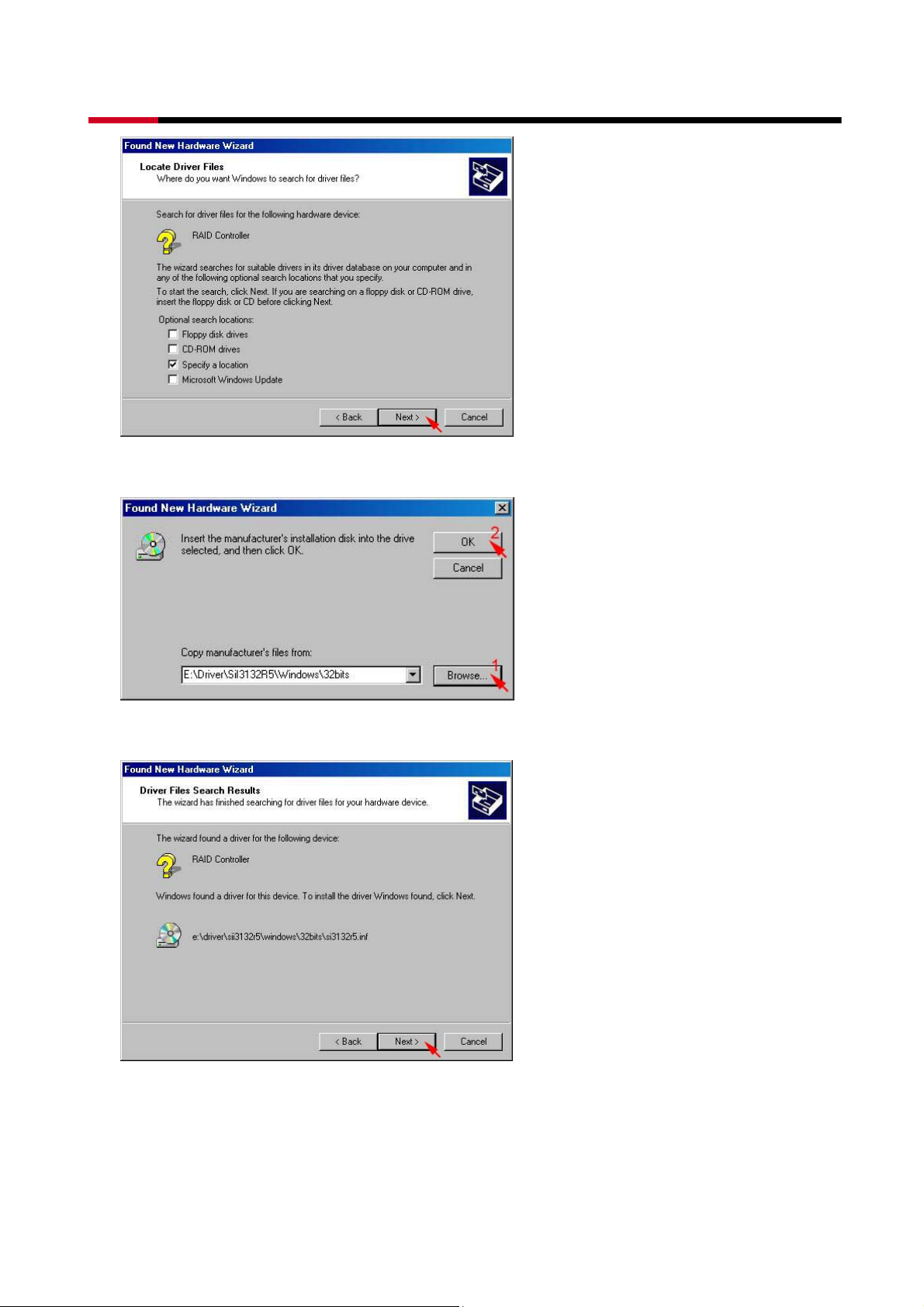
z Click Browse… to select to driver path, than click OK.
z Click Next> to install the Silicon Image Sil3132 SoftRaid 5 Controller driver.
z Click Yes to pass the Microsoft digital signature and continue the installation.
17
Page 18
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
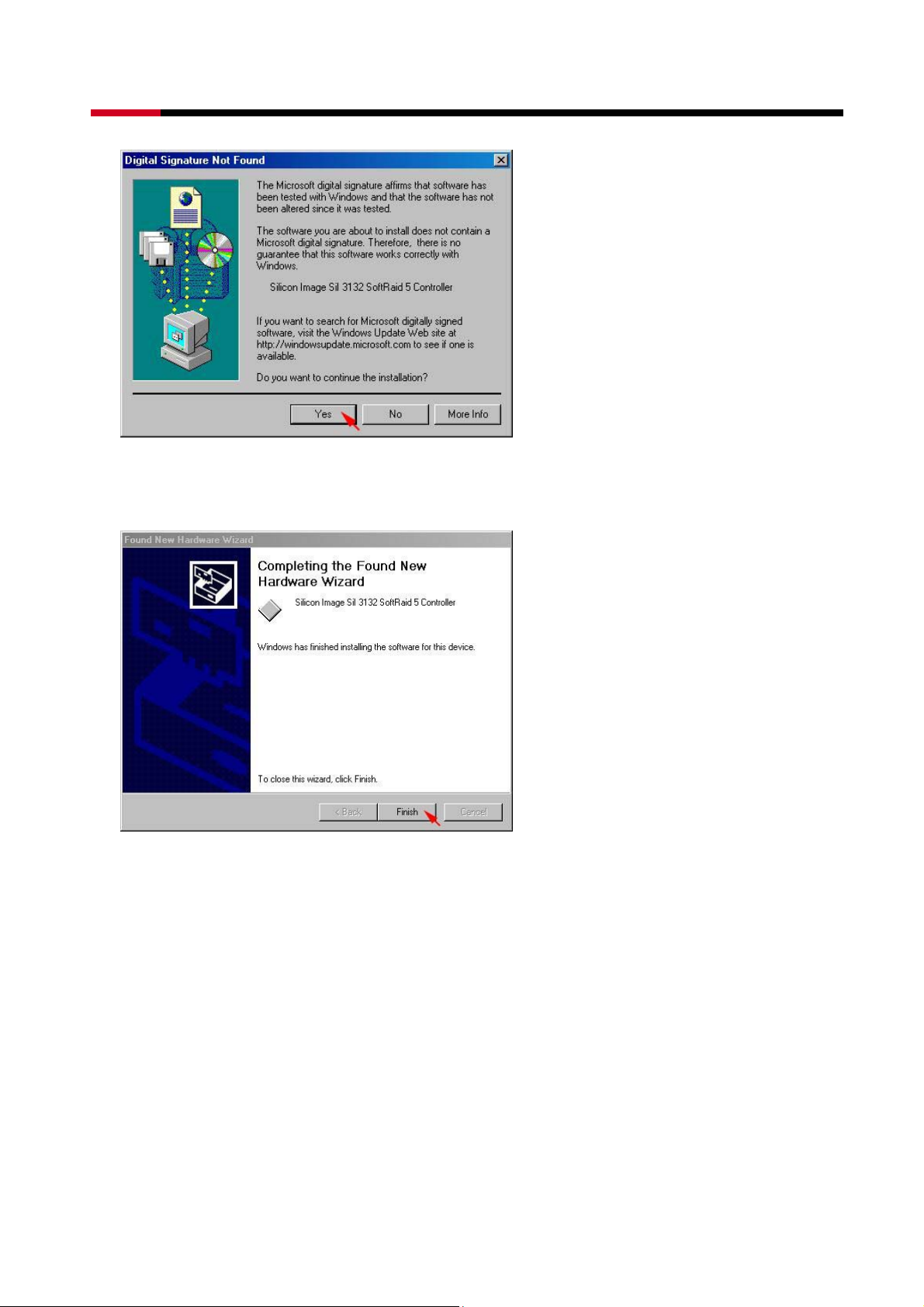
z When the Silicon Image Sil3132 SoftRaid 5 Controller installation has completed, click
Finish, and begin to the Silicon Image’s Pseudo Processor Device driver installation.
z Windows will find the Silicon Image’s Pseudo Processor Device hardware, click Next>.
18
Page 19
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
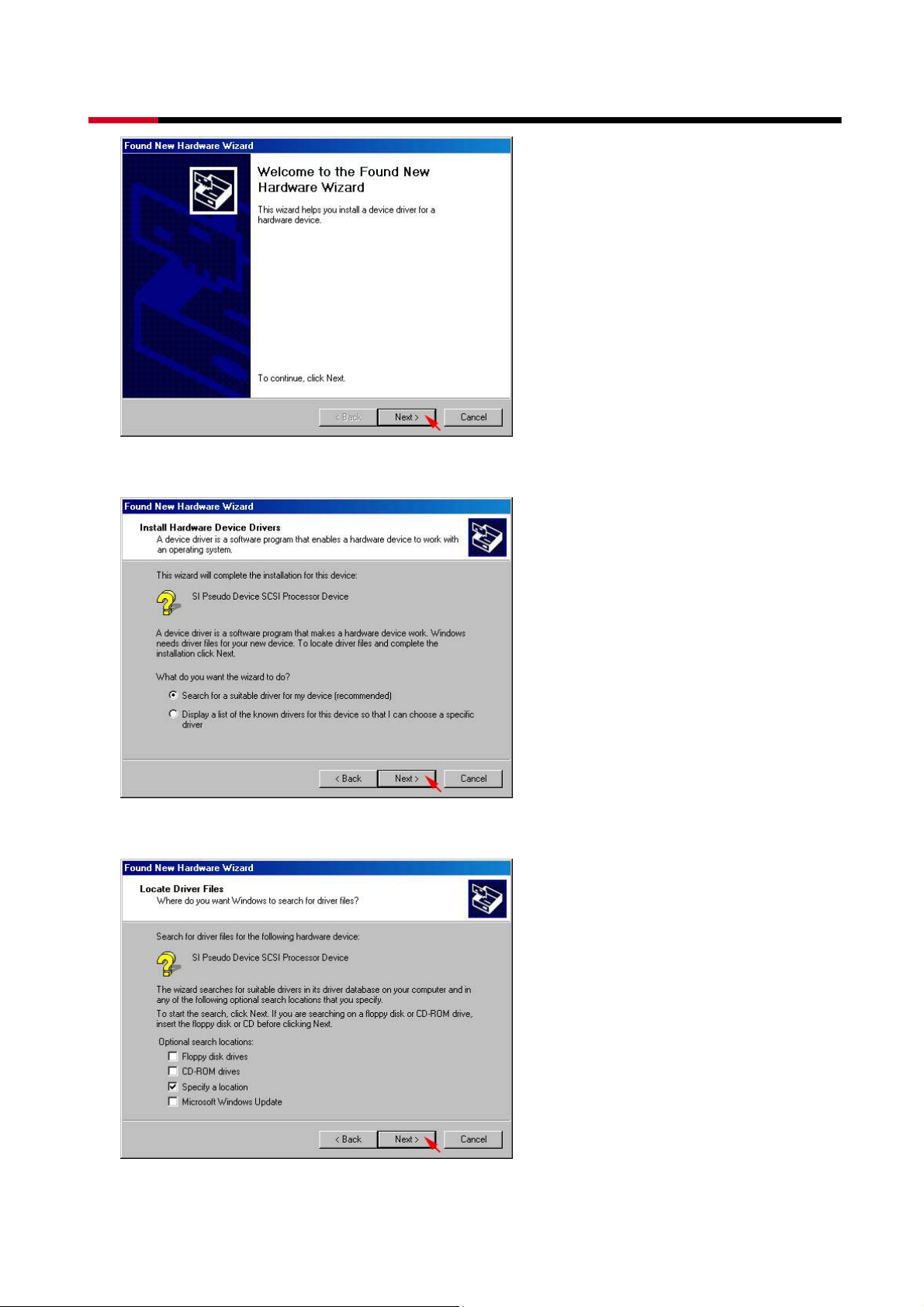
z Select Search for a suitable driver for my device (recommended), than click Next>.
z Select Specify a location, than click Next>.
19
Page 20
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
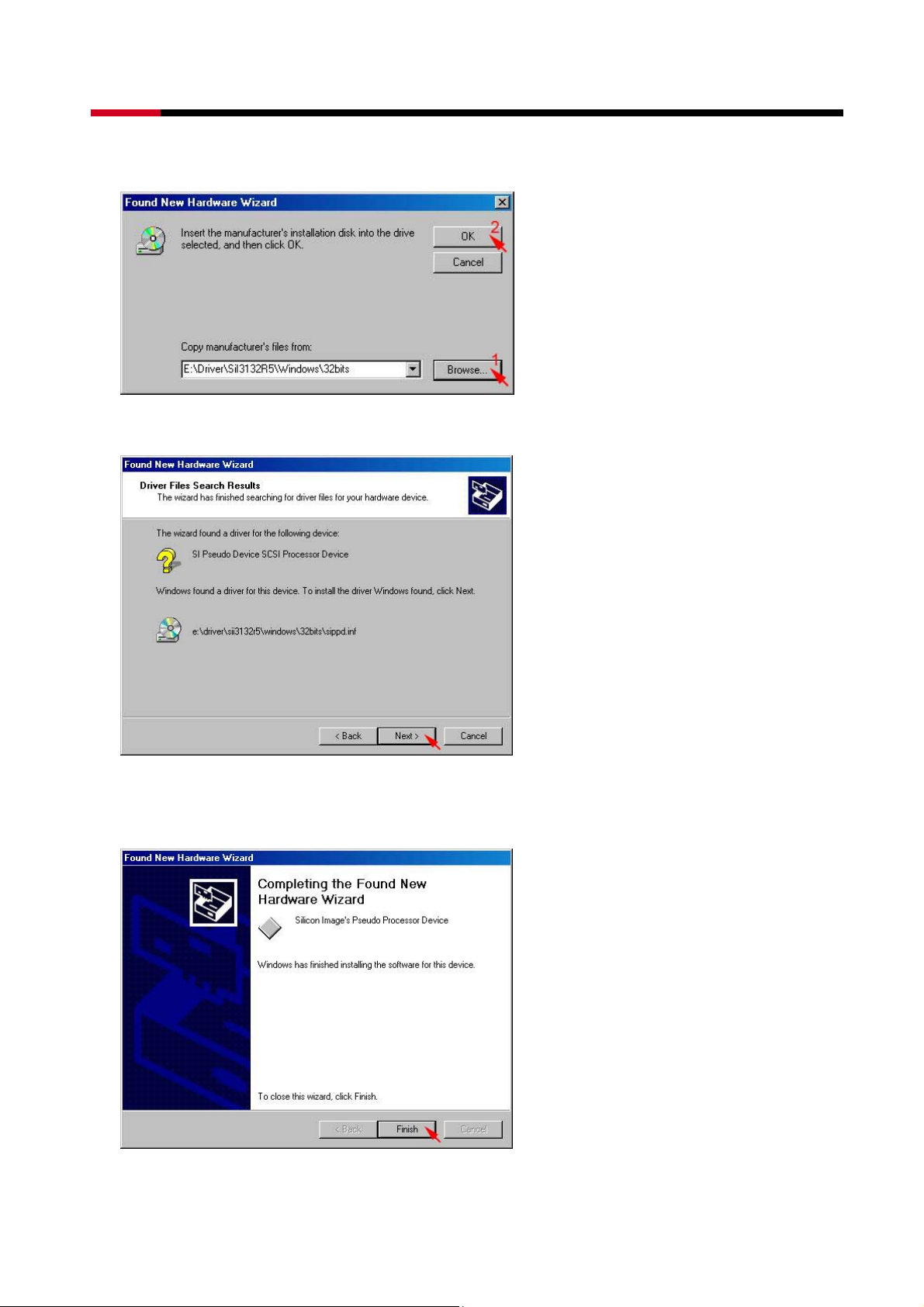
z Click Browse… to select to driver path, than click OK.
z Click Next> to install the Silicon Image’s Pseudo Processor Device driver.
z When the Silicon Image’s Pseudo Processor Device installation has completed, click
Finish.
20
Page 21
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
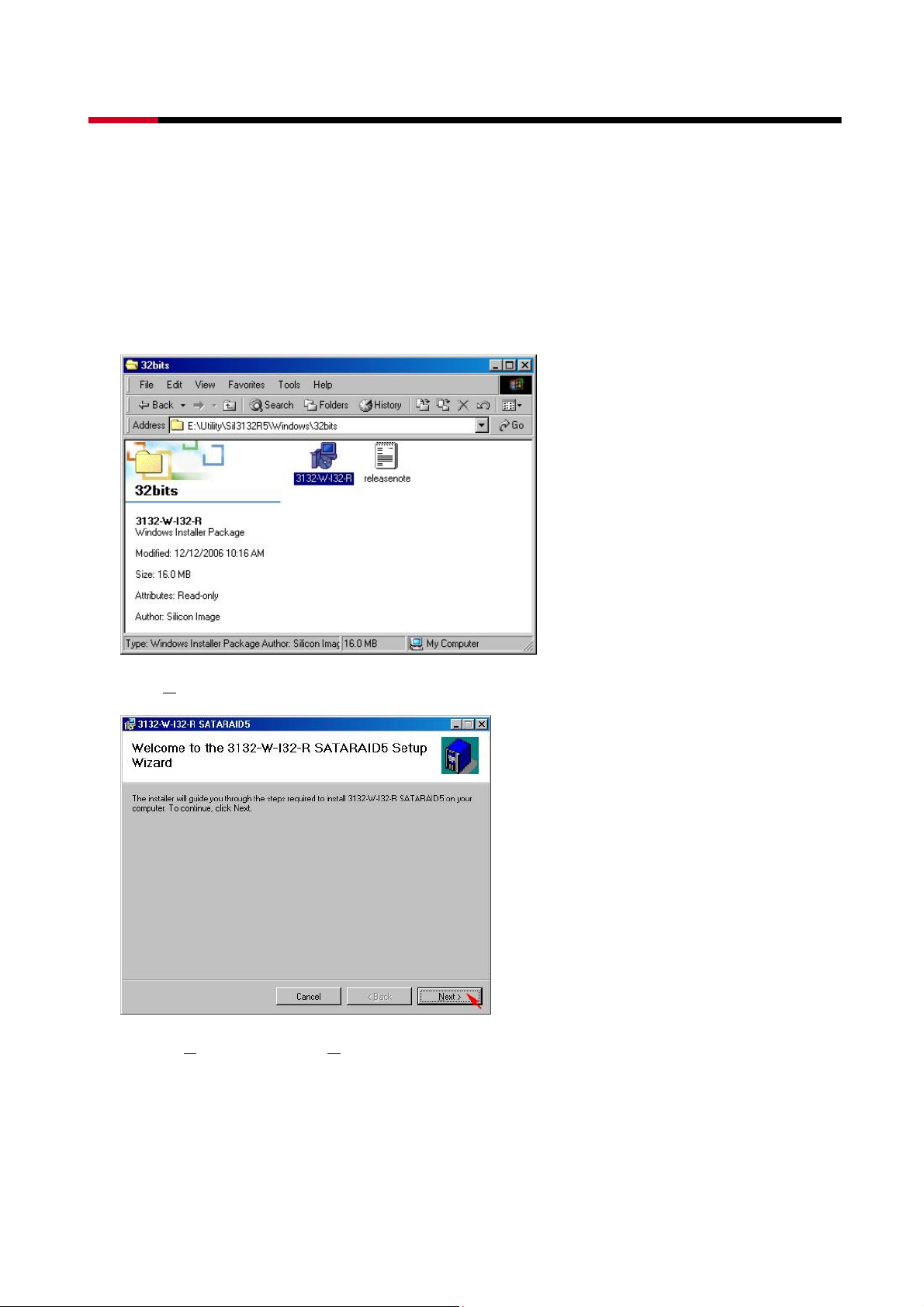
3.3.2 INSTALLING SATARAID5 UTILITY
Follow the descriptions below, and step by step to complete the installation.
z Open the Setup and Installation Repository CD and select the SATARAID5 Array
Manager software from the Utility folder.
z Double-click the 3132-W-I32-R.exe file.
z Click N
ext> to begin setup.
z Select I A
gree, than click Next>.
21
Page 22
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
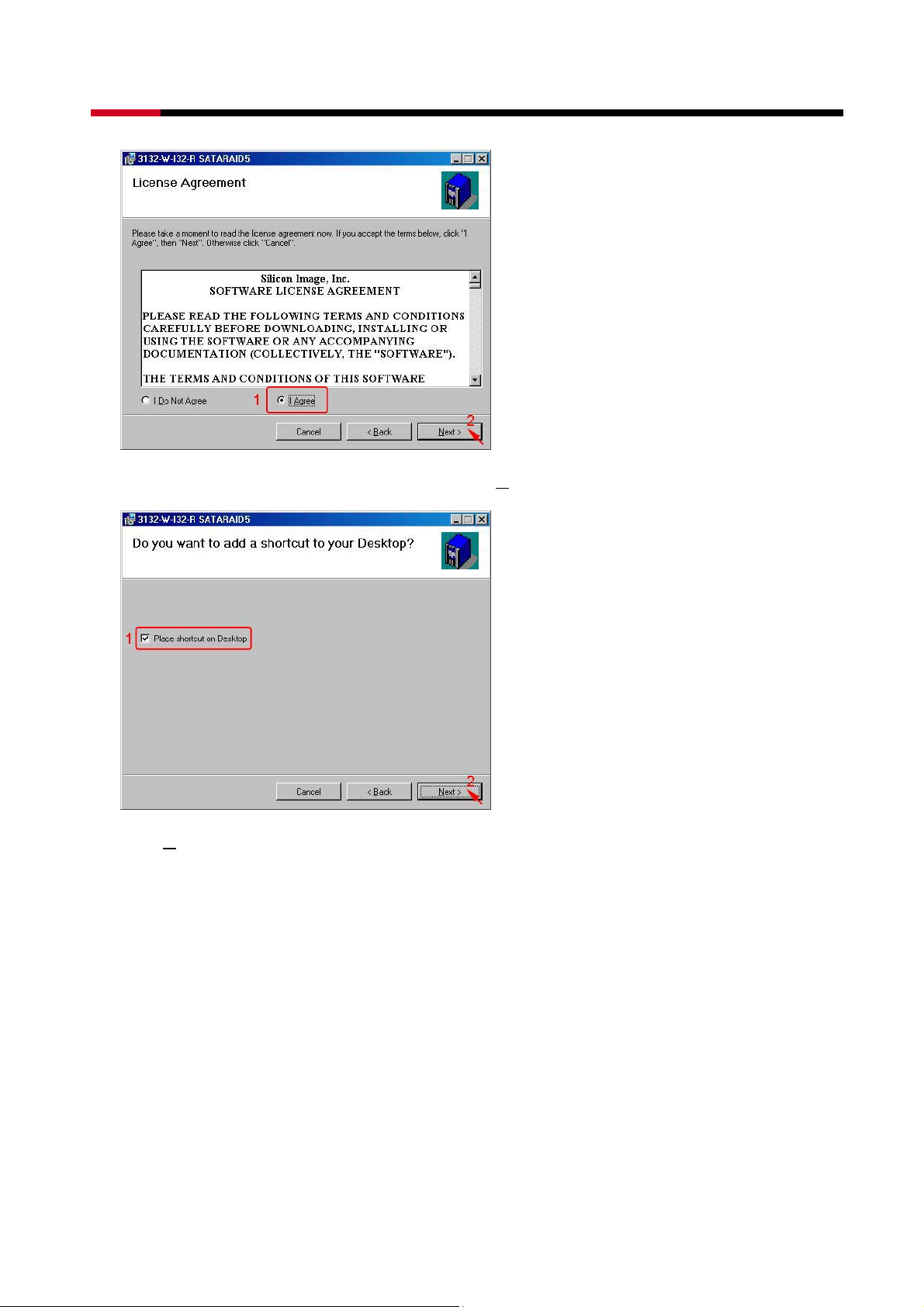
z Select Place shortcut on Desktop, than click N
z Click N
ext> to use the default installation folder.
ext> to create a shortcut on the desktop.
22
Page 23
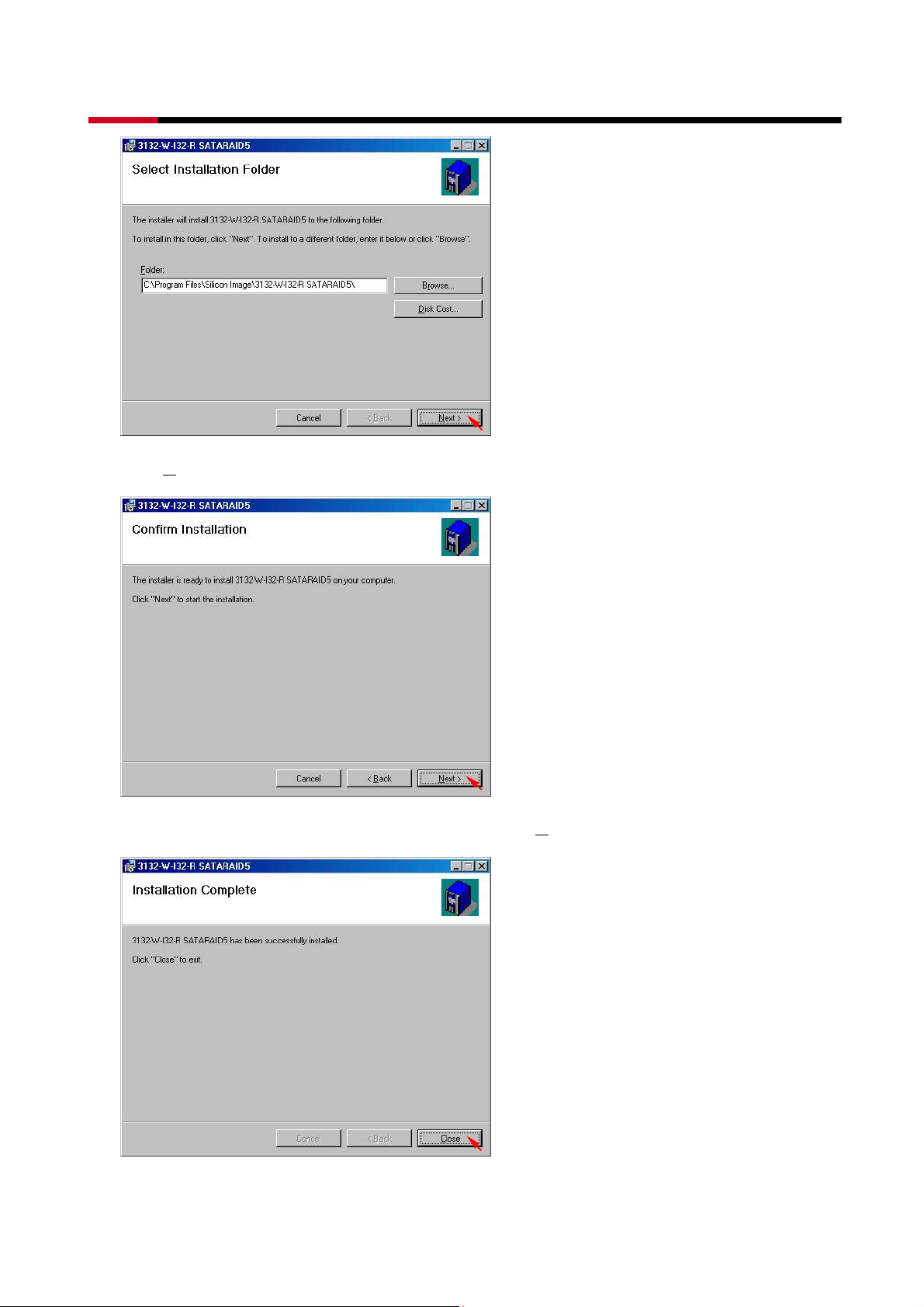
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Click N
ext> to begin the installation.
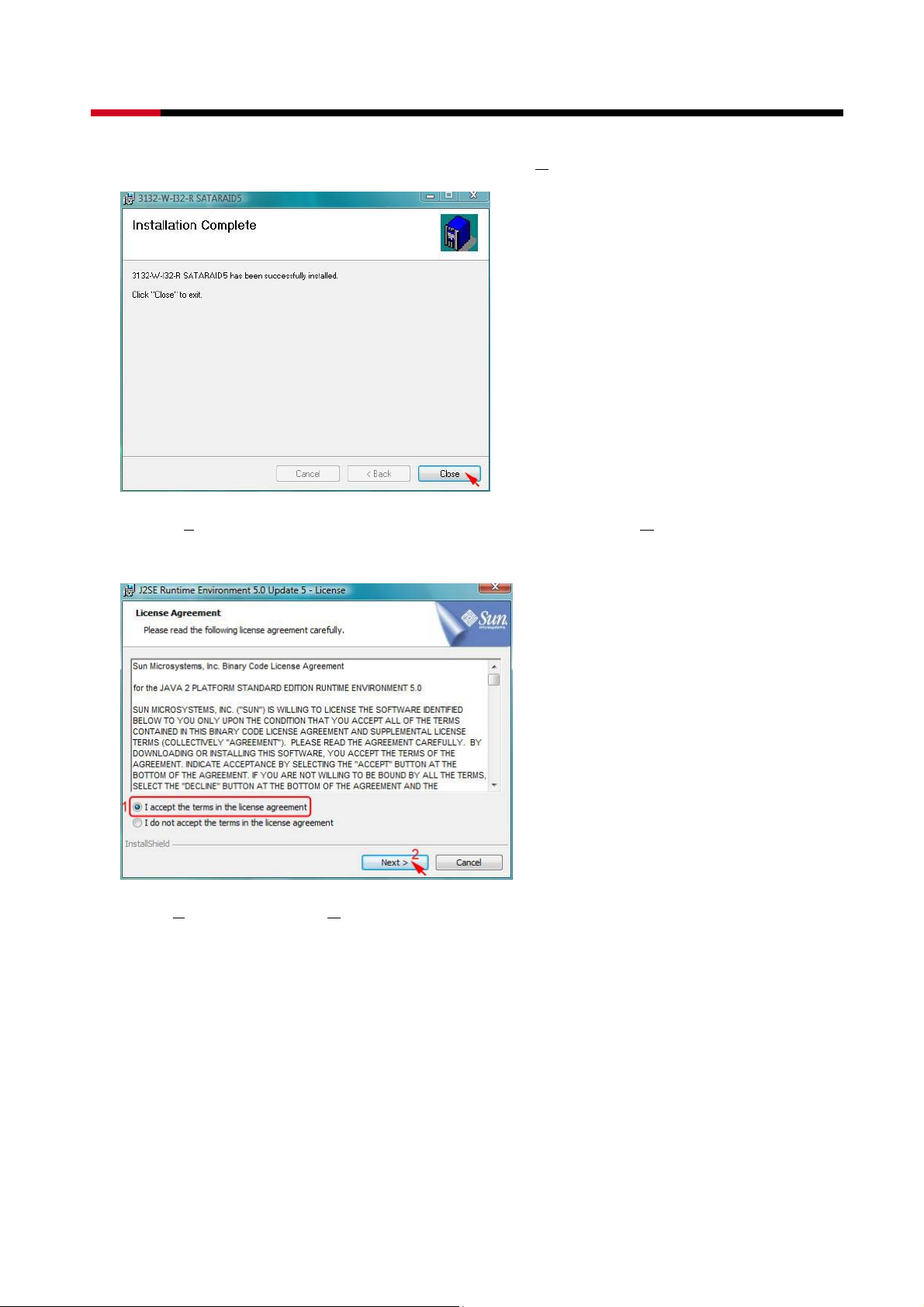
z When SATARAID5 installation has completed, click C
lose to exit.
23
Page 24
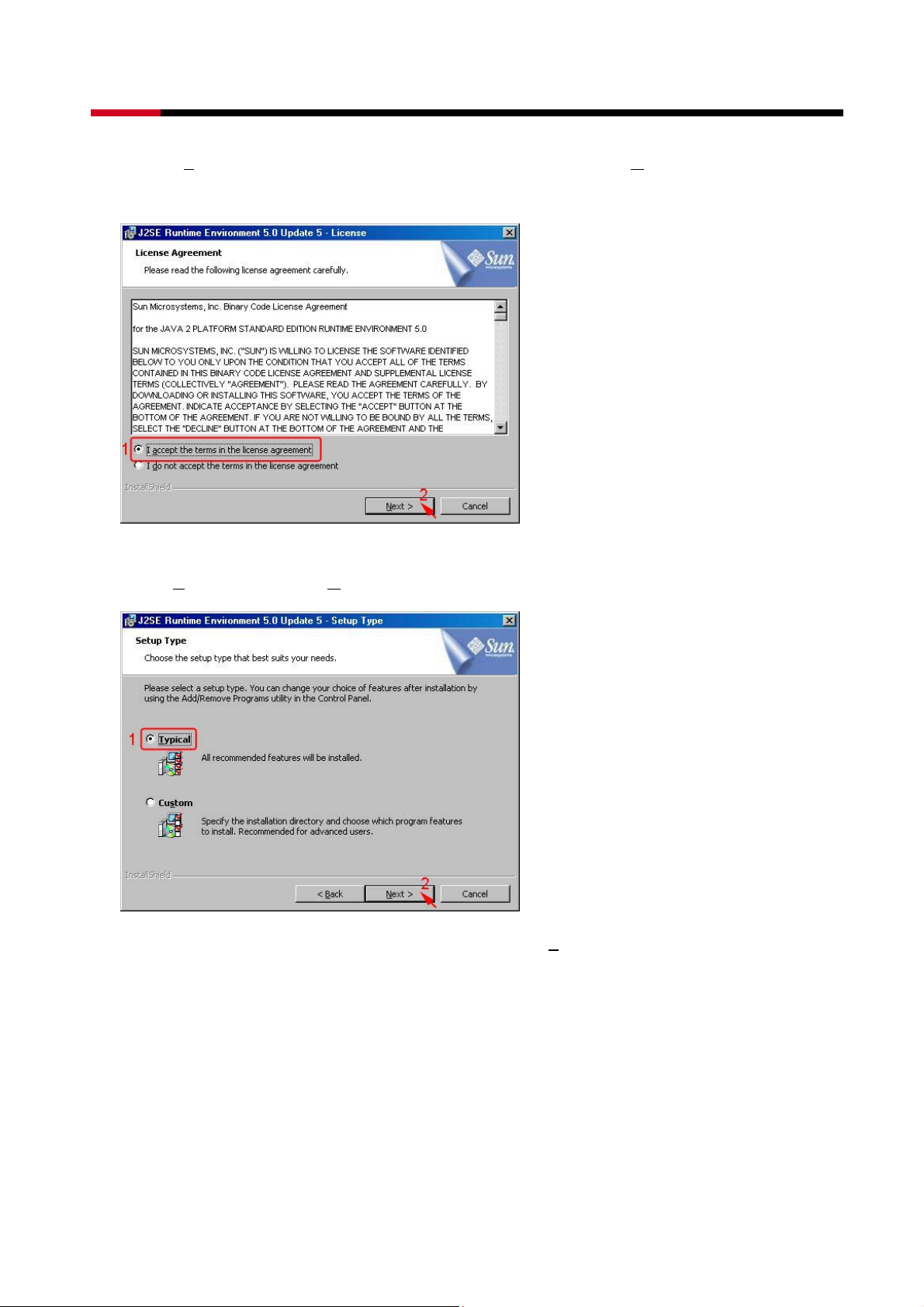
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select I agree the terms in the license agreement, than click Next> to begin the Java
platform installation.
z Select Typical, than click Next>.
z When Java platform installation has completed, click F
inish to exit.
24
Page 25
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select Start > Programs > Silicon Image > SATARaid5Manager to start the Array
Manager software.
3.3.3 DISK DRIVE MODE SETUP
Please refer to the chapter 4.
3.3.4 ALLOCATING PARTITION
Before creating any partitions, RAID groups must first be created using the
SATARaid5Manager utility. Once the sets have been created, allow the system to load
Windows.
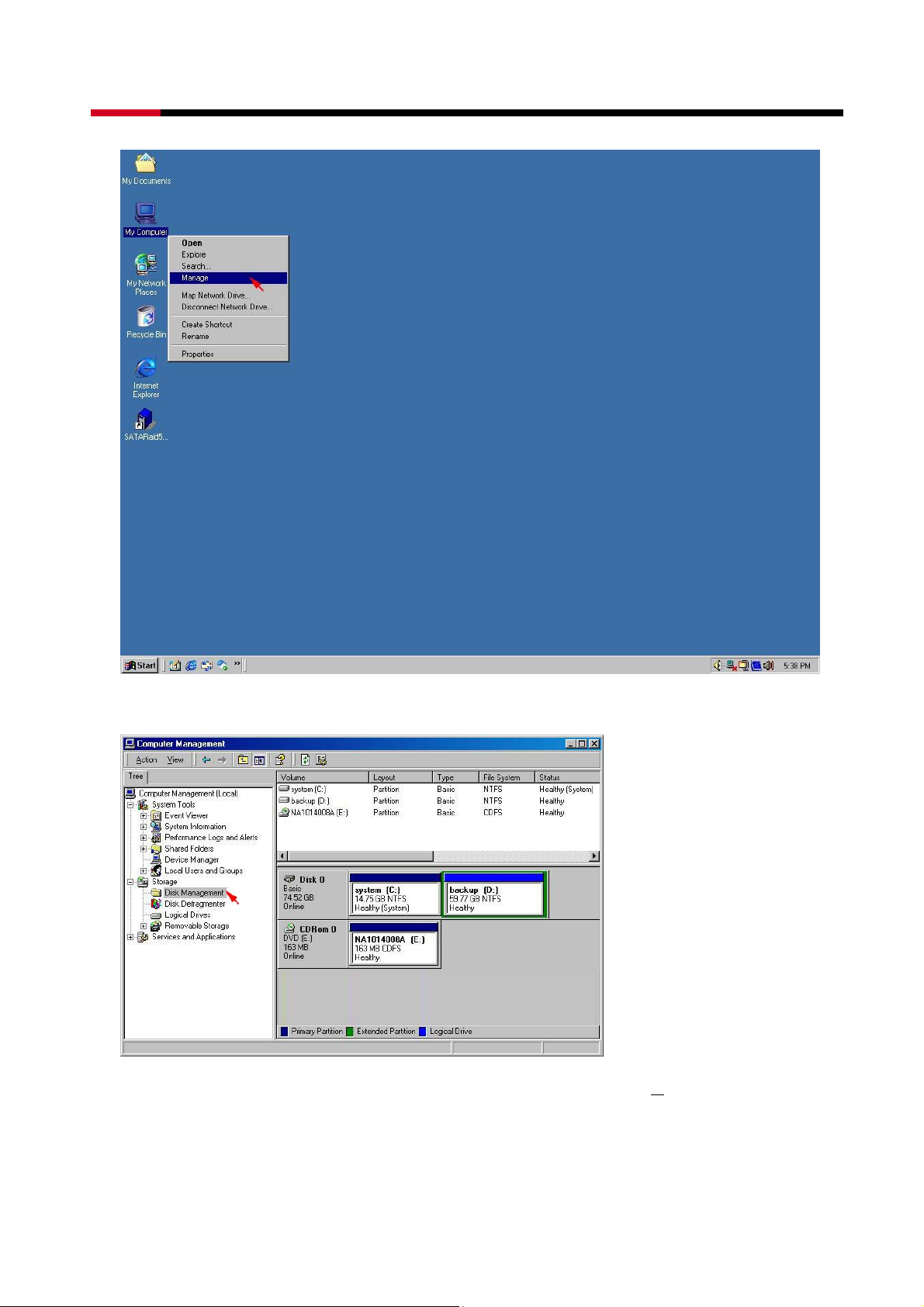
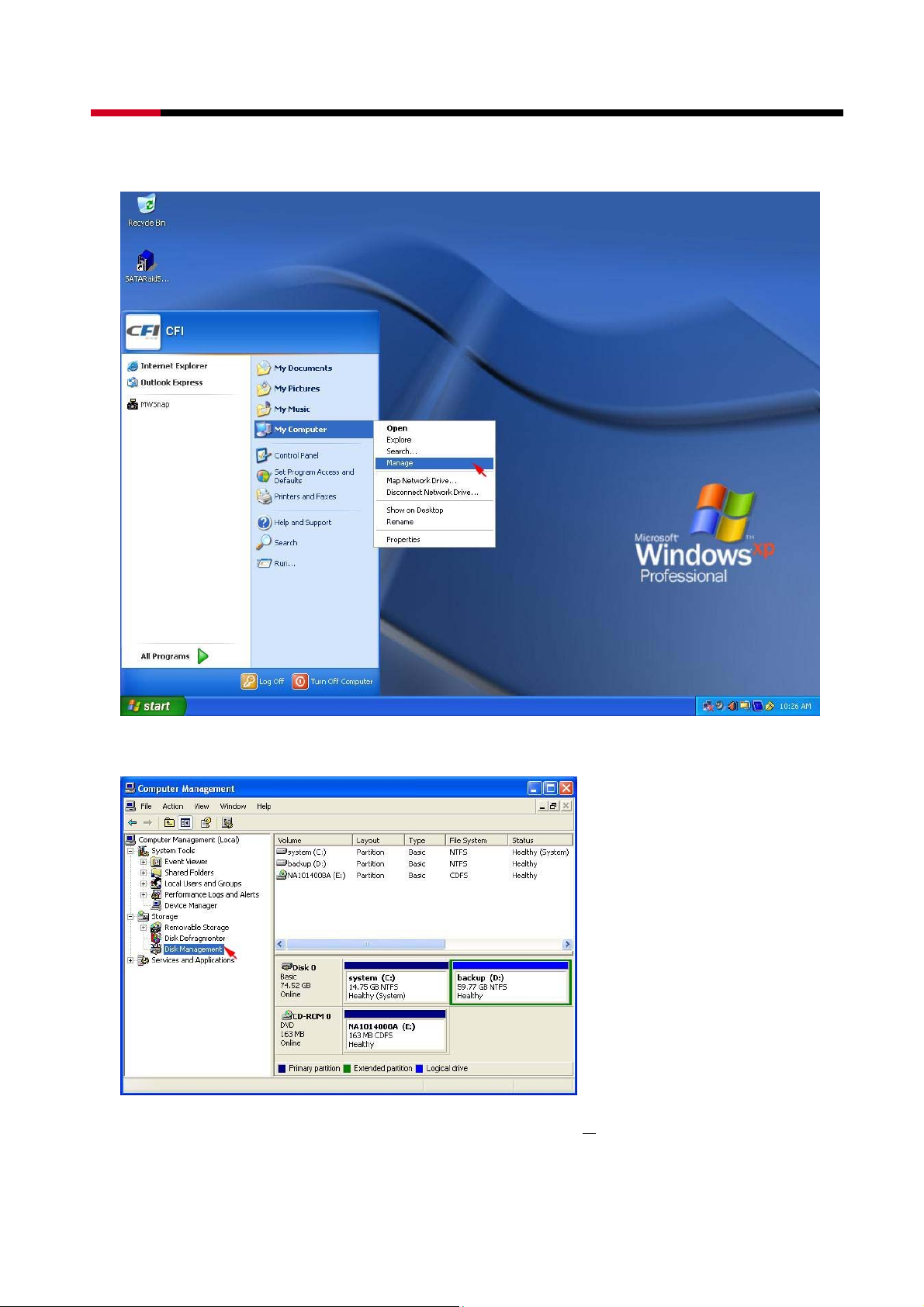
z Right-click on My Computer icon and select Manage from the pop-up menu.
25
Page 26
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select Disk Management under Storage to view the disk drives.
z When Write Signature and Upgrade Disk Wizard appears, click N
ext>.
26
Page 27
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
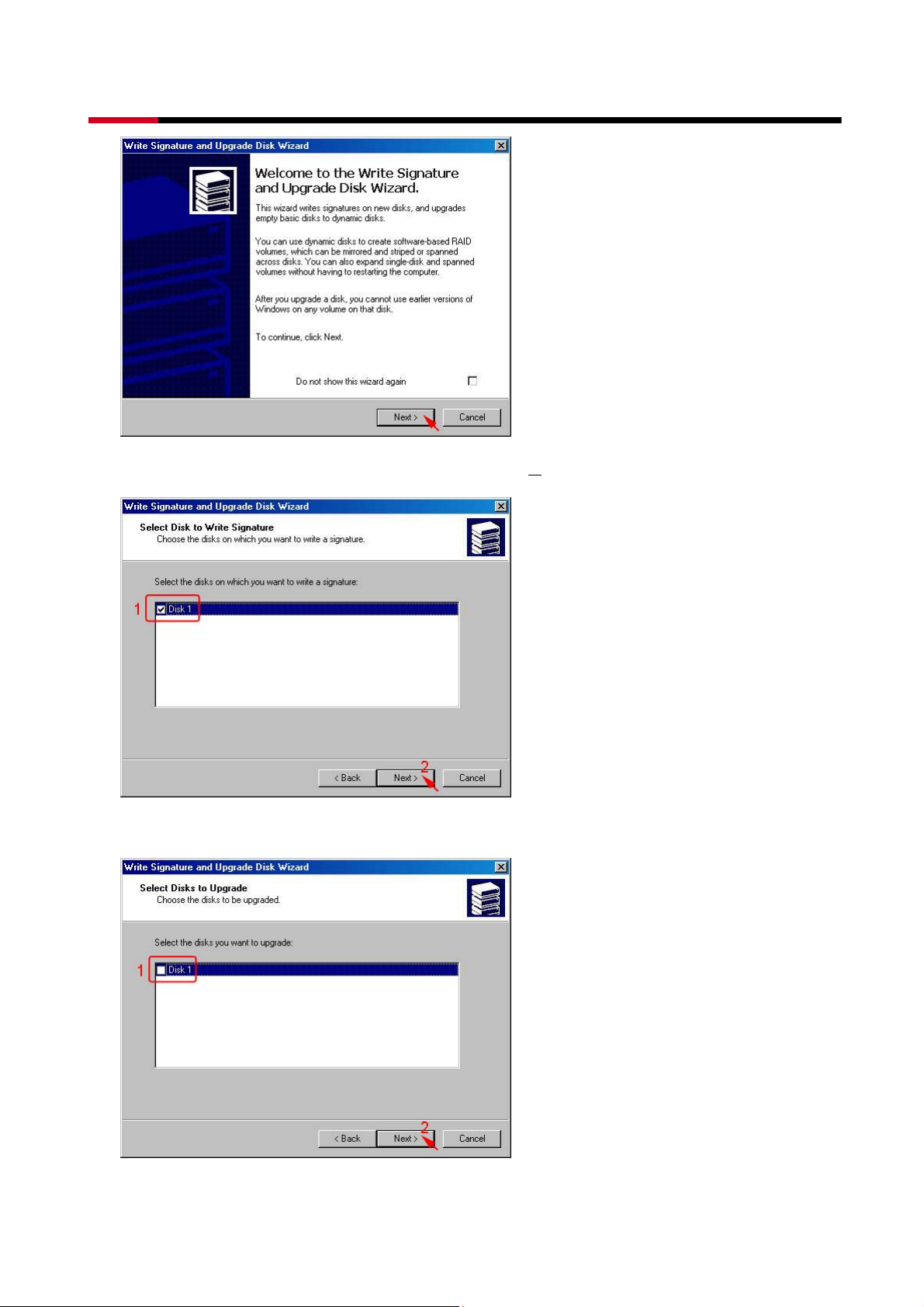
z Select the new disk to write a signature, than click N
ext>.
z Do not click any disk to upgrade to dynamic disk, than click Next>.
27
Page 28
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
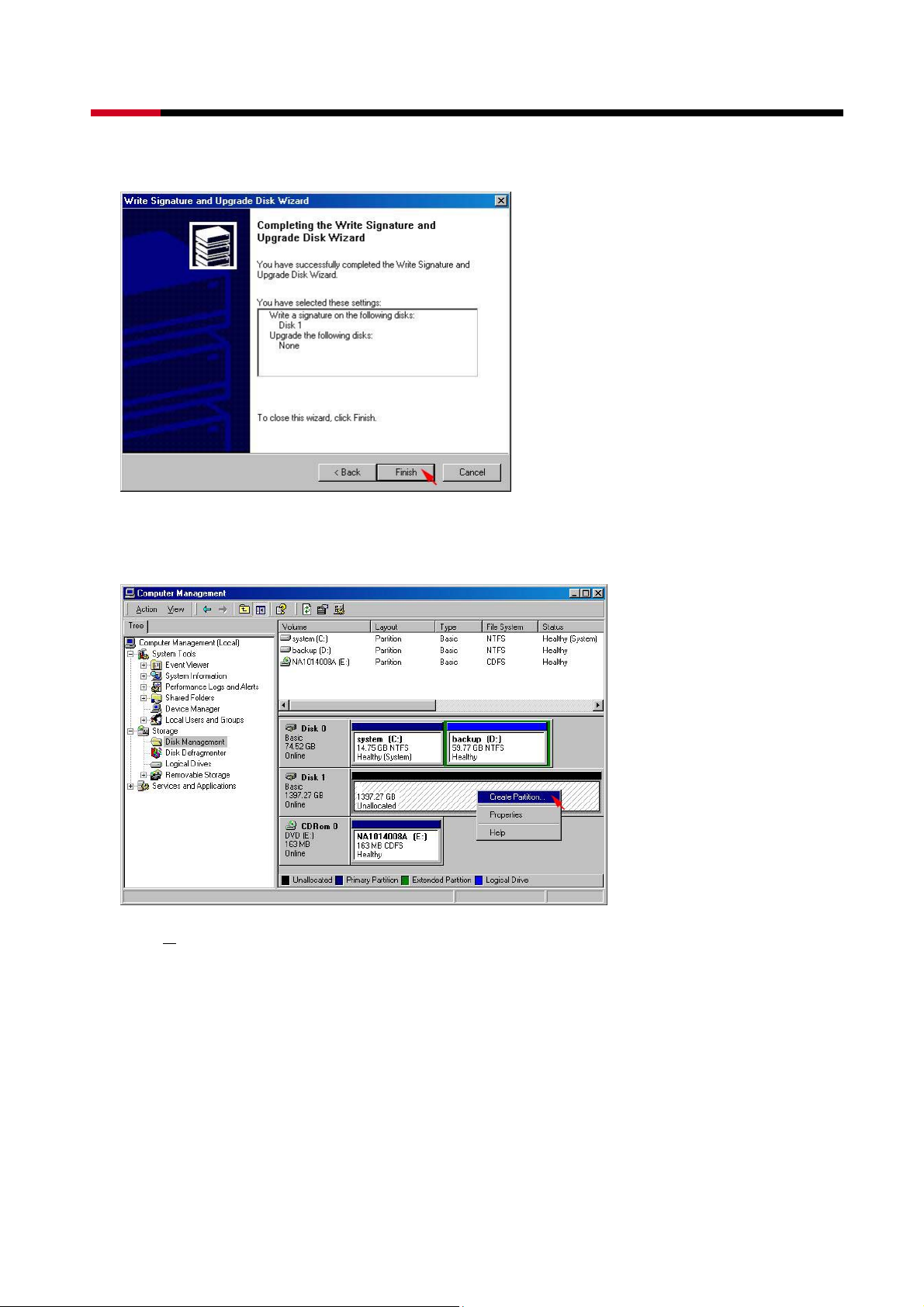
z When the Write Signature and Upgrade Disk Wizard has completed, click Finish.
z Right-click on the Unallocated partition and select Create Partition… from the pop-up
menu.
z Click N
ext> to create a partition on a basic disk.
28
Page 29
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
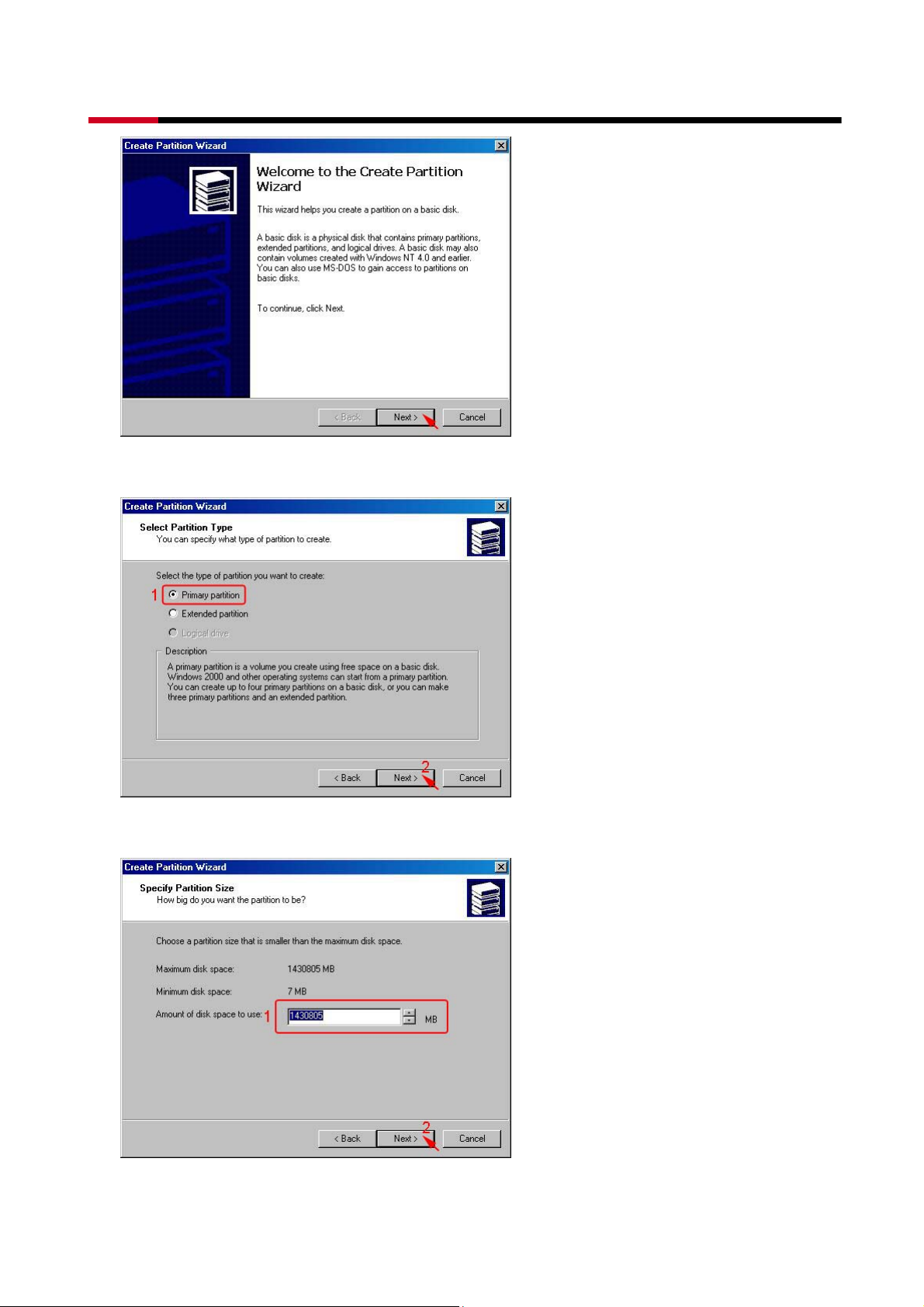
z Select the partition type you want to create, than click Next>.
z Specify the partition size you want to create, than click Next>.
29
Page 30
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
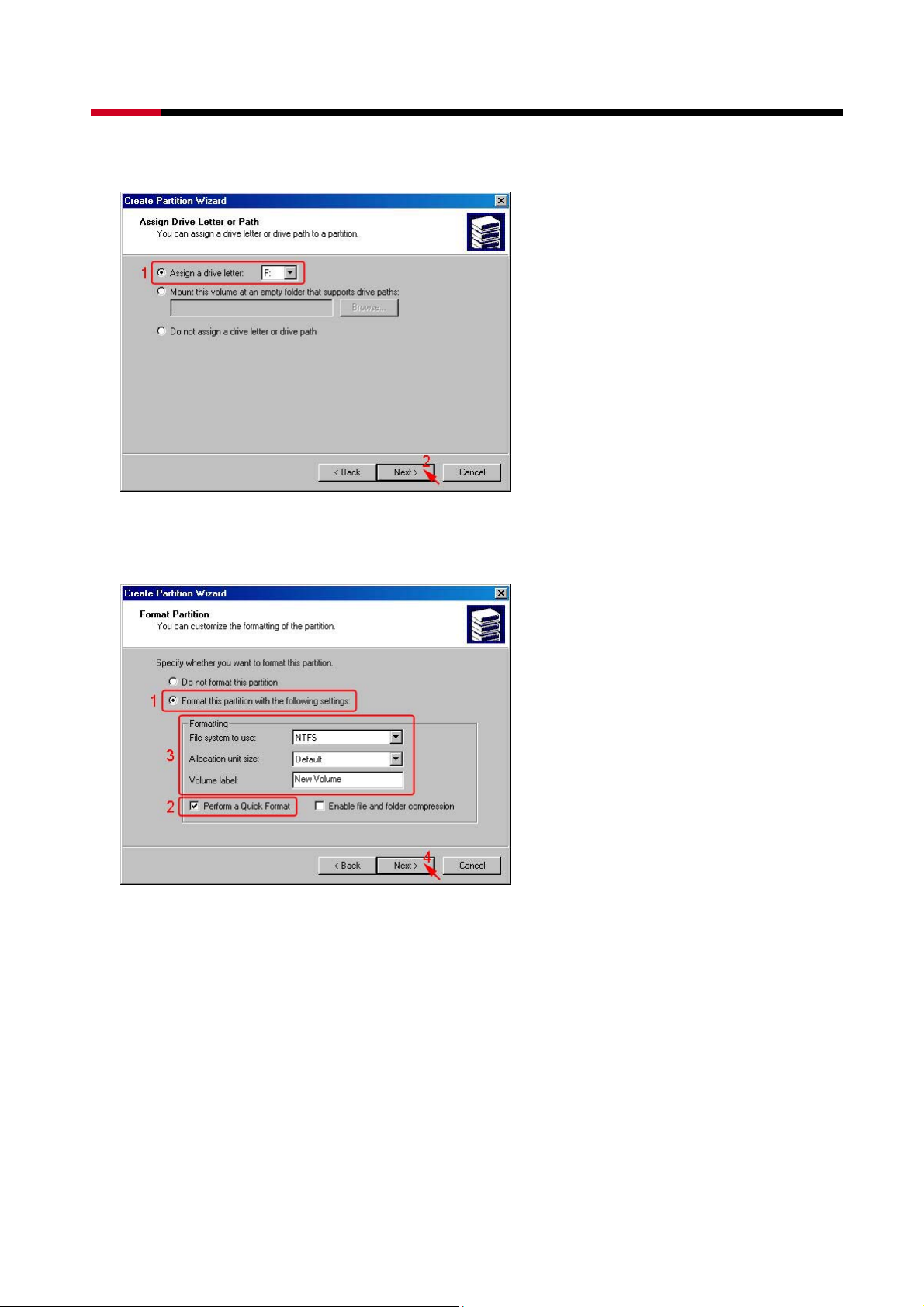
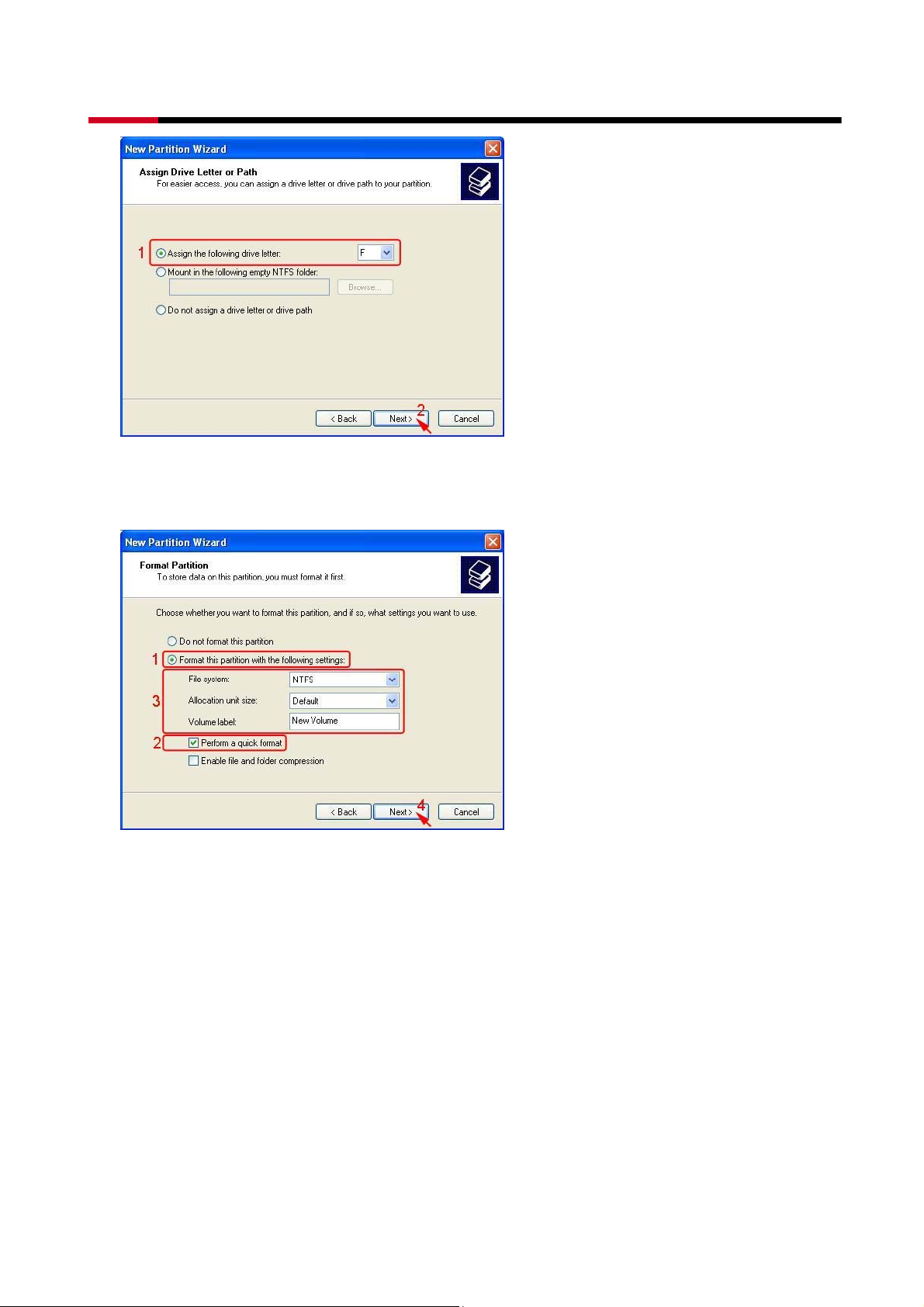
z Assign the drive letter or path you want to create, than click Next>.
z Click Format this partition with the following settings and Perform a Quick Format,
setup the File system to use, Allocation unit size, Volume label, than click Next>.
z When the Create Partition Wizard has completed, click Finish.
30
Page 31

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
The status of the newly created partition in the Disk Management window should change to
Formatting and the percentage complete will be displayed. Depending upon the size of the
partition, the format process may take several minutes. When complete, the status will
change to “Healthy” and the name and drive letter will be updated. Once the disk reports
Healthy, it appears in the listing in System Listing section with all of its pertinent information
as well.
Repeat the above procedure as needed for any other partitions. Close the Data
Management window by clicking on the small boxed “X” in the top right corner of the
31
Page 32

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
window. Click on the “My Computer” icon on the Desktop. The new drives will be visible
and properly named. The new disks are available for use.
3.4 INSTALLING ON WINDOWS XP (32/64-BIT)
3.4.1 INSTALLING SATA RAID HOST BUS ADAPTER
Follow the descriptions below, and step by step to complete the setup.
z Insert the Setup and Installation Repository CD in the CD-ROM drive.
z When start the Windows O/S, new hardware will be found; Select No, not this time, than
click Next>.
32
Page 33

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
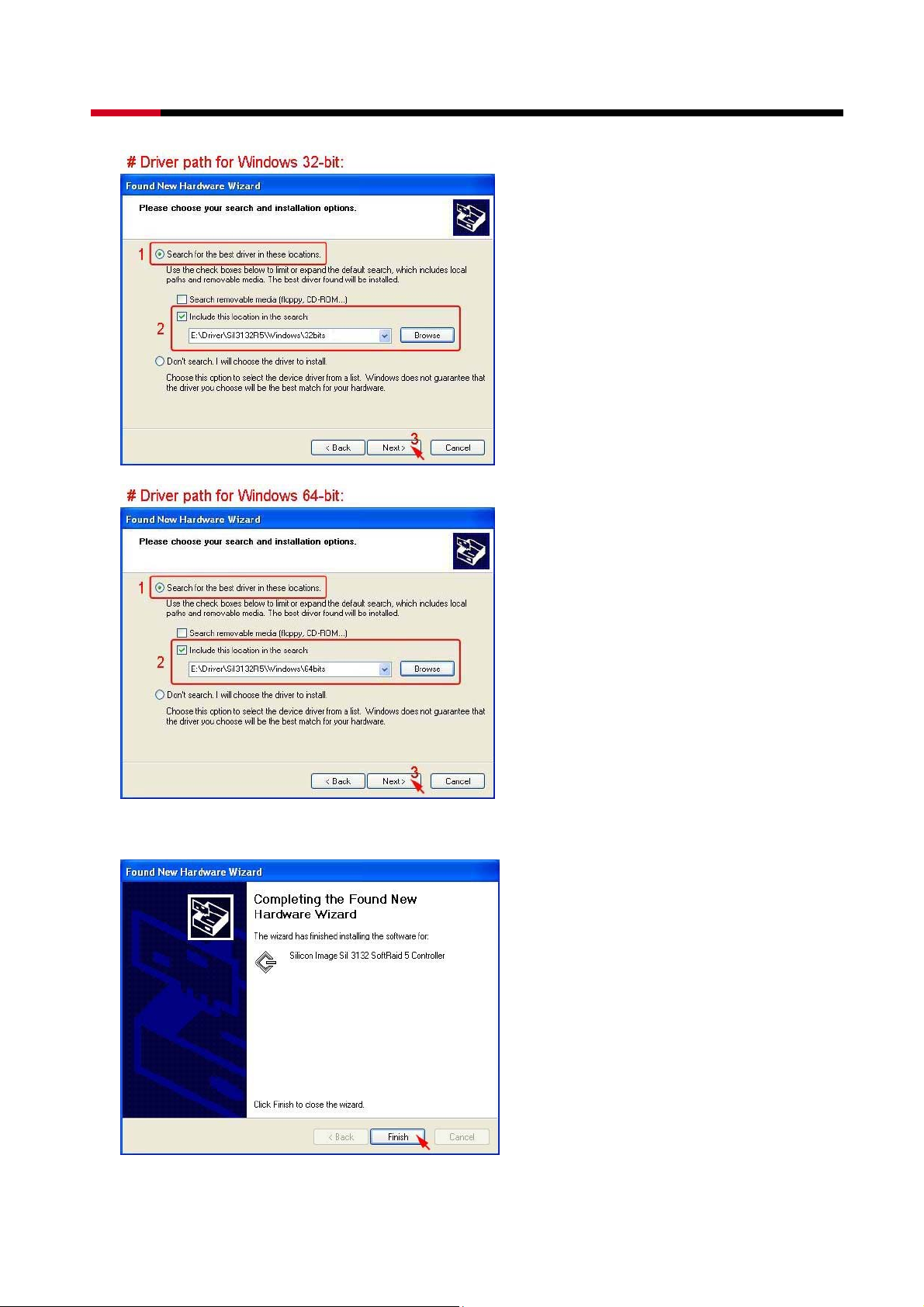
z Select Install from a list or specific location (Advanced), than click Next>.
z Select Search for the best driver in there location, Include this location in the search,
and click Browse to select the driver path, than click Next>.
33
Page 34
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z When the installation has completed, click Finish.
34
Page 35

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
3.4.2 INSTALLING SATARAID5 UTILITY
Follow the descriptions below, and step by step to complete the installation.
z Open the Setup and Installation Repository CD and select the SATARAID5 Array
Manager software from the Utility folder.
z Double-click the utility file.
z Click N
ext> to begin setup.
35
Page 36

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select I A
gree, than click Next>.
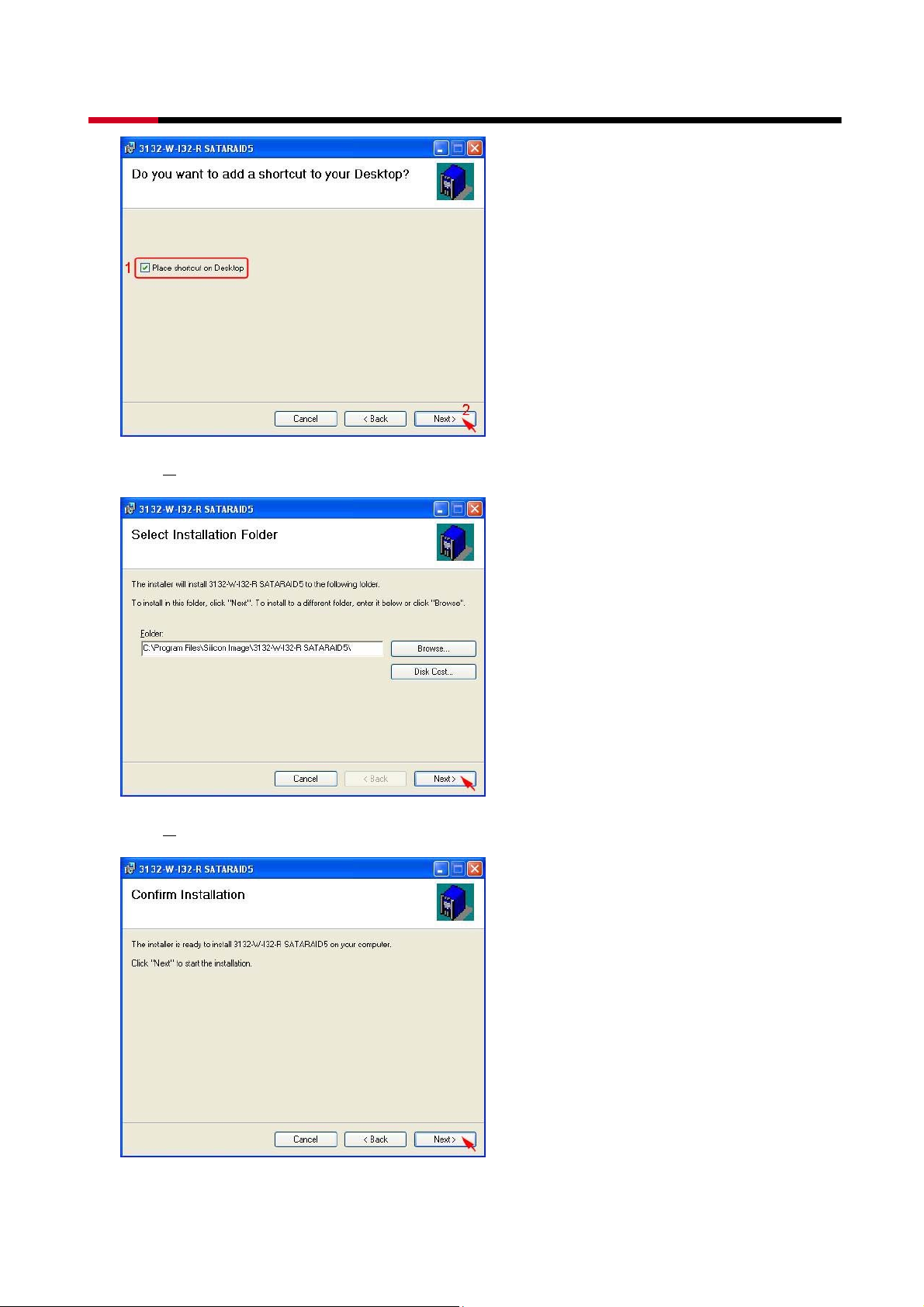
z Select Place shortcut on Desktop, than click N
ext> to create a shortcut on the desktop.
36
Page 37
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Click N
z Click N
ext> to use the default installation folder.
ext> to begin the installation.
37
Page 38

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z When SATARAID5 installation has completed, click Close to exit.
z Select I a
ccept the terms in the license agreement, than click Next> to begin the Java
platform installation.
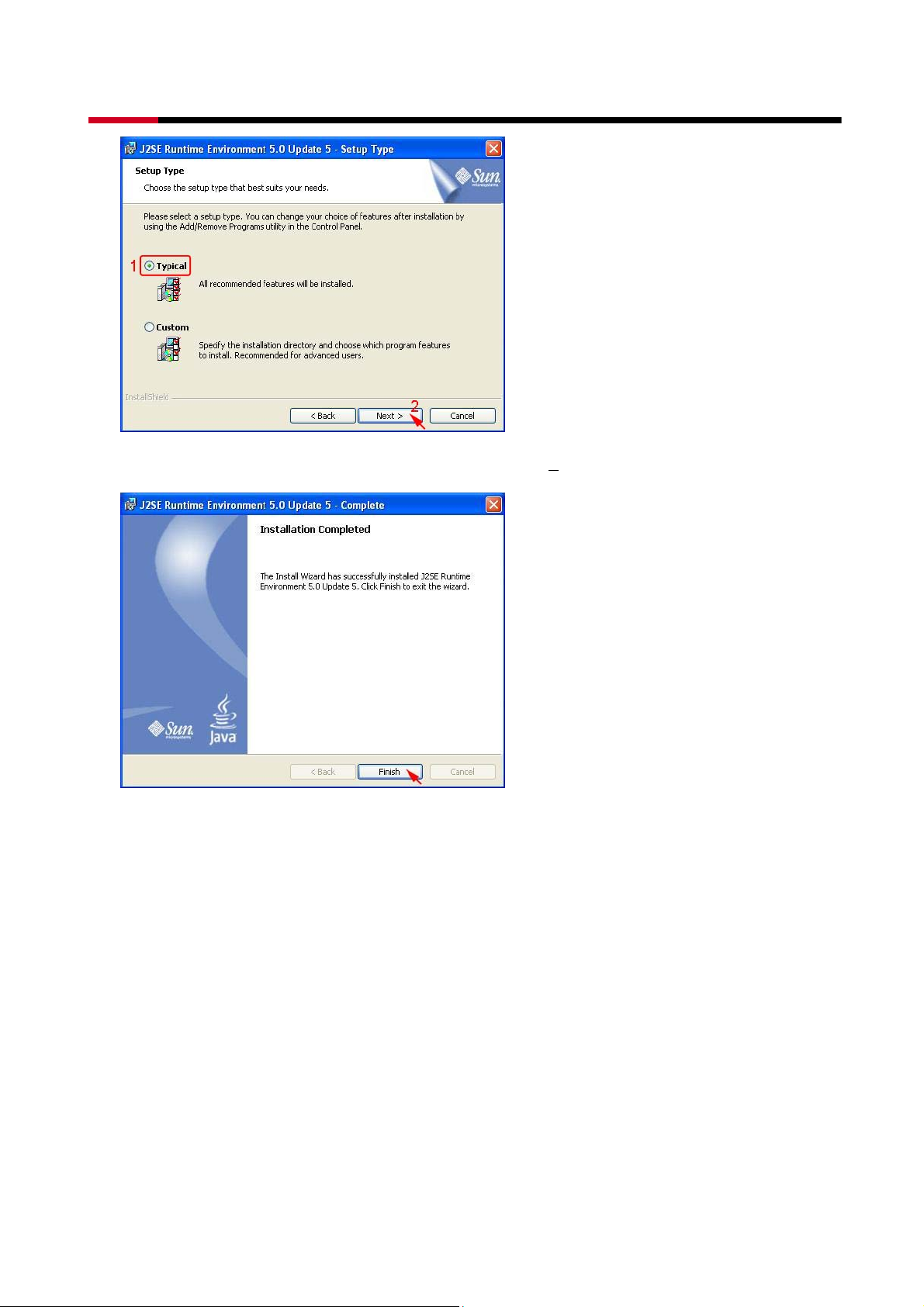
z Select T
ypical, than click Next>.
38
Page 39
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z When Java platform installation has completed, click F
inish to exit.
z Select Start > All Programs > Silicon Image > SATARaid5Manager to start the Array
Manager software.
3.4.3 DISK DRIVE MODE SETUP
Please refer to the chapter 4.
3.4.4 ALLOCATING PARTITIONS ON WINDOWS XP 32-BIT
Before creating any partitions, RAID groups must first be created using the
SATARaid5Manager utility. Once the sets have been created, allow the system to load
Windows.
39
Page 40
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Right-click on My Computer icon and select Manage from the pop-up menu.
z Select Disk Management under Storage to view the disk drives.
z When Initialize and Convert Disk Wizard appears, click N
ext>.
40
Page 41

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select the new disk to initialize, than click N
ext>.
z Do not click any disk to convert, than click Next>.
41
Page 42

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z When the Initialize and Convert Disk Wizard has completed, click Finish.
z Right-click on the Unallocated partition and select New Partition… from the pop-up
menu.
z Click N
ext> to create a partition on a basic disk.
42
Page 43

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select the partition type you want to create, than click Next>.
z Specify the partition size you want to create, than click Next>.
43
Page 44
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
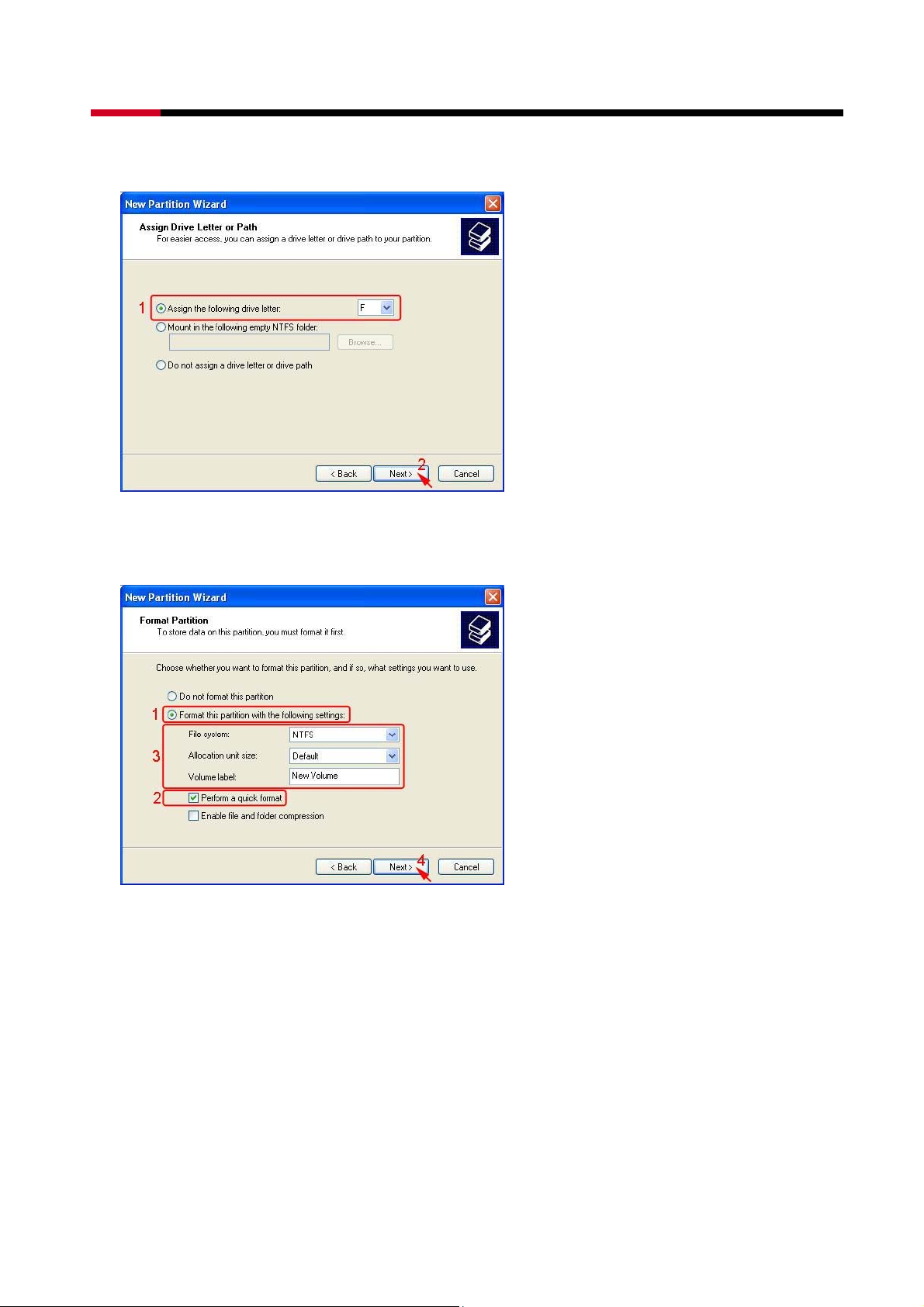
z Assign the drive letter or path you want to create, than click Next>.
z Click Format this partition with the following settings and Perform a quick format,
setup the File system, Allocation unit size, Volume label, than click Next>.
z When the New Partition Wizard has completed, click Finish.
44
Page 45
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
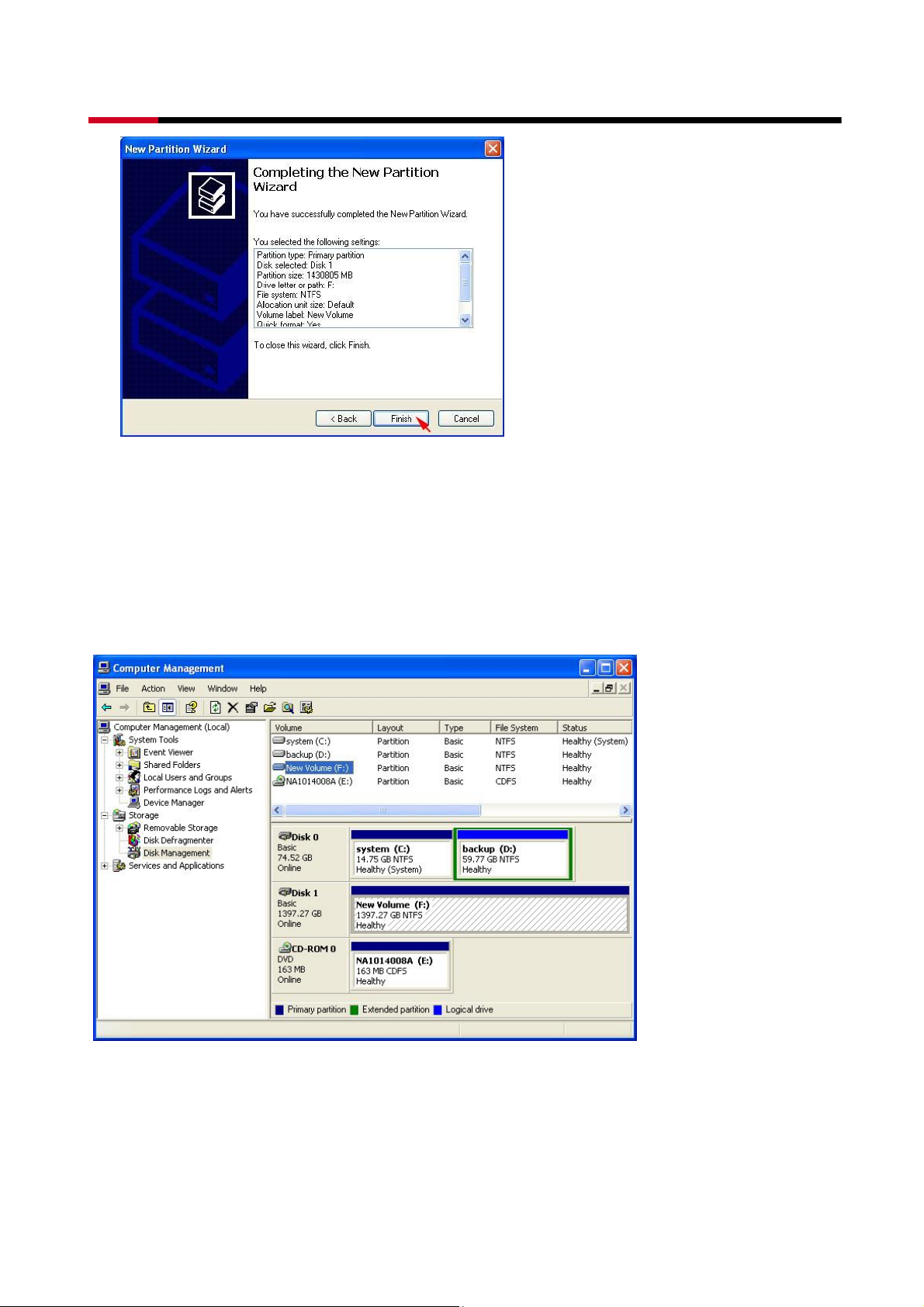
The status of the newly created partition in the Disk Management window should change to
Formatting and the percentage complete will be displayed. Depending upon the size of the
partition, the format process may take several minutes. When complete, the status will
change to “Healthy” and the name and drive letter will be updated. Once the disk reports
Healthy, it appears in the listing in System Listing section with all of its pertinent information
as well.
Repeat the above procedure as needed for any other partitions. Close the Data
Management window by clicking on the small boxed “X” in the top right corner of the
45
Page 46
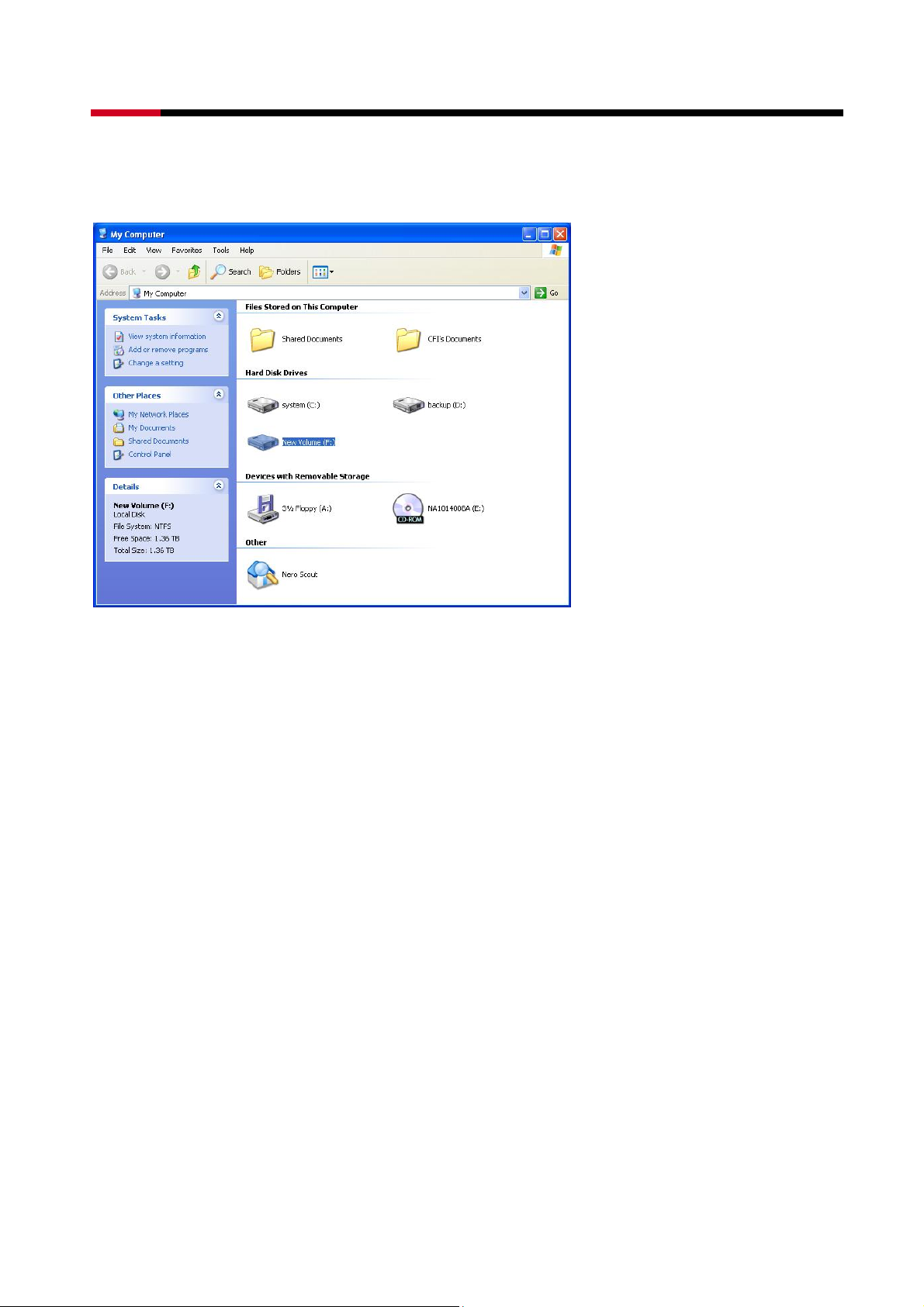
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
window. Click on the “My Computer” icon on the Desktop. The new drives will be visible
and properly named. The new disks are available for use.
3.4.5 ALLOCATING PARTITIONS ON WINDOWS XP 64-BIT
Before creating any partitions, RAID groups must first be created using the
SATARaid5Manager utility. Once the sets have been created, allow the system to load
Windows.
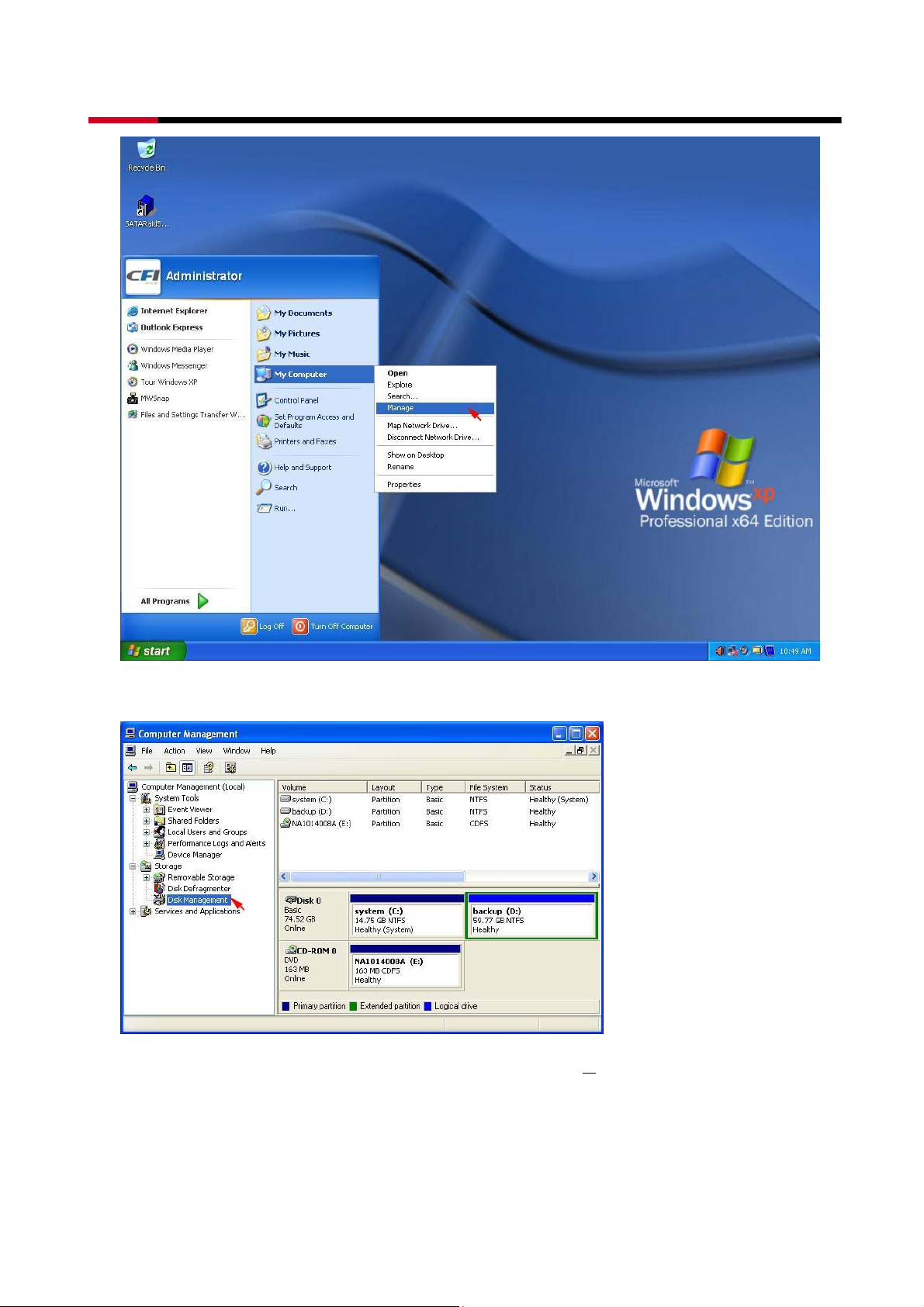
z Right-click on My Computer icon and select Manage from the pop-up menu.
46
Page 47
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select Disk Management under Storage to view the disk drives.
z When Initialize and Convert Disk Wizard appears, click N
ext>.
47
Page 48
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
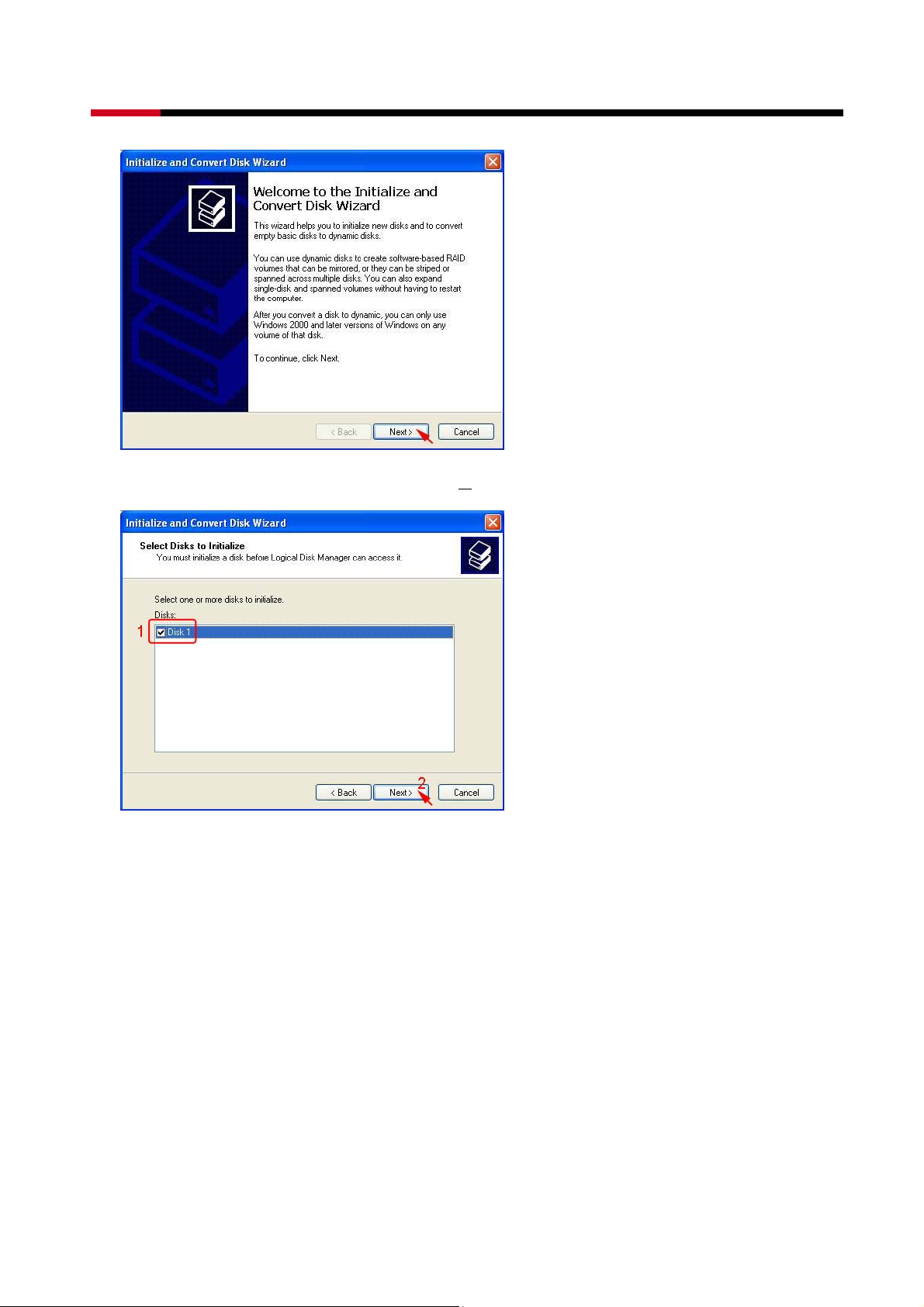
z Select the new disk to initialize, than click N
ext>.
z Do not click any disk to convert, than click Next>.
48
Page 49

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
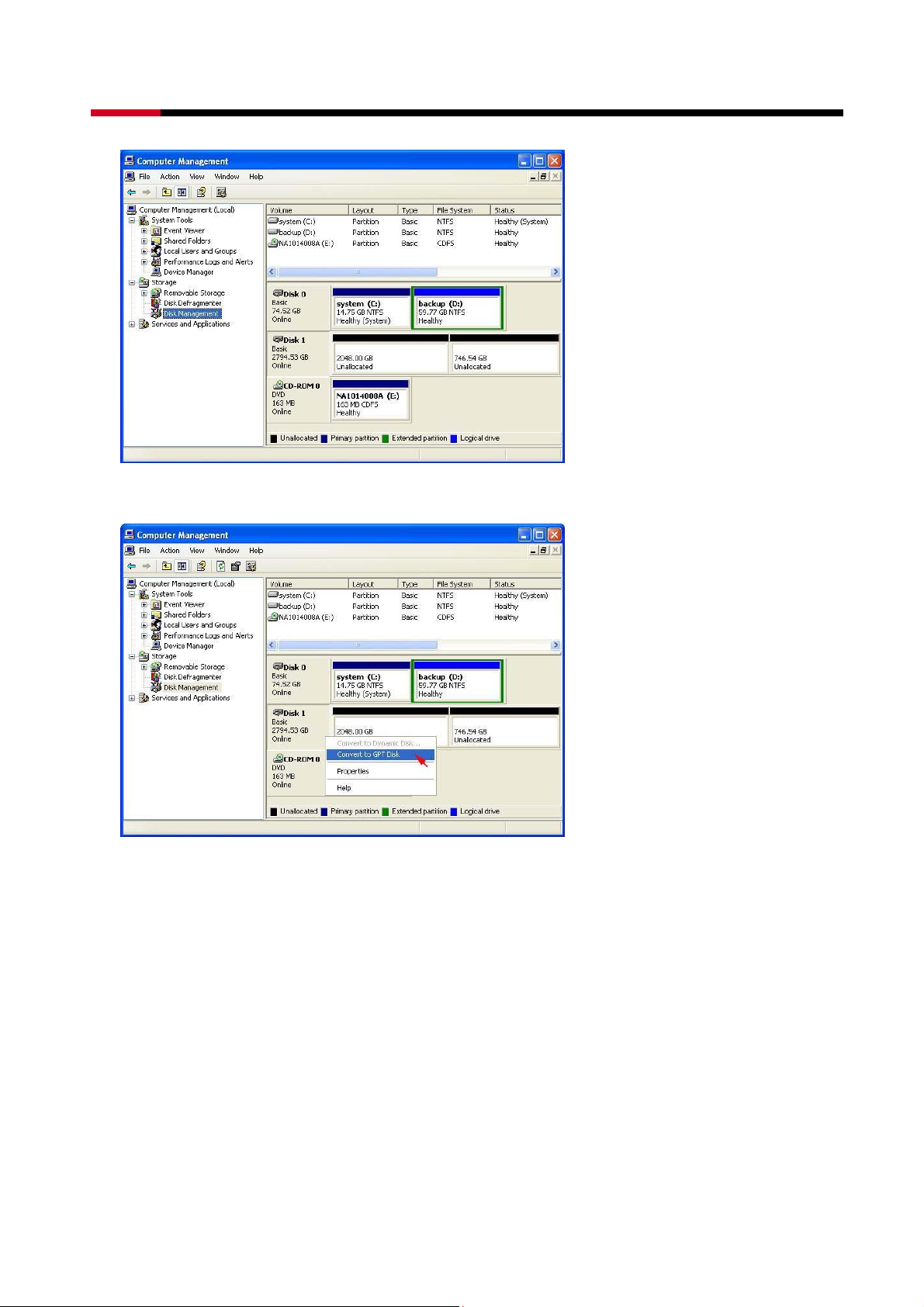
z When the Initialize and Convert Disk Wizard has completed, click Finish.
z Windows 64-bit system supports GPT disk which supports disk volume greater than 2TB.
49
Page 50
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Right-click on the Basic disk and select Convert to GPT disk from the pop-up menu.
z Right-click on the Unallocated partition and select New Partition… from the pop-up
menu.
50
Page 51

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Click N
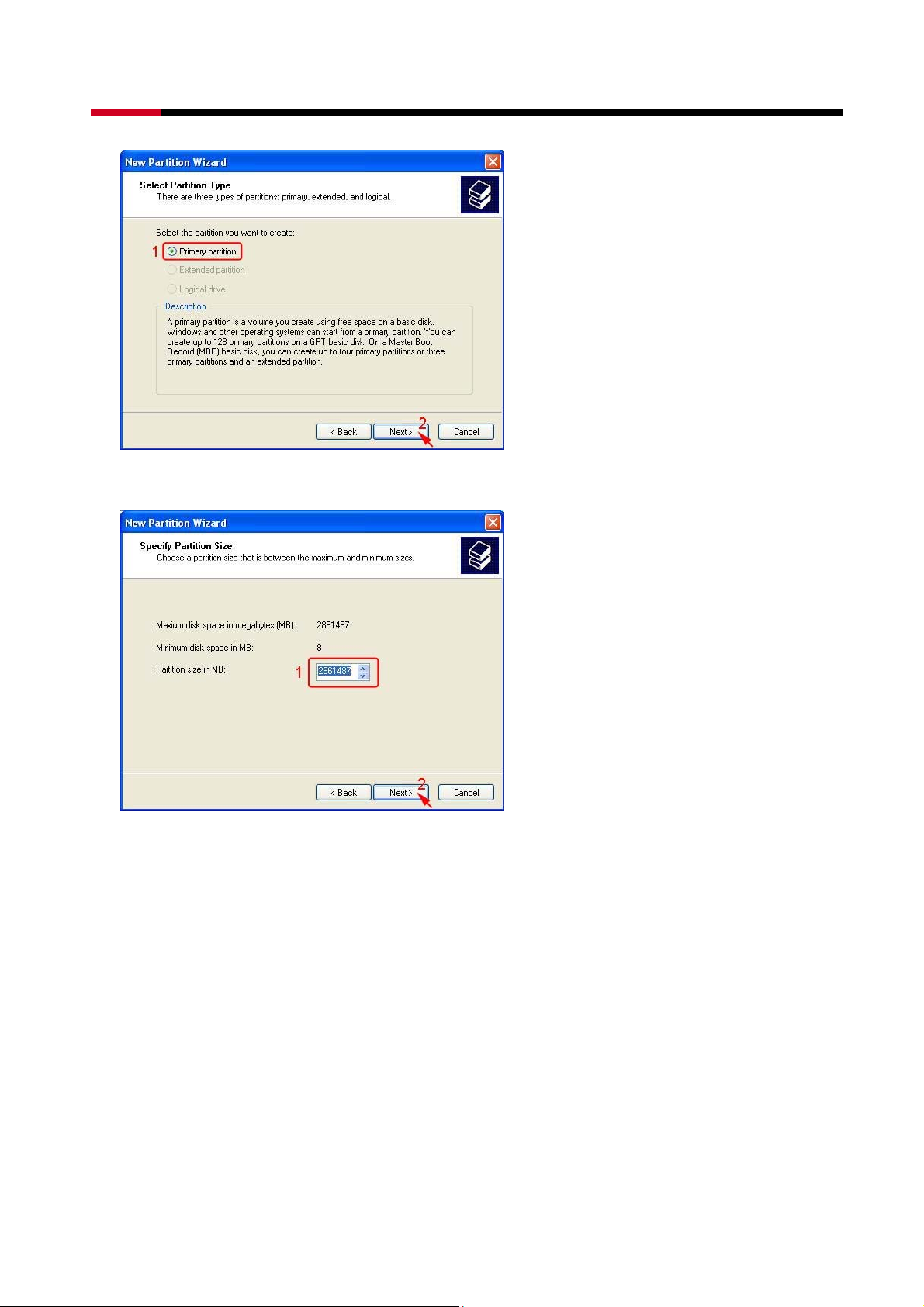
ext> to create a partition on a basic disk.
z Select the partition to create, than click Next>.
51
Page 52
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Specify the partition size you want to create, than click Next>.
z Assign the drive letter or path you want to create, than click Next>.
52
Page 53
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Click Format this partition with the following settings and Perform a quick format,
setup the File system, Allocation unit size, Volume label, than click Next>.
z When the New Partition Wizard has completed, click Finish.
53
Page 54

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
The status of the newly created partition in the Disk Management window should change to
Formatting and the percentage complete will be displayed. Depending upon the size of the
partition, the format process may take several minutes. When complete, the status will
change to “Healthy” and the name and drive letter will be updated. Once the disk reports
Healthy, it appears in the listing in System Listing section with all of its pertinent information
as well.
Repeat the above procedure as needed for any other partitions. Close the Data
Management window by clicking on the small boxed “X” in the top right corner of the
54
Page 55
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
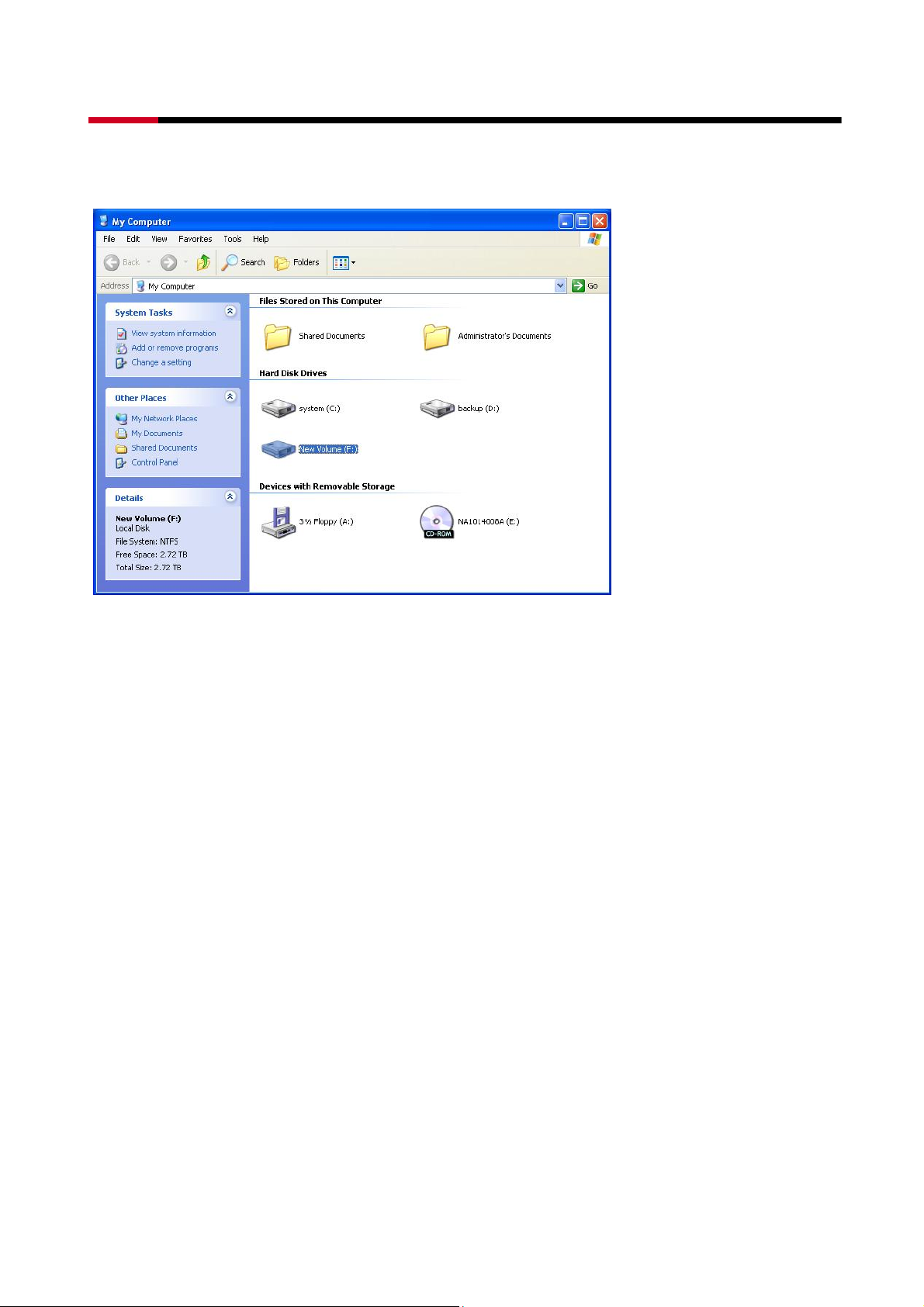
window. Click on the “My Computer” icon on the Desktop. The new drives will be visible
and properly named. The new disks are available for use.
3.5 INSTALLING ON WINDOWS SERVER 2003
(32/64-BIT)
3.5.1 INSTALLING SATA RAID HOST BUS ADAPTER
Follow the descriptions below, and step by step to complete the setup.
z Insert the Setup and Installation Repository CD in the CD-ROM drive.
z When start the Windows O/S, new hardware will be found; Select No, not this time, than
click Next>.
55
Page 56

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select Install from a list or specific location (Advanced), than click Next>.
z Select Search for the best driver in there location, Include this location in the search,
and click Browse to select the driver path, than click Next>.
56
Page 57

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z When the installation has completed, click Finish.
57
Page 58

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
3.5.2 INSTALLING SATARAID5 UTILITY
Follow the descriptions below, and step by step to complete the installation.
z Open the Setup and Installation Repository CD and select the SATARAID5 Array
Manager software from the Utility folder.
z Double-click the utility file.
z Click N
ext> to begin setup.
58
Page 59

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select I A
gree, than click Next>.
z Select Place shortcut on Desktop, than click N
ext> to create a shortcut on the desktop.
59
Page 60

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Click N
z Click N
ext> to use the default installation folder.
ext> to begin the installation.
z When SATARAID5 installation has completed, click C
lose to exit.
60
Page 61

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select I accept the terms in the license agreement, than click Next> to begin the Java
platform installation.
z Select T
ypical, than click Next>.
61
Page 62

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z When Java platform installation has completed, click F
inish to exit.
z Select Start > All Programs > Silicon Image > SATARaid5Manager to start the Array
Manager software.
3.5.3 DISK DRIVE MODE SETUP
Please refer to the chapter 4.
3.5.4 ALLOCATING PARTITIONS
Before creating any partitions, RAID groups must first be created using the
SATARaid5Manager utility. Once the sets have been created, allow the system to load
Windows.
62
Page 63

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Right-click on My Computer icon and select Manage from the pop-up menu.
z Select Disk Management under Storage to view the disk drives.
z When Initialize and Convert Disk Wizard appears, click N
ext>.
63
Page 64
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
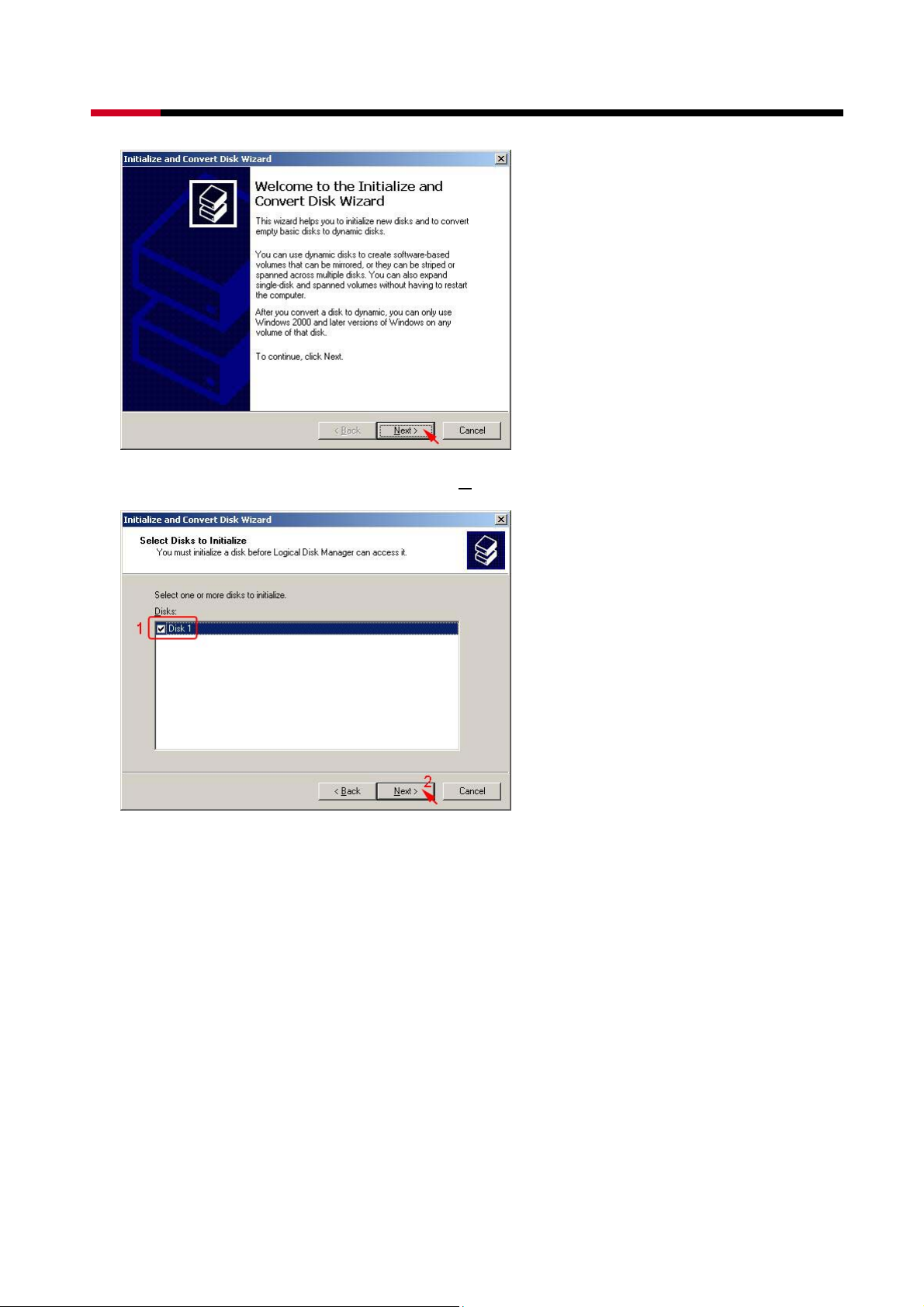
z Select the new disk to initialize, than click N
ext>.
z Do not click any disk to convert, than click Next>.
64
Page 65

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z When the Initialize and Convert Disk Wizard has completed, click Finish.
z Windows Server 2003 SP1 or later system supports GPT disk which supports disk
volume greater than 2TB.
65
Page 66

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Right-click on the Basic disk and select Convert to GPT disk from the pop-up menu.
z Right-click on the Unallocated partition and select New Partition… from the pop-up
menu.
66
Page 67

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Click N
ext> to create a partition on a basic disk.
z Select the partition to create, than click Next>.
67
Page 68

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Specify the partition size you want to create, than click Next>.
z Assign the drive letter or path you want to create, than click Next>.
68
Page 69

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
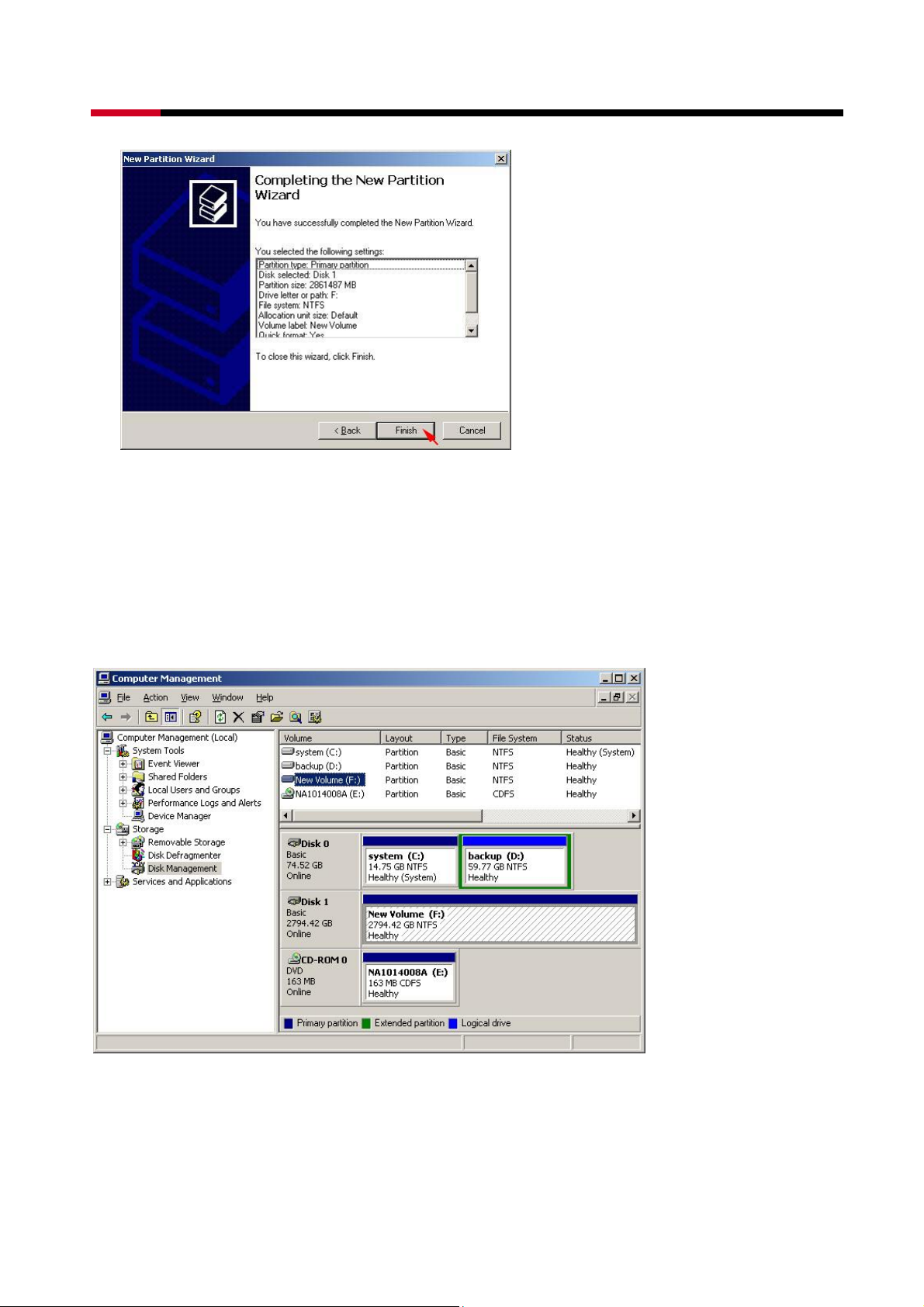
z Click Format this partition with the following settings and Perform a quick format,
setup the File system, Allocation unit size, Volume label, than click Next>.
z When the New Partition Wizard has completed, click Finish.
69
Page 70
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
The status of the newly created partition in the Disk Management window should change to
Formatting and the percentage complete will be displayed. Depending upon the size of the
partition, the format process may take several minutes. When complete, the status will
change to “Healthy” and the name and drive letter will be updated. Once the disk reports
Healthy, it appears in the listing in System Listing section with all of its pertinent information
as well.
Repeat the above procedure as needed for any other partitions. Close the Data
Management window by clicking on the small boxed “X” in the top right corner of the
70
Page 71

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
window. Click on the “My Computer” icon on the Desktop. The new drives will be visible
and properly named. The new disks are available for use.
3.6 INSTALLING ON WINDOWS VISTA (32/64-BIT)
3.6.1 INSTALLING SATA RAID HOST BUS ADAPTER
Follow the descriptions below, and step by step to complete the setup.
z Insert the Setup and Installation Repository CD in the CD-ROM drive.
z When start the Windows O/S, new hardware will be found; Select Locat and install
driver software (recommended).
71
Page 72

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Insert the disc that came with your RAID Controller, than click Next.
z When the installation has completed, click Close.
72
Page 73

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
3.6.2 INSTALLING SATARAID5 UTILITY
Follow the descriptions below, and step by step to complete the installation.
z Open the Setup and Installation Repository CD and select the SATARAID5 Array
Manager software from the Utility folder.
z Double-click the utility file.
z Click N
ext> to begin setup.
73
Page 74

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Select I A
gree, than click Next>.
z Select Place shortcut on Desktop, than click N
ext> to create a shortcut on the desktop.
74
Page 75

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Click N
z Click N
ext> to use the default installation folder.
ext> to begin the installation.
75
Page 76
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z When SATARAID5 installation has completed, click Close to exit.
z Select I a
ccept the terms in the license agreement, than click Next> to begin the Java
platform installation.
z Select T
ypical, than click Next>.
76
Page 77

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z When Java platform installation has completed, click F
inish to exit.
z Select Start > All Programs > Silicon Image > SATARaid5Manager to start the Array
Manager software.
3.6.3 DISK DRIVE MODE SETUP
Please refer to the chapter 4.
3.6.4 ALLOCATING PARTITIONS
Before creating any partitions, RAID groups must first be created using the
SATARaid5Manager utility. Once the sets have been created, allow the system to load
Windows.
77
Page 78

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Right-click on My Computer icon and select Manage from the pop-up menu.
z Select Disk Management under Storage to view the disk drives.
z When Initialize Disk Wizard appears, select Disk 1 and GPT (GUID Partition Table),
than click OK.
78
Page 79

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Windows Vista system supports GPT disk which supports disk volume greater than 2TB.
z Right-click on the Unallocated partition and select New Single Volume… from the pop-
up menu.
79
Page 80

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Click N
ext> to create the partition.
z Specify the partition size you want to create, than click Next>.
80
Page 81

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z Assign the drive letter or path you want to create, than click Next>.
z Click Format this partition with the following settings and Perform a quick format,
setup the File system, Allocation unit size, Volume label, than click Next>.
81
Page 82

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
z When the New Partition Wizard has completed, click Finish.
The status of the newly created partition in the Disk Management window should change to
Formatting and the percentage complete will be displayed. Depending upon the size of the
partition, the format process may take several minutes. When complete, the status will
change to “Healthy” and the name and drive letter will be updated. Once the disk reports
Healthy, it appears in the listing in System Listing section with all of its pertinent information
as well.
82
Page 83

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
Repeat the above procedure as needed for any other partitions. Close the Data
Management window by clicking on the small boxed “X” in the top right corner of the
window. Click on the “My Computer” icon on the Desktop. The new drives will be visible
and properly named. The new disks are available for use.
83
Page 84

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
4 SATA RAID5 ARRAY MANAGER
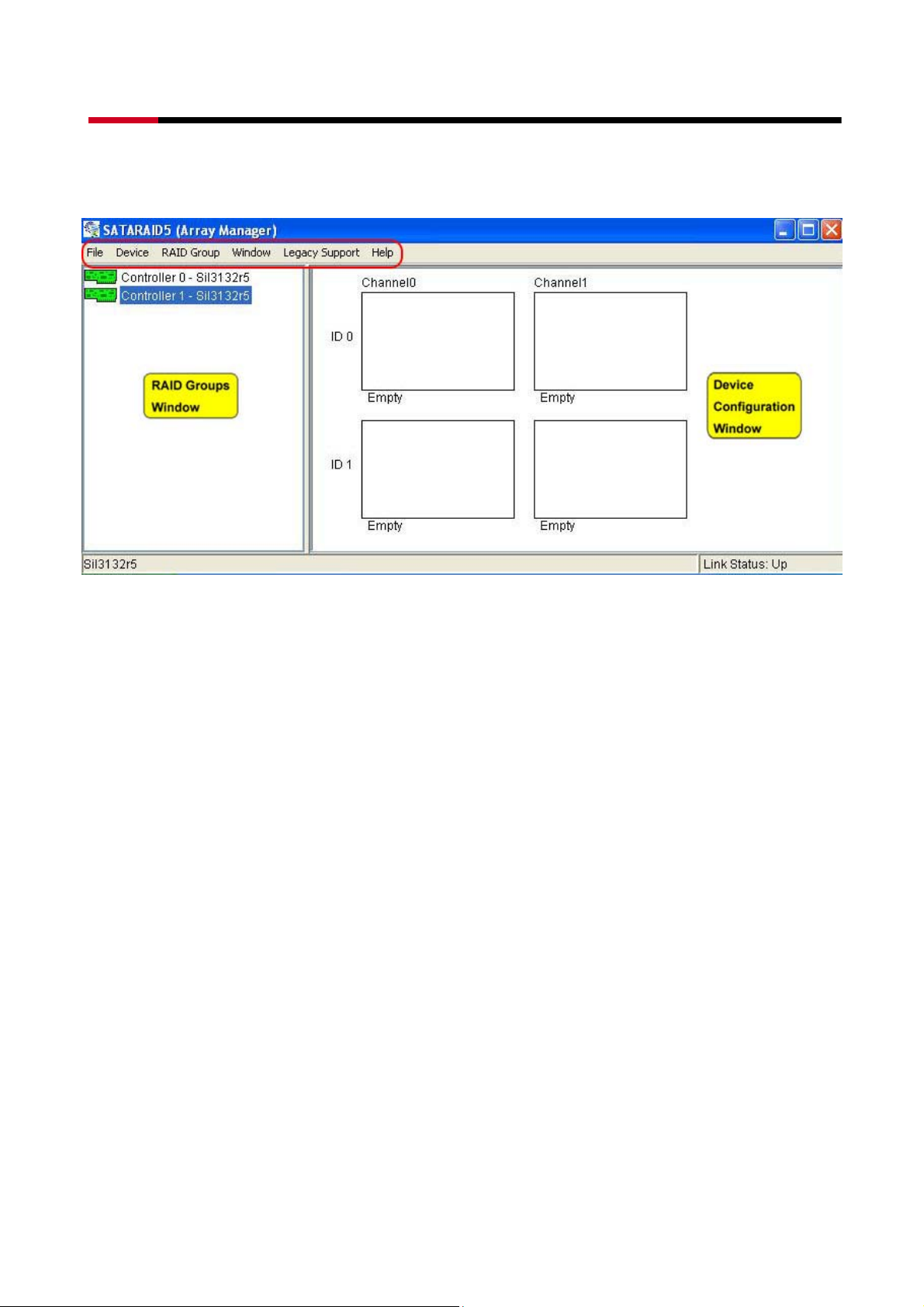
4.1 OVERVIEW
The SATARAID5 Array Manager is the Graphical User Interfaces (GUI) which allows you to
create and manage RAID volumes. The Manager initially shows two windows as seen below.
The RAID Groups window identifies SATA host adapters and configured RAID groups. For
systems with more than one Silicon Image Host Bus Adapter installed, you can switch
between cards by selecting the desired card in the RAID Groups Window.
When a controller is selected, the RAID Groups currently defined on that controller are also
shown in the RAID Groups Window. Selecting a specific RAID Group will highlight the
segments associated with that volume in the Device Configuration Window.
The Device Configuration window identifies all physical drives and their partitions.
84
Page 85

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
Throughout the Manager, different colors are used to indicate the status of the components.
The meanings of the colors are:
COLOR STATUS
Green Good. The component and all subcomponents are okay.
Yellow Warning. This component or at least one subcomponent
has become degraded and requires service.
Red Failed. This component or at least one subcomponent
has failed.
Grey Unused.
4.2 CREATING RAID GROUPS
To begin creating a new RAID Group, select “Create RAID Group” from the RAID Group menu
or right click on a controller in the RAID Groups window and select “Create RAID Group” from
the pop-up menu. This will cause the Create RAID Group dialog to appear.
Note: The term “right-click” refers to using the secondary button on your mouse to
perform the indicated operation. On a Windows system, use the mouse button that
you have defined to be the secondary button (by default, that button is on the right
side of the mouse, unless you have reconfigured the primary and secondary mouse
buttons using Control Panel > Mouse). On a Macintosh system, press and hold the
Command (Apple) key and click the mouse.
4.2.1 CONTIGUOUS RAID GROUPS
Contiguous RAID Groups allow the user to select a segment of disk drive or a disk drive.
Select the disk and enter the desired values and press Create to create the RAID Group
(Example below).
85
Page 86

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
4.2.2 CONCATENATED RAID GROUPS
Concatenated RAID Groups allow the user to select different sized segments for each
member of the volume. For Concatenated volumes only, a dialog box will appear allowing the
user to select the individual segment sizes from each disk. Enter the desired values and
press Create to create the RAID Group (Example below).
4.2.3 STRIPED RAID GROUPS
Striped RAID Groups allow the user to select minimum of 2 or more disks for each member of
the volume. Enter the desired values and press Create to create the RAID Group (Example
below).
86
Page 87

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
4.2.4 MIRRORED RAID GROUPS
Mirrored RAID Groups allow the user to select 2 disks for each member of the volume. Enter
the desired values and press Create to create the RAID Group (Example below).
4.2.5 MIRRORED STRIPED RAID GROUPS
Mirrored Striped RAID Groups allow the user to select minimum of 4 disks for each member
of the volume. Enter the desired values and press Create to create the RAID Group (Example
below).
87
Page 88

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
4.2.6 PARITY RAID GROUPS
Parity RAID Groups allow the user to select minimum of 3 or more disks for each member of
the volume. Enter the desired values and press Create to create the RAID Group (Example
below).
88
Page 89
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
4.2.7 RAID GROUPS OVERVIEW
RAID Groups allow Enter values in all fields and click Create to create the RAID Group.
FIELD DEFINITION
RAID Group
Label
RAID Group
Configuration
Capacity
Enter an identifiable name for the RAID group. This value can be any string (up to 8
characters including blank spaces) to help users identify this volume.
Select a Group ID from the available ID list. The maximum number of RAID Groups
per controller is 8, so Group ID can be any number between 0 and 7, inclusive.
Select which RAID level is to be used to configure these members:
• Contiguous (for virtual disk).
• Concatenated (for multiple concatenated segments).
• Striped (for RAID 0)
• Mirrored (for RAID 1)
• Mirrored Striped (for RAID 10)
• Parity RAID (for RAID 5)
Select a value to define the total usable capacity of the RAID Group or manually
enter the volume size in gigabytes (GB). Selecting MAX will create the largest RAID
Chunk Size
Rebuild
Priority
set possible with the drive(s) selected.
Select a value to define the chunk size (stripe size) for performance tuning. In
general, large stripe sizes are best for large files that are accessed sequentially (for
example, media streaming files) and smaller sizes are better for randomly accessed
data like databases. This parameter is not used for Contiguous (JBOD),
Concatenated, and Mirrored configurations.
Select a value to identify how quickly the controller should rebuild data on a disk
after a hardware failure. A value of 1 is the lowest priority and will take the longest
to rebuild. A value of 10 is the highest priority and will rebuild the fastest, but may
require more CPU resources, which might affect the computer’s performance. This
parameter is not used for Contiguous (JBOD), Concatenated, and Striped
configurations.
89
Page 90

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
Click the On or Off button to enable or disable the Check Pointing feature. When
Check Pointing is enabled, restoring data is very fast after an unexpected power
Check
Pointing
Parity
Devices
loss, although normal performance may be slightly reduced. When Check Pointing
is disabled, normal performance is improved, but restores can take a long time to
complete. This selection is only available when the selected RAID configuration is
Mirrored, Mirrored Striped or Parity RAID, and the “Advanced RAID Features”
checkbox in the Configuration/Advanced Options dialog is checked.
Click the On or Off button to enable or disable the ability to return “dirty” data after
an unexpected power loss and all of the data could not be written to disk, rather
than taking the volume off-line. This selection is only available when the selected
RAID configuration is Parity RAID and the “Advanced RAID Features” checkbox in
the Configuration/Advanced Options dialog is checked.
Select the RAID member devices from the available device segment grid. Up to five
members can be selected for Contiguous, Concatenated, Mirrored, Striped or
Parity RAID modes (although Mirrored RAID Groups will typically contain only two
members). Exactly four members must be selected for Mirrored Striped mode.
RAID Level Min # of
Disks
0 2
1 2
5 3*
10 4*
Contiguous 1
Concatenated 1
Once all parameters have been selected, select “Create” to create the RAID Group. When
finished, press Cancel to exit the Create RAID Group Dialog.
*
For 3132, this requires the use of a Port Multiplier device to access more than one disk per SATA channel.
90
Page 91
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
4.3 ADDITIONAL MENU COMMANDS
The Main menu commands are shown below
File Device RAID Group Window Legacy Support Help
Configuratio
n…
Exit Delete Spare Rebuild RAID
Delete
Delete Orphan Bring RAID Group
Make Pass-
Device
Create Spare Create RAID Group Task
Manager
Event Log Rebuild Legacy RAID
Group
Delete RAID Group Resources Delete Legacy RAID Group
Member
Convert Legacy RAID
Online
Thru
RAID Group
Summary
Create Legacy Spare
Bring Legacy RAID Group
Create Legacy RAID Group Help
Topics
About
Group
Group
Online
Summary
Delete Legacy Spare
Convert Legacy Spare
The commands are documented on the pages that follow.
91
Page 92
4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
4.3.1 CONFIGURATION
SATARAID5 configuration options include customization of the settings for Log File, Popup,
and Advanced Options. This command displays a dialog box to let user set different
configurations for SATARAID5 with the following three tabs:
Log File Tab
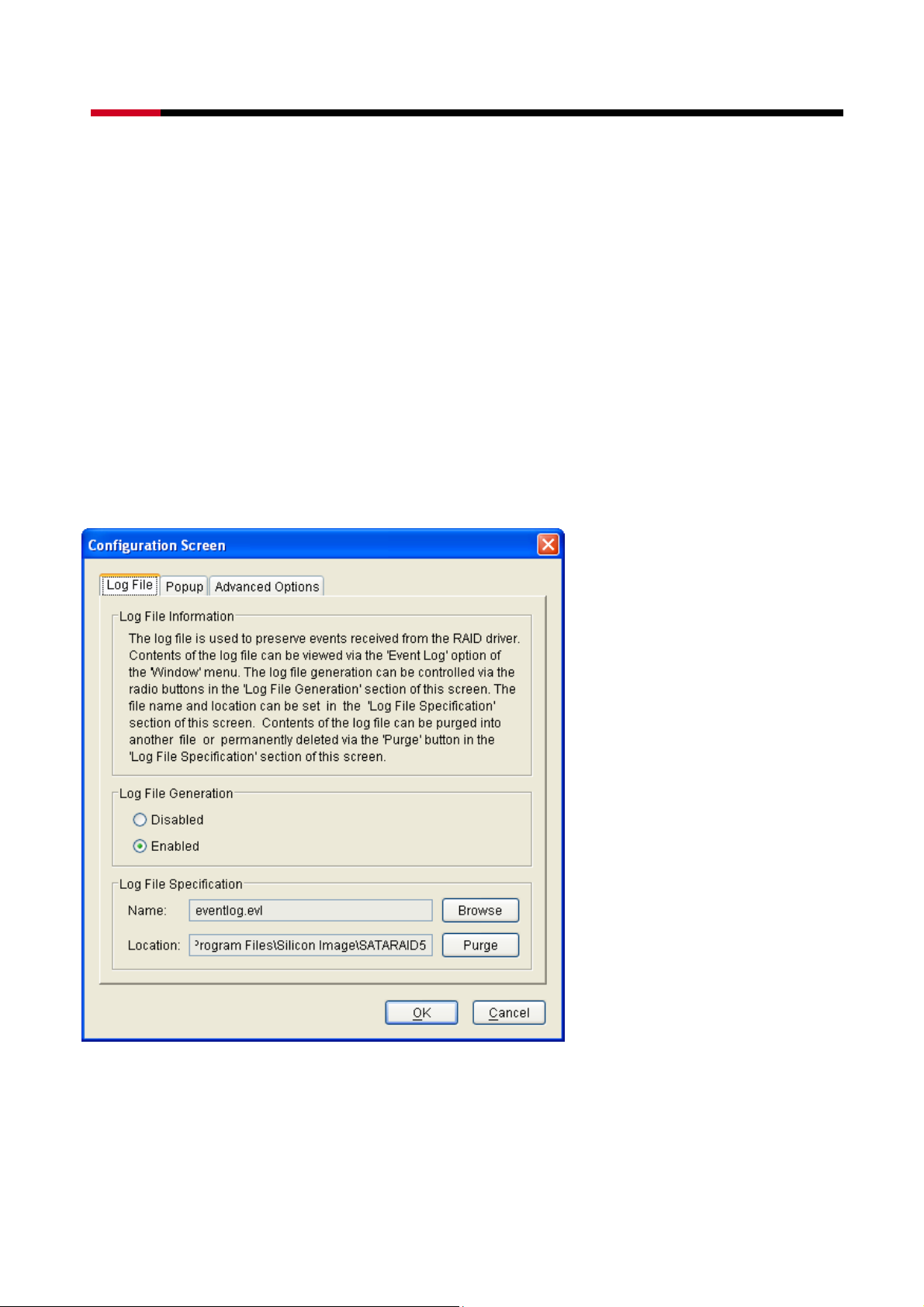
The Log File tab allows you to define the location and name of the log file. The log file is used
to store event information received from all Silicon Image RAID drivers. The log file is a text
file and can be viewed with any text viewer (such as “Notepad” on Windows platforms) or
with the Event Log window of the SATARAID5 Manager. Use the Log File tab to set the
location and the desired filename for the log file.
To specify whether the Log File is generated, click on either the Disabled or Enabled radio
button. If Log File generation is enabled, you can click the Browse button to specify the file
92
Page 93

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
name and location of the Log File. You can also use the Purge button to delete the contents
of the Log File.
93
Page 94

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
Popup Tab
SATARAID5 can be configured to notify the user of events using messages in popup windows.
Use the slider control to set the event level for popups to occur:
- Information Level - The following events will trigger a popup window:
Informational
Warnings
Errors
- Warning Level - The following events will trigger a popup window:
Warnings
Errors
- Error Level - The following events will trigger a popup window:
Errors
- Disable All - No events will trigger a popup window.
94
Page 95

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
95
Page 96

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
Advanced Options
The Advanced Options tab is used to control advanced features of the RAID driver. By default,
all these advanced options are disabled.
The Advanced Options tab allows you to enable the following advanced features.
FEATURE EXPLANATION
When this feature is selected, Legacy Support menu will be available in
Legacy (Bootable)
Support
Delete Member
Support
the menu bar. Enables the Legacy Support menu to support RAID
functions for legacy RAID groups (available on Windows platforms
only). See Legacy Support menu options.
When this feature is selected, Delete Member menu item will be
available under the Device menu. Enables the Delete Member option
on the Device menu to delete a member from RAID 1 (Mirrored), RAID 5
(Parity RAID), and RAID 10 (Striped and Mirrored) groups. See Delete
Member menu option.
96
Page 97

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
When this feature is selected and user selects to create RAID group, if
the RAID group to be created is fault tolerance group (RAID 1, RAID 5,
or RAID 10), user will be able to select Improper Shutdown Policy in
Advanced RAID
the Create RAID Group dialog box. Enables the selection of an
Improper Shutdown Policy (including Check-Pointing and Dirty Parity
Features
handling) in the Create RAID Group dialog box when the selected RAID
Group type is a fault-tolerant configuration (Mirrored, Mirrored/Striped
and Parity RAID). This feature is not supported for Legacy RAID
groups.
When this feature is selected, Resources menu item will be available
Resources Info
under the Window menu. Enables the Resources option on the
Support
Window menu for debugging purposes. See Resources menu option.
4.3.2 EXIT
This command terminates the SATARAID5 program.
97
Page 98

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
4.3.3 CREATE SPARE
This command displays a dialog box to let user create spare drive, user needs to select the
following parameters:
PARAMETER DESCRIPTION
Choose one of:
Spare Type
Capacity
RAID Group
Device
Segment
• Global - If the spare drive is for all RAID groups in the system.
• Dedicated - If the spare drive is dedicated to the specified RAID group.
If you select Global for the Spare Type, current options from a list of capacity
are from 128 MB to 100 GB, HALF and MAX.
If you select Dedicated for the Spare Type, please selected RAID group to
which this spare drive is dedicated.
Select one device segment from the available spare type only.
4.3.4 DELETE SPARE
This menu option displays a dialog box to select (highlight) one or more spare drives to delete.
98
Page 99

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
4.3.5 DELETE MEMBER
This menu option displays a dialog box to select (highlight) RAID group members to delete.
Because RAID 0 is not fault tolerant, RAID 0 members are not shown in the list.
Note: Deleting members will demote the RAID group to a non-fault-tolerant RAID group.
4.3.6 DELETE ORPHAN
This menu option displays a dialog box to select (highlight) orphan segments to delete. An
orphan segment is part of a RAID group that cannot access other segments within the same
99
Page 100

4 Bay SATA to eSATA 3.5” HDD RAID Storage System RSV-S4-X User Manual
RAID group. When a member of a RAID group fails in a severe manner (such as a loss of
power or a complete hard disk failure), it becomes an orphan.
This command displays the Delete Orphan Segment window to show all orphan segments
and allow user to delete selected orphan segments.
4.3.7 MAKE PASS-THRU
This menu option is not available in this product.
4.3.8 DEVICE SUMMARY
This command displays the Segment Summary window to show all physical devices’
segments.
The Segment Summary window has its own menu bar. All options available via the menu bar
are shown below
100
 Loading...
Loading...