
RAMAN PROCESS ANALYZER
Instruction Bulletin IB-103-300 Rev 1.0


HIGHLIGHTS OF CHANGES
Effective May, 2001 Rev. 1.0
PAGE SUMMARY
Throughout Added information as needed to meet CE mark certification.
5-1 through 5-5 Added Analog Output section to manual.


ROSEMOUNT WARRANTY
The Raman Process Analyzer is designed for industrial applications. Treat with
care to avoid physical damage. THE WARRANTY DOES NOT COVER
DAMAGE FROM MISHANDLING.
Rosemount warrants that the equipment manufactured and sold by it will, upon
shipment, be free of defects in workmanship or material. Should any failure to conform to
this warranty become apparent during a period of one year after the date of shipment,
Rosemount shall, upon prompt written notice from the purchaser, correct such
nonconformity by repair or replacement, F.O.B. factory of the defective part or parts.
Correction in the manner provided above shall constitute a fulfillment of all liabilities of
Rosemount with respect to the quality of the equipment.
THE FOREGOING WARRANTY IS EXCLUSIVE AND IN LIEU OF
ALL OTHER WARRANTIES OF QUALITY WHETHER WRITTEN, ORAL,
OR IMPLIED (INCLUDING ANY WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY
OF FITNESS FOR PURPOSE).
The remedy(ies) provided above shall be purchaser’s sole remedy(ies) for any failure
of Rosemount to comply with the warranty provisions, whether claims by the purchaser are
based in contract or in tort (including negligence).
Rosemount does not warrant equipment against normal deterioration due to
environment. Factors such as corrosive gases and solid particulates can be detrimental and
can create the need for repair or replacement as part of normal wear and tear during the
warranty period.
Equipment supplied by Rosemount Analytical Inc. but not manufactured by it will be
subject to the same warranty as is extended to Rosemount by the original manufacturer.
At the time of installation it is important that the required services are supplied to the
system. This will ensure, that should there be a delay between installation and full
commissioning that the analyzer being supplied with ac power will not be subjected to
component deterioration.
IB-103-300
i

PURPOSE
The purpose of this manual is to provide a comprehensive understanding of the Raman Process Analyzer
components, functions, installation, and maintenance.
This manual is designed to provide information about the Raman Process Analyzer. We recommend that
you thoroughly familiarize yourself with the Description and Installation sections before installing your analyzer.
The description presents the basic principles of the analyzer along with its performance characteristics
and components. The remaining sections contain detailed procedures and information necessary to install and
service the analyzer.
Before contacting Rosemount concerning any questions, first consult this manual. It describes most
situations encountered in your equipment’s operation and details necessary action.
DEFINITIONS
The following definitions apply to WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, and NOTES found throughout this
publication.
Highlights an operation or maintenance
procedure, practice, condition, statement,
etc. If not strictly observed, could result
in injury, death, or long-term health
hazards of personnel.
Highlights an essential operating procedure,
condition, or statement.
Highlights an operation or maintenance
procedure, practice, condition, statement,
etc. If not strictly observed, could result
in damage to or destruction of
equipment, or loss of effectiveness.
NOTE
NOTE TO USERS
The number in the lower right corner of each illustration in this publication is a manual illustration
number. It is not a part number, and is not related to the illustration in any technical manner.
IB-103-300
ii

IMPORTANT
LASER SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
The Raman Process Analyzer uses a Class IV Diode Laser with a maximum output of 1 Watt at a wavelength of 810 nm (invisible, near-infrared light). The light is transmitted through fiber optic cables to and
from the probe. The Raman Process Analyzer contains a Laser Safety Device that detects the return intensity of the laser light. If the return light diminishes below a certain level, the device reduces the laser
power to Class I. This safety feature reduces the chance of personnel injury from contact with the laser.
Take the following precautions when working around the Raman Process Analyzer:
Invisible laser light — avoid exposure to operating laser. A Class IV laser is used in
this analyzer. The laser has a maximum output of 1 Watt at a wavelength of
810 nm.
1. Only service this product if you have completed formal training in laser safety and
safe servicing techniques on this unit.
2. Never look at the probe tip when the probe is connected to the analyzer. Disconnect
the fiber optic cables before examining the probe.
3. Always clean the probe tip when removed from process. It may be possible for liquid droplets or particles to attach to the tip of the probe, allowing light “reflection”
to return to the Laser Safety Device. Use only appropriate material that will not
scratch or otherwise damage the probe tip.
4. Do not bring the probe tip in contact with any surfaces when removed from the process. Any “scattered” light returned by the probe may trigger the laser back to Class
IV.
5. All personnel working in the area of the laser must wear laser safety goggles (fullgoggle type with side shields). Goggles must have a minimum attenuation factor of
100,000 (optical density 5) for an 810 nm wavelength.
IB-103-300
iii
IMPORTANT
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS FOR THE WIRING AND
INSTALLATION OF THE LASER
The following safety instructions apply specifically
to all EU member states. They should be strictly
adhered to in order to assure compliance with the
Low Voltage Directive. Non-EU states should also
comply with the following unless superseded by
local or National Standards.
1. Adequate earth connections should be made to all earthing points, internal and external,
where provided.
2. After installation or troubleshooting, all safety covers and safety grounds must be
replaced. The integrity of all earth terminals must be maintained at all times.
3. Mains supply cords should comply with the requirements of IEC227 or IEC245.
4. All wiring shall be suitable for use in an ambient temperature of greater than 75°C.
5. All cable glands used should be of such internal dimensions as to provide adequate cable
anchorage.
6. To ensure safe operation of this equipment, connection to the mains supply should only
be made through a circuit breaker which will disconnect all circuits carrying conductors
during a fault situation. The circuit breaker may also include a mechanically operated
isolating switch. If not, then another means of disconnecting the equipment from the
supply must be provided and clearly marked as such. Circuit breakers or switches must
comply with a recognized standard such as IEC947 (properly grounded three wire source
of electrical power). All wiring must conform with any local standards.
7. Warning - Electrical Shock Hazard. Where equipment or covers are
marked with the symbol to the right, hazardous voltages are likely to
be present beneath. These covers should only be removed when
power is removed from the equipment — and then only by trained
service personnel.
8. Caution - Hot Surface Hazard. Where equipment or covers are
marked with the symbol to the right, there is a danger from hot
surfaces beneath. These covers should only be removed by trained
service personnel when power is removed from the equipment.
Certain surfaces may remain hot to the touch.
9. Where equipment or covers are marked with the symbol to the
right, refer to the Operator Manual for instructions.
10. Warning - Laser Light Warning. Where equipment or covers
are marked with the symbol to the right, high powered laser
light is beneath. These covers should only be removed by
trained service personnel when power is removed from the
equipment.
11. All graphical symbols used in this product are from one or more of the following
standards: EN61010-1, IEC417, and ISO3864.
IB-103-300
iv

ESSENTIAL INSTRUCTIONS
READ THIS PAGE BEFORE PROCEEDING
Rosemount Analytical designs, manufactures, and tests all its products to meet
many national and international standards. Because these instruments are sophisticated
technical products, you must properly install, use, and maintain them to ensure they
continue to operate within their normal specifications. The following instructions must
be adhered to and integrated into your safety program when installing, using, and
maintaining Rosemount Analytical products. Failure to follow the proper instructions
may cause any one of the following situations to occur: loss of life, personal injury,
property damage, damage to the instrument, and warranty invalidation.
• Read all instructions prior to installing, operating, and servicing the product. If this
Instruction Bulletin is not the correct manual, telephone 1-800-654-7768 and the required manual will be provided. Save this instruction manual for future reference.
• If you do not understand any of the instructions, contact your Rosemount represen-
tative for clarification. Refer to the technical support hotline on page ix.
• Follow all warnings, cautions, and instructions marked on and supplied with the
product.
• Inform and educate your personnel in the proper installation, operation, and mainte-
nance of the product.
!
• Install your equipment as specified in the installation instructions of the appropriate
Instruction Bulletin and per applicable local and national codes. Connect all products to the proper electrical and pressure sources.
• This product must only be used in the manner prescribed by Rosemount. To ensure
proper performance, use qualified personnel to install, operate, update, program,
and maintain this product.
• The environmental conditions in which this equipment is designed to operate is
within an ambient operating temperature of 32° to 122°F (0° to 50°C) at 20 to 100%
relative humidity.
• There are no operator-replaceable parts.When replacement parts are required, en-
sure that the qualified people use replacement parts specified by Rosemount. Unauthorized parts and procedures can affect the product’s performance and place the
safe operation of your process at risk. Look alike substitutions may result in fire,
electrical hazards, or improper operation.
• To prevent electrical shock and personal injury, ensure that all equipment doors are
closed and protective covers are in place. Only qualified persons are authorized to
open equipment doors and remove protective covers for equipment service or
maintenance.
IB-103-300
v

WHAT YOU NEED TO KNOW
BEFORE INSTALLING AND WIRING A ROSEMOUNT
RAMAN PROCESS ANALYZER
1. What is the line voltage being supplied to the Raman Process Analyzer?
Write the line voltage here __________ .
2. Is the analyzer being controlled at the analyzer cabinet or by network connection?
3. Is the conduit set-up and all wiring for the analyzer run?
CAN YOU USE THE FOLLOWING
QUICK START GUIDE?
Use the Quick Start Guide if....
1. You are familiar with the Raman Process Analyzer installation requirements.
2. All wiring and conduit are in place for installation of the analyzer.
3. A configuration set exists for the process to be analyzed.
4. You are familiar with the SURE calibration procedures.
If you cannot use the Quick Start Guide, turn to Section II, Installation, in
this Instruction Bulletin.
IB-103-300
vi

QUICK START GUIDE
RAMAN PROCESS ANALYZER
Before using the Quick Start Guide, please read “WHAT YOU
NEED TO KNOW BEFORE INSTALLING AND WIRING A
ROSEMOUNT RAMAN PROCESS ANALYZER” on the preceding page.
1. Mount the analyzer cabinet. Refer to Section II, paragraph 2-3.a.
2. Install the Raman probes. Refer to Section II, paragraph 0.
3. Install the fiber optic cable conduits. Refer to Section II, paragraph 0.
4. Connect the fiber optic cables. Refer to Section II, paragraph 1-1.a.
5. Connect the cooling air supply and filters to the analyzer cabinet. Refer to Section
II, paragraph 2-3.e.
6. Connect line voltage to the analyzer cabinet. Refer to Section II, paragraph 2-4.
7. Connect the network cable or computer peripherals to the analyzer cabinet. Refer
to Section II, paragraphs 0 and 2-6.
8. Turn power on to the analyzer cabinet.
9. If using a network connection to control the analyzer, use the NetSupport software
to enable communication with the analyzer. Refer to Section III, paragraph 3-1.
10. Use MAINCFG to select the desired configuration set. Refer to Section III, para-
graph 3-3.a.
11. Perform a dark scan and photometric calibration procedure. Refer to Section III,
paragraph 3-3.b.
12. Select the QUIT option to start the MAIN program and monitor the process.
IB-103-300
vii

QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE
RAMAN PROCESS ANALYZER SOFTWARE
Select a configuration set
1. Close the MAIN program.
2. Start the MAINCFG program.
3. Select SYSTEM CONFIGURATION.
4. Select ENABLE A CONFIGURATION.
5. Select the configuration file to be used.
Calibrate the analyzer
1. Use the MAINCFG program and load the correct configuration set for the process
to be monitored.
2. Remove the probe from the process and ensure the probe is clean of any liquid or
foreign material.
3. Mount the probe in the SURE calibration kit.
4. Select PHOTOMETRIC CALIBRATION from the MAIN Setup Menu screen.
5. A prompt to verify that the probe is connected to the calibration kit is displayed.
Click the CONTINUE button.
6. Select the appropriate channel to be calibrated. Set the number of scans to 1 and
click CONTINUE.
7. The system auto-ranges and acquires the dark scan current, then displays the pho-
tometric curve. Make sure the curve is not saturated (have a flat region). If flat regions appear in the scan, back out the calibration kit two or three turns and press
RE-SAMPLE. Repeat the calibration kit adjustments and re-sampling until a
smooth photometric curve is measured.
8. Make sure the appropriate channel is selected and set the number of scans to 10.
Press RE-SAMPLE, then press CONTINUE.
9. Press STORE to save this scan for future use. The selected channel photometrics
are calibrated.
10. To calibrate the photometrics of another channel, repeat steps 1 through 9.
IB-103-300
viii

Technical Support Hotline:
For assistance with technical problems, please call the Customer Support Center (CSC).
Phone: 1-800-433-6076
In addition to the CSC, you may also contact Emerson Process Management North
American Response Center (NARC). North American Response Center coordinates
Rosemount’s field service throughout the US and abroad.
Phone: 1-800-654-RSMT (1-800-654-7768)
Rosemount may also be reached via the Internet through e-mail and the World Wide
Web:
E-mail: GAS.CSC@emersonprocess.com
World Wide Web: www.processanalytic.com
Manufacturer’s Address
Rosemount Analytical Inc.
1201 N. Main Street
Orrville, Ohio 44667
IB-103-300
ix/x


TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section Page
Rosemount Warranty ................................................................................................................................... i
Section I. System Overview....................................................................................................................1-1
1-1. Scope Of Manual...........................................................................................................1-1
1-2. Components Checklist (Package Contents)...................................................................1-1
1-3. Functional Equipment Description................................................................................ 1-1
1-4. Equipment Specifications............................................................................................... 1-5
Section II. Installation .............................................................................................................................2-1
2-1. Overview ......................................................................................................................... 2-1
2-2. Typical Installation......................................................................................................... 2-1
2-3. Mechanical Installation ..................................................................................................2-2
2-4. Electrical Installation...................................................................................................... 2-5
2-5. Computer Network.........................................................................................................2-6
2-6. Computer Peripherals..................................................................................................... 2-6
2-7. Installation Inspections...................................................................................................2-7
Section III. Setup...................................................................................................................................... 3-1
3-1. Communication Software............................................................................................... 3-1
3-2. MAINCFG Program....................................................................................................... 3-3
3-3. Setup................................................................................................................................ 3-8
Section IV. Operation .............................................................................................................................. 4-1
4-1. Overview ......................................................................................................................... 4-1
4-2. Software Usage Conventions ........................................................................................4-1
4-3. MAIN Program Startup................................................................................................. 4-3
Section V. ANALOG OUTPUT .............................................................................................................5-1
5-1. Introduction ..................................................................................................................... 5-1
5-2. Analog Output Scaling Setup ....................................................................................... 5-1
5-3. Access The Scaling Setup Screen................................................................................5-1
5-4. Save (or Replace) Configuration..................................................................................5-3
5-5. How Scaling is Applied................................................................................................... 5-3
5-6. Analog Output Diagnostic Screen................................................................................ 5-4
5-7. Accessing the Diagnostic Screen..................................................................................5-4
5-8. Concentration Values ......................................................................................................5-5
5-9. Outputs ............................................................................................................................5-5
Section VI. Preventive Maintenance .....................................................................................................6-1
6-1. General ............................................................................................................................6-1
6-2. Cleaning ..........................................................................................................................6-1
Section VII. Troubleshooting.................................................................................................................. 7-1
7-1. General ............................................................................................................................7-1
7-2. Alarm Messages .............................................................................................................7-1
7-3. Troubleshooting ..............................................................................................................7-1
Section VIII. Service ................................................................................................................................8-1
8-1. General ............................................................................................................................8-1
8-2. Analyzer Component Replacement............................................................................... 8-1
8-3. Analyzer Calibration ......................................................................................................8-6
IB-103-300
xi/xiv

TABLE OF CONTENTS (Continued)
Section Page
Section IX. Replacement Parts...............................................................................................................9-1
Section X. Returning Equipment to the Factory .............................................................................10-1
10-1. Returning Equipment....................................................................................................10-1
Glossary..........................................................................................................................................................1
Index............................................................................................................................................................... 1
LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS
Figure Page
Figure 1-1. Typical Raman Process Analyzer System Package..............................................................1-1
Figure 1-2. Functional Equipment Diagram............................................................................................1-2
Figure 1-3. Analyzer Cabinet..................................................................................................................1-4
Figure 2-1. Typical Installation...............................................................................................................2-1
Figure 2-2. Analyzer Cabinet Installation...............................................................................................2-2
Figure 2-3. Raman Probe ........................................................................................................................2-2
Figure 2-4. Cable Pull Box .....................................................................................................................2-3
Figure 2-5. Cable to Pull Tape Connection.............................................................................................2-3
Figure 2-6. Probe Connections................................................................................................................2-4
Figure 2-7. Air Supply Hookup ..............................................................................................................2-5
Figure 2-8. Conduit Ports........................................................................................................................2-5
Figure 2-9. Input Power Terminal...........................................................................................................2-6
Figure 2-10. Computer Connections.........................................................................................................2-6
Figure 3-1. NETSUPPORT CONTROL Screen ...................................................................................3-1
Figure 3-2. KNOWN CLIENTS Screen ...............................................................................................3-1
Figure 3-3. MAINCFG Program Structure .............................................................................................3-2
Figure 3-4. SETUP MENUS Screen.....................................................................................................3-3
Figure 3-5. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MENU Screen ................................................................3-3
Figure 3-6. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION Screen...............................................................................3-3
Figure 3-7. PLS SETUP Screen ............................................................................................................3-4
Figure 3-8. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION Screen...............................................................................3-4
Figure 3-9. CCD MAP Screen ...............................................................................................................3-5
Figure 3-10. CONFIGURE MODBUS Screen ........................................................................................3-5
Figure 3-11. SYSTEM CONFIGURATION MENU Screen .................................................................3-6
Figure 3-12. SETUP MENUS Screen......................................................................................................3-6
Figure 3-13. Calibration Message.............................................................................................................3-6
Figure 3-14. PHOTOMETRIC CALIBRATION Screen........................................................................3-7
Figure 3-15. DARK CURRENT CALIBRATION Screen ....................................................................3-8
Figure 4-1. MAIN Program Structure.....................................................................................................4-2
Figure 4-2. RAMAN PROCESS ANALYZER Screen........................................................................4-3
Figure 4-3. PASSWORD VERIFICATION Screen..............................................................................4-3
Figure 4-4. OPERATOR MENUS Screen ............................................................................................4-4
Figure 4-5. SETUP MENUS Screen.....................................................................................................4-4
Figure 4-6. ZERO CLIP OPTION Screen............................................................................................4-4
Figure 4-7. RAMAN ANALYZER DATALOG UTILITY Screen....................................................4-5
Figure 4-8. OPERATOR MENUS Screen ............................................................................................4-5
IB-103-300
xii

LIST OF ILLUSTRATIONS (Continued)
Figure Page
Figure 4-9. GRAB SCAN MENUS Screen .........................................................................................4-5
Figure 4-10. GRAB SCAN Screen .......................................................................................................... 4-6
Figure 4-11. SAVE AS Screen ...............................................................................................................4-6
Figure 4-12. OPERATOR MENUS Screen.............................................................................................4-7
Figure 4-13. DIAGNOSTIC MENUS Screen..........................................................................................4-7
Figure 4-14. VIEW CALCULATIONS Screen.......................................................................................4-7
Figure 4-15. DIAGNOSTIC MENUS Screen..........................................................................................4-8
Figure 4-16. ANALOG INPUT MEASUREMENTS Screen.................................................................4-9
Figure 4-17. DIGITAL I/O STATE Screen............................................................................................ 4-9
Figure 4-18. SMART DIAGNOSTICS MENU Screen........................................................................ 4-10
Figure 4-19. ANALYZER SOFTWARE STATUS Screen.................................................................. 4-10
Figure 4-20. ANALYZER ALARMS STATUS Screen....................................................................... 4-11
Figure 4-21. PASSWORD VERIFICATION Screen ............................................................................4-12
Figure 4-22. TRENDS Screen ................................................................................................................4-12
Figure 4-23. SMART DIAGNOSTICS MENU Screen....................................................................... 4-13
Figure 4-24. PERFORMANCE MEASURES Screen ...........................................................................4-13
Figure 4-25. DARK CURRENT & PHOTOMETRIC CORRECTION Screen .................................4-14
Figure 4-26. CALIBRATION PATH & MODEL Screen ..................................................................4-14
Figure 4-27. DIAGNOSTICS MENUS Screen ....................................................................................4-15
Figure 4-28. OPERATOR MENUS Screen...........................................................................................4-15
Figure 4-29. SET SECURITY Screen ...................................................................................................4-16
Figure 4-30. SET PASSWORDS Screen...............................................................................................4-16
Figure 4-31 GRAB DARK SCAN Screen.......................................................................................... 4-16
Figure 4-32. ABOUT Screen .................................................................................................................. 4-16
Figure 5-1. RAMAN PROCESS ANALYZER Screen ........................................................................5-1
Figure 5-2. PASSWORD VERIFICATION Screen ..............................................................................5-2
Figure 5-3. OPERATOR MENUS Screen.............................................................................................5-2
Figure 5-4. SETUP MENUS Screen...................................................................................................... 5-2
Figure 5-5. ANALOG OUTPUT SCALING SETUP Screen ............................................................... 5-2
Figure 5-6. SAVE Prompt ......................................................................................................................5-3
Figure 5-7. DIAGNOSTIC MENUS Screen..........................................................................................5-4
Figure 5-8. ANALOG OUTPUT DIAGNOSTIC Screen ..................................................................... 5-4
Figure 7-1. Raman Troubleshooting Flowchart #1.................................................................................7-2
Figure 7-2. Raman Troubleshooting Flowchart #2.................................................................................7-3
Figure 7-3. Raman Troubleshooting Flowchart #3.................................................................................7-4
Figure 8-1. Fuse Locations .....................................................................................................................8-2
Figure 8-2. CCD Camera Thermocouple Removal.................................................................................8-2
Figure 8-3. Laser Cooling Fan Removal.................................................................................................8-3
Figure 8-4. Laser Removal .....................................................................................................................8-4
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
Table 1-1. Raman Process Equipment Specifications (Analyzer)*...................................................... 1-5
Table 9-1. Replacement Parts for the Raman Process Analyzer ...........................................................9-1
IB-103-300
xiii/xiv


1
SECTION I. SYSTEM OVERVIEW
1-1. SCOPE OF MANUAL
This instruction bulletin covers installation, setup,
operation, troubleshooting, and maintenance of the
Raman Process Analyzer manufactured by Rosemount Analytical. The troubleshooting and service
procedures in this manual are limited to those that
can be performed by most equipment operators.
1-2. COMPONENTS CHECKLIST
(PACKAGE CONTENTS)
The Raman Process Analyzer system includes the
items listed in Figure 1-1. The SURE Calibration Kit
contains all the necessary components for quickly
calibrating the analyzer.
1-3. FUNCTIONAL EQUIPMENT DESCRIPTION
When properly configured, the analyzer detects and
measures the concentration of sample components
that inelastically scatter light. Access for the detection of the process components is accomplished with
one to four analyzer probes installed in or around the
process flow.
Functional components of the analyzer are shown in
the electronic diagram of Figure 1-2. The important
components of the diagram include the process
probes, the diode lasers, the laser safety device,
spectrograph, vortex cooler, CCD camera, and the
industrial computer. Brief descriptions of the analyzer component functions are provided in the following paragraphs.
1. Analyzer
2. Analyzer Test Records
3. Instruction Bulletin
4. Backup Software
5. SURE Calibration Kit
6. Oil Filter
7. Water Filter
8. In Situ Probe (1 per channel)
9. Fiber Optic Cables (3 per probe)
Figure 1-1. Typical Raman Process Analyzer System Package
IB-103-300
1-1

PRESSURE
REGULATOR
AIR
SUPPLY
OIL
FILTER
VORTEX
COOLING
CHAMBER
AIR
VALV E
HOT
AIR
USER
INTERFACE
ANALYZER CABINET
INDUSTRIAL
COMPUTER
LASER
CONTROL
MODULE
WATER
FILTER
CONTROLLER
PROCESS PROBES
LASER
SAFETY
BOARD
DIAMOND
REFERENCE 1
FILTER
CCD
CAMERA
1
OPTIC
SPECTROGRAPH
DIODE
LASER 1
SPLITTER
OPTIC
FILTER
DIODE
LASER 2
DIAMOND
REFERENCE 2
CCD
CAMERA
HEAD
SPLITTER
SPLITTER
2
3
4
Figure 1-2. Functional Equipment Diagram
IB-103-300
1-2
SPLITTER
27320024
The following are brief descriptions of analyzer component functions. A listing of components in the
analyzer cabinet is provided in Figure 1-3.
a. Diode Lasers and Probes. The analyzer uses
one or two diode lasers and up to four process
probes. Each diode laser generates a light beam.
The light beam is split in a 10/90 optic splitter.
Fiber optic cables transmit ten percent of the
beam to a diamond reference circuit and the remaining ninety percent to a 50/50 optic splitter.
A fiber optic cable from the diamond reference
transmits the reference beam to the spectrograph.
The ninety percent portion of the beam is evenly
split to provide excitation energy for two process
probes. Each beam is filtered at the probe to
eliminate stray radiation. The probe emits the
filtered laser beam into the process flow.
The process components inelastically scatter distinct wavelengths. Two return cables transmit
scattered light from the probe to the analyzer.
The unfiltered S cable transmits all scattered
light to the Laser Safety Device. The filtered R
cable transmits only a specific range of nearinfrared wavelengths to the spectrograph.
b. Laser Safety Device. To minimize operator
hazards, the laser safety device monitors the intensity of the scattered laser light from the process flow. If the safety device receives less than
an acceptably large part of the scattered light, it
reduces the laser power output from Class IV to
Class I.
The laser safety device continues to regulate the
output of the diode lasers at pulsed Class I power
levels until the device detects an acceptable
amount of scattered light from the process.
Low light scatter may indicate a broken fiber optic cable, a bad cable connection, or removal of
the probe from the process. Refer to the “Laser
Safety Instructions” in the front of this manual
for more information.
c. Vortex Cooler. The vortex cooler helps control
the temperature of the CCD (charge coupled device) camera and the cabinet interior. The main
function of the vortex cooler is to maintain the
ambient temperature near the camera at 30°C so
that the internal CCD chip temperature will remain at –30°C.
Incoming instrument air is dried, filtered, and
routed through a temperature-controlled air valve
to the vortex cooler. The vortex effect separates
the forced air into warm and cold air flows. The
chilled air is routed to the CCD camera.
As the cabinet air gets warmer, the air valve
opens a larger flow of forced air to the vortex
chamber, providing more cooling air to the camera. As the cabinet air cools, a proportional air
valve partly closes to slow the flow of cooling
air.
d. Spectrograph and CCD Camera. Filtered light
from the diamond reference and the R probe is
transmitted by fiber optic cable to the spectrograph. The spectrograph separates incoming light
into distinct wavelengths. Each wavelength of
light is sent to the CCD camera head where the
spectral image is decoded and electronically transferred to the CCD camera controller. The controller processes the spectral image into numerical
data. The data is sent to the industrial computer for
interpretation and display.
e. Industrial Computer. The industrial computer
converts data points into light intensity with respect to frequency. The histogram of each predicted component is displayed on the CRT. The
spectra are processed by the prediction’s algorithm in accordance with the calibration file.
Each application requires its own calibration file.
The output data is stored for further analysis.
f. User Interface. An interface device is required
to set up and operate the analyzer using the
MAIN and MAINCFG software programs. The
user interface device can be a remote computer
connected through a network modem, Ethernet,
RF antenna and laptop computer, or a monitor,
keyboard, and mouse connected at the analyzer
cabinet.
g. Analyzer Outputs. The available analyzer out-
puts are MODBUS and/or analog, 4 to 20 mA.
h. SURE Calibration Kit. The SURE calibration
kit is a light proof housing that secures the probe
tip above a fluorescent glass. The kit uses no
external light source or power source. When the
fluorescent glass and probe are properly assembled in the light-proof housing, the analyzer can
be calibrated using the MAINCFG software program.
IB-103-300
1-3

1. Hoffman Enclosure 10. Temperature Controller
2. Computer Power Supply 11. Enclosure Backplate
3. Computer 12. CCD Camera Controller
4. Disk Drives 13. Spectrograph Assembly
5. Optics Assembly Tray 14. Laser Pedestal Assembly
6. CCD Camera 15. Laser Safety Device
7. CCD Camera Hood 16. Proportional Air Valve
8. Termination Board 17. Raman Power Supply
9. Peripheral Device Connector 18. Vortex Cooler Assembly
Figure 1-3. Analyzer Cabinet
IB-103-300
1-4

1-4. EQUIPMENT SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1-1. Raman Process Equipment Specifications (Analyzer)*
Spectral Range ........................................................................................................... 500 cm
-1
to 2000 cm-1 Raman Shift
Spectral Resolution .................................................................................................................................................. ∼2 nm
Typical Error ...................................................................................... Less than 1% of full-scale, application dependent
Operating Temperature ............................................................................................................. 32° to 122°F (0° to 50°C)
Storage Temperature ................................................................................................................ 32° to 122°F (0° to 50°C)
Relative Humidity .......................................................................................................................................... 20 to 100%
Warm-up Time ................................................................................................................................................ 60 minutes
Input Power ........................................................................................................... 115 VAC, 60 Hz or 230 VAC, 50 Hz
Power Rating ......................................................................................................................................... 250 VA (250 W)
Electrical Classification ................................................................... General Purpose or Class I, Div II, Type “Z” Purge
Environmental Classification .......................................................................................................................... NEMA-4X
Dimensions (H x W x D) .................................................................................. 48 x 24 x 12 in. (1219 x 610 x 305 mm)
Weight ...................................................................................................................................................... 165 lbs (75 kg)
Certification ........................................................................................................................................................ CE Mark
*Probe specifications may vary from probe to probe. Refer to the material supplied with probe for specifications.
1-5. CERTIFICATIONS
Emerson Process Management has satisfied all obligations coming from the European legislation to harmonize the product requirements in Europe.
IB-103-300
1-5/1-6


2
SECTION II. INSTALLATION
2-2. TYPICAL INSTALLATION
Before starting to install this equipment,
read the “Safety instructions for the
wiring and installation of the laser” at
the front of this Instruction Bulletin.
Failure to follow the safety instructions
could result in serious injury, death, or
substantial property damage.
2-1. OVERVIEW
This section covers installation of the Rosemount
Raman Process Analyzer. Included are a typical installation, common requirements, what you need to
have on hand to start an installation, and the mechanical and electrical installation instructions. An
authorized Rosemount service representative must
complete the analyzer installation. You must complete the mechanical installation before calling the
service representative for final check-out and installation commissioning.
A typical system installation is shown in Figure 2-1.
When properly installed, the analyzer cabinet is securely mounted to a wall in the process control area.
The cabinet should not be mounted in the path of direct sunlight.
Process probes are installed in the process flow (usually a sampling flow). Up to four process probes may
be installed for each analyzer. The installed probes
should be adequately shielded from accidental impact, rainfall, and direct sunlight. Ready access for
probe removal, cleaning, and replacement is recommended.
Fiber optic cable lengths are per customer specification. Make sure the correct cables are selected for
each run. One inch or larger diameter conduits or cable troughs are recommended for shielding the fiber
optic cables. Pull boxes are needed when successive
cable bend angles exceed 180 degrees. Conduit ends
should point down to protect against water accumulation. Sharp conduit edges must be avoided and the
cables should be lubricated before pulling.
Figure 2-1. Typical Installation
IB-103-300
2-1
2-3. MECHANICAL INSTALLATION
a. Analyzer Cabinet.
Lift the cabinet with the upper brackets. Avoid
contact with the vortex cooler. Position and securely mount the cabinet using appropriate
screws and flat washers.
b. Raman Probe.
Never rest the cabinet standing up.
Damage to conduit fittings can occur.
The analyzer is housed in a NEMA-4X cabinet.
The NEMA-4X cabinet is suitable for wall
mounting in a Class I, Division II environment
when equipped with an ISA Type Z-Purge.
When lifting, the cabinet door must be closed
and latched. Make sure the mounting brackets
are installed and tight.
The analyzer cabinet weighs approximately 165
lbs (75 kg). Analyzer cabinet mounting dimensions are provided in Figure 2-2. Mark the position for cabinet hanger mounting on center with
wall studs or a securely mounted plywood backplate.
24.0
(609.6)
12.0
(304.8)
Each analyzer system includes up to four process
probes designed for mounting in a flow line or
tank. Install each process probe according to the
following instructions:
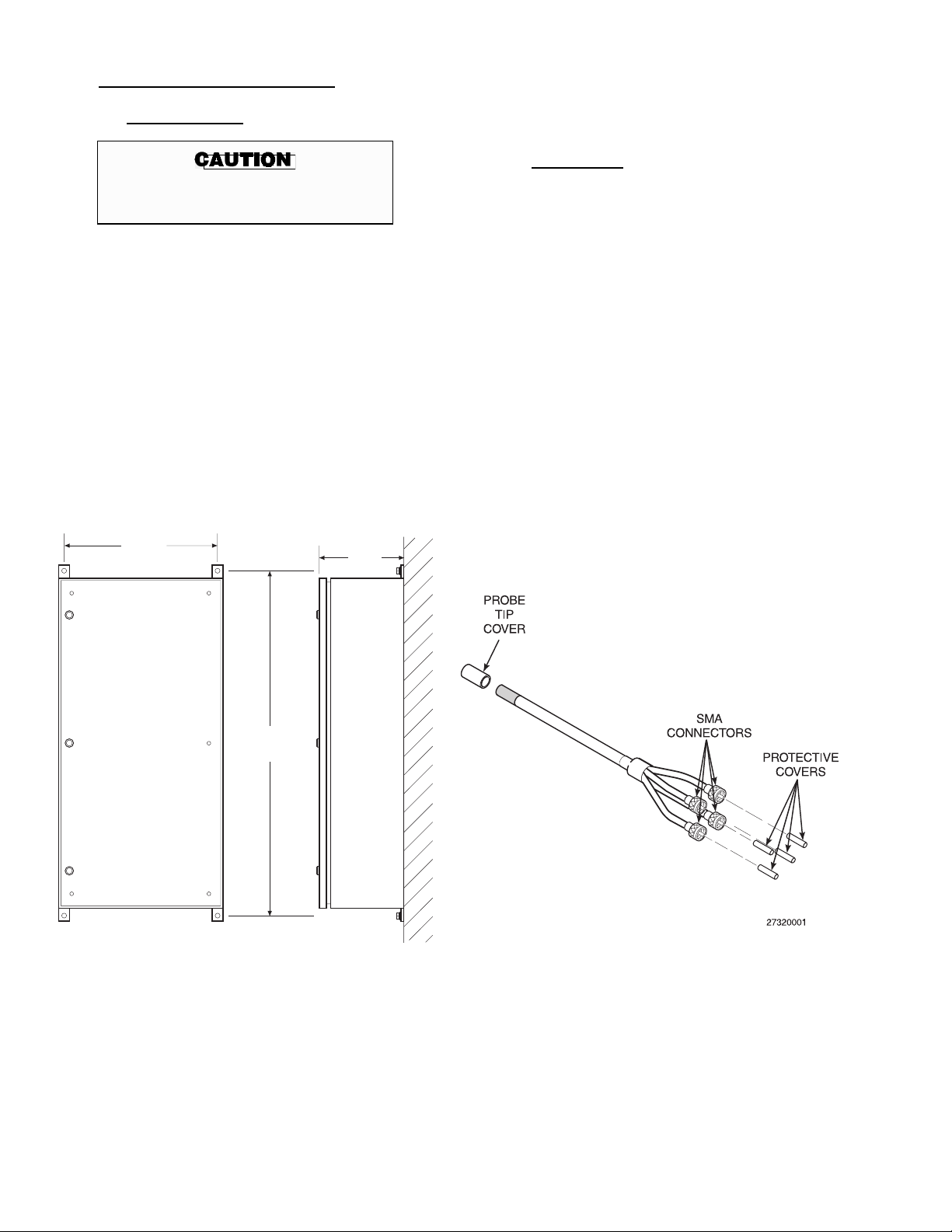
1.
Remove the protective covers from the
probe tip, Figure 2-3.
2. Install a bored through compression fitting
of compatible metallurgy in the process
line, tee, or process tank wall.
3.
Insert the probe to the desired depth in the
compression fitting.
4. If compatible with the process, apply a suit-
able sealant around the seal diameter of the
probe.
5. Tighten the compression fitting to secure
the probe. Do not over-tighten the fitting.
48.0
(1219.2)
NOTE:
DIMENSIONS ARE IN INCHES WITH
MILLIMETERS IN PARENTHESIS.
Figure 2-2. Analyzer Cabinet Installation
27320025
IB-103-300
Figure 2-3. Raman Probe
2-2
ENDPLATE
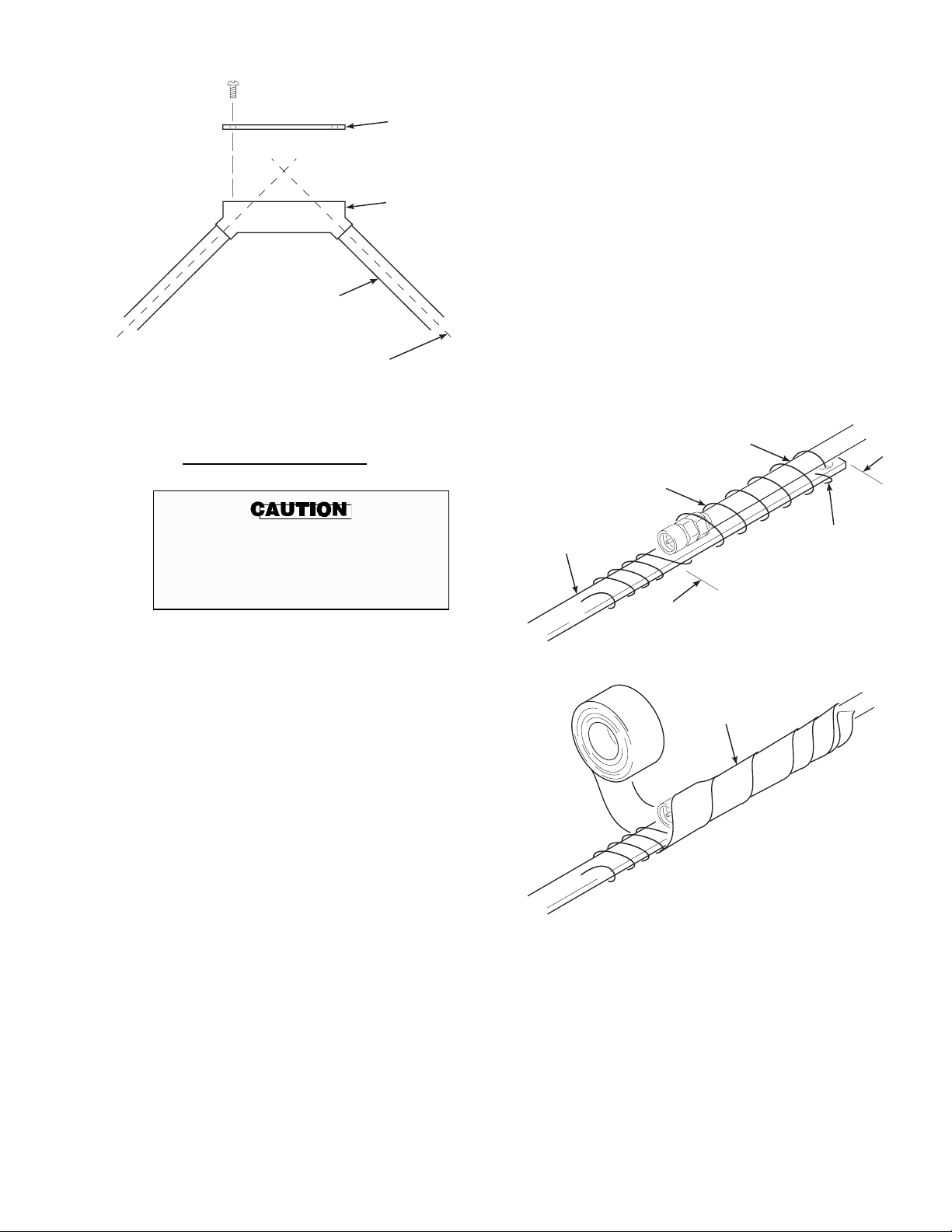
4. Overlay 3 ft (91.4 cm) of the fiber optic ca-
ble onto the pull tape and wrap with nylon
string to hold in place. Wrap and tape the
fiber optic cable to the pull tape as shown in
Figure 2-5.
CABLE PULL
BOX (90 TURN
CONDUIT
FIBER OPTIC
CABLE
Figure 2-4. Cable Pull Box
c. Fiber Optic Cable Conduits.
Fiber optic cables are precision optics
devices. Careless handling or installation of a fiber optic cable can result in
permanent cable damage.
1.
Install a 3/4 in. (19 mm) diameter minimum
conduit from the analyzer cabinet to each
process probe. The minimum radius for all
conduit bends is 10 in. (254 mm). For fiber
optic cable runs, it is not required to connect the conduit to the analyzer cabinet.
o
FITTING)
27320060
NYLON STRING
(WRAP TIGHTLY)
PULL TAPE
5.
Carefully pull the cable through the conduit; pull enough cable to allow for cable
slack when connecting at the analyzer cabinet or probe.
6.
When using cable pull boxes, turn the
coiled cable over. Feed the pull tape to the
opposite side of the pull box. Wrap and tape
the cable to the pull tape and pull the free
end through the next section of conduit.
Repeat the cable pulling instructions as
needed to install all fiber optic cables.
FIBER OPTIC
CABLE
FEED STRING
THROUGH PULL
TAPE EYELET
3FT
(91.4 CM)
WRAP WITH
ELECTRICAL
TAPE
2.
Install a cable pull box following a series of
conduit bends totaling 180 degrees. A 90
degree turn fitting (Figure 2-4) is recommended for use as a cable pull box.
3.
When using pull boxes, coil the fiber optic
cable into a figure eight below the pull box.
Feed a cable pull tape from one conduit end
to the pull box.
27320031
Figure 2-5. Cable to Pull Tape Connection
IB-103-300
2-3
 Loading...
Loading...