ROHM 2SB852K Technical data
2SB852K
Transistors
High-gain Amplifier Transistor (−32V, −0.3A)
2SB852K
zFeatures
1) Darlington connection for high DC current gain.
2) Built-in 4kΩ resistor between base and emitter.
3) Complements the 2SD1383K.
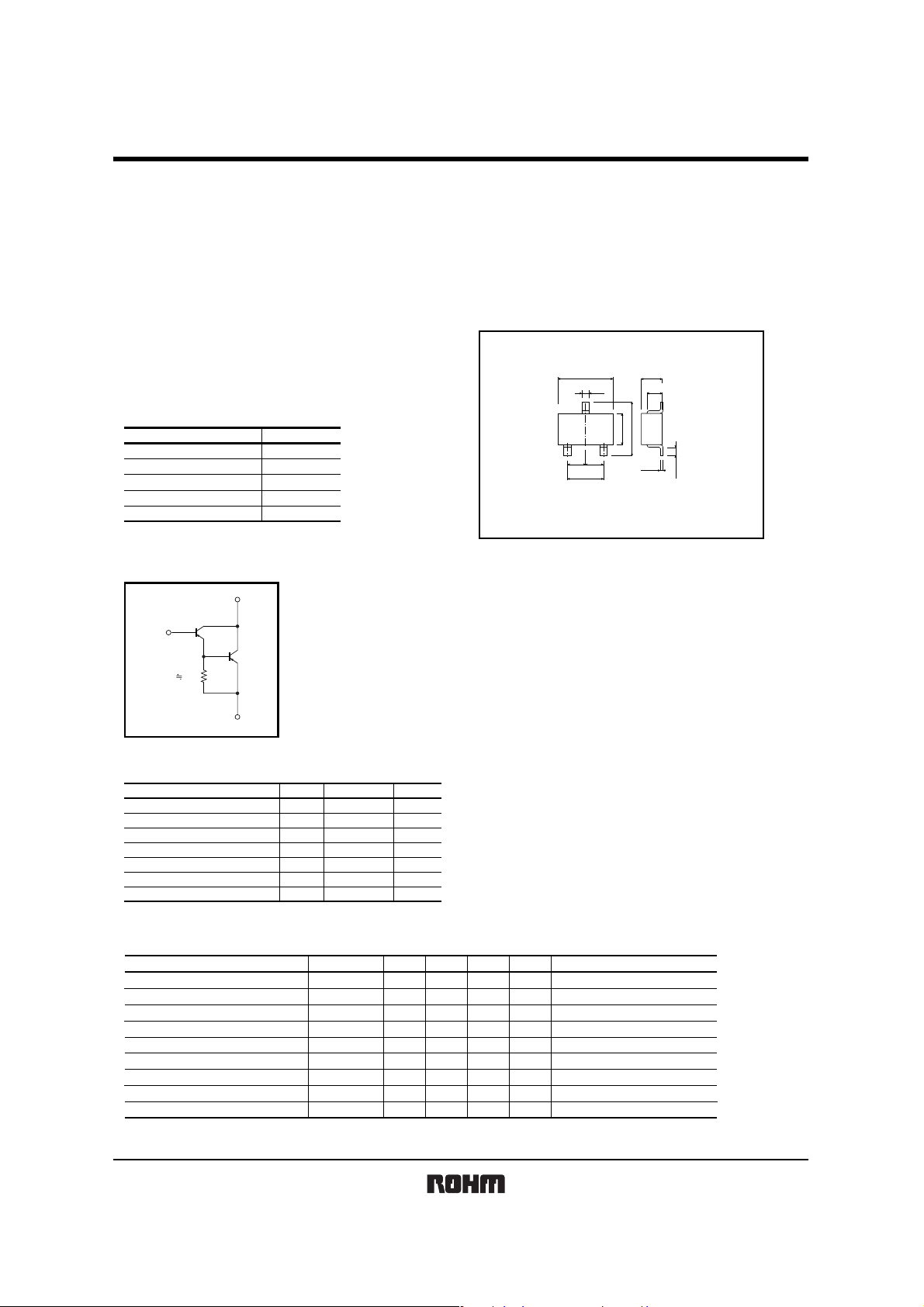
zPackaging specifications
Type
Package
FE
h
Marking
Denotes h
Code
FE
Basic ordering unit (pieces)
∗
2SB852K
SMT3
B
U
∗
T146
3000
zCircuit diagram
C
zExternal dimensions (Unit : mm)
2SB852K
(1)Emitter
(2)Base
(3)Collector
2.9
(3)
(2)
0.95 0.95
1.9
0.4
1.1
0.8
1.6
2.8
(1)
0.15
Each lead has same dimensions
0.3Min.
B
R
BE
4kΩ
E : Emitter
B : Base
C : Collector
E
zAbsolute maximum ratings (Ta=25°C)
C
C
Limits
−40
−32
−6
−0.3
0.2
150
−55 to +150
Unit
V
V
V
A
W
°C
°C
∗
Collector-base voltage
Parameter Symbol
Collector-emitter voltage
Emitter-base voltage
Collector current
Collector power dissipation
Junction temperature
Storage temperature
∗ RBE=0Ω
V
V
V
P
Tstg
CBO
CES
EBO
I
Tj
zElectrical characteristics (Ta=25°C)
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit Conditions
Collector-base breakdown voltage
Collector-emitter breakdown voltage
Emitter-base breakdown voltage
Collector cutoff current
Emitter cutoff current
DC current transfer ratio
Collector-emitter saturation voltage
Transition frequency
Output capacitance
∗
1 Measured using pulse current.
∗
2 Transition frequency of the device.
CBO
BV
BV
CES
BV
EBO
I
CBO
EBO
I
FE
h
CE(sat)
V
T
f
Cob − 3 −
−40
−32
−6
−−
−−
−−
−−
−−
5000 −
−−−1.5
200
−
V
V
V
−1
µAVCB= −24V
−1
µAVEB= −4.5V
−−
V
MHz
−
pF
C
= −100µA
I
C
= −1mA
I
E
= −100µA
I
V
CE
= −5V, IC= −0.1A
C
= −200mA, IB= −0.4mA
I
VCE= −5V, IE=10mA, f=100MHz
V
CB
= −10V, IE=0A, f=1MHz
∗
1
∗
2
Rev.B 1/2
2SB852K
Transistors
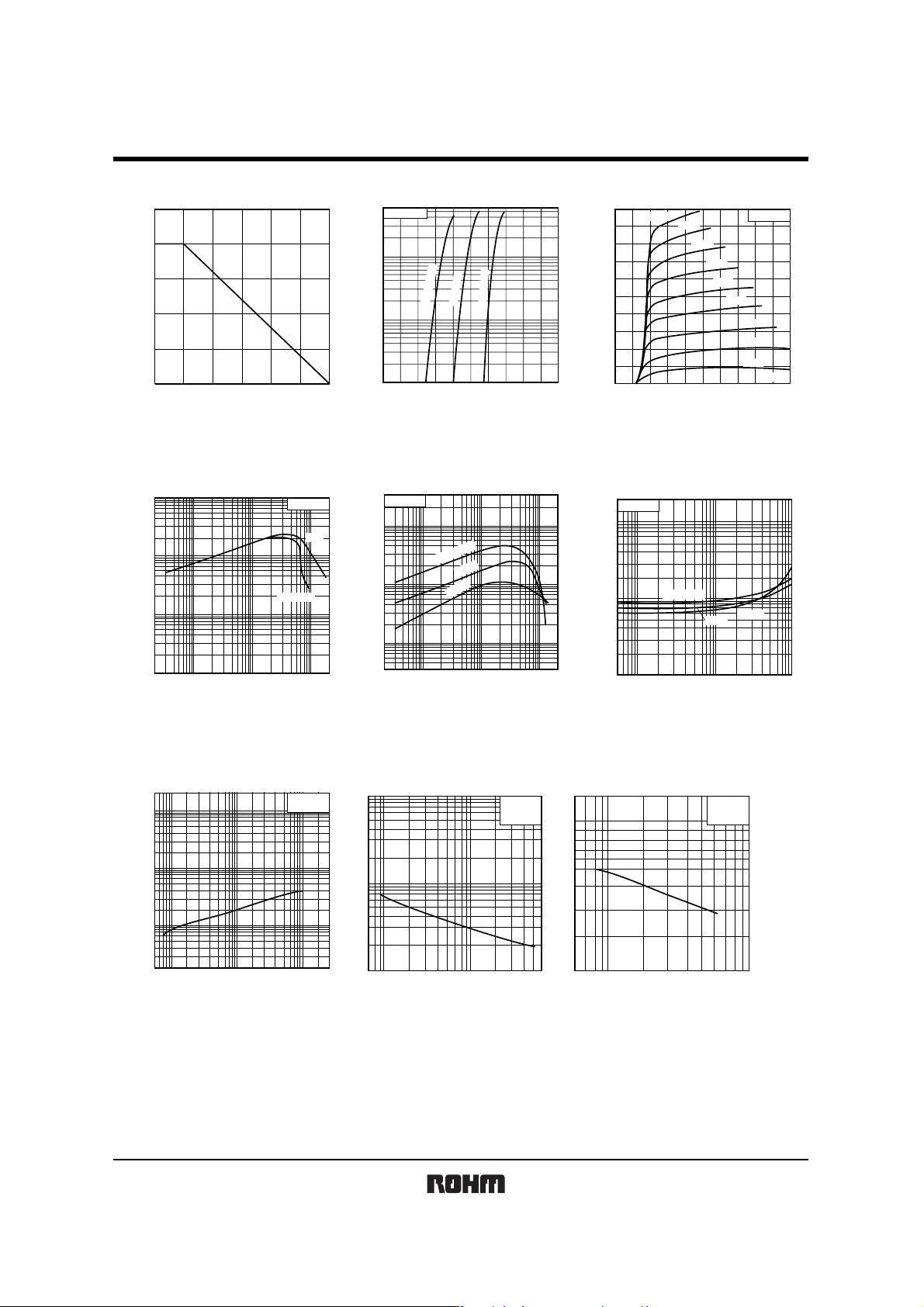
zElectrical characteristic curves
125
(%)
100
CMax
/P
C
75
50
25
POWER DISSIPATION : P
0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE : Ta (°C)
Fig.1 Power dissipation curves
100000
50000
20000
10000
5000
2000
1000
DC CURRENT GAIN : hFE
500
200
100
−2 −5 −10 −20 −50 −100 −200 −500
COLLECTOR CURRENT : I
Fig.4 DC current gain vs. collector current ( Ι )
Ta=25°C
VCE= −3V
C
(mA)
−5V
−1000 −2000
−500
VCE= −6V
(mA)
−200
C
−100
−50
−20
−10
−5
COLLECTOR CURRENT : I
−2
0
−0.4 −0.8 −1.2 −1.6 −2.0 −2.4
C
=100°
Ta
BASE TO EMITTER VOLTAGE : V
C
°
°C
55
Ta=25
Ta= −
BE
(V)
Fig.2 Ground emitter propagation characteristisc
VCE= −5V
FE
50000
20000
10000
5000
DC CURRENT GAIN : h
2000
1000
500
−5 −10 −20 −50 −100 −200 −500
COLLECTOR CURRENT : I
Ta=100
55°C
−
25°C
C
°
−1000 −2000
C
(mA)
Fig.5 DC current gain vs. collector current ( ΙΙ )
−100
(mA)
−80
C
−60
−40
−20
COLLECTOR CURRENT : I
−10µA
−9µA
−8µA
0
0 −1
COLLECTOR TO EMITTER VOLTAGE : V
−2 −3 −4 −5
Ta=25°C
−7µA
−6µA
−5µA
−4µA
−3µA
−2µA
IB=0
CE
Fig.3 Ground emitter output characteristics
−20
IC/IB=500
−10
FE
−5
−2
−1
−0.5
DC CURRENT GAIN : h
−0.2
−0.1
−5
Ta= −55°C
100°C
25°C
−10 −20 −50 −100 −200 −500
COLLECTOR CURRENT : I
C
(mA)
Fig.6 Collector-emitter saturation voltage
vs. collector current
(V)
−1000
10000
(MHz)
T
5000
2000
1000
500
200
100
TRANSISION FREQUWNCY : f
50
1 2 5 10 20 50 100 200
EMITTER CURRENT : I
E
(mA)
Ta=25°C
VCE= −5V
100
OUTPUT CAPACITANCE : Cob (pF)
Fig.7 Gain bandwidth product vs. emitter current
50
20
10
5
2
1
−1 −2 −5 −10 −20 −50
COLLECTOR TO BASE VOLTAGE : V
Fig.8 Collector output capacitance
vs. collector-base voltage
Ta=25°C
f=1MHz
I
E
=0A
20
10
5
2
EMITTER INPUT CAPACITANCE : Cib (pF)
1
−1 −2 −5 −10
CB
(V)
EMITTER TO BASE VOLTAGE : V
Fig.9 Emitter input capacitance
vs. emitter-base voltage
Ta=25°C
f=1MHz
I
E
=0A
EB
(V)
Rev.B 2/2
 Loading...
Loading...