
R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
1xEV-DO Rev A, Rev B
User Manual
(;ÜÞì2)
1178809402
Version 06

This document describes the following software options:
●
R&S®SMBVB-K47 1xEV-DO Rev. A (1423.7776.xx)
●
R&S®SMBVB-K87 1xEV-DO Rev. B (1423.7930.xx)
This manual describes firmware version FW 5.00.044.xx and later of the R&S®SMBV100B.
© 2021 Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co. KG
Mühldorfstr. 15, 81671 München, Germany
Phone: +49 89 41 29 - 0
Email: info@rohde-schwarz.com
Internet: www.rohde-schwarz.com
Subject to change – data without tolerance limits is not binding.
R&S® is a registered trademark of Rohde & Schwarz GmbH & Co. KG.
Trade names are trademarks of the owners.
1178.8094.02 | Version 06 | R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
The following abbreviations are used throughout this manual: R&S®SMB100B is abbreviated as R&S SMBVB, R&S®WinIQSIM2TM is
abbreviated as R&S WinIQSIM2; the license types 02/03/07/11/13/16/12 are abbreviated as xx.

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Contents
1 Welcome to the 1xEV-DO digital standard...........................................5
1.1 Accessing the 1xEV-DO dialog....................................................................................6
1.2 What's new.....................................................................................................................6
1.3 Documentation overview..............................................................................................6
1.3.1 Getting started manual....................................................................................................6
1.3.2 User manuals and help................................................................................................... 6
1.3.3 Service manual............................................................................................................... 7
1.3.4 Instrument security procedures.......................................................................................7
1.3.5 Printed safety instructions............................................................................................... 7
1.3.6 Data sheets and brochures............................................................................................. 7
1.3.7 Release notes and open source acknowledgment (OSA).............................................. 7
Contents
1.3.8 Application notes, application cards, white papers, etc...................................................8
1.4 Scope............................................................................................................................. 8
1.5 Notes on screenshots...................................................................................................8
2 About the 1xEV-DO options.................................................................. 9
2.1 Required options...........................................................................................................9
2.2 Modulation system........................................................................................................9
2.3 Traffic scheduling process.........................................................................................11
3 1xEV-DO configuration and settings..................................................12
3.1 General settings.......................................................................................................... 12
3.2 Trigger settings........................................................................................................... 15
3.3 Marker settings............................................................................................................19
3.4 Clock settings..............................................................................................................20
3.5 Global connectors settings........................................................................................21
3.6 Traffic channel settings..............................................................................................22
3.7 Multi-carrier configuration settings...........................................................................34
3.8 Access network settings............................................................................................ 36
3.9 Access terminal settings............................................................................................40
3.10 Filter / clipping / ARB settings................................................................................... 55
3.10.1 Filter settings.................................................................................................................56
3.10.2 Clipping settings............................................................................................................57
3User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
3.10.3 ARB settings................................................................................................................. 58
3.10.4 I/Q setting......................................................................................................................59
4 Remote-control commands.................................................................61
4.1 Programming examples............................................................................................. 62
4.2 General commands.....................................................................................................64
4.3 Filter / clipping / ARB commands..............................................................................68
4.4 Trigger commands......................................................................................................73
4.5 Marker commands...................................................................................................... 76
4.6 Clock commands........................................................................................................ 77
4.7 Access network commands.......................................................................................78
4.8 Multi-carrier configuration commands..................................................................... 82
4.9 Configure traffic user commands..............................................................................85
Contents
4.10 Configure access terminal commands..................................................................... 95
List of commands...............................................................................117
Index....................................................................................................120
4User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
1 Welcome to the 1xEV-DO digital standard
The R&S SMBV100B-K47/-K87 is a firmware application that adds functionality to generate signals in accordance to the CDMA2000® 1xEV-DO (Evolution-Data Optimized),
Rev. A and Rev. B.
CDMA2000® 1xEV-DO is the North American standard for the third mobile radio generation (3G). CDMA2000® 1xEV-DO is a high-speed packet-switched transmission technique with forward peak data rates of 4.9152 Mbps per carrier, designed and optimized
for a data-centric broadband network.
The R&S SMBV100B simulates 1xEV-DO signal at the physical layer. In forward link
(downlink) mode, the signal is generated in real time. Parameter changes during active
signal output take effect immediately without signal interruption. In reverse link (uplink)
mode, the signal is precalculated and played from the ARB memory. Parameter
changes result in a recalculation of the signal.
The following list gives an overview of the main feature provided by the
R&S SMBV100B for generating an 1xEV-DO signal in accordance with 3GGP2
C.S0024-B.v3.0.
●
Generation of 1xEV-DO signals with a chip rate of 1.2288 Mcps
●
Independent configuration of up to four traffic channels or four access terminals
●
Support of physical layer subtypes 0, 1, 2 and 3
●
Support of multi-carrier operation with up to 16 simultaneous carriers
●
Operating modes "Traffic" and "Access" on the uplink
●
Simulation of up to 360 additional MAC users
●
Generation of standard compliant forward/downlink and reverse/uplink channel
types
●
Supports configuration of public data as defined in the standard, such as Long
Code Masks for I and Q channel, Preamble Length, DRCLength.
●
Filling the data files for data channels from the following standard sources: pattern
(all1, all0, user-defined up to 64 bits), PN data or data lists
●
Clipping for reducing the crest factor
Welcome to the 1xEV-DO digital standard
This user manual contains a description of the functionality that the application provides, including remote control operation.
All functions not discussed in this manual are the same as in the base unit and are
described in the R&S SMBV100B user manual. The latest version is available at:
www.rohde-schwarz.com/manual/SMBV100B
Installation
You can find detailed installation instructions in the delivery of the option or in the
R&S SMBV100B service manual.
5User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
1.1 Accessing the 1xEV-DO dialog
To open the dialog with 1xEV-DO settings
► In the block diagram of the R&S SMBV100B, select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO".
A dialog box opens that display the provided general settings.
The signal generation is not started immediately. To start signal generation with the
default settings, select "State > On".
1.2 What's new
This manual describes firmware version FW 5.00.044.xx and later of the
R&S®SMBV100B.
Compared to the previous version there are editorial changes only.
Welcome to the 1xEV-DO digital standard
Documentation overview
1.3 Documentation overview
This section provides an overview of the R&S SMBV100B user documentation. Unless
specified otherwise, you find the documents on the R&S SMBV100B product page at:
www.rohde-schwarz.com/manual/smbv100b
1.3.1 Getting started manual
Introduces the R&S SMBV100B and describes how to set up and start working with the
product. Includes basic operations, typical measurement examples, and general information, e.g. safety instructions, etc. A printed version is delivered with the instrument.
1.3.2 User manuals and help
Separate manuals for the base unit and the software options are provided for download:
●
Base unit manual
Contains the description of all instrument modes and functions. It also provides an
introduction to remote control, a complete description of the remote control commands with programming examples, and information on maintenance, instrument
interfaces and error messages. Includes the contents of the getting started manual.
●
Software option manual
Contains the description of the specific functions of an option. Basic information on
operating the R&S SMBV100B is not included.
6User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
The contents of the user manuals are available as help in the R&S SMBV100B. The
help offers quick, context-sensitive access to the complete information for the base unit
and the software options.
All user manuals are also available for download or for immediate display on the Internet.
1.3.3 Service manual
Describes the performance test for checking compliance with rated specifications, firmware update, troubleshooting, adjustments, installing options and maintenance.
The service manual is available for registered users on the global Rohde & Schwarz
information system (GLORIS):
https://gloris.rohde-schwarz.com
1.3.4 Instrument security procedures
Welcome to the 1xEV-DO digital standard
Documentation overview
Deals with security issues when working with the R&S SMBV100B in secure areas. It
is available for download on the Internet.
1.3.5 Printed safety instructions
Provides safety information in many languages. The printed document is delivered with
the product.
1.3.6 Data sheets and brochures
The data sheet contains the technical specifications of the R&S SMBV100B. It also
lists the options and their order numbers and optional accessories.
The brochure provides an overview of the instrument and deals with the specific characteristics.
See www.rohde-schwarz.com/brochure-datasheet/smbv100b
1.3.7 Release notes and open source acknowledgment (OSA)
The release notes list new features, improvements and known issues of the current
firmware version, and describe the firmware installation.
The open-source acknowledgment document provides verbatim license texts of the
used open source software.
See www.rohde-schwarz.com/firmware/smbv100b
7User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
1.3.8 Application notes, application cards, white papers, etc.
These documents deal with special applications or background information on particular topics.
See www.rohde-schwarz.com/application/smbv100b
1.4 Scope
Tasks (in manual or remote operation) that are also performed in the base unit in the
same way are not described here.
In particular, it includes:
●
Managing settings and data lists, like saving and loading settings, creating and
accessing data lists, or accessing files in a particular directory.
●
Information on regular trigger, marker and clock signals and filter settings, if appropriate.
●
General instrument configuration, such as checking the system configuration, configuring networks and remote operation
●
Using the common status registers
Welcome to the 1xEV-DO digital standard
Notes on screenshots
For a description of such tasks, see the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
1.5 Notes on screenshots
When describing the functions of the product, we use sample screenshots. These
screenshots are meant to illustrate as many as possible of the provided functions and
possible interdependencies between parameters. The shown values may not represent
realistic usage scenarios.
The screenshots usually show a fully equipped product, that is: with all options installed. Thus, some functions shown in the screenshots may not be available in your particular product configuration.
8User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
2 About the 1xEV-DO options
This section provides an overview of required options and background information on
the CDMA2000® 1xEV-DO standard.
2.1 Required options
The basic equipment layout for generating 1xEV-DO signals includes the:
●
Base unit
●
Baseband realtime extension (R&S SMBVB-K520)
●
Digital standard 1xEV-DO Rev. A (R&S SMBVB-K47)
●
Digital standard 1xEV-DO Rev. B (R&S SMBVB-K87)
You can generate signals via play-back of waveform files at the signal generator. To
create the waveform file using R&S WinIQSIM2, you do not need a specific option.
About the 1xEV-DO options
Modulation system
To play back the waveform file at the signal generator, you have two options:
●
Install the R&S WinIQSIM2 option of the digital standard, e.g. R&S SMBVB-K255
for playing LTE waveforms
●
If supported, install the real-time option of the digital standard, e.g. R&S SMBVBK55 for playing LTE waveforms
For more information, see data sheet.
2.2 Modulation system
The following table gives an overview of parameters of the modulation system 1xEVDO.
9User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Table 2-1: Parameters of the modulation system 1xEV-DO
Parameter Value
Chip rate 1.2288 Mcps
About the 1xEV-DO options
Modulation system
Channel types
Generation mode
Data rates
Forward link:
●
Pilot channel
●
Forward Traffic Channel (Rev. A)
●
Reverse Activity
●
DRCLock
●
Reverse Power Control
●
ARQ (Rev. A)
●
Control Channel
Reverse link, access mode:
●
Pilot Channel
●
Data Channel
Reverse link, traffic mode:
●
Pilot Channel
●
Auxiliary Pilot Channel (Rev. A)
●
Reverse Rate Indicator
●
Data Rate Control
●
Data Source Control (Rev. A)
●
ACK Channel
●
Data Channel
Forward link:
●
Realtime mode
Reverse link:
●
Arbitrary waveform mode
●
Multicarrier operation
Up to 16 concurrent carriers supported
Requires option R&S SMBVB-K87
Forward link:
●
38.4 .. 2457.6 kbps (Rev. 0)
●
4.8 .. 3072 kbps (Rev. A)
●
4.8 .. 4915 kbps (Rev. B)
Requires option R&S SMBVB-K87
Reverse link:
●
9.6 .. 153.6 kbps (Rev. 0)
●
4.8 .. 1843.2 kbps (Rev. A)
Frame length 26.67 ms (1 frame = 16 slots)
Slot duration 1.67 ms (1 slot = 2048 PN chips)
PN offset 0 .. 511
Channel coding All channel coding modes defined in the standard (channel encoding,
block interleaving, repetition, modulation, orthogonal spreading by
Walsh function)
Modulation BPSK, QPSK, 8PSK, 16QAM, 64QAM
Requires option R&S SMBVB-K87
Multi-code modulation B4, Q2, Q4, Q4Q2, E4E2
Long Code Mask Separate Long Code Masks for I and Q channel. The Long Code Gen-
erator is reloaded at every PN rollover with 0x24B91BFD3A8.
Walsh covers Different Walsh functions for the different channels
10User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
2.3 Traffic scheduling process
In the 1xEV-DO system, the Forward Link is governed by a time division multiple
access technique. Access to Forward Link bandwidth by a user channel is governed by
a scheduling process. The schedule process determines who gets access to Forward
Link slots to carry user data.
The traffic scheduling process in this instrument follows a number of rules to schedule
which user's data is sent for each slot.
The rules are listed in order of priority, with the highest priority rules being listed first. In
the event that two rules contradict each other, the circumstances invoking the lower priority rule must be altered to resolve the contradiction.
●
A channel with "State = Off" is never transmitted.
●
The first slot of the control channel packet is always transmitted at its specified offset at the start of the control channel cycle.
●
Once the first slot of a multiple slot packet is sent, the remaining slots are always
transmitted with the proper interlace (three slots skipped after one slot sent).
●
Packets for a user can be transmitted on 1 to 4 interlaces (there are a total of 4
interlaces in the 1xEV-DO system). Packets on the different interlaces are duplicates of the packets sent on the other interlaces for a given user. The interleave
factor user interface parameter is used to control the number of interlaces used for
each user.
●
Immediately after the transmission of the last slot of a multiple slot packet, a lockout period of three slots is created. No additional packets from the same source
can be scheduled before the three slot period expires.
●
A control channel packet has priority over all other traffic channels. This excludes
transmission of user channels in advance of the control channel packet, if the other
channel would require a slot that the control channel packet would require.
●
User1 traffic has priority over User2, User3, and User4 traffic.
●
User2 traffic has priority over User3 and User4 traffic.
●
User3 traffic has priority over User4 traffic.
●
If no traffic is scheduled for a slot, an idle slot is transmitted.
About the 1xEV-DO options
Traffic scheduling process
11User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
3 1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access:
► Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO".
The remote commands required to define these settings are described in Chapter 4,
"Remote-control commands", on page 61.
3.1 General settings
The tab provides access to the default and the "Save/Recall" settings. The selected
link direction determines the available parameters.
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
General settings
State..............................................................................................................................12
Set To Default................................................................................................................13
Save/Recall...................................................................................................................13
Generate Waveform......................................................................................................13
1xEV-DO Version.......................................................................................................... 13
Link Direction................................................................................................................ 14
PN Offset.......................................................................................................................14
System Time................................................................................................................. 14
Multicarrier Configuration..............................................................................................14
Access Network Settings.............................................................................................. 14
Filter / Clipping / ARB Settings......................................................................................14
State
Activates the standard and deactivates all the other digital standards and digital modulation modes in the same path.
12User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:STATe on page 67
Set To Default
Calls the default settings. The values of the main parameters are listed in the following
table.
Parameter Value
State Not affected by "Set to default"
Link Direction Downlink/ Forward
PN Offset 0
System Time 0
Predefined Settings User Defined
Multicarrier State off
Filter CdmaOne + Equalizer
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
General settings
Clipping Off
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:PRESet on page 65
Save/Recall
Accesses the "Save/Recall" dialog, that is the standard instrument function for saving
and recalling the complete dialog-related settings in a file. The provided navigation
possibilities in the dialog are self-explanatory.
The settings are saved in a file with predefined extension. You can define the filename
and the directory, in that you want to save the file.
See also, chapter "File and Data Management" in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:CATalog? on page 65
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:LOAD on page 66
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:STORe on page 66
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:DELete on page 66
Generate Waveform
With enabled signal generation, triggers the instrument to save the current settings of
an arbitrary waveform signal in a waveform file with predefined extension *.wv. You
can define the filename and the directory, in that you want to save the file.
Using the ARB modulation source, you can play back waveform files and/or process
the file to generate multi-carrier or multi-segment signals.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:WAVeform:CREate on page 68
1xEV-DO Version
Displays the current version of the standard.
13User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
The default settings and parameters provided are oriented towards the specifications
of the version displayed.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:VERSion? on page 67
Link Direction
Selects the link direction.
The settings of the traffic channels per user and the access terminals are provided in
the following menu section in accordance with the selection.
"Downlink/Forward"
"Uplink/Reverse"
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:LINK on page 65
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
General settings
The link direction selected is base station to access terminal. The signal corresponds to that of a base station.
The link direction selected is access terminal to base station. The signal corresponds to that of an access terminal.
PN Offset
Sets the PN Offset of the 1xEV-DO signal.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:PNOFfset on page 65
System Time
Sets the system time value of the 1xEV-DO signal and the base station. The system
time is expressed in units of 1.67 ms intervals (80 ms/ 48).
Note: In uplink, the value selected for system time must be multiple of 16.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:STIMe on page 67
Multicarrier Configuration
Provides access to the "Multicarrier Configuration" dialog, see Chapter 3.7, "Multi-car-
rier configuration settings", on page 34.
Access Network Settings
In downlink direction, provides access to the "Access Network Settings" dialog, see
Chapter 3.8, "Access network settings", on page 36.
Filter / Clipping / ARB Settings
Provides access to the settings dialogs for configuring baseband filtering, clipping and
the sequence length of the arbitrary waveform component, see Chapter 3.10, "Filter /
clipping / ARB settings", on page 55.
14User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
3.2 Trigger settings
Access:
► Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Trigger In".
This tab provides access to the settings necessary to select and configure the trigger,
like trigger source, mode, trigger delay, trigger suppression, as well as to arm or trigger
an internal trigger manually. The current signal generation status is displayed in the
header of the tab together with information on the enabled trigger mode. As in the
"Marker" and "Clock" tabs, this tab provides also access to the settings of the related
connectors.
This section focuses on the available settings.
For information on how these settings affect the signal, refer to section "Basics on ..."
in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Trigger settings
Routing and enabling a trigger
The provided trigger signals are not dedicated to a particular connector. Trigger signals
can be mapped to one or more User x connectors.
The provided trigger signals are not dedicated to a particular connector. Trigger signals
can be mapped to one or two User x connectors.
Use the Global connectors settings to configure the signal mapping, the polarity, the
trigger threshold and the input impedance of the input connectors.
To route and enable a trigger signal, perform the following general steps:
●
Define the signal source and the effect of a trigger event.
Select the "Trigger In > Mode" and "Trigger In > Source".
●
Define the connector where the selected signal is provided.
Use the "Global Connectors" settings.
Settings:
Trigger Mode.................................................................................................................16
Signal Duration Unit...................................................................................................... 16
Trigger Signal Duration................................................................................................. 16
15User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Running/Stopped.......................................................................................................... 16
Arm................................................................................................................................17
Execute Trigger.............................................................................................................17
Trigger Source...............................................................................................................17
Sync. Output to External Trigger/Sync. Output to Trigger.............................................17
External Trigger Inhibit..................................................................................................18
Trigger Delay.................................................................................................................18
Trigger Mode
Selects trigger mode, i.e. determines the effect of a trigger event on the signal generation.
●
"Auto"
The signal is generated continuously.
●
"Retrigger"
The signal is generated continuously. A trigger event (internal or external) causes a
restart.
●
"Armed Auto"
The signal is generated only when a trigger event occurs. Then the signal is generated continuously.
An "Arm" stops the signal generation. A subsequent trigger event (internal or external) causes a restart.
●
"Armed Retrigger"
The signal is generated only when a trigger event occurs. Then the signal is generated continuously. Every subsequent trigger event causes a restart.
An "Arm" stops signal generation. A subsequent trigger event (internal or external)
causes a restart.
●
"Single"
The signal is generated only when a trigger event occurs. Then the signal is generated once to the length specified at "Signal Duration".
Every subsequent trigger event (internal or external) causes a restart.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO[:TRIGger]:SEQuence on page 73
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Trigger settings
Signal Duration Unit
Defines the unit for describing the length of the signal sequence to be output in the
"Single" trigger mode.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SLUNit on page 74
Trigger Signal Duration
Enters the length of the signal sequence to be output in the "Single" trigger mode.
Use this parameter to output part of the signal deliberately, an exact sequence of the
signal, or a defined number of repetitions of the signal.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SLENgth on page 74
Running/Stopped
With enabled modulation, displays the status of signal generation for all trigger modes.
16User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
●
"Running"
The signal is generated; a trigger was (internally or externally) initiated in triggered
mode.
●
"Stopped"
The signal is not generated and the instrument waits for a trigger event.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:RMODe? on page 74
Arm
Stops the signal generation until subsequent trigger event occurs.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:ARM:EXECute on page 73
Execute Trigger
For internal trigger source, executes trigger manually.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXECute on page 74
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Trigger settings
Trigger Source
The following sources of the trigger signal are available:
●
"Internal"
The trigger event is executed manually by the "Execute Trigger".
●
"External Global Trigger"
The trigger event is the active edge of an external trigger signal provided and configured at the User x connectors.
●
"Baseband Sync In"
In primary-secondary instrument mode, secondary instruments are triggered by the
active edge of the synchronization signal.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SOURce on page 75
Sync. Output to External Trigger/Sync. Output to Trigger
Enables signal output synchronous to the trigger event.
●
"On"
Corresponds to the default state of this parameter.
The signal calculation starts simultaneously with the trigger event. Because of the
processing time of the instrument, the first samples are cut off and no signal is output. After elapsing of the internal processing time, the output signal is synchronous
to the trigger event.
17User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
●
"Off"
The signal output begins after elapsing of the processing time. Signal output starts
with sample 0. The complete signal is output.
This mode is recommended for triggering of short signal sequences. Short sequences are sequences with signal duration comparable with the processing time of the
instrument.
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Trigger settings
In primary-secondary instrument mode, this setting ensures that once achieved, synchronization is not lost if the baseband signal sampling rate changes.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXTernal:SYNChronize:OUTPut
on page 74
External Trigger Inhibit
Applies for external trigger signal.
Sets the duration with that any following trigger event is suppressed. In "Retrigger"
mode, for example, a new trigger event does not cause a restart of the signal generation until the specified inhibit duration does not expire.
For more information, see chapter "Basics" in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger[:EXTernal]:INHibit on page 75
Trigger Delay
Delays the trigger event of the signal from:
●
The external trigger source
18User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Use this setting to:
●
Synchronize the instrument with the device under test (DUT) or other external devices
●
Compensate delays and align the signal generation start in multi-instrument setup
For more information, see chapter "Basics on ..." in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger[:EXTernal]:DELay on page 75
3.3 Marker settings
This tab provides access to the settings necessary to select and configure the marker
output signal, like the marker mode or marker delay settings.
This section focuses on the available settings.
For information on how these settings affect the signal, refer to section "Basics on ..."
in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Marker settings
Routing and enabling a marker
The provided marker signals are not dedicated to a particular connector. They can be
mapped to one or more User x connectors.
To route and enable a marker signal, perform the following general steps:
●
Define the shape of the generated marker, i.e. select the "Marker > Mode".
●
Define the connector where the selected signal is provided.
Use the Global connectors settings.
Marker Mode.................................................................................................................20
Marker x Delay..............................................................................................................20
19User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Marker Mode
Marker configuration for up to 3 markers. The settings are used to select the marker
mode defining the shape and periodicity of the markers. The contents of the dialog
change with the selected marker mode.
"Slot (1.67 ms)"
"PN Sequence Period (26,67 ms)"
"Even Second Mark (2 s)"
"Chip Sequence Period (ARB)"
"On/Off Ratio"
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Clock settings
A marker signal is generated at the start of each slot (every 1.67 ms).
A marker signal is generated every 26.67 ms (PN Sequence Period).
A marker signal is generated every 2 seconds.
(For reverse link mode)
A marker signal is generated at the beginning of every Arbitrary
Waveform sequence (depending on the set sequence length). The
marker signal is generated regardless of whether an ARB component
is used.
A regular marker signal that is defined by an On/Off ratio is generated. A period lasts one ON and OFF cycle.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:ONTime on page 76
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:OFFTime on page 76
"User Period"
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:PERiod on page 77
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:MODE on page 76
Marker x Delay
Delays the marker signal at the marker output relative to the signal generation start.
Variation of the parameter "Marker x Delay" causes signal recalculation.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:DELay on page 77
A marker signal is generated at the beginning of every user-defined
period ("Period").
3.4 Clock settings
This tab provides access to the settings necessary to select and configure the clock
signal, like the clock source and clock mode.
20User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
This section focuses on the available settings.
For information on how these settings affect the signal, refer to section "Basics on ..."
in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
Defining the clock
The provided clock signals are not dedicated to a particular connector. They can be
mapped to one or more User x connectors.
Use the Global connectors settings to configure the signal mapping, the polarity, the
trigger threshold, and the input impedance of the input connectors.
To route and enable a trigger signal, perform the following general steps:
●
Define the signal source, that is select the "Clock > Source".
●
Define the connector where the selected signal is provided.
Use the Global connectors settings.
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Global connectors settings
Clock Source.................................................................................................................21
Clock Source
Selects the clock source.
●
"Internal"
The instrument uses its internal clock reference.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLOCk:SOURce on page 77
3.5 Global connectors settings
Each of the "Trigger In", "Marker" and "Clock" dialogs and the "Trigger Marker Clock"
dialog provides a quick access to the related connector settings.
See also chapter "Global connectors settings" in the user manual.
21User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
3.6 Traffic channel settings
Access:
1. Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Link Direction > Downlink"
2. Select "Traffic Channels".
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
Four "User (1 to 4)" are available.
3. To activate a user, set e.g. "User 1 > On".
4. To access the settings of a user, select the corresponding field, e.g. "User 1".
The corresponding "Configure Traffic User 1 .. 4" dialog opens. The user number is
indicated in the panel headline.
22User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
The dialog comprises the settings of the traffic channel and of the forward MAC
channel settings, such as Reverse Power Control (RPC) and DRCLock.
Common........................................................................................................................23
RPC (MAC)................................................................................................................... 30
DRC Lock (MAC).......................................................................................................... 31
ARQ (MAC)...................................................................................................................33
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
└ State (User).....................................................................................................23
└ Physical Layer Subtype (User)....................................................................... 23
└ Number of Packets to Send - Infinite.............................................................. 23
└ Number of Packets to Send - Value................................................................24
└ Packet Start Offset..........................................................................................24
└ Rate Index.......................................................................................................25
└ Packet Size.....................................................................................................28
└ Data Rate........................................................................................................29
└ Slot Count....................................................................................................... 29
└ Data Pattern (hex)...........................................................................................29
└ MAC Index...................................................................................................... 29
└ MAC Level...................................................................................................... 29
└ Interleave Factor.............................................................................................29
└ RPC Mode...................................................................................................... 30
└ RPC Range Count.......................................................................................... 31
└ RPC Pattern....................................................................................................31
└ DRC Lock State.............................................................................................. 32
└ DRC Lock Period............................................................................................ 32
└ DRC Lock Length............................................................................................33
└ Frame Offset...................................................................................................33
└ H-ARQ Mode.................................................................................................. 33
Common
Comprises the common traffic channel settings:
State (User) ← Common
Enables or disables the selected user.
If the user is enabled, the proper "MAC Index" is placed within the MAC channel and
packets can be sent to the user. If disabled, the "MAC Index" is not present within the
MAC channel and packets cannot be sent to the user.
Note: Disabling the state of a user during a transfer aborts all transfers to the user.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:STATe on page 94
Physical Layer Subtype (User) ← Common
Displays the physical layer subtype selected in the menu "Access Network Settings".
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:SUBType on page 82
Number of Packets to Send - Infinite ← Common
Enables or disables sending an unlimited number of packets to the selected user.
23User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
If "Infinite" is enabled, there is no limit to the number of packets sent to the user.
If "Infinite" is disabled, the number of packets to be sent to the selected "User" can be
specified.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PACKet:INFinite on page 89
Number of Packets to Send - Value ← Common
Sets the number of packets to send to the selected user.
The number of packets to be sent depends on whether the parameter "Infinite" is
enabled or disabled. If "Infinite" is enabled, there is no limit to the number of packets
sent to the user.
If "Infinite" is disabled and a value is specified while packets are being sent, the new
count value is used at the end of transmission of the current packet. If a value of zero
is specified, the transmission to the user is stopped at the end of the current packet.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PACKet:INFinite on page 89
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PACKet:COUNt on page 89
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
Packet Start Offset ← Common
Sets the minimum number of slots between the end of one packet and the beginning of
the next.
For single slot packets, a value of zero will cause the next packet to be sent in the
immediate next slot (subject to scheduling).
For multiple slot packets, a value of zero will cause the next packet transmission to
start three slots after the end of the previous packet. The three slot delay is identical to
the interleaving delay between slots for multiple slot packets. The offset value is
attached to the end of the preceding packet.
24User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Note: An offset value of zero with a rate change from a single slot packet to multiple
slot packets causes the first slot of the multiple slot packets to be transmitted in the slot
immediately following the single slot packet.
See Chapter 2.3, "Traffic scheduling process", on page 11 for an explanation on how
the control and traffic channels are transmitted over time.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PACKet:SOFFset on page 90
Rate Index ← Common
Sets an index into the table of rates and slot counts.
Note: Selected rate becomes effective at the beginning of the next packet transmitted
to the selected user.
For physical layer 0&1, the parameter "Rate Index" alone automatically set the packet
size, data rate and the slot count for the packets sent to the selected user. Parameters
"Packet Size", "Data Rate" and "Slot Count" are read-only.
Table 3-1: Rate index for Physical Layer subtype 0&1
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
Rate index Packet size index Packet size, bits Data Rate, kbps Slot count
1 0 1024 38.4 16
2 0 1024 76.8 8
3 0 1024 153.6 4
4 0 1024 307.2 2
5 0 2048 307.2 4
6 0 1024 614.4 1
7 0 2048 614.4 2
8 0 3072 921.6 2
9 0 2048 1228.8 1
10 0 4096 1228.8 2
11 0 3072 1843.2 1
12 0 4096 2457.6 1
For physical layer subtype 2, a combination of the parameters "Rate Index" and
"Packet Size" sets the data rate and the slot count for the packets sent to the selected
user.
25User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Table 3-2: Rate index for Physical Layer subtype 2
Rate index Packet size index Packet size, bits Data Rate, kbps Slot count
1 3 128 4.8 16
1 2 256 9.6 16
1 1 512 19.2 16
1 0 1024 38.4 16
2 3 128 9.6 8
2 2 256 19.2 8
2 1 512 38.4 8
2 0 1024 76.8 8
3 3 128 19.2 4
3 2 256 38.4 4
3 1 512 76.8 4
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
3 0 1024 153.6 4
4 3 128 38.4 2
4 2 256 76.8 2
4 1 512 153.6 2
4 0 1024 307.2 2
5 2 512 76.8 4
5 1 1024 153.6 4
5 0 2048 307.2 4
6 3 128 76.8 1
6 2 256 153.6 1
6 1 512 307.2 1
6 0 1024 614.4 1
7 2 512 153.6 2
7 1 1024 307.2 2
7 0 2048 614.4 2
8 1 1024 307.2 2
8 0 3072 921.6 2
9 2 512 307.2 1
9 1 1024 614.4 1
9 0 2048 1228.8 1
10 0 4096 1228.8 2
11 1 1024 614.4 1
26User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Rate index Packet size index Packet size, bits Data Rate, kbps Slot count
11 0 3072 1843.2 1
12 0 4096 2457.6 1
13 0 5120 1536 2
14 0 5120 3072 1
Table 3-3: Rate index for Physical Layer subtype 3 (requires the appropriate Rev. B option)
Rate index Packet size index Packet size, bits Data Rate, kbps Slot count
1 3 128 4.8 16
1 2 256 9.6 16
1 1 512 19.2 16
1 0 1024 38.4 16
2 3 128 9.6 8
2 2 256 19.2 8
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
2 1 512 38.4 8
2 0 1024 76.8 8
3 3 128 19.2 4
3 2 256 38.4 4
3 1 512 76.8 4
3 0 1024 153.6 4
4 3 128 38.4 2
4 2 256 76.8 2
4 1 512 153.6 2
4 0 1024 307.2 2
5 2 512 76.8 4
5 1 1024 153.6 4
5 0 2048 307.2 4
6 3 128 76.8 1
6 2 256 153.6 1
6 1 512 307.2 1
6 0 1024 614.4 1
7 2 512 153.6 2
7 1 1024 307.2 2
7 0 2048 614.4 2
8 1 1024 307.2 2
27User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Rate index Packet size index Packet size, bits Data Rate, kbps Slot count
8 0 3072 921.6 2
9 2 512 307.2 1
9 1 1024 614.4 1
9 0 2048 1228.8 1
10 0 4096 1228.8 2
11 1 1024 614.4 1
11 0 3072 1843.2 1
12 0 4096 2457.6 1
13 0 5120 1536 2
14 0 5120 3072 1
15 0 1024 153.6 4
16 0 2048 307.2 4
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
17 0 3072 460.8 4
18 0 4096 614.4 4
19 0 5120 768 4
20 0 6144 921.6 4
21 0 6144 1843.2 2
22 0 6144 3686.4 1
23 0 7168 1075.2 4
24 0 7168 2150.4 2
25 0 7168 4300.8 1
26 0 8192 1228.8 4
27 0 8192 2457.6 2
28 0 8192 4915.2 1
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RATE:INDex on page 91
Packet Size ← Common
Sets the packet size for the packets sent to the selected user.
For physical layer 0&1, the parameter "Packet Size" is read-only. The value is automat-
ically set depending on the selection for the parameter "Rate Index". (see Table 3-1)
For physical layer subtypes 2 and 3, a combination of the parameter "Packet Size" and
the parameter "Rate Index" sets the data rate and the slot count for the packets sent to
the selected user, see Table 3-2.
Note: Selected rate becomes effective at the beginning of the next packet transmitted
to the selected user.
28User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PSIZe on page 90
Data Rate ← Common
Displays the data rate of the packets sent to the selected user. This parameter is readonly. The value is set automatically, depending on the selected "Rate Index " and
"Packet Size", see Table 3-1 and Table 3-2.
Note: Selected rate becomes effective at the beginning of the next packet transmitted
to the selected user.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RATE? on page 91
Slot Count ← Common
Displays the slot count of the packets sent to the selected user.
This parameter is read-only. The value is set automatically, depending on the selected
"Rate Index" and "Packet Size", see Table 3-1 and Table 3-2.
Note: Selected rate becomes effective at the beginning of the next packet transmitted
to the selected user.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:SCOunt? on page 94
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
Data Pattern (hex) ← Common
Sets the data pattern for the data portion of the packets sent to the user.
The most significant bit (MSB) of this value is the MSB of the packet and the word is
repeated to fill all space within the packet. This parameter is in a hexadecimal format.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DATA:PATTern on page 85
MAC Index ← Common
Sets the MAC index used for the selected user.
MAC indexes have to be different for the different users. However, in case that two
users are using the same value for MAC index, the lower priority user is disabled, or be
unable to enable.
The values for the MAC indexes for the other users (see parameter Other Users
Count) are assigned from a pool of valid MAC indexes, that exclude the MAC indexes
specified for each of the four configurable users.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:MAC:INDex on page 88
MAC Level ← Common
Sets the power within the MAC channel that is dedicated to the selected user.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:MAC:LEVel on page 89
Interleave Factor ← Common
Controls the number of interleave slots used for the selected user on the forward link.
29User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Four interleave slots are defined in the 1xEV-DO system. By default, only 1 interleave
slot ("Interleave Factor" = 1) for an access terminal is configured and transmission to
that access terminal every fourth slot is selected. For an interleave factor > 1, packets
on multiple interleave slots are sent, increasing the data throughput to the access terminal.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:IFACtor on page 88
RPC (MAC)
Access: "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Traffic Channels > User > RPC (MAC)".
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
RPC Mode ← RPC (MAC)
Sets the operation mode for the Reverse Power Control (RPC) Channel within the
MAC channel for the selected user.
"Hold"
"All up"
"All down"
An alternating series of up and down power control bits are transmitted. The intent is to hold the access terminal at a constant power
level. This mode always starts with an up bit, and ends with the following down bit. This mode is 2 bits long.
A continuous stream of up (0) power control bits are transmitted. The
intent is to force the access terminal to the highest transmit power
level.
This mode is a single bit long.
A continuous stream of down (1) power control bits are transmitted.
The intent is to force the access terminal to the lowest transmit power
level.
This mode is a single bit long.
30User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
"Range"
"Pattern"
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:MODE on page 92
RPC Range Count ← RPC (MAC)
Sets the number of Reverse Power Control (RPC) bits sent in each direction when the
"RPC Mode" is set to "Range". The specified value is used immediately.
Note: This parameter is displayed in RPC mode "Range" only.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:RANGe on page 93
A sequence of up power control bits is sent followed by an equal
number of down power control bits. The intent is to force the access
terminal to ramp its power from one extreme to another. The number
of power control bits in each direction is specified by the "RPC Range
Count" parameter. (see RPC Range Count). Each time that the range
mode is specified, the sequence is restarted.
The range mode starts with the first up bit and ends with the last
down bit.
The length of the mode is two times the RPC range Count.
A user-defined sequence of RPC bits is sent. The mode starts with
the bit defined in the first (0) zone, and ends with the last bit of the
last (3) zone. The length of the pattern is the sum of the Count values
for each RPC zone.
RPC Pattern ← RPC (MAC)
Defines the Reverse Power Control (RPC) pattern in form of table with four zones
(zone 0 .. 3).
For each zone, a bit and a count can be defined.
"Bit"
"Count"
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:ZONE<ch0>:BIT on page 93
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:ZONE<ch0>:COUNt on page 94
DRC Lock (MAC)
Access: "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Traffic Channels > User > DRC Lock (MAC)".
Defines the RPC bits sent within the specific zone of the RPC pattern.
Defines the number of RPC bits sent within the specific zone of the
RPC pattern.
31User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
DRC Lock State ← DRC Lock (MAC)
Sets the state of the DRC (Data Rate Control) lock bit for the selected user.
Note: Changes in the DRC lock state are only considered at the interval defined by the
parameter DRC lock length.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:STATe on page 87
DRC Lock Period ← DRC Lock (MAC)
Sets the period (measured in slots) of time between successive transmissions of the
DRC (Data Rate Control) lock bit for the selected user.
Note: A value of zero disables the DRC lock subchannel and the MAC RPC channel of
the selected user is not punctured with the DRC lock subchannel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:PERiod on page 86
32User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
DRC Lock Length ← DRC Lock (MAC)
Sets the number of DRC (Data Rate Control) lock Periods that the state of the DRC
lock for the selected user is held constant.
Note: Changes in the DRC lock state are only considered at the interval defined by the
parameter "DRC Lock Length".
A value of one allows updating of the DRC lock bit at anytime.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:LENGth on page 86
Frame Offset ← DRC Lock (MAC)
Sets the reverse link frame offset for the reverse link.
The frame offset is used to position the DRC lock bit within the MAC channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:OFFSet on page 86
ARQ (MAC)
Access: "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Traffic Channels > User > ARQ (MAC)".
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Traffic channel settings
H-ARQ Mode ← ARQ (MAC)
Enables or disables the H-ARQ Channel.
The H-ARQ channel is used by the access network to transmit positive acknowledge-
ment (ACK) or a negative acknowledgement (NAK) in response to a physical layer
packet.
Note: This parameter is enabled for Physical Layer "Subtype 2 "only.
"Off"
"ACK"
"NAK"
Disables transmission of the H-ARQ channel.
The channel is transmitted with all bits set to ACK.
The channel is transmitted with all bits set to NAK.
33User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06
R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:HARQ:MODE on page 87
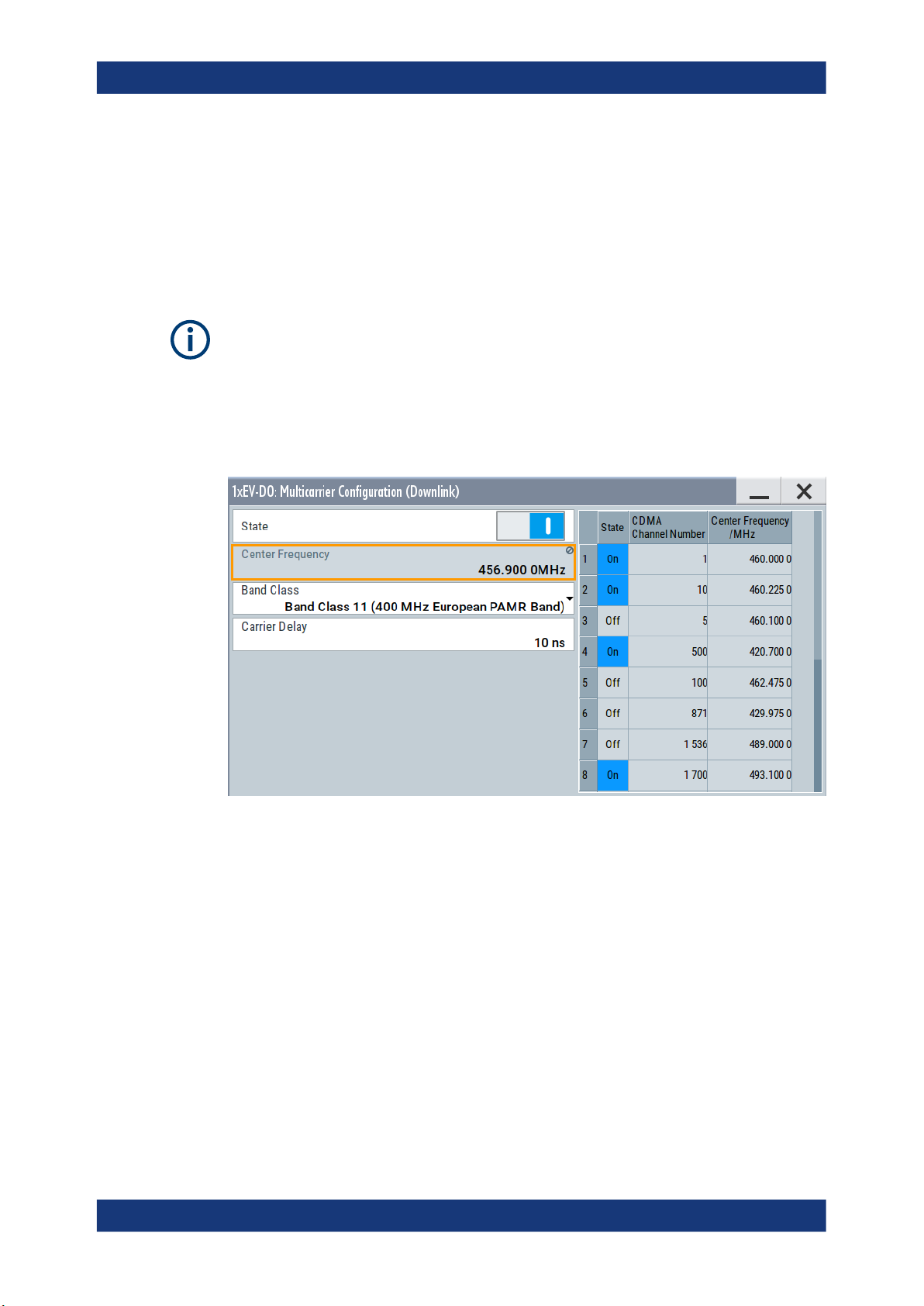
3.7 Multi-carrier configuration settings
Multi-Carrier Configuration requires option R&S SMBVB-K87
In multi-carrier mode, up to 16 modulated carriers can be generated with one baseband. Each carrier’s center frequency is input via it’s "CDMA Channel Number" or by
directly entering the RF "Center Frequency / MHz". The carriers can be activated or
deactivated separately.
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Multi-carrier configuration settings
State..............................................................................................................................34
Center Frequency (band)..............................................................................................34
Band Class....................................................................................................................35
Carrier Delay.................................................................................................................35
State..............................................................................................................................35
CDMA Channel Number............................................................................................... 35
Center Frequency......................................................................................................... 35
State
Enables or disables multi-carrier operation.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CARRier<ch>:STATe on page 84
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier<ch>:STATe on page 84
Center Frequency (band)
Shows the center frequency of the band resulting from the set active carriers.
34User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CFRequency? on page 83
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CFRequency? on page 83
Band Class
Selects the band class for operation, as defined in 3GPP2 C.S0057-E.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:BCLass on page 83
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:BCLass on page 83
Carrier Delay
Applies a delay to each carrier in order to reduce the crest factor of the sum signal.
The delay increases by the given value on each active carrier. Inactive carriers are not
accounted.
Example:
"Carrier Delay = 1000 ns"
The first active carrier is delayed by 0 ns, the second by 1000 ns, the third by 2000 ns,
etc.
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Multi-carrier configuration settings
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CDELay on page 83
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CDELay on page 83
State
Switches the selected carrier on or off.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CARRier<ch>:STATe on page 84
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier<ch>:STATe on page 84
CDMA Channel Number
Selects the carrier’s channel number.
The selected channel numbers are directly translated into center frequencies, accord-
ing to the used band class. In some cases, not all channel numbers in the range that is
indicated by the tool tip are allowed. In case a non-existing channel is selected, the
software selects the next available channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CARRier<ch>:CHANnel on page 84
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier<ch>:CHANnel on page 84
Center Frequency
Sets the center frequency of the carrier.
In some cases, not all center frequencies in the range that is indicated by the tool tip
are defined by the selected band class. In case a non-existing frequency is selected,
the software selects the next available frequency.
35User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CARRier<ch>:FREQuency on page 84
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier<ch>:FREQuency on page 84
3.8 Access network settings
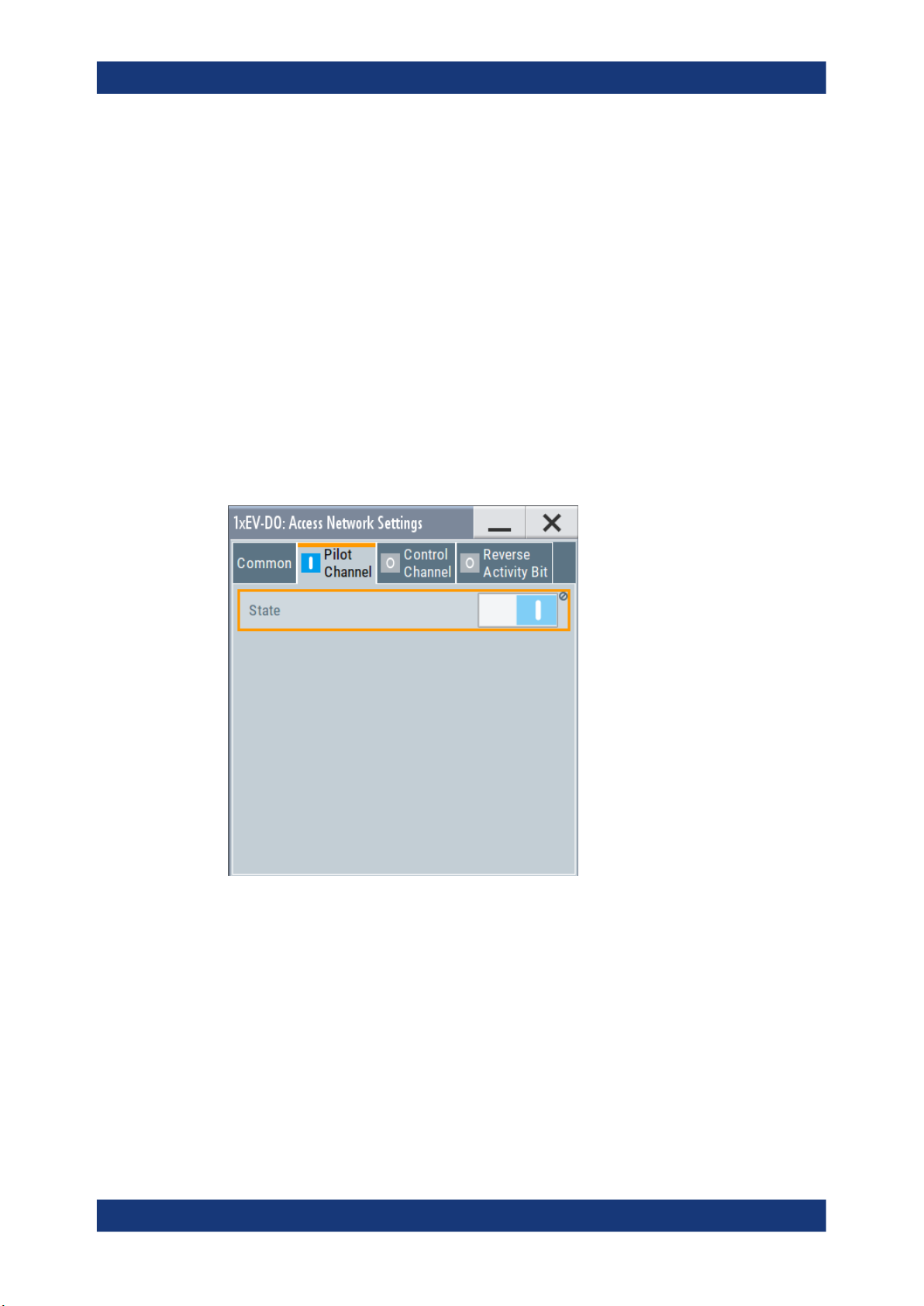
The "Access Network Settings" dialog is available at Downlink only and allows configuration of physical layer subtype, the pilot and control channels and reverse activity bit.
"Access Network Settings" consists of three main sections, "Pilot Channel", "Control
Channel" and "Reverse Activity Bit (MAC)".
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access network settings
Physical Layer Subtype (Access Network Settings)
Defines the physical layer subtype for the forward link direction.
Physical layer subtype 0 is the original (release "0").
Physical layer subtype 1 and 2 are the revision "A" physical layers.
Physical layer subtype 3 is the revision "B" physical layer.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:SUBType on page 82
Continuous Pilot Mode
Enables or disables a special mode within the 1xEV-DO generator. When the state is
off, normal operation is selected. When the state is on, a special mode is selected.
In this special mode, the 1xEV-DO generator generates a pilot signal only.
Note: During the special mode, all other parameters do not affect the signal output.
36User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06
R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CPMode on page 79
Other Users Count
Sets the number of additional users (beyond the four defined users) that appear in the
MAC Channel.
These additional users never have a packet addressed to them, but are used to fill in
the MAC channel code domain.
These Other Users are used to distribute the excess power (beyond what is required
by the "User 1..4" and RAB channels).
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:OUCount on page 80
Pilot Channel
Access:
"Baseband > 1xEV-DO > General > Access Network Settings > Pilot Channel"
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access network settings
State ← Pilot Channel
Displays the state of the pilot channel. Pilot channel is transmitted by sector on each
active forward channel. It is present always and transmitted at the full sector power.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:PCHannel:STATe? on page 80
Control Channel
Access:
"Baseband > 1xEV-DO > General > Access Network Settings > Control Channel"
37User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access network settings
State ← Control Channel
Enables or disables the control channel messages.
The only control channel message that is ever sent is the Sync Message. When this is
enabled, the control channel messages have the highest priority for placement within
the slots. The Sync Message is updated constantly, even when the control channel is
not enabled.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:STATe on page 79
Rate ← Control Channel
Sets the rate that the control channel messages are transmitted at.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:RATE on page 78
Packet Start Offset ← Control Channel
Sets the offset (in slots) from the start of control channel cycle to the start of the synchronous message capsule that contains the Sync Message.
SeeChapter 2.3, "Traffic scheduling process", on page 11 for an explanation on how
the control and traffic channels are transmitted over time.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:PSOFfset on page 78
Minimum Revision ← Control Channel
Sets the value of the minimum revision field within the control channel message.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:REVision:MINimum
on page 79
38User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Maximum Revision ← Control Channel
Sets the value of the maximum revision field within the control channel message.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:REVision:MAXimum
on page 79
Reverse Activity Bit
Access:
"Baseband > 1xEV-DO > General > Access Network Settings > Reverse Activity Bit"
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access network settings
State ← Reverse Activity Bit
Activates or deactivates the reverse activity bit (RAB).
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:STATe on page 82
RAB Level ← Reverse Activity Bit
Sets the power within the MAC block for the Reverse Activity Channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:LEVel on page 81
RAB Length ← Reverse Activity Bit
For physical layer subtype 0&1 only
Sets the duration (in slots) of a Reverse Activity bit.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:LENGth on page 80
RAB Offset ← Reverse Activity Bit
For physical layer subtype 0&1 only
39User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Sets the starting time offset of the Reverse Activity (RA) bit in slots. The command is
specified in Reverse Activity Length/8 units.
The RA bit starts when the following equation is satisfied:
●
System Time mod RAB length = RAB Offset,
where System Time is expressed in slots.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:OFFSet on page 81
RAB MAC Index ← Reverse Activity Bit
For physical layer subtype 3 only sets the RAB MAC Index.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:MAC:INDex on page 81
3.9 Access terminal settings
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
Access:
1. Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Link Direction > Uplink"
2. Select "Access Terminals".
Four terminals are available.
3. To enable a subset of predefined settings for faster configuration, select "Predefined Settings".
4. To activate a terminal, set its state to "On", e.g. "Terminal 1 > On".
5. To access the settings of a terminal, select the corresponding field, e.g. "Terminal
1".
The corresponding "Configure Access Terminal 1 .. 4" dialog opens. The access
terminal number is indicated in the panel headline.
40User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
The dialog comprises the settings of the access terminal mode, of the data channel
and configuration of the different channels.
The available channels depend on the selected "Physical Layer Subtype" and the
selected "Access Terminal Mode", see Table 3-4.
Table 3-4: Overview on available channels, depending on physical layer subtype and access terminal
Physical
layer
subtype
0&1 Traffic X - X - X X Packet 1
mode
Access
terminal
mode
Access X - - - - - Packet 1
Pilot
channel
Auxiliary
pilot
channel
RRI
channel
DSC
channel
DRC
channel
ACK
channel
Data
channel
41User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
Physical
layer
subtype
2 Traffic X X X X X X Packet
Access
terminal
mode
Access X - - - - - Packet 1
Pilot
channel
Auxiliary
pilot
channel
RRI
channel
DSC
channel
DRC
channel
ACK
channel
Data
channel
1..3
Predefined Settings
Uplink only
Enables selection of UL predefined settings for Terminal 1 for faster configuration.
The predefined settings are made according to 3GPP2 C.S0032-A to allow easy
receiver testing.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:PREDefined on page 96
State
Enables or disables the selected access terminal.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:STATe on page 116
Mode
Sets the mode ("Traffic" or "Access") of the selected access terminal.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:MODE on page 114
Physical Layer Subtype
Selects the physical layer subtype for the selected access terminal.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:SUBType on page 116
Disable Quadrature Spreading
Disables the quadrature spreading (complex multiply) with PN sequences and long
code.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DQSPreading on page 110
Long Code Mask I (hex)
Sets the long code mask of the I channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:IMASk on page 114
Long Code Mask Q (hex)
Sets the long code mask of the Q channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:QMASk on page 115
42User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Preamble Length
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode only)
Specifies the length of the preamble in frames (16 slots each) of the access probe (see
figure below).
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:PLENgth on page 115
Access Cycle Duration
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode only)
Sets the access cycle duration in slots. Access probes are repeated with a period of
access cycle duration slots.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACYCle:DURation on page 99
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
Access Cycle Offset
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode only)
The access channel transmission starts with this number of slots relative to the begin-
ning of each access cycle duration.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACYCle:OFFSet on page 99
Pilot Channel
Access:
Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Access Terminals > Terminal > Pilot Channel".
State ← Pilot Channel
Displays the state of the pilot channel.
Note: The pilot channel is always switched on.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:PCHannel:STATe? on page 115
Gain ← Pilot Channel
Sets the gain of the pilot channel.
43User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Gains of other channels are relative to the pilot channel power. This setting is used to
distinguish the power between access terminals, when more than one access terminal
is active.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:PCHannel:GAIN on page 114
Auxiliary Pilot Channel
Access:
Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Access Terminals > Terminal > Auxiliary Pilot Chan-
nel".
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
State ← Auxiliary Pilot Channel
(enabled for Physical Layer subtype 2 and an access terminal working in traffic mode
only)
Enables or disables the state of the auxiliary pilot channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:APCHannel:STATe on page 100
Relative Gain ← Auxiliary Pilot Channel
Sets the gain of the auxiliary pilot channel relative to the data channel power.
Note: All other channel gains are specified relative to the pilot channel power, but the
auxiliary pilot gain is specified relative to the data channel power. This parameter is
only enabled for Physical Layer subtype 2 and for an access terminal working in traffic
mode.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:APCHannel:GAIN on page 100
Minimum Payload ← Auxiliary Pilot Channel
(enabled for Physical Layer subtype 2 and an access terminal working in traffic mode
only)
Sets the minimum payload size in bits of the data channel that activates the transmission of the auxiliary pilot channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:APCHannel:PAYLoad:MINimum
on page 100
RRI Channel
Access:
44User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Access Terminals > Terminal > RRI Channel".
State ← RRI Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Enables or disables the state of the reverse rate indicator (RRI) channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:RRIChannel:STATe on page 116
Relative Gain ← RRI Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Sets the gain of the reverse rate indicator (RRI) channel relative to the pilot channel
power.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:RRIChannel:GAIN on page 115
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
DSC Channel
Access:
Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Access Terminals > Terminal > DSC Channel".
State ← DSC Channel
(enabled for Physical Layer subtype 2 and an access terminal working in traffic mode
only)
Enables or disables the state of the data source control (DSC) channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DSCChannel:STATe on page 113
Relative Gain ← DSC Channel
(enabled for Physical Layer subtype 2 and an access terminal working in traffic mode
only)
Sets the gain of the data source control (DSC) channel relative to the pilot channel
power.
45User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DSCChannel:GAIN on page 112
Length ← DSC Channel
(enabled for Physical Layer subtype 2 and an access terminal working in traffic mode
only)
Specifies the transmission duration of the data source control (DSC) channel in slots.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DSCChannel:LENGth on page 113
Values (OCT) ← DSC Channel
(enabled for Physical Layer subtype 2 and an access terminal working in traffic mode
only)
Specifies the pattern transmitted on the data source control (DSC) Channel.
The sequence starts at frame 0 and slot 0 and is repeated with the length of the pat-
tern. Each specified value is transmitted for DSC length slots.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DSCChannel:VALues on page 113
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
DRC Channel
Access:
Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Access Terminals > Terminal > DRC Channel".
State ← DRC Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Enables or disables the state of the data rate control (DRC) channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:STATe on page 112
Relative Gain ← DRC Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Sets the gain of the data rate control (DRC) channel relative to the pilot channel power.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:GAIN on page 111
46User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Length ← DRC Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Specifies the transmission duration of the data rate control (DRC) channel in slots.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:LENGth on page 111
Values (hex) ← DRC Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Specifies the pattern transmitted on the data rate control (DRC) channel.
The sequence starts at frame 0 and slot 0 and is repeated with the length of the pat-
tern. Each specified value is used for DRC length slots.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:VALues on page 112
Cover ← DRC Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Selects the data rate control (DRC) channel Walsh cover.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:COVer on page 110
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
Gating Active ← DRC Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Activates or deactivates the data rate control (DRC) Channel gating.
With deactivated gating, each DRC value is repeated for DRC length slots.
If gating is active, each value of the DRC channel is transmitted for one slot followed
by DRCLenght-1 empty slots.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:GATing[:STATe]
on page 111
47User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
ACK Channel
Access:
Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Access Terminals > Terminal > ACK Channel".
State ← ACK Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Enables or disables the ACK channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:STATe on page 98
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
Relative Gain ← ACK Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Sets the gain of the ACK channel relative to the pilot channel power.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:GAIN on page 97
Mode ← ACK Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Specifies the modulation mode of the ACK channel.
"BPSK"
"OOK"
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:MODE on page 98
Gating (bin) ← ACK Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Sets the active and inactive slots of the ACK channel.
The sequence starts at frame 0 and slot 0 and is repeated with the length of the pat-
tern.
A 0 gates the ACK channel off for the corresponding slot, a 1 activates the channel.
Sets the modulation to BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying).
With BPSK modulation, a 0 (ACK) is mapped to +1 and a 1 (NAK) to
-1 respectively.
Sets the modulation to OOK (On/Off keying). With OOK modulation, a
0 (ACK) is mapped to ON and a 1 (NAK) to OFF.
Note: OKK modulation is only enabled for physical layer subtype 2.
48User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:GATing on page 97
Values ← ACK Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Specifies the data pattern transmitted on the ACK Channel.
The sequence starts at frame 0 and slot 0 and is repeated with the length of the pat-
tern. A 0 specifies an ACK, a 1 specifies a NAK. This pattern is only read for slots that
are gated on.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:VALues on page 99
Data Channel
Access:
Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > Access Terminals > Terminal > Data Channel".
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
State ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Enables or disables the state of the packets.
There are three configurable packets ("Packet 1… 3") for physical layer subtype 2.
When more than one packet is active, packet 1 is sent on the first subframe (first four
slots). Packets 2 and 3 are sent respectively on the second and the third subframe
(see figure below).
49User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
When only one packet is active and "Number of Subpackets" is set to 1, no interleaving
is performed between the packets. In this case, the data channel is active continuously
(see figure below).
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
When only one packet is active but the number of subpackets is larger than one, interleave subframe. In this case, two subframes are left empty in-between every two subpackets (see figure below).
Only one configurable packet is available for physical layer subtype 0&1, the data
channel is continuously active for the number of packets to send.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:STATe
on page 109
Gain/db ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Sets the gain in dB of the selected packet relative to the pilot channel power.
Note: Configuration of "Packet 2" and "Packet 3" transmitted on the second and the
third subframe, is only enabled for physical layer subtype 2.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:GAIN
on page 107
50User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Infinite Packets ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Enables or disables sending an unlimited number of packets.
If "Infinite Packets" is disabled, the number of packets to send can be specified with
the parameter "Number of Packets to Send".
Note: Configuration of "Packet 2" and "Packet 3" transmitted on the second and the
third subframe, is only enabled for physical layer subtype 2.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:INFinite
on page 107
Packets To Send ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Sets the number of packets to be sent.
The number of packets to send depends on whether the parameter "Infinite Packets" is
enabled or disabled. If "Infinite Packets" is enabled, there is no limit to the number of
packets sent.
If "Infinite Packets" is disabled, the number of packets can be specified. The data
channel will be switched off after the specified "Number of Packets" have been sent.
Note: Configuration of "Packet 2" and "Packet 3" transmitted on the second and the
third subframe, is only enabled for physical layer subtype 2.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:COUNt
on page 104
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
Subpackets ← Data Channel
(enabled for physical layer subtype 2 and an access terminal working in traffic mode
only)
Sets the number of subpackets to be sent.
Example:
If number of subpackets is 4, then subpacket 0, 1, 2 and 3 of a packet is sent in a subframe each (with two subframes interleaving between). Afterward the next packet is
started. It simulates a situation where three times NAK has been received from the
base station with an ACK after the fourth subpacket.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:
SUBPackets[:COUNt] on page 109
Payload Size/bits ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Sets the payload size in bits for the selected packet.
Note: Configuration of "Packet 2" and "Packet 3" transmitted on the second and the
third subframe, is only enabled for physical layer subtype 2.
51User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:PSIZe
on page 108
Modulation ← Data Channel
(enabled for physical layer subtype 2 and an access terminal working in traffic mode
only)
Displays the modulation type per packet.
The modulation type is set automatically according to the selected payload size. The
value is read-only.
Remote-control command: SOUR:BB:EVDO:TERM2:DCH:PACK3:MOD?
"B4"
"Q4"
"Q2"
"Q4Q2"
"E4E2"
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:
MODulation? on page 108
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
The modulation type is set to BPSK modulation with 4-ary Walsh
cover.
The modulation type is set to QPSK modulation with 4-ary Walsh
cover.
The modulation type is set to QPSK modulation with 2-ary Walsh
cover.
Sum of Q4 and Q2 modulated symbols.
Sum of E4 (8-PSK modulated with 4-ary Walsh cover) and E2 (8-PSK
modulated with 2-ary Walsh cover) modulated symbols.
Data Rate/kbps ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Displays the resulting data rate for the selected packet.
The data rate is the effective data rate achieved for the specific packet. Sum up the
data rates of all three packets to obtain the total effective data rate for the uplink data
channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:DRATe?
on page 106
Channel Coding ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Activates or deactivates channel coding, including scrambling, turbo encoding and
channel interleaving.
Note: Configuration of "Packet 2" and "Packet 3" transmitted on the second and the
third subframe, is only enabled for physical layer subtype 2.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:CCODing
on page 104
52User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Data Source ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Selects the data source.
The number of bits read from the data source for each packet depends on the payload
size, channel coding state and FCS state. The following table gives an overview on the
number of bits read.
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
Channel Coding ON PayloadSize - FCSSize - 6 PayloadSize - 6
Channel Coding OFF (PayloadSize/CodeRate) -
FCS ON FCS OFF
(PayloadSize/CodeRate)
FCSSize
FCSSize and code rate depend on the physical layer subtype (see that table bellow).
FCSSize 16 24
Code rate 1/4 or 1/2 1/5 or 1/3
Physical layer subtype 0&1 Physical layer subtype 2
Note: Configuration of "Packet 2" and "Packet 3" transmitted on the second and the
third subframe, is only enabled for physical layer subtype 2.
The following standard data sources are available:
●
"All 0, All 1"
An internally generated sequence containing 0 data or 1 data.
●
"PNxx"
An internally generated pseudo-random noise sequence.
●
"Pattern"
An internally generated sequence according to a bit pattern.
Use the "Pattern" box to define the bit pattern.
●
"Data List/Select DList"
A binary data from a data list, internally or externally generated.
Select "Select DList" to access the standard "Select List" dialog.
– Select the "Select Data List > navigate to the list file *.dm_iqd > Select" to
select an existing data list.
– Use the "New" and "Edit" functions to create internally new data list or to edit
an existing one.
– Use the standard "File Manager" function to transfer external data lists to the
instrument.
See also:
●
Section "Modulation Data" in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
●
Section "File and Data Management" in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
●
Section "Data List Editor" in the R&S SMBV100B user manual
53User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:DATA
on page 105
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:DATA:
DSELection on page 105
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:DATA:
PATTern on page 105
FCS ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode only)
Enables or disables appending a standard frame check sequence (FCS) to the MAC
layer packet.
Note: Configuration of "Packet 2" and "Packet 3" transmitted on the second and the
third subframe, is only enabled for physical layer subtype 2.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:FCS[:
STATe] on page 106
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Access terminal settings
State ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode only)
Enables or disables the state of the data channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:STATe on page 110
Relative Gain ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode only)
Sets the gain in dB of the data channel relative to the pilot channel power.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:GAIN on page 103
Capsule Length ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode only)
Sets the number of frames (16 slots each) to be transmitted after the preamble. Each
frame contains one data packet.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:CLENgth on page 101
Data Rate ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode only)
Selects the data rate for the data channel.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:DRATe on page 102
Data Source ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode only)
54User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Selects the data source.
The following standard data sources are available:
●
"All 0, All 1"
An internally generated sequence containing 0 data or 1 data.
●
"PNxx"
An internally generated pseudo-random noise sequence.
●
"Pattern"
An internally generated sequence according to a bit pattern.
Use the "Pattern" box to define the bit pattern.
●
"Data List/Select DList"
A binary data from a data list, internally or externally generated.
Select "Select DList" to access the standard "Select List" dialog.
– Select the "Select Data List > navigate to the list file *.dm_iqd > Select" to
– Use the "New" and "Edit" functions to create internally new data list or to edit
– Use the standard "File Manager" function to transfer external data lists to the
See also:
●
Section "Modulation Data" in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
●
Section "File and Data Management" in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
●
Section "Data List Editor" in the R&S SMBV100B user manual
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Filter / clipping / ARB settings
select an existing data list.
an existing one.
instrument.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:DATA on page 101
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:DATA:PATTern
on page 102
Append FCS ← Data Channel
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode only)
Enables or disables appending a standard frame check sequence (FCS) to the MAC
layer packet.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:FCS[:STATe]
on page 103
3.10 Filter / clipping / ARB settings
Access:
► Select "General > Filter/Clipping/ARB/IQ Settings".
The dialog comprises the settings, necessary to configure the baseband filter, sample rate variation and clipping.
55User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
3.10.1 Filter settings
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Filter / clipping / ARB settings
Settings:
Filter
Selects the baseband filter.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:TYPE on page 72
Roll Off Factor or BxT
Sets the filter parameter.
The filter parameter ("Roll off Factor" or "BxT") depends on the currently selected filter
type. This parameter is preset to the default for each of the predefined filters.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:APCO25 on page 70
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:COSine on page 70
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:GAUSs on page 70
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:PGAuss on page 71
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:RCOSine on page 72
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:SPHase on page 72
Cut Off Frequency Factor
Sets the value for the cutoff frequency factor. The cutoff frequency of the filter can be
adjusted to reach spectrum mask requirements.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:LPASs on page 71
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:LPASSEVM on page 71
56User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Chip Rate Variation
Enters the chip rate.
The chip rate entry changes the output clock and the modulation bandwidth.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CRATe:VARiation on page 69
3.10.2 Clipping settings
► Access:
Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > General > Filter/Clipping/ARB/IQ Settings > Clipping"
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Filter / clipping / ARB settings
Provided are the following settings for configuring the clipping settings:
Clipping State
(For reverse link mode only)
Switches baseband clipping on and off.
Baseband clipping is a simple and effective way of reducing the crest factor of the sig-
nal. Since clipping is done before to filtering, the procedure does not influence the
spectrum. The EVM however increases.
1xEV-DO signals can have high crest factors particularly with many channels and long
sequences.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLIPping:STATe on page 69
57User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Clipping Level
(For reverse link mode only)
Sets the limit for clipping.
This value indicates at what point the signal is clipped. It is specified as a percentage,
relative to the highest level. 100% indicates that clipping does not take place.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLIPping:LEVel on page 68
Clipping Mode
(For reverse link mode only)
Selects the clipping method. The dialog displays a graphical illustration on how this two
methods work.
●
"Vector | i + jq |"
The limit is related to the amplitude | i + q |. The I and Q components are mapped
together, the angle is retained.
●
"Scalar | i | , | q |"
The limit is related to the absolute maximum of all the I and Q values | i | + | q |.
The I and Q components are mapped separately, the angle changes.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLIPping:MODE on page 69
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Filter / clipping / ARB settings
3.10.3 ARB settings
► Access:
Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > General > Filter/Clipping/ARB/IQ Settings > ARB"
58User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Provided are the following settings for configuring the ARB settings:
Sequence Length ARB
(For reverse link mode only)
Changes the sequence length of the arbitrary waveform component of the 1xEV-DO
signal. This component is calculated in advance and output in the arbitrary waveform
generator. It is added to the realtime signal components.
The number of chips is determined from this sequence length. One slot of 1.67ms
duration equals 2048 chips.
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SLENgth on page 66
3.10.4 I/Q setting
► Access:
Select "Baseband > 1xEV-DO > General > Filter/Clipping/ARB/IQ Settings > IQ"
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Filter / clipping / ARB settings
Provided are the following settings for configuring the IQ settings:
Invert Q for Correct Baseband Output
With its default 1xEV-DO settings, the R&S SMBV100B generates a standard compliant RF signal.
If a standard compliant baseband signal is required, enable this parameter to invert the
Q-part of the baseband signal.
If both, the RF signal and baseband signal have to be compliant with the 1xEV-DO
standard:
●
Set "Invert Q for Correct Baseband Output > On"
59User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
●
Set "I/Q Mod > I/Q Settings > I/Q Swap > On"
See also R&S SMBV100B user manual, section "Applying I/Q Vector Modulation".
Remote command:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:IQSWap:STATe on page 72
1xEV-DO configuration and settings
Filter / clipping / ARB settings
60User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
4 Remote-control commands
The following commands are required to generate signals with the 1xEV-DO options in
a remote environment. We assume that the R&S SMBV100B has already been set up
for remote operation in a network as described in the R&S SMBV100B documentation.
A knowledge about the remote control operation and the SCPI command syntax are
assumed.
Conventions used in SCPI command descriptions
For a description of the conventions used in the remote command descriptions, see
section "Remote Control Commands" in the R&S SMBV100B user manual.
Common Suffixes
The following common suffixes are used in remote commands:
Suffix Value range Description
Remote-control commands
ENTity<ch>
SOURce<ch>
OUTPut<ch>
CARRier<Ch>
USER<ST>
TERMinal<ST>
1 Optional keyword, provided for compatibility with
R&S®SMW200A
ENTity1:SOURce1 = SOURce1
1 available baseband signals
1 to 3 available markers
0 to 21 band class
1 to 4 user
1 to 4 terminal
The following commands specific to the 1xEV-DO are described here:
● Programming examples.......................................................................................... 62
● General commands.................................................................................................64
● Filter / clipping / ARB commands............................................................................68
● Trigger commands.................................................................................................. 73
● Marker commands.................................................................................................. 76
● Clock commands.....................................................................................................77
● Access network commands.................................................................................... 78
● Multi-carrier configuration commands.....................................................................82
● Configure traffic user commands............................................................................ 85
● Configure access terminal commands....................................................................95
61User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
4.1 Programming examples
Example: Performing general tasks
This example shows how to enable the option with predefined settings as basis for further customization (e.g. defining the transmission direction, etc.). Results and configuration are stored with the save/recall function.
// ******************************************************************
// Reset instrument first
// ******************************************************************
*RST; *CLS
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:PRESet
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:STATe ON
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:SETTing:STORe "/var/user/1xEVDO_def"
// ******************************************************************
// Recall settings
// ******************************************************************
MMEM:CDIR "/var/user/"
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:SETTing:CATalog?
// 1xEVDO_def,1xEVDO_dl,1xEVDO_test
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:SETTing:DELete "1xEVDO_test"
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:SETTing:LOAD "1xEVDO_dl"
Remote-control commands
Programming examples
// ******************************************************************
// Change the data transmission direction
// queries PN offset, sets the system time
// queries version and ARB sequence length
// generates and stores an waveform file in the current directory
// ******************************************************************
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:LINK?
// DOWN
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:LINK UP
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:PNOFfset?
// 0
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:STIMe 32
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:SLENgth?
// 48
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:VERSion?
// Release B
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:WAVeform:CREate "wv1xEVDO_ul"
Example: Adjusting clock and trigger settings
The following example lists the provided commands:
// ******************************************************************
// Clock settings
// ******************************************************************
62User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:CLOCk:SOURce INTernal
// ******************************************************************
// Configure and enable signal generation
// ******************************************************************
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SOURce INTernal
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SEQuence ARETrigger
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:STAT ON
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXECute
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:ARM:EXECute
// :SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SEQuence SING
// :SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SLUNit CHIP
// :SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SLENgth 2
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:RMODe?
// Stopped
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXECute
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:RMODe?
// Run
Remote-control commands
Programming examples
// :SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SOURce EGT1
// :SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXTernal:SYNChronize:OUTPut ON
// :SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXTernal:INHibit 200
// :SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXTernal:DELay 100
Example: Configure and enable standard marker signals
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut1:MODE RATio
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut1:ONTime 40
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut1:OFFTime 20
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut3:MODE USER
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut3:PERiod 100
Example: Generating a downlink multicarrier signal
This example shows how to enable the multi-carrier configuration and generate a signal composed of four carriers within a selected band class.
// ******************************************************************
// Reset instrument first
// ******************************************************************
*RST; *CLS
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:LINK?
// DOWN
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:BCLass BC11
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier1:STATe 1
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier2:CHANnel 10
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier2:STATe 1
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier3:CHANnel 5
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier4:CHANnel 500
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier4:STATe 1
63User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier5:CHANnel 100
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier6:CHANnel 1200
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier6:CHANnel?
// Response: 871
// channel 1200 is not valid, the firmware selects the next available channel.
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier7:CHANnel 1536
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier8:CHANnel 1700
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier8:STATe 1
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier9:CHANnel 240
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:STATe 1
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:STATe 1
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CFRequency?
// 456900000
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier1:FREQuency?
// 460000000
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier2:FREQuency?
// 460225000
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier4:FREQuency?
// 420700000
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier8:FREQuency?
// 493100000
Remote-control commands
General commands
// apply a carrier delay to reduce the crest factor
:SOURce1:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CDELay 0.000001
// Carrier#1 is delayed by 0 ns, carrier#2 by 1000 ns,
// carrier#4 by 2000 ns, carrie#8 by 3000 ns
4.2 General commands
This section contains commands for the primary and general settings of the 1xEV-DO
standard. These settings concern activation of the standard, setting the transmission
direction, defining the chip rate and the sequence length, as well as the preset and
power adjust setting.
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:LINK....................................................................................... 65
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:PNOFfset................................................................................ 65
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:PRESet................................................................................... 65
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:CATalog?................................................................... 65
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:DELete...................................................................... 66
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:LOAD........................................................................ 66
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:STORe.......................................................................66
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SLENgth..................................................................................66
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:STATe..................................................................................... 67
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:STIMe..................................................................................... 67
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:VERSion?................................................................................67
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:WAVeform:CREate................................................................... 68
64User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:LINK <Link>
Defines the transmission direction.
Parameters:
<Link> FORWard/DOWN | REVerse/UP
Example: see Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Manual operation: See "Link Direction" on page 14
Remote-control commands
General commands
*RST: DOWN
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:PNOFfset
Sets the PN Offset of the 1xEV-DO signal.
Parameters:
<PnOffset> integer
Range: 0 to 511
*RST: 0
Example: see Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Manual operation: See "PN Offset" on page 14
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:PRESet
Sets the parameters of the digital standard to their default values (*RST values specified for the commands).
Not affected is the state set with the command SOURce<hw>:BB:EVDO:STATe.
Example:
Usage: Event
Manual operation: See "Set To Default" on page 13
see Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
<PnOffset>
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:CATalog?
Queries the files with 1xEV-DO settings (file extension *.1xevdo) in the default or the
specified directory.
Return values:
<Catalog> "<filename1>,<filename2>,..."
Returns a string of filenames separated by commas.
Example: See Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Usage: Query only
Manual operation: See "Save/Recall" on page 13
65User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:DELete <Filename>
Deletes the selected file from the default or specified directory. Deleted are files with
the file extension *.1xevdo.
Setting parameters:
<Filename> string
Example: See Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Usage: Setting only
Manual operation: See "Save/Recall" on page 13
Remote-control commands
General commands
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:LOAD
Loads the selected file from the default or the specified directory. Loads are files with
extension *.1xevdo.
Setting parameters:
<Filename> string
Example: See Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Usage: Setting only
Manual operation: See "Save/Recall" on page 13
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SETTing:STORe <Filename>
Stores the current settings into the selected file; the file extension *.1xevdo is
assigned automatically.
Setting parameters:
<Filename> string
Example: See Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Usage: Setting only
Manual operation: See "Save/Recall" on page 13
<Filename>
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:SLENgth <SLength>
(For reverse link mode only)
Sets the sequence length of the arbitrary waveform component of the 1XEV-DO signal
in number of frames. This component is calculated in advance and output in the arbitrary waveform generator. It is added to the real time signal components. The number
of chips is determined from this sequence length. One slot of 1.67ms duration equals
2048 chips.
66User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<SLength> integer
Example: See Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Manual operation: See "Sequence Length ARB" on page 59
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:STATe <State>
Activates the standard and deactivates all the other digital standards and digital modulation modes in the same path.
Parameters:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Example: see Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Remote-control commands
General commands
Range: 4 to dynamic
Increment: 4
*RST: 48
*RST: 0
Manual operation: See "State" on page 12
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:STIMe <STime>
Sets the System Time value of the 1xEV-DO signal and the base station. The System
Time value is expressed in units of 1.67 ms intervals (80 ms/ 48).
Note: In uplink, the value selected for system time must be multiple of 16.
Parameters:
<STime> integer
Range: 0 to 2199023255551
*RST: 0
Example: see Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Manual operation: See "System Time" on page 14
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:VERSion?
Queries the version of the 1xEV-DO standard underlying the definitions
Return values:
<Version> string
Example: see Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Usage: Query only
Manual operation: See "1xEV-DO Version" on page 13
67User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:WAVeform:CREate <Filename>
Creates a waveform using the current settings. The file is stored with the predefined
file extension *.wv. The filename and the directory it is stored in are user-definable.
Setting parameters:
<Filename> string
Example: See Example "Performing general tasks" on page 62
Usage: Setting only
Manual operation: See "Generate Waveform" on page 13
4.3 Filter / clipping / ARB commands
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLIPping:LEVel........................................................................68
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLIPping:MODE.......................................................................69
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLIPping:STATe....................................................................... 69
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CRATe:VARiation......................................................................69
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:APCO25.......................................................70
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:COSine........................................................ 70
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:GAUSs.........................................................70
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:LPASs..........................................................71
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:LPASSEVM.................................................. 71
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:PGAuss........................................................71
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:RCOSine......................................................72
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:SPHase........................................................72
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:TYPE............................................................................ 72
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:IQSWap:STATe........................................................................ 72
Remote-control commands
Filter / clipping / ARB commands
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLIPping:LEVel <Level>
(For reverse link mode only)
The command sets the limit for level clipping (Clipping). This value indicates at what
point the signal is clipped. It is specified as a percentage, relative to the highest level.
100% indicates that clipping does not take place.
Level clipping is activated with the command SOUR:BB:EVDO:CLIP:STAT ON
Parameters:
<Level> integer
Range: 0 PCT to 100 PCT
Increment: 1 PCT
*RST: 100 PCT
Example:
BB:EVDO:CLIP:LEV 80PCT
sets the limit for level clipping to 80% of the maximum level.
BB:EVDO:CLIP:STAT ON
activates level clipping.
68User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Manual operation: See "Clipping Level" on page 58
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLIPping:MODE <Mode>
(For reverse link mode only)
Sets the method for level clipping.
Parameters:
<Mode> VECTor | SCALar
Remote-control commands
Filter / clipping / ARB commands
VECTor
The reference level is the amplitude | i+jq |
SCALar
The reference level is the absolute maximum of the I and Q values.
*RST: VECTor
Example:
Manual operation: See "Clipping Mode" on page 58
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLIPping:STATe <State>
(For reverse link mode only)
The command activates level clipping (Clipping). The value is defined with the command BB:EVDO:CLIPping:LEVel, the mode of calculation with the command
BB:EVDO:CLIPping:MODE.
Parameters:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Example:
Manual operation: See "Clipping State" on page 57
BB:EVDO:CLIP:MODE SCAL
BB:EVDO:CLIP:LEV 80PCT
Sets the limit for level clipping to 80% of this maximum level.
BB:EVDO:CLIP:STAT ON
*RST: OFF
BB:EVDO:CLIP:STAT ON
activates level clipping.
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CRATe:VARiation <Variation>
Enters the output chip rate.
The output chip rate changes the output clock and the modulation bandwidth, as well
as the synchronization signals that are output. It does not affect the calculated chip
sequence.
69User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<Variation> float
Remote-control commands
Filter / clipping / ARB commands
Range: 1 Mcps to 5 Mcps
Increment: 1E-6 Mcps (1cps)
*RST: 1.2288 Mcps
Example:
Manual operation: See "Chip Rate Variation" on page 57
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:APCO25
Sets the rolloff factor for filter type APCO25.
Parameters:
<Apco25> float
Example:
Manual operation: See "Roll Off Factor or BxT" on page 56
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:COSine <Cosine>
Sets the rolloff factor for the Cosine filter type.
BB:EVDO:CRAT:VAR 4086001
sets the chip rate to 4.08 Mcps.
<Apco25>
Range: 0.05 to 0.99
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 0.2
BB:EVDO:FILT:PAR:APCO25 0.2
Sets the rolloff factor to 0.2 for filter type APCO25.
Parameters:
<Cosine> float
Range: 0.05 to 1
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 0.1
Example:
Manual operation: See "Roll Off Factor or BxT" on page 56
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:GAUSs <Gauss>
Sets the rolloff factor for the Gauss filter type.
Parameters:
<Gauss> float
BB:EVDO:FILT:PAR:COS 0.35
Sets the rolloff factor to 0.35 for filter type Cosine.
Range: 0.15 to 2.5
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 0.5
70User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote-control commands
Filter / clipping / ARB commands
Example:
Manual operation: See "Roll Off Factor or BxT" on page 56
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:LPASs <LPass>
Sets the cutoff frequency factor for the lowpass filter (ACP Opt.) type.
Parameters:
<LPass> float
Example:
Manual operation: See "Cut Off Frequency Factor" on page 56
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:LPASSEVM <LPassEvm>
Sets the cutoff frequency factor for the lowpass filter (EVM Opt.) type.
BB:EVDO:FILT:PAR:GAUS 0.5
Sets BxT to 0.5 for the Gauss filter type.
Range: 0.05 to 2
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 0.5
BB:EVDO:FILT:PAR:LPAS 0.5
The cut of frequency factor is set to 0.5.
Parameters:
<LPassEvm> float
Range: 0.05 to 2
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 0.5
Example:
Manual operation: See "Cut Off Frequency Factor" on page 56
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:PGAuss <PGauss>
Sets the rolloff factor for the Pure Gauss filter type.
Parameters:
<PGauss> float
Example:
Manual operation: See "Roll Off Factor or BxT" on page 56
BB:EVDO:FILT:PAR:LPASSEVM 0.5
The cut of frequency factor is set to 0.5.
Range: 0.15 to 2.5
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 0.5
BB:EVDO:FILT:PAR:GAUS 0.5
Sets BxT to 0.5 for the Pure Gauss filter type.
71User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:RCOSine <RCosine>
Sets the rolloff factor for the Root Cosine filter type.
Parameters:
<RCosine> float
Remote-control commands
Filter / clipping / ARB commands
Range: 0.05 to 1
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 0.15
Example:
Manual operation: See "Roll Off Factor or BxT" on page 56
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:PARameter:SPHase
Sets BxT for the Split Phase filter type.
Parameters:
<SPhase> float
Example:
Manual operation: See "Roll Off Factor or BxT" on page 56
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:FILTer:TYPE <Type>
The command selects the filter type.
BB:EVDO:FILT:PAR:RCOS 0.22
Sets the rolloff factor to 0. 22 for filter type Root Cosine.
<SPhase>
Range: 0.15 to 2.5
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 2
BB:EVDO:FILT:PAR:SPH 0.5
Sets BxT to 0.5 for the Split Phase filter type.
Parameters:
<Type> RCOSine | COSine | GAUSs | LGAuss | CONE | COF705 |
COEQualizer | COFequalizer | C2K3x | APCO25 | SPHase |
RECTangle | PGAuss | LPASs | DIRac | ENPShape |
EWPShape | LPASSEVM
*RST: Downlink: COEQ; Uplink: CONE
Example:
Manual operation: See "Filter" on page 56
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:IQSWap:STATe <State>
Inverts the Q-part of the baseband signal
BB:EVDO:FILT:TYPE CONE
Sets the filter type CdmaOne. This filter type is defined by the
standard for the uplink.
72User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Manual operation: See "Invert Q for Correct Baseband Output" on page 59
4.4 Trigger commands
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO[:TRIGger]:SEQuence................................................................73
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:ARM:EXECute............................................................73
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXECute....................................................................74
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXTernal:SYNChronize:OUTPut................................... 74
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:RMODe?....................................................................74
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SLENgth.................................................................... 74
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SLUNit....................................................................... 74
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SOURce.....................................................................75
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger[:EXTernal]:DELay........................................................75
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger[:EXTernal]:INHibit........................................................75
Remote-control commands
Trigger commands
*RST: 0
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO[:TRIGger]:SEQuence <Sequence>
Selects the trigger mode:
●
AUTO = auto
●
RETRigger = retrigger
●
AAUTo = armed auto
●
ARETrigger = armed retrigger
●
SINGle = single
Parameters:
<Sequence> AUTO | RETRigger | AAUTo | ARETrigger | SINGle
*RST: AUTO
Example: See Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62.
Manual operation: See "Trigger Mode" on page 16
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:ARM:EXECute
Stops signal generation; a subsequent internal or external trigger event restart signal
generation.
Example:
see Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62
Usage: Event
Manual operation: See "Arm" on page 17
73User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXECute
Executes a trigger.
Example: see Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62
Usage: Event
Manual operation: See "Execute Trigger" on page 17
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:EXTernal:SYNChronize:OUTPut <Output>
Enables signal output synchronous to the trigger event.
Parameters:
<Output> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Example: See Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62
Manual operation: See "Sync. Output to External Trigger/Sync. Output to Trigger"
Remote-control commands
Trigger commands
*RST: 1
on page 17
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:RMODe?
Queries the signal generation status.
Return values:
<RMode> STOP | RUN
Example: see Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62
Usage: Query only
Manual operation: See "Running/Stopped" on page 16
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SLENgth <SLength>
Defines the length of the signal sequence that is output in the SINGle trigger mode.
Parameters:
<SLength> integer
Range: 1 to 4294967295
*RST: 1
Example: See Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62
Manual operation: See "Trigger Signal Duration" on page 16
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SLUNit <SLunit>
Defines the unit for the entry of the length of the signal sequence.
74User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<SLunit> SLOT | CHIP | SEQuence
Example: See Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62
Manual operation: See "Signal Duration Unit" on page 16
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:SOURce <Source>
Selects the trigger signal source and determines the way the triggering is executed.
Provided are:
●
Internal triggering by a command (INTernal)
●
External trigger signal via one of the User x connectors
EGT1: External global trigger
●
In primary-secondary instrument mode, the external baseband synchronization signal (BBSY)
●
EXTernal: Setting only
Provided only for backward compatibility with other Rohde & Schwarz signal generators.
The R&S SMBV100B accepts this value and maps it automatically as follows:
EXTernal = EGT1
Remote-control commands
Trigger commands
*RST: SEQuence
Parameters:
<Source> INTernal|EGT1|EXTernal|BBSY
*RST: INTernal
Example: See Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62
Manual operation: See "Trigger Source" on page 17
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger[:EXTernal]:DELay <Delay>
Sets the trigger delay.
Parameters:
<Delay> float
Range: 0 to 2147483647
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 0
Default unit: samples
Example: See Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62.
Manual operation: See "Trigger Delay" on page 18
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger[:EXTernal]:INHibit <Inhibit>
Specifies the duration by which a restart is inhibited.
75User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<Inhibit> integer
Example: See Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62.
Manual operation: See "External Trigger Inhibit" on page 18
4.5 Marker commands
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:MODE....................................................76
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:ONTime..................................................76
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:OFFTime................................................76
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:PERiod...................................................77
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:DELay....................................................77
Remote-control commands
Marker commands
Range: 0 to 21.47*chipRate
*RST: 0
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:MODE <Mode>
Defines the signal for the selected marker output.
Parameters:
<Mode> SLOT | PNSPeriod | ESM | CSPeriod | USER | RATio
SLOT
Each slot (every 1.67 ms)
PNSPeriod
Every 26.67 ms (PN Sequence Period)
ESM
Every 2 s (even second mark).
CSPeriod
Each arbitrary waveform sequence
RATio
Regular marker signal
USER
Every user-defined period.
SLOT
Example:
*RST:
SOURce:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut2:MODE ESM
selects the even second mark clock (every 2 seconds) on the
output for marker signal 2
Manual operation: See "Marker Mode" on page 20
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:ONTime <OnTime>
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:OFFTime <OffTime>
Sets the duration during which the marker output is on or off.
76User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<OffTime> integer
Example: See Example "Configure and enable standard marker signals"
Manual operation: See "Marker Mode" on page 20
Remote-control commands
Clock commands
Range: 1 to 16777215
*RST: 1
on page 63.
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:PERiod
Sets the repetition rate for the signal at the marker outputs.
Parameters:
<Period> integer
Range: 1 to 16777215
*RST: 2
Example: See Example "Configure and enable standard marker signals"
on page 63.
Manual operation: See "Marker Mode" on page 20
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TRIGger:OUTPut<ch>:DELay <Delay>
Defines the delay between the signal on the marker outputs and the start of the signals.
Parameters:
<Delay> float
Range: 0 to 16777215
Increment: 1
*RST: 0
<Period>
Example: See Example "Configure and enable standard marker signals"
on page 63
Manual operation: See "Marker x Delay" on page 20
4.6 Clock commands
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLOCk:SOURce...................................................................... 77
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:CLOCk:SOURce <Source>
Selects the clock source:
●
INTernal: Internal clock reference
77User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<Source> INTernal
Example: See Example "Adjusting clock and trigger settings" on page 62.
Manual operation: See "Clock Source" on page 21
4.7 Access network commands
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:PSOFfset.................................................78
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:RATE...................................................... 78
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:REVision:MAXimum..................................79
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:REVision:MINimum...................................79
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:STATe..................................................... 79
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CPMode..................................................................79
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:OUCount.................................................................80
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:PCHannel:STATe?....................................................80
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:LENGth........................................................... 80
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:LEVel.............................................................. 81
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:MAC:INDex......................................................81
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:OFFSet............................................................81
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:STATe..............................................................82
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:SUBType.................................................................82
Remote-control commands
Access network commands
*RST: INTernal
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:PSOFfset <PSoffset>
Sets the offset (in slots) from the start of control channel cycle to the start of the synchronous message capsule that contains the Sync Message.
Parameters:
<PSoffset> integer
Range: 0 to 3
*RST: 0
Example:
BB:EVDO:ANET:CCH:PSOF 2
sets the packet start offset for the control channel to 2.
Manual operation: See "Packet Start Offset" on page 38
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:RATE <Rate>
Sets the rate that the control channel messages are transmitted at.
Parameters:
<Rate> DR4K8 | DR9K6 | DR19K2 | DR38K4 | DR76K8 | DR153K6 |
DR307K2 | DR614K4 | DR921K6 | DR1228K8 | DR1536K |
DR1843K2 | DR2457K6 | DR3072K | DR460K8 | DR768K |
DR1075K2 | DR2150K4 | DR3686K4 | DR4300K8 | DR4915K2
*RST: 38.4 kbps
78User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote-control commands
Access network commands
Example:
Manual operation: See "Rate" on page 38
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:REVision:MAXimum
<Maximum>
Sets the value of the maximum revision field within the control channel message.
Parameters:
<Maximum> integer
Example:
Manual operation: See "Maximum Revision" on page 39
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:REVision:MINimum <Minimum>
Sets the value of the minimum revision field within the control channel message.
BB:EVDO:ANET:CCH:RATE DR76K8
sets the control channel rate to 76.8 kbps.
Range: 0 to 255
*RST: 1
BB:EVDO:ANET:CCH:REV:MAX 10
sets the value of the maximum revision field to 10.
Parameters:
<Minimum> integer
Range: 0 to 255
*RST: 1
Example:
Manual operation: See "Minimum Revision" on page 38
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CCHannel:STATe <State>
Enables or disables the control channel messages.
Parameters:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Example:
Manual operation: See "State" on page 38
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:CPMode <CpMode>
BB:EVDO:ANET:CCH:REV:MIN 1
sets the value of the minimum revision field to 1.
*RST: 0
BB:EVDO:ANET:CCH:STAT ON
enables the control channel message.
Enables or disables a special mode within the 1xEV-DO generator.
Note: During the special mode, all other parameters do not affect the signal output.
79User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<CpMode> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Remote-control commands
Access network commands
*RST: 0
Example:
Manual operation: See "Continuous Pilot Mode" on page 36
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:OUCount <OuCount>
Sets the number of additional users (beyond the four defined users) that appear in the
MAC Channel.
Parameters:
<OuCount> integer
Example:
Manual operation: See "Other Users Count" on page 37
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:PCHannel:STATe?
BB:EVDO:ANET:CPM ON
enables the special mode.
Range: 0 to 55 for physical layer subtype 0&1) , 0 to 110 for
physical layer subtype 2, 0 to 360 for physical layer
subtype 3
*RST: 1
BB:EVDO:ANET:OUC 5
sets the number of additional users to 5.
Displays the state of the pilot channel. Pilot channel is transmitted by sector on each
active forward channel. It is present always and transmitted at the full sector power.
Return values:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
*RST: ON
Example:
Usage: Query only
Manual operation: See "State" on page 37
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:LENGth <Length>
Sets the duration (in slots) of a Reverse Activity bit.
Note: This parameter is available for physical layer subtype 0&1 only.
Parameters:
<Length> RL8 | RL16 | RL32 | RL64
BB:EVDO:ANET:PCH:STAT?
displays the state of the pilot channel.
*RST: 8
80User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote-control commands
Access network commands
Example:
Manual operation: See "RAB Length" on page 39
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:LEVel <Level>
Sets the power within the MAC block for the Reverse Activity channel.
Parameters:
<Level> float
Example:
Manual operation: See "RAB Level" on page 39
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:MAC:INDex <Index>
For physical layer, subtype 3 only sets the RAB MAC Index.
BB:EVDO:ANET:RAB:LENG RL16
sets the duration of the Reverse Activity Bit (RAB) to 16 slots.
Range: -25 to -7
Increment: 0.01
*RST: -7
BB:EVDO:ANET:RAB:LEV -7.0
sets the power of the MAC block for the Reverse Activity Channel to -7.0 dB.
Parameters:
<Index> integer
Range: 4 to 127
*RST: 4
Manual operation: See "RAB MAC Index" on page 40
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:OFFSet <Offset>
Sets the starting time offset of the Reverse Activity bit in slots. The command is specified in Reverse Activity Length/8 units. The RA bit starts when the following equation is
satisfied:
System Time mod RAB length = RAB Offset, where System Time is expressed in slots.
Note: This parameter is available for physical layer subtype 0&1 only.
Parameters:
<Offset> integer
Range: 0 to 7
*RST: 0
Example:
BB:EVDO:ANET:RAB:OFFS 1
Sets the starting time offset of the Reverse Activity bit to 1.
Manual operation: See "RAB Offset" on page 39
81User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:RAB:STATe <State>
Activates or deactivates the reverse activity bit (RAB).
Parameters:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Remote-control commands
Multi-carrier configuration commands
*RST: OFF
Example:
BB:EVDO:ANET:RAB:STAT ON
activates the Reverse Activity Bit.
Manual operation: See "State" on page 39
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:ANETwork:SUBType <Subtype>
Selects the physical layer subtype.
Note: The physical layer subtype settings can be queried per user.
Parameters:
<Subtype> S1 | S2 | S3
*RST: S2
Example:
BB:EVDO:ANET:SUBT S2
sets the physical layer subtype to 2.
Options: S3 requires option R&S SMBVB-K87
Manual operation: See "Physical Layer Subtype (User)" on page 23
See "Physical Layer Subtype (Access Network Settings)"
on page 36
4.8 Multi-carrier configuration commands
Multi-Carrier Configuration requires option R&S SMBVB-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:BCLass........................................................................83
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:BCLass.................................................................. 83
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CFRequency?...............................................................83
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CFRequency?.........................................................83
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CDELay....................................................................... 83
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CDELay................................................................. 83
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CARRier<ch>:STATe..................................................... 84
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier<ch>:STATe............................................... 84
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CARRier<ch>:CHANnel.................................................84
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier<ch>:CHANnel........................................... 84
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CARRier<ch>:FREQuency.............................................84
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier<ch>:FREQuency.......................................84
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:STATe..........................................................................85
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:STATe.................................................................... 85
82User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:BCLass <BandClass>
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:BCLass <BandClass>
Selects the band class for operation, as defined in 3GPP2 C.S0057-E.
BC17 is supported in downlink only.
Parameters:
<BandClass> BC0 | BC1 | BC2 | BC3 | BC4 | BC5 | BC6 | BC7 | BC8 | BC9 |
Example: see Example "Generating a downlink multicarrier signal"
Options: R&S SMBVB-K87
Manual operation: See "Band Class" on page 35
Remote-control commands
Multi-carrier configuration commands
BC10 | BC11 | BC12 | BC13 | BC14 | BC15 | BC16 | BC17 |
BC18 | BC19 | BC20 | BC21
*RST: BC0
on page 63
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CFRequency?
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CFRequency?
Queries the center frequency of the band resulting from the set active carriers.
Return values:
<CenterFrequency> integer
Example: see Example "Generating a downlink multicarrier signal"
on page 63
Usage: Query only
Options: R&S SMBVB-K87
Manual operation: See "Center Frequency (band)" on page 34
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CDELay <CarrierDelay>
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CDELay <CarrierDelay>
Sets a delay to each active carrier.
Parameters:
<CarrierDelay> float
Range: 0 to 10E-6
Increment: 1E-9
*RST: 0
Example: see Example "Generating a downlink multicarrier signal"
on page 63
Options: R&S SMBVB-K87
Manual operation: See "Carrier Delay" on page 35
83User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CARRier<ch>:STATe <State>
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier<ch>:STATe <State>
Switches the selected carrier on or off.
Parameters:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Example: see Example "Generating a downlink multicarrier signal"
Options: R&S SMBVB-K87
Manual operation: See "State" on page 34
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CARRier<ch>:CHANnel <Channel>
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier<ch>:CHANnel <Channel>
Sets carrier’s CDMA channel number.
Remote-control commands
Multi-carrier configuration commands
*RST: 0
on page 63
See "State" on page 35
The available Channel values depend on the selected Band Class.
In some cases, not all channel numbers can be used. In case a non-existing channel is
input, the next available channel is used.
Parameters:
<Channel> integer
Range: 0 to 3000
*RST: 1
Example: See Example "Generating a downlink multicarrier signal"
on page 63
Options: R&S SMBVB-K87
Manual operation: See "CDMA Channel Number" on page 35
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:CARRier<ch>:FREQuency <Frequency>
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:CARRier<ch>:FREQuency <Frequency>
Sets the center frequency of the carrier in MHz. In some cases, not all center frequencies are defined by the selected band class. In case a non-existing frequency is input,
the next available frequency is used.
Parameters:
<Frequency> float
Range: 100 to 3000
Increment: 1E-4
*RST: 870.03
Example: See Example "Generating a downlink multicarrier signal"
on page 63
84User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Options: R&S SMBVB-K87
Manual operation: See "Center Frequency" on page 35
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:UP:MC:STATe <State>
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:DOWN:MC:STATe <State>
Enables or disables multi-carrier operation.
Parameters:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Example: See Example "Generating a downlink multicarrier signal"
Options: R&S SMBVB-K87
Remote-control commands
Configure traffic user commands
*RST: 0
on page 63
4.9 Configure traffic user commands
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DATA:PATTern......................................................... 85
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:LENGth.................................................... 86
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:OFFSet.................................................... 86
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:PERiod.....................................................86
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:STATe...................................................... 87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:HARQ:MODE.......................................................... 87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:IFACtor................................................................... 88
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:MAC:INDex............................................................. 88
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:MAC:LEVel..............................................................89
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PACKet:COUNt........................................................89
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PACKet:INFinite.......................................................89
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PACKet:SOFFset..................................................... 90
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PSIZe..................................................................... 90
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RATE?....................................................................91
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RATE:INDex............................................................ 91
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:INJect..............................................................92
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:MODE.............................................................92
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:RANGe............................................................93
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:ZONE<ch0>:BIT...............................................93
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:ZONE<ch0>:COUNt......................................... 94
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:SCOunt?................................................................. 94
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:STATe..................................................................... 94
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DATA:PATTern <Pattern>, <BitCount>
Sets the data pattern for the data portion of the packets sent to the user. The most significant bit (MSB) of this value is the MSB of the packet and the word is repeated to fill
all space within the packet.
85User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<Pattern> numeric
<BitCount> integer
Remote-control commands
Configure traffic user commands
*RST: #H00000000,
Range: 32 to 32
*RST: 32
Example:
Manual operation: See "Data Pattern (hex)" on page 29
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:LENGth <Length>
Sets the number of DRC (Data Rate Control) Lock periods that the state of the DRC
Lock for the selected user is held constant.
Note: Changes in the DRC Lock state are only considered at the interval defined by
the parameter DRC Lock Length.
A value of one allows updating of the DRC Lock bit at anytime.
Parameters:
<Length> DL1 | DL4 | DL8 | DL16 | DL32 | DL64
Example:
Manual operation: See "DRC Lock Length" on page 33
BB:EVDO:USER2:DTA:PATT #H55aa55aa
Sets the data pattern for user 2.
*RST: 1
BB:EVDO:USER2:DRCL:LENG DL8
Sets eight DRCLock periods for holding the state of user 2 constant.
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:OFFSet <Offset>
Sets the reverse link frame offset for the reverse link. The frame offset is used to position the DRC Lock bit within the MAC channel.
Parameters:
<Offset> integer
Range: 0 to 15
*RST: 0
Example:
Manual operation: See "Frame Offset" on page 33
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:PERiod <Period>
Sets the period (measured in slots) of time between successive transmissions of the
DRC (Data Rate Control) Lock bit for the selected user.
BB:EVDO:USER2:DRCL:OFFS 5
Sets the reverse link frame offset to 5.
86User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Note: A value of zero disables the DRC Lock subchannel and the MAC RPC channel
of the selected user is not punctured with the DRC Lock subchannel.
Parameters:
<Period> DP0 | DP4 | DP8 | DP16
Remote-control commands
Configure traffic user commands
*RST: DP4
Example:
Manual operation: See "DRC Lock Period" on page 32
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:DRCLock:STATe <State>
Sets the state of the DRC (Data Rate Control) Lock bit for the selected user.
Note: Changes in the DRC Lock state are only considered at the interval defined by
the parameter DRC Lock Length.
Parameters:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Example:
Manual operation: See "DRC Lock State" on page 32
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:HARQ:MODE <Mode>
Enables or disables the H-ARQ Channel. The H-ARQ channel is used by the access
network to transmit positive acknowledgement (ACK) or a negative acknowledgement
(NAK) in response to a physical layer packet.
BB:EVDO:USER2:DRCL:PER DP8
Sets the DRC Lock period for user 2 to 8 slots.
*RST: OFF
BB:EVDO:USER2:DRCL:STAT ON
activates the DRC Lock bit for user 2.
Note: This parameter is enabled for Physical Layer Subtype 2 only.
Parameters:
<Mode> OFF | ACK | NAK
OFF
Disables transmission of the H-ARQ channel.
ACK
Enables transmission of H-ARQ. The channel is transmitted with
all bits set to ACK.
NAK
Enables transmission of H-ARQ. The channel is transmitted with
all bits set to NAK
*RST: OFF
87User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote-control commands
Configure traffic user commands
Example:
Manual operation: See "H-ARQ Mode" on page 33
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:IFACtor <IFactor>
Controls the number of interleave slots used for the selected user on the forward link.
Four interleave slots are defined in the 1xEV-DO system.
By default, only 1 Interleave slot (Interleave Factor = 1) for an access terminal is configured and transmission to that access terminal every fourth slot is selected.
For an interleave factor > 1, packets on multiple interleave slots are sent, increasing
the data throughput to the access terminal.
Parameters:
<IFactor> integer
BB:EVDO:USER2:SUBT S2
Sets the physical layer subtype for user 2 to 2.
BB:EVDO:USER2:HARQ:MODE ACK
Enables ARQ channel. The channel is transmitted with all bits
set to ACK.
Range: 1 to 4
*RST: 1
Example:
Manual operation: See "Interleave Factor" on page 29
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:MAC:INDex <Index>
Sets the MAC Index used for the selected user.
MAC Index has to be different for the different users. However, in case that two users
are using the same value for MAC Index, the lower priority user is disabled, or be
unable to enable.
The values for the MAC Indexes for the other users (see [:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:
ANETwork:OUCount) are assigned from a pool of valid MAC Indexes.
Parameters:
<Index> integer
BB:EVDO:USER2:IFAC 2
Sets two interleaved slots for user 2 on the forward link.
Range: 5 to 63 for physical layer subtype 0&1, 6 to 127 for
physical layer subtype 2, 4 to 383 for physical layer
subtype 3
*RST: Physical layer subtype 0&1: 5 for user 1; 6 for user
2; 7 for user 3; 8 for user 4; / physical layer subtype
2: 6 for user 1; 7 for user 2; 8 for user 3; 9 for user
4
Example:
BB:EVDO:USER2:MAC:IND 6
Sets the MAC index for user 2 to 16.
88User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Manual operation: See "MAC Index" on page 29
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:MAC:LEVel <Level>
Sets the power within the MAC channel that is dedicated to the selected user.
Parameters:
<Level> float
Remote-control commands
Configure traffic user commands
Range: -25 to -7
Increment: 0.01
*RST: -7
Example:
Manual operation: See "MAC Level" on page 29
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PACKet:COUNt
Sets the number of packets to send to the selected user.
The number of packets to be send depends on whether the parameter "Infinite" is
enabled or disabled.
If "Infinite" is enabled, there is no limit to the number of packets sent to the user.
If "Infinite" is disabled and a value is specified while packets are being sent, the new
count value is used at the end of transmission of the current packet. If a value of zero
is specified, the transmission to the user is stopped at the end of the current packet.
Parameters:
<Count> integer
Example:
BB:EVDO:USER2:MAC:LEV -7.0
sets the power within the MAC channel to -7.0 dB.
<Count>
Range: 0 to 65536
*RST: 65536
BB:EVDO:USER2:PACK:INF OFF
Disables sending of unlimited number of packets.
BB:EVDO:USER2:PACK:COUNT 10
Sets the number of packets to be sent to 10.
Manual operation: See "Number of Packets to Send - Value" on page 24
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PACKet:INFinite <Infinite>
Enables or disables sending an unlimited number of packets to the selected user.
Parameters:
<Infinite> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
ON
Enables sending of an unlimited number of packets to the user.
89User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote-control commands
Configure traffic user commands
OFF
Disables sending of an unlimited number of packets to the user.
The number of packets to be sent can be specified.
*RST: 1
Example:
Manual operation: See "Number of Packets to Send - Infinite" on page 23
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PACKet:SOFFset
Sets the minimum number of slots between the end of one packet and the beginning of
the next.
For single slot packets, a value of zero will cause the next packet to be sent in the
immediate next slot (subject to scheduling).
For multiple slot packets, a value of zero will cause the next packet transmission to
start three slots after the end of the previous packet. The three slot delay is identical to
the interleaving delay between slots for multiple slot packets. The offset value is
attached to the end of the preceding packet.
Parameters:
<SOffset> integer
BB:EVDO:USER2:PACK:INF OFF
Disables sending of unlimited number of packets for user 2.
BB:EVDO:USER2:PACK:COUNT 10
Sets the number of packets to be sent to user 2 to10.
See "Number of Packets to Send - Value" on page 24
<SOffset>
Range: 0 to 255
*RST: 0
Example:
Manual operation: See "Packet Start Offset" on page 24
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:PSIZe <PSize>
Sets the packet size for the packets sent to the selected user.
Note: Selected rate becomes effective at the beginning of the next packet transmitted
to the selected user.
Parameters:
<PSize> PS128 | PS256 | PS512 | PS768 | PS1024 | PS1536 | PS2048 |
BB:EVDO:USER2:PACK:SOFF 10
Sets the packet start offset for user 2 to10.
PS3072 | PS4096 | PS5120 | PS6144 | PS8192 | PS12288 |
PS7168
*RST: PS128
90User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote-control commands
Configure traffic user commands
Example:
Manual operation: See "Packet Size" on page 28
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RATE?
Queries the data rate of the packets sent to the selected user.
Note: Selected rate becomes effective at the beginning of the next packet transmitted
to the selected user.
Return values:
<Rate> DR4K8 | DR9K6 | DR19K2 | DR38K4 | DR76K8 | DR153K6 |
BB:EVDO:ANET:SUBT S2
sets the physical layer subtype to 2.
BB:EVDO:USER2:RATE:IND 4
sets the rate index of user 2 to 4.
BB:EVDO:USER2:PSIZ PS256
sets the packet size for user 2 to 256.
SOUR:BB:EVDO:USER2:RATE?
queries the data rare for user 2.
Response: 76.8 kbps
DR307K2 | DR614K4 | DR921K6 | DR1228K8 | DR1536K |
DR1843K2 | DR2457K6 | DR3072K | DR460K8 | DR768K |
DR1075K2 | DR2150K4 | DR3686K4 | DR4300K8 | DR4915K2
*RST: DR4K8
Example:
Usage: Query only
Manual operation: See "Data Rate" on page 29
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RATE:INDex <Index>
Determines the rate index.
Note: Selected rate becomes effective at the beginning of the next packet transmitted
to the selected user.
BB:EVDO:ANET:SUBT S2
sets the physical layer subtype.
BB:EVDO:USER2:RATE:IND 4
sets the rate index of user 2.
BB:EVDO:USER2:PSIZ PS256
sets the packet size for user 2.
SOUR:BB:EVDO:USER2:RATE?
queries the data rate for user 2.
Response: 76.8 kbps
91User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<Index> integer
Remote-control commands
Configure traffic user commands
Range: 1 to 12 (physical layer subtype 0&1), 1 to 14 (physi-
cal layer subtype 2), 1 to 28 (physical layer subtype
3)
*RST: 1
Example:
Manual operation: See "Rate Index" on page 25
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:INJect
Enables sending of user defined Reverse Power Control (RPC) pattern at the end of
the current RPC mode.
The former RPC mode is restart at the end of the pattern transmission.
Example:
BB:EVDO:ANET:SUBT S2
sets the physical layer subtype.
BB:EVDO:USER2:RATE:IND 4
sets the rate index of user 2.
BB:EVDO:USER2:PSIZ PS256
sets the packet size for user 2.
SOUR:BB:EVDO:USER2:RATE?
queries the data rate for user 2.
Response: 76.8 kbps
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:MODE PATT
Sets the mode of the Reverse Power Control (RPC) Channel
within the MAC channel for user 2 to pattern, i.e. a user-defined
sequence is transmitted.
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:ZONE0:BIT 1
Sets the bit for zone 0 to 1
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:ZONE0:COUNT 10
Sets the number of RPC bits for zone 0 to 10.
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:ZONE1:BIT 0
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:ZONE1:COUNT 100
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:ZONE2:BIT 1
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:ZONE2:COUNT 50
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:ZONE3:BIT 0
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:ZONE3:COUNT 10
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:INJ
The user defined RPC pattern is inserted at the end of the current RPC mode.
Usage:
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:MODE <Mode>
Sets the operation mode for the Reverse Power Control (RPC) Channel within the
MAC channel for the selected user.
Event
92User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<Mode> HOLD | UP | DOWN | RANGe | PATTern
Remote-control commands
Configure traffic user commands
*RST: HOLD
Example:
Manual operation: See "RPC Mode" on page 30
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:RANGe <Range>
Sets the number of Reverse Power Control (RPC) bits sent in each direction when the
"RPC Mode = Range". The specified value is used immediately.
Parameters:
<Range> integer
Example:
Manual operation: See "RPC Range Count" on page 31
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:MODE UP
a continuous stream of Up (0) are transmitted on the Reverse
Power Control (RPC) Channel within the MAC channel for user
2.
Range: 1 to 256
*RST: 1
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:MODE RANG
Sets the mode of the Reverse Power Control (RPC) Channel
within the MAC channel for user 2 to range.
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:RANG:COUN 200
Sets the number of RPC bits to 200.
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:ZONE<ch0>:BIT <Bit>
The Reverse Power Control (RPC) pattern is defined in form of table with four zones
(zone 0 .. 3). For each zone, a bit and a count can be defined.
This parameter defines the RPC bits sent within the specific zone of the RPC Pattern.
Parameters:
<Bit> 0 | 1
Range: 0 to 1
*RST: 0
Example:
Manual operation: See "RPC Pattern" on page 31
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:MODE PATT
Sets the mode of the Reverse Power Control (RPC) Channel
within the MAC channel for user 2 to pattern, i.e. a user-defined
sequence is transmitted.
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:ZONE1:BIT 1
Sets the bit for zone 1 to 1.
93User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:RPC:ZONE<ch0>:COUNt <Count>
The Reverse Power Control (RPC) pattern is defined in form of table with four zones
(zone 0 .. 3). For each zone, a bit and a count can be defined.
This parameter defines the number of RPC bits sent within the specific zone of the
RPC Pattern.
Parameters:
<Count> integer
Remote-control commands
Configure traffic user commands
Range: 1 to 128
*RST: 0
Example:
Manual operation: See "RPC Pattern" on page 31
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:SCOunt?
Queries the slot count of the packets sent to the selected user.
Return values:
<SCount> integer
Example:
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:MODE PATT
Sets the mode of the Reverse Power Control (RPC) Channel
within the MAC channel for user 2 to pattern, i.e. a user-defined
sequence is transmitted.
BB:EVDO:USER2:RPC:ZONE1:COUNT 10
Sets the number of RPC bits for zone 1 to 10.
BB:EVDO:ANET:SUBT S2
Sets the physical layer subtype to 2.
BB:EVDO:USER2:RATE:IND 4
Sets the rate index of user 2 to 4.
BB:EVDO:USER2:PSIZ PS256
Sets the packet size for user 2 to 256.
SOUR:BB:EVDO:USER2:SCO?
Queries the number of slots for user 2.
Response: 2
Usage: Query only
Manual operation: See "Slot Count" on page 29
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:USER<st>:STATe <State>
Enables or disables the selected user. If the user is enabled, the proper MAC Index is
placed within the MAC channel and packets can be sent to the user. If disabled, the
MAC Index is not present within the MAC channel and packets cannot be sent to the
user.
Note: Disabling the state of a user during a transfer aborts all transfers to the user.
94User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
Remote-control commands
Configure access terminal commands
*RST: ON (user 1); OFF (user 2 .. 4)
Example:
BB:EVDO:USER2:STAT ON
Activates user 2.
Manual operation: See "State (User)" on page 23
4.10 Configure access terminal commands
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:PREDefined.............................................................................96
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:GAIN..............................................97
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:GATing........................................... 97
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:MODE............................................98
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:STATe............................................ 98
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:VALues.......................................... 99
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACYCle:DURation...............................................99
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACYCle:OFFSet................................................. 99
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:APCHannel:GAIN............................................. 100
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:APCHannel:PAYLoad:MINimum......................... 100
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:APCHannel:STATe............................................ 100
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:CLENgth.......................................... 101
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:DATA............................................... 101
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:DATA:DSELection............................. 102
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:DATA:PATTern..................................102
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:DRATe............................................. 102
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:FCS[:STATe].....................................103
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:GAIN............................................... 103
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:CCODing......................104
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:COUNt..........................104
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:DATA............................105
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:DATA:DSELection..........105
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:DATA:PATTern...............105
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:DRATe?........................ 106
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:FCS[:STATe]..................106
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:GAIN............................107
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:INFinite.........................107
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:MODulation?.................108
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:PSIZe...........................108
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:STATe...........................109
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:PACKet<ch>:SUBPackets[:COUNt].....109
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DCHannel:STATe.............................................. 110
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DQSPreading....................................................110
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:COVer..........................................110
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:GAIN............................................111
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:GATing[:STATe]............................. 111
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:LENGth........................................ 111
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:STATe.......................................... 112
95User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DRCChannel:VALues........................................ 112
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DSCChannel:GAIN............................................112
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DSCChannel:LENGth........................................ 113
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DSCChannel:STATe.......................................... 113
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:DSCChannel:VALues.........................................113
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:IMASk..............................................................114
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:MODE..............................................................114
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:PCHannel:GAIN................................................114
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:PCHannel:STATe?.............................................115
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:PLENgth...........................................................115
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:QMASk............................................................ 115
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:RRIChannel:GAIN.............................................115
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:RRIChannel:STATe............................................116
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:STATe.............................................................. 116
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:SUBType..........................................................116
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:PREDefined <Predefined>
Sets the UL setting of Terminal 1 to one of the predefined configurations.
Remote-control commands
Configure access terminal commands
The predefined settings are made according to 3GPP2 C.S0032-A to allow easy
receiver testing.
Parameter Description
USER
ULS1DR9K6
ULS1DR19K2
ULS1DR38K4
ULS1DR76K8
ULS1DR153K6
ULS2PS128LL
ULS2PS256HC
ULS2PS256LL
ULS2PS512LL
ULS2PS768LL
ULS2PS1024LL
ULS2PS1536LL
There are no predefined settings
UL, Subtype 1, 9.6 kbps.
UL, Subtype 1, 19.2 kbps.
UL, Subtype 1, 38.4 kbps.
UL, Subtype 1, 76.8 kbps.
UL, Subtype 1, 153.6 kbps.
UL, Subtype 2, 128 bits payload, Low Latency.
UL, Subtype 2, 256 bits payload, High Capacity.
UL, Subtype 2, 256 bits payload, Low Latency.
UL, Subtype 2, 512 bits payload, Low Latency.
UL, Subtype 2, 768 bits payload, Low Latency.
UL, Subtype 2, 1024 bits payload, Low Latency.
UL, Subtype 2, 1536 bits payload, Low Latency.
ULS2PS2048LL
ULS2PS3072LL
ULS2PS4096LL
ULS2PS6144LL
UL, Subtype 2, 2048 bits payload, Low Latency.
UL, Subtype 2, 3072 bits payload, Low Latency.
UL, Subtype 2, 4096 bits payload, Low Latency.
UL, Subtype 2, 6144 bits payload, Low Latency.
96User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameter Description
Remote-control commands
Configure access terminal commands
ULS2PS8192LL
ULS2PS12288LL
UL, Subtype 2, 8192 bits payload, Low Latency.
UL, Subtype 2, 12288 bits payload, Low Latency.
Parameters:
<Predefined> USER | ULS1DR9K6 | ULS1DR19K2 | ULS1DR38K4 |
ULS1DR76K8 | ULS1DR153K6 | ULS2PS128LL |
ULS2PS256HC | ULS2PS256LL | ULS2PS512LL |
ULS2PS768LL | ULS2PS1024LL | ULS2PS1536LL |
ULS2PS2048LL | ULS2PS3072LL | ULS2PS4096LL |
ULS2PS6144LL | ULS2PS8192LL | ULS2PS12288LL
*RST: USER
Example:
BB:EVDO:PRED ULS2PS256HC
Sets the UL settings of Terminal 1 to UL of Subtype 2 with 256
bits payload and High Capacity.
BB:EVDO:TERM1:SUBT?
Response: S2.
BB:EVDO:TERM1:DCH:PACK1:PSIZ?
Response: 256
Manual operation: See "Predefined Settings" on page 42
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:GAIN <Gain>
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode)
Sets the gain of the ACK channel relative to the pilot channel power.
Parameters:
<Gain> float
Range: -80 to 30
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 0
Example:
BB:EVDO:TERM2:ACKC:GAIN -10
Sets the relative gain of ACK channel to -10 dB
Manual operation: See "Relative Gain" on page 48
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:GATing <Gating>
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode)
Sets the active and inactive slots of the ACK channel. This parameter is in binary format and has a maximal length of 16 bits.
The sequence starts at frame 0 and slot 0 and is repeated with the length of the pattern. A 0 gates the ACK channel off for the corresponding slot, a 1 activates the channel.
97User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Parameters:
<Gating> integer
Remote-control commands
Configure access terminal commands
*RST: 0001
Example:
Manual operation: See "Gating (bin)" on page 48
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:MODE <Mode>
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode)
Specifies the modulation mode of the ACK channel.
With BPSK modulation, a 0 (ACK) is mapped to +1 and a 1 (NAK) to -1.With OOK
modulation, a 0 (ACK) is mapped to ON and a 1 (NAK) to OFF.
Parameters:
<Mode> BPSK | OOK
Example:
BB:EVDO:TERM2:ACKC:GAT #B11001100,8
Sets slots 3, 4, 7 and 8 of ACK channel as inactive.
BPSK
Sets the modulation to BPSK (Binary Phase Shift Keying).
OOK
Sets the modulation to OOK (On-Off Keying).
Note: This value is only enabled for physical layer subtype 2.
*RST: BPSK
BB:EVDO:TERM2:MODE TRAF
sets the mode of terminal 2 to traffic.
BB:EVDO:TERM2:SUBT S2
sets the physical layer subtype of terminal 2 to 2.
BB:EVDO:TERM2:ACKC:MODE OOK
selects OOK modulation for ACK channel of terminal 2.
Manual operation: See "Mode" on page 48
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:STATe <State>
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode)
Enables or disables the ACK channel.
Parameters:
<State> 1 | ON | 0 | OFF
*RST: 1
Example:
Manual operation: See "State" on page 48
BB:EVDO:TERM2:ACKC:STAT OFF
Deactivates the ACK channel for terminal 2.
98User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACKChannel:VALues <Values>
(enabled for access terminal working in traffic mode)
Specifies the data pattern transmitted on the ACK Channel.
The sequence starts at frame 0 and slot 0 and is repeated with the length of the pattern.A 0 specifies an ACK, a 1 specifies a NAK. The pattern is only read for slots that
are gated on. This parameter is in binary format and has a maximal length of 16 bits.
Parameters:
<Values> integer
Remote-control commands
Configure access terminal commands
*RST: #H1
Example:
Manual operation: See "Values" on page 49
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACYCle:DURation
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode)
Sets the access cycle duration in slots. Access probes are repeated with a period of
access cycle duration slots.
Parameters:
<Duration> integer
Example:
Manual operation: See "Access Cycle Duration" on page 43
BB:EVDO:TERM2:ACKC:VAL #B011,3
Sets the data pattern transmitted on the ACK channel for terminal 2.
<Duration>
Range: 1 to 255
*RST: 16
BB:EVDO:TERM2:MODE ACC
enables terminal 2 to work in access mode.
BB:EVDO:TERM2:ACYC:DUR 20
sets the duration of the access cycle for terminal 2 to 20 slots.
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:ACYCle:OFFSet <Offset>
(enabled for access terminal working in access mode)
The Access Channel transmission starts with this number of slots relative to the beginning of each access cycle duration.
Parameters:
<Offset> integer
Range: 0 to 12
Increment: 4
*RST: 0
99User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06

R&S®SMBVB-K47/-K87
Remote-control commands
Configure access terminal commands
Example:
Manual operation: See "Access Cycle Offset" on page 43
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:APCHannel:GAIN <Gain>
(enabled for Physical Layer subtype 2 and for an access terminal working in traffic
mode)
Sets the gain of the auxiliary pilot channel relative to the data channel power.
Note: All other channel gains are specified relative to the pilot power, but the auxiliary
pilot gain is specified relative to the data channel power.
Parameters:
<Gain> float
Example:
BB:EVDO:TERM2:MODE ACC
Enables terminal 2 to work in access mode.
BB:EVDO:TERM2:ACYC:OFFS 10
Sets the offset of the Access Channel to 10.
Range: -80 to 30
Increment: 0.01
*RST: 0
BB:EVDO:TERM2:APCH:GAIN -10
sets the relative gain of auxiliary pilot channel to -10 dB
Manual operation: See "Relative Gain" on page 44
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:APCHannel:PAYLoad:MINimum
<Minimum>
(enabled for Physical Layer subtype 2 and for an access terminal working in traffic
mode)
Sets the minimum payload size in bits of the data channel that activates the transmission of the auxiliary pilot channel.
Parameters:
<Minimum> PS128 | PS256 | PS512 | PS768 | PS1024 | PS1536 | PS2048 |
PS3072 | PS4096 | PS6144 | PS8192 | PS12288
*RST: PS128
Example:
Manual operation: See "Minimum Payload" on page 44
[:SOURce<hw>]:BB:EVDO:TERMinal<st>:APCHannel:STATe <State>
BB:EVDO:TERM2:APCH:PAYL:MIN PS256
Sets the minimum payload of the auxiliary pilot channel to 256
bits.
(enabled for Physical Layer subtype 2 and for an access terminal working in traffic
mode)
100User Manual 1178.8094.02 ─ 06
 Loading...
Loading...