Page 1
Installation Instructions
TL-Series Servo Motor
(Catalog Numbers TL-A110, -A120, -A130, -A220, -A230, -A2530, -A2540, A310, and
-A410)
This publication provides installation instructions for the TL-Series motors.
®
Use this document if you are responsible for installing these Allen-Bradley
motor products. Please read all instructions before installing this motor.
For: See Page
Receiving and Storage 2
Environmental Ratings 2
Operating Temperature and Shaft Materials 3
Motor Catalog Number Identification 4
Before You Install the Motor 5
Motor Installation and Maintenance Guidelines 5
Prolonging Motor Life 6
Making Mechanical Connection to the Motor Shaft 7
Installing Cables 8
Preventing Electrical Noise 8
Using Shaft Seals 9
Installing the TL-Series Motor 9
Motor Load Force Ratings 11
Connector Data 13
Mounting Dimensions 15
Metric Frame 16
NEMA Frame 18
Removing and Installing a Shaft Key 20
Accessories 21
Related Documentation 23
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 2
2 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
Receiving and Storage
The customer is responsible for inspecting the equipment before accepting the
shipment from the freight company. Check the item(s) you receive against your
purchase order. Notify the carrier of shipping damage or missing items
immediately. Store your motor in a clean and dry location within the following
environmental conditions:
Environmental Condition Description
Storage Temperature -10° to 85° C (14° to 185° F)
Relative Humidly 20% to 85% non-condensing
Atmosphere non-corrosive
Environmental Ratings
The TL-Series motors, connectors, and flying leads are separately rated for
environmental protection per Ingress Protection standards (IP ratings).
TL-Series Motor
Rating Description 1
Motor with optional shaft seal 2
Motor without a shaft seal, and
the mounted in the direction:
shaft down
shaft horizontal
shaft up
Flying leads and connectors IP30 protected from objects greater than 12.5 mm (0.5 in.)
1 IP rating descriptions are for reference only. Refer to the international standards for more complete rating descriptions.
2 An optional shaft seal kit is required to provide the IP65 rating. See Accessories on page 21.
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
IP65 dust tight, water jets
IP53
IP51
IP50
dust protected, spraying water
dust protected, vertically falling water
dust protected, no special moisture protection
in diameter, no special moisture protection
Page 3

TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 3
Operating Temperature and Shaft Materials
Condition or Material Description
Operating Temperature 0° to 40° C (32° to 104° F)
Shaft Material carbon steel
Shaft Key Material carbon steel
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 4
4 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
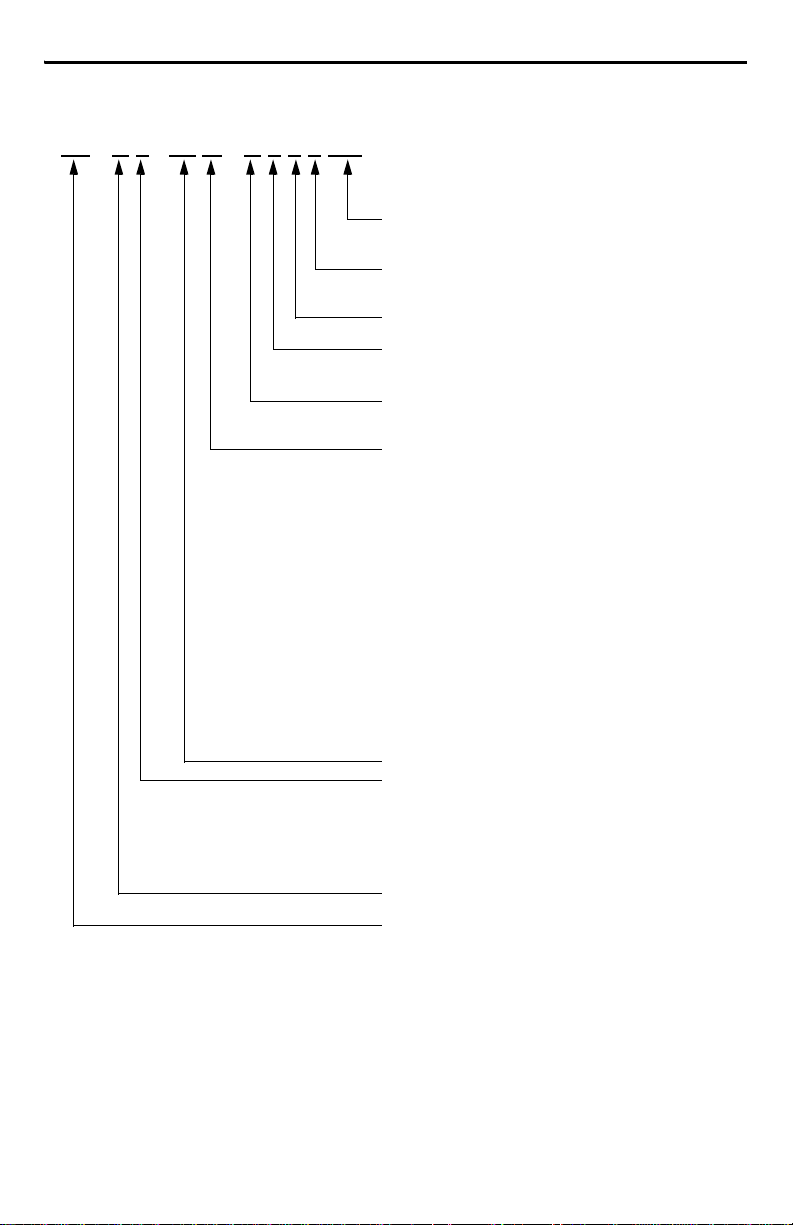
TL - A 4 10 M - B J 3 2 AA
Motor Catalog Number Identification
FACTORY DESIGNATED OPTIONS
AA = Standard
AN = NEMA Mounting Flange/Shaft
BRAKE
2 = No Brake
4 = 24VDC Brake
CONNECTORS
3 = Flying Leads with Connectors
ENCLOSURE/SHAFT KEY/SHAFT SEAL
J = IP65 Housing/Shaft Key/No Shaft Seal
K = IP65 Housing/No Shaft Key/No Shaft Seal
FEEDBACK
B = Absolute Encoder, Battery-backed Multi-turn
H = Incremental Encoder (2000 lines)
RATED SPEED
A = 500 rpm
B = 1000 rpm
C = 1500 rpm
D = 2000 rpm
E = 2500 rpm
F = 3000 rpm
G = 3250 rpm
H = 3500 rpm
J = 3750 rpm
K = 4000 rpm
L = 4250 rpm
M = 4500 rpm
N = 4750 rpm
P = 5000 rpm
Q = 5250 rpm
R = 5500 rpm
S = 5750 rpm
T = 6000 rpm
MAGNET STACK LENGTH DESIGNATOR
FLANGE SIZE
Diameter of Mounting Bolt Circle for Metric Motors, or NEM A size
1 = 46 mm or NEMA 17
2 = 70 mm or NEMA 23
25 = 90 mm or NEMA 34
3 = 100 mm
4 = 115 mm
VOLTAGE RATING
A = 230 VAC
SERIES DESIGNATOR
TL = Low Inertia
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 5
TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 5
!
!
Before You Install the Motor
1. Remove the motor carefully from its shipping container.
2. Visually inspect the motor for any damage.
3. Examine the motor frame, front output shaft, and mounting pilot for any
defects.
4. Notify the carrier of any shipping damage immediately.
ATTENTION
Do not attempt to open and modify the motor. Modifications
that can be performed in the field are described in this manual,
other changes should not be attempted.
Only a qualified Allen-Bradley employee can service this type
of motor.
Failure to observe these safety procedures could result in
personal injury, damage to equipment, and void warranty
coverage.
Motor Installation and Maintenance Guidelines
The following sections provide general installation and maintenance information.
The information should assist you to correctly install and to provide maintenance
that will prolong the lifetime of your TL servo motor.
ATTENTION
Ensure that cables are installed and restrained to prevent
uneven tension or flexing at the cable connectors.
Excessive and uneven force at the cable connectors may result
in damage to the connector housings and contacts as the cable
flexes.
Failure to observe these safety procedures could result in
damage to the motor and its components.
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 6

6 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
Prolonging Motor Life
Thoughtful design and proper maintenance can increase the life of a servo motor.
The following are guidelines to maximize the life of a servo motor.
• Always provide a drip loop in each cable to carry liquids away from connections.
• If design requirements permit, provide shields that protect the motor housing,
shaft seals, and their junctions from product contamination and fluids.
• Inspect the motor and seals for damage or wear at 6-month intervals. Replace
damaged items.
A dry and dusty environment will cause a seal to wear more rapidly than a wet or
oily environment. However, fluids can be forced around worn seals more easily
than dry particles. Replace a shaft seal at or before its expected lifetime, as
bearing contamination significantly shortens the life of a servo motor.
• Brakes on these servo motors are holding brakes. The brakes are spring-set, and
release when voltage is applied to the brake coil. A separate power source is
required to disengage the brake. This power source may be applied by a servo
motor controller, in addition to manual operator control.
The recommended method of preventing shaft rotation is:
1. Command the servo drive to 0 rpm.
2. Verify the motor is at 0 rpm.
3. Engage the brake.
4. Disable the drive.
Disabling the drive removes the potential for brake wear caused by a poorly
tuned servo system oscillating the shaft.
If system main power fails, holding brakes can withstand occasional use as
stopping brakes. This situation allows some shaft rotation as the braking occurs,
and also may create mechanical backlash within the system. Braking with power
applied to the motor is potentially damaging to the system, increases brake wear,
and reduces brake life.
IMPORTANT
Holding brakes are not designed to stop rotation of the
motor shaft, nor are they intended to be used as a safety
device. They will hold a motor shaft at 0 rpm for up to the
rated brake holding torque.
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 7
TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 7
!
Making Mechanical Connection to the Motor Shaft
Mechanical connections to the motor shaft, such as couplings and pulleys, require a
torsionally rigid coupling or a reinforced timing belt. The high dynamic
performance of servo motors can cause couplings, pulleys or belts to loosen or slip
over time. A loose or slipping connection will cause system instability and may
damage the motor shaft. All connections between the system and the servo motor
shaft must be rigid to achieve acceptable response from the system. Periodically
inspect connections to verify their rigidity.
When mounting couplings or pulleys to the motor shaft, ensure that the
connections are properly aligned and that axial and radial loads are within the
specifications of the motor. Refer to Motor Load Force Ratings on page 11 for
guidelines on how to achieve 20,000 hours of motor bearing life.
ATTENTION
A shaft key provides a rigid mechanical connection with the potential for
self-alignment, but the key must be properly installed in the keyway. Refer to:
• Mounting Dimensions on page 15 for dimensional information about the key and
shaft keyway, and
• Removing and Installing a Shaft Key on page 20 for recommendations on how to
remove and install a shaft key.
Damage may occur to the motor bearings and the feedback
device if sharp impact to the shaft is applied during installation
of couplings and pulleys, or a shaft key. Damage to the
feedback device may result by applying leverage from the
motor mounting face to remove devices mounted on the motor
shaft.
Do not strike the shaft, key, couplings, or pulleys with tools
during installation or removal. Apply a constant pressure (e.g.,
with a wheel puller) to the user end of the shaft to remove any
friction fit or stuck device from the motor shaft.
Failure to observe these safety procedures could result in
damage to the motor and its components.
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 8
8 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
!
Installing Cables
Knowledgeable cable routing improves system electromagnetic compatibility
(EMC). To install the cables:
1. Keep wire lengths as short as physically possible.
2. Route signal cables (encoder, serial, analog, etc.) away from motor and power
wiring.
3. Separate cables by 0.3 m (1 ft) minimum for every 9 m (30 ft) of parallel run.
4. Ground both ends of the cable shield and twist the signal wire pairs to prevent
electromagnetic interference (EMI) from other equipment.
ATTENTION
High voltage can be present on the shields of a power cable, if
the shields are not grounded.
Ensure there is a connection to ground for all shields in the
power cable.
Failure to observe these safety procedures could result in
personal injury or damage to equipment.
Preventing Electrical Noise
Electromagnetic interference (EMI), commonly called noise, may adversely impact
motor performance by inducing stray signals. Effective techniques to counter EMI
include filtering the AC power, shielding and separating signal carrying lines, and
practicing good grounding techniques.
Effective AC power filtering can be achieved by using isolated AC power
transformers or properly installed AC line filters.
To help avoid EMI:
• Physically separate signal lines from motor cabling and power wiring. Do not
route signal wires with motor and power wires, or over the vent openings of
servo drives.
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 9

TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 9
!
• Ground all equipment using a single-point parallel ground system that employs
ground bus bars or large straps. If necessary, use additional electrical noise
reduction techniques to reduce EMI in noisy environments.
Using Shaft Seals
An additional seal is required on the motor shaft near the motor front bearing, if
the shaft is exposed to fluids or significant amounts of fine dust.
An IP65 rating for the motor, exclusive of flying leads, requires the use of shaft
seals.
• Refer to Environmental Ratings on page 2 for brief descriptions of IP ratings.
• Refer to Shaft Seal Kits on page 21 or the Motion Control Selection Guide
(publication GMC-SG001x-EN-P) to find the catalog numbers of seal kits
available for your motor.
Installing the TL-Series Motor
All TL-Series motors include a mounting pilot for aligning the motor on a
machine. Preferred fasteners are stainless steel. The installation must comply with
all local regulations and use of equipment and installation practices that promote
electromagnetic compatibility and safety.
ATTENTION
Unmounted motors, disconnected mechanical couplings, loose
shaft keys, and disconnected cables are dangerous if power is
applied.
Disassembled equipment should be appropriately identified
(tagged-out) and access to electrical power restricted
(locked-out).
Before applying power to the motor, remove the shaft key and
other mechanical couplings which could be thrown from the
shaft.
Failure to observe these safety procedures could result in
personal injury.
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 10

10 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
!
!
Recommendations on Installing TL-Series Motors
Observe the following recommendations when installing the motor.
ATTENTION
1. Allow sufficient clearance around motor to keep it from exceeding its maximum
operating temperature range. Refer to Receiving and Storage on page 2 for the
operating range. Do not install the motor in an area with restricted airflow. Keep
other heat producing devices away from the motor.
To obtain the specified motor thermal rating, mount the motor on a surface
with heat dissipation equivalent to an aluminum heatsink of the following
dimensions:
Motor Frame Size Heatsink Dimensions
TL-A1xx 203.2 x 203.2 x 6.35 8 x 8 x 0.25
TL-A2xx 254.0 x 254.0 x 6.35 10 x 10 x 0.25
TL-Series motors are not for direct connection to an AC power
line.
Servo motors are designed for connection to a servo drive that
controls the application of AC power. Failure to observe these
safety procedures could result in damage to the motor and
equipment.
millimeters inches
TL-A25xx, TL-3xx, and TL-A4xx 304.8 x 304.8 x 12.7 12 x 12 x 0.50
ATTENTION
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Outer surfaces of motor can reach high temperatures, 125° C
(257° F) during motor operation.
Take precautions to prevent accidental contact with hot
surfaces. Locate the motor and route cable connections to avoid
contact with hot surfaces.
Failure to observe these safety procedures could result in
personal injury or damage to equipment.
Page 11

TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 11
!
2. Refer to Motor Load Force Ratings on page 11 to determine the radial and axial
shaft load limitations of your motor.
3. Position the motor with the cable mounts pointing downward.
4. Properly mount and align the motor.
5. Connect the feedback, power, and brake cables after the motor is mounted.
ATTENTION
Mount the motor so exposure to dust and liquids is minimized
for both the motor and its cable connections, and restrain cables
to prevent uneven tension or flexing at the connectors.
Short circuits in the feedback, power, or brake circuits may
result from exposure of the unsealed motor cable connectors to
dust or liquids, or by uneven forces at the connector housing.
Failure to observe these safety procedures could result in
personal injury or damage to the motor and equipment.
Motor Load Force Ratings
Motors are capable of operating with a sustained shaft load. The radial and axial
load force location is shown in the figure, and maximum values are in the tables.
Note: Loads are measured in pounds, kilograms are mathematical conversions.
Figure 1
Load Forces on Shaft
Radial load force applied at center of shaft extension
Axial load force
The following tables represent 20,000 hour L10 bearing fatigue life at various loads
and speeds. The 20,000 hour life does not account for application-specific life
reduction that may occur due to bearing grease contamination from external sources.
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 12

12 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
Radial Load Force Ratings
Motor 1000 rpm 2000 rpm 3000 rpm 4500 rpm 5000 rpm
kg (lb) kg (lb) kg (lb) kg (lb) kg (lb)
TL-A110P 11 (24) 9 (19) 7 (16) – – 6 (14)
TL-A120P 12 (26) 10 (21) 8 (18) – – 7 (15)
TL-A130P 13 (29) 10 (23) 9 (20) – – 8 (17)
TL-A220P 27 (60) 22 (48) 19 (42) – – 16 (35)
TL-A230P 31 (68) 24 (54) 21 (47) – – 18 (40)
TL-A2530P 48 (106) 38 (84) 34 (74) – – 28 (62)
TL-A2540P 50 (110) 39 (87) 34 (76) – – 29 (64)
TL-A310M 80 (177) 64 (140) 56 (123) 47 (103) – –
TL-A410M 76 (168) 60 (133) 53 (117) 44 (98) – –
Axial Load Force Ratings (Maximum Radial Load)
Motor 1000 rpm 2000 rpm 3000 rpm 4500 rpm 5000 rpm
kg (lb) kg (lb) kg (lb) kg (lb) kg (lb)
TL-A110P 8 (18) 6 (14) 5 (10) – – 4 (9)
TL-A120P 9 (20) 7 (16) 5 (12) – – 5 (10)
TL-A130P 10 (22) 8 (17) 6 (13) – – 5 (11)
TL-A220P 15 (32) 11 (24) 9 (20) – – 7 (16)
TL-A230P 15 (34) 12 (26) 10 (21) – – 8 (17)
TL-A2530P 18 (39) 13 (29) 11 (24) – – 9 (19)
TL-A2540P 18 (39) 13 (29) 11 (25) – – 9 (20)
TL-A310M 24 (54) 18 (40) 15 (34) 12 (27) – –
TL-A410M 29 (64) 21 (47) 18 (40) 14 (31) – –
Axial Load Force Ratings (Zero Radial Load)
Motor 1000 rpm 2000 rpm 3000 rpm 4500 rpm 5000 rpm
kg (lb) kg (lb) kg (lb) kg (lb) kg (lb)
TL-A110P 12 (26) 9 (20) 7 (16) – – 6 (13)
TL-A120P 12 (26) 9 (20) 7 (16) – – 6 (13)
TL-A130P 12 (26) 9 (20) 7 (16) – – 6 (13)
TL-A220P 19 (41) 14 (30) 11 (25) – – 9 (20)
TL-A230P 19 (41) 14 (30) 11 (25) – – 9 (20)
TL-A2530P 23 (50) 17 (37) 14 (31) – – 11 (25)
TL-A2540P 23 (50) 17 (37) 14 (31) – – 11 (25)
TL-A310M 29 (65) 22 (48) 19 (41) 15 (32) – –
TL-A410M 34 (75) 25 (55) 21 (47) 17 (37) – –
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 13

TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 13
!
Connector Data
This table provides signal descriptions for the flying leads on all TL-Series motors.
Absolute Encoder Incremental Encoder
Feedback Connector Feedback Connector Connector Housings
Pin Signal Pin Signal
6
1-6 Reserved — 1 A+ green
7 EPWR red 2 A- green/blk
8 ECOM and brown/blk 3 B+ blue
BAT- blk 4 B- blue/blk
9 SHIELD blk shrink 5 I+ yellow
10-11 Reserved — 6 S1 gray/blk
12 SD+ blue 7 +5V DC red
13 SD- blue/blk 8 ECOM black
14 BAT+ brown 9 SHIELD blk shrink
15 Reserved — 10 I- yellow/blk
Power Connector 11 S2 brown/blk
Pin Signal 12-14 Reserved —
1 U phase red 15 S3 white/blk
2 V phase white Power Connector
3 W phase black Pin Signal
4 Ground yellow/grn 1 U phase red
Brake Connector 2 V phase black
Pin Signal 3 W phase white
1 BR+ yellow 4 Ground yellow/grn
2BR-
-A410 only
See page 14 for additional
information about these
AMP™ connectors.
blue
yellow
Brake Connector
Pin Signal
1BR+ yellow
2BR-
-A410 only
blue
yellow
11
12
13
14
15
AMP HOUSING
P/N 172171-1
AMP HOUSING
P/N 350779-1
AMP HOUSING
P/N 172165-1
1
7
2
8
3
9
4
10
5
1
2
3
4
1
2
ATTENTION
Ensure that cables are installed and restrained to prevent
uneven tension or flexing at the cable connectors.
Excessive and uneven force at the cable connector may result in
damage to the housing and contacts as the cable flexes.
Failure to observe these safety procedures could result in
damage to the motor and its components.
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 14

14 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
Connector Type Feedback
(15 Position)
Brake
(2 Position)
Power
(4 Position)
Motor Connectors (on flying leads):
Plug Housing 172171-1 172165-1 350779-1
Power Contacts
Reel
Loose
Ground Contacts
Reel
Loose
1
770835-1
794059-1
2
5
5
170359-1
170360-1
170363-1
170364-1
— —
7
8
7
8
350218-3
350547-3
350654-1 10
350669-1
Compatible Receptacles (on mating cables):
Cap (receptacle) Housing 172163-1 172157-1 350780-1
Socket Contacts
Reel
Loose
170361-1
170365-1
6
6
170362-1
170366-1
9
9
350536-3
350550-3
Tooling (Motor Connectors and/or Compatible Receptacles):
Hand Crimp Tool
90870-1 90758-1 90546-1
for Motor Connectors
Hand Crimp Tool
90758-1 90759-1
for Compatible Receptacles
Contact Extraction Tool
Contact Insertion Tool
1 For U, V, W in Power connector.
2 For Motor Frame GND in Power connector.
3 The locking/retention tangs on pin and socket contacts may become
deformed by use of the Contact Extraction Tool. Ensure that the tangs
are positioned slightly outward before re-inserting the contact into the
connector housing.
After contacts are inserted into the connector housing, gently pull
backward on each wire to ensure that contacts are fully seated and
latched into position.
4 Use of the Contact Insertion Tool is optional, as contacts are readily
pushed by hand into the connector housing.
Note: AMP specifies wire sizing in AWG, mm
3
4
189727-1 318851-1
455830-1
5 Wire range 0.05 - 0.14 mm
6 Contacts and AWG in Rockwell manufactured cables may
vary by cable conductor. For reference only, the wire range
of the above contacts is 0.14 - 0.34 mm
7 Used on TL-A1xx through TL-A25xx motors
Wire range is 0.14 - 0.34 mm
8 Used on TL-A4xx motors.
Wire range 0.34 - 0.75 mm
9 Wire range 0.34 - 0.75 mm
10Wire range 0.50 - 2.5 mm
2
is a conversion from AWG.
2
(30-26 AWG)
2
(26-22 AWG)
2
(22-18 AWG)
2
(22-18 AWG)
2
(20-14 AWG)
2
(26-22 AWG).
10
10
10
10
10
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 15

TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 15
Mounting Dimensions
The dimension symbols and actual dimensions for the different frame sizes and
stack lengths in the TL motors are referenced in tables on the following pages.
Figure 2
References for Motor Mounting Dimensions
Mounting pattern has two holes
for A110 through A130 (shown).
All others have four holes.
HD
AD
BE
Motor Dimensions for
Metric Frame
Mounting pattern has two threaded
holes for A120 and A130 (shown).
All others have four holes.
AC
L
T
LA
Connector
for Brake
option
only
L
CAB
L-LB
TB
L-LB
T
D
Key (supplied)
S dia. holes on
M dia. bolt circle
S dia. holes on
M dia. bolt circle
F
LB
LE
LB
P
N
NB
G
P
N
AD
BE
Motor Dimensions for
NEMA Frame
HD
LE
CAB
D
Key supplied with
LA
TL-A2xx and -A25xx
(NEMA 23 and 34) only.
TL-A120 or -A130 (NEMA 17)
is not available with key slot.
G
F
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 16

16 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
Metric Frame
Dimensions are for non-brake motors. Footnotes provide additional dimensions
for brake motors, and tolerances for common dimensions.
Motor
Series
TL-A
110
130
220
230
2530
2540
310
410
NOTE: Metric motor frames are designed to metric dimensions. Inch dimensions are a mathematical conversion.
AD
mm
(in.)
31.1
(1.22)
43.0
(1.69)
53.0
(2.09)
56.0
(2.20)
67.0
(2.64)
BE
mm
(in.)
21.0
(0.83)
27.6
(1.09)
38.4
(1.51)
D 1
mm
(in.)
8.0
(0.315)
12.0
(0.472
4)
16.0
(0.629
9)
22.0
(0.
87)
HD
mm
(in.)
51.1
(2.01)
73.0
(2.87)
93.0
(3.66)
99.0
(3.90)
117.0
(4.61)
L 2
mm
(in.)
78.5
(3.09)
84.5
(3.33)
98.5
(3.88)
106.1
(4.18)
128.1
(5.04)
134.7
(5.30)
143.7
(5.66)
179.2
(7.06)
216.0
(8.50)
L-LB
mm
(in.)
25.0
(0.984)
30.0
(1.181)
35.0
(1.378)
40.0
(1.57)
3
LA
LB 2
mm
(in.)
LE 2
mm
(in.)
mm
(in.)
53.5
(2.11)
39.1
59.5
5.0
(1.54)
(2.34)
(0.20)
73.5
(2.89)
76.1
6.0
(0.24)
(3.00)
98.1
42.8
(1.69)
(3.86)
99.7
8.0
(0.32)
17. 0
(0.67)
(3.93)
108.7
(4.28)
144.2
(5.68)
176.0
(6.93)
43.8
(1.72)
57.1
(2.25)
102.0
(4.02)
M
mm
(in.)
46.0
(1.811) 120
70.0
(2.76)
90.0
(3.54)
100.0
(3.94)
115.0
(4.53)
1 Tolerance for this dimension is: TL-A1xx -0.009 mm (-0.0004 in.); TL-A2xx -0.011 mm (-0.0004 in.); TL-A25xx -0.011 mm (-0.0004 in.);
TL-A310 -0.011 mm (-0.0004 in.); TL-A410 -0.013 mm (-0.0005 in.).
2 If ordering a TL-A110, TL-A120, or TL-A130 motor with brake, add 35.6 mm (1.40 in.) to L, LB, and LE.
If ordering a TL-A220, or TL-A230 motor with brake, add 34.6 mm (1.36 in.) to L, LB, and LE.
If ordering a TL-A2530, or TL-A2540 motor with brake, add 36.6 mm (1.44 in.) to L, LB, and LE.
If ordering a TL-310 motor with brake, add 23.0 mm (0.90 in.) to L, LB, and LE.
If ordering a TL-410 motor with brake, add 32.0 mm (1.26 in.) to L, LB, and LE.
3 Tolerance for this dimension is: ±1.0 mm (±0.039 in.)
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 17

Motor
Series
TL-A
110
120
130
N 4
mm
(in.)
30.0
(1.1811)
NB
mm
(in.)
20.0
(0.79)
P
mm
(in.)
40.0
(1.57)
TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 17
S 5
mm
(in.)
4.5
(0.177)
T
mm
(in.)
2.5
(0.10)
TB
mm
(in.)
4.5
(0.18)
CAB 6
mm
(in.)
G 7
mm
(in.)
6.2
(0.244)
F 8
mm
(in.)
3.0
(0.118)
9
Key
mm
(in.)
3 x 3 x 15
(0.118 x 0.118 x
0.59)
220
230
2530
2540
310
410
NOTE: Metric motor frames are designed to metric dimensions. Inch dimensions are a mathematical conversion.
4 Tolerance for this dimension is: TL-A1xx -0.021 mm (-0.0008 in.); TL-A2xx -0.025 mm (-0.001 in.); TL-A25xx -0.03 mm (-0.0012 in.);
TL-A310 -0.03 mm (-0.0012 in.); TL-A410 -0.035 mm (-0.0014 in.).
5TL
-A1xx has 2 mounting holes, TL-A2xx through TL-A410 have 4 mounting holes.
Mounting holes are S diameter on M diameter bolt circle.
6 Tolerance for cable length is ±50.0 mm (±1.97 in.). Minimum bend radius is 15.00 mm (0.59 in.).
7 Tolerance for this dimension is: -0.20 mm (-0.008 in.).
8 Tolerance for this dimension is: TL-A1xx -0.006 to -0.031 mm (-0.0002 to -0.0012 in.); TL-A2xx and -A25xx -0.012 to -0.042 mm (-0.0005 to
-0.0017 in.); TL-A310 -0.012 to -0.042 mm (-0.0005 to -0.0017 in.); TL-A410 -0.015 to -0.051mm (-0.0006 to -0.0020 in.).
9 Tolerance for x and y dimensions is: TL-A1xx -0.025 mm, TL-A2xx -0.030 mm, TL-A25xx -0.030 mm, TL-A3xx -0.030 mm, and TL-A410
-0.036 mm, length is untoleranced.
50.0
(1.9685)
70.0
(2.7556)
80.0
(3.15)
95.0
(3.74)
27.0
(1.06)
34.0
(1.34)
—
60.0
(2.36)
80.0
(3.15)
86.0
(3.39)
100.0
(3.94)
5.5
(0.217)
6.6
(0.260)
9.0
(0.354)
3.0
(0.12)
7.0
(0.28)
300
(11.8)
7.0
(0.28)
—
9.5
(0.374)
13.0
(0.512)
18.0
(0.709)
4.0
(0.157)
5.0
(0.197)
8.0
(0.315)
4 x 4 x 15
(0.158 x 0.158 x
0.59)
5 x 5 x 20
(0.197 x 0.197 x
0.79)
8 x 7 x 25
(0.315 x 0.276 x
0.985)
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 18

18 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
NEMA Frame
Dimensions are for non-brake motors. Footnotes provide additional dimensions
for brake motors, and tolerances for common dimensions.
Motor
Series
TL-A
AC
mm
(in.)
AD
mm
(in.)
BE
mm
(in.)
D 1
mm
(in.)
HD
mm
(in.)
L 2
mm
(in.)
L-LB
mm
(in.)
3
LA
LB 2
mm
mm
(in.)
(in.)
LE
mm
(in.)
2
mm
(in.)
M
5.0
6.0
8.0
64.5
(2.54)
78.5
(3.09)
99.8
(3.93)
121.8
(4.80)
104.7
(4.12)
113.7
(4.48)
39.1
(1.54)
43.3
(1.70)
43.8
(1.72)
91.5
120
130
—
31.10
(1.22)
21.0
(0.83)
6.35
(0.25)
52.0
(2.05)
(3.603)
105.5
(4.153)
27.0
(1.063)
(0.20)
137.9
220
230
60
(2.36)
43.0
(1.69)
12.70
(0.50)
27.6
(1.09)
2530
—
53.0
(2.09)
15.875
(0.625)
2540
NOTE: NEMA motor flanges and shafts are designed to inch dimensions. Other frame areas are designed to metric dimensions.
Conversions are mathematically calculated.
1 Tolerance for this dimension is: TL-A1xx -0.009 (-0.0004); TL-A2xx -0.011 (-0.0004); TL-A25xx -0.011 (-0.0004).
2 If ordering a TL-A120, or TL-A130 motor with brake, add 35.6 mm (1.40 in.) to L, LB, and LE.
If ordering a TL-A220, or TL-A230 motor with brake, add 34.6 mm (1.36 in.) to L, LB, and LE.
If ordering a TL-A2530, or TL-A2540 motor with brake, add 36.6 mm (1.44 in.) to L, LB, and LE.
3 Tolerance for this dimension is: ±1.0 mm (±0.039 in.).
73.0
(2.87)
96.0
(3.78)
(5.43)
159.9
(6.30)
149.2
(5.872)
158.2
(6.205)
38.1
(1.50)
44.5
(1.752)
(0.24)
(0.32)
43.8
(1.725)
66.7
(2.625)
98.4
(3.875)
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 19

Motor
Series
TL-A
N 4
mm
(in.)
NB
mm
(in.)
P
mm
(in.)
TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 19
5
S
mm
(in.)
T
TB
mm
(in.)
CAB
mm
(in.)
mm
(in.)
7
8
6
G
mm
(in.)
F
mm
(in.)
Key 9
mm
(in.)
120
22.0
(0.8661)
—
42.0
(1.65)
8-32
Thread
2.0
(0.08)
—
300
(11.8)
— — —
130
220
38.1
(1.50)
—
56.4
(2.22)
5.5
(0.217)
1.5
(0.06)
—
300
(11.8)
10.92
(0.43)
3.175
(0.125)
(0.125 x 0.125
x 0.9375)
230
2530
73.02
(2.875)
—
86.0
(3.39)
5.5
( 0 . 2 1 7 )
1.6
(0.06)
—
300
(11.8)
13.13
(0.517)
4.763
(0.1875)
(0.187 x 0.187
x 1.156)
2540
NOTE: NEMA motor flanges and shafts are designed to inch dimensions. Other frame areas are designed to metric dimensions.
Conversions are mathematically calculated.
4 Tolerance for this dimension is: TL-A1xx -0.021 mm (-0.0008 in.); TL-A2xx -0.025 mm (-0.001 in.); -A25xx -0.03 mm (-0.0012 in.);.
5TL
-A1xx has 2 threaded holes, TL-A2xx and TL-A25xx have 4 mounting holes.
Mounting holes are S diameter on M diameter bolt circle.
6 Tolerance for cable length is ±50.0 mm (±1.97 in.). Minimum bend radius is 15.00 mm (0.59 in.).
7 Tolerance for this dimension is: -0.38 mm (-0.015 in.).
8 Tolerance for this dimension is: +0.051 mm (+0.002 in.)
9 Tolerance for x and y dimensions is: (-0.002 in.), length is untoleranced.
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 20

20 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
!
Removing and Installing a Shaft Key
TL shaft keys are constructed of carbon steel. Keys for metric mount motors are
toleranced for interference fit (slightly larger than the opening) to ensure a secure
and rigid fit for the mating connection. Keys for NEMA mount motors are
toleranced for a slightly loose (slip) fit.
ATTENTION
To remove an interference fit key:
• Lift the key by grasping it with a plier or similar tool.
• Lever the key with a flat blade screwdriver inserted between the key and the slot.
To install an interference fit key:
• Verify the replacement key matches the keyway in the shaft and the mating
mechanical connection (e.g., coupling or pulley) before proceeding.
• Support the underside of the shaft diameter with a fixture (Figure 3), and use a
controlled press device to apply a constant force across the top surface to press
the key into the shaft.
Damage may occur to the motor bearings and the feedback
device if sharp impact to the shaft is applied during installation
of couplings and pulleys, or a shaft key. Damage to the feedback
device may result by applying leverage from the motor
mounting face to remove devices mounted on the motor shaft.
Failure to observe these safety procedures could result in
damage to the motor and its components.
Figure 3
Key Alignment and Shaft Support
Shaft
Support for shaft
and/or motor
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 21

TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 21
Accessories
Factory available accessories for the TL motors are described below.
Motor Cables
Factory manufactured feedback, brake, and power cables are available in standard
cable lengths. Transition cables are available to allow connection of a TL-Series
motor to existing N-Series or Y-Series power, feedback, and brake cables. Factory
cables provide proper shield termination which reduces the potential for EMI.
For a complete listing of available cables refer to your drive’s installation manual,
contact your nearest Rockwell Automation sales office, or access the information
from the web sites referenced in Related Documentation on page 23.
Shaft Seal Kits
Catalog numbers and dimensions for TL shaft seals are shown below.
Motor Catalog Number
TL-A110,
TL-A120,
TL-A130
TL-A220,
TL-A230
TL-A2530,
TL-A2540,
TL-A310
TL-A410 TL-SSN-4
1 Shaft seals require a lubricant to reduce wear. Lubricant is provided with kit.
TL-SSN-1
TL-SSN-2
TL-SSN-3
1
Inside Diameter Outside Diameter Width
mm (in.) mm (in.) mm (in.)
8.9 (0.35) 16 (0.71) 3 (0.12)
14.0 (0.55) 24 (0.95) 5 (0.20)
19.8 (0.78) 30 (1.18) 5 (0.20)
24.0 (0.95) 40 (1.57) 10 (0.39)
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 22

22 TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions
Transition Plates
Transition plates allow a TL-Series NEMA motor to physically replace N-Series
motors.
Compatible Motors
Catalog Number Description
TL-TRPLAT-17-23 TL-Series Transition Plate, NEMA 17 to 23 N-23xx TL-A1xxP-xxxxN
TL-TRPLAT-23-34 TL-Series Transition Plate, NEMA 23 to 34 N-34xx TL-A2xxP-xxxxN
TL-TRPLAT-34-42 TL-Series Transition Plate, NEMA 34 to 42 N-42xx TL-A25xxP-xxxxN
Transition plates are not available for the N-56xx motors.
N-Series TL-Series
NEMA
Transition Cables
Transition cables interface between existing N-Series and Y-Series motor cables
and the flying lead cables on TL-Series motors with incremental encoders.
Motor Type Cable Length Feedback Cable Power Cable Brake Cable
N-Series
Y-S eri es
1. Transition cables are only for use on TL-Series motors with incremental encoders.
2. Y-Series transition cables have Power and Brake connections combined in one cable.
305 mm (12.0 in.) 2090-XXNFTN-S 1 2090-XXNPTN-16S 1 2090-XXNBTN-S 1
610 mm (24.0 in.) 2090-XXNFTY-S 1
2090-XXNPTY-16S
1, 2
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 23

TL-Series Servo Motor Installation Instructions 23
Related Documentation
These publications provide additional information; specifically about TL motors
and compatible Rockwell Automation drives. To obtain a copy, contact your local
Rockwell Automation office or distributor, or access the documents on-line at
http://
For information about: Read this document: Publication Number
Connecting to Ultra1500™
Digital Servo Drives
www.rockwellautomation.com
/literature.
Quick Start Instructions
User Manual
2092-QS001x-EN-P
2092-IN001x-EN-E
Connecting to Ultra3000™
Digital Servo Drives
Connecting to Kinetix
Multi-Axis Servo Drives
TL-Series Motor Transition Plates Installation Instructions TL-IN001x-EN-P
A glossary of industrial automation terms
and abbreviations
How to minimize and control
system-level noise.
An overview of Allen-Bradley motion
controls and systems, including
information about the this and other
motors.
®
6000
Installation Manual
Integration Manual
Installation Manual
Integration Manual
Allen-Bradley Industrial
Automation Glossary
System Design for Control
of Electrical Noise
Reference Manual
Motion Control Selection
Guide
2098-IN003x-EN-P
2098-IN005x-EN-P
2094-IN001x-EN-P
2094-IN002x-EN-P
AG-7.1
GMC-RM001x-EN-P
GMC-SG001x-EN-P
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005
Page 24

For more information refer to our web site:
For Rockwell Automation Technical Support information refer to:
Allen-Bradley and Kinetix are registered trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
Ultra1500 and Ultra3000 are registered trademarks of Rockwell Automation, Inc.
AMP and TYCO are trademarks of Tyco International, Ltd.
www.ab.com/motion
www.ab.com/support
or Tel: (1) 440.646.5800
Publication TL-IN001C-EN-P — March 2005 PN 0013-2067-001-03
Supersedes publication TL-IN001B-EN-P — December 2004 Copyright © 2005 Rockwell Auto mation, Inc. All rights reserved. Printed in the USA.
 Loading...
Loading...