Page 1

IISSUE EM D-GS08591
6
mEab
E
HRdi!!!I!@MGASOLINEENGINEGENERATQ
SERVICE MANUAL
@FUJl HEAVYINDUSTRIESLTD.
Page 2

CONTENTS
Section
Title Page
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
10.
11.
12.
SPECIFICATIONS ..........." ....". """.......".. "". . ..... . .. . . ........ ...." ...."" . ... . . . .. 1
PERFORMANCE CURVES .. ..." .. ... . ....."... "....".. "... "...... ......... .... ........" 3
FEATURES .. . . .......... ......" ......" ...."... "". "....... . . ......... . ..... .... .." ......... . . 5
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE GENERATOR ...-”” .”... -. ...”. o........”...... 6
4-1
External View of Generator
.. . ...... . . . . . .... . . . . . . . . . . . . ..... . ... . ... . .... . .... . . . ...
6
4-2 Control Panel
.... . .... . . ... . ... . .... ....... . . . ..... . . . . . . . . ...... . ... . .... ... . .... . . ...
7
4-3 Location of Serial Number and Specification Number . . . . . . . ...”...............”.. 20
Construction AND FUNCTION .. . . . . .."... ".- ... . . . . . . .....-. -C.---... -"--------- 21
5-1
Construction
... .. . ...." .. ..."... ".... . . .." .. ..". . ....." .. . . . . . ...." .. . . ... . ... . . .... . 21
5-2 Function . ... . . . ...... . .... . ..." .. . ... . . . ..... . . .." ...."" . . . . . . ...." ... . ... . ... . . ... . . . 21
5-3 Description of Generator Operation
..... .... . . . . . . . . . . . ..... . . . ... . ....... .... . . . .. 25
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS ................" ..... ..." . ............. . . ............. ..... . . . 28
RANGE OF APPLICATIONS .. ... . .... . ....... . . . . . .......... . .." . . ... . .... . ... . .... ..- 29
MEASURING PROCEDURES ..".. ".. .." . . . ... . . . . . . .. . . . . .... . . . . ... . .... .... . .... . . . 32
8-1
Measuring Instruments ..... . ... . .... . . . . .... . . . ..... ..... . ....... C.. . . ..... . . .... ..- 32
8-2 AC Output Measuring
.. . ...... . .." . ....... ....... . . . . . . . . ....... ....... ..". "........ 35
8-3 Measuring Insulation Resistance .. ....... .... ... . . . ....... . . . . . ... .... . ... . .... ...- 35
CHECKING FUNCTIONAL MEMBERS ..... . .. . ............ . .................... .... 37
9-1
Pilot LamP .. . . . . ..... . .... . ... . ... ... . . . . . .... . . . . . ..... ..... ..... . .... . .... .... . . .... 37
9-2 AC Receptacles
.... . ... ... . . ... . ... . . . . . ... . . . . . ... . . . . . . . . .. ....... ... .... .... . . ....
9-3 Circuit Breaker
37
.. . . . ... . ... . ... . . ... . ...... . . ... ... . . . . . . . ....... . . ... . ... . ... .... . . . . 38
9-4 Stator . .... . . . ....... . .... . . ... .... . ... . . . . .. .. ....... . . . . . . . . . ... .. C... . .... .... . . .... 38
9-5 Rotor . ...... . . . . . .... . . ....... .... . .... . . . . .... . . . . . ........ . . . . . ... . ... . . .. C. . . ... . .. 39
9-6 Condenser .... . . . . .... . . ... . ... . ....... ... . .... . . . . . .. . . . .... . . . . ... . ....... .... . . ... 39
9-7 Diode Rectifier
.... . ... . .... . ... . .... . .. ..... . . . .... . . . . . . . ....... .... . . ... .... .... . . .
40
Disassembly AND ASSEMBLY ... . .. ..... . . . . . .... . .... ........ C... . . ... . .... . . ... 41
10-1 Preparation and Precautions . . ... . . ....."... ".. ".. "... .... . . . . . .. . .... ... . .... . . ... 41
10-2 Special Tools for Disassembly and Assembly
.... . . . . . ...... . . .... . .... ... . . ..... . 41
10-3 Disassembly Procedures . . ... . ....... . . . . . .... .. . .......... . . . . ... . ....... .... . . .... 42
10-4 Assembly Procedures .." . . ... ... . .... . . . . .... . . . . . . . . . . .... . . . . ... . .... . ... . .... . . . . 51
10-5 Checking, Disassembly and Reassembly of the Control Box . ... . . ... . ... ....--.. 58
Troubleshooting .. . ...." .. . ....." . . . . . .... . . . . . ... . . . . . . . . ...... .... . .... .... ... . . . 59
11-1 No AC Output . . . . . ... . . .... . ... . ... ....... . . ....... . . . . . . . . ...... ... . .... .... . . .... . . 59
11-2 AC voltage is too high or too low
... . . . .... . . . . . .... . .. . . . ...... .... . .... .... .... . . .
’61
11-3 AC voltage is normal at no-load, but the load cannot be applied ..-. ---... ”...-”. 62
11-4 No DC Output ..... . .... . . .... ........ . . . . . ... . . . . . . ... .. .... . .. .... .... . ... . .... . . ... 63
11-5 idle Control . .. ..... . .... . . .... .... . .... . . . .... . . . . . .......... . . . . ...... . . .. . ..... . . ..- 64
WIRING DIAGRAM
.. . . .... ..... . . .... . . .... . . . .... . . . .... . . . ....... . . .... . ... . . ... .... . .
67
NOTE: As for the servicing information on engine portion, please refer to the
EHI 7, EH25 and EH34 engine service manual.
Page 3
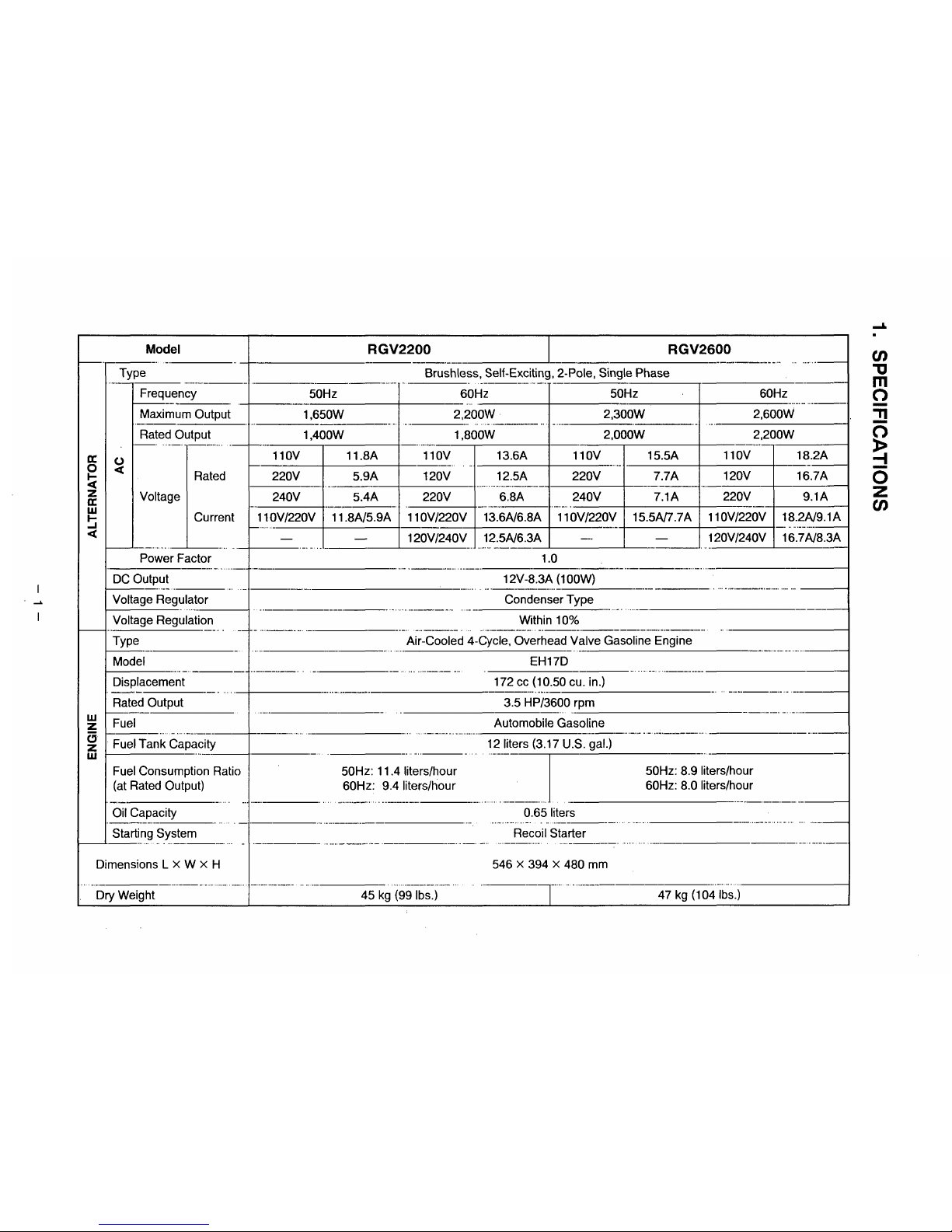
1.
SPECIFICATIONS
-
I
!
T
i
i
j
r
I
i
I
I
T
-r
NN
IoIo
IncD
E
E
0
a3
w
X
d
a,
m
X
(D
d
In
a,
a
D
8
C
U
a
c
I I !I
I
II
-
c
i
.-
-
C
m
U
I
3V
I
3NIDN3
UOlVNU3llV
I
-1-
L
Page 4
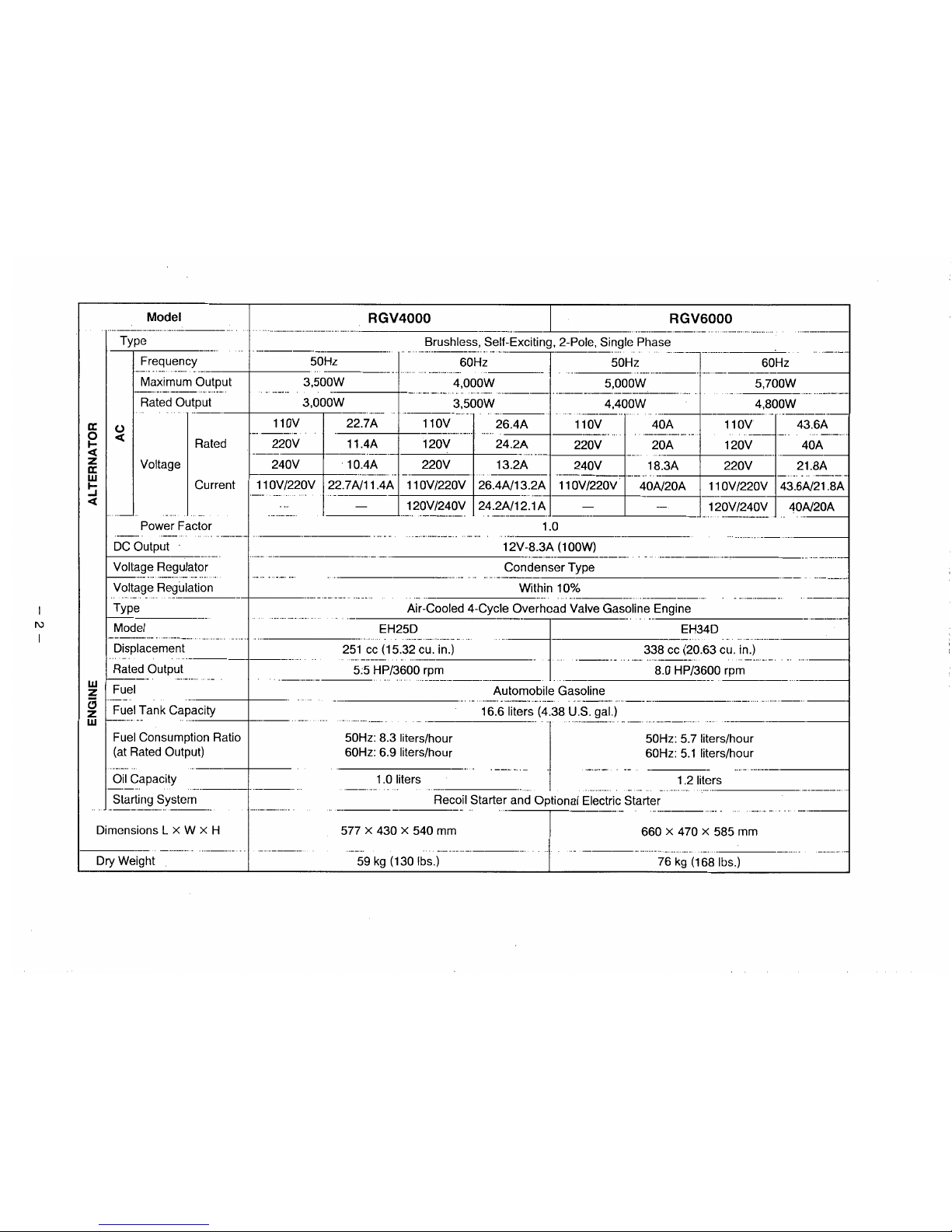
I
i
I
I
-
N
I
0
co
I
0 0 0
>
(D
0
PC
0
0
0
9
0
I
i
I
IS
7
I
:d
i
I
N
0
m
!
a,
n
C
a,
U
S
s
i:
j:
T
I
i
I
E
E
0
d
m
X
0
m
d
X
b
m
b
I
!
..
,:
..
s
I
.!
:j:
I
I
I
!
!
-
.-
c
0
n3
U
-I
tlOlVNtl3llV
3N13N3
I
-2-
Page 5
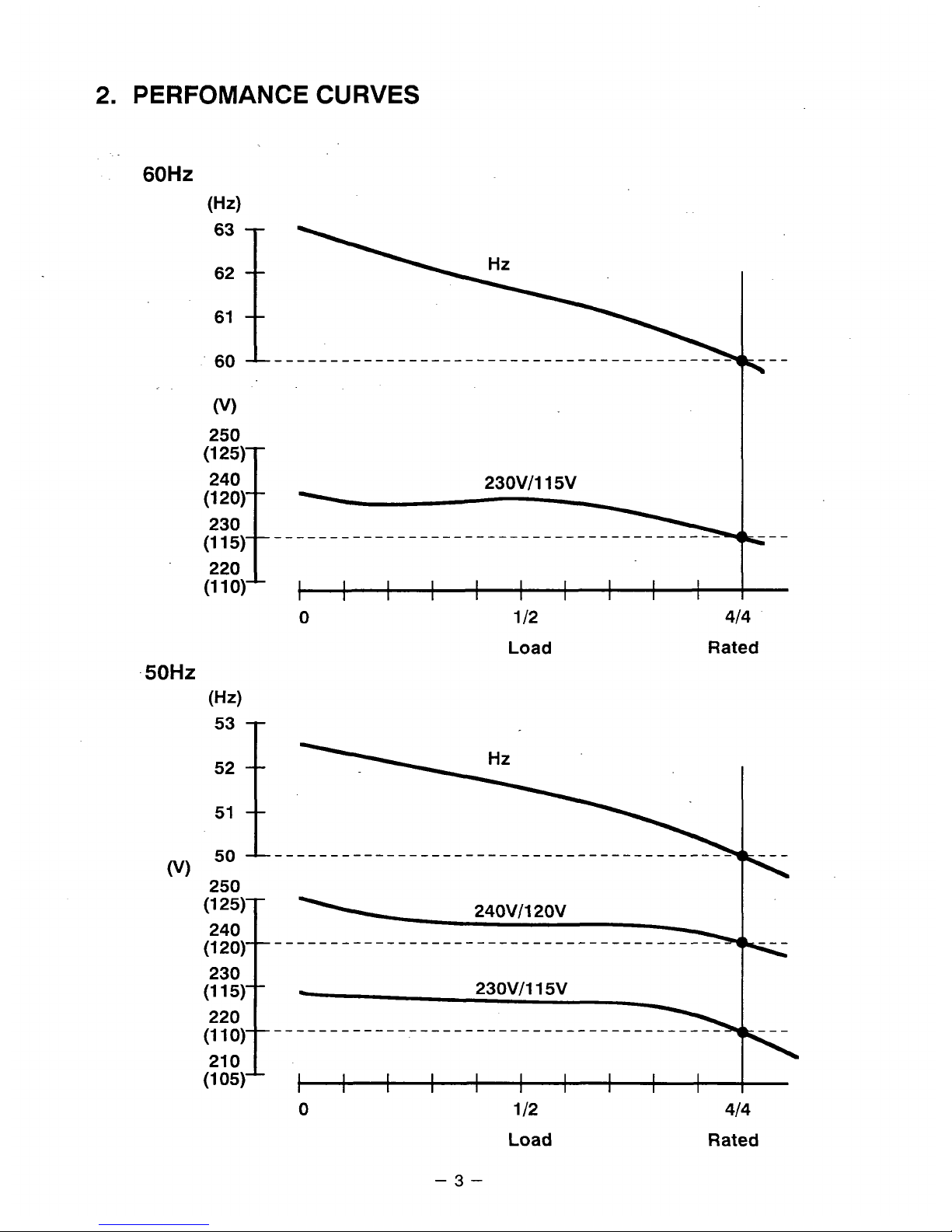
2.
PERFOMANCE CURVES
63T
\
250
(1 25)
23ov/115v
220
0
1 /2
414
Load Rated
50Hz
(Hz)
Hz
51
00
250
(1 25) 24ov/12ov
230V/115V
220
21
0
(1
05)
0
1 12
414
Load Rated
-3-
Page 6
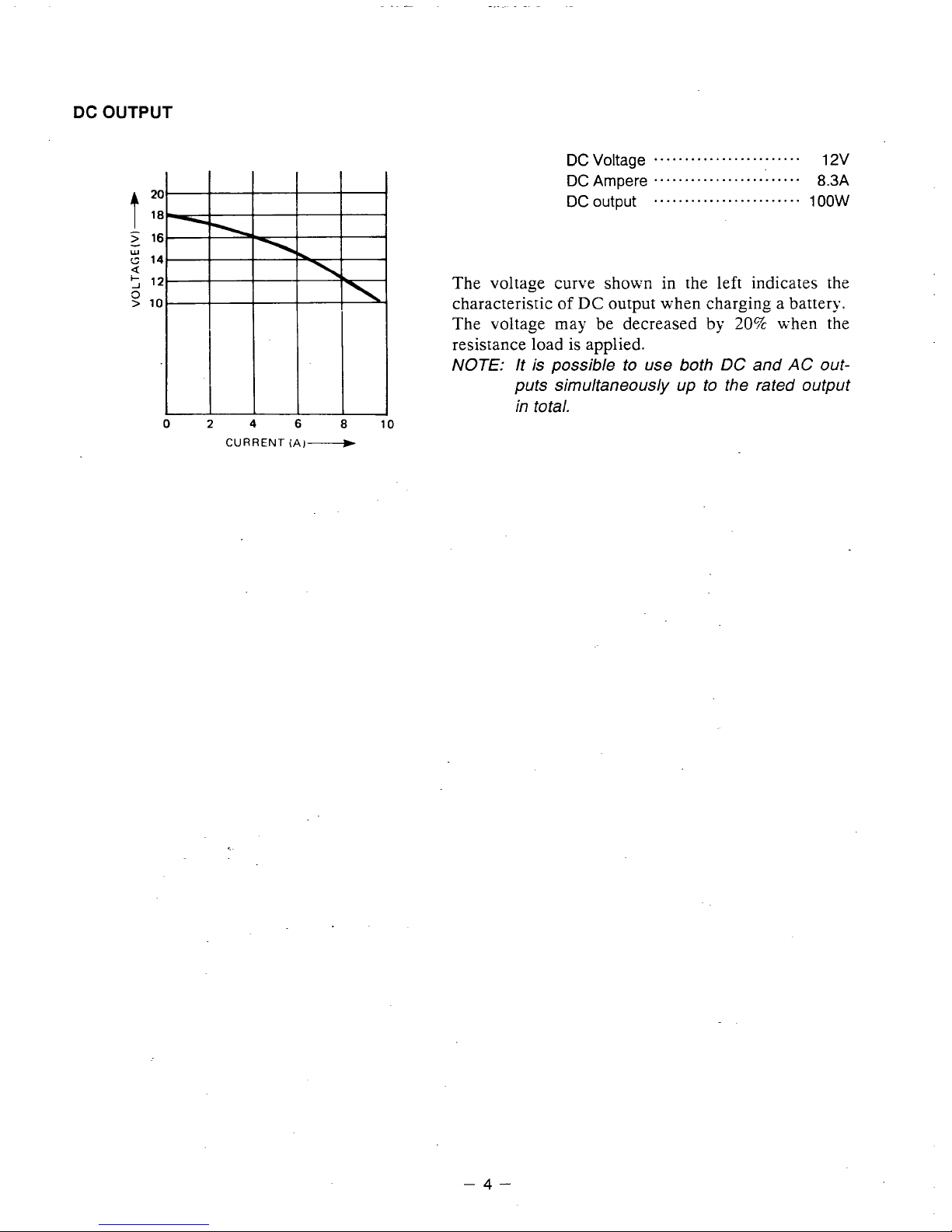
DC
OUTPUT
DC Voltage
........................
DCAmpere
........................
DC output
........................
12v
8.3A
1
oow
The voltage curve shown in the left indicates the
characteristic
of
DC output when charging a battery.
The voltage may be decreased
by
20%
when the
resistance load is applied.
NOTE:
It is possible to use both DC and
AC
out-
puts simultaneously up to the rated output
in total.
CURRENT
(AI&
-4-
Page 7

3.
3-1
3-2
3-3
3-4
3-5
3-6
3-7
3-8
3-9
FEATURES
BRUSHLESS ALTERNATOR
Newly developed brushless alternator eliminates troublesome brush maintenance.
CONDENSER TYPE VOLTAGE REGULATOR
A
trouble free condenser type voltage regulator ensures a stable voltage under all working
conditions.
OIL SENSOR
Oil sensor automatically shuts off the engine whenever the oil level falls down below the lower limit
to protect the engine from seizure.
QUIET OPERATION
Robin RGV series generator delivers a quiet operation with
:
0
A large super silent muffler.
0
A quiet 4-stroke Robin Rro OHV engine.
0
A
silent cyclone air cleaner.
NO RADIO NOISE
Noise suppressor spark plug and spark plug cap are equipped standard to prevent radio frequency
interfe.rence.
LARGE FUEL TANK
The large fuel tank allows more than 5 to
11
hours
of
continuous operation which
is
sufficient for a
half day or one day work without refueling.
RUGGED TUBULAR FRAME
Full cradle type rugged tubuler frame protects the generator all around.
COMPACT AND LIGHT WEIGHT
Newly developed brushless alternator enabled the
RGV
generators to be very compact
in
size and
light
in
weight.
MINIMAL MAINTENANCE
0
A brushless alternator release the operator from periodical brush maintenance.
0
A trouble free condenser type voltage regulator.
0
A drip-proof alternator design.
0
No-fuse circuit breakers.
0
An electronic pointless ignition system.
0
A
dust-proof cyclone air cleaner.
3-10 LONG-LIFE DURABILITY
The heavy-dut! 4 stroke Robin Rro
OHV
engine and virtually maintenance-free brushless alternator
ensure greater durability with
:
0
A brushless alternator with a condenser voltage regulator.
Full
rubber mount
in
a sturdy tubular frame.
0
A
forged ste.el crankshaft supported by two main ball bearings.
A
pointless electronic ignition system.
0
A
cast-iron cylinder liner.
0
A
forged aluminum connecting rod.
-5-
Page 8

4.
4-1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
OF
THE GENERATOR
EXTERNAL VIEW
of
GENERATOR
VOLT?JETER FUEL LEVEL GAUGE TANK CAP
STOP
BUTON
CHOKE KNOB
kC
AIR CLEANER
..
DC
RECOIL STARTER
,
DC CIRCUIT BREAKEFi AC CIRCUIT BREAKER
OIL SENSOR
SPARK PLUG MUFFLER
31L DRAIN PLUG OIL LEVEL GAUGE
-6-
Page 9
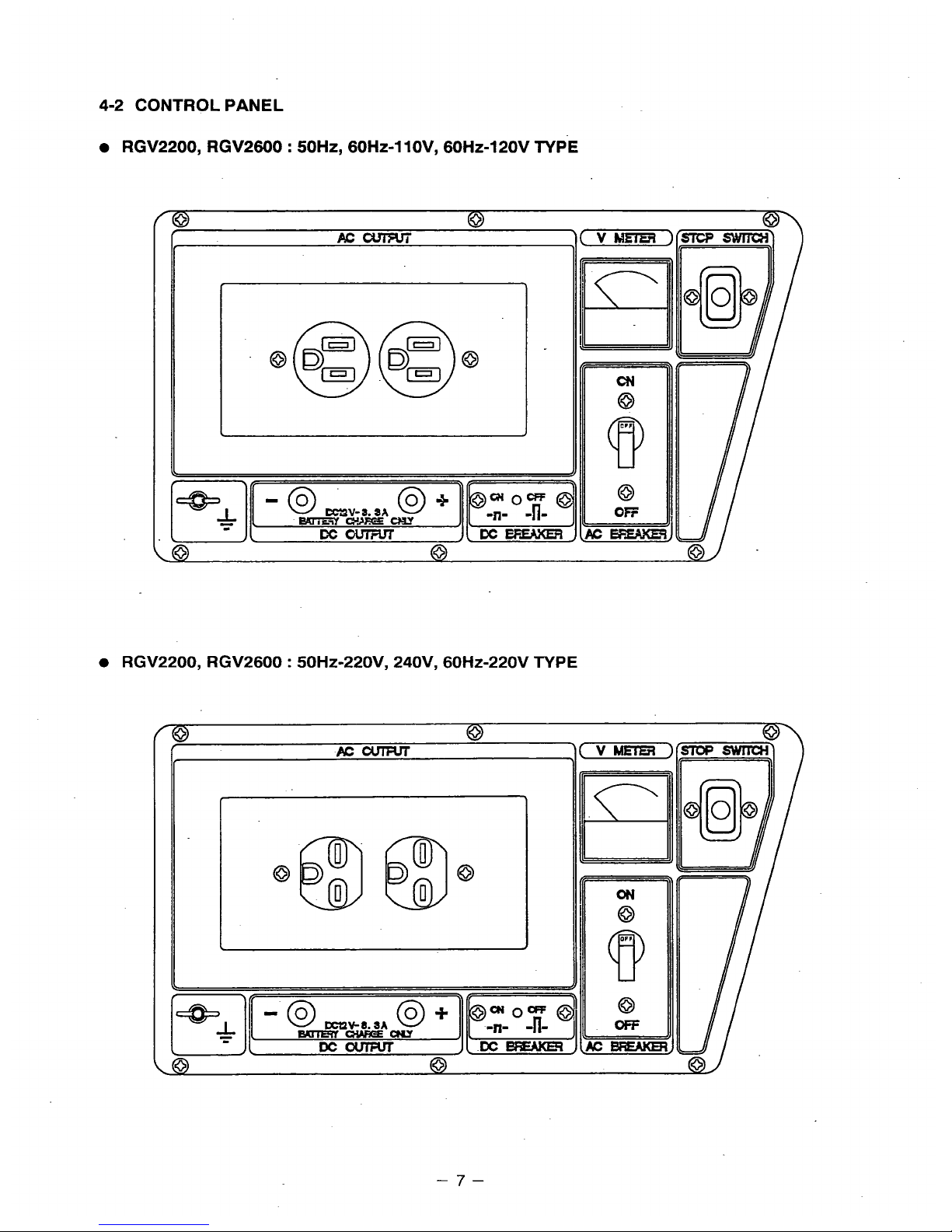
4-2 CONTROL PANEL
RGV2200, RGV2600 : SOHz, 60HZ-1 lOV, 60Hz-120V TYPE
RGV2200, RGV2600 : 50H~-220V, 240V, 60HZ-220V TYPE
-7-
Page 10
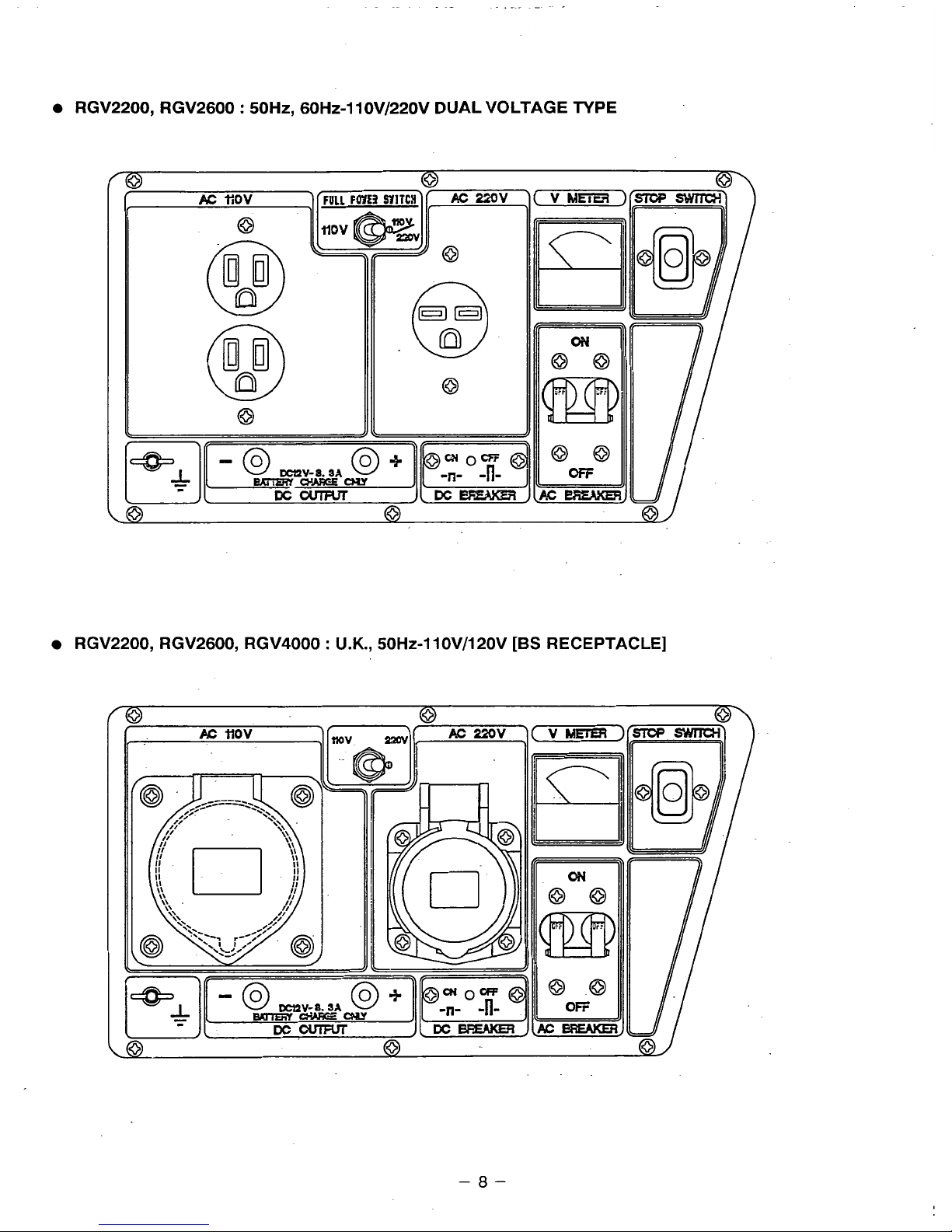
RGV2200, RGV2600 : SOHZ, 60H~-lIOV/220V DUAL VOLTAGE TYPE
RGV2200, RGV2600, RGV4000
:
U.K.,
50H~-110V/120V
[BS
RECEPTACLE]
-8-
Page 11
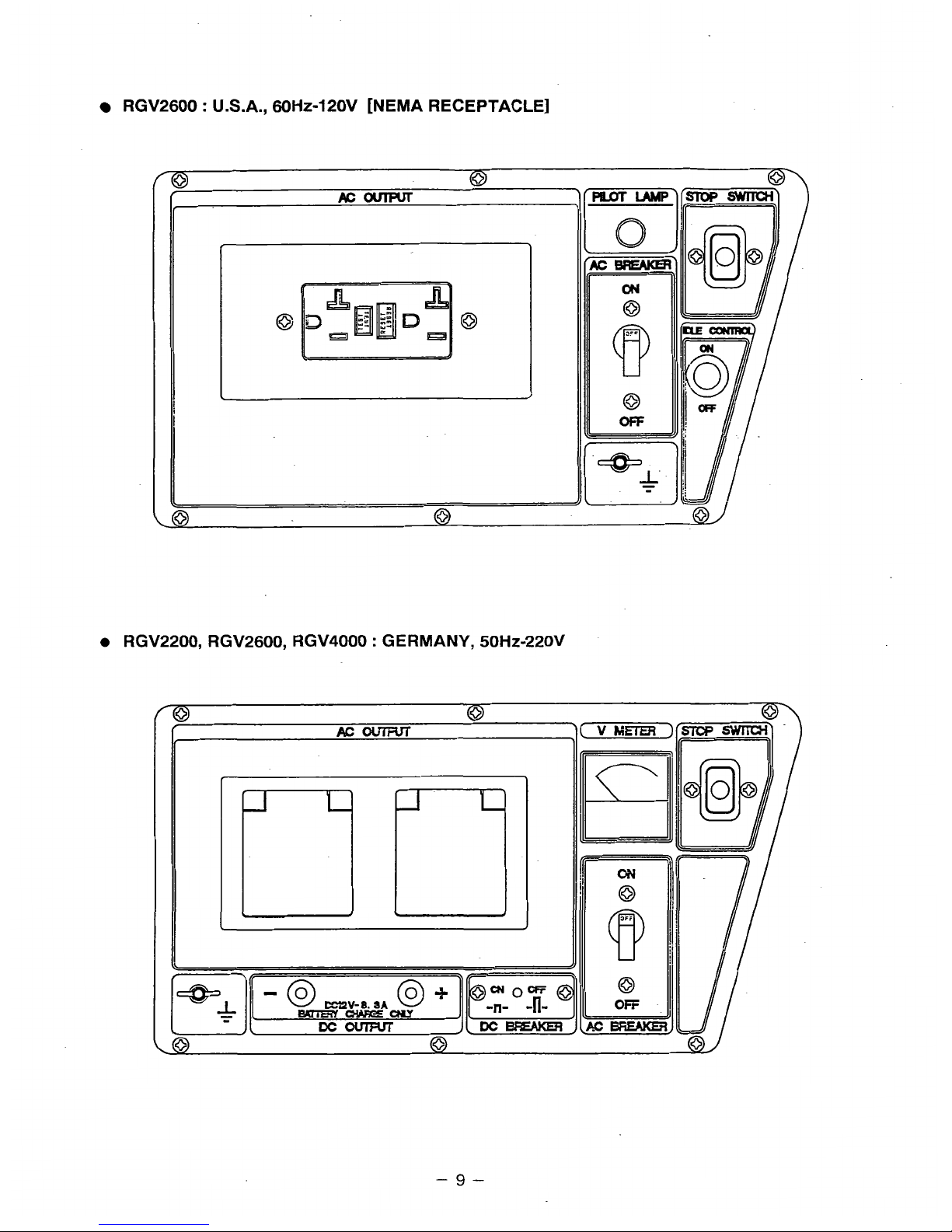
RGV2600 : U.S.A., 60Hz-120V [NEMA RECEPTACLE]
RGV2200, RGV2600, RGV4000
:
GERMANY, 50Hz-220V
-9-
Page 12
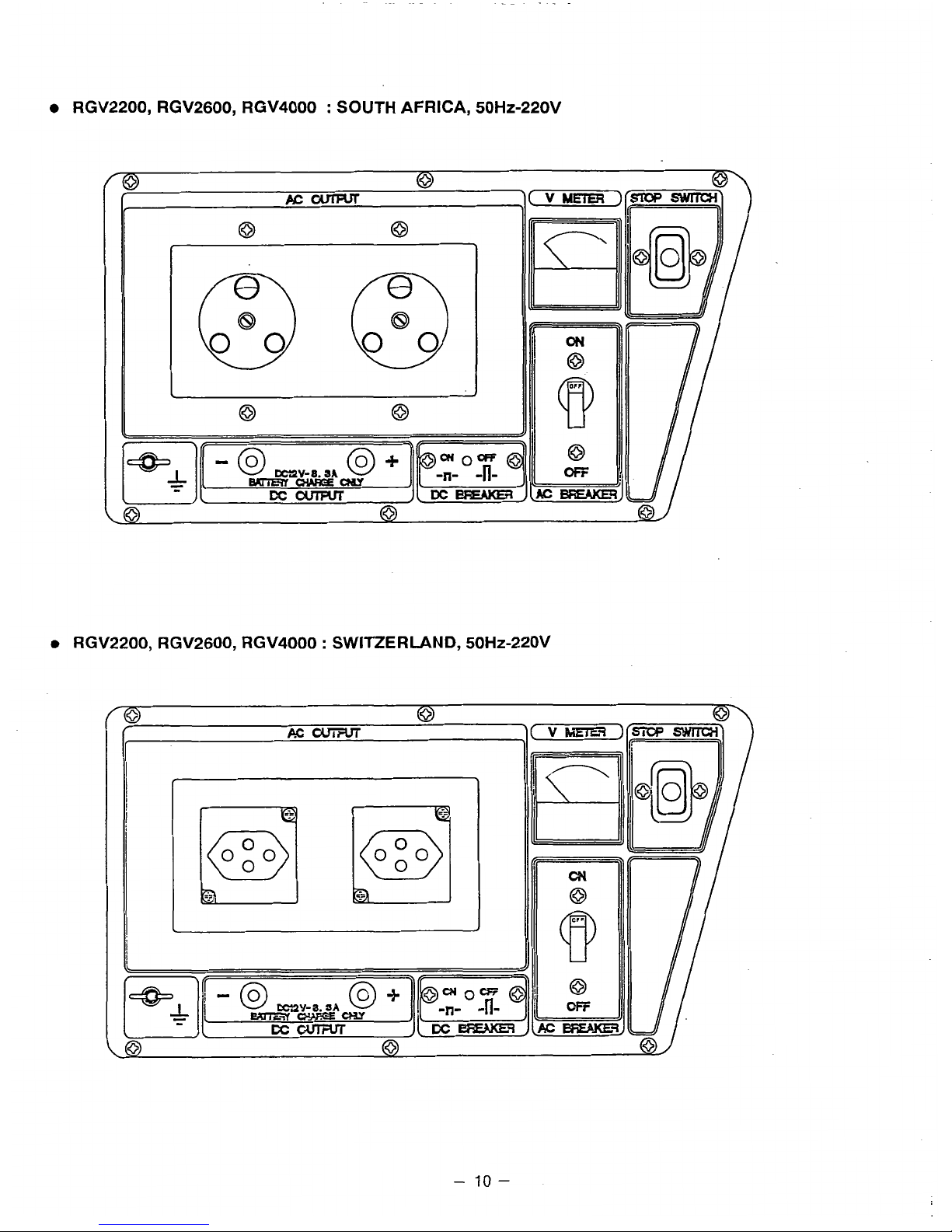
RGV2200, RGV2600, RGV4000 : SOUTH
AFRICA,
50HZ-220V
I
RGV2200, RGV2600, RGV4000 SWITZERLAND, 50HZ-22OV
-
10
-
Page 13
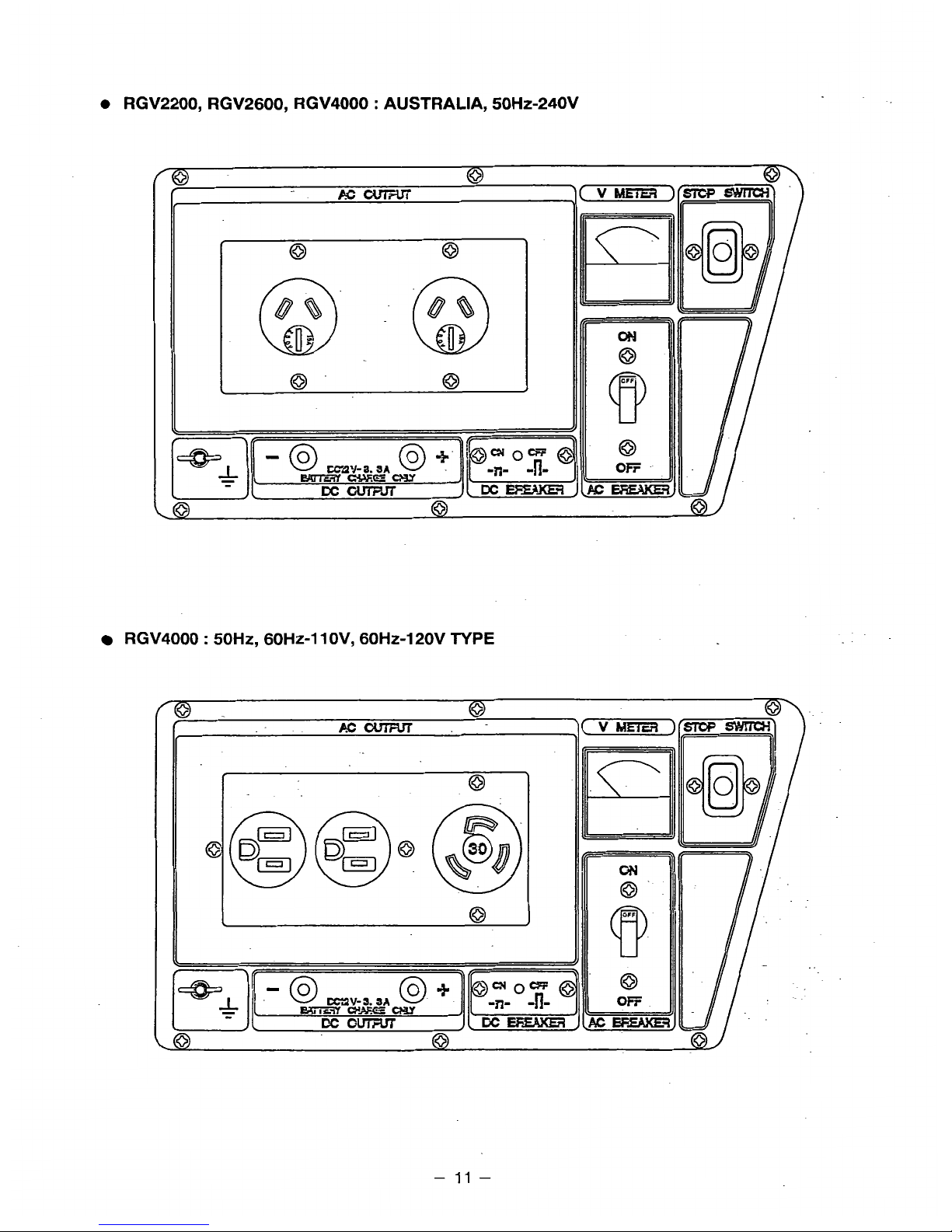
RGV2200, RGV2600, RGV4000
:
AUSTRALIA,
50HZ-240V
RGV4000 : 5OHZ, 60Hz-11 OV, 60HZ-120V
TYPE
-
11
-
Page 14
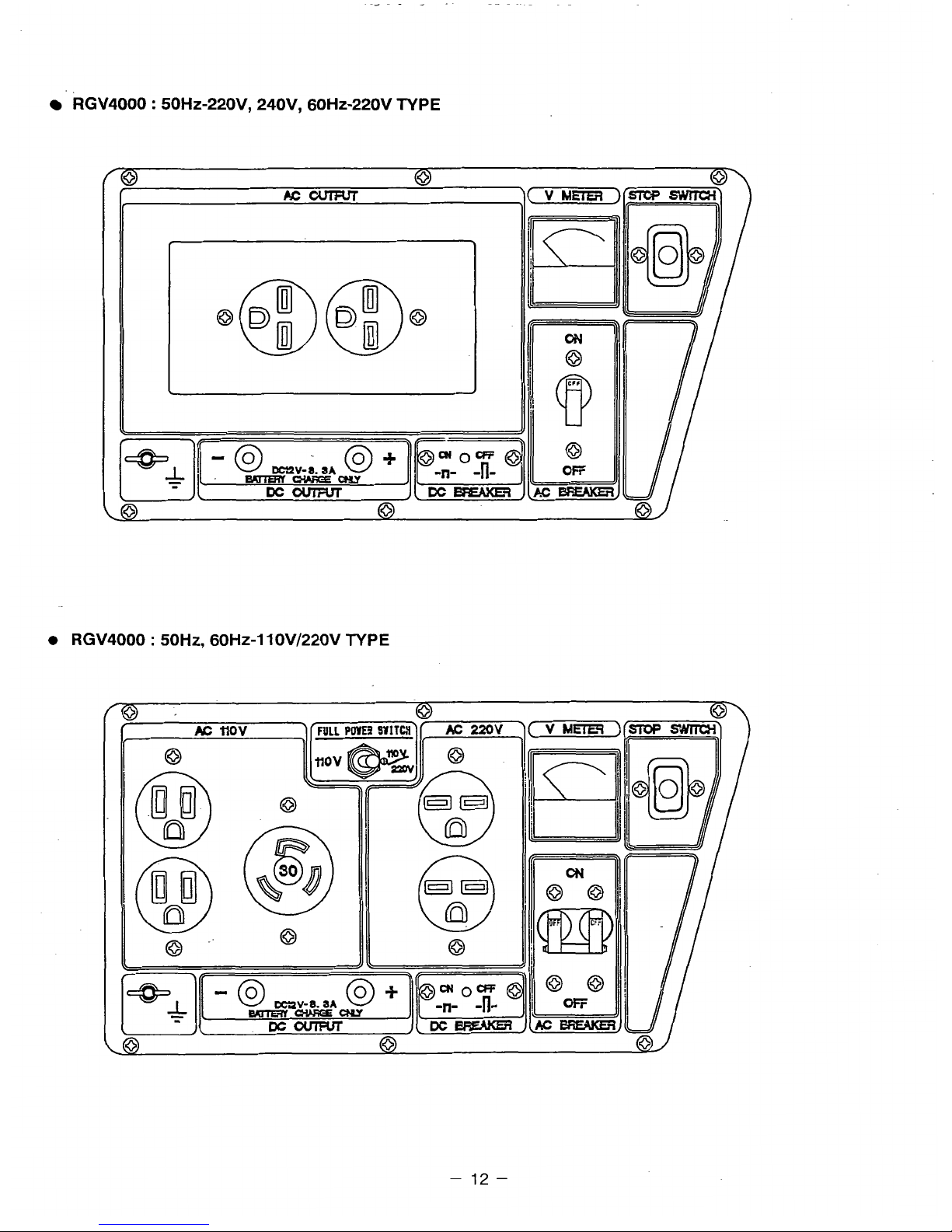
RGV4000 : 50H~-220V, 240V, 60HZ-220V
TYPE
0
RGV4000 : SOHZ, 6OHZ-l10V/220V
TYPE
-
12
-
Page 15
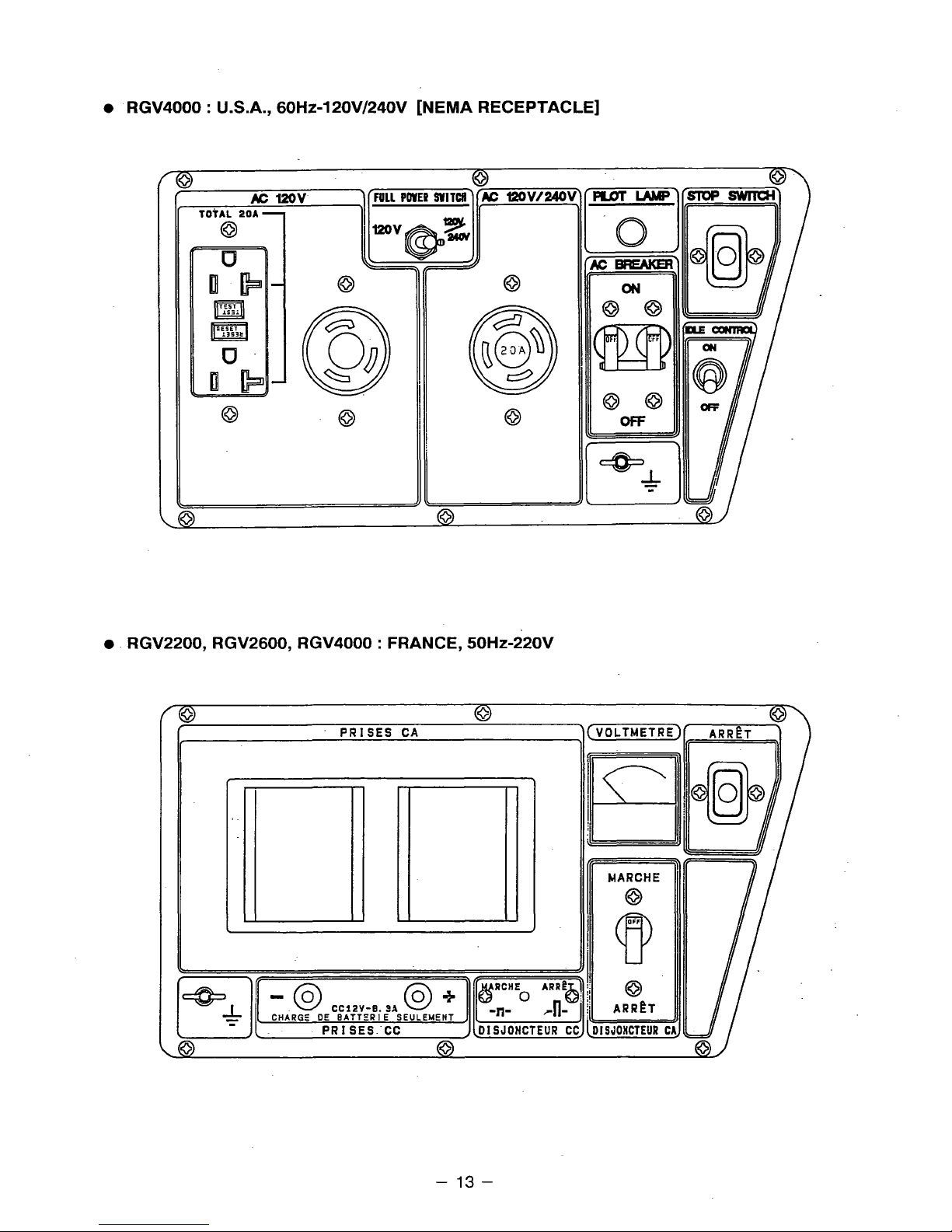
RGV4000 : U.S.A., 60H~-120V/240V [NEMA RECEPTACLE]
@I
.
RGV2200, RGV2600, RGV4000 : FRANCE, 50Hz-220V
L
PRISES
CA
CHARGE
DE
BATTERIE
SEULEMENT
-
13-
Page 16
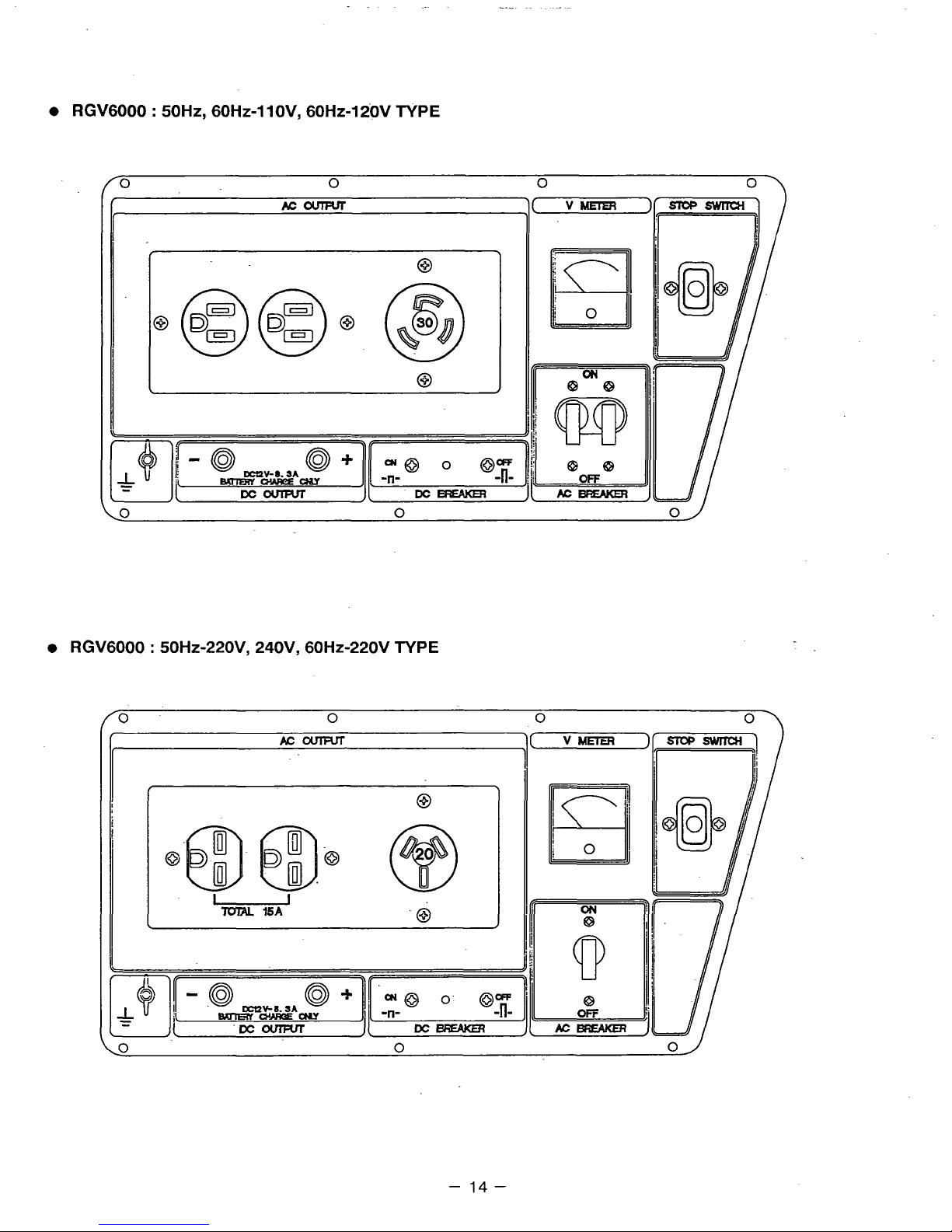
0
RGV6000 : 50Hz, 60Hz-1 lOV, 60Hz-IiOV TYPE
I
!
L
!
@
1
0
I
U
VMEIER
1
RGV6000 : 50H~-220V, 240V, 60Hz-220V TYPE
f0
0 0
o\
\O
~
0
0)
-
14-
Page 17
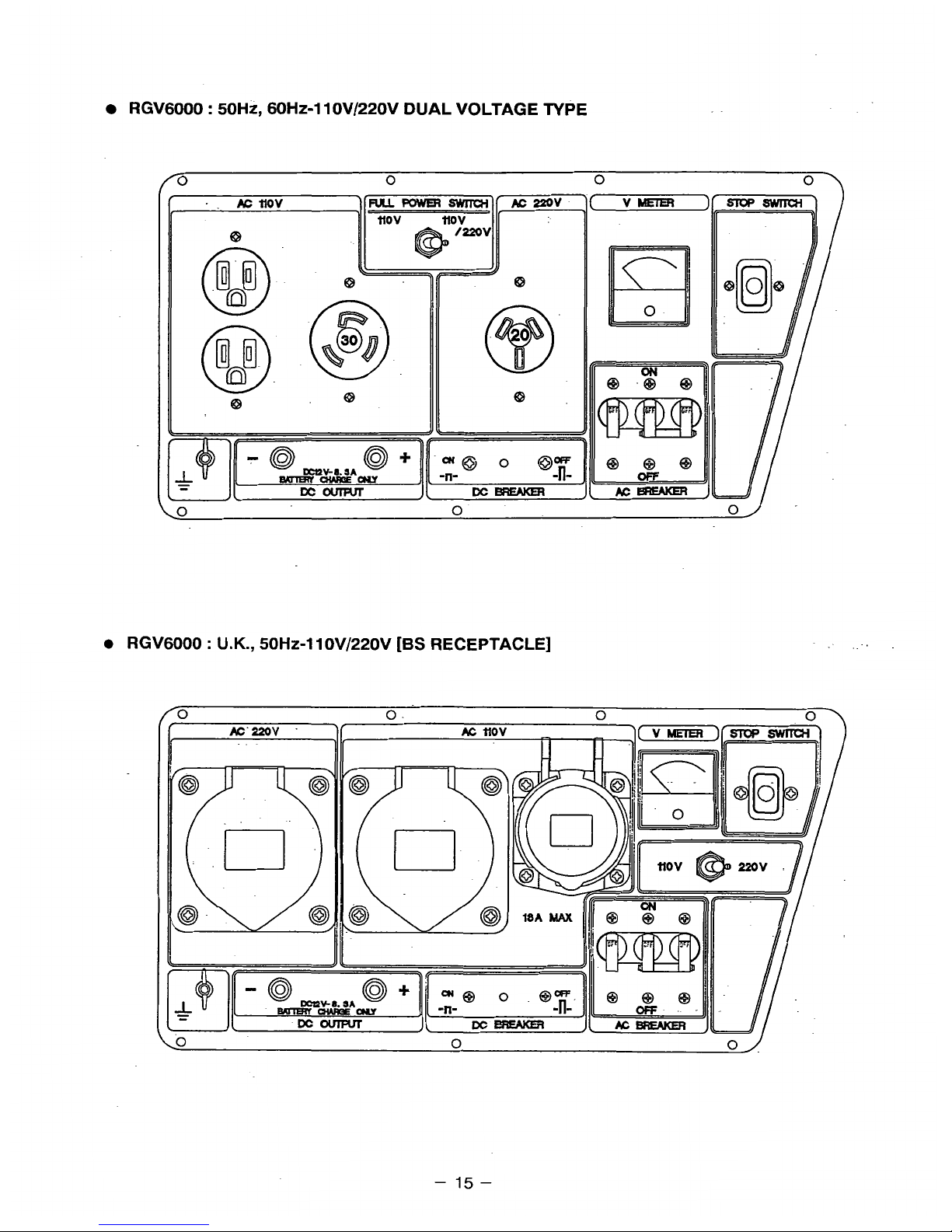
RGV6000 : 50Hz, 60H~-llOV/220V DUAL VOLTAGE
TYPE
..
-
15
-
Page 18
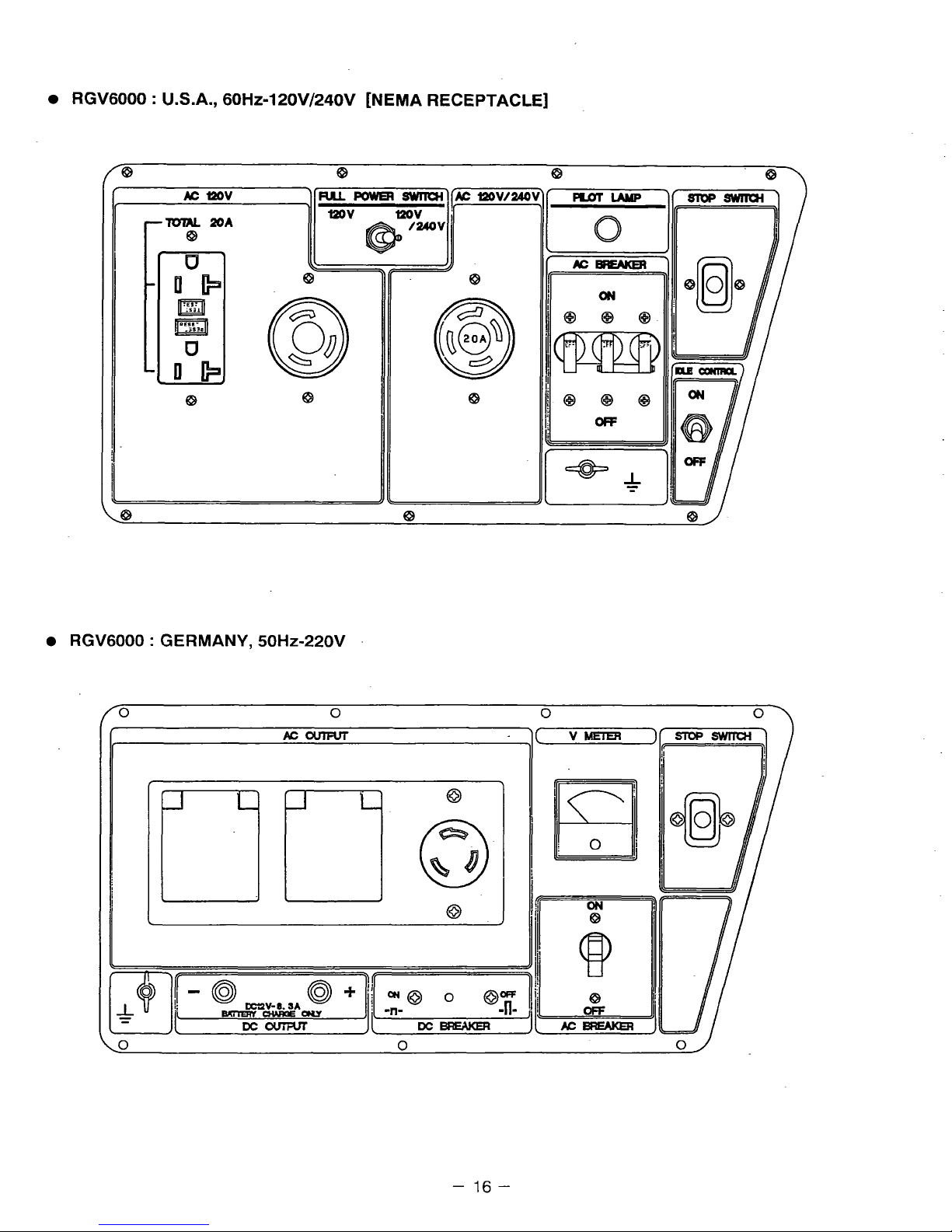
RGV6000 : U.S.A., 60H~-120V/240V [NEMA RECEPTACLE]
RGV6000
:
GERMANY,
50Hz-220V
f0 0 0
I
\O
0
-
16
-
Page 19
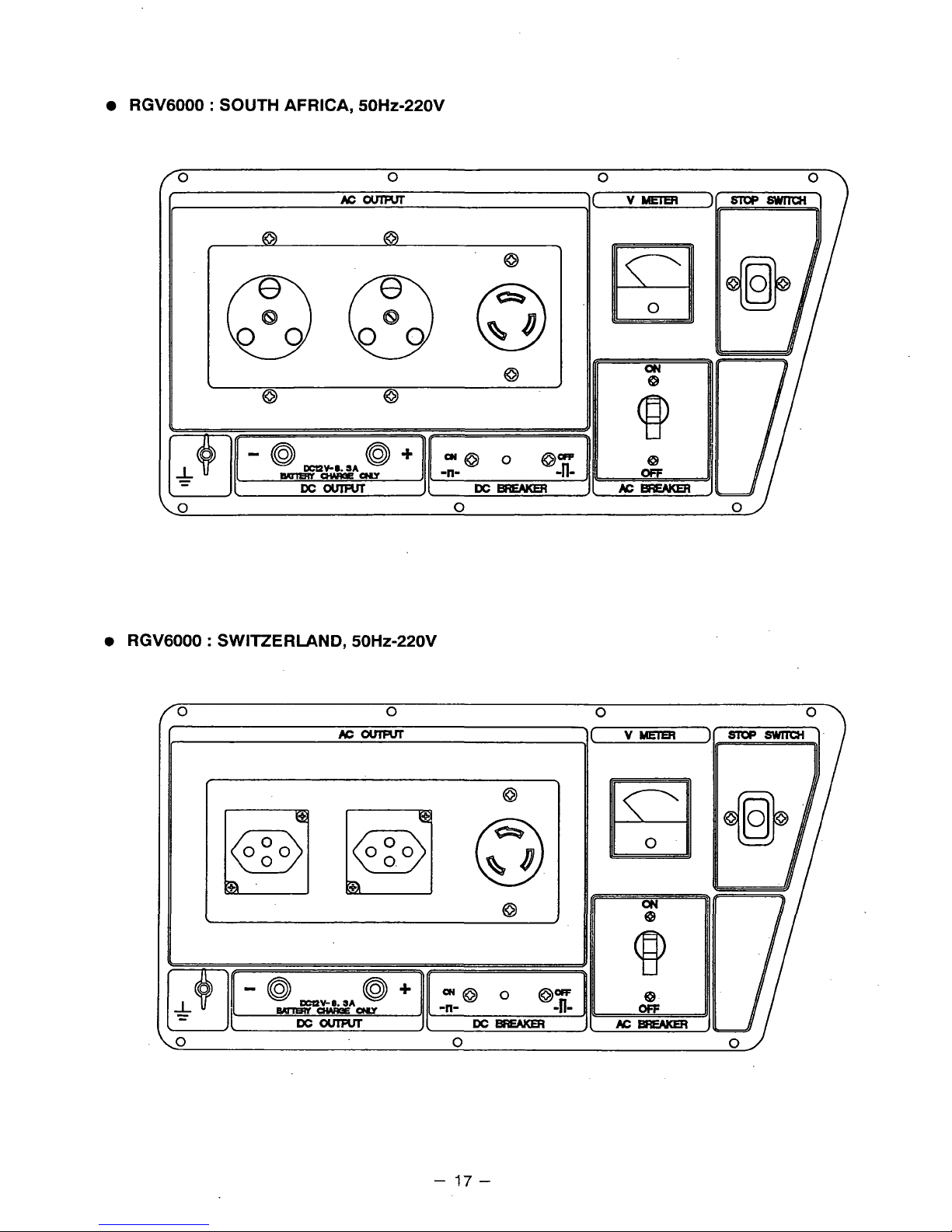
RGV6000 : SOUTH
AFRICA,
50Hz-220V
h
A
J
U
U
kEm
,
VMEtER
I
I
63
0
RGV6000 : SWITZERLAND,
50Hz-220V
f0
0
0
o\
ON
0
E
-
17
-
Page 20
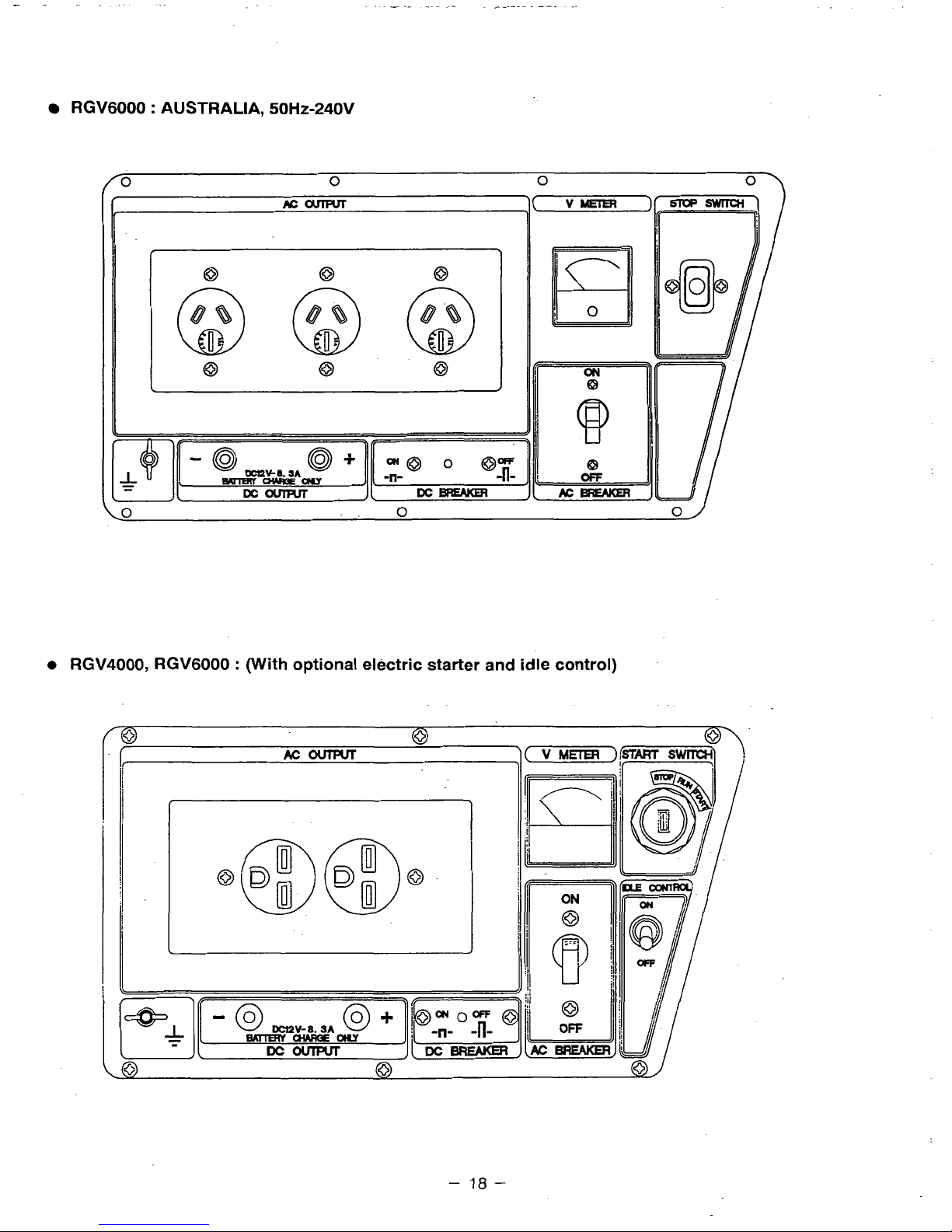
RGV6000
:
AUSTRALIA,
50HZ-240V
0
RGV4000, RGV6000 : (With optional electric starter and idle control)
-
la
-
Page 21
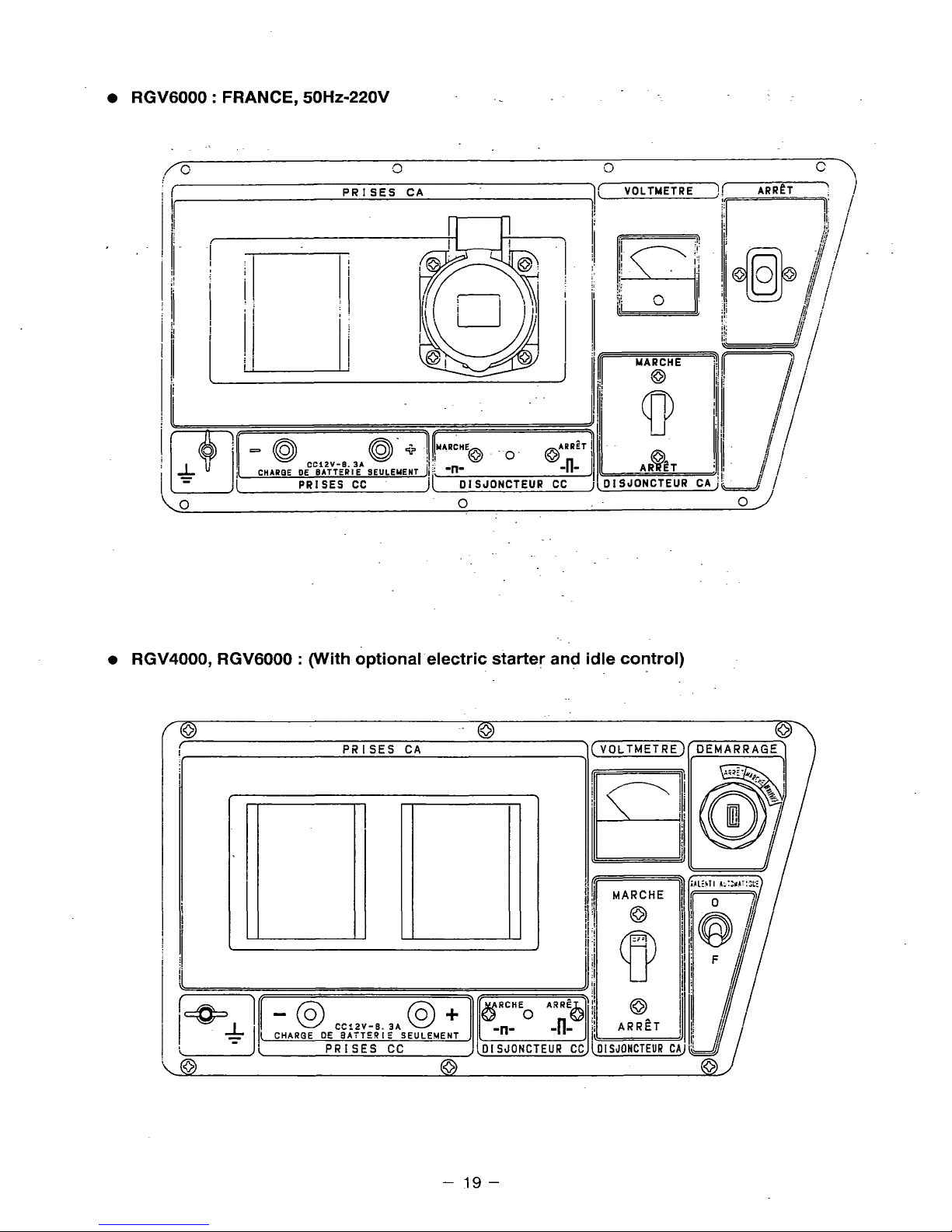
RGV6000
:
FRANCE,
50H~220V
VOLTMETRE
0
0
RGV4000, RGV6000 : (With optional electric starter and idle control)
/@
PRlSES
CA
-
19
-
Page 22
4-3
LOCATION
of
SERIAL NUMBER
and
SPECIFICATION NUMBER
Serial number and specification number are stamped
on
the
LABEL
(MODEL
NAME)
stuck on the end
cover.
NOTE:
Always specify these numbers when inquiring about the generator or ordering spare parts in
order
to
get correct parts and accurate service.
MODEL
NAME
-
20
-
Page 23
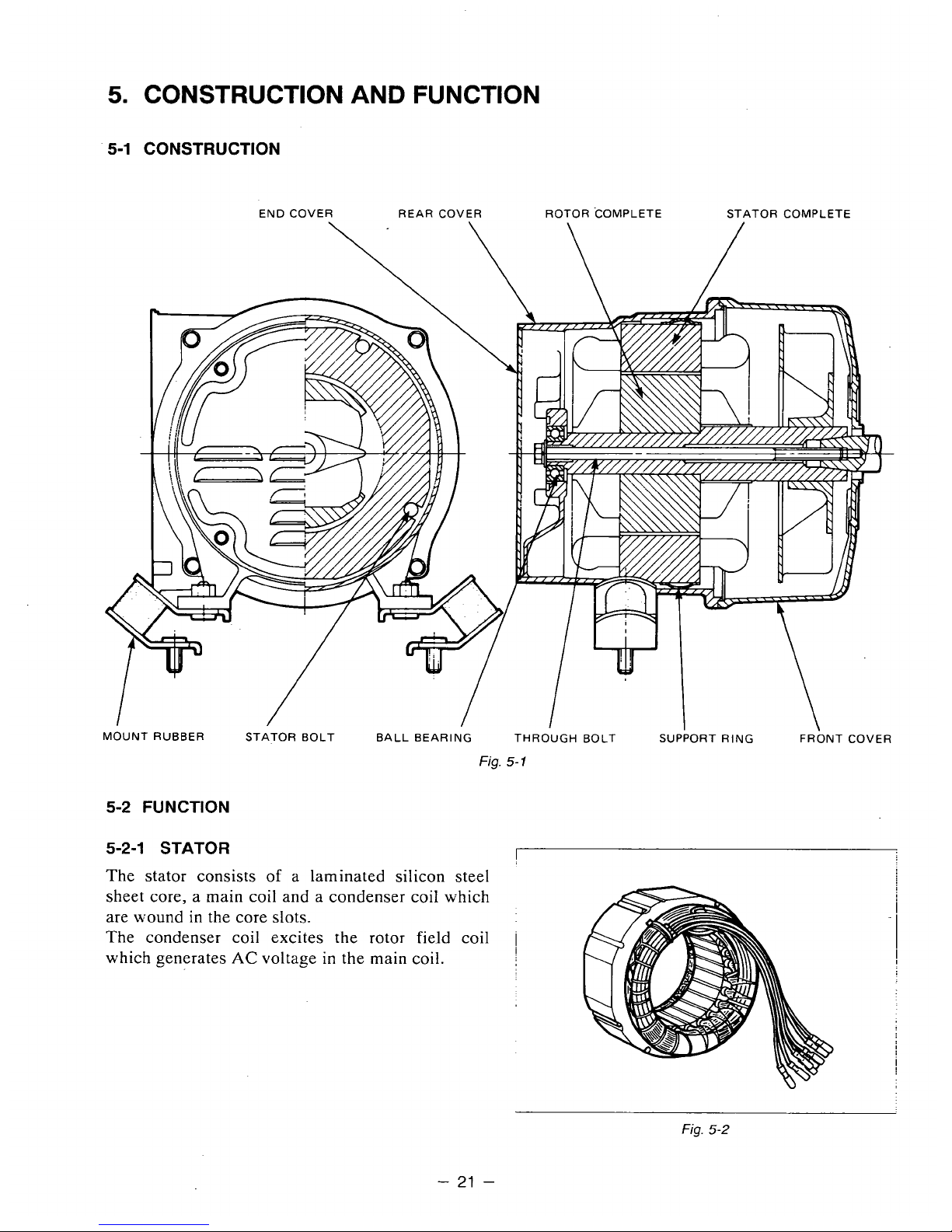
5.
CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION
5-1
CONSTRUCTION
END
COVER
REAR
COVER
ROTOR
COMPLETE
STATOR
COMPLETE
MOUNT
RUBBER
STATOR
BOLT
BALL
BEARING
THROUGH
BOLT SUPPORT
RING
FRONT
COVER
Fig.
5-7
5-2 FUNCTION
5-2-1 STATOR
I
The stator consists
of
a laminated silicon steel
sheet core, a main coil and a condenser coil which
are wound
in
the core slots.
The condenser coil excites the rotor field coil
i
-I
which generates
AC
voltage
in
the
main
coil.
i
1
I
I
I
Fig.
5-2
-
21
-
Page 24
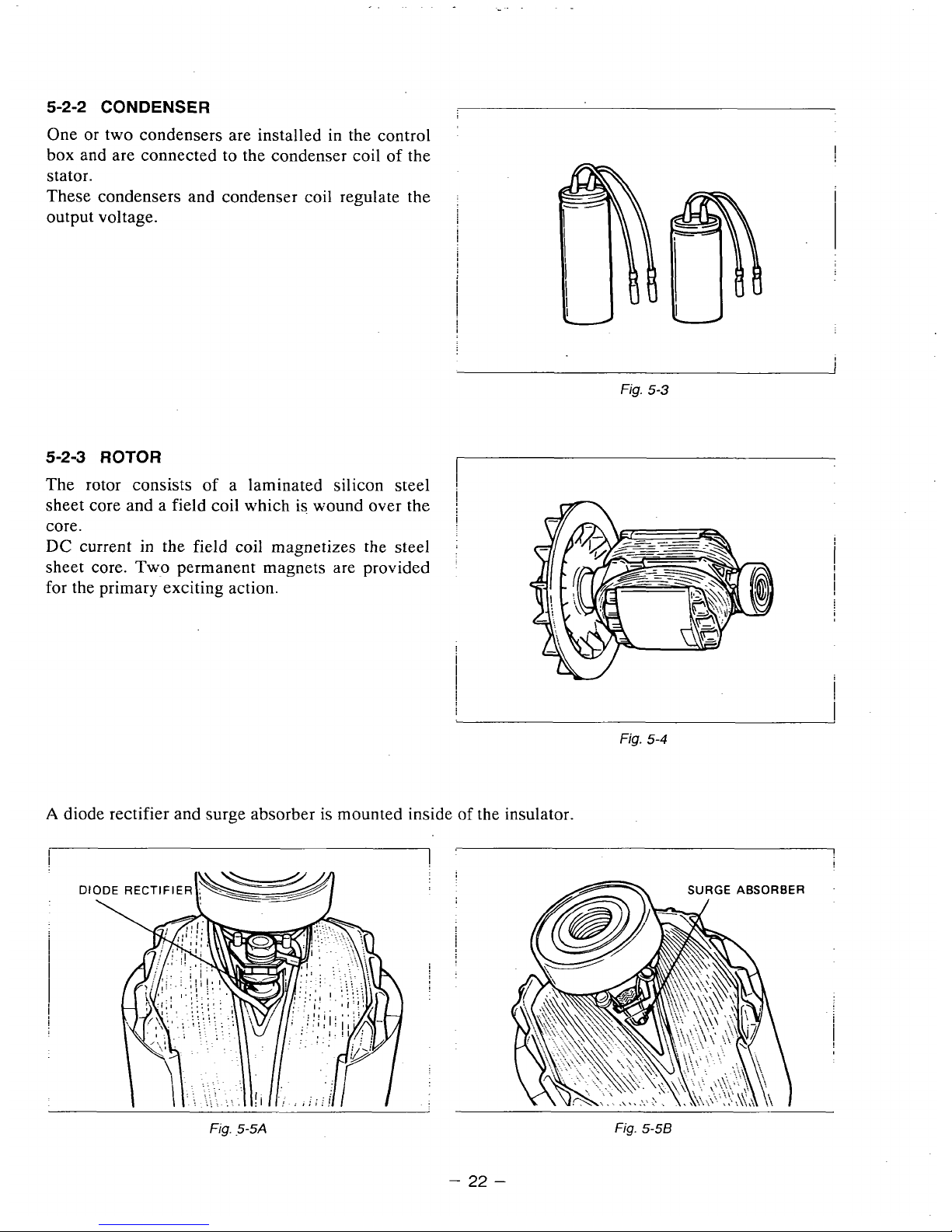
5-2-2 CONDENSER
One
or
two condensers are installed
in
the control
box and are connected to the condenser coil
of
the
stator.
These condensers and condenser coil regulate the
:
output voltage.
5-2-3
ROTOR
The rotor consists
of
a laminated silicon steel
sheet core and a field coil which is xound over the
core.
DC
current in the fie.ld coil magnetizes the steel
sheet core.
Tw~o
permanent magnets are provided
for the primary exciting action.
Fig.
5-4
A
diode rectifier and surge absorber is mounted inside
of
the insulator.
1
!
!.
-
22
-
Page 25
5-2-4
DC CIRCUIT
BREAKER
(1)
The
10
ampere
DC
circuit breaker mounted
on
the control panel protects whole
DC
circuit
from getting damage by overload or short
circuit.
j
Fig.
5-6
5-2-5
NO-FUSE BREAKER
The no-fuse breaker protects the generator from getting damage by overloading or short circuit'in the
appliance.Table
5-1
shows
the capacity of no-fuse breaker by each spec. and their object of protection.
I
MODEL
1
SPECIFICATION
I
NO-FUSE
BREAKER
j
OBJECT
of
PROTECTION
I
50HZ-11 OV
Total output amperage
6.5A 50HZ-220V, 240V
Total output amperage
15A
60Hz-11 OV, 120v
Total output amperage
12A
60HZ-220V
8A
Total output amperage
RGV2200
'
I
50HZ-11 OVI22OV
'
Total output amperage
6.5A (2-Pole, 2-Element)
60HZ-120VI240V
'
I
8A (2-Pole. 2-Element)
Total output amperage
.
50HZ-11 OV.
I
18A
Total output amperage
9A 50Hz-220V
Total output amperage
..
20A 60HZ-11 OV. 12Ov
Total output amperage
RGV2600
1 OA
.i
Total output amperage 60HZ-220V
!
60HZ-240V
50HZ-11 OVl220V
.
9A (2-Pole. 2-Element) Total output amperage
. .
aA
I
Total output amperage
I
~
60Hz-11 OVi22OV, 12OVi24OV
i
1
OA (2-Pole. 2-Element)
1
Total output amperage
50HZ-11 OV
!
27A Total output amperage
I
I
60142-1
lov,
120v
.
j
30A Total output amperage
.
50Hz-220V
I
14A
Total output amperage
I
RGV4000
60HZ-220V 15A
!
!
Total output amperage
.12A Total output amperage
..
-5OHZ-240V
I
50HZ-11 OVi220V
I
14A (2-Pole, 2-Element)
i
Total output amperaqe
I
.60Hz-11 OV!22OV. 120V!240V
[
15A (2-Pole, 2-Element) Total output amperage
Total output amperage
50HZ-11 OV
40A
1
60HZ-11 OV. 120V
50HZ-220V. 60Hz-220V
50HZ-240V
50HZ- 1
1
OV/22OV.
.I
!
.
30A
Output from 30A receptacle
RGV6000
I
20A
20A (2-Pole. 2-Element) Total output amperage
18A
I
Total output amperage
Total output amperage
I
60HZ- 1 1 OVi22OV.
.
60Hz-120Vi240V 30A
i
Output from 30A receptacle
Table
5-
1
-
23
-
Page 26
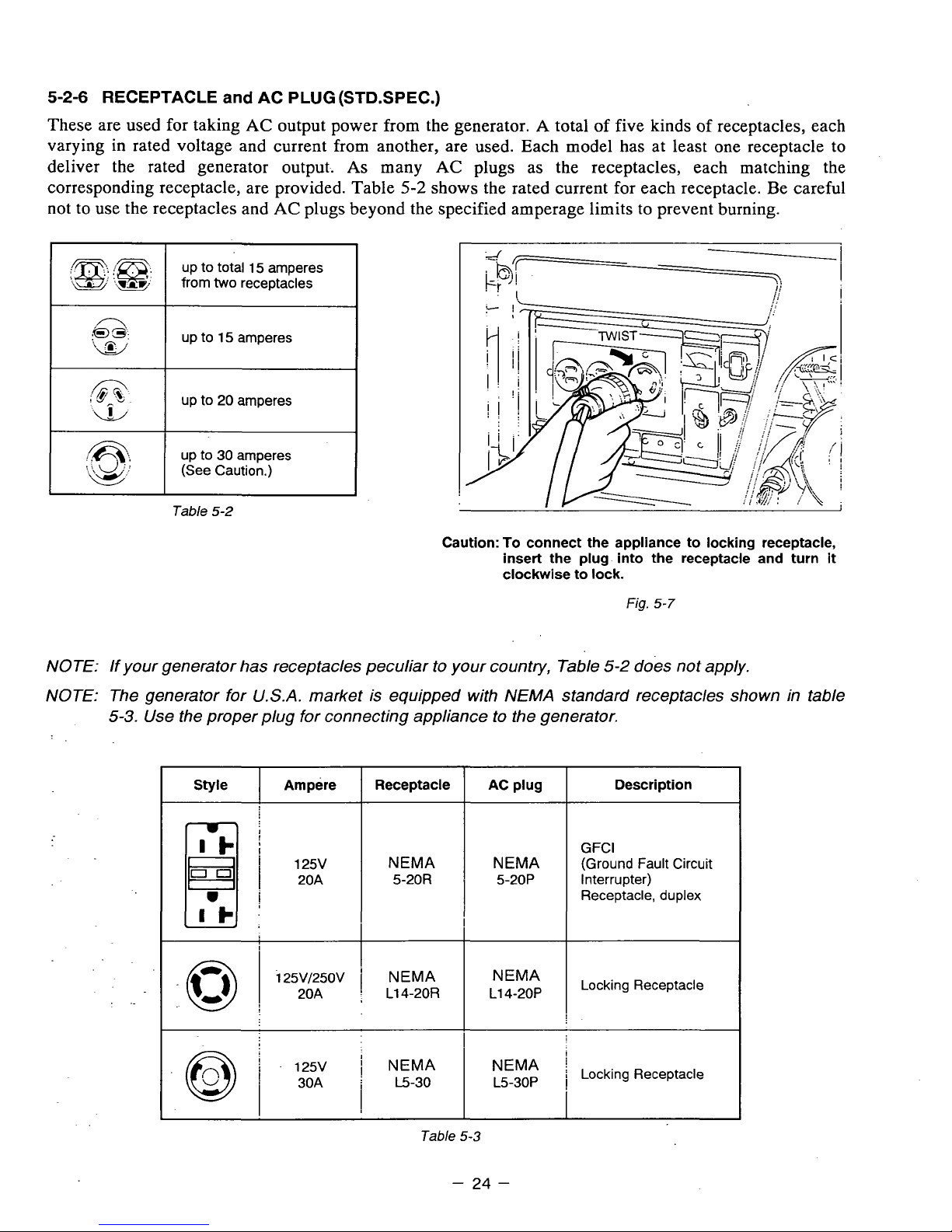
5-2-6
RECEPTACLE
and
AC PLUG (STD.SPEC.)
These are used for taking
AC
output power from the generator. A total
of
five kinds of receptacles, each
varying in rated voltage and current from another, are used. Each model has at least one receptacle to
deliver the rated generator output.
As
many
AC
plugs as the receptacles, each matching the
corresponding receptacle, are provided. Table
5-2
shows the rated current for each receptacle. Be careful
not to use the receptacles and
AC
plugs beyond the specified amperage limits to prevent burning.
I
I
up
to
30
amperes
(See Caution.)
I
I
Table
5-2
Caution:
To
connect the appliance to locking receptacle,
insert the plug into the receptacle and turn it
clockwise to lock.
Fig. 5-7
NOTE: If your generator has receptacles peculiar to your country, Table
5-2
does not apply.
NOTE: The generator for
U.S.A.
market is equipped with
NEMA
standard receptacles shown in table
5-3.
Use the proper plug for connecting appliance to the generator.
Style
Ampere
125V
20A
Receptacle
NEMA
5-20R
NEMA
L14-20R
AC plug
NEMA
5-20P
NEMA
L14-20P
Description
GFCl
(Ground Fault Circuit
Interrupter)
Receptacle, duplex
Locking Receptacle
NEMA
Locking Receptacle
L5-30P
Table
5-3
-
24
-
Page 27
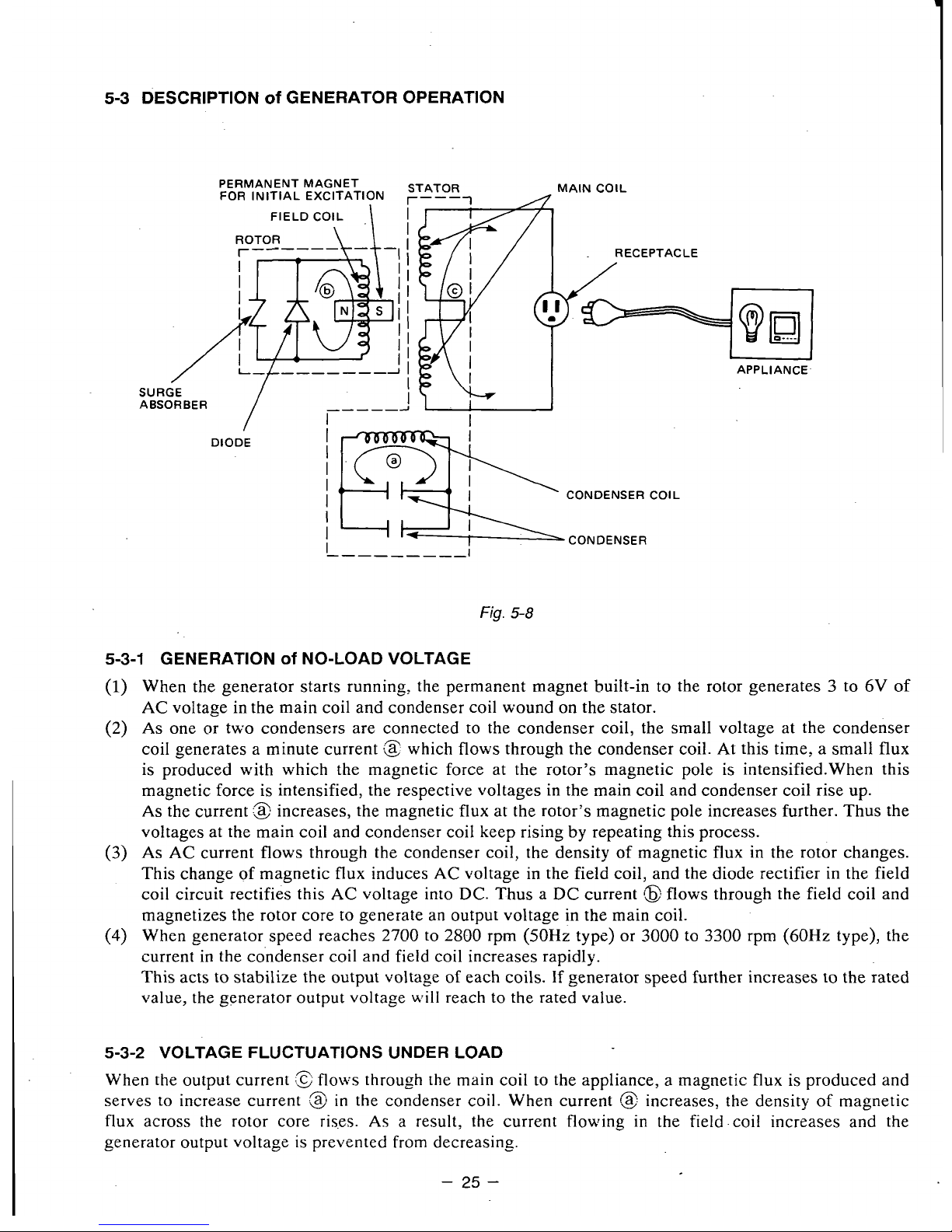
5-3
DESCRIPTION
Of
GENERATOR OPERATION
PERMANENT MAGNET
FOR
INITIAL EXCITATION
STATOR MAIN COIL
.
RECEPTACLE
SURGE
ABSORBER
'""""_I
Fig.
5-8
5-3-1
GENERATION
Of
NO-LOAD VOLTAGE
When the generator starts running, the permanent magnet built-in to the
rotor
generates 3 to 6V of
AC voltage in the main coil and condenser coil wound
on
the stator.
As
one
or
two condensers are connected
to
the condenser coil, the small voltage at the condenser
coil generates a minute current
!z
which
flows
through the condenser coil. At this time: a small
flux
is produced with which the magnetic force
at
the rotor's magnetic pole is intensified.When this
magnetic force
is
intensified, the respective voltages
in
the main coil and condenser coil rise up.
As
the current
:s
increases, the magnetic
flux
at the
rotor's
magnetic pole increases further. Thus the
voltages at the main coil and condmser coil keep rising
by
repeating this process.
As AC current flows through the condenser coil, the density of magnetic
flux
in the rotor changes.
This change of magnetic
flux
induces
AC
voltage in the field coil, and the diode rectifier
in
the field
coil circuit rectifies this AC voltage into DC. Thus a DC current
(8
flows
through the field coil and
magnetizes the rotor core
to
generate
an
output voltage
in
the main coil.
When generator speed reaches
2700
to
2800
rpm (50Hz type)
or
3000
to
3300
rpm (60Hz type), the
current
in
the condenser coil and field coil increases rapidly.
This acts to stabilize the output voltage of each coils.
If
gene.rator speed further increases to the rated
value, the generator output voltage
will
reach to the rated value.
5-3-2
VOLTAGE FLUCTUATIONS UNDER LOAD
When the output current
:g
flows through the
main
coil to the appliance, a magnetic
flux
is
produced and
serves to increase current
;zn
in
the condenser coil. When current
83
increases, the density
of
magnetic
flux
across the rotor core rises.
As
a
result, the current flowing
in
the field -coil increases and the
-
generator output voltage is prevented from decreasing.
-
25
-
Page 28

i
5-3-3
FULL
POWER
SWITCH
(Dual Voltage Type)
The full power switch is provided for the dual voltage type to take out the full rated power from
one
receptacle
in
each voltage.
1201240V
r
"-:(or
11OI220V)
I
43l
240V
(or
220V)
Fig.
5-9
MC,
I
Rec.
1
1
Fig.
5-
10
-
I
"
-
Switch
:
LOWER VOLTAGE
HIGHER VOLTAGE
Position
I
RECEPTACLE
1
RECEPTACLE
ll0V
I
or
:
Rated output
No
output can
be
:aken.
120v
:
1 10:'220v
120i240V
or
I
Half
of
rated
output
Rated output
I
1
Table
5-4
-
26
-
Page 29

Two main coils
are
wound over stator core. Each main coil outputs half the rated power at the 1owe.r
voltage (llOV or 120V). These main coils are wound to be in the same phase. The full power switch
reconnects these main coils in parallel or in series.
Fig.
5-9
shows a circuit diagram.When the full power switch is set for single lower voltage indication
(11OV or
12OV),
the switch position is as indicated by the lower solid line in the diagram. Fig.
5-10
is
a
simplified representation of this circuit, showing the two main coils connected in parallel.In this case, the
higher voltage -(220V or 240V) at Rec.
3
cannot be taken out. Rec. 2 for the lower voltage can output up
to the rated power (up to
30A
if the rated current is over
30A),
and Rec. 1 can output up to a total of
15A.
When the full power switch is
set
for double voltage indication (110V/220V or 120V/240V), the switch
position is as indicated
by
the upper dotted line in Fig.
5-9.
Fig.
5-11
is a simplified representation of this
circuit, showing the two main coils connectea in series. In this case, power can be taken simultaneously
from the receptacles for the both voltages. Rec.
3
for the higher voltage can output up to the rated power,
but Rec.
1
and Rec. 2 for the lower voltage can output only up to half the rated power each.
Table
5-4
is a summary of the above explanation. Select the proper output voltage by full power switch in
accordance with the appliance to be used.
5-3-4
VOLTAGE CHANGEOVER SWITCH
The generator of
50Hz
110V/220V dual voltage type for
U.K.
is provided with voltage changeover
switch instead
of
full power switch.
The output voltage
is
selected from llOV and 220V by turning this switch and both voltages cannot be
taken out simultaneously.
CHANGEOVER
VOLTAGE
11ov
SWITCH
RECEPTACLE
PTACLE
-
-
-
Fig.
5-
12
-
27
-
Page 30

6.
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Use extreme caution near fuel. A constant danger of explosion or fire exists.
Do
not fill the fuel tank while the engine is running.
Do
not smoke
or
use opern flame near the fuel
tank. Be careful not to spill fuel when refueling.
If
spilt, wipe it and let dry before starting the engine.
Do
not place inflammable materials near the generator.
Be careful not to put fuel, matches, gunpowder, oily cloth, straw, and any other inflammables near the
generator.
Do
not operate the generator in a room,cave or tunnel. Always operate in a well-ventilated area.
Otherwise the engine may overheat and also, the poisonous carbon monoxide contained
in
the exhaust
gases will endanger human lives. Keep the generator at least
1
m
(4
feet) away from structures or
facilities during use.
Operate the generator on a level surface.
If
the generator is tilted or moved during use, there is a danger of fuel spillage and a chance that the
generator may tip over.
Do
not operate with wet hands or in the rain.
Severe electric shock may occur.
If
the generator is wet by rain or
snow,
wipe it and thoroughly dry
it
before starting.
Don't pour water over the generator directly nor wash
it
with water.
If
the generator
is
wet with water, the insulations will be adversely affected and may cause current
leakage and electric shock.
Do not connect the generator to-the commercial power lines.
This
may cause a short-circuit or damage to the generator.Use a transfer switch for connecting with
indoor wiring.
NOTE: The parts numbers of the transfer switches and of the plastic box to store them are as
shown in Table
6-1.
!
Part No.
j
Part Name
'
Q'ty
'
Phase
Allowable Current
!
365-45604-08
1j1j
60A
340-45606-08
j
Transfer Switch
30A
1
I
367-45605-08
,
Transfer Switch
I
1
15A
1
1
Transfer Switch
!
367-43008-08
I
Plastic
Box
30A
1
1
i
348-43009-08
j
Plastic
Box
I
1'1
i
60A
Table
6-
7
Be
sure to check and remedy
the
cause
of
circuit breaker tripping before re-setting
it
on.
CAUTION
:If the circuit breaker tripped
off
as a result of using an electrical appliance,the cause
can be an overload
or
a short-circuit. In such a case, stop operation immediately and carefully
check the electrical appliance and
AC
plugs for faulty wiring.
-
28
-
Page 31

7.
RANGE
OF
APPLICATIONS
Generally, the power rating of an electrical appliance indicates the amount
of
work that can be done by
it.The electric power required for operating an electrical appliance is not always equal to the output
wattage of the appliance. The electrical appliances generally have a label showing their rated voltage,
frequency, and power consumption (input wattage). The power consumption
of
an electrical appliance is
the power necessary for using it.When using a generator
for
operating an electrical appliance,the power
factor and starting wattage must be taken into consideration.
In
order to determine the right size generator, it is necessary to add the total wattage of all appliances to
be connected
to
the unit.
Refer to the followings to calculate the power consumption of each appliance or equipment by
its
type.
Incandescent lamp, heater, etc. with a power factor
of
1
.O
Total power consumption must be equal to or less than. the rated output of the generator.
Example:
A
rated 3000W generator can turn thirty lOOW incandescent lamps
on.
Fluorescent lamps,mercury lamps, etc. with a smaller power factor
Select a generator with a rated output equivalent to 1.2 to 2 times
of
the power consumption of the
load.
Example:
A
400W mercury lamp requires 600W to 700W power source to be turned
on.
A
rated 3000W generator can power four or five 400W mercury lamps.
NOTE1: If
a
power factor correction capacitor is not applied to the mercury lamp or fluorescent
lamp, the more power shall be required to drive those lamps.
A
rated
3000
W
generator can drive one or
two
400
W
mercury lamps without power factor
correction capacitors.
NOTE2: Nominal wattage
of
the fluorscent lamp generally indicates the output wattage
of
the
lamp.
Therefore, if the fluorescent lamp has no special indication
as
to the power consumption,
efficiency should be taken into account
as
explained in Item
(5)
on
the following page.
Motor driven tools and light electrical appliances
Generally the starting wattage
of
motor driven tools and light electrical appliances are 1.2 to 3 times
lager than their running wattage.
Example:
A
rated 250W electric drill requires a 400W generator to start it.
Initially loaded motor driven appliances such as water pumps,compressors,etc.
These appliances require large starting wattage which
is
3
to 5 times of running wattage.
Example:
A
rated
900W
compressor requires a 4500W generator to drive it.
NOTEi: Motor-driven appliances require the aforementioned generator output only at the starting.
Once their motors are started, the appliances consume about
1.2
to 2 times their rated
power consumption
so
that the excess power generated by the generator can be used
for other electrical appliances.
NOTE2
Motor-driven appliances mentioned
in
ltems
(3)
and
(4)
vary
in
their required motor
starting power depending on the kind of motor and start-up load. If it is difficult to
determine the optimum generator capacity, select a generator with
a
larger capacity.
-
29
-
Page 32

(5)
Appliances without any indication as to power consumption
Some appliances have no indication as to power consumption; but instead the work load (output) is
indicated. In such a case, power consumption is to
be
worked out according to the numerical formula
mentioned below.
(Output
of
electrical appliance)
(Efficiency)
=
(Power consumption)
Example
1
:
Example
2:
Efficiencies of some electrical appliances are as follows:
Single-phase motor
- - - - - -
.
.
- -
- -
-
-
0.6
-
0.75
The smaller the motor, the
Three-phase motor
- - -
- -
- - - -
- -
-
0.65
-
0.9
lower the efficiency.
Fluorescent lamp
.
. . . . . .
. . . .
.
. . . .
. .
.
0.7
-
0.8
A
40W fluorescent lamp means that its luminous output
is
40W.
Its
efficiency
is
0.7
and
accordingly, power consumption will be 40
+
0.7=
57W.
As
explained in
Item(2),
multiply
this power consumption value
of
57W by
1.2
-
2 and you will get the figure
of
the necessary
capacity of a generator. In other words, a generator with a rated output
of
1000Wcapacity
can light nine to fourteen 40W fluorescent lamps.
Generally speaking, a
400W
motor means that its work load
is
400W. Efficiency of this
motor is
0.7
and power consumption will be
400
+
0.7= 570W. When this motor
is
used for
a motor-driven tool: the capacity of the generator should be multiple of 570W by 1.2 to
3
as
explained
in
the
Itern(3).
570(W) X 1.2-3=684(W)-1710(W)
MODEL
1
I
RGV2200
Frequency 50Hz
i
60Hz
i
lncandesent lamp,
heater, etc.
1
14OOW I 1800W
Fluorescent lamp,
mercury lamp, etc.
Electric tool etc.
approx.
I
approx.
1
700W
1
9OOW
approx.
I
approx.
400W
'
400W
RGV2600 RGV4000 RGV6000
I
I
I
I
-
I
50Hz 60HZ
1
50Hz
!
60Hz
1
50Hz
'
i
60Hz
I
I
2000w
2200w
3000W j 3500W
1
4400W I 4800W
I
i
I
I I I
I
I
approx. approx.
I
approx.
I
approx.
I
approx.
approx.
lOOOW
j
1100W
1
1500W
1
1800W
\
2000W
I
2350W
!
I
i
approx. 1 approx.
1600W
!
16OOW 18OOW
I
2000W
800W
i
800W
approx.
1
approx. 1 approx. j approx.
approx.
I
approx. approx. approx. approx. approx. approx. app:ox.
Pump. compressor, etc.
I
300W
i
400W
I
400W
I
400W
:
750W
I
750W 800W
1
800W
i
Table
7-1
-
30
-
Page 33

NOTES: Wiring between generator and electrical appliances
1.
Allowable current of cable
Use a cable with an allowable current that
is
higher than the rated input current of the load
(electrical appliance).
If
the input current
is
higher than the allowable current of the cable used, the
cable will become excessively heated and deteriorate the insulation, possibly burning. it out.
Table 7-2 shows cables and their allowable currents for your reference.
If a long cable is used, a voltage drop occurs 'due to the increased resistance in the conductors
decreasing the input voltage to the load (electrical product). As a result, the load can be damaged.
Table 7-2 shows voltage drops per
100
meters of cable.
2.
Cable length
Nominal
cross
dia.
mm2
I
No.
1
A
I
No.
lmm
I
0.75
2.0
8
13
i
17
i
3710.26
50
/
0.18
12 16 1.27
18 7
1
3010.18
3.5
1
12-10
I
23
45 10.32
5.5
70 10.32
25 10-8
T
I
Resistance Flowing Current
Qil00m
1
1A
1
3A
I
5A
I
8A
1
10A
1.486 1.5V 5V
1
7.5V 12V 15V
2.477 2.5V 8V 12.5V
,
-
-
0.952
I
1 V 1 3V
8V
1
1OV 5V
I
0.517
j
-
!
1.5~ j 2.5V , 4~ 1 5~
I I
I
0.332
I
-
1V ! 2V I 2.5V
3.5V
I
I
Table
7-2
1
Voltage drop indicates as
V
=
100
XRXIXl
R
means resistance
( 0 !lo0
m)
on
the above table.
I
means electric current through the wire
(A).
8
means the length
of
the wire (m).
The length of wire indicates round length,it means twice the length from generator to electrical tools.
-
31
-
Page 34

8.
MEASURING PROCEDURES
8-1
MEASURING INSTRUMENTS
8-1-1
“Dr.
ROBIN”
GENERATOR TESTER
The “Dr. Robin”generator tester
is
exclusively
designed for fast, easy diagnosis and repair of.
Robin generators.
The “Dr. Robin” has the following features:
(1)
Functions of voltmeter, frequency meter,
meggertester, capacitance meter and circuit
tester are combined in one unit.
(2)
Fast and easy readout by- digital indicator.
(3)
Built-in automatic battery checker indicates
(4)
Tester and accessories are installed
in
a
the time to change batterie.s.
handy, sturdy case
for
easy carring.
0
SPECIFICATIONS
Fig.
8-1
Model
-I
Dr.
Robin
~
Part Number 388-47565-08
Voltage
0-5OOV AC
Q)
p!
,
Frequency
25-70HZ
[r
.G
Resistance
-
m
z
Condenser Capacity
m1
0.1 -1.999
Q
10-1
00
,E
F
L
3
m
a,
I
I
lnsuiation Resistance
3M
R
_____
Circuit Protector
1
Fuse
Power Source
I
2 x 6F44P (006P)
Dry
Cell Battery
I
Test leads with needie probes
.
.
‘1
set
Test leads with jack plugs
. .
. .
.
.
1
set
Accessories
Dimensions
(L
X
W X H)
i
285 mrnx200 rnmxl10
rnrn
Weight
1.6kg
Table
8-
1
The
“Dr.
Robin”generator tester can be ordered from Robin generator distributors by the following part
number.
I
Dr. Robin
Part
Number
:
388-47565-08
I
If
you do not
have
a
”Dr.
Robin“generator tester,use the instruments described
in
the following section
for
checking generator
parts.
-
32
-
Page 35

8-1-2
INSTRUMENTS
(1)
VOLTMETER
AC voltmeter
is
necessary.The approximate
AC voltage ranges
of
the
voltmeters to be
used for various types
of
generators are as
follows:
0
to 15OV: Type with an output voltage
of
110
or
120V
0
to 300V: Type with an output voltage
of
220,230 or 240V
0
to 15OV, 0 to 330V: Dual voltage type
(2)
AMMETER
AC ammeter
is
necessary. An AC ammeter
with a range. that can be changed according to
the current rating of a given generator
is
most
desirable. (About 10A, 20A, 100A)
FREQUENCY METER
Frequency range
:
About
45
to
65Hz
NOTE:
Be careful of the frequency
input voltage range.
meter’s
.-
””-
I
FOR
AC
Fig.
8-2
FOR
AC
Fig.
8-3
.,
r
I
!
Fig.
8-4
-
33
-
Page 36

(4)
CIRCUIT TESTER
Used for measuring resistance,
etc.
Fig.
8-5
(5)
MEGGER TESTER
!
Used for measuring generator insulation
resistance.
Select one with testing voltage range of
5OOV.
I
Fig.
8-6
(6)
ENGINE TACHOMETER
There are various types of tachometers,
such
as contactlzss type, contact type, and strobe
type. The contact type can be used only when
the generator and engine have been dis-
assembled. The contactless type
is
recommended.
The PET-2100E engine tachometer
is
available from your Robin distributors.
Please inquire by the part number PET-2100E.
I I
!
I
Fig.
8-7
!
-
34
-
Page 37

8-2
AC OUTPUT MEASURING
TO
AC
RECEPTACLE
Fig.
8-8
Use a circuit like the shown in Fig.8-8 for measuring AC output. A hot plate
or
lamp with a power factor
of
1.0
may be used as a load. Adjust the load and rpm. and check that the voltage range is as specified in
Table
8-2
at the rated amperage and rated rpm.
Rated
voltage
21 6-264V 198-242V 108-1 32V 99-121V
Voltage range
240V
220v
1 20v 110v
Table
8-2
8-3
MEASURING INSULATION RESISTANCE
Use a "Dr. Robin"generator tester in megger tester
mode
or
use a megger tester to check the
insulation resistance. Connect a megger tester to
one of receptacle. output terminals and the ground
terminal, then measure the insulation resistance.
An insulation resistance
of
1
megohm
or
more is
normal. (The original insulation resistance at the
time of shipment from the factory
is
10
megohm
or more.)
If
it is less than 1 megohm, disassemble the
generator and measure the insulation resistance of
the stator, rotor and control panel individually.
0
STATOR
(1)
Measure the insulation resistance between
(2)
Measure the insulation resistance between
(3)
Measure the insulation resistance between
(4)
lMeasure the insulation resistance between
BLUE lead and the core.
WHITE lead and the core.
YELLOW lead and -the core.
BROWN lead and the core.
Fig.
8-10
-
35
-
Page 38

0
ROTOR
.
..
Measure the insulation across one
of
the soldered
terminals
of
the rotor and the core.
0
CONTROL PANEL
Measure the insulation resistances between the
live parts and the grounded parts.
I\
I
Fig.
8-
1
1
Any part where the insulation resistance is less than 1MQ has faulty insulation, and may cause electric
leakage and electric shock.
Replace the faulty part.
-
36
-
Page 39

9.
CHECKING FUNCTIONAL MEMBERS
9-1
PILOT LAMP
and
VOLTMETER
Check the pilot lamp and the voltmeter if it is
turned
on
by applying specific voltage.
Pilot lamp and voltmeter cannot be checked with
'
circuit tester because its resistance is too large.
I
(See Fig.9-1.)
Fig.
9-1
Pilot lamp should be turned
on
at
70
to
12OV.
9-2
AC RECEPTACLES
Using a "Dr. Robin"or a circuit tester, check continuity between the two terminals at the rear of the
AC
receptacles while the receptacle
is
mounted on the control panel. When continuity
is
found between the
output terminals of the rece.ptacle with a wire connected across these terminals, the
AC
receptacle is
normal. When the wire
is
removed and no continuity
is
found between these terminals, the receptacles
are also normal.
&
.I:
AC RECEPTACLE
.:
I
I
Fig.
9-2A
Fig.
9-28
-
37
-
Page 40

9-3
CIRCUIT BREAKER
Check continuity between each
of
two terminals at
the rear
of
the circuit breaker while it is mounted
on
the control panel. Normally, there is continuity
be.tween each
of
the two when the circuit breaker
is
on
while there
is
no
continuity when the circuit
breaker is off.
-
..
..
..
9-4
STATOR
Disengage connectors
on
the wires from stator and
check the resistance between wires with a "Dr.
Robin"
or
a
circuit tester refering
to
the following
table.
Fig.
9-3
Fig.
9-4
(Rxl!!
+lo%)
I
Specification
AC Winding
I
i
Hz
I
I
Condenser Winging
Voltaae
Black!
Blue
.
I
~ Yellow
iYellow
White / Red
...
I
11 ov, 220v, 1.1 OVl22OV
4.48
..
1.96
j
1.96
50
I
I.
.,
I
240V
1.24
!
220V,~ llOV/220V
.
1
.
1.24
4.48.
. .
2.33
2.33
RGV2200
'
.
60
3.46
..
-
1
~OV.
I~OV~~~OV
..I
1.24
.
3.46.
.
-,
1.24
I
I
11
ov.
220v, 11 OV/220V
2.64
:
1
.oo
1
.oo
i
50
RGV2600
240v 2.64 1.19
1.19
..
220v, 1 1 OV:'220V
i
0.75
0.75
.
.!
1
;99.
60
I
I
120V, 120Vi240V 0.75
.
0.75
.
:
..
-!
1.99
I
r;n
I
110V. 220V. 110Vj220V
.
0.70
I
.
0.70
1.
".
1 :44
I
I
j
4"
240V 0.83
I
0.83 1.44
RGV4000
.
'
'
-1
-
..
I
220v. 1 1 OV!220V
0.54
.
__
j
-
0.54
j.
1.03
I
-60
j
120V. 120V/240V 0.54 0.54
i
'
-1.03
I
11
ov.
220v. 11 ovi220v
i
!
0.33 0.33
0.39
.j
50.
0.79
240V
!
RGV6000
.
.
I
.
0.39
0.79
..
220v. 1 lOV/220V
.
I
0.24 0.56 0.24
::
60
,
. .-
.r
!.
!
120v. 120vi240v 0.24
.
-0.56
:.
.
.
-0.24
..
.
.
Table
9-
1
NOTE:-
If--the--circuit tester is not sufficiently accurate, it may not show the values given and may give
erroneous readings.
Erroneous readings will also occur when there is a wide variation
0-f
resistance among coil
windings or when measurement is performed
at
ambient temperatures different from
ZO"C(68"F).
..
-
38
-
Page 41

9-5
ROTOR
ASSEMBLY
(1)
Using a "Dr.
Robin"
or a circuit tester, measure the resistance
of
the field coil
at
the terminals.
(RxlQ
&lo%)
MODEL
RGV6000
RGV4000 RGV2600
RGV2200
RESISTANCE
I
2.52
R
1.60
R
1.77
R
2.04
R
I
Table
9-2
NOTE
1:
Because a diode is soldered to the coil
ends at the terminals, resistance may
be measured only when tester probes
touche the terminals in one combination of polarity. Therefore, if no resistance reading appears, try checking
in reverse polarity.
NOTE
2:
If the circuit tester is not sufficiently
accurate, it may not show the values
given and may give erroneous
readings.
Erroneous reading will also occur when
there is a wide variation of resistance
among coil windings or when meas-
urement is performed at embient temperatures different from
2OoC(68"F).
9-6
CONDENSER
W
Use a
"Dr.
Robin" in capacitance meter mode
to
check the capacity
of
condensers. (See Fig.9-6).
Fig.
9-6
3
RGV4000, RGV6000
I
NOTE:
Be sure to discharge condensers by shorting condenser leads each other before checking their
capacitance,or the accurate reading cannot be obtained.
-
39
-
Page 42

I
W
NORMAL CAPACITY OF CONDENSER
MODEL
RGV6000 RGV4000
RGV2600
RGV2200
Resistance
282FX2
202FX2
.
24kF
17~F
Table
9-3
I
If
such
an instrument is unavailable, the condenser can be checked
by
replacing with a new one.
If the generator performs good with new condenser, the cause of trouble
is
defect
in
original
condenser.
.
-
..
9-7
DIODE
RECTIFIER
DIODE RECTIFIER
Brown
Brown/
White
..
Brown
Orange
Brown
Brown
CIRCUIT TESTER
~.
Fig.
9-9
Fig.
9-
10
..
Circuit -inside
of
the diode rectifiers is
as
shown
in
Fig.
9-9.
Check continuity between each terminal
b!
using a circuit tester as shown
in
Fig.
9-10.
The rectifier is normal when condtinuity
is
as
follows:
.
..
..
...
W
Checking table
..
for analogue c.ircuit tester.
I
Apply black Sneedle
of
the circuit tester
.
-
Analogue. circuit tester
i
I
Brown
i
Brown
i
Orange
i
Brown:White
i
I
!
:
Brown
I
No
continuity
No
continuity
j
Continuity
.. . .
..
I
I
r-"
I
..
I
Brown
Apply red
3
.needle
No
continuity
Orange
I
Continuity
I
Continuity
,
Continuity
-of
ttie circuit tester
I
NO
continuity Continuity
Brown;White
No
continuity
j
No
continuity
j
No
continuity
?"-..,
I
-
40
-
Page 43

W
Checking table for digital circuit tester.
Apply red
@J
needle
of
the circuit tester
Digital circuit tester
Brown
1
Brown
BrownWhite
Orange
Brown
Continuity
No
continuity
No
continuity
-
Apply black @ needle
of
the circuit tester
Brown
Continuity Continuity Continuity
Orange
No
continuity Continuity
NO
continuity
1
!
I
Brown,White
No
continuity
No
continuity
No
continuity
NOTE
1:
NOTE
2:
NOTE
3:
Table
9-4-2
Because of the difference of measuring method between the analogue circuit tester and the
digital circuit tester, polarity
of
tester needles should be reversed.
“Continuity” means forward direction characteristics of the diode, and different from short
circuit condition (in which a pointer of the tester goes out of its normal scale), shows
resistance to some extent. When results of the checking indicates failure even in one
section,replace with a new one.
Some analogue testers like “Simpson” brand operate as same as digital testers.
10.
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
10-1
PREPARATION
and
PRECAUTIONS
1)
Be sure to memorize the location of individual parts when disassembling the generator
so
that. the
generator can be reassembled correctly. Tag the disassembled part with the necessary information to
facilitate easier and smoother reassembly.
2)
For more convenience,divide the parts into several groups and store them in boxes.
3)
To
prevent bolts and nuts from being misplaced
or
installed incorrectly, replace them temporarily to
4)
Handle disassembled parts with care; clean them before reassembly using a neutral cleaning fluid.
5)
Use
all disassembly .‘assembly
tools
properly, and
use
the proper tool
for
each specific job.
their original position.
10-2
SPECIAL TOOLS
for
DISASSEMBLY
and
ASSEMBLY
Part Number
:
388-95001
-07
Part Name
:
REAR COVER PULLER
REAR
COVER
PULLER
-
41
-
Page 44

-
Step
Description
I
Remarks
Part
to
remov
Front Panel
.-
'.
Tool
..
10
mm spanner
or
box wrench
(1)
Take off
the
four
bolts
and remove the
-
.
front panel
from
the frame.
~
-
(See Fig.
10-
1
.)
..-
.
.
.
..
t
t
i
.-
.
..
.
.
..
..
.
(2)
Disconnect the connectors on the wiring
.
~~
beween the-front panel and the engine.
. - .
-
-
(SeeFig.
10-2.)
.
.
..
-1
." .
.-
,
..
.-
.
..
..
..
i.
..
.
...
..
.
,.
Fig.
10-1
f
..
1.
."
(.3)
Take
off
the bushing from the bottom of
.-
the front panel.
.
(See
Fig.
10-2.:)
(4)
Disconnect the connectors on the wiring
from
the front panel to'the alternator.
'(See
Fig.
10-1.)
..
-
..
.
:..
:
!
.
.-
Press the upper end of
the bushing and pull
out:
I
-.-
:.
i..
..
.
-.
...
..
..
FIG.
10-3
-
42
-
Page 45

Step
2.
..
I
..
.
.
..
.
'art to remove
Fuel Tank
-
..
.
..
..
-
-Description
.
-1
..Remarks
(I)
Discharge fuel from the
tank:
-
.
Use utmost .care about
1:
Shut the fuel strainer. .fire hazard.
.
-
2.
Remove the-strainer cup.
3.
Put a vessel to receive fuel under the - Wipe off spilt fuel
strainer and open the -fuel. cock to thoroughly.
discharge fuel:(See Fig.
10-4.)
body.
screen.
4.
Attach the strainer cup
to
the strainer Do not lose the filter
..
I
:I
.
;;
.
1;
Fig.
10-4
-
I
(2)
Disconnect fuel hose from. the strainer.
'
Loosen the hose clamp on the top of the
i
strainer and
pull
out the fuel hose
from
the strainer. (See
Fig.
10-5.)
(3j
Take
off
the four
nuts
and remove the
fuel tank. (See Fig.
10-6.1
I
T
I
Tool
-.
Pliers
10
mm
spanner
or
box
wrench
Fig.
10-5
Fig.
10-6
-
43
-
Page 46

Step
3.
Part
to remove
Muffler and
l4uffler
Cover
Description
!
Remarks
(1)
Remove the rear plate from the frame.
The rear plate
is
welded
(Except for
RGV6000)
to the frame of the
6X 12mm
flange bolt
.........
.2
pcs.
I
RGV6000.
(2)
Remove the two bolts which
fix
the muffler to the alternator.
Loosen the two
nuts
on the muffler flange and remove the muffler
from the engine.
8X20mm
bolt and washer ass'y
.....
2
pcs.
8mm
stainless
nut
................
2
pcs.
8mm
spring washer
for
RGV4000
and
RGV6000
.......
2
pcs.
Muffler gasket
..................
1
PC.
(3)
Remove
the
muffler
cover 1 and the muffler cover 2 from the muffler.
6X lOmm
bolt and washer ass'y
-
.
8
pcs.
(See
Fig.
10-8.)
(3)
For
RGV6000
only:
Remove
the muffler bracket from the rear cover.
8X20mm
bolt and washer ass'y
...
2
pcs.
~cIUFFLER COVER
1
A
M.ilL!FFLER COVER
2
for
RGV6000
only
FAUFFLER BRACKET
Tool
10
mm
spanner
or
box wrench
12
mm
spanner
or
box
wrench
10
mm
spanner
or
box wrench
12
mm
spanner
or
box
wrench
FIG.
10-7
-
44
-
Page 47

Dart to remove
Pipe Frame
Description
(1)
For RGV6000:
Remove
the
fuel strainer from
the
frame.
(2)
Remove the
nuts
which are fixing engine
and alternator to
the
mount rubbers.
(See Fig.
10-8.)
(3)
Using a chain-block, sling up
the
engine
and alternator and dismount from
the
frame.
Remarks
Remove the
air
cleaner
cover for easier
dismounting.
Fig.
10-8
(3)
Remove the mount rubbers from the
’
frame.
Loosen the
nuts
on
the bottom side
of
the frame. (See Fig.
10-9.)
Tool
12
rnm spanner
12
mm spanner
or
box wrench
MOUNT
RUBBER
,
0
Fig.
10-9
-
45
-
Page 48

'art
to remove
Rear Cover
-
Description
(1)
Remove the end cover. (See Fig.
10-10.)
64
bolt.
..............
.4
pa.
(2)
Take off the rear cover.
1.
Remove the four bolts which fasten
the rear cover to the front cover.
64
bolt.
...............
.4
PC-,
2.
Use. a special tool "REAR COVER
PULLER" to remove
the
rear cover.
a) Insert the two screws of the special
tool into the thread holes of
the
rear
cover.
b)Apply the center bolt of the special
tool on the head of the through bolt.
c)Tighten the center bolt to
pull
out
the rear cover.
Remarks
Insert the
two
screws
sufficiently and evenly,
or
the thread hole may be
damaged at removing.
Tool
10
mm
spanner
or
box wrench
10
mm spanner
or
box wrench
Fig.
10-10
Fig.
10-1
1
!
In
the case that
"RE.AR
COLER PULLER'' is unavailable, remove the
I
rear cover
by
the follow-ing instructions.
I
3.
Hit
on
the
boss
and legs of rear
Do
not give a
strong
hit
Box
Lvrench
cover with a plastic hammer to
;
on the boss
or
legs.
I
Plastic hammer
loosen.
i
i
Fig.
10-12
Fig.
10-13
-
46
-
Page 49

-
Step
6.
'art
to
remove
Startor
.
. - .
.Description
~
.
Tool
. .~
-
-
Remarks
I
I
(1)
Remove
the
four bolts which fasten
the
stator
to
the
rear cover.
(See Fig. 10-14.)
~~~ ~ ~ ~~~~~~~~~
6~
BOLT
. . . . .
.
4
pcs.
..
,60
SPRING
WASHER
. . . . .
.
.
.
.4
pcs.
-.
.
Fig.
10-14
(2)
Put a piece of .lumber
on
the floor
in.
I
upright position.
I.
-.
(See Fig.
10-15.)
I
I
(3)
Hold
the
rear cover and stator upside
down
with
both hands.
(4)
Down
the rear cover and stator over a
lumber lightly hitting
the
bottom of rear
I
cover to the top end of lumber to pull out
I
the
stator.
I
(See FIE. 10-16.)
i
I
~.
10
mm socket
wrench
I
I
"[NOTES]
1
1.
Apply
fingers- to stator coil to keep the stator from dr-opping
on
the floor.
2.
Gently
hit
the bottom of rear cover to-.the top end
of
lumber several times until the stator
comes out loose:'
I!
Fig.
10-15
Fig.
10-16
-
47
-
Page 50

-
Step
6.
-
-
..
Part to remove
I
Description
Remarks
Tool
Stator
Rotor
..
(5)
Take apart the
support
ring
and
stator
from
rear
cover.
SUPPORT
RING
\
60
BOLT
......
4
pcs.
60
SPRING
WASHER
.........
.4
pcs.
Q
WASHER
....
4
pcs.
Fig.
10-1
7
i
1
i
Take
off
the through
Dolt.
.Apply
a
box
nrench
on
the
head
of
I
through bolt. Hit the Lvrench handle
with
1
a hammer counter-clockwise to loosen.
j
Fig.
10-18
Box
lvrench
Plastic hammer
-
48
-
Page 51

Step
I.
-
I
Dart to remove
Rotor
Description
(3)
Use a bolt and oil as
a
tool for pulling
out rotor
in
the following procedures
:
1. Pour engine oil into the center hole of
rotor shaft.
Fill with oil
to
the shaft end.
(See Fig. 10-19.)
thread size:
2.
Prepare a bolt with the following
RGV2200,2600.
......
MIOXP1.25
RGV4000,6000..
....
.M12XP1.50
3.
Apply a few turns of seal tape around
the tip of the bolt.
Remarks
Tool
Fig.
10-19
4.
Screw~the bolt into the thread of the
rotor shaft.
5.
Torque the bolt using a socket wrench
until
the rotor comes
off
loose.
*
The hydraulic pressure inside the rotor
shaft takes apan the rotor from the
engine shaft.
Fig.
10-20
Do
not stick out your
face over the rotor.
It
may
jump
up
on
separation.
Socket wrench
(4)
Wipe .off oil thoroughly from rotor shaft
and
engine-PTO shaft.
I
Fig.
10-21
-
49
-
Page 52

-
Step
8.
-
Part
to
remove
Front Cover
Description Remarks
(1)
Remove the front cover.
Loosen the four
bolts
and
remove the
front cover.
86
bolt
.
. . .
. . . . . . . . . . . .4
PC-.
Fig.
10-22
Tool
12
mm
Socket
wrench
-
50
-
Page 53

10-4
ASSEMBLY PROCEDURES
10-4-1
FRONT
COVER
Attach the front cover to the engine main bearing
cover. Match the faucet joint and tighten the bolts.
M8
X
18mm bolt.
. . . .
.
4
pcs.
M8 spring washer
. . . .
.
4
pcs.
Tightening torque
120-1
40
kg-crn
11.8-13.7
Nm
8.7-10.1
ft4bS
10-4-2
ROTOR
(1)
Wipe off oil, grease and dust from the tapered
portion of engine shaft and matching tapered
hole of rotor shaft.
Tighten the through bolt.
Apply a wrench on the through bolt and hit
wrench handle clockwise with a hammer
to
tighten.
If
an impact wrench
is
available, use it.
(2)
Mount the rotor
to
the engine shaft.
Tightening torque
:
I
Tightening torque
IRGV
I
115-135
kg-cm
2200.2600
1 1.3-1 3.2
Nom
I
I
8.7-10.8
ft4bs
230-250
kgwn
RGV
4000,6000
22.5-24.5
Nom
16.6-1 9.5
ft*lbs
Fig.
10-23
Fig.
10-24
-
51
-
Page 54

10-4-3
STATOR
1
(1)
Put
the
stator
in
the
rear
cover
setting
the
four
i
grooves
on
the
side
of
stator
with
thread
holes
of
the
rear
cover.
i
......
e"----
60
BOLT
4
pcs.
60
SPRING
WASHER
/
..........
.4
pcs.
I
Tighten
the
four
bolts
tentatively
to
check
if
I
the
grooves
and thread
holes
are
aligned
I
correctly.
(See
Fig.10-25.)
!
pulling them out from the rear cover.
I
....
B-
60
WASHER
4
pcs.
NOTE : Be careful not to give cuts to wires when
(2) Remove
the
four
bolts.
i
a.
L
-
I
Fig.
10-25
(3)
Apply
the
support
ring
between
the
rear
cover
and
I
/
Tap on
the
support
ring
evenly
using
an
aluminum
bar
and a hammer
to
press
into
the
rear
cover.
(See
Fig.lO-26.)
(4)
Join
the
stator
to
rear
cover
with
four
bolts,
washers
and
spring
washers.
(See
Fig.
10-25.)
M6
bolt
.......................
M6
washer
....................
4
pcs.
4
pcs.
M6
spring
washer
...........
4
pcs.
80-1
00
kgwn
7.8-9.8
Nom
5.8L7.2
ft-lbs
NOTE: Tighten
four
bolts evenly taking several
steps.
The
dimensions
of
the
stator
bolts
are
shown
in
Table
10-1.
;
ALUMINUM
I
Fig.
10-26
MODEL
'
lI
S
id
!
65mm
1
15mm
RGV2200
,
2.56
inch i 0.59 inch
,
i
RGV2600
3.35
inch
'
85mm
!
20mm
j
M6x
,.o
'
2o
mm
I
M6
X
1.0
0.79 inch
I
95
mm
RGV4000
I
3.74 inch
;
0.79 inch
!
I
RGV6000
1
4.53 inch 1.57 irxh
:
115mm
I
40
mm
b.16
X
1.0
-1
Tab!e
70-
7
-
52
-
Page 55

10-4-4
REAR
COVER
(1)
Attach the bushing over the lead wire drawn out from the rear cover.
Press the smaller end
of
the bushing into the window
of
the rear cover. (See Fig.10-27.)
Fig.
10-27
Put the rear cover with stator over the rotor.
Tap
on
the rear cover evenly with a plastic
hammer to press the rotor bearing into the rear
cover.
Fig.
10-28
Fix
the rear cover to the adaptor with
bolts,
spring
washers, and washers.
M6
x
25
mm
bolt
..............
4
pcs.
4
pcs.
M6
spring washer
.............
4
pcs.
346
washer
.....................
50-60
kg-cm
4.9-5.9
Nom
3.6-4.3
ft-lbs
four
Fig.
10-29
-
53
-
Page 56

10-4-5
END
COVER
Attach the end cover
to
the rear cover.
M6
X
8mm flange bolt
-----.---..
4
pcs.
40-60 kg*cm
3.9-5.9 N-m
2.9-4.3
ft-lbs
10-4-6
FRAME
(1)
Attach the mount rubbers
to
the frame.
Insert the setting tongue of mount rubber into
the hole on the frame and tighten the nut from
the bottom of the frame.
M8
flange nut
. . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. .
.
.
4
pcs.
Tightening torque
120-1
40 kg-cm
1
1.8-1 3.7
Nom
8.7-1 0.8
ft*lbS
Fig.
10-30
r-
FRAME
UPPER
Fig.
10-31
NOTE
:
The mount rubbers are selected to reduce vibration most effectively by model.
Be sure to use the correct mount rubber for your generator.
Although mount rubbers have the same appearance, their characteristics are different.
(2)
Attach the 5 mm terminal
of
the grounding wires (green.:pellow) to the unpainted thread hole of the
frame base plate using
a
5
mm brass
scrsLv.
-
54
-
Page 57

(3)
Install the engine and alternator assembly into the frame.
Put the engine and alternator assembly into the frame from the side of
it.
Tighten the nuts over the mount rubber bolts to fix.
Mgnuts
..........................
4
pcs.
I
Tightening torque
1
120-1
40
kgwn
11.8-1.3.7
Nom
8.7-1
0.1
ftolbs
NOTE : Remove the air cleaner cover for easier installation.
NOTE
:
When tightening the nuts, slightly lift the engine and alternator assembly
so
that the weight is
not applied to the mount rubbers.
(4)
Fasten the other earth cable with 5 mm terminal
to the unpainted bolt hole on the frame.
(See Fig.10-32.)
(5)
Attach the rear plate frame.
(For
RGV2200,2600,4000 only)
"6 x 10
mm
bolt
..............
2 pcs.
Attach fuel tank mount rubbers to rear plates.
The nuts
€or
mount rubbers are welded
to
rear
plates.
I
Tightening torque
I
40-60
kg-cm
3.9-5.9
N-rn
2.9-4.3
f?*lbs
EARTH
CABLE
Fig.
10-32
REAR
PLATE
I
...
Fig.
10-33
-
55
-
Page 58

104-7
MUFFLER
and
MUFFLER COVER
(1)
For RGV6000 only:
(2) Attach the muffler cover
1
and the muffler cover 2 to the muffler.
Attach the muffler bracket to the rear cover. Tighten the bolts temporarily.
M6
X
lOmm bolt and washer Ass'y
-.-----
8
pcs.
7.9-9.8 Nom
5.8-7.2
ft*lbs
(3)
Put the muffler gasket
to
the engine.
(4)
Attach the muffler with muffler cover to the engine and the rear cover.
:&
Tighten the two nuts fou the muffler first.
P
Use
the spring washers €or RGV4000 and
RGV6000.
8mm
stainless nut.
...................
8mm spring washer..
.................
2 pcs.
2
pcs.
(for RGV4000 and RGV6000 only)
220-280
kgwn
21.6-27.4 Nom
15.8-20.2
ft-lbs
:z
Tighten the bolts to fix the muffler to the
A
rear cover.
M8
X20mm bolt and washer
Ass')'
.-.-.
2 pcs. (for RGV2200, 2600,
4000)
190-250
kg-crn
18.6-24.5 Nom
13.7-1 8.0
ft*lbS
is
For RGV6000 only:
Tighten the two bolts
to
fix
the muffler
bracket to.the 'rear cover: and .then the two
-..
bolts-for the muffler to the muffler bracket.
M8
X20mm
bolt and Lvasher
Ass'y
.....
-
.
3-pcs.
(for RGV6000 only)
190-250
kg-cm
18.6-24.5 Nom
13.7-1 8.0
ft*lbS
Fig.
10-35
-
56
-
Page 59

(5)
For
RGV2200, RGV2600 and RGV4000 only
:
Attach the rear plate to the frame.
M6
X
1Omm bolt
...............
2 pcs.
I
Tightening torque
I
40-60 kg-cm
3.9-5.9 Nom
2.9-4.3
ft*lbs
10-4-8
FUEL
TANK
(1)
For
RGV2200, RGV2600 and RGV4000 only
:
Attach the fuel strainer to the bottom
of
the fuel tank.
Screw in the fuel strainer all the way and return
one to two turns, and then lock it with the lock nut.
For
RGV6000
only
:
Attach the fuel strainer
to
the frame.
FUEL TAXK CAP
FUEL GAUGE
4.9-6.9 Nom
(2)
Mount the fuel tank
on
the frame with rubber
washers between the tank flange
and
the frame.
M6 X20mm bolt (black)
...........
Rubber \%-asher
........................
NOTE
:
For easy tank assembly, glue the rubber
/;.
washers over the mounting holes
of
the
Y'
frame.
(3)
Connect the rubber pipe.
First,
€it
the hose clamps
on
the rubber pipe
and connect
it
to
the strainer and the
carburetor. Then fasten
it
with the hose
HOSE
CUMP
clamps.
For
RGV6000,
connect the rubber pipe
to
the
strainer and the fuel tank
in
the same wag.
easier connection.
-
57
-
Fig.
10-36
Page 60

10-4-9 FRONT PANEL
-Mount the front panel assembly to the frame.
Refer to Section
10-5
for disassembly, checking and reassembly procedures of the front panel.
(1)
Connect the wires from the front panel and the
engine.
(2) Connect the wires drawn out from the stator
to
the wires from the front panel.
NOTE : Connect the wires of the same color.
(3)
Press the upper end of the bushing into the
bottom window of the front panel.
(4) Mount the front panel to the frame.
M6
X
12
mm flange bolt
....................
4 pcs.
3.9-5.9
Nom
Fig.
10-37
10-5 CHECKING, DISASSEMBLY
and
REASSEMBLY
of
the
FRONT PANEL
10-5-1 CHECKING OF THE FRONT PANEL
Dismount the front panel from frame.
Remove the control panel and check each components and wiring.
Refer to Section
9
for the detail of checking procedure for the components in the front panel.
10-5-2
DISASSEMBLY
(1)
Remove the control panel from the front panel.
344scre~~
..............
6
pcs. (RGV2200, RGV2600, RGV4000)
344screLy
..............
7
pcs. (RGV6000)
(2) Disconnect-the connectors on the wires to detach the control panel and front panel.
(3)
Remove the condensers and diode rectifier from the front panel.
(4) After disconnecting individual wires, remove the control panel components.
NOTE : Full power switch and pilot lamp have their wires soldered. Unsolder them to remove those
parts if necessary.
10-5-3 REASSEMBLY
(1)
Install the receptacles, no-fuse breaker, terminals, switches, etc. on the control panel and wirz them.
NOTE
:
Circuit diagrams are shown in Section
12.
Colored wires are used for easy identification, and
are of the correct capacity and size. Use heat-resistant type wires (permissible temperature
range 75°C or over) in the specified gauge shown. in the circuit diagrams.
(2)
Install condensers, and diode rectifier into the front panel.
(3)
Connect the wires of control panel components and front panel.
(4)
Attach the control panel to the front panel.
M4 screw
.....
6 pcs. (RGV2200, RGV2600, RGV4000)
M4 Screw
..............
7
pcs. (RGV6000)
1.2-1.5
Nom
-
58
-
Page 61

11.
TROUBLESHOOTING
11-1 NO AC
OUTPUT
11 -1 -1 CHECKING CONDENSER
Check the capacity
of
condensers using a “Dr. Robin”generator tester in capacitance meter mode.
NOTE : Be sure to discharge condensers by shorting condenser leads each other before checking their
capacitance, or the accurate reading cannot be obtained.
Fig.
11-1
NORMAL CAPACITY
OF
CONDENSER
I
MODEL
’
RGV2200
I
RGV2600
I
RGV4000
1
RGV6000
I
CAPACITY
j
17.2
F 20,2Fx2
i
28cFX2
24y
F
!
Table
11-1
If such an instrument
is
unavailable,the condenser can be checked
by
replacing with a new one.If the
generator performs
good
with new condenser, the cause
of
trouble
is
defect in original condenser.
11-1-2 CHECKING
STATOR
~.
Remove control panel and disconnect stator
wires at the connectors.
Measure the resistance between terminals
on
stator leads. (See Fig1 1-2)
Refer to Table
9-1
for
normal resistance.
If
stator
is
faulty: replace
it
\vith
a new one.
Fig.
1
1-2
-
59
-
Page 62

Check the insulation resistance between
!
stator core and each stator lead using a
Dr.
Robin generator tester
in
msgger tester mode
or
a megger tester.
(Fig.
11-3)
If
insulation
is
bad, replace stator with a new
one.
Fig. 1 1-3
1
!
11 -1
-3
CHECKING
ROTOR
(1)
CHECKING FIELD COIL
W
Remove rear cover and stator.
Fig.
1
1-4
W
Using a Dr. Robin
or
a circuit tester, measure the resistance
of
the field coil at the terminals.
(RXlQ
*lo%)
t
MODEL
RGV6000 RGV2200 RGV2600
'
RGV4000
RESISTANCE
2.52
Q
I
2.01
ST
'
1.77
R
I
1.60
Q
..
T&de
1
1-2
NOTE
1
:
Because a diode is soldered to the coil
ends at the terminals, resistance may
be measured only when tester probes
touch the terminals in one combination
of polarity. Therefore, if no resistance
reading appears, try checking in
reverse polarity.
[Remedy]
If
the resistance
is
not
normal, replace
rotor
with a
I
new one.
Fig.
11
-5
-
60
-
Page 63

Measure the insulation across one
of
the
soldered terminals
of
the rotor and the core.
(Fig.
11-6)
If
insulation is bad, replace rotor with a new
one.
Fig.
11
-6
11-2
AC VOLTAGE
IS
TOO HIGH
OR
TOO LOW
11-2-1
CHECKING ENGINE SPEED
If
the engine speed is too high or too low, adjust it
to the rated r.p.m.
[How
to
adjust
engine
r.p.m.1
Loosen the lock nut on the adjusting screw.
Turn the adjusting screw clockwise
to
de-
crease engine speed
or
counter-clockwise to
increase engine speed.
Normal engine speed at no load
is
:
3100 - 3150
r.p.m. for 50Hz type
3700
-
3750
r.p.m. for 6OHz type
11
-2-2 CHECKING CONDENSER
Check condenser referring to Step
11-1-1
11 -2-3 CHECKING STATOR
Check stator referring to Step
11-1-2.
11-2-4 CHECKING
ROTOR
Check
rotor
referring to Step
11-1-3.
.
..
.
..
;
;;
I
Fig.
1
1
-7
-
61
-
Page 64

11-3 AC VOLTAGE
IS
NORMAL AT NO-LOAD, BUT THE LOAD CANNOT BE APPLIED.
11-3-1 CHECK THE ENGINE SPEED.
If the engine speed is low, adjust it to the rated r.p.m.
*
Refer to Step 11-2-1 for engine speed adjustment.
11-3-2 CHECK THE TOTAL WATTAGE
OF
APPLIANCES CONNECTED TO THE GENERATOR.
Refer
to
Section 7 "RANGE
OF
APPLICATIONS" for the wattage of the appliances.
If the generator
is
over-loaded, reduce the load to the rated output
of
the generator.
11-3-3 CHECK THE APPLIANCE
FOR
TROUBLE.
If the appliance is faulty, repair it.
11-34 CHECK
IF
THE ENGINE
IS
OVER-
HEATED.
If the cooling air inlet and/or cooling air outlet is
clogged with dirt, grass, chaff or other debris..
remove it.
11-3-5 CHECK THE INSULATION
OF
THE
GENERATOR.
Stop the engine. Measure the insulation resistance
between- the live terminal of the receptacle and
the ground terminal.
If
the insulation resistance is less than
1
MQ:
disassemble the generator and check the insulation
resistance
of
the stator, rotor and the live parts
in
the control box. (Refer to Section
8-3.)
Any part where the insulation resistance
is
less
than
1
ME,
the insulation is faulty
and
may cause
electric leakage.
Replace the faulty part.
AIR
OUTLET
(GENERATOR!
.
Fig.
11-8
..
Fig.
1
1-9
-
62
-
Page 65

11
-4
NO
DC OUTPUT
11-4-1 CHECK THE AC OUTPUT.
Check the generator by following Step
11-1-1
through Step
11-1-3.
114-2 CHECK THE DC BREAKER.
If
the DC breaker turned
off
while charging a
battery, check the cables for short-circuit or
connection in reverse polarity before resetting
it
on.
NOTE : If the DC output is used
to
charge a
large capacity battery
or
an over-discharged battery, an excessive current
may flow causing.
11-4-3 CHECK THE
WIRING.
Check all the wires to be connected correctly.
11-44 CHECK THE DIODE RECTIFIER.
Remove the control panel and che-ck the diode
rectifier with a circuit tester.
Refer to Section
9-7
"DIODE RECTIFIER'' for the
checking procedure.
11-4-5 CHECK THE DC COIL
I
I
Fig.
17-10
Check the resistance between two brown leads from stator with a circuit tester.
I
MODEL SPECIFICATION
I
RESISTANCE
I
i
50Hz
!
11 OV. 220V. 240V, 11 OVl22OV
0.3652
i
60Hz i 120V, 220V, 11 OV/22OV, 12OVl24OV 0.32R
I
RGV2200
I
i
50Hz
1
110V. 220V, 240V. 110V/220V
1
0.260
:
60Hz I 120V. 220V, 110V/220V. 120Vi240V
1
0.21
0
RGV2600
~
:
50Hz
;
1 1 OV. 220V, 240V. 11 OV!220V 0.24R
60Hz
i
120V. 220V, 11 OVi22OV, 12OVl24OV
5OHz
0.200
0.150
1 1 OV. 220V, 240V,
1
1 OVi22OV
8
60Hz I 120V. 220V. 11 OVl22OV. 120V/240V 0.13R
RGV4000
:
RGV6000
Table
11-3
If
the resistance reading is much larger
or
smaller than the specified value, the DC coil
of
the stator
is
faulty. Replace stator with a new one.
-
63
-
Page 66

11-5
IDLE CONTROL (OPTIONAL EQUIPMENT)
11-5-1
ENGINE SPEED
IS
NOT INCREASED WHEN A LOAD
IS
APPLIED
(1)
Inspect the solenoid bracket.
Check the bend angle of solenoid bracket.
If the bracket is distorted, correct the angle
with proper tool.
.
(2)
Check the wattage
of
load appied
to
the
v
generator.
If
the generator is loaded over the rated
wattage, the engine speed can not be increased.
lMost induction loads such as electric motor
or
electric tools or welding machine require three
to five times large wattage
of
their ratings at
starting.
This starting wattage must not exceed the rated
output of the generator.
(3)
Check the slow set r.p.m.
The normal idling speed by the
IDLE
CONTROL is as follows
:
RGV2200,
2600
-----.
1900
-
2100
r.p.m.
RGV4000,
6000
---.-.
2000
-
2200
r.p.m.
The above speed setting is for
cold
engine
condition.
If
the engine speed is out
of
adjusting range
of
the adjusting screw, move the solenoid
backward.
Fig.
11-12
ADJUSTING
SCREW
Fig.
77-73
-
64
-
Page 67

IDLE
CONTROL
UNIT
i
(4)
Check the wiring through ZCT on the IDLE
CONTROL UNIT.
A)
Single Voltage Type
Make sure that an output wire from main coil
is
passing through the. ZCT on the IDLE
COKTROL UNIT.
B)
Dual Voltage Type
Check that two output wires (black wire and
red wire) from main coils are passing through
the ZCT on the IDLE COKTROL UKIT in the
same direction.
(5)
Checking the IDLE CONTROL UNIT
Check the resistance between six leads
of
IDLE CONTROL UNIT with circuit tester.
11”-
I
Terminal number
of
the
IDLE
CONTROL UNIT
I
/
ZCT
\\\
Fig.
17-14
IDL
Fig.
11-15-
Circuit tester
(with battery power source
1
SV)
Apply black 3 needle
of
the circuit tester
1
I
:g
A
.a
n
L.
\I
I
250 kR
.
250 kR
i
75kQ
!
Q
1
00
22
I
00
Apply red
@
needle
!
I
of
the circuit tester
3
1
250 kR
1
250 kQ 75 kR
,”.
I
75 kR
I
:
I-
250 kR
-
.n
f
.&
I
8.5 kR
30-
!
7.8kR 7.8kQ
11
*
Teste:
measuring
range
:
1000
k
0
Tabi‘e
11-4
NOTE : The resistance readings vary depending on the types
of
circuit testers.
The above table shows an example
of
the resistance readings measured by an ordinary
analogue circuit tester with
1.5
volt battery power source.
It is advisable
for
you to check the resistance readings using your standard circuit tester and
revise the checking table.
-
65
-
Page 68

11-5-2
ENGINE SPEED
IS
NOT REDUCED WHEN LOAD
IS
OFF.
(1) Check the distortion of the SOLEKOID BRACKET as shown in step
11-5-1-(1).
(2)
Check the wiring
of
SOLENOID.
Check two leads from SOLENOID are securely connected.
(3)
Check the wiring
of
IDLE CONTROL
USIT.
Check all leads from IDLE CONTROL UNIT are securely and correctly connected.
(4)
Checking the SOLEKOID.
-
Measure the resistance between two leads from
SOLENOID.
I
NORMAL
RESISTANCE
I
25-31
O
If
the resistance. is larger or smaller than th-is
range, SOLENOID
..
is
defective,
Replace \vith a new one.
SOLEXOID
\
Fig.
11-17
.-
.
..
-
66
-
Page 69

12.
WIRING
DIAGRAM
0
RGV2200,2600 : 50Hz-11 OV, 60H~-11 OV, 60HZ-120V
TYPE
ENGINE CONT-BOX
r--------
~
r""""""--
1
ET
I
-
67
-
Page 70

RGV2200,2600 : 50H~-220V, 240V, 60Hz-220V
TYPE
ENGINE
CONT-BOX
r""""~
r"""""""
1
..
..
.,
I,
?@
II
STOP
SW
I
b
i
,
i
L"
CB T
fix:
I
I
-
68
-
Page 71

RGV2200,2600 : 50Hz, 60H~-llOV/22OV
TYPE
ENGINE CONT-BOX
r--------
~
r"""""-"""
1
ET
1.
25mm2
-
69
-
Page 72

RGV2200,2600
:
U.K.,
50H~-llOV/22OV
[BS
RECEPTACLE]
ENGINE CONT-BOX
r””“”~
r”””””“””-
1
II
STOP
SW
“-3
Black
I
c
CB
.
T
I1
II
Brown/White
-
70
-
Page 73

0
RGV2600 U.S.A., 60Hz-12OV [NEMA RECEPTACLE]
ENGINE
~
r""""""""-
CONT-BOX
1
I
I
ET
-
71
-
Page 74

0
RGV4000 : 50H~-11 OV, 60Hz-11 OV, 60Hz-120V-TYPE
ENGINE CONT-BOX
r--------
1
r--
1
STOP
SW
I
I
ET
!I
Ii
Piii
I
-
72
-
Page 75

RGV4000 50H~-220V, 240V, 60HZ-220V
TYPE
ENGINE
CONT-BOX
7
r--
1
II
I
II
-
Brown/White
L
1-L
-
I
J
I
I
i
I
I
I
I
I
i
I
ET
..
-
73
-
Page 76

0
RGV4000
:
5OHZ,
6OHZ-l1OV/220V
TYPE
ENGINE
CONT-BOX
r--------
7
r--
1
ET
-
74
-
Page 77

RGV4000
:
U.K..,
50H~-llOV/220V
[BS
RECEPTACLE]
ENGINE
CONT-BOX
r--------
1
r----------
-
-
-
-
-
- -
1
STOP
SW
Black
I
II
Ii
PI
i
i
I
I
I
J
-
75
-
Page 78

0
RGV4000
:
U.S.A.,
60Hz-l20V/240V
[NEMA RECEPTACLE
with
IDLE CONTROL]
ENGINE
CONT-BOX
r--
~
r"""-"""""""""-
1
I
I
STOP
SW
A
'I
ET
Green/
Yellow
!
L""""II""""-"""""""""""---l
I
-
76
-
Page 79

RGV6000 : 5OHZ-1 lOV, 6OHZ-1 lOV, 60Hz-120V
TYPE
ENGINE-
CONT-BOX
r--
1
r---
1
I
I
STOP
SW
I
Brown/White
I
-
-
- - - - - -
-
-
0.75mm2 2.00mm2
ET
-
77
-
Page 80

RGV6000 : 50H~-220V,
240V,
60HZ-22OV
TYPE
ENGINE
CONT-BOX
r""""7
r""""""""-
1
I
I
I
.
-1
I
:I
Brown/White
I
-
-
- - - - - - -
-
0.
75mm2
2.
Omm"
ET
1.25mm'
-
78
-
Page 81

0
RGV6000 : 50Hz, 60HZ-11 OV/22OV
TYPE
ENGINE
CONT-BOX
r--
r""""""""""
1
I
STOP
SW
?
I
I I
L--J
Green/
II
-
Brown/White
I
1
ET
I
-
79
-
Page 82

RGV6000
:
U.K.,
50H~-lIOV/220V
[BS
RECEPTACLE]
ENGINE
CONT-BOX
~
r""""""""""
1
L
- -
-
-
-
-
-
II
GENERATOR
II
r--------
I
II
I
II
Brown/White
I
STOP
SW
Green/Yellow
I
T
I
Trl
ET
-
80
-
Page 83

0
RGV6000 : U.S.A., 60Hz-l20V/240V [NEMA RECEPTACLE
with
IDLE CONTROL]
ENGINE
CONT-BOX
r--
1
r--
1
I
II
I'
I
II
White
II
I
I
J
-
81
-
Page 84

a
TYPE
WITH
ELECTRIC STARTER (Optional Equipment)
15mm2
ENGINE
,~
CONT-BOX
-Black
1;
!
Green/Yellow
I
4
ET
!
Key
switch
-M
ST
IG
6
I
I I
I
OFF
ON
I
START
-
a2
-
Page 85

TYPE
WITH ELECTRIC STARTER AND IDLE CONTROL (Optional Equipment)
+M
-M
B
IG
ST
I
ET
L
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
II""""""""""
blue
!
Key
switch
-
a3
-
Page 86

0
TYPE
WITH
IDLE CONTROL (Optional Equipment)
ENGINE
CONT-BOX
r---
""-~
r"""""""""""""
1
,-
I,
I
"-
""
I
I
Green/
Yellow
I
SOL
.-
I
"I
I
I
CHG
-
84
-
Page 87

Symbols
Part Name
MC
AC Winding
cc
Circuit Breaker
CB
DC Output Terminal T
Pilot Lamp
L
Diodes Stack Assy D
Condenser C
Field Winding
FC
DC Winding
DC
Condenser Winding
N FB No-Fuse Breaker
vc
sw
Voltage Changeover Switch sw1
Voltage Changeover Switch
STOP SW
Engine Stop Switch
0.s
Oil Sensor Control Unit
so
L
Solenoid
Idle Control Unit
Spark Plug
Charge Coil
Ignition Coil
ET Earth Terminal (Ground Terminal)
ST. M Starting Motor
KEY
SW
BAT
:
Battery
Key Switch
V
Voltmeter
REC
Control Box (Front Panel) CONT.BOX
AC Output Receptacle
-
85
-
Page 88

0
FUJI
HEAVY
-INDUSTRIES
LTD.
INDUSTRIAL
PRODUCTS
DIV.
Subaru
Bldg.
1-7-2, Nishi-Shinjuku, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo 160, Japan
CABLE ADDRESS
:
FUJIHEAVY
TOKYO
TEL : (Tokyo 03) 3347-241 4,5 TELEX 232-2401 FUJI
J
FACSIMILE:
(TOKYO
03)
3347-2418
PRINTED
IN
JAPAN
June-1993
 Loading...
Loading...