Page 1

Page 2
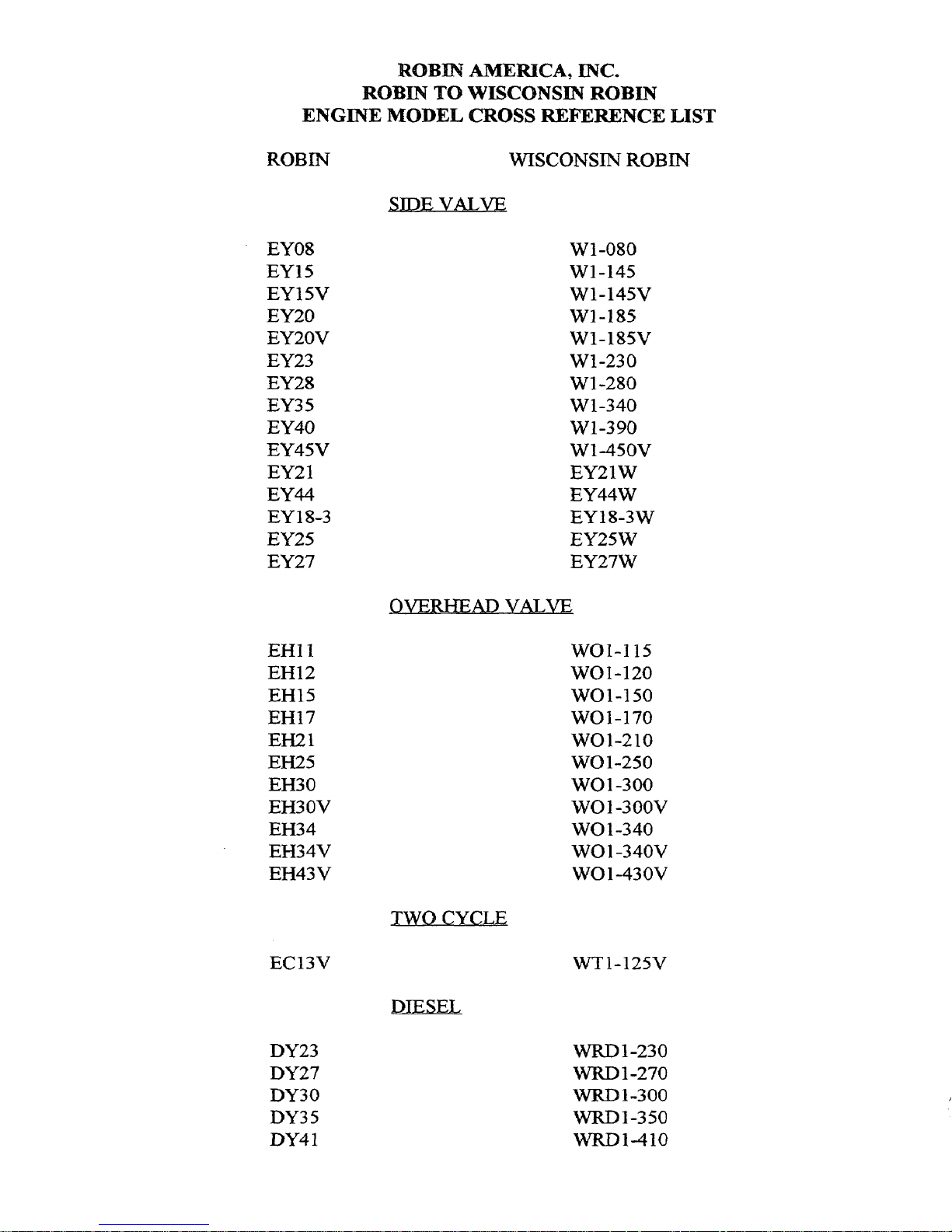
ROBIN
ENGINE
ROBIN
MODEL CROSS
AMERICA,
TO
WISCONSIN
mc.
ROBIN
REFERENCE
LIST
ROBIN
EY08
EYl5
15V
EY
EY20
EY2OV
EY23
EY28
EY35
EY40
EY45V
1
EY2
EY44
EY 18-3
EY25
EY27
-
WISCONSIN
W1-080
W1-145
W1-145V
w1-185
W1-185V
Wl-230
W
1-280
W1-340
W1-390
W1-450V
EY21W
EY44W
18-3W
EY
EY25W
EY27W
ROBIN
EHl 1
EH12
EH15
EH17
EH21
EH25
EH30
EH3OV
EH34
EH34V
EH43V
EC13V
DY23
DY27
DY30
DY35
DY4
1
TWO
CYCLE
WOl-115
WOl-120
WO1-150
WO1-170
wo1-210
WO1-250
WO
1-300
WO
1
-300v
WO
1-340
WO
1 -340V
WO
1 -430V
WT1-125V
WRD
WRD
WRD
WRD1-350
wRDl-410
1-230
1-270
1-300
Page 3

CONTENTS
Section Title Page
...........................................
1
.
SPECIFICATIONS
1
2
.
PERFORMANCE
...........................................
2
2-1 Maximum Output
........................................
2
2-2 Continuous Rated Output
..................................
2
2-3
Maximum Torque and Fuel Consumption Ratio
at
Max . Output
.........
2
3
.
FEATURES
................................................
4
4
.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
of
ENGINE CONSTRUCTION
...............
4
4-1
Cylinder Crankcase
......................................
4
4-2 Main Bearing Cover
.......................................
4
4-3 Crankshaft
...........................................
4
4-5 Camshaft
.............................................
4
4-7 Cylinder Head
..........................................
5
4-8 Governor
.............................................
5
4-9 Cooling
...............................................
5
4-10
Lubrication
............................................
5
4-11 Ignition
..............................................
5
4-13 Air Cleaner
............................................
5
4-14 Sectional View
of
Engine
...................................
6
4.4 Connecting Rod and Piston
.................................
4
4-6 Valve Arrangement
.......................................
5
4-12 Carburetor
............................................
5
5.lNSTALLATlON
............................................
14
5-1 Installing
..............................................
14
5-2 Ventilation
............................................
14
5-3 Exhaust Gas Evacuation
....................................
14
5-4
Fuel System
...........................................
14
5-5 Power Transmission to Driven Machines
.........................
14
5-6
Wiring
.............................................
15
6
.
DISASSEMBLY
and
REASSEMBLY
..............................
21
6-1 Preparation and Suggestions
.................................
21
6-2 Special Tools
...........................................
21
6-3
Disassembly and Ressembly Procedures
.........................
22
Page 4

7.MAGNETO
................................................
29
7-1 Magneto
7-2
Breaker Point Adjustment
7-3
Timing
74 Magneto Trouble Shooting
8
.
GOVERNOR ADJUSTMENT
9.
CARBURETOR
9-1
Operation and Construction
9-2
Disassembly
9-3 Adjustment
10
.
RUN-IN OPERATION
11
.
TROUBLE SHOOTtNG
11
-1 Starting Difficulties
11
-2
Engine Misses
11-3
Engine Stops
114
Engine Overheats
11-5
Engine Knocks
11-6 Engine Backfires Through Carburetor
.............................................
Adjustment
.......................................
.............................................
and
Reassembly
............................................
of
REASSEMBLED ENGINE
.......................................
.......................................
...........................................
...........................................
........................................
.........................................
..................................
...................................
...................................
.................................
................................
...................
...........................
29
29
30
31
32
33
33
34
36
37
38
38
39
39
39
40
40
12
.
CHECKS AND CORRECTIONS
13 . CORRECTION TABLE
14
.
MAINTENANCE
14-1 Daily Checks and maintenance (Every 8 Hours)
14-2
Every
14-3 Every
14-4
Every
14-5 Every 500
14-6 Every 1000 Hours (Yearly) Checks
14-7
Preparation for Long-Term Storage
20
50
100
and
Hours
Hours
.
.
.......................................
STORING
Checks and Maintenance
(10
Day)
200 Hours (Monthly) Checks
600 Hours (Semianual) Checks and Maintenance
.................................
.................................
Checks and Maintenance
and
....................
........................
..................
and
Maintenance
............
...........
Maintenance
.................
............................
41
42
48
48
48
48
48
49
49
49
Page 5
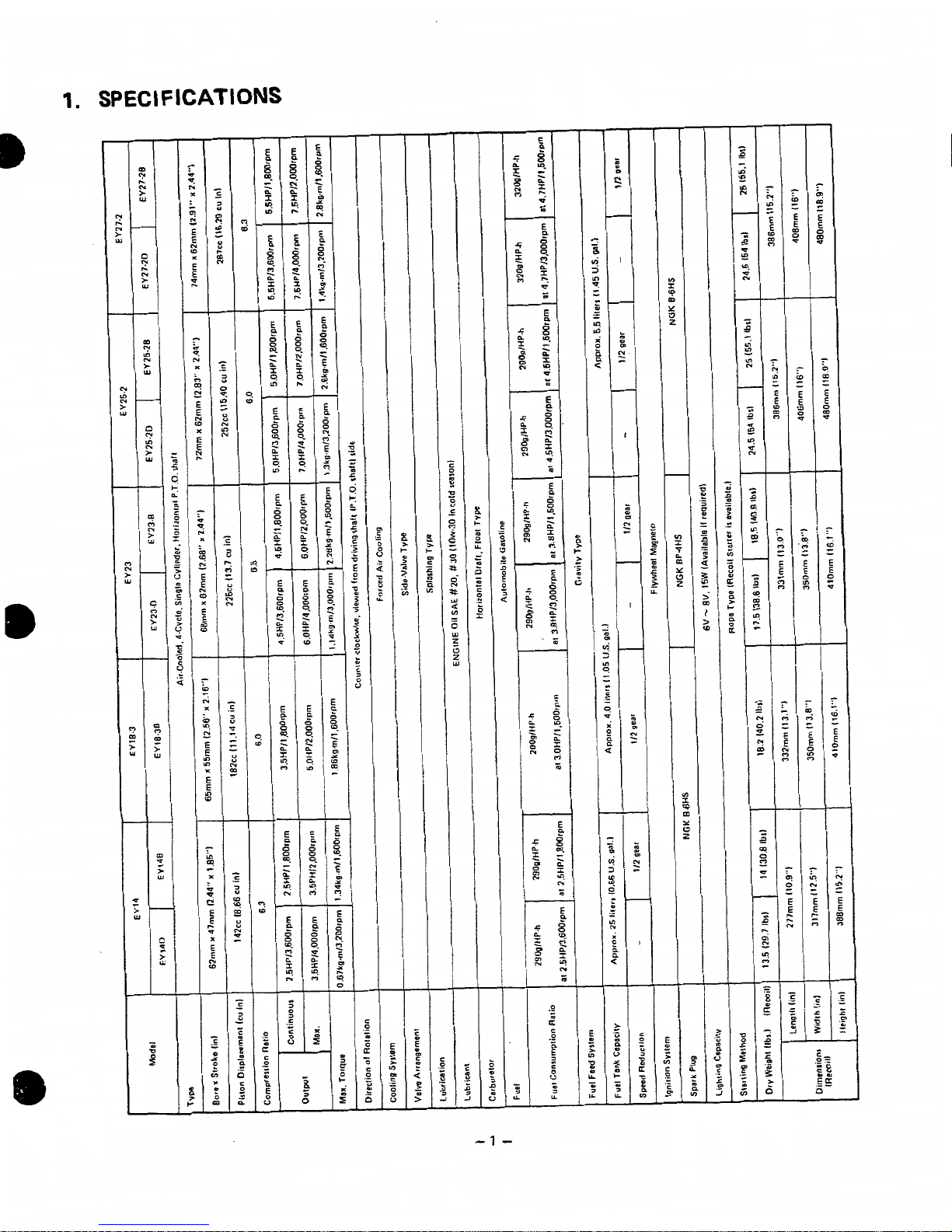
1.
SPEC1
FICATIONS
[
N
m
p
52
0
n
0"
V
t
1
c
t
I
I
i
-1
-
Page 6
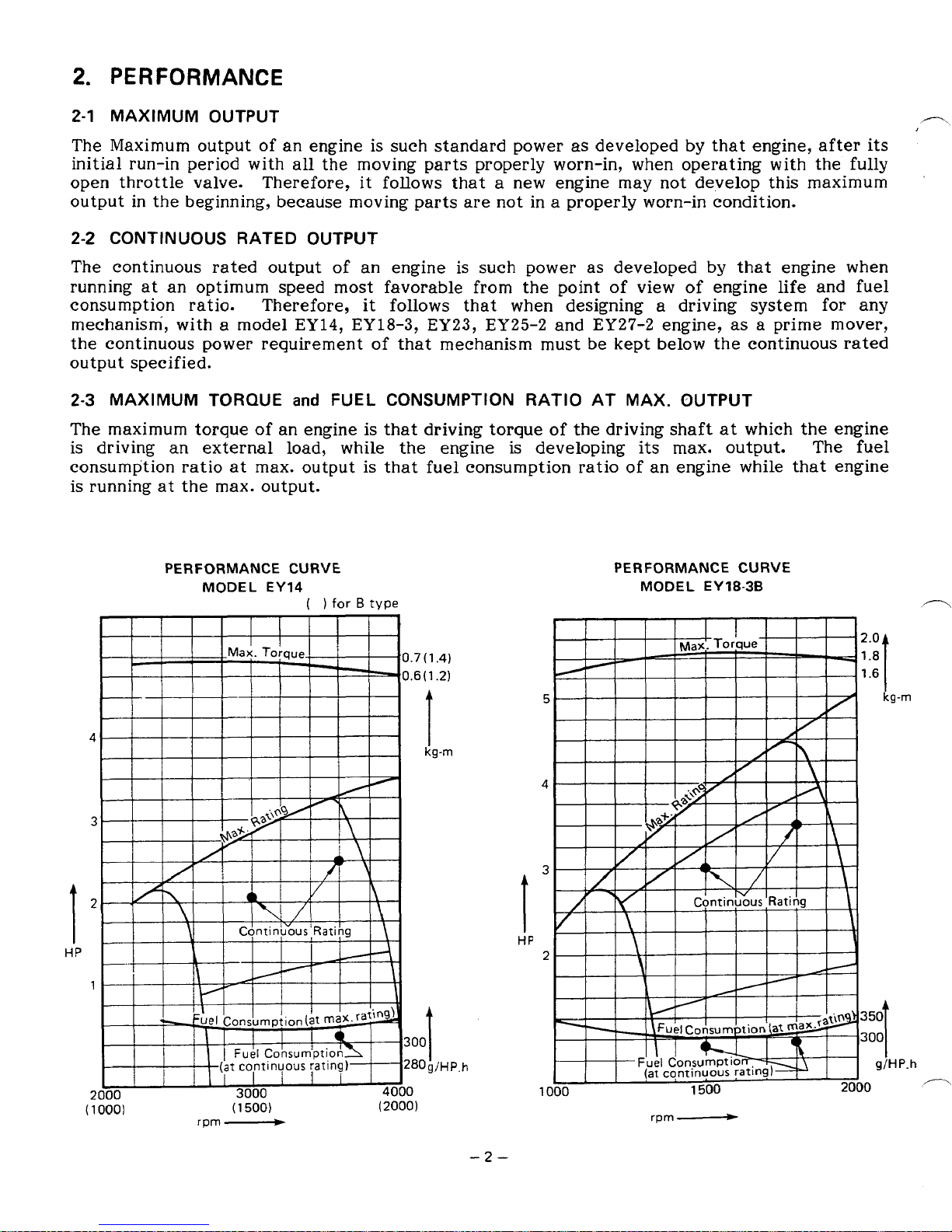
2.
PERFORMANCE
2-1
MAXIMUM OUTPUT
n
The Maximum output of an engine is
initial run-in period with
all
the
open throttle valve. Therefore, it
the
output in
2-2
CONTINUOUS RATED OUTPUT
The continuous
running
beginning, because moving parts are not in a properly worn-in condition.
rated
at
an optimum speed most favorable from the point of view of engine life and fuel
output of an engine
consumption ratio. Therefore, it follows that when designing
such
standard power
as
developed
by
that engine,
moving parts properly worn-in, when operating with the fully
follows
that
is
such
a
new engine may not develop this maximum
power as developed
a
by
driving system for any
mechanism, with a model EY14, EY18-3, EY23, EY25-2 and EY27-2 engine,
the
continuous power requirement of
that
mechanism must
be
kept below
the
output specified.
2-3
MAXIMUM TORQUE
The maximum torque of an engine is
is
driving an external load,
consumption ratio
is
running
at
the
PERFORMANCE CURVE
at
rnax. output.
and
FUEL CONSUMPTION RATIO
while
max. output
is
AT
MAX. OUTPUT
that
driving torque of the driving shaft
the
engine
that
fuel consumption ratio
is
developing
its
of
PERFORMANCE CURVE
MODEL EY18-38
max. output. The fuel
an engine while
after
that
engine when
as
a
prime
mover,
continuous
at
which the engine
that
engine
its
rated
-2-
Page 7
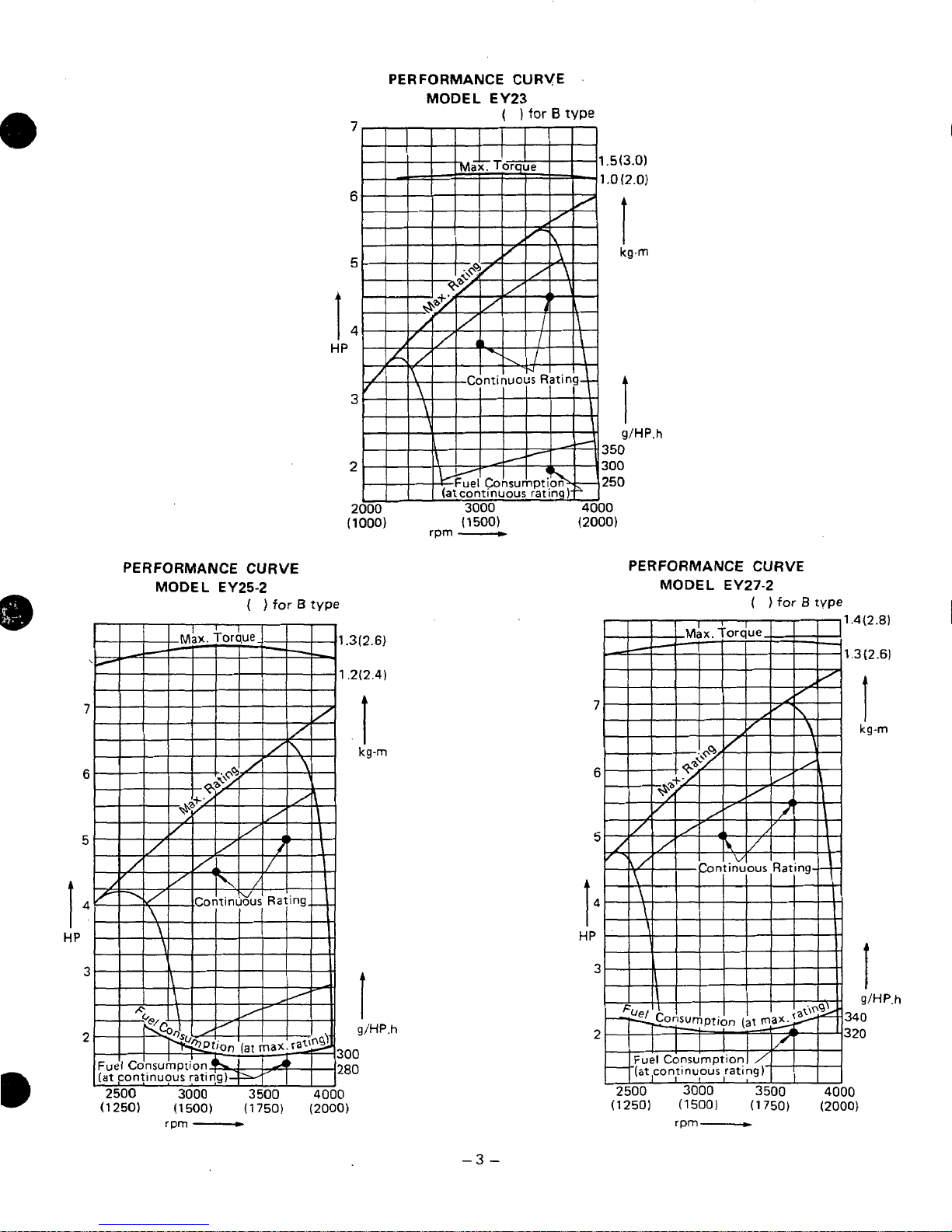
PERFORMANCE
CURVE
MODEL
EY23
7
( )
for
B
type
1.5(3.0)
1.0
(2.0)
6
I
5
kg-m
HP
I4
3
I
g1HP.h
3
50
2
300
250
2000
3000
4000
(1
000)
(1
500)
(2000)
rpm
__c
PERFORMANCE CURVE
MODEL EY25-2
(
)
for
B
type
.h
PERFORMANCE CURVE
MODEL EY27-2
(
)
for
8
type
1.4(2.8)
1.3(2.6)
7
I
kg-m
6
5
HP
I4
3
I
g1HP.h
340
2
320
2500
3000
3500
4000
(1250)
(1500)
(1750)
(2000)
rpm
-
-3
-
Page 8

FEATURES
A
compact, lightweight and durable 4-cycle air-cooled engine with high power output,
embodying ingenious design technique and advanced production skill.
n
Simple construction, smart appearance, easy
start.
Reliable power for wide. variety of purposes, with smooth speed controll by
a
governor,
under varying
load
conditions.
Economical advantage through low fuel consumption.
Great versatility in installation through
a
360°
belt
extension possibility and a two side
oil
fill and drain arrangement.
GENERAL DESCRIPTJON
of
ENGINE CONSTRUCTION
CYLINDER, CRANKCASE
The
cylinder and
the
crankcase
are
die-cast
as
a
compact aluminium mono-block piece.
The
cylinder liner and
the
valve
seats
are
made of special alloy
cast
iron and
are
imbedded in
the
aluminium casting
as
inserts. The intake and exhaust ports
are
located
at
one side
of
the
cylinder and
are
also
made
of
inserted pieces in
the
casting.
The crankcase
is
separable
at
the driving
shaft
side and this separable piece constitutes
the
main bearing cover.
4-2
MAIN BEARING COVER
As
the aluminium die-cast main bearing cover
is
built onto the crankcase on the driving shaft
side, the engine 'inside
are
reached
for inspection, easily by simply removing it. It
is
also
provided with
a
flange and
boss
for directly mounting operating machines such
as
generators
and pumps.
There
are
two
oil filters serving also
as
oil gauges provided
at
two locations.
(However, in
EY18-3
or
EY23
engine,
at
one location in
the
carburetor
side.)
4-3
CRANKSHAFT
The crankshaft is machined from
a
carbon
steel
forging with
an
induction hardened crank pin.
On
the
fan side,
the
breaker
cam is provided and on
the
driving side,
the
crankshaft
gear
is
force-fit.
44
CONNECTING ROD
and
PISTON
The connecting rod
is
machined from an aluminium alloy forging in which the
forged
alloy itself
serves
as
the
bearing metal
at
both
ends. On
the
large end, an oil scraper
for
splashing
the
lubricating
oil
is
provided.
The piston is machined from an aluminium alloy casting and
is
provided with two grooves
for
compression rings and one groove
for
the
oil ring.
4-5
CAMSHAFT
The camshaft is machined from
a
carbon
steel
forging with integral intake and exhaust cams
and
is
provided with a force-fit cam gear.
In
the
model B engine,
the
camshaft
serves
also
as
the
driving shaft, being driven
at
half
the
crankshaft speed.
In
the
EY14D, EY23D, EY25-2D
and
EY27-2D
engines,
the
camshaft is machined from a special alloy
cast
iron with an integral
camshaft
gear,
and is supported by aluminium bearing metals machined integral with
the
crankcase
at
both ends. (no
ball
bearing is used)
n
-4
-
Page 9

4-6
VALVE ARRANGEMENT
The exhaust valve is positioned
in
the
upstream side of the cooling air with the result that the
exhaust valve
is
intensively cooled for engine life improvement.
-
4-7
CYLINDER
HEAD
A
Ricardo type combustion chamber
of
ample area is employed for good combustion efficiency.
The spark plug
is
mounted obliquely to facilitate fuel tank mounting.
4-8
GOVERNOR
The flyweight type governor effectively operates to maintain
the
selected speed at varying
load.
The model
EY14, EY18-3
and
EY23
engine
is
equipped with a separate gearing for the governor
to
secure better performance.
4-9
COOLING
Cooling is accomplished
by
a
flow
of air circulated past the cylinder walls and head
fins
from a
combination fan-flywheel. The air
is
guided
by
a cylinder buffle
and
a head cover. The
EY14,
EY18-3,
EY23,
EY25-2
and
EY27-2
engines are equipped with curved vane fans made
in
two
modifications, each
for
direct drive and reduction drive engines.
4-10
LUBRICATION
Lubrication for rotating and sliding parts is accomplished
by
scooping and splashing the
oil
in
the crankcase
with
oil scraper attached to connecting rod.
4-11 IGNITION
The ignition system
is
of the flywheel magneto type
with
the ignition timing set
230
before
T.D.C. The magneto comprises a flywheel, ignition coil and a breaker, of which the flywheel
(serving also as a fan)
is
mounted on the crankshaft and the two other members are mounted
directly
in
the crankcase. (for details, refer
to
7.
MAGNETO
section)
The model
EY23
engine normally incorporates an electronic ignition system.
4-12 CARBURETOR
A
horizontal draft carburetor
is
employed. Its setting has been carefully determined after
through testing to achieve best starting, accelerating, fuel consumption, output and other
performances.
For
other details such as construction, refer to
9.
CARBURETOR
section.
4-13
AIR
CLEANER
The model
EY
14,
EY18-3
and
EY23
engines are equipped with an oval air cleaner incorporating
8
sponge element.
The cycl.one type air cleaner with a semi-wet double element is optional.
The
model
EY25-2,
EY27-2
engines are equipped
with
an
cyclone type semi-wet double element
air cleaner.
-5-
Page 10

4-14
SECTIONAL
VIEW
of
ENGINE
4-14-1
MODEL
EY14
FI
Blower
ywheel
(Cooling
Housing
Starting
Pulley-
MODEL
EY14
ver
-6-
Page 11
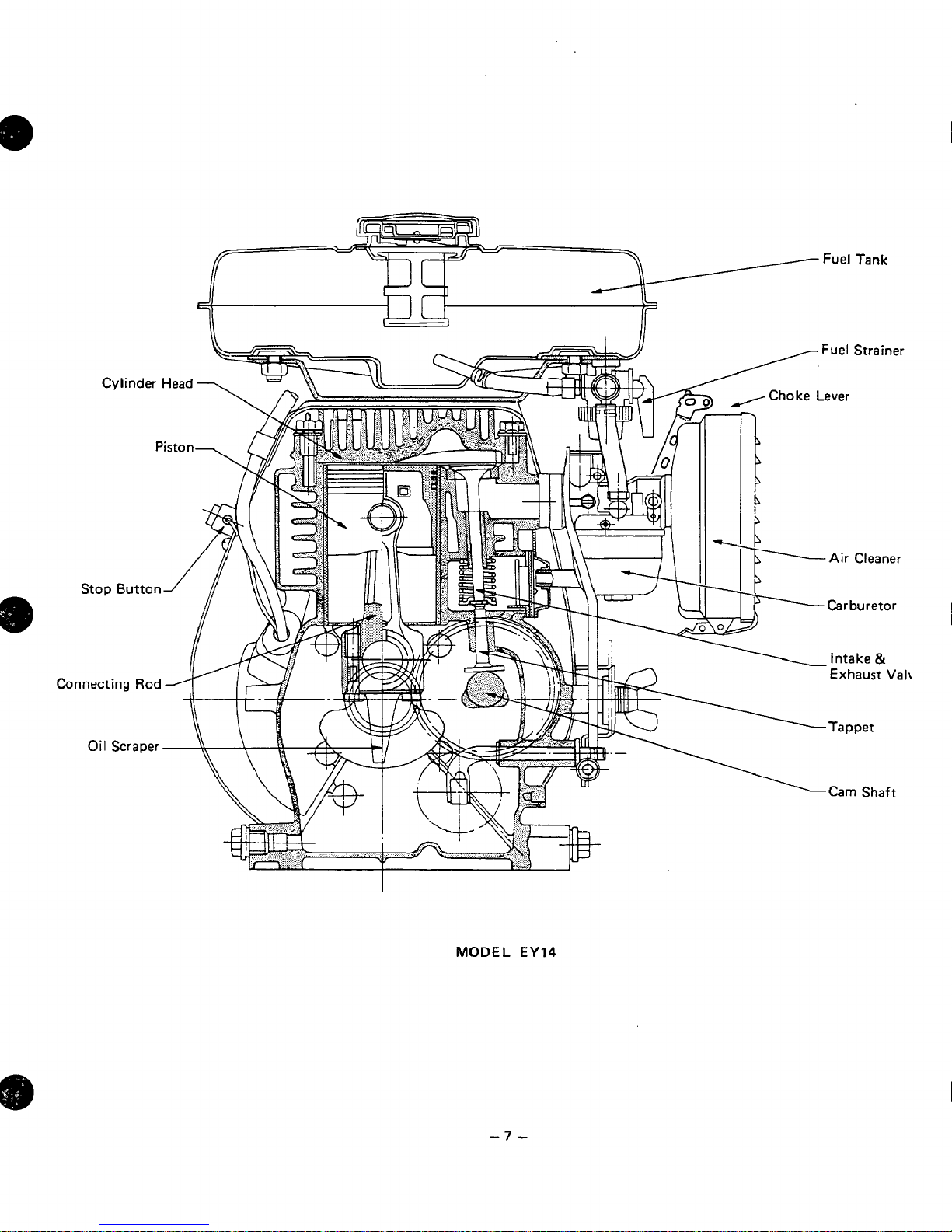
Fuel
Tank
MODEL
-7
EY14
-
Page 12
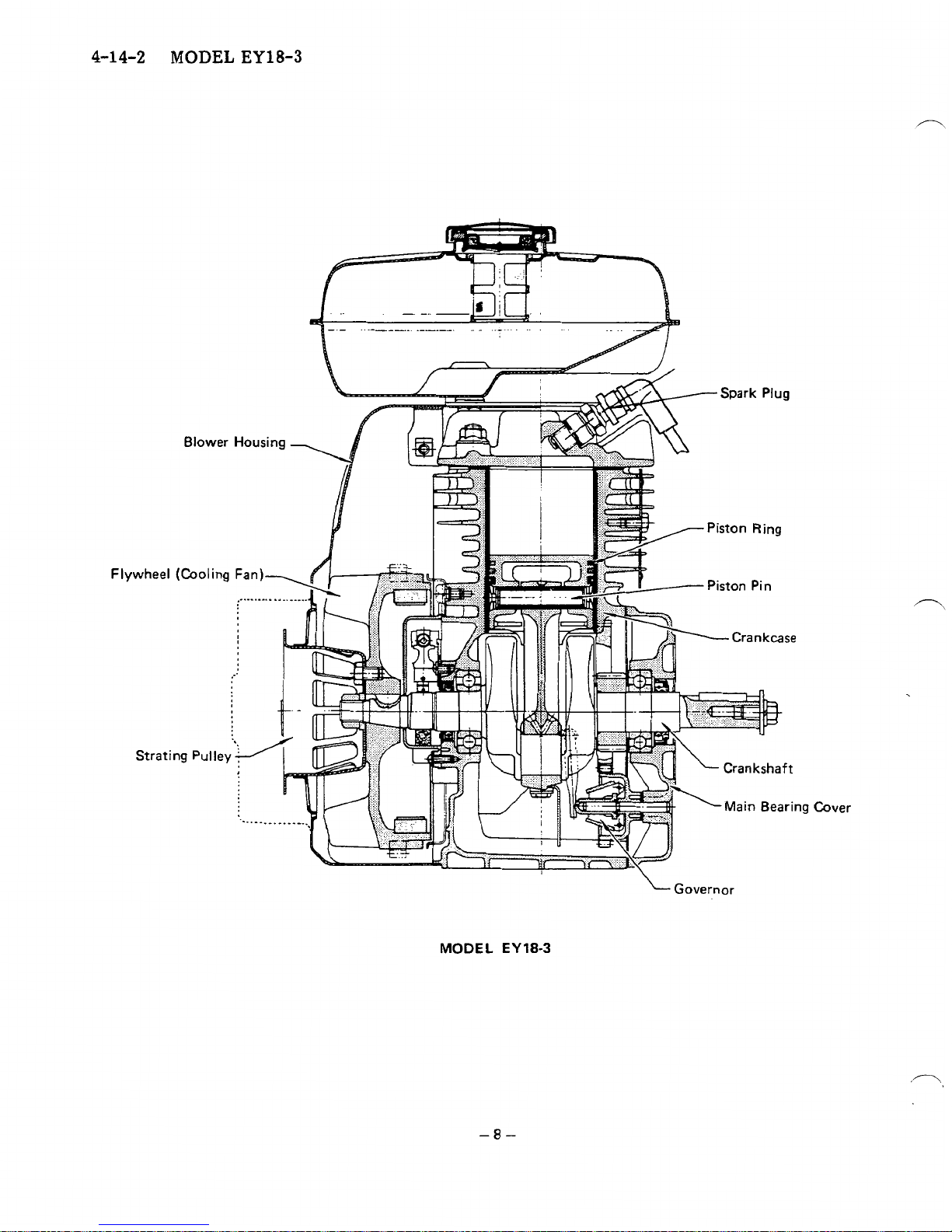
4-14-2
MODEL
EY18-3
Cover
MODEL
EY18-3
-a-
Page 13
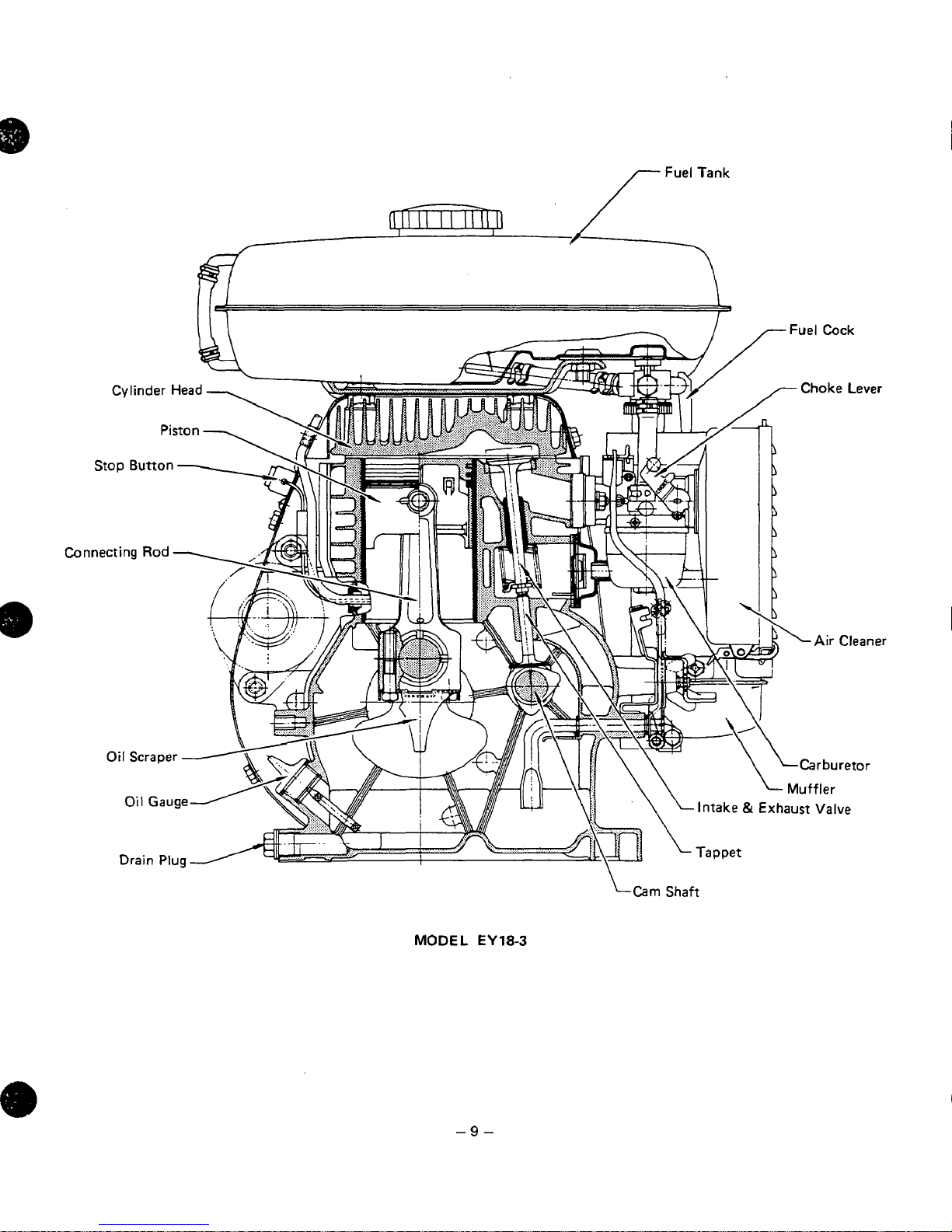
/
/-
Tank
MODEL EY18-3
-9-
Page 14
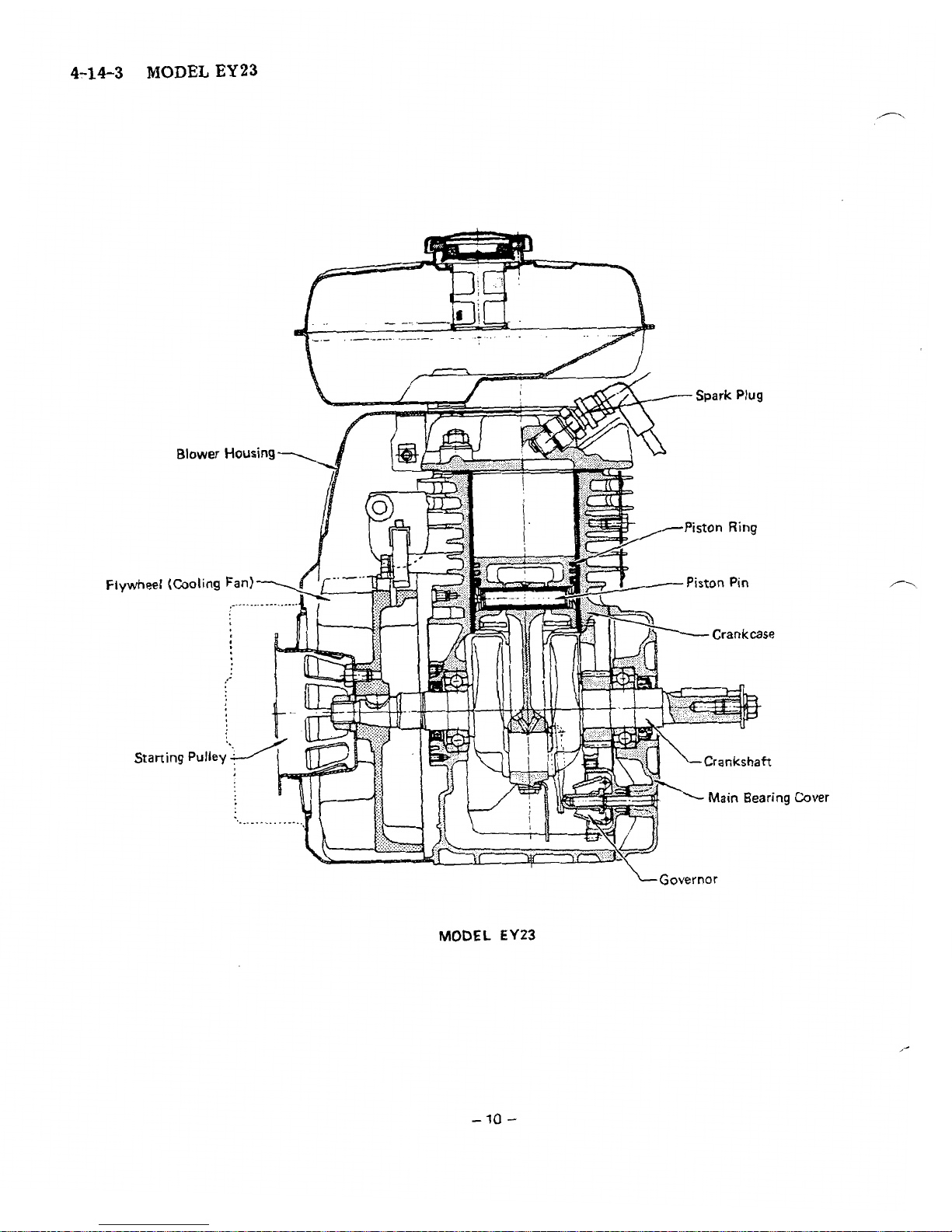
4-14-3
MODEL
EY23
Flywheel
Star
MODEL
EY23
7g
Cover
-
10
-
Page 15
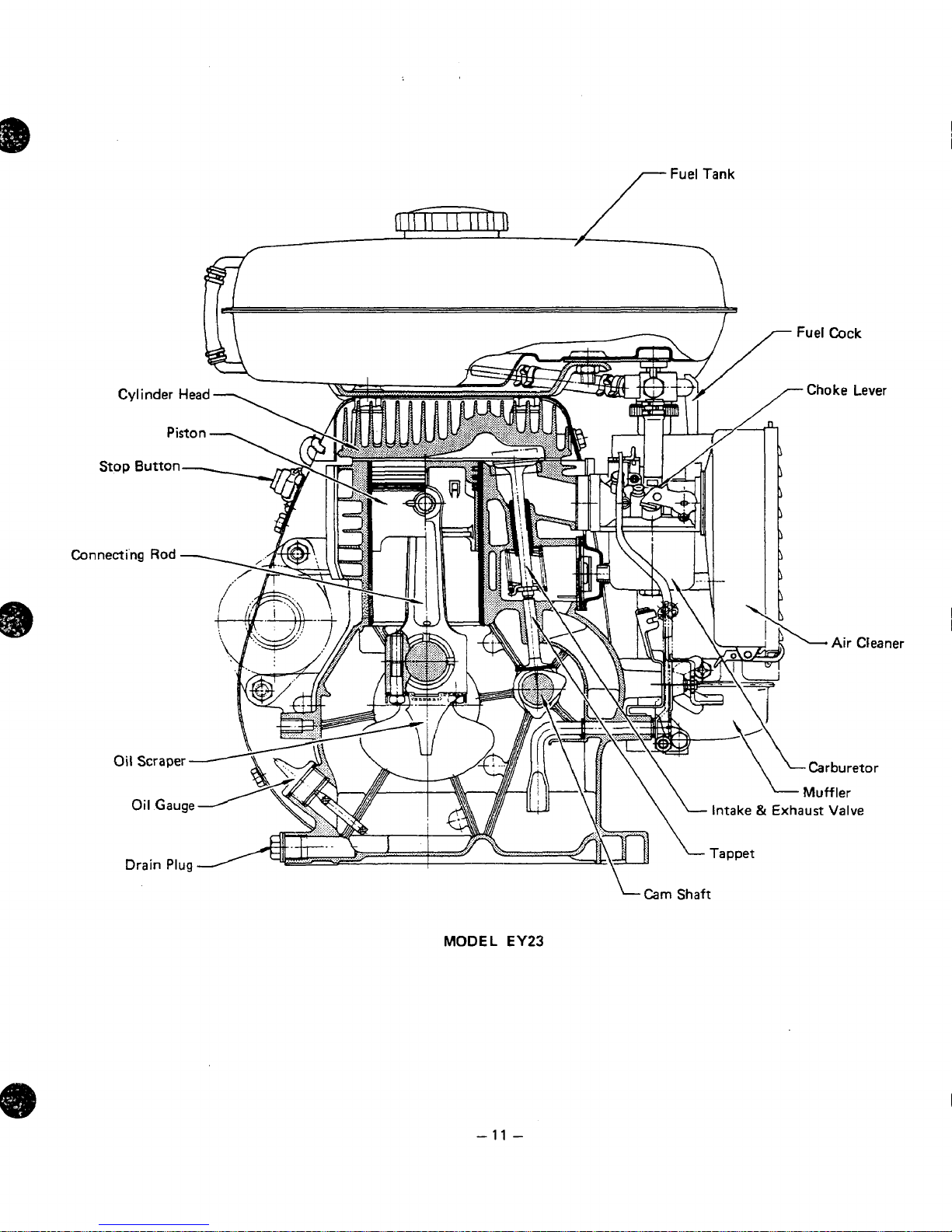
Con
/"
Tank
MODEL
-
EY23
11
Cam
Shaft
-
Page 16
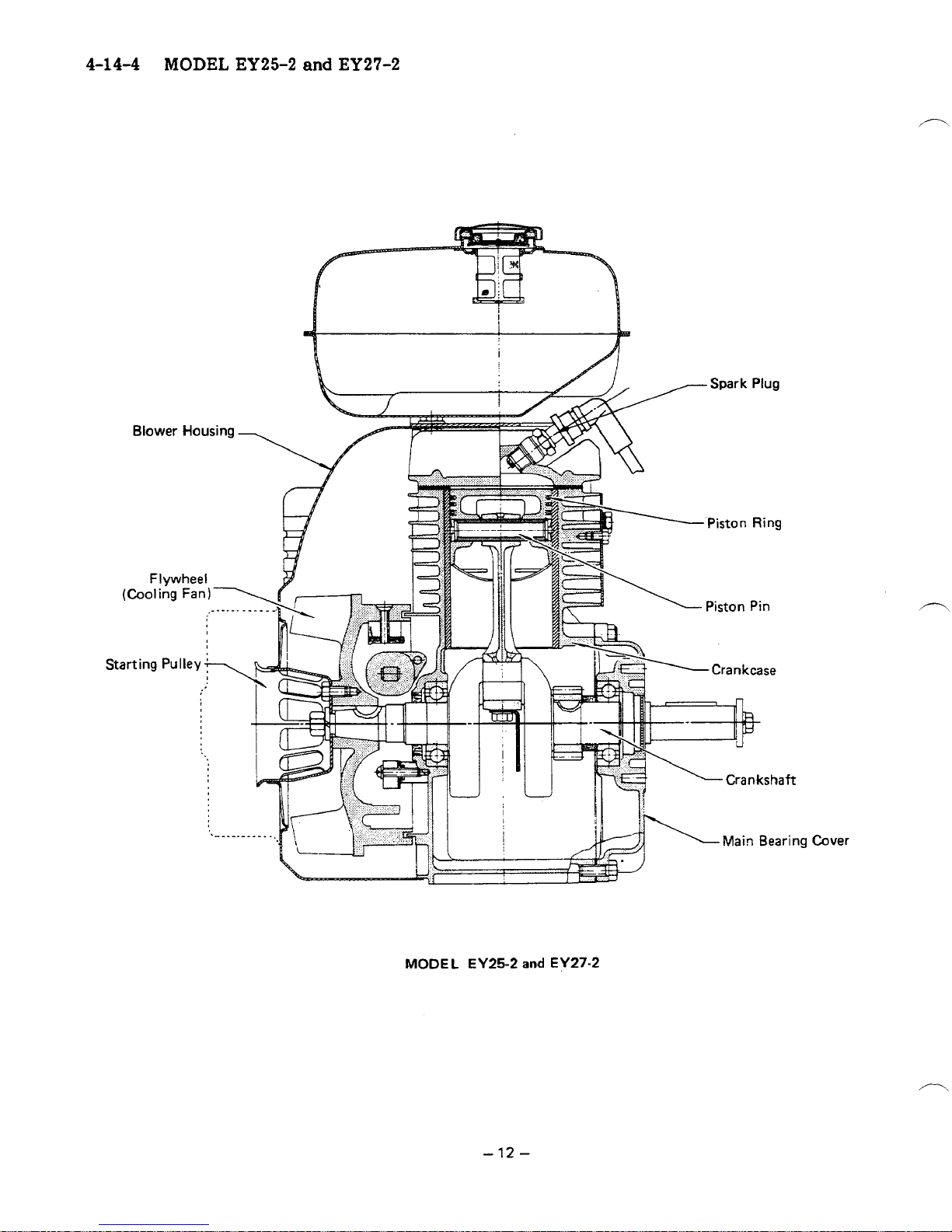
4-14-4
MODEL
EY25-2
and
EY27-2
MODEL
EY25-2
-
12
and
-
Cover
EY27-2
Page 17
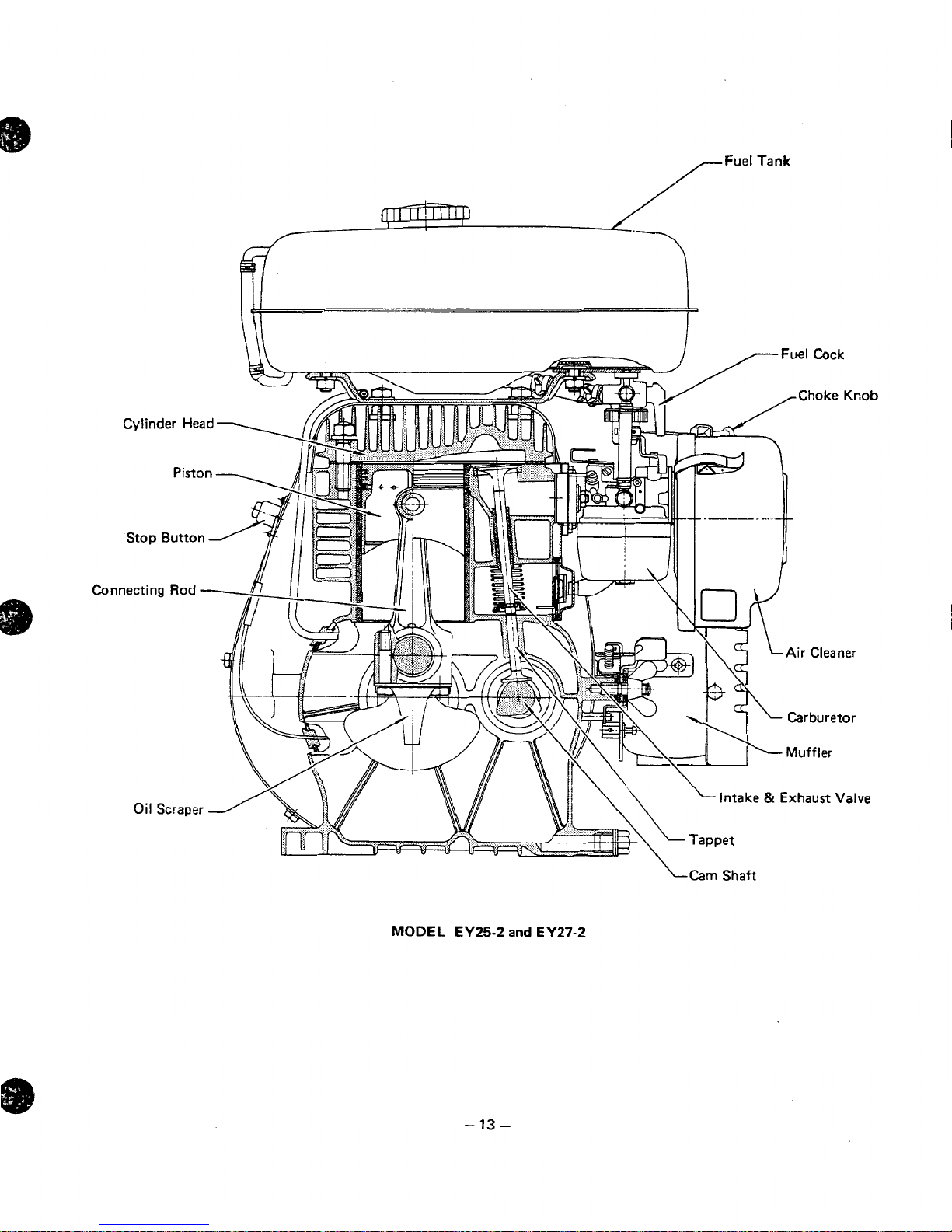
I
ti
I
I
\Cam
Shaft
MODEL
EY25-2
and
EY27-2
-
13
-
Page 18

5.
INSTALLATION
The life,
affected by
contents must
5-1
When
anchoring
ease
of
maintenance, frequency of
the
way
the
be
studied carefully.
INSTALLING
installing the engine,
or
supporting method must
check
and repair, and operating
engine is installed. When installing the engine, therefore, the following
its
position, coupling conditions with the operating machine and
be
carefully studied.
Especially, when deciding the installing position, consideration must
routines such
maintenance of
5-2
VENTILATION
The
engine must
to
be
operated in a cover
re-circulation
the engine compartment
consumption, power reduction, seizure,
proper
below
5-3
Since
gas
operation
50OC
EXHAUST GAS EVACUATION
the
must
influenced
as
filing and checking
air
cleaner and oil draining.
be
supplied with fresh air
or
in a small room, a proper means must
or
ducts and baffle plates
is
allowed
is
harmed. The temperature
of
gasoline
for
for
to
rise, vapor lock, oil deterioration, increase of
loss
and
oil,
checking of spark plug and breaker,
cooling and fuel combustion. When
guiding a cooling
of
engine life
of
the engine compartment must
air,
or
other troubles
even in summer with necessary ventilation arrangement.
exhaust
be
by
gas
from
evacuated
the
length
the
engine is toxic, when
to
outside. Since the output power
of
the
exhaust duct, its diameter must
the
engine
is
be
length.
cost
are
greatly
be
given
be
provided for cooling
to
facilitate
the
its
engine
air
because if the temperature in
oil
are
caused, and
be
maintained
operated indoors,
of
an engine
increased in proportion
the
exhaust
is
considerably
to
its
n
is
F-,
5-4
FUEL SYSTEM
When
bottom surface lies within
When
the
When connecting
the
standard fuel tank is installed separate from
the
fuel tank is installed too low, fuel is not fed properly and if it is positioned
carburetor overflow
the
fuel pipe,
the
is
caused.
height
to
the
of
5
CL
50
cm from
the
eliminate air lock and vapor
engine, it must
fuel joint of the carburetor.
carefully examined for heat conductivity, diameter, bending, and
standard I.D. of the fuel pipe is
5-5
5-5-1
Take
o
V-belts
o
The
o
The
POWER
BELT
the
driving shaft
driving pulley of
TRANSMISSION
DRIVE
following notes into condition:-
are preferred to
of
the
the
4
‘L
5
to
DRIVEN
flat
belts.
engine and
engine and
mm.
MACHINES
the
driven
the
shaft
of
the
driven pulley of
driven machine must
the
correctly.
o
The driving pulley must
o
As
far
as
possible,
o
When starting
the
engine,
the
be
mounted
belt
is spanned horizontally.
the
load must
as
near
be
the
engine
as
possible.
disconnected from
be
so
lock,
leakage
located
the
piping must
through fittings. The
be
that
too
high,
parallel.
its
be
driven machine must be aligned
the
engine.
o
If a clutch is
not
available, a tension pulley
or
-
other
14
-
means must
be
employed.
Page 19

5-5-2
FLEXIBLE COUPLING
When
a
flexible coupling
is
engine driving shaft must
The
tolerances on
5-6
WIRING
5-6-1
The
dotted
1)
START
wiring
line
Point system
MODEL
is
are
EY14
the
runout and mis-alignment
by
RECOIL
indicated in
not wired in
Spark Plug
used,
be
STARTER,
the
the
runout and mis-alignment between
made
as
small
or
by ROPE
as
possible.
are
specified by
wiring diagram given below. Normally,
the
engine
at
the
\
'Ignition Coil
Lighting
factory.
~
Lighting
Coil
(Optional Equipment, available
Stoo Button
Switch
each
Lamp
the
driven
shaft
coupling maker.
the
portions indicated by
(6V-8V
',15W)
if
required)
and
the
MODEL
MODEL EY25-2, EY27-2
EY18-3
Contact Breaker
'
Lighting
,Condenser
la"
"-7
Coil
(Optional Equipment, available if
required)
ir
.ed
)
Fig.
-
5-6-
7
15
-
Page 20

2)
Electronic ignition system
MODEL
Optional
Lamp
EY14:
Coil
CDI (Capacitor Discharge Ignition)
Stop
Button
Pulser
Coil
""".J
Fig.
58-2
system
BlackMlhite
MODEL
EY23
m7
STD:
"
L
TIC
Spark
(Transistor Ignition Circuit) system
Ignition Coil Connector
Plug
Fig.
i
5-6-3
Stop
Button
-
16
-
Page 21

MODEL
EY23:
TIC
with
Lamp
Spark Plug
Lamp
Coil
Coil
System
/
Ignition Coil
Flywheel
Fig.
5-64
Stop Button
77!7
MODEL EY25-2, EY27-2:
Optional
Lamp
Coil
PIT
(Pulser
Ignition Pulser
etc.
\
Flywheel
Ignition Transistor)
Coil
Fig.
Spark Plug
I
5-6-5
system
1
Stop
Button
-
17
-
Page 22

5-6-2
The wiring is
lines
CELL
is
normally not prepared
.
START
as
shown in the figure below. The section, in the figure, described with dotted
in
the
engine side.
,~
MODEL
EY18-3,
Plug
Spark
EY25-2, EY27-2:
Magneto Black
a
Point with
Starting Motor Magnetic Switch
Black
Cell
System
7777
EY18-3D,
-
8
BS
Wiring
JIS
CB Female
JIS
CA
JIS
LA106
Diagram
Terminal
Male Terminal
Board Terminal
-
18
-
Page 23

MODEL
EY23,
EY25-2,
EY27-2:
PIT
with
Cell
System
Spark
plug
-
Flywheel
i
Magnetic
Switch
Starting
Motor
F&.
5-6-7
-19-
Page 24

1)
Specifications
Parts
No.
Name
Manufacturer
Voltage
Output
Weight
2147050110
(Model
EY18-3BS, 23BS,
2147050210
(Model
EY23DS, 25-2DS,
Starting
Motor
HITACHI
12v
0.6
kW
14
131.5
31.5
-
-
F&.
5-6-8
25-2BS, 27-2BS),
2
7-2DS)
2)
Operation
The battery
is
connected
to
the terminal
66
of
the magnetic switch.
The condition when
the
starting motor is
ON
is
as
shown in
the
figure below.
t
iM
“S
;.
Ijl
Starting
Motor
tM
Switch
4
Key
Switch
Fig.
5-6-9
This circuit consists
of
a
magnetic
switch
operating circuit and
a
starting motor operating
circuit.
When
the
key
switch
is
turned
ON,
the
-
circuit is closed, and electricity
flows
to
the
direction directed
by
an arrow,
thus the coil
of
the magnetic switch being excited
to
absorbe
the contact.
Then, power is supplied to
the
starting motor, and engine cranking
is
started.
so,
low
voltage
current
flows
in the
M
circuit, while
starter
current
for
a
large
current
flows
in
the
S
circuit.
M
*
Pinion
gear
engagement
When
the
starting motor
is
started,
the
wait assembled
with
the
helical
spline on
the
shaft
is
T-”.
moved
to
the
axial direction
by
centrifugal
force,
and push out the pinion gear
to
be
engaged in
the
ring gear.
-20
-
Page 25

6.
DISASSEMBLY
and
REASSEMBLY
6-1
PREPARATION
and
SUGGESTIONS
0
1)
When
disassembling the engine, memorize the locations of individual parts
so
as to be able
to reassemble them correctly. Tag parts
if
there is a possibility
of
confusion.
'2)
Prepare several boxes
to
keep parts beginning to certain groups together.
3)
Group those parts related each other, tentatively assembling where they belong,
im-
mediately after removing,
in
order to prevent missing
and
misplacing.
4)
Handle the disassembled parts carefully and wash them
in
kerosene.
5)
Use
the correct
tools
in
the correct way.
6)
Standard tools required for disassembling and reassembling:
a)
Work
table
b)
Washing pan
c)
Disassembling tools
d)
Washing
oil
(kerosene
or
gasoline), Mobile oil
e)
Emery
paper, cloth
when the oil drain plug on the crankcase side wall
on
the carburetor side
is
unscrewed.
and flywheel to the specified
torque
values.
7)
Before starting
to
disassemble the engine, drain fuel and lubricant.
Oil
can be drained
8)
Tighten the screws
of
the cylinder head, main bearing cover, connecting rod, spark plug,
9)
Use new packings and gaskets
in
reassembly.
10)
Immedaitely before assembling parts, wash them
in
fresh gasoline
or
kerosene and blow
them dry.
0
11)
Apply Mobile oil
on
rotating and sliding parts.
12)
Take care not to contaminate the parts
by
dust during assembling.
13)
Tighten bolts, nuts and screws with proper torque according to the their sizes.
If
small
14)
After completely assembling the engine, turn it
by
hand and check
if
there
is
any
screws are tightened too tight, they may get broken.
abnormality
or
loose members.
6-2
SPECIAL
TOOLS
Flywheel Puller
Valve
Guide Puller
Valve
Valve
Seat Cutter
Spring Compressor
Fig.
6-2
-21
-
Page 26

Description
Part
No.
QtY
Remarks
1
Flywheel Puller
Bolt
Spring
Compressor
I
Valve Guide Puller
(Plate,
Shaft,
Nut)
Valve Seat Cutter
6-3
DISASSEMBLY
6-3-1 FUEL
1)
Disconnect fuel pipe between strainer and carburetor
2)
Remove fuel tank from
3)
Remove tank
EY27-2: 10 mm flange nut, 4 pieces)
6-3-2 BLOWER HOUSING and HEAD COVER
1)
Remove blower housing from crankcase and head cover (cylinder baffle).
(EY14: 6
bolt, 6 pieces)
2)
Remove head cover (cylinder baffle) from cylinder head.
TANK
x
and
REASSEMBLY
and FUEL TANK BRACKET
bracket.
bracket
8
mm Flange bolt, 6 pieces/EY18-3,
from cylinder
209 95004 07
001
6608500
2079500307 Valve
I
205 95001
206 95001 07 EY 18-3, EY 23
207 95001 07
2079500207
07
PROCEDURES
(8
mm
nut,
head
1
3
1
I
1
I
1
1
1
4
pieces)
(EY14: 8 mm flange nut/EY18-3, EY23, EY25-2,
EY23,
EY14, EY18-3, EY23, EY25-2, EY27-2
EY14, EY18-3, EY23, EY25-2, EY27-2
I
EY
I
at
(EY14:
14
EY25-2, EY27-2
EY14, EY18-3, EY23, EY25-2, EY27-2
carburetor side.
3
pieces)
EY25-2, EY27-2: 6 x 12 mm Flange
I
-
6-3-3 AIR CLEANER
1)
Remove air cleaner cover and element.
2)
Loosen two bolts and remove air cleaner
2
pieces/EY18-3, EY23, EY25-2, EY27-2:
same
3)
Disconnect breather
4)
In
element thoroughly and apply mixture'of 4
excess oil before reinstalling it.
6-3-4 MUFFLER
Remove muffler from cylinder part of crankcase. (EY14, EY18-3, EY23, EY25-2, EY27-2:
nut,
6-3-5 GOVERNOR LEVER and CARBURETOR
1)
Remove governor lever from governor
2)
Remove governor rod and
3) Remove carburetor from cylinder part
In
6-3-6 STARTING PULLEY and MAGNETO
1)
Remove starting pulley from flywheel.
bolt, 3 pieces)
time,
reassembly, wash element in kerosene shaking well until
2
pieces)
reassembly, refer
disconnect choke knob
pipe.
rod
spring from carburetor.
to
8.
GOVERNOR ADJUSTMENT section.
that
case
6
x
10 mm bolts,
is
connected
part
shaft.
of
(EY14:
(6
crankcase.
from carburetor. (EY14: 6 x 8 mm Flange bolt
'2
pieces) (EY25-2, EY27-2:
to
carburetor choke lever.)
dirt
is
sufficiently removed. Dry
kerosene and 1 part Mobile oil. Squeeze out
mm
bolt,
6 x 12
1
pieces)
(6mm
nut, 2 pieces)
mm bolt/EY25-2,
EY27-2:
8
x
at
8
12
the
mm
mm
-
-
22
-
Page 27

0
Remove flywheel
2)
a
Apply
socket wrench over the flywheel
nut and give the wrench
a
soft hammer. Remove nut and spring
washer. (EY14:
from
crankshaft.
a
sharp blow with
12
mm nut/EY18-3, EY23,
EY25-2, EY27-2: 14 mm nut)
to
Attached flywheel puller
flywheel
illustrated in Fig. 6-3-1, turn center
clockwise until flywheel becomes
enough
Remove spark plug cap from high tension
3)
cable
coil from crankcase.
and washer,
Take off the point cover and remove
4)
to
be
removed.
of ignition
2
pieces)
coil
and remove ignition
(6
x
25 mm screw
as
bolt
loose
I
Flywheel Puller Flywheel
Fig.
6-3-
7
contact breaker and condenser, from
crankcase (All models of the EY23 engine
are
electronicallv ignited.)
In reasseambling magneto, refer
5)
"
to
7-2 BREAKER POINT ADJUSTMENT, and 7-3 TIMING
ADJUSTMENT.
6-3-7 CYLINDER HEAD and SPARK PLUG
1)
Remove spark plug from cylinder head.
2)
Unscrew mounting nuts/bolts and remove cylinder head from crankcase. (EY14: 8 mm flange
10
bolt/EY18-3, EY23, EY25-2, EY27-2:
mm flange nut)
3) Remove cylinder head gasket and baffle (head cover) from crankcase.
4) In reassembly;
*
Clean carbon from combustion chamber and dirt from between the cooling fins
its
head. Check
*
Torque 8 mm flange bolt in EY14
3,
EY23 to 330 % 360 kg-cm (23.8% 25.9 ft-lb), and those in EY25-2, EY27-2
mounting face for distortion. Use new head gasket.
to
190 2.20 kg-cm (13.7.> 16.6 ft-lb),
10
rnm
of
nuts in EY18-
to
340 % 370 kg-
cm (24.6 -26.8 ft-lb).
*
Leave spark plug out temporarily, for
and
for
timing adjustments. When mounting spark plug, tighten
ease
in turning engine over for remainder
it
to
230
of
assembly
Q,
270 kg-cm
(16.6 %19.5 ft-lb) torque in models EY14, EY18-3, EY23, EY25-2 and EY27-2.
cylinder
6-3-8 INTAKE and EXHAUST VALVES
1)
Remove tappet cover and breather plate
from crankcase.
2) Lift valve spring
by
means
tool (valve spring compressor) and remove
retainer locks and valves.
same way both
haust valve.
(See
for
intake valve and ex-
Fig.
6-3-2)
Then, remove valve springs and spring
retainers.
CAUTION:
DO
SURFACE
THE COMPRESSOR
3)
In
reassembly;
*
Clean carbon and gum deposits from the
NOT DAMAGE GASKET
OF
TAPPET CHAMBER WITH
TOOL.
of
compressor
Proceed
in
the
I
Fig.
6-3-2
-
23
-
Page 28

Replace valves if
or
warped.
Correct
cutter
the
tool
as
The finished
the
valve
valve
seat
by
using
illustrated in Fig.
seat
width should
face
be
is
pitted
4S0
6-3-3.
1.2
seat
~1.5
mrn.
Valve guides should
be
replaced when
valve stem clearance becomes excessive.
(See
Fig.
6-34)
Draw valve guides out using -valve guide
puller
tool
as
shown
in
Fig.
6-3-4
and
press new guides in, using the same puller
tool.
Assemble valve springs and spring
tainers
after
adjusting tappet
t3"
1
clearance.
re-
Valve Seat Cutter
Fig.
6-3-3
A
-
VALVE FACE ANGLE
B
-
SEAT ANGLE
/
C
-
GUIDE INSIDE DIA.
D
-
VALVE
MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE
CLEARANCE BETWEEN Cand
STEM
DIA.
(
D
):
EY14
INTAKE
EXHAUST
i
INTAKE
I
EXHAUST
VALVE
Guide
EY14 EY18-3, E23, EY25-2, EY27-2
45O
45"
+0.015
6
dia.
0
-0.025
6
dia.
-0.040
-0.075
6
dia.
-0.095
i
0.025L-
0.075L-
and
VALVE GUIDE CLEARANCE
Fig.
6-3-5
0.055L
0.1
1OL
I
I
Fig.
6-3-4
7
.7
0.056L- 0.098L
4
45O
dia.
dia.
5O
N.036
N.016
-0.040
-0.062
L:
Loose
-
24
-
Page 29

4)
Tappet Adjustment (See Fig.
6-3-6)
With tappet
in
its lowest position, hole
valve down and insert feeler gauge
between valve and tappet stem. The
clearance
for
both intake and exhaust,
with engine cold, must be and
0.16
%
0.20
mm
for
EY14,
EY18-3,
EY23, EY25-2
and
EY27-2.
If
the clearance is less than it
should be, grind the end
of
valve stem a
very little at a time and remeasure.
If
the clearance
is
too large, sink valve
seat with seat cutter tool.
After obtaining correct clearance, assemble valve springs and spring retainers,
and
secure them
in
place with the re-
tainer
locks.
Check
operation
of
valves
by
turning crankshaft over
by
hand and
remeasure tappet clearance.
6-3-9
MAIN BEARING COVER
Fig.
6-3-6
Remove mounting screws.
(EY14:
6
mm
bolt and washer
7
pieces/EY18-3,
EY23, EY25-2,
EY27-2:
8
mm
bolt 8 pieces)
Tap around outer surface
of
main bearing cover with a soft hammer to break it loose and
carefully remove it,
so
as not to damage oil seal.
In
reassembling
EY14,
EY18-3
and
EY23
main bearing cover, install governor gear and governor
sleeve inside it
first,
and make sure that governor shaft is already installed in crankcase.
In
this case,
in
order to prevent damage
of
governor gear (made
of
plastics) which has been
installed inside main bearing cover, reassemble main bearing cover to crankcase, making sure
that governor gear mesh
with
cam gear.
In
reassembling
EY25-2,
EY27-2
main bearing cover, mount governor yoke inside main bearing
cover before remounting it. (See Fig.
6-3-7)
If
oil seal must
be
replaced, force fit
a
new
oil seal
in
main bearing cover before mounting it.
In
reassembling main bearing cover, apply oil to bearing surfaces, gear train, tappets and oil
seal lips and form a light film
of
oil
on
main bearing cover face to hold gasket in place. Mount
an
oil
seal guide
on
to the crankshaft to prevent damage to the oil.seal lips. (Fig.
6-3-8)
Confirm that crankshaft end play is
0
~0.2
mm.
If
necessary, adjust it with adjusting collar.
(See
Fig.
6-3-9)
Fig.
6-3-7A
(EY14, EY18-3, EY231
(Model
Bl
Fig.
6-3-
7B
(E
Y25-2, E Y27-21
(Model
D)
-
25
-
Page 30

Fig.
6-3-8
*
Correct fastening torque
Adjusting
Collar
for
main bearing cover mounting screws is:
EY 14 80 %lo0 kg-cm (5.7% 7.2
EY18-3, EY23, EY25-2 and EY27-2
170 ~190
kg-cm
(12.2 Q 13.7
Fig.
ft-lb)
6-3-9
ft-lb)
CAUTION: Fig. 6-3-9 SHOWS ONE METHOD
PLAY.
THE DISTANCE BETWEEN THE MACHINED SURFACE
ADJUSTING COLLAR IS MEASURE’D. THE COMPRESSED THICKNESS
COVER
PACKING IS 0.25
mm
(EY14, EY18-3 and EY23) and 0.15
OF
MEASURING THE CRANKSHAFT END
OF
CRANKCASE AND
mm
(EY25-2, EY27-2)
OF
TAKE THIS THICKNESS INTO CALCULATION WHEN DETERMINING THE END PLAY.
6-3-10 CAMSHAFT and TAPPETS
1)
Remove
In
this
on its side
2)
Withdraw tappets and
camshaft from crankcase.
ease,
as
to
prevent tappets from falling out and becoming damaged, turn crankcase over
shown in Fig. 6-3-10.
mark
them
for
identification with the hole
from
which they were
removed.
3)
In reassembly; *put tappets
Do not forget
*
Timing
If valve timing
6-3-1
1)
to
marks
mount thrust sleeve on camshaft.
on camshaft gear and crankshaft gear must
is
off,
back
engine
in their corresponding
will
not function properly
hole
first and then mount
be
matched
or
may not
up.
run
at
all.
BEARING
camshaft.
(See
Fig.
-,
F3.
6-3-
70
I
Fig.
6-3-
1
1
-
26
-
Page 31

6-3-11
1)
2)
3)
CONNECTING
Straighten
Take off
oil
Scrape off
ROD
out
the
bent
scraper, rod
all
carbon deposits
and
tabs
lock
PISTON
of
rod lock washer and remove
washer and connecting
that
might interfere with removal
cylinder.
4)
Turn crankshaft until piston is
and
out
through top
5)
Remove piston from connecting rod by taking out
of
cylinder.
at
top, then
pin.
6)
Remove piston rings from piston by widening
In
7)
reassembly;
push
connecting
the
open ends.
bolts
rod
cap..
two
clips and then removing
from connecting rod.
of
piston from upper end of
rod
and piston assembly
the
upward
piston
PISTON RINGS (See Fig.
a)
If an expander
tool
is not available, install
rings by placing the open ends
on first land
far enough
to
of
piston, spread ring only
slip
over piston and carry it
6-3-12)
of
into correct groove.
Be extremely careful not
brake ring. Assemble rings in
oil
ring, second ring and top ring. (See
Fig.
6-3-13)
PISTON and CONNECTING
b)
to
distort and
the
ROD
order
Assemble piston and connecting rod
inserting piston pin. Be sure
at
clips
both ends of piston pin.
to
When installing connecting rod, use
piston ring compressor
Fig.
rod
6-3-14
so
that
and position
the
as
mark
illustrated in
the
connecting
on
it
faces
flywheel side.
Prior
to
installing
the
connecting rod, oil
the piston rings, large end bearing and
cylinder wall amply.
Stagger the piston ring gaps
around
To
the
piston.
.determine
the
clearance between
900
piston and cylinder, measure the diameter
of
the piston in the center
at
faces
Turn crankshaft
the bottom
to
of
the piston skirt.
bottom of stroke and
of
the
tap piston down until rod contacts crank
pin.
Mount connecting rod cap matching
marks on connecting rod.
*
Install
tabs
*
Check
a
new rod
positively.
for
free
lock
washer
movement
and
bend the
of
connecting
rod after assembling.
the
insert
apart
thrust
ring
of
by
a
the
the
/I
Fa.
6-3-
F
is.
6-3-
F
is.
6-3-
12
...
...
...
.......
.......
.......
.......
!"&
.......
I
13
13
Second
Oil
Ring
Piston
Ring
Ring
Guide
Fig.
6-3-
14
-
27
-
Page 32

The
correct
torque values
EY
14
EY18-3
EY
23
EY25-2
EY
27-2
90
%
170 % 200
200 % 25Okg-m (14.4 % 18.0 ft-lb)
connecting
are
as
115
kg-cm
rod
follows:
(6.5
cap fastening
%
kg-cm (12.3 % 14.4 ft-lb)
8.3
ft-lb)
Refer
to
chart
Fig.
6-3-15
for
clearance
between piston, cylinder and connecting
I
D
(crankshaft pin Dial
I
I
W
(crankshaft
I
~~&~N$~>!~~~~R
I
PISTON RING GAP
PISTON RING SiDE
CLEARANCE IN
GROOVES
CONNECTING
TO
CRANK PIN
CONNECTING
PISTON PIN TO PISTON 10.009T-0.01 L )0.009T-O.01 L 10.009T-0.01 L 10.004T-0.015L
L:
LOOSE,
pin
ROD
ROD
T: TIGHT
Width)
TO
AT
PISToN
TOP RING
RING
OIL
SIDE
PISTON PIN
EY14
23.4
kO.1
10.037L-0.075L
1
0.20L-0.40L
0.05L-0.095L
0.04L-0.085L SECOND RING
0.01
L-0.055L
0.05L-0.076L
0.01 L-0.029L
rod.
EY
18-3 EY 23 EY25-2 EY27-2
25
+0.1
1
0.03L-0.069L I 0.03L-0.069L
1
o.o~L-o.~~L
0.04L-0.085L.
0.1L-0.3L 0.2L-0.7L
0.01L-0.029L
1
25
2.'
1
o.o~L-o.~~L
0.04L-0.085L
0.037L-0.063L 0.037L-0.063L
If
JWL
I
27
2.'
1
0.06L-0.99L ~0.072L-O.111L
I
o.o~L-o.~~L
0.04L-0.085L
0.1
L-0.3L 0.1 L-0.3L
0.021 L-0.04OL 0.01 L-O.C29L
1
27
2.'
1
o.o~L-o,~~L
0.05L-0.095L 0.05L-0.095L 0.05L-O.OQ5L 0.05L-0.095L
0.04L-0.085L
0.01 L-0.055L 0.01 L-0.055L 0.01 L-0.065L 0.01 L-O.055L
0.04L-0.066L 0.04L-0.066L
0.1
L-0.3L
0.021 L-0.040L
I
0.004T-0.015L
I
I
I
I
I
6-3-12
1)
2)
3)
*
CRANKSHAFT
Remove woodruff key
Remove crankshaft from crankcase
tapping lightly
damage
In
reassembly; Attach
of
the
crankshaft and mount crankshaft in
crankcase
If
an
oil
seal
crankshaft
damage lips of
at
its end. Take
oil
seal.
as
shown in Fig.
guide
with
extreme
oil
seal.
is
(for
magneto).
care
oil
seal
guide on end
6-3-16.
not available,
care
so
as
Fig.
by
not
to
mount
not
to
-
6-3-
75
I
28
-
Crankshaft
Fig.
6-3-
16
Page 33

7.
MAGNETO
7-1
MAGNETO
The spark for ignition
is
furnished by a magneto in models EY14,
EY18-3,
EY23, EY25-2 and
EY27-2. In these models, magnetos manufactured
by
KOKUSAN DENKI K.K.
are
used.
(The
model
EY23
is
based on noncontact ignition system.)
The
magneto consists
of
a
flywheel, ignition coil, and breaker assembly (including condenser),
of
which flywheel
is
mounted on crankshaft and ignition
coil
and
breaker
assembly
are
mounted in
crankcase directly.
7-2
BREAKER POINT ADJUSTMENT
The
breaker points, which
are
mounted in
the
crankcase inside the flywheel should
be
checked twice
a
season
or
whenever the
ignition
spark
becomes weak. If
there
is
evidence
of
pitting
or
pyramidding,
the
breaker points must
be
corrected, and then
it
becomes necessary
to
readjust
the
gap
to
its
proper clearance. (0.35 mm, 0.014 inch)
The
normal
breaker
point opening
is
0.35
mm
at
full
separation. Since
the
spark timing
of
23O
is
regulated by
the
point opening, use
a
timing
light
to
obtain an accurate
spark
advance.
To
adjust
breaker
point opening, remove
starting pulley, blower housing and flywheel
from
the
engine and proceed
as
follows.
(See
Fig.
7-2)
1)
Remove
breaker
cover
from
contact
breaker.
2)
Turn crankshaft over until
breaker
arm
comes in contact with
the
high
point
of
the
breaker cam. (maximum point opening
of
0.35
mm)
3)
Loosen contact support plate
lock
screw,
just enough
so
that
bracket
can
be
moved.
4) Insert
a
0.35
mm feeler gauge between
the
points.
CAUTION: ADJUST BREAKER POINT GAP
WITHOUT OPENING
IT
MORE THAN
2
mm,
OTHERWISE RATED
HEEL-
PRESSING FORCE
MAY
NOT OBTAINED
DUE TO
THE
BENDING OF CONTACT
BREAKER ARM.
5) Insert
a
0.35
mm feeler gauge between
the points.
I
Fig.
7-2-A
(EY74, EY
18-31
Fig.
7-2-6
(E
Y25-2, E y27-21
6)
Apply a screw driver
to
adjusting
tab
and move
the
contact support plate just enough
so
that
7)
Tighten
lock
screw and
recheck
breaker
point
gap.
8)
Pull a strip
of
8
%lo
rnm wide white paper through
the
closed
points
to
remove oil and dust.
CAUTION: IN THIS CASE NEVER OPEN THE BREAKER POINT
GAP
MORE
THAN 2
mm.
9)
Mount flywheel, blower housing and starting pulley on engine after adjustment.
a
slight
drag
is
felt while sliding
the
feeler gauge
from
between
the
points.
-
29
-
Page 34

7-3
TIMING
With
the
before
the
controlled by
opening
However,
using a timing
For
timing adjustment, the following alignment
EY
14:
EY25-2
EY25-2
EY18-3:
ADJUSTMENT
Model
EY14, EY18-3, EY25-2
piston reaches TDC on
the
breaker point opening and
is
adjusted according
the
advance timing
light
as
shown
D
&
B
&
EY27-2
EY27-2 B
D
type: D mark
type: 3 mark
the
to
the
BREAKER
is
more accurately adjusted through
in
Fig.
7-3-1.
Projection
M
mark and
at
M
mark and
at
M
mark and
M
mark and relief line
M
mark and
and
compression
at
lower left crankcase
upper
slit
EY27-2
this
POINT
marks
upper left
slit
on flywheel circumference
engines,
stroke.
advance
are
is
ADJUSTMENT
provided.
crankcase
the
This spark advance
obtained when
(see
slit
on flywheel circumference
left
crankcase
slit
on flywheel circumference.
at
upper left crankcase
on flywheel circumference
spark
Fig.
is
timed
to
0.35
the
following procedures,
7-3-2)
the
mm
to
breaker
(0.014
occur
of
23O
point
inch).
23O
is
n
Flywheel
Fig.
7-3-1
For
timing adjustment, the following procedures using a timing light:
the
Disconnect
stop button
Remove blower housing
of
the
Connect one
crankcase. (See Fig.
While
the
points
timing
7-3-1)
are
open, the
W
lead
from
engine.
light
light
wires and
leads
the
coil primary wire.
to
the coil primary wire and ground
remains on and when
the
extinguished.
(D
Turn flywheel slowly counter-clockwise
the
light extinguishes.
Then, turn flywheel very slowly clockwise
the
mark
moment
on
engines) and stop immediately
flywheel
the
If
the
the
procedures
After
primary
is
in
the line with
timing
is
cowect.
timing mark lines are not in alignment, then re-adjust the point opening according
BREAKER
completing
lead
POINT
3)
through
to
the
ADJUSTMENT,
5).
the
timing adjustment, re-mount
stop button.
the
type engines)
(D
type engines)
the
light lights
the
crankcase. When the mark line is
by
removing
the
or
the
flywheel and repeat
blower housing and connect
Fig.
7-3-2
points are
clockwise
or
up.
!I3
counter+lockwise
Check if tine
the
other
closed,
the
lead
light
to
is
type engines) until
(B
type
slit
on
the
in
alignment,
to
the
checking
the
coil
/1
-30
-
Page 35

7-4
MAGNETO TROUBLE SHOOTING
When the engine does
following
1)
Check ignition cable for possible corrosion, broken, worn insulator
2)
Check the sparking
3)
Check if the breaker points require cleaning,
tests wiU clarify if they are caused
corroded or pitted. (Condenser may have
Refer to
4)
If
no
*
SPARK
Remove spark
"BREAKER POINT ADJUSTMENT".
spark takes place, replace ignition coil.
TESTING
plug
not
as
from
start
described later
or
starts
with
in
this
difficulty,
by
a defect
section.
or
to
be replaced.)
cylinder head and place it
or
in
the magneto.
adjusting
on
blower housing, with the ignition cable
connected to it.
Crank the engine several times
spark plug.
If
the
spark
is
by
starting pulley and observe the spark
strong, the ignition system can be eliminated as the source
trouble.
If
the spark is weak or there is
through
3)
above.
The
correct electrode gap
no
spark at
all,
repeat the checks according to the procedures
is
0.6
Q
0.7
mm
(0.024
when
or
its
operation is unstable, the
or
loose connection.
not.
%
If the points are badly
in
the spark gap
0.028
inch).
of
of
1)
-31
-
Page 36

8.
GOVERNOR
ADJUSTMENT
In
the model
EY
14,
EY 18-3, EY23, EY25-2
and
EY27-2
engines, a centrifugal flyweight type
1’1
governor
is
used. The flyweight assembly is mounted
on
a
separate governor gear
in
EY14,
EY18-3
and
EY23
and on the camshaft gear
in
EY25-2
and
EY27-2,
and automatically regulate
the throttle valve
of
the carburetor
in
such a way that the engine speed is maintained constant
under varying loads.
1)
Connect carburetor throttle lever and governor lever with governor
rod
and mount governor
2)
Connect the governor lever and the rotation adjusting lever with a governor
spring,
and set
the rotation adjusting lever to the crankcase.
3)
Turn
control lever clockwise
(EY14,
EY18-3, EY23)
or counterclockwise
(EY25-2,.
EY
27-2)
until throttle valve
in
carburetor is opened
fully.
Lock
control lever in this
position.
4)
With a screw driver inserted
in
the groove of govenor shaft, turn it clockwise
(EY14,
EY18-
3,
EY23)
or
counter-clockwise
(EY25-2,
EY27-2)
fully
(until it will not turn any more) and
then lock governor lever to governor shaft by tightening clamp bolt.
lever
on
governor shaft.
Governor
Rod
\
Governor Spring
Fig.
8-1
-
32
-
Page 37

9.
CARBURETOR
9-1
OPERATION
and
CONSTRUCTION
(See
Figs.
9-1-1
and
9-1-2)
9-1-1
FLOAT
SYSTEM
The float chamber located directly beneath the main carburetor structure serves to maintain
at
a
the fuel level
incorporated in
it.
constant height by a joint action
Fuel from the fuel tank enters
while
cousing
the
fuel level
the
Throttle
Pilot
is
low
float to move up.
Valve
Outlet
but is
the
float chamber through the needle valve, which
closed
when
the
fuel
of
level
the
reaches
float
and the needle valve
is
kept open
a
predetermined level
I
F
is.
-33
9-
7
-2
-
Page 38

9-1-2
The
through
jet
outlet
PILOT
SYSTEM
pilot system supplies fuel
the
main
jet
and
is
then regulated by
and
by-pass.
is
measured by
the
to
the
engine during idle and low
the
pilot screw
pilot jet
before
to
mix with
the
being supplied
speed
air
to
operation.
The
fuel taken
measured by the pilot air
the
engine through
the
,-
pilot
During
9-1-3
idle
operation, the engine
MAIN
SYSTEM
is
supplied with fuel mainly through the pilot outlet.
During medium and high-speed operation, fuel supply
system, in which fuel flow
supplied through the main
where
main nozzle the
mixture
with intake
9-1-4
The
the
is
CHOKE
choke
fuel
is
mixed with air, the flow
metered
then discharged through the top of the main nozzle
air
to
become
SYSTEM
system aides starting in
engine is cranked with
so
that
more fuel
9-2
DISASSEMBLY
is
introduced into
and
Besides mechanical failures, most troubles
most common
causes
of
passages, and variations in
carburetor,
without restriction.
the
air cleaner and carburetor must
(See
rate
is
controlled by the main
jet
where
the
flow
rate
air
is
admitted through the bleed holes
the
optimum air-fuel mixture
the
cold
season by enriching
the
choke
REASSEMBLY
closed,
the
the
vacuum applied
air flow
are
incorrect fuel-air mixtures
the
fuel level.
Fig.
9-2-A,
9-2-B
or
9-2-C.)
rate
of
to
In
to
the engine
jet.
is
controlled, and through the main nozzle,
which is controlled
as
to
be
supplied
the
to
the
is
controlled in the main
In
the main system, fuel
by
the main
to
mix with the fuel. The
air
atomized fuel where it mixes
to
the
engine.
air-fuel mixture. When
main nozzle is made higher
make a starting easy.
attributed
are
order to obtain
be
maintained clean
to
an incorrect mixing ratio.
clogged
jets,
the
restricted
full
performance
so
that
air
air and fuel
jet.
and fuel
In
of
is
the
the
The
the
flow
n\
9-2-1
1)
2)
9-2-2
1)
2)
9-2-3
1)
2)
3)
THROTTLE
Unscrew Philips
Take
care
not
SYSTEM
head
screw
to
damage ends
(16)
and remove
of
throttle valve.
throttle
Remove throttle stop screw (20) to remove spring
CHOKE
Unscrew Philips screw
model
Remove them beforehand
When assembling
PILOT
Remove pilot jet
Unscrew pilot screw
SYSTEM
EY25-2,
SYSTEM
(lo),
remove
EY27-2 engines have
to
prevent them from being
choke
(23).
shaft,
Use
(22)
the
flat on
correct
and
remove spring
tool to prevent damage.
choke
choke
choke
valve
ball
(21).
Reassembly
a.
Tighten
b.
Replace pilot screw
pilot
jet firmly
if
to
prevent
fuel
leakage
tapered end is diformed.
valve
(19).
(11)
and
(24)
and
choke
lost.
valve must
and
a
possible
Do
not overtighten.
(17)
and throttle shaft
take
out
choke
be
toward
spring
(25)
the
poor
engine performance.
shaft
in
the
main
(18).
(12).
carburetor.
air
jet
side-
The
-
34
-
Page 39

9-2-4
MAIN
SYSTEM
1)
Remove main jet holder
(9)
and dismount
2)
Remove main
jet
(8)
from main jet holder
'3)
Remove main nozzle
(2)
from carburetor
4)
Reassembly
float chamber-bowl
(6).
(9).
body.
a.
Tighten main jet securely to main jet
holder.
If
not tightened securely an
engine disorder may result through a
too rich
fuel
mixture.
b.
Tighten main jet holder to
90
kg-cm
(6.5
ft.
lbs)
torque.
9-2-5
FLOAT SYSTEM
1)
Extract float
pin
(5)
and remove float
(4)
2)
Reassembly
and needle valve
(14).
Whenever needle valve
is
replaced, re-
place valve seat as well, installing a
matching needle valve and seat assembly.
CAUTION: NEVER USE A DRILL OR A
METAL WIRE
TO
CLEAN JETS. THEY
ARE LIABLE
TO
DAMAGE
THE ORIFICE
AND CAUSE AN ENGINE MALFUNCTION. BLOW AIR
TO
CLEAN THEM.
23
17
rn
18
12
11
7
10
13
Fig.
9-2-A
(EY74, EY18-31
7
8
9
Fig.
9-2-C
(E Y25-2,
EY27-21
Fig.
9-2-6
(E
Y23/
-35
-
Page 40

9-3
ADJUSTMENTS
1)
Pilot screw is adjusted by'back screwing (counter-clockwise)
after
closing
it
fully once.
EY14
...................
1
turn
EY 18-3
BV18 2
turn
BV21
...........
1
turn
EY23 BV21
...........
1-3/8
turn
EY25-2 BV24
............
1-5/8
turn
EY27-2 BV24
...........
1-1/2
turn
...........
CAUTION:
DO
NOT OVERTIGHTEN PILOT SCREW WHEN CLOSING IT FULLY.
2)
Turn
throttle
stop screw clockwise until
the
specified idling speed
of
1200
+loo
rpm
is
THE NEEDLE POINT MIGHT BE DAMAGED BY OVERTIGHTENING.
obtained.
When
the
idling speed
is
higher
than
1200
+io'
rpm turn
it
counter-clockwise.
and engine
at
8
normal operating temperature.
3)
,
Make
final adjustments to
the
pilot
screw
and
throttle
stop
screw
with air cleaner mounted
-36
-
Page 41

10.
RUN-IN OPERATION
of
REASSEMBLED
ENGINE
An overhauled engine must be carefully run-in
to
get
proper surface condition on newly
installed parts.
Especially when
cylinder,
piston, piston rings
or
valves
are
replaced, a thorough run-in operation
is
indispensable.
The recommended run-in schedule is
as
follows:
r
I
I
1
LOAD
EY14 EY27-2 EY25-2
EY 23
EY18-3
SPEED
TIME
NO
LOAD
10
minutes
NO
LOAD
3,000
rpm
10
minutes 2,500 rpm
I
NO
LOAD
I
3,600
rpm
I
10
minutes
I
1.25 HP
60 minutes
3,600 rpm
5.5
HP
5
HP
4.5
PS
3.5
HP
2.5
HP
30
minutes 3,600 rpm 2.75 HP
2.5 HP
2.25
PS
1.75
HP
-
37
-
Page 42

11.
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
For
a
satisfactory
starting
and running conditions of
a
gasoling
engine, the following three
requirements must be met:
1.
The cylinder filled with a proper fuel-air mixture.
2.
An appropriate compression
3.
Good
If
are
back
troubles
11-1
11-1-1
1)
'No
2)
Carburetor insufficiently choked, especially when engine is cold.
3)
Water, dirt
4)
Inferior
5)
Needle valve in carburetor held open by
continuous fuel drip
all
spark
three
also
at
correct time
requirements
other
factors
pressure, which contribute
are
given below.
STARTING
FUEL
DIFFICULTIES
SYSTEM
gasoline in fuel tank,
or
gum in gasoline hindering flow
or
poor
grade
from
gasoline not vaporizing satisfactorily
Sometimes, this trouble is remedied by lightly tapping
handle
6)
Due to carburetor flooding,
making
When
pulley
or
the like.
the
mixture
this
happens, remove spark plug and turn
to
evacuate over-rich mixture through the plug
too
in
the cylinder.
to
ignite the mixture.
are
not met simultaneously, an engine can not be started.
such
as
or
heavy load
fuel
cock
to
at
starting and too long exhaust pipe causing
hard starting.
closed.
of
dirt
the carburetor during idling.
too
much fuel introduced in
rich
to
be
ignited.
The
most common
fuel
to
carburetor.
to
produce
or
gum.
This
condition
the
float chamber with
the
the
engine over several times with starting
hole.
Keep carburetor choke open
during this operation. Dry spark plug thoroughly and reinstall, and try
There
high
causes
correct
is
cylinder through cranking,
to
start
of engine
fuel mixture.
ascertained by
a
screw
driver
again.
c\
n
11-1-2
When the fuel system and the ignition system are eliminated
and
1)
2)
3)
COMPRESSION
loss
of
power, the following
SYSTEM
are
to be checked
for
Cylinder dry after long interruption of operation.
Loose
escaping mixture gas in compression
Damaged
or
broken spark plug. In
head
gasket
or
slack
this
case,
stroke.
cylinder
a
hissing noise is audible, during cranking, made by
head
tightening. A similar hissing noise
as
possible
lack
during compression stroke.
4)
Tappet clearance incorrect. (See
If
the
compression
dismantled and
1)
Valve
2)
Piston rings stuck
stuck
from engine and clean,
is
the
foliowing
open
not recovered after correcting the above faults,
due
to
carbon
in
piston
correct
must
due
"6-3-8,
be
checked.
or
gum
to
carbon accumulation. Remove pistor! and connecting
or
replace parts.
4)
Tappet Adjustment'!)
OR
valve stem.
-38
-
the
cause of starting difficulties
of compression.
is
produced
the
engine must
be
partly
rod
n
Page 43

11-1-3
ELECTRIC
SYSTEM
When there is no spark, the following must be checked.
1)
Disconnected cable leading to ignition coil, spark plug or contact breaker.
2)
Broken ignition coil winding, causing short circuit.
3)
Wet
or
oil soaked spark. plug cable.
4)
Dirty
or
wet
spark plug.
5)
Incorrect spark plug electrode gap.
6)
Short connection
of
spark plug.electrodes.
7)
.Pitted
or
fused
breaker points.
8)
Sticking breaker
arm.
9)
Leaking
or
grounded condenser.
10)
Incorrect ignition timing.
11-2
ENGINE
MISSES
1)
Incorrect spark plug electrode gap.
2)
Worn and leaking ignition cable.
3)
Weak spark.
4)
Loose connections
in
ignition wire.
5)
Pitted
or
worn breaker points.
6)
Gasoline containing water.
7)
Poor compression.
11-3
ENGINE
STOPS
1)
Fuel tank empty. Gasoline contaminated
with
water, dirt
or
gum.
2)
Gasoline vaporized
in
fuel lines due to excessive heating around engine. (Vapor lock)
.3)
Vapor lock in
fuel
lines or carburetor due to the use of too volatile winter
gas
in the hot
4)
Air vent hole in fuel tank cap plugged.
5)
Seizure in rotating
or
sliding pairs
in
engine due to lack
of
oil.
6)
Ignition troubles.
season.
114
ENGINE OVERHEATS
1)
Crankcase oil supply
low.
Replenish immediately.
2)
Incorrect spark timing
3)
Low
grade gasoline
is
used.
Engine overloaded.
4)
Restricked cooling air circulation.
5)
Cooling air partly misdirected causing loss to cooling efficiency.
6)
Cylinder head cooling fins blocked with dirt.
-39
-
Page 44

7)
Engine operated
in
closed space without fresh
supply
of
cooling air.
8)
Restricked exhaust gas outlet.
9)
Engine detonating due to low octane gasoline
with
heavy load at low speed.
Carbon deposit in combustion space.
11-5
ENGINE KNOCKS
1)
Gasoline
of
poor
quality
or
low octane rating.
2)
Engine operating under heavy-load at
low
speed.
3)
Carbon
or
lead deposits
in
cylinder head.
4)
Incorrect spark timing.
5)
Lose
or
burnt out connecting rod be.aring.
6)
Worn
or
loose piston pin.
7)
Engine overheated.
11-6
ENGINE BACKFIRES THROUGH CARBURETOR
1)
Water
or
dirt in gasoline
or
poor grade
of
gasoline.
2)
Sticky intake valve.
3)
Overheated valves,
or
hot
carbon particles in engine.
4)
Engine cold.
-
40
-
Page 45

12.
CHECKS
and
CORRECTIONS
After'dismantling and cleaning the engine parts,
check
them, and
if
necessary, correct them,
according
to
the correction table.
The
correction
table
applies whenever
the
engines
are
repaired. Its contents should
be
thoroughly understood by those
who
undertake the repairing. Its specifications must be abided
by to effect correct maintenance.
Below,
terms
employed
in
the correction table
are
explained.
1)
CORRECTION
All operations performed on the engine parts
for
the purpose
of
improving
or
recovering
the
engine performance, consisting
of
repair, readjustment, and replacement.
2)
STANDARD SIZE
Design dimension
of
the part without the tolerance.
3)
CORRECTION TOLERANCE
Tolerance on the re-finished part dimension
or
on the readjustment dimension.
4)
CORRECTION LIMIT
Limit on
the
part and adjustment, beyond which any dimensional and functional change, due to
wear, burn and other causes
will
adversely affect
the
normal engine performance.
5)
USE LIMIT
Limit, beyond which the part
is
no longer usable, due to defects in function
or
strength.
NOTE:
All
dimensions in
the
"13.
CORRECTION TABLE"
are
given in millimeter, except where
otherwise specified.
-41
-
Page 46

13.
CORRECTION TABLE
7
CORRECTION
METHOD
t
ITEM
Flatness
of
cylinder
head
ENGINE
MODEL
CORRECT1
STANDARD
TOLERANCE
SIZE
N
LIMIT
USE
"IT
REMARKS
TOOL
surface
,late,
'eeler
0.1
5
Correct
EY25-2
EY27-2
M.018
EY 18-3
EY23
EY25-2
EY27-2
EY14
EY23
EY18-3
EY27-2
EY25-2
65
dia.
68
dia.
72 dia.
74 dia.
4.0.01
9
0
0.01
Bore
0.1
5
1.15
Roundness
Boring
EY14
EY18-3
EY23 0.01 5
EY25-2
EY27-2
EY14
EY 23
EY18-3
EY25-2
EY27-2
1.2-
1.5
EY14
N.015 6
dia.
EY18-3
EY23
EY25-2
EY27-2
7 dia. +0.036-+0.016
S.T.D.
61.963 dia.
EY14
C 62.463
dia.
B
62.213dia.
Cylindricity
Valve seat contact
width
Correct
2.5
0.1 5
0.15
9t
middle
>onion
Valve guide
I.D.
Replace
0.2
0.2
I
I
S.T.D.
64.980
dia.
EY18-3
I
B
64.230
dia.
~~ ~~
1
C 65.480 dia.
I
O.D.
at
skirt,
in
thrust
direction
(over
size)
EY23
S.T.D.
67.970 dia.
B
68.220dia.
C
68.470
dia.
-0.02
Micrometer
Vernier
calipers
"0.1
Replace
-0.1
0.15
0.035
EY25-2
1
B
72.19dia.
I
S.T.3.71.94
dia.
C
72.44 dia.
S.T.D. 73.928
dia.
EY27-2
1
0
74.178dia.
EY25-2
y:p
l::
1
EY23 2nd
2.0
+O
.02
5
0
Width
of
ring
groove
0.15
Replace
EY18-3 Oil
+0.035
0
I
oil
2.8
I
I
Top
2.0
EY27-2 2nd
2.0
I
Oil 4.0
EY14
EY18-3
,
14 dia.
P.,"
+0.002
Cylinde
gauge
Piston pin hole 0.035
Replace
--.-"I
-0.009
EY25-2
EY27-7
16dia.
I
-
"
-
I
EY14
I
0.037L-0.075L
Max. cylinder dia. and
piston dia.
at
skirt in
thrust direction
EY18-3
EY23
I
I
0.030L-0.069L
Cylinde
Micro-
meter
gauge, Clearance between
piston and cylinde
0.025
0.025
Replace
EY25-2
0.072L-0.111
L
EY27-2
0
06
L-
0.099
L
-42
-
Page 47

Clearance between EY27-2
piston ring and
ring groove
Fit between piston EY23
&
piston
pin
Ring gap
Ring width
pin
Piston
O.D.
I
Fl
1
I
lame end
I.D.
1.D.
I
Large end
Clearance between
rod
and cr& kpin
EY25-2 2nd
EY14
EY18-3
EY23
EY 14
EY 18-3 0.009T-0.010L
EY25-2
EY27-2
EY18-3 EY25-2
EY2722
EY25-2
EY27-2
EY14
EY 18-3
EY23
EY25-2
EY27-2
EY14 0.05L-0.076L
E??!-3
EY25-2
EY27-2
I
Top
Oil
2:
TOP
Oil
2nd
2
.a
14 dia.
I
16 dia
I I I
I
,
24 dia.
26 dia. +0.013
28
dia.
I
-~
0.050L-0.095L
0.040 L- 0.085 L
0.01OL-0.055L
0.050L-0.095L
0.04OL-0.085L
0.01OL-0.065L
0.004T- 0.01 5 L
0.20-0.40
rl
0.05-0.25
-0.05h -0.07
-0.04-
4.01--0.03 Top 2.5
-0.05-
-0.04-
-0.01-4.03
I
-0.060
-0.07
-0.06
0
4.008
-0.005
-0.01
~~
3
1
0
0.04L-0.066L
'
0.15L
0.06L
-0.1
-0.04
0.1
1
1.5
USE
I
L,MIT
-0.1
REMARKS
0.15
0.06L
1.5 Replace
o*2
1
TOOL
Feeler
ww
Cylinder
gauge
Micrometer
Feeler
gauge
Micrometer
Micrometer
Cylinder
gauge
Cylinder
gauge
Micrometer
CORRECTION
METHOD
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Small end
Clearance between 0.01 L-0.029L
small
and piston
clearance
Parallelism between
large end and
small end bores
Distance between
large end and
small
end
end
I.D.
1.0.
pin
bores
EY25-2
EY27-2
EY25-2
EY27-2
EY 18-3
EY14
'
EYf8-3
E
Y23
EY25-2
EY27-2
EY25-2
EY27-2
14 dia. i-o.021-+0.01
16 dia. M.027-+0.016
I
0.021 L-0.WOL
L- 0.7
L
0.1
0.05
-0.1
-43
Cylinder
gauge
Cylinder
wage
Micrometer
Feeler
gauge
Test bar
&
Dial
indicatol
Replace
Replace 0.1
Remachine
or Replace
Remachine
or
Replace
0.12
0.1
0.08
2
0.15
1
-
Page 48

ITEM
Crankpin
Crankpin O.D. EY 23
roundness EY25-2
Crankpin O.D. EY23
cylindricity
Crankpin O.D.
parallelism
O.D.
ENGINE STANDARD CORRECTION
1
MODEL
4
EY -1
EY 18-3
EY25-2
zi
I
EY14
EY18-3
EY27-2
EY14
I
EY18-3
EY25-2
I
EY*7-2
I
EY14
EY 18-3
EY25-2
1
EY23
I
EY27-2
1
SIZE
24 dia. -0.050-0.063
26 dia. -0.037-0.050
28
dia.
TOLERANCE
-0.040.-
0.053
I
LIMIT
0.15 0.15 EY27-2
1
I
below
0.005
I I I I
below 0.005
I
I
below
1
I
0.008
I
USE
LIMIT
?
EMAR KS
CORRECTION
I
METHOO
Micro- Remachine
meter or Replace
Micrometer
Micrometer
Dial
indicato
4
Crankshaft
journal O.D.
Cam lobe height
Journal
O.D.
Squareness
-0.003-
EY25-2
EY27-2 Mag.
EY14
EY 18-3
EY25-2
1
EY23
EY14D
EY 18-38 Drive
EY23B Mag.s. 17dia. "0.016--0.027
-1
EY18-3D Drive
EY23D !Mag.
EY25-2B j Drive
EY27-28 iMaq.
EY25-20 Drive
EY27-2D Mag.
I
EY14
1
EY18-3
I
EY14
EY18-3
I
EY23
'
EY25-2
EY27-2
1
Drive
s.
3o
dia
s.
I
24.95
1
30.8
s.
22 dia. "0.003-"0.012
Drive
Mag.
s.
15dia.
{:;e:'
I
I I
I I
I
I
I
I
!Intake
1
15 dia. --0.016~--0.027
s.
25 dia. "0.003~-0.012
s.
s.
l7
dia.
s.
30
dia.
s.
20 dia.
s.
15 dia.
s.
15
dia.
32
-
Exhaust
dia.
-0.003--0.012
-0.009-0
I
I
4.016-"0.027
-0.016~-0.027
1
-0.003--0.012
I I I
~o~032~~o~043
I
I
I
j
20.025,b -0.040
0.075~-0.095
4.01
fl.1
2
-0.05 -0.05
I
1
-0.25
'
]
0.05
I
'
0.05
I
j
-1-5
I
,
I
-0.25
I
0.05
0.05
I
1
I
i
l.o
I
1
i
~ ~~~
:or total
ength
Micro-
meter
Micro-
meter
calipers
Square Replace
Replace
Replace
,-
Clearance between
stem and guide
I
EY18-3
EY23 Intake
EY25-2 Exhaust
EY27-2
ilntake
/Exhaus7
I
0.025L-O.C)55L
0.075L-0.110L
1
0.056L-0.098L
-44
j
.
0.3
-
0.3
4t
middle
~
Cylinder Replace
Page 49

ENGINE
MODEL
I
CORRECTION
REMARKS
TOOL
CORRECTION
METHOD
STANDARD
SIZE LIMIT
USE
ITEM
TOLERANCE
0.10L-0.14L
0.16L-0.2OL
LIMIT
below
above
0.0:
0.25
EY14
EY 18-3
EY 23
Tappet clearance
Correct
E Y 25-2
EY27-2
EY14
2.5 0.04L-0.12L
EY18-3
FY23 Clearance between
groove and retainer
0.5
0.5
-2
.o
Correct
Replace
EY25-2
EY27-2
2.5
0.04L-0.15L
EY14
Venier
calipers
Stem
end
length
4.0 -2
.o
EY27-2
EY 14
EY18-3
EY 23
38.12
46
0
-
+Q.06
Venier
calipers
Total length
-0.5
-0.5
Replace
E Y 25-2
EY27-2
50.9
20.05
EY14
Cylinder
gauge
&
Micrometer
0.013L-0.037L
0.025L-0.062L
Clearance between
stem
and guide
EY18-3
EY23
EY27-2
EY
14
EY 23
EY 25-2
EY 18-3
0.2 0.2
Replace
Metering needle
unscrew
Fixed
EY25-2
EY27-2
f1f4
EY 14
EY18-3
EY 23
1
BV18 2
BV21
1
BV21 1-3B
Pilot screw
unscrew
E Y 25-2
EY27-2
1-518
1-1/2
EY14
EY18-3
NGK
34HS
Spark plug
NG
K
BP4HS
EY14
EY 18-3
Adjust or
Replace
Spark gap
EY23
-
EY25-2
EY27-2
0.6-
0.7
1
EY 14
EY 183
2
5O
Timing
tester
Spark timing EY23
EY27-2
EY25-2
23' before T.D.C.
Adjust
0.4
EY14
EY 18-3
EY25-2
EY27-2
kO.1
20.05
Contact
breaker
spanner
Point opening
50.1
Adjust
0.35
-
45
-
Page 50

ITEM
Max.
Output
Continuous Rated
output
MODEL
EY14D
EY183D
EY23D
EY25-2D
EY27-2D
EY14D
EY18-3D
EY23D
EY25-2D
EY27-2D
HPIrpm
3.5l4.000
5.0/4,000
6.014,OOO
7.014,000
7.514.000
2.513.600
3.513.600
4.513.600
5.013.600
5.513.600
CORRECTION LIMIT
Below 110%
of
rated output
REMARKS
,”.
ITEM
Fuel Consumption
ITEM
Lubricant
Consumption
ITEM
Special Lubricant
Quality
MODEL
EY14
EY 18-3
EY25-2
EY27-2
MODEL
EY14
EY 18-3
EY23 50 15
EY25-2
”-
EY27-2
MODEL
EY14
’
EYl8-3
E
Y23
EY25-2
EY27-2
,
literlhr
.o
1
1.5
1.9 EY23
2.2
2.3
ahr
15
28
30
liter
0.50
0.70
0.65
0.85
REMARKS
USE
LIMIT
cc/hr
REMARKS
50
50 15
-
60
REMARKS
or
Use the class SC
Below
-1OOC (14’F) SAE 1OW-30
-1OOC (14OF) -2OoC I68OF) SAE
2OoC
/6S0F)
nigher grade Engine Oil
-4OOC (104OF)
SA€
#20
#30
ITEM
Oil Change First
I
EY14
MODEL
I
1
FREQUENCY
Time:
Change
oil
Second Time and Thereafter: Change
after 20 hours operation.
-46
-
oil
OF
every
OIL
50
CHANGING
hours
operation.
Page 51

I
ITEM
I
MODEL I kg/ud/rpm
I
CORRECTION LIMIT
I
TOOL
EY 14 4.61420
EY 18-3 5.91360
Cylinder Pressure EY23 6.7
1380
70%
of
normal value
EY25-2 5.51420
EY27-2 5.51420
Pressure gauge
ITEM MODEL
TOOL REMARKS
EY 14D
EY183D
EY23D
EY25-2D
1,200- 1,300
EY27-2D
Min.
accelerating
revolution
Tachometer
EY14B
EY23B
EY 18-38
EY25-2B
EY27-2B
600-
650
ITEM MODEL
1
kg-crn
I
ft-ib
1
TOOL
I
REMARKS
Cylinder head
clamp
nuts
EY14 190- 230 13.7- 16.6
EY18-3
EY23
1
330-360
I
23.8-25.9
I
Torquewrench
I
I
I
EY25-2
EY27-2
340-370
I
24.6-26.7
I
I
EY14
I
90-115
1
6.5-8.3
I
I
EY
18-3
EY23
170- 200
I
12.3-14.4
1
Torque wrench
Connecting rod
2
bolts
P
I-
I
I
I
I
EY27-2
1
200-250
1
14.4- 18.0
1
F
:Lz-
nuts
EY14
I
450-500
I
32.6-36.1
I
EY18-3
EY23
EY 27-2
EY25-2
43.5-47.0
Torque wrench
600-
650
EY14
I
80-100
I
5.8-7.2
I
Main bearing cover
bolts
EYl8-3
1
170- 190
12.3- 13.7
Torque wrench
EY25-2
EY14
I
250-290
I
I I
230-270
Spark plug
I
EY25-2
EY27-2
260- 300 18.8-21.7
-47
-
Page 52

14.
MAINTENANCE
and
STORING
The following maintenance jobs apply when the engine is operated correctly under normal
conditions.
The
indicated maintenance intervals are by no means guarantees
for
maintenance
free operations during these intervals.
For
example, if
the
engine is operated in extremely dusty conditions, the
air
cleaner should be
cleaned every day, instead of every
50
hours.
n
14-1
DAILY CHECKS
and
MAINTENANCE (EVERY
8
HOURS)
Checks and maintenance
Reasons for requiring them
Remove dust from whatever parts which
ceptible
to
dust.
accumulated dust.
The
governor linkage is especially sus-
Check
external fuel
leakage.
If
any, re-
tighten
or
replace.
Not
only wasteful but
also
dangerous
Check
screw tightening. If any
loose
one
vibration accidents.
is
found, re-tighten.
Loose screws and nuts
will
result in
as
necessary.
I
ficient oil, it
will
fail.
If
the
engine
is
operated without suf-
Check oil level in crankcase and
add
up
14-2 EVERY
20
HOURS CHECKS and MAINTENANCE
Checks and maintenance
Reasons for requiring
them
-\
Change crankcase oil.
To
remove run-in wear particles.
14-3
EVERY
50
HOURS
(10
DAY) CHECKS and MAINTENANCE
Checks and maintenance
!
I
Reasons for requiring them
Change crankcase oil.
Contaminated
oil
accelerates
wear.
Clean air cleaner
Clogged air cleaner harms engine opera-
tion.
-
-
Check spark plug.
If
contaminated,
wash
made difficult.
in
gasoline or polish with emery paper.
Output power is reduced and starting
is
,
14-4 EVERY
100
-
200
HOURS (MONTHLY) CHECKS and MAINTENANCE
I
Checks and maintenance
i
I
Reasons for requiring them
””
Clean
fuel
filter and
fuel
tank. =engine will
be
out
of
wder.
Clean contact breaker points.
The engine output drops.
_”
”
”
-
48
-
Page 53

14-5
EVERY
500
-600
HOURS (SEMIANUAL) CHECKS
and
MAINTENANCE
Remove cylinder
deposit.
Disassemble and clean carburetor.
14-6 ~ EVERY
Perform overhauls, clean
replace parts.
Change piston rings
Replace fuel pipe once
14-7
1)
PREPARATION
Perform
the
Checks
1000
Checks
above
and maintenance
head
and remove carbon
HOURS (YEARLY) CHECKS
and maintenance
correct
a
year.
for
LONG-TERM STORAGE
13-1
and
13-2
or
maintenance
Reasons
The
engine will
and
MAINTENANCE
Reasons
The engine output
of
order.
To
prevent-
fuel
leakage.
jobs.
for
requiring them
be
out of order.
for
requiring them
drops
from
danger caused by the
and become out
>
2)
Drain fuel from
3)
To
prevent rust in
the
fuel tank and carburetor
the
cylinder bore, apply oil through
crankshaft several turns by hand. Re-install
4)
Turn
the
starting pulley by hand and leave it where
5)
Clean
6)
Put a vinyl
the
engine outside with oiled cloth.
or
other cover over
the
engine and
float
the
store
chamber.
plug.
the
resistance
the
the
spark plug
is
the
hole
heaviest.
engine in dry place.
and turn
the
-49
-
Page 54

Page 55

Industrial
Engines
 Loading...
Loading...