Page 1

Page 2
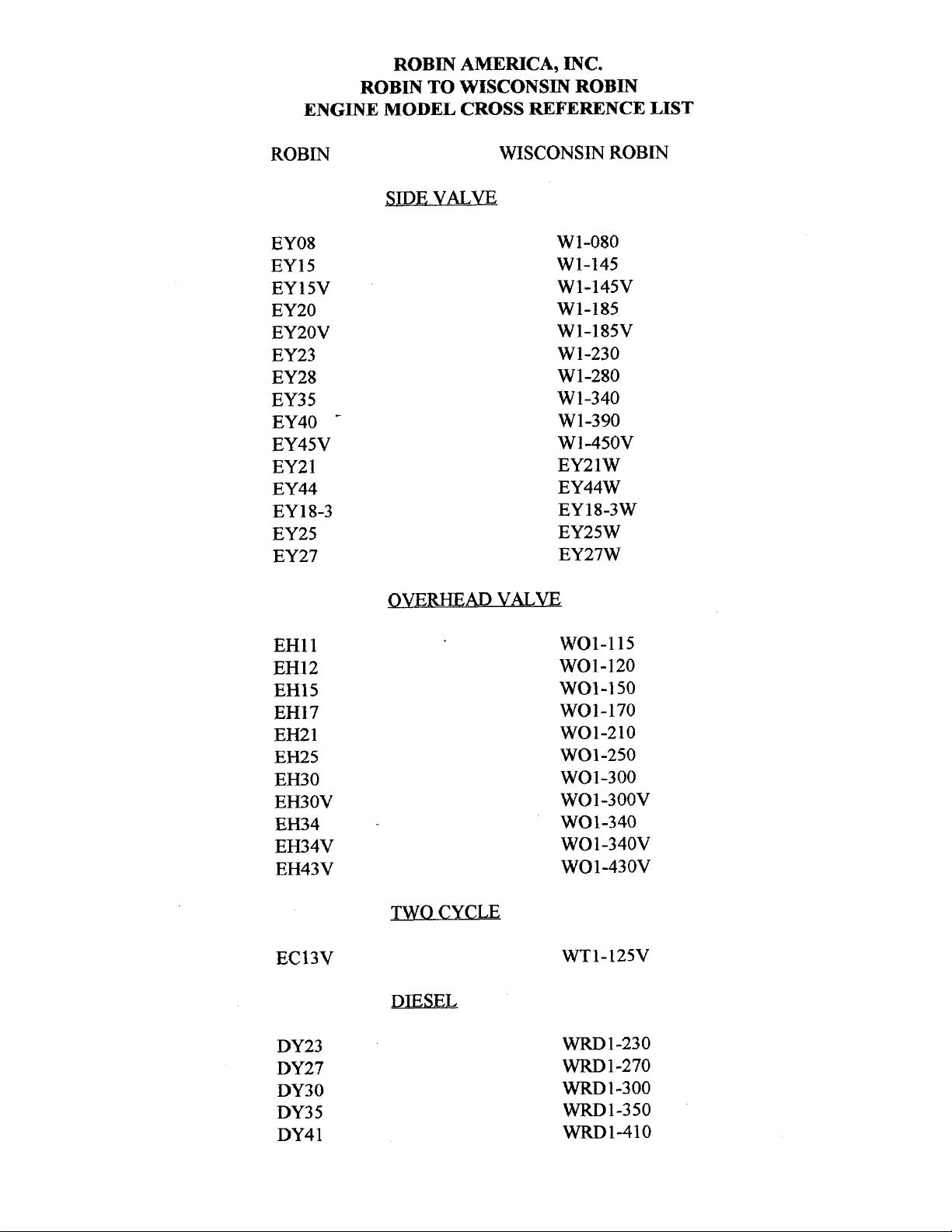
ROBIN
AMERICA, INC.
ROBIN
TO
WISCONSIN
ROBIN
ENGINE
MODEL
CROSS REFERENCE
LIST
ROBIN
EY08
EY15
EY 15V
EY20
EY2OV
EY23
EY28
EY3
5
EY40
-
EY45V
EY2
1
EY44
EY 18-3
EY25
EY27
EH11
EH12
EH15
EH17
EH21
EH25
EH30
EH30V
EH34
EH34V
EH43V
EC13V
DY23
DY27
DY30
DY3
5
DY4 1
WISCONSIN
ROBIN
SIDE
VALVE
W
1-080
W1-145
W1-145V
W1-185
W1-185V
W1-230
W 1-280
W
1-340
W 1-390
Wl-45OV
EY21W
EY44W
EY18-3W
EY25W
EY27W
OVERHEAD
VALVE
WO1-115
wo1-120
WO1-150
WO1-170
wo1-210
WOl-250
WO 1-300
WO1-300V
WO1-340
WO
1
-340V
WO 1-43 OV
TWO CYCLE
WT1-125V
DIESEL
WRD
1-230
WRD
1-270
-1-300
WRD1-350
WRD1-410
0
0
0
Page 3

CONTENTS
Section
1
.
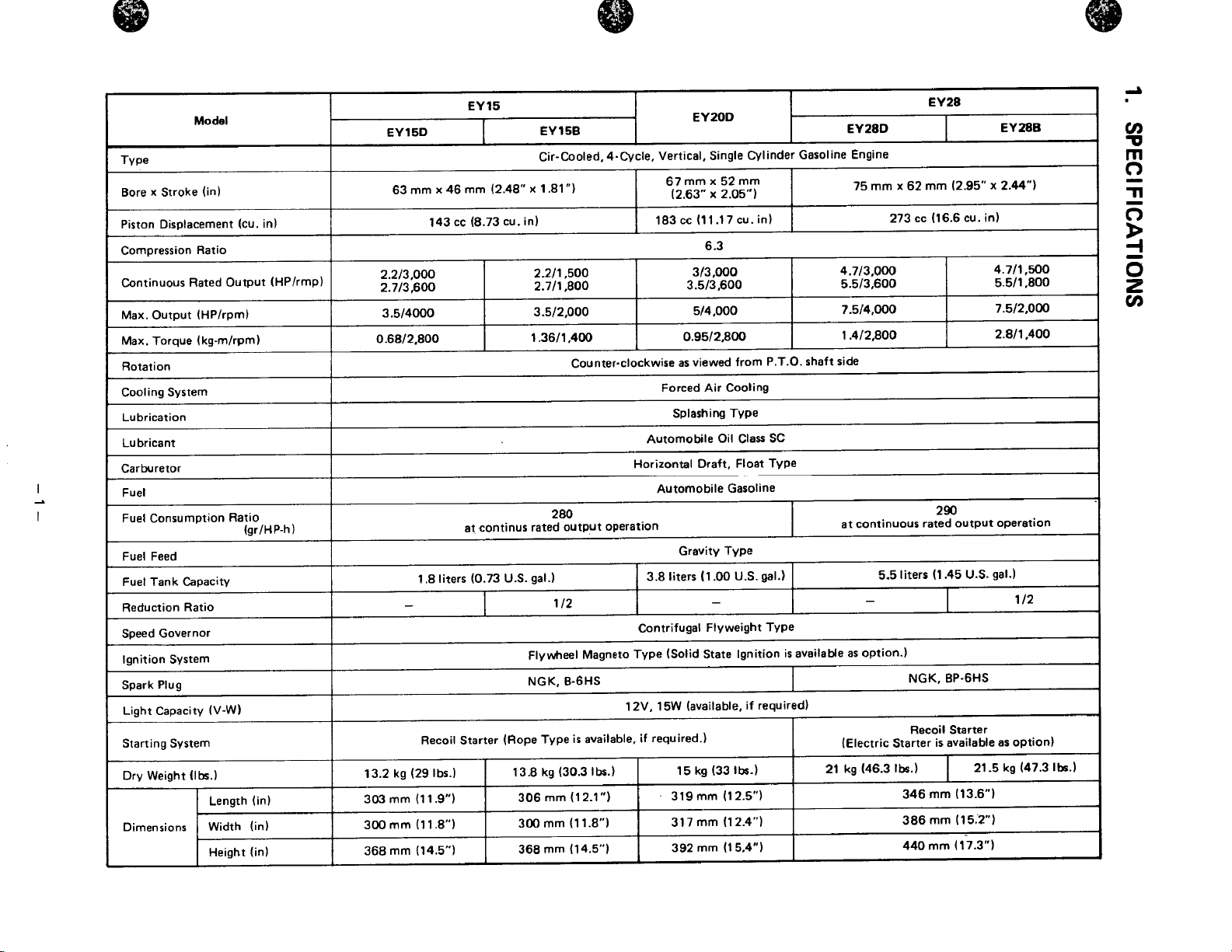
SPECIFICATIONS
2
.
PERFORMANCE
2-
1
Maximum Output
2-2
Continuous Rated Output
2-3
Maximum Torque
3 . FEATURES
4
.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Cylinder. Crankcase
4- 1
Main Bearing Cover
4-2
Crankshaft
4-3
Connecting Rod and Piston
4-4
Camshaft
4-5
Valve Arrangement
4-6
4-7
Cylinder Head
Governor
4-8
Cooling
4-9
Lubrication
4-10
4-1
1
Ignition
Carburetor
4-12
Air Cleaner
4-
13
4-14
Sectional View
Title
...............................................
............................................
............................................
..............................................
.............................................
Page
...........................................
1
...........................................
.......................................
.................................
.......................................
3
of
ENGINE CONSTRUCTION
...............
.....................................
......................................
...........................................
................................
......................................
.........................................
...........................................
...........................................
...........................................
of
Engine
..................................
4
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
8
9
9
10
5
.
DISASSEMBLY
5-1
Preparation and Suggestion
5-2
Special
5-3
Haw
5-4
How To Reassemble
6
.
MAGNETO
6-1
Magneto
6-2
Breaker Point Adjustment
6-3
Timing Adjustment for
6-4
Magneto Trouble Shooting
6-5
Solid
7 .
GOVERNOR ADJUSTMENT
8
.
CARBURETOR
8-
1
Operation and Construation
8-2
Disassembly and Reassembly
9 . BREAK-IN OPERATION
and
REASSEMBLY
Tools
..........................................
To
Disassemble
...............................................
.............................................
State
Ignition
............................................
...............................
.................................
.....................................
.....................................
.................................
EY15. EY20
.................................
......................................
...................................
................................
Of
REASSEMBLED ENGINE
Point Type Ignition System
........
...............................
................
18
18
18
20
27
37
37
37
38
39
39
40
42
42
43
45
Page 4

Section
10
.
ROBIN SOLID STATE IGNITION ENGINE
Features
10-1
10-2
Basic Theory of T
Basic Theory of
10-3
11
.
TROUBLE SHOOTING
.
1
Starting Difficulties
11
11
-2
Engine Misfires
1
1 -3
Engine Stops
11
-4
Engine Overheats
Engine Knocks
11-5
11
-6
Engine Backfires through Carburetor
12
.
INSTALLATION
12-1
Installing
12-2
Ventilation
Exhaust Gas Discharge
12-3
12-4
Power Transmission to Driven Machines
12-5
Wiring
13
.
ELECTRIC STARTING MOTOR
13-
1
Specifications
Operation
13-2
Title
.............................................
.
I.C.
...................................
P
.
I.T.
...................................
.......................................
......................................
.........................................
..........................................
.......................................
.........................................
............................................
.............................................
...........................................
....................................
..............................................
.........................................
............................................
(Option)
(T.I.C. and P.I.T.)
............
..........................
........................
..........................
pese
46
46
46
46
47
47
48
48
48
49
49
50
50
50
50
50
51
53
53
53
14
.
RECOIL STARTER DISASSEMBLY
14-1
How
To Disassemble (Type D)
How
14-2
14-3
14-4
15
.
CHECKS
16
.
TABLE
17
.
MAINTENANCE
17-1
17-2
17-3
17-4
17-5
17-6
17- 7 Preparation for
To Reassemble (Type
Check Items after Reassembly
How
To Do in Such
and
CORRECTIONS
of
CORRECTION STANDARDS
and
STORING
Daily Checks and Maintenance
Every
20
Hours
Checks and Maintenance
Every
50
Hours Checks and Maintenance
Every
100
-
200
Every
500 - 600
Every
1000
Hours (Yearly) Checks and Maintenance
Long
and
REASSEMBLY
................
..............................
D)
...............................
...............................
Cases!
.................................
...................................
...........................
.................................
..............................
.......................
.......................
Hours (Monthly) Checks and Maintenance
Hours (Semiannual) Checks and Maintenance
................
Abeyance
..............................
...........
.........
54
54
55
57
57
58
59
65
65
65
65
65
66
66
66
.
Page 5
Page 6
2.
PERFORMANCE
2-1
MAXIMUM
OUTPUT
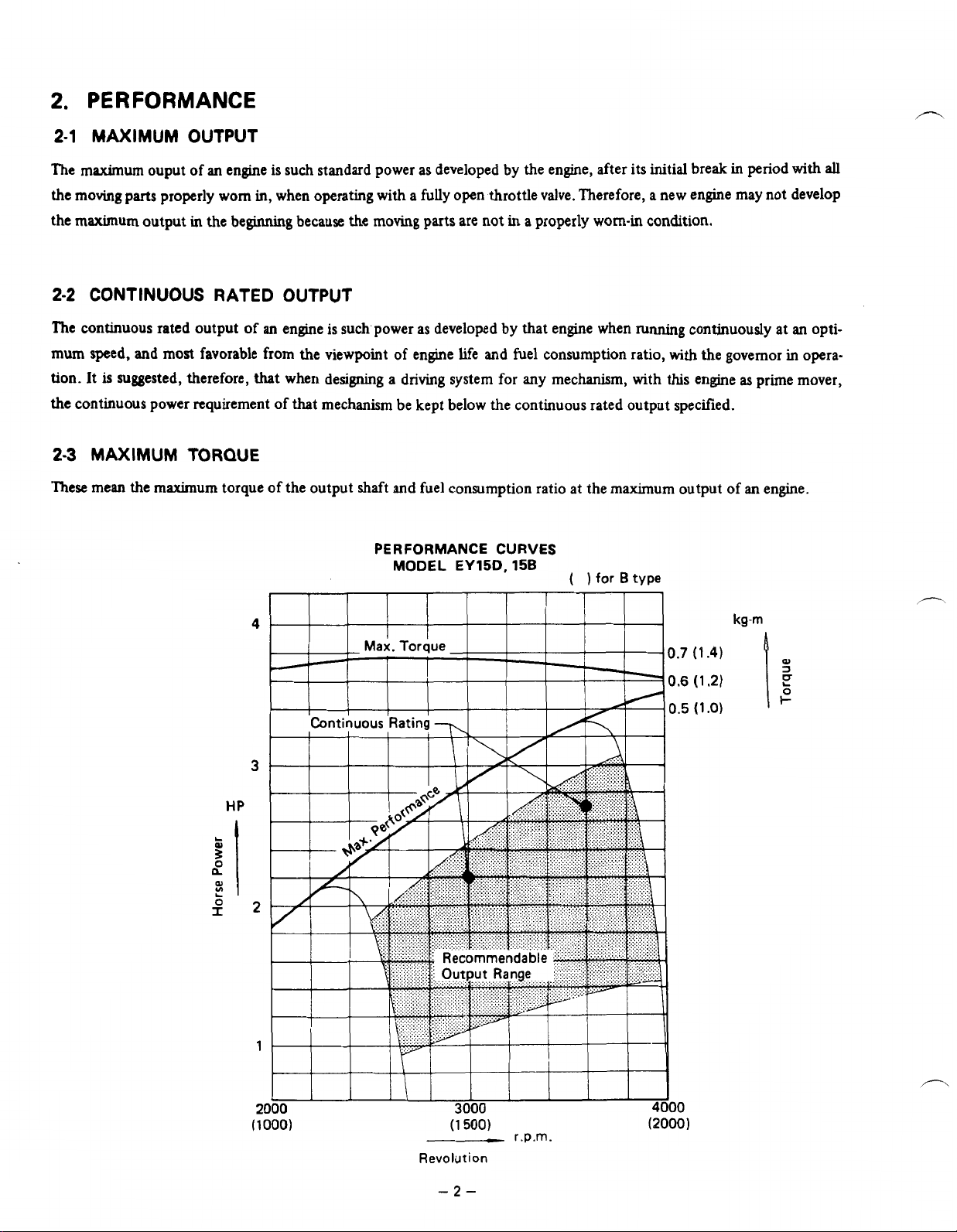
The maximum ouput of an engine is such standard power as developed by the engine, after its initial break in period
the
moving
the maximum output
2-2
The continuous rated output of
mum
tion. It
the continuous power requirement
23
These mean the maximum torque
parts properly
CONTINUOUS
speed,
and
most favorable from the viewpoint of engine life and fuel consumption ratio,
is
suggested, therefore, that when designing a
MAXIMUM
worn
in, when operating with a fully open throttle valve. Therefore, a new engine may not develop
in
the beginning because the moving
RATED
OUTPUT
an
engine
is
of
that mechanism be kept below
TORQUE
of
the output shaft and fuel consumption ratio at the maximum output of an engine.
4
parts
are not
sudrpower as developed
driving
PERFORMANCE
MODEL EY15D,
Ma;.
Torque
system
the
in
a
properly
by
that engine when
worn-in
running
condition.
continuously at
with
for
any mechanism, with this engine
continuous rated output specified.
CURVES
15B
(
1
for
B
type
~
0.7
the governor
as
prime mover,
kg-m
-
I
I
7
0.6
with
an
in
opera-
all
opti-
HP
I\ I
tii
2000
(1
000)
Revolution
3000
(1
500)
-2-
I
I
I
I
I
I
4000
r.p.m.
(20001
Page 7
5
4
3
HP
L.
B
w
r
22
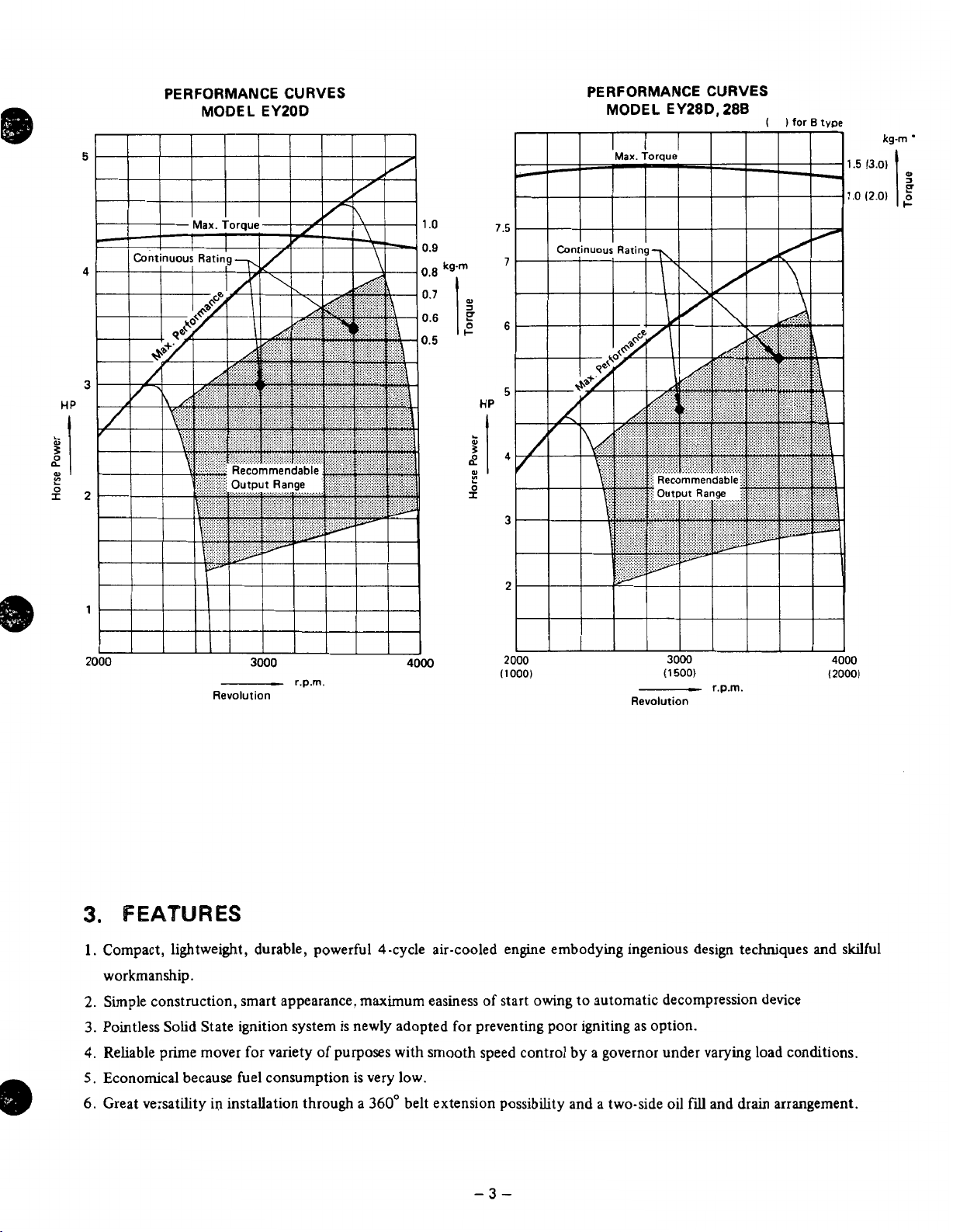
PERFORMANCE CURVES
MODEL EYZOD
Max.
Toraue
PERFORMANCE CURVES
MODEL
1
.o
EY28D,
288
I
)
for B tvm
1
2000
3.
FEATURES
1.
Compact, lightweight, durable, powerful 4-cycle air-cooled engine embodying ingenious design techques
3000
Revolution
4000
r.p.m.
2000
(1
000)
3000
(
15001
Revolution
r.p.rn.
and
workmanship.
2.
Simple construction, smart appearance, maximum easiness of start owing to automatic decompression device
3.
Pointless
4.
Reliable prime mover for variety of purposes with smooth speed control by a governor under varying load conditions.
5.
Economical because fuel consumption is very low.
6.
Great ve:satility in installation through a
Solid
State ignition system is newly adopted
for
preventing poor igniting as option.
360"
belt extension possibihty and a two-side
oil
fill
and drain arrangement.
4000
I20001
skilful
-3-
Page 8
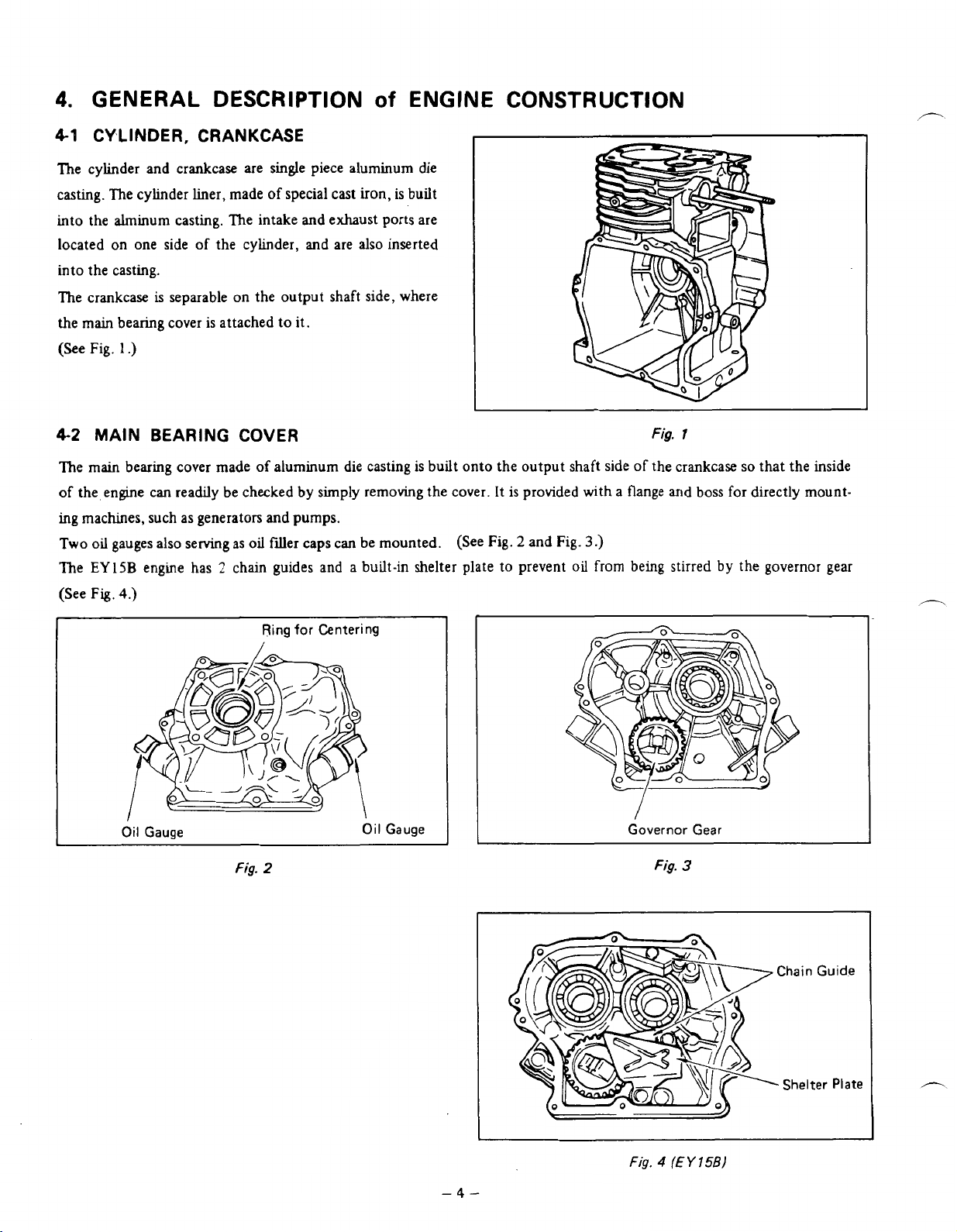
4.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
4-1
CYLINDER, CRANKCASE
The cylinder and crankcase are single piece aluminum die
casting. The cyhder liner, made of special cast
into the alminum casting. The intake
located on one side
into the casting.
of
the cyhder,
and
exhaust
and
of
ENGINE CONSTRUCTION
iron,
is built
ports
are
are also inserted
The crankcase
the main bearing cover
(See Fig.
4-2
MAIN
The main
of
the engine can readily be checked by simply removing the cover. It
ing machmes, such as generators and pumps.
Two
oil
The
EY
(See
Fig.
is
separable on the output shaft side, where
is
attached to it.
1
.)
BEARING
bearing
gauges also serving as
15B engine has 2 chain guides and a built-in shelter plate to prevent
4.)
cover made
COVER
of
aluminum die casting is built
oil
filler caps can be mounted. (See Fig. 2 and Fig.
Ring
for
/
Centering
Fig.
onto
the output shaft side of the crankcase
is
provided with a flange
3.)
oil
from
being
1
and
boss
stirred
so
that the inside
for directly mount-
by
the governor gear
Oil
Gauge
Fig.
2
Oil
Gauge
-4-
I
Governor Gear
Fig.
3
Chain
Guide
-
Shelter
1
Fig.
4
(E
Y
15B)
Plate
Page 9
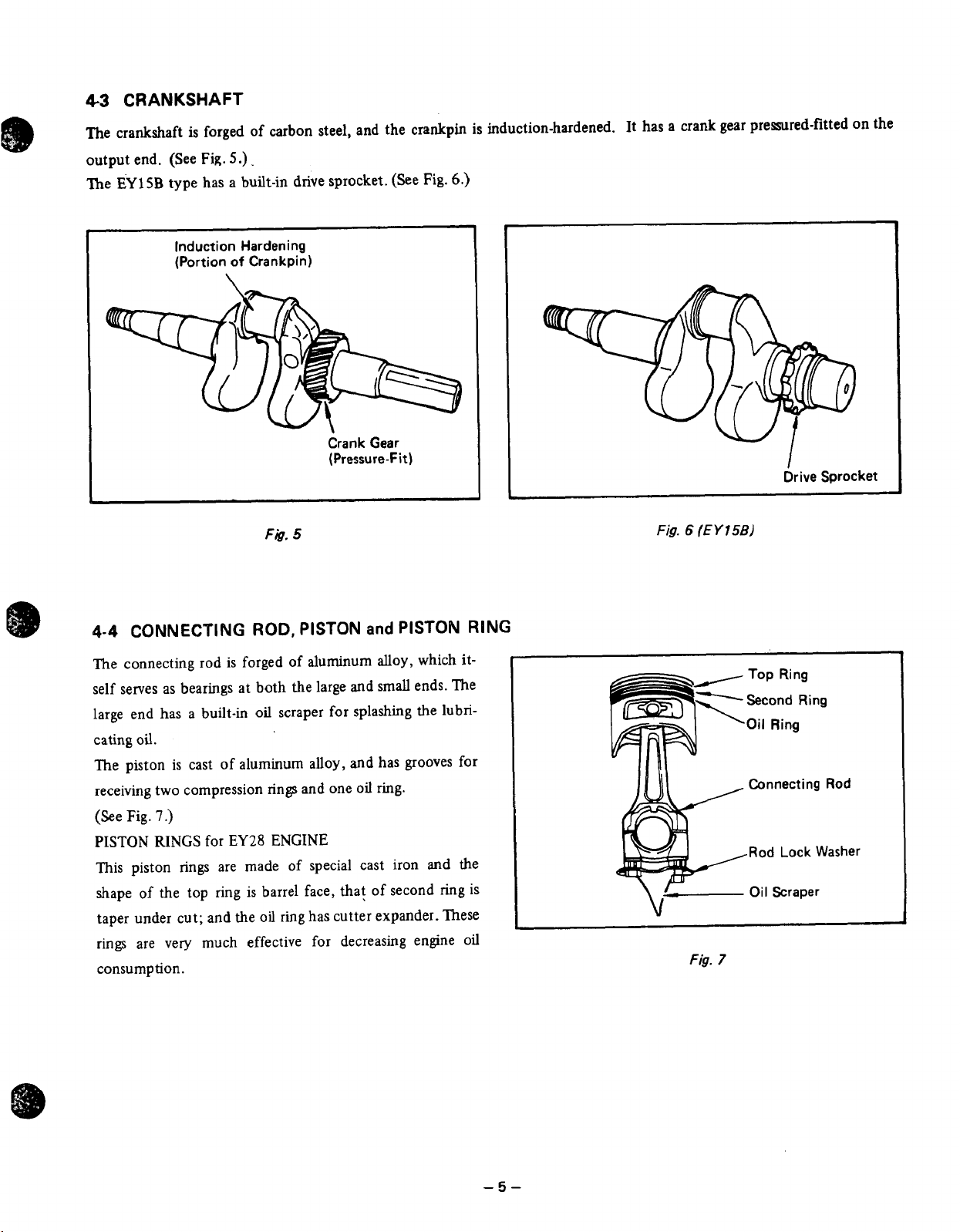
4-3
CRANKSHAFT
The crankshaft
output end.
"he
EY
(See
15B
type has a built-in drive sprocket. (See Fig.
Induction Hardening
(Portion
is
forged of carbon steel, and the crankpin
Fig.
5.).
of
Crankpin)
Crank Gear
(Pressure-Fit)
Fig.
5
is
induction-hardened. It has a crank gear premred-fitted on the
6.)
Drive Sprocket
-
Fig.
6
(E
Y
158)
4-4
CONNECTING
ROD,
PISTON
and
PISTON
The connecting rod is forged of aluminum alloy, which itself serves as bearings at both the large and
has
a
large end
cating
oil.
built-in
oil
scraper for splashing the lubri-
small
ends. The
The piston is cast of aluminum alloy, and has grooves for
rings
receiving two compression
(See
Fig.
7.)
PISTON RINGS
for
EY28 ENGINE
and one
This piston rings are made of special cast iron
shape
of
the top ring
taper under cut; and the
is
barrel face, that of second
oil
ring has cutter expander. These
rings are very much effective for decreasing engine
oil
ring.
and
ring
the
oil
consumption.
RING
is
1
Fig.
Connecting
Rod
Oil Scraper
7
Lock
Rod
Washer
-5-
Page 10
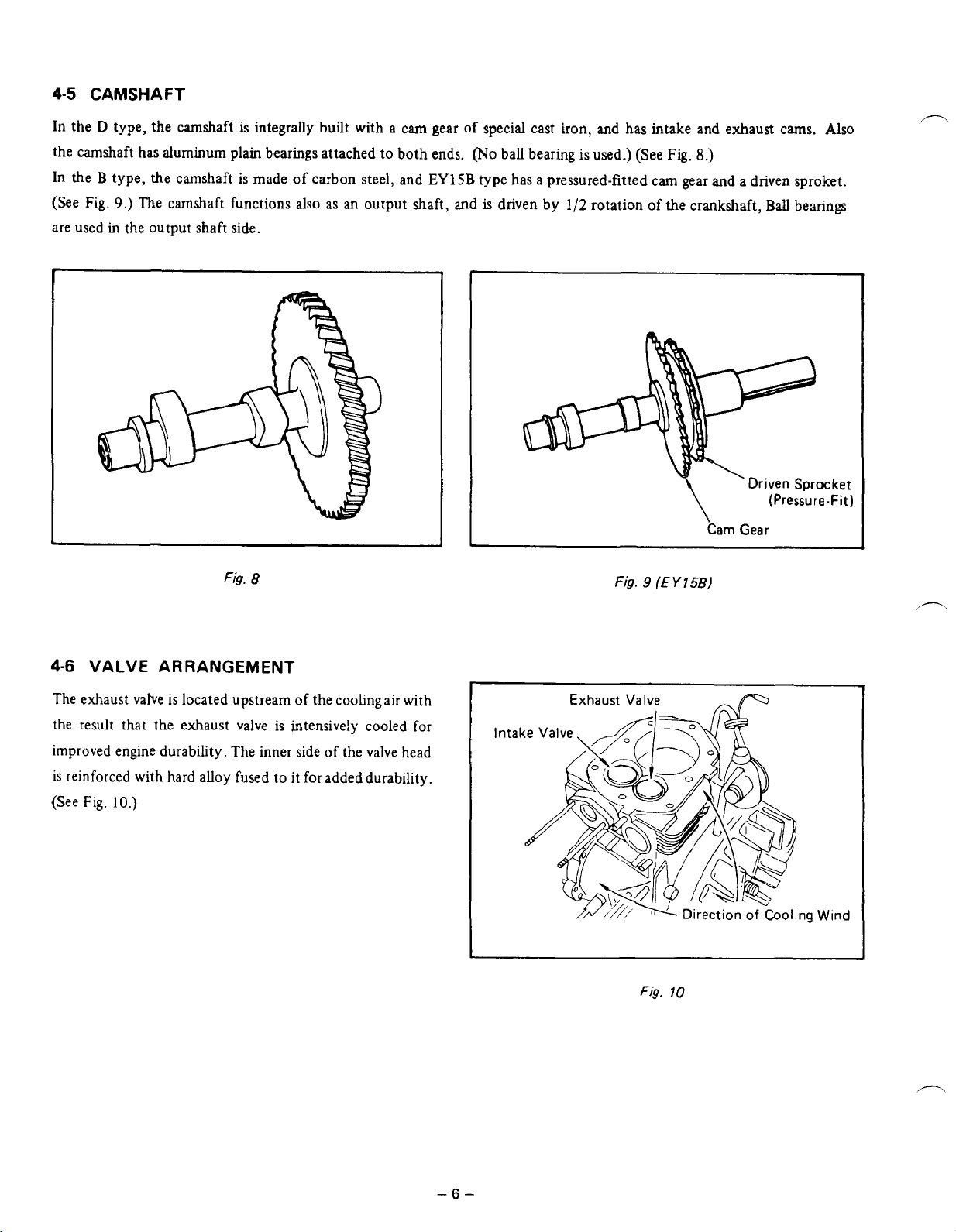
4-5
CAMSHAFT
In
the D type, the camshaft
the camshaft has aluminum
In
the B type, the camshaft is made of carbon steel, and
9.)
(See Fig.
are used
The camshaft functions also as an output shaft, and is driven by
in
the output shaft side.
is
integrally built with a cam gear
plain
bearings attached to both ends.
of
(No
EYlSB
J
special cast iron, and has intake and exhaust cams. Also
ball bearing is used.) (See Fig.
8.)
type has a pressured-fitted cam gear and a driven sproket.
1/2
rotation
of
the crankshaft,
Ball
bearings
Driven Sprocket
(Pressure-Fit)
Cam
Gear
Fig.
8
4-6
VALVE ARRANGEMENT
The exhaust vahe is located upstream
the result that the exhaust valve
improved engine durability. The inner side
of
the coolingair with
is
intensiveiy cooled
of
the valve head
for
is reinforced with hard alloy fused to it for added durability.
(See Fig.
10.)
I
Fig.
9
Exhaust Valve
Fig.
(E
Y
70
156)
Direction
of
Cooling
Wind
-6-
Page 11
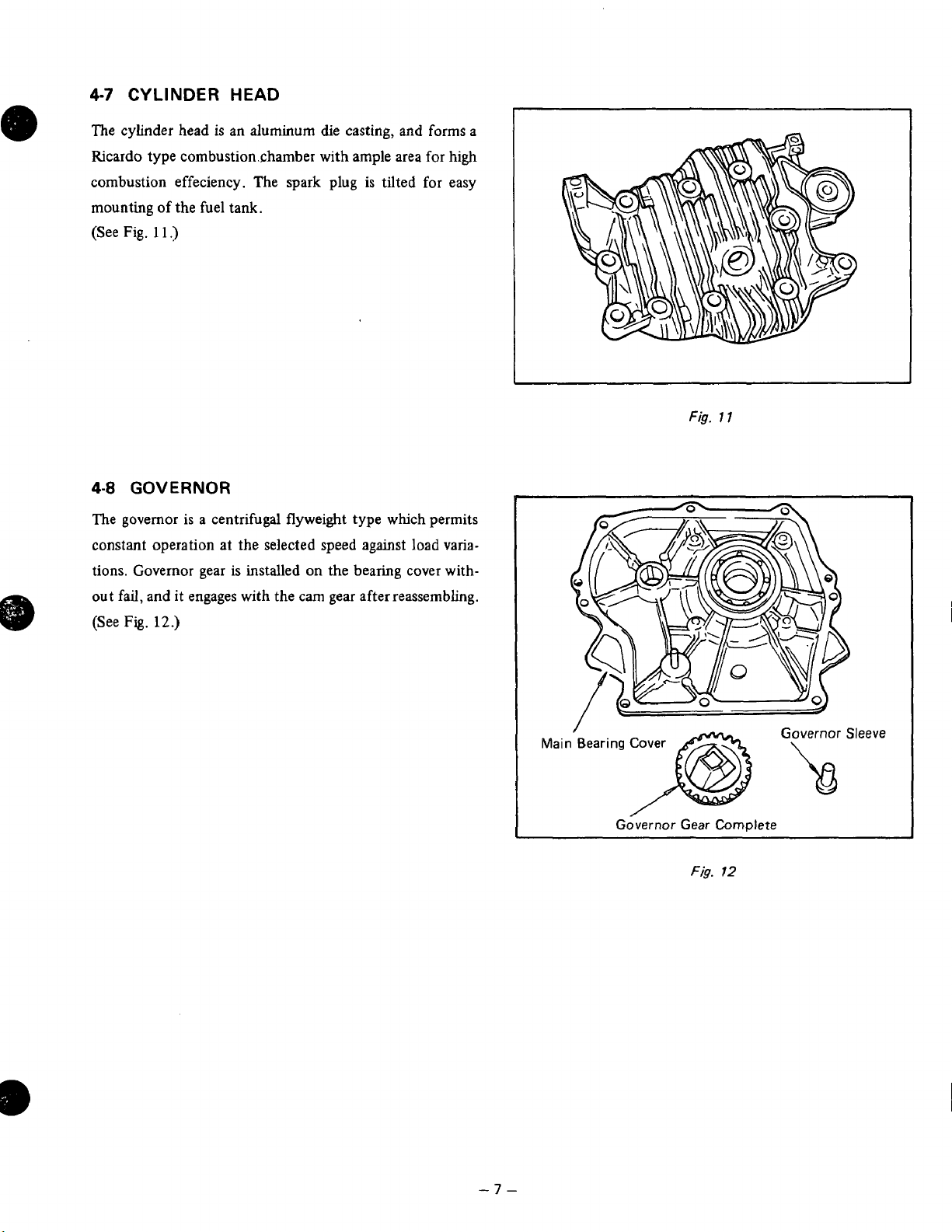
4-7
CYLINDER
HEAD
The cylinder head
is
an aluminum die casting,
and
forms a
Ricardo type combustion.chamber with ample area for high
is
combustion effeciency. The spark plug
mounting
(See Fig.
4-8
of
the fuel tank.
11.1
GOVERNOR
tilted for easy
The governor is a centrifugal flyweight type which permits
constant operation at the selected speed against load variations. Governor gear
out fail, and
Fig.
(See
it
12.)
is
installed on the bearing cover with-
engages with the cam gear afterreassembling.
Fig.
1
1
1
/
Main
Bearing Cover
Governor Gear
Fig.
Complete
12
Governor
Sleeve
-7-
Page 12
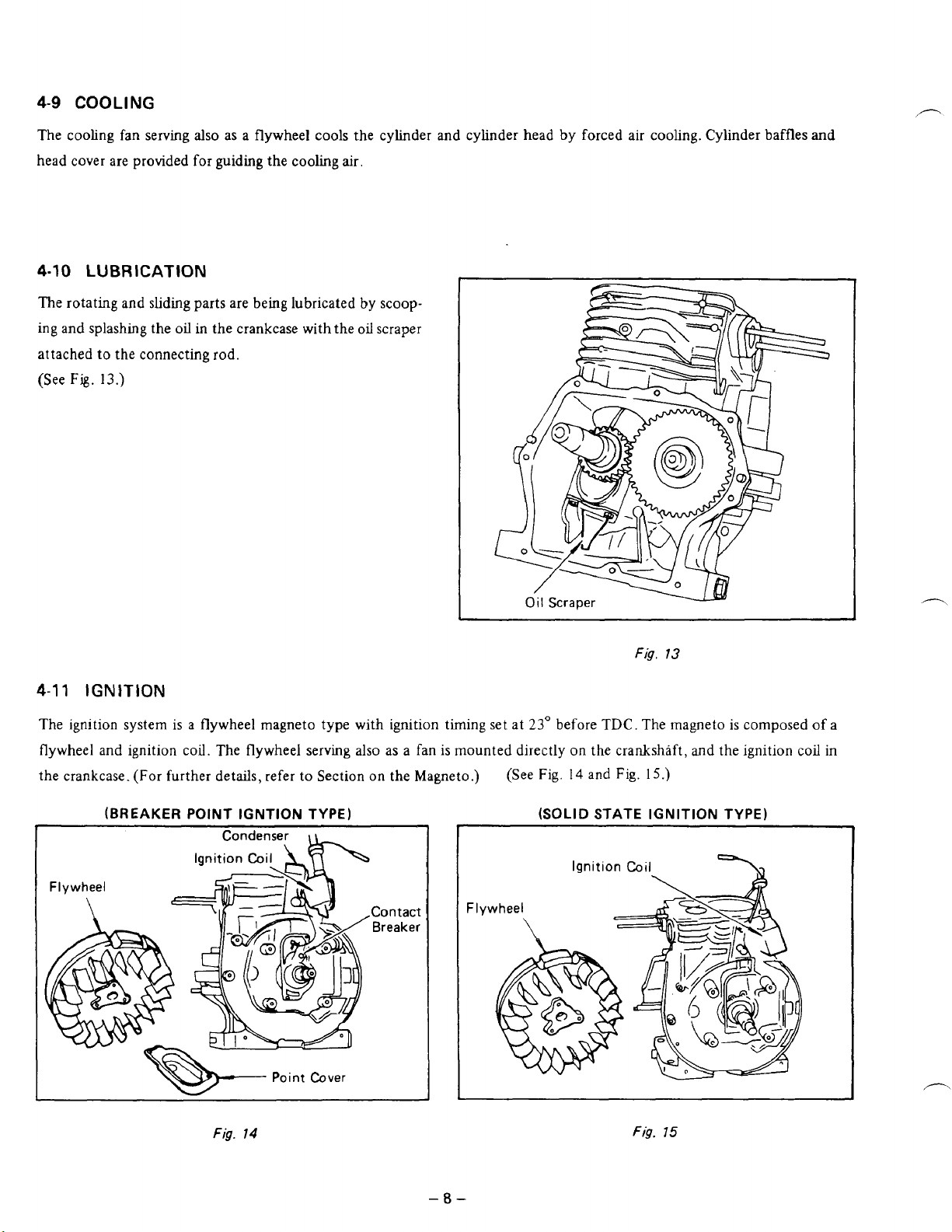
4-9
COOLING
The cooling fan serving
also
as a flywheel
cools
head cover are provided for guiding the coohg
4-10
The
ing and splashing the
attached
(See Fjg.
LUBRICATION
rotating and sliding parts are being lubricated by
oil
in the crankcase with the
to
the connecting
13.)
rod.
the cyhder and cylinder head by forced air cooling. Cylinder baffles
air.
scoop-
oil
scraper
and
4-1
1
IGNITION
The ignition system is a flywheel magneto type with ignition timing set at
flywheel and ignition
the crankcase.
(For
(BREAKER
coil.
The flywheel serving also as a fan is mounted directly
further detds, refer to Section on the Magneto.) (See Fig.
POINT IGNTION TYPE)
23"
before
(SOLID
Fig.
13
TDC.
The magneto
on
the crankshaft, and the ignition
14
and Fig.
STATE IGNITION TYPE)
Ignition
15.)
Coil
is
composed
Ea\?
of
coil
a
in
Fig.
14
-8-
Fig.
15
Page 13
D
4-12
A
CARBURETOR
horizontal draft carburetor is employed. It
fully set after thorough tests to assure satisfactory start up,
acceleration, fuel consumption, output performance etc.
For construction and order details, refer to the Section on
Carburetor Construction, Disassembly
(See
Fig.
i6.)
has
and
Reassembly.
been care-
Fig.
16
m
4-13
The air cleaner
type using a sponge element.
double element air cleaner is optionally available.)
(See
AIR
Fig.
CLEANER
of
17.)
the standard type engine is an oblong
(A
cyclone type semi-wet
Air
Cleaner for
Standard Type
Cyclone Type
(Option)
Mushroom Cyclone Type
(Option)
Fig.
17
-9-
Page 14
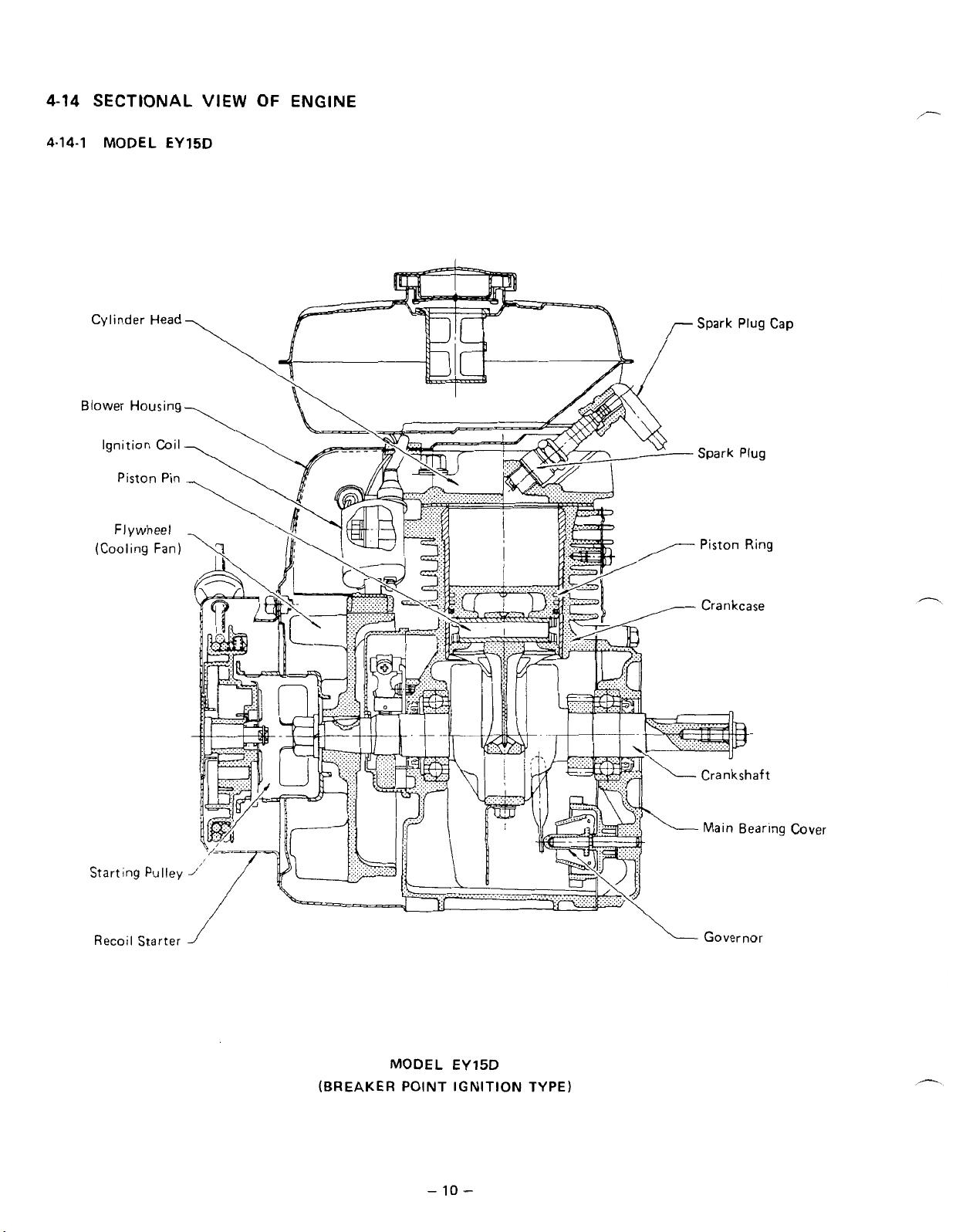
4-14
SECTIONAL
VIEW
OF
ENGINE
4-14-1
Blower
MODEL
Cylinder
Ignition
Head
Housing
Coil
Piston
Flywheel
(Cooling Fan)
EY15D
Pin
Starting
Recoil
Pulley
Starter
MODEL
(BREAKER POINT IGNITION TYPE)
-
EY15D
10
-
Governor
Page 15
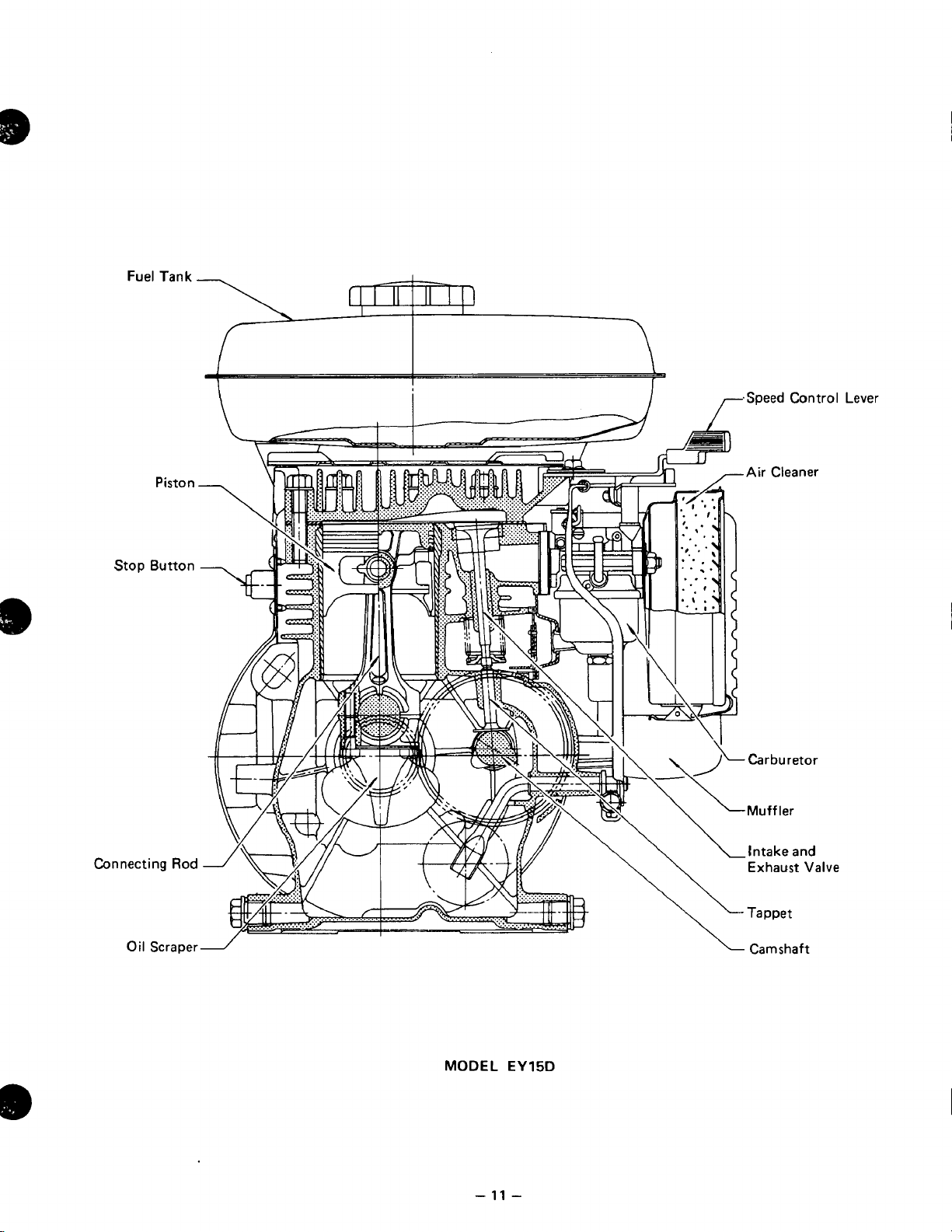
\
I
i
/-Speed Control Lever
Piston
Stop Button
Connecting
Rod
Air Cleaner
'Carburetor
.Muffler
.Intake and
Exhaust Valve
Tappet
Oil
Scraper-
MODEL
-
11
EY15D
-
1
Camshaft
Page 16
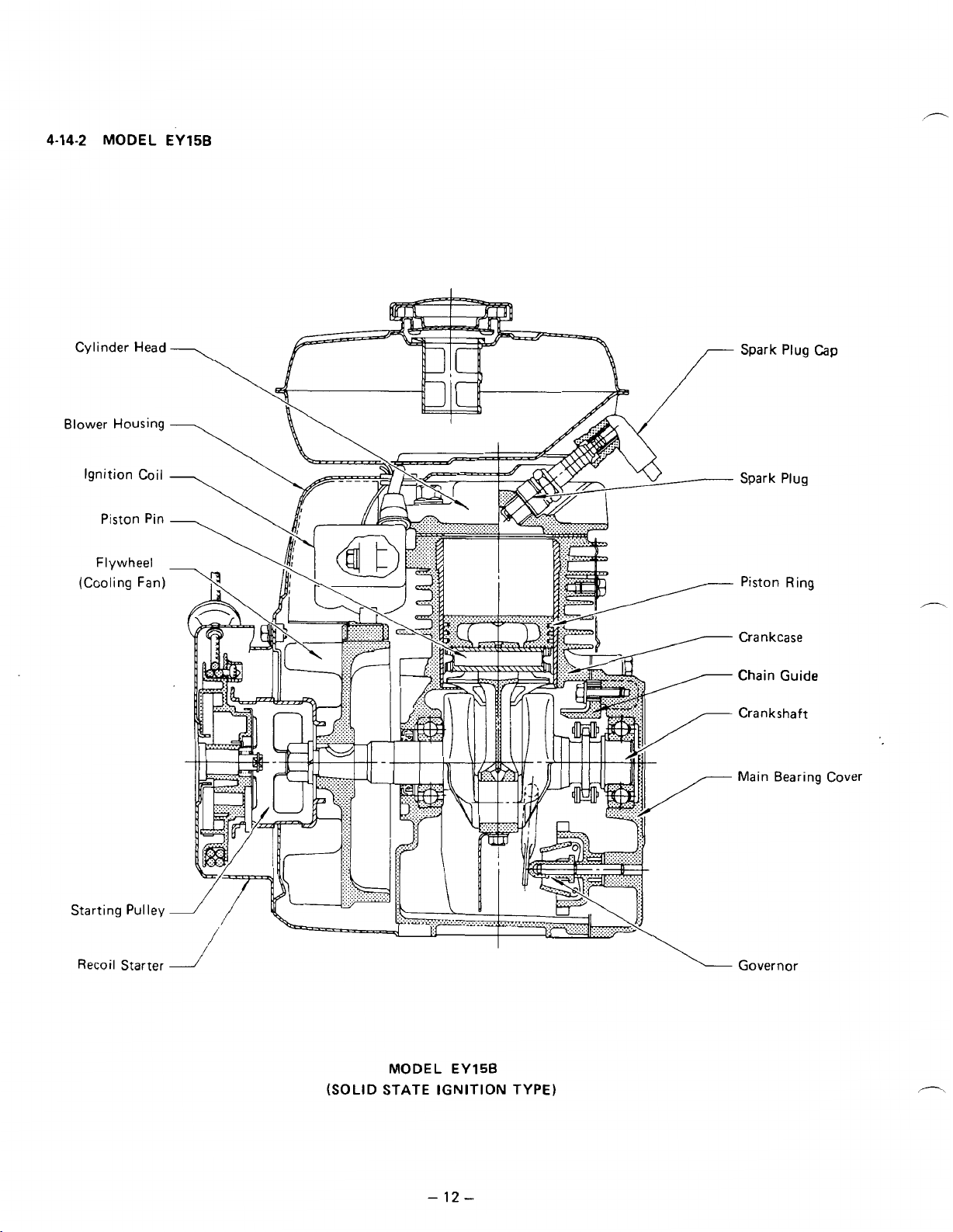
4-14-2
MODEL
EY15B
Cvlinder Head
Blower Housing
Ignition
(Cooling Fan)
Coil
Piston Pin
Flywheel
Spark Plug Cap
Spark Plug
Piston Ring
Crankcase
Chain Guide
Crankshaft
Main Bearing Cover
Starting Pulley
Recoil
Starter
--/
MODEL
(SOLID STATE
EY15B
IGNITION
-
12
-
TYPE)
L
Governor
Page 17
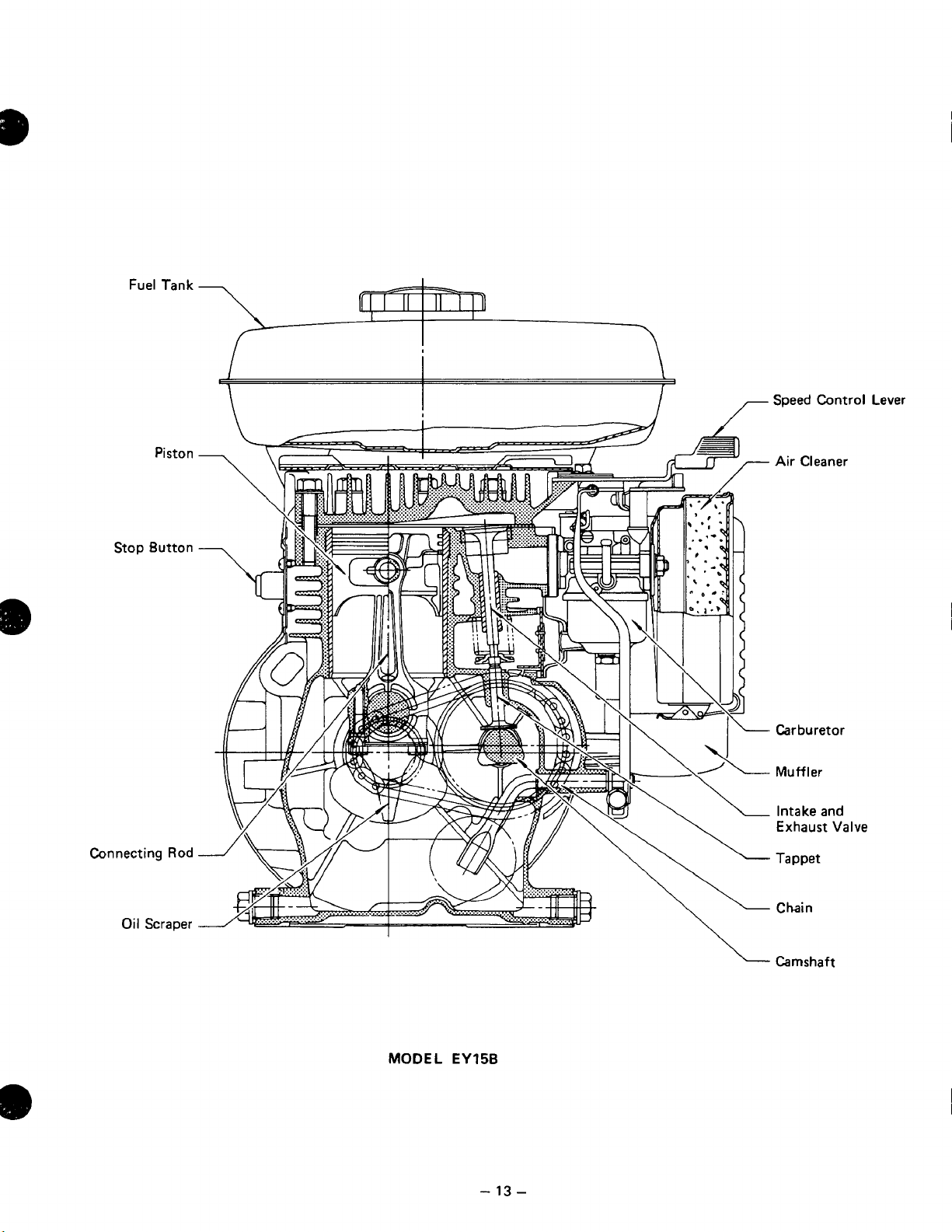
Fuel
Tank
I
1
Piston
Stop Button
Connecting Rod
\r
Speed Control Lever
Air Cleaner
Carburetor
Muff
I
er
Intake and
Exhaust Valve
Tappet
Oil
Scraper
MODEL
EY15B
-
13
Chain
-
Page 18
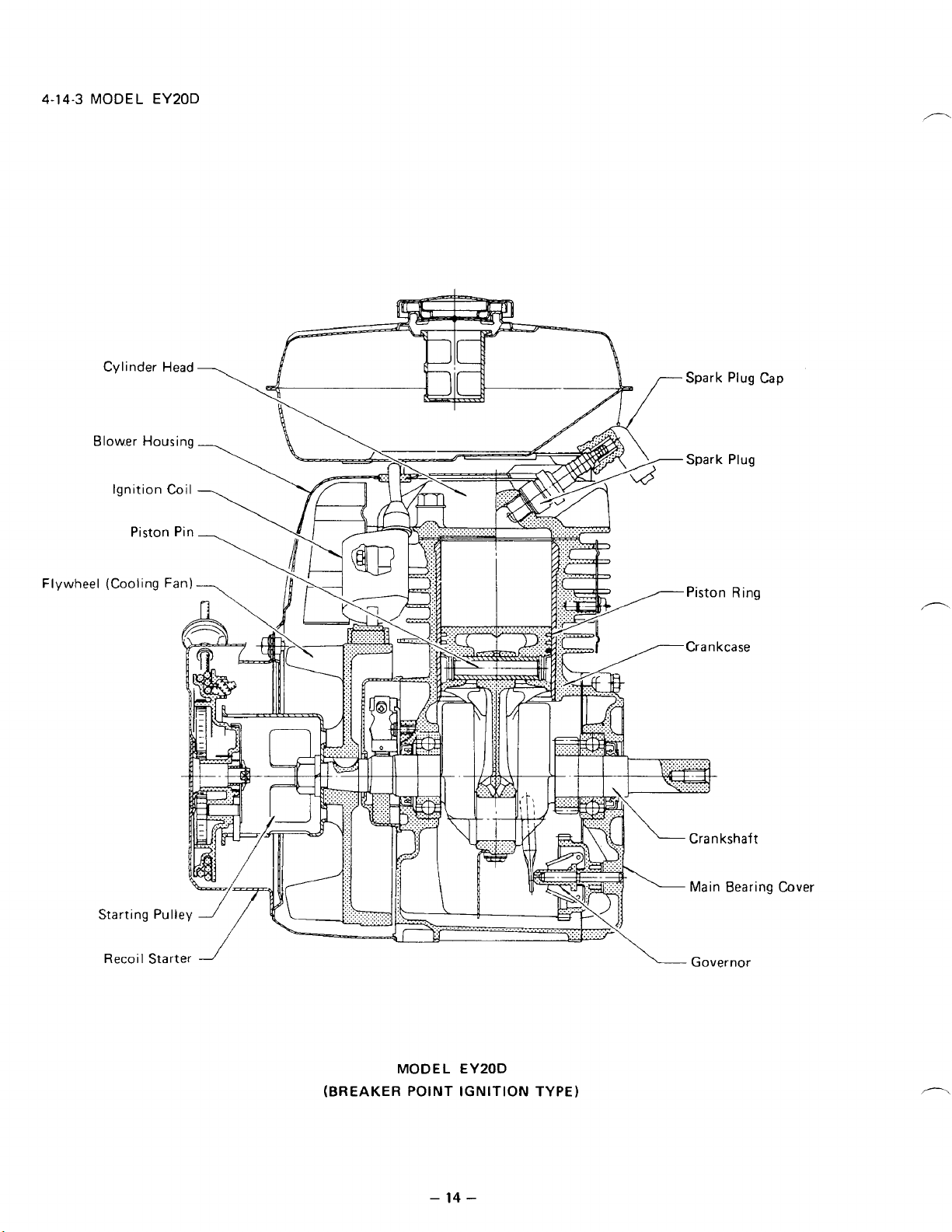
4-14-3
MODEL
EY20D
Recoil
Starter
(BREAKER
MODEL EYPOD
POINT IGNITION
-
14
-
Cover
Governor
TYPE)
Page 19
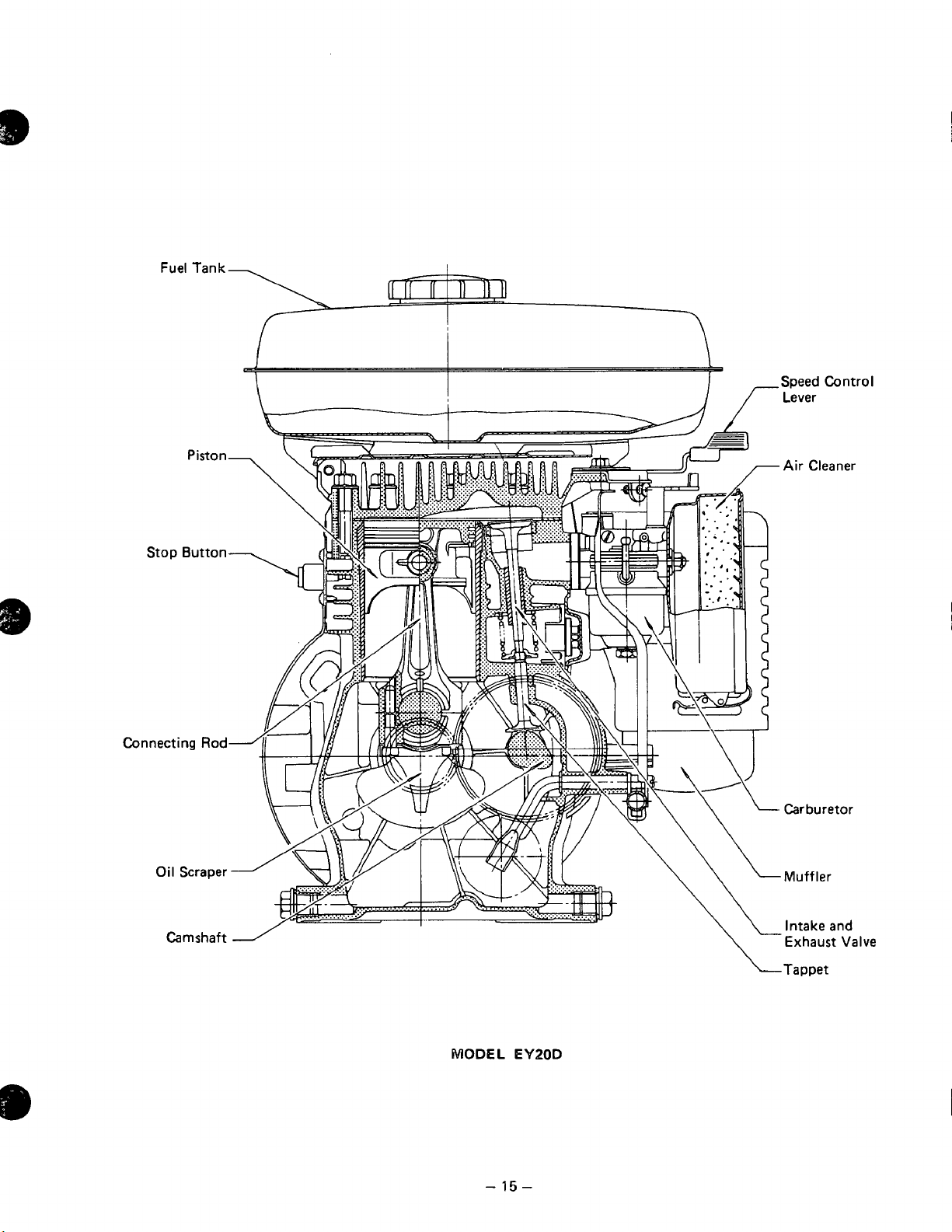
Speed Control
Lever
Piston
Stop Button
Connecting
Oil Scraper
Air Cleaner
Rod
Carburetor
.Muffler
Camshaft
1
MODEL
-
EY20D
15
-
\-
\“Tappet
Intake and
Exhaust Valve
Page 20
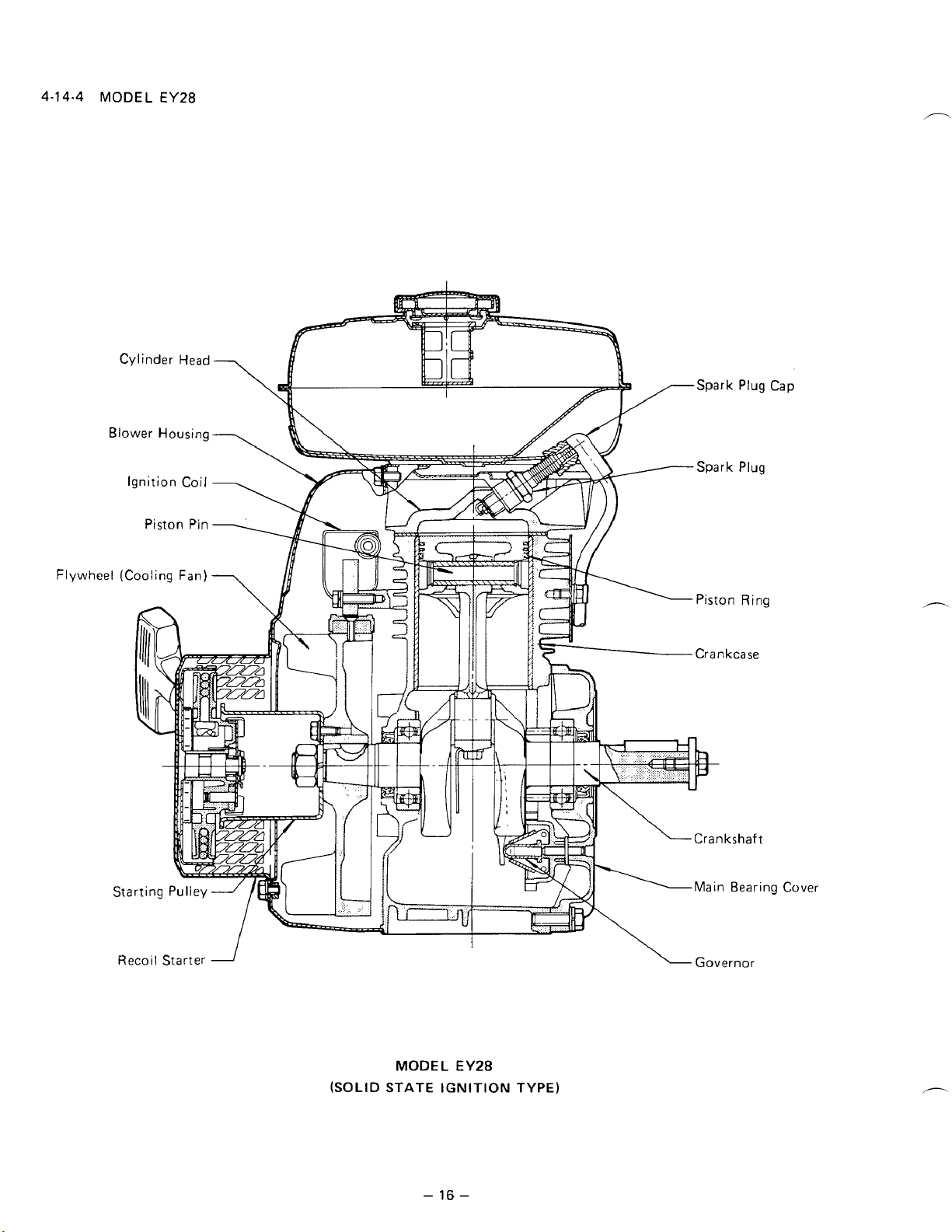
4-14-4
MODEL
EY28
,Spark
Spark
Plug
Plug
Cap
Flywhe
Piston
Crankcase
-Governor
Ring
lg
Cover
(SOLID
MODEL
EY28
STATE IGNITION TYPE)
-
16
-
Page 21
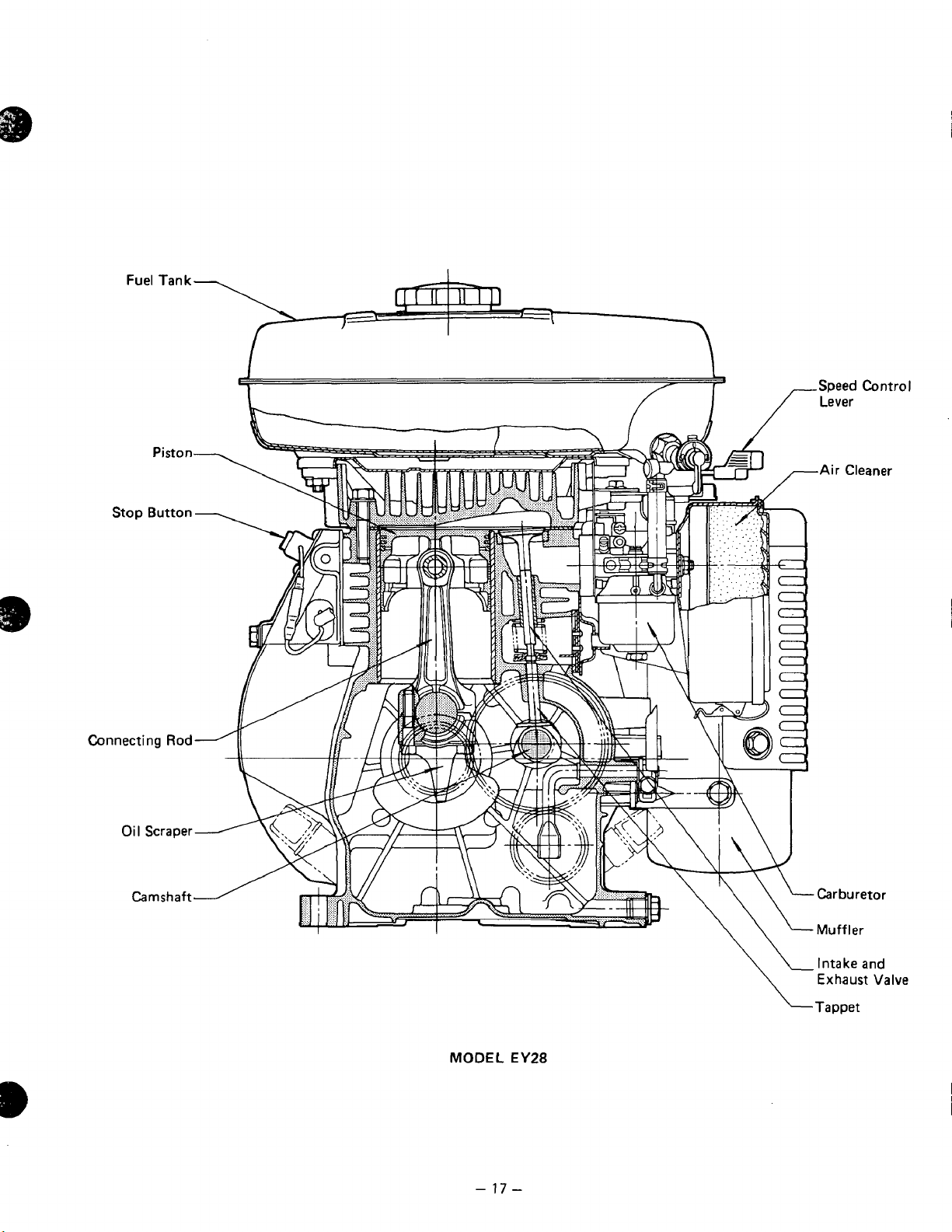
Fuel Tank
-0
I
MODEL
-
17
EY28
-
Intake and
Exhaust
Tappet
Valve
Page 22
PREPARATIONS
and
SUGGESTIONS
When disassembling the engine, remember well the
correctly.
Have boxes ready
To
If
you are uncertain
to
keep disassembled parts by group.
of
identifying some parts, it is suggested that tags be attached
prevent missing and misplacing, temporarily assemble each
locations
Carefully handle disassembled parts, and clean them with washing oil.
Use the correct
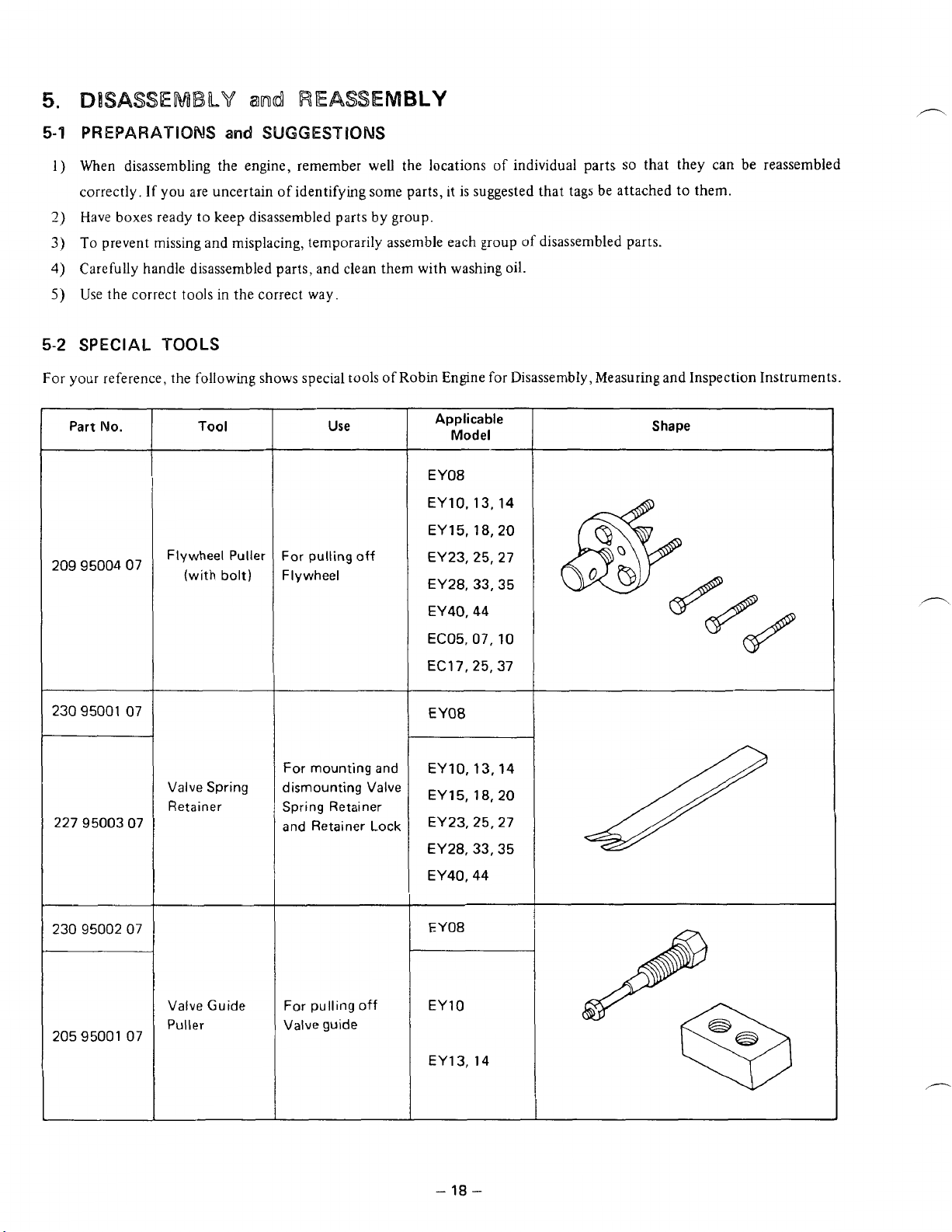
SPECIAL
For
your reference, the following shows special tools
Part
No.
2099500407
tools
in the correct way.
TOOLS
Tool
Flywheel Puller
bolt)
(with
Use
For pulling
Flywheel
of
off
Robin Enpne
Applicable
E
YO8
EY10,13,14
EY 15,18,20
EY23,25,27
EY28,33,35
EY40,44
group
Model
of
individual parts
of
disassembled parts.
for
Disassembiy, Measuring and Inspection Instruments.
so
that they can
to
Shape
them.
be
reassembled
23095001
227 95003
230
95002
205 95001
07
07
07
07
Valve
Spring
Retainer
Valve
Guide
Puller
For mounting and
dismounting Valve
Spring Retainer
and Retainer
For pulling
Valve
guide
Lock
off
EC05.07,lO
EC17,25,37
€YO8
EY10,13,14
EY 15,18,20
EY23,25,27
EY28,33,35
EY40,44
EY08
EYlO
EY13, 14
-
18-
Page 23

Part
No.
2069500107
Tool
Use
Applicable
Model
I
EY
18,23
2279500107
2349500107
2079500107
226
9500
1
07
Valve Guide
Puller
Guide
(Chain Guide)
For
pulling
Valve guide
For mounting
chain guide
off
EY
1
5,20
EY28
EY25,27
EY15B
“20248
Timing Tester
For
qdjusting
timing
EY10,13,14
EY 15,18,20
EY25,27
EY33,35,40
EY44
EC03,04,05
EC07,10,17
EC25,37
-
19
-
Page 24

5-3
HOW
TO
DISASSEMBLE
I
Order
I:
1
Item
Drain plug
Recoil starter
*Length
(1)
(1)
of
the bolt indicates the length from the bolt head bottom surface
Procedures
Drain engine oil.
8
mm
on
Flange
Drain plugs
crankcase.
Remove the recoil starter.
6@
x
both sides of
bolt: 4 pcs.
the
Remarks
the gasket.
to
lose
to
the threaded end.
Tool
14
mm spanner Be careful not
10
mm box spanner
Gasket
-
20
-
Page 25

Order
3
4
Item
~~
Blower housinl
Fuel tank and
head cover
Air cleaner
Muffler cover
Procedures
(1)
Remove the Blower housing from the
crankcase
EY15,20
EY28
(1)
Close the fuel cock.
(2)
From the carburetor disconnect the fuel
and
head cover.
...
64
6q5
......
6q5
x
12 mm bolt: 2 pcs.
x
14
mm bolt: 2 pcs.
x
12
mm
bolt:
4
pcs.
pipe between the fuel strainer and carburetor
on
the side
(3)
Remove the fuel tank from the cylinder
of
the fuel strainer.
head.
EY15,20
EY28
(4)
Remove the head cover from the cylinder
...
......
64
nut: 2 pcs.
84
nut: 4 pcs.
head.
(1)
Remove the air cleaner cover and element.
(2) Remove the air cleaner case from the car-
buretor.
6rp
nut: 2 pcs.
(3)
Disconnect the breather pipe.
(1)
From the muffler remove muffler cover.
EYl5,20
EY
28
...
.....
64
x
8
mm bolt: 3 pcs.
6q5
x
8
mm bolt: 4 pcs.
Remarks
Fastened together
with the fuel tank
Air cleaner is fastened together with the
carburetor.
Tool
10
mm box spanner
10
mm spanner or
12 mm spanner
10
mm box spanner
10
mm box spanner
~
7
Muffler
(1)
Remove the muffler from the cylinder
portion of the crankcase.
8q5
nut: 2 pcs.
Brass nut
Muffler
Cover
6”.
12 mm spanner
/I
Mu’ffler
-
21
-
Page 26

Order
8
9
I
Item
Governor lever
and the relative
parts
Carburetor
Procedunx
(1)
Remove the governor lever from the
governor lever shaft.
6$1
x
25
mm bolt: 1 pce.
(2)
Remove the governor
spring
from the carburetor.
(1)
Remove the carburetor from the cylinder
rod
and
rod
portion of the crankcase.
Remarks
Just
loosen the bolt,
unnecessary to take
out
the bolt.
10
or
mm
10
Tool
box
spanner
mm spanner
~ ~~
1
Lever
Fig.
-
22
18
-
Page 27

Order
I
10 Starting pulley
11 Flywheel
12 Ignition coil
Spark
Item
"
(1)
Remove the starting pulley from the fly-
wheel.
64
x
Fit a box or socket wrench over the
flywheel nut, and strike it hard with
hammer to remove the nut
14
mrn,
"
"
-
Plug
washer.
(1) Remove the flywheel from
(1)
Remove the ignition plug cap from
ignition plug; and remove the iption
coil
64
x
Cap
Rocedu~s
12 mm bolt: 3 pcs.
EY28:
from the crankcase.
25 mm bolt: 2 pcs.
18
mm)
(EY
15,20:
and spring
the
crankshaft
a
the
I
Remarks
Be
careful not to
damage the blades
of
the
flywheel
a driver and a like.
Strike counterclock-
wise with
(See Fig.
Fit the flywheel puller
as
shown
turn the center bolt
clockwise and pull
out the flywheel.
Sems bolt
a
hammer.
19.)
in
Fig.20,
with
I
~
~
Tool
10
rnm
box
spanner
19
mm
box
spanner
24
mm box
or
spanner
Flywheel puller
I
1
10
mm box spanner
(Solid
State lgnitio
Flywheel Puller
Fig.
-
23
-
\
0
20
\
Flywheel
Page 28

Order
13
14
Item
Spark plug
~~ ~~
Cylinder head
Procedures
(1)
Remove the spark plug from the
cylinder head.
(1)
Remove the 8 mm bolt and remove the
~~ ~~ ~
cylinder head from the crankcase.
89
x
40
mm bolt: 8 pcs.
(2)
Remove the cylinder head gasket
the crankcase.
from
Remarks
21
mm
12 mm
Tool
box
box
spanner
spanner
I
,”-.
15
Intake and
exhaust valve
16 Main bearing
cover
(1)
Remove the inner and outer tappet
covers from the crankcase.
69
x
I2
mm bolt: 2 pcs.
(2)
Pull out the intake and exhaust valve.
(3)
Remove the valve spring and the valve
retainer
(1)
From the crankcase remove the bolt
.
fastening the main bearing cover.
EY
15,20
EY28
(2)
Remove the cover,
.
. . .
. .
. .
.
6$
x
30
mm bolt: 8 pcs.
8$
x
28 mm bolt: 8 pcs.
lightly
tapping the
cover evenly with a plastic hammer.
Spark
Plug
Put the notch on the
outer circumference
of the
spring
retainer
on this side.
Hook
the medium
size
(-)
drive at the
dent (lower side)
of
the spring retainer
and pull out the
valves, while pulling
the spring retainer
toward
(See Fig. 2
you.
1
.)
Sems bolt
Be careful not
damage the
oil
to
seal.
(See Fig. 22.)
Cvlinder Head
10
mm
box
spanner
The front
is
this
side.
(-)
driver
10
mm box spanner
Crankcase
Cyclone
Cleaner
I
Drain
Plug
-
24
-
Page 29

Oil
Seal
Guide
18
Tappet
J
Fig.
21
Procedules
(1)
Remove the camshaft from the crankcase.
~ ~~ ~~~~ ~~~~~
(1)
Remove the tappets from the crankcase.
Main Bearing
L
F&.
22
Remarks
To
prevent the tap-
pets from falling
or
Tool
Cover
damaging, place the
~~ ~
crankcase
side. (See Fig.
on
the
23.)
Before removing put
a mark
of
intake
or
exhaust on each tappet.
In
the
EY
15B
type, remove the tappets after step
2
1.
Intake Valve,
9
!
GoGernor Gear
1-
I
Camshaft
Exhaust Valve
Valve Spring
Spring
Retainer
Tappet
-
25
-
I
Fig.
Tappet
23
Page 30

Order
19
Item
I
Connecting rod
and piston
Procedures
I
(1)
Scrape off carbon and other foreign deposits from the upper parts of the cylin-
der and piston, and then straighten out
the bent tabs of the lock washers
the connecting
rod,
and remove two
pieces of the bolt.
(2)
Remove the
oil
scraper, lock washer and
connecting rod cap from the crankshaft.
(3)
Turn the crankshaft until the piston
I
raised up
to
the highest position,
the connecting rod up, and remove the
piston out of the top of the cylinder.
on
is
push
Remarks
I
In
the
EYI
5B type,
rod to the position
shown in
Fig.
24.
Tool
i
10
mm box spanner
or
10
mm spanner move the connecting
20
22
Piston and
piston pin
(1
j
Remove the two clips, pull out the piston
pin, and take the piston off from the
small end of the connecting rod.
Be careful not
damage the inside
of
the small end of
the connecting rod.
(2)
Spread the open ends
and remove them frGm the piston.
of
the piston rings
Be careful not
break the rings
spreading too much.
(1)
I
Remove the woodruff
magneto).
(2)
Lightly hammer the magneto end
key
(for the Be careful not
damage the
of
oil
the crankshaft, and pull it out of the
crankcase.
(1)
Remove the woodruff key (for the Crankshaft
Camshaft Chain damage the oil seal.
(for
EY15B)
magneto).
(2)
Remove the crankshaft and the camshaft
at the same time from the crankcase,
tapping the crankshaft tip in the magneto
side.
Piston
Ring
Be careful not to
To
prevent the tappets
from
failing or
aging, place the crank-
on
case
the side.
Piston
to
to
by
to
seal.
dam-
Connecting
Rod
iston Pin
"
joodruff
\
Key
Crankshaft
Fig.
24
(E
Y
15B)
-
26
-
Page 31

5-4
HOW
.Precaution
TO
REASSEMBLE
in
reassembling
Every and each part should be cleaned thoroughly. Especially, pay utmost care and attention to the cleanliness of the
piston, cylinder, crankshaft, connecting rod and bearings.
Scrape completely off carbons from the cylinder head and the upper part of the piston; especially the carbon adhered
in
the groove
Carefully check the lip portion of every
Apply enough
Replace
of
the piston ring should be carefully and completely taken out.
oil
to the lip portion of the oil seal when reassembling.
all
the gaskets with new ones.
oil
seal. If faulty one is found, replace it without any hesitation.
Replace the key, pin, bolt, nuts, etc. with new one, if necessary.
Whenever tightening torque is specified, conform to the specified figures.
Apply
oil
to the revolutionary parts and friction surfaces, when reassembling.
Check and adjust the clearances of various portions and then reassemble.
or
When some main portions are assembled in the course of reassembling, turn
move the gadgets by hand and pay at-
tention to the frictional noise and resistance.
*Sequence and precautions in reassembling
5-4-
1
CRANKSHAFT
1)
Fit the
oil
seal guide onto the end of the crankshaft,
and insert the crankshaft into the crankcase as shown
in
Fig.
25.
NOTE:
2)
Put woodruff key (for magneto)
In case
ful
not
of
not
using the oil seal guide, be care-
to
damage
the
oil
seal
in
place.
lip.
I.
Fig.
25
-
27
-
Page 32

3)
DIMENSIONS
D
(Crankshaft pin
PISTON RING GAP
of
CRANKSHAFT PIN
Dia.)
PISTON RING
CLEARANCE
CONNECTING
CRANK PIN
CONNECTING
PISTON
54-2
CRANKSHAFT, CAMSHAFT, CHAIN
TAPPET
1)
Set
the chamshaft, as
NOTE:
2)
Put
crankshaft and the camshaft parallel. Then mount
them
SIDE
IN
GROOVES
ROD
ROD
PIN
TO PISTON
(for
the
chain
Set
matches
shaft
the tappets
onto
the
TO
TO PISTON PIN
EYISB)
in
the sprockets
shown
in
the chain
and
crankcase.
so
to
the timing marks
the
camshaft.
in
the crankcase, and then set the
OIL
RING
DIA.
SI
DE
of
the crankshaft and
Fig.
27.
that the white
and
link
of
the crank-
0.090L - 0.135L 0.050L
OL
-
0.065L
Table
1
plate
-
0.063L
0.1
0.01OL - 0.029L
0.009T
&A
-
0.095L 0.050L
-
0.065L 0.01
L - 0.3L
-
0.01
OL
-
0.09OL
0.01OL - 0.065L 0.01OL
0.020L - 0.046L 0.037L
L: LOOSE
T: TIGHT
Ling Plate (White)
V
Timing Mark
,”--
Fig.
27
(EY
15s)
-
28
-
Page 33

54-3
1)
PISTON and
If
no
ring expander
spreading
NOTE:
PISTON
the
rings only far enough to
Pay attention not to break the rings
top ring. Meantime, the surfaces
RING
is
available,
install
the
slip
them
of
rings
by
placing
over
the
by
twisting. Install the oil ring
the second ring and the top ring with carved marks
the
open
ring
correct kg grooves.
ends over
first
followed
the
first land
by
of
the
piston
the
second ring and then
are
to
be
faced
and
up.
I
Top Ring
Second Ring
Oil Ring
Piston Ring
Fig.
28
I
I
Taper Barrel Face
Cutter Ring
(without expander) (with expander)
Fig.
29
I
EY15,20
I
I
Taper Under Cut
EY28
I
.
-
.
..
J
2)
Reassemble
NOTE:
the
piston and connection
Apply enough oil to the small top end
Be
sure
to
place the clips on
rod
both
by means
ends
of
the
piston
of
the connecting rod.
of
the
piston pin.
-
29
-
pin.
Page 34

3)
When installing the connecting rod into place, hold
piston rings with the
(if
no
ring guide is available, keep pressing the piston
rings with finger tips and gently strike the top
piston with a wooden piece
and check that the symbol
necting rod is in the direction
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE:
Apply enough oil
ing
rod
reassembling.
The open ends
apart from one another
ery
.
The clearance between the piston and cylinder must be measured
ring
guide
as
shown in Fig.
or
the like
@or
mark
MA
of
the flywheel magneto.
to
the piston rings, connect-
plain bearings and cylinder wall before
of
the piston rings must be
on
the piston periph-
of
to
push
it in),
on the con-
30
the
90"
I
Piston
Fig.
30
at
the piston skirt thrust surface.
Ring Guide
544
CONNECTING
1)
Turn
the crankshaft to the bottom dead center, light-
ly
hammer the piston head
contacts the crankpin, and assemble.
2)
When reassembhg the connecting
alignment projection mark on the
3)
Oil scraper
Fig.
31
.)
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE:
Use new lock washers, and bend the tabs securely.
After reassembly, confirm that the connecting
rod moves lightly.
Connection rod cap tightening torque:
EY15
EY20
EY28
For the piston, piston ring and rod clearance, see Fig.
ROD
is
to be set on the side
.
,
. . . . . . . .
. .
. . .
+-
until
.
. . .
the
connecting
rod
cap, match the
rod.
of
magneto. (See
90-
115
170
-
200
kg-cm
kg-cm
rod
I
26.
Alignment
Mark
Fig.
31
Oil
Scraper
-
30
-
Page 35

5-4-5
Insert
the
camshaft.
NOTE:
NOT€:
TAPPET and CAMSHAFT
the
tappets back into their holes first,
Align the timing mark
cam gear with the one on the crank gear.
is
timing
or
In the EY158,
sprocket’s timing mark.
If the intake tappet and exhaust tappet were
assembled contrarily each other, the tappet clearance cannot be kept correctly.
wrong, the engine cannot operate properly
at
all.
(See
Fig.
at
the root of a tooth of the
32.)
set
the white link plate
(See
Fig.
and
27.)
then
If
thevalve
mount
at
the
Fig.
32
5-4-6
Install
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE:
MAIN
BEARING COVER
the
main
bearing cover
When the chain guide
the clearance between the chain and the chain guids
CHAIN GUIDE tightening torque
As
the governor gear
{See
side,
Fig.
ing cover
checking that
gear.
replaced, pressure-fit
the main bearing cover.
to
the
crankcase.
is
replaced in the EY158, use the guide (chain guide)
70
to
90
kgcm.
Chain Guide
n
Fig.
33
(E
Y
75B)
is
mounted on the main bear-
install the main bearing cover while
it
meshes with the teeth of the cam
35.) Meantime, if the oil
a
new
oil
n
seal
seal
before installing
need be
is
from 0 to 0.5mm.
I
\
(See
(See
Fig.
33.1,
or
set
the chain
Fig.
34.)
Fig.
34
(E
Y
156)
Pay attention
the governor gear and cam gear
to
the engagement
so
that
of
-
31
-
Page 36

NOTE:
When installing main bearing cover, apply oil to the
bearing and oil
the crankshaft or camshaft to protect the oil
lip from damage. Then place the main bearing
cover on.
Check the crankshaft and camshaft their side clear-
ance are
the adjusting shims. (See Fig.
adjustment of the camshaft
0
seal
lip.
Fit
the oil
-
0.2
mm; and if not adjust them with
seal
36.)
is
not necessary)
guide over
seal
(In D type,
Fig.
36
NOTE:
NOTE:
Main bearing cover tightening torque:
EY15,
EY20.
EY28
Fig.
crankshaft and camshaft side clearance between the
machined face of the crankcase and adjusting collar.
As
the crankcase, adjust the clearance
thickness
. . . . . .
37
a
paper packing
. . . . .
shows one
of
0.22
.
80-
100
. . . . .
170 - 190
of
the methods measuring the
is
used on
mm into account.
the
kg-cm
kgcm
machined face
by
taking this
(See
Fig.
37.)
of
I
11
II
Y=II
Dial Indicator
Ground Surface of Crankcase
(The surface
1
1
put together with the
main bearing cover.)
of
the crankcase
is
surface of
to be
the
-32
-
Page 37

5-4-7
Remove carbon
NOTE:
NOTE:
INTAKE and EXHAUST VALVES
and
If
the
valve face
If
there
is
placing,
new valve guide
gum deposite
is
dinted
an excessive clearance between the valve guide and valve stem, replace the valve guide
pull
out
the valve guide, using the valve guide pulling base and
into
or
place.
from
the valves, valve seats, intake
warped, replace the valves with new ones.
Valve Guide Puller
and
exhaust
bolts
ports
and
valve guides.
as
shown
in
with
a spare. For
Fig.
38,
and pressure-fit a
Valve Guide Puller
Crankcase
E
Valve Guide
re-
F&.
39
A-VALVE FACE ANGLE
B
-SEAT ANGLE
C-GUIDE INSIDE DIA.
D-VALVE STEM OUTSIDE
MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE
CLEARANCE BETWEEN C and D
€-VALVE STEM
TILT
DIA.
ANGLE
INTAKE
EXHAUST
INTAKE
EXHAUST
VALVE
EY15
Fig.
38
and
VALVE GUIDE CLEARANCE
EY20
45O
45O
dia.
dia.
dia.
+0.022
1::::;
1:::;
-
0.062L
-
0.looL
3"
6.5
6.5
6.5
0.025L
0.056L
53'
Nut
EY28
3"30"
L:
LOOSE
Table
-
33
2
-
Page 38

5-4-8
Lower
the
NOTE: The correct tappet clearance for
TAPPET ADJUSTMENT
the
tappet
all
the
clearance.
is
cold.
(See
Fig.
way
40.)
down,
push
the
valve,
both
intake and exhaust
and
insert a feeler gauge between
valves
is
0.1
Intake, Exhaust Valve Valve Spring
Grinding Face
mm
*
the
0.02
valve
mm
and
tappet stem to
as
measured when
measure
the
engine
..
i
I
Fig.
40
NOTE:
NOTE: After the tappet clearance adjustment, install the
NOTE: INSTALLATION of SPRING RETAINERS
If
the clearance
trary, if the ciearance
a
obtain
tappet clearance once again if
Place the notch on the outer circumference of the
retainer toward this side and insert the retainer, like
pushing in, using
used for
insertion may be easier.
good fit. Then adjust the clearance.
EY18
is
smaller than specified, slightly grind the top
is
too large, replace the
it
a
special tool. (This special tool
and other models.)
(See
Fig.
-
Tappet
is
correct.
If
adriver isused,
42.)
valve
vT/
Spring Retainer
Fig.
41
of
the
valve
stem, and measure
with new one, and polish its contact surface with a compound to
valve
spring retainers, and turn the crankshaft, and measure the
is
it
again. On the con-
Front should be this side.
I
Fig.
-
34
-
Valve Spring Retainer
42
Page 39

I
54-9
Remove carbon from the cylinder head, particularly
I
the head
NOTE:
NOTE:
CYLINDER HEAD
its
combustion chamber, and make clean the cooling
for
distortion.
Replace the cylinder head gasket with a new one.
DlSTlNGTlON between the GASKET of EY15, EY20and EY28
The pitch
for EY15 and EY20 are same. However, the inner dimensions are different each other. The gasket for EY15
red mark while the gasket for EY20 has a green mark.
of
the holes
for
the bolts fastening cylinder head and the outer circumference dimensions
fins.
of
Also
the
check
gasket
has
a
43.
is
15K. and
Red
mark
NOTE:
NOTE:
NOTE:
5-4-10
For EY28, refer to Fig.
Cylinder head tightening torque:
DISCRIMINATION of CYLINDER HEAD
As stated above, the pitch
head
is
common to both EY15 and EYZO. For en-
abling
to
discriminate the cylinder head
from that of EY20, an embossed mark 15
to the former, while no embossed mark
the
latter.
For EY28, an embossed mark "EY28"
the combustion chamber side of the cylinder head.
Meantime, embossed mark forEY15 Kerosene engine
EY20 Kerosene engine is 20K.
SPARK PLUG
Tightening torque of the spark plug:
5-4-1
EYl5, EY20
EY28
1 IGNITION
...........
...............
COIL,
FLYWHEEL and STARTER PULLEY
Green
mark
190
-
230 kg-cm
of
the holes of cylinder
of
is
is
given on
120 - 150
230
-
250
kg-cm
kg-cm
EY15
is
given
given to
Fig.
43
Fig.
44
Embossed
EY28
-
mark
1)
Temporarily fasten the ignition
ened together with the flywheel.
NOTE:
NOTE:
Before installing, wipe out oil from the crankshaft and the tapered portion of the flywheel.
Flywheel tightening torque:
coil
to
the crankcase, and install the flywheel
600
-
650
kg-cm
-
35
-
to
the crankshaft. Starting pulley
is
fast-
Page 40

2)
After measuring the
air
gap between the ignition coil
and flywheel, retighten the ignition coil. (See Fig.
Air gap:
0.5
mm
45.)
.
/"
\
45
54-12
To
the
54-13
When reassemblying, refer to the
5-4-14
CARBURETOR
the cylinder portion of the crankcase. install
air
cleaner and fasten with two
GOVERNOR LEVER
MUFFLER and MUFFLER COVER
pieces
7. GOVERNOR
in
the order of the gasket, insulator, gasket and carburetor, and then mount
of 6 mm nut.
ADJUSTMENT.
1
\
Fig.
With two pieces of the brass nut fasten the muffler to the crankcase and then install the muffler cover.
54-15
Install
NOTE:
54-16
With 4 pieces
NOTE:
HEAD COVER, FUEL TANKand FAN COVER
in
the order
If
these items are installed in the order of the head cover, fan cover and fuel tank, removal of the fan cover
be impossible.
RECOIL
It
is
of
69
feared
of
the
head cover, fuel tank
STARTER
x
8
mm bolt fasten the recoil starter.
that
the
bolt
longer
than
8
and
mm
fan
may
cover.
damage
the
blades.
I
,"-
would
-
36
-
Page 41

6.
MAGNETO
6-1
MAGNETO
The spark for ignition is furnished by a magneto assembly. The magneto consists of a flywheel, ignition
breaker assembly (including condenser),
mounted in crankcase directly, The
ed in
6-5.
The
breaker points, whch are mounted in the crankcase inside the flywheel should be checked twice a season or whenever the ignition spark becomes weak.
of pitting
rected, and then it becomes necessary to readjust the gap to
its proper clearance.
The normal breaker point opening (point gap) is
at full separation. Since the spark timing of
by the point opening,
curate spark advance. (Refer to
or
pyramidding, the breaker points must be cor-
use
a timing light to obtain an ac-
EYl5B
If
'6
-3
of
which flywheel
type engine normally incorporates a solid state ignition system
there
is
an evidence
0.35
23"
is regulated
TIMING
ADJUST-
is
mounted on crankshaft and ignition coil contact breaker are
mm
MENT.")
coil
and contact
(T.1.C)
Contact
describ-
Breaker
Fig.
46
To
adjust breaker point opening, remove starting pulley, blower housing and flywheel from the engine and proceed
follows: (See Fig.
1)
Remove breaker cover from contact breaker.
2)
Turn crankshaft over until breaker arm comes in contact with the
opening of
3)
Loosen contact support plate lock screw just enough
4)
Insert a
CAUTION:
obtained due
5)
Apply a screw driver to adjusting tab and move the contact support plate just enough
sliding the feeler gauge from between the points.
6)
Tighten lock screw and recheck breaker point gap.
7)
Pull
a strip of
CAUTION:
8)
Mount flywheel, blower housing and starting pulley on engine after adjustment.
46.)
0.35
mm)
0.35
mm feeler gauge between the points.
Adjust breaker point gap without opening
to
the bending
8
-
10
mm wide white paper through the closed points to remove oil and dust
When inserting a sheet
of
contact
of
breaker arm.
paper, never open the breaker point gap more than 2 mm.
high
point of the breaker cam. (Maximum point
so
that bracket can be moved.
it
more than 2 mm, otherwise rated heel-pressing force may not
so
that a slight drag
on
the point surfaces.
is
felt while
as
be
.'
'
-
37
-
Page 42

6-3
TIMING ADJUSTMENT
(See
Figs.
47,48
and
49)
The spark is timed to occur at
23”
before the piston reaches
TDC
on the compression stroke.
This
spark advance of
23”
is
controlled by the breaker point opening and tius advance is obtained when the breaker point opening is adjusted according
to
the
BREAKER
justed through the following procedures using a timing tester as
NOTE: Refer
6-3-1
ALIGNMENT
(See Fig.
For timing adjustment, the
marks are provided as shown
*
‘M”
*
‘P-
6-3-2
TIMING ADJUSTMENT
1)
Bsconnect the stop button lead wires
2)
Remove blower housing
3)
Connect the timing tester lead with red rubber cap
to
the crankcase. (See Fig.
While the points are open, the buzzer within tester remains ringing and when the
silent. (See Fig.
4)
Turn
POINT ADJUSTMENT
to
section
47.)
“4-1’1
MARK
IGNITION”
for TIMING ADJUSTMENT
to its proper point gpening. However, the advance timing is more accurately ad-
shown
in Fig.
48.
and
“13.
CHECKS
and
CORRECTIONS.”
1
following
in
Fig.
alignment
47.
mark and line on the crankcase
mark and line on fhe flywheel cooling fan
with
TIMING TESTER
and
the coil primary wire.
from
engine.
to
the coil primary wire and ground the lead with b!ack rubber cap
48.)
48.)
the flywheel slowly until alignment mark on the flywheel is in the line
Fig.
47
points
are closed, the tester remains
with
alignment mark on the carankcase.
/-
Fig.
48
Fig.
49
-
38
-
Page 43

Remove the flywheel without turning crankshaft at all.
Loosen the lock screw of the breaker point support plate
so
that the breaker point can be rotated.
By rotating the support plate
ringmg from being silent. (See Figs.
Put the flywheel back and check by rotating flywheel slowly. If the buzzer in timing tester starts ringing when line
mark
on
the flywheel is in the line with line mark
is correct.
If the timing mark lines are not in alignmnent, then readjust the point opening according to the
ADJUSTMENT, by removing the flywheel and repeat the checking procedure
After completing the timing adjustment remount the blower housing and connect the coil primary lead to the stop
button.
of
the breaker point, fmd the exact point when the buzzer within timing tester starts
48
and
49.)
on
the crankcase. When the line marks are in alignment, the timing
BREAKER
3)
through
5).
MAGNETO TROUBLE SHOOTING
When the engine does not,start
they are caused by
1) Check igntion cable for possible corrosion, broken, worn insulator or loose connection.
2) Check the sparking as described later in this section.
3)
Check if the breaker points require cleaning, or adjusting
may have to be replaced too.
Refer to ‘BREAKER POINT ADJUSTMENT.”
4)
If no spark takes place, replace igntiion coil.
*SPARK
Remove spark plug from cylinder head and place it on blower housing, with the ignition cable connected to it.
Crank the engine several times by starting pulley and observe the spark
strong, the ignition system can be eliminated as the source
If the spark is weak or there is
The correct electrode gap is
a
defect
TESTING
or
starts with difficulty, or when its operation is unstable, the following tests will clarify if
in
the magneto.
no
0.6
or
not. If the points are badly corroded or pitted, condenser
in
the spark gap of spark plug. If the spark is
of
trouble.
spark at all, repeat the checks according to the procedures 1) through
-
0.7
mm. (Refer to section
“15.
CHECKS
and
CORRECTIONS.”)
3)
POINT
above.
6-5
SOLID
STATE
IGNITION (See Section
10
“ROBIN
SOLID
STATE
IGNITION ENGINE”
details.)
The following solid state ignition systems are available as optional or standard:
1) T.I.C. (TRANSISTOR IGNITION CIRCUIT)
On the outside
standard type engine, and the exciter coil (primary-excitation) is available as an optional part. (The flywheel is for
common use.) (See Fig.
2) P.
I.
T.
(PULSER IGNITION TRANSISTOR) (EY 15, EY20)
The ignition coil and lighting coil are installed inside the flywheeel. Thls built-in type ignition system is installed to
the engine in whch lighting coil is requested. (P.I.T. unit is installed on the outside of the flywheel,)
of
the flywheel, an igntiion coil is installed, which is so-called outer coil type. This is equipped to the
59.)
(EY15,
EY20, EY28)
-
39
-
for
Page 44

7.
GOVERNE
Models
gear and the throttle valve
EY
15,
EY20
and
EY28
employ a centrifugal flyweight type governor. The governor
of
the carburetor
is
automatically regulated
by
order to maintain constant engine speed against load variations.
The adjustment procedure
1)
Connect the carburetor throt?le lever to the governor lever with the connecting link,
or
shaft.
2)
Install the speed control lever to the cylinder head.
3)
Connect the governor lever to the control lever with the governor spring.
of
the governor is as follows (See
Figs.
50
and
5
1.):
is
mounted on the governor
a
lever which is connected to the governor
and
mount them onto the govern
in
*The
For
hooked at
point
4)
Turn
firm
Control lever
Fig.
50
point
where the governor spring
EY15
and
EY28
the governor spring
the
point
1,
while
it
is
to
2
for
EY20.
rhe
control lever
towards
high
that the carburetor throttle valve
can
stay wherever it
is
is
to
be hooked
be
hooked at the
speed, and
is
fully
required.
is
to
be
con-
opened.
I'
An
example
Fig.
51
Governor Lever
of
the governor spring being hooked
Fig.
52
I
-40
-
Page 45

5)
With a screwdriver in the groove
turn it 'clockwise"
longer moves, and then lock the governor lever to the
governor shaft with the governor lever tightening bolt.
(See Fig.
*Dimensions of the governor spring for the engine to be connected to the generator:
Both
EY
governor spring to be hooked are different each other according to the hertz. Meantime, the dimensions
or
spring
53.)
15
and EY20 engines can be connected to the generators
for the standard engine is same as those
fully
of
the governor shaft,
until the governor shaft no
of
the
spring
Governor Lever
Fig.
53
of
both
50Hz
and
60Hz;
and the'dimensions of the
for the engine to be connected to the
60Hz
of
the govern-
generator.
EY28 engine
to the right generator. Meantime, standard type engine is for
Discrimination according to the dimensions:
can
be connected
to
the generators
EY15/60Hz
EY20/60Hz
"
EY28/60Hz(
of
both
(Standard)
-I
--I
(Longer
(a)
(all"
Hook
(Longer Hook Side)
(Standard)
STD)
50
Side)
Hz
the
and
60
60
Hz;
Hz
generator.
-::-
but it is necessary to select the right engine
EY 15/50Hz
I4Al-l
(Longer
EY20/50Hz
"
(Longer Hook Side)
EY28/50Hz
Hook
(A)
Side)
*For EY15,
*Both ends
ed
to
contrary directions.
EY20
and
of
the spring for
Fig.
54
EY28
it is commonly said that the governor spring longer in the length of
EYI 5 are bended to the same direction, while both ends of
-41
-
the
spring for
(A)
is
for
EY20
50
Hz.
are bend-
Page 46

8.
CARBURETOR
8-1
OPERATION
8-1
-1
FLOAT SYSTEM
The float chamber
level during engine operation.
The fuel
float rises; and when its buoyancy and fuel pressure are balanced, the needle valve close
keeping the fuel at the reference level.
flows
from the fuel tank into the
and
CONSTRUCTION
is
located just below the carburetor body and, with a float and a needle valve, maintains a constant fuel
float
r
By-Pass Choke
(See
Fig.
55
and
Fig.
56.)
chamber through the needle valve. When the fuel rises to a specific level, the
,-
Pilot Jet
to
the shut
n
off
the fuel, thereby
Throttle
Pilot Outlet
Valve
I
I
Fig.
55
.
Main
Main
Air
Body
Float
Main Jet
Nozzle
Jet
/-'-
Needle
Float
-
42
-
Page 47

8-
1-2
PILOT SYSTEM
The pilot system feeds the fuel
The fuel is fed through the
The fuel-air mixture is fed to the engine through the pilot outlet and the by-pass.
During
8-1
The fuel is metered by the
The choke
8-2
engine
-3
The main system feeds the fuel to the engine during medium- and high-speed operation.
through the bleed holes in the main nozzle, and the mixture
taken through the air cleaner into an optimum fuel-air mixture, which
8-
1-4
sure applied to the main nozzle increases
idling,
the fuel is mainly fed from the pilot outlet.
MAIN
SYSTEM
CHOKE
is
used for easy start in the cold season. When the recoil starter
DISASSEMBLY
Apart
from
mechanical failures, most
due to a clogged up air or fuel passage in jets, or fuel level variations.
buretor must be kept clean at all times. The carburetor
to
the engine during idling and low-speed operation.
main
jet to the pilot jet, where it is metered, and mixed
main
jet and fed to the main nozzle.
and
REASSEMBLY
The
is
atomized out of the main bore. It is mixed again with the
and
draws much fuel accordingly; thus easily start up the engine.
of
carburetor troubles are caused by
disassembly
with
air metered by the main
is
supplied to the engine.
is
pulled
with
an
incorrect mixing ratio, which may arise mainly
In
order to assure proper
reassembly procedures are
and
the air metered by.the pilot air jet.
air
jet is mixed
a
closed choke, the negative pres-
flow
of
air
as
follows:
with
the fuel
air
and fuel, the car-
(See
Figs.
57
and
58.)
7
8
-4gJ
29
"i
134
I
7
8*
12
Fig.
A
57
(EY
15,201
-43
l0e
l1
"---@
12
4
Fig.
58
(E
Y28)
-
Page 48

8-2-1
THROTTLE SYSTEM
1)
Remove the Philips screw (27) and throttle valve (22), and
2)
The spring
(24)
can be taken out by removing the throttle stop screw
pull
out the throttle shaft (23).
(25).
*Exercise care not to damage throttle valve ends.
8-2-2
CHOKE
1)
Remove the Philips screw
2)
When reassembling the choke shaft, make sure that the cutout in the choke valve faces the main air jet.
SYSTEM
(14)
and choke valve
(1
9,
and pull
out
the choke shaft
(1
6).
Meantime, when reassembling the moderation regulating ball (20) and the spring (21), set these parts at the
positions with the rings
8-2-3
PILOT
1)
Remove the pilot jet (26),
2)
Reassembly
SYSTEM
(1
8)
and (19) and then reassemble.
using
correct tool to avoid damage to it.
Tighten the pilot-jet securely. Otherwise, the fuel may leak, causing engine malfunction.
8-2-4
MAIN
SYSTEM
1)
Remove the bolt
2)
Re-move the main jet (13) from the body
and then remove the pipe assy
3)
Reassembly
(1
2)
and take out float chamber body
(29)
(lo).
(6).
[In
case
of
EY28,
remove the main jet (13) from the pipe assy (29),
and the nozzle (28) from the carburetor body
(6).]
a) Fasten the main jet securely to the body. Otherwise, the fuel may become too rich and cause engine malfunction.
b)
The bolt tightening torque
is
70
kg-cm.
right
8-2-5
FLOAT SYSTEM
I
j
Pull
out the float pin
it
with rubber needle.
CAUTION:
When cleaning the jets, use neither a drill
adversely affect fuel
2)
When removing the needle valve and floats, gently tap the reverse side using the
and remove because the float pin is calked
(9)
and remove the float
flow).
Be sure to use compressed air
(8)
and needle valve
nor
a wire (because of possible damage
to
blow them clean.
to
the carburetor body.
(1
7).
If
the needle valve need be replaced, replace
of
the orifice which will
rod
more slender than the float
pin
-
44
-
Page 49

9.
BREAK-IN OPERATION
An
overhauled engine must be operated at low speed break-in the parts. A thorough break-in is indispensable particularly
when
the
cylinder, piston,:piston rings
The recommended break-in schedule is shown below.
or
of
REASSEMBLED ENGINE
valves are replaced with new ones.
I
I
I
EY15
HP
1.35
2.7 HP
1
I
LOAD
EY20 EY28
NO
LOAD 2,500 rpm
NO
LOAD
NO
LOAD
1.75 HP
3.5
HP
I
I
2.75 HP
5.5
HP
CRANKSHAFT REV.)
3,000
I
3,600 rpm
I
3,600 rpm
I
3,600 rpm,
SPEED
rpm
10
10
1
10
I
30 minutes
I
60
TIME
minutes
minutes
minutes
minutes
-45
-
Page 50

10.
10-1
Model
breaker type ignition device, utilizing the power transistor as an element for controling eiectric current. There are two types
of this system, the one is outer coil type without pulser and is called
type has a built-in pulser coil and is called P.I.T. (Pulser transistor type). T.I.C. is a standard ignition system for
ROBIN
FEATURES
EYl5D
and
EY20D
SOLID
can employ as option a pointless ignition system, called Solid State Ignition, whch is the circuit
STATE
IGNITION
ENGINE
T.I.C.
(Transistor ignition circuit type) and the other
('F.I.C.
and
P.I.T.)
EY28D,
B.
r
Being different from the breaker point type ignition system, this brand-new system
startingup failure owing to dirty, burnt or oxidized point surface, lowering of ignition efficiency being caused by moisture,
rough
surface of breaker point and incorrect timing resultant from worn mechanical parts.
10-2
BASIC
T.I.C. (Transistor ignition type) consists ofthe flywheel and
ignition coil with built-in transistor; and its basic theory is as
follows:
Revolution
primary side of the ignition coil, and the electric current
the electric current
The flywheel goes round further, and at the time
ignition the electric current C runs, then the electric
current
electric current
tor,
electricity
ignition coil and it sparks at the plug.
THEORY
of
the flywheel generates electricity on the
A
runs. A makes the power transistor
D
runs
is
abruptly cut; and as a result, the
is
generated on the secondary side of the
of
T.I.C.
B
passes.
to
the signal transistor,
B,
passing through the power transis-
(See
Fig.
'ON"
by
which the
high
59.)
and
of
voltage
I
Resister
is
completely free from such troubles as
-
1
T
Ignition
11
.-
&
Coil
m
C
8
01
v)
I
X
I"
Fig.
59
10-3
BASIC
P.1.T
@her ignition transistor type) consists of the igni-
tion coil,
as
follows:
1) Revolution of the
primary side
rent
the electric current
2)
The flywheel goes round further, and at the time of
ignition, the pulser coil generates electricity, and the
electric current
Then, the electric current D runs, by which the electric current
voltage electricity is generated on the secondary side
of
the ignition coil and it sparks at the plug.
THEORY
P.I.T.
unit and flywheel; and its basic theory is
of
the ignition coil, and the electric cur-
A
runs. A makes the power transistor
B
is cut abruptly, and as a result the high
of
P.I.T.
flywheelgenerateselectricity
B
passes.
C
runs;
and
(See
SCR
becomes
Fig.
"ON"
60.)
on the
and
"ON."
Fig.
60
-
46
-
Page 51

11.
TRQU
The following three conditions must be satisfied for satisfactory engine start.
1. The cylinder filled with a proper fuel-air mixture.
2.
An
appropriate compression in the cylinder.
3.
Good sparks at the correct time to ignite the mixture.
The engine cannot be started unless these three conditions are met. There are also other factors which make engine start difficult, e.
pipe, just to
The most common causes of engine troubles are given below:
11-1
g.,
a heavy load on the engine when it is about to start at low speed, and a
say
a few.
STARTING
DIFFICULTIES
high
back pressure due to a long exhaust
11-1-1
7)
11-1-2
If starting difficulties and loss of power are not due to the fuel system or ignition system, the following must be checked for
possible lack
1)
2)
3)
4)
FUEL SYSTEM
No
gasoline in th fuel tank;
The carburetor is not choked enough, particularly when the engine is cold.
Water, dust
Inferior grade gasoline or poor quality gasoline is not gasfied enough to produce the correct fuel-air mixture.
The carburetor needle valve is held open by dirt or gum.
carburetor when the engine is idling. (Overflow)
Th~s
of the like.
If the carburetor overflows, excessive fuel runs into the cyhder when starting the engine, making the fuel-air mixture
too rich to burn. If this happens, remove the spark plug, and turn the starting pulley a few turns in order to let the
rich fuel-air mixture out of the spark plug hole into the atmosphere. Keep the carburetor choke open during this
operation. Dry the spark plug well, screw
When the engine is cold, pull the carburetor knob to let the gasoline
COMPRESSION SYSTEM
Engine inside is completely dried up because of a long period
Loose or broken spark plug. This causes a hissing noise made by mixture gas running out
stroke during cranking.
Damaged head gasket
Incorrect Tappet Clearance
If the correct compression is not obtained even after remedying the above, disassemble the engine and check further
or
gum
in the gasoline block flow
trouble may be remedied, depending on cases, by lightly tapping the float chamber with the grip of a screwdriver
of
compression.
or
the fuel cock is closed.
of
the fuel to the carburetor.
This
trouble can be detected as the fuel flows out
it
into place, and try to start again.
flow
into the carburetor.
of
non-operation.
of
cylinder in compression
or
loose cylinder head. A similar hissing noise is produced during compression stroke.
of
the
as follows:
a) Valve stuck open due
b) If the piston rings are stuck on the piston, remove the piston and connecting rod from the engine, and clean, remedy
or replace the parts.
to
carbon
or
gum on the valve stem.
-
47
-
Page 52

11-1-3
ELECTRICAL SYSTEM
Check the following for lack
1) Leads
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
8)
9)
10) Incorrect spark timing.
11-2
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7) Insufficient compression.
of
the ignition coil, spark plug
Ignition coil damaged and shorted.
Spark plug cable wet or soaked with
Spark plug dirty or wet.
Spark plug electrode gap incorrect.
Spark plug electrodes in contact with each other.
Contact breaker points pitted or fused.
Breaker arm stuck.
Condenser leaking
ENGINE MISFIRES
Incorrect spark plug electrode gap. Adjust it to anywhere between
Ignition cable worn and leaking.
Sparks weak.
Ignition wire connections loose.
Pitted or
Water in gasoline.
worn
breaker points.
of
sparks.
or
grounded.
or
contact breaker disconnected.
oil.
0.6
and
0.7
mm.
11-3
ENGINE
1)
Fuel tank empty. Water, dirt, gum, etc. in gasoline.
2)
Vapor lock,
3)
Vapor lock in the fuel lines or carburetor due to the use of too volatile winter gas
4)
Air
vent hole in the fuel tank cap plugged.
5)
Bearing parts seized due to lack
6)
Magneto
114
ENGINE OVERHEAT
Crankcase
Spark timing incorrect.
Low
grade gasoline is used, or engine
Cooling air circulation restricted.
Cooling
Cylinder head
Engine operated in
Exhaust gas discha'rge restricted,
Engine running on low-octane gasoline detonates due
STOPS
i.
e., gasoline evaporating
or
ignition coil faulty.
oil
level
low,
Add
oil
air
party misdirected causes loss of coohg efficiency.
cooling
fins
clogged up with dirt.
an
enclosed space without fresh supply of cooling air.
in
the fuel lines due to overheat around
of
oil.
immediately.
is
overloaded.
or
carbon deposits in the combustion chamber.
to
heavy load at low speed.
the
engine.
in
the hot season.
-
48
-
Page 53

11-5
ENGINE
1)
Low-quahty gasoline.
2)
Engine operating under heavy load
3)
Carbon or lead deposits
4)
Spark timing incorrect.
5)
Loose connecting
6)
Loose piston
7)
Causes
KNOCKS
rod
pin
due to wear.
of
engine overheat.
at
low speed.
in
the cylinder head.
bearing due to wear.
11-6
ENGINE
1)
Water
2)
Intake valve stuck.
3)
Valves overheated,
4)
Engine cold.
BACKFIRES
or
dirt in gasoline,
through
or
low-grade gasoline.
or
red-hot carbon particles in the combustion chamber.
CARBURETOR
-49
-
Page 54

12.
in whch the engine
INSTALLATION
Engine life, ease of maintenance and inspection, frequency of checks and repairs, and operating cost all depend on the way
is
installed. Carefully observe the following instructions for installing the engine.
12-1 INSTALLING
,-
When mouhting the engine, carefully examine its position, the method
and the method of supporting the engine.
When determining its mounting position, in particular, make sure that gasoline and oil can easily be supplied andchecked, the
spark plug and breaker can easily be checked, the
air
cleaner can easily be serviced, and that the oil can easily be discharged.
of
connecting it to a load (machine), the foundation,
12-2 VENT1 LATlON
Fresh
air
is necessary for coohg the engine and burning the fuel.
In cases where the engine is operated under a hood
lock,
oil
deterioration, increased
to operate the engme properly, It is necessary, therefore, to provide a duct
prevent recirculation
Take steps as necessary to keep the engine room temperature below
of
the hot air used for engme cooling, and temperature rise of the load (machme).
oil
consumption,lossaof power, piston seizure, shorter engine life, etc., making
or
in a small room, temperature rise
or
baffle to guide cooling
50°C
even in the hottest period
in
the engine room can cause vapor
it
impossible
air
to the engine to
of
the year.
12-3 EXHAUST GAS DISCHARGE
Exhaust gas is noxious. When operating the engine indoors, be sure to discharge the exhaust gas
pipe
is
used in such a case, the internal resistance increases causing loss of engine power.
crease
in
proportion
Exhaust pipe:
to
exhaust pipe length.
Less
than 3 m long, pipe inside diameter
Less
than 5 m long, pipe inside diameter
25
rnm,
30 mm.
Thus
outdoors.
pipe inside diameter must in-
If
a long exhaust
12-4 POWER TRANSMISSION
12-4-1
Take the following notes into consideration.
If
12-4-2
When using a flexible coupling, runout and misalignment between the driven shaft and engine shaft must be minimized.
Runout and misalignment tolerance are specified by the couphg manufacturer.
BELT
DRIVE
*
V-belts are preferable to flat belts.
*
The driving shaft
*
The driving pulley of the engine must be in line with the driven pulley of the load.
*
Install the engine pulley as close to the engine as possible.
*
If
possib!e, span the belt horizontally.
*
Disengage the load when starting the engine.
no clutch
is
used, use a belt tension pulley
FLEXIBLE
of
the engine must be parallel to the driven shaft
COUPLING
to
DRIVEN MACHINES
or
the like.
of
the load.
-
50
-
Page 55

12-5
WIRING
RECOIL STARTER OPERATION
Wire as shown
ing
coil
for
Models
an
intermediate tap.
[BREAKER
POINT IGNITION TYPE]
in
the wiring diagram below. Normally, those indicated
EY15,.EY20 and EY28
Condenser
(an
optional, not standard accessory) permits installation
Ignition
Magneto
Fig.
61
by
dotted lines are not included in engine wiring. Light-
of
an
AC
buzzer with
Coil
2
m
3
-
n
?
m
P
v)
[SOLID
1.
T.
STATE IGNITION TYPE for
I.C.
(Standard)
MODELS
EY15
and
EY201
2.
P. I.T. (with lighting coil)'
BlacklYellow
Spark Plug
Buzzer Switch
Fig.
62
""
Fig.
63
-
51
-
Page 56

[SOLID STATE IGNITION TYPE for MODEL EY28l
1.
T.
I.
C.
(Standard)
Ignition Coil Connecter
Spark
Plug
Exciter Coil
(Option)
Flywheel
Fig.
c
Stop Button
l-
Black
rrm
64
[ELECTRIC STARTER TYPE for MODEL EY281
Ignition
S
r-----
77h
I""
Battery
(12V
Coil
Unit
24AH)
Key Switch
Black
Starting Motor
/"-
Fig.
-
65
52
-
Page 57

13.
ELECTRIC
SBA
TBNG
MOTOR
(OPVBO
for
EV28
ONLY)
13-1
SPECIFICATIONS
Part Name
Maker
Voltage
output
Weight
Starting Motor
Nihon Denso
12v
0.6
kW
3.0
kg
K.
K.
Bolt
Drive Lever
13-2
Connect the
ing motor magnet switch.
The state
ing figure:
When the key switch is put to
closed and the current flows
The magnet switch coil is excited, and the contact
UP.
Then the continuity
pinion gear
The pinion gear is engaged with the ring gear, and the
engine cranking is made.
This means that the lower current flows in the
and
OPERATION
(t)
of
starting motor
is
instantaneously pushed out
in
the
S-+
circuit larger starter current
side
of
battery to the
“ON”
to
is
made to the starting motor, and the
8$
terminal
is as shown in the follow-
“ON,”
the
M+
the arrowhead direction.
by
the drive lever.
flows.
of
circuit is
is
drawn
M+
circuit,
start-
Stop
Collar
Fig.
66
From Rectifier
Battery
Magnet Switch
Fig.
67
1
Key Switch
B
-
53
-
Page 58

14.
RECOIL
STARTER DISASSEMBLY
and
REASSEMBLY
The recoil starter hardly
form disassembly and reassembly in the following procedures:
Tools to be used:
14-1
HOW
TO
Remove the recoil starter from the engine with a box
spanner.
Pull
the starting knob and pull out the starter rope
30
to
40
cm. Firmly press the reel with a thumb as
shown in
verse turn ai the place where the reel notch comes to
the outlet
the inside
utilize the reel notch, and rewind it until the rotation
stops in the arrowhead direction, braking the reel rotation with
Fig.
of
of
a
thumb.
has
a trouble in the normal use, however, in case
Box
spanner (spanner), Cutting pliers (pliers) and Screw driver
DISASSEMBLE
68
so
that the reel should not make re-
starter rope. Pull out the starter rope
recoil starter with a screwdriver. Then,
(D
Type)
for
to
it
has a trouble
Starter
or
at the time
Rope
Starter
Fig.
68
Notch
of
lubrication, per-
%
Knob
'4
3)
When removing, take out the parts in the order
numbering in Fig.
1.
U
2.
Thrust washer
3.
Friction spring cover
4.
Return spring
5.
Friction spring
6.
Ratchet
Meantime,
shaft with cutting pliers
69.
type snap ring
for
removing the U type snap ring, nip the
and
push it out.
of
the
2
@-"
353
Fig.
69
-54-
Page 59

b
Take out the reel from the starter case as shown
4)
70:
In this case, slowly take out it turning the reel lightly
toward left and right
so
that the spring is removed
from the reel hook section.
If the reel is suddenly taken out, there is
spring jumps out in the form as it
so
very dangerous,
(If
the spring jumped out, house it in the starter
instructed in Fig.
be carefuly of it.
75.)
a
fear that the
is
hooked, whch is
Finally, release and take out the starter rope tied to
both the reel side and the starting knob side.
Thus, the disassembly work ends.
in
Fig.
case
as
I
Starter Case Spring
Fig.
70
14-2
1)
HOW
TO
REASSEMBLE
(Type
D)
First, have the starter rope pass through the starting
knob, and tie the rope as shown in Fig.
Then, have the opposite side
of
71
No.1.
the rope pass through
the starter case and the reel, and tie it as shown in
Fig.
71
No.2.
(In
the Fig.
you see
Then surely house the end
71
both the ropes
in
figures
No.
1
and
are
tied quite lightly, as
No.2.
in
Please note this is
just for the purpose of easy understanding. Therefore,
when actually tying, tie the rope as tighteiy as possible.
2)
Confirm that the spring
housing section, and have the spring to form
inner edge will be about
and that it
hooks
surely the reel hook.
is
surely set in the starter case
so
1
mm from the starter shaft
Meantime, with the pliers about 10 cm long spring
the inner edge can easily be formed.
the reel.
that its
from
No.2
Outer
Edge
Fig.
of
Spring
71
Good
No.1
/
Reel
Hook
-
55
Starter Shaft
-
4cm
\
Inner Edge
Fig.
72
of
Spring
Page 60

3)
Before putting the reel in the starter case, wind the
starter rope in the arrowhead direction as shown
73,
and at
2.5
windings take out the rope from the reel
hook
notch. Set the reel
to the inner end of the spring,
in
and put the reel in the starter case.
(At this time, confirm that the reel hook is duly set
the spring.)
in
Fig.
Then, hold the starter rope as shown
4
turn the reel
times in the arrowhead direction, When
wound up, firmly press the reel not
to
73,
allow reverse
turn, and pull the starting knob. Then, pull out from
the starter case the starter rope utilized for winding,
and slowly return khe starting
4)
When reassembling the parts, follow up in the reverse
order
to
Fig.
69.
knob.
When putting the friction plate in the hole for it, set
the return spring
a
little upward as shown in
Fig.
74
that the friction plate can easily be put in the hole for
it.
Next, turn the friction plate in the arrowhead direction
till the position where its notch matches with the ratchet. Push firmly the friction plate to the reel side, and
a
U
put the thrust washer and then clamp it with
shape
snap ring.
U
(Clamp the
shape snap ring with cutting pliers.)
Fig.
to
and
so
Fig.
73
t
With the above, the disassembly and reassembly
assembled. Therefore, for caution's sake check the function
in
described
the next page.
works
end, however, there
-
56
Fig.
74
is a case that the parts are
of
the recoil starter following the confirmation items
-
not
properly re-
Page 61

14-3
CONFIRMATION ITEMS AFTER REASSEMBLY (Type
1)
Pull
the starting knob
i)
If
the starting knob is felt heavy to pull and cannot be pulled, check whether the parts were reassembled correctly
2
or
3
times, and pull out the starter rope a little.
as instructed.
n)
If the ratchet does not function, check whether the spring is hooked properly.
2)
Pull the starting knob, and pull out the starter rope all the way long.
i)
If
the starter rope remains left in the reel or the starter rope does not return at all, immoderate strain is imposed on
the spring.
ii)
If the return power of the starter rope is weak
mobile
tions explained in the paragraph
iii)
If the sound is heard that the spring is falling off, and the starter rope cannot.be wound in relay, reassemble once
So
rewind the starter rope
oil
in the frictional portions. If it does not revive yet, wind it
1
or
i)
above and
2
times as per instruction in Fig.
or
the starting knob is drooped
confirm
again from the biginning.
D)
68.
on
the way, inject a few drops
1
or
2
times.
(In
this case, refer to the instruc-
whether or not immoderate strain is imposed
on
the spring.)
of
14-4
HOW
TO
DO
IN
SUCH
1)
In case the spring jumps out when disassembling
CASES!
With thin wire make a ring smaller than the case for
spring, and hook the outer edge of spring on the part
of the ring
as
shown
in
Fig. 75. House it in the spring
housing section of the reel, and calmly remove the
ring, pressing the spring with fingers
so
as not
out.
The ring can easily be removed by gouging it with the
tip of the screwdriver or the like.
Meantime, refer to Fig.
72
for
not
to mistake the hous-
ing direction of the spring.
2)
In
case of lubricating
Lubricate the rotating parts, frictional parts and spring
with heat resistant grease, if possible,
the time of disassembly
3)
In
case the direction of rotation
or
at the end
or
mobile oil at
of
season for use.
is
reverse (Type
to
come
B)
Fig.
75
As
this manual is
for
right rotation
recoil
starter, perform reverse
work
for
left rotation recoil starter.
-
57
-
Page 62

15.
After disassembling and cleaning the engine, check and repair, if necessary, according to the correction table. The correction
table applies whenever the engines are repaired.
table. Correct maintenance
The meanings of the terms
CHECKS
Correction
Repair, adjustment
Correction Limit
The limit on wear, damage or functional deterioration of engine parts beyond which normal engine performance cannot be expected without repairing such parts.
Use Limit
The limit beyond which parts can
Standard Dimensions
The design dimensions
Correction Tolerance
Tolerance on the dimensions
and
CORRECTIONS
It
is important for the servicemen to be familiar with the contents of this
is
recommended by observing the correction standards specified.
used
in the correction table
or
replacement
of
new parts minus tolerance.
of
any engine parts.
no
longer be used in respect of performance
of
engine parts refinished or adjusted.
are
as follows:
or
strength.
P
-
58
-
Page 63

16.
TABLES
OF
CORRECTION STANDARDS
ITEM
Flatness of cylinder
head
Bore
Roundness 0.01
Cylindricity
Valve seat contact
width
at skirt,
0.25
I.D.
in
Valveguide
O.D.
thrust direction
(incl. over size)
0
C 0.5
ENGINE
I
MODEL
I
EY20
EY28
EY 15
EY
20
EY28
EYl5
EY 20
EY
EY15
EY20
EY 28
EY 15
EY15
I
EY20
EY 28
EY15
EY28
1
1
28
1
1
S.T.D.62.98 dia.
B
S.T.D.66.98dia.
S.T.D.
B
C
STANDARD
SiZE
Less
than 0.1
S.T.D. 63 dia.
67 dia. rnax.
S.T.D.
75
dia.
6.5@
63.23 dia.
67.23 dia.
74.98 dia.
75.23 dia.
75.48 dia.
.
-
+0.019
I
Dif.
0.01
1.2
+0.022
-
between
&
rnin.
5
-1.5
0
0.02
0
1
0.15
0.1
5
2.5
0.1
5
-0.1
USE
LIMIT
0.65
0.1
-0.1
REMARKS
7
I
5
At middle
portion
1
plate,
Cylinder
gauge
Micrometer
TOOL
CORRECTION
METHOD
Correct
Boring
Correct
Replace
Replace
EY15
I
EY2O
Width
of
ring
groove
1
Piston
pin
hole
EY15
Clearance between
piston
and
cylinder
Clearance between
pisition ring and
ring groove To
EY20
EY
EY 20 0.010-0.055
28
I
I
I
Oil
Top 1.5
Oil
"*
14 dia.
16
30
dia.
P
I
+0.060
t0.040
+0.002
I
-0.009
+0.002
-
0.009
0.020-0.059
0.040-0.079
0.090-0.135
0.060-0.1
0.010-0.065
0.050-0.095
0.010-0.065
-
59
05
-
I
0.035
-
0.025
0.1 5
Replace
0.035
Max. cylin-
thrust direction
5
0.1
5
Micrometer
Replace
Replace 0.1
Page 64

Clearance between
pirition ring and
ring groove
Fit between piston
and piston
Ring
Ring width 2nd
pin
gap
ENGINE STANDARD CORRECTI,
MODEL TOLERANCE
EY28 0.01 0-0.065
EY15
1
EY20
1
EY
28
EYZO
I
EY28
TEY15
1
1
Oil
2nd
2;
Oil 2.8 -0.010--0.030
TOP
2.0
2.0
011
2.8
Top
1.5
2nd 1.5 4.010-
Oil
3.0
0.050-0.090
0.01 0-0.065
-0.009-0.010
0.20
0.05
0.1
~~~
-0.090--0.110
-0.060--0.080
T
-0.050--0.070
-0.010--0.030
-0.010--0.030
-
-
-
0.40
0.25
0.3
0.030
Y
LIMIT
0.1
5
0.06L
1.5
-0.1
I
USE
LIMIT
0.1
0.06L
1.5
-0.1
5
REMARKS
I
1
TOOL
Feeler
gauge.
Micrometer
Feeler
CORRECTION
METHOD
Replace
Replace
Replace
0
-
I
I
end
Large
Clearance between EY20
rad large end
and crankpin EY28 0.020-0.046
Small end I.D. 0.010-0.021
Clearance between
small
and pinston pin
Large
clearance
Parallelism between
large end and
small
I.D.
end I.D.
end
side
end bores
I.D.
1
1
EY28
EY15 24 dia.
EY
20 26 die.
EY
28
EY15
EY
28
Ey15
EY20 0.010-0.029
EY28
EY15
EY
15
EY28
EY20
14 dia.
16 dia.
I I
28
dia.
14 dia.
16
dia.
1
I
I
-0.008
+0.013
0.037-0.063
0.1
-
0.3
0.05
-
0.04
0.1
0.2
0.08
0.1 2
1
0.1
.o
-0.04
0.1
0.2
0.08
0.1
2
1
.o
0.1
Micrometer
Cylinder
Cylinder
gauge,
Micrometer
Cylinder
gauge
Cylinder
gauge.
Micro-
meter
Feeler
gauge
Test
bar
and Dial
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Replace
Rernachine
or Replace
Re-machine
or Replace
Distance between
large
end
small
and
end bores
EY
28
100
0.15
-
60
-
Page 65

ITEM
Crankpin
roundness
0.D
AODEL
EY28
EYt5
EY20
EY 28
24
1
28
1
die.
dia.
l-
CORRECT1
TOLERANCE
-0.037
-0.050
-0.020
-0.033
Less
than 0.005
N
LIMIT
0.1 5
TOOL
0.5 Crankpin O.D.
Micrometer
Micro.
meter
CORRECTION
METHOD
Re-machine
or
Replace
Crankpin O.D.
cylindricity
Crankpin O.D.
parallelism
Crankshaft
journal
O.D.
lobe
Cam
Journal
height
O.D.
EY15
EY 20
EY28
EY20
EY15
EY 158
EY 28D
Drive
Mag.
8.
Drive
Mag.
s.
Drive
Mag.
s.
Drive
s.
Mag.
t-
Drive
Mag.
s.
Drives. 15dia.
s.
Mag.
s.
25
25
s.
25 die.
25
s.
30 dia.
30 dia.
s.
15
15
s.
25 dia.
15 die.
25
die.
dia.
die.
dia.
dia.
dia
Less
than 0.005
Less
than
0.008
-
O.OO3
-
0.01
2
io.1
-0.01
6--0.027
-0.003--0.012
-0.016--0.027
-0.016--0.027
-0.020--0,033
-
0.05
-
0.25
-0.05
Micrometer
Dial
wuge
-
0.05
-
0.25
I-
-0.05
Micrometer
Micro-
meter
Micrometer
Replace
Replace
Replace
length
Free
Squareness
EY28B
EY15
EY 20
EY 28
EY15
EY 20
EY 28
Drive
Mag.
s.
30 dia.
s.
37
25 dia.
-0.003--0.012
-0.020--0.033
-61
-1.5
,
,o
1
For total
length
Vernier
calipers
Square
Replace
Replace
-
Page 66

ITEM
ENGINE STANDARD CORRECT1
1
MODEL
I
SIZE TOLERANCE
N
LIMIT
USE
LIMIT
REMARKS
CORRECTION
I
METHOD
Clearance between
stem and guide
Clearance between
groove and retainer
Stem
end length
EY15
EYrn Intake
EY 28 Exhaust
EY15
Intake 0.025
Exhaust
I I
I
EY,5
I
Intake Exhaust 5.9
I
EY2O
I
Intake
Exhaust
Tntake
Exhaust
I
EY15
I
EY28
35.6
43.7
5.9
6'2
6.4
4.45
0.056
0.025
0.056
1
I
I
When
0.10
0.1
-
0.062
0.1
-
0.062
-
0.100
cold
*0.02
-
0.3
00
-0.15
"
0.3
blow
0.05
abow
0.25
0.5
-1
.o
-
0.5
0.3
0.5
-1
-
0.5
.o
At middle
Micro-
meter
Cylinder
gauge
Feeler
gauge
Feeler
gauge
Vernier
calipers
Vernier
calipers
Replace
Replace
Correct
Replace
Replace
Replace
stem and guide
Spark plug
Spark gap
Spark timing
Point opening
EY28
1
I
EY28
EY15
I
:;:
EY15
EY 28
I
EY20
I
NGKBBHS
I
NGK
I
23'before
I
BPBHS
T.D.C.
1
0.013
0.013-0.043
1
I
0.6
f
-
-
0.05
0.037
0.7
0.2
t
f
1
5"
0.1
0.2
Feeler
Timing
tester
breaker Adjust
spanner
I
1
Adjust
replace
Adjust
or
-
62
-
Page 67

tTEM
MODEL
HP/rpm
CORRECTION
LIMIT
REMARKS
Max.
output
Continuous
Output
ITEM
Fuel
Consumption
ITEM
Lubricant
Consumption
Rated
EYISD
EYl5B
EY2OD
EY28D
EY 288
EY15D
EYl58
EY2OD
EY 28D
EY28B
EY15
EY20
EY28
MODEL
EY15
EY20
EY28
3.514000
3.512000
5.0/4000
7.514000
7.512000
2.713600
800
2.711
3.513600
5.513600
800
5.511
liter/hr MODEL
1.1
1.2
2.7
cc/hr
10
15
Below
110%
of
rated
output
CORRECTION PRECISENESS
135%
of
the
standard value
LIMIT
50
60
cc/hr
and
up
CORRECTION PROCEDURE
3600
rPm at cOnthuOuS rated
REMARKS USE
Output
c
*Use the
ITEM
Fixed quantity
of
Lubricant
SC
ITEM
Specified Lubricant
Qualiw
MODEL
EY15
EY20
EY28
or higher grade engine oil.
MODEL
EY15
EY20
EY28
Q
0.6
0.85
Comparison between oil viscosity and temparature
r
Single
grade
Multigrade
-20
?,I,
I
I
I
-10
1OW-30
I
0
10
I
I
!,
#30
1
#40.
1
I
30 4OoC
I
20
I
I
REMARKS
I
When the peripheral temparature
below -2OoC, use the oil
and
quality fitted to the local conditions.
When the peripheral temparature
I
than 4OoC. use the oil
I
quality fitied to
The oil consumption
when
used
rature,
day.
REMARKS
the
local conditibns.
under high peripheral tempa-
so
it
is
necessary to check every
of
viscosity
of
vismsitv and
is
apt to increase,
is
is
more
I
I
I
~~.
1
If
quality and quantity
of
the engine oil become lower or less, burning might be caused
-
63
-
Page 68

ITEM FREOUEMCYOFOILCHANGE
Oil Chaw
ITEM
Cylinder prowre
ITEM
Mn. acderating
molution
ITEM
Cylinder haad EY
bolts
EY15
EY 20
EY
28
MODEL
EY15
EY2O
28
EY
MODEL
EY 15D
EY
15B
EYZOD
EY28D
EY28B
I
MODEL
20
EY28 220
kglcm'lrpm
00
514
61400
rpm
1200
600
1200
1200
600
I
kgem
190
-
-
First time: Change
Second Time and Thereafter: Change
CORRECTION LIMIT
70%
of
and down
TOOL
I
I
ft-lb
230
260
oil
after
normal value
I
TOOL
20
houn operation.
oil
every
50
hours operation.
TOOL
Pressure gauge
REMARKS
I
I
REMARKS
Torque wrench
REMARKS
Reference value
Crankshaft
Rev.
-_
Connectin0
twin
Magneto clamp
nuts
..
WlfS
Smrk
rod
Plug
EY15
EY 28
EY15
I
Ff;:
I
EY28
EY28
SO-
-
170
1
600-
1
170-
120
-
230
-
115
200
650
190
150
270
I
1
Torque wrench
Toraue wrench
Torque wrench
-64-
Page 69

&
-
17.
me following maintenance jobs apply when the engine
tenance intervals are by no means guarantees for maintenance free operations during these intervals.
17-1 DAILY CHECKS and MAINTENANCE
MAINTENANCE
For
example,
every
50
if
hours.
the engine is operated
and
STORING
is
operated correctly under normal conditions. The indicated main-
in
extremely dusty conditions, the
air
cleaner should be cleaned every day instead
of
I
Remove dust from whatever parts which
accumulated dust.
I
Check external fuel leakage. If any, retighten
replace.
I
Check screw tightening. If
re-tighten.
Check
17-2 EVERY
I
Change crankcase
Checks and maintenance
any
loose one
oil
level in crankcase and add up as necessary.
20
HOURS CHECKS
Checks and maintenance
oil.
is
found,
and
MAINTENANCE
I
The governor linkage
Not
or
only
Loose
accidents.
If
the engine
I
To
remove run-in wear particles
Reasons for requiring them
is
especially susceptible to dust.
wasteful but also dangerous
screws and nuts
is
operated without sufficient
Reasons for requiring them
will
result
in
vibration
oil,
it
will
1
17-3 EVERY
Change crankcase
Clean
air
Check spark plug.
gasoline
17-4 EVERY 100
or
I
I
Clean fuel filter and fuel tank.
Clean contact breaker points.
50
HOURS (10 DAYS) CHECK and MAINTENANCE
Checks and maintenance
cleaner.
polish
-
Checks
oil.
If
contaminated, wash in
with
emery paper.
200
HOURS (MONTHLY) CHECKS
and
maintenance
Contaminated
Clogged
Output power is reduced and starting
is
air
made difficult.
and
~~ ~ ~~~
I
1
The engine
I
The engine output drops.
-
65
-
Reasons for requiring them
oil
accelerates wear.
cleaner harms engine operation.
MAINTENANCE
Reasons for requiring them
will
be out
of
order.
Page 70

17-5 EVERY
500-
600
HOURS (SEMIANNUAL) CHECKS
and
MAINTENANCE
Checks
Remove cylinder head and remove carbon
deposit.
Disassemble and clean carburetor.
77-6
EVERY 1000 HOURS (YEARLY) CHECKS
Checks and maintenance
Perform overhauls, clean, correct
parts.
Change piston
Replace fuel
rings.
pipe
17-7 PREPARATION
1)
Perform the above
2)
Drain
fuel from the fuel tank and carburetor
3)
To
prevent rust in the cylinder bore, apply oil through the spark plug hole and turn the crankshaft several turns by
hd. Reinstall the plug.
4)
Turn the starting pulley by
5)
Clean the engine outside
6)
Put a vinyl
or
17-1
other cover
and
maintenance
The engine
and
MAINTENANCE
or
replace
once a year. To prevent
for
and
with
over
LONG
17-2
hand
ABEYANCE
maintenance
and leave
oiled cloth.
the engine and store the engine
jobs.
float
chamber.
it
where the resistance
The engine output drops and become out
is
the heaviest.
in
dry place.
Reasons for requiring them
will
be out of order.
for
Reasons
from
danger caused by the fuel leakage.
requiring them
of
order.
1
-
66
-
Page 71

Industrial
Engines
 Loading...
Loading...