Page 1

35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw
Part Number: 71-0220RK
Revision: B
Released: 9/10/12
Detector
www.rkiinstruments.com
Page 2

WARNING
Read and understand this instruction manual before operating
detector . Improper use of the dete ctor could result in bodily harm
or death.
Periodic calibration and maintenance of the detector is essential
for proper operation and correct readings. Please calibrate and
maintain this detector regularly! Frequency of calibration
depends upon the type of use you have and the sensor types.
T ypical calibration frequencies for most applications a re between
3 and 6 months, but can be required more often or less often
based on your usage.
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector
Page 3

Product Warranty
RKI Instruments, Inc. warrants gas alarm equipment sold by us to be free fro m defects in
materials, workmanship, and performance for a period of one year fr o m date of shipment
from RKI Instruments, Inc. Any parts found defective withi n tha t period will be repaired
or replaced, at our option, free of charge. This warranty does not apply to those items
which by their nature are subject to deterioration or consumption in normal ser v ice, and
which must be cleaned, repaired, or replaced on a routine basis. Examples of such items
are:
W arranty is voided by abuse including mechanical damage, alteration, rough handling, or
repair procedures not in accordance with the operator’s manual. This warranty indicates
the full extent of our liability , a nd we are not r esponsible for removal or r eplacement costs,
local repair costs, transportation costs, or contingent expenses incurred without our prior
approval.
a) Absorbent cartridges d) Batteries
b) Pump diaphragms and valves e) Filter elements
c) Fuses
THIS WARRANTY IS EXPRESSLY IN LIEU OF ANY AND ALL OTHER
WARRANTIES AND REPRESENTATIONS, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED,
AND ALL OTHER OBLIGATIONS OR LIABILITIES ON THE PART OF
RKI INSTRUMENTS, INC. INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL RKI INSTRUMENTS,
INC. BE LIABLE FOR INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
LOSS OR DAMAGE OF ANY KIND CONNECTED WITH THE USE OF
ITS PRODUCTS OR FAILURE OF ITS PRODUCTS TO FUNCTION OR
OPERATE PROPERLY.
This warranty covers instruments and parts sold to users by authorized distributors,
dealers, and representatives as appointed by RKI Instruments, Inc.
We do not assume indemnification fo r any accident or dama g e ca u s e d by the operation of
this gas monitor, and our warranty is limited to the replacement of parts or our complete
goods.
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector
Page 4

Table of Contents
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Housing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Flow System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Detection System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Mounting the Sample-Draw Detector . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Connecting the Sample Lines to the Sample-Draw Detector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Wiring the Sample-Draw Detector to a Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Start Up. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Introducing Incoming Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Setting the Zero Reading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Normal Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Low Flow Alarm. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Maintenance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Preventive Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Replacing Components of the Sample-Draw Detector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Adjusting the Low Flow Setting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Calibration Frequency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Calibration, IR CH4 and H2S Detectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Preparing for Calibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Setting the Zero Reading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Setting the Response Reading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Returning to Normal Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Calibration, Oxygen Detector. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Preparing for Calibration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Setting the Zero Reading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Setting the Fresh Air Reading. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Returning to Normal Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Parts List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector
Page 5

Overview
This manual describes the 35-3010RKA-07 sample-draw detector. This manual also
describes how to install, start up, maintai n, and calibrate the detector. A parts list at the
end of this manual lists replacement parts and accessories for the sample-draw detector.
Specifications
Table 1 lists specifications for the 35-3010RKA-07.
Table 1: Specifications
Target Gases & Detection Ranges Methane (CH
): 0 - 100% LEL
4
Oxygen: 0-25% volume
Hydrogen Sulfide (H
S): 0 - 100 ppm
2
Input Power 24 VDC
Current Draw 275 mA
Output Signals 4-20 mA each channel
Construction (housing) Fiberglass/polyester (NEMA 4X)
Dimensions 15.44 in. H x 12.55 in. W x 8.31 in. D
Weight 14 lbs.
Sampling Method Sample-draw
Sample Flow 1.2 SCFH (nominal)
Response Time 90% in 30 seconds
Accuracy Methane
:
± 5% of reading or ± 2% of full scale (whichever is greater)
Oxygen
± 0.5% O
:
2
Hydrogen Sulfide (H2S):
± 5% of reading or ± 2 ppm H
S (whichever is greater)
2
WARNING: When using the 35-3010RKA-07, you must follow the instructions and
warnings in this manual to assure proper and safe opera tion of the
35-3010RKA-07 an d to minimize the ris k of personal injury. Be sure to
maintain and periodically calibrate the 35-3010RKA-07 as described in this
manual.
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 1
Page 6

Description
Hydrophobic
Filter ( AcroPak)
Flow B lock
for IR CH4
IR CH4
Sensor
H2S Sensor
Amp 1
Pum p
Charcoal Filter
LEL Transm itter
CO Sensor
Combustible
Sensor
Oxygen S ensor
Amp 2
Inlet Fitting For 1/4"
OD Rigid Tubing
Exhaust F itting For 1/4"
OD Rigid Tubing
3/4 ConduitH ub, 2X
Flow
Block
Main Circuit Board
Oxygen
Transmitter
Reset Switch
Preamp
Circuit
Board
This section describes the components of the 35-3010RKA-07 sample-draw detector. The
sample-draw detector consists of the housing, flow system, and detection system.
Figure 1: Sample-Draw Detector Component Location
Housing
The sample-draw detector’s fibe rglass housing is weather- and corrosion-resistant. It is
suitable for installation where general purpose equipment is in use. The housing door is
hinged on the left side and is secured by two latches on the right side.
Four mounting feet are attached to the back of the housing (one at each corner). Use the
mounting feet to install the housing to a vertical surface. Use the two conduit hubs on the
bottom of the housing to make wiring connections.
An aluminum subpanel is mounted to th e interior of the housing. The sample-draw
detector’s internal components are mounted to the subpanel.
2 • 35 -3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detec tor
Page 7
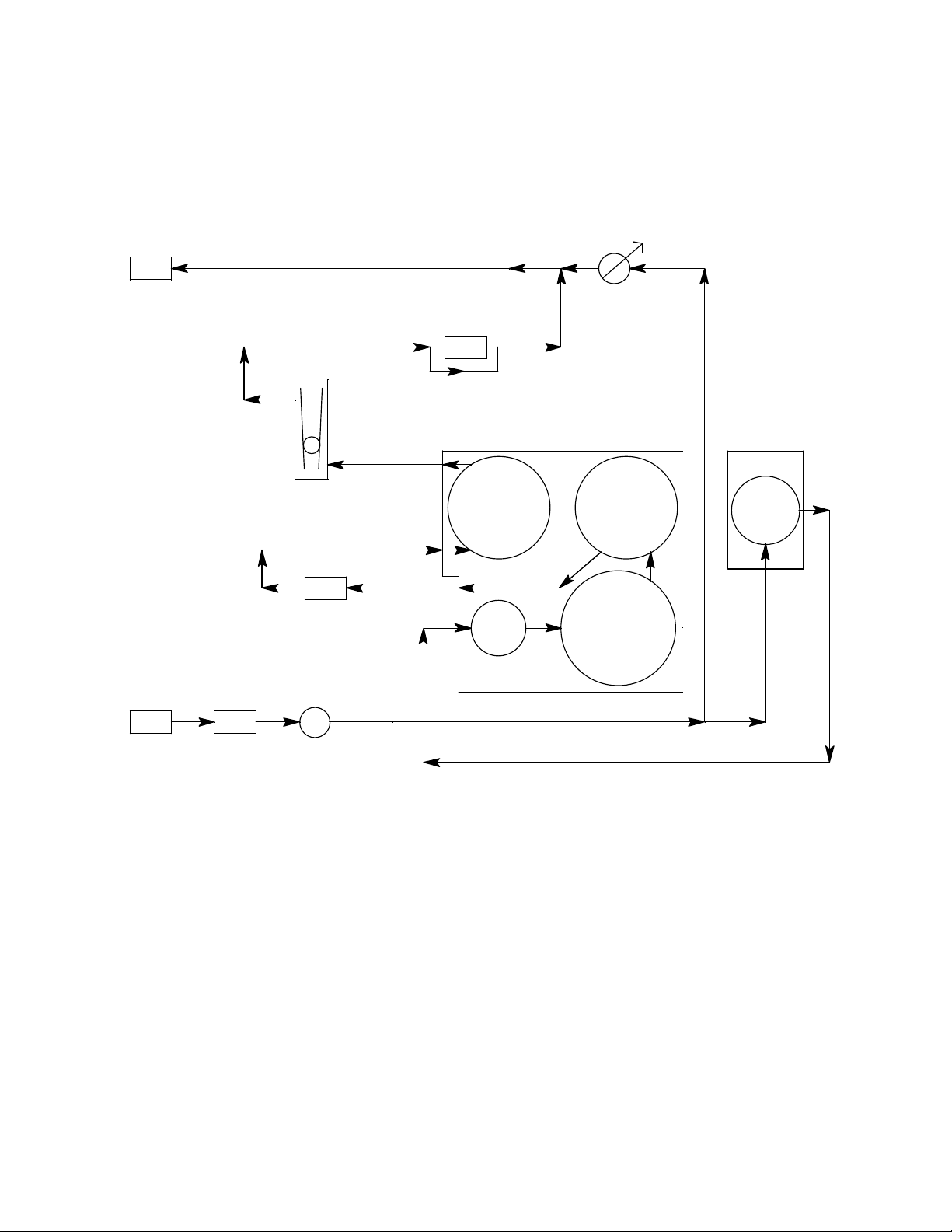
Flow System
Oxygen
IR CH4
Hydrophobic
Filter
Inlet
Exhaust
Pump
LEL
Dummy
Plug
H2S
Flow meter
Flo w Block
Bypass
Valve
Pressu re Swi tch
CO
Dummy
Plug
Charcoal
Filter
The sample-draw detector’s flow system consists of the INLET fitting, hydrophobic filter,
charcoal filter, pump, flowmeter, bypass valve, status lights, pressure switch, flow blocks,
and EXHAUST fitting (see Figure 1). Figure 2 illustrates how the gas sample moves
through the flow system.
Figure 2: Sample-Draw Detector Flow Diagram
INLET Fitt i n g
The INLET fitting on the bottom of the housing allows the gas sample to enter the sampledraw detector. The INLET fitting accepts 1/4 in. rigid tubing. See “Installation” on page 9
for instructions to connect tubing to the INLET fitting.
Hydrophobic Filter
The hydrophobic filter is to the left of the main circuit board. It is held in place by a metal
clip. It prevents water and other liquids from contaminating the flow system. Replace the
filter when it appears dirty, discolored, or clogged. If a liquid other than water is drawn
into the filter, repl ace the filter as soon as possible.
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 3
Page 8

Charcoal Filter
The charcoal filter is located above the LEL transmitter. It is held in place by a metal clip.
The charcoal filter is placed after the H
S sensor and before the CO sensor (if one is
2
installed) in the flow system. It scrubs out interfering gases which may cause the CO
sensor to respond, such as H
S or certain hydrocarbons. It is included in this version of
2
the sample draw detector in cas e a CO sensor i s added i n the fi eld. If a CO sens or i s adde d
in the field, a new charcoal filter should also be installed.
Pump
The pump is located to the left of the main circuit board near the bottom left of the
sample-draw detector. The pump pulls the gas sample into the sample-draw detector. The
pump operates on 24 VAC, which is generated from the 24 VDC supplie d to the sample
draw detector.
Flowmeter
The flowmeter is attached to the main circuit board near the top left corner (see Figure 1).
A ball in the flowmeter column indicates the flow rate of the sample-draw detector. The
flowmeter measures the flow in the range 0.2 to 2.0 SCFH (Standard Cubic Feet per Hour).
Although the sample-draw detector will operate down to a flow of 0.6 SCFH, the
optimum flow rate is 1.2 SCFH.
Bypass Valve
The bypass valve is to the left of the flowmeter. The bypass valve adjusts the flow rate to
the sensor. Use a flat-blade screwdriver to adjust the bypass valve.
NOTE: The bypass valve allows fine adjustments of the flow rate. For a wider range of
adjustment, use the flow adjust potentiometer (see Figure 1).
Status Lights
Two status lights are above the flowmeter.
Pilot Light
The green Pilot light is on when the sample-draw detector is receiving power.
Fail Light
The red Fail light is on when the sample flow rate is below the low flow level.
NOTE: The factory set low flow level is 0.6 SCFH (±0.2). See “Adj usting the Low Flow
Setting” on page 18 for instructions to adjust this setti ng.
Pressure Switch
The pressure switch is mounted to the opposite side of the main circuit board. The
pressure switch monitors the flow rate of the incoming gas sample.
If the flow rate falls below the preset low flow level, the pressure switch causes the fail
relay to interrupt the signal in the 4-20 mA line for the H
downscale reading at the monitor on these channels. The low flow level is factory-set at
0.6 SCFH (±0.2 SCFH).
NOTE: There is no low flow indication for the LEL channel.
4 • 35 -3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detec tor
S channel. This causes a
2
Page 9

Flow Blocks
BATT 24V
Test Point TP-
Sensor Terminal
Strip
Oxygen
Transmitter
FB
+
+
TOXIC
OXY
G
Transmitter T ype Selector,
Set To OXY
Intercon nect
Terminal Strip
Span Pot
Zero P ot
TP +
TP -
4/20
TOXIC
Test Point TP+
RD BK
W
OXY
SPAN
LEL Transmitter
Interconnect
Terminal Strip
Test Point TP-
Span Pot
Zero P ot
ZERO
Test Point TP+
Both flow blocks are located in the lower right corner of the sample-draw detector. The
oxygen and H
houses the IR CH
S sensors are installed in the larger flow block. The smaller flow block
2
sensor. The flow blocks route the sampled air to each sensor.
4
EXHAUST Fitting
The EXHAUST fitting on the bottom of the housing allows the gas sample to exit the
sample-draw detector. The EXHAUST fitting accepts 1/4 in. rigid tubing. See
“Installation” on page 9 to connect tubing to the EXHAUST fitting.
Detection System
The detection system consists of the gas sensors, LEL and oxygen transmitters, preamp
circuit board, and the main circuit board.
IR CH
The infrared CH
Sensor
4
sensor is installed in the smaller flow block in the lower right corner. A
4
small circuit board with a cable mates to it and retains it in the block. The cable is wired to
the main PCB.
Oxygen Sensor
The oxygen sensor is installed in the lower right of the larger flow block. It consists of a
cylindrical body which houses the detection elements and a cable which terminates in a
round 7-pin male connector. The sensor connector mates to a 7-position socket that is
wired to the main PCB.
Carbon Monoxide Sensor
The CO sensor position in the flow block is occupied by a plastic dummy plug in the
35-3010RKA-07.
Hydrogen Sulfide Gas Sensor
The hydrogen sulfide gas sensor is installed in the upper right side of the flow block. It
has 4 pins which mate with sockets in th e preamp circuit board.
Figure 3: LEL & Oxygen Transmitters
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 5
Page 10

LEL Transmitter
The LEL transmitter is mounted to the left of the oxygen transmitter and above the main
circuit board. It consists of the span pot, zero pot, one internally wired terminal strip, and
the test points.
Span/Zero Pots
The span and zero pots are located at the bottom edge of the transm itter and are used for
calibration. Use the span pot to make adjustments to gas response readings and the zero
pot to make adjustments to the zero reading
Transmitter Interconnect Terminal Strip
The transmitter interconnect terminal strip is the seven-point terminal strip near the right
edge of the transmitter. The transmitter is factory wired to the sensor and main circuit
board.
T est Points
The test points are located on the left side of the transmitter and are labeled TP+ and TP-.
A 100 mV - 500 mV outpu t is available at these test points for use during calibration.
Oxygen Transmitter
The oxygen transmitter is mounted to the right of th e LEL transmitter and ab ove the main
circuit board. The amplifier includes the amplifier type selector, two internally wired
terminal strips, span pot, zero pot, and test points.
Transmitter Type Selector
The transmitter type selector is near the bottom left corner of the amplifier. It is to the left
of the detector terminal strip and below the span pot.
The transmitter included with the sample-draw detector is designed for use with RKI’s
oxygen and toxic gas sensors. The transmitter type selector determines for which sensor
the amplifier is intended. For oxygen transmitters, a jumper blo c k is installed over the
OXY selector.
Detector Terminal Strip
The detector terminal strip is the four-point terminal strip near the bottom edge of the
transmitter. It is factory wired to the transmitter.
Interconnect Terminal Strip
The interconnect terminal strip is the four-point terminal strip near the top edge of the
transmitter. It is factory wired to the main circuit board.
Span/Zero Pots
The span and zero pots are located on the left side of the transmitter and are used for
calibration. Use the span pot to make adjustments to gas response readings and the zero
pot to make adjustments to the zero reading
T est Points
The test points are located on the top of the transmitter on either side of the transmitter
interconnect terminal strip. They are labeled TP+ and TP-. A 100 mV - 500 mV output is
available a t these test p o ints for use during cali bration.
Preamp Circuit Board
The preamp circuit is used to connect the CO and H
and to secure the sensors in the flow block. Two cables mate to the main circuit board: the
one on the left is for the CO sensor signal and the one on the right is for the H
6 • 35 -3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detec tor
S sensors to the main circuit board
2
S sensor
2
Page 11
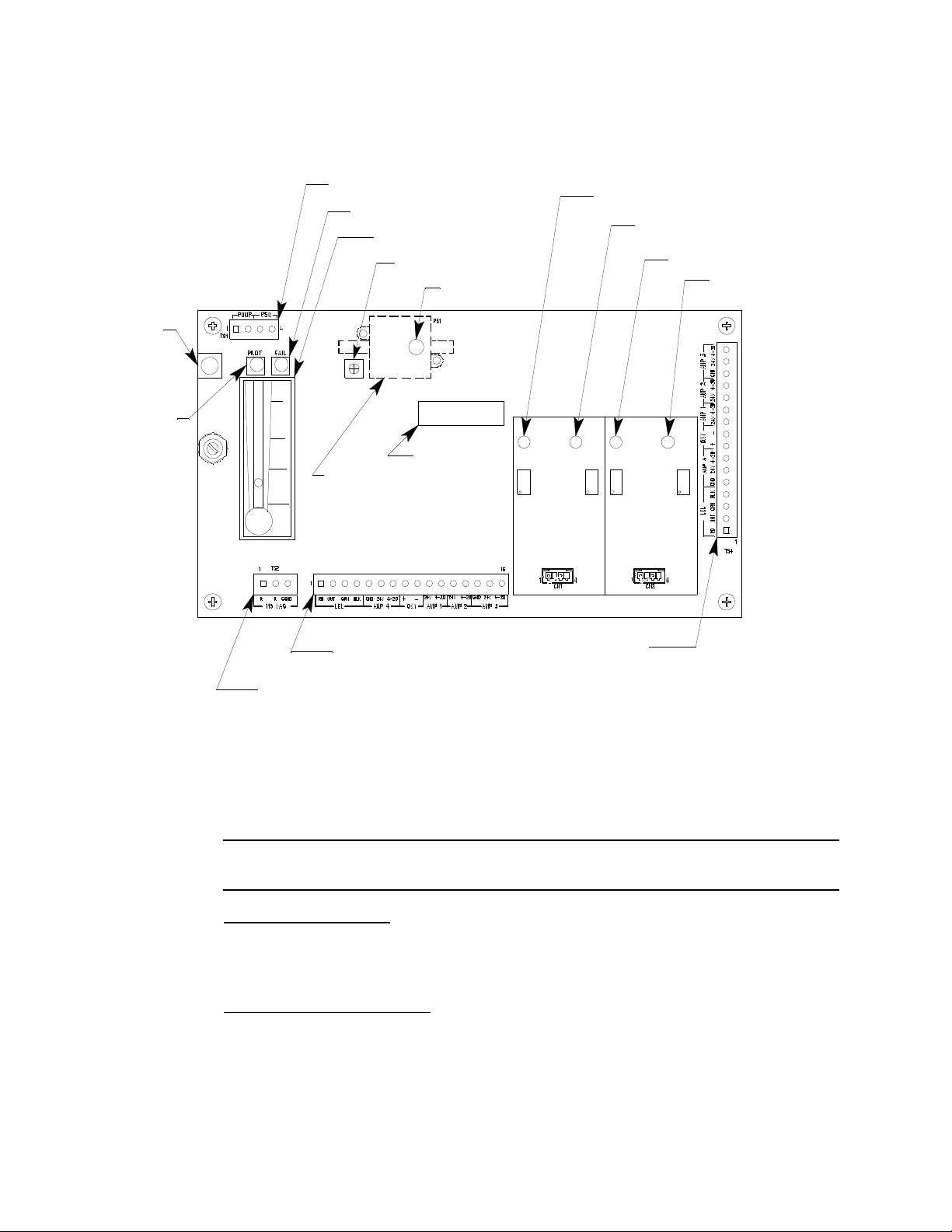
signal. Since the CO sensor is replaced with a dummy plug in the 35-3010RKA-07 the CO
Test Point CAL + 2
Amp 1
(CO)
Zero Span Zero
Fail LED
Sensor/Transmitter
Terminal Strip
Pressure Switch
Reset
Switch
Pilot LED
Amp 2
(H2S)
Span
Test Point CAL + 1
Test Point CAL - 2
Te st Point CAL - 1
AC Terminal
Strip Not Used
Interconnect Terminal
Strip
Low Flow Adjust
Flow Adjust Pot
Flowmeter
Pump Term in al Stip
Relay
sensor signal cable carries no signal in this version of the 35-3010RK.
Main Circuit Board
The main circuit board includes the interconnect terminal strip, sensor/transmitter
terminal strip, amp 1 circuit, amp 2 circuit, pump terminal strip, relay, and reset switch
(see Figure 4).
Figure 4: Main Circuit Board
NOTE: The flowmeter and status lights are mounted to the main circuit board but are
considered part of the flow system.
Interconnect Terminal Strip
The interconnect terminal strip is the sixteen-point terminal strip near the bottom edge of
the main circuit board. Use the interconnect terminal strip to connect the sample-draw
detector to power and an external device.
Sensor/Transmitter Terminal Strip
The sensor/transmitter terminal strip is the sixteen-point terminal strip near the right
edge of the circuit board. Use the transmitter terminal strip to connect sensors or
transmitters to the main circuit board.
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 7
Page 12
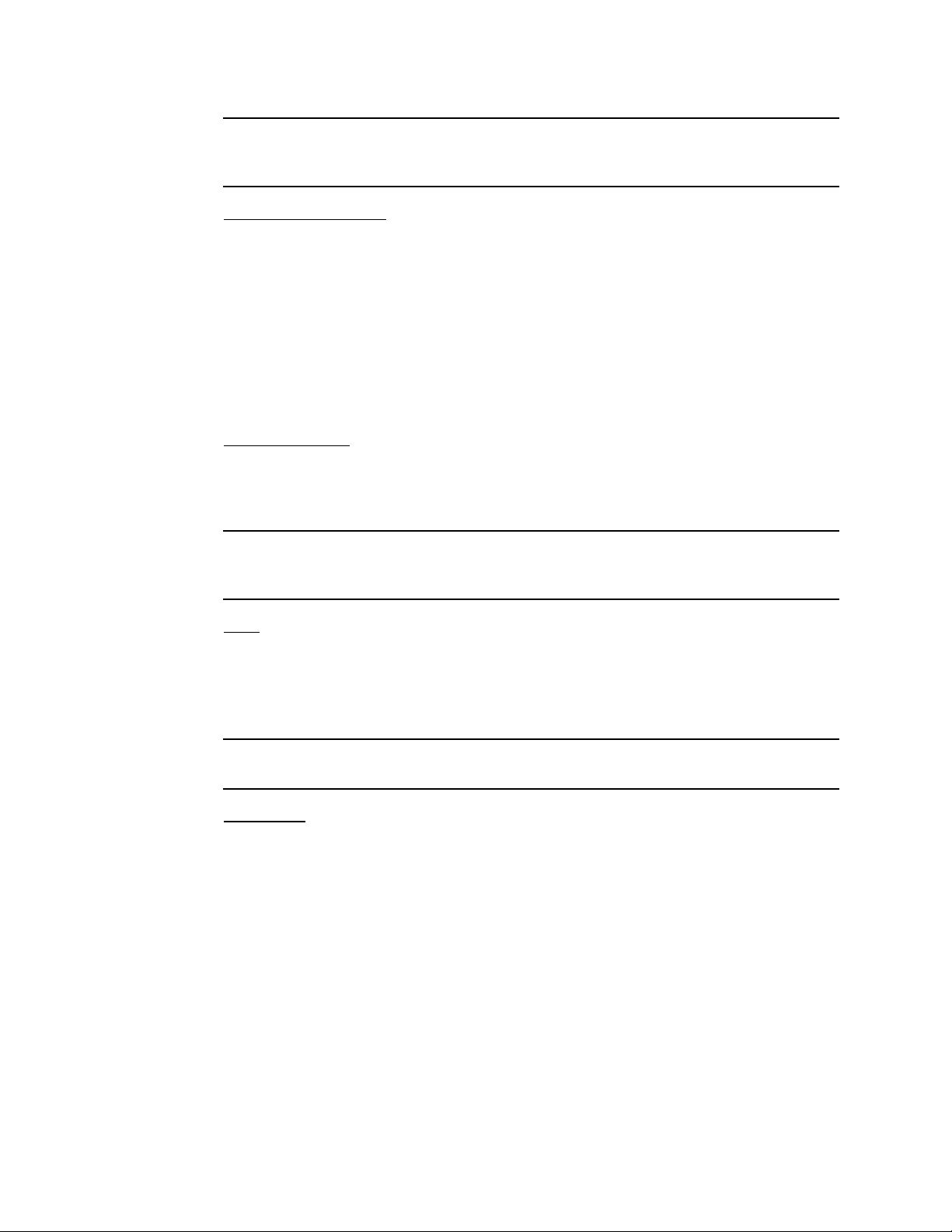
NOTE: The sensors and transmitters are factory wired to the sensor/transmitter
terminal strip. See “Wiring the Sample-Draw Detector” on page 10 fo r all wiring
procedures related to the sample-draw detector.
Amp 1 and Amp 2 Circuits
These circuits are located to the left of the sensor/transmitter terminal strip. They each
include test points, a zero pot, and a span pot. Amp 1 is on the left and is for the CO
channel. Amp 2 is on the right and is for the H
S channel. Since there is no CO channel in
2
the 35-3010RKA-07, Amp 1 is not used.
The zero and span po ts are used during calibration. Use th e span pot t o mak e adj ustment s
to gas response readings and the zero pot to make adjustments to the zero reading.
The test points are labeled CAL-1 and CAL+1 for the CO channel and CAL-2 and CAL+2
for the H
S channel. A 10 0 mV - 500 mV out put is available at the H2S test points for use
2
during calibration. No output is ava ilable at the CO test points.
Pump Terminal Strip
The pump terminal strip is the four-point terminal in the top left corner of the circuit
board. Use the pump terminal strip to connect the pump and pressure switch to the main
circuit board.
NOTE: The pump and pressure switch are factory-wired to the circuit board. See
“Installation” on page 9 for all wiring procedures related to the sample-draw
detector.
Relay
The relay is approximately in the middle of the circuit board. The relay is a four pole,
double-throw (4PDT) relay and is rated for 2 amps at 25 VDC (resistive). If the pressure
switch senses a low flow condition, the relay interrupts the 4-20 mA signal from the H
S
2
channel which will cause a downscale reading at the controller or recording device.
NOTE: There is no flow fail indication for the LEL and oxygen channels on the
35-3010RKA-07 Sample Draw Adapter.
Reset Switch
A small reset button is located in the upper left corner of the main PCB. When a low flow
condition occurs, the pump will be shut off. To reset the low flow condition and sta r t the
pump again, press and hold the reset sw itch for about 2 seconds, then release.
8 • 35 -3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detec tor
Page 13
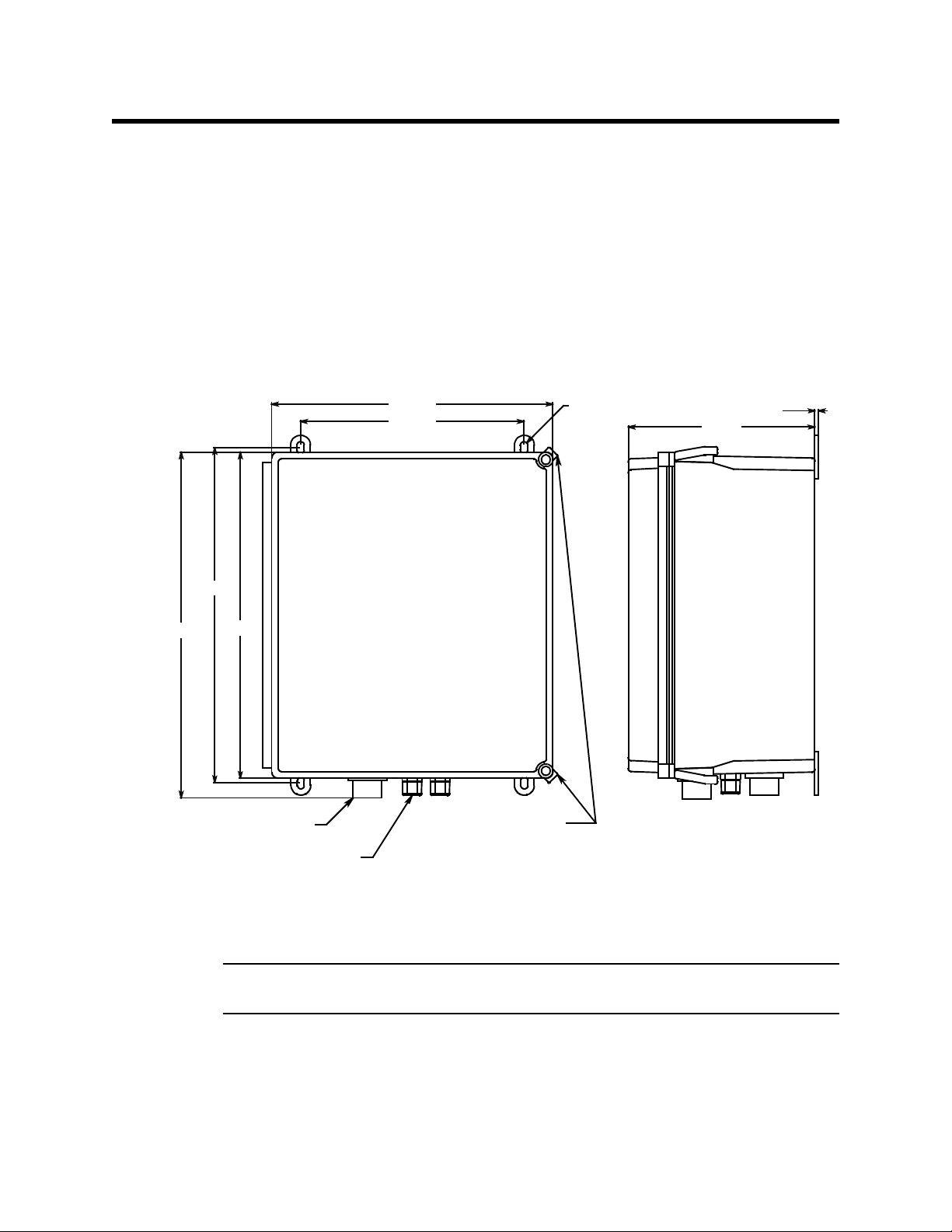
Installation
Ø .31 x .50 slot, 4X
8.31
.18
Tube Fitting for 1/4"
OD tube, 2X
3/4" Conduit Hub, 2X
10.00
12.55
Door Latch
15.44
14.94
14.55
This section describes procedures to mount the sample-draw gas detector in the
monitoring environment and wire the sample-draw detector to power and an external
device.
Mounting the Sample-Draw Detector
1. Select the mounting site. Consider the following when you select the mountin g site.
• Is there enough room to open the housing door and make wiring connections at
the bottom of the housing and tubing connections at the right of the housing?
• Make sure there is sufficient room to perform start-up, maintenance, and
calibration procedures.
Figure 5: Mounting the Sample-Draw Detector
2. Clos e and latch the housing door.
NOTE: The sample-draw detector is shipped with the mounting feet “tucked under” the
housing to protect the mounting feet during shipment.
3. Slightly loo sen the screw that secures one of the mounting feet to the housing, then
rotate the mounting foot 180 degrees (see Figure 3).
4. Tighten the screw that secures the mounting foot to the housing.
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 9
Page 14

5. Repeat steps 3 and 4 for the remaining three mounting feet.
6. Position the sample-d raw housing on a vertical surf ace at eye level (4 1/2 to 5 feet
from the floor).
7. Ins ert 1/4 in. or 5/16 in. screws through the slots in the mounting feet to secure the
housing to the mounting surface.
Connecting the Sample Lines to the Sample-Draw Detector
1. Attach 1/4 in. O.D. rigid polypropylene or rigid Teflon sample tubing to the INLET
fitting.
CAUTION: If you use flexible sample tubing (polyurethane is acceptable), use an appropriate
insert to seal the connection between the tubing and th e INLET fitting.
2. Place the opposite end of the tubing at the sampling area.
CAUTION: Avoid loops or slumps in the incoming sample line. T o r educe response time, keep the
incoming sample line as short as possibl e.
3. Attach rigid sample tubing to the EXHAUST fitting.
4. Route the opposite end of the tubing to an open area where the sample can safely
disperse.
Wiring the Sample-Draw Detector
WARNING: Always verify that the power source is OFF before you make wiring
connections.
1. Turn off the controller.
2. Turn off or unplug incoming power to the controller.
3. Unlatch and op en the housing door of the sample-draw de tector.
4. Guide an eight-conductor 18 gauge, shielded cable or eight 18 gauge wires in conduit
through one of the conduit hubs at the bottom of the sample-draw housing. If
necessary, use both hubs to bring the wires in making sure that all the wires for a
particular channel go through the same hub.
5. Connect the cable to the sample-draw detector’s interconnect terminal strip as shown
in Figure 6.
6. Close and latch the housing door of the sample-draw detector.
CAUTION: Leave the cabl e shield drain wire insulated and disconnected at the sample-draw
detector. You will connect the op posite end of the dra i n wire at the controller.
7. Route the cable or wires in conduit leadin g from the sample-draw detector to the
controller.
8. Connect the drain wire to an available chassis ground at the controller end. RKI
controllers typically have a ground stud that can be used to ground the cable’s drain
wire.
10 • 35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector
Page 15
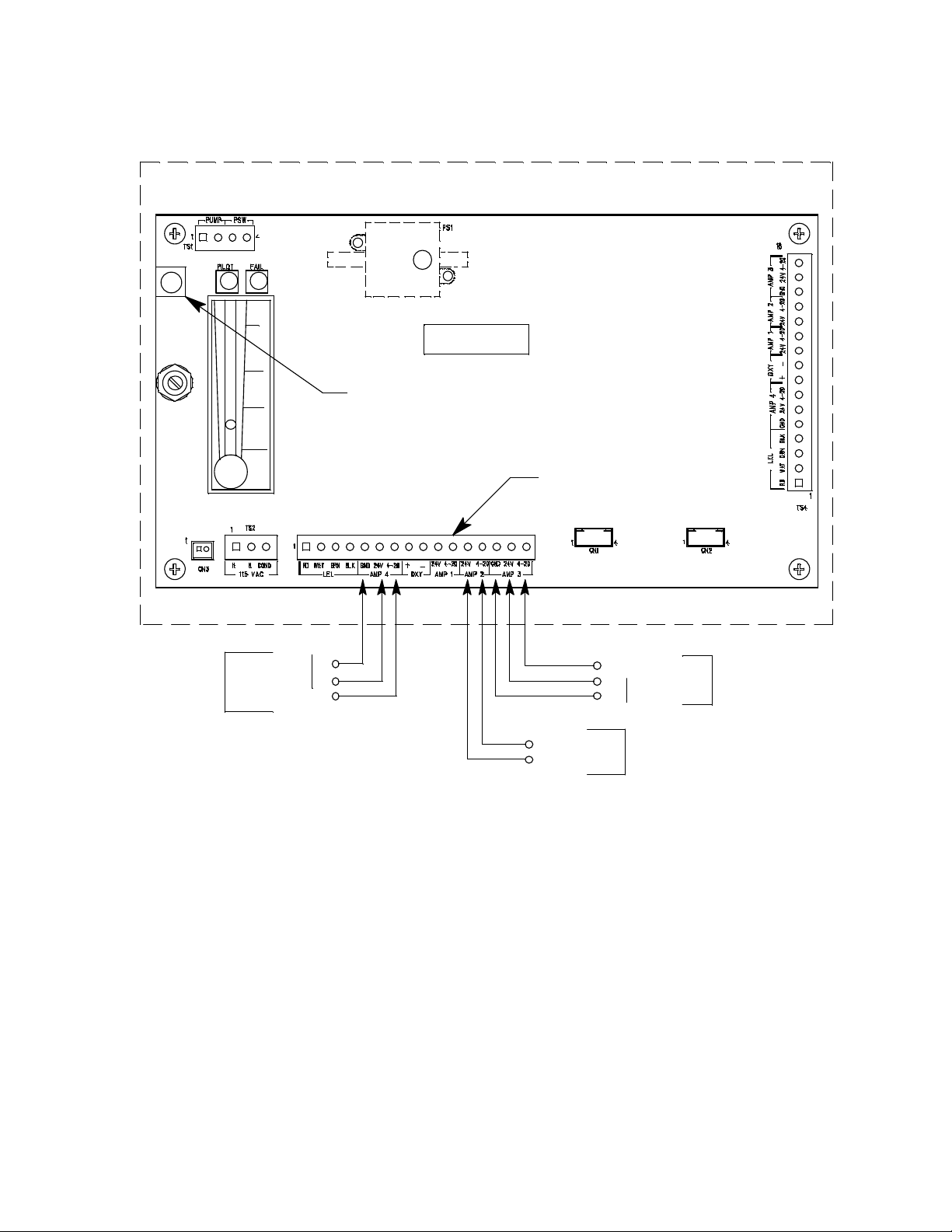
LEL (Controller
Transmitter
Terminals)
Intercon nect Terminal Strip
4/20 Feedback
+
-
24 VDC
24 VDC +
4/20 Feedback
H2S
(Controller Transmitter
Terminals)
Oxygen
(Controller
Transmitter
Terminals)
4-20 (Feedback)
24 VDC
-
+
Reset Switch
Sample Draw Housing
Main CircuitBoard
Figure 6: Extern al (Field) Wiring, Sa mple-Draw Dete ctor
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 11
Page 16

White
SPAN
ZERO
G
OXY
BK WRD
OXY
TOXIC
TOXIC
24V4/20
+
+
FB
TP -
BATT
TP +
CO
(Not
Used)
H2S
Pump
Factory
Wired
Pressure Switch
Fact o ry W ire d
White
Red
Green
IR LEL Sensor
Connector
IR LEL
Detector
Black
INSTR UM EN TS
SENSOR
GRN
TP-
BLK
SPAN Z ERO
POWER/SIG
P/N 57 -1 05 0R K
REV. 0
TP+
GND
24V
4-20
RED
WHT
Oxygen Sensor
Green
CO and H2S Sensors Plug Into
FarSide of Pr eamp
Circuit Board
Figure 9: Internal (Factory) Wiring, Sample-Draw Det ector
12 • 35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector
Page 17

Start Up
This section describes procedures to start up the sample-draw detector and place t he
sample-draw detector into normal operation.
Introducing Incoming Power
1. Complete the installation procedures described earlier in this manual.
2. Verify that the power wiring to the controller is correct and secure. See the controller
operator’s ma nual.
3. Turn on or plug in the incoming power at the controller, then turn on the controller.
4. Verify that the Pilot light is on at the sa mple draw detector.
5. Verify that the controller is on and operating properly.
6. Verify tha t the f lo wmeter indicates a flow rate of approximately 1.2 SCFH. If
necessary, use the bypass valve or flow adjust potentiom eter to adjust the flow rate.
NOTE: The following step tests for leaks in the sample line. This test may cause a low
flow condition at the sample-draw detector.
7. Verify that the incoming sample line is not leaking. To test the sample line, plug the
open end of the sample line with your thumb. If the flowmeter ball drops to the
bottom of the flowmeter, the incoming sample line is not leaking.
8. Remove your thumb from the sample line, press the pump reset switch, and verify the
flowmeter returns to a normal flow rate.
Setting the Zero Reading
CAUTION: If you suspect the presence of combustible gas, hydrogen sulfide, or an abnormal
oxygen condi tion (no t 20.9% ) in the monitori ng env iro nment, u se the c alib ration k it
and the zero air calibration cylinder to int roduce “fresh air” to the sample draw
adapter and verify an accurate zero setting.
1. Verify that the sample-draw detector is sampling a fresh air environment
(environment known to be free of combustible gas, H
content, 20.9%).
2. Open the housing door.
3. Set a voltmeter to measure in the millivolt (mV) range.
4. Check the zero reading for each channel.
•For the IR CH
transmitter. Plug the positive lead into the test point labeled TP+; plug the
negative lead into the test point labeled TP-.
• For the oxygen channel, plug the voltmeter into the test points on the oxygen
transmitter. Plug the positive lead into the test point labeled TP+; plug the
negative lead into the test point labeled TP-.
channel, plug the voltmeter leads into the test points on the LEL
4
S, and of normal oxygen
2
•For the H
of the main circuit board. Plug the positive lead into the test point labeled CAL+2;
plug the negative lead into the test point labeled CAL-2.
5. Verify a voltmeter reading of 100 mV (± 2 mV) .
S channel, plug the voltmeter into the test points in the A MP 2 section
2
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 13
Page 18
Operation
6. If necessary, use a small flat-blade screwdriver to adjust the zero pot until the
voltmeter reading is 100 mV (± 2 mV).
7. Close the housing door.
Normal Operation
During normal operation, the Pilot LED will be on and the flowmeter will indicate about
1.2 SCFH. The current gas readings will be indicated at the controller. See the controller’s
operator’s manual for a description of the reading indications.
Low Flow Alarm
If the flowrate falls below 0.6 SCFH (±0.2 SCFH), then the sample draw detector will
initiate a low flow alarm. In a low flow alarm the Fail LED will turn on and the pump will
shut off. In addition, the H
sample draw detector resulting in a failure indication for the H
If a low flow alarm occurs, press the pump reset switch fo r about 2 seconds to restart the
pump, turn off the Fail LED, and resume proper sensor signal transmission to the
controller. If the condition continues, find the cause of the reduced flow, correct it, and
restart the pump with the pump reset switch. A flow reduction can be caused by a flow
blockage, a leak in the flow system, a malfunctioning pressure switch, or a malfunctioning
pump.
S sensor signals to the controller will be interrupted by the
2
S channel at the controller.
2
NOTE: There is no flow fail indication for the LEL and oxygen channels on the 35-
Maintenance
This section describes maintenance procedures. It includes preventive maintenance
procedures. This section also includes procedures to troubleshoot the sample-draw
detector, replace components of the sample-draw detector, and adjust the low flow
setting.
Preventive Maintenance
This section describes a preventive maintenance schedule to ensure the optimum
performance of the sample-draw detector. It includes daily, monthly, and quarterly
procedures.
Daily
1. Ve ri fy that the pilot light is on.
2. Verify that the flowmeter indicates a flow rate of approximately 1.2 SCFH.
3. Verify a reading of 0%LEL for the IR CH
3010RKA-07.
If necessary use the bypass valve or flow ad just potentiometer to adjust the flow rate
to 1.2 SCFH.
channel (100 mV at the LEL transmitter test
4
points), 20.9% for the oxygen channel (434 mV at the oxygen transmitter test points),
and 0 ppm for the H
significant changes in the reading.
S channel (100 mV at the amp 2 test points). Investigate
2
14 • 35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector
Page 19
Monthly
This pr oc edure describes a test to verify that the sample-draw detector responds properly
to the target gases.
Preparing for the response test
CAUTION: This procedure may cause alarms at the controller. Take appropriate action to avoid
this, such as entering the calibration mode at the controller.
1. Ver ify that the controller is reading 0 for the IR CH
and H2S channels and 20.9 for the
4
oxygen channel.
If the reading is not 0 on the IR CH
or H2S channels or 20.9 on the oxygen channel, set
4
the zero reading as described in “Start Up” on page 13, then continue this procedure.
2. Assemble the calibra tion kit as described in the Calibration section of this ma nual.
Use of a 4-gas cylinder is recommended so that all channels may be checked at once.
Performing the response test
NOTE: This procedure describes the RKI calibration kit that includes a demand flow
regulator.
1. Screw the regulator into the calibration cylinder.
2. Connect the c ali brat io n tu bi ng fr om the r e gul ator to the inlet line at or near the INLET
fitting. Gas will begin to flow.
3. After approximately one minute, verify that the reading for each channel at the
controller stabilizes within ± 10% of the concentration of the test sample. If the
reading is not within ± 10% of the test sample, calibrate the sample-draw detecto r as
described in the Calibration section of this manual.
4. Remove the calibrati on tubing from the inlet line, then reconnect the inlet line.
Quarterly
Calibrate the sample-draw detector as described in the “Calibration” section on page 14.
Troubleshooting
The troubleshooting guide describes symptoms, probable causes, and recommended
action for problems you may encounter with the sample-draw gas detect or.
NOTE: This troubleshooting guide describes sample-draw detector problems only. See
the instruction manual for the controller if it exhibits any problems.
Fail Condition
Symptoms
• The sample-draw detector’s Fail light is on.
• The controller is operating properly but indicates a reading well below zero on one or
more channels.
Probable Causes
• The sample-draw detector’s flow rate is too low because of an obstructed sample line,
failed pump, etc.
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 15
Page 20

• The sample-draw detector is malfunction ing.
• The sensor or transmitter wiring is disconnected or misco nnected.
Recommended Action
1. At the sample-draw detector, set the correct flow rate with the bypass valve or flow
adjust potentiometer.
2. If you cannot set the correct flow rate, check the sample lines for obstructions or kinks.
3. Verify tha t the sensor and transmitter wiring are correct and secure. “Wiring the
Sample-Draw Detector” on page 10 describes detector wiring connections.
4. Calibrate the problem channel or channels as described in the Calibration section.
5. If the fail condition continues, replace the sensor from the problem channel or
channels as described later in this section.
6. If the fail condition continues, contact RKI Instruments, Inc. for further instruction.
Slow or No Response/Difficult or Unable to Calibrate
Symptoms
• One or more of the sensors respond slowly or does not respond during the monthly
response test.
• Unable to accurately set the zero or response reading on one or more of the channels
during the calibration procedure.
• One or more of the sensors requires frequent calibration.
NOTE: Under “normal” circumstances, the sample- draw de tector requires calibration
once a quarter. Some applications may require a more frequent calibration
schedule.
Probable Causes
• The calibration cylinder is low, out-dated, or defective.
• The sample-draw detector’s flow rate is too low because of an obstructed sample line,
failed pump, etc.
• The sample-draw detector is malfunction ing.
Recommended Action
1. Verify that the calibration cylinder contains an adequate supply of a fresh test sample.
2. If necessary, set the correct flow rate with the bypass valve or flow adjust
potentiometer.
3. If you cannot set the correct flow rate, check the sample line for obstructions or kinks.
4. If the calibration/response difficulties continue, replace the sensor as described later
in this section.
5. If the calibration/response difficulties continue, contact RKI Instruments, Inc. for
further instruction.
16 • 35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector
Page 21

Replacing Components of the Sample-Draw Detector
This section includes procedures to replace the sensors, the hydrop hobic filter, and the
charcoal filter.
Replacing the IR CH
Sensor
4
1. Turn off or unplug incoming power.
2. Unscrew the four screws that hold the circuit board on the flow block.
3. Pull the circuit board off the flow block.
4. Unplug the infrared detector from the circuit board.
5. Plug the new detector into the circuit board.
6. Reinstall the circuit board to the flow block.
7. Turn on or plug in power.
8. Calibrate the replacement sensor as described in “ C alibration, IR CH
and H2S
4
Detectors” on page 19.
Replacing the Oxygen Sensor
1. Turn off incoming po wer.
2. Open the housing door of the sample-draw detector.
3. Unscrew and remove the two screws that secure the retaining plate, then lift the plate,
connector, and sensor out of the housing.
4. Unplug the connector from the socket th at lead s from the sensor.
5. Plug the socket of the replacement sensor into the connector.
6. Place the sensor in the oxygen sensor cavity, then position the retaining plate on the
two standoffs.
7. Secure the retaining plate to the standoffs with the two screws you removed in step 3.
8. Turn on incoming power.
9. Calibrate the replacement sensor as described in “Calibration, Oxygen Detector” on
page 21.
Replacing the Hydrogen Sulfide Sensor
1. Turn off incoming po wer.
2. Open the housing door of the sample-draw detector.
3. Unscrew the 5 screws that retain the preamp circuit board.
4. Lift the preamp circuit board away from the flow block.
Be careful not to pull on the cables that connect the preamp circuit to the main circuit
board.
There is a foam gasket in the bottom of each flow cavity beneath the circuit board.
Make sure the gaskets stay in place.
5. Pull the H
S sensor off the preamp circuit board. It is located in the amp 2 position
2
(right side) of the preamp circuit board.
6. Plug the new sensor into the preamp board.
7. Reinstall the preamp circuit board with the sensors onto the flow block.
8. Turn on incoming power.
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 17
Page 22

9. Calibrate the replacement sensor as described in “Parts List” on page 23.
Replacing the Hydrophobic Filter
1. Turn off or unplu g power to the controller.
2. Locate the hydrophobic filter. It is just to the left of the main circuit board.
3. Grasp the hydrophobic filter and pull it out of its metal clamp.
4. Remove the rubber seals from each end of the hydrophobic filter and remove the
filter.
5. Place the new hydrophobic filter in the same orientation as the one that was removed.
6. Place the new hydrophobic filter back into the metal clamp.
Replacing the Charcoal Filter
NOTE: The charcoal filter does not normally need to be replaced in the 35-3010RKA-07
because it does not include a CO sensor.
1. Turn off or unplu g power to the controller.
2. Locate the charcoal filter. It is located along the upper edge of the detector housing.
3. Grasp the charcoal filter and pull it out of its metal clamp.
4. Remove the rubber seals from each end of the charcoal filter and remove the filter.
5. Place the new charcoal filter in the same orientation as the one that was removed.
6. Place the new charcoal filter back into the metal clamp.
Adjusting the Low Flow Setting
The factory-set low flow setting is 0.6 SCFH (±0.2). To adjust the low flow setting:
1. Use the flow adjust potentiom e ter (VR1) to set the f low to 0.6 SCFH.
If the sample-draw detector goes into low f low alarm before you can adjust the flow
down to 0.6 SCFH, adjust the low flow potentiometer 1/4 turn clockwise, then
attempt to set the flow again. Repeat this step until you are able to adjust the flow to
0.6 SCFH.
2. Slowly turn the low flow potentiometer counterclockwise just until the sample-draw
detector goes into low flow alarm.
NOTE: The low flow potentiometer is accessible through a circular cutout in the main
circuit board. The cutout is labeled PS1.
3. Verify that the low flow alarm is 0.6 SCFH (±0.2). Repeat steps 3 and 4 if necessary.
4. Use the flow adjust potentiom e ter (VR1) to set the f low to 1.2 SCFH.
5. Make sure the sample-draw detector’s Fail light is off.
Calibration Frequency
Although there is no particular calibration frequency that is correct for all applications, a
calibration frequency of every 3 months is adequate for most sample draw detector
applications. Unless experience in a particular application dictates otherwise, RKI
Instruments, Inc. recommends a calibration frequency of every 3 months for the oxygen
18 • 35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector
Page 23
and H2S sensors and every 6 months for the IR CH4 sensor in the sample draw dete ctor.
If an application is not very demanding, for example detection in a clean, temperature
controlled environment, and calibration adjustments a re minima l at calibration, then a
calibration frequency of every 6 months for the oxygen and H
months for the IR CH
sensor is adequate for the sample draw detector.
4
If the application is very demanding, for example if the environment is not well
controlled, then more frequent calibration than every 3 months for the oxygen and H
sensors and every 6 months for the IR CH
detector.
Calibration, IR CH4 and H2S Detectors
This section describes how to calibrate the IR CH4 and H2S sensors in the sample draw
detector. It includes procedures to prepare for calibration, set the zero reading, set the
response reading, and return to nor mal operation.
NOTE: This procedure describes calibration using a demand flow regulator, a zero air
calibration cylinder, and a 4-gas calibration cylinder.
S sensors and every 12
2
2
sensor may be necessary for the samp le draw
4
S
Prepari ng for Ca libration
CAUTION: This procedure may cause alarms at the controller. Take appropriate action to avoid
this, such as entering the calibration mode at the controller.
1. Open the housing door.
2. Set a voltmeter to measure in the millivolt (mV) range.
• When checking the mV output of the IR CH
test points on the LEL transmitter. Plug the positive lead into the test point labeled
TP+; plug the negative lead into the test point labeled TP-.
• When checking the mV output of the H
the test points in the AMP 2 section of the main circuit board. Plug the positive
lead into the test point labeled CAL+2; plug the negative lead into the test point
labeled CAL-2.
3. Use the following formula to determine the correct test points output for the
calibrating sample.
Output (mV) = (calibrating sample/fullscale) X 400 + 100
For example, with a calibrating sample of 50 %LEL methane and a fullscale setting of
100%LEL, the correct output for the LEL test points is 300 mV.
300 (mV) = (50/100) X 400 +100
channel, plug the voltmeter into the
4
S channel, plug the voltmeter leads into
2
Setting the Zero Reading
NOTE: If you can verify a fresh air environment, it is not necessary to use the zero air
calibration cylinder to set the zero reading.
1. Screw the regulator into the zero air calibration cyli nd er.
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 19
Page 24

2. Connect the calibration kit sample tubing to the regulator.
3. Connect the sample tubing from the regulator to the inlet line at or near the INLET
fitting.
4. Allow the gas to flow for one minute.
5. Verify a voltmeter reading of 100 mV ± 2 mV at the LEL test point s as described in the
Preparing for Calibration section above.
6. If necessary, use a small flat-blade screwdriver to adjust the zero pot for the IR CH
4
channel until the voltmeter reading is 100 mV ± 2 mV.
7. Verify a voltmeter reading of 100 mV ± 2 mV at the AMP 2 test points for the H
S
2
channel as described in the Preparing for Calibration section above.
8. If necessary, use a small flat-blade screwdriver to adjust the zero pot for the H
S
2
channel until the voltmeter reading is 100 mV ± 2 mV.
9. Disconnect the sample tubing from the inlet line.
10. Unscrew the regulator from the zero air calibration cylinder. Leave the sample tubing
connected to the regulator.
Setting the Response Reading
1. Screw the regulator into the 4-gas calibration cylinder.
2. Connect the sample tubing from the regulator to the inlet line at or near the sa mpledraw detector’s INLET fitting.
3. Allow the calibra tion gas to flow for one minute.
4. Check the mV output on the LEL transmitter test points and verify that the reading
matches the response reading (±2 mV) you determined earlier.
5. If necessary, use the span pot on the LEL transmitter to adjust the reading to match the
correct response reading.
6. Check the mV output on the AMP 2 test poi nts for H
matches the response reading (±2 mV) you determined earlier.
7. If necessary, use the AMP 2 span pot to adjust the reading to match the correct
response reading.
S and verify that the reading
2
8. Disconnect the sample tubing from the sample-draw detector’s inlet line.
9. Unscrew the regulator from the calibration cylinder.
NOTE: For convenience, leave the regulator connected to the sample tubing.
Returning to Normal Operation
1. Remove the voltmeter leads from the test points.
2. Reconnect the in coming sample line.
3. Wait 1 to 2 minutes to allow the calibration gas to be drawn out and the reading to
stabilize.
4. Close the housing door.
5. Store the components of the calibration kit in a safe and convenient place.
20 • 35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector
Page 25
Calibration, Oxygen Detector
This secti on de scri be s h ow t o c ali br ate the ox ygen detector in the sample-draw detector . It
includes procedures to prepare for calibration, set the fresh air reading, set the zero
reading, and return to normal operation.
NOTE: This procedure describes calibration using a demand flow regulator, a zero air
calibration cylinder, and a 4-gas calibration cylinder to set the zero reading. A 4gas cylinder is used to set the zero reading since it is already used to calibrate the
IR CH
used to set the zero reading.
Prepari ng for Ca libration
CAUTION: This procedure may cause alarms at the controller. Take appropriate action to avoid
1. Open the housing door.
2. Set a voltmeter to measure in the millivolt (mV) range.
and oxygen channels. A 100% nitrogen calibration cylinder could also be
4
this, such as entering the calibration mode at the controller.
3. Plug the voltmeter into the test points on the oxygen transmitter. Plug the positive
lead into the test point labeled TP+; plug the negative lead into the test point labeled
TP-.
4. Use the following formula to determine the correct test points output for the
calibrating sample.
Output (mV) = (calibrating sample/fullscale) X 400 + 100
For example, with a calibrating sample of 12% and a fullscale setting of 25%, the
correct output for the oxygen test points is 292 mV.
292 (mV) = (12/25) X 400 +100
Setting the Zero Reading
NOTE: The 4-gas calibration cylinder included in the calibration kit may be used to zero
the oxygen channel. Keep in mind that the oxygen concentration in that cylinder
is 12%, not 0%. Be sure to set the controller appropriately.
1. Screw the regulator into the 4-gas calibration cylinder.
2. Connect the calibration kit sample tubing to the regulator.
3. Allow the sample-draw detector to respond to the calibrating sample for
approximately 1 minute.
4. After one minute, check the mV output on the oxygen transmitter test points and
verify that the reading matches the response reading (±2 mV) you determined earlier
(292 mV for 12% oxygen).
5. If necessary, use the span pot on the transmitter to adjust the reading to match the
correct response reading.
6. Disconnect the sample tubing from the inlet line.
7. Unscrew the regulator from the 4-gas calibra tion cylinder.
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 21
Page 26

8. For convenience, leave the regulator attached to the sample tubing.
Setting the Fresh Air Reading
CAUTION: This procedure may cause alarms at the controller. Take appropriate action to avoid
this, such as entering the calibration mode at the controller.
NOTE: If you can verify a fresh air environment, it is not necessary to use the zero air
calibration cylinder to set the zero reading.
1. Screw the regulator into the zero air calibration cyli nd er.
2. Connect the calibration kit sample tubing to the regulator.
3. Connect the sample tubing from the regulator to the inlet line at or near the INLET
fitting.
4. Allow the gas to flow for one minute.
5. Verify a voltmeter reading of 434 mV ± 2 mV at the test points as described in the
Preparing for Calibration section above.
6. If necessary, use a small flat-blade screwdriver to adjust the zero pot until the
voltmeter reading is 434 mV ± 2 mV.
7. Disconnect the sample tubing from the inlet line.
8. Unscrew the regulator from the zero air calibration cylinder. Leave the sample tubing
connected to the regulator.
Returning to Normal Operation
1. Reconnect the in coming sample line.
2. Wait 1 to 2 minutes to allow the calibration gas to be drawn out and the reading to
stabilize.
3. Close the housing door.
4. Store the components of the calibration kit in a safe and convenient place.
22 • 35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector
Page 27
Parts List
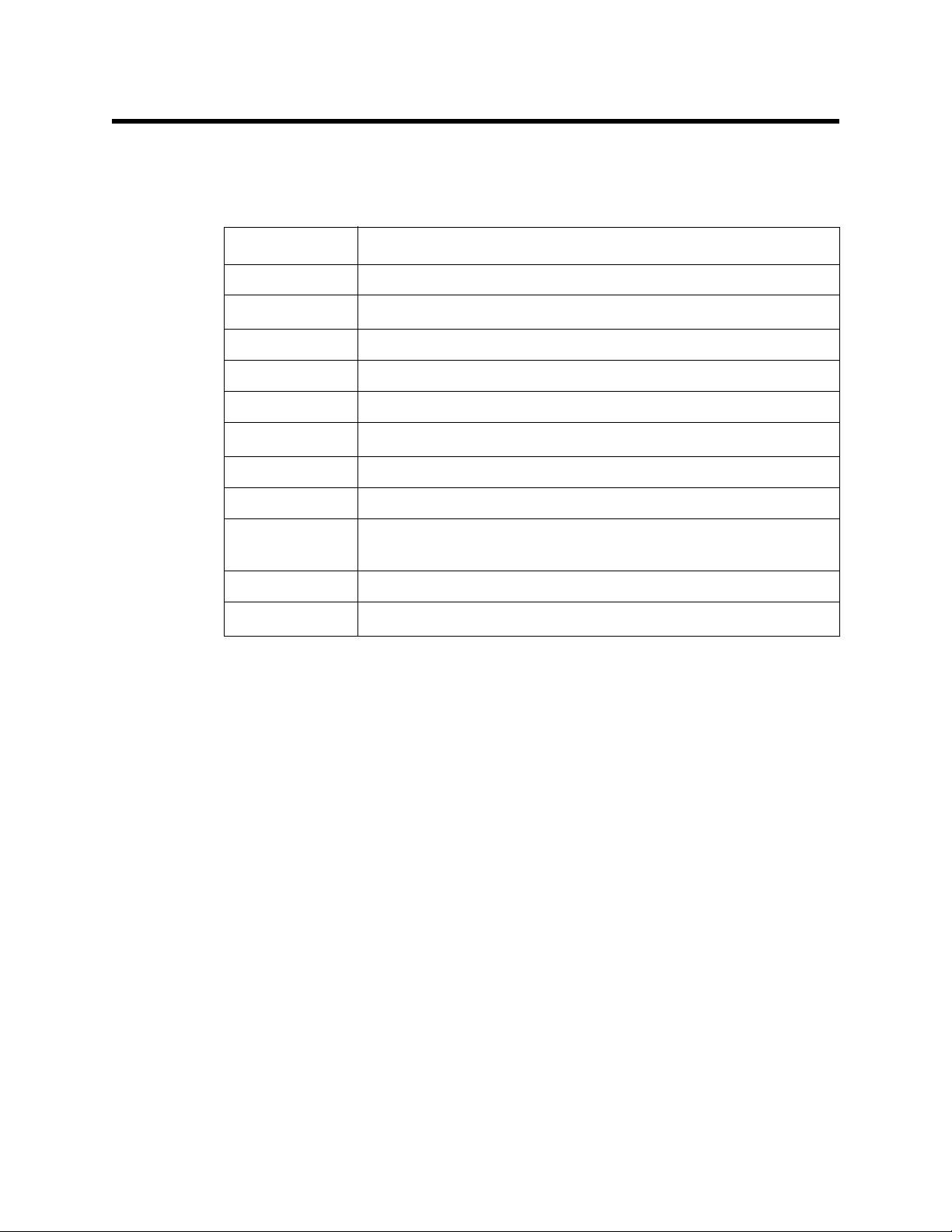
Table 4 lists replacement parts and accessories for the sample-draw gas detector.
Table 2: Parts List
Part Number Description
06-1248RK Sample tubing, 3/16 x 5/16, specify length, (for calibra tion kit)
07-0034RK Sealing gasket, for H
S flow block cavity
2
30-0610RK Pump
33-0171RK Hydrophobic filter (AcroPak)
33-6095RK Charcoal filter, CF-188
61-5039RK-CH4 Infrared CH
sensor, 0 - 100% LEL
4
65-0601RK Oxygen sensor
81-0076RK-01 Zero air calibration cylinder (34 liter)
81-0154RK-04 4-gas calibration gas cylinder, 50% LEL methane/12% oxygen/25
ppm H
S/50 ppm CO, 34 liter
2
81-1055RK Regulator, demand flow, for 17 and 34 liter steel cylinders
ES-1537-H2S H
S sensor
2
35-3010RKA-07 Sample-Draw Detector • 23
 Loading...
Loading...