
RIGOL
User’s Guide
MSO7000/DS7000 Series Digital
Oscilloscope
Apr. 2018
RIGOL TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL
Guaranty and Declaration
Copyright
© 2018 RIGOL TECHNOLOGIES, INC. All Rights Reserved.
Trademark Information
RIGOL is a registered trademark of RIGOL TECHNOLOGIES, INC.
Publication Number
UGA22101-1110
Software Version
00.01.01.SP5
Software upgrade might change or add product features.
Notices
RIGOL products are covered by P.R.C. and foreign patents, issued and pending.
RIGOL reserves the right to modify or change parts of or all the specifications
and pricing policies at the company’s sole decision.
Information in this publication replaces all previously released materials.
Information in this publication is subject to change without notice.
RIGOL shall not be liable for either incidental or consequential losses in
connection with the furnishing, use, or performance of this manual, as well as
any information contained.
Any part of this document is forbidden to be copied, photocopied, or rearranged
without prior written approval of RIGOL.
Product Certification
RIGOL guarantees that this product conforms to the national and industrial
standards in China as well as the ISO9001:2008 standard and the ISO14001:2004
standard. Other international standard conformance certifications are in progress.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide I
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL
Safety Requirement
General Safety Summary
Please review the following safety precautions carefully before putting the
instrument into operation so as to avoid any personal injury or damage to the
instrument and any product connected to it. To prevent potential hazards, please
follow the instructions specified in this manual to use the instrument properly.
Use Proper Power Cord.
Only the exclusive power cord designed for the instrument and authorized for use
within the local country could be used.
Ground the Instrument.
The instrument is grounded through the Protective Earth lead of the power cord. To
avoid electric shock, connect the earth terminal of the power cord to the Protective
Earth terminal before connecting any input or output terminals.
Connect the Probe Correctly.
If a probe is used, the probe ground lead must be connected to earth ground. Do not
connect the ground lead to high voltage. Improper way of connection could result in
dangerous voltages being present on the connectors, controls or other surfaces of
the oscilloscope and probes, which will cause potential hazards for operators.
Observe All Terminal Ratings.
To avoid fire or shock hazard, observe all ratings and markers on the instrument and
check your manual for more information about ratings before connecting the
instrument.
Use Proper Overvoltage Protection.
Ensure that no overvoltage (such as that caused by a bolt of lightning) can reach the
product. Otherwise, the operator might be exposed to the danger of an electric
shock.
Do Not Operate Without Covers.
Do not operate the instrument with covers or panels removed.
Do Not Insert Objects Into the Air Outlet.
Do not insert anything into the holes of the fan to avoid damaging the instrument.
Use Proper Fuse.
Please use the specified fuses.
II MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL
Avoid Circuit or Wire Exposure.
Do not touch exposed junctions and components when the unit is powered on.
Do Not Operate With Suspected Failures.
If you suspect that any damage may occur to the instrument, have it inspected by
RIGOL authorized personnel before further operations. Any maintenance,
adjustment or replacement especially to circuits or accessories must be performed
by RIGOL authorized personnel.
Provide Adequate Ventilation.
Inadequate ventilation may cause an increase of temperature in the instrument,
which would cause damage to the instrument. So please keep the instrument well
ventilated and inspect the air outlet and the fan regularly.
Do Not Operate in Wet Conditions.
To avoid short circuit inside the instrument or electric shock, never operate the
instrument in a humid environment.
Do Not Operate in an Explosive Atmosphere.
To avoid personal injuries or damage to the instrument, never operate the
instrument in an explosive atmosphere.
Keep Product Surfaces Clean and Dry.
To avoid dust or moisture from affecting the performance of the instrument, keep the
surfaces of the instrument clean and dry.
Prevent Electrostatic Impact.
Operate the instrument in an electrostatic discharge protective environment to avoid
damage induced by static discharges. Always ground both the internal and external
conductors of cables to release static before making connections.
Use the Battery Properly.
Do not expose the battery (if available) to high temperature or fire. Keep it out of the
reach of children. Improper change of a battery (lithium battery) may cause an
explosion. Use the RIGOL specified battery only.
Handle with Caution.
Please handle with care during transportation to avoid damage to keys, knobs,
interfaces, and other parts on the panels.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide III
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation or practice which, if not
avoided, will result in serious injury or death.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation or practice which, if not
avoided, could result in damage to the product or loss of important data.
DANGER
It calls attention to an operation, if not correctly performed, could
result in injury or hazard immediately.
WARNING
It calls attention to an operation, if not correctly performed, could
result in potential injury or hazard.
CAUTION
It calls attention to an operation, if not correctly performed, could
result in damage to the product or other devices connected to the
product.
Hazardous
Voltage
Safety Warning
Protective Earth
Terminal
Chassis Ground
Test Ground
Safety Notices and Symbols
Safety Notices in this Manual:
Safety Terms on the Product:
Safety Symbols on the Product:
IV MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL
WARNING
This oscilloscope can only be used for measurements within its specified
measurement categories.
WARNING
Inadequate ventilation may cause an increase of temperature in the
instrument, which would cause damage to the instrument. So please
keep the instrument well ventilated and inspect the air outlet and the fan
regularly.
Measurement Category
Measurement Category
MSO7000/DS7000 series digital oscilloscopes can make measurements in
Measurement Category I.
Measurement Category Definitions
Measurement category I is for measurements performed on circuits not directly
connected to MAINS. Examples are measurements on circuits not derived from
MAINS, and specially protected (internal) MAINS derived circuits. In the latter case,
transient stresses are variable. Thus, you must know the transient withstand
capability of the equipment.
Measurement category II is for measurements performed on circuits directly
connected to low voltage installation. Examples are measurements on household
appliances, portable tools and similar equipment.
Measurement category III is for measurements performed in the building installation.
Examples are measurements on distribution boards, circuit-breakers, wiring
(including cables, bus-bars, junction boxes, switches and socket-outlets) in the fixed
installation, and equipment for industrial use and some other equipment. For
example, stationary motors with permanent connection to a fixed installation.
Measurement category IV is for measurements performed at the source of a
low-voltage installation. Examples are electricity meters and measurements on
primary overcurrent protection devices and ripple control units.
Ventilation Requirement
This oscilloscope uses a fan to force cooling. Please make sure that the air intake and
exhaust areas are free from obstructions and have free air. When using the
oscilloscope in a bench-top or rack setting, provide at least 10 cm clearance beside,
above and behind the instrument for adequate ventilation.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide V
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL
WARNING
To avoid short circuit inside the instrument or electric shock, never
operate the instrument in a humid environment.
WARNING
Ensure that no overvoltage (such as that caused by a bolt of lightning)
can reach the product. Otherwise, the operator might be exposed to the
danger of an electric shock.
Working Environment
Temperature
Operating: 0℃ to +50℃
Non-operating: -30℃ to +70℃
Humidity
Operating:
Below +30℃: ≤95%RH (without condensation)
+30℃ to +40℃: ≤75%RH (without condensation)
+40℃ to +50℃: ≤45%RH (without condensation)
Non-operating:
Below 65℃: ≤95% RH (without condensation)
Altitude
Operating: below 3 km
Non-operating: below 15 km
Installation (Overvoltage) Category
This product is powered by mains conforming to installation (overvoltage) category
II.
Installation (Overvoltage) Category Definitions
Installation (overvoltage) category I refers to signal level which is applicable to
equipment measurement terminals connected to the source circuit. Among these
terminals, precautions are done to limit the transient voltage to a low level.
Installation (overvoltage) category II refers to the local power distribution level
which is applicable to equipment connected to the AC line (AC power).
Pollution Degree
Pollution Degree 2
Pollution Degree Definition
Pollution Degree 1: No pollution or only dry, nonconductive pollution occurs. The
VI MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL
CAUTION
To avoid damage to the instrument, do not expose it to caustic liquids.
WARNING
To avoid short-circuit resulting from moisture or personal injuries, ensure
that the instrument is completely dry before connecting it to the power
supply.
pollution has no effect. For example, a clean room or air-conditioned office
environment.
Pollution Degree 2: Normally only nonconductive pollution occurs. Temporary
conductivity caused by condensation is to be expected. For example, indoor
environment.
Pollution Degree 3: Conductive pollution or dry nonconductive pollution that
becomes conductive due to condensation occurs. To be found in industrial
environment or construction sites (harsh environments). For example, sheltered
outdoor environment.
Pollution Degree 4: The pollution generates persistent conductivity caused by
conductive dust, rain, or snow.
For example, outdoor areas.
Safety Class
Class 1 – Grounded Product
Care and Cleaning
Care
Do not store or leave the instrument where it may be exposed to direct sunlight for
long periods of time.
Cleaning
Clean the instrument regularly according to its operating conditions.
1. Disconnect the instrument from all power sources.
2. Clean the external surfaces of the instrument with a soft cloth dampened with
mild detergent or water. When cleaning the LCD, take care to avoid scarifying it.
Environmental Considerations
The following symbol indicates that this product complies with the WEEE Directive
2002/96/EC.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide VII
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL
Product End-of-Life Handling
The equipment may contain substances that could be harmful to the environment or
human health. To avoid the release of such substances into the environment and
avoid harm to human health, we recommend you to recycle this product
appropriately to ensure that most materials are reused or recycled properly. Please
contact your local authorities for disposal or recycling information.
VIII MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL
MSO7000/DS7000 Series Overview
MSO7000/DS7000 series is a multifunctional and high-performance digital
oscilloscope designed on the basis of the unique Ultra Vision II technique developed
by RIGOL. Integrating 6 independent instruments into one, the MSO7000/DS7000
series is equipped with super sample bandwidth ratio, extremely high memory depth,
clear display, excellent waveform capture rate, and powerful data analysis functions.
Many of its specifications have reached the top level in the industry. It provides
sound solutions for mainframes, optional & accessories, and application software. It
has aroused great attention from customers in the areas such as industrial control,
power supply, and automotive electronics.
Main Features:
Analog bandwidth: 500 MHz, 350 MHz, 200 MHz, and 100 MHz; bandwidth
upgrade option supported
4 analog channels, 1 EXT channel, and 16 optional digital channels
Up to 10 GSa/s real-time sample rate
Up to 500 Mpts memory depth (option)
High waveform capture rate (over 600,000 wfm/s)
Up to 450,000 frames of hardware real-time and ceaseless waveforms recording
and playing functions
Integrates 6 independent instruments into 1, including digital oscilloscope,
16-channel logic analyzer, dual-channel Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator,
digital voltmeter, 6-digit frequency counter and totalizer, and protocol analyzer
A variety of serial protocol triggers and decodes
Auto measurement of 41 waveform parameters; full-memory hardware
measurement function
A variety of math operations, built-in enhanced FFT analysis, and peak search
function
Waveform histogram analysis (standard)
Independent search, navigation keys, and event table
Built-in advanced power analysis software (option)
User-defined one-key quick operation
10.1-inch capacitive multi-touch screen, 256-level intensity grading display, with
color persistence
Multiple interfaces available: USB HOST & DEVICE, LAN(LXI), HDMI, TRIG OUT,
and USB-GPIB
Web Control remote command
Unique online version upgrade
Novel and delicate industrial design, easy to operate
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide IX
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL
Label
Knob
Label
Knob
Horizontal SCALE
Horizontal Time
Base Knob
Vertical SCALE
Vertical Scale
Knob
Horizontal
POSITION
Horizontal Position
Knob
Vertical OFFSET
Vertical
Offset Knob
Wave Vertical SCALE
Waveform Vertical
Scale Knob
Trigger LEVEL
Trigger Level
Knob
Wave Vertical
POSITION
Waveform Vertical
Position Knob
Multifunction
Knob
Model
Analog
Bandwidth
No. of
Analog
Channels
No. of
Channels of
Function/AWG
No. of
Digital
Channels
DS7054
500 MHz
4
——
——
DS7034
350 MHz
4
——
——
DS7024
200 MHz
4
——
——
DS7014
100 MHz
4
——
——
MSO7054
500 MHz
4
2, Opt.
16
MSO7034
350 MHz
4
2, Opt.
16
MSO7024
200 MHz
4
2, Opt.
16
MSO7014
100 MHz
4
2, Opt.
16
Format Conventions in this Manual:
1. Key
The key on the front panel is denoted by the format of "Key Name (Bold) + Text
Box" in the manual. For example, Utility denotes the "Utility" key.
2. Menu
The menu items are denoted by the format of "Menu Word (Bold) + Character
Shading". For example, System denotes the "System" menu item under
Utility.
3. Operation Procedures:
denotes the next step of operation. For example, Utility System denotes
that first press Utility, and then press the System key.
4. Connector:
The connectors on the front or rear panel are usually denoted by the format of
"Connector Name (Bold) + Square Brackets (Bold)". For example, [TRIG OUT].
5. Knob
Content Conventions in this Manual:
MSO7000/DS7000 series includes the following models. Unless otherwise specified,
this manual takes MSO7054 as an example to illustrate the functions and operation
methods of MSO7000/DS7000 series.
XII MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Contents
Contents
Guaranty and Declaration ......................................................................... I
Safety Requirement ................................................................................. II
General Safety Summary........................................................................... II
Safety Notices and Symbols ..................................................................... IV
Measurement Category ............................................................................. V
Ventilation Requirement ............................................................................ V
Working Environment .............................................................................. VI
Care and Cleaning .................................................................................. VII
Environmental Considerations .................................................................. VII
MSO7000/DS7000 Series Overview ....................................................... IX
Document Overview ................................................................................ X
Chapter 1 Quick Start ........................................................................ 1-1
General Inspection ................................................................................. 1-2
Appearance and Dimensions ................................................................... 1-3
To Prepare for Use ................................................................................. 1-4
To Adjust the Supporting Legs .......................................................... 1-4
To Connect to AC Power ................................................................... 1-4
Turn-on Checkout ............................................................................ 1-5
To Replace the Fuse ......................................................................... 1-5
To Connect the Probe ....................................................................... 1-6
Function Inspection ......................................................................... 1-9
Probe Compensation ...................................................................... 1-10
Front Panel Overview ........................................................................... 1-11
Rear Panel Overview ............................................................................ 1-12
Front Panel Function Overview .............................................................. 1-15
Vertical ......................................................................................... 1-15
Horizontal ..................................................................................... 1-16
Wave ............................................................................................ 1-17
Trigger ......................................................................................... 1-18
Clear ............................................................................................ 1-18
Auto ............................................................................................. 1-18
RUN/STOP .................................................................................... 1-18
Single ........................................................................................... 1-19
Multifunction knob ......................................................................... 1-19
Function Menu .............................................................................. 1-20
Touch Lock Key ............................................................................. 1-20
Quick Key (Shortcut Key) ................................................................ 1-21
User Interface ...................................................................................... 1-22
Touch Screen Controls .......................................................................... 1-26
Tap .............................................................................................. 1-26
Pinch & Stretch ............................................................................. 1-27
XIV MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Contents RIGOL
Drag ............................................................................................. 1-27
Rectangle Drawing ......................................................................... 1-28
Parameter Setting Method ..................................................................... 1-29
To Use the Security Lock ....................................................................... 1-30
To Use the Built-in Help System ............................................................. 1-31
To View the Option Information and the Option Installation ...................... 1-32
Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System ................................................. 2-1
To Enable or Disable the Analog Channel ................................................. 2-2
To Adjust the Vertical Scale .................................................................... 2-3
Vertical Expansion ................................................................................. 2-4
To Adjust the Vertical Offset ................................................................... 2-4
Channel Coupling .................................................................................. 2-5
Bandwidth Limit .................................................................................... 2-5
Probe Ratio ........................................................................................... 2-6
Input Impedance ................................................................................... 2-7
Waveform Invert ................................................................................... 2-8
To Set the Probe ................................................................................... 2-8
Passive Probe ................................................................................. 2-9
Active Probe ................................................................................... 2-9
Amplitude Unit ..................................................................................... 2-10
Channel Delay ...................................................................................... 2-10
Offset Cal ............................................................................................ 2-11
Channel Label ...................................................................................... 2-11
Chapter 3 To Set the Horizontal System ............................................. 3-1
To Adjust the Horizontal Time Base ......................................................... 3-2
To Adjust the Horizontal Position ............................................................. 3-3
Delayed Sweep ..................................................................................... 3-4
Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System .................................................. 4-1
Timebase Mode ..................................................................................... 4-2
YT Mode ........................................................................................ 4-2
XY Mode ........................................................................................ 4-2
ROLL Mode .................................................................................... 4-4
Acquisition Mode ................................................................................... 4-5
Normal .......................................................................................... 4-5
Average ......................................................................................... 4-5
Peak .............................................................................................. 4-6
Sampling Mode ..................................................................................... 4-6
Sample Rate ......................................................................................... 4-7
LA Sample Rate ..................................................................................... 4-8
Memory Depth ...................................................................................... 4-9
LA Memory Depth ................................................................................. 4-10
Anti-Aliasing ......................................................................................... 4-10
Horizontal Expansion ............................................................................ 4-10
Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope ................................................ 5-1
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide XV
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Contents
Trigger Source ....................................................................................... 5-2
Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level ................................................................ 5-3
Trigger Mode ......................................................................................... 5-4
Trigger Coupling..................................................................................... 5-6
Trigger Holdoff ....................................................................................... 5-6
Noise Rejection ...................................................................................... 5-7
Trigger Type .......................................................................................... 5-8
Edge Trigger ................................................................................... 5-9
Pulse Trigger ................................................................................. 5-10
Slope Trigger ................................................................................. 5-12
Video Trigger................................................................................. 5-15
Pattern Trigger .............................................................................. 5-17
Duration Trigger ............................................................................ 5-19
Timeout Trigger ............................................................................. 5-21
Runt Trigger .................................................................................. 5-23
Window Trigger ............................................................................. 5-25
Delay Trigger ................................................................................ 5-27
Setup/Hold Trigger......................................................................... 5-29
Nth Edge Trigger ........................................................................... 5-32
RS232 Trigger (Option) .................................................................. 5-33
I2C Trigger (Option) ....................................................................... 5-36
SPI Trigger (Option) ....................................................................... 5-38
CAN Trigger (Option) ..................................................................... 5-40
FlexRay Trigger (Option) ................................................................ 5-43
LIN Trigger (Option) ...................................................................... 5-45
I2S Trigger (Option) ....................................................................... 5-47
MIL-STD-1553 Trigger (Option) ....................................................... 5-50
Zone Trigger ................................................................................. 5-52
Trigger Output Connector...................................................................... 5-54
Chapter 6 Operations and Measurements .......................................... 6-1
Math Operation ...................................................................................... 6-2
Addition .......................................................................................... 6-2
Subtraction ..................................................................................... 6-3
Multiplication ................................................................................... 6-4
Division .......................................................................................... 6-5
FFT ................................................................................................ 6-6
"AND" Operation ............................................................................. 6-9
"OR" Operation ............................................................................. 6-10
"XOR" Operation ............................................................................ 6-12
"NOT" Operation............................................................................ 6-13
Intg.............................................................................................. 6-14
Diff .............................................................................................. 6-15
Sqrt .............................................................................................. 6-16
Lg (Base 10 Exponential) ................................................................ 6-16
Ln ................................................................................................ 6-17
XVI MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Contents RIGOL
Exp .............................................................................................. 6-18
Abs .............................................................................................. 6-18
Low Pass ....................................................................................... 6-19
High Pass ...................................................................................... 6-20
Band Pass ..................................................................................... 6-20
Band Stop ..................................................................................... 6-21
AX+B ............................................................................................ 6-22
Math Operation Label ..................................................................... 6-23
Auto Measurement ............................................................................... 6-24
Quick Measurement after AUTO....................................................... 6-24
Measurement Parameter ................................................................. 6-26
Measurement Settings .................................................................... 6-32
Remove the Measurement Result ..................................................... 6-35
Statistical Function ......................................................................... 6-36
All Measurement ............................................................................ 6-36
Cursor Measurement............................................................................. 6-36
Manual Mode ................................................................................. 6-38
Track Mode ................................................................................... 6-41
XY Mode ....................................................................................... 6-44
Chapter 7 Digital Voltmeter (DVM) and Frequency Counter ............... 7-1
Digital Voltmeter (DVM) ......................................................................... 7-2
To Enable or Disable DVM Measurement............................................ 7-2
To Select the Measurement Source ................................................... 7-2
To Select Measurement Mode ........................................................... 7-3
To Set the Limits ............................................................................. 7-3
Frequency Counter ................................................................................ 7-4
To Enable or Disable the Frequency Counter ...................................... 7-4
To Select the Measurement Source ................................................... 7-4
To Select the Measurement Item ...................................................... 7-4
To Set Resolution ............................................................................ 7-5
To Clear Count ................................................................................ 7-5
To Enable or Disable the Statistical Function ...................................... 7-5
Chapter 8 Power Analysis (Option) ..................................................... 8-1
Power Quality ....................................................................................... 8-2
Ripple .................................................................................................. 8-4
Chapter 9 Histogram Analysis ............................................................ 9-1
To Enable or Disable the Histogram Function ............................................ 9-2
To Select the Histogram Type ................................................................. 9-2
To Select the Histogram Source .............................................................. 9-2
To Set the Histogram Height ................................................................... 9-3
To Set the Histogram Range ................................................................... 9-3
To Enable or Disable the Statistical Function............................................. 9-3
To Reset ............................................................................................... 9-4
Chapter 10 Digital Channel ................................................................. 10-1
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide XVII
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Contents
To Select the Digital Channel ................................................................. 10-2
To Enable/Disable the Digital Channel .................................................... 10-2
To Set the Threshold ............................................................................ 10-3
Auto Arrangement Setting ..................................................................... 10-4
To Set the Waveform Display Size .......................................................... 10-4
To Set the Label ................................................................................... 10-4
Group Setting ...................................................................................... 10-5
Waveform Color of the Digital Channel ................................................... 10-6
Chapter 11 Protocol Decoding ........................................................... 11-1
Parallel Decoding ................................................................................. 11-2
RS232 Decoding (Option) ..................................................................... 11-7
I2C Decoding (Option) ........................................................................ 11-14
SPI Decoding (Option) ........................................................................ 11-18
LIN Decoding (Option) ........................................................................ 11-23
CAN Decoding (Option) ....................................................................... 11-28
FlexRay Decoding (Option) .................................................................. 11-33
I2S Decoding (Option) ........................................................................ 11-37
1553B Decoding (Option) .................................................................... 11-41
Chapter 12 Reference Waveform ....................................................... 12-1
To Enable Ref Function ......................................................................... 12-2
To Select the Reference Channel ............................................................ 12-2
To Select the Ref Source ....................................................................... 12-2
To Adjust the Ref Waveform Display ....................................................... 12-2
To Save to Internal Memory .................................................................. 12-3
To Clear the Display of the Reference Waveform ..................................... 12-3
To View Details of the Reference Waveform ............................................ 12-3
To Reset the Reference Waveform ......................................................... 12-4
Color Setting........................................................................................ 12-4
Label Setting ....................................................................................... 12-4
To Export to Internal or External Memory ............................................... 12-5
To Import from Internal or External Memory ........................................... 12-5
Chapter 13 Pass/Fail Test .................................................................. 13-1
To Enable or Disable the Pass/Fail Test Function ...................................... 13-2
To Start or Stop the Pass/Fail Test Operation ........................................... 13-2
To Select the Source ............................................................................. 13-2
To Create a Mask ................................................................................. 13-3
To Save the Mask ................................................................................. 13-3
To Load a Mask .................................................................................... 13-3
To Set the Output Form of the Test Results ............................................. 13-4
To Enable or Disable the Display of the Statistics of the Test Results ......... 13-5
Statistics Reset .................................................................................... 13-5
Chapter 14 Waveform Recording & Playing ....................................... 14-1
Common Settings ................................................................................. 14-2
Record Options .................................................................................... 14-3
XVIII MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Contents RIGOL
Play Options ........................................................................................ 14-4
Chapter 15 Search and Navigation Function ....................................... 15-1
Search Function ................................................................................... 15-2
Navigation Function .............................................................................. 15-4
Chapter 16 Display Control ................................................................. 16-1
To Select the Display Type ..................................................................... 16-2
To Set the Persistence Time .................................................................. 16-2
To Set the Waveform Intensity ............................................................... 16-3
To Set the Screen Grid .......................................................................... 16-3
To Set the Grid Brightness ..................................................................... 16-3
Scale ................................................................................................... 16-3
Color Grade ......................................................................................... 16-3
Waveform Freeze ................................................................................. 16-4
Chapter 17 Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator (MSO7000 Option)
17-1
To Output Basic Waveforms ................................................................... 17-2
To Output Sine .............................................................................. 17-2
To Output Square .......................................................................... 17-3
To Output Ramp ............................................................................ 17-4
To Output Pulse ............................................................................. 17-4
To Output DC ................................................................................ 17-5
To Output Noise ............................................................................. 17-5
Sinc .............................................................................................. 17-6
Exp.Rise ........................................................................................ 17-6
Exp.Fall ......................................................................................... 17-7
ECG .............................................................................................. 17-7
Gauss ........................................................................................... 17-7
Lorentz ......................................................................................... 17-8
Haversine ...................................................................................... 17-8
To Output the Arbitrary Waveform .......................................................... 17-9
To Load the Channel and Waveform ................................................. 17-9
To Create the Waveform ............................................................... 17-10
To Edit Waveforms ....................................................................... 17-12
Modulation ........................................................................................ 17-13
AM ............................................................................................. 17-14
FM ............................................................................................. 17-15
FSK ............................................................................................ 17-15
Sweep ............................................................................................... 17-16
Burst ................................................................................................. 17-18
Chapter 18 Store and Load ................................................................. 18-1
Storage System .................................................................................... 18-2
Storage Type ....................................................................................... 18-2
Load Type ............................................................................................ 18-3
Internal Storage and Load ..................................................................... 18-4
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide XIX
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Contents
External Storage and Load .................................................................... 18-6
Disk Management ................................................................................ 18-6
To Select a File Type ...................................................................... 18-7
To Create a Folder ......................................................................... 18-7
To Delete a File or Folder .............................................................. 18-11
To Copy and Paste a File or Folder ................................................. 18-12
To Rename a File or Folder ........................................................... 18-12
To Clear the Internal Memory Safely .............................................. 18-13
Factory Settings ................................................................................. 18-13
Chapter 19 System Utility Function Setting ....................................... 19-1
Remote Interface Configuration ............................................................. 19-2
LAN Configuration ......................................................................... 19-2
To Set the GPIB Address ................................................................ 19-5
USB Connection ............................................................................. 19-5
System-related .................................................................................... 19-6
Beeper ......................................................................................... 19-6
Language ..................................................................................... 19-6
System Information ....................................................................... 19-6
Power On ...................................................................................... 19-6
Power Status ................................................................................. 19-7
Aux Output ................................................................................... 19-7
Key Locker .................................................................................... 19-8
HDMI Setting ................................................................................ 19-8
Self-calibration .............................................................................. 19-8
Auto Config ................................................................................... 19-9
Print Setting .................................................................................. 19-9
Email .......................................................................................... 19-11
Screen Saver ............................................................................... 19-12
Quick Operation .......................................................................... 19-13
Self-check ................................................................................... 19-15
System Time ............................................................................... 19-16
Chapter 20 Remote Control ............................................................... 20-1
Remote Control via USB ........................................................................ 20-2
Remote Control via LAN ........................................................................ 20-6
Remote Control via GPIB ....................................................................... 20-7
Chapter 21 Troubleshooting .............................................................. 21-1
Chapter 22 Appendix ......................................................................... 22-1
Appendix A: Accessories and Options ..................................................... 22-1
Appendix B: Warranty ........................................................................... 22-3
Index ........................................................................................... 1
XX MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
General Inspection
1. Inspect the packaging
If the packaging has been damaged, do not dispose the damaged packaging or
cushioning materials until the shipment has been checked for completeness and
has passed both electrical and mechanical tests.
The consigner or carrier shall be liable for the damage to the instrument
resulting from shipment. RIGOL would not be responsible for free
maintenance/rework or replacement of the instrument.
2. Inspect the instrument
In case of any mechanical damage, missing parts, or failure in passing the
electrical and mechanical tests, contact
3. Check the accessories
Please check the accessories according to the packing lists. If the accessories
are damaged or incomplete, please contact your
1-2 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
134.2
Appearance and Dimensions
Figure 1-1 Front View Unit: mm
Figure 1-2 Vertical View Unit: mm
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-3
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
(a) To unfold the supporting legs
(b) To fold the supporting legs
AC 100-240V , 45-440Hz
~Line:200W Max
~Fuse:AC 250VT3.15A
HAZARDOUS VOLTAGE INSIDE
DO NOT REMOVETHE COVER UNLESS BY SPECIFIED PERSONNEL.
WARNING: MAINTAIN GROUND TOAVOID ELECTRIC SHOCK
EXTTRIG
TRIG OUT
HOST
DEVICE
LAN
CAUTION
To avoid electric shock, ensure that the instrument is correctly grounded.
Power Cord Connector
Supporting Legs
To Prepare for Use
To Adjust the Supporting Legs
Adjust the supporting legs properly to use them as stands to tilt the oscilloscope
upwards for stable placement of the oscilloscope as well as better operation and
observation. Users can also fold the supporting legs when the instrument is not in
use for easier storage or shipment, as shown in Figure 1-3.
Figure 1-3 To Adjust the Supporting Legs
To Connect to AC Power
The input AC power requirements of the oscilloscope are 100~240 V, 45~440 Hz.
Please use the power cord provided in the accessories to connect the oscilloscope to
the AC power source via the power cord connector, as shown in Figure 1-4. After you
turn on the power switch, the oscilloscope is connected to power, and the Power key
located at the lower-left corner of the front panel is blinking.
Figure 1-4 To Connect to AC Power
1-4 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
Tip
Restart and Shutdown:
1. Enable the touch screen and then tap the function navigation icon at the
lower-left corner of the screen to enable the function navigation.
2. Tap the "Restart" icon, and then the "Restart" selection menu is displayed,
as shown in the figure below:
3. If you tap the "Restart" icon , the oscilloscope will be powered off and
then automatically restart again. If you tap the "Shutdown" icon , the
oscilloscope is powered off (you can also press the Power key at the
lower-left corner of the front panel to turn off the oscilloscope).
Turn-on Checkout
When the oscilloscope is connected to power, press the Power key at the lower-left
corner of the front panel to start the oscilloscope. (You can also press Utility
System Power status, and select "Switch On". After the instrument is
connected to power source, it will start directly. You can also enable the touch screen
to perform the above operations.) During the start-up process, the oscilloscope
performs a series of self-tests. After the self-test, the welcome screen is displayed.
To Replace the Fuse
If you need to replace the fuse, use only the specified fuse (AC 250V, T3.15A;
5.2mm× 20mm) and perform the following operations (as shown in Figure 1-5):
1. Turn off the instrument, cut off the power and remove the power cord.
2. Insert a slotted screwdriver into the slot of the fuse holder to pry it out.
3. Take out the fuse.
4. Replace the old fuse with a specified fuse.
5. Install the fuse holder.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-5
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
WARNING
To avoid electric shock, please ensure that the instrument has been turned
off, the power source has been cut off, and the fuse to be used conforms
to the fuse rating.
Fuse Holder
Fuse
Figure 1-5 To Replace the Fuse
To Connect the Probe
RIGOL provides the passive probe, the active probe, and the logic probe for
MSO7000/DS7000 series. For specific probe models, please refer to
MSO7000/DS7000 Series Datasheet
please refer to the specified Probe User’s Guide.
Connect the passive probe:
1. Connect the BNC terminal of the probe to an analog channel input terminal of
the oscilloscope on the front panel, as shown in Figure 1-6.
2. Connect the ground alligator clip or spring of the probe to the circuit ground
terminal, and then connect the probe tip to the circuit point to be tested.
. For detailed technical information of the probes,
Figure 1-6 To Connect the Passive Probe
After you connect the passive probe, check the probe function and probe
compensation adjustment before making measurements. For detailed procedures,
1-6 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
refer to "Function Inspection" and "Probe Compensation".
Connect the active probe:
Take RP7080 (active differential probe head) as an example.
1. Connect the probe head to the preamp of the active probe, as shown in Figure
1-7.
Figure 1-7 To Connect the Probe Head to the Preamp of the Active Probe
2. Connect the other end of the preamp to an analog channel input terminal of the
oscilloscope on the front panel, as shown in Figure 1-8. Note that you should
push the probe to the end to ensure that it is tightly connected.
Figure 1-8 To Connect the Active Probe
3. Use the probe auxiliary equipment to connect the probe front to the circuit
under test. For details about the probes, refer to
User's Guide
After connecting the active probe, you can perform probe calibration and offset
voltage adjustment if necessary. For detailed procedures, refer to the "Active
Probe" section.
Connect the logic probe:
1. Connect the single-wire terminal of the logic probe to the digital channel input
terminal on the front panel of the oscilloscope in the correct direction, as shown
in Figure 1-9.
2. Connect the other terminal of the logic probe to the signal terminal under test.
RIGOL's MSO7000 series has a standard configuration of a logic probe RPL2316.
To apply to different application scenarios, RPL2316 provides three connection
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-7
.
RP7000 Series Active Probe
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
methods to connect the signal under test. For details, refer to
Probe User’s Guide
Note:
Before you connect the logic probe to the signal under test, connect logic
probe's adapter provided in the accessories to its corresponding channel group.
The digital channel input terminal does not support hot plugging. Please do not
insert or pull out the logic probe when the instrument is in power-on state.
.
Figure 1-9 To Connect the Logic Probe
RPL2316 Logic
1-8 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
WARNING
To avoid electric shock when using the probe, please make sure that the
insulated wire of the probe is in good condition. Do not touch the
metallic part of the probe when the probe is connected to high voltage
source.
Compensation Signal Output Terminal
Ground Terminal
Function Inspection
1. Press Default on the front panel, then a prompt message "Restore default?" is
displayed. Press OK or tap OK to restore the instrument to its factory default
settings.
2. Connect the ground alligator clip of the probe to the "Ground Terminal" as
shown in Figure 1-10 below.
3. Use the probe to connect the input terminal of CH1 of the oscilloscope and the
"Compensation Signal Output Terminal" of the probe, as shown in Figure 1-10.
Figure 1-10 To Use the Compensation Signal
4. Set the probe attenuation to 10X, and then press AUTO.
5. Observe the waveform on the display. In normal condition, the square waveform
as shown in Figure 1-11 should be displayed.
Figure 1-11 Square Waveform Signal
6. Use the same method to test the other channels. If the square waveforms
actually shown do not match that in the figure above, please perform "Probe
Compensation" introduced in the next section.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-9
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
Tip
The probe compensation signal can only be used for probe compensation
adjustment and cannot be used for calibration.
Over compensated Perfectly compensated Under compensated
Probe Compensation
When the probes are used for the first time, you should compensate the probes to
make them match the input channels of the oscilloscope. Non-compensated or
poorly compensated probes may cause measurement inaccuracy or errors. The
probe compensation procedures are as follows:
1. Perform Step 1, 2, 3 and 4 specified in "Function Inspection".
2. Check the displayed waveforms and compare them with Figure 1-12.
Figure 1-12 Probe Compensation
3. Use a nonmetallic screwdriver to adjust the low-frequency compensation
adjustment hole on the probe until the waveform is displayed as "Perfectly
compensated" in the figure above.
1-10 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
Horizontal
OFFSET
Zero
OFFSET
Zero
Intensity
OFFSET
Zero
50%
Wave
Vertical
Menu
T
rigger
Navig ate
Digital Oscilloscope
500MHz 10GSa/s
GⅠ GⅡ
For output only
Default
Touch
Lock
Menu
Mode
Force
Math L A
CLEAR
Cursor
Quick
Utility
Display
Zoom
Ref
1 2
G GⅠ Ⅱ
3 4
Decode
StorageAcquire
Measure
AUTO
RUN
STOP
SINGLE
Off
Back
Menu
Search
No.
Description
No.
Description
1
Capacitive Touch Screen
11
RUN/STOP Key
2
Function Menu Operation Keys
12
Single Trigger Control Key
3
Quick Key (Shortcut Key)
13
Trigger Control System
4
Multifunction Knob
14
Vertical Control System
5
Common Operation Keys
15
Analog Channel Input
Terminals
6
Touch Lock Key
16
Probe Compensation Signal
Output Terminal/Ground
Terminal
7
Horizontal Control System
17
Digital Channel Input
Interface
[1]
8
CLEAR Key
18
Dual-channel
Function/Arbitrary
Waveform Generator Output
Terminals
[2]
9
Auto Waveform Display Key
19
USB HOST Interface
10
Waveform Control System
20
Power Key
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
20 19 18 17 16 15 14
Front Panel Overview
Figure 1-13 Front Panel
Table 1-1 Front Panel Description
Note:
Note:
[1]
This function is only available for the MSO7000 model.
[2]
This function is only available for the MSO7000 model installed with the
Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator option.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-11
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
1 2 3 4 5
10 9 8 7 6
Rear Panel Overview
Figure 1-14 Rear Panel
1. Handle
Rotate the handle upright to carry the instrument easily. Rotate it
downward if you do not need to carry it.
2. LAN Interface
Connect the instrument to network via this interface. The instrument is in
compliance with the standards specified in LXI Device Specification 2011. It
can be used to set up a test system.
When you access to the Internet, you can use the Web Control or PC
software Ultra Scope to send the SCPI commands or use the user-defined
programming to control the instrument. When update is available, you can
perform online upgrading for the system software of the instrument via the
LAN interface. After it is connected to the network, you can print the
waveform displayed on the screen when you use the network printer.
1-12 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
Tip
After the oscilloscope is connected to network (if you do not have the access
to the Internet, please ask the administrator to open the specified network
authority), you can perform online upgrading for the system software:
1) Enable the touch screen function. Tap the function navigation icon
at the lower-left corner of the touch screen to enable the function
navigation.
2) Tap the "Help" icon, and then the "Help" menu is displayed on the
screen.
3) Press Online upgrade or enable the touch screen to tap "Online
upgrade", then a "System Update Information" window is displayed,
requesting you whether to accept or cancel "RIGOL TERMS OF ONLINE
UPGRADE SERVICE". Tap "Accept" to start online upgrade. Tap "Cancel"
to cancel the online upgrade.
Tip
Perform local upgrading for the system software:
1) Insert the USB storage device (stored with upgrading files under its root
directory) into the USB HOST interface, and then the "Help" menu is
automatically displayed.
2) Press Local upgrade or enable the touch screen to tap "Local
upgrade", then a dialog box "Upgrade system firmware?" is displayed.
3) Press OK or enable the touch screen to tap "OK" to start local upgrade
for the oscilloscope. If you tap "Cancel", the local upgrade will be
cancelled.
3. USB DEVICE Interface
You can connect the instrument to the PC via this interface. Then you can
use the PC software Ultra Scope to send the SCPI commands or use the
user-defined programming to control the instrument.
4. USB HOST Interface
You can connect the storage device that is compatible with the USB to the
instrument via the USB HOST interface.
Connecting the storage device can save or recall the waveform files and
setup files; as well as save the data and screen image. When update is
available, you can perform local upgrading for the system software of the
instrument via the USB HOST interface.
I
n
s
e
r
t
t
h
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
5. HDMI Video Output
You can connect the instrument to an external display equipped with the
HDMI interface (e.g. monitor or projector) via the Video Output interface
to better observe the waveform display clearly. At this time, you can also
view the waveforms on the LCD of the instrument.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-13
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
6. EXT TRIG
Inputs the external signal via the external input terminal.
7. Trigger Out and Pass/Fail
TRIG OUT:
The oscilloscope can output a signal that can reflect the current
capture rate of the oscilloscope at each trigger via this interface.
Connect the signal to a waveform display device and measure the
frequency of the signal. The measurement result is the same as the
current capture rate.
Pass/Fail
The instrument can output a pulse from the [TRIG OUT] connector
when a pass/failed event is detected during the pass/fail test.
8. Lock Hole
You can lock the instrument to a fixed location by using the security lock
(please purchase it by yourself) via the lock hole.
9. Fuse
If you need to replace the fuse, use only the specified fuse. For details,
refer to descriptions in "To Replace the Fuse".
10. AC Power Cord Connector
Indicates the input terminal where AC power source is connected. The
power supply requirements of the instrument are: 100 V~240 V; 45
Hz~440 Hz. Please use the power cord provided in the accessories to
connect the oscilloscope to the AC power source.
1-14 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
OFFSET
Zero
OFFSET
Zero
OFFSET
Zero
Vertical
Default
1 2
G GⅠ Ⅱ
3 4
1, 2, 3, 4: indicates the analog channel switch key. The four channels are
marked by different colors which are also used to mark both the corresponding
waveforms of the specified channel on the screen and the channel input
connectors.
GI, GII: indicates the Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator setting key.
Press GI to enable or disable the output of the [GI] connector on the front
panel; press GII to enable or disable the output of the [GII] connector on the
front panel; and then enter the corresponding Function/Arbitrary Waveform
Generator setting interface. Enable or disable the status display of the current
signal.
Note: This function is only available for the MSO7000 model installed with the
Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator option.
Default: indicates the default setting key. Press this key to restore the
instrument to its factory default settings.
Vertical OFFSET: indicates the channel vertical offset knob. You can
rotate the knob to modify the vertical offset of the current channel waveform.
Each analog channel is configured with an independent vertical offset
adjustment knob. Turn it clockwise to increase the offset, and turn it
counterclockwise to decrease the offset. During the modification, the waveform
would move up and down. Meanwhile, the offset information in the
corresponding status label would change accordingly. Press down this knob to
quickly reset the vertical offset to zero.
Vertical SCALE: indicates the channel vertical scale knob. Modify the
vertical scale of the current channel. Each analog channel is configured with an
independent vertical scale adjustment knob. Turn it clockwise to decrease the
scale, and turn it counterclockwise to increase the scale. During the
Front Panel Function Overview
Vertical
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-15
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
modification, the display amplitude of the waveform will enlarge or reduce. The
scale information in the corresponding status label will change accordingly.
Press down this knob to quickly switch the vertical scale adjustment mode
between "Coarse" and "Fine".
Horizontal
Na vigat e
Zoom
Search
Nav igate
Horizontal
Zoom: indicates the delayed sweep key. Press this key to enable or disable the
delayed sweep function.
Search: indicates the Search key. Press this key to enter the search setting
menu. The search function allows you to search for relevant events from the
collected data based on the search condition that you set.
: indicates the navigation combination key. With the
combination keys, you can perform recording & playing navigation, time
navigation, and event navigation.
Horizontal POSITION: indicates the horizontal position knob. You can
rotate the knob to modify the horizontal position (i.g. trigger position). The
trigger point would move left or right relative to the center of the screen when
you rotate the knob. During the modification, waveforms of all the channels
would move left or right, and the horizontal position message (e.g. )
at the upper-right corner of the screen would change accordingly. Press down
this knob to quickly reset the horizontal position (or the delayed sweep
position).
Horizontal SCALE: indicates the horizontal time base knob. You can rotate
the knob to modify the horizontal time base. Turn it clockwise to decrease the
time base, and turn it counterclockwise to increase the time base. During the
modification, waveforms of all the channels will be displayed in expanded or
compressed form, and the time base message (e.g. ) at the upper
section of the screen would change accordingly. Press down this knob to quickly
switch the horizontal time base adjustment mode between "Coarse" and "Fine".
1-16 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
W
ave
Math L A
Ref Decode
Wave
Math: indicates the math operation key. Press this key to enable the math
operation function. The math operations include A+B, A-B, A× B, A/B, and FFT.
Besides, you can also set the math operation label.
LA: indicates the logic analyzer key. Press this key to open the logic analyzer
control menu. You can enable or disable any channel or channel group, modify
the waveform sizes of the digital channel, modify the threshold of the digital
channel, and group the 16 digital channels. Besides, you can also set a label for
each digital channel.
Note: This function is only available for the MSO7000 model.
Ref: indicates the reference waveform key. Press this key to open the reference
waveform setting menu. You can compare the actually measured waveform with
the reference waveform to locate the circuit failure.
Decode: indicates the decode key. Press this key to open the decode setting
menu, and then you can set the decode options. MSO7000/DS7000 series
supports the parallel decoding and many protocol decodings. (For details, refer
to the descriptions in "Protocol Decoding").
Wave Vertical POSITION: indicates the waveform vertical position knob.
Rotate the knob to adjust the vertical position of the current digital channel
waveform, the vertical position of the math operation waveform, the vertical
position of the reference waveform, or the vertical display position of the bus
decoding.
Wave Vertical SCALE: indicates the waveform vertical scale knob. Rotate
the knob to adjust the vertical scale of math operation waveform or the vertical
scale of the reference waveform, and also can adjust the size of the displayed
digital channel waveforms.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-17
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
50%
T
rigger
Menu
Mode
Force
Menu: Press this key to open the trigger operation menu.
This oscilloscope provides various trigger types.
Mode: Press this key to switch the trigger mode to Auto
Normal, or Single.
Force: Press this key to generate a trigger signal
forcefully.
Trigger LEVEL: modifies the trigger level/threshold
level. Turn it clockwise to increase the level, and turn it
counterclockwise to decrease the level. During the
modification, the trigger level line would move up and
down and the trigger level/threshold level value at the
upper-right corner of the screen would change accordingly.
Press down the knob to quickly set the trigger level to 50%
of the waveform peak-peak value.
Press this key to clear all the waveforms on the screen. If the
oscilloscope is in the "RUN" state, new waveforms will
continue being displayed.
Press this key to enable the waveform auto setting function.
The oscilloscope will automatically adjust the vertical scale,
horizontal time base, and trigger mode according to the input
signal to realize optimal waveform display.
Press this key to set the operating state of the oscilloscope to
"RUN" or "STOP". In the "RUN" state, the key is illuminated
in yellow. In the "STOP" state, the key is illuminated in red.
Trigger
Clear
Auto
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
RUN/STOP
1-18 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
Press this key to set the trigger mode to "Single".
Intensity
Single
Multifunction knob
Non-menu Operation:
In non-menu-operation mode, rotate this knob to adjust the brightness of
waveform display. The settable screen brightness ranges from 1% to 100%.
Turn it clockwise to increase the brightness, and turn it counterclockwise to
decrease the brightness. Press down this knob to reset the brightness to 60%.
Press Display Intensity to adjust the waveform brightness. You can also
use the knob to adjust it.
Menu Operation:
When you operate on the menu, the backlight of the knob is illuminated. For the
menu item that has multiple parameters under it, when you press the menu
softkey, rotate the knob to select the parameter item, then press down the knob
to select it (sometimes, the specified parameter item can be selected by rotating
the knob). The knob can also be used to modify parameters, input the filename,
etc.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-19
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
Menu
Cursor
Utility
Display
StorageAcquire
Measure
Press this key to disable the touch screen function.
Function Menu
Measure: Press this key to enter the measurement setting menu. You can set the
measurement source, enable or disable the all measurement function, the statistical
analysis function, and etc. You can make a quick measurement for 41 waveform
parameters.
Acquire: Press this key to enter the acquisition setting menu. You can set the time
base mode, the acquisition mode, memory depth, and etc.
Storage: Press this key to enter the file or waveform storage and load interface.
The file types for storage include image, waveform, and setups. Besides, waveform
load and setup load are supported. The disk management and file auto naming
function are also supported in this menu.
Cursor: Press this key to enter the cursor measurement menu. The oscilloscope
provides three cursor modes: Manual, Track, and XY. Note that XY cursor mode is
only available when the horizontal time base is set to "XY".
Display: Press this key to enter the display setting menu. You can set the display
type, persistence time, wave intensity, and etc.
Utility: Press this key to enter the system function setting menu. You can set
system-related functions or parameters, such as I/O, sound, language, and etc.
Besides, some advanced functions (such as the pass/fail test, waveform recording,
and self-calibration) are also supported.
Touch Lock Key
Note: By default, the touch screen function of the oscilloscope is always enabled. If
you disable the function, press the key again to enable it.
1-20 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
Press this key to perform the quick operation, including screenshot,
waveform saving, setup saving, all measurement, and statistics reset.
Press Utility More Quick settings to set the quick shortcut
keys.
Quick Key (Shortcut Key)
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-21
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13
User Interface
MSO7000/DS7000 series has a 10.1-inch WSVGA (1024× 600) LCD, with 256 level
gray-scale display. The user interface displays the acquired waveforms, the setting
information, and the measurement results.
Figure 1-15 User Interface
1. Digital Channel Label/Waveform
The logic high and low level of the digital waveform are displayed in green. Its
edge is displayed in white. The color of the currently selected waveform of the
digital channel is consistent with that of the channel label, being displayed in red.
The grouping setting function under the logic analyzer function menu can divide
the digital channels into 4 channel groups. The channel label of the same
channel group is displayed in the same color; different channel groups are
marked with different colors.
Note: This function is only available for the MSO7000 model.
2. Operating Status
Available states include RUN, STOP, T’D (triggered), WAIT, and AUTO.
1-22 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
screen waveform
waveform in the memory
3. Horizontal Time Base
Represents the time length per grid in the horizontal axis of the screen.
Use Horizontal SCALE to modify this parameter. The adjustable range
of the horizontal time base is different for different models.
4. Sample Rate/Memory Depth
Displays the current sample rate and memory depth of the analog channel.
The sample rate and the memory depth will change along with the horizontal
time base.
5. Auto Measurement Label
Enable the touch screen, and then tap the label. Up to 41 waveform parameters
are available for auto measurement. It also offers full-memory hardware
measurement function.
6. Waveform Memory
Provides a diagram of the position of the screen waveform in the memory.
7. Trigger Position
Displays the trigger position of the screen waveform and that of the waveform in
the memory.
8. Run/Stop Label
In the run state, the label is displayed in green; while in the stop state, it is
displayed in red. You can enable the touch screen to tap the icon "STOP/RUN" to
control its operating status.
9. Horizontal Position
Use Horizontal POSITION to modify this parameter. Press down this knob
to quickly reset the horizontal position.
10. Trigger Type
Displays the currently selected trigger type and trigger condition setting. When
you select different trigger types, different labels are displayed. For example,
represents triggering on the rising edge in "Edge" trigger.
11. Trigger Source
Displays the currently selected trigger source (CH1-CH4, AC, EXT, or D0-D15).
When you select different trigger sources, different labels are displayed. For
example, denotes that CH1 is selected as the trigger source.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-23
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
12. Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level
When CH1-CH4 or EXT is selected as the trigger source, you need to set a
proper trigger level.
When D0-D15 is selected as the trigger source, you need to set a proper
threshold level.
The trigger level label is displayed at the left section of the screen, and
the trigger level/threshold level value is displayed at the upper-right corner
of the screen.
When you use Trigger LEVEL to modify the trigger level/threshold
level, the trigger level/threshold level value will change with the up and
down of .
Note: In Slope Trigger, Runt Trigger, and Window trigger, you need to set the
upper and lower limits of the trigger level, and two trigger level labels ( and
) are displayed.
13. Operation Menu
Press any softkey on the front panel to activate the corresponding menu.
14. Notification Area
Displays the beeper icon, the USB storage device icon, time, and the LAN
connection icon.
Beeper icon: Press Utility Beeper to turn on or off the beeper. When
the beeper is turned on, will be displayed; when off, will be
displayed.
USB storage device icon: When a USB storage device is detected, will be
displayed.
Time: displays the system time. For the system time setting, refer to
descriptions in "System Time".
LAN connection icon: When the LAN interface is successfully connected,
will be displayed.
15. AWG 2
Displays the on/off status of AWG 2.
Displays the waveform type set for the current AWG2.
It is only available for the MSO7000 model installed with the
Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator option.
16. AWG 1
Displays the on/off status of AWG 1.
Displays the waveform type set for the current AWG1.
It is only available for the MSO7000 model installed with the
Function/Arbitrary Waveform Generator option.
1-24 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
17. Digital Channel Status Area
Displays the current status of the 16 digital channels. The digital channels
currently turned on are displayed in green, and the currently selected digital
channel is highlighted in red. The digital channels turned off are displayed in
gray.
Note: This function is only available for the MSO7000 model.
18. CH4 Status Label
Displays the status of CH4.
Displays the vertical scale of CH4. That is, the voltage value per grid of CH4
in the vertical axis.
Displays the offset of CH4, i.g. the vertical offset of CH4 waveform.
Different labels will be displayed according to the current channel setting.
For example, if you select "DC" for channel coupling, is displayed; if you
enable the bandwidth limit, is displayed; if you select "50 Ω" for
impedance, is displayed.
19. Message Box
Displays the prompt messages.
20. CH3 Status Label
Displays the status of CH3.
Displays the vertical scale of CH3. That is, the voltage value per grid of CH3
in the vertical axis.
Displays the offset of CH3, i.g. the vertical offset of CH3 waveform.
Different labels will be displayed according to the current channel setting.
For example, if you select "DC" for channel coupling, is displayed; if you
enable the bandwidth limit, is displayed; if you select "50 Ω" for
impedance, is displayed.
21. CH2 Status Label
Displays the status of CH2.
Displays the vertical scale of CH2. That is, the voltage value per grid of CH2
in the vertical axis.
Displays the offset of CH2, i.g. the vertical offset of CH2 waveform.
Different labels will be displayed according to the current channel setting.
For example, if you select "DC" for channel coupling, is displayed; if you
enable the bandwidth limit, is displayed; if you select "50 Ω" for
impedance, is displayed.
22. CH1 Status Label
Displays the status of CH1.
Displays the vertical scale of CH1. That is, the voltage value per grid of CH1
in the vertical axis.
Displays the offset of CH1, i.g. the vertical offset of CH1 waveform.
Different labels will be displayed according to the current channel setting.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-25
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
Tip
The touch screen function is available for all the menus displayed on the screen
and the buttons enabled. In this manual, key operation descriptions are illustrated
in details, and as for the touch screen function about some operations, refer to
descriptions in relevant chapters.
For example, if you select "DC" for channel coupling, is displayed; if you
enable the bandwidth limit, is displayed; if you select "50 Ω" for
impedance, is displayed.
23. Analog Channel Label/Waveform
Different channels are marked with different colors. The color of the channel
label is the same as that of the waveform.
24. Function Navigation
Enable the touch screen and then tap this icon to enable the function navigation.
Touch Screen Controls
MSO7000/DS7000 series provides a 10.1-inch super large capacitive touch screen,
which supports multi-touch and gesture operation. It has strong waveform display
capability and excellent user experience. It features great convenience, high
flexibility, and great sensitivity. The actions supported by the touch screen controls
include tapping, pinching & stretching, dragging, and rectangle drawing.
Tap
Use one finger to touch the symbol or characters on the screen slightly, as shown in
Figure 1-16. The functions of the tap action include:
Tap the menu displayed on the screen to operate on the menu.
Tap the function navigation icon at the lower-left corner of the touch screen
to enable the function navigation.
Tap the displayed numeric keypad to set the parameters.
Tap the virtual keypad to set the label name and the filename.
Tap the close button at the upper-right corner of the message box to close the
prompt window.
Tap other windows on the touch screen and operate on the windows.
1-26 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
Figure 1-16 Tap Gesture
Pinch & Stretch
Pinch or stretch two points on the screen with two fingers to zoom in or out the
waveform. To zoom in the waveform, first pinch the two fingers and then stretch the
fingers; to zoom out the waveform, first stretch the two fingers, and then pinch the
fingers together, as shown in Figure 1-17. The functions of the pinch & stretch action
include:
Pinching & stretching in the horizontal direction can adjust the horizontal time
base of the waveform.
Pinching & stretching in the vertical direction can adjust the vertical scale of the
waveform.
Figure 1-17 Pinch & Stretch Gesture
Drag
Use one finger to select the object, and then drag the object to a destination place,
as shown in Figure 1-18. The functions of the drag action include:
Drag the waveform to change its position or offset.
Drag the window controls to change the positions of the window (e.g. numeric
keypad).
Drag the marker to change the position of the marker.
Figure 1-18 Drag Gesture
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-27
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
Tip
Tap the "Draw rect" icon to switch between the rectangle drawing and waveform
operation modes.
Tap the "Draw rect" icon, if is displayed, it indicates that the rectangle
drawing mode is enabled. Tap the "Draw rect" icon, if is displayed, it indicates
that the waveform operation mode is enabled. By default, the waveform operation
mode is enabled.
Rectangle Drawing
Enable the function navigation, and then tap the "Draw rect" icon to switch to the
rectangle drawing mode. Drag to draw a rectangle on the screen, as shown in Figure
1-19. Move your finger away from the screen, and then a menu is displayed on the
screen. At this time, you can tap to select "Trigger zone A", "Trigger zone B",
"Histogram", "Horizontal zoom", "Vertical zoom", or "Waveform zoom".
Figure 1-19 Rectangle Drawing Gesture
Select "Trigger zone A":
Draw the region for Trigger zone A;
Open Trigger zone A;
Open the "Zone Trigger" menu.
Select "Trigger zone B":
Draw the area for Trigger zone B;
Open Trigger zone B;
Open the "Zone Trigger" menu.
Select "Histogram":
Draw the region for the histogram;
Open the "Histogram" menu.
Select "Horizontal zoom": expands the waveforms in the horizontal direction.
Select "Vertical zoom": expands the waveforms in the vertical direction.
Select "Waveform zoom": expands the waveforms both in the horizontal and
vertical direction.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
1-28 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
Parameter
Input Field
Delete key
Max. value
Min. value
Default
Clear key
Parameter Setting Method
You can use the knob or enable the touch screen to set the parameters of
MSO7000/DS7000 series. The common parameter setting methods are as follows:
Method 1:
For the parameters with the sign , rotate the multifunction knob on the front
panel directly to select the parameter item or modify the parameter value.
Method 2:
For the parameters with the sign , rotate the multifunction knob on the front
panel and press it down to select the parameter item or modify the parameter value.
Method 3:
For the parameters with displayed on the menu, rotate the multifunction knob
on the front panel directly to set the parameter, or press down the multifunction
knob or the specified menu softkey, and then the numeric keypad is shown in
Figure 1-20 below.
Figure 1-20 Numeric Keypad
In the numeric keypad, rotate the multifunction knob to select the parameter, then
press down the knob to select it. Then input the value or the unit. You can also
enable the touch screen and tap the value or unit in the numeric keypad to input
them. After you input all the values and select the desired units, the numeric keypad
is turned off automatically. This indicates that you have completed parameter setting.
Besides, after you have input the values, you can also press OK directly to close the
numeric keypad. At this time, the unit of the parameter is the default unit. In the
numeric keypad, you can also perform the following operations:
Delete the parameter value that has been input.
Set the parameter to a maximum or minimum value (sometimes, the maximum
or minimum value are the specified one for the current state).
Set the parameter to a default value.
Clear the parameter input field.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-29
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
Tip
The above method is commonly used for the parameter settings of the
oscilloscope. For other methods of parameter settings, refer to details in relevant
chapters.
Security Lock Hole
Method 4:
For the parameters without the above signs, press the desired menu softkey to
switch between the parameter items. This method is applicable to the parameters
with only two available options.
To Use the Security Lock
If necessary, you can lock the instrument to a fixed location by using the security lock
(please purchase it by yourself), as shown in Figure 1-21. The method is as follows:
align the lock with the lock hole and plug it into the lock hole vertically, turn the key
clockwise to lock the oscilloscope and then pull the key out.
Figure 1-21 To Use the Security Lock
Note: Please do not insert other objects into the security lock hole to avoid
damaging the instrument.
1-30 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
Help Options Help Display Area
To Use the Built-in Help System
The help system of this oscilloscope provides instructions for all the function keys on
the front panel and their corresponding menu keys. The steps for opening the built-in
help system are as follows:
1. Enable the touch screen function, and tap the function navigation icon at
the lower-left corner of the touch screen to enable the function navigation.
2. Tap the "Help" icon, and then the "Help" menu is displayed on the screen.
3. Press Help on the front panel or tap the "Help" menu item, and then the help
information is displayed on the screen, as shown in Figure 1-22. The help
interface mainly consists of two sections. The left section lists "Help Options",
and the right section is the "Help Display Area".
Figure 1-22 Help Information
After opening the help interface, you can get its help information in the "Help Display
Area" through the following three methods:
Method 1: For the keys, you can directly press the front-panel keys (except the
Power key, the Menu Off key, and the Back key) to obtain the help information. For
the buttons, you can rotate the knob or press down the knob to get the help
information (except the multifunction knob , Wave Vertical POSITION
knob, and Wave Vertical SCALE knob). As the function of rotating the knob is
different from that of pressing down the knob, these two operations will give you
different help information.
Method 2: In the "Help Options", rotate the multifunction knob to switch among
the help options to get the corresponding help information.
Method 3: Enable the touch screen and tap the desired help option to get the
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-31
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 1 Quick Start
Tip
Help information for other keys and buttons:
Power key: powers on/off the instrument.
Menu Off key: displays or hides menus. Pressing this key can hide the
menus.
Back key: returns to the previous menu or last set function menu.
Multifunction knob : In non-menu-operation mode, rotate this knob to
adjust the brightness of waveform display. When you operate on the
menu, this knob is illuminated. For the menu that has multiple
sub-menus, press the corresponding softkey of the sub-menu, and then
rotate this knob to select the specified parameter item and press down
the knob to select it (sometimes you need to rotate the knob to select the
parameter item). It can also be used to modify parameters, input a
filename, etc.
Wave Vertical POSITION: rotating the knob can adjust the
vertical position of the waveform of the current digital channel, the
vertical position of the math operation waveform, the vertical position of
the reference waveform, or the vertical display position of the decoding
bus.
Wave Vertical SCALE: rotating the knob can adjust the vertical
scale of the math operation waveform or the vertical scale of the
reference waveform; adjust the display size of the waveform of the digital
channel.
If the menu item is grayed out, you cannot press the corresponding
front-panel menu key to obtain the help information. What you can do is only
to follow the above Method 2 or 3 to get the help information.
corresponding help information.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
To View the Option Information and the Option
Installation
MSO7000/DS7000 series oscilloscope provides multiple options to fulfill your
measurement requirements. If you need any of these options, order them according
to the Order No. available in "Appendix A: Accessories and Options", and then
install the options according to this section. Besides, you can also view the options
currently installed on the oscilloscope or activate the newly purchased option.
1. View the installed option
The instrument is installed with the trial versions of the options before leaving
factory. When you power on the instrument for the first time, the trial time is
about 2,160 minutes. If your instrument has currently installed the option,
perform the following operations to view the name of the installed option and
other detailed information about the option from the option list.
(1) Enable the touch screen function, and tap the function navigation icon
1-32 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 1 Quick Start RIGOL
Tip
Only 1 option license file of one instrument is allowed to be stored in the
same USB storage device, but the USB storage device can store the option
license file of several different instruments. You are not allowed to modify
the licensed filename.
During the installation process, you are not allowed to power off the
instrument or pull out the USB storage device.
Installing options by inputting the license code manually and sending the
SCPI commands is not supported.
at the lower-left corner of the touch screen to enable the function
navigation.
(2) Tap the "Help" icon, and then the "Help" menu is displayed on the screen.
(3) Press the Option list key or tap the Option list menu item, and then a list
of the options installed is displayed on the screen for users to view.
2. Install the option
The option license is a string of fixed characters. Each instrument has one
unique license. The license file should be in specific format, with the filename
extension ".lic". After you purchase an option, you will obtain a key (used for
obtaining the license). Then, you can install the option according to the
following steps.
1) Obtain an option license
(2) In the software license registration interface, input the correct key,
serial number (press Utility System About to obtain the serial
number of the instrument. You can also open the "Help" function menu,
and then press About to obtain the serial number), and the
verification code. Click Generate to obtain the download link of the
option license file. If you need to use the option license file, please
click the link to download the file to the root directory of the USB
storage device.
2) Install the option
(1) Confirm that the option license file is located in the root directory of
the USB storage device, and connect the USB storage device to the
oscilloscope properly.
(2) The Option setup key is activated, and press this menu key to start
installing the option.
(3) After installation, a prompt message "Option activated successfully" is
displayed.
Note: After the option has been installed, you need to restart the
instrument.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 1-33
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System RIGOL
Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System
MSO7000/DS7000 series provides four analog input channels (CH1-CH4), and each
channel is equipped with an independent vertical control system. The setting
methods for the vertical systems of the four channels are the same. This chapter
takes CH1 as an example to introduce the setting method for the vertical system.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 2-1
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System
To Enable or Disable the Analog Channel
Enable the analog channel:
Connect a signal to the channel connector of CH1, and then press 1 in the vertical
control area (Vertical) on the front panel to enable CH1. Then, the backlight of the
channel is illuminated. At this point, the channel setting menu is displayed at the
right section of the screen and the channel is activated. The channel status label at
the bottom of the screen is shown in the figure below. You can also enable the touch
screen to tap the channel status label to enable the channel.
The information displayed in the channel status label is related to the current channel
setting but irrelevant with the on/off status of the channel. After the channel is
turned on, modify the parameters such as the vertical scale, horizontal time base,
trigger mode, and trigger level according to the input signal for easy observation and
measurement of the waveform.
If CH1 is enabled but not activated, the channel status label is shown in the following
figure. To activate the channel, press 1 on the front panel in the vertical control area
(Vertical) or enable the touch screen to tap the waveform activation channel
displayed on the screen.
Disable the analog channel:
If the setting menu of the channel that needs to be disabled (the current channel is
activated) is displayed at the right section of the screen, press the channel key to
disable the channel. If the setting menu of the channel that needs to be disabled is
not displayed at the right section of the screen, first open the setting menu of the
channel to be disabled (activate the channel), then press the channel key to disable
the channel. You can also enable the touch screen to tap the channel status label to
disable the channel. For example, if CH1 and CH2 are enabled, and CH2 channel
setting menu is displayed on the screen, then if you need to disable CH1, first
activate CH1, and then press 1 or enable the touch screen to tap the CH1 channel
status label to disable CH1. If CH1 is disabled, the channel status label is shown in
the following figure.
2-2 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System RIGOL
Vertical Scale
Value Input Field Decrease Increase
To Adjust the Vertical Scale
Vertical scale indicates the voltage value per grid in the vertical axis of the screen. It
is often expressed in V/div. While you adjust the vertical scale, the display amplitude
of the waveform would enlarge or reduce. The scale information of the channel
status label (e.g. as shown in the following figure) at the lower section of the screen
would change accordingly.
The adjustable range of the vertical scale is related to the currently set probe ratio
and input impedance. By default, the probe ratio is 1X and the input impedance is 1
MΩ. In this case, the adjustable range of the vertical scale is from 1 mV/div to 10
V/div.
When CH1 is turned on, you can adjust the vertical scale with the following three
methods:
Rotate Vertical SCALE that corresponds to CH1 to adjust the vertical scale
(clockwise to reduce the scale and counterclockwise to increase).
Enable the touch screen function and adjust the vertical scale with the pinch &
stretch gesture on the touch screen. For details, refer to the "Pinch & Stretch"
section.
Enable the touch screen function, and tap the channel status label at the bottom
of the screen. The following window is displayed. Tap the icon at the
right side of the Scale input field to increase or decrease the scale. You can also
tap the Scale input field to input a specific value with the displayed numeric
keypad.
In the vertical control area (Vertical) on the front panel, press Vertical SCALE to
adjust the vertical scale in "Coarse" (by default) or "Fine" mode. You can also press
1 More Fine to enable or disable fine adjustment.
Fine adjustment: Rotate Vertical SCALE to further adjust the vertical scale
within a relatively smaller range to improve vertical resolution. If the amplitude
of the input waveform is a little bit greater than the full scale under the current
scale and the amplitude would be a little bit lower if the next scale is used, fine
adjustment can be used to improve the amplitude of waveform display to view
signal details.
Coarse adjustment (take counterclockwise as an example): Rotate Vertical
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 2-3
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System
Vertical Offset
SCALE to set the vertical scale at 1-2-5 step, i.e. 1 mV/div, 2 mV/div, 5 mV/div,
10 mV/div…10 V/div.
Vertical Expansion
When changing the vertical scale of the analog channel by rotating the Vertical
SCALE knob, you can select to expand or compress the waveform around the
"Center" or "GND" (Ground). By default, "GND" is selected under Expand.
Press 1 More, then press Expand continuously to select "Center" or "GND".
Center: when the vertical scale is changed, the waveform will be expanded or
compressed around the screen center.
GND: when the vertical scale is changed, the waveform will be expanded or
compressed around the signal ground level position.
To Adjust the Vertical Offset
Vertical offset indicates the offset of the signal ground level position of the waveform
from the screen center in the vertical direction. Its unit is consistent with the
currently selected amplitude unit (refer to "Amplitude Unit"). When adjusting the
vertical offset, the waveforms of the corresponding channel moves up and down.
The vertical offset information (as shown in the following figure) in the channel
status label at the bottom of the screen will change accordingly.
The adjustable range of the vertical offset is related to the current input impedance,
probe ratio, and vertical scale.
When CH1 is turned on, you can adjust the vertical offset with the following four
methods:
Rotate Vertical OFFSET that corresponds to CH1 to adjust the vertical
offset within the adjustable range. Rotate this knob clockwise to increase the
vertical offset, and rotate it counterclockwise to reduce the vertical offset.
Pressing down the knob can quickly reset the vertical offset (set the vertical
offset to 0).
Menu setting: Press 1 More Offset, and then the numeric keypad is
displayed. Input the offset value with the numeric keypad.
Enable the touch screen, and then adjust the vertical offset with the drag
gesture. For details, refer to the "Drag" section.
Enable the touch screen function, and tap the channel status label at the bottom
of the screen. The following window is displayed. Tap the icon at the
2-4 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System RIGOL
Value Input Field Decrease Increase
right side of the Scale input field to increase or decrease the offset. You can
also tap the Scale input field to input a specific value with the displayed
numeric keypad.
Channel Coupling
The undesired signals can be filtered out by setting the coupling mode. For example,
the signal under test is a square waveform with DC offset.
When the coupling mode is "DC": the DC and AC components of the signal under
test can both pass the channel.
When the coupling mode is "AC": the DC components of the signal under test
are blocked.
Press 1 to open the setting menu of CH1. Then, press Coupling continuously or
rotate the multifunction knob to select the desired coupling mode (by default, it
is DC). The current coupling mode is displayed in the channel status label at the
bottom of the screen, as shown in the figure below. You can also enable the touch
screen, and then touch the CH1 setting menu to select the desired coupling mode.
DC AC
Note:
When the input impedance is set to "50 Ω", the channel coupling is set to DC
coupling by force, and the Coupling menu is grayed out and cannot be
modified.
When the coupling mode is "AC", the input impedance is set to 1 MΩ by force,
and the Impedance menu is grayed out and cannot be modified.
Bandwidth Limit
MSO/DS7000 series supports the bandwidth limit function. Setting the bandwidth
limit can reduce the noises in the displayed waveforms. For example, the signal
under test is a pulse with high frequency oscillation.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 2-5
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System
Bandwidth of the Oscilloscope
Model
Available Bandwidth Limit
100 M (MSO7014/DS7014)
20 M
200 M (MSO7024/DS7024)
20 M
350 M and 500 M
(MSO7034/MSO7054/DS7034/DS7054)
20 M, 250 M
When the bandwidth limit is disabled, the high frequency components of the
signal under test can pass the channel.
When you enable the bandwidth limit and limit it to 20 MHz or 250 MHz, the high
frequency components found in the signal under test that are greater than 20
MHz or 250 MHz are attenuated.
Press 1 to open the setting menu of CH1.Then, press BW Limit continuously or
rotate the multifunction knob to select the desired bandwidth limit. Press down
the knob to select it. By default, it is OFF. When the bandwidth limit is enabled, the
character "B" will be displayed in the channel status label at the bottom of the screen,
as shown in the figure below. You can also enable the touch screen, and then tap the
CH1 setting menu to select the desired bandwidth limit.
The bandwidth limit that you select is based on the bandwidth of your oscilloscope
model, as shown in Table 2-1.
Table 2-1 Bandwidth Limit
Note: Bandwidth limit can not only reduce the noise, but also can attenuate or
eliminate the high frequency components of the signal.
Probe Ratio
MSO/DS7000 series allows you to set the probe attenuation manually. To obtain the
correct measurement results, you must set the probe ratio properly. By default, the
probe ratio is 1X.
Press 1 to open the setting menu of CH1.Then, press Attenuation continuously or
rotate the multifunction knob to select the desired probe ratio. You can also
enable the touch screen, and then touch the CH1 setting menu to select the desired
probe ratio. The probe ratio values available are as shown in Table 2-2.
2-6 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System RIGOL
Menu
Attenuation Ratio
(display amplitude of the signal: actual amplitude
of the signal)
0.01X
0.02X
0.05X
0.1X
0.2X
0.5X
1X (default)
2X
5X
10X
20X
50X
100X
200X
500X
1000X
50000X
0.01:1
0.02:1
0.05:1
0.1:1
0.2:1
0.5:1
1:1
2:1
5:1
10:1
20:1
50:1
100:1
200:1
500:1
1000:1
50000:1
Table 2-2 Probe Ratio
Note: After the oscilloscope auto-recognized certain probes with a fixed attenuation
ratio, the probe ratio will also be auto recognized. You do not have to set it
manually.
Input Impedance
To reduce the circuit load between the oscilloscope and the circuit under test, this
oscilloscope provides two input impedance modes: 1 MΩ (default) and 50 Ω.
1 MΩ: The input impedance of the oscilloscope is very high, and the current
flowed from the circuit under test can be ignored.
50 Ω: makes the oscilloscope match with the device whose input impedance is
50 Ω.
Press 1 to open the setting menu of CH1. Then, press Impedance continuously to
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
select the input impedance of the oscilloscope. If you select "50 Ω", the channel
status label at the bottom of the screen will display the icon .
Note:
After the oscilloscope recognizes the probe automatically, the input impedance
will also be auto recognized. You do not have to set it manually.
The setting of the input impedance will affect the ranges of channel vertical
scale and offset.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 2-7
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System
(a) "Invert" Off
(b) "Invert" On
Waveform Invert
Press 1 to open the setting menu of CH1. Then, press Invert continuously to enable
or disable the waveform invert. When enabled, the channel label is displayed, as
shown in the following figure.
When disabled, the waveform is displayed normally; when enabled, the voltage
values of the displayed waveform are inverted (as shown in Figure 2-1). Enabling the
waveform invert will also change the result of math function and waveform
measurement.
Figure 2-1 Waveform Invert
Note: When the waveform invert is enabled, the trigger edge or the trigger polarity
will change (e.g. Edge trigger, Pulse trigger, or Slope trigger).
To Set the Probe
The analog channel of this oscilloscope not only supports the common passive probe,
but also the active probe. It can automatically recognize the currently connected
probe type and its probe ratio. For detailed technical information of the probes,
please refer to the corresponding Probe User’s Guide.
Press 1 to open the setting menu of CH1. Then, press Probe to open the probe
menu. If different probes are connected to the oscilloscope, different information
about the probe will be displayed, and you can perform the different operations on
the menu.
2-8 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System RIGOL
Tip
For some of the ordinary passive probes, the oscilloscope can recognize their
probe ratio automatically. If not recognized, please refer to "Probe Ratio" to set
the probe ratio.
Tip
When a 50 Ω active probe is connected, the input impedance (refer to "Input
Impedance") of the channel will be automatically set to "50 Ω".
For the active probe, the oscilloscope can recognize the probe ratio
automatically. If the currently connected probe supports a variety of probe
ratios, please refer to "Probe Ratio" to set the probe ratio.
Passive Probe
If a passive probe is connected, for example, when RIGOL's RP3500A probe model
is connected to the oscilloscope, press Probe to open the probe menu. Its
sub-menus are grayed out and disabled.
Active Probe
If an active probe is connected, for example, when RIGOL's RP7150 probe model is
connected to the oscilloscope, press Probe to open the probe menu, and you can
operate on the menu item.
Probe Delay
To avoid measurement result errors arising from the transmission delay of the
probe cable, the oscilloscope provides the probe delay adjustment function for
the active probe. Press Skew, and then rotate the multifunction knob or
use the numeric keypad to set the probe delay time.
Bias Voltage
The oscilloscope provides the bias voltage adjustment function for active probes.
This function is used to adjust the signal under test that exceeds the input
dynamic range of the probe amplifier to an appropriate range to ensure the
integrity of the signal under test. Press Bias, rotate the multifunction knob
or use the numeric keypad to set the DC bias voltage.
Probe Information
Press About to view information about the probe currently connected, such as
the manufacturer, model, serial number, and the last calibration date.
Probe Calibration
Press Calibration to start zero calibration automatically for the probe.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 2-9
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System
Actual Trigger Position
Trigger
Level
Amplitude Unit
Select the amplitude display unit for the current channel. The available units are W, A,
V, and U. When the unit is changed, the unit related to the relevant functions of the
channel will change accordingly.
Press 1 More Unit, press Unit continuously or rotate the multifunction knob
to select a unit. You can also enable the touch screen to select the desired unit
with touch gestures. The default unit for the value is V.
Channel Delay
When using an oscilloscope for actual measurement, the transmission delay of the
probe cable may bring relatively greater errors (zero offset). MSO7000/DS7000
allows you to set a delay time for calibrating the zero offset of the corresponding
channel. Zero offset is defined as the offset of the crossing point of the waveform
and trigger level line relative to the trigger position, as shown in Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2 Zero Offset
Press 1 More Ch-Ch Skew, rotate the multifunction knob or use the
numeric keypad to set the desired delay calibration time. The available range of the
delay calibration time is from -100 ns to 100 ns.
Note: This parameter is related to the instrument model and the current horizontal
time base setting. The larger the horizontal time base is, the larger the setting
step will be.
2-10 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System RIGOL
Offset Cal
When you use an oscilloscope to make actual measurements, a small offset that
arises from the temperature drift of the component or external environment
disturbance may occur on the zero-cross voltage of the channel, which will affect the
measurement results of the vertical parameters. MSO7000/DS7000 allows you to set
an offset calibration voltage for calibrating the zero point of the corresponding
channel, so as to improve the accuracy of the measurement results.
Note: If the zero-cross voltage of the channel has a larger amplitude offset that
exceeds the adjustable null range, please perform self-calibration for the
instrument to ensure the measurement accuracy. For details, refer to
descriptions in "Self-calibration".
Press 1 More Offset Cal, rotate the multifunction knob or use the
numeric keypad to set the offset calibration value.
Channel Label
The instrument uses the channel number to mark the corresponding channel by
default. For ease of use, you can also set a label for each channel. For example,
" ".
Press 1 More Label to enter the label setting menu. You can use the built-in
label or manually input a label. Three input methods are available for you to input a
label name, including Chinese, English, and Traditional Chinese.
The label setting menu includes the following menu items.
Press Display to turn on or off the display of the channel label. If it is enabled,
the label will be displayed at the left side of the waveform. When on, CH1 is, by
default, displayed to be the channel label.
Press Library to select the preset labels such as CH1, ACK, ADDR, BIT, CLK, CS,
DATA, IN, MISO, MOSI, OUT, RX and TX.
Press Label and the label editing interface is automatically displayed as shown in
Figure 2-3. You can input the label manually. For the label input method, refer to
"To Create a Folder".
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 2-11
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 2 To Set the Vertical System
Label Input Area Input Selection Area Virtual Keypad Delete Key
Upper-lower
Case Switch
Figure 2-3 Label Editing Interface
For example, set the label to " ". In the virtual keypad, rotate the multifunction
knob to select "Caps" and press down the knob to switch the uppercase or
lowercase mode. Rotate the multifunction knob and select "C", press down the knob.
Then, in the input selection area, rotate the multifunction knob and select "C". Press
down the knob to input "C". Use the same method to input "hn1". After finishing the
input, press OK to finish the editing. You can also enable the touch screen to operate
by touch gestures. If Display is enabled, the label will be displayed at the left
of CH1 waveform.
To delete or modify the input characters, rotate the multifunction knob or enable
the touch screen to realize it.
Rotate the multifunction knob : use the delete key to delete or modify the
characters. To modify the characters, input the desired characters again.
Enable the touch screen: use the touch gestures to directly move the cursor to
the right side of the character required to be deleted or modified, and then tap
the delete key to delete the character. To modify the characters, input the
desired character again or delete the character.
2-12 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 3 To Set the Horizontal System
Decrease the timebase Increase the timebase
To Adjust the Horizontal Time Base
Horizontal time base, also called the horizontal scale, refers to the time of each grid
in the horizontal direction of the screen. It is usually expressed in s/div. The
adjustable range of the horizontal time base is related to the model type.
While you change the horizontal time base, the displayed waveforms of all channels
are expanded or compressed horizontally relative to the current selected horizontal
reference baseline (refer to "Horizontal Expansion"). The horizontal time base at
the upper-left corner of the screen will be changed accordingly, as shown in the
figure below.
You can adjust the horizontal time base with the following three methods:
Rotate Horizontal SCALE to adjust the horizontal time base within the
available range (clockwise to reduce the horizontal time base and
counterclockwise to increase).
Enable the touch screen function and adjust the horizontal time base with the
pinch & stretch gesture on the touch screen. For details, refer to the "Pinch &
Stretch" section.
Enable the touch screen function, and tap the horizontal time base label
at the top of the screen. The following window is displayed. Tap the
icon at the right side of the Timebase input field to increase or
decrease the horizontal time base. You can also tap the Timebase input field to
input a specific value with the displayed numeric keypad.
In the Horizontal control area (Horizontal), rotate the Horizontal SCALE knob
to switch the adjustment mode between "Coarse" and "Fine" (by default, it is Coarse).
You can also press Acquire More Fine to enable or disable the fine
adjustment of the horizontal time base.
Coarse adjustment: Rotate the Horizontal SCALE knob will adjust the
horizontal time base of the waveforms of all channels at 1-2-5 step within the
adjustable range. Rotate it clockwise to reduce the horizontal time base, and
counterclockwise to increase the horizontal time base.
Fine adjustment: Rotate the Horizontal SCALE knob will adjust the
horizontal time base of the waveforms of all channels with a minor step value
within the adjustable range. Rotate it clockwise to reduce the horizontal time
3-2 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 3 To Set the Horizontal System RIGOL
Decrease the position Increase the position
base, and counterclockwise to increase the horizontal time base.
Note: When the delayed sweep is enabled, rotate the Horizontal SCALE knob
to adjust the time base for the delayed sweep. The delayed sweep time base
displayed in the center of the screen will be changed accordingly, as shown in
the following figure.
To Adjust the Horizontal Position
Horizontal position, also called trigger position, refers to the trigger point position of
the waveforms of all channels in the horizontal direction relative to the screen center.
When the waveform trigger point is at the left (right) side of the screen center, the
horizontal position is a positive (negative) value.
While you change the horizontal position, the waveform trigger points and the
displayed waveforms of all channels are moved left and right. The horizontal position
at the right-upper corner of the screen changes accordingly, as shown in the figure
below.
You can adjust the horizontal position with the following three methods:
Rotate Horizontal POSITION to adjust the horizontal position of the
waveforms of all channels. When you rotate it clockwise, the waveform trigger
point moves right on the screen; when you rotate it counterclockwise, the
waveform trigger point moves left on the screen. Pressing down the knob can
quickly reset the horizontal position (reset to 0).
Enable the touch screen function and adjust the horizontal position with the
drag gesture on the touch screen. For details, refer to the "Drag" section.
Enable the touch screen function, and tap the horizontal position label
at the top of the screen. The following window is displayed. Tap the
icon at the right side of the Pos input field to increase or decrease the horizontal
position. You can also tap the Pos input field to input a specific value with the
displayed numeric keypad.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 3-3
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 3 To Set the Horizontal System
Waveform Before Enlargement
Horizontal Position of the
Delayed Sweep
Main
Time
Base
Time
Base of
the
Delayed
Sweep
Waveform After Enlargement
Note: When the delayed sweep is enabled, rotate the Horizontal POSITION
knob to adjust the horizontal position of the delayed sweep (press down the knob to
quickly reset it). The horizontal position of the delayed sweep at the upper-right
corner of the screen changes accordingly.
Delayed Sweep
Delayed sweep can be used to enlarge a length of waveform horizontally to view
waveform details.
In the horizontal control area on the front panel, press Zoom to enable or disable
the delayed sweep. By default, it is disabled. You can also press Acquire More
Zoom to enable or disable the delayed sweep function.
Note: To enable the delayed sweep, you must ensure that the current time base
mode is "YT".
In delayed sweep mode, the screen is divided into two display areas as shown in
Figure 3-1.
Figure 3-1 Delayed Sweep Mode
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
3-4 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 3 To Set the Horizontal System RIGOL
Waveform before enlargement:
The waveform in the area that is not covered by subtransparent blue in the upper
part of the screen is the waveform before enlargement. Its horizontal time base (also
called main time base) is displayed at the upper-left corner of the screen. You can
rotate the Horizontal POSITION knob to move the area left and right or rotate
the Horizontal SCALE knob to enlarge or reduce this area.
Note: If you need to modify the horizontal time base (also called main time base) of
the normal sweep, please disable the delayed sweep function first. Rotate the
Horizontal SCALE knob to set the required main time base, and then
enable the delayed sweep function.
Waveform after enlargement:
The waveform in the lower part of the screen is the horizontally expanded delayed
sweep waveform. Its horizontal time base (also called the time base of the delayed
sweep) is displayed on the screen. Compared with the main time base, the time
based of the delayed sweep has increased the waveform resolution, as shown in
Figure 3-1. At this time, you can rotate the Horizontal SCALE knob to adjust
the time base of the delayed sweep, and rotate the Horizontal POSITION
knob to adjust the horizontal position of the delayed sweep.
Note: The time base of the delayed sweep should be smaller than or equal to the
main time base.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 3-5
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System
II I
III IV
A
B
C
D
Signal must be
centered horizontally
Timebase Mode
MSO7000/DS7000 series supports three available time base modes: YT mode, XY
mode, and ROLL mode. By default, the time base mode is YT.
Press Acquire Timebase Mode on the front panel, and then rotate the
multifunction knob to select the desired time base mode. Then, press down the
knob to select the mode. You can also press Timebase Mode continuously to select
the mode or enable the touch screen to tap the desired mode and select it.
YT Mode
In this mode, the Y axis represents voltage, and the X axis represents time.
Note: Only when this mode is enabled, can delayed sweep be turned on. In this
mode, when the horizontal time base is equal to or greater than 200 ms/div,
the instrument enters slow sweep mode. For details, refer to descriptions in
"ROLL Mode".
XY Mode
In this mode, both the X axis and the Y axis represent the voltage. The mode
changes the display from voltage-time display mode to voltage-voltage display. You
can use the Lissajous method to measure the phase deviation of the two input
signals whose frequencies are the same. The following figure shows the
measurement schematic diagram of phase deviation.
Figure 4-1 Measurement Schematic Diagram of Phase Deviation
4-2 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System RIGOL
According to sin=A/B or C/D, is the phase deviation angle between the two
channels. The definitions of A, B, C, and D are shown in the above figure. The phase
deviation angle is obtained, that is:
=arcsin(A/B) or arcsin(C/D)
If the principal axis of the ellipse is within Quadrant I and III, the phase deviation
angle obtained should be within Quadrant I and IV, namely within (0 to π/2) or (3π/2
to 2π). If the principal axis of the ellipse is within Quadrant II and IV, the phase
deviation angle obtained should be within Quadrant II and III, namely within (π/2 to
π) or (π to 3π/2).
The XY function can be used to measure the phase deviation occurred when the
signal under test passes through a circuit network. Connect the oscilloscope to the
circuit to monitor the input and output signals of the circuit.
Application example: measures the phase deviation between the input signals of
two channels.
Use Lissajous method
1. Connect one sine signal to CH1, and then connect another sine signal (with the
same frequency and amplitude as the previous one but a 90° phase deviation
from the previous one) to CH2.
2. Press AUTO, after you select "XY" mode, rotate the Horizontal SCALE to
adjust the sample rate properly to obtain a better view of Lissajous graph for
observation and measurement.
3. Rotate the Vertical SCALE knob that corresponds to CH1 and CH2
respectively to make the signals easy to observe. Then, a circle, as shown in the
figure below, should be displayed.
4. Observe the measurement result shown in the figure above. According to the
measurement schematic diagram of the phase deviation (as shown in Figure
4-1), A/B(C/D)=1. Thus, the phase deviation angle of the two channel input
signals is =arcsin1=90°.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 4-3
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System
Slow Sweep
It is similar to the ROLL mode. In YT mode, when the horizontal time base is set to
200 ms/div or smaller, the instrument enters the "slow sweep" mode in which the
instrument first acquires the data at the left of the trigger point and then waits for
a trigger event. After the trigger occurs, the instrument continues to finish the
waveform at the right of the trigger point. When observing the low-frequency
signal in the slow sweep mode, it is recommended that you set "Channel
Coupling" to "DC".
Note:
The maximum sample rate in XY mode is 2.5 GSa/s. In this mode, CH1 and CH2
are forced to be enabled; CH3 and CH4 are forced to be disabled. Generally, a
longer sample waveform can ensure better display effect of Lissajous figure. But
due to the limitation of the memory depth, you have to reduce the waveform
sample rate to acquire a longer waveform (refer to the introduction in "Memory
Depth"). Therefore, during the measurement, reducing the sample rate
properly can achieve better display effect of Lissajous figure.
The following functions are disabled in XY mode:
"Delayed Sweep", "Vector display", "Scale", "Protocol Decoding",
"Acquisition Mode", "Pass/Fail Test", "Waveform Recording &
Playing", "Digital Channel", and "To Set the Persistence Time".
ROLL Mode
In this mode, the waveform scrolls from right to left to update the display. The
available range of the horizontal scale is from 200 ms to 1 ks. Press More Auto
ROLL to select "ON". The system automatically enters the ROLL mode, and there is
no slow sweep.
Note:
If the current delayed sweep is enabled, then when you enable the ROLL mode,
the delayed sweep is disabled automatically. When you re-enable the "YT" mode,
the delayed sweep will be re-enabled.
The following functions cannot be set in ROLL mode:
"To Adjust the Horizontal Position" (available when the oscilloscope is in
"Stop" operating status), "Delayed Sweep", "To Trigger the Oscilloscope",
"Protocol Decoding", "Pass/Fail Test", "Waveform Recording &
Playing", and "To Set the Persistence Time".
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
4-4 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System RIGOL
Acquisition Mode
The acquisition mode is used to control how to generate waveform points from the
sample points.
MSO7000/DS7000 supports the following three acquisition modes: Normal, Average,
and Peak. By default, the acquisition mode is Normal.
Press Acquire Acquisition on the front panel, and then rotate the multifunction
knob to select the desired acquisition mode. Then, press down the knob to
select the mode. You can also press Acquisition continuously to select the mode or
enable the touch screen to tap the desired mode and select it.
Normal
In this mode, the oscilloscope samples the signal at a specified fixed time interval to
rebuild the waveform. For most of the waveforms, using this mode can produce the
optimal display effects.
Average
In this mode, the oscilloscope averages the waveforms from multiple samples to
reduce the random noise of the input signal and improve the vertical resolution.
Greater number of averages can lower the noise and increase the vertical resolution;
while at the same time, it will slow the response of the displayed waveform to the
waveform changes.
When you select "Average" mode, press Averages and rotate the multifunction
knob or use the numeric keypad to set the desired number of averages. You can
also use the pop-up numeric keypad to input the average count. When the average
count value is in power-of-2 increments, a prompt message "Trim average count" is
displayed. At this time, a value that is smaller than the one you input and the closest
to power-of-2 increments will be input automatically. For example, if you input 9 with
the numeric keypad, the average count will be input 8 automatically.
The number of averages can be set to 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048,
4096, 8192, 16384, 32768, or 65536. By default, it is 2.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 4-5
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System
Figure 4-2 Waveforms before Averaging
Figure 4-3 Waveforms after 128 Times of Averaging
Peak
In this mode, the oscilloscope acquires the maximum and minimum values of the
signal within the sample interval to get the envelope of the signal or the narrow pulse
that might be lost. In this mode, signal aliasing can be prevented, but the noise
displayed would be larger.
In this mode, the oscilloscope can display all the pulses whose pulse widths are at
least the same as the sample period.
Sampling Mode
This oscilloscope only supports the real-time sampling mode. In this mode, the
oscilloscope produce the waveform display from samples collected during one trigger
4-6 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System RIGOL
Tip
Press RUN/STOP on the front panel to stop sampling, and then the oscilloscope
will maintain its last captured graph. You can still expand or zoom the waveforms
by using the horizontal and vertical control knobs.
Tip
Single-channel mode: only one of the four channels (CH1/CH2/CH3/CH4) is
enabled.
Dual-channel mode: either CH1 or CH2 is enabled; and either CH3 or CH4 is
enabled.
4-channel mode: CH1/CH2 are both enabled or CH3/CH4 are both enabled.
event. The highest real-time sample rate on the analog channel of MSO7000/DS7000
series is 10 GSa/s. The current sample rate is displayed under CH Sa Rate.
Sample Rate
Sampling is the process of converting the analog signal into the digital signal at a
specified time interval and then restoring them in sequence. The sample rate is the
reciprocal of the time interval.
The sample rate of the analog channel is related to the current channel mode. The
maximum real-time sample rate in the single-channel mode of the oscilloscope is 10
GSa/s. The maximum real-time sample rate in the dual-channel mode is 5 GSa/s, and
the maximum real-time sample rate in the 4-channel mode is 2.5 GSa/s.
Note: The sample rate is displayed both in the status bar at the upper part of the
screen and in the CH Sa Rate menu. To indirectly modify the sample rate,
rotate the Horizontal SCALE knob to adjust the horizontal time base or
modify the memory depth.
The impact of low sample rate on the waveform:
1. Waveform Distortion: when the sample rate is too low, some waveform
details are lost, and the sample waveform displayed is rather different from the
actual waveform of the signal.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 4-7
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System
Pulse
disappeared
2. Waveform Aliasing: when the sample rate is twice lower than the actual
signal frequency (Nyquist Frequency), the frequency of the waveform rebuilt from
the sample data is smaller than the actual signal frequency.
3. Waveform Leakage: when the sample rate is too low, the waveform rebuilt
from the sample data does not reflect all the actual signal information.
LA Sample Rate
LA sampling is the process of sampling on the compared digital signals at a certain
time interval. LA sample rate is the reciprocal of the time interval. For example, if the
LA sample rate is 500 MSa/s, it indicates that the oscilloscope will make data
acquisition on the digital signals at an interval of 2 ns. The maximum LA sample rate
of the oscilloscope is 1.25 GSa/s, and its display value is related to the sample rate of
the current analog channel.
Note:
1. The digital signals here mentioned refers to the signal obtained from the
comparison between the input signal and the user-defined threshold level. The
rule of the comparison is that when the amplitude of the input signal is greater
than the threshold level, it is judged to be the logic high level; when the
amplitude of the input signal is smaller than the threshold level, it is judged to
be the logic low level.
4-8 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System RIGOL
T
Trigger Point
Pre-sample Delayed Sample
Memory Depth
MDepth SRate TScale HDivs
MDepth
SRate
TScale
HDivs
2. LA sample rate is displayed under the LA Sa Rate menu. To indirectly modify
the LA sample rate, rotate the Horizontal SCALE knob to adjust the
horizontal time base or modify the memory depth.
Memory Depth
Memory depth refers to the number of points of the oscilloscope that can store in one
trigger acquisition. It reflects the storage capability of the acquisition storage. This
oscilloscope is equipped with a standard memory depth of up to 500 Mpts.
Figure 4-4 Memory Depth
The following equation shows the relations among memory depth, sample rate, and
horizontal time base scale:
——indicates the memory depth. The unit is pts.
——indicates the sample rate. The unit is Sa/s.
——indicates the horizontal time base scale. The unit is s/div.
——indicates the number of grids in the horizontal direction. The unit is div.
Therefore, under the same horizontal time base scale, a higher memory depth can
ensure a higher sample rate.
Press Acquire Mem Depth, then rotate the multifunction knob to switch to
the desired memory depth, and then press down the knob to select the option. You
can also press the Mem Depth key continuously or enable the touch screen to
select the memory depth. By default, the memory depth is Auto.
For analog channels:
― In single-channel mode, the memory depths available include Auto, 1 Kpts, 10
Kpts, 100 Kpts, 1 Mpts, 10 Mpts, 25 Mpts, 50 Mpts, 100 Mpts, 125 Mpts
(optional), 250 Mpts (optional), and 500 Mpts (optional).
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 4-9
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System
― In dual-channel mode, the memory depths available include Auto, 1 Kpts, 10
Kpts, 100 Kpts, 1 Mpts, 10 Mpts, 25 Mpts, 50 Mpts, 100 Mpts, 125 Mpts
(optional), and 250 Mpts.
― In 4-channel mode, the memory depths available include Auto, 1 Kpts, 10 Kpts,
100 Kpts, 1 Mpts, 10 Mpts, 25 Mpts, 50 Mpts, 100 Mpts, and 125 Mpts
(optional).
Note: In "Auto" mode, the oscilloscope selects the memory depth automatically
according to the current sample rate.
LA Memory Depth
Press Acquire More to view the memory depth of the current digital channel
under LA Mem Depth. The LA memory depth will change with the memory depth of
the analog channel, and cannot be set separately. The maximum LA memory depth is
62.5 Mpts.
Anti-Aliasing
At a slower sweep speed, the sample rate is reduced, and a dedicated display
algorithm can be used to minimize the possibility of aliasing.
Press Acquire Anti-aliasing to enable or disable the anti-aliasing function. By
default, anti-aliasing is disabled. In this case, it is more likely to generate waveform
aliasing.
Note: This function should be enabled when the horizontal time base has a large
deviation from the period of the signal under test (e.g. when the horizontal
time base is greater than five-fold the period of the signal under test).
Horizontal Expansion
Horizontal expansion indicates the reference position that the screen waveform is
referenced to when it is horizontally expanded or compressed in adjusting the
Horizontal SCALE knob. In YT mode, press Acquire More Expand and
then rotate the multifunction knob to select the desired reference position. Press
down the knob to select it. You can also press Expand continuously to select it or
enable the touch screen to tap the desired reference. The horizontal expansion
reference supported by the oscilloscope includes Center, Left, Right, Trigger, and User.
The default is "Center".
Center: when the horizontal time base is modified, the waveform will be
4-10 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 4 To Set the Sample System RIGOL
expanded or compressed horizontally relative to the screen center.
Left: when the horizontal time base is modified, the waveform will be expanded
or compressed horizontally relative to the leftmost position of the screen.
Right: when the horizontal time base is modified, the waveform will be
expanded or compressed horizontally relative to the rightmost position of the
screen.
Trigger: when the horizontal time base is modified, the waveform will be
expanded or compressed horizontally relative to the trigger point.
User: when the horizontal time base is modified, the waveform displayed will be
expanded or compressed horizontally relative to the user-defined reference
position.
After you select "User", press Expand User and then rotate the multifunction
knob to set the expansion reference. Its available range is from the
rightmost position of the screen to the leftmost position of the screen. By default,
it is the screen center. Pressing down the multifunction knob can quickly
reset the user-defined reference position to 0.
Note: This function is unavailable in YT mode with the delayed sweep being enabled,
XY mode, and ROLL mode.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 4-11
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
As for trigger, you set certain trigger condition according to the requirement and
when a waveform in the waveform stream meets this condition, the oscilloscope
captures this waveform as well as the neighboring part, and displays them on the
screen. For the digital oscilloscope, it samples waveform continuously no matter
whether it is stably triggered, but only stable trigger can be stably displayed. The
trigger module ensures that every time base sweep or acquisition starts from the
user-defined trigger condition, namely every sweep is synchronous with the
acquisition and the waveforms acquired is overlapped so as to display the stable
waveforms.
Trigger settings should be based on the features of the input signal. To quickly
capture the desired waveform, you need to understand the signal under test. This
oscilloscope provides abundant trigger types that help you focus on the desired
waveform details.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-1
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Trigger Source
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Menu Source to
select the desired source, or rotate the multi-function knob to select a desired
source, then press down the knob to select it. You can also press Source
continuously to select the trigger source or enable the touch screen to tap the
desired trigger source and select it.
Analog channels (CH1-CH4), digital channels (D0-D15, available for the MSO7000
series), EXT (external trigger), or AC Line can all be selected as the trigger source.
Analog channel input:
Signals input from analog channels CH1-CH4 can all be used as trigger sources. No
matter whether the channel selected is enabled, the channel can work normally.
Digital channel input:
Signals input from digital channels D0-D15 can all be used as trigger sources. No
matter whether the channel selected is enabled, the channel can work normally.
External trigger input:
The external trigger source can be used to trigger on the fifth channel while all the
other four channels are acquiring data. The trigger signal (e.g. external clock or
signal of the circuit under test) will be connected to EXT trigger source via the
external trigger input terminal [EXT TRIG] connector. You can set the trigger
conditions within the range of the trigger level (from 8 V to +8 V).
AC line input:
The trigger signal is obtained from the AC power input of the oscilloscope. AC trigger
is usually used to measure signals relevant to the AC power frequency. For example,
stably triggering the waveform output from the transformer of a transformer
substation. It is mainly used in related measurements of the power industry.
5-2 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level
The adjustment of the trigger level/threshold level is related to the type of the trigger
source.
When the trigger source is selected from CH1 to CH4, rotate the Trigger
LEVEL knob to adjust the trigger level. During the adjustment, a trigger level
line (the color of the trigger level line should be consistent with that of the
channel color) and a trigger label " " are displayed on the screen, and they
move up and down with the variation of the trigger level. When you stopping
modifying the trigger level, the trigger level line disappears in about 2 s. The
current trigger level value is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Note: In Runt Trigger, Slope Trigger, and Window trigger, you need to set the
upper and lower limits of the trigger level. You can modify the level by rotating
the Trigger LEVEL knob. The difference between the current upper limit
and lower limit of the trigger level is displayed at the upper-right side of the
screen. Two trigger level labels ( and ) are displayed at the left side of the
screen. Meanwhile, the real-time trigger level information is displayed at the
lower-left side of the screen, as shown in the figure below. H indicates the upper
limit of the trigger level, L indicates the lower limit of the trigger level, and △
indicates the deviation of the trigger level.
When the trigger source is EXT, rotate the Trigger LEVEL knob to adjust
the trigger level. The current trigger level value is displayed at the upper-right
corner of the screen.
Note: For this trigger source, only the variation of the trigger level value is
displayed on the screen during the adjustment of the trigger level, without
displaying the trigger level lines on the screen.
When the trigger source is AC Line, there is no trigger level.
When the trigger source is selected from D0 to D15, rotate the Trigger
LEVEL knob to adjust the threshold level. The current threshold level value is
displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen. In addition, you can also press
LA to enter the LA logic analysis setting menu. Then set the threshold level of
the digital channel in the sub-menu threshold setting. For the setting method,
refer to "To Set the Threshold".
You can also enable the touch screen function to adjust the trigger
level/threshold level. Two methods are available for you:
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-3
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Pre-trigger Buffer
Post-trigger Buffer
Trigger Event
Acquisition Memory
Level Input Field Decrease the level Increase the level
Method 1: Enable the touch screen and drag the trigger level line to adjust the
trigger level. For details about the operations, refer to descriptions in "Drag"
section.
Method 2: Enable the touch screen function, and tap the trigger setting label
at the upper-right corner of the screen. The following window is
displayed. Tap the icon at the right side of the Level input field to
increase or decrease the trigger level. You can also tap the Level input field to
input a specific value with the displayed numeric keypad.
Trigger Mode
The following is the schematic diagram of the acquisition memory. To easily
understand the trigger event, we classify the acquisition memory into the pre-trigger
buffer and post-trigger buffer.
Figure 5-1 Schematic Diagram of the Acquisition Memory
After the system runs, the oscilloscope operates by first filling the pre-trigger buffer.
It starts searching for a trigger after the pre-trigger buffer is filled. While searching
for the trigger, the data sampled will still be transmitted to the pre-trigger buffer (the
new data will continuously overwrite the previous data). When a trigger is found, the
pre-trigger buffer contains the data acquired just before the trigger. Then, the
oscilloscope will fill the post-trigger buffer and display the data in the acquisition
memory. If the acquisition is activated via RUN/STOP, the oscilloscope will repeat
this process; if the acquisition is activated via SINGLE, the oscilloscope will stop
after finishing a single acquisition (you can pan and zoom the currently displayed
waveform).
5-4 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
MSO7000/DS7000 provides three trigger modes: Auto, Normal, and Single. The
default is Auto.
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Mode to quickly switch
the current trigger mode. The trigger mode is displayed at the upper-right corner of
the screen: A (Auto), N (Normal), and S (Single).
Auto: In this trigger mode, if the specified trigger conditions are not found, triggers
are forced and acquisitions are made so as to display the waveforms. This trigger
mode should be used when the signal level is unknown or the DC should be
displayed as well as when forcible trigger is not necessary as the trigger condition
always occurs.
Normal: In this trigger mode, triggers and acquisitions only occur when the specified
trigger conditions are found. This trigger mode should be used when the signal is
with low repetition rate or only the event specified by the trigger setting needs to be
sampled as well as when auto trigger should be prevented to acquire stable display.
Single: In this trigger mode, the oscilloscope performs a single trigger and
acquisition when the specified trigger conditions are found, and then stops. This
trigger mode should be used when you need to perform a single acquisition of
the specified event and analyze the acquisition result (you can pan and zoom
the currently displayed waveform, and the subsequent waveform data will not
overwrite the current waveform). After a single trigger mode is initiated, the
operating status of the oscilloscope is in "STOP" state.
Note: In "Normal" and "Single" trigger modes, pressing Force can generate a
trigger signal forcibly.
In addition, you can enable the touch screen to set the trigger mode. Enable the
touch screen and tap the trigger setting label at the upper-right
corner of the screen. Then the following window is displayed. Tap to select "Auto",
"Normal", or "Single" as the trigger mode.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-5
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Tip
When "AC" or "LFR" is selected under Coupling, no trigger level lines and trigger
icons are displayed. When you adjust the trigger level, you can only see the changes
of the trigger level values at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Holdoff Time
Trigger Position
t1
t2
Trigger Coupling
Trigger coupling decides which kind of components will be transmitted to the trigger
module. Please distinguish it from "Channel Coupling".
Note: Trigger coupling is only valid when the trigger type is Edge and the trigger
source is an analog channel.
Press Menu Coupling in the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel.
Then, rotate the multifunction knob to select the desired coupling mode (by
default, it is DC). You can also press Coupling continuously to select it or enable the
touch screen to select the desired coupling mode with touch gestures.
DC: allows DC and AC components to pass the trigger path.
AC: blocks the DC components and attenuates signals.
LFR: blocks the DC components and rejects the low-frequency components.
HFR: rejects the high frequency components.
Trigger Holdoff
Trigger holdoff can be used to stably trigger on complex repetitive waveforms that
have multiple edges (or other events) between waveform repetitions (such as pulse
series). Holdoff time indicates the time that the oscilloscope waits for re-arming the
trigger module after generating a correct trigger. The oscilloscope will not trigger
even if the trigger condition is met during the holdoff time and will only re-arm the
trigger module after the holdoff time expires.
For example, to stably trigger the repetitive pulse series as shown in the figure below,
the holdoff time should be set to a value that is greater than t1 and smaller than t2.
Figure 5-2 Schematic Diagram of Trigger Holdoff
5-6 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Menu Holdoff (for
some trigger, Holdoff is a sub menu under More, at this time, press Menu More
Holdoff) and then rotate the multifunction knob at a small step to modify the
holdoff time (the holdoff to this time when the waveforms are stably triggered; by
default, the holdoff time is 16 ns). Also, you can use the numeric keypad to set the
holdoff time. The adjustable range of holdoff time is from 8 ns to 10 s.
Noise Rejection
Noise rejection can reject the high frequency noise in the signal and reduce the
possibility of miss-trigger of the oscilloscope.
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Menu to enter the
trigger setting menu, then press Noise Reject continuously (for some trigger,
Noise Reject is a sub menu under More, at this time, press Menu More
Noise Reject) to enable or disable noise rejection.
Note: This function is only available when the trigger source is an analog channel.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-7
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Trigger Type
MSO7000/DS7000 series ocilloscope provides the following trigger functions (all the
triggers are hardware triggers, except the zone trigger).
Edge Trigger
Pulse Trigger
Slope Trigger
Video Trigger
Pattern Trigger
Duration Trigger
Timeout Trigger
Window Trigger
Delay Trigger
Setup/Hold Trigger
Nth Edge Trigger
RS232 Trigger (Option)
I2C Trigger (Option)
SPI Trigger (Option)
CAN Trigger (Option)
FlexRay Trigger (Option)
LIN Trigger (Option)
I2S Trigger (Option)
MIL-STD-1553 Trigger (Option)
Zone Trigger
5-8 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
Edge Trigger
Triggers on the trigger level/threshold level of the specified edge of the input signal.
Trigger Type:
Press Menu Type in the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel and
rotate the multifunction knob to select "Edge", then press down the knob to
select it. You can also press Type continuously or enable the touch screen to tap the
desired trigger type and select it. At this time, the current trigger setting information
(including trigger type, trigger source, and trigger level/threshold level) is displayed
at the upper-right corner of the screen, as shown in the figure below. The
information will change based on the trigger settings.
Source Selection:
Press Source to open the signal source list and select CH1-CH4, AC Line, EXT, or
D0-D15. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Source". The current trigger
source is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Note: Only when we select the channel (that has been input with signals) as the
trigger source, can we obtain a stable trigger.
Edge Type:
Press Slope, and then rotate the multifunction knob to select the input signal
the edge on which the oscilloscope triggers. Then, the current edge type is displayed
at the upper-right corner of the screen. You can also press the Slope key
continuously or enable the touch screen to select the desired edge type.
Rising: triggers on the rising edge of the input signal when the voltage level
meets the specified trigger level.
Falling: triggers on the falling edge of the input signal when the voltage level
meets the specified trigger level.
Either: triggers on the rising or falling edge of the input signal when the
voltage level meets the preset trigger level.
Trigger Mode:
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Mode to quickly switch
the current trigger mode. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Mode".
Trigger Parameter Setting:
Set the trigger parameters (trigger coupling, trigger holdoff, and noise rejection)
under this trigger type. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Coupling",
"Trigger Holdoff", and "Noise Rejection".
Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level:
Rotate the Trigger LEVEL knob to adjust the trigger level or threshold level.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-9
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
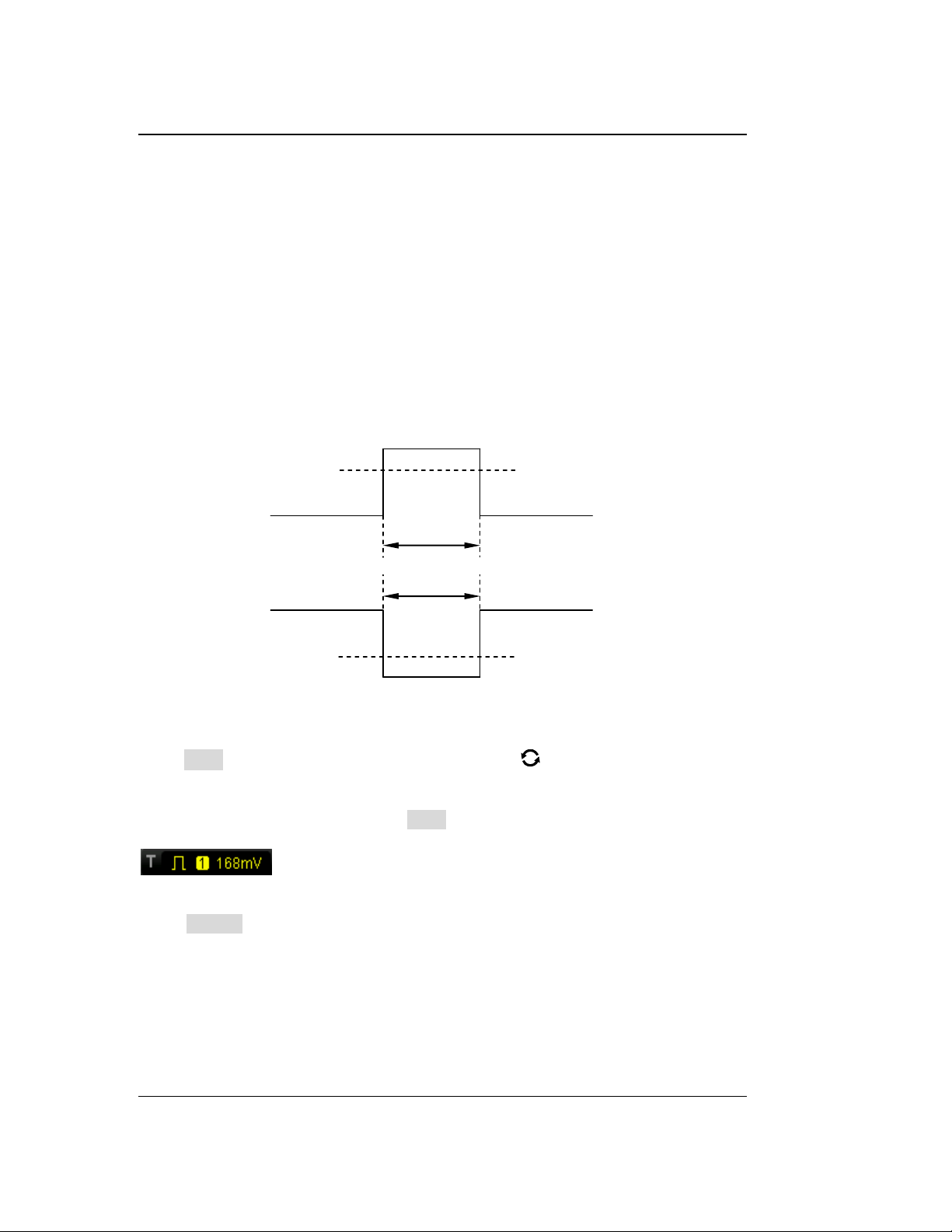
RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Trigger
Level
Trigger
Level
+Width
A
B
-Width
A
B
Please refer to descriptions in "Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level". The current
trigger level/threshold level value is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Pulse Trigger
Triggers on the positive or negative pulse with a specified width. In this mode, the
oscilloscope will trigger when the pulse width of the input signal satisfies the
specified pulse width condition.
In this oscilloscope, positive pulse width is defined as the time difference between
the two crossing points of the trigger level and positive pulse; negative pulse width is
defined as the time difference between the two crossing points of the trigger level
and negative pulse, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 5-3 Positive Pulse Width/Negative Pulse Width
Trigger Type:
Press Type, and then rotate the multifunction knob to select "Pulse". Press
down the knob to select the trigger type. Then, the current trigger setting
information is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen, as shown in the
figure below. You can also press the Type key continuously or enable the touch
screen to select the desired trigger type.
Source Selection:
Press Source to open the signal source list and select CH1-CH4 or D0-D15. For
details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Source". The current trigger source is
displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Note: Only when we select the channel (that has been input with signals) as the
trigger source, can we obtain a stable trigger.
5-10 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
Polarity:
Press Polarity continuously to select the desired polarity. The polarities available are
positive polarity ( ) and negative polarity ( ).
Trigger Condition:
Press When, then rotate the multifunction knob to select the trigger condition,
and then press down the knob to select the trigger condition. You can also press
When continuously to select the trigger condition or enable the touch screen to tap
the desired trigger condition and select it.
When you select "Positive" for polarity, ">" for trigger condition, the oscilloscope
triggers when the positive pulse width of the input signal is greater than the
specified pulse width.
When you select "Positive" for polarity, "<" for trigger condition, the oscilloscope
triggers when the positive pulse width of the input signal is smaller than the
specified pulse width.
When you select "Positive" for polarity, "<>" for trigger condition, the
oscilloscope triggers when the positive pulse width of the input signal is greater
than the specified lower limit of pulse width and smaller than the specified
upper limit of pulse width.
When you select "Negative" for polarity, ">" for trigger condition, the
oscilloscope triggers when the negative pulse width of the input signal is greater
than the specified pulse width.
When you select "Negative" for polarity, "<" for trigger condition, the
oscilloscope triggers when the negative pulse width of the input signal is smaller
than the specified pulse width.
When you select "Negative" for polarity, "<>" for trigger condition, the
oscilloscope triggers when the negative pulse width of the input signal is greater
than the specified lower limit of pulse width and smaller than the specified
upper limit of pulse width.
Pulse Width Setting:
When ">" or "<" is set to the trigger condition, press Lower or Upper, and
then rotate the multifunction knob to set the desired value; or press down the
multifunction knob to set the lower limit value or the upper limit value. You
can also use the pop-up numeric keypad to set it. The pulse range available is
from 800 ps to 10 s.
When "<>" is set to the trigger condition, press Upper and Lower, and then
rotate the multifunction knob to set the lower limit value and the upper limit
value. You can also use the pop-up numeric keypad to set them.
Note: The lower limit of the pulse width must be smaller than the upper limit.
Trigger Mode:
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Mode to quickly switch
the current trigger mode. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Mode".
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-11
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Upper Limit of Trigger Level
(Up Level)
Lower Limit of Trigger Level
(Low Level)
A
B
Positive Slope Time
Negative Slope Time
Trigger Parameter Setting:
Set the trigger parameters (trigger holdoff and noise rejection) under this trigger
type. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Holdoff" and "Noise
Rejection".
Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level:
Rotate the Trigger LEVEL knob to adjust the trigger level or threshold level.
Please refer to descriptions in "Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level". The current
trigger level/threshold level value is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Slope Trigger
In Slope trigger, the oscilloscope triggers on the positive or negative slope of the
specified time. This trigger mode is applicable to ramp and triangle waveforms.
In this oscilloscope, positive slope time is defined as the time difference between the
two crossing points of trigger level line A and B with the rising edge; negative slope
time is defined as the time difference between the two crossing points of trigger level
line A and B with the falling edge, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 5-4 Positive Slope Time/Negative Slope Time
Trigger Type:
Press Type, and then rotate the multifunction knob to select "Slope". Press
down the knob to select the trigger type. Then, the current trigger setting
information is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen, as shown in the
figure below. You can also press Type continuously or enable the touch screen to tap
the desired trigger type and select it.
Source Selection:
Press Source to switch the trigger source and select CH1-CH4. For details, refer to
descriptions in "Trigger Source". The current trigger source is displayed at the
upper-right corner of the screen.
Note: Only when we select the channel (that has been input with signals) as the
trigger source, can we obtain a stable trigger.
5-12 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
Edge Type:
Press Slope continuously to select the input signal edge on which the oscilloscope
triggers.
Rising: triggers on the rising edge of the input signal.
Falling: triggers on the falling edge of the input signal.
Slope Condition:
Press When, then rotate the multifunction knob to select the trigger condition,
and then press down the knob to select the trigger condition. You can also press
When continuously to select the trigger condition or enable the touch screen to tap
the desired trigger condition and select it.
When you select "Rising" for the edge type, ">" for trigger condition, the
oscilloscope triggers when the positive slope time of the input signal is greater
than the specified time.
When you select "Rising" for the edge type, "<" for trigger condition, the
oscilloscope triggers when the positive slope time of the input signal is smaller
than the specified time.
When you select "Rising" for the edge type, "<>" for trigger condition, the
oscilloscope triggers when the positive slope time of the input signal is greater
than the specified lower limit time and smaller than the specified upper limit
time.
When you select "Falling" for the edge type, ">" for trigger condition, the
oscilloscope triggers when the negative slope time of the input signal is greater
than the specified time.
When you select "Falling" for the edge type, "<" for trigger condition, the
oscilloscope triggers when the negative slope time of the input signal is smaller
than the specified time.
When you select "Falling" for the edge type, "<>" for trigger condition, the
oscilloscope triggers when the negative slope time of the input signal is greater
than the specified lower limit time and smaller than the specified upper limit
time.
Slope Time Setting:
When ">" or "<" is set to trigger condition, press Lower or Upper, and then
rotate the multifunction knob to set the lower limit value or the upper limit
value. You can also use the pop-up numeric keypad to set it. The available range
of the slope time is from 800 ps to 10 s.
When "<>" is set to trigger condition, press Upper and Lower, and then rotate
the multifunction knob to set the upper limit value and the lower limit value.
You can also use the pop-up numeric keypad to set them.
Note: The lower slope time limit must be smaller than the upper slope time
limit.
Level Selection and Adjustment of Trigger Level:
After the trigger condition setting is completed, you need to adjust the trigger level
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-13
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
to correctly trigger the signal and obtain a stable waveform. Press Level Select
(when "<>" is selected as the trigger condition, Level Select is a sub-menu under
More), then rotate the multifunction knob to select the desired level type for
adjustment, and then press down the knob to select the type. You can also press
Level Select continuously to select the level type or enable the touch screen to tap
the desired level type and select it.
Level A: only adjusts the upper limit of the trigger level, and the lower limit of
the trigger level remains unchanged.
Level B: only adjusts the lower limit of the trigger level, and the upper limit of
the trigger level remains unchanged.
Level AB: adjusts the upper and lower limits of the trigger level at the same time,
and the trigger level deviation (the difference between the upper limit and lower
limit of the trigger level) remains unchanged.
Note: In Slope trigger, pressing Trigger LEVEL can quickly switch the current
level adjustment type.
Rotate the Trigger LEVEL knob to adjust the corresponding trigger level. During
the adjustment of trigger level, two trigger level lines appear on the screen, and they
move up and down with the change of the trigger level. At the same time, the
real-time trigger level information is displayed at the lower-left corner of the screen
(as shown in the figure below, H indicates the upper limit of the trigger level, L
indicates the lower limit of the trigger level, and △ indicates the trigger level
deviation). When you stopping modifying the trigger level, the trigger level line and
the trigger level information at the lower-left corner of the screen disappear in about
2 s. The current trigger level deviation is displayed at the upper-right corner of the
screen.
Trigger Mode:
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Mode to quickly switch
the current trigger mode. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Mode".
Trigger Parameter Setting:
Set the trigger parameters (trigger holdoff and noise rejection) under this trigger
type. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Holdoff" and "Noise
Rejection".
5-14 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
Video Trigger
The video signal can include image information and timing information, which adopts
different standards and formats. MSO7000/DS7000 series can trigger on the
standard video signal field or line of NTSC (National Television Standards Committee),
PAL (Phase Alternating Line), or SECAM (Sequential Couleur A Memoire).
Trigger Type:
Press Type, and then rotate the multifunction knob to select "Video". Press
down the knob to select the trigger type. Then, the current trigger setting
information is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen, as shown in the
figure below. You can also press Type continuously or enable the touch screen to tap
the desired trigger type and select it.
Source Selection:
Press Source to switch the trigger source and select CH1-CH4. For details, refer to
descriptions in "Trigger Source". The current trigger source is displayed at the
upper-right corner of the screen.
Note: Only when we select the channel (that has been input with signals) as the
trigger source, can we obtain a stable trigger.
Video Polarity:
Press Polarity continuously to select the desired video polarity. The polarities
available are positive polarity ( ) and negative polarity ( ).
Video Standard:
Press Standard and rotate the multifunction knob to select the desired video
standard. You can also press Standard continuously to select the video standard or
enable the touch screen to tap the desired video standard and select it.
NTSC: indicates that the field frequency is 60 fields per second, and the frame
frequency is 30 frames per second. The TV scan line is 525, with the even field
going first and the odd field following behind.
PAL/SECAM:
PAL: indicates that the frame frequency is 25 frames per second. The TV
scan line is 625, with the odd field going first and the even field following
behind.
SECAM: indicates that the frame frequency is 25 frames per second. The TV
scan line is 625 with interlaced scan.
480P: indicates that the frame frequency is 60 frames per second. The TV scan
line is 525, with progressive scan; the line frequency is 31.5 kHz.
576P: indicates that the frame frequency is 60 frames per second. The TV scan
line is 625; with progressive scan.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-15
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Tip
For a better observation of the waveform details in the video signal, you can
set a larger memory depth first.
In the trigger debugging process of video signals, the frequency in different
part of the signal can be reflected by a different brightness, as RIGOL digital
oscilloscope provides the intensity graded color display function. Experienced
users can quickly judge the signal quality and discover abnormalities during
the debugging process.
Sync:
Press Sync, then rotate the multifunction knob to select the sync type, and then
press down the knob to select the type. You can also press Sync continuously to
select the sync type or enable the touch screen to tap the desired sync type and
select it.
All Lines: triggers on the first line found.
Line: for NTSC and PAL/SECAM video standards, trigger on the specified line.
When this sync type is selected, you can specify a line number. Press Line, then
rotate the multifunction knob or use the pop-up numeric keypad to modify
the line number. The range of the line number is related to the currently selected
video standards. The range is from 1 to 525 (NTSC), 1 to 625 (PAL/SECAM), 1 to
525 (480P), and 1 to 625 (576P).
Odd: triggers on the rising edge of the first ramp pulse in the odd field.
Even: triggers on the rising edge of the first ramp pulse in the even field.
Noise Rejection:
Set the trigger parameter (noise rejection) under this trigger type. For details, refer
to descriptions in "Noise Rejection".
Trigger Mode:
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Mode to quickly switch
the current trigger mode. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Mode".
Trigger Setting:
Press Noise Reject to set the trigger parameter (noise rejection) under this trigger
type. For details, refer to descriptions in "Noise Rejection".
Trigger Level:
Use Trigger LEVEL to modify the level. For details, refer to descriptions in
"Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level".
5-16 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
Pattern Trigger
Identifies a trigger condition by searching for a specified pattern. This pattern is a
logical "AND" combination of channels. Each channel can be set to H (high), L (low),
or X (don't care). A rising or falling edge (you can only specify a single edge) can be
specified for one channel included in the pattern. When an edge is specified, the
oscilloscope will trigger at the edge specified if the pattern set for the other channels
are true (namely the actual pattern of the channel is the same as the preset pattern).
If no edge is specified, the oscilloscope will trigger on the last edge that makes the
pattern true. If all the channels in the pattern are set to "X", the oscilloscope will not
trigger.
Figure 5-5 Pattern Trigger
Trigger Type:
Press Type, and then rotate the multifunction knob to select "Pattern". Press
down the knob to select the trigger type. Then, the current trigger setting
information is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen, as shown in the
figure below. You can also press Type continuously to select the trigger type or
enable the touch screen to tap the desired trigger type and select it.
Source Selection:
Press Source to open the signal source list and select CH1-CH4 or D0-D15. For
details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Source". The current trigger source is
displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Note: Only when we select the channel (that has been input with signals) as the
trigger source, can we obtain a stable trigger.
Pattern Setting:
Press Code, and rotate the multifunction knob to select the pattern of the
currently selected channel. Press down the knob to select the pattern. You can also
press Code continuously to select the pattern or enable the touch screen to select it.
The available patterns include the following five types:
H: sets the pattern of the channel selected to "1", i.g. the voltage level is higher
than the trigger level/threshold level of the channel.
L: sets the pattern of the channel selected to "0", i.g. the voltage level is lower
than the trigger level/threshold level of the channel.
X: sets the pattern of the channel selected to "X", i.g. this channel is not used as
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-17
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Confirmation Key
All Bits
Move the cursor to
the left
Move the cursor to
the right
Pattern
a part of the pattern. When all channels in the pattern are set to "X", the
oscilloscope will not trigger.
Rising: sets the pattern to the rising edge ( ) of the channel selected.
Falling: sets the pattern to the falling edge ( ) of the channel selected.
The corresponding pattern is displayed at the bottom of the screen. The patterns of
channels CH1-CH4 and D0-D15 are presented from left to right, as shown in the
figure below.
You can also set the pattern with the virtual keypad. The setting methods are as
follows:
Enable the touch screen to tap the channel pattern. Then, a virtual keypad is
displayed. Set the channel pattern with the keypad. For example, tap CH2 pattern,
then the virtual keypad for setting the channel pattern is displayed, as shown in
Figure 5-6. Tap the left arrow key to move the cursor to the left or tap the right
arrow key to move the cursor to the right. Then select a pattern. After the
pattern of the current channel is set completely, the cursor goes to the next pattern
bit automatically. Set them respectively. After all the pattern bits are set completely,
tap OK to confirm the setting, and close the virtual keypad. You can also tap All to
apply the current pattern to all the channels. This key function the same as the All
Bits menu key.
Figure 5-6 Virtual Keypad for Pattern Setting
Note: Only one edge (rising or falling edge) can be specified in the pattern. If one
edge item is currently defined and then another edge item is defined in another
channel in the pattern, then a prompt message "Invalid input" is displayed. Then the
latter defined edge item will be replaced by X.
All Bits:
Press All Bits to set the patterns of all channels to the currently selected pattern.
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
5-18 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
Trigger Mode:
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Mode to quickly switch
the current trigger mode. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Mode".
Trigger Parameter Setting:
Set the trigger parameters (trigger holdoff and noise rejection) under this trigger
type. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Holdoff" and "Noise
Rejection".
Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level:
Rotate the Trigger LEVEL knob to adjust the trigger level/threshold level. Refer
to "Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level". The current trigger level/threshold level
value is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Duration Trigger
In duration trigger, the instrument identifies a trigger condition by searching for the
duration of a specified pattern. This pattern is a logical "AND" combination of the
channels. Each channel can be set to H (high), L (low), or X (don't care). You can
specify a channel in the pattern to be the rising or falling edge (only one edge can be
specified). When the duration (△T) of this pattern meets the preset time, the
oscilloscope initiates a trigger, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 5-7 Duration Trigger
Trigger Type:
Press Type, and then rotate the multifunction knob to select "Duration". Press
down the knob to select the trigger type. Then, the current trigger setting
information is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen, as shown in the
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-19
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
figure below. You can also press Type continuously to select the trigger type or
enable the touch screen to tap the desired trigger type and select it.
Source Selection:
Press Source to open the signal source list and select CH1-CH4 or D0-D15. For
details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Source". The current trigger source is
displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Note: Only when we select the channel (that has been input with signals) as the
trigger source, can we obtain a stable trigger.
Pattern Setting:
Press Code, and rotate the multifunction knob to select the pattern of the
currently selected channel. Press down the knob to select the pattern. The
corresponding pattern is displayed at the bottom of the screen. The patterns of
channels CH1-CH4 and D0-D15 are presented from left to right, as shown in the
figure below. You can also press Code continuously to select the pattern or enable
the touch screen to select it.
H: sets the pattern of the channel selected to "H", i.g. the voltage level is higher
than the trigger level/threshold level of the channel.
L: sets the pattern of the channel selected to "L", i.g. the voltage level is lower
than the trigger level/threshold level of the channel.
X: sets the pattern of the channel selected to "X", i.g. this channel is not used as
a part of the pattern. When all channels in the pattern are set to "X", the
oscilloscope will not trigger.
Rising: sets the pattern to the rising edge of the channel selected.
Falling: sets the pattern to the falling edge of the channel selected.
Trigger Condition:
Press When, then rotate the multifunction knob to select the trigger condition,
and then press down the knob to select the trigger condition. You can also press
When continuously to select the trigger condition or enable the touch screen to tap
the desired trigger condition and select it.
>: triggers when the duration of the pattern is greater than the preset time.
Press Lower to set the lower limit of the duration of the pattern. Its range is
from 800 ps to 10 s.
<: triggers when the duration of the pattern is smaller than the preset time.
Press Upper to set the upper limit of the duration of the pattern. Its range is
from 800 ps to 10 s.
<>: triggers when the duration of the pattern is smaller than the upper limit of
the preset time and greater than the lower limit of the preset time. Press Upper
to set the upper limit of the duration of the pattern, and the range is from 1.2 ns
5-20 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
to 10 s. Press Lower to set the lower limit of the duration of the pattern, and
the range is from 800 ps to 10 s.
><: triggers when the duration of the pattern is greater than the upper limit of
the preset time and smaller than the lower limit of the preset time. Press Upper
to set the upper limit of the duration of the pattern, and the range is from 800 ps
to 10 s. Press Lower to set the lower limit of the duration of the pattern, and
the range is from 800 ps to 9.99 s.
Note: The lower time limit must be smaller than the upper time limit.
All Bits:
Press All Bits to set the pattern of all trigger sources to the pattern setting selected
currently.
Trigger Mode:
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Mode to quickly switch
the current trigger mode. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Mode".
Trigger Parameter Setting:
Set the trigger parameters (trigger holdoff and noise rejection) under this trigger
type. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Holdoff" and "Noise
Rejection".
Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level:
Rotate the Trigger LEVEL knob to adjust the trigger level/threshold level. Refer
to "Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level". The current trigger level/threshold level
value is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Timeout Trigger
In Timeout trigger, the oscilloscope triggers when the time interval (△T) (the time
from when the rising edge (or falling edge) of the input signal passes through the
trigger level to the time from when the neighboring falling edge (or rising edge)
passes through the trigger level) is greater than the preset timeout value, as shown
in the figure below.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-21
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
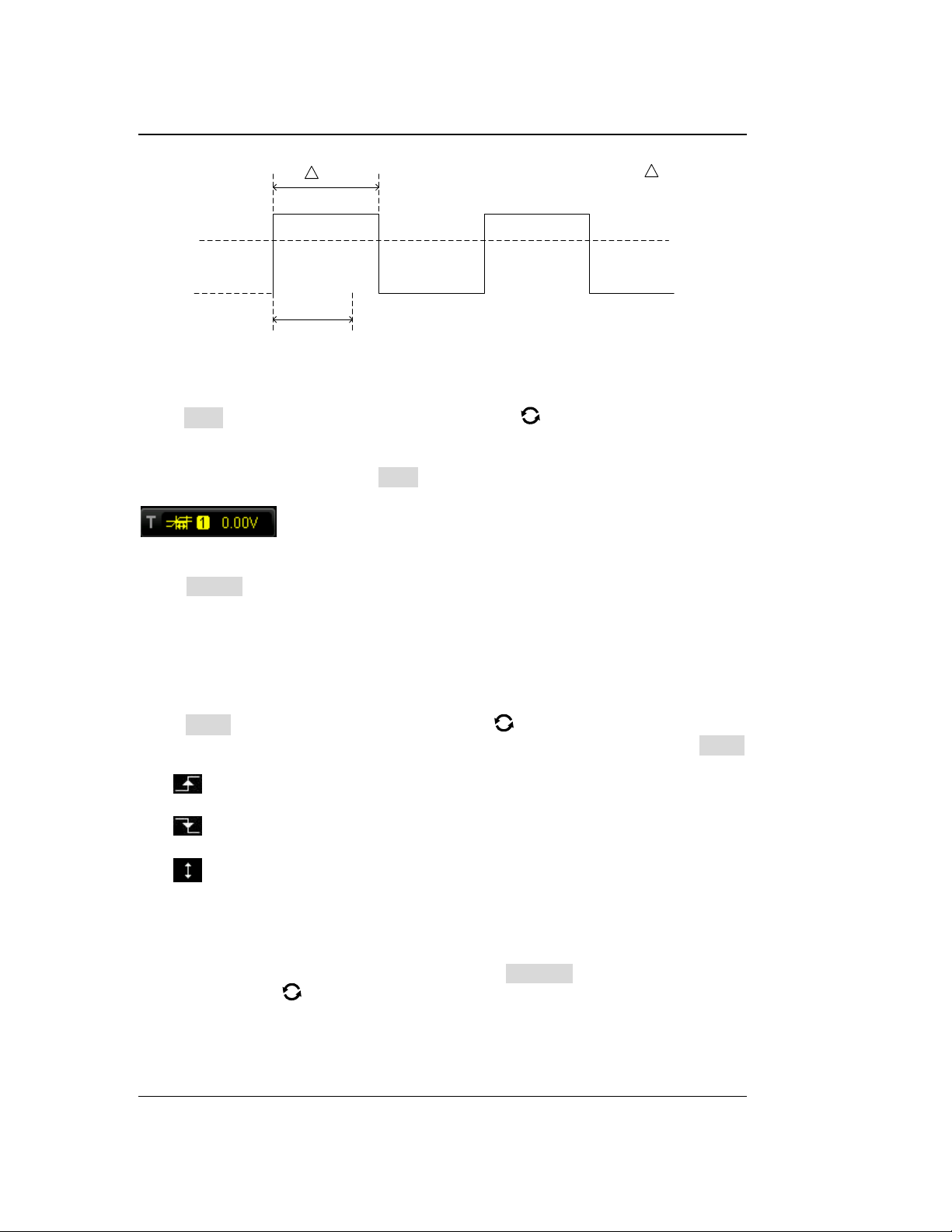
RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Time Out
T
Time Out< T
Figure 5-8 Timeout Trigger
Trigger Type:
Press Type, and then rotate the multifunction knob to select "Timeout". Press
down the knob to select the trigger type. Then, the current trigger setting
information is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen, as shown in the
figure below. You can also press Type continuously to select the trigger type or
enable the touch screen to tap the desired trigger type and select it.
Source Selection:
Press Source to open the signal source list and select CH1-CH4 or D0-D15. For
details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Source". The current trigger source is
displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Note: Only when we select the channel (that has been input with signals) as the
trigger source, can we obtain a stable trigger.
Edge Type:
Press Slope and rotate the multifunction knob to select the edge type of the
input signal that starts to pass through the trigger level. You can also press Slope
continuously to enable the touch screen to select the edge type.
Rising: starts timing when the rising edge of the input signal passes through
the trigger level.
Falling: starts timing when the falling edge of the input signal passes
through the trigger level.
Either: starts timing when either edge of the input signal passes through the
trigger level.
Timeout Value:
Timeout value represents the maximum time that the signal remains idle before the
signal passes through the trigger level. Press Timeout, and then rotate the
multifunction knob or use the pop-up numeric keypad to set the timeout value of
Timeout trigger. The available range is from 16 ns to 10 s.
5-22 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope RIGOL
Lower Limit of
the Trigger Level
Upper Limit of the
Trigger Level
Negative Runt Pulse
Positive Runt Pulse
Trigger Mode:
In the trigger control area (Trigger) on the front panel, press Mode to quickly switch
the current trigger mode. For details, refer to descriptions in "Trigger Mode".
Trigger Parameter Setting:
Set the trigger parameter (noise rejection) under this trigger type. For details, refer
to descriptions in "Noise Rejection".
Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level:
Rotate the Trigger LEVEL knob to adjust the trigger level/threshold level. Refer
to "Trigger LEVEL/Threshold Level". The current trigger level/threshold level
value is displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen.
Runt Trigger
This trigger mode is used to trigger pulses that pass through one trigger level but fail
to pass through another trigger level, as shown in the figure below.
Figure 5-9 Runt Trigger
Trigger Type:
Press Type, and then rotate the multifunction knob to select "Runt". Press down
the knob to select the trigger type. Then, the current trigger setting information is
displayed at the upper-right corner of the screen, as shown in the figure below. You
can also press Type continuously to select the trigger type or enable the touch
screen to tap the desired trigger type and select it.
Source Selection:
Press Source to switch the trigger source and select CH1-CH4. For details, refer to
descriptions in "Trigger Source". The current trigger source is displayed at the
upper-right corner of the screen.
Note: Only when we select the channel (that has been input with signals) as the
trigger source, can we obtain a stable trigger.
MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide 5-23
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com

RIGOL Chapter 5 To Trigger the Oscilloscope
Polarity:
Press Polarity continuously to select the pulse polarity of Runt trigger.
Positive: triggers on the positive runt pulse.
Negative: triggers on the negative runt pulse.
Trigger Condition:
Press When and rotate the multifunction knob to set the trigger conditions of
Runt trigger. You can also press When continuously or enable the touch screen to
select it.
None: indicates not setting the trigger condition of Runt trigger.
>: triggers when the runt pulse width is greater than the lower limit of pulse
width. Press Lower to set the minimum pulse width of Runt trigger.
<: triggers when the runt pulse width is smaller than the upper limit of pulse
width. Press Upper to set the maximum pulse width of Runt trigger.
<>: triggers when the runt pulse width is greater than the lower limit and
smaller than the upper limit of pulse width. Press Upper to set the maximum
pulse width of Runt trigger. Press Lower to set the minimum pulse width of
Runt trigger.
Note: The lower limit of the pulse width must be smaller than the upper limit.
Level Selection and Adjustment of Trigger Level:
After the trigger condition setting is completed, you need to adjust the trigger level
to correctly trigger the signal and obtain a stable waveform. Press Level Select
(when "<>" is selected as the trigger condition, Level Select is a sub-menu under
More), then rotate the multifunction knob to select the desired level type for
adjustment, and then press down the knob to select the type. You can also press
Level Select continuously to select the level type or enable the touch screen to tap
the desired level type and select it.
Level A: only adjusts the upper limit of the trigger level, and the lower limit of the
trigger level remains unchanged.
Level B: only adjusts the lower limit of the trigger level, and the upper limit of the
trigger level remains unchanged.
Level AB: adjusts the upper and lower limits of the trigger level at the same time, and
the trigger level deviation (the difference between the upper limit and lower limit of
the trigger level) remains unchanged.
Note: In Runt trigger, pressing Trigger LEVEL can quickly switch the current
level adjustment type.
Rotate the Trigger LEVEL knob to adjust the corresponding trigger level. During
the adjustment of trigger level, two trigger level lines appear on the screen, and they
move up and down with the change of the trigger level. At the same time, the
real-time trigger level information is displayed at the lower-left corner of the screen
(as shown in the figure below, H indicates the upper limit of the trigger level, L
indicates the lower limit of the trigger level, and △ indicates the trigger level
deviation). When you stopping modifying the trigger level, the trigger level line and
5-24 MSO7000/DS7000 User's Guide
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
 Loading...
Loading...