ULTRA-COMPACT
REAL-TIME CLOCK IC
RS5C314
EK-082-9908
1
OUTLINE
The RS5C314 is a CMOS type real-time clock which is connected to the CPU via three signal lines and capable of
serial transmission of clock and calendar data to the CPU. The RS5C314 can generate various interrupt clock pulses
lasting for long periods (one month). Driving an oscillation circuit at constant voltage, the circuit undergoes few
voltage fluctuations and consequently realizes low current consumption (TYP. 0.7µA at 3 V). It also provides an
oscillator halt sensing function for application to data validity at power-on and other occasions. Integrated into an
ultra-compact and ultra-thin 8pin SSOP (0.65mm pitch), the RS5C314 is the optimum choice for equipment requiring
small size and low power consumption.
There is RS5C313 reversing the logic of serial clock for series goods.
• Time Keeping Supply Voltage: 1.6 to 6.0 V • Operating Supply Voltage: 2.7 to 6.0 V
• Low Current Consumption: TYP. 0.7µA (MAX. of 1.5µA) at 3V
• Connection to the CPU via only three pins: CE, SCLK, and SIO (for addressing and data read and write opera-
tions)
• A clock counter (counting hours, minutes, and seconds) and a calendar counter (counting leap years, years,
months, days, and days of the week) in binary-coded decimal (BCD) code
• Generation of interrupt pulses to the CPU with cycles ranging from 1 month to 1/1024 Hz, interrupt flags, and
interrupt halt
• Software-based alarming through clock-interlocked interrupt operation
• Oscillator halt sensing to judge internal data validity
• Second digit adjustment by ±30 seconds • 12-hour or 24-hour time display selectable
• Automatic leap year recognition up to the year 2099 • CMOS logic • Package: 8pin SSOP (0.65mm pitch)
FEATURES
PIN CONFIGURATION
1
2
3
4
CE
SCLK
SIO
VSS
8
7
6
5
VDD
OSCIN
OSCOUT
INTR
• 8pin SSOP
RS5C314
2
A DIFFERENCE WITH RS5C313
The logic of serial clock is point that it become that RS5C313 reverses RS5C314 with SCLK for SCLK and differ-
ence point of RS5C314 and RS5C313, describe is the master of by it being different in the following 3 items
(Give RS5C313 application manual absolutely reference in electric characteristic / the thing AC/DC require-
ments rating / recommendation gesture a maximum.)
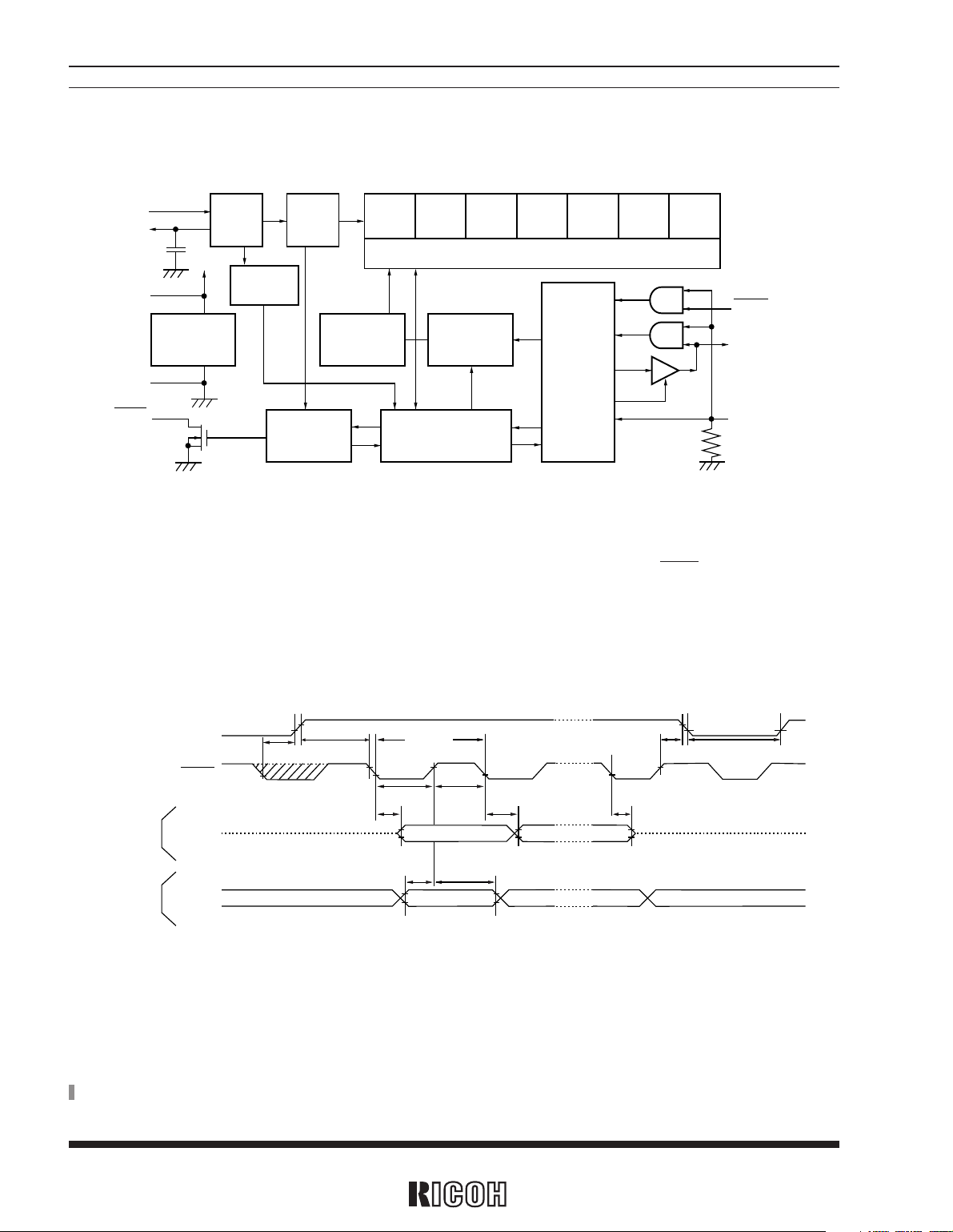
BLOCK DIAGRAM
SEC. MIN. HOUR WEEK DAY
MONTH
YEAR
OSCIN
OSCOUT
VDD
VSS
INTR
OSC DIV
OSC
DETECT
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
ADDRESS
DECODER
INTERRUPT
CONTROL
SHIFT REGISTER
I/O
CONTROL
ADDRESS
REGISTER
SIO
SCLK
CE
TIME COUNTER
1.
Timing Chart
Input/output conditions
V
IH = 0.8 × VDD
VIL = 0.2 × VDD
VOH = 0.8 × VDD
VOL = 0.2 × VDD
tSCK
tCES
tCKS
tCEH
tCR
tRE
tRZ
tCKL tCKH
tRR
Read Data
Write Data
t
DS tDH
CE
SCLK
SIORead cycle
Write cycle
SIO
*
) The ability that is fair in “H” or “L” slanted line department

RS5C314
3
The real-time clock becomes accessible by switching the CE pin from the low level to high level to enable
interfacing with the CPU and then inputting setting data (control bits and address bits) to the SIO pin in synchronization with
shift clock pulses from the SCLK pin.
The input data are registered in synchronization with the rising edge of the SCLK. When the data is read, the read cycle shall
be set by control bits.
2.1 Read Cycle Flow
1. The CE pin is switched from the low level to the high level.
2. Four control bits (with the first bit ignored) and four read address bits are input from the SIO pin. At this time,
control bits R/W and AD are set equally to 1 while a control bit DT is set to 0.
3. The SIO pin enters the output mode at the falling edge of the shift clock pulse 2B from the SCLK pinwhile the
four read bits (MSB→LSB) at designated addresses are output at the falling edge of the shift clock pulse 5B (see
the figure below).
4. Then, the SIO pin returns to the input mode at the falling edge of the shift clock pulse 1C. Afterwards control bits
and address bits are input at the shift clock pulses 1C in the same manner as at the shift clock pulse 1A.
5. At the end of read cycle, the CE pin is switched from the high level to the low level (after
tCEH from the rising edge
of the eighth shift clock pulse from the SCLK pin). (Following on read cycle, write operation can be performed by
setting control bits in the write mode at the shift clock pulse 1C and later with the CE pin held at the high level.)
R/W: Establishes the read mode when set to 1, and the write mode when set to 0.
AD: Writes succeeding address bits (A3 to A0) to the address register when set to 1 with the DT
bit set to 0 and performs no such write operation in any other case.
DT: Writes data bits (D3 to D0) to the counter or the register specified by the address register
which has written just before when set to 1 with the R/W and AD bits set equally to 0 and
performs no such write operation in any other case.
A3 to A0: Inputs the bits MSB to LSB in the address table describing the functions.
• Control bits
• Address bits
2. Read Data
1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A 8A 1B 2B 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B 8B 1C 2C 3C
R/W
AD DT A3 A2 A1 A0
— — — D3 D2 D1 D0
R/W
AD
*
CE
SCLK
Input to
SIO pin
Output from
SIO pin
(Internal processing)
Reading to shift register
Writing to
address resister
Setting of
control bit
Control bits Address bits
(Hi-z) (Hi-z)
(Hi-z)
Read data
Setting of
SIO pin in
output mode
Shifting data Setting of SIO pin in
input mode
*
*
) In the above figure, the “*” mark indicates arbitrary data; the “—” mark indicates unknown data;
the mark indicates data which are available when the SIO pin is held at the high, low, or Hiz level ;
and the diagonaliy shaded area indicates high or low.
“ ”

RS5C314
Writing data to the real-time clock requires inputting setting data (control bits and address bits) to the SIO pin and
then establishing the write mode by using a control bit R/W in the same manner as in read operation.
*
) Control bits and address bits are described in the previous section on read cycle.
• Data bits D3 to D0 : inputs writing data to the counter or the register describing the functions in order of
MSB to LSB.
3.1 Write Cycle Flow
1. The CE pin is switched from the low level to the high level.
2. Four control bits (with the first bit ignored) and four write address bits are input from the SIO pin. At this
time, control bits R/W and DT are set equally to 0 while a control bit AD is set to 1 (at the shift clock pulses
1A to 8A from the SCLK pin).
3. Four control bits and four bits of data to be written are input in the descending order of their significance. At
this time, control bits R/W and AD are set equally to 0 while a control bit DT is set to 1 (at the shift clock pulses
1B to 8B from the SCLK pin).
4. When write cycle is continued, control bits and address bits are input at the shift clock pulse 1C and later in the
same manner as at the shift clock pulse 1A.
5. At the end of write operation, control bits R/W, AD, and DT are set equally to 0 (at the rising edge of the fifth
shift clock pulse and later from the SCLK pin) or the CE pin is switched from the high level to the low level (after
tCEH from the rising edge of the eighth shift clock pulse from the SCLK pin).
3.
Write Data
1A 2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A 8A 1B 2B 3B 4B 5B 6B 7B 8B 1C 2C 3C
R/W
AD DT A3 A2 A1 A0
R/W AD DT D3 D2 D1 D0
R/W
AD
CE
SCLK
Input to
SIO pin
Output from
SIO pin
(Internal processing)
Reading from shift register
Writing to
address register
Setting of
control bits
End of write operationSetting of
control bits
Control bits Address bits
Control bits Data bits
(Hi-z) (Hi-z)
*
*
*
*
*
) In the above figure, the “*” mark indicates arbitrary data; and the diagonally shaded area indicates the high or low level.
RICOH COMPANY, LTD.
ELECTRONIC DEVICES DIVISION
HEADQUARTERS
13-1, Himemuro-cho, Ikeda City, Osaka 563-8501, JAPAN
Phone +81-727-53-6003 Fax +81-727-53-2120
YOKOHAMA OFFICE (International Sales)
3-2-3, Shin-Yokohama, Kohoku-ku, Yokohama City, Kanagawa 222-8530,
JAPAN
Phone +81-45-477-1697 Fax +81-45-477-1694 · 1695
http://www.ricoh.co.jp/LSI/english/
RICOH CORPORATION
ELECTRONIC DEVICES DIVISION
SAN JOSE OFFICE
1996 Lundy Avenue, San Jose, CA 95131, U.S.A.
Phone +1-408-944-3306 Fax +1-408-432-8375
http://www.ricoh-usa.com/semicond.htm
 Loading...
Loading...