Page 1
Network Interface Board
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
Read this manual carefully before you use this product and keep it handy for future
reference.
For safety, please follow the instructions in this manual.
Page 2
Introduction
To get maximum versa tility from this machin e all opera tors shoul d carefull y read and f ollow th e instructions in this manual. Please keep this manual in a handy place near the machine.
Please read the Safety Info rmation in the “Printer Referen ce” before u sing this machine. It c ontains important information related to USER SAFETY and PREVENTING EQUIPMENT PROBLEMS.
Important
Parts of this manual are subject to change without prior notice. In no event will the company be liable
for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages as a result of handling or operating
the machine.
Note
The names of the applications do not appear in the following pages. Confirm which applications you
will be using before reading this manual.
Descriptions in this manual Application
PRINTER MANAGER FOR ADMINISTRATOR
Aficio Manager for Admin
Net Vision for Admin
infotec NetPrint Manager for Admin
Lanier Net Manager for Admin
PRINTER MANAGER FOR CLIENT Aficio Manager for Client
Net Vision for Client
infotec NetPrint Manager for Client
Lanier Net Manager for Client
Software Versions Conventions Used in this Manual
• NetWare 3.x means NetWare 3.11, 3.12 and 3.2.
• NetWare 4.x means NetWare 4.1, 4.11 and IntranetWare.
Trademarks
Apple, AppleTalk, EtherTa lk, LaserWriter an d Macintosh are reg istered trademarks of Apple Computer,
Incorporated.
Ethernet is a registered trademark of Xerox Corporation.
Microsoft, Windows and Windo ws NT are re giste red trade marks of Mi croso ft Corpora tion in the Unit ed
States and/or other countries.
Netscape and Netscape Navigator are registered trademarks of Netscape Communications Corpora-
tion.
Novell, NetWare, Client32 and NDS are registered trademarks of Novell, Inc.
PostScript is a registered trademark of Adobe Systems, Incorporated.
Sun is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
SunOS is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Solaris is a registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States and other countries.
Other product names us ed herei n are for iden tifica tion purp oses on ly and migh t be tradem arks of th eir
respective companies. We disclaim any and all rights in those marks.
Note
The proper names of the Windows operating systems are as follows:
• Microsoft Windows 95 operating system
• Microsoft Windows 98 operating system
• Microsoft Windows for Workgroups operating system Version 3.11
• Microsoft Windows NT Server operating system Version 4.0
• Microsoft Windows NT Workstation operating system Version 4.0
Page 3
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction................................................................................................ 1
Setting up the Printer in a Network.......................................................... 2
Printing without Using a Print Server ............................................................ 2
Printing with a Windows NT Print Server...................................................... 2
Printing as a NetWare Print Server............................................................... 3
1.Windows 95/98 Configuration
Configuring Windows 95/98..................................................................... 6
Preparing to Use the TCP/IP Protocol for Printing........................................ 6
Preparing to Use the NetBEUI Protocol for Printing...................................... 7
Installing Multidirect Print.............................................................................. 8
Setting up the Printer Driver.......................................................................... 9
Uninstalling Multidirect Print........................................................................ 11
2.Windows NT 4.0 Configuration
Preparing for a Network Connection..................................................... 14
Preparing to Use the TCP/IP Protocol for Printing...................................... 14
Preparing to Use the NetBEUI Protocol for Printing.................................... 15
Installing Multidirect Print............................................................................ 17
Setting up the Printer Driver........................................................................ 18
Uninstalling Multidirect Print........................................................................ 20
Setting up a Client Computer................................................................. 21
Windows 95/98............................................................................................ 21
Windows NT 4.0.......................................................................................... 22
Configuring LPR Port Printing............................................................... 23
3.NetWare Configuration
Installing NIB Setup Tool........................................................................ 26
Installing the PRINTER MANAGER FOR ADMINISTRATOR..................... 26
Running NIB Setup Tool ............................................................................. 27
Quick Setup Using the NIB Setup Tool Wizard..................................... 28
NetWare 3.x - Advanced Settings.......................................................... 31
Setting up as Print Server........................................................................... 31
Setting up as Remote Printer...................................................................... 34
NetWare 4.x, 5 - Advanced Settings ...................................................... 37
Setting up as Print Server........................................................................... 38
Setting up as Remote Printer...................................................................... 40
Setting up a Client Computer................................................................. 44
Windows 95/98............................................................................................ 44
Windows NT 4.0.......................................................................................... 45
ii
Page 4

4.Macintosh Configuration
Configuring a Macintosh........................................................................ 47
Changing to EtherTalk ................................................................................ 47
Configuring the Printer................................................................................ 48
Changing Printer Name............................................................................... 48
Changing Zone............................................................................................ 48
5.Appendix
Multidirect Print......................................... .... ..... ............................ ..... .... 51
Select Printer
[
Network
[
Configuring the Network Interface Board with a Web Browser.......... 54
Going to the Top Page................................................................................ 54
Assigning IP Address with ARP+PING.................................................. 57
Remote Maintenance by Telnet (mshell)............................................... 58
Operation Flow............................................................................................ 58
Command List............................................................................................. 59
SNMP........................................................................................................ 66
Understanding the Displayed Information............................................ 67
Print Job Information................................................. .................................. 67
Print Log Information................................................................................... 67
Network Statistical Information.................................................................... 68
Configuring the Network Interface Board.................................................... 69
]
................ ............................................................................... 51
]
............... ................................................................................. ...... 52
Message List............................................................................................ 72
System Log Information.............................................................................. 72
Precautions.............................................................................................. 77
Connecting a Dial up Router to a Network.................................................. 77
When Printing PostScript from Windows .................................................... 78
When Printing it with NetWare.................................................................... 78
When Using DHCP ..................................................................................... 79
When Using NIB Setup Tool....................................................................... 80
Specifications.......................................................................................... 81
INDEX........................................................................................................ 82
iii
Page 5
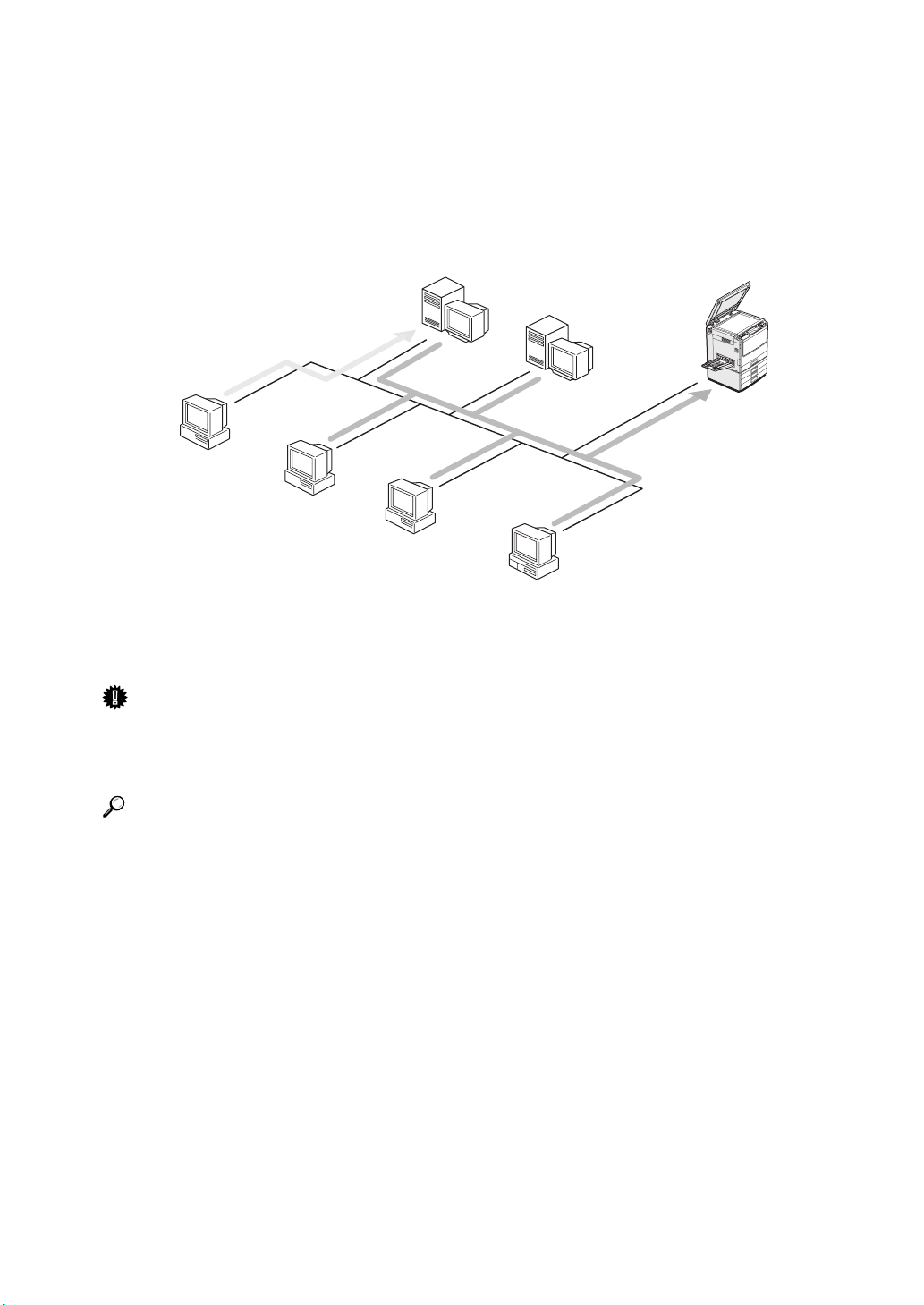
Introduction
This manual contains detailed instructions on configuring the printer to use it as
a network printer. The actual procedures may differ depending on your network environment. Use the procedure appropriate for your network environment.
Windows NT (Server)
NetWare (Server)
Windows 95/98
Windows NT
NetWare
(Client)
Macintosh
Important
❒
The procedures in this manual assume that you are a network administrator.
If you are not, be sure to consult your network administrator before configuration.
Reference
For more information on physically installing the Network Interface Board
and cabling, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
For more information on configuring the Network Interface Board with the operation panel, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
Features
❖
• Support for 100BASE-TX and 10BASE-T
• The Network Interface Board is compatible with NetWare (IPX/SPX),
Windows NT (TCP/IP, NetBEUI), Windows 95/98 (TCP/IP, NetBEUI) ,
and Macintosh (AppleTalk) protocols. This allows you to use the printer in
a network that uses different protocols and operating systems.
• A computer used as a dedicated print server is not required because the
Network Interface Board can be configured as a NetWare print server.
• The Network Interface Board can connect the printer to the network without requiring its own power supply because the Network Interface Board
is installed inside the printer.
1
Page 6
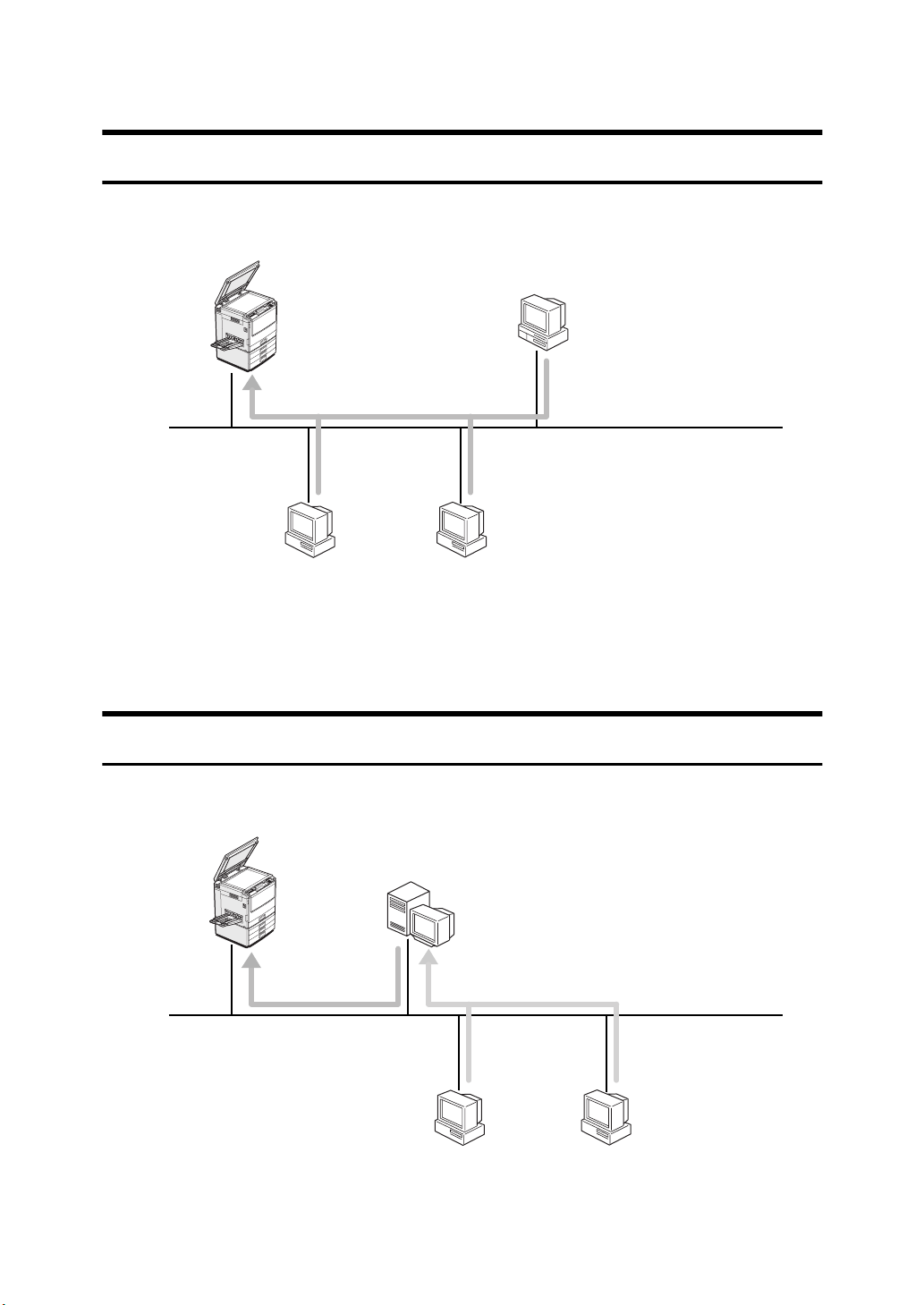
Setting up the Printer in a Network
Printing without Using a Pri nt Server
You do not need to use a print server. The actual procedure may differ depending on your operating system.
Macintosh
AppleTalk
TCP/IP
NetBEUI
Windows 95/98
Windows NT 4.0
TCP/IP
NetBEUI
• Windows 95/98 ⇒ P.5
• Windows NT 4.0 ⇒ P.14
• Macintosh ⇒ P.47
Printing with a Windows NT Print Server
When Windows NT Server or Workstation is the operating system used on the
print server, TCP/IP or NetBEUI protocols are used.
Windows NT Server (or Workstation) 4.0
Print Server
TCP/IP
NetBEUI
Windows 95/98
Windows NT 4.0
2
Page 7
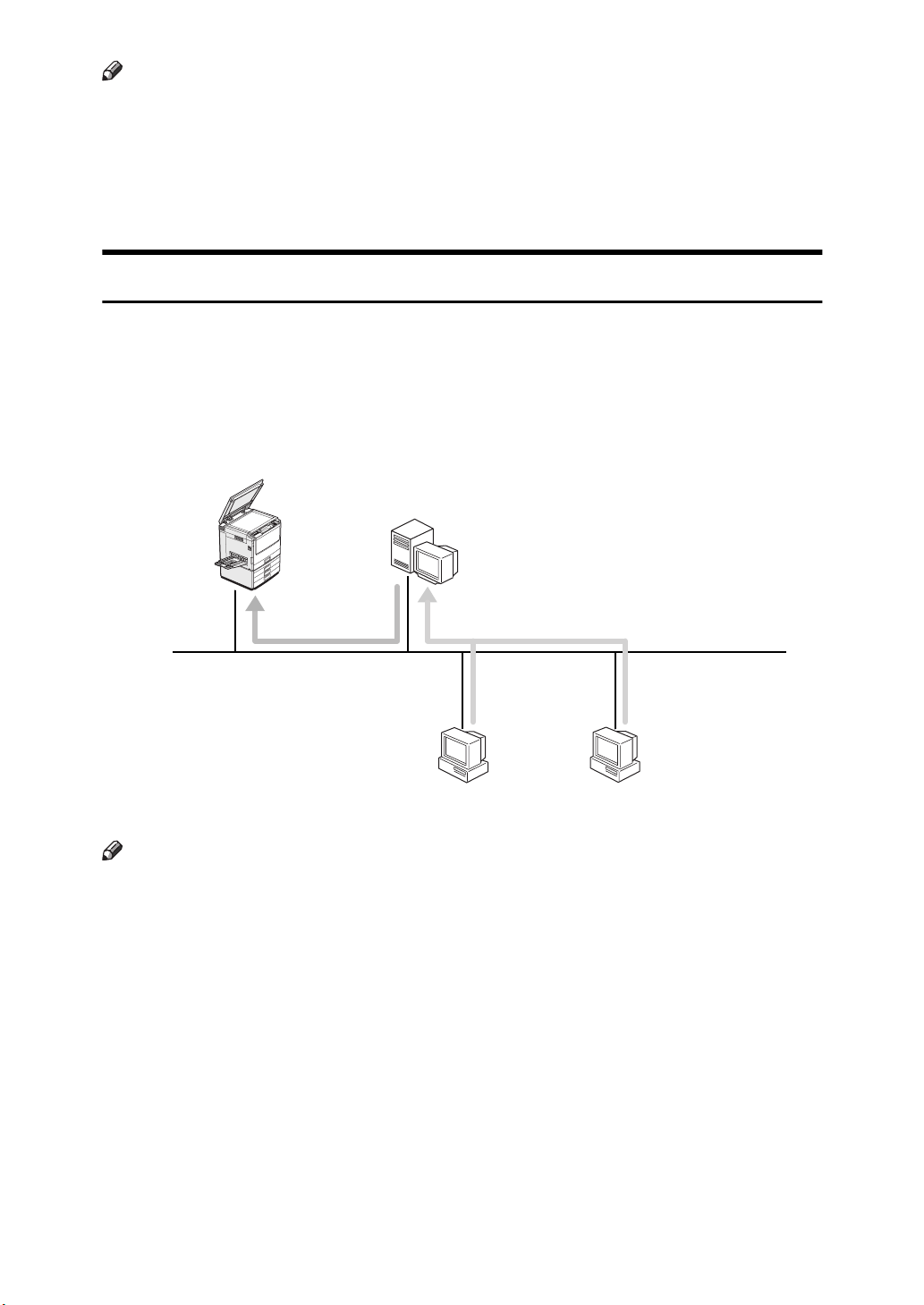
Note
❒
For more information on setting up TCP/IP or NetBEUI in a Windows NT environment, see P.14
❒
Client setup instructions are different for each type of Windows OS.
“Preparing for a Network Connection”
.
• Windows 95/98 ⇒ P.21
• Windows NT 4.0 ⇒ P.22
Printing as a NetWare Print Server
The Network Interface Board allows you to set up the printer in a NetWare environment as either a print server or a remote printer. A dedicated NetWare
print server is not required. If a dedicated print server is being used, the printer
should be configured as a remote printer.
Configure as Print Server
❖
Print Server
NetWare
File Server
Windows 95
Note
❒
The actual procedures for configuring the printer may differ depending on
Windows 98
the version of NetWare.
• NetWare 3.x ⇒ P.31
• NetWare 4.x, 5 ⇒ P.37
❒
The actual procedures for configuring your client computer may differ de-
“NetWare 3.x - Advanced Settings”
“NetWare 4.x, 5 - Advanced Settings”
pending on the operating system.
• Windows 95/98 ⇒ P.44
“Windows 95/98”
3
Page 8
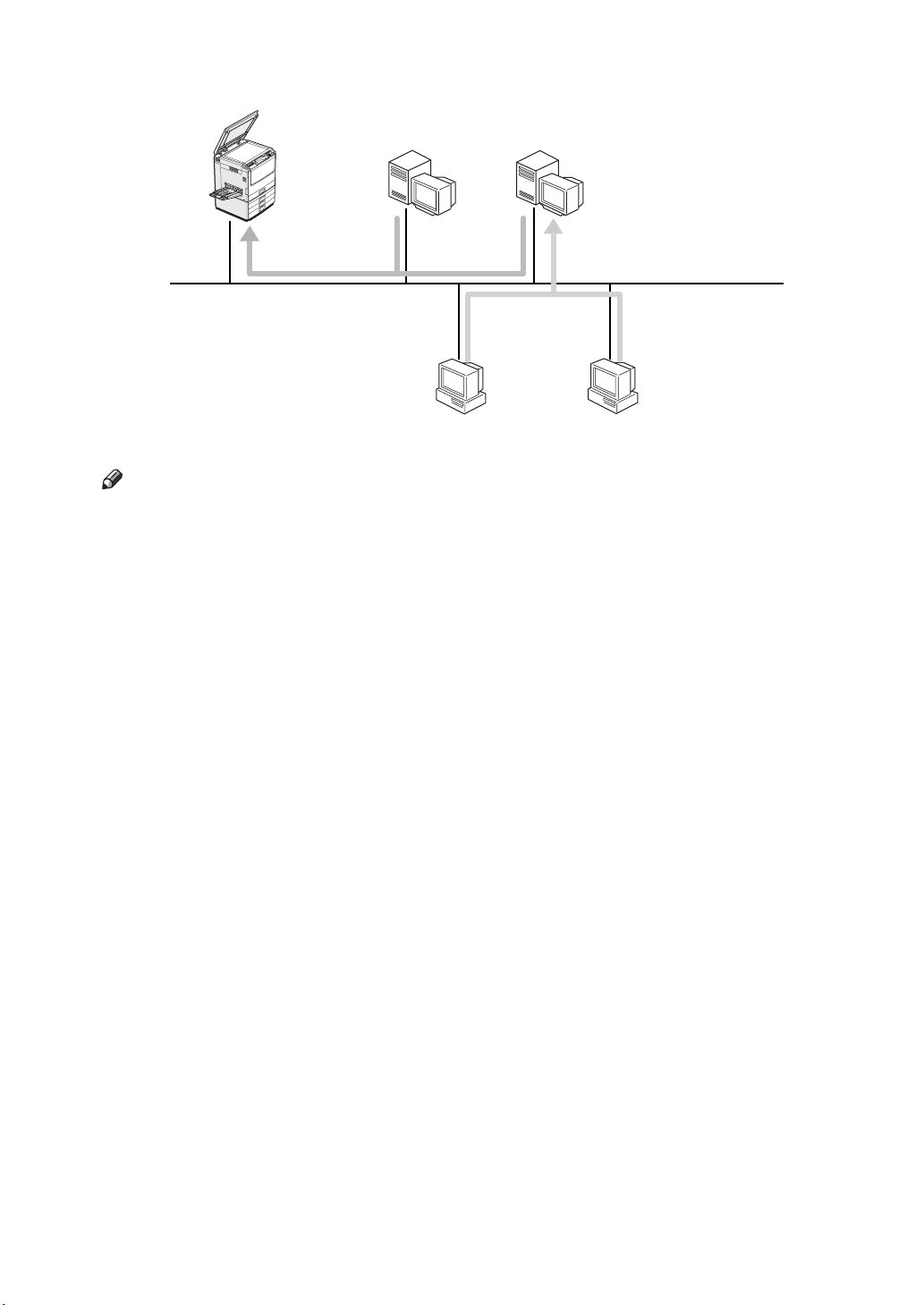
Configure as Remote Printer
❖
Remote Printer
NetWare
Print Server
NetWare
File Server
Windows 95
Windows 98
Note
❒
The actual procedures for configuring the printer may differ depending on
the version of NetWare.
• NetWare 3.x ⇒ P.34
“Setting up as Remote Printer”
• NetWare 4.x, 5 ⇒ P.40
❒
The actual procedures for configuring your client computer may differ depending on the operating system.
• Windows 95/98 ⇒ P.44
“Windows 95/98”
4
Page 9

1. Windows 95/98
Configuration
You can use the printer as a network printer with Windows 95/98 using Multidirect Print, and the TCP/IP or NetBEUI protocols. This chapter explains how to
configure your printer and Windows.
5
Page 10
Windows 95/98 Configuration
Configuring Windows 95/98
1
Basic Procedure
Selecting the protocol
TCP/IP NetBEUI
Assigning the IP address
TCP/IP
NetBEUI
Windows 95/98
Preparation
Configuring Windows environment
Installing Multidirect Print
Installing the printer driver
Changing the port
Multidirect Print supports the TCP/IP protocol and the NetBEUI protocol.
Consult the network administrator before selecting the protocol.
Limitation
❒
When you use the NetBEUI protocol, you cannot print to a printer which is
located on the other side of a router.
Note
❒
You can use both TCP/IP and NetBEUI protocols in a computer. To use both
protocols, you must first install them.
Preparing to Use the TCP/IP Protocol for Printing
To use the TCP/IP protocol to print, the network must be configured as described below.
Configuring the printer
Configure your printer to use the TCP/IP protocol.
• Confirm that the TCP/IP protocol is set to active. (The default setting is active.)
• Assign an IP address and make other settings required for using the TCP/IP
protocol.
6
Page 11

Configuring Windows 95/98
Reference
For more information on how to make the above settings, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
If DHCP is used to assign IP addresses, see P.79
Note
❒
After setting the IP address, use the PING command to confirm that it has
been set correctly.
A
Click
B
Type the following. (Example IP address is 192.168.15.16)
C:> ping 192.168.15.16
If the address has been configured correctly, the following message appears.
Reply from 192.168.15.16 : bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=32
If the address has been configured incorrectly, the following message appears.
Request timed out.
Start
[
]
, point to
Programs
[
]
, and then click
“When Using DHCP”
MS-DOS Prompt
[
]
.
.
Configuring a Windows 95/98 computer
1
Follow these steps to configure a Windows 95/98 computer to use the TCP/IP
protocol.
Double-click the
A
is in the
tab.
Note
❒
If the TCP/IP protocol is not installed, click
and install it. For more information on installing the TCP/IP protocol, see
the Windows 95/98 online help.
Configure the TCP/IP protocols with the appropriate IP address, subnet
B
mask and other settings.
Confirm with the network administrator that the settings are correct.
The following network components are instal led
[
Network
[
icon of
]
Control Panel
[
, and confirm that “TCP/IP”
]
Add
[
box of the
]
]
in the
Configuration
[
Configuration
[
]
tab,
Preparing to Use the NetBEUI Protocol for Printing
To use the NetBEUI protocol to print, the network must be configured as described below.
]
Configuring the printer
Configure your printer to use the NetBEUI protocol.
7
Page 12

1
Windows 95/98 Configuration
• Confirm that the NetBEUI protocol is set to active. (The factory default is active.)
Reference
For more information on how to make the above settings, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
Configuring a Windows 95/98 computer
Install the NetBEUI protocol into a Windows 95/98 computer, and configure
NetBEUI as the default protocol.
Double-click the
A
BEUI” is in the
figuration
Note
❒
If the NetBEUI protocol is not installed, click
and install it. For more information on installing the NetBEUI protocol, see
the Windows 95/98 online help.
❒
If there is “NetBEUI ->Dial-Up Adaptor” in the
ponents are installed:
Configure the NetBEUI protocol as the default protocol. Click the
B
ration
stalled:
Click the
C
click
Click
D
After confirming the message to restart, click
E
tab.
]
tab, select “NetBEUI” in the
]
box, and click
]
Advanced
[
.
OK
[
]
to close the
OK
[
]
Network
[
The following network components ar e installe d:
[
tab, select
]
icon in
]
]
box, select it and click
Properties
[
Network
[
]
Control Panel
[
The following network components are in-
[
.
]
Set this protocol to be the default protocol
[
dialog box.
, and confirm that “Net-
]
box in the
]
Add
[
Remove
[
Yes
[
]
in the
The following network com-
[
]
.
]
Configuration
[
to remove the binding.
Installing Multidirect Print
Con-
[
]
tab,
Configu-
[
, and
]
Follow these instructions to install Multidirect Print.
Preparation
You must restart the computer after installing Multidirect Print. Be sure to
close all applications before beginning the installation process.
Note
❒
You must install Multidirect Print and the appropriate printer driver in order
to print. If you print, using the TCP/IP protocol, to be able to browse the
printer via the network, PRINTER MANAGER FOR CLIENT (⇒see the inside of the front cover of this manual) needs to be installed. If the installer
starts automatically with the Auto Run program, you can install both of these
programs. For more information on how to install these programs, see the
"Printer Reference" that comes with the printer.
8
Page 13

Close all the applications that are currently running.
A
Insert the CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
B
Configuring Windows 95/98
Note
❒
If the installer starts automatically, you can use it to install Multidirect
Print, and set up the printer driver, and then go to step F.
Open
C
In the
D
Click
E
Type the name of the CD-ROM drive in the
F
gram
clude the quotation marks), and then click
❒
From the
G
After the
H
After the
I
computer now.
Control Panel
[
Install/Uninstall
[
Next >
[
box, followed by “\NETWORK\MDP\DISK1\SETUP” (do not in-
]
Note
An example would be “D:\NETWORK\MDP\DISK1\SETUP” when the
drive letter is “D”.
.
]
Choose Setup Language
[
Welcome
[
Setup Complete
[
, and click
]
, and double click the
]
tab, click
]
dialog box appears, click
]
dialog box appears, click
]
Finish
[
Install
[
list, select the language you use.
]
.
]
[
.
]
Add/Remove Programs
Command line for installation pro-
[
Next >
[
.
]
.
]
Yes, I want to restart my
[
Finish
[
icon.
]
1
The computer restarts, and Multidirect Print can now be used. If you select
“No”, be sure to restart the computer manually before launching Multidirect
Print for the first time.
Go to P.9
“Setting up the Printer Driver”
after the computer restarts.
Setting up the Printer Driver
Using Multidirect Print to print is not possible until the printer driver is installed
and the correct port selected.
Preparation
The target printer must be turned on before starting the installation process.
Install the printer drivers.
A
If the printer drivers have already been installed, you can go to the next step.
Reference
For more information on installing the printer drivers, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
9
Page 14

Windows 95/98 Configuration
Note
❒
Any port can be selected during the installation, however, LPT1 is recommended.
1
In the
B
the
Click the
C
In the
D
OK
[
The
can print with TCP/IP appear.
❒
❒
To print using the NetBEUI protocol, click
E
Click the printer you want to use, and click
F
Printers
[
menu, click
File
]
[
Add Port
[
.
]
Select Printer
[
Limitation
If PRINTER MANAGER FOR CLIENT is not installed in your computer,
printers which can print with TCP/IP do not appear.
Note
The printers which have replied to a broadcast from the computer are listed here. To print to a printer that is not on this list, or to directly type the
port name, click
name in step G.
window, click the icon of the printer you want to use. On
]
Other
[
.
]
Add Port
[
, and click
]
]
, and click
.
]
Multi Direct Print
[
Next >
[
[
]
NetBEUI
Next >
[
, and then type the port
.
]
.
]
, and then click
]
Details
[
Properties
[
tab, and then click
]
box, click
]
]
dialog box appears, and the names of the printers which
New Printer
[
10
Reference
For more information on a particular item in the dialog box, see P.51
tidirect Print”
Note
❒
You can identify the “Printer Name” and “Address” on the configuration
page printed by the printer.
❒
You cannot add the partly same address that was already used. For example, when “192.168.0.2” was already used, “192.168.0.2xx” cannot be used.
Similarly, when “192.168.0.20” was already used, “192.168.0.2” cannot be
used.
Confirm that the port name of the printer is correct, and click
G
If you did not select a printer in step F, you must type the port name.
.
[
Typing the port name for use with the TCP/IP protocol
Type the IP address of the Network Interface Board into the
A
box.
You can type the host name or a domain name instead of an IP address into
Host Name
the
[
]
box.
Next >
]
IP address
[
“Mul-
.
]
Page 15

Limitation
❒
You cannot use a host name that begins with “%%”.
❒
You cannot use the port name that is already in use.
Configuring Windows 95/98
Note
❒
When you use DHCP to assign IP addresses to Network Interface
Boards, you can use a printer name (Current Hostname on the network
configuration page) as the host name.
Typing the port name for use with the NetBEUI protocol
Print a configuration page, and confirm the Network path name.
A
Reference
For more information on printing a configuration page, see the "Printer
Reference" included as a PDF file in the CD-ROM.
Type the printer's network path name in the form of “%%Computer
B
name \Share name”. Do not type “\\” as head characters but “%%”.
Confirm the port name in the
H
Confirm that the port name is displayed in the
I
and click
Configuration is complete.
When you print, the printing procedure is no different. When you select the
printer configured here, the computer automatically uses Multidirect Print.
OK
[
.
]
Port Name
[
box, and click
]
Print to the following port
[
Finish
[
.
]
box,
]
1
Uninstalling Multidirect Print
Open
A
With the
B
After a confirmation message appears, click
C
UninstallShield removes all of the components of Multidirect Print.
When the uninstallation is complete, restart the computer.
D
Control Panel
[
Install/Uninstall
[
, and double-click the
]
tab, click
]
Multi Direct Print
[
Add/Remove Programs
[
, and click
]
.
Yes
[
]
icon.
]
Add/Remove
[
.
]
11
Page 16

1
Windows 95/98 Configuration
12
Page 17

2. Windows NT 4.0
Configuration
You can use the printer as a network printer with Windows NT 4.0 using Multidirect Print, and the TCP/IP or NetBEUI protocols. This chapter explains how to
configure the printer and Windows NT.
13
Page 18
Windows NT 4.0 Configuration
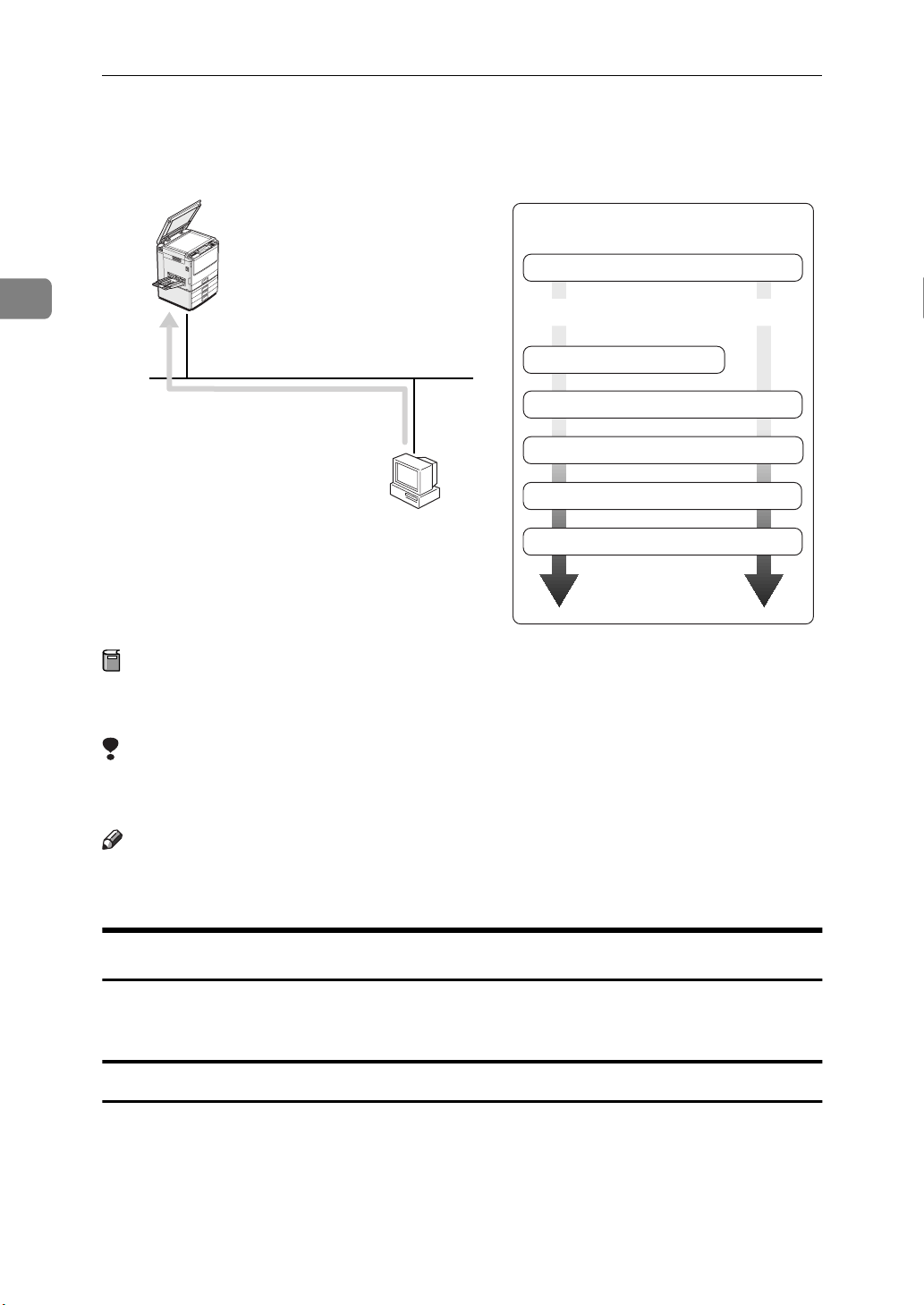
Preparing for a Network Connection
Basic Procedure
Selecting the protocol
2
TCP/IP NetBEUI
Assigning the IP address
TCP/IP
NetBEUI
Windows NT 4.0
Preparation
Configuring Windows environment
Installing Multidirect Print
Installing the printer driver
Changing the port
Multidirect Print supports the TCP/IP protocol and the NetBEUI protocol.
Consult the network administrator before selecting the protocol.
Limitation
❒
When you use the NetBEUI protocol, you cannot print to a printer which is
located on the other side of a router.
Note
❒
You can use both TCP/IP and NetBEUI protocols, in a computer. To use both
protocols, you must first install them.
Preparing to Use the TCP/IP Protocol for Printing
Follow these instructions to configure the Network Interface Board and Windows NT to use the TCP/IP protocol.
Configuring the printer
Configure your printer to use the TCP/IP protocol.
• Confirm that the TCP/IP protocol is set to active. (The default setting is active.)
• Assign an IP address and make other settings required for using the TCP/IP
protocol.
14
Page 19

Preparing for a Network Connection
Reference
For more information on how to make the above settings, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
If DHCP is used to assign IP addresses, see P.79
Note
❒
After setting the IP address, use the PING command to confirm that it has
been set correctly.
A
Click
B
Type the following. (Example IP address is 192.168.15.16)
C:> ping 192.168.15.16
If the address has been configured correctly, the following message appears.
Reply from 192.168.15.16 : bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=32
If the address has been configured incorrectly, the following message appears.
Request timed out.
Start
[
]
, point to
Programs
[
]
, and then click
“When Using DHCP”
Command Prompt
[
]
.
.
Configuring a Windows NT computer
2
Follow these steps to configure Windows NT to use the TCP/IP protocol.
Double-click the
A
Protocol” is in the
Note
❒
If the TCP/IP protocol is not installed, click
install it. For more information on installing the TCP/IP protocol, see the
Windows NT online help.
Configure the TCP/IP protocols with the appropriate IP address, subnet
B
mask and other settings.
Confirm with the network administrator that the settings are correct.
Click the
C
installed.
If “Microsoft TCP/IP Printing” is not installed, click
and install it. For more information on installing and configuring network
services, see the Windows NT online help.
Services
[
Network
[
Network protocols
[
tab, and confirm that the “Microsoft TCP/IP Printing” is
]
icon of
]
Control Panel
[
box in the
]
, and confirm that “TCP/IP
]
Add
tab.
]
Protocols
[
]
in the
]
tab, and
Services
[
Protocols
[
Add
[
]
in the
[
Preparing to Use the NetBEUI Protocol for Printing
]
tab,
Follow these instructions to configure the Network Interface Board and Windows NT to use the NetBEUI protocol.
15
Page 20

2
Windows NT 4.0 Configuration
Configuring the printer
Configure your printer to use the NetBEUI protocol.
• Confirm that the NetBEUI protocol is set to active. (The factory default is active.)
Reference
For more information on how to make the settings above, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
Configuring a Windows NT computer
Install the NetBEUI protocol into a Windows NT computer, and type the LAN
adapter number (Lana Number).
Double-click the
A
Protocol” is in the
Note
❒
If the NetBEUI protocol is not installed, click
and install it. For more information on installing the NetBEUI protocol, see
the Windows NT online help.
Change the Lana Number. Click the
B
in the
face
]
Select the Lana Number corresponding
C
headline, and click
Type “0” as the Lana Number.
D
Note
❒
If the other protocol's Lana Number is configured with “0”, you must
change the Lana Number with a number other than “0”.
Click
E
Click
F
After confirming the message for restart, click
G
[
[
Network Services
[
.
OK
]
Close
]
Network
[
Network protocols
[
[
, and close the
Edit
icon of
]
]
.
]
[
[
box , and click
Network
Control Panel
box in the
]
Services
[
Properties
[
Nbf protocol
[
dialog box.
]
, and confirm that “NetBEUI
]
]
in the
.
]
of the
]
.
tab.
]
Protocols
[
NetBIOS inter-
[
Network route
[
Protocols
[
Add
[
tab, select the
]
Yes
[
]
]
tab,
]
16
Note
❒
When you change the Lana Number, you must restart.
Page 21

Preparing for a Network Connection
Installing Multidirect Print
Follow these instructions to install Multidirect Print.
Preparation
You must restart the computer after installing Multidirect Print. Be sure to
close all applications before beginning the installation process.
Note
❒
You must install Multidirect Print and the appropriate printer driver in order
to print. If you print, using the TCP/IP protocol, to be able to browse the
printer via the network, PRINTER MANAGER FOR CLIENT (⇒see the inside of the front cover of this manual) needs to be installed. If the installer
starts automatically with the Auto Run program, you can install both of these
programs. For more information on how to install these programs, see the
"Printer Reference" that comes with the printer.
❒
To install this software, you must be logged on as a member of the Administrators group.
Close all applications that are currently running.
A
2
Insert the CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
B
Note
❒
If the installer starts automatically, you can use it to install Multidirect
Print, and set up the printer driver, and then go to step F.
Open
C
In the
D
Click
E
Type the name of the CD-ROM drive in the
F
gram
clude the quotation marks), and then click
❒
From the
G
After the
H
Control Panel
[
Install/Uninstall
[
Next >
[
box, followed by “:\NETWORK\MDP\DISK1\SETUP” (do not in-
]
Note
An example would be “D:\NETWORK\MDP\DISK1\SETUP” when the
drive letter is “D”.
.
]
Choose Setup Language
[
Welcome
[
, and double-click the
]
tab, click
]
dialog box appears, click
]
Install
[
list, select the language you use.
]
.
]
Add/Remove Programs
[
Command line for installation pro-
[
Next >
[
.
]
.
]
Finish
[
icon.
]
17
Page 22

Windows NT 4.0 Configuration
2
After the
I
computer now.
The computer restarts, and Multidirect Print can now be used. If you select
“No”, be sure to restart the computer manually before launching Multidirect
Print for the first time.
Go to P.18
Setup Complete
[
, and click
]
“Setting up the Printer Driver”
dialog box appears, click
]
Finish
[
.
]
after the computer restarts.
Yes, I want to restart my
[
Setting up the Printer Driver
Using Multidirect Print to print is not possible until the printer driver is installed
and the correct port is selected.
Preparation
The target printer must be turned on before starting the installation process.
Install the printer drivers.
A
If the printer drivers have already been installed, you can go to the next step.
Reference
For more information on installing the printer driver, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
Note
❒
Any port can be selected during the installation, however, LPT1 is recommended.
In the
B
the
Click the
C
In the
D
Port
The
can print with TCP/IP appear.
❒
❒
❒
Printers
[
menu, click
File
[
]
Available Printer Ports
[
.
]
Select Printer
[
Limitation
If PRINTER MANAGER FOR CLIENT is not installed in your computer,
printers which can print with TCP/IP do not appear.
You cannot add to type the port name that was already used.
Note
The printers which have replied to a broadcast from the computer are listed here. To print to a printer that is not on this list, or to directly type the
port name, click
name in step G.
window, click the icon of the printer you want to use. On
]
.
]
Add Port
[
box, click
]
]
, and click
.
]
Multi Direct Print
[
Next >
[
]
, and then type the port
, and then click
]
Ports
[
Properties
[
tab, and click
]
]
dialog box appears, and the names of the printers which
New Printer
[
New
[
18
Page 23

Preparing for a Network Connection
To print using the NetBEUI protocol, click
E
Click the printer you want to use, and click
F
Reference
For more information on a particular item in the dialog box, see P.51
tidirect Print”
Note
❒
You can identify the “Printer Name” and “Address” on the configuration
page printed by the printer.
Confirm that the port name of the printer is correct, and click
G
If you did not select a printer in step F, you must type the port name.
.
NetBEUI
[
Next >
[
.
]
.
]
[
Typing the port name for use with the TCP/IP protocol
Type the IP address of the Network Interface Board into the
A
box.
You can type the host name or a domain name instead of an IP address into
Host Name
[
the
Limitation
❒
You cannot use a host name that begins with “%%”.
❒
You cannot use a port name that is already in use.
]
box.
Next >
]
IP address
[
“Mul-
2
.
]
Note
❒
When you use DHCP to assign IP addresses to Network Interface
Boards, you can use a printer name (Current Hostname on the network
configuration page) as the host name.
Typing the port name for use with the NetBEUI protocol
Print a configuration page, and confirm the Network path name.
A
Reference
For more information on printing a configuration page, see the "Printer
Reference" included as a PDF file in the CD-ROM.
Type the printer's network path name in the form of “%%Computer
B
name \Share name”. Do not type “\\” as head characters but “%%”.
Confirm the port name in the
H
I
In the
Printer Ports
[
dialog box, click
]
Port Name
[
box, and click
]
Close
[
.
]
Finish
[
]
.
19
Page 24

Windows NT 4.0 Configuration
2
Confirm that the port name appears in the
J
and that it is selected. And then click
Configuration is complete.
When you print, the printing procedure is no different. When you select the
printer configured here, the computer automatically uses Multidirect Print.
OK
[
Print to the following port(s)
[
.
]
Uninstalling Multidirect Print
Open
A
In the
B
After a confirmation message appears, click
C
UninstallShield removes all of the components of Multidirect Print.
When the uninstallation is complete, restart the computer.
D
Control Panel
[
Install/Uninstall
[
, and double-click the
]
tab, click
]
Multi Direct Print
[
Add/Remove Programs
[
, and click
]
.
Yes
[
]
Add/Remove
[
icon.
]
box
]
.
]
20
Page 25
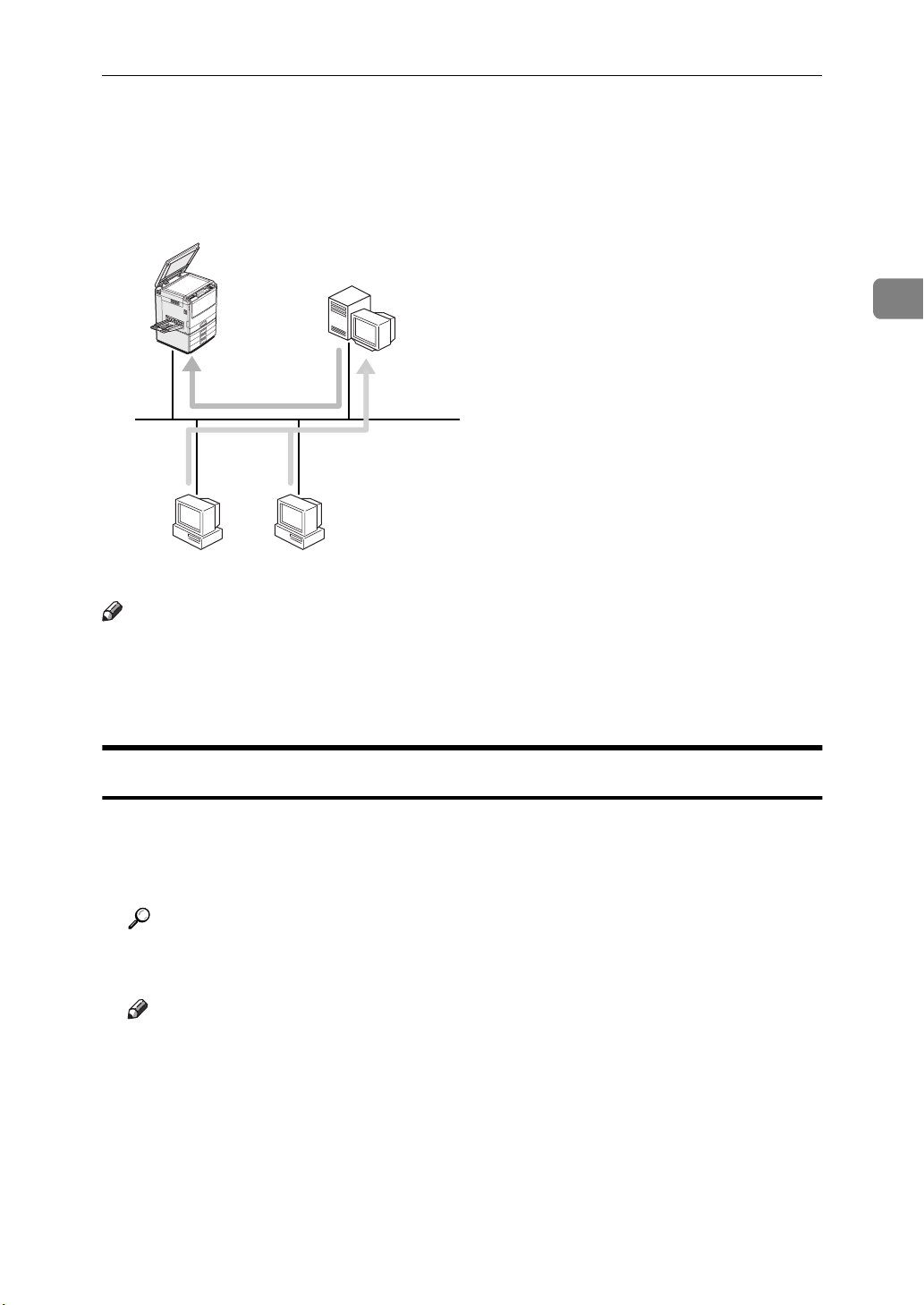
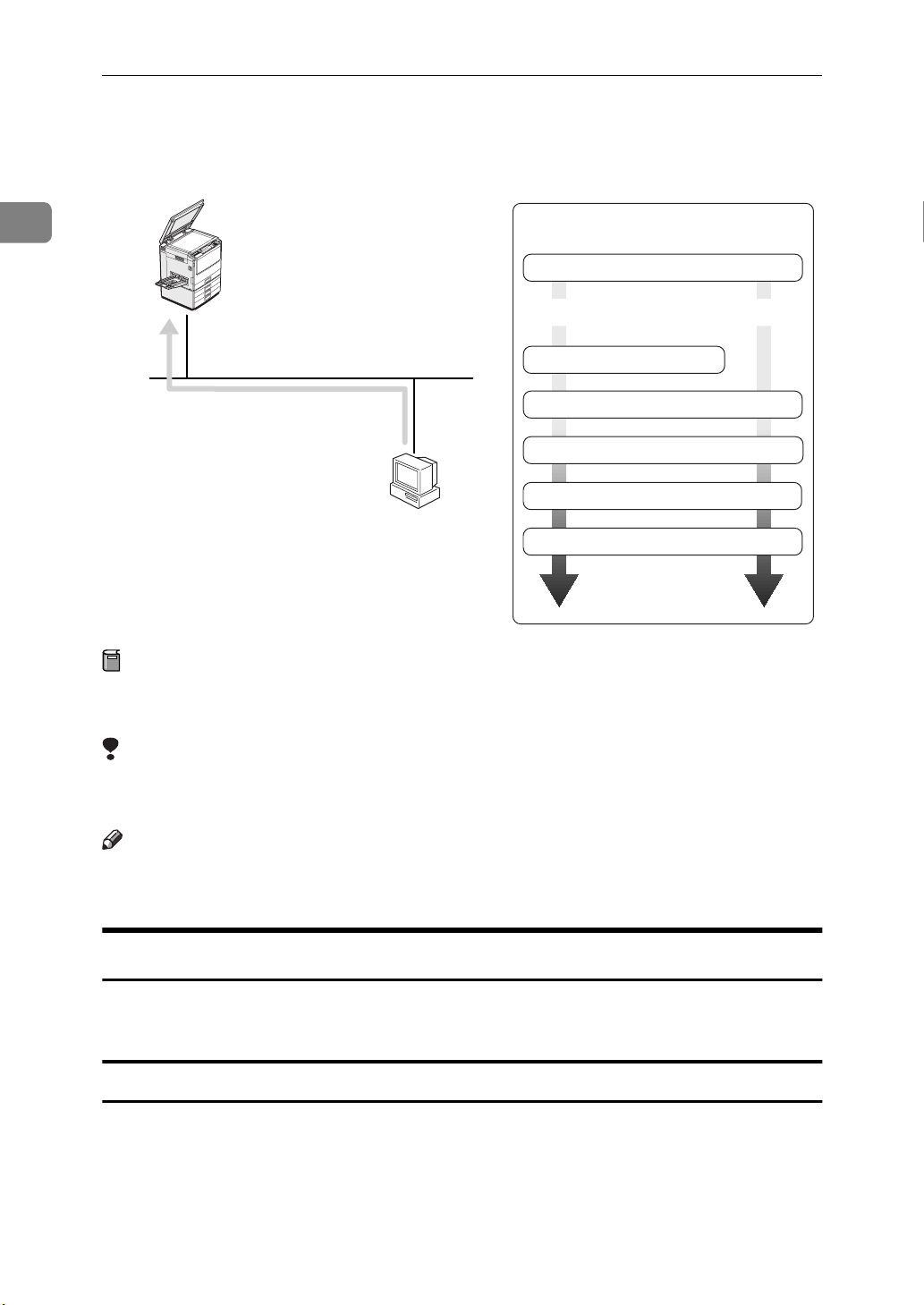
Setting up a Client Computer
Setting up a Client Computer
This section describes the procedures for setting up a client in a network that
uses Windows NT Server or Windows NT Workstation as a print server.
Windows NT 4.0
Print Server
Windows 95/98 Windows NT 4.0
2
Note
❒
All of the procedures in this section assume that the client has already been
configured to communicate with a Windows NT print server. Do not proceed
with the following instructions until the client has been set up and configured
correctly.
Windows 95/98
To print from Windows 95/98, you must install the printer driver and change
the printer port to the print server.
Install the printer driver as a local printer.
A
Reference
For more information on installing the printer driver, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
Note
❒
Any port can be selected during the installation, however, LPT1 is recommended.
B
Click
Start
[
, point to
]
Settings
[
, and then click
]
Printers
[
.
]
Click the icon of the printer you want to use. On the
C
.
erties
]
Click the
D
Details
[
tab, and click
]
Add Port
[
.
]
menu, click
File
[
]
Prop-
[
21
Page 26

Windows NT 4.0 Configuration
2
Click
E
On the network tree, double-click the name of the computer used as the
F
print server.
The names of the printers attached to the network appear.
Click the name of the printer you want to use, and click
G
Click
H
Confirm that the port name appears in the
I
click
Network
[
OK
[
OK
[
.
]
.
]
, and click
]
Browse
[
.
]
.
OK
[
]
Print to the following port
[
box, and
]
Windows NT 4.0
Printers
Use the
A
B
C
[
Click
Double-click the
This launches the Add Printer Wizard.
Click
Start
[
Network printer server
[
]
window to set up the printer.
, point to
]
[
Settings
[
Add Printer
, and then click
]
icon.
]
, and click
]
Next >
[
Printers
[
.
]
.
]
In the
D
print server.
The names of the printers attached to the network appear.
Click the name of the printer you want to use, and click
E
❒
❒
Select whether you use this printer as the default printer, and click
F
After installation is complete, click
G
The icon of the newly installed printer appears in the
Shared Printers
[
Note
If the printer driver is not installed in the print server, a message appears.
If a driver has been installed on the client, click
structions on the screen.
There is a Windows NT printer driver in the CD-ROM that comes with the
machine.
box, double-click the name of the computer used as a
]
.
OK
[
]
OK
]
[
, and follow the in-
Finish
[
.
]
Printers
[
]
window.
Next >
[
.
]
22
Page 27

Configuring LPR Port Printing
Configuring LPR Port Printing
This section explains the procedure for printing to a LPR port from Windows
NT.
Preparation
The TCP/IP protocols must be installed and configured correctly. ⇒ P.14
“Preparing to Use the TCP/IP Protocol for Printing”
Note
❒
The following instructions assume that the printer drivers have already been
installed. This is a procedure to change the printer port to LPR.
2
Click
A
Click the icon of the printer you want to use. On the
B
.
erties
]
Click the
C
In the
D
Note
❒
If “LPR Port” does not appear, “Microsoft TCP/IP Printing” has not been
installed.
Type the IP address of the Network Interface Board into the
E
of server providing lpd
Type “lp” into the
F
.
OK
]
[
Click
G
Confirm that the port name is displayed in the
H
box and the check mark is inside the check box. Then click
, point to
Start
[
]
tab, and then click
Ports
[
]
Available Printer Ports
[
.
Close
[
]
Settings
[
box.
]
Name of printer or print queue on that server
[
, and then click
]
Add Port
[
box, click
]
.
]
LPR Port
[
Printers
[
, and then click
]
.
]
menu, click
File
[
]
Name or address
[
box, and click
]
print to the following port(s)
[
OK
[
New Port
[
.
]
Prop-
[
.
]
]
23
Page 28

2
Windows NT 4.0 Configuration
24
Page 29

3. NetWare Configuration
This chapter describes how to configure the printer to use it as a print server or
a remote printer in a NetWare environment.
Note
❒
NetWare must be set to active using the operation panel of the printer. For
more information on how to set it, see the "Printer Reference" included as a
PDF file in the CD-ROM.
25
Page 30

3
NetWare Configuration
Installing NIB Setup Tool
A utility called NIB Setup Tool is provided to configure your printer to work in
a NetWare environment. Installing the PRINTER MANAGER FOR ADMINISTRATOR (⇒see the inside of the front cover of this manual) installs NIB Setup
Tool on the computer. This section describes how to install the PRINTER MANAGER FOR ADMINISTRATOR, and how to run NIB Setup Tool.
Limitation
❒
NetWare 3.x, 4.x or 5 must be functional to run NIB Setup Tool.
❒
NIB Setup Tool is supported to work with the following operating systems.
• Microsoft Windows 95/98
• Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
Installing the PRINTER MANAGER FOR ADMINISTRATOR
Follow these steps to install the PRINTER MANAGER FOR ADMINISTRATOR.
Preparation
You should install the PRINTER MANAGER FOR ADMINISTRATOR on
your computer. If you install the PRINTER MANAGER FOR ADMINISTRATOR from a file server or run it via the network, the PRINTER MANAGER
FOR ADMINISTRATOR might not work correctly.
Be sure to close all applications before starting the installation procedure.
Close all the applications that are currently running.
A
Insert the CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
B
If the setup menu starts automatically, follow the instructions on the screen.
Otherwise, go to step C.
Open
C
In the
D
Click
E
In the
F
drive followed by “:\NETWORK\PRINTMAN\XXXADMIN\DISK1\SETUP” (do not include the quotation marks) and then click
Control Panel
[
Install/Uninstall
[
Next >
[
command line f or installa tion pro gram
[
.
]
and double-click the
]
tab, click
]
Install
[
]
Add/Remove Programs
[
.
box, type the name of the CD-ROM
]
Finish
[
icon.
]
.
]
26
Note
❒
An example would be “D:\\NETWORK\PRINTMAN\XXXADMIN\DISK1\
SETUP” when the CD-ROM drive name is “D”.
From the
G
Choose Setup Language
[
list, select the language you use.
]
Page 31

Installing NIB Setup Tool
In the
H
The Software License Agreement appears.
I
After reading through all of the contents by clicking
agree with the License Agreement.
Select a folder to install it in, and then click
J
To change the displayed folder, click
The installation program starts.
After the confirmation dialog box appears, the installation is complete.
Welcome
[
dialog box, click
]
Next >
[
Browse
[
.
]
PageDown
[
Next >
[
]
to select another one.
.
]
]
, click
Running NIB Setup Tool
Click
A
ER MANAGER FOR ADMINISTRATOR
Start
[
, point to
]
Programs
[
, and then click
]
program folder.
]
NIB Setup Tool
[
in the
]
Yes
[
PRINT-
[
]
to
3
27
Page 32

3
NetWare Configuration
Quick Setup Using the NIB Setup Tool Wizard
Using NIB Setup Tool, you can easily set up a NetWare printing environment.
Reference
For more information on setting up NIB Setup Tool, see P.26
Setup Tool”
You can select
When you configure the Network Interface Board for the first time, use the Wiz-
ard method.
If you want to use the Property Sheet method, see P.31
Settings”
Note
❒
This section assumes that NetWare is functional and that the necessary environment for the NetWare Print Services is available.
❒
If you configure the Network Interface Board in a NetWare environment using NIB Setup Tool, you should install the client software released from Novell in the following cases.
• Windows 95/98 in NDS mode
.
Wizard
[
and P.37
Property Sheet
]
[
or
“NetWare 4.x, 5 - Advanced Settings”
]
as an installation method.
“NetWare 3.x - Advanced
.
“Installing NIB
• Windows NT 4.0 in NDS mode
• Windows NT 4.0 in Bindery mode
Log in to the Netware file server or the NDS tree as an Admin or Admin
A
equivalent.
Run NIB Setup Tool.
B
Reference
⇒
Click
C
[
The
Click
D
Click the IPX address of the Network Interface Board you are configuring,
E
and click
Note
❒
If you do not know which Network Interface Board you are configuring,
see a network configuration page to confirm the MAC address (Network
address).
“Running NIB Setup Tool”
P.27
Wizard
[
Network board list
IPX protocol
[
and click
]
Next >
[
]
dialog box of the Network Interface Board appears.
.
]
.
]
[OK]
.
28
Page 33

Quick Setup Using the NIB Setup Tool Wizard
Confirm that the MAC address and IPX address are correct, and click
F
.
ish
]
Fin-
[
Type the print server name into the
G
The factory default is RDP_ followed by the 6 digit serial number. We recommend that you change it to something that is easier to remember or something
based on the structure of your network.
In the dialog box for selecting a network environment, click to select
H
and clear
Ware
]
Click
I
A dialog box for configuring the NetWare environment appears.
Select
J
when printing under the NDS mode.
When you are using NetWare version 4.x, you should select
❒
If you selected
K
file server in which a print server is to be created.
Clicking
Browse
[
Next >
[
Bindery
[
Note
When configuring the NDS mode, if
check the version of the client software released from Novell. It is recommended that you install the latest version of the client software released
from Novell.
Browse
[
]
dialog box.
TCP/IP
[
.
]
when printing under the Bindery mode, or select
]
Bindery
[
]
.
]
, type into the
]
, you can select a file server among those listed in the
Device Name
[
NDS
[
]
File Server Name:
[
box, and click
]
cannot be selected, you need to
box the name of the
]
NDS
[
Next >
[
]
.
.
]
Net-
[
NDS
[
3
]
If you selected
L
which the print server is created, and type the context into the
Browse
Clicking
listed in the
As a context, object names are typed from a lower object and divided by a period. For example, if you want to create a print server into NET under DS,
type “NET.DS”.
Click
M
[
Next >
[
Browse
[
.
]
, type into the
NDS
[
]
]
, you can select a NDS tree and a NDS context among those
]
dialog boxes.
[
box the name of the NDS tree in
Tree:
]
Context:
[
box.
]
29
Page 34

NetWare Configuration
3
Type the name of the printer into the
N
print queue into the
The default for the Printer Name is “Print Server Name” followed by “_1”
and that the default for the Print Queue Name is “Print Server Name” followed by “_Q” ( quotation marks are not included). You can change them, if
necessary.
If you have selected the NDS mode, type the volume of the print queue into
O
the
Queue Volume
[
Browse
Clicking
box.
Click
P
A dialog box to confirm the printing environment appears.
After confirming the environment, click
Q
If you want to change the settings, click
Clicking
Printer and the Print Queue in the NetWare network.
After a confirmation dialog box appears, select
R
exit NIB Setup Tool.
[
Next >
[
[
.
]
Next >
]
Print Queue Name
[
box.
]
]
, you can select one of those shown in the
, NIB Setup Tool automatically creates the Print Server, the
Printer Name
[
box.
]
Next >
[
< Back
[
box, and the name of the
]
Browse
[
.
]
]
and make the settings again.
and click
Quit
[
]
]
Finish
[
dialog
to
]
30
Page 35

NetWare 3.x - Advanced Settings
NetWare 3.x - Advanced Settings
The actual procedures for configuring the printer may differ depending on
whether the Network Interface Board is configured as a print server or as a remote printer. This section describes how to configure it in the NetWare 3.x environment.
Basic Procedure
Installing NIB Setup Tool
Print Server Remote Printer
Configuring the Network Interface Board
Configuring the NetWare
3
Turning the power
off and on
Preparation
The following procedures use the Property Sheet method in configuring the
Network Interface Board. When you configure the Network Interface Board
as a NetWare print server for the first time, we recommend that you use the
Wizard method. ⇒ P.28
Note
❒
This section assumes that NetWare is functional and that the necessary environment for the NetWare Print Service is available.
Starting the print server
“Quick Setup Using the NIB Setup Tool Wizard”
Setting up as Print Server
Log in to the file server as a Supervisor or a Supervisor equivalent.
A
Run NIB Setup Tool.
B
Reference
⇒
“Running NIB Setup Tool”
P.27
C
D
Click
[
The
Click
Property Sheet
[
Browse
]
dialog box of the Network Interface Board appears.
IPX protocol
[
and click
]
.
]
[OK]
.
31
Page 36

3
NetWare Configuration
Click the IPX address of the Network Interface Board which is to be config-
E
ured, and then click
Note
❒
If you do not know which Network Interface Board you are configuring,
see a network configuration page to confirm the MAC address (Network
Address).
Confirm that the MAC address and the IPX address are correct, and click
F
Finish
[
The
Click
G
The property sheet appears.
.
]
NIB Setup Tool
[
Configure
[
]
Next >
[
]
window appears.
.
.
]
Click the
H
Name
Click the
I
Select
A
In the
B
print server is to be created.
Click
log box.
Click
C
After a confirmation dialog box appears, click
D
On the
J
Type “PCONSOLE” from the command prompt.
K
F:> PCONSOLE
Create a print queue as follows.
L
Note
❒
If you use the currently defined print queue, go to step M.
From the
A
the
Press the
B
Press the
C
General
[
box.
]
NetWare
[
Bindery
[
File Server Name:
[
Browse
[
OK
[
NIB
[
]
ENTER
{
tab, and type the name of the print server into the
]
tab, and make the following settings.
]
.
]
box, type the name of the file server in which a
]
]
to select a file server among those listed in the
to close the property sheet.
]
menu, click
Available Options
[
key.
}
{
INSERT
{
ESC
key and type a print queue name.
}
key to return to the
}
to exit NIB Setup Tool.
Exit
[
]
menu, select
]
Available Options
[
Print Queue Information
[
OK
[
.
]
]
menu.
[
Browse
[
and press
]
Device
]
dia-
32
Create a printer as follows.
M
From the
A
the
{
Available Options
[
ENTER
key.
}
menu, select
]
Print Server Inf ormat ion
[
and press
]
Page 37

NetWare 3.x - Advanced Settings
To create a new print server, press the
B
server name.
If you use the currently defined print server, select one of the print servers
Print Server
shown in the
Important
❒
Use the same name as that specified in NIB Setup Tool. ( Step H)
From the
C
From the
D
Select the printer which is indicated as “Not Installed”.
E
If you change the name of the printer, type a new name.
F
A name "Printer x" is assigned to the printer. “x” stands for the number of
the selected printer.
As Type, select
G
The IRQ, Buffer size, Starting form and Queue service modes are automatically configured.
Press the
H
Press the
I
Assign print queues to the created printer as follows.
N
From the
A
Select the printer created in step M.
B
Press the
C
[
Print Server Information
[
Print Server Configuration
[
Remote Other/Unkown
[
key, and click
ESC
}
{
{
[
{
key to return to the
ESC
}
Print Server Configuration
INSERT
}
]
list.
menu, select
]
menu, select
]
Yes
]
[
menu, select
]
key to select a queue serviced by the printer.
{
INSERT
.
]
in the confirmation dialog box.
Print Server Configuration
[
key and type a print
}
Print Server Configuration
[
Printer Configuration
[
]
Queues Serviced By Printer
[
menu.
.
]
.
]
3
.
]
Note
❒
You can select more than one queue at a time.
Follow the instructions on the screen to make other necessary settings.
D
When you have finished the previous steps, confirm that the queues are assigned.
Press the
O
SOLE.
Turn the printer power off and on.
P
Note
❒
To confirm that the printer is configured correctly, type the following from
the command prompt.
F:> USERLIST
❒
If the printer works as configured, the name of the print server appears as
an attached user.
{
key until “Exit?” appears, and select
ESC
}
to exit PCON-
Yes
]
[
33
Page 38

NetWare Configuration
Setting up as Remote Printer
Log in to the file server as a Supervisor or a Supervisor equivalent.
A
Run NIB Setup Tool.
B
Reference
⇒
“Running NIB Setup Tool”
P.27
3
Click
C
The
Click
D
Click the IPX address of the Network Interface Board which is to be config-
E
ured, and click
❒
Confirm that the MAC address and IPX address are correct, and click
F
ish
The
Click
G
The property sheet appears.
Click the
H
Name
Property Sheet
[
Browse
[
Note
If you do not know which Network Interface Board you are configuring,
see a network configuration page to confirm the MAC address (Network
Address).
.
]
NIB Setup Tool
[
box.
]
]
dialog box of the Network Interface Board appears.
IPX protocol
[
Configure
[
General
[
and click
]
.
]
Next >
[
.
]
.
]
]
window appears.
tab, and type the name of the print server into the
]
[OK]
.
Fin-
[
Device
[
34
Click the
I
In the
A
In the
B
print server is to be created.
Clicking
Browse
[
In the
C
In the
D
❒
Click
E
After a confirmation dialog box appears, click
F
NetWare
[
Print Server Name
[
File Server Name
[
Browse
[
]
dialog box.
Print Server Operation Mode
[
Remote Printer No.
[
Important
Use the same printer number as that to be created in the printer server.
OK
[
]
tab, and make the following settings.
]
box, type the name of the print server.
]
box, type the name of the file server in which a
]
]
, you can select a file server among those listed in the
group, click
]
box, type the printer number.
]
to close the property sheet.
As Remote Printer
[
.
OK
[
]
.
]
Page 39

NetWare 3.x - Advanced Settings
On the
J
Type “PCONSOLE” from the command prompt.
K
F:> PCONSOLE
Create a print queue as follows.
L
Note
❒
If you use the currently defined print queue, go to step L.
From the
A
the
Press the
B
Press the
C
Create a printer as follows.
M
From the
A
the
To create a new print server, press the
B
server name.
If you use an currently defined print server, select one of the print servers
shown in the
NIB
[
{
ENTER
{
ENTER
]
menu, click
Available Options
[
key.
}
{
INSERT
{
[
key to return to the
ESC
}
Available Options
key.
}
Print Server
[
Exit
[
key and type a print queue name.
}
to exit NIB Setup Tool.
]
menu, select
]
menu, select
]
]
list.
Print Queue Information
[
Available Options
[
Print Server Inf ormat ion
[
{
INSERT
menu.
]
key and type a print
}
and press
]
and press
]
3
Important
❒
Use the same name as that specified in NIB Setup Tool. (Step H)
From the
C
From the
D
Select the printer which is indicated as “Not Installed”.
E
Important
❒
Use the same number as that was used as the Remote Printer No. using
NIB Setup Tool. (Step I-D)
If you change the name of the printer, type a new name.
F
A name "Printer x" is assigned to the printer. x stands for the number of the
selected printer.
As type, select
G
The IRQ, Buffer size, Starting form, and Queue service mode are automatically configured.
Press the
H
Press the
I
Assign print queues to the created printer as follows.
N
From
A
Select the printer created in step L.
B
Print Server Information
[
Print Server Configuration
[
Remote Parallel, LPT1
[
{
{
Print Server Configuration Menu
[
key, and click
ESC
}
key to return to
ESC
}
menu, select
]
menu, select
]
.
]
in the confirmation dialog box.
Yes
]
[
Print Server Configuration Menu
[
, select
]
Print Server Configuration
[
Printer Configuration
[
Queues Serviced By Printer
[
.
]
.
]
.
]
.
]
35
Page 40

NetWare Configuration
3
Press the
C
Note
❒
You can select more than one queue at a time.
Follow the instructions on the screen to make other necessary settings.
D
When you have finished the previous steps, confirm that the queues are assigned.
Press the
O
SOLE.
Start the print server by typing the following from the console of the Net-
P
Ware Server.
If it is running, restart it after exiting it.
To exit
❖
CAREE: unload ps er ver
To start
❖
CAREE: load pser ve r
Note
❒
If the printer works as configured, “Waiting for job” appears.
{
ESC
{
INSERT
}
key to select a queue serviced by the printer.
}
key until “Exit?” appears, and select
print_server_name
[
to exit PCON-
Yes
]
36
Page 41

NetWare 4.x, 5 - Advanced Settings
NetWare 4.x, 5 - Advanced Settings
The actual procedures for configuring the printer may differ depending on
whether the Network Interface Board is configured as a print server or as a remote printer. This section describes how to configure it in the NetWare 4.x and
5 environment.
To use NetWare 5
❖
• Load the IPX protocol into the file server in advance.
• You cannot use the NDPS (Novell Distributed Print Services) mode.
Basic Procedure
Installing NIB Setup Tool
Print Server Remote Printer
Configuring the Network Interface Board
Configuring the NetWare
Turning the power
off and on
Preparation
Starting the print server
The following procedures use the Property Sheet method in configuring the
Network Interface Board. When you configure the Network Interface Board
as a NetWare print server for the first time, we recommend that you use the
Wizard method. ⇒ P.28
“Quick Setup Using the NIB Setup Tool Wizard”
3
Note
❒
This section assumes that NetWare is functional and that the necessary environment for the NetWare Print Service is available.
❒
You should install the client software released from Novell on Windows before running NIB Setup Tool for configuring in NDS mode or using Windows
NT 4.0.
37
Page 42

3
NetWare Configuration
Setting up as Print Server
Important
❒
You can set up the print server using the NDS or Bindery mode in NetWare
4.x, 5. The following procedure is for setting up the print server using the
NDS mode in NetWare 4.1. When you set up the print server using the Bindery mode, use the NIB Setup Tool Wizard. ⇒ P.28
Setup Tool Wizard”
Log in to the file server as an Admin or an Admin equivalent.
A
Run NIB Setup Tool.
B
Reference
⇒
“Running NIB Setup Tool”
P.27
.
“Quick Setup Using the NIB
Click
C
The
Click
D
Select the IPX address of the Network Interface Board which is to be con-
E
figured by clicking it, and click
❒
Confirm that the MAC address and the IPX address are correct, and click
F
Finish
[
The
Click
G
The property sheet appears.
Click the
H
Name
Property Sheet
[
Browse
[
Note
If you do not know which Network Interface Board you are configuring,
see a network configuration page to confirm the MAC address (Network
Address).
NIB Setup Tool
[
box.
]
]
dialog box of the Network Interface Board appears.
IPX protocol
[
.
]
Configure
[
General
[
and click
]
.
]
]
window appears.
.
]
tab and type the name of the print server into the
]
[OK]
Next >
[
.
.
]
Device
[
38
Click the
I
A
Select
NetWare
[
NDS
[
]
tab, and make the following settings.
]
.
Page 43

NetWare 4.x, 5 - Advanced Settings
Type into the
B
server is created, and type the context into the
Clicking
those listed in the
As a context, object names are typed from a lower object and divided by a
period. For example, if you want to create a print server into NET under
DS, type "NET.DS".
Click
C
After a confirmation dialog box appears, click
D
On the
J
From Windows, run NWAdmin.
K
Reference
For more information on NWAdmin, see the documentation that comes
with NetWare.
NIB
[
OK
[
]
[
Browse
[
to close the property sheet.
]
menu, click
box the name of the NDS tree in which the print
Tree:
]
Context:
[
]
, you can select a NDS tree and a NDS context among
Browse
[
]
dialog box.
to exit NIB Setup Tool.
Exit
[
]
OK
[
box.
]
.
]
3
Create a print queue as follows.
L
Select the container object the print queue is located in among those in
A
the directory tree, and click
In the
B
In the
C
In the
D
In the
E
created, and click
After confirming the settings, click
F
Create a printer as follows.
M
Select the container object the printer is located in, and click
A
the
In the
B
are using NetWare 5, click “Printer (Non NDPS)”.
In the
C
Click to select
D
Assign print queues to the created printer as follows.
N
Click
A
Class of new object
[
Print Queue name
[
Print Queue Volume
[
Available objects
[
Object
[
menu.
]
Class of new object
[
Printer name
[
Define additional properties
[
Assignments
[
]
box, click the volume in which the print queue is
]
.
OK
[
]
box, type the name of the printer.
]
, and click
]
Create
[
box, click “Print Queue”, and click
]
box, type the name of the print queue.
box, click the
]
box, click “Printer”, and click
]
Add
[
on the
]
Create
[
in the
]
Object
[
Browse
[
.
]
to check a box, and click
]
Assignments
[
menu.
]
button.
]
[OK]
group.
]
.
[OK]
Create
[
on
]
Create
[
. When you
.
]
39
Page 44

NetWare Configuration
3
In the
B
OK
[
Click
C
drop-down menu, and then click
Click
D
After confirming the settings, click
E
Create a print server as follows.
O
Select the context specified using NIB Setup Tool (step I-A) and on the
A
Object
[
In the
B
you are using NetWare 5, click “Print Server (Non NDPS)”.
In the
C
❒
Click to select
D
Assign the printer to the created print server as follows.
P
Click
A
In the
B
and click
After confirming the settings, click
C
Available objects
[
.
]
Configuration
[
Manual load
[
menu, click
]
Class of new object
[
Print Server name
[
Important
Use the same name as that specified using NIB Setup Tool. (Step H)
Assignments
[
Available objects
[
OK
[
]
Define additional properties
[
.
]
box, click the queue created in step L, and click
]
, and in the
]
in the
, and click
]
Communication type
[
Create
[
box, click “Print Server”, and click
]
box, type the name of the print server.
]
box, click to select the printer created in step M,
]
.
]
[
Printer type
[
Communication
[
OK
[
in the
Add
]
OK
[
box, select
]
.
]
group, and click
]
.
]
, and click
]
Assignments
[
.
]
[
Create
[
group.
]
Parallel
.
]
using the
]
.
[OK]
. When
[OK]
Turn the printer power off and on.
Q
Note
❒
If the printer works as configured, the name of the print server appears as
an attached user.
Setting up as Remote Printer
Log in to the file server as Admin or an Admin equivalent.
A
Run NIB Setup Tool.
B
Reference
C
D
⇒
Click
[
The
Click
“Running NIB Setup Tool”
P.27
Property Sheet
[
Browse
]
dialog box of the Network Interface Board appears.
IPX protocol
[
and click
]
.
]
[OK]
.
40
Page 45

NetWare 4.x, 5 - Advanced Settings
Select the IPX address of the Network Interface Board which is to be con-
E
figured by clicking it, and click
Note
❒
If you do not know which Network Interface Board you are configuring,
see a network configuration page to confirm the MAC address (Network
Address).
Confirm that the MAC address and the IPX address are correct, and click
F
Finish
[
The
Click
G
The property sheet appears.
.
]
NIB Setup Tool
[
Configure
[
.
]
]
window appears.
Next >
[
.
]
3
Click the
H
Name
Click the
I
In the
A
In the
B
print server is to be created.
Clicking
Browse
[
In the
C
be created.
Clicking
Browse
[
As a context, object names are typed from a lower level object and divided
by a period. For example, if you want to create a print server into NET under DS, type “NET.DS”.
General
[
box.
]
NetWare
[
Print Server Name
[
File Server Name
[
[
]
dialog box.
NDS Context
[
]
dialog box.
tab, and type the name of the print server into the
]
tab, and make the following settings.
]
box, type the name of the print server.
]
box, type the name of the file server in which a
]
Browse
Browse
[
]
, you can select a file server among those listed in the
box, type the context in which the print server is to
]
]
, you can select a context among those listed in the
Device
[
In the
D
In the
E
❒
Click
F
After the confirmation dialog box appears, click
G
Print Server Operation Mode
[
Remote Printer No.
[
Important
Use the same number as that of the printer to be created in the print
server.
to close the property sheet.
OK
[
]
box, type the number of the printer.
]
group, click
]
As Remote Printer
[
.
OK
[
]
.
]
41
Page 46

NetWare Configuration
3
On the
J
From Windows, run NW Admin.
K
Reference
For more information on NWAdmin, see the documentation that comes
with NetWare.
Create a print queue as follows.
L
Select the container object the print queue is located in among those in
A
the directory tree, and click
In the
B
OK
]
[
In the
C
In the
D
In the
E
queue is created, and click
After confirming the settings, click
F
Create a printer as follows.
M
Select the container object the printer is located in, and click
A
the
In the
B
When you are using the NetWare 5, click “Printer (Non NDPS)”.
In the
C
Click
D
menu, click
NIB
[
]
Class of new object
[
.
Print Queue name
[
Print Queue Volume
[
Available objects
[
Object
[
menu.
]
Class of new object
[
Printer name
[
Define additional properties
[
Exit
[
box, type the name of the print queue.
]
box, click to select the volume in which the print
]
box, type the name of the printer.
]
to exit NIB Setup Tool.
]
Create
[
box, click to select “Print Queue”, and click
]
box, click the Browse button.
]
OK
[
box, click to select “Printer”, and click
]
on the
]
.
]
Create
[
to check a box, and click
]
Object
[
.
]
menu.
]
Create
[
Create
[
.
]
in
]
[OK]
.
42
Assign print queues to the created printer as follows.
N
Click
A
In the
B
OK
[
Click
C
drop-down menu, and then click
Click
D
After confirming the settings, click
E
Create a print server as follows.
O
Select the context specified using NIB Setup Tool (Step H), and on the
A
Object
[
In the
B
you are using the NetWare 5, click “Print Server (Non NDPS)”.
In the
C
Assignments
[
Available objects
[
.
]
Configuration
[
Manual load
[
menu, click
]
Class of new object
[
Print Server name
[
, and click
]
box, click the queue created in step K, and click
]
, and in the
]
in the
]
[
Create
[
box, click “Print Server”, and click
]
box, type the name of the print server.
]
in the
Add
[
]
Printer type
[
Communication
[
Communication type
OK
[
.
]
Assignments
[
box, select
]
.
]
group.
]
Parallel
[
.
]
group, and click
]
using the
]
.
[OK]
. When
[OK]
Page 47

NetWare 4.x, 5 - Advanced Settings
Important
❒
Use the same name as that specified using NIB Setup Tool. (Step H)
Click to select
D
Assign the printer to the created print server as follows.
P
Click
A
In the
B
OK
[
In the
C
Printer Number
[
Type the printer number and click
D
❒
After confirming the settings, click
E
Start the print server by typing as follows from the console of the NetWare
Q
Server.
Assignments
[
Available objects
[
.
]
Printers
[
Important
Use the same number as that specified as Remote Printer No. using NIB
Setup Tool. (Step H-E)
Define additional properties
[
, and click
]
box, click the queue created in step L, and click
]
group, click the printer assigned in step B, and click
]
.
]
Add
[
]
]
in the
.
OK
[
]
.
OK
[
]
, and click
Assignments
[
Create
[
group.
]
.
]
3
If it is running, restart it after exiting it.
To exit
❖
CAREE: unload ps er ver
To start
❖
CAREE: load pser ve r
print_server_name
43
Page 48

NetWare Configuration
Setting up a Client Computer
This section describes how to set up a client computer when you use a NetWare
print server.
Note
❒
This section assumes that the client has NetWare client applications installed
and is correctly configured to communicate with a NetWare print server. If
not, install necessary applications before starting the set up procedure.
3
Windows 95/98
Follow these steps to set up a Windows 95/98 client.
Preparation
Log in to the NetWare file server before starting the following procedure.
Install the printer driver of the printer you want to use as “Local printer”.
A
Reference
For more information on installing the printer driver, see the "Printer Reference" that comes with the printer.
Note
❒
Any port can be selected during the installation, however, LPT1 is recommended.
Click
B
In the
C
On the
D
Click the
E
Start
[
Printers
[
File
[
[
, point to
]
window, click the icon of the printer you want to use.
]
menu, click
]
Details
Settings
[
tab, and click
]
, and then click
]
Properties
[
Add Port
[
Printers
[
.
]
.
]
.
]
44
Click
F
On the network tree, double-click the name of the file server.
G
The queues appear.
Click the queue you want to print, and click
H
Click
I
In the
Click
J
Click the
K
Network
[
OK
[
Print to the following port
[
OK
[
and click
]
.
]
to close the printer property, and again, open it.
]
Printer Settings
[
Browse
[
tab.
]
.
]
.
OK
[
]
]
box, a network path to the printer appears.
Page 49

Setting up a Client Computer
Clear the
L
Note
❒
You should not select these check boxes because they should be specified
using the printer driver. If they are checked, the printer might not print
correctly.
When using the PostScript printer driver
Follow these steps to set up for the PostScript printer driver.
Click the
A
Click
B
Remove the check marks from the
C
CTRL+D after job
Click
M
Form feed
[
PostScript
[
Advanced
[
to close the property.
OK
[
]
and the
]
tab.
]
.
]
check boxes.
]
Enable banner
[
Send CTRL+D before job
[
check boxes.
]
and the
]
Windows NT 4.0
Follow these steps to set up a Windows NT 4.0 client.
Preparation
Log in to the NetWare file server before starting the following procedure.
Send
[
3
Double-click the
A
the queue you want to use, and then double-click it.
Printers
[
The
Click
B
Close all the applications that are currently running.
C
Insert the CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
D
If the setup menu starts automatically, you can proceed to the next step. If not,
see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
The
E
From the
F
Follow the instructions on the screen to finish the installation of the printer
G
driver.
[
Printer Installation
[
No
.
]
Port
[
]
Network Neighborhood
[
dialog box appears.
dialog box appears.
]
list, select the queue you selected in step A, and click
]
icon on the desktop and navigate to
]
[
Next >
.
]
45
Page 50

3
NetWare Configuration
46
Page 51

4. Macintosh Configuration
Configuring a Macintosh
This chapter explains how to configure a network printer in a Macintosh EtherTalk environment. The actual procedures to configure a network printer may
differ depending on the version of the Mac OS. This chapter describes how to
configure your printer for Mac OS 8. If you use a different version, see the manual that comes with your version of the Mac OS for more information.
Basic Procedure
Changing to EtherTalk
Configuring the printer
Changing printer name
Changing zone
Limitation
❒
To print from a Macintosh, you must use RICOH-SCRIPT2.
Changing to EtherTalk
Follow these steps to configure a Macintosh computer to use EtherTalk.
Reference
For more information on installing the software required for EtherTalk, see
the Macintosh manuals.
Open
A
From the
B
If you change zones, select a name from the
C
Control Panels
[
Connect via:
[
, and double-click the
]
menu, select “Ethernet”.
]
AppleTalk
[
zone
[
]
icon.
]
menu.
Close the
D
Restart the Macintosh.
E
AppleTalk
[
control panels.
]
47
Page 52

4
Macintosh Configuration
Configuring the Printer
Use the operation panel to activate the EtherTalk protocol (The default setting is
active).
Reference
For more information on configuration, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
Changing Printer Name
If the network has several same model printers, the names will be the same.
Printers that have the same name will have their names changed slightly in the
Chooser. For example, three printers named “printer” will appear in the chooser
as “printer0”, “printer1” and “printer2”.
Use an application such as
change printer names in the Macintosh EtherTalk environment. These utilities
are distributed by Apple Computer, Inc.
Apple Printer Utility
LaserWriter Utility
or
to
Changing Zone
It may be necessary to change the zone configuration.
Use an application such as
change the zone configuration in the Macintosh EtherTalk environment. These
utilities are distributed by Apple Computer, Inc.
Note
❒
If your Macintosh is configured to use TCP/IP, you can change the zone configuration with a Web browser. ⇒ P.54
Board with a Web Browser”
Follow these steps to use the Apple Printer Utility.
A
Insert the CD-ROM in the CD-ROM drive.
B
Copy the “Zone Name.ps” file in the “Zone Name” folder to the hard disk.
C
Open the copied “Zone Name.ps” file using a text editor, and change “NewZone” , which is in the second line from the bottom, to the name of the new
zone.
%!PS-Adobe2.0 %%
Title: Changing Zone (EtherNet only)
%%CreationDate: Tue Dec 16 1997
%%EndComments
true 0 startjob not {ERROR}if
(%EtherTalk%) << /EtherTalkZone (
%%EOF
D
Save “Zone Name.ps”.
Apple Printer Utility
“Configuring the Network Interface
NewZone
) >> setdevparams
LaserWriter Utility
or
to
48
Page 53

Configuring a Macintosh
E
Run the Apple Printer Utility, and select the printer for which the new zone
name is to be used.
F
Select
the printer.
Send PostScript File
[
]
in the
Utilities
[
]
menu, and send “Zone Name.ps” to
4
49
Page 54

4
Macintosh Configuration
50
Page 55

5. Appendix
6
Multidirect Print
Multidirect Print is a Windows program that allows you to print on a Peer-toPeer network. This program allows you to print directly to a network printer,
even if there is no print server.
OS Protocol Stack
Microsoft Windows 95/98 The Microsoft version of TCP/IP that comes with
Windows.
Microsoft Windows NT 4.0
Note
❒
If the printer is in the middle of warming up or printing, an error message
might appear for a short time after you request a print job. You can change
how long the printer should wait to display the message by clicking
tings
]
in the
tab on Windows NT 4.0.
Details
[
]
tab on Windows 95/98, and
The Microsoft version of NetBEUI that comes with
Windows.
Port Set-
[
Configure Port
[
]
in the
Ports
[
]
Select Printer
[
A list of available printers appears on this screen. This example is for the English
version.
Printer Name
1.
The contents of this list are different for
the TCP/IP and NetBEUI protocols.
]
1
4
2 3
5
TCP/IP
If you select
the Network Interface Board appears. If
you select
of the Network Interface Board appears.
[
NetBEUI
[
]
, the printer name of
]
, the computer name
51
Page 56

Appendix
5
Note
The printer name can be found on the
❒
printer configuration page.
The printer name is set to “RNP” and
❒
the last 6 digits of the MAC address of
the Network Interface Board. For example, a board with a MAC address of
00:00:74:62:5C:65, would be named
RNP625C65. You can change this
name to something more convenient.
Address
2.
The contents of this list are different for
the TCP/IP and NetBEUI protocols.
TCP/IP
If you select
the Network Interface Board appears. If
you select
of the Network Interface Board appears.
Network
[
[
NetBEUI
[
]
]
, the printer name of
]
, the computer name
Note
The form of the Network path name is
❒
“%% computer name \ name of printer type”.
Comment
3.
Comments that are registered on the Network Interface Board.
4.
Refresh
[
Click to refresh the contents of the display. When refreshing, the name of this
button changes to
the refresh.
5.
About
[
Version and copyright information.
Protocol
6.
Select to display the printers which can
print using the selected protocol.
]
Stop
]
[
. Click it to stop
]
When you select a printer with the
[
]
dialog box, the port name is en-
Select Printer
tered automatically. These examples are for the English version.
❖ TCP/IP ❖ NetBEUI
1 3
2
Host name
1.
If you print using the TCP/IP protocol, to
select a printer using a host name or a domain name, type the name here. Type the
IP address
IP address into the
selecting a printer by an IP address.
Limitation
❒
You cannot use a host name that
[
begins with “%%”.
]
box when
Note
When you use DHCP to assign IP ad-
❒
dresses to Network Interface Boards,
you can use a printer name (Current
Hostname on the network configuration page) as the host name.
IP address
2.
If you print using the TCP/IP protocol,
type the IP address of the printer.
52
Page 57

Printer name
3.
Type the printer's Network path name in
form of “%%Computer name \Share
name”. Do not type “\\” as head characters but “%%”.
Multidirect Print
5
53
Page 58

5
Appendix
Configuring the Network Interface Board with a Web Browser
The Network Interface Board functions as a Web server in addition to allowing
a printer to function as a network printer. You can use a Web browser to view
the printer status and configure the Network Interface Board.
Configuring the Printer
❖
This facility requires the TCP/IP protocol to be installed. After the printer has
been configured to use the TCP/IP protocol, it will be possible to adjust the
settings using a web browser.
Reference
For more information on configuring the printer to use the TCP/IP protocol, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
Operating System Browser Requirements
❖
OS Browser
Microsoft Windows 95/98
Microsoft Windows NT 3.51/4.0
Mac OS 7.6 ∼ 8.6
Solaris 2.5 ∼ 2.6
Limitation
❒
Using Windows NT 3.51 with Internet Explorer 3.02 may cause problems.
❒
Sometimes after clicking
Refresh
case, click
❒
The text on the screen may disappear or be aligned incorrectly if the font
size settings of the browser are set to be too large. It is recommended that
you use a font size equal to or smaller than “10 point” with Netscape Navigator, and “Medium” or smaller with Internet Explorer.
[
]
or
Back
[
Reload
[
]
Microsoft Internet Explorer 3.02/4.0
Netscape Navigator 3.0/4.0
]
, the previous page may not appear. In this
.
Going to the Top Page
After launching your Web browser, type the IP address of the printer. See the example below. This example is for the English version.
http://192.168.15.16/
(In this example, the IP address of the Network Interface Board is 192.168.15.16.)
54
Page 59

Configuring the Network Interface Board with a Web Browser
Note
❒
If a DNS server is used in the network, you can type the host name as an URL.
For example, http://webmonitor.netprinter.com/. In order to do this, you
must register the IP address and host name of the Network Interface Board
with the DNS server. Consult the network administrator for information on
how to do this.
❒
If the network uses proxy servers, the browser may run slowly.
1
2
3
Header Button
1.
You can register favorite URLs with
URL
]
[
. To view the help section, click
Help
[
]
.
Important
❒
There may be a fee in using the
browser to access a website on the
internet.
Note
The help file is stored in the CD-ROM
❒
in the HTML format.
Menu Button
2.
Buttons to configure the Network Interface Board and confirm the status of the
printer.
Note
Network Config
When you click
❒
log box appears requesting the user
name and password. Type only the
password in this dialog box. The factory default password is “password”.
The password is the same as that used
❒
in the remote maintenance (mshell)
and that used in NIB Setup Tool. If
you change a password on the Web
browser, the other passwords are also
changed.
Representation Area
3.
Displays the name and comments of the
Network Interface Board and the status
of the printer.
[
]
, a dia-
5
-Linking the Address (URL) to the
You can link the address (URL) of the
Help
Button
[
]
Help
[
]
button to the help files on your com-
puter or on a Web server.
A
Copy the help file on the CD-ROM to the desired location. The help files are
located in folders labeled with abbreviated language names. For example, English help files are in the
]
folder. Be sure to copy the entire
[EN]
folder to
EN
[
the new location.
B
Using a web browser, navigate to the Top Page and click
C
Type your password, (it is not necessary to type a user name) and click
Network config
[
]
.
[
OK
]
.
55
Page 60

Appendix
5
D
Type the path to the help file in the
If you copied the help file to "C:\HELP\EN", then type "file://C:/HELP/".
For example, if you copied the file to a web server, the address (URL) that will
be linked to the help files is "http://a.b.c.d/HELP/EN/index.html", type "http://a.b.c.d/HELP/".
E
Click
When a warning message appears, select to continue configuring.
Apply
[
]
.
Help URL
[
]
box.
56
Page 61

Assigning IP Address with ARP+PING
Assigning IP Address with ARP+PING
Using TCP/IP, you can assign the IP address using ARP and PING. The following example is for a BSD UNIX workstation (SunOS 4.x).
Preparation
ARP+PING should be set to active in the network boot configuration before
assigning the IP address using ARP+PING. For more information on setting
it to active, see the "Printer Reference" that is provided as a paper manual.
Log in to the workstation as root.
A
Use the arp command to assign the IP address to the MAC address of the
B
Network Interface Board.
# arp -s 192.168.15.16 00:00:74:62:5C:65
Note
❒
192.168.15.16 is the IP address, and 00:00:74:62:5C:65 is the MAC address.
Assign the IP address using the PING command.
C
# ping 192.168.15.16
5
Use the PING command again to confirm the address.
D
# ping 192.168.15.16
If the address has been configured correctly, the following message appears.
192.168.15.16 is alive
If the address has been configured incorrectly, the following message appears.
no answer from 192.168.15.16
-How to Confirm the MAC Address
The MAC address (Ethernet address) of the Network Interface Board is required
in order to use ARP and PING to assign the IP address.
The MAC address can be seen on the printer configuration page.
Reference
For more information on printing a configuration page, see the "Printer Reference" included as a PDF file in the CD-ROM.
57
Page 62

Appendix
Remote Maintenance by Telnet (mshell)
You can view the printer status and configure the network interface board using
telnet.
Note
❒
You should use a password so that only the network administrator, or a person having network administrator privileges, can use remote maintenance
(mshell).
Operation Flow
The following is a sample procedure using telnet.
Limitation
❒
Only one person at a time can log on to do remote maintenance.
5
Using the IP address or host name of the printer, start telnet.
A
% telnet
Note
❒
In order to use the host name instead of the IP address, you must write it
to the /etc/hosts file.
Type the password.
B
Note
❒
The factory default is “password”.
Type a command.
C
Reference
For more information on telnet commands, see P.59
Finish telnet.
D
msh> logout
When the configuration is revised, a confirmation message requests whether
or not the changes should be saved.
Type “yes” to save the changes and press the
E
If you do not want to save the changes, type “no”and press the
If you want to make additional changes, type “return” at the command line,
and press the
IP_address
{
ENTER
}
key.
{
ENTER
“Command List”
key.
}
{
ENTER
.
}
key.
58
Note
❒
If the “Can not write NVRAM information” message appears, the changes
are not saved. Repeat the steps above.
Page 63

Remote Maintenance by Telnet (mshell)
❒
The Network Interface Board is reset automatically when the settings are
changed.
❒
When the Network Interface Board is reset, the active print job which has
already been sent to the printer will finish printing. However, jobs that
have not been sent yet will be cancelled.
Command List
This is a list of commands that can be used via remote maintenance.
Note
❒
Type “help” to see a list of commands that can be used.
msh> help
❒
Type “help command_name” to display information on the syntax of that
command.
msh> help
TCP/IP address
command_name
5
Use the ifconfig command to configure TCP/IP (IP address, subnet mask, broadcast address, default gateway address).
Reference
❖
msh> ifconfig
Configuration
❖
msh> ifconfig le 0
Parameter Configuration Item
(no parameter) IP address
netmask subnet mask
gateway default gateway address
The following is an example for configuring an IP address of 192.168.15.16.
msh> ifconfig le0 192.168.15.16
The following is an example for configuring a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0.
msh> ifconfig le0 netmask 255.255.255.0
Note
❒
This affects the configuration of the Network Board of the IP address that is
used.
❒
To type an address using hexadecimal, add “0x” to the first command.
parameter address
59
Page 64

5
Appendix
-Address
Subnet Mask
❖
A number used to mathematically “mask” or hide the IP address on the network by eliminating those parts of the address that are alike for all the machines on the network.
Default Gateway Address
❖
A gateway is a connection or interchange point that connects two networks.
A gateway address is for the router or host computer used as a gateway.
Note
❒
To get the addresses above, contact your network administrator.
Access control
Use the access command to view and configure access control.
Reference
❖
msh> access
Configuration
❖
msh> access
Parameter Configuration Method
control Access Control Address
mask Access Control Mask
Note
❒
The Access Control Address and the Access Control Mask are used to limit
access to the computer used for printing by denying access to users based on
their IP address. If it is not necessary to limit access, set the Access Control
Mask to “0.0.0.0”.
❒
When the Access Control Address matches the masked result of the IP address of the computer attempting to print, print jobs from that IP address can
be accepted by the Network Interface Board.
❒
For example, if you assign 192.168.15.16 as the Access Control Address to the
Network Interface Board, the combination of the Access Control Mask and
the IP addresses that can be printed are as follows. The XXX is a variable that
means any number from 1 to 255 is acceptable.
parameter address
60
Page 65

Access Control Mask IP Addresses that can
Access the Printer
0. 0. 0. 0 XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX
255. 0. 0. 0 192.XXX.XXX.XXX
255.255. 0. 0 192.168.XXX.XXX
255.255.255. 0 192.168. 15.XXX
255.255.255.255 192.168. 15. 16
Network boot
Use the set command to configure a network boot.
msh> set
“On” means active and “Off” means inactive.
parameter
{on | off}
Remote Maintenance by Telnet (mshell)
Parameter Configuration Method
ping ARP+PING
tftp RARP+TFTP
bootp BOOTP
dhcp DHCP
Note
❒
When you use RARP+TFTP, BOOTP or DHCP, the server also needs to be
configured.
❒
DHCP takes precedence over all other settings.
Protocol
Use the set command to allow/prevent remote access for each protocol.
msh> set
protocol
{up | down}
5
61
Page 66

Appendix
Protocol
5
appletalk
tcpip
netware
netbeui
lpr
ftp
rsh
diprint
web
Note
❒
If you prohibit remote access using TCP/IP and then log out, you cannot use
“Up” means active. “Down”
means inactive.
remote access. If this was a mistake, you can use the printer operation panel
to allow access by TCP/IP.
❒
When you prevent access via TCP/IP, you are also prevented from using lpr,
ftp, rsh, diprint, and web.
Status of printer
The following commands can be used to get information about the current status
of the printer.
msh>
command
62
Command Information that is Displayed
status Status of printer.
Information about the print job.
info Information about the paper tray, output
tray, emulation and program of printer.
prnlog [ID] Lists the last 10 print jobs.
netstat Information on the Network Interface
Board.
Note
❒
More information on the print job appears when the ID number is added after
the prnlog command.
Reference
For more information on the meaning of the data returned with these commands, see P.69
“Configuring the Network Interface Board”
.
Page 67

Remote Maintenance by Telnet (mshell)
Information about the Network Interface Board configuration settings
Use the show command to display the Network Interface Board configuration
settings.
msh> show [-p]
Note
❒
Add “-p” to the show command to have the information displayed on one
screen at a time.
Reference
For more information on the meaning of the data returned with this command, see P.69
“Configuring the Network Interface Board”
.
System log information
Use the syslog command to display information stored in the printer's system
log.
msh> syslog
5
Reference
For more information on the displayed information, see P.72
formation”
.
“System Log In-
SNMP
Use the snmp command to display and edit SNMP configuration settings such
as the community name.
Note
❒
You can configure from No. 1 to 10 SNMP settings.
❒
The default settings for No. 1 and 2 are as follows.
Number 1 2
community name public admin
IP address 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0
access type read-only
trap off
Display
❖
Shows the SNMP information and available protocols.
msh> snmp ?
msh> snmp [-p] [
registered_number
read-write
trap off
]
63
Page 68

Appendix
Note
❒
If the -p option is added, you can view the displays one by one.
❒
If the registered number is not added, you can view the status of all the registered numbers.
Community name configuration
❖
You can set the community name of the Network Interface Board.
msh> snmp
Note
❒
The community name must consist of 15 characters or less.
Access type configuration
❖
You can select the access type from those listed below.
msh> snmp
Access Type Type of Access Which is Permitted
number
number
name
type
community_name
access_type
5
read Read only access is permitted.
write Read and write access is permitted.
trap User is notified of trap messages.
no All access is denied.
Protocol configuration
❖
You should use the following command to set the protocols to active or inactive. If you set a protocol to inactive, you cannot use all the registered numbers for it.
msh> snmp {ip | ipx} {o n | off }
• “On” means active and “Off” means inactive
If you want to change the protocol settings for each registered number, use
the following command. Confirm that the protocol set to inactive using the
above command, are not set to active using this command.
msh> snmp
Access configuration
❖
You can configure the address of a host depending on the protocols used.
The Network Interface Board accepts requests only from hosts having addresses with access types of “read-only” or “read-write”. Type “0” to have the
Network Interface Board accept requests from any host without requiring a
specific type of access.
number
active {ip | ipx} {on | off}
64
The following example shows how to set the protocol for an address.
msh> snmp
number
{ip | ipx}
address
Page 69

Remote Maintenance by Telnet (mshell)
Note
❒
When using the TCP/IP protocol, type ip followed by a space and then the
IP address.
❒
When using the IPX/SPX protocol, type ipx followed by a space, the IPX
address followed by a decimal and then the MAC address of the Network
Interface Board.
The following is an example of how to configure registration number 3 with
the IP address 192.168.15.16.
msh> snmp 3 ip 192.168.15.16
The following is an example of how to configure registration number 3 with
the IPX address 7390A448, and the MAC address 00:00:74:62:5C:65.
msh> snmp 3 ipx 7390A 44 8. 00 007 46 25 C6 5
Changing the password
Use the passwd command to change the remote maintenance password.
Important
❒
Be sure not to forget or lose the password.
Note
❒
The default factory password is “password”.
Type “passwd”.
A
msh> passwd
Type the current password.
B
Old password:
Type the new password.
C
New password:
Note
❒
The password must consist of 3 to 8 alphanumeric characters and symbols.
Upper and lower case characters are considered unique. For example, R is
different from r.
❒
The password is the same as that used in the configuration of the Network
Interface Board using a Web browser and that used in NIB Setup Tool. If
you change a password on the mshell, the other passwords are also
changed.
5
Type the new password again.
D
Retype new password:
65
Page 70

5
Appendix
SNMP
The Network Interface Board functions as a SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) agent using the UDP and IPX protocols. Using the SNMP manager you can get information on the printer.
The factory default community names are “public” and “admin”. You can get
MIB information using these community names.
Reference
For more information on configuring the community name, see P.63
in “Remote Maintenance by Telnet (mshell)”.
Limitation
❒
The supported MIBs may differ depending on your printer.
Supported MIBs
❖
• MIB-II
• PrinterMIB
• HostResourceMIB
“SNMP”
• RicohPrivateMIB
66
Page 71

Understanding the Displayed Information
Understanding the Displayed Information
This section describes how to read the displayed information on the status of the
Network Interface Board.
Print Job Information
The status of the print job can be viewed using the following commands.
• mshell : Use the status command. ⇒ P.62
Item Name Meaning
ID Number of the print request.
Source The name of the host requesting the print job.
Process The type of print command.
“Status of printer”
Status Status of print job.
• Active
Printing or preparing to print.
•Waiting
Waiting to be transferred to the printer.
Time The time when the print request was received.
Print Log Information
This is a record of jobs that have been printed up to now. The most recent ten
records appear.
This record appears with the following commands.
• mshell : Use the prnlog command. ⇒ P.62
Item Name Meaning
ID Printing request number.
Source The user name, workstation name or address of the host
that sent the print job.
Process The type of print command used.
“Status of printer”
5
Bytes The size of the file in bytes.
67
Page 72

5
Appendix
Item Name Meaning
Result Communication result.
•OK
Indicates that the print job was completed correctly.
•NG
Indicates that the print job was not completed normally.
• Canceled
rcp, rsh or lpr print commands were stopped. A problem
occurred with the printing application. This message
does not appear when ftp or RPRINTER is used.
Time The time when the print request was received.
User Code The user name, workstation name or address of the host
that sent the print job.
Address IP address.
Process The type of print command used.
Print Start Time The time the print process was started.
Print End Time The time the print process was completed.
Open Count The number of print processes that the application made.
Eof Count The reception number of file unit.
Data Size The number of bytes of received data.
Network Statistical Information
This section is about the information provided about the Network Interface
Board.
Detailed information on the words used to describe the status of the Network Interface Board are described below.
• mshell : Use info command. ⇒ P.62
Item Name Meaning
System elapsed time The time that has passed since the network interface board
started.
Total printing time The total time spent in processing the print data.
Total open count The total number of open (printing process) count that the
application requires.
Current connection
count
The number of jobs currently connected with the Network
Interface Board.
“Status of printer”
68
Total connection count The total number of print jobs sent to the Network Interface
Board.
Page 73

Understanding the Displayed Information
Item Name Meaning
Print error count The number of times the printing process sent an error mes-
sage.
Access error count The number of times the connection was refused because of
the value of the access control.
Print request full count The number of times a connection was refused because the
number of print requests exceeded the number of allowed
sessions.
Configuring the Network Int erface Board
Network Interface Board settings can be displayed and confirmed using the
commands below.
• mshell : Use the show command. ⇒ P.63
face Board configuration settings”
Item Name Meaning
“Information about the Network Inter-
5
Common
Mode
Protocol Up/Down
AppleTalk
TCP/IP
NetWare
NetBEUI
NVRAM version
Device name
Comment
Location
Contact
Soft switch
AppleTalk
Mode
Net
Object
Type
Zone
Up means active. Down means inactive.
Internal version number.
AppleTalk protocol in selection.
Network number.
Macintosh printer name.
The type of printer.
Name of the zone that the printer belongs to.
69
Page 74

Appendix
Item Name Meaning
5
TCP/IP
Mode
ftp
lpr
rsh
diprint
web
telnet
download
EncapType
Network boot
Filter
Max DSTs
Address
Netmask
Broadcast
Gateway
AccessCtrl
AccessMask
Time server
Home page URL
Home page link name
Help page URL
SNMP protocol
Up means active. Down means inactive.
Frame type.
Network boot.
Internal parameter.
IP address.
Subnet mask.
Broadcast address.
Default gateway address.
Access control address.
Access control mask.
URL of homepage.
URL name of homepage.
URL of help page.
Protocol used with SNMP.
70
Page 75

Item Name Meaning
Understanding the Displayed Information
NetWare
Mode
EncapType
RPRINTER number
RPRINTER name
Print server name
Fileservername
Context name
Switch
Mode
NDS/Bindery
Packet negotiation
Print job timeout
NetBEUI
Mode
Switch
Mode
Direct print
Notification
Workgroup name
Computer name
Comment
Share name[1]
(This value is fixed)
Frame type.
Remote printer number.
Remote printer name.
Print server name.
Name of the connect file server.
Context of print server.
Active mode.
(This value is fixed)
Time of the job timeout.
(This value is fixed)
(This value is fixed)
(This value is fixed)
Notices of finishing to print.
Name of the workgroup.
Name of the computer.
Comment.
Share name. (name of the printer type)
5
Shell mode Mode of the remote maintenance tool.
71
Page 76

Appendix
Message List
This is a list of messages recorded to the printer's system log. The system log can
be viewed using the syslog command.
System Log Information
You can use the following methods to view the system log.
• mshell : Use the syslog command. ⇒ P.63
Message when the Network Interface Board starts or restarts
“System log information”
5
RICOH Network Interface Board
Ver.x.x.x
PRINTER SYSTEM “system name”
Ver.x.x.x
Attach FileServer=“file server name” The printer is attached to “file server
Current Interface Speed:xxxMbps The speed of the network (10 Mbps or 100
Current IPX address The current IPX address.
Frametype=“frame type name” The "frame type name" is configured to be
NetBEUI Computer Name=“computer
name”
Start httpd The Web server has been started.
Start npmpd for IPX The npmpd for the IPX protocol has been
Start npmpd for TCP/IP The npmpd for the TCP/IP protocol has
Start smbd direct print mode(NetBEUI) You can print from a client on the Win-
The version number of the Network Interface Board.
The system name and version of the printer.
name” as the nearest server.
Mbps).
used on NetWare.
The NetBEUI Computer Name is defined
as "computer name".
started.
been started.
dows network via the print server.
72
Start snmpd Ver.2.0 The SNMP agent of the displayed version
has been started.
Vendor= , Country= , Lang= The vendor, the country code and the lan-
guage.
Page 77

NetWare (When the Network Interface Board is started)
When working as a print server
❖
Message List
Access to NetWare server “file server
name” denied. Either there is no account
for this print server on the NetWare server
or the password was incorrect.
Attach to print queue “print queue name” Attached to the print queue.
File server is empty The file server is not registered. Register
Log in to the file server “file server name”
(“NDS|BINDERY”)
Open log file “file name” The selected log file has been opened.
Printer “printer name” has no queue The print queue is not assigned to the
Print queue “print queue name” cannot
be serviced by printer 0, “print server
name”
The print server received error “error
number” during attempt to log in to the
network. Access to the network was denied. Verify that the print server name
and password are correct.
Cannot log in to the file server. Confirm
that the print server is registered on the
file server. If a password has been configured for the print server, delete it.
your file server using the utility.
Logged in to the file server with NDS or
BINDERY mode.
printer. Using NWAdmin, assign the
print queue to the printer, and then restart
it.
Print services are not available for the
print queue. Confirm that the volume of
the print queue exists on the selected file
server.
Cannot log in to the file server. The print
server is not registered or the password
has been set. Register the print server
without setting a password.
5
When working as a remote printer
❖
Cannot create service connection Cannot establish a connection with the file
server. Your request may exceed the maximum number of connections that the file
server can deal with at a time.
Cannot find the printer (“print server
name”/”printer number”)
Establish a connection with the print server, “print server name”
The printer having the number displayed
on the print server does not exist. Confirm
the number of the printer registered to the
print server.
A connection with the print server has
been established.
73
Page 78

Appendix
No local target for “print server name” Cannot get routing information on the file
server. If a different frame type is configured from that used on the network, you
should select "Auto Select" as a frame
type.
5
Required file server (“file server name”)
not found
Required print server (“print server
name”) not found
Unable to attach to print server (“print
server name”)
Cannot find the required file server.
Cannot find the print server. Confirm the
name of the print server.
Cannot connect to the print server. The
print server refuses a connection for some
reason. Confirm the configuration of the
print server.
NetBEUI (When the Netw ork Interface Board is started)
Back to default name (<Computer name>) The same Computer name is detected on
the network. As unable to add computer
name to the suffix, the computer name
changed to the default name. Configure a
new computer name that is unique.
Print session full Cannot accept the print session.
Required computer name (<Computer
name>) is duplicated name
The same Computer name is detected on
the network. The start job determines the
computer name by adding the computer
name to the suffix (0,1....). Configure a
new computer name that is unique.
74
TCP/IP
When the address is configured
❖
Invalid gateway address The Gateway address is not correct for the
selected IP address.
When using lpr
❖
filter data error Some data cannot be handled by the filter
option. Confirm the file code and the set-
tings of the filter option.
lost connection The connection was cut by a counterpart.
Check the printer to which you requested
to print.
Page 79

Message List
print requests full Cannot accept the print request (max. 5 re-
quests). Confirm the status of the printer
with mshell, and print it again after the
number of print requests becomes less
than 5.
printer permission denied Cannot get a permission to use the print-
er. Confirm the access rights with the ac-
cess control address and the access control
mask.
printer refuse Something is wrong with the printer.
Confirm the status of the printer.
At the beginning of the message, the IP address of the client is displayed within parentheses.
When using SNMP
❖
Exit snmpd The agent is complete. Reset the printer
or turn the printer off and on.
5
recvfrom:packet discarded,length(Reception packet length)> (Packet size),from
addr <Address of partner point>
session <Community name appointed>
not defined
snmpin:Bad use of session <community
Name> from <Address>
snmpin:error in snmpdecipher,code (<Error No.>)
snmpin:error in snmpservsend,code (<Error No.>)
The received packet was ignored since
the length of the packet exceeds the limit.
Confirm whether the administration station sent a packet whose length was longer than 1025 bytes.
The community name of the received
packet is not defined. Confirm that the
community name of the administration
station is the same as that of the printer.
The community name of the received
packet is not the same as that of the administration station. Confirm the community name of the printer.
An error occurred on the received packet.
Check if the number of the objects sent
from the administration station is more
than 31 and if there are wrong MIB requests.
Cannot send a response packet. Normally, this message is followed by the messages below *1 *2.
snmpin:pkt too large,code (<Error num-
*1
ber>)
The response packet to the request is too
big to send. Reduce the number of the objects per request.
75
Page 80

Appendix
5
snmpin:error in sending too large request
back,code (<Error number>),giving up
snmpin:received bad version The version of the received packet is in-
The packet notifying the error is too big to
*2
send. Reduce the number of the objects
per request.
valid. Confirm that the version of the administration station is version-1(0).
Error numbers in the messages are codes for internal use.
76
Page 81

Precautions
Precautions
Please pay attention to the following when using a network interface board.
When configuration is necessary, follow the appropriate procedures below.
Connecting a Dial up Router to a Network
When the NetWare file server and the printer are on the opposite side of a router,
packets are continuously sent back and forth, possibly causing communications
charges to increase. Because the packet transmission is a specification of NetWare, you need to change the configuration of the router. If the network you are
using does not allow you to configure the router, configure the printer.
Configuring the router
Filter the packets so that they do not pass over the dial up router.
Note
❒
The MAC address of the printer doing the filtering is printed on the printer
configuration page. For more information on printing a configuration page,
see the "Printer Reference" that comes with the printer.
❒
For more information on configuring the printer if the router cannot be configured, see the instructions below.
Configuring the printer with NetWare
Following the setup method in this manual, configure the file server.
A
Set the frame type for a NetWare environment.
B
Reference
For more information on selecting a frame type, see the "Printer Reference"
that is provided as a paper manual.
Configuring the printer without NetWare
While not printing, the Network Interface Board sends packets on the net-
A
work. Set NetWare to inactive.
5
Reference
For more information on selecting a protocol, see the "Printer Reference"
that is provided as a paper manual.
77
Page 82

5
Appendix
When Printing PostScript fr om Windows
When printing PostScript from Windows, see the “Printer Reference” that comes
with your machine, and configure it to use the Network Interface Board with the
printer driver.
When Printing it with NetWare
Config u r ing the fo r m feed
You should not configure the form feed on NetWare. You do not need to configure on NetWare in order to control a new page with the printer driver of Windows. If this setting is configured, the printer might not print properly. If you do
not want to use the form feed, configure it according to the OS you are using as
follows.
Form feed
• With Windows 95/98, clear the
tab in the printer properties dialog box.
[
]
check box with the
Printer Settings
[
]
Configuring the banner page
Do not configure a banner page on NetWare.
If you do not want to add a banner page, configure it according to the OS you
are using as follows.
Form feed
• With Windows 95/98, clear the
tab in the printer properties dialog box.
• With Windows NT 4.0, click
Network
and click it. Select
NT
]
in the
appears. Clear the
vell Client Configuration
Service
[
[
]
tab and click
Enable banner
[
]
.
[
Start
[
]
and select
Properties
[
]
check box with the
]
, point to
[
]
check box in the
Setting
[
Novell Client Configuration for Windows
]
. The
[
]
, point to
Novell Client Configuration
Default Capture
[
Printer Settings
[
Control Panel
[
]
box
]
tab in
No-
[
Printing after resetti ng the printer
After resetting the remote printer, it will be cut off from the print server for about
30-40 seconds before connecting again. Due to the NetWare specification, print
jobs may be accepted, but they will not be printed during this interval.
When using the printer as a remote printer, wait about 2 minutes after resetting
the printer before attempting to print.
]
]
78
Page 83

Precautions
When Using DHCP
Note the following points when using DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol).
Supported systems
Windows NT Server 4.0 can be configured as a DHCP server.
Configuring the printer with a reserved IP address
To always assign the same IP address, configure a reserved IP address using the
DHCP server.
Note
❒
When multiple DHCP servers are used, reserve the same address with each
DHCP server. The Network Interface Board needs to receive information
from the DHCP server that it contacts.
Follow these steps to configure the printer with a reserved IP address.
5
Start the DHCP manager.
A
Select the scope that will be used, and on the
B
.
tion
]
Type the IP address into
C
Type the MAC address of the Network Interface Board into
D
.
er
]
Note
❒
Do not use hyphens to separate the numbers.
❒
If you do not know the MAC address, it can be found on the configuration
page printed by the printer.
Type a name and comment into the
E
box.
Note
❒
For more information on client names, see P.80
Click
F
An IP address is reserved.
Add
[
.
]
IP Address
[
.
]
Client Name
[
Scope
[
box and the
]
menu, click
]
Unique Identifi-
[
Client Comment
[
“Additional information”
Reserva-
[
.
]
G
Click
Close
[
to close the dialog box.
]
79
Page 84

Appendix
Additional information
5
Active Lease
• When you click
client leases appears. When the reserved IP address is not active, the name of
the reservation is the name entered in the Client Name field of the Add Reserved Clients dialog box. When the reserved IP address becomes active, the
client name changes to the printer name configured by the Network Interface
Board. Only the first 13 letters of the printer name appear here. When you use
the printer with Multidirect Print, use the host name of the printer as the
ent Properties
• When the DHCP server does not assign an IP address, the Network Interface
Board uses 11.22.33.44 as a temporary IP address. You can confirm the printer's IP address on the network configuration page.
• Because 11.22.33.44 is a special IP address, you cannot print using this address.
• When using the DHCP relay agent in a network environment that uses a dial
up router to connect to the Network Interface Board, an increase in communication fees can occur.
[
]
Client Properties dialog box.
]
on the
Scope
[
]
menu of DHCP manager, a list of
[
Cli-
When Using NIB Setup Tool
If the Network Interface Board cannot browse using the TCP/IP protocol, confirm that the TCP/IP environment is correctly configured in your computer.
80
Page 85

Specifications
Specifications
LAN interface 100BASE-TX, 10BASE-T
Frame type EthernetII, IEEE802.2, IEEE802.3, SNAP
Protocol • TCP/IP
Windows 95
Windows 98
Windows NT 4.0
•IPX/SPX
NetWare 3.11, 3.12, 3.2, 4.1, 4.11, 5, IntranetWare
• NetBEUI
Windows 95
Windows 98
Windows NT 4.0
• AppleTalk
Mac OS 7.6 ∼ 8.6
SNMP MIB-II, PrinterMIB, HostResourceMIB, RicohPrivateMIB
5
81
Page 86

INDEX
A
61
,
,
60
60
access control address
access control mask
ARP+PING
, 57,
B
BOOTP
,
61
C
client computer, setup
,
,
25
47
,
,
,
,
31
,
54
,
64
,
37
,
21
22
5
13
Windows 95/98
Windows NT 4.0
community name
configuration
LPR port printing, Windows NT 4.0
23
Macintosh
NetWare
NetWare 3.x
NetWare 4.x, 5
Web browser
Windows 95/98
Windows NT 4.0
L
LPR port Printing, Windows NT 4.0
,
23
M
,
72
,
57
,
51
,
,
,
47
8
17
MAC address
Macintosh, configuration
message
,
MIB
66
Multidirect Print
Multidirect Print, install
Windows 95/98
Windows NT 4.0
N
,
NetWare 3.x, configuration
NetWare 4.x, 5, configuration
NetWare, configuration
,
,
26
61
,
,
28
80
network boot
NIB Setup Tool
install
precautions
,
25
,
31
,
37
P
D
default gateway address
, 61,
DHCP
dial up router, precautions
79
,
60
,
E
EtherTalk
,
47
I
information
Network Interface Board configura-
, 63,
tion
Network Statistics
print job
print log
system log
,
install
Multidirect Print, Windows 95/98
Multidirect Print, Windows NT 4.0
17
IP address
26
,
,
, 57,
69
67
67
, 63,
59
72
,
68
77
,
password
precautions
, 55,
,
65
77
R
RARP+TFTP
Remote Maintenance by Telnet (mshell)
58
remote printer, setup
NetWare 3.x
NetWare 4.x, 5
,
61
,
34
,
,
40
S
setup
,
,
,
21
,
22
9
18
client computer, Windows 95/98
client computer, Windows NT 4.0
printer driver, Windows 95/98
printer driver, Windows NT 4.0
, 63,
SNMP
8
,
specifications
status of printer
subnet mask
66
,
,
60
81
,
62
82
Page 87

U
uninstall
Multidirect Print, Windows 95/98
Multidirect Print, Windows NT 4.0
20
W
,
11
,
Web browser
Windows 95/98, configuration
Windows NT 4.0, configuration
,
54
Z
,
Zone
48
,
,
5
13
83
Page 88

84 EE GB UE USA G528
Page 89

Note to users in the United States of America
Notice:
This equipment has be en tes ted and found t o com ply w ith the limi ts for a Cl ass B d igital devic e, purs uant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against
harmful interference i n a resid ential instal lation . This e quipm ent gene rates, u ses an d can rad iate rad io
frequency energy and, if not instal led and used in accorda nce with the ins tructions , may caus e harmful
interference to radio communications.
However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmfu l interference to radio or television reception, whic h can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one more of
the follo wing measures:
Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the recei ver is
connected.
Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Warning
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void
the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Caution (in case of 100BASE-TX environment):
Properly shielded and grounded cables (STP) and connectors must be used for connections to host
computer (and/or peripheral) in order to meet FCC emission limits.
STP with ferrite core must be used for RF interference suppression.
Declaration of Conformity
Product Name: Printer Controller
Model Number: Color Controller RC-200
Responsible party: Ricoh Corporation
Address: 5 Dedrick Place, West Caldwell, NJ 07006
Telephone number: 973-882-2000
This device complies with part 15 of FCC Rules.
Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Note to users in Canada
Note:
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Remarque concernant les utilisateurs au Canada
Avertissement:
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Declaration of Conformity
“The Product complies with the requirements of the EMC Directive 89/336/EEC and the Low Voltage
Directive 73/23/EEC.”
Warning
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void
the user's authority to operate the equipment.
Copyright © 1999
Page 90

Network Interface Board 185
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
EE GB
UE USA G528-8640
 Loading...
Loading...