Page 1

DOCUMENT FEEDER
Page 2

24 June 1994 SPECIFICATIONS
1. SPECIFICATIONS
Original Size: Maximum: A3 or 11" x 17"
Minimum: A5 Lengthwise or 51/2" x 81/2"
Original Weight: 53 to 105 g/m2 (14 to 28 lb)
Original Feed: Automatic Feed - ADF mode
Original Tray Capacity: 30 sheets - 80 g/m2 (20 lb)
Original Set: Face up - First sheet on top
Original Transport: One flat belt
Copying Speed: 13 copies/min ute
(A4 lengthwise or 81/2" x 11" lengthwise)
Power Consumption: 35 W
Dimensions (W x D x H): 590 x 443 x 100 mm (23.3" x 17.5" x 4.0")
Weight: Approximately 7 kg (15.5 lb)
• Specifications are subject to change without notice.
1
Page 3

COMPONENT LAYOUT 24 June 1994
2. COMPONENT LAYOUT
2.1 MECHANICAL COMPONENTS
1
234 65
8
910
7
1. Pulse Generator Disk
2. Friction Belt
3. Pick-up Lever
4. Pick-up Roller
5. Original Table
6. Exit Roller
7. Transport Belt
8. Transport Belt Roller
9. Feed Roller
10. Relay Roller
2.2 ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
45
6
7
3
2
1
8
9
10
12
11
1. Pick-up Solenoid
2. Registration Sensor
3. Original Set Sensor
4. Feed Clutch
5. Pulse Generator Sensor
6. DF Motor
7. Insert Original Indicator
8. Original Misfeed Indica to r
9. Lift Switch
10. DF Main Board
11. DF Transformer
12. DF Interface Board
2
Page 4

24 June 1994 ELECTRICAL COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS
3. ELECTRICAL COMPONENT DESCRIPTIONS
SYMBOL NAME FUNCTION LOCATION
Motor
M1 DF Drives all the document feeder components. 6
Solenoid
SOL1 Pick-up Solenoid Energizes to press the pick-up lever against
the stack of originals in preparation for
original feed-in.
Clutch
CL1 Feed Clutch Turns on to transmit main motor rotation to
the feed roller.
Switch
SW1 Lift Switch Informs the CPU when the DF is lifted and
also serves as the misfeed reset switch for
the DF.
Sensors
S1 Pulse Generator
Sensor
S2 Original Set
Sensor
S3 Registration
Sensor
Printed Circuit Board
PCB1 DF Main Board Controls all DF functions. 10
PCB2 DF Interface
Board
Transformer
TR1 DF Transformer Steps down the wall voltage to 25 volts ac. 11
LEDs
LED1 Original Misfeed
Indicator
LED2 Insert Original
Indicator
Supplies timing pulse to the DF main board. 5
Informs the copier CPU that originals have
been placed and causes the Insert Original
indicator to go out.
Sets original stop timing and checks for
original misfeeds.
Interfaces between the copier main board
and the DF.
Turns on when an original is misdeed. 8
Turns off when the originals are inserted into
the original table.
1
4
9
3
2
12
7
3
Page 5

POWER DISTRIBUTION 24 June 1994
4. POWER DISTRIBUTION
+24 V (VA)
Regulator
+5 V (VC)
Rectifier
AC Drive Board
(PCB2)
115 Vac
220–230 Vac
240 Vac
DF
Transformer
(TR1)
25 Vac
Smoothing
Rectifier
DF Main Board (PCB1)
The document feeder uses two dc powe r levels: +24 volts, and +5 volts.
When the main switch is turned on, th e DF t ran sfo rmer receives the wall
outlet ac power thro ugh the ac drive board and output s 2 5 volt s ac to th e DF
main board. Then, the dc power supply circuit on the DF main board con vert s
the 25 volts ac input to +24 volts and +5 volts.
+24 volts is used by the DF moto r, th e pick-up solenoid, and the feed clut ch.
+5 volts is used by other electrical components.
4
Page 6

24 June 1994 BASIC OPERATION
5. BASIC OPERATION
When the main switch is turned on, the DF CPU sends the "DF installed"
signal to the copier CPU. Receivin g th is sig nal, the copier CPU recognizes
that the document fee de r is inst alle d an d sen ds the "DF confirmed" signal to
the DF CPU.
When originals are placed on the origin al ta ble, the Insert Original ind icat or
turns off and the DF CPU sends the "original set" signal to the copier CPU to
inform that the orig ina ls h ave bee n set .
When the Start key is pressed, the copier CPU sends the "feed-in" signal to
the document feeder. On rece ipt of th is signa l, th e DF CPU e nergizes the DF
motor, the pick-up sole no id, and the fee d clut ch to fee d in th e bo ttom sheet of
the original stack onto the exposu re glass. The pick-up solenoid, and the
feed clutch remain energized until t he origin al’s leading edge reaches the
registration sensor. The DF motor tu rns off shortly after the original’s trailing
edge passes the registration sensor. Then, the DF mo to r pau ses an d
reverses for a moment to alig n th e ed ge of th e original with the scale.
The scanner starts, and the start timing does not depe nd on th e pro gress of
the original through the DF. When the scanner reaches the return position,
the copier CPU sends the "origina l chan ge" sign al to the DF CPU in order to
exchange the current origin al with the next origin al.
5
Page 7

Fiber Optics
Fiber Optics
INTERFACE CIRCUIT 24 June 1994
6. INTERFACE CIRCUIT
Copier Main Board (PCB1) DF Interface Board (PCB4)
CPU
TXD
RXD
+5V
CN120-2
CN120-5
CN120-4
CN120-1
CN2-1
CN2-4
CN1
CN2-2
CN2-3
DF Main Board (PCB1)
CN118
RXD
CPU
TXD
The copier CPU and the DF CPU communicate via the interface board usin g
fiber optics. The interfa ce bo ard chan ge s the opt ical sign als to electrical
signals (and vice versa).
6
Page 8
[A]
[D]
24 June 1994 ORIGINAL FEED
7. ORIGINAL FEED
7.1 ORIGINAL PICK-UP MECHANISM
[C]
[B]
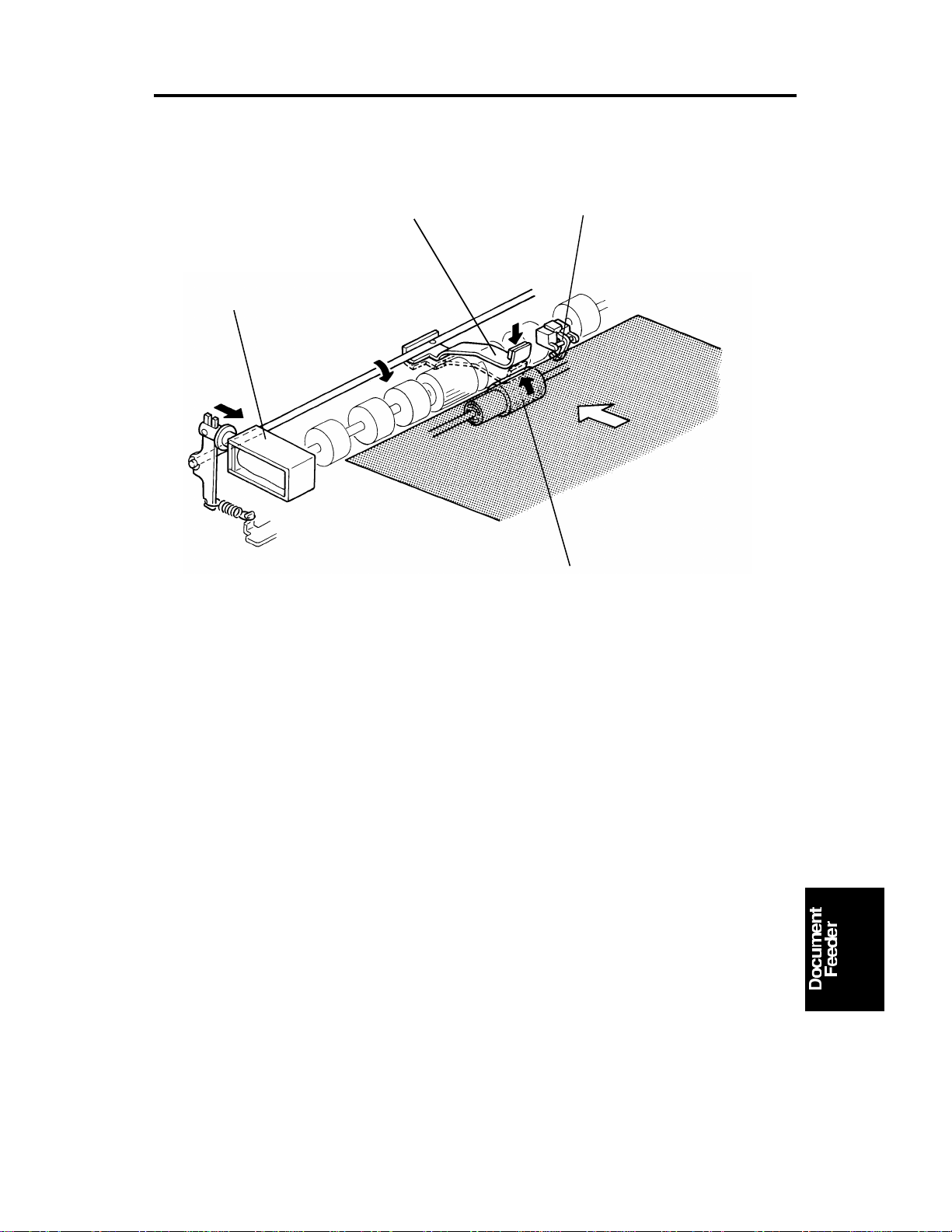
After setting the origina ls on th e orig ina l tab le, the origin als con ta ct th e feeler
[A] of the original se t sen sor an d cau se the feeler to move out of th e sensor.
The DF CPU then sends the origina l set signal to the copier CPU to inform it
that the document fee de r will be used . When the Start key is pressed , th e
pick-up solenoid [B] is energized. The original stack is then pressed be twe en
the pick-up lever [C] and pick-up roller [D]. The rota tio n of the pick-up roller
advances the bottom original.
7
Page 9

[B]
[D]
ORIGINAL FEED 24 June 1994
7.2 ORIGINAL SEPARATION ME CHANI SM
[A]
[C]
[E]
[B]
[D] [C]
[A]
[E]
The feed roller [A] and the friction belt [B] are use d to feed in an d separate
the originals [C]. Only the bottom original is fed beca use the frictio n belt
prevents any other origin als fro m f eeding.
Original feed starts when the pick-up lever [D] presses the original stack and
the rotation of the pick-up roller [E] advances the bo tt om original of the stack.
The feed roller moves the original pa st th e friction belt because the driving
force of the feed roller is greater than the resistan ce of the friction belt. The
friction belt prevents multiple feeds becau se th e resist ance of the frictio n belt
is greater than the friction between original she et s.
8
Page 10

24 June 1994 ORIGINAL FEED
7.3 ORIGINAL FEED-IN MECHANIS M
[C]
[G]
[E]
[A]
[D]
[B]
[F]
The DF motor [A] drives the feed roller [B], the pick-up roller [C] , th e relay
rollers [D], and the transport belt roller [E] via timing belts and a gear train.
The feed roller and the pick-up roller are controlled by the feed clutch [F] , but
the relay rollers and the transport roller are dire ctly driven by the DF motor.
The idler rollers [G] on the feed roller shaf t are free from the shaft.
When the Start key is pressed, the DF mot or is energized and the relay
rollers and transport belt roller start tu rnin g. 100 millisecon ds af ter t he DF
motor starts turning, the pick-up solenoid an d th e feed clutch is energized.
The pick-up and feed rollers then start turning and carry the original be twe en
the relay rollers and the idler rollers. The pick-up solen oid and the fee d clutch
are de-energized when the origin al’s leading edge passes thro ugh the
registration sensor.
The DF motor remains energized to deliver the original to the exposure glass
until a certain number of pulses (10 to 25 pulse s) aft er the original’s trailing
edge passes through the regist rat ion sensor. Then, the DF motor pauses and
reverses for 15 pulses to align the edge of the original wit h th e scale.
To feed the second original, the DF mot or sta rts rot at ing when the scanner
reaches the return position. (The copier CPU sends the original cha ng e
signal to the DF CPU.) At this time, the transport belt start s carrying the first
original on the exposure glass to the exit rolle r. The timing for when the
pick-up solenoid and the fee d clut ch are ene rgize d for the second original
depends on the length of the first origin al dete cte d by th e reg istra tio n sen sor.
9
Page 11

[D]
ORIGINAL FEED 24 June 1994
7.4 ORIGINAL FEED- OUT ME CHANI SM
[A] [B] [C]
The exit rollers are driven by the DF motor through a gear train , the tra nsp ort
belt roller, the transport be lt [A ], the transport belt idler roller [B ], and the exit
roller drive belt [C]. When the DF CPU receives the original change signal
from the copier CPU, the DF motor starts turning. Simult aneo usly, the
transport belt carries the original to the exit rolle rs [D] an d the exit ro llers take
over the original feed-out.
10
Page 12

+24 V (VA)
+5 V (VC)
R x D
CN117-1
CN117-2
Forward: +24 V
Reverse: 0 V
Forward: 0 V
Reverse: +24 V
24 June 1994 ORIGINAL FEED
7.5 DF MOTOR CIRCUIT
DF Main Board (PCB1)
Original
Change
Signal
CPU
Forward
Reverse
ON/OFF
GATE
IC
Forward
Reverse
DRIVER
IC
DF Motor
(M1)
Timing Pulse
A 24 volt dc motor is used as the DF moto r. When the CPU receives the feed
signal from the copier, the CPU out pu ts the ON signal and the Forward sign al
to the gate IC. On receipt of the forward signal from the gate IC, the driver IC
outputs 24 volts to CN117-1 and 0 volt s to CN11 7-2 . This cau ses the DF
motor to start turning in the forward direction .
Within 10 to 25 pulses after the original’s trailing edge passes throu gh the
registration senso r, the CPU stops sending the ON signal and the Forward
signal. The DF motor stops turnin g. Then the CPU outputs the ON signal an d
the reverse signal for 15 pulses. The n th e drive r I C out puts 0 volts to
CN117-1 and +24 volts to CN117-2 to reverse the DF motor.
Pulse
Generator
Sensor
(S1)
11
Page 13

DF Motor
ORIGINAL FEED 24 June 1994
7.6 ORIGINAL FEED AND MIS FEED DETECTION TIMING
Feed Signal (Start key) Original Change Signal
0 500 1000 0 500 1000
Timing (ms)
10 to 25 pulses
10 to 25 pulses
❋
15 pulses
J0
Pick-up Sol.
and
Feed Clutch
100 ms
15 pulses
J0
J0
Registration
Sensor
500 ms
500 ms
1,500 ms
❋: The timing depends on the length of the first original.
1,500 ms
The above chart shows the origina l fee d timin g for the origin al size of A4
lengthwise or 8.5" x 11" and the detection timing.
The registration sensor is used for a misfe ed det ect ion. If the DF CPU
detects that a misfeed exists, the DF CPU lights the Origina l Misfeed
indicator and sends the origin al misfe ed signa l to th e cop ier CPU. Then the
copier CPU lights the check paper p ath an d th e Misfe ed Loca tio n Number
(JO) on the operation panel. When the main switch is turn ed on, the DF CPU
checks the registration sensor output for initial original misfeed. During the
original feed-in, the DF CPU perfo rms two kind s of original misfeed detection:
1. Whether the registration senso r is actua ted with in 500 milliseco nds aft er
the pick-up solenoid and the feed clut ch turn on.
2. Whether the original has passed through the re gist ration sensor 1,500
milliseconds after the regist rat ion sensor has been actuated.
12
Page 14

[A]
24 June 1994 INSTALLATION PROCEDURE
8. INSTALLATION PROCEDURE
NOTE: This procedure is for the machin e code A152 copier.
[B]
[C]
[F] 230~240 V
[D] 220~230 V
[E]
CAUTION: When installing the DF, make sure that the copie r is
unplugged.
1. Remove the platen cover [A] from the copier.
2. Replace the 2 screws with the 2 stud screws [B].
3. Remove the strips of tape from the DF.
CAUTION: This procedure (step 3) must be done only in 240 volt areas
4. Perform the conversion fro m 220∼230 V to 240 V as follows:
1) Remove the main board cover [C] (2 screws).
2) Disconnect the connector for 220∼230 V [D] (Black Wire ) from th e ac
harness connector [E] an d reco nn ect the connector for 240 V [F]
(White Wire) to the ac harness connecto r.
3) Reinstall the cover.
13
Page 15

INSTALLATION PROCEDURE 24 June 1994
[E]
[A]
[I]
[C]
[B]
[D]
[F]
[G]
[K]
[J]
[H]
5. Insert the DF [A] into the holes [B] in the copier upper cover.
6. Secure the DF to the copier (2 thumb screws [ C]).
7. Remove the upper rear cover [D] (2 screws).
[H]
8. Remove the ADF bracket [E ] (1 screw an d 1 clamp ).
9. Locate the 4P connector [F] and connect it to the ADF interface board
[G], then fix the ADF interface unit [H] to the copier (1 screw) while
securing the harnesses through the wire clamp.
NOTE: Use the screw that secured th e ADF bracket [I].
10. Plug in the connector [J] (3 P/ Bla ck) t o CN41 8 on the ac drive board [K].
14
Page 16

[B]
24 June 1994 INSTALLATION PROCEDURE
[D]
[A]
[C]
11. Reinstall the upper rear cove r.
12. Plug the optics fiber cable [A] into the DF and the copier.
13. Plug the power supply cord [B] of the DF into th e outle t in th e cop ier rea r
cover.
14. Attach the volta ge reference decal [C].
15. Install the origina l tab le [D] .
15
Page 17

INSTALLATION PROCEDURE 24 June 1994
[D]
[A]
[E]
[C]
[A]
[B]
16. Open the front cover.
17. Lift the upper unit.
18. Remove 2 screws [A].
19. Tighten the shorter stepped screw [B].
20. Install the upper u nit stan d [C]
(1 longer stepped screw [D]).
21. Attach th e magnet [E].
22. Attach th e decal [F].
23. Close the uppe r u nit and t he front cover.
24. Check the operatio n of the DF.
25. Instruct key operators ho w to use the uppe r unit stand.
[F]
16
Page 18

15 January 1992 INSTALLATION PROCEDURE
8. INSTALLATION PROCEDURE
NOTE: This procedure is for machine code A077/A078 copiers.
8.1 INSTALLATION
[A]
[B]
[D]
CAUTION: When installing the DF, make sure that the copie r is
unplugged.
1. Remove the platen cover [A] from the copier.
2. Remove the strips of tape from the DF.
CAUTION: This procedure (step 3) must be done only in 240 volts
areas.
[E] 230~240 V
[C] 220~230 V
3. Perform the conversion fro m 220 ~23 0 V to 240 V as follo ws:
1) Remove the main board cover [B ] (2 screws).
2) Disconnect the connector for 2 20~230 V [C] (Black Wire) from ac
harness connector [ D] and reconnect the connector for 240 V [E]
(White Wire) to the ac harness connect or.
3) Reinstall the cover.
13
Page 19

[E]
INSTALLATION PROCEDURE 15 January 1992
[G]
[A]
[C]
[B]
[D]
[F]
4. Insert the DF [A] into the hole s [B] of th e copier up pe r cover.
5. Secure the DF to the copier (2 thumb screws [ C]).
6. Remove the seal [D] from th e ou tle t of the copier.
7. Plug in the optics fiber cable [E] to the DF and the copier as shown.
8. Plug in the power supply cord [F] of the DF to the outlet of the copier rear
cover as shown.
9. Install the orig ina l t ab le [G ] as shown.
10. Check the operatio n of the DF.
14
Page 20

[D] 230~240 V
[B] 220~230 V
15 January 1992 INSTALLATION PROCEDURE
8.2 220 ~ 230 V/24 0 V CONV ERSION
[A]
[C]
1. Remove the main board cover [A] (2 screws).
2. Disconnect the connect or for 2 20~230 V [B] (Black Wire) from ac harness
connector [C] and reconne ct th e con nector for 240 V [D] (White Wire) to
the ac harness connector.
3. Reinstall the cove r.
15
Page 21

[B]
24 June 1994 REPLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
9. REPLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
9.1 TRANSPORT BELT REPLACEMENT
[A]
[E]
[F]
[I]
[D]
[G]
[H]
[C]
1. Turn off the main switch.
2. Remove the original table [A].
3. Remove the DF [B] from t he copier (2 knob screws, 1 power supply cord
and 1 optics harness).
4. Remove the grip guide [C] (2 screws).
5. Remove the transfo rmer cove r [D] (3 screws), DF motor cover [E]
(4 screws) and main board cover [F] (2 screws).
6. Remove the transpo rt belt assembly [G] (5 screws and 1 drive belt [H]).
NOTE: When installing the tra nsport belt assembly, make sure th at the
positioning pin [I] fits into the DF frame.
17
Page 22

REPLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENT 24 June 1994
[A]
[B]
7. Remove the transpo rt rolle r holder [A] (1 screw, 1 snap ring and 1
bushing).
8. Pull out the transport belt [B].
NOTE: After reinstalling the transport belt, make sure that the bushings
of the transport rollers set correctly an d the tra nsport belt turns
smoothly.
18
Page 23

[C]
24 June 1994 REPLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
9.2 FEED-IN UNIT REMOVAL
[A]
[B]
1. Turn off the main switch.
2. Remove the transport belt assembly. (See Transport Belt Replacement.)
3. Remove the left hinge bracket [A] (4 screws and 1 connector).
4. Disconnect five connectors from th e main board [B ] (CN111, CN113,
CN115, CN116 and CN117).
5. Remove the feed-in unit [C] (5 screws).
NOTE: When reinstalling the feed-in unit , th e harne ss mu st be
positioned underneath the right hinge bracket.
19
Page 24

[C]
REPLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENT 24 June 1994
9.3 PICK-UP ROLLER REPLACEMENT
[D]
[B]
[A]
1. Turn off the main switch.
2. Remove the feed-in unit . (Se e Feed-in Unit Removal.)
3. Remove the DF motor [A] (2 screws an d 1 timin g be lt [B ]).
4. Remove the pick-up roller [C] (2 E-rings and 1 bushing) from the shaft [D].
20
Page 25

24 June 1994 REPLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
9.4 FEED ROLLER REPLACEMENT
[E]
[H]
[G]
[I]
[F]
[B]
[C]
[A]
[D]
1. Turn off the main switch.
2. Remove the feed-in unit . (Se e Feed-in Unit Removal.)
3. Remove the feed roller timing belt [A] , fe ed roller ge ar [B ] (1 E-rin g an d 1
spring pin [C]) and 1 bushing [D].
NOTE: Be careful not to lose the spring pin.
4. Slide the feed roller shaft [E ] to ward s t he fron t an d remo ve th e feed clutch
[F] (1 E-ring and 1 connector).
5. Take out the feed roller shaft (1 spacer and 1 bushing ----- from the rear
side).
6. Remove the feed roller [G] from th e shaft (3 idler rollers [H], 7 E-rings and
1 spring pin [I]).
NOTE: Be careful not to lose the spring pin.
21
Page 26

REPLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENT 24 June 1994
9.5 FRICTION BELT REPLACEMENT
[C]
[A]
[B]
1. Turn off the main switch.
2. Remove the friction belt asse mbly [A] (1 screw).
3. Remove the friction belt [B ] (2 springs, 1 pin).
NOTE: When installing the frict ion belt assembly, make sure the fe ed
roller [C] is set in the correct position. (See the illustra tio n. )
22
Page 27

[D]
24 June 1994 REPLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
9.6 PICK-UP SOLENOID ADJUSTMENT
[F]
[E]
[B]
[C]
[A]
1. Turn off the main switch.
2. Remove the feed-in unit. (See Feed-in Unit Removal.)
3. Loosen two screws [A] secu ring the pick-up solenoid [B] .
4. Place a 1.2 mm thickness gauge [C] between the plunger and the
solenoid.
5. Turn the solenoid leve r [D] clockwise until the plunger touches the
thickness gauge. Just at this po int , tig hten two screws.
6. Make sure that the pick-u p leve r [E] is to uch ing the pick-up roller [F] when
the plunger is pushed. If not, repeat steps 3 to 5.
7. Reassemble the DF.
8. Turn on the main switch and check th e orig ina l f eed-in operation.
23
 Loading...
Loading...