
1800MHz - 1900MHz ADJUSTABLE BANDWIDTH
OFF-AIR REPEATERS
OR1-SBHP1-1800
OR2-SBHP1-1800
OR1-SBHP1-1900
OR2-SBHP1-1900
Doc. code 91 080 0701F - Rel. 04
TECHNICAL HANDBOOK
Radio Frequency Systems
Kabelkamp 20
30179 Hannover, Germany
Tel.: +49 511 676 2731
Fax: +49 511 676 2515
E-mail: sales.europe@rfsworld.com

INDEX
1) SAFETY RULES................................................................................................................................... 1
2) STANDARDS........................................................................................................................................ 2
2.1) MANUFACTURE LABELS
2.2) SYMBOLS
3) GENERAL DESCRIPTION................................................................................................................... 3
3.1) EXAMPLE: USE IN TUNNELS
3.2) OPERATING PRINCIPLE - 1800MHz - 1900MHz ADJUSTABLE BAND OFF-AIR REPEATERS
3.3) ATTACHED DOCUMENTS
4) INSTALLATION AND POWER-UP PROCEDURES............................................................................ 4
4.1) INSTALLATION
A - INITIAL CHECK
B - POSITIONING THE REPEATER
C - POWER SUPPLY SOURCE CONNECTIONS AND ALARMS CONNECTIONS
D.C. POWERED EQUIPMENT
AC POWERED EQUIPMENT (ALTERNATE CURRENT)
4.2) POWER-UP
4.3) ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
1800MHz – 1900MHZ Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
INDEX
1

1

1) SAFETY RULES
1.1 Introduction
The equipment described in this technical handbook has been designed and tested in conformity of
international safety standards IEC215 / EN60215 and IEC950 / EN60950; the equipment has to be used
under the responsibility of specialised personnel only. In accordance with IEC215 / EN60215, adjustment,
maintenance and repair of the exposed equipment shall be carried out only by qualified personnel, who are
aware of the hazards involved. The minimum qualifications are established in the standard.
Final installation of the systems must fulfil the EMF emission levels, as requested by regulations in force
(recommendation n. 1999/519/EC).
WARNING: Installation Notes
Modular equipment, intended to be housed insidea rack cabinet, must be installed within a protected
access area only.
This area must be opportunely protected by security system that will exclude the entry, even if accidental, to
not authorized and trained personnel. Alternatively, the cabinet, in which the equipment is housed, must be
closed on all sides, to allow the access to internal parts to authorized personnel only
1.2 AC Power supply
When working on the equipment always make sure that the equipment is not connected to the mains
supply.
Before power up always make sure that the equipment is connected to earth by using the equipment
grounding bolt.
If it is necessary to fit an AC power supply plug to power cable, the User must observe the following colour
codes: LIVE terminal to BROWN lead NEUTRAL terminal to BLUE lead EARTH terminal to GREEN/YELLOW
lead The User must also ensure that the protective earth wire would be the last to break, should the cable be
subject to excessive strain.
1.3 Safety precautions
For the correct and safe use of the equipment it is essential that both operation personnel and services
personnel follow generally accepted safety procedures (see IEC Publications 215: "Safety measures for
radio transmitting equipment" and 61010-1: "Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measureme nt,
control, and laboratory use") in addition to the safety precautions specified in this technical handbook.
Specific warnings and caution statements, where applicable, can be found throu ghout this technical
handbook. Warning and caution statements and/or symbols are ma rked on the equipment where is
necessary. (see also ANNEX n°1).
As far as the equipment safety devices are concerned please remind that: -periodic functional check shall be
carried out on protective devices; -functional check shall be carried out on protective devices, when they
have operated under fault conditions; -safety devices shall not be altered or disconnected except for
replacement; -safety circuit shall not be modified.
SAFETI RULES ENG

1.4 Caution and warning statements
Caution
destruction of equipment or other property. Warning of danger
requires correct procedures or practices in order to avoid personal injury.
It's used to indicate the correct operation and maintenance, in order to prevent damage or
Used to indicate the potential hazard that
1.5 Impaired safety protection
Whenever it is likely that safe operation is impaired, the apparatus must be in-operative and secured against
unintended operation. The appropriate servicing staff authority must be informed.
For instance, the safety is likely to be impaired if the equipment fails to perform the prescribed
measurements, or shows visible damages.
1.6 Electrostatic sensitive devices
In case of electrostatic sensitive devices ( for instance all ICs and many other semicondu ctor devices belong
to this class) it is essential to use a right protection to reduce the risk of personal injury. Careless handling,
during repair, may imply life danger. When repairing, make sure that you are connected with the same
potential as the ground of the equipment by means of the right devices, i.e. a GIRDLE (a wrist wrap with
resistance) and a WINDING CORD to be connected to the girdle and to the relevant socket placed on the
equipment.
You must also keep components and tools at this potential.
1.7 Electrolytic Capacitors
Non-solid electrolytic capacitors must not contain chemicals, which may be regarded as hazardous, if
incorrectly handled. Caution is necessary, should the outer case be fractured.
1.8 Electric shock
In case of electric shock it is recommended not to touch the person before breaking the circuit by means of
the power supply switch; should it be not possible to break the circuit power supply it would be advisable to
try to rescue the person by means of some insulating materials: e.g. a wood stick, a nylon cord or a suitable
service made of plastics, etc.
NEVER TOUCH ELECTROCUTED PEOPLE WITH YOUR HAND AS LONG AS THEIR BODIES ARE
SUBJECTED TO VOLTAGE, OTHERWISE YOU TOO WOULD GET ELECTOCUTED.
Call the doctor and then immediately perform the artificial respiration as described here belo w:
SAFETI RULES ENG

Lay the patient on his back with his arms parallel to his body; if the patient lies on an
inclined plane, please make sure that his stomach be slightly lower than his breast.
Open the patient's mouth and check if there are foreign bodies. Kneel down near the
patient at the same level as his head's, put one of your hands under his head and the
other one under his neck. Lift the patient's neck and let his head fall backwards the
most possible.
Shift your hand from the patient's neck to his chin; put your thumb between his chin
and his mouth, your forefinger along his jawbone, keep your other fingers tight. By
doing these operations start the self-oxygenation by means of deep breathings in
standing open-mouthed. With your thumb between the patient's chin and his mouth,
keep the patient's lips closed and blow into his nasal cavities.
During these operations see if the patient's breast rises. If it is not so, his nose may be
obstructed; in this case, by levering on his chin with your hand, open the patient's
mouth, put your lips on and blow into his oral cavity. Look at the patient's breast and
see if it rises. One can use this second method instead of the first one also if the
patient's nose is not obstructed, provided that his nose be occluded by squeezing his
nostrils with your hand after shifting it from his head. The patient's head must be kept
bent backwards the most possible.
Start with ten fast and deep expirations, then go on at the rhythm of twelve/fifteen expirations per minute.
Continue as long as the patient has recovered consciousness, or a doctor has ascertained his death.
1.9 Burns
As far as burns are concerned: Don't try to take off clothes from the burnt
parts; Pour some cold water on body burnt areas and ask immediately for a
doctor; Don't apply ointments or oily tinctures.
SAFETI RULES ENG
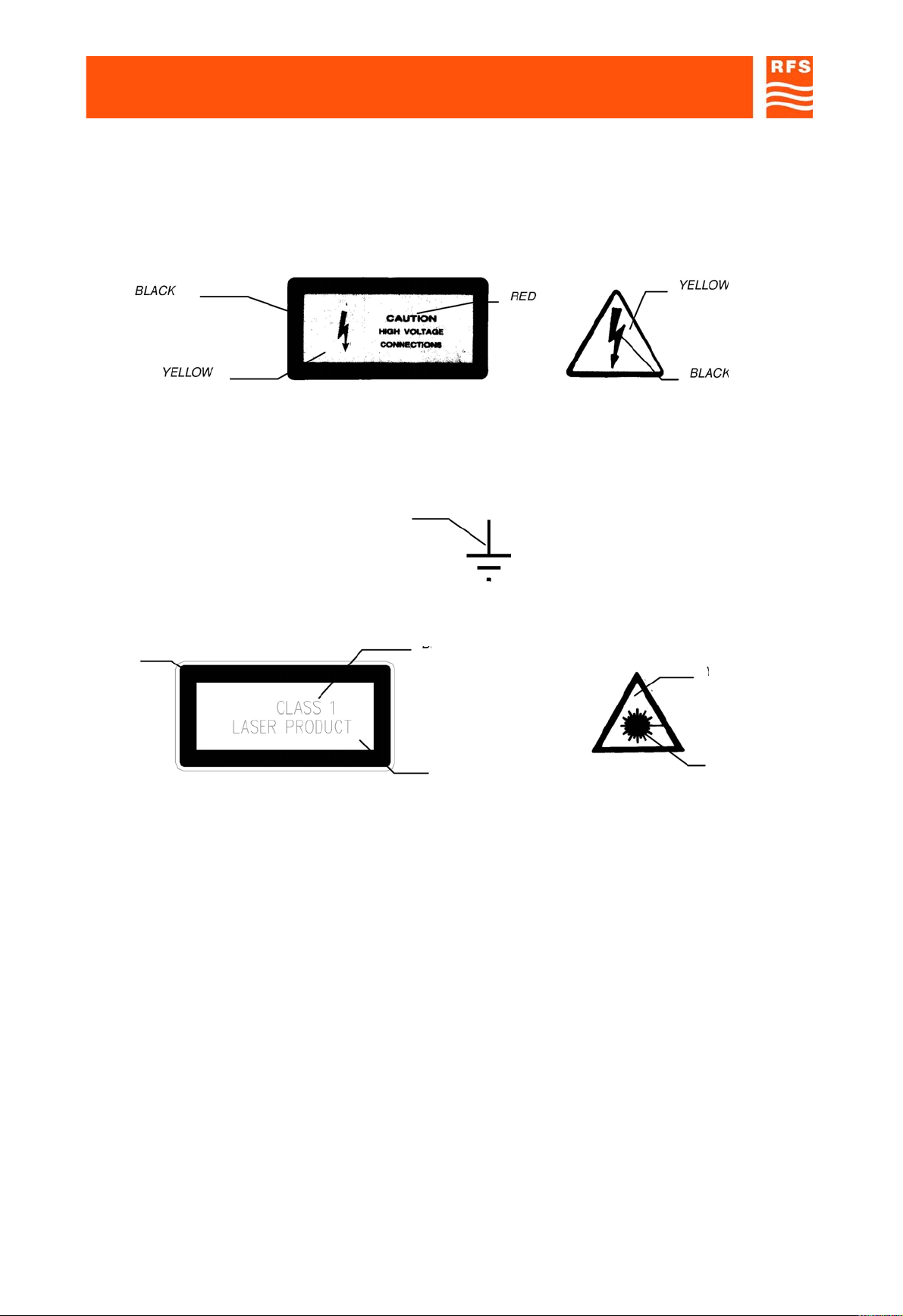
ANNEX 1 When the equipment or the modules are equipped with the labels as shown here below, it is essential to
observe the warnings contained
-LIVE VOLTAGE POINT
-PROTECTIVE EARTHING TERMINAL
BLACK
-CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT
YELLOW
BLA
CK
BLACK
EXPLANATORY LABEL (affixed to the WARNING LABEL (affixed to the CLASS 1 product side)
CLASS 1 product front)
Products which are of CLASS 1 as defined in the IEC EN 60825-1, fourth edition “Safety of laser
products -Part 1: Equipment classification, requirements and user's guide”. Even if the product is of
CLASS 1, please observe the following safety procedures, prescribed in the cited norm:
• do not observe directly the laser beam,
• do not use observation optics (lens, microscopes, telescopes, etc.),
• do not expose eyes directly.
YELLO
W
BLACK
SAFETI RULES ENG

-DEVICES SENSITIVE TO THE ELECTROSTATICS
WARNING: Please observe the due precautions in handling devices which are sensitive to the
electrostatics.
-NON-SOLID ELECTROLYPTIC CAPACITORS MAY CONTAIN CHEMICALS TO BE REGARDED AS
HAZARDOUS, IF INCORRECTLY HANDLED.
WARNING
THE MAXIMUM CAUTION IS REQUIRED IF THE OUTER CASE IS FRACTURED
SAFETI RULES ENG

2

2) STANDARDS
2.1. MANUFACTURE LABELS
2.1.1 BAR CODE LABEL
Fig. 1
Label fields (ref. Fig.1):
a) Serial number: this field contains the serial number (made up of a 7-digit sequential group) of the
module or equipment.
b) F (final test tracing out): this field contains an F letter that has been barred to certify that the item has
been successfully tested in the factory Final Test Dept.
c) Customer order reference.
d) Equipment acronym or manufacture part number.
e) ICS (Item Change Status): this field contains the item ICS, made up of 2 digits, starting from 01, of the
manufacture part number or equipment.
Fig.2 shows an example of bar code label applied:
Fig. 2
On equipment other labels may be present, as integration of what reported in bar code label (fig.1);
see following pages.
STANDARDS Page 1

2.1.2 MANUFACTURE LABELS FOR RACK CABINETS AND EQUIPMENT
(1)
(4)
(9)
(2)
(5) (6)
(10)
90mm
(7)
(3)
(8)
(11)
Fig. 3
Label fields (ref. Fig.3):
(1) SYSTEM (it will be filled in only if the rack cabinet or the equipment belong to a system):
this field contains the system acronym.
(2) EQUIPMENT:
This field contains the acronym of the rack cabinet or equipment.
(3) MANUFACTURE PART NUMBER:
This field contains the manufacture part number either of the rack cabinet or the equipment.
(4) SERIAL NUMBER:
This field contains the serial number (made up of a 5-digit sequential group) of the rack cabinet or
equipment.
The serial number of each item comes from the manufacture orders print-out (for domestic and foreign
markets).
(5) QIF (Quality Identification Factor):
FACTORY USE ONLY
(6) ICS (Item Change Status):
This field contains the item ICS, made up of 2 digits, of the rack cabinet or equipment.
(7) ORIGIN CODE:
FACTORY USE ONLY
(8) MANUFACTURE YEAR AND WEEK:
This field contains the manufacture year and week of the rack cabinet or equipment (4 digits, the first two
of which indicate the year, while the last two digits indicate the relevant week) e.g. 9515: 15th week of
1995.
STANDARDS Page 3

(9) SUPPLY VOLTAGE (from MAINS and/or from DC SOURCE)
(10) ABSORBED CURRENT
(11) MAINS FREQUENCY
F (final test tracing out):
This field contains an F letter that has been barred to certify that the item has been successfully tested in
the factory Final Test Dept.
Fig.4 shows an example of manufacture label as applied to a RACK CABINET or to an EQUIPMENT.
58822 A0122
230Vac/48Vdc
00021 01
0.5Aac/0.89Adc
50/60 Hz
Fig. 4
(•) System acronym (if any)
For instance, you will find the manufacture label placed:
- on the upper left corner of the rack cabinet frame;
- on the rear side (or on the external right side) of the equipment rack.
9515
STANDARDS Page 4

2.1.3 MANUFACTURE LABELS FOR RACKS AND PLUG-IN, OR WIRING TYPE, MODULES
(1)
(4)
(2)
(5) (6) (8)
(3)
(7)
Fig. 5
Label fields (ref. Fig.5):
(1) SYSTEM (it will be filled in only if the rack or the module to be label belong to a system):
this field contains the system acronym.
(2) EQUIPMENT:
This field contains the acronym of the rack, or module.
(3) MANUFACTURE PART NUMBER:
This field contains the manufacture part number of the rack or module.
(4) SERIAL NUMBER:
This field contains the serial number (made up of a 5-digit sequential group) of the rack or module.
The serial number of each item comes from the manufacture orders print-out (for domestic and foreign
markets).
(5) QIF (Quality Identification Factor)
FACTORY USE ONLY
(6) ICS (Item Change Status):
This field contains the item ICS, made up of 2 digits, of the rack or module.
(7) ORIGIN CODE:
FACTORY USE ONLY
(8) MANUFACTURE YEAR AND WEEK:
This field contains the manufacture year and week of the rack or module (4 digits, the first two of which
indicate the year, while the last two digits indicate the relevant week) e.g. 9515: 15th week of 1995.
STANDARDS Page 5

F (final test tracing out):
This field contains an F letter that has been barred to certify that the item (rack or module) has been
successfully tested in the factory Final Test Dept.
Fig.6 shows an example of manufacture label as applied to a RACK or PLUG-IN, or WIRING TYPE
MODULES.
58822 A012200021 01 9515
Fig. 6
(•) System acronym (if any)
For instance, you will find the manufacture label placed:
- on the topside of the plug-in module, right or left;
- on the topside of the wiring-type module.
2.1.4 SUB-MODULES MANUFACTURE LABEL
F
Fig. 7
Label fields (ref. Fig.7):
(3) MANUFACTURE PART NUMBER:
This field contains the sub-module manufacture part number.
(5) QIF (Quality Identification Factor)
FACTORY USE ONLY
(6) ICS (Item Change Status):
This field contains the item ICS, made up of 2 digits, of the sub-module.
(7) ORIGIN CODE:
FACTORY USE ONLY
STANDARDS Page 6
(8) MANUFACTURE YEAR AND WEEK:
This field contains the manufacture year and week of the submodule (4 digits, the first two of which
indicate the year, while the last two digits indicate the relevant week) e.g. 9542: 42nd week of 1995.
F (final test tracing out):
This field contains an F letter that has been barred to certify that the item (sub-module) has been
successfully tested in the factory Final Test Dept.
Fig. 8 shows an example of manufacture label as applied to a SUB-MODULE.
00081.01 B0111
Fig. 8
You will find the manufacture label placed on the sub-module top, left, or right side.
F
STANDARDS Page 7

2.2) SYMBOLS
EQUIPMENT FRONT SYMBOLS
SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION
Earth connection Impulsive command Band-stop filter
Ground Fuse Low-pass filter
Chassis ground Thermal breaker High-pass filter
AC Failure Modulator,
demodulator
DC Overtemperature Stereo
Pulse current Output monitoring
signal
Battery / accumulator Input monitoring
signal
Positive connector
P
Negative connector
P
OFF
L.O.
Direct power
monitoring socket
Reflected power
monitoring socket
Local oscillator
monitoring socket
ON Gating as opening
criterion
STAND-BY Gating as closing
criterion
Balance
Amplifier
Adjustable gain
amplifier
Loudspeaker
connection
Audio connection
Headphone
connection
Stereo headphone
ON push-button Channel / band filter Star connection
STANDARDS Page 8

EQUIPMENT FRONT SYMBOLS
f
5MHz
SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION
Delta connection Receiving antenna Dual sound
High voltage Linearization
Start push-button Limiter upper
threshold
Local, manual
command
Automatic Adjusting
OFF / inhibited
(function)
ON / active
(function)
Stand-by
(function)
Output connector
Input connector
Limiter lower
threshold
Max adjusting
Min adjusting
Adjusting
Frequency adjusting
Xtal adjusting
Clock display
(operation time
counter)
Fan, blower Amplitude tuning
Antenna Band tuning
Transmission antenna Mono
STANDARDS Page 9
Freq. tuning

BLOCK DIAGRAM SYMBOLS
dB
THERMAL
SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION
Linear variability 2-way switch NAND general symbol
Automatic adjustment Voltage control
NOT general symbol
electromagnetic relay
Combiner general
Transformer Preemphasis
sign
2-way power divider Rectifier general
Deenphasis
symbol
2-way power
combiner
=
DC/DC converter Delay line general
symbol
=
3-way power divider Bridge rectifier Coaxial type time
delay limiter
4-way power divider
REG
3dB Hybrid Zener regulator
Voltage regulator Resistive attenuator
Pad
LIM.
WHITE
White limiter
Constant current bias
Fixed phase shifter
device
BIAS
Positive peak clipper Sinusoidal oscillator
SWITCH
Thermal switch
Negative peak clipper Ex-OR Band-pass filter
Circulator OR general symbol Band-stop filter
Isolator NOR general symbol Low-pass filter
Switch AND general symbol High-pass filter
STANDARDS Page 10

BLOCK DIAGRAM SYMBOLS
SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION SYMBOLS DESCRIPTION
f
f/n
Divider by n DC amplifier Optical amplifier
f/n
FI
OL
RF FI
OL
f
Multiplier by n Differential
f
comparator
Mixer general symbol Phase comparator
Up-converter from IF
to RF
RF
Down-converter from
RF to IF
P. SYNC
CLAMP
Voltage / frequency
V
converter
Detector amplifier
Lamped to the
syncrhronizing signal
peak
Schmitt’s trigger
Directional coupler Amplitude linearity
precorrector
Double directional
coupler
Amplitude limiter
without distortion
Directional coupler
Equalizer general sign
with double detector
Detector
A
Amplitude equalizer
Peak detector Phase equalizer
3
X
X
To rise to cubical
power
Amplifier general
T
RF
symbol
Multistage amplifier
RF
Propagation time
equalizer
Laser diode electricaloptical transmitter
Optical-electrical
receiver
STANDARDS Page 11

3

μ
p
μ
3) GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Mobile phone systems have increasingly been spreading in these last years.
Besides providing reliable and good quality connections, telecommunication system services should cover
as widest territory as possible.
It is well-known that connections to users’ terminals are obtained on air by means of steady stations named
radio bases, located through the whole territory so as to obtain a continuous covering through cells one next
to another.
That allows a great number of users to enter the system using few channels.
It is important to maintain the continuity of radio-electrical coverage (and consequently, of service within
each cell) in order to guarantee an acceptable level of communication.
BTS Tri-cellular
FIGURE 1 – SUBDIVISION OF THE TERRITORY IN CELLS
Off-Air Repeaters are proposed as a valid and economical solution to optimize the cell coverage of the
territory and irradiate shadow area as an alternative to solutions requiring dedicated Radio-Bases (Figure 2).
MicroBTS solution Repeater solution
2Mbit radio connection
The repeater costs are 50% lower
BTS
than with the solution
BTS
Shadow Zone
BTS
Shadow Zone
BTS
Re
eater
Source
FIGURE 2 – RADIO-ELECTRICAL PROBLEMS IN CELL NETWORK COVERAGE
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 3
3.1

Off-Air Repeaters on one side receive the signals from the radio base station, amplify them and re-transmit
them in the direction of the shadow area (down-link path). On the other side Off-Air Repeaters receive the
signals from the mobiles (MS), amplify them and re- transmit them to the base station (up-link path).
When a single Off-Air Repeater does not provide satisfactory coverage, the repeater can be used along with
other equipment. Different solutions are provided: cascade systems, based on Bi-Directional Amplifiers, and
optical fibre solutions, based on Remote Units.
3.1) EXAMPLE: USE IN TUNNELS
The Off-Air Repeater interfaces directly with the BTS of the provider of the services to be extended, and can
be used along with other equipment distributed inside the tunnels. Such equipment can be divided into two
types, according to the radio-coverage system used:
- Bi-directional amplifiers, for cascade systems.
- Remote Units, for optical systems.
The following are a few examples of general projects for radio-elec tric coverage in tunnels.
• Tunnels with a length of less than 300 meters.
In this case, one single Off-Air Repeater is sufficient. It is located at the entrance to the tunnel, equipped
with an antenna which irradiates in the direction of the shadow zone (Figure 3).
DO
W
N
L
I
N
U
K
P
L
I
N
K
OFF-AIR
REPEATER
DOWN
UP
Power Supply
(230Vac)
48Vdc Power Supply
and external signals
DOWN
UP
FIGURE 3
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
3.2
CHAPTER 3

• Tunnels with a length in the 300-meter to 600-meter range.
Also in this case, one single Off-Air Repeater is sufficient. The repeater is located at the entrance to the
tunnel and equipped with a leaky cable. This cable can be combined with a directional antenna to
irradiate a portion of the area in front of the tunnel exit (Figure 4).
DO
W
N
L
I
N
U
K
P
L
I
N
K
OFF-AIR
REPEATER
DOWN
UP
Power Supply
(230Vac)
48Vdc Power Supply
and external signals
DOWN
UP
FIGURE 4
• Tunnels with a length of more than 600 meters.
The signal can be enhanced in two ways:
a) By an Off-Air Repeater at the entrance to the tunnel, connected to a cascade of bi-directional
amplifiers inside the tunnel which re-generate the signal with amplification steps at a distance of
250mt. ÷ 400mt. from one another (Figure 5).
D
O
WN
L
I
N
U
P
K
L
I
N
K
OFF-AIR
REPEATER
DOWN
RF
UP
DC
POWER
SUPPLY
BF
BF
DC
RF
RF-DC-BF
Bias-T
DOWN
UP
RF-DC-BF
BI-DIRECTIONAL
AMPLIFIER
RF-DC-BF
BI-DIRECTIONAL
AMPLIFICATION STEP
RF-DC-BF
RF-DC-BF
AMPLIFIER
FIGURE 5
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 3
3.3

b) By an Off-Air Repeater connected to master unit and optical remote units with amplification steps of
no more than 1200mt. each. The optical fiber system extends the signal through an antenna or a
passive distribution system (Figure 6).
D
OW
N
L
I
N
K
U
P
L
I
N
K
OFF-AIR
REPEATER
DOWN
RF
UP
Power Supply
(230Vac)
DOWN
UP
48Vdc Power
Supply and external
signals
MASTER
UNIT
REMOTE
UNIT
FIGURE 6
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
3.4
CHAPTER 3

3.2) OPERATING PRINCIPLE – 1800/1900MHz ADJUSTABLE BANDWIDTH OFF-AIR REPEATERS
The repeaters described in this handbook have been developed to permit cell coverage as set forth by the
DCS (Digital Cellular System) standard for cell phones operating on the 1800MHz band or by the PCS
(Personal Communications Service) standard for cell phones operating on the 1900MHz band. The DC
powered repeater can be power-fed by a 48Vdc power supply source only. The AC powered repeater can be
power-fed from MAINS (230Vac) or from a 48Vdc power supply source or both from MAINS and from a
48Vdc source. The presence of both power supply voltages guarantees the continuity of the coverage
service even in case of failure of one source. The commutation is handled automatically by the repeater.
Off-Air Repeaters are bi-directional amplifiers. The signal to be extended follows two distinct paths: the uplink path, from the mobiles to the radio base station, and the down-link path, from the radio base station
towards the mobiles.
Figure 7 provides a block-diagram of the 1800/1900MHz adjustable band Off-Air Repeater.
NETWORK
RS232
G
MANAGEMENT
MODEM
5.5Vdc
UNIT
5.5Vdc
10.5Vdc
DC/DC
CONVERTER
48Vdc
IN
48Vdc
230Vac
LF
AC/DC
CONVERTER
IN
MANAGEMENT BUS
E1
LNA UP
dB
5.5Vdc
HPA
DOWN
10.5Vdc
B2
DOWN
MS
UP
A2
BTS
DOWN
UP
ALC
5.5Vdc
LNA DOWN
C1 D1
dB
B1
10.5Vdc
5.5Vdc
HPA UP
E2
A1
5.5Vdc
10.5Vdc
BAND SELECTIVE 1
DOWN LINK
UP LINK
5.5Vdc
D2
BAND SELECTIVE 2
DOWN LINK
UP LINK
ALC
10.5Vdc
5.5Vdc
C2
FIGURE 7 – 1800/1900MHz OFF-AIR REPEATERS BLOCK-DIAGRAM
In down-link the RF signal from the donor antenna is filtered and pre-amplified by a low-noise amplifier (LNA,
ref. C1).
The selection of the band of frequencies to be extended is handled by two band-selective modules, ref. D1
and ref. D2, which make the band-pass and frequency center programmable entities.
The band of frequencies to be extended can be managed by the user by means of the management system.
The signal is then amplified by the High power amplifier (ref. E1) filtered by the MS side duplexer, ref.
B2,and transmitted by an antenna or a passive distribution system.
A VSWR detector is equipped.
The up-link path is identical to the down-link path described above.
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
3.5
CHAPTER 3

The 48Vdc powered repeater is equipped with a DC/DC converter, ref. F.
The A.C. powered repeater is equipped also with an AC/DC converter, ref. L.
The management module, ref. G, makes it possible to manage the repeater in remote mode via a built-in
modem, or in local mode through the RS232 connector, available on the management module.
The repeater management is performed by means of the Operation and Maintenance Terminal software,
both in local mode and in remote mode (ref. Chap. 4).
3.3) ATTACHED DOCUMENTS
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
1800MHz 48Vdc/230Vac ADJUSTABLE BAND OFF-AIR REPEATERS
ILL DCS OFF-AIR REPEATERS (ILLUSTRATIVE DRAWINGS)
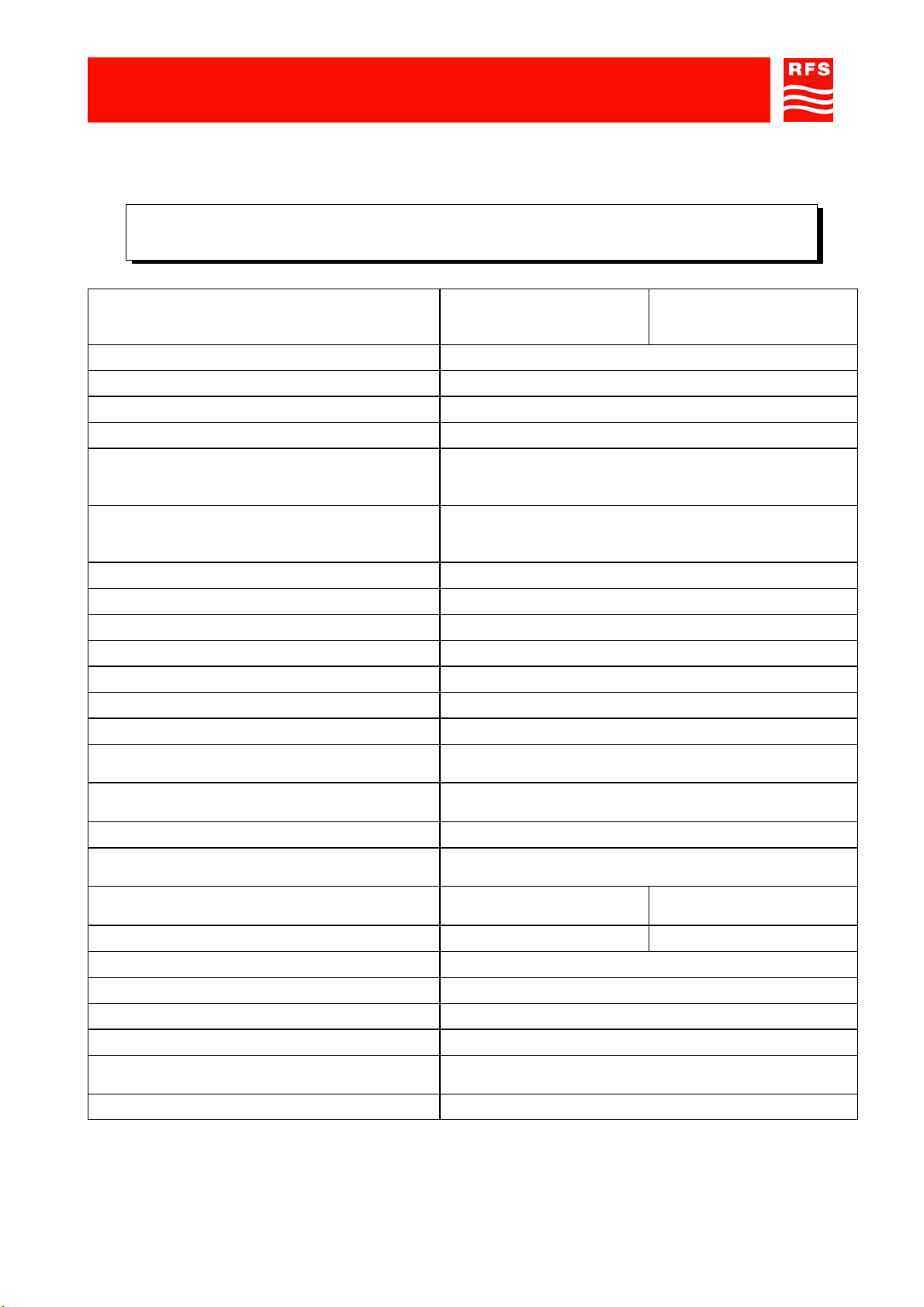
Sheet 1, equipment composition and backplane access points map
Sheet 2, modules access points map and external access points m ap
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
1900MHz 48Vdc/230Vac ADJUSTABLE BAND OFF-AIR REPEATERS
ILL PCS OFF-AIR REPEATERS (ILLUSTRATIVE DRAWINGS)
Sheet 1, equipment composition and backplane access points map
Sheet 2, modules access points map and external access points m ap
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 3
3.6
ANNEX 1
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
1800MHz 48Vdc/230Vac ADJUSTABLE BAND OFF-AIR REPEATERS
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Up Link operating frequency band
Down Link operating frequency band
Number of amplified bands
1800MHz OFF-AIR
REPEATER
48Vdc MODEL
1710 ÷ 1785MHz
1805 ÷ 1880MHz
1800MHz OFF-AIR
REPEATER
230Vac MODEL
1
Programmable Bandwidth / steps From 1MHz to 16.5MHz / 10kHz step adjustable
Output Power 28dBm (2 carriers)
3rd Order Intercept Point (OIP3) 57dBm
Output Power at 1dB compression point
36dBm
Noise Figure @ max. gain 8dB
Gain / Step
50 ÷ 80dB / 1dB step
Ripple into operating band ± 2dB
Total processing delay
6μs
Return Loss 14dB
ALC threshold (default value)
Spurious emissions and intermodulation products
< -36dBm (in the frequency band 9kHz ÷ 1GHz)
< -30dBm (in the frequency band 1GHz ÷ 12.75GHz)
3dB over nominal output power
(this value can be changed on site)
Local Control Interface RS232
Remote Control Interface PSTN – GSM/DCS modem
Power Supply
-72 ÷ -36Vdc
-72 ÷ -36Vdc
85÷265Vac (50-60Hz)
Power Consumption 110W @ 48Vdc 140VA @ 230Vac
MTBF 50 000 hours
Operating Temperature (*) -20°C up to +55°C
Degree of protection provided by enclosure IP65
RF connectors 7/16 female
Dimensions (h-w-d)
(max. volume - heat sinks included)
423x395x230mm
Weight 23Kg
All values are typical at 25°C unless otherwise specified
(*) Degraded performances from +50°C to +55°C
1800MHz-1900MHz ADJUSTABLE BAND Annex TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
OFF-AIR REPEATERS
1

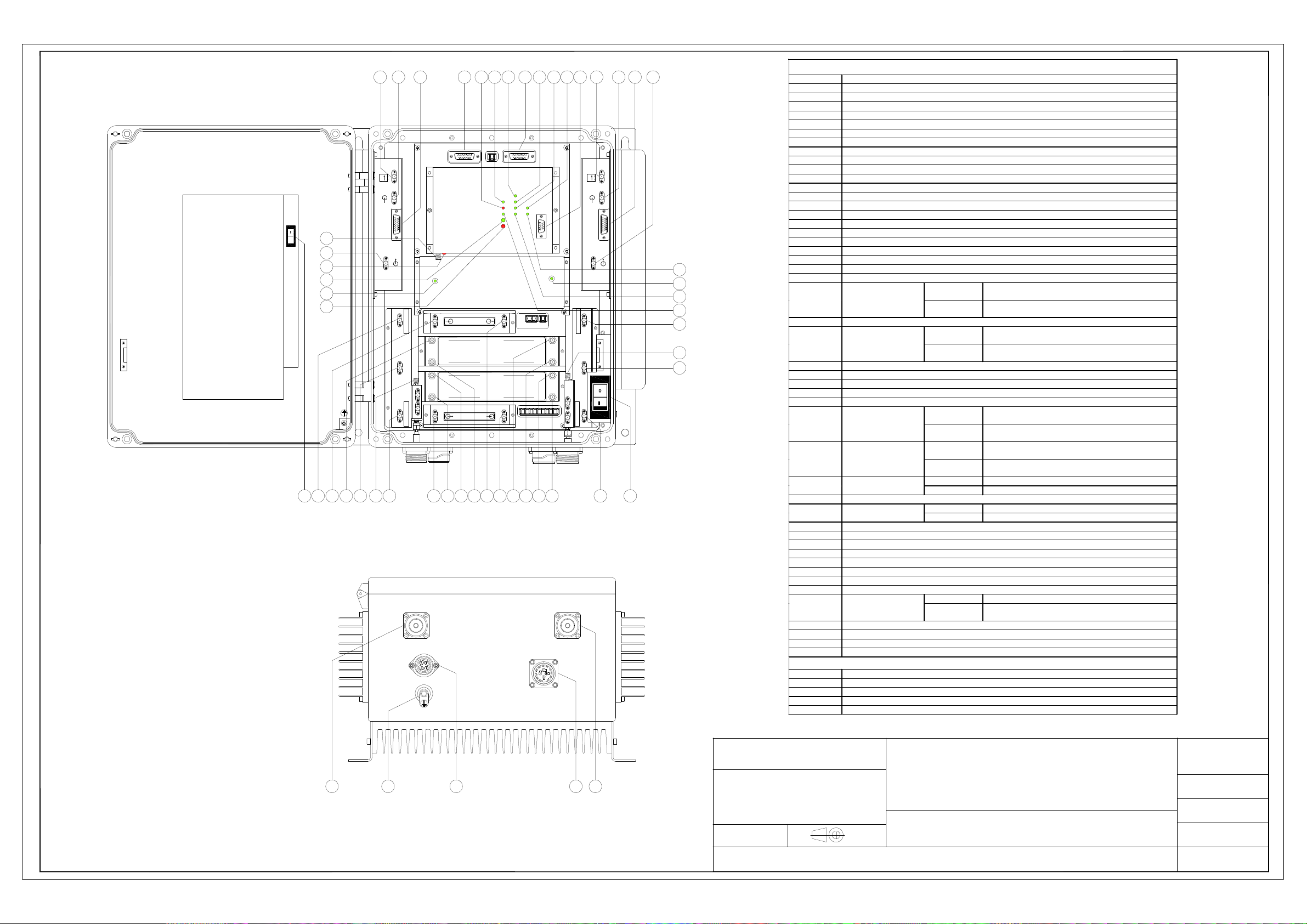
HPA - UP LINK - communicates with management
HPA - UP LINK - does not communicate with
HPA - DOWN LINK - communicates with
HPA - DOWN LINK - does not communicate with
LNA - DOWN LINK - communicates with
LNA - DOWN - does not communicate with
LNA - UP LINK - communicates with management
LNA - UP LINK - does not communicate with
45 44 43 42 40 39 33 32 30
41 35
37
38
34 3136
Ref. DESCRIPTION
1 DUPLEXER - BTS side - Up Link path SMA connector
2 LNA - Down Link - input
3 Band Selective 2 Up-Link path output
4 DUPLEXER - BTS side - input/output SMA connector
5 Directional coupler - BTS side - SMA (f) input/output connector
6 DUPLEXER - BTS side - SMA Down Link connector
9 LNA - Up Link path - output
10 Band Selective 1 Up Link Input
11 Band Selective 1 Down Link Output
MODULES ACCESS POINTS MAP
P
IN
UP LINK
46
0
SPV BUS
HIGH POWER AMPLIFIER
OPERATING
132KHz
ALARM
BS 2
BS 1
RL
U LNA
+5V
D
U
HPA D
RS232
P
IN
SPV BUS
DOWN LINK
HIGH POWER AMPLIFIER
47
48
49
OUT
5V5
POWER SUPPLY
10V5
50
51
1710-1785MHz
1805-1880MHz
57
1
5
4 6 9 10 14 15
LNA DOWN
Out
Out
In
UP-LINK
BAND-SELECTIVE 2
DOWN-LINK
DOWN-LINK
BAND-SELECTIVE 1
UP-LINK
LNA UP
In
OutIn
In
Out
1805-1880MHz
1710-1785MHz
OUT
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
2111 16 18172 13
223 12
INTERNAL VIEW - MODULES ACCESS POINTS
12 Band Selective 2 Down Link Input
13 LNA - Down Link path - output
14 LNA - Up Link path - input
15 Band Selective 2 Up Link path input
16 Band Selective 2 Down Link path output
17 Band Selective 1 Down Link path Input
18 Band Selective 1 Up Link path output
21 DUPLEXER - MS side - Up Link path SMA connector
22 48Vdc ONLY circuit breaker
23 DUPLEXER - MS side - input/output SMA connector
24 Directional coupler - MS side - SMA (f) input/output connector
25 DUPLEXER - MS side - Down Link path SMA connector
26 GREEN LED: +5Vdc available
27
GREEN / RED LED
HPA UP
GREEN
RED
unit
management unit
28 GREEN LED: +10.5V available
29
GREEN / RED LED
HPA DOWN
GREEN
RED
management unit
management unit
30 HPA Down Link output
31 Sub-D 15-pole management link between Down Link HPA and management unit
32 HPA Down Link input
33 HPA Down Link monitoring SMA connector
34 Sub-D 9-poles RS232 connector
35
36
37
GREEN / RED LED
LNA DOWN
GREEN / RED LED
LNA UP
GREEN / RED LED
Band Selective 1
GREEN
RED
GREEN
RED
GREEN BS1 communicates with management unit
RED BS1 does not communicate with management unit
management unit
management unit
unit
management unit
38 Sub-D 15-pole management link between Down Link HPA and management unit
39
GREEN / RED LED
Band Selective 2
GREEN BS2 communicates with management unit
RED BS2 does not communicate with management unit
40 GREEN LED 132kHz: 132kHz (line amplifier management carrier) correctly operating
41 RED LED: Return Loss alarm
42 Sub-D 15-pole management link between Up Link HPA and management unit
43 Sub-D 15-pole management link between Up Link HPA and management unit
44 HPA Up Link input
45 HPA Up Link monitoring SMA connector
46 GSM modem RF output
47 HPA Up Link output
48
RED LED: modem
operation
RED ON Trying to connect to network
BLINKING
RED
Modem correctly operating
49 GREEN LED: equipment correctly operating
50 GREEN LED: 5.5V available
51 RED LED: equipment fault
57 (*) AC voltage ONLY circuit breaker
EXTERNAL ACCESS POINTS MAP
52 BTS side 7/16 RF connector
53 Equipment Grounding
54 (*) AC voltage input (230Vac)
55 48Vdc input / external alarms Connector
56 MS side 7/16 RF connector
(*) 230VAC MODEL ONLY
Part Number
ILL DCS OFF-AIR REPEATERS
Title
1800MHz ADJUSTABLE BAND OFF-AIR REPEATERS
MODULES ACCESS POINTS MAP AND EXTERNAL
52
53 54
BOTTOM VIEW - REPEATER CASE CLOSED
EXTERNAL ACCESS POINTS
55 56
Scale
Copyright protection according to law
Revisions
ACCESS POINTS MAP
ED. 01-1
29/09/2006
Date
31/01/2007
Drawn by
Checked by
Approved by
Sheet
ED. 02
CG
MN
AV
2/2
ANNEX 2
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
1900MHz 48Vdc/230Vac ADJUSTABLE BAND OFF-AIR REPEATERS
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Up Link operating frequency band
Down Link operating frequency band
Number of amplified bands
1900MHz OFF-AIR
REPEATER
48Vdc MODEL
1850 ÷ 1910MHz
1930 ÷ 1990MHz
1900MHz OFF-AIR
REPEATER
230Vac MODEL
1
Programmable Bandwidth / steps From 1MHz to 16.5MHz / 10kHz step adjustable
31dBm (1 carrier)
Output Power (GSM/TDMA)
28dBm (2 carriers)
25dBm (4 carriers)
26dBm (1 carrier)
Output Power (CDMA)
23dBm (2 carriers)
20dBm (4 carriers)
3rd Order Intercept Point (OIP3) 57dBm
Output Power at 1dB compression point
36dBm
Noise Figure @ max. gain 8dB
Gain / Step
50 ÷ 80dB / 1dB step
Ripple into operating band ± 2dB
Total processing delay
6μs
Return Loss 14dB
ALC threshold (default value)
Spurious emissions and intermodulation products
< -13dBm (in the frequency band 9kHz ÷ 1GHz)
< -13dBm (in the frequency band 1GHz ÷ 12.75GHz)
3dB over nominal output power
(this value can be changed on site)
Local Control Interface RS232
Remote Control Interface
Power Supply
PSTN – GSM (850, 900, 1800, 1900)
or CDMA (850, 1900) modem
-72 ÷ -36Vdc
-72 ÷ -36Vdc
85÷265Vac (50-60Hz)
Power Consumption 110W @ 48Vdc 140VA @ 230Vac
MTBF 50 000 hours
Operating Temperature (*) -20°C up to +55°C
Degree of protection provided by enclosure IP65
RF connectors 7/16 female
Dimensions (h-w-d)
(max. volume - heat sinks included)
423x395x230mm
Weight 23Kg
All values are typical at 25°C unless otherwise specified
(*) Degraded performances from +50°C to +55°C
1800MHz-1900MHz ADJUSTABLE BAND Annex TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS
OFF-AIR REPEATERS
2


4

4) INSTALLATION AND POWER-UP PROCEDURES
Ref.: ILL DCS OFF-AIR REPEATERS / ILL PCS OFF-AIR REPEATERS
WARNING:
Before installing the equipment, carefully read the safety norms herewith attached.
A correct repeater installation and setting procedure requires a good knowledge and experience in
installing telecommunication equipment. These activities should be performed by skilled personnel
only. Remember that if the equipment is not installed correctly, it may:
- put the donor BTS temporary out of service,
- be damaged by excessively high input or output signal levels.
4.1) INSTALLATION
1. INITIAL CHECK
Make sure that the supply is complete and/or that the material has not been damaged during transport.
The list of the materials that make up the equipment is described in the relative PACKING LIST.
Should any parts be missing, or should some be damaged, kindly inform the Sales Dept. of RFS
immediately, in order to facilitate replacing and/or repairing the parts involved.
WARNING:
Before installing the equipment, always make sure that the repeater is not powered up:
- Check that both ON/OFF switches located inside the alternate current powered repeater are
in the OFF position (AC voltage circuit breaker, ref. 59 and 48Vdc circuit breaker, ref. 22
FIGURE 1a).
- Check that the ON/OFF switch (48Vdc circuit breaker, ref. 22, FIGURE 1b) located inside the
direct current powered repeater is in the OFF position.
The LEDs inside the repeater must be turned off.
P
IN
UP LINK
0
SPV BUS
HIGH POWER AMPLIFIER
AC voltage
circuit breaker
ref. 59
a) 230Vac MODEL
INTERNAL VIEW
OUT
1710-1785MHz1805-1880MHz
BS 2
132KHz
BS 1
RL
ULNA
+5V
U
HPA D
OPERATING
ALARM
POWER SUPPLY
5V5 10V5
LNA DOWN
Out
UP-LINK
BAND-SELECTIVE 2
In
DOWN-LINK
Out
DOWN-LINK
BAND-SELECTIVE 1
In
UP-LINK
LNA UP
48Vdc circuit
breaker
ref. 22
P
IN
D
SPV BUS
DOWN LINK
HIGH POWER AMPLIFIER
OUT
In
Out
In
Out
1710-1785MHz 1805-1880MHz
P
IN
UP LINK
SPV BUS
HIGH POWER AMPLIFIER
OUT
5V5 10V5
1710-1785MHz1805-1880MHz
Out
In
Out
In
LNA DOWN
LNA UP
OPERATING
POWER SUPPLY
UP-LINK
BAND-SELECTIVE 2
DOWN-LINK
DOWN-LINK
BAND-SELECTIVE 1
UP-LINK
132KHz
ALARM
BS 2
BS 1
RL
ULNA
+5V
U
HPA D
48Vdc circuit
breaker
ref. 22
P
IN
D
SPV BUS
DOWN LINK
HIGH POWER AMPLIFIER
OUT
In
Out
In
Out
1710-1785MHz 1805-1880MHz
b) 48Vdc MODEL
INTERNAL VIEW
FIGURE 1 – EQUIPMENT POWER SWITCHES
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.1

2. POSITIONING THE REPEATER
The Off-Air Repeater is housed inside a case which provides high-degree environmental protection (IP65).
Therefore it is suitable for outdoor wall mount installation. It can also be installed inside specific cabinets
equipped with UPS units.
Fix the Off-Air Repeater in vertical position on the wall, or on the vertical guides present inside the cabinet:
• Lift the equipment and fix its position with four M8 bolts, which are to be inserted in the pre-cut slots
(ref. A, FIGURE 2).
• After checking the correct positioning of the equipment, fully tighten the bolts.
334.00 mm (13.15 in.)
A A
366.00 mm (14.41 in.)
AA
FIGURE 2 - POSITION OF THE HOLES IN THE SUPPORT BRACKETS FOR THE EQUIPMENT
3. POWER SUPPLY SOURCE CONNECTIONS AND ALARMS CONNECTIONS
• Before carrying out any other electrical connection connect the rack to the station ground, using the
ground bolt on the bottom of the repeater (ref. 53, FIGURE 3).
• Make sure that the power supply source provides the prescribed nominal voltage.
If so, connect the equipment to the power supply source, as described below.
MS side
RF connector
ref. 56
BTS side
RF connector
ref. 52
MS side
RF connector
ref. 56
BTS side
RF connector
ref. 52
Equipment
Grounding
ref. 53
AC voltage input
from MAINS
a) 230Vac MODEL
BOTTOM VIEW
ref. 54
48Vdc input and
external alarms
Connector
ref. 55
Equipment
Grounding
ref. 53
b) 48Vdc MODEL
BOTTOM VIEW
48Vdc input and
external alarms
Connector
ref. 55
FIGURE 3 – EXTERNAL CONNECTORS
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.2

• D.C. POWERED EQUIPMENT
- Connect the 15-pole (f) connector on the bottom of the repeater (ref. 55, FIGURE 3) to the 48Vdc/Alarm
cable (supplied with the equipment).
The cable permits D.C power supply (48Vdc) to the equipment. It also makes available the remote
signals detailed into Table 1.
- Connect the cable to the power supply source (48Vdc) and connect the external signals.
PLEASE NOTE:
The 48Vdc power supply cable (also including the external alarms), provided standard with the
equipment, must never be longer than 3 meters in length (connectors included).
48Vdc POWER SUPPLY AND EXTERNAL ALARMS CONNECTOR
WIRES COLOR OF 48VDC
PIN TYPE OF SIGNAL
POWER SUPPLY AND
EXTERNAL ALARMS
CABLE
0 0Vdc RED
1 0Vdc RED
2 - 48Vdc BLACK
3
48Vdc
POWER SUPPLY
- 48Vdc BLACK
4 EXTERNAL ALARM 3 GRAY
5 EXTERNAL ALARM 4 BROWN
6 EXTERNAL ALARM 2 ORANGE
7 EXTERNAL ALARM 1 PINK
EXTERNAL ALARMS
8 GROUND - GND GREEN
9
+5Vdc EXT. ALM.
COMMON
WHITE
10 NOT CONNECTED
11 BLUE
12
SPV CARRIER FOR BDAs
(IF ANY)
132kHz
VIOLET
13 NOT CONNECTED
14 NOT CONNECTED
TABLE 1 – 48Vdc POWER SUPPLY AND REMOTE SIGNALS CONNECTOR PIN-OUT
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.3

• AC POWERED EQUIPMENT (ALTERNATE CURRENT)
- Connect the 230Vac power cable to the connector located on the bottom of the repeater (ref. 54,
FIGURE 3). The connector pin assignments is detailed in Table 2.
230Vac POWER SUPPLY CONNECTOR
PIN CABLE 230VAC POWER SUPPLY
CABLE COLOR
1 LINE BROWN
2 NEUTRAL BLUE
3 GROUND (GND) YELLOW / GREEN
4 NOT CONNECTED
TABLE 2 – 230Vac POWER SUPPLY CONNECTOR PIN-OUT
- Connect the other end of the cable to the power supply source (230Vac).
- Also connect the 48Vdc power and alarms cable, provided standard, to the 15-pin connector located on
the bottom of the equipment (ref. 55, FIGURE 3).
The cable makes remote signals available. The connector pin-out is detailed into table 1.
The cable can also be connected to a 48Vdc power supply, to feed the equipment with a D.C. voltage.
PLEASE NOTE:
The 48Vdc power supply cable (also including the external alarms), provided standard with the
equipment, must never be longer than 3 meters in length (connectors included).
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.4

4.2) POWER-UP
Warning: before power up, make sure that the isolation between the donor antenna and the
service antenna is at least 15dB greater than the repeater gain.
1. Connect the cable from the donor antenna to a spectrum analyzer and check input signal presence and
level. After measurement disconnect the spectrum analyzer.
2. Switch on the equipment by means of the switches placed inside the repeater (FIGURE 1a and b).
3. Check the LEDs status on the management module: FIGURE 4 and Table 3 show LEDs status on the
management module under normal operating conditions.
11S
132KHz
RL
+5V
OPERATING
ALARM
1S 2S 4S3S 5S
U
U
BS 2
BS 1
HPA D
6S10S 9S 8S 7S
DLNA
FIGURE 4 – MANAGEMENT MODULE: LEDS STATUS - CORRECT POWER UP
REF. STATUS MEANING
LED 1S OFF
LED 2S ON
Equipment correctly operating
LED 3S ON Management module: +5Vdc available
LED 4S ON, GREEN
LED 5S ON, GREEN
LED 6S ON, GREEN
LED 7S ON, GREEN
LED 8S ON, GREEN
LED 9S ON, GREEN
HPA (High Power Amplifier) - UP LINK -
communicates with management module
HPA (High Power Amplifier) - DOWN LINK -
communicates with management module
LNA (Low Noise Amplifier) - DOWN LINK -
communicates with management module
BS1 communicates with management module
BS2 communicates with management module
LNA (Low Noise Amplifier) - UP LINK - communicates
with management module
LED 10S ON, GREEN 132kHz correctly operating
LED 11S OFF
NO Return Loss alarm
TABLE 3 - MANAGEMENT MODULE: LEDS STATUS - CORRECT POWER UP
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.5
4. Check that the green LED on the 230Vac power supply module (when equipped) is ON (ref. 60, ILL
DCS OFF-AIR REPEATERS, sheet 2).
5. Check LEDs status on the 48Vdc power supply module: FIGURE 5 and Table 4 show LEDs status on
the power supply module (DC/DC converter) under normal operating conditions.
POWER SUPPLY
5V5 10V5
1A 2A
FIGURE 5 – DC/DC CONVERTER: LEDS STATUS - CORRECT POWER UP
REF. STATUS MEANING
LED 1A ON 5.5Vdc from DC/DC converter available
LED 2A ON 10.5Vdc from DC/DC converter available
TABLE 4 - DC/DC CONVERTER: LEDS STATUS - CORRECT POWER UP
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.6

6. WIRELESS MODEMS
a. Models equipped with CDMA modem
data communication between repeater (via built-in CDMA modem) and management workstation
(PC where OMT/OMC management softw ares have been previously installed) via PSTN and/or
CDMA modem, must be established in CSD (CIRCUIT-SWITCHED DATA) mode only. All other
modalities are not allowed.
As CDMA modems don’t use SIMs, the network’s parameters have to be set manually by using the
HyperTerminal. Please contact your local Operator, communicating modem’s ESN (check the sticker at the
top of the management module), to get the needed parameters. Most common parameters are:
Typical CDMA Network Parameters
Acronyms Full name
MSL
MDN
MTN
Master Subsidy
Lockcode
Mobile Data Number Provided by the Operator Modem phone number
Mobile Telephone
Number
Network's setting /
Terminal's setting
Provided by the Operator Modem lock / unlock code -
Provided by the Operator Modem phone number
Description Notes
MDN & MTN are
synonyms
MDN & MTN are
synonyms
MNC
MCC
ESN
MIN
IMSI
(Home) SID
(Home) NID
PRI
PRL
PCA
PCB
SCA
SCB
A-key
Mobile Network Code Provided by the Operator
Mobile Country Code Provided by the Operator
Electronic Serial Number
Mobile Identification
Number
International Mobile
Subscription Identity
System ID Provided by the Operator
Network ID Provided by the Operator
Product Release
Instruction
Preferred Roaming List Provided by the Operator List of NIDs/SIDs -
Primary Channel A Provided by the Operator RF primary channel -
Primary Channel B Provided by the Operator RF primary channel Secondary Channel A Provided by the Operator RF secondary channel Secondary Channel B Provided by the Operator RF secondary channel -
Autenthification key Provided by the Operator Key for the autenthification
Proprietary of the modem
(factory setting)
Provided by the Operator Subscriber's account number -
Provided by the Operator International modem ID
Provided by the Operator Carrier information -
2 digit number that represents a
sub-network in the IMSI
Predefined number that
represents a Country in the IMSI
Modem internal proprietary ID
(factory setting)
ID of the sub-network where
modem can operate
ID of the sub-network where
modem can operate
-
-
It can be found into the
sticker at the top of the
management module
IMSI = MCC + MNC +
MIN
SID & NID are synonyms
SID & NID are synonyms
Built-in modem's one is
random
Note: not all parameters could be needed
In normal operating conditions the jumper must remain connected (if removed, the remote management will
be avoided). It can be temporary removed to set the Operator’s parameters into the built-in modem by using
the RS232 modem port. The same serial cable used for local management, can be used to set the modem.
Once the modem setting is complete, reconnect the jumper to the normal operating position
.
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
4.7
CHAPTER 4

The following procedure explains how to set the modem’s parameters.
Please note: AT commands, contained between the inverted commas, must be strictly typed as it follows.
1) Switch-off the repeater
2) Remove the jumper at RS232 (modem) connector
3) Connect the serial cable (supplied with repeater) with your laptop and RS232 (modem) connector
4) Switch-on the repeater and wait for the complete auto-diagnostic test
5) Run HyperTerminal software on your laptop (if you’re using Microsoft XP, run HyperTerminal from
start/programs/accessories/communication/HyperTerminal)
6) Type the connection’s name (e.g. repeater’s modem) and press OK
7) Chose the right PC’s serial port (COM) and press OK
8) Set the bit-rate at “9600” baud
9) Set the number of bits at “8”
10) Set the parity at “no parity”
11) Set the bit stop at “1”
12) Set the flow control at “no flow control”
13) Press OK
14) Type “AT” and press ENTER (modem should reply with “OK”)
15) Type “AT+E1” and press ENTER (modem should reply with “OK”)
16) Type “AT+CGSN” and press ENTER to display the ESN number (if needed)
17) Type “AT+WSPC=1,000000” and press ENTER to get access to CDMA AT commands
18) Type “AT+WMDN=xxx” where xxx is the MDN number (10 to 15 digits) and press ENTER
If needed, to get current MDN number, type “AT+WMDN?” and press ENTER
19) Type “AT+WIMI=xxx” where xxx is the IMSI number (15 digits) and press ENTER
If needed, to get current IMSI number, type “AT+WIMI? and press ENTER
20) Type “AT+WSID=, xxx, yyy” where xxx is the SID number (1 up to 5 digits / 0 up to 32767) and yyy
is the NID number (1 up to 5 digits / 0 up to 65535 – if not provided, set 65535
) and press ENTER
If needed, to get current IMSI number, type “AT+WIMI? and press ENTER
With the this command you’ve set SID & NID number in first memory location. Up to 20 (0 up to 19)
locations are supported. To set other SIDs & NIDs, please use the following sintax:
Type “AT+WSID=zz, xxx, yyy” where zz is the location (up to 2 digits / 1 up to 19) where these SIDs
& NIDs have to be stored, xxx is the SID number (1 up to 5 digits / 0 up to 32767) and yyy is the NID
number (1 up to 5 digits / 0 up to 65535 – if not provided, set 65535
) and press ENTER
Please note: to set both SID & NID at 0 in location 2, type “AT+WSID=2”
21) Type “AT+WPCC=xxx,yyy” where xxx is primary channel “a” (up to 4 digits / 0 up to 2047) and yyy
is primary channel “b” (up to 4 digits / 0 up to 2047) and press ENTER
If needed, to get current primary channels, type “AT+WPCC? and press ENTER
22) Type “AT+WSCC=xxx,yyy” where xxx is secondary channel “a” (up to 4 digits / 0 up to 2047) and
yyy is secondary channel “b” (up to 4 digits / 0 up to 2047) and press ENTER
If needed, to get current secondary channels, type “AT+WSCC? and press ENTER
23) Type “AT+WCMT=1” and press ENTER to store these settings into the modem. The modem will be
automatically re-start with new settings. Please wait for 10-20 seconds prior to type other commands
24) Type “AT” and press ENTER (modem should reply with “OK”)
25) Type “AT+E1” and press ENTER (modem should reply with “OK”)
26) Type “AT+CICB=0” and press ENTER to allow CSD data connections
27) Close the HyperTerminal
28) Remove the serial cable
29) Switch-off the equipment
30) Reconnect the existing jumper cable with RS232 (modem)
Please note: not all the above mentioned parameters could be necessary. For any problem, please contact
our local subsidiary.
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.8

b. Models equipped with GSM modem
How to install/remove the SIM card from the built-in modem
• Open the repeater.
• Check that the switches inside the repeater are set to 0 - OFF (FIGURE 1a and b).
• Insert the SIM enabled to data transmission in not transparent mode 9600BPS (FIGURE 6)
FIGURE 6 – DETAIL OF THE SIM INSERTION
• Close the Management Module
• Switch on the equipment (AC voltage circuit breaker, ref. 57, 48Vdc circuit breaker, ref. 22, FIGURE
1a-b).
• Close the repeater.
7. INSTALL THE OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE SOFTWARE OMT REPEATER
Install on your PC the Operation and Maintenance Terminal software to set and manage the equipment
(please refer to the software User’s manual). The repeater can be managed in remote mode via a builtin modem, or in local mode.
8. START OMT Repeater IN LOCAL MODE
In LOCAL mode the notebook is connected to the repeater via RS232 serial cable.
- Open the repeater door (by unscrewing four screws located on the equipment front door).
Connect your notebook to the management module (connector RS232, ref. 34, FIGURE 7) using the provided
serial cable (null-modem type).
RS232
Modem
ref. 58
P
IN
UP LINK
SPV BUS
HIGH POWER AMPLIFIER
OUT
OPERATING
POWER SUPPLY
5V5 10V5
RS232
Link
ref. 59
BS 2
132KHz
BS 1
RL
ULNA
D
+5V
U
HPA D
ALARM
RS232 (Repeater) RS232 (Modem)
RS232
Repeater
ref. 34
P
IN
SPV BUS
DOWN LINK
HIGH POWER AMPLIFIER
OUT
LNA DOWN
Out
BAND-SELECTIVE 2
Out
BAND-SELECTIVE 1
In
LNA UP
UP-LINK
DOWN-LINK
DOWN-LINK
UP-LINK
In
OutIn
In
Out
FIGURE 7 – RS232 CONNECTORS
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.9
- The connector RS232 (ref. 58,FIGURE 7) and the connector RS232 (ref. 59, FIGURE 7) are
connected with a cable (only in models equipped with CDMA modem).
- Switch on your notebook and start Windows.
- To Run the program select the related folder in the Windows ‘Start’ menu and click.
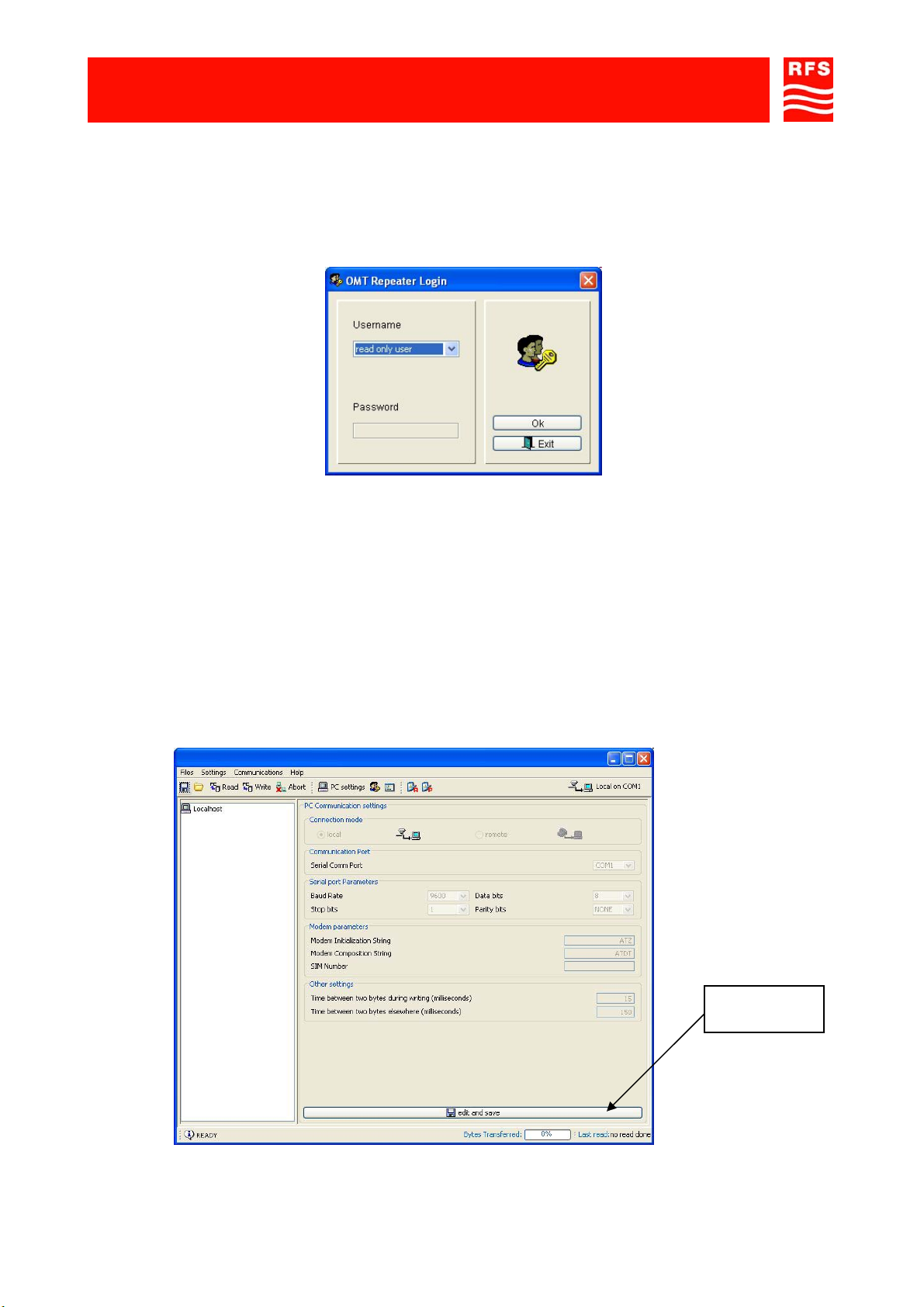
- The ‘Login panel’ is displayed (FIGURE 8).
- Select read/write user.
PLEASE NOTE It’s not requested to insert the password the first opening of the program. It’s recommended
to change the password to avoid undesired accesses to the program (to change the password, please refer
to the Operation and Maintenance Terminal Software User’s manual).
- Click ‘Ok’ to start the software.
The window ‘Communication settings’ is displayed: check that local ‘Connection mode’ is selected.
If remote Connection mode is selected it is possible to change the Connection mode as follows:
- select the ‘Edit and save’ button in the lower part of the panel to enable changes;
- select local Connection mode;
- press the ‘Edit and save’ button again to confirm.
FIGURE 8 – LOGIN PANEL
Edit and save
button
FIGURE 9 – ‘COMMUNICATION SETTINGS’ PANEL
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.10

9. SET THE REPEATER GAIN, FREQUENCY CENTER AND BANDWIDTH
- Select the menu entry ‘Read’ in the ‘Device’ menu, or click the ‘
Read’ button, to read the
equipment configuration and status.
The software main window is displayed.
By means of the software set the repeater gain as described below.
NOTE
How to modify parameters:
- Click on the ‘edit and save’ button, in the lower part of the window, to enable changes to the repeater
parameters.
- Click again on the ‘edit and save’ button to save changes.
- The menu entry ‘Write’, in the ‘Device’ menu, makes it possible to apply changes to the repeater. A
password is required: default password is blank. To change the password please refer to the
software User’s manual.
a) In the tree structure of the repeater system (FIGURE 9) select the repeater (double click on
‘Repeater’): on the right side of the window, the configuration and status panels of the repeater
will be shown (Description, Spectrum, Parameters, Alarms, Communications, Advanced).
b) In the description panel, the user should select ( FIGURE
10) if the system is TDMA or CDMA.
This selection allows to load the right values of RF power transmitted by the HPAs (only for
1900MHz repeaters)
.
FIGURE 10 – Selection TDMA / CDMA
c) In the ‘Spectrum’ panel (FIGURE 11)set both ‘UL-attenuation’ and ‘DL-attenuation’ to 30 (dB) -
maximum attenuation, i.e. minimum gain.
d) Connect the cable from the donor antenna to the BTS connector on the bottom of the repeater
(ref. 52, FIGURE 3).
e) Connect the MS connector on the bottom of the repeater (ref. 56, FIGURE 3) to a spectrum
analyzer.
f) In the Spectrum panel, set the Up-link frequency center and bandwidth.
In the same panel set the repeater gain (UL-Up-link- attenuation, DL-Down-link- attenuation).
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.11

PLEASE NOTE:
should it be necessary to set an attenuation greater than 15dB it is strongly recommended to
connect a fixed attenuator between donor antenna and the repeater BTS side port to avoid
BTS desensitisation due to excessive radiated up-link noise.
g) Check via the spectrum analyzer that the output signal level (MS side) is correct.
When the output signal level is correct, disconnect the spectrum analyzer.
FIGURE 11 – ‘SPECTRUM’ PANEL
If the repeater is used in stand-alone configuration, connect the cable from the service antenna to
the MS connector on the bottom of the repeater (ref. 56, FIGURE 3).
If the repeater is the head station of an optical fiber system, refer to the OPTICAL FIBER COVERAGE
SOLUTIONS technical handbook to install and set Master Unit and Remote Units.
If the repeater is part of a cascade system, refer to the IN-LINE AMPLIFIERS technical handbook to
install and set in-line amplifiers.
During operation the equipment can be managed, both in LOCAL and in REMOTE mode, via the software.
In REMOTE mode the equipment is managed via a modem link. On the repeater side the modem is
installed within the equipment management module.
If installing /removing the SIM card from the built-in modem is necessary, please refer to the following
procedure 6b (HOW TO INSTALL/REMOVE THE SIM CARD FROM THE BUILT-IN MODEM).
For details regarding the software, please refer to the software User’s manual.
4.3) ROUTINE MAINTENANCE
This equipment does not require any ORDINARY MAINTENANCE (or preventive maintenance) servicing.
1800MHz-1900MHz Off-Air Repeaters (OR Series) Page 91 080 0701F – Rel.04
CHAPTER 4
4.12

ABBREVIATIONS AND ACRONYMS
AC Alternating Current
ALC Automatic Level Control
BDA Bi-Directional Amplifier
BTS Base Transceiver Station
DC Direct Current
DCS Digital Cellular System
EGSM Enhanced Global System for Mobile Communications
EMC Electro-Magnetic Compatibility
FET Field-Effect Transistor
GSM Global System for Mobile Communications
GSM-R GSM - Railway
HPA High Power Amplifier
IF Intermediate Frequency
IP3 Third order Intercept Point
LNA Low Noise Amplifier
MMIC Monolithic Microwave Integrated Circuit
MS Mobile Station
MTBF Mean Time Between Failures
MU Master Unit
NF Noise Figure
OMC Operation and Maintenance Center
OMT Operation and Maintenance Terminal
PC Personal Computer
PEP Peak Envelope Power
PLL Phase-Locked Loop
PSTN Public Switched Telephone Network
RAM Random Access Memory
RF Radio Frequency
RL Return Loss
RU Remote Unit
SAW Surface Acoustic Wave
SIM Subscriber Identity Module
SPV Supervision
TTL Transistor, Transistor, Logic
UMTS Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply
VCO Voltage Controlled Oscillator
ABBREVIATIONS AND ACRONYMS
 Loading...
Loading...