Page 1

REJ09B0124-0200
M16C/6N Group
(M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM)
16
Hardware Manual
RENESAS 16-BIT SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER
M16C FAMILY / M16C/60 SERIES
Before using this material, please visit our website to verify that this is the most
updated document available.
Rev. 2.00
Revision date: Nov. 28, 2005
www.renesas.com
Page 2
Keep safety first in your circuit designs!
•
Renesas Technology Corporation puts the maximum effort into making semiconductor products better and more reliable, but there is always the possibility that trouble may occur with
them. Trouble with semiconductors may lead to personal injury, fire or property damage.
Remember to give due consideration to safety when making your circuit designs, with appropriate measures such as (i) placement of substitutive, auxiliary circuits, (ii) use of nonflammable material or (iii) prevention against any malfunction or mishap.
Notes regarding these materials
• These materials are intended as a reference to assist our customers in the selection of the
Renesas Technology Corporation product best suited to the customer's application; they do
not convey any license under any intellectual property rights, or any other rights, belonging
to Renesas Technology Corporation or a third party.
• Renesas Technology Corporation assumes no responsibility for any damage, or infringement of any third-party's rights, originating in the use of any product data, diagrams, charts,
programs, algorithms, or circuit application examples contained in these materials.
• All information contained in these materials, including product data, diagrams, charts, programs and algorithms represents information on products at the time of publication of these
materials, and are subject to change by Renesas Technology Corporation without notice
due to product improvements or other reasons. It is therefore recommended that customers contact Renesas Technology Corporation or an authorized Renesas Technology Corporation product distributor for the latest product information before purchasing a product
listed herein.
The information described here may contain technical inaccuracies or typographical errors.
Renesas Technology Corporation assumes no responsibility for any damage, liability, or
other loss rising from these inaccuracies or errors.
Please also pay attention to information published by Renesas Technology Corporation by
various means, including the Renesas Technology Corporation Semiconductor home page
(http://www.renesas.com).
• When using any or all of the information contained in these materials, including product
data, diagrams, charts, programs, and algorithms, please be sure to evaluate all information as a total system before making a final decision on the applicability of the information
and products. Renesas Technology Corporation assumes no responsibility for any damage, liability or other loss resulting from the information contained herein.
• Renesas Technology Corporation semiconductors are not designed or manufactured for
use in a device or system that is used under circumstances in which human life is potentially at stake. Please contact Renesas Technology Corporation or an authorized Renesas
Technology Corporation product distributor when considering the use of a product contained herein for any specific purposes, such as apparatus or systems for transportation,
vehicular, medical, aerospace, nuclear, or undersea repeater use.
• The prior written approval of Renesas Technology Corporation is necessary to reprint or
reproduce in whole or in part these materials.
• If these products or technologies are subject to the Japanese export control restrictions,
they must be exported under a license from the Japanese government and cannot be imported into a country other than the approved destination.
Any diversion or reexport contrary to the export control laws and regulations of Japan and/
or the country of destination is prohibited.
• Please contact Renesas Technology Corporation for further details on these materials or
the products contained therein.
Page 3

How to Use This Manual
1. Introduction
This hardware manual provides detailed information on the M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) of
microcomputers.
Users are expected to have basic knowledge of electric circuits, logical circuits and microcomputers.
2. Register Diagram
The symbols, and descriptions, used for bit function in each register are shown below.
XXX Register
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
00
Symbol
XXX
XXX
(b2)
(b4-b3)
*1
Symbol
XXX
Bit
0
1
-
-
Bit Name
XXX Bit
Nothing is assigned. When write, set to "0",
When read, its content is indeterminate.
Reserved Bit Set to "0"
Address
XXX
Function
b1b0
0 0: XXX
0 1: XXX
1 0: Do not set a value
1 1: XXX
After Reset
00h
*5
RW
RW
RW
WO
*2
*3
*4
XXX5
XXX
XXX
XXX Bit
6
7
XXX Bit
Function varies depending on
mode of operation
0: XXX
1: XXX
*1
Blank:Set to “0” or “1” according to the application
0 : Set to “0”
1 : Set to “1”
X : Nothing is assigned
*2
RW : Read and write
RO : Read only
WO: Write only
– : Nothing is assigned
*3
• Reserved bit
Reserved bit. Set to specified value.
*4
• Nothing is assigned
Nothing is assigned to the bit concerned. As the bit may be use for future functions, set to “0” when
writing to this bit.
• Do not set to this value
The operation is not guaranteed when a value is set.
• Function varies depending on mode of operation
Bit function varies depending on peripheral function mode.
Refer to respective register for each mode.
*5
Follow the text in each manual for binary and hexadecimal notations.
RW
RW
RO
Page 4
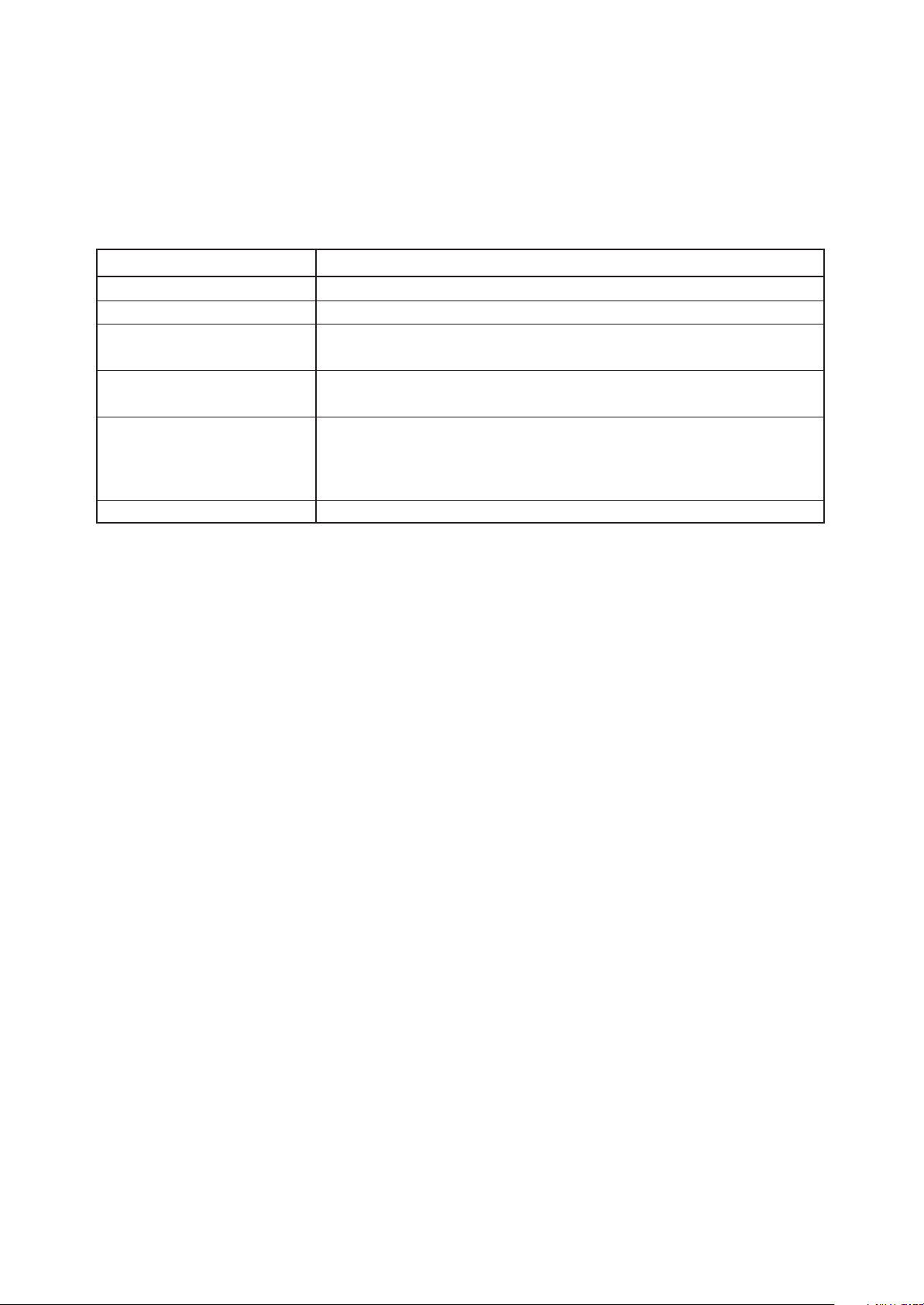
3. M16C Family Documents
The following documents were prepared for the M16C family
Document Contents
Short Sheet Hardware overview
Data Sheet Hardware overview and electrical characteristics
Hardware Manual Hardware specifications (pin assignments, memory maps, peripheral
specifications, electrical characteristics, timing charts)
Software Manual Detailed description of assembly instructions and microcomputer
performance of each instruction
Application Note • Application examples of peripheral functions
• Sample programs
• Introduction to the basic functions in the M16C family
• Programming method with Assembly and C languages
RENESAS TECHNICAL UPDATE
Preliminary report about the specification of a product, a document, etc.
NOTE:
1. Before using this material , please visit our website to verify that this is the most updated document
available.
(1)
.
Page 5

Table of Contents
SFR Page Reference ............................................................................................................ B-1
1. Overview ............................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Applications ..................................................................................................................................................1
1.2 Performance Outline ....................................................................................................................................2
1.3 Block Diagram .............................................................................................................................................. 4
1.4 Product List ..................................................................................................................................................5
1.5 Pin Configuration .........................................................................................................................................6
1.6 Pin Description ........................................................................................................................................... 13
2. Central Processing Unit (CPU) ........................................................................................... 16
2.1 Data Registers (R0, R1, R2, and R3) ........................................................................................................ 16
2.2 Address Registers (A0 and A1) .................................................................................................................. 16
2.3 Frame Base Register (FB) .........................................................................................................................17
2.4 Interrupt Table Register (INTB) ..................................................................................................................17
2.5 Program Counter (PC) ...............................................................................................................................17
2.6 User Stack Pointer (USP), Interrupt Stack Pointer (ISP) ........................................................................... 17
2.7 Static Base Register (SB) .......................................................................................................................... 17
2.8 Flag Register (FLG) ................................................................................................................................... 17
2.8.1 Carry Flag (C Flag) ............................................................................................................................ 17
2.8.2 Debug Flag (D Flag) .......................................................................................................................... 17
2.8.3 Zero Flag (Z Flag) ..............................................................................................................................17
2.8.4 Sign Flag (S Flag) ..............................................................................................................................17
2.8.5 Register Bank Select Flag (B Flag).................................................................................................... 17
2.8.6 Overflow Flag (O Flag)....................................................................................................................... 17
2.8.7 Interrupt Enable Flag (I Flag) .............................................................................................................17
2.8.8 Stack Pointer Select Flag (U Flag)..................................................................................................... 17
2.8.9 Processor Interrupt Priority Level (IPL) .............................................................................................. 17
2.8.10 Reserved Area .................................................................................................................................17
3. Memory ............................................................................................................................... 18
4. Special Function Register (SFR)......................................................................................... 19
5. Reset ................................................................................................................................... 35
5.1 Hardware Reset .........................................................................................................................................35
5.1.1 Reset on a Stable Supply Voltage ..................................................................................................... 35
5.1.2 Power-on Reset ................................................................................................................................. 35
5.2 Software Reset .......................................................................................................................................... 37
5.3 Watchdog Timer Reset ............................................................................................................................... 37
5.4 Oscillation Stop Detection Reset ............................................................................................................... 37
5.5 Internal Space ............................................................................................................................................ 37
6. Processor Mode ..................................................................................................................38
6.1 Types of Processor Mode ..........................................................................................................................38
6.2 Setting Processor Modes ........................................................................................................................... 39
7. Bus ......................................................................................................................................45
7.1 Bus Mode ................................................................................................................................................... 45
7.1.1 Separate Bus ..................................................................................................................................... 45
7.1.2 Multiplexed Bus.................................................................................................................................. 45
A-1
Page 6

7.2 Bus Control ................................................................................................................................................ 46
7.2.1 Address Bus ....................................................................................................................................... 46
7.2.2 Data Bus ............................................................................................................................................ 46
7.2.3 Chip Select Signal.............................................................................................................................. 46
7.2.4 Read and Write Signals ..................................................................................................................... 48
7.2.5 ALE Signal ......................................................................................................................................... 48
________
7.2.6 RDY Signal ........................................................................................................................................49
7.2.8 BCLK Output ...................................................................................................................................... 50
__________
7.2.7 HOLD Signal ......................................................................................................................................50
7.2.9 External Bus Status When Internal Area Accessed ...........................................................................52
7.2.10 Software Wait...................................................................................................................................52
8. Clock Generating Circuit .....................................................................................................56
8.1 Types of Clock Generating Circuit .............................................................................................................. 56
8.1.1 Main Clock ......................................................................................................................................... 64
8.1.2 Sub Clock........................................................................................................................................... 65
8.1.3 On-chip Oscillator Clock .................................................................................................................... 66
8.1.4 PLL Clock ........................................................................................................................................... 66
8.2 CPU Clock and Peripheral Function Clock ................................................................................................ 68
8.2.1 CPU Clock and BCLK ........................................................................................................................68
8.2.2 Peripheral Function Clock .................................................................................................................. 68
8.3 Clock Output Function ............................................................................................................................... 68
8.4 Power Control ............................................................................................................................................ 69
8.4.1 Normal Operation Mode..................................................................................................................... 69
8.4.2 Wait Mode .......................................................................................................................................... 71
8.4.3 Stop Mode.......................................................................................................................................... 73
8.5 Oscillation Stop and Re-oscillation Detection Function ............................................................................. 78
8.5.1 Operation When CM27 Bit = 0 (Oscillation Stop Detection Reset) .................................................... 78
8.5.2 Operation When CM27 Bit = 1 (Oscillation Stop, Re-oscillation Detection Interrupt) ........................ 78
8.5.3 How to Use Oscillation Stop and Re-oscillation Detection Function .................................................. 79
9. Protection ............................................................................................................................80
10. Interrupt ............................................................................................................................. 81
10.1 Type of Interrupts ..................................................................................................................................... 81
10.2 Software Interrupts ................................................................................................................................... 82
10.2.1 Undefined Instruction Interrupt......................................................................................................... 82
10.2.2 Overflow Interrupt ............................................................................................................................ 82
10.2.3 BRK Interrupt ................................................................................................................................... 82
10.2.4 INT Instruction Interrupt ................................................................................................................... 82
10.3 Hardware Interrupts ................................................................................................................................. 83
10.3.1 Special Interrupts .............................................................................................................................83
10.3.2 Peripheral Function Interrupts.......................................................................................................... 83
10.4 Interrupts and Interrupt Vector .................................................................................................................84
10.4.1 Fixed Vector Tables .......................................................................................................................... 84
10.4.2 Relocatable Vector Tables ............................................................................................................... 84
10.5 Interrupt Control .......................................................................................................................................86
10.5.1 I Flag ................................................................................................................................................88
10.5.2 IR Bit ................................................................................................................................................ 88
10.5.3 ILVL2 to ILVL0 Bits and IPL ............................................................................................................. 88
A-2
Page 7

10.5.4 Interrupt Sequence .......................................................................................................................... 89
10.5.5 Interrupt Response Time.................................................................................................................. 90
10.5.6 Variation of IPL when Interrupt Request is Accepted ....................................................................... 90
10.5.7 Saving Registers .............................................................................................................................. 91
10.5.8 Returning from an Interrupt Routine ................................................................................................ 92
10.5.9 Interrupt Priority ............................................................................................................................... 92
10.5.10 Interrupt Priority Resolution Circuit ................................................................................................ 92
______
10.6 INT Interrupt ............................................................................................................................................. 94
______
10.7 NMI Interrupt ............................................................................................................................................98
10.8 Key Input Interrupt ...................................................................................................................................98
10.9 CAN0/1 Wake-up Interrupt ....................................................................................................................... 98
10.10 Address Match Interrupt ......................................................................................................................... 99
11. Watchdog Timer .............................................................................................................. 101
11.1 Count Source Protective Mode ..............................................................................................................102
12. DMAC.............................................................................................................................. 103
12.1 Transfer Cycle ........................................................................................................................................ 108
12.1.1 Effect of Source and Destination Addresses .................................................................................. 108
12.1.2 Effect of BYTE Pin Level................................................................................................................ 108
12.1.3 Effect of Software Wait................................................................................................................... 108
________
12.1.4 Effect of RDY Signal ...................................................................................................................... 108
12.2 DMA Transfer Cycles ............................................................................................................................. 110
12.3 DMA Enable ........................................................................................................................................... 111
12.4 DMA Request ......................................................................................................................................... 111
12.5 Channel Priority and DMA Transfer Timing............................................................................................ 112
13. Timers ............................................................................................................................. 113
13.1 Timer A ................................................................................................................................................... 115
13.1.1 Timer Mode .................................................................................................................................... 119
13.1.2 Event Counter Mode ......................................................................................................................120
13.1.3 One-shot Timer Mode ....................................................................................................................125
13.1.4 Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Mode ...........................................................................................127
13.2 Timer B................................................................................................................................................... 130
13.2.1 Timer Mode ....................................................................................................................................133
13.2.2 Event Counter Mode ......................................................................................................................134
13.2.3 Pulse Period and Pulse Width Measurement Mode ...................................................................... 135
14. Three-Phase Motor Control Timer Function .................................................................... 138
15. Serial Interface ................................................................................................................149
15.1 UARTi.....................................................................................................................................................149
15.1.1 Clock Synchronous Serial I/O Mode ..............................................................................................159
15.1.2 Clock Asynchronous Serial I/O (UART) Mode ............................................................................... 167
15.1.3 Special Mode 1 (I2C Mode) ............................................................................................................175
15.1.4 Special Mode 2 .............................................................................................................................. 184
15.1.5 Special Mode 3 (IE Mode) ............................................................................................................. 189
15.1.6 Special Mode 4 (SIM Mode) (UART2) ........................................................................................... 191
15.2 SI/Oi .......................................................................................................................................................196
15.2.1 SI/Oi Operation Timing................................................................................................................... 200
15.2.2 CLK Polarity Selection ................................................................................................................... 200
15.2.3 Functions for Setting an SOUTi Initial Value .................................................................................. 201
A-3
Page 8

16. A/D Converter .................................................................................................................. 202
16.1 Mode Description ...................................................................................................................................206
16.1.1 One-shot Mode .............................................................................................................................. 206
16.1.2 Repeat Mode ................................................................................................................................. 208
16.1.3 Single Sweep Mode .......................................................................................................................210
16.1.4 Repeat Sweep Mode 0 .................................................................................................................. 212
16.1.5 Repeat Sweep Mode 1 .................................................................................................................. 214
16.2 Function ................................................................................................................................................. 216
16.2.1 Resolution Select Function ............................................................................................................ 216
16.2.2 Sample and Hold ........................................................................................................................... 216
16.2.3 Extended Analog Input Pins........................................................................................................... 216
16.2.4 External Operation Amplifier (Op-Amp) Connection Mode ............................................................216
16.2.5 Current Consumption Reducing Function ...................................................................................... 217
16.2.6 Output Impedance of Sensor under A/D Conversion..................................................................... 217
17. D/A Converter.................................................................................................................. 219
18. CRC Calculation.............................................................................................................. 221
19. CAN Module .................................................................................................................... 223
19.1 CAN Module-Related Registers ............................................................................................................. 224
19.1.1 CAN Message Box......................................................................................................................... 224
19.1.2 Acceptance Mask Registers........................................................................................................... 224
19.1.3 CAN SFR Registers .......................................................................................................................224
19.2 CANi Message Box ................................................................................................................................ 225
19.3 Acceptance Mask Registers...................................................................................................................227
19.4 CAN SFR Registers ...............................................................................................................................228
19.5 Operational Modes ................................................................................................................................. 234
19.5.1 CAN Reset/Initialization Mode ....................................................................................................... 234
19.5.2 CAN Operation Mode..................................................................................................................... 235
19.5.3 CAN Sleep Mode ........................................................................................................................... 235
19.5.4 CAN Interface Sleep Mode ............................................................................................................ 235
19.5.5 Bus Off State.................................................................................................................................. 236
19.6 Configuration CAN Module System Clock ............................................................................................. 237
19.7 Bit Timing Configuration ......................................................................................................................... 237
19.8 Bit-rate ................................................................................................................................................... 238
19.8.1 Calculation of Bit-rate..................................................................................................................... 238
19.9 Acceptance Filtering Function and Masking Function............................................................................239
19.10 Acceptance Filter Support Unit (ASU)..................................................................................................240
19.11 Basic CAN Mode ..................................................................................................................................241
19.12 Return from Bus Off Function .............................................................................................................. 242
19.13 Time Stamp Counter and Time Stamp Function ..................................................................................242
19.14 Listen-Only Mode ................................................................................................................................. 242
19.15 Reception and Transmission................................................................................................................243
19.15.1 Reception ..................................................................................................................................... 244
19.15.2 Transmission ................................................................................................................................ 245
19.16 CAN Interrupt .......................................................................................................................................246
A-4
Page 9

20. Programmable I/O Ports ................................................................................................. 247
20.1 PDi Register ........................................................................................................................................... 248
20.2 Pi Register, PC14 Register ....................................................................................................................248
20.3 PURj Register ........................................................................................................................................ 248
20.4 PCR Register .........................................................................................................................................248
21. Flash Memory Version .................................................................................................... 260
21.1 Memory Map ..........................................................................................................................................261
21.1.1 Boot Mode...................................................................................................................................... 262
21.2 Functions to Prevent Flash Memory from Rewriting ..............................................................................262
21.2.1 ROM Code Protect Function .......................................................................................................... 262
21.2.2 ID Code Check Function ................................................................................................................ 262
21.3 CPU Rewrite Mode ................................................................................................................................ 264
21.3.1 EW0 Mode ..................................................................................................................................... 265
21.3.2 EW1 Mode ..................................................................................................................................... 265
21.3.3 FMR0, FMR1 Registers ................................................................................................................. 266
21.3.4 Precautions on CPU Rewrite Mode ............................................................................................... 271
21.3.5 Software Commands ..................................................................................................................... 273
21.3.6 Data Protect Function .................................................................................................................... 278
21.3.7 Status Register (SRD Register) .....................................................................................................278
21.3.8 Full Status Check ........................................................................................................................... 280
21.4 Standard Serial I/O Mode ...................................................................................................................... 282
21.4.1 ID Code Check Function ................................................................................................................ 282
21.4.2 Example of Circuit Application in Standard Serial I/O Mode .......................................................... 286
21.5 Parallel I/O Mode ................................................................................................................................... 287
21.5.1 User ROM and Boot ROM Areas ................................................................................................... 287
21.5.2 ROM Code Protect Function .......................................................................................................... 287
21.6 CAN I/O Mode ........................................................................................................................................ 288
21.6.1 ID Code Check Function ................................................................................................................ 288
21.6.2 Example of Circuit Application in CAN I/O Mode ...........................................................................291
22. Electrical Characteristics ................................................................................................. 292
22.1 Electrical Characteristics (Normal-ver.)..................................................................................................292
22.2 Electrical Characteristics (T/V-ver.) ........................................................................................................ 328
23. Usage Precaution............................................................................................................ 338
23.1 SFR ........................................................................................................................................................ 338
23.1 External Bus ........................................................................................................................................... 339
23.3 External Clock ........................................................................................................................................ 340
23.4 PLL Frequency Synthesizer ...................................................................................................................341
23.5 Power Control ........................................................................................................................................ 342
23.6 Oscillation Stop, Re-oscillation Detection Function ............................................................................... 344
23.7 Protection ............................................................................................................................................... 345
23.8 Interrupt .................................................................................................................................................. 346
23.8.1 Reading Address 00000h............................................................................................................... 346
23.8.2 Setting SP ......................................................................................................................................346
_______
23.8.3 NMI Interrupt ..................................................................................................................................346
23.8.4 Changing Interrupt Generate Factor ..............................................................................................347
23.8.5 INT Interrupt ................................................................................................................................... 347
23.8.6 Rewrite Interrupt Control Register ................................................................................................. 348
23.8.7 Watchdog Timer Interrupt .............................................................................................................. 348
_____
A-5
Page 10

23.9 DMAC .................................................................................................................................................... 349
23.9.1 Write to DMAE Bit in DMiCON Register ........................................................................................ 349
23.10 Timers .................................................................................................................................................. 350
23.10.1 Timer A ......................................................................................................................................... 350
23.10.2 Timer B.........................................................................................................................................354
23.11 Thee-Phase Motor Control Timer Function ..........................................................................................356
23.12 Serial Interface ..................................................................................................................................... 357
23.12.1 Clock Synchronous Serial I/O Mode ............................................................................................357
23.12.2 Special Modes ............................................................................................................................. 358
23.12.3 SI/Oi .............................................................................................................................................359
23.13 A/D Converter ...................................................................................................................................... 360
23.14 CAN Module ......................................................................................................................................... 362
23.14.1 Reading CiSTR Register.............................................................................................................. 362
23.14.2 Performing CAN Configuration .................................................................................................... 364
23.14.3 Suggestions to Reduce Power Consumption .............................................................................. 365
23.14.4 CAN Transceiver in Boot Mode.................................................................................................... 366
23.15 Programmable I/O Ports ...................................................................................................................... 367
23.16 Dedicated Input Pin .............................................................................................................................. 368
23.17 E
23.18 Mask ROM Version ............................................................................................................................. 370
23.19 Flash Memory Version .........................................................................................................................371
23.20 Flash Memory Programming Using Boot Program .............................................................................. 373
23.21 Noise .................................................................................................................................................... 374
lectrical Characteristic Differences Between Mask ROM and Flash Memory Version Microcomputers ....
23.19.1 Functions to Prevent Flash Memory from Rewriting ....................................................................371
23.19.2 Stop Mode.................................................................................................................................... 371
23.19.3 Wait Mode .................................................................................................................................... 371
23.19.4 Low Power Dissipation Mode and On-Chip Oscillator Low Power Dissipation Mode ................. 371
23.19.5 Writing Command and Data......................................................................................................... 371
23.19.6 Program Command...................................................................................................................... 371
23.19.7 Lock Bit Program Command ........................................................................................................ 371
23.19.8 Operation Speed .......................................................................................................................... 371
23.19.9 Prohibited Instructions ................................................................................................................. 372
23.19.10 Interrupt...................................................................................................................................... 372
23.19.11 How to Access............................................................................................................................ 372
23.19.12 Rewriting in User ROM Area...................................................................................................... 372
23.19.13 DMA Transfer .............................................................................................................................372
23.20.1 Programming Using Serial I/O Mode ........................................................................................... 373
23.20.2 Programming Using CAN I/O Mode ............................................................................................. 373
369
Appendix 1. Package Dimensions ........................................................................................ 375
Register Index ....................................................................................................................... 377
Specifications written in this manual are believed to be accurate, but are not guaranteed to be entirely free
of error. Specifications in this manual may be changed for functional or performance improvements.
Please make sure your manual is the latest edition.
A-6
Page 11
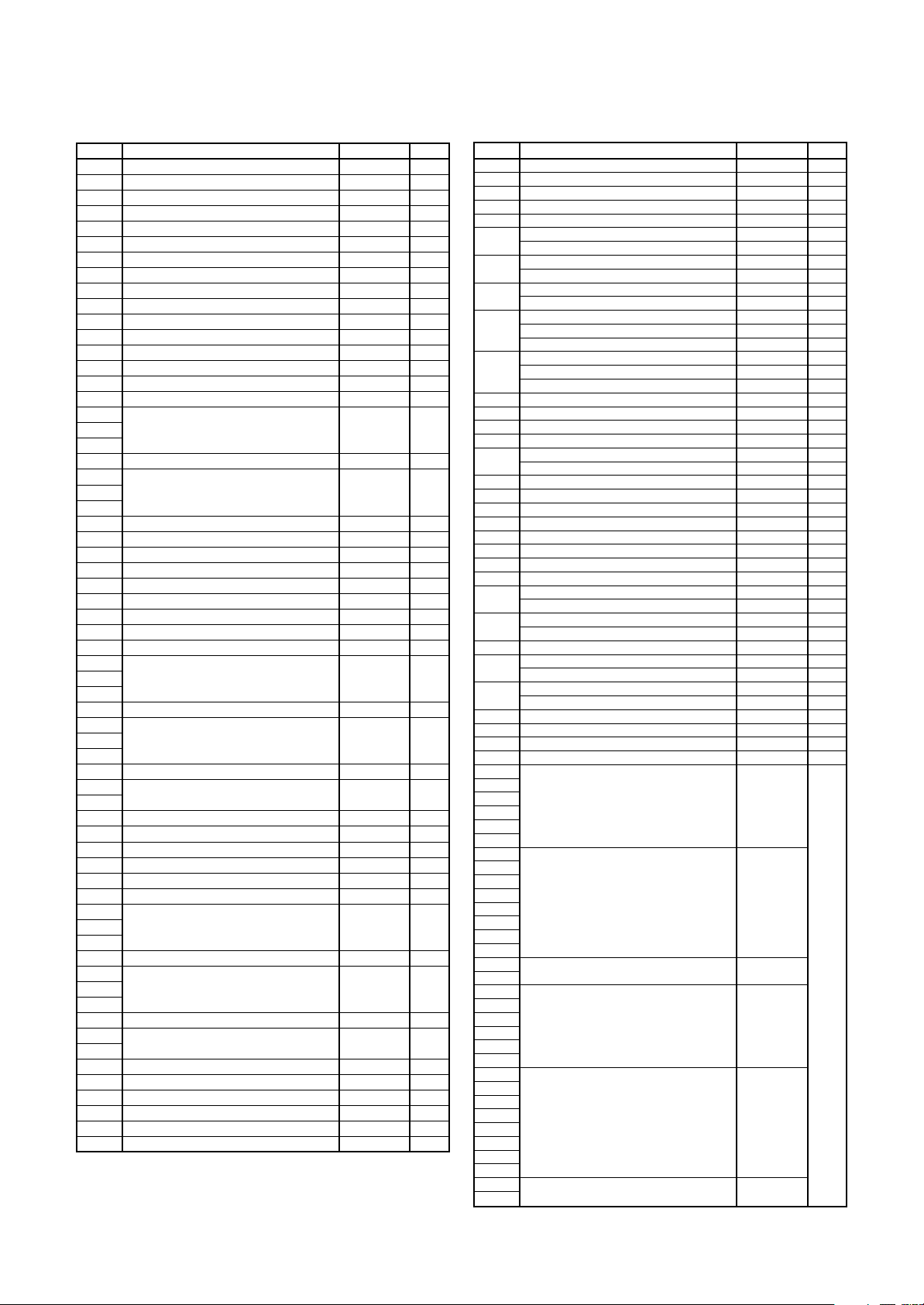
SFR Page Reference
Address Register Symbol Page
C01WKIC
C0RECIC
C0TRMIC
INT3IC
TB5IC
S5IC
TB4IC
U1BCNIC
TB3IC
U0BCNIC
C1RECIC
S4IC
INT5IC
C1TRMIC
S3IC
INT4IC
U2BCNIC
DM0IC
DM1IC
C01ERRIC
ADIC
KUPIC
S2TIC
S2RIC
S0TIC
S0RIC
S1TIC
S1RIC
TA0IC
TA1IC
TA2IC
INT7IC
TA3IC
INT6IC
TA4IC
TB0IC
S6IC
TB1IC
INT8IC
TB2IC
INT0IC
INT1IC
INT2IC
0040h
0041h
0042h
0043h
0044h
0045h
0046h
0047h
0048h
0049h
004Ah
004Bh
004Ch
004Dh
004Eh
004Fh
0050h
0051h
0052h
0053h
0054h
0055h
0056h
0057h
0058h
0059h
005Ah
005Bh
005Ch
005Dh
005Eh
005Fh
0060h
0061h
0062h
0063h
0064h
0065h
0066h
0067h
0068h
0069h
006Ah
006Bh
006Ch
006Dh
006Eh
006Fh
0070h
0071h
0072h
0073h
0074h
0075h
0076h
0077h
0078h
0079h
007Ah
007Bh
007Ch
007Dh
007Eh
007Fh
CAN0/1 Wake-up Interrupt Control Register
CAN0 Successful Reception Interrupt Control Register
CAN0 Successful Transmission Interrupt Control Register
INT3 Interrupt Control Register
Timer B5 Interrupt Control Register
SI/O5 Interrupt Control Register
Timer B4 Interrupt Control Register
UART1 Bus Collision Detection Interrupt Control Register
Timer B3 Interrupt Control Register
UART0 Bus Collision Detection Interrupt Control Register
CAN1 Successful Reception Interrupt Control Register
SI/O4 Interrupt Control Register
INT5 Interrupt Control Register
CAN1 Successful Transmission Interrupt Control Register
SI/O3 Interrupt Control Register
INT4 Interrupt Control Register
UART2 Bus Collision Detection Interrupt Control Register
DMA0 Interrupt Control Register
DMA1 Interrupt Control Register
CAN0/1 Error Interrupt Control Register
A/D Conversion Interrupt Control Register
Key Input Interrupt Control Register
UART2 Transmit Interrupt Control Register
UART2 Receive Interrupt Control Register
UART0 Transmit Interrupt Control Register
UART0 Receive Interrupt Control Register
UART1 Transmit Interrupt Control Register
UART1 Receive Interrupt Control Register
Timer A0 Interrupt Control Register
Timer A1 Interrupt Control Register
Timer A2 Interrupt Control Register
INT7 Interrupt Control Register
Timer A3 Interrupt Control Register
INT6 Interrupt Control Register
Timer A4 Interrupt Control Register
Timer B0 Interrupt Control Register
SI/O6 Interrupt Control Register
Timer B1 Interrupt Control Register
INT8 Interrupt Control Register
Timer B2 Interrupt Control Register
INT0 Interrupt Control Register
INT1 Interrupt Control Register
INT2 Interrupt Control Register
CAN0 Message Box 0: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 0: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 0: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 1: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 1: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 1: Time Stamp
86
86
86
87
86
86
86
86
86
86
87
87
87
87
87
87
86
86
86
86
86
86
86
86
86
86
86
86
86
86
87
87
87
87
86
86
86
87
87
86
87
87
87
225
226
Address Register Symbol Page
0000h
0001h
0002h
0003h
Processor Mode Register 0
0004h
Processor Mode Register 1
0005h
System Clock Control Register 0
0006h
0007h
The blank areas are reserved.
System Clock Control Register 1
0008h
Chip Select Control Register
0009h
Address Match Interrupt Enable Register
000Ah
Protect Register
000Bh
000Ch
Oscillation Stop Detection Register
000Dh
000Eh
Watchdog Timer Start Register
000Fh
Watchdog Timer Control Register
0010h
0011h
Address Match Interrupt Register 0
0012h
0013h
0014h
0015h
Address Match Interrupt Register 1
0016h
0017h
0018h
0019h
001Ah
001Bh
Chip Select Expansion Control Register
001Ch
PLL Control Register 0
001Dh
001Eh
Processor Mode Register 2
001Fh
0020h
0021h
DMA0 Source Pointer
0022h
0023h
0024h
0025h
DMA0 Destination Pointer
0026h
0027h
0028h
DMA0 Transfer Counter
0029h
002Ah
002Bh
002Ch
DMA0 Control Register
002Dh
002Eh
002Fh
0030h
0031h
DMA1 Source Pointer
0032h
0033h
0034h
0035h
DMA1 Destination Pointer
0036h
0037h
0038h
DMA1 Transfer Counter
0039h
003Ah
003Bh
003Ch
DMA1 Control Register
003Dh
003Eh
003Fh
PM0
PM1
CM0
CM1
CSR
AIER
PRCR
CM2
WDTS
WDC
RMAD0
RMAD1
CSE
PLC0
PM2
SAR0
DAR0
TCR0
DM0CON
SAR1
DAR1
TCR1
DM1CON
40
41
58
59
46
100
80
60
102
102
100
100
52
63
62
107
107
107
106
107
107
107
106
B-1
Page 12
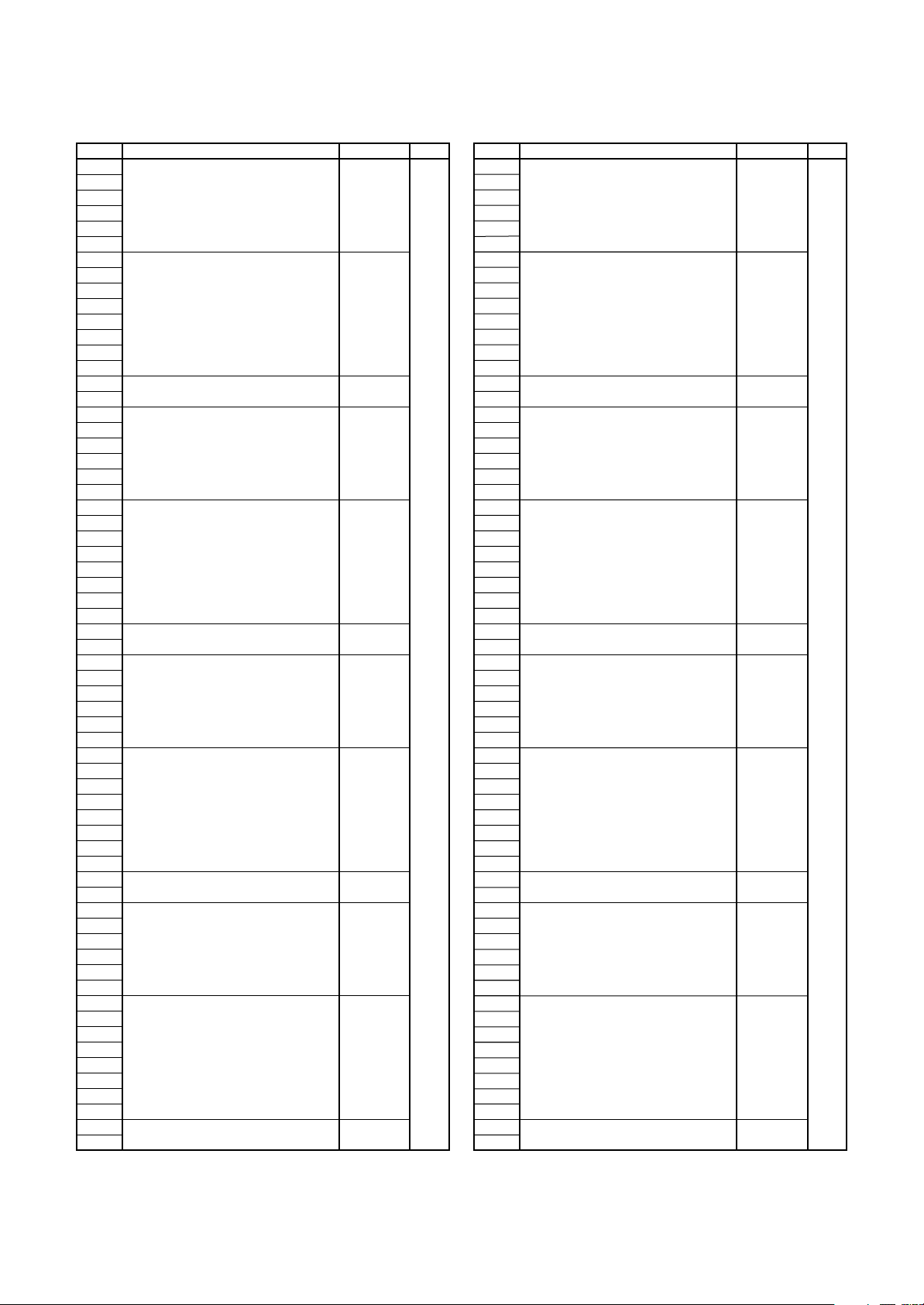
Address Register Symbol Page
Address Register Symbol Page
00C0h
00C1h
00C2h
00C3h
00C4h
00C5h
00C6h
00C7h
00C8h
00C9h
00CAh
00CBh
00CCh
00CDh
00CEh
00CFh
00D0h
00D1h
00D2h
00D3h
00D4h
00D5h
00D6h
00D7h
00D8h
00D9h
00DAh
00DBh
00DCh
00DDh
00DEh
00DFh
00E0h
00E1h
00E2h
00E3h
00E4h
00E5h
00E6h
00E7h
00E8h
00E9h
00EAh
00EBh
00ECh
00EDh
00EEh
00EFh
00F0h
00F1h
00F2h
00F3h
00F4h
00F5h
00F6h
00F7h
00F8h
00F9h
00FAh
00FBh
00FCh
00FDh
00FEh
00FFh
CAN0 Message Box 6: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 6: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 6: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 7: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 7: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 7: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 8: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 8: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 8: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 9: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 9: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 9: Time Stamp
225
226
0080h
0081h
0082h
CAN0 Message Box 2: Identifier / DLC
0083h
0084h
0085h
0086h
0087h
0088h
0089h
CAN0 Message Box 2: Data Field
008Ah
008Bh
008Ch
008Dh
008Eh
CAN0 Message Box 2: Time Stamp
008Fh
0090h
0091h
0092h
CAN0 Message Box 3: Identifier / DLC
0093h
0094h
0095h
0096h
0097h
0098h
0099h
CAN0 Message Box 3: Data Field
009Ah
009Bh
009Ch
009Dh
009Eh
CAN0 Message Box 3: Time Stamp
009Fh
00A0h
00A1h
00A2h
CAN0 Message Box 4: Identifier / DLC
00A3h
00A4h
00A5h
00A6h
00A7h
00A8h
00A9h
CAN0 Message Box 4: Data Field
00AAh
00ABh
00ACh
00ADh
00AEh
CAN0 Message Box 4: Time Stamp
00AFh
00B0h
00B1h
00B2h
CAN0 Message Box 5: Identifier / DLC
00B3h
00B4h
00B5h
00B6h
00B7h
00B8h
00B9h
CAN0 Message Box 5: Data Field
00BAh
00BBh
00BCh
00BDh
00BEh
CAN0 Message Box 5: Time Stamp
00BFh
225
226
B-2
Page 13
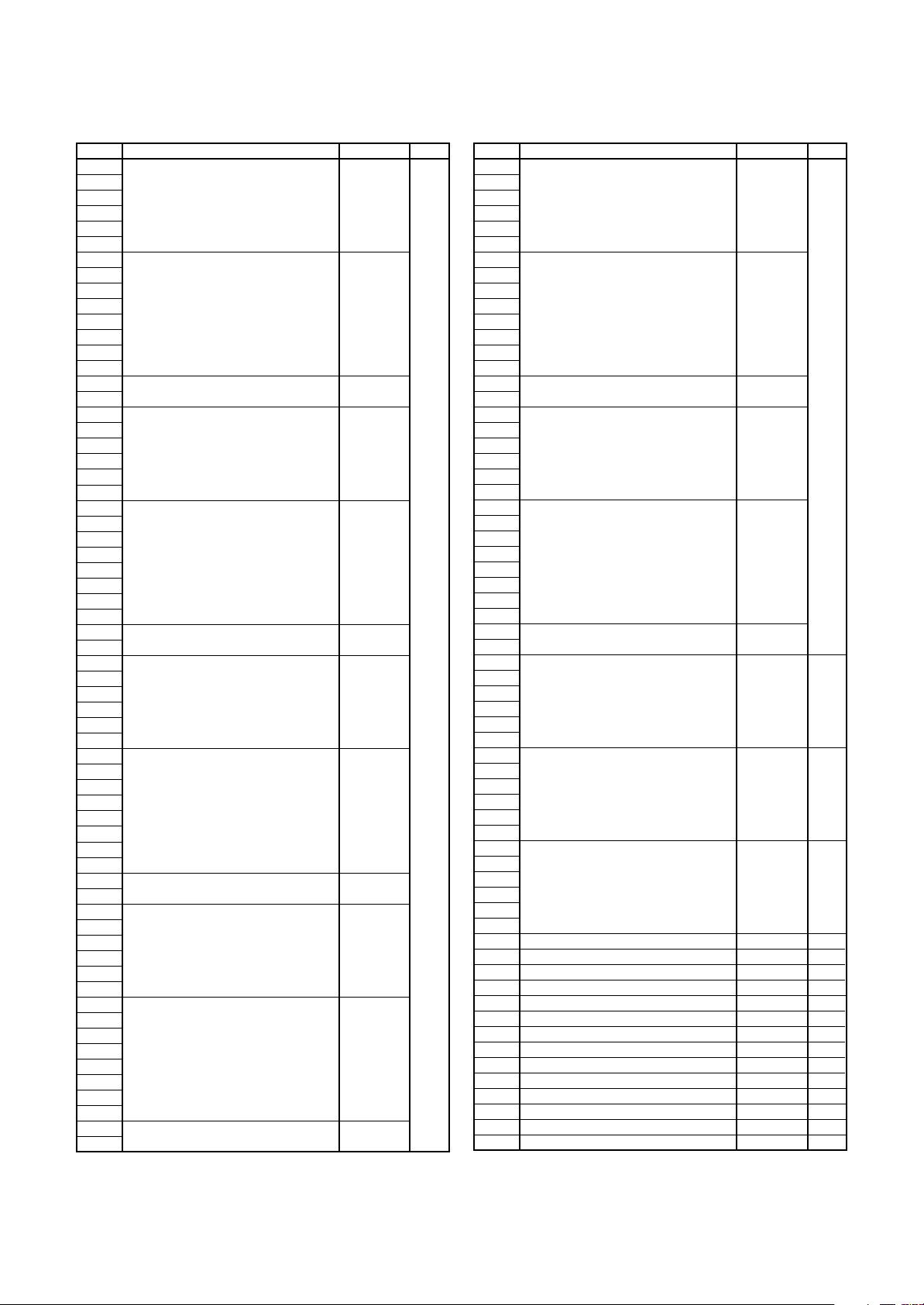
Address Register Symbol Page
C0GMR
C0LMAR
C0LMBR
Address Register Symbol Page
0140h
0141h
0142h
0143h
0144h
0145h
0146h
0147h
0148h
0149h
014Ah
014Bh
014Ch
014Dh
014Eh
014Fh
0150h
0151h
0152h
0153h
0154h
0155h
0156h
0157h
0158h
0159h
015Ah
015Bh
015Ch
015Dh
015Eh
015Fh
0160h
0161h
0162h
0163h
0164h
0165h
0166h
0167h
0168h
0169h
016Ah
016Bh
016Ch
016Dh
016Eh
016Fh
0170h
0171h
0172h
0173h
0174h
0175h
0176h
0177h
0178h
0179h
017Ah
017Bh
017Ch
017Dh
017Eh
017Fh
CAN0 Message Box 14: Identifier /DLC
CAN0 Message Box 14: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 14: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 15: Identifier /DLC
CAN0 Message Box 15: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 15: Time Stamp
CAN0 Global Mask Register
CAN0 Local Mask A Register
CAN0 Local Mask B Register
225
226
227
227
227
0100h
0101h
0102h
CAN0 Message Box 10: Identifier / DLC
0103h
0104h
0105h
0106h
0107h
0108h
0109h
CAN0 Message Box 10: Data Field
010Ah
010Bh
010Ch
010Dh
010Eh
CAN0 Message Box 10: Time Stamp
010Fh
0110h
0111 h
0112h
CAN0 Message Box 11: Identifier / DLC
0113h
0114h
0115h
0116h
0117h
0118h
0119h
CAN0 Message Box 11: Data Field
011Ah
011Bh
011Ch
011Dh
011Eh
CAN0 Message Box 11: Time Stamp
011Fh
0120h
0121h
0122h
CAN0 Message Box 12: Identifier / DLC
0123h
0124h
0125h
0126h
0127h
0128h
0129h
CAN0 Message Box 12: Data Field
012Ah
012Bh
012Ch
012Dh
012Eh
CAN0 Message Box 12: Time Stamp
012Fh
0130h
0131h
0132h
The blank areas are reserved.
CAN0 Message Box 13: Identifier / DLC
0133h
0134h
0135h
0136h
0137h
0138h
0139h
CAN0 Message Box 13: Data Field
013Ah
013Bh
013Ch
013Dh
013Eh
CAN0 Message Box 13: Time Stamp
013Fh
225
226
B-3
Page 14
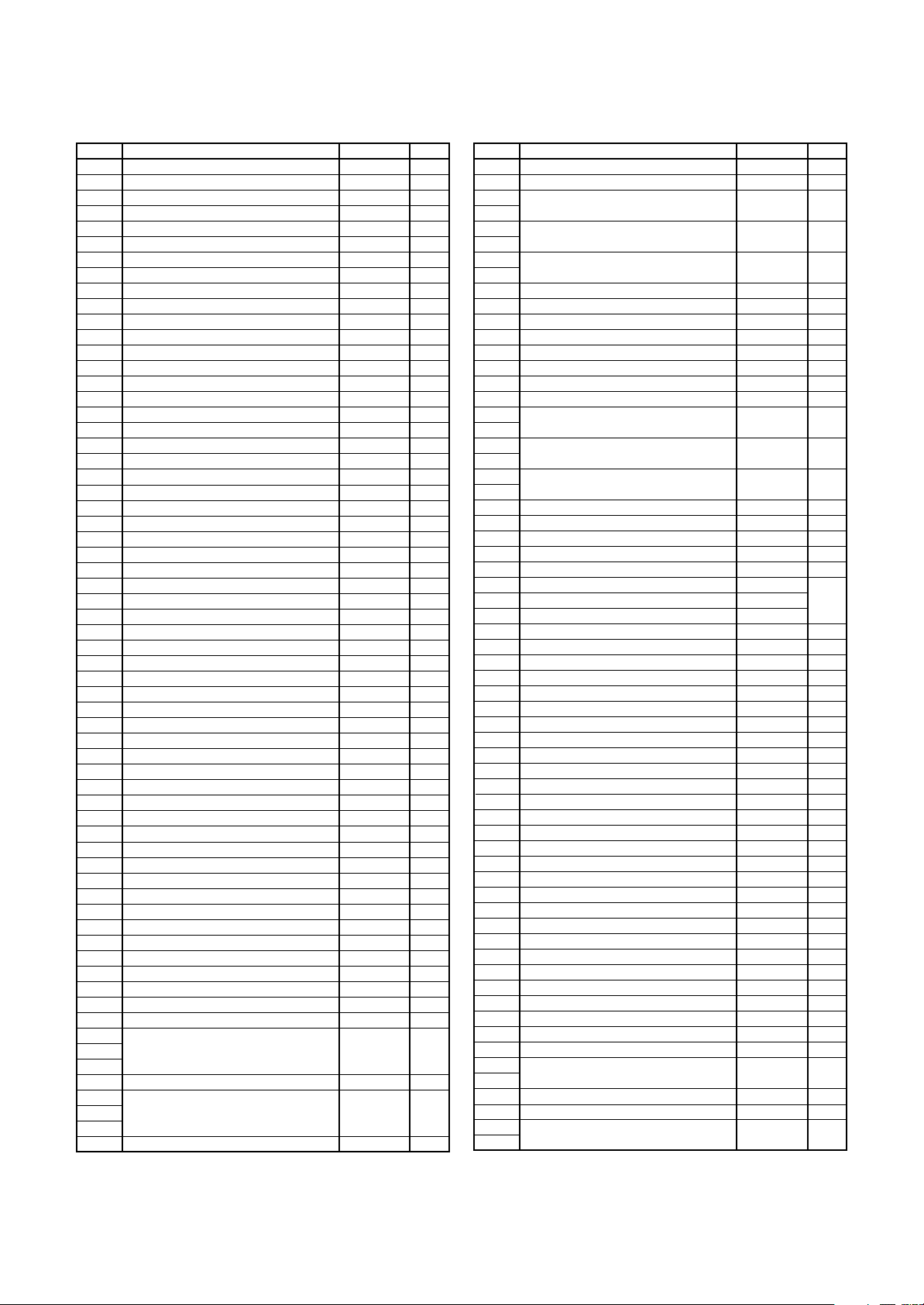
Address Register Symbol Page
Address Register Symbol Page
TBSR
TA11
TA21
TA41
INVC0
INVC1
IDB0
IDB1
DTT
ICTB2
IFSR2
TB3
TB4
TB5
S6TRR
S6C
S6BRG
S3456TRR
TB3MR
TB4MR
TB5MR
IFSR0
IFSR1
S3TRR
S3C
S3BRG
S4TRR
S4C
S4BRG
S5TRR
S5C
S5BRG
U0SMR4
U0SMR3
U0SMR2
U0SMR
U1SMR4
U1SMR3
U1SMR2
U1SMR
U2SMR4
U2SMR3
U2SMR2
U2SMR
U2MR
U2BRG
U2TB
U2C0
U2C1
U2RB
01C0h
01C1h
01C2h
01C3h
01C4h
01C5h
01C6h
01C7h
01C8h
01C9h
01CAh
01CBh
01CCh
01CDh
01CEh
01CFh
01D0h
01D1h
01D2h
01D3h
01D4h
01D5h
01D6h
01D7h
01D8h
01D9h
01DAh
01DBh
01DCh
01DDh
01DEh
01DFh
01E0h
01E1h
01E2h
01E3h
01E4h
01E5h
01E6h
01E7h
01E8h
01E9h
01EAh
01EBh
01ECh
01EDh
01EEh
01EFh
01F0h
01F1h
01F2h
01F3h
01F4h
01F5h
01F6h
01F7h
01F8h
01F9h
01FAh
01FBh
01FCh
01FDh
01FEh
01FFh
Timer B3, B4, B5 Count Start Flag
Timer A1-1 Register
Timer A2-1 Register
Timer A4-1 Register
Three-Phase PWM Control Register 0
Three-Phase PWM Control Register 1
Three-Phase Output Buffer Register 0
Three-Phase Output Buffer Register 1
Dead Time Timer
Timer B2 Interrupt Occurrence Frequency Set Counter
Interrupt Cause Select Register 2
Timer B3 Register
Timer B4 Register
Timer B5 Register
SI/O6 Transmit/Receive Register
SI/O6 Control Register
SI/O6 Bit Rate Generator
SI/O3, 4, 5, 6 Transmit/Receive Register
Timer B3 Mode Register
Timer B4 Mode Register
Timer B5 Mode Register
Interrupt Cause Select Register 0
Interrupt Cause Select Register 1
SI/O3 Transmit/Receive Register
SI/O3 Control Register
SI/O3 Bit Rate Generator
SI/O4 Transmit/Receive Register
SI/O4 Control Register
SI/O4 Bit Rate Generator
SI/O5 Transmit/Receive Register
SI/O5 Control Register
SI/O5 Bit Rate Generator
UART0 Special Mode Register 4
UART0 Special Mode Register 3
UART0 Special Mode Register 2
UART0 Special Mode Register
UART1 Special Mode Register 4
UART1 Special Mode Register 3
UART1 Special Mode Register 2
UART1 Special Mode Register
UART2 Special Mode Register 4
UART2 Special Mode Register 3
UART2 Special Mode Register 2
UART2 Special Mode Register
UART2 Transmit/Receive Mode Register
UART2 Bit Rate Generator
UART2 Transmit Buffer Register
UART2 Transmit/Receive Control Register 0
UART2 Transmit/Receive Control Register 1
UART2 Receive Buffer Register
132
143
143
143
140
141
142
142
142
144
97
131
131
131
197
197
197
198
131
133
135
136
95
96
197
197
197
197
197
197
197
197
197
158
157
157
156
158
157
157
156
158
157
157
156
154
153
153
154
155
153
0180h
0181h
0182h
0183h
0184h
0185h
0186h
0187h
0188h
0189h
018Ah
018Bh
018Ch
018Dh
018Eh
018Fh
0190h
0191h
0192h
0193h
0194h
0195h
0196h
0197h
0198h
0199h
019Ah
019Bh
019Ch
019Dh
019Eh
019Fh
01A0h
01A1h
01A2h
01A3h
01A4h
01A5h
01A6h
01A7h
01A8h
01A9h
01AAh
01ABh
01ACh
01ADh
01AEh
01AFh
01B0h
01B1h
01B2h
01B3h
01B4h
01B5h
The blank areas are reserved.
Flash Memory Control Register 1
01B6h
01B7h
Flash Memory Control Register 0
01B8h
01B9h
Address Match Interrupt Register 2
01BAh
01BBh
Address Match Interrupt Enable Register 2
01BCh
01BDh
Address Match Interrupt Register 3
01BEh
01BFh
FMR1
FMR0
RMAD2
AIER2
RMAD3
266
266
100
100
100
B-4
Page 15
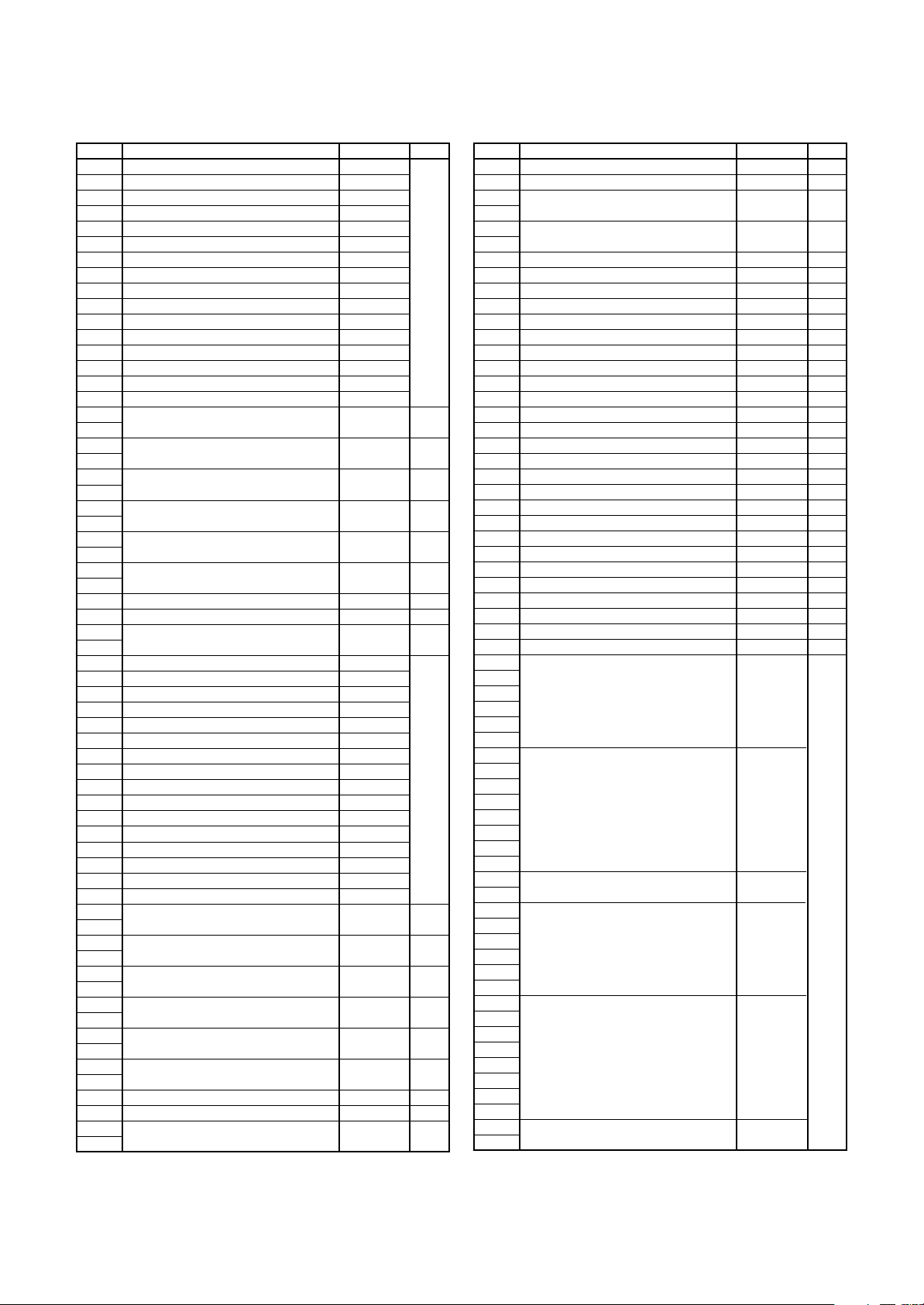
Address Register Symbol Page
C0AFS
C1AFS
PCLKR
CCLKR
Address Register Symbol Page
0240h
0241h
0242h
0243h
0244h
0245h
0246h
0247h
0248h
0249h
024Ah
024Bh
024Ch
024Dh
024Eh
024Fh
0250h
0251h
0252h
0253h
0254h
0255h
0256h
0257h
0258h
0259h
025Ah
025Bh
025Ch
025Dh
025Eh
025Fh
0260h
0261h
0262h
0263h
0264h
0265h
0266h
0267h
0268h
0269h
026Ah
026Bh
026Ch
026Dh
026Eh
026Fh
0270h
0271h
0272h
0273h
0274h
0275h
0276h
0277h
0278h
0279h
027Ah
027Bh
027Ch
027Dh
027Eh
027Fh
CAN0 Acceptance Filter Support Register
CAN1 Acceptance Filter Support Register
Peripheral Clock Select Register
CAN0/1 Clock Select Register
CAN1 Message Box 0: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 0: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 0:Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 1: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 1: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 1:Time Stamp
233
233
61
62
225
226
0200h
CAN0 Message Control Register 0
CAN0 Message Control Register 1
0201h
CAN0 Message Control Register 2
0202h
0203h
CAN0 Message Control Register 3
0204h
CAN0 Message Control Register 4
0205h
CAN0 Message Control Register 5
0206h
CAN0 Message Control Register 6
0207h
CAN0 Message Control Register 7
0208h
The blank areas are reserved.
CAN0 Message Control Register 8
0209h
CAN0 Message Control Register 9
020Ah
CAN0 Message Control Register 10
020Bh
CAN0 Message Control Register 11
020Ch
CAN0 Message Control Register 12
020Dh
CAN0 Message Control Register 13
020Eh
CAN0 Message Control Register 14
020Fh
CAN0 Message Control Register 15
0210h
CAN0 Control Register
0211h
0212h
CAN0 Status Register
0213h
0214h
CAN0 Slot Status Register
0215h
0216h
CAN0 Interrupt Control Register
0217h
0218h
CAN0 Extended ID Register
0219h
021Ah
CAN0 Configuration Register
021Bh
021Ch
CAN0 Receive Error Count Register
021Dh
CAN0 Transmit Error Count Register
021Eh
CAN0 Time Stamp Register
021Fh
0220h
CAN1 Message Control Register 0
0221h
CAN1 Message Control Register 1
0222h
CAN1 Message Control Register 2
0223h
CAN1 Message Control Register 3
0224h
CAN1 Message Control Register 4
0225h
CAN1 Message Control Register 5
0226h
CAN1 Message Control Register 6
0227h
CAN1 Message Control Register 7
0228h
CAN1 Message Control Register 8
0229h
CAN1 Message Control Register 9
022Ah
CAN1 Message Control Register 10
022Bh
CAN1 Message Control Register 11
022Ch
CAN1 Message Control Register 12
022Dh
CAN1 Message Control Register 13
022Eh
CAN1 Message Control Register 14
022Fh
CAN1 Message Control Register 15
0230h
CAN1 Control Register
0231h
0232h
CAN1 Status Register
0233h
0234h
CAN1 Slot Status Register
0235h
0236h
CAN1 Interrupt Control Register
0237h
0238h
CAN1 Extended ID Register
0239h
023Ah
CAN1 Configuration Register
023Bh
023Ch
CAN1 Receive Error Count Register
023Dh
CAN1 Transmit Error Count Register
023Eh
CAN1 Time Stamp Register
023Fh
C0MCTL0
C0MCTL1
C0MCTL2
C0MCTL3
C0MCTL4
C0MCTL5
C0MCTL6
C0MCTL7
C0MCTL8
C0MCTL9
C0MCTL10
C0MCTL11
C0MCTL12
C0MCTL13
C0MCTL14
C0MCTL15
C0CTLR
C0STR
C0SSTR
C0ICR
C0IDR
C0CONR
C0RECR
C0TECR
C0TSR
C1MCTL0
C1MCTL1
C1MCTL2
C1MCTL3
C1MCTL4
C1MCTL5
C1MCTL6
C1MCTL7
C1MCTL8
C1MCTL9
C1MCTL10
C1MCTL11
C1MCTL12
C1MCTL13
C1MCTL14
C1MCTL15
C1CTLR
C1STR
C1SSTR
C1ICR
C1IDR
C1CONR
C1RECR
C1TECR
C1TSR
228
229
230
231
231
231
232
233
233
233
228
229
230
231
231
231
232
233
233
233
B-5
Page 16

Address Register Symbol Page
Address Register Symbol Page
02C0h
02C1h
02C2h
02C3h
02C4h
02C5h
02C6h
02C7h
02C8h
02C9h
02CAh
02CBh
02CCh
02CDh
02CEh
02CFh
02D0h
02D1h
02D2h
02D3h
02D4h
02D5h
02D6h
02D7h
02D8h
02D9h
02DAh
02DBh
02DCh
02DDh
02DEh
02DFh
02E0h
02E1h
02E2h
02E3h
02E4h
02E5h
02E6h
02E7h
02E8h
02E9h
02EAh
02EBh
02ECh
02EDh
02EEh
02EFh
02F0h
02F1h
02F2h
02F3h
02F4h
02F5h
02F6h
02F7h
02F8h
02F9h
02FAh
02FBh
02FCh
02FDh
02FEh
02FFh
CAN1 Message Box 6: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 6: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 6: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 7: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 7: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 7: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 8: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 8: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 8: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 9: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 9: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 9: Time Stamp
225
226
0280h
0281h
0282h
CAN1 Message Box 2: Identifier / DLC
0283h
0284h
0285h
0286h
0287h
0288h
0289h
CAN1 Message Box 2: Data Field
028Ah
028Bh
028Ch
028Dh
028Eh
CAN1 Message Box 2: Time Stamp
028Fh
0290h
0291h
0292h
CAN1 Message Box 3: Identifier / DLC
0293h
0294h
0295h
0296h
0297h
0298h
0299h
CAN1 Message Box 3: Data Field
029Ah
029Bh
029Ch
029Dh
029Eh
CAN1 Message Box 3: Time Stamp
029Fh
02A0h
02A1h
02A2h
CAN1 Message Box 4: Identifier / DLC
02A3h
02A4h
02A5h
02A6h
02A7h
02A8h
02A9h
CAN1 Message Box 4: Data Field
02AAh
02ABh
02ACh
02ADh
02AEh
CAN1 Message Box 4: Time Stamp
02AFh
02B0h
02B1h
02B2h
CAN1 Message Box 5: Identifier / DLC
02B3h
02B4h
02B5h
02B6h
02B7h
02B8h
02B9h
CAN1 Message Box 5: Data Field
02BAh
02BBh
02BCh
02BDh
02BEh
CAN1 Message Box 5: Time Stamp
02BFh
225
226
B-6
Page 17
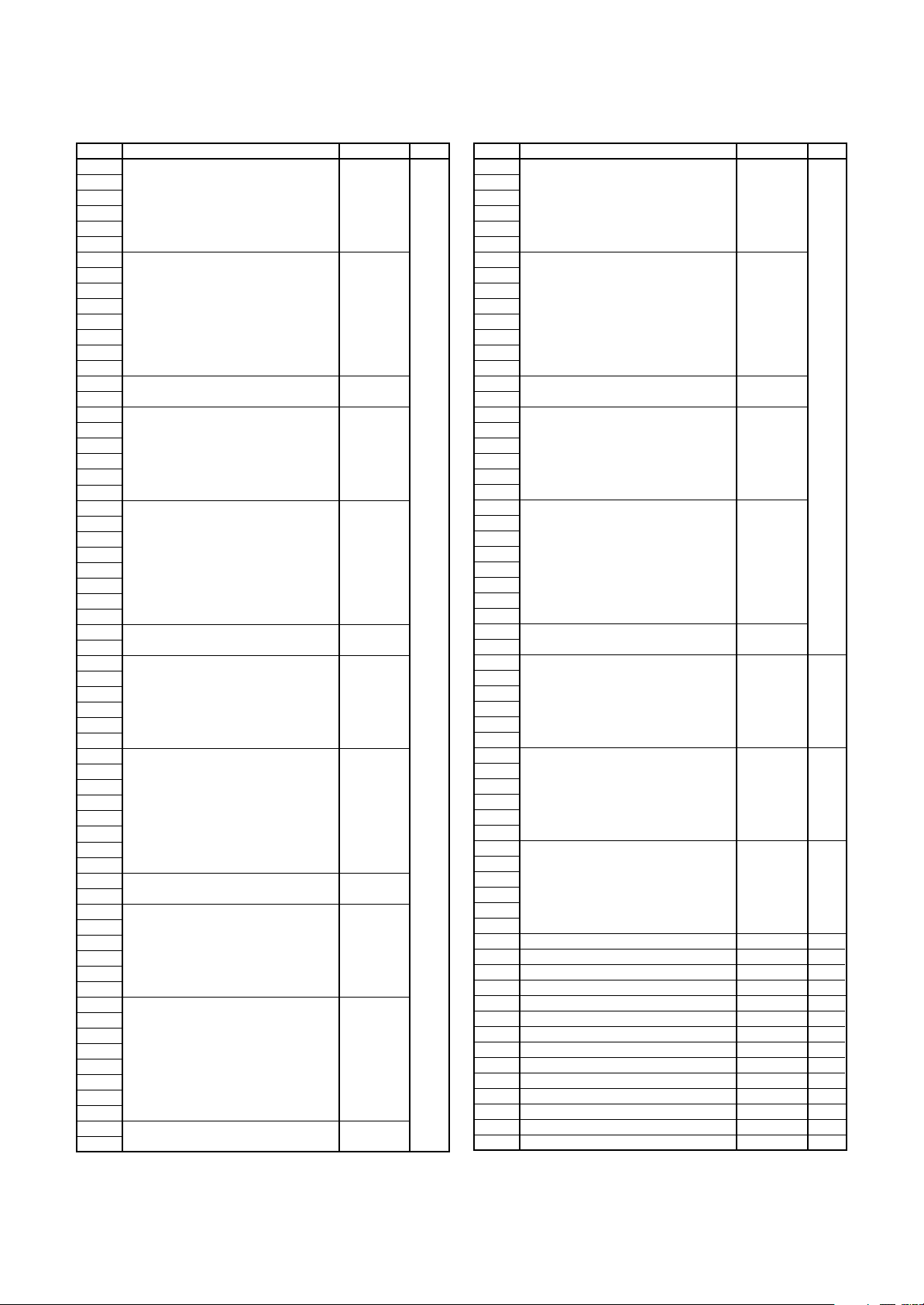
Address Register Symbol Page
C1GMR
C1LMAR
C1LMBR
Address Register Symbol Page
0340h
0341h
0342h
0343h
0344h
0345h
0346h
0347h
0348h
0349h
034Ah
034Bh
034Ch
034Dh
034Eh
034Fh
0350h
0351h
0352h
0353h
0354h
0355h
0356h
0357h
0358h
0359h
035Ah
035Bh
035Ch
035Dh
035Eh
035Fh
0360h
0361h
0362h
0363h
0364h
0365h
0366h
0367h
0368h
0369h
036Ah
036Bh
036Ch
036Dh
036Eh
036Fh
0370h
0371h
0372h
0373h
0374h
0375h
0376h
0377h
0378h
0379h
037Ah
037Bh
037Ch
037Dh
037Eh
037Fh
CAN1 Message Box 14: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 14: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 14: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 15: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 15: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 15: Time Stamp
CAN1 Global Mask Register
CAN1 Local Mask A Register
CAN1 Local Mask B Register
225
226
227
227
227
0300h
0301h
0302h
CAN1 Message Box 10: Identifier / DLC
0303h
0304h
0305h
0306h
0307h
0308h
0309h
CAN1 Message Box 10: Data Field
030Ah
030Bh
030Ch
030Dh
030Eh
CAN1 Message Box 10: Time Stamp
030Fh
0310h
0311h
0312h
CAN1 Message Box 11: Identifier / DLC
0313h
0314h
0315h
0316h
0317h
0318h
0319h
CAN1 Message Box 11: Data Field
031Ah
031Bh
031Ch
031Dh
031Eh
CAN1 Message Box 11: Time Stamp
031Fh
0320h
0321h
0322h
CAN1 Message Box 12: Identifier / DLC
0323h
0324h
0325h
0326h
0327h
0328h
0329h
CAN1 Message Box 12: Data Field
032Ah
032Bh
032Ch
032Dh
032Eh
CAN1 Message Box 12: Time Stamp
032Fh
0330h
0331h
0332h
The blank areas are reserved.
CAN1 Message Box 13: Identifier / DLC
0333h
0334h
0335h
0336h
0337h
0338h
0339h
CAN1 Message Box 13: Data Field
033Ah
033Bh
033Ch
033Dh
033Eh
CAN1 Message Box 13: Time Stamp
033Fh
225
226
B-7
Page 18
Address Register Symbol Page
Address Register Symbol Page
AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
AD4
AD5
AD6
AD7
ADCON2
ADCON0
ADCON1
DA0
DA1
DACON
PC14
PUR3
P0
P1
PD0
PD1
P2
P3
PD2
PD3
P4
P5
PD4
PD5
P6
P7
PD6
PD7
P8
P9
PD8
PD9
P10
P11
PD10
PD11
P12
P13
PD12
PD13
PUR0
PUR1
PUR2
PCR
03C0h
03C1h
03C2h
03C3h
03C4h
03C5h
03C6h
03C7h
03C8h
03C9h
03CAh
03CBh
03CCh
03CDh
03CEh
03CFh
03D0h
03D1h
03D2h
03D3h
03D4h
03D5h
03D6h
03D7h
03D8h
03D9h
03DAh
03DBh
03DCh
03DDh
03DEh
03DFh
03E0h
03E1h
03E2h
03E3h
03E4h
03E5h
03E6h
03E7h
03E8h
03E9h
03EAh
03EBh
03ECh
03EDh
03EEh
03EFh
03F0h
03F1h
03F2h
03F3h
03F4h
03F5h
03F6h
03F7h
03F8h
03F9h
03FAh
03FBh
03FCh
03FDh
03FEh
03FFh
A/D Register 0
A/D Register 1
A/D Register 2
A/D Register 3
A/D Register 4
A/D Register 5
A/D Register 6
A/D Register 7
A/D Control Register 2
A/D Control Register 0
A/D Control Register 1
D/A Register 0
D/A Register 1
D/A Control Register
Port P14 Control Register
Pull-Up Control Register 3
Port P0 Register
Port P1 Register
Port P0 Direction Register
Port P1 Direction Register
Port P2 Register
Port P3 Register
Port P2 Direction Register
Port P3 Direction Register
Port P4 Register
Port P5 Register
Port P4 Direction Register
Port P5 Direction Register
Port P6 Register
Port P7 Register
Port P6 Direction Register
Port P7 Direction Register
Port P8 Register
Port P9 Register
Port P8 Direction Register
Port P9 Direction Register
Port P10 Register
Port P11 Register
Port P10 Direction Register
Port P11 Direction Register
Port P12 Register
Port P13 Register
Port P12 Direction Register
Port P13 Direction Register
Pull-up Control Register 0
Pull-up Control Register 1
Pull-up Control Register 2
Port Control Register
205
205
204,207,209
211,213,215
220
220
220
255
257
255
255
254
254
255
255
254
254
255
255
254
254
255
255
254
254
255
255
254
254
255
255
254
254
255
255
254
254
256
256
256
257
0380h
Count Start Flag
0381h
Clock Prescaler Reset Flag
0382h
One-Shot Start Flag
0383h
Trigger Select Register
0384h
Up/Down Flag
TABSR
CPSRF
ONSF
TRGSR
UDF
0385h
0386h
Timer A0 Register
0387h
0388h
The blank areas are reserved.
Timer A1 Register
0389h
038Ah
Timer A2 Register
038Bh
038Ch
Timer A3 Register
038Dh
038Eh
Timer A4 Register
038Fh
0390h
Timer B0 Register
0391h
0392h
Timer B1 Register
0393h
0394h
Timer B2 Register
0395h
Timer A0 Mode Register
0396h
Timer A1 Mode Register
0397h
Timer A2 Mode Register
0398h
Timer A3 Mode Register
0399h
Timer A4 Mode Register
039Ah
Timer B0 Mode Register
039Bh
Timer B1 Mode Register
039Ch
Timer B2 Mode Register
039Dh
Timer B2 Special Mode Register
039Eh
039Fh
UART0 Transmit/Receive Mode Register
03A0h
UART0 Bit Rate Generator
03A1h
03A2h
UART0 Transmit Buffer Register
03A3h
UART0 Transmit/Receive Control Register 0
03A4h
UART0 Transmit/Receive Control Register 1
03A5h
03A6h
UART0 Receive Buffer Register
03A7h
03A8h
UART1 Transmit/Receive Mode Register
03A9h
UART1 Bit Rate Generator
03AAh
UART1 Transmit Buffer Register
03ABh
03ACh
UART1 Transmit/Receive Control Register 0
03ADh
UART1 Transmit/Receive Control Register 1
03AEh
UART1 Receive Buffer Register
03AFh
03B0h
UART Transmit/Receive Control Register 2
03B1h
03B2h
03B3h
03B4h
03B5h
03B6h
03B7h
03B8h
DMA0 Request Cause Select Register
03B9h
03BAh
DMA1 Request Cause Select Register
03BBh
03BCh
CRC Data Register
03BDh
03BEh
CRC Input Register
03BFh
TA0
TA1
TA2
TA3
TA4
TB0
TB1
TB2
TA0MR
TA1MR
TA2MR
TA3MR
TA4MR
TB0MR
TB1MR
TB2MR
TB2SC
U0MR
U0BRG
U0TB
U0C0
U0C1
U0RB
U1MR
U1BRG
U1TB
U1C0
U1C1
U1RB
UCON
DM0SL
DM1SL
CRCD
CRCIN
117,132,145
118,132
118
118,145
117
116
116
143
116
143
116
116
143
131
131
131
143
116
119
146
121
123,146
126
123
128
123,146
131,133
134,136
146
144
154
153
153
154
155
153
154
153
153
154
155
153
156
105
106
221
221
B-8
Page 19

M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM)
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change
SINGLE-CHIP 16-BIT CMOS MICROCOMPUTER
Nov 28, 2005
1. Overview
The M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) of single-chip microcomputers are built using the
high-performance silicon gate CMOS process using an M16C/60 Series CPU core and are packaged in
100-pin and 128-pin plastic molded LQFP. These single-chip microcomputers operate using sophisticated
instructions featuring a high level of instruction efficiency. With 1 Mbyte of address space, they are capable
of executing instructions at high speed. Being equipped with two CAN (Controller Area Network) modules in
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM), the microcomputer is suited to car audio and industrial control
systems. The CAN modules comply with the 2.0B specification. In addition, this microcomputer contains a
multiplier and DMAC which combined with fast instruction processing capability, makes it suitable for control
of various OA and communication equipment which requires high-speed arithmetic/logic operations.
1.1 Applications
• Car audio and industrial control systems, other (Normal-ver. product)
• Automotive, industrial control systems and other automobile, other (T/V-ver. product)
Rev.2.00
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 1 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 20
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
1.2 Performance Outline
Tables 1.1 and 1.2 list a performance outline of M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM).
Table 1.1 Performance Outline of M16C/6N Group (100-pin Version: M16C/6NK)
Item
Normal-ver. T/V-ver.
CPU Number of Basic Instructions 91 instructions
Minimum Instruction 41.7ns (f(BCLK) = 24MHz, 50.0ns (f(BCLK) = 20MHz,
Execution Time
Operation Mode
1/1 prescaler, without software wait) 1/1 prescaler, without software wait)
Single-chip, memory expansion
and microprocessor modes
Address Space 1 Mbyte
Memory Capacity See Table 1.3 Product List
Peripheral Port Input/Output: 87 pins, Input: 1 pin
Function Multifunction Timer Timer A: 16 bits ✕ 5 channels
Timer B: 16 bits ✕ 6 channels
Three-phase motor control circuit
Serial Interface 3 channels
Clock synchronous, UART, I2C-bus
2 channels
Clock synchronous
A/D Converter 10-bit A/D converter: 1 circuit, 26 channels
D/A Converter 8 bits ✕ 2 channels
DMAC 2 channels
CRC Calculation Circuit CRC-CCITT
CAN Module 2 channels with 2.0B specification
Watchdog Timer 15 bits ✕ 1 channel (with prescaler)
Interrupt Internal: 32 sources, External: 9 sources
Software: 4 sources, Priority level: 7 levels
Clock Generating Circuit 4 circuits
• Main clock oscillation circuit (*)
• Sub clock oscillation circuit (*)
• On-chip oscillator
• PLL frequency synthesizer
(*) Equipped with a built-in feedback resistor
Oscillation Stop Detection Main clock oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection function
Function
Electrical Supply Voltage
Characteristics
VCC = 3.0 to 5.5V (f(BCLK) = 24MHz, VCC = 4.2 to 5.5V (f(BCLK) = 20MHz,
1/1 prescaler, without software wait) 1/1 prescaler, without software wait)
Power Mask ROM 21mA (f(BCLK) = 24MHz, Consumption PLL operation, no division)
Flash Memory
23mA (f(BCLK) = 24MHz, 21mA (f(BCLK) = 20MHz,
PLL operation, no division) PLL operation, no division)
Mask ROM 3µA
Flash Memory
Flash Memory Program/Erase Supply Voltage
Version
Program and Erase Endurance
(f(BCLK) = 32kHz, Wait mode, Oscillation capacity Low)
0.8µA (Stop mode, Topr = 25°C)
3.0 ± 0.3V or 5.0 ± 0.5V 5.0 ± 0.5V
100 times
I/O I/O Withstand Voltage 5.0V
Characteristics
Output Current 5mA
Operating Ambient Temperature -40 to 85°C T version: -40 to 85°C
Device Configuration CMOS high performance silicon gate
Package 100-pin plastic mold LQFP
NOTES:
1. I2C-bus is a registered trademark of Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V.
2. IEBus is a registered trademark of NEC Electronics Corporation.
option: All options are on request basis.
Performance
Single-chip mode
V version: -40 to 125°C
(1)
, IEBus
(2)
(option)
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 2 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 21
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
Table 1.2 Performance Outline of M16C/6N Group (128-pin Version: M16C/6NM)
Item
Normal-ver. T/V-ver.
Performance
CPU Number of Basic Instructions 91 instructions
Minimum Instruction 41.7ns (f(BCLK) = 24MHz, 50.0ns (f(BCLK) = 20MHz,
Execution Time
Operation Mode
1/1 prescaler, without software wait) 1/1 prescaler, without software wait)
Single-chip, memory expansion
Single-chip mode
and microprocessor modes
Address Space 1 Mbyte
Memory Capacity See Table 1.3 Product List
Peripheral Port Input/Output: 113 pins, Input: 1 pin
Function Multifunction Timer Timer A: 16 bits ✕ 5 channels
Timer B: 16 bits ✕ 6 channels
Three-phase motor control circuit
Serial Interface 3 channels
Clock synchronous, UART, I2C-bus
(1)
, IEBus
(2)
4 channels
Clock synchronous
A/D Converter 10-bit A/D converter: 1 circuit, 26 channels
D/A Converter 8 bits ✕ 2 channels
DMAC 2 channels
CRC Calculation Circuit CRC-CCITT
CAN Module 2 channels with 2.0B specification
Watchdog Timer 15 bits ✕ 1 channel (with prescaler)
Interrupt Internal: 34 sources, External: 12 sources
Software: 4 sources, Priority level: 7 levels
Clock Generating Circuit 4 circuits
• Main clock oscillation circuit (*)
• Sub clock oscillation circuit (*)
• On-chip oscillator
• PLL frequency synthesizer
(*) Equipped with a built-in feedback resistor
Oscillation Stop Detection Main clock oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection function
Function
Electrical Supply Voltage
Characteristics
VCC = 3.0 to 5.5V (f(BCLK) = 24MHz, VCC = 4.2 to 5.5V (f(BCLK) = 20MHz,
1/1 prescaler, without software wait) 1/1 prescaler, without software wait)
Power Mask ROM 21mA (f(BCLK) = 24MHz, Consumption PLL operation, no division)
Flash Memory
23mA (f(BCLK) = 24MHz, 21mA (f(BCLK) = 20MHz,
PLL operation, no division) PLL operation, no division)
Mask ROM 3µA
Flash Memory
Flash Memory Program/Erase Supply Voltage
Version
Program and Erase Endurance
(f(BCLK) = 32kHz, Wait mode, Oscillation capacity Low)
0.8µA (Stop mode, Topr = 25°C)
3.0 ± 0.3V or 5.0 ± 0.5V 5.0 ± 0.5V
100 times
I/O I/O Withstand Voltage 5.0V
Characteristics
Output Current 5mA
Operating Ambient Temperature -40 to 85°C T version: -40 to 85°C
V version: -40 to 125°C
(option)
Device Configuration CMOS high performance silicon gate
Package 128-pin plastic mold LQFP
NOTES:
1. I2C-bus is a registered trademark of Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V.
2. IEBus is a registered trademark of NEC Electronics Corporation.
option: All options are on request basis.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 3 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 22
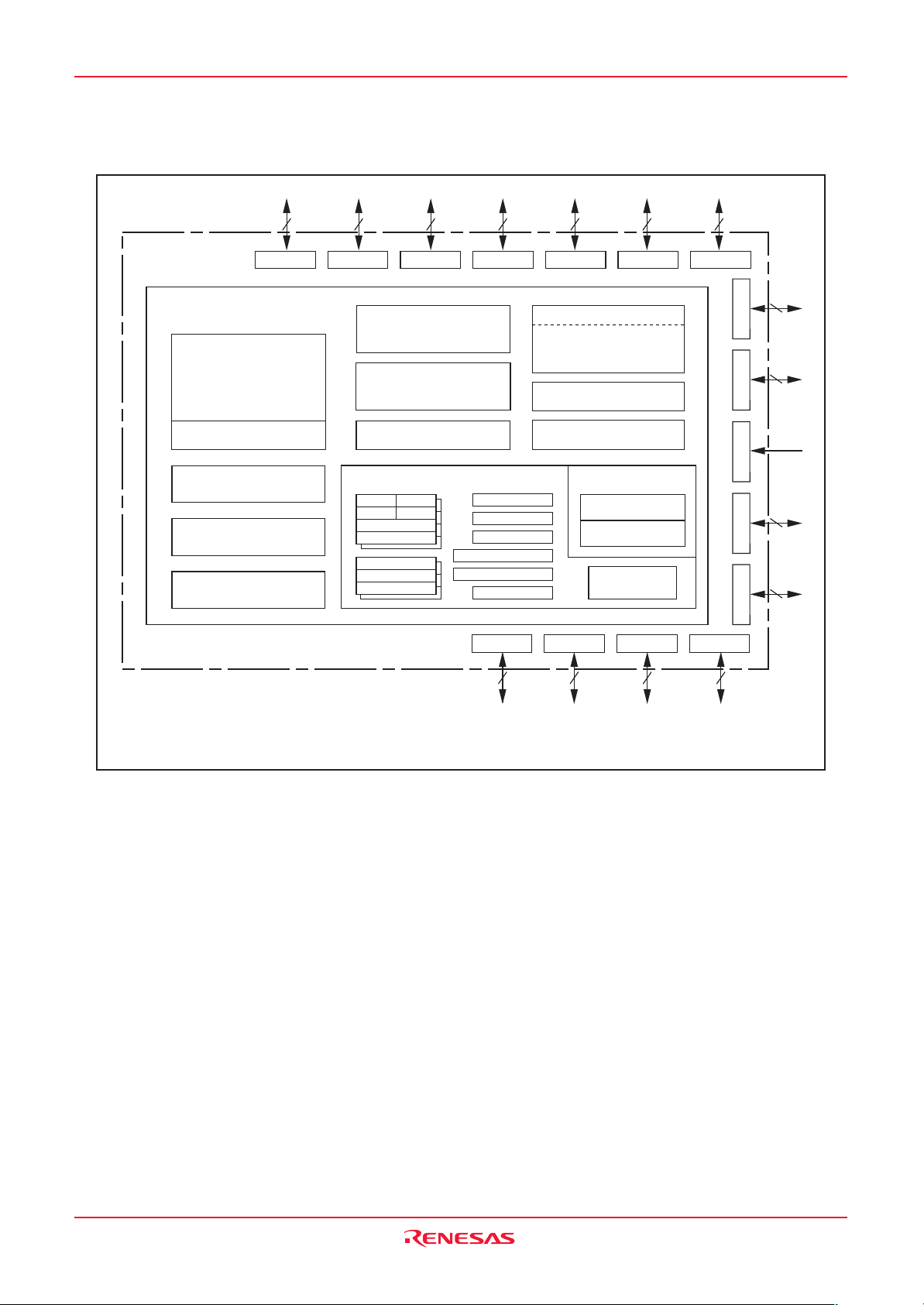
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
1.3 Block Diagram
Figure 1.1 shows a block diagram of M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM).
8
Port P0
Port P18Port P2
Internal peripheral functions
Expandable up to 26 channels)
Timer (16 bits)
Output (timer A): 5
Input (timer B): 6
Three-phase motor
control circuit
Watchdog timer
(15 bits)
DMAC
(2 channels)
D/A converter
(8 bits ✕ 2 channels)
NOTES:
1: ROM size depends on microcomputer type.
2: RAM size depends on microcomputer type.
3: Ports P11 to P14 are only in the 128-pin version.
4: 8 bits ✕ 2 channels in the 100-pin version.
Clock synchronous serial I/O
CRC arithmetic circuit (CCITT)
8 8 8 8
A/D converter
(10 bits ✕ 8 channels
UART or
(3 channels)
(Polynomial: X
R0H R0L
R1H R1L
R2
R3
A0
A1
FB
16+X12+X5
+1)
SB
USP
ISP
INTB
PC
FLG
Port P14
(3)
2
Port P5Port P4Port P3
System clock generating circuit
XIN-XOUT
XCIN-XCOUT
PLL frequency synthesizer
On-chip oscillator
Clock synchronous serial I/O
(8 bits ✕ 4 channels)
CAN module
(2 channels)
(4)
MemoryM16C/60 series CPU core
(1)
ROM
(2)
RAM
Multiplier
Port P13
Port P12
(3)
8
(3)
8
8
Port P6
Port P7
8
Port P8
7
Port P8_5
Port P9
8
Port P10
8
Port P11
(3)
8
Figure 1.1 Block Diagram
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 4 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 23
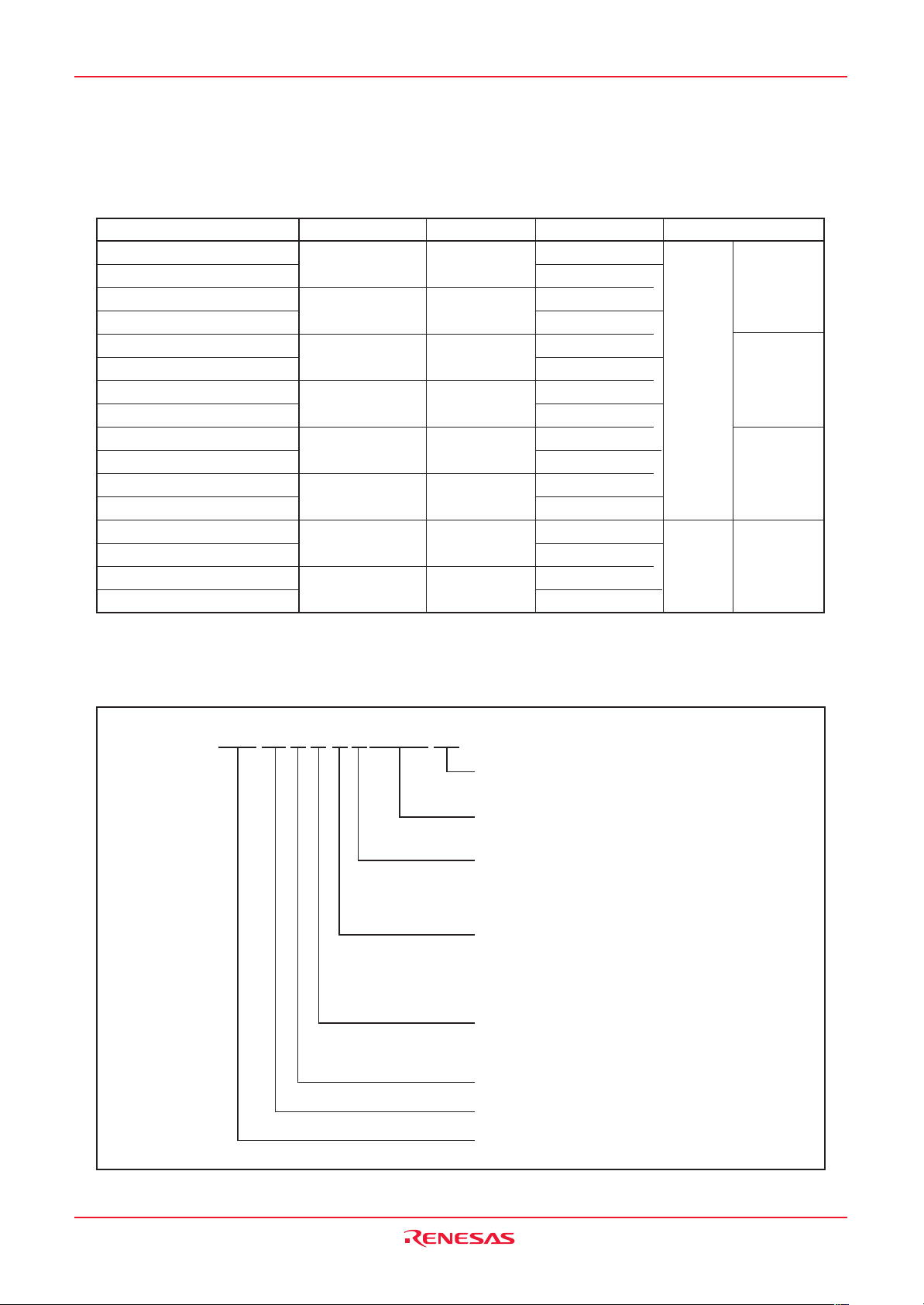
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
1.4 Product List
Table 1.3 lists the M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) products and Figure 1.2 shows the type numbers,
memory sizes and packages.
Table 1.3 Product List
Type No. ROM Capacity RAM Capacity Package Type Remarks
M306NKFHGP
384 K + 4 Kbytes 31 Kbytes
PLQP0100KB-A
M306NMFHGP PLQP0128KB-A
M306NKFJGP
(D) 512 K + 4 Kbytes 31 Kbytes
PLQP0100KB-A
M306NMFJGP PLQP0128KB-A
M306NKFHTGP
M306NMFHTGP
M306NKFJTGP
M306NMFJTGP
M306NKFHVGP
M306NMFHVGP
M306NKFJVGP
M306NMFJVGP
M306NKME-XXXGP
(D) 384 K + 4 Kbytes 31 Kbytes
(D)
(D) 512 K + 4 Kbytes 31 Kbytes
(D)
(D) 384 K + 4 Kbytes 31 Kbytes
(D)
(D) 512 K + 4 Kbytes 31 Kbytes
(D)
192 Kbytes
16
Kbytes
PLQP0100KB-A T-ver.
PLQP0128KB-A
PLQP0100KB-A
PLQP0128KB-A
PLQP0100KB-A V-ver.
PLQP0128KB-A
PLQP0100KB-A
PLQP0128KB-A
PLQP0100KB-A
M306NMME-XXXGP PLQP0128KB-A
M306NKMG-XXXGP
256 Kbytes
20
Kbytes
PLQP0100KB-A
M306NMMG-XXXGP PLQP0128KB-A
(D): Under development
NOTE:
1. In the flash memory version, there is 4-Kbyte space (block A).
As of Nov. 2005
Flash
memory
version
(1)
Mask
ROM
version
Normal-ver.
Normal-ver.
Type No.
M30 6N K M G T - XXX GP
Figure 1.2 Type No., Memory Size, and Package
Package type:
GP: Package PLQP0100KB-A, PLQP0128KB-A
ROM No.
Omitted on flash memory version
Characteristics
(no): Normal-ver.
T : T-ver. (Automotive 85°C version)
V : V-ver. (Automotive 125°C version)
ROM capacity:
E : 192 Kbytes
G: 256 Kbytes
H : 384 Kbytes
J : 512 Kbytes
Memory type:
M : Mask ROM version
F : Flash memory version
Shows the number of CAN module, pin count, etc.
6N Group
M16C Family
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 5 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 24
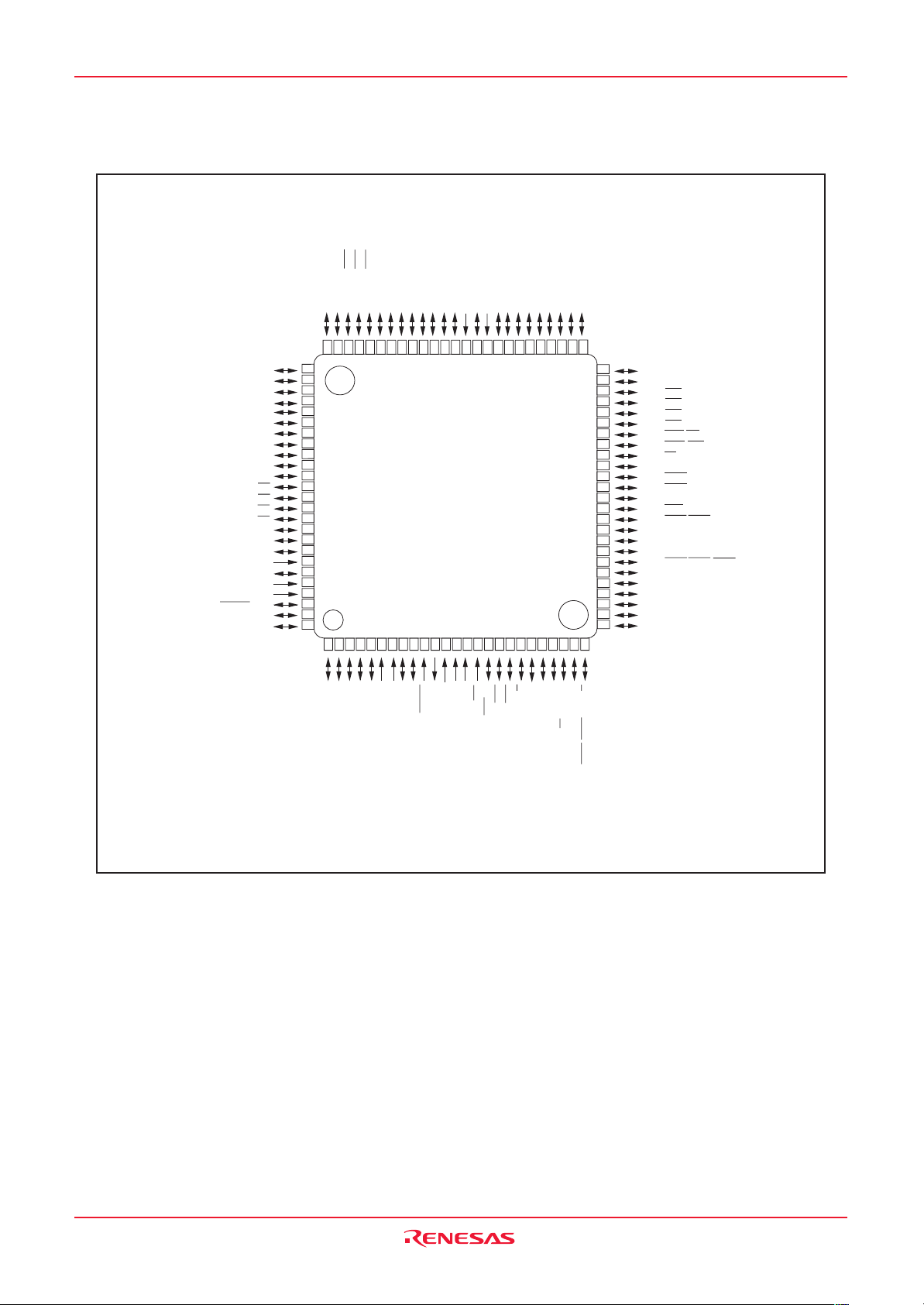
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
1.5 Pin Configuration
Figures 1.3 and 1.4 show the pin configuration (top view). Tables 1.4 to 1.8 list the pin characteristics.
PIN CONFIGURATION (top view)
P1_2/D10
P1_1/D9
P1_0/D8
P0_7/AN0_7/D7
P0_6/AN0_6/D6
P0_5/AN0_5/D5
P0_4/AN0_4/D4
P0_3/AN0_3/D3
P0_2/AN0_2/D2
P0_1/AN0_1/D1
P0_0/AN0_0/D0
P10_7/AN7/KI3
P10_6/AN6/KI2
P10_5/AN5/KI1
P10_4/AN4/KI0
P10_3/AN3
P10_2/AN2
P10_1/AN1
AVSS
P10_0/AN0
VREF
P9_7/ADTRG/SIN4
P9_6/ANEX1/CTX0/SOUT4
P9_5/ANEX0/CRX0/CLK4
AVCC
P2_3/AN2_3/A3(/D3/D2)
P2_7/AN2_7/A7(/D7/D6)
P2_2/AN2_2/A2(/D2/D1)
P1_4/D12
P1_3/D11
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10111213141516171819202122232425
P9_3/DA0/TB3IN
P9_4/DA1/TB4IN
P2_1/AN2_1/A1(/D1/D0)
P2_0/AN2_0/A0(/D0/-)
P1_5/D13/INT3
P1_6/D14/INT4
P1_7/D15/INT5
M16C/6N Group
(M16C/6NK)
BYTE
CNVSS
P8_7/XCIN
P8_6/XCOUT
P9_1/TB1IN/SIN3
P9_0/TB0IN/CLK3
P9_2/TB2IN/SOUT3
(1)
P2_4/AN2_4/A4(/D4/D3)
RESET
P3_0/A8(/-/D7)
P2_6/AN2_6/A6(/D6/D5)
P2_5/AN2_5/A5(/D5/D4)
XIN
VSS
XOUT
VSS
VCC1
P8_5/NMI
P3_2/A10
VCC2
P3_1/A9
57585960616263646566676869707172737475
P8_2/INT0
P8_3/INT1
P8_4/INT2/ZP
P3_3/A11
P8_1/TA4IN/U
P3_4/A12
P8_0/TA4OUT/U(SIN4)
P4_1/A17
P4_0/A16
P3_7/A15
P3_6/A14
P3_5/A13
515253545556
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
P7_7/TA3IN/CRX1
P7_6/TA3OUT/CTX1
P7_5/TA2IN/W(SOUT4)
P7_4/TA2OUT/W(CLK4)
P7_3/CTS2/RTS2/TA1IN/V
1. P7_1 and P9_1 are N channel open-drain pins.
2. Not available the bus control pins (except CLKOUT pin) in T/V-ver..
P4_2/A18
P4_3/A19
P4_4/CS0
P4_5/CS1
P4_6/CS2
P4_7/CS3
P5_0/WRL/WR
P5_1/WRH/BHE
P5_2/RD
P5_3/BCLK
P5_4/HLDA
P5_5/HOLD
P5_6/ALE
P5_7/RDY/CLKOUT
P6_0/CTS0/RTS0
P6_1/CLK0
P6_2/RXD0/SCL0
P6_3/TXD0/SDA0
P6_4/CTS1/RTS1/CTS0/CLKS1
P6_5/CLK1
P6_6/RXD1/SCL1
P6_7/TXD1/SDA1
P7_0/TXD2/SDA2/TA0OUT
P7_1/RXD2/SCL2/TA0IN/TB5IN
P7_2/CLK2/TA1OUT/V
Package: PLQP0100KB-ANOTES:
(1)
Figure 1.3 Pin Configuration (Top View) (1)
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 6 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 25
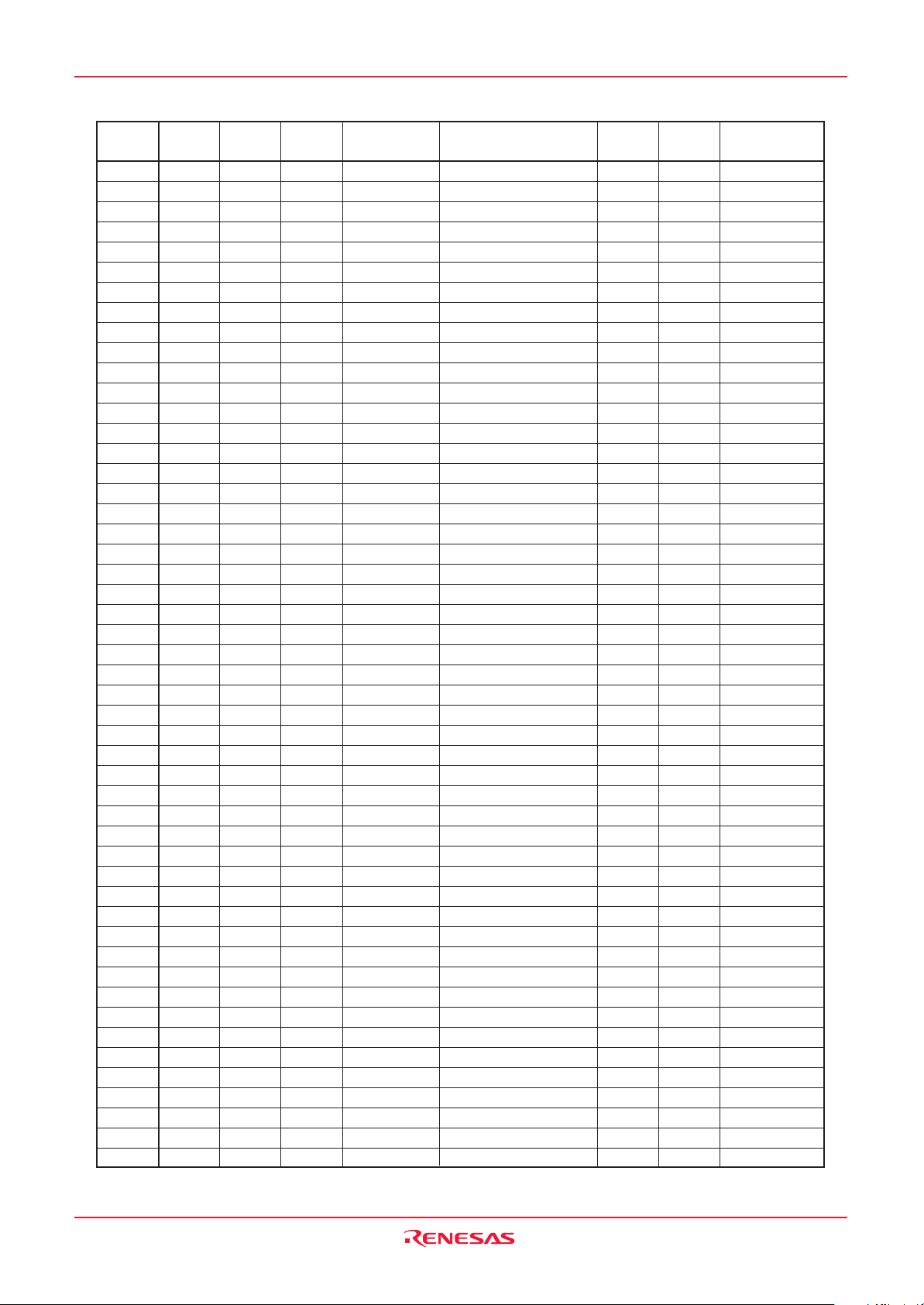
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
Table 1.4 Pin Characteristics for 100-Pin Package (1)
Pin No.
Control
Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin
1 P9_4 TB4IN DA1
Port
2 P9_3 TB3IN DA0
3 P9_2 TB2IN SOUT3
4 P9_1 TB1IN SIN3
5 P9_0 TB0IN CLK3
6 BYTE
7 CNVSS
8 XCIN P8_7
9 XCOUT P8_6
_____________
10
RESET
11 XOUT
12 VSS
13 XIN
14 VCC1
15 P8_5
16 P8_4
17 P8_3
18 P8_2
19 P8_1
20 P8_0 TA4OUT/U (SIN4)
21 P7_7 TA3IN CRX1
22 P7_6 TA3OUT CTX1
23 P7_5
24 P7_4 TA2OUT/W (CLK4)
25 P7_3
26 P7_2 TA1OUT/V CLK2
27 P7_1 TA0IN/TB5IN RXD2/SCL2
28 P7_0 TA0OUT TXD2/SDA2
29 P6_7 TXD1/SDA1
30 P6_6 RXD1/SCL1
31 P6_5 CLK1
32 P6_4
33 P6_3 TXD0/SDA0
34 P6_2 RXD0/SCL0
35 P6_1 CLK0
36 P6_0
37 P5_7
38 P5_6 ALE
39 P5_5
40 P5_4
41 P5_3 BCLK
42 P5_2
43 P5_1
44 P5_0
45 P4_7
46 P4_6
47 P4_5
48 P4_4
49 P4_3 A19
50 P4_2 A18
Interrupt
________
NMI
_________
INT2 ZP
_________
INT1
_________
INT0
TA4IN/U
TA2IN/W (SOUT4)
TA1IN/V
Timer Pin UART Pin
___
____
___
__________ __________
CTS2/RTS2
_________ __________________
CTS1/RTS1/CTS0/CLKS1
__________ __________
CTS0/RTS0
Analog
CAN Module
_________
RDY/CLKOUT
___________
HOLD
___________
HLDA
______
RD
__________________
WRH/BHE
_________ ______
WRL/WR
_______
CS3
_______
CS2
_______
CS1
_______
CS0
Bus Control
(1)
NOTE:
1. Not available the bus control pins (except CLKOUT pin; Pin No.37) in T/V-ver..
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 7 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 26
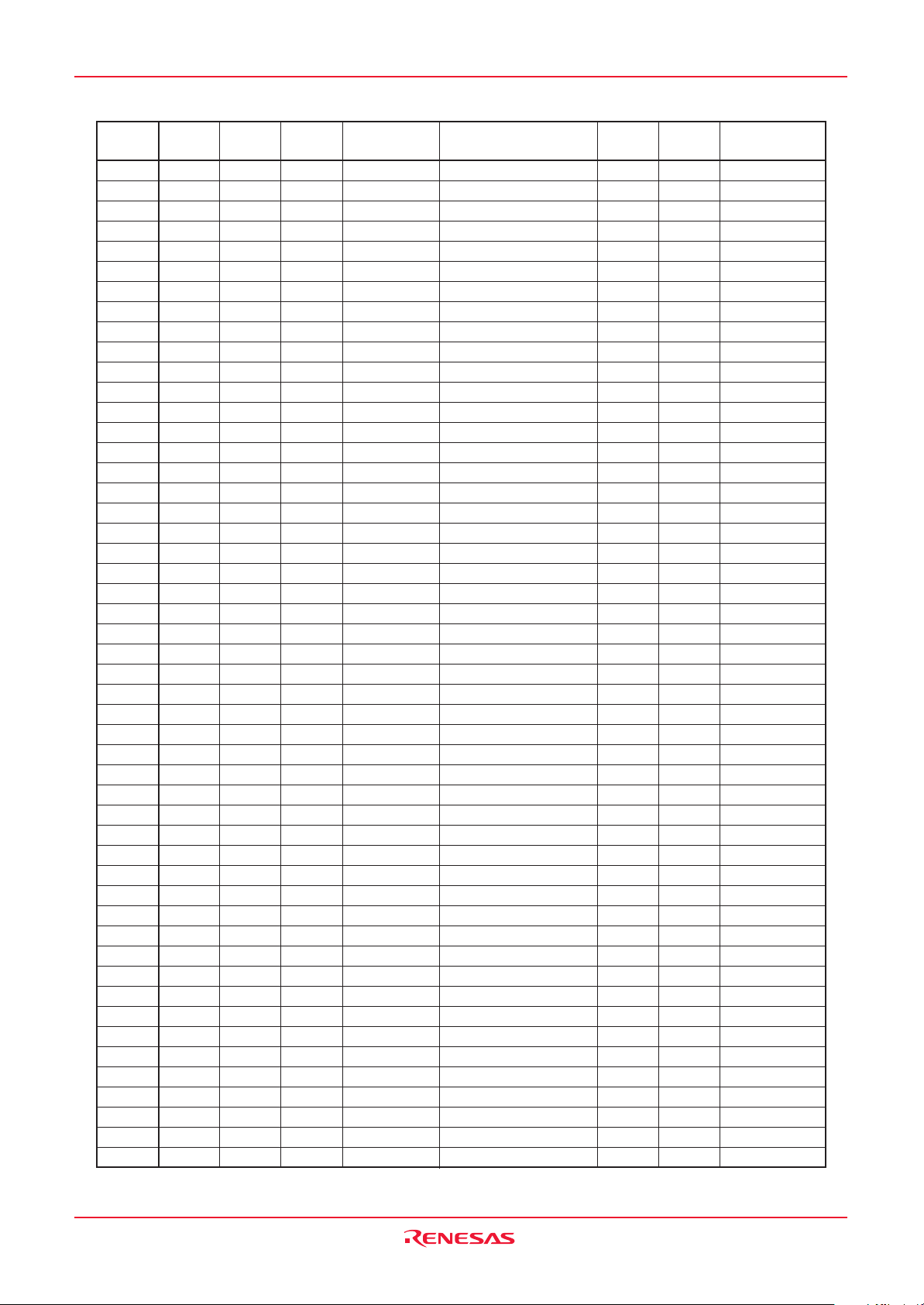
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
Table 1.5 Pin Characteristics for 100-Pin Package (2)
Pin No.
Control
Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin
51 P4_1 A17
Port
52 P4_0 A16
53 P3_7 A15
54 P3_6 A14
55 P3_5 A13
56 P3_4 A12
57 P3_3 A11
58 P3_2 A10
59 P3_1 A9
60 VCC2
61 P3_0 A8(/-/D7)
62 VSS
63 P2_7 AN2_7 A7(/D7/D6)
64 P2_6 AN2_6 A6(/D6/D5)
65 P2_5 AN2_5 A5(/D5/D4)
66 P2_4 AN2_4 A4(/D4/D3)
67 P2_3 AN2_3 A3(/D3/D2)
68 P2_2 AN2_2 A2(/D2/D1)
69 P2_1 AN2_1 A1(/D1/D0)
70 P2_0 AN2_0 A0(/D0/-)
71 P1_7
72 P1_6
73 P1_5
74 P1_4 D12
75 P1_3 D11
76 P1_2 D10
77 P1_1 D9
78 P1_0 D8
79 P0_7 AN0_7 D7
80 P0_6 AN0_6 D6
81 P0_5 AN0_5 D5
82 P0_4 AN0_4 D4
83 P0_3 AN0_3 D3
84 P0_2 AN0_2 D2
85 P0_1 AN0_1 D1
86 P0_0 AN0_0 D0
87 P10_7
88 P10_6
89 P10_5
90 P10_4
91 P10_3 AN3
92 P10_2 AN2
93 P10_1 AN1
94 AVSS
95 P10_0 AN0
96 VREF
97 AVCC
98 P9_7 SIN4
99 P9_6 SOUT4 ANEX1 CTX0
100 P9_5 CLK4 ANEX0 CRX0
Interrupt
_________
INT5 D15
_________
INT4 D14
_________
Timer Pin UART Pin
Analog
CAN Module
Bus Control
INT3 D13
______
KI3 AN7
______
KI2 AN6
______
KI1 AN5
______
KI0 AN4
______________
ADTRG
(1)
NOTE:
1. Not available the bus control pins in T/V-ver..
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 8 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 27
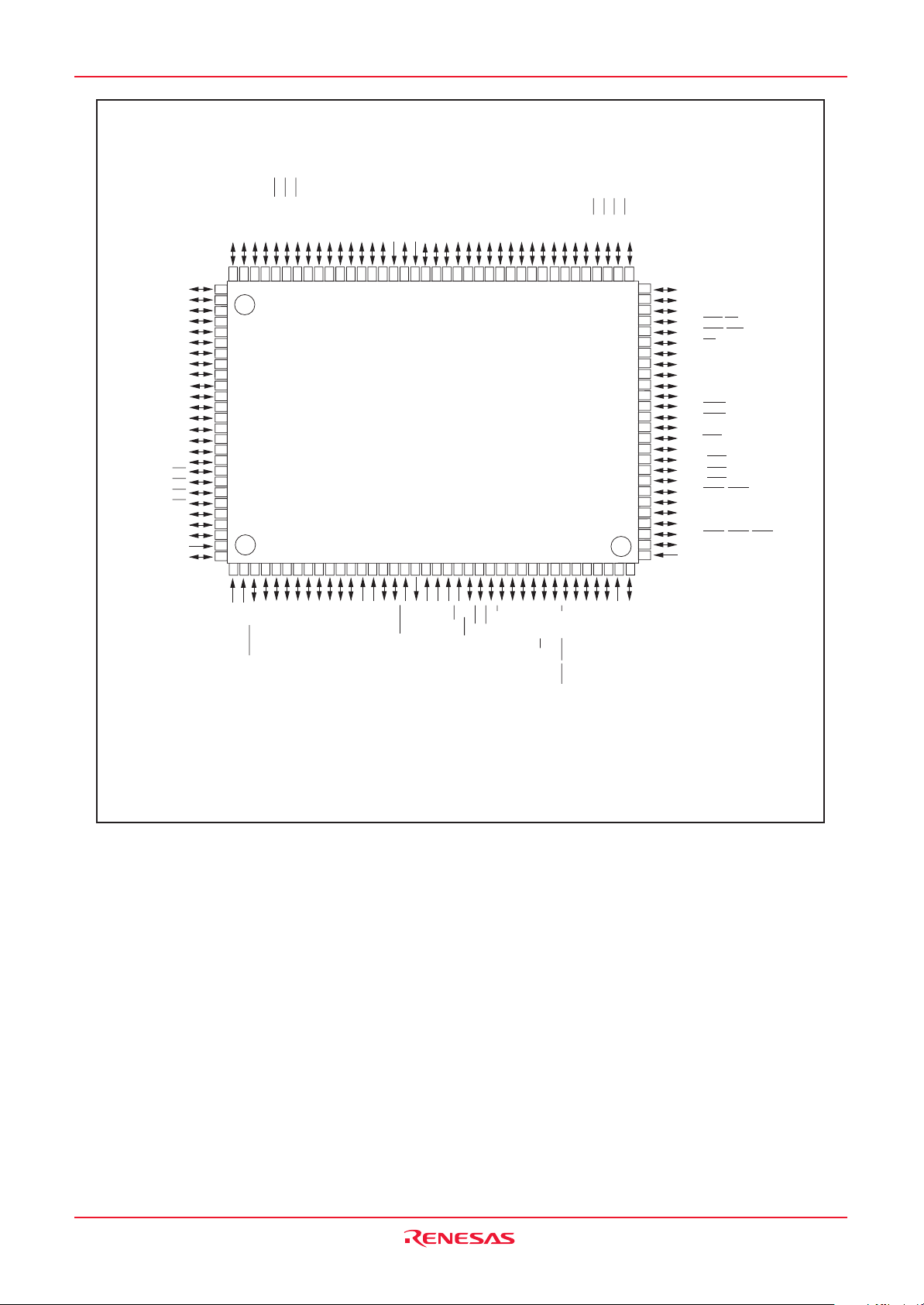
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
PIN CONFIGURATION (top view)
P1_0/D8
P0_7/AN0_7/D7
P0_6/AN0_6/D6
P0_5/AN0_5/D5
P0_4/AN0_4/D4
P0_3/AN0_3/D3
P0_2/AN0_2/D2
P0_1/AN0_1/D1
P0_0/AN0_0/D0
P11_7/SIN6
P11_6/SOUT6
P11_5/CLK6
P11_4
P11_3
P11_2/SOUT5
P11_1/SIN5
P11_0/CLK5
P10_7/AN7/KI3
P10_6/AN6/KI2
P10_5/AN5/KI1
P10_4/AN4/KI0
P10_3/AN3
P10_2/AN2
P10_1/AN1
AVSS
P10_0/AN0
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
P1_1/D9
P1_2/D10
P1_5/D13/INT3
P1_4/D12
P1_3/D11
P1_6/D14/INT4
100101102
VREF
AVCC
P9_4/DA1/TB4IN
P9_7/ADTRG/SIN4
P9_5/ANEX0/CRX0/CLK4
P9_6/ANEX1/CTX0/SOUT4
P2_3/AN2_3/A3(/D3/D2)
P2_2/AN2_2/A2(/D2/D1)
P2_1/AN2_1/A1(/D1/D0)
P1_7/D15/INT5
P2_0/AN2_0/A0(/D0/-)
P2_4/AN2_4/A4(/D4/D3)
P14_1
P14_0
P9_3/DA0/TB3IN
P9_0/TB0IN/CLK3
P9_1/TB1IN/SIN3
P9_2/TB2IN/SOUT3
(1)
P2_5/AN2_5/A5(/D5/D4)
M16C/6N Group
BYTE
VCC2
VSS
P2_7/AN2_7/A7(/D7/D6)
P2_6/AN2_6/A6(/D6/D5)
P12_2
P12_1
P12_0
P3_0/A8(/-/D7)
(M16C/6NM)
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 3011 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 2012345678910
XIN
VSS
VCC1
XOUT
RESET
CNVSS
P8_7/XCIN
P8_6/XCOUT
P12_3
P12_4
P3_1/A9
P8_5/NMI
P8_3/INT1
P8_2/INT0
P8_4/INT2/ZP
P3_7/A15
P3_6/A14
P3_5/A13
P3_4/A12
P3_3/A11
P3_2/A10
737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899
31 32 33 34 35 36 37
P8_1/TA4IN/U
P7_7/TA3IN/CRX1
P7_6/TA3OUT/CTX1
P8_0/TA4OUT/U(SIN4)
P7_5/TA2IN/W(SOUT4)
P4_1/A17
P4_0/A16
P7_4/TA2OUT/W(CLK4)
P7_3/CTS2/RTS2/TA1IN/V
1. P7_1 and P9_1 are N channel open-drain pins.
2. Not available the bus control pins (except CLKOUT pin) in T/V-ver..
P4_7/CS3
P4_6/CS2
P4_5/CS1
P4_3/A19
P4_2/A18
P4_4/CS0
66676869707172
65
64
63
62
61
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
VCC1
P6_6/RXD1/SCL1
P6_7/TXD1/SDA1
P7_2/CLK2/TA1OUT/V
P7_0/TXD2/SDA2/TA0OUT
P7_1/RXD2/SCL2/TA0IN/TB5IN
(1)
Package: PLQP0128KB-ANOTES:
P12_5
P12_6
P12_7
P5_0/WRL/WR
P5_1/WRH/BHE
P5_2/RD
P5_3/BCLK
P13_0
P13_1
P13_2
P13_3
P5_4/HLDA
P5_5/HOLD
P5_6/ALE
P5_7/RDY/CLKOUT
P13_4
P13_5/INT6
P13_6/INT7
P13_7/INT8
P6_0/CTS0/RTS0
P6_1/CLK0
P6_2/RXD0/SCL0
P6_3/TXD0/SDA0
P6_4/CTS1/RTS1/CTS0/CLKS1
P6_5/CLK1
VSS
Figure 1.4 Pin Configuration (Top View) (2)
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 9 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 28
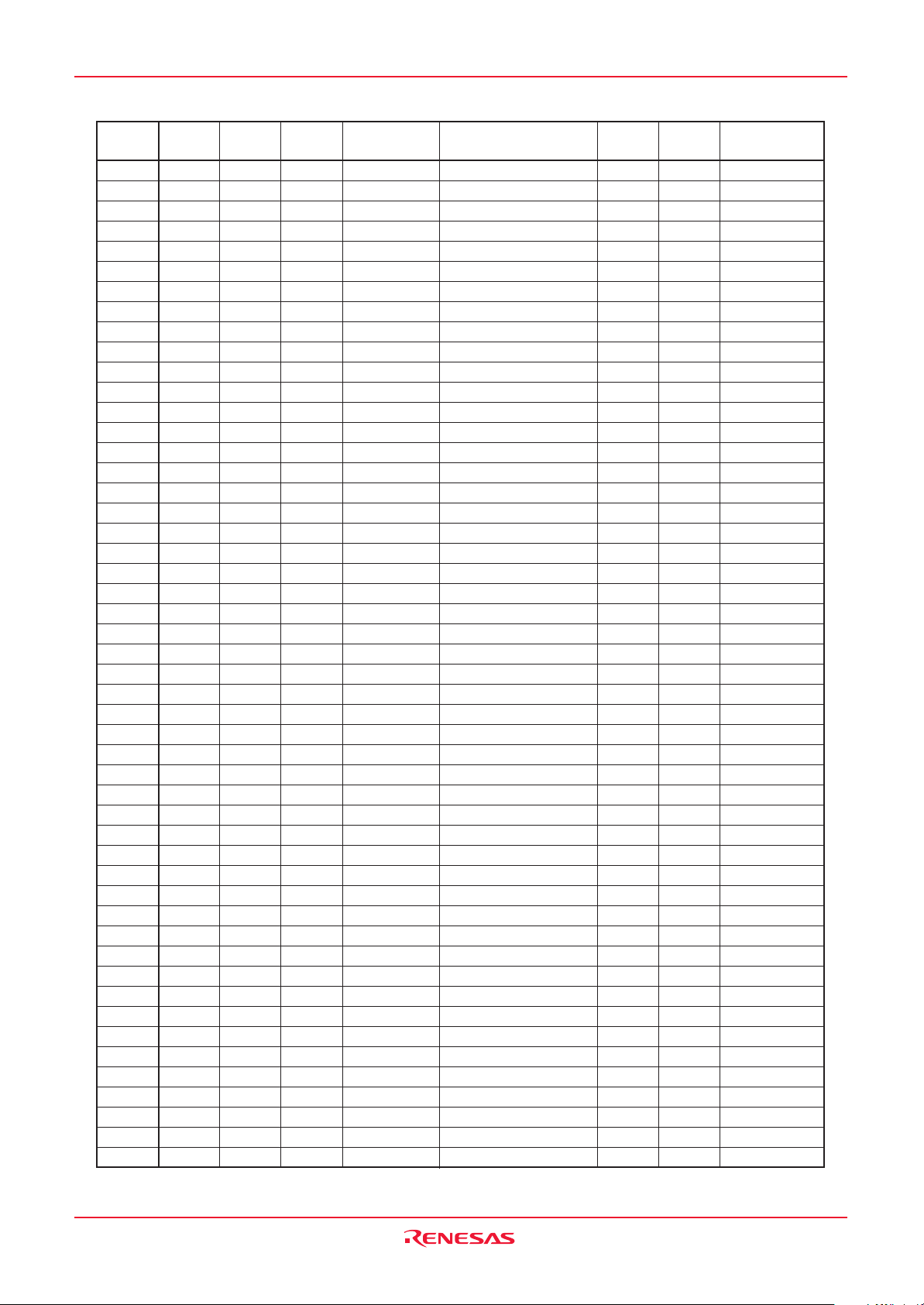
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
Table 1.6 Pin Characteristics for 128-Pin Package (1)
Pin No.
Control
Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin
1 VREF
Port
2 AVCC
3 P9_7 SIN4
4 P9_6 SOUT4 ANEX1 CTX0
5 P9_5 CLK4 ANEX0 CRX0
6 P9_4 TB4IN DA1
7 P9_3 TB3IN DA0
8 P9_2 TB2IN SOUT3
9 P9_1 TB1IN SIN3
10 P9_0 TB0IN CLK3
11 P14_1
12 P14_0
13 BYTE
14 CNVSS
15 XCIN P8_7
16 XCOUT P8_6
_____________
17
RESET
18 XOUT
19 VSS
20 XIN
21 VCC1
22 P8_5
23 P8_4
24 P8_3
25 P8_2
26 P8_1
27 P8_0 TA4OUT/U (SIN4)
28 P7_7 TA3IN CRX1
29 P7_6 TA3OUT CTX1
30 P7_5
31 P7_4 TA2OUT/W (CLK4)
32 P7_3
33 P7_2 TA1OUT/V CLK2
34 P7_1 TA0IN/TB5IN RXD2/SCL2
35 P7_0 TA0OUT TXD2/SDA2
36 P6_7 TXD1/SDA1
37 VCC1
38 P6_6 RXD1/SCL1
39 VSS
40 P6_5 CLK1
41 P6_4
42 P6_3 TXD0/SDA0
43 P6_2 RXD0/SCL0
44 P6_1 CLK0
45 P6_0
46 P13_7
47 P13_6
48 P13_5
49 P13_4
50 P5_7
Interrupt
________
NMI
_________
INT2 ZP
_________
INT1
_________
INT0
TA4IN/U
TA2IN/W (SOUT4)
TA1IN/V
_________
INT8
_________
INT7
_________
INT6
Timer Pin UART Pin
___
____
___
__________ __________
CTS2/RTS2
_________ __________________
CTS1/RTS1/CTS0/CLKS1
__________ __________
CTS0/RTS0
Analog
______________
ADTRG
CAN Module
_________
RDY/CLKOUT
Bus Control
(1)
NOTE:
1. Not available the bus control pins (except CLKOUT pin; Pin No.50) in T/V-ver..
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 10 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 29
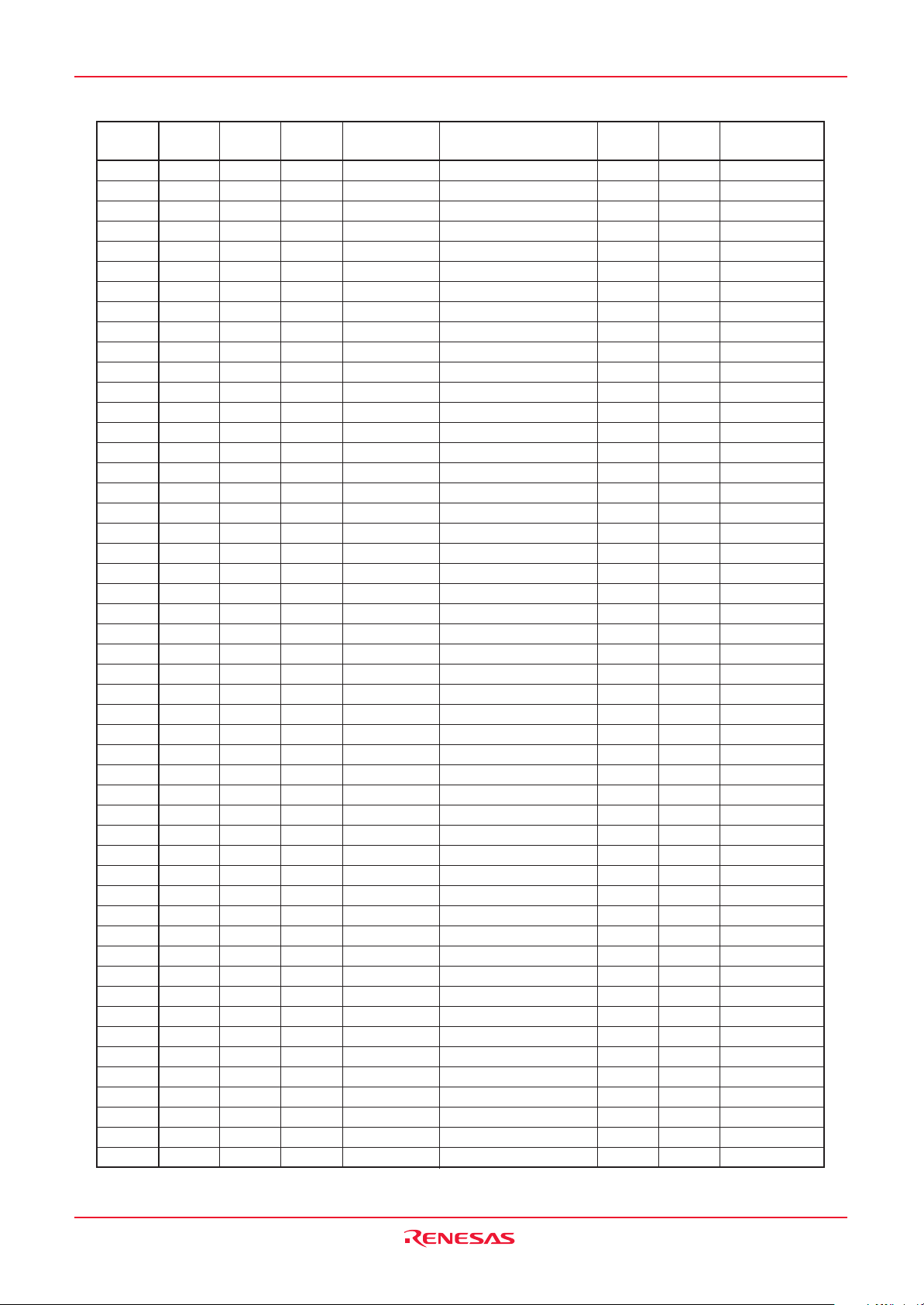
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
Table 1.7 Pin Characteristics for 128-Pin Package (2)
Pin No.
Control
Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin
51 P5_6 ALE
Port
52 P5_5
53 P5_4
54 P13_3
55 P13_2
56 P13_1
57 P13_0
58 P5_3 BCLK
59 P5_2
60 P5_1
61 P5_0
62 P12_7
63 P12_6
64 P12_5
65 P4_7
66 P4_6
67 P4_5
68 P4_4
69 P4_3 A19
70 P4_2 A18
71 P4_1 A17
72 P4_0 A16
73 P3_7 A15
74 P3_6 A14
75 P3_5 A13
76 P3_4 A12
77 P3_3 A11
78 P3_2 A10
79 P3_1 A9
80 P12_4
81 P12_3
82 P12_2
83 P12_1
84 P12_0
85 VCC2
86 P3_0 A8(/-/D7)
87 VSS
88 P2_7 AN2_7 A7(/D7/D6)
89 P2_6 AN2_6 A6(/D6/D5)
90 P2_5 AN2_5 A5(/D5/D4)
91 P2_4 AN2_4 A4(/D4/D3)
92 P2_3 AN2_3 A3(/D3/D2)
93 P2_2 AN2_2 A2(/D2/D1)
94 P2_1 AN2_1 A1(/D1/D0)
95 P2_0 AN2_0 A0(/D0/-)
96 P1_7
97 P1_6
98 P1_5
99 P1_4 D12
100 P1_3 D11
Interrupt
Timer Pin UART Pin
Analog
CAN Module
___________
HOLD
___________
Bus Control
HLDA
______
RD
__________________
WRH/BHE
_________ ______
WRL/WR
_______
CS3
_______
CS2
_______
CS1
_______
CS0
_________
INT5 D15
_________
INT4 D14
_________
INT3 D13
(1)
NOTE:
1. Not available the bus control pins in T/V-ver..
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 11 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 30
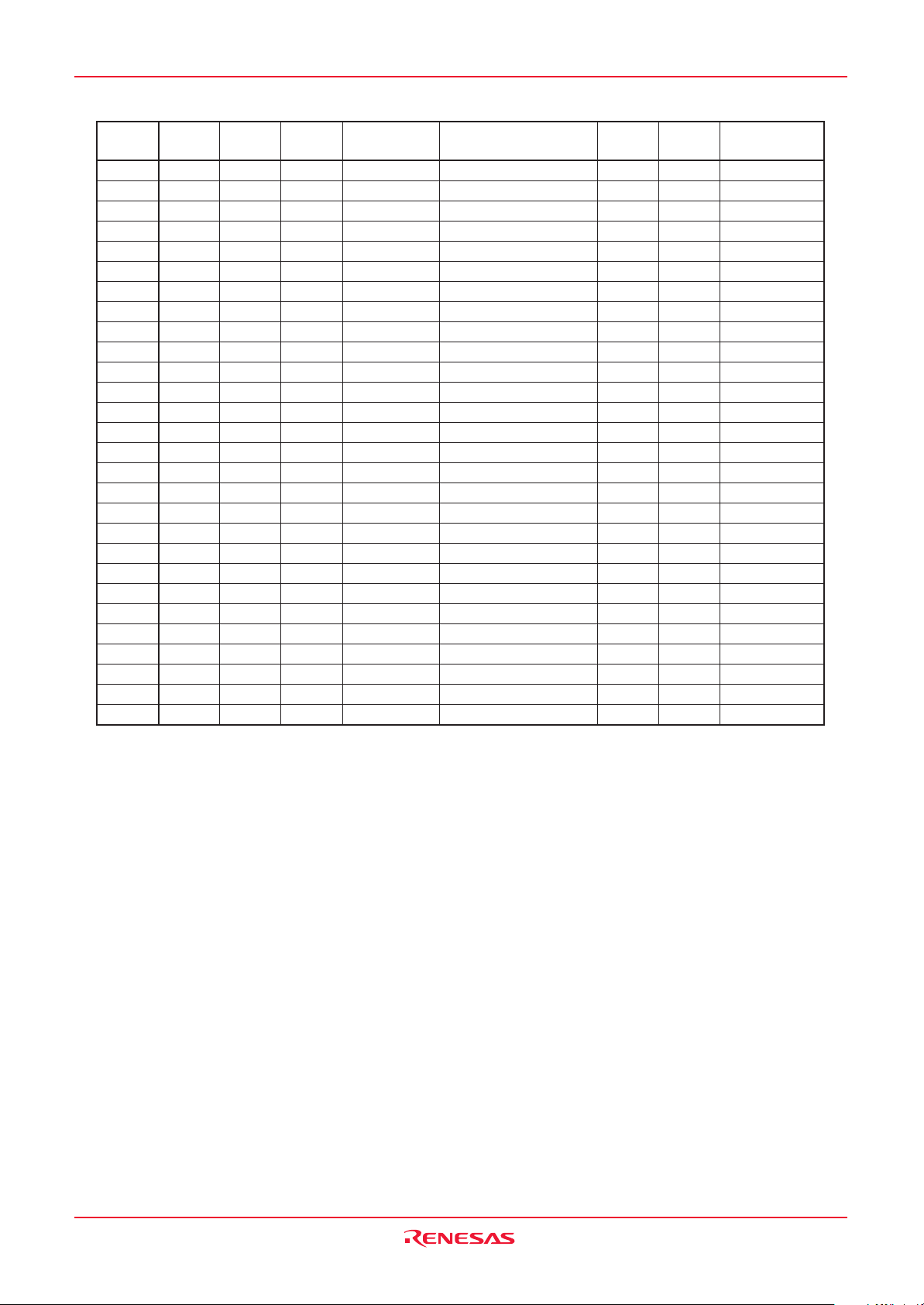
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
Table 1.8 Pin Characteristics for 128-Pin Package (3)
Pin No.
101 P1_2 D10
Control
Pin Pin Pin Pin Pin
Port
102 P1_1 D9
103 P1_0 D8
104 P0_7 AN0_7 D7
105 P0_6 AN0_6 D6
106 P0_5 AN0_5 D5
107 P0_4 AN0_4 D4
108 P0_3 AN0_3 D3
109 P0_2 AN0_2 D2
110 P0_1 AN0_1 D1
111 P0_0 AN0_0 D0
112 P11_7 SIN6
113 P11_6 SOUT6
114 P11_5 CLK6
115 P11_4
116 P11_3
117 P11_2 SOUT5
118 P11_1 SIN5
119 P11_0 CLK5
120 P10_7
121 P10_6
122 P10_5
123 P10_4
124 P10_3 AN3
125 P10_2 AN2
126 P10_1 AN1
127 AVSS
128 P10_0 AN0
Interrupt
______
KI3 AN7
______
KI2 AN6
______
KI1 AN5
______
Timer Pin UART Pin
Analog
KI0 AN4
CAN Module
Bus Control
(1)
NOTE:
1. Not available the bus control pins in T/V-ver..
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 12 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 31

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
1.6 Pin Description
Tables 1.9 to 1.11 list the pin descriptions.
Table 1.9 Pin Description (100-pin and 128-pin Versions) (1)
Signal Name Pin Name I/O Type Description
Power supply
input
Analog power
supply input
Reset input
CNVSS
(2)
External data
bus width
select input
Bus control
(3)
pins
VCC1, VCC2,
VSS
AVCC, AVSS
_____________
RESET
CNVSS
BYTE
(2)
D0 to D7
D8 to D15
A0 to A19
A0/D0 to A7/D7
A1/D0 to A8/D7
_______ _______
CS0 to CS3
_________ ______
WRL/WR
_________ ________
WRH/BHE
______
RD
ALE
__________
HOLD
__________
HLDA
________
RDY
I: Input O: Output I/O: Input/Output
I
I
I
I
I
I/O
I/O
O
I/O
I/O
O
O
O
I
O
I
Apply 3.0 to 5.5V to the VCC1 and VCC2 pins and 0V to the VSS
pin. The VCC apply condition is that VCC2 = VCC1
(1)
.
Applies the power supply for the A/D converter. Connect the AVCC
pin to VCC1. Connect the AVSS pin to VSS.
The microcomputer is in a reset state when applying “L” to the this pin.
Switches processor mode. Connect this pin to VSS to when after
a reset to start up in single-chip mode. Connect this pin to VCC1
to start up in microprocessor mode.
Switches the data bus in external memory space. The data bus
is 16-bit long when the this pin is held “L” and 8-bit long when
the this pin is held “H”. Set it to either one. Connect this pin to
VSS when an single-chip mode.
Inputs and outputs data (D0 to D7) when these pins are set as
the separate bus.
Inputs and outputs data (D8 to D15) when external 16-bit data
bus is set as the separate bus.
Output address bits (A0 to A19).
Input and output data (D0 to D7) and output address bits (A0 to
A7) by time-sharing when external 8-bit data bus are set as the
multiplexed bus.
Input and output data (D0 to D7) and output address bits (A1 to
A8) by time-sharing when external 16-bit data bus are set as the
multiplexed bus.
_______ _______ _______ _______
Output CS0 to CS3 signals. CS0 to CS3 are chip-select signals
to specify an external space.
Output WRL, WRH, (WR, BHE), RD signals. WRL and WRH or
________ ______
BHE and WR can be switched by program.
• WRL, WRH and RD are selected
• WR, BHE and RD are selected
ALE is a signal to latch the address.
While the HOLD pin is held “L”, the microcomputer is placed in
a hold state.
In a hold state, HLDA outputs a “L” signal.
While applying a “L” signal to the RDY pin, the microcomputer
________ _________ ______ ________ _____ ________ _________
________ _________ _____
________
The WRL signal becomes “L” by writing data to an even address
in an external memory space.
_________
The WRH signal becomes “L” by writing data to an odd address
in an external memory space.
_____
The RD pin signal becomes “L” by reading data in an external
memory space.
______ ________ _____
______
The WR signal becomes “L” by writing data in an external
memory space.
_____
The RD signal becomes “L” by reading data in an external
memory space.
________
The BHE signal becomes “L” by accessing an odd address.
______ ________ _____
Select WR, BHE and RD for an external 8-bit data bus.
__________
__________
________
is placed in a wait state.
NOTES:
1. In this manual, hereafter, VCC refers to VCC1 unless otherwise noted.
2. Connect to VSS in T/V-ver..
3. Not available the bus control pins in T/V-ver..
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 13 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 32

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
Table 1.10 Pin Description (100-pin and 128-pin Versions) (2)
Signal Name Pin Name I/O Type Description
Main clock
input
Main clock
output
Sub clock
input
Sub clock
output
BCLK output
(3)
Clock output
INT interrupt input
_______
NMI interrupt
input
Key input
XIN
XOUT
XCIN
XCOUT
BCLK
CLKOUT
NT0 to INT8
________
NMI
______ ______
KI0 to KI3
(3)
I/O pins for the main clock oscillation circuit. Connect a ceramic
I
resonator or crystal oscillator between XIN and XOUT
To use the external clock, input the clock from XIN and leave
O
XOUT open.
I/O pins for a sub clock oscillation circuit. Connect a crystal
I
oscillator between XCIN and XCOUT
To use the external clock, input the clock from XCIN and leave
O
(1)
.
XCOUT open.
Outputs the BCLK signal.
O
The clock of the same cycle as fC, f8, or f32 is output.
O
Input pins for the INT interrupt.
I
Input pin for the NMI interrupt.
I
Input pins for the key input interrupt.
I
______
_______
(1)
.
interrupt input
Timer A
TA0OUT to TA4OUT
TA0IN to TA4IN
ZP
Timer B
Three-phase motor
control output
Serial interface
TB0IN to TB5IN
U, U, V, V, W, W
__________ __________
CTS0 to CTS2
__________ __________
RTS0 to RTS2
CLK0 to CLK6
RXD0 to RXD2
SIN3 to SIN6
TXD0 to TXD2
SOUT3 to SOUT6
CLKS1
___ ___ ____
(3)
(3)
I/O
I/O
(3)
These are timer A0 to timer A4 I/O pins.
These are timer A0 to timer A4 input pins.
I
Input pin for the Z-phase.
I
These are timer B0 to timer B5 input pins.
I
These are Three-phase motor control output pins.
O
These are send control input pins.
I
These are receive control output pins.
O
These are transfer clock I/O pins.
These are serial data input pins.
I
These are serial data input pins.
I
These are serial data output pins.
O
These are serial data output pins.
O
This is output pin for transfer clock output from multiple pins
O
function.
2
I
C mode
SDA0 to SDA2
SCL0 to SCL2
I/O
I/O
These are serial data I/O pins.
These are transfer clock I/O pins. (however, SCL2 for
the N-channel open drain output.)
Reference
voltage input
A/D converter
VREF
AN0 to AN7
Applies the reference voltage for the A/D converter and D/A
I
converter.
Analog input pins for the A/D converter.
I
AN0_0 to AN0_7
AN2_0 to AN2_7
_____________
ADTRG
ANEX0
I/O
This is an A/D trigger input pin.
I
This is the extended analog input pin for the A/D converter,
and is the output in external op-amp connection mode.
This is the extended analog input pin for the A/D converter.
I
These are the output pins for the D/A converter.
O
These are the input pins for the CAN module.
I
These are the output pins for the CAN module.
O
D/A converter
CAN module
ANEX1
DA0, DA1
CRX0, CRX1
CTX0, CTX1
I: Input O: Output I/O: Input/Output
NOTES:
1. Ask the oscillator maker the oscillation characteristic.
________ ________
2. INT6 to INT8, CLK5, CLK6, SIN5, SIN6, SOUT5, SOUT6 are only in the 128-pin version.
3. Not available the bus control pins in T/V-ver..
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 14 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 33

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 1. Overview
Table 1.11 Pin Description (100-pin and 128-pin Versions) (3)
Signal Name Pin Name I/O Type Description
I/O port
P0_0 to P0_7
P1_0 to P1_7
P2_0 to P2_7
P3_0 to P3_7
P4_0
to
P4_7
P5_0 to P5_7
P6_0 to P6_7
I/O
8-bit I/O ports in CMOS, having a direction register to select
an input or output.
Each pin is set as an input port or output port. An input port
can be set for a pull-up or for no pull-up in 4-bit unit by
program.
(however P7_1 and P9_1 for the N-channel open drain
output.)
P7_0 to P7_7
P8_0 to P8_4
P8_6, P8_7
P9_0 to P9_7
P10_0 to P10_7
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
I
Input pin for the NMI interrupt.
_______
Input port
P11_0 to P11_7
P12_0 to P12_7
P13_0 to P13_7
P14_0, P14_1
P8_5
Pin states can be read by the P8_5 bit in the P8 register.
I: Input O: Output I/O: Input/Output
NOTE:
1. Ports P11 to P14 are only in the 128-pin version.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 15 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 34

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 2. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
2. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Figure 2.1 shows the CPU registers. The CPU has 13 registers. Of these, R0, R1, R2, R3, A0, A1 and FB
comprise a register bank. There are two register banks.
b31 b15 b8 b7 b0
R2
R3
R0H (R0's high bits) R0L (R0's low bits)
R1H (R1's high bits) R1L (R1's low bits)
R2
R3
A0
A1
FB
Data Registers
Address Registers
Frame Base Registers
(1)
(1)
(1)
b19 b15
INTBLINTBH
The upper 4 bits of INTB are INTBH and the lower 16 bits of INTB are INTBL.
b19
PC
b15 b0
USP
ISP
SB
b15 b0
FLG
b15 b0
IPL U I O B S Z D C
NOTE:
1. These registers comprise a register bank. There are two register banks.
b7b8
b0
Interrupt Table Register
b0
Program Counter
User Stack Pointer
Interrupt Stack Pointer
Static Base Register
Flag Register
Carry Flag
Debug Flag
Zero Flag
Sign Flag
Register Bank Select Flag
Overflow Flag
Interrupt Enable Flag
Stack Pointer Select Flag
Reserved Area
Processor Interrupt Priority Level
Reserved Area
Figure 2.1 CPU Registers
2.1 Data Registers (R0, R1, R2, and R3)
The R0 register consists of 16 bits, and is used mainly for transfers and arithmetic/logic operations. R1 to
R3 are the same as R0.
The R0 register can be separated between high (R0H) and low (R0L) for use as two 8-bit data registers.
R1H and R1L are the same as R0H and R0L. Conversely R2 and R0 can be combined for use as a 32-bit
data register (R2R0). R3R1 is the same as R2R0.
2.2 Address Registers (A0 and A1)
The A0 register consists of 16 bits, and is used for address register indirect addressing and address
register relative addressing. They also are used for transfers and arithmetic/logic operations. A1 is the
same as A0.
In some instructions, A1 and A0 can be combined for use as a 32-bit address register (A1A0).
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 16 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 35

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 2. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
2.3 Frame Base Register (FB)
FB is configured with 16 bits, and is used for FB relative addressing.
2.4 Interrupt Table Register (INTB)
INTB is configured with 20 bits, indicating the start address of an interrupt vector table.
2.5 Program Counter (PC)
PC is configured with 20 bits, indicating the address of an instruction to be executed.
2.6 User Stack Pointer (USP), Interrupt Stack Pointer (ISP)
Stack pointer (SP) comes in two types: USP and ISP, each configured with 16 bits.
Your desired type of stack pointer (USP or ISP) can be selected by the U flag of FLG.
2.7 Static Base Register (SB)
SB is configured with 16 bits, and is used for SB relative addressing.
2.8 Flag Register (FLG)
FLG consists of 11 bits, indicating the CPU status.
2.8.1 Carry Flag (C Flag)
This flag retains a carry, borrow, or shift-out bit that has occurred in the arithmetic/logic unit.
2.8.2 Debug Flag (D Flag)
This flag is used exclusively for debugging purpose. During normal use, it must be set to “0”.
2.8.3 Zero Flag (Z Flag)
This flag is set to “1” when an arithmetic operation resulted in 0; otherwise, it is “0”.
2.8.4 Sign Flag (S Flag)
This flag is set to “1” when an arithmetic operation resulted in a negative value; otherwise, it is “0”.
2.8.5 Register Bank Select Flag (B Flag)
Register bank 0 is selected when this flag is “0” ; register bank 1 is selected when this flag is “1”.
2.8.6 Overflow Flag (O Flag)
This flag is set to “1” when the operation resulted in an overflow; otherwise, it is “0”.
2.8.7 Interrupt Enable Flag (I Flag)
This flag enables a maskable interrupt.
Maskable interrupts are disabled when the I flag is “0”, and are enabled when the I flag is “1”. The I flag is
set to “0” when the interrupt request is accepted.
2.8.8 Stack Pointer Select Flag (U Flag)
ISP is selected when the U flag is “0” ; USP is selected when the U flag is “1”.
The U flag is set to “0” when a hardware interrupt request is accepted or an INT instruction for software
interrupt Nos. 0 to 31 is executed.
2.8.9 Processor Interrupt Priority Level (IPL)
IPL is configured with three bits, for specification of up to eight processor interrupt priority levels from level
0 to level 7.
If a requested interrupt has priority greater than IPL, the interrupt request is enabled.
2.8.10 Reserved Area
When white to this bit, write “0”. When read, its content is indeterminate.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 17 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 36

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 3. Memory
3. Memory
Figure 3.1 shows a memory map of the M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM). The address space
extends the 1 Mbyte from address 00000h to FFFFFh.
The internal ROM is allocated in a lower address direction beginning with address FFFFFh. For example, a
512-Kbyte internal ROM is allocated to the addresses from 80000h to FFFFFh.
As for the flash memory version, 4-Kbyte space (block A) exists in 0F000h to 0FFFFh. 4-Kbyte space is
mainly for storing data. In addition to storing data, 4-Kbyte space also can store programs.
The fixed interrupt vector table is allocated to the addresses from FFFDCh to FFFFFh. Therefore, store the
start address of each interrupt routine here.
The internal RAM is allocated in an upper address direction beginning with address 00400h. For example, a
31-Kbyte internal RAM is allocated to the addresses from 00400h to 07FFFh. In addition to storing data, the
internal RAM also stores the stack used when calling subroutines and when interrupts are generated.
The SFR is allocated to the addresses from 00000h to 003FFh. Peripheral function control registers are
located here. Of the SFR, any area which has no functions allocated is reserved for future use and cannot be
used by users.
The special page vector table is allocated to the addresses from FFE00h to FFFDBh. This vector is used by
the JMPS or JSRS instruction. For details, refer to M16C/60, M16C/20, M16C/Tiny Series Software Manual.
In memory expansion and microprocessor modes, some areas are reserved for future use and cannot be
used by users.
Use T/V-ver. in single-chip mode. The memory expansion and microprocessor modes cannot be used.
00000h
SFR
Internal RAM
Capacity
16 Kbytes 043FF
20 Kbytes
31 Kbytes
Address XXXXX
053FF
07FFF
h
Capacity
h
192 Kbytes D0000
h
256 Kbytes C0000
h
384 Kbytes A0000
512 Kbytes 80000
Internal ROM
Address YYYYY
00400h
XXXXX
0F000h
0FFFFh
10000h
27000h
(1)
h
h
h
h
h
28000h
80000h
YYYYY
FFFFFh
h
Reserved area
Reserved area
h
(program area)
Internal RAM
Internal ROM
(data area)
External area
Reserved area
External area
Internal ROM
(1)
(3)
FFE00h
Special page
vector table
FFFDCh
(2)
(4)
FFFFFh
Undefined instruction
Overflow
BRK instruction
Address match
Single step
Oscillation stop and re-oscillation
detection / watchdog timer
DBC
NMI
Reset
NOTES:
1. During memory expansion mode or microprocessor mode, cannot be used.
2. In memory expansion mode, cannot be used.
3. As for the flash memory version, 4-Kbyte space (block A) exists.
4. When using the masked ROM version, write nothing to internal ROM area.
5. Shown here is a memory map for the case where the PM10 bit in the PM1 register is "1" (block A enabled, addresses 10000h to
26FFFh for CS2 area) and the PM13 bit in the PM1 register is "1" (internal RAM area is expanded over 192 Kbytes).
* Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
And not available external area in T/V-ver..
Figure 3.1 Memory Map
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 18 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 37

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
4. Special Function Register (SFR)
SFR (Special Function Register) is the control register of peripheral functions.
Tables 4.1 to 4.16 list the SFR information.
Table 4.1 SFR Information (1)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0000h
0001h
0002h
0003h
0004h
0005h
0006h
0007h
0008h
0009h
000Ah
000Bh
000Ch
000Dh
000Eh
000Fh
0010h
0011h
0012h
0013h
0014h
0015h
0016h
0017h
0018h
0019h
001Ah
001Bh
001Ch
001Dh
001Eh
001Fh
0020h
0021h
0022h
0023h
0024h
0025h
0026h
0027h
0028h
0029h
002Ah
002Bh
002Ch
002Dh
002Eh
002Fh
0030h
0031h
0032h
0033h
0034h
0035h
0036h
0037h
0038h
0039h
003Ah
003Bh
003Ch
003Dh
003Eh
003Fh
X: Undefined
Processor Mode Register 0
Processor Mode Register 1
System Clock Control Register 0
System Clock Control Register 1
Chip Select Control Register
Address Match Interrupt Enable Register
Protect Register
Oscillation Stop Detection Register
Watchdog Timer Start Register
Watchdog Timer Control Register
Address Match Interrupt Register 0
Address Match Interrupt Register 1
Chip Select Expansion Control Register
PLL Control Register 0
Processor Mode Register 2
DMA0 Source Pointer
DMA0 Destination Pointer
DMA0 Transfer Counter
DMA0 Control Register
DMA1 Source Pointer
DMA1 Destination Pointer
DMA1 Transfer Counter
DMA1 Control Register
(1)
(4)
(2)
PM0
PM1
CM0
CM1
CSR
AIER
PRCR
CM2
WDTS
WDC
RMAD0
RMAD1
(4)
CSE
PLC0
PM2
SAR0
DAR0
TCR0
DM0CON
SAR1
DAR1
TCR1
DM1CON
00000000b (CNVSS pin is "L")
00000011b (CNVSS pin is "H")
00001000b
01001000b
00100000b
00000001b
XXXXXX00b
XX000000b
0X000000b
XXh
00XXXXXXb
00h
00h
X0h
00h
00h
X0h
00h
0001X010b
XXX00000b
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
00000X00b
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
00000X00b
(3)
NOTES:
1. The PM00 and PM01 bits in the PM0 register do not change at software reset, watchdog timer reset and oscillation stop detection reset.
* Effective when memory expansion and microprocessor modes (= Normal-ver.).
2. The CM20, CM21, and CM27 bits in the CM2 register do not change at oscillation stop detection reset.
3. CNVSS pin = H is not available in T/V-ver.. Do not set a value.
4. These registers are not available in T/V-ver.
5. The blank areas are reserved and cannot be accessed by users.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 19 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 38

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.2 SFR Information (2)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0040h
0041h
0042h
0043h
0044h
0045h
0046h
0047h
0048h
0049h
004Ah
004Bh
004Ch
004Dh
004Eh
004Fh
0050h
0051h
0052h
0053h
0054h
0055h
0056h
0057h
0058h
0059h
005Ah
005Bh
005Ch
005Dh
005Eh
005Fh
0060h
0061h
0062h
0063h
0064h
0065h
0066h
0067h
0068h
0069h
006Ah
006Bh
006Ch
006Dh
006Eh
006Fh
0070h
0071h
0072h
0073h
0074h
0075h
0076h
0077h
0078h
0079h
007Ah
007Bh
007Ch
007Dh
007Eh
007Fh
X: Undefined
CAN0/1 Wake-up Interrupt Control Register
CAN0 Successful Reception Interrupt Control Register
CAN0 Successful Transmission Interrupt Control Register
INT3 Interrupt Control Register
Timer B5 Interrupt Control Register
SI/O5 Interrupt Control Register
Timer B4 Interrupt Control Register
UART1 Bus Collision Detection Interrupt Control Register
Timer B3 Interrupt Control Register
UART0 Bus Collision Detection Interrupt Control Register
CAN1 Successful Reception Interrupt Control Register
SI/O4 Interrupt Control Register
INT5 Interrupt Control Register
CAN1 Successful Transmission Interrupt Control Register
SI/O3 Interrupt Control Register
INT4 Interrupt Control Register
UART2 Bus Collision Detection Interrupt Control Register
DMA0 Interrupt Control Register
DMA1 Interrupt Control Register
CAN0/1 Error Interrupt Control Register
A/D Conversion Interrupt Control Register
Key Input Interrupt Control Register
UART2 Transmit Interrupt Control Register
UART2 Receive Interrupt Control Register
UART0 Transmit Interrupt Control Register
UART0 Receive Interrupt Control Register
UART1 Transmit Interrupt Control Register
UART1 Receive Interrupt Control Register
Timer A0 Interrupt Control Register
Timer A1 Interrupt Control Register
Timer A2 Interrupt Control Register
INT7 Interrupt Control Register
Timer A3 Interrupt Control Register
INT6 Interrupt Control Register
Timer A4 Interrupt Control Register
Timer B0 Interrupt Control Register
SI/O6 Interrupt Control Register
Timer B1 Interrupt Control Register
INT8 Interrupt Control Register
Timer B2 Interrupt Control Register
INT0 Interrupt Control Register
INT1 Interrupt Control Register
INT2 Interrupt Control Register
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
CAN0 Message Box 0: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 0: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 0: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 1: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 1: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 1: Time Stamp
C01WKIC
C0RECIC
C0TRMIC
INT3IC
TB5IC
S5IC
TB4IC
U1BCNIC
TB3IC
U0BCNIC
C1RECIC
S4IC
INT5IC
C1TRMIC
S3IC
INT4IC
U2BCNIC
DM0IC
DM1IC
C01ERRIC
ADIC
KUPIC
S2TIC
S2RIC
S0TIC
S0RIC
S1TIC
S1RIC
TA0IC
TA1IC
TA2IC
INT7IC
TA3IC
INT6IC
TA4IC
TB0IC
S6IC
TB1IC
INT8IC
TB2IC
INT0IC
INT1IC
INT2IC
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XX00X000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XX00X000b
XX00X000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XX00X000b
XX00X000b
XXXXX000b
XXXXX000b
XX00X000b
XXXXX000b
XX00X000b
XX00X000b
XX00X000b
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
NOTES:
1. These registers exist only in the 128-pin version.
2. The blank area is reserved and cannot be accessed by users.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 20 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 39

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.3 SFR Information (3)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0080h
0081h
0082h
0083h
0084h
0085h
0086h
0087h
0088h
0089h
008Ah
008Bh
008Ch
008Dh
008Eh
008Fh
0090h
0091h
0092h
0093h
0094h
0095h
0096h
0097h
0098h
0099h
009Ah
009Bh
009Ch
009Dh
009Eh
009Fh
00A0h
00A1h
00A2h
00A3h
00A4h
00A5h
00A6h
00A7h
00A8h
00A9h
00AAh
00ABh
00ACh
00ADh
00AEh
00AFh
00B0h
00B1h
00B2h
00B3h
00B4h
00B5h
00B6h
00B7h
00B8h
00B9h
00BAh
00BBh
00BCh
00BDh
00BEh
00BFh
X: Undefined
CAN0 Message Box 2: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 2: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 2: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 3: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 3: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 3: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 4: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 4: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 4: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 5: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 5: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 5: Time Stamp
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 21 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 40

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.4 SFR Information (4)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
00C0h
00C1h
00C2h
00C3h
00C4h
00C5h
00C6h
00C7h
00C8h
00C9h
00CAh
00CBh
00CCh
00CDh
00CEh
00CFh
00D0h
00D1h
00D2h
00D3h
00D4h
00D5h
00D6h
00D7h
00D8h
00D9h
00DAh
00DBh
00DCh
00DDh
00DEh
00DFh
00E0h
00E1h
00E2h
00E3h
00E4h
00E5h
00E6h
00E7h
00E8h
00E9h
00EAh
00EBh
00ECh
00EDh
00EEh
00EFh
00F0h
00F1h
00F2h
00F3h
00F4h
00F5h
00F6h
00F7h
00F8h
00F9h
00FAh
00FBh
00FCh
00FDh
00FEh
00FFh
X: Undefined
CAN0 Message Box 6: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 6: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 6: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 7: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 7: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 7: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 8: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 8: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 8: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 9: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 9: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 9: Time Stamp
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 22 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 41

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.5 SFR Information (5)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0100h
0101h
0102h
0103h
0104h
0105h
0106h
0107h
0108h
0109h
010Ah
010Bh
010Ch
010Dh
010Eh
010Fh
0110h
0111 h
0112h
0113h
0114h
0115h
0116h
0117h
0118h
0119h
011Ah
011Bh
011Ch
011Dh
011Eh
011Fh
0120h
0121h
0122h
0123h
0124h
0125h
0126h
0127h
0128h
0129h
012Ah
012Bh
012Ch
012Dh
012Eh
012Fh
0130h
0131h
0132h
0133h
0134h
0135h
0136h
0137h
0138h
0139h
013Ah
013Bh
013Ch
013Dh
013Eh
013Fh
X: Undefined
CAN0 Message Box 10: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 10: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 10: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 11: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 11: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 11: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 12: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 12: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 12: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 13: Identifier / DLC
CAN0 Message Box 13: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 13: Time Stamp
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 23 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 42

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.6 SFR Information (6)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0140h
0141h
0142h
0143h
0144h
0145h
0146h
0147h
0148h
0149h
014Ah
014Bh
014Ch
014Dh
014Eh
014Fh
0150h
0151h
0152h
0153h
0154h
0155h
0156h
0157h
0158h
0159h
015Ah
015Bh
015Ch
015Dh
015Eh
015Fh
0160h
0161h
0162h
0163h
0164h
0165h
0166h
0167h
0168h
0169h
016Ah
016Bh
016Ch
016Dh
016Eh
016Fh
0170h
0171h
0172h
0173h
0174h
0175h
0176h
0177h
0178h
0179h
017Ah
017Bh
017Ch
017Dh
017Eh
017Fh
X: Undefined
CAN0 Message Box 14: Identifier /DLC
CAN0 Message Box 14: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 14: Time Stamp
CAN0 Message Box 15: Identifier /DLC
CAN0 Message Box 15: Data Field
CAN0 Message Box 15: Time Stamp
CAN0 Global Mask Register
CAN0 Local Mask A Register
CAN0 Local Mask B Register
C0GMR
C0LMAR
C0LMBR
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
NOTE:
1. The blank areas are reserved and cannot be accessed by users.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 24 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 43

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.7 SFR Information (7)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0180h
0181h
0182h
0183h
0184h
0185h
0186h
0187h
0188h
0189h
018Ah
018Bh
018Ch
018Dh
018Eh
018Fh
0190h
0191h
0192h
0193h
0194h
0195h
0196h
0197h
0198h
0199h
019Ah
019Bh
019Ch
019Dh
019Eh
019Fh
01A0h
01A1h
01A2h
01A3h
01A4h
01A5h
01A6h
01A7h
01A8h
01A9h
01AAh
01ABh
01ACh
01ADh
01AEh
01AFh
01B0h
01B1h
01B2h
01B3h
01B4h
01B5h
01B6h
01B7h
01B8h
01B9h
01BAh
01BBh
01BCh
01BDh
01BEh
01BFh
X: Undefined
Flash Memory Control Register 1
Flash Memory Control Register 0
Address Match Interrupt Register 2
Address Match Interrupt Enable Register 2
Address Match Interrupt Register 3
(1)
(1)
FMR1
FMR0
RMAD2
AIER2
RMAD3
0X00XX0Xb
00000001b
00h
00h
X0h
XXXXXX00b
00h
00h
X0h
NOTES:
1. These registers are included in the flash memory version. Cannot be accessed by users in the mask ROM version.
2. The blank areas are reserved and cannot be accessed by users.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 25 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 44

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.8 SFR Information (8)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
01C0h
Timer B3, B4, B5 Count Start Flag
TBSR
01C1h
01C2h
01C3h
01C4h
01C5h
01C6h
01C7h
01C8h
01C9h
01CAh
01CBh
01CCh
01CDh
Timer A1-1 Register
Timer A2-1 Register
Timer A4-1 Register
Three-Phase PWM Control Register 0
Three-Phase PWM Control Register 1
Three-Phase Output Buffer Register 0
Three-Phase Output Buffer Register 1
Dead Time Timer
Timer B2 Interrupt Occurrence Frequency Set Counter
TA11
TA21
TA41
INVC0
INVC1
IDB0
IDB1
DTT
ICTB2
01CEh
01CFh
01D0h
01D1h
01D2h
01D3h
01D4h
01D5h
01D6h
01D7h
01D8h
01D9h
01DAh
01DBh
01DCh
01DDh
01DEh
01DFh
01E0h
Interrupt Cause Select Register 2
Timer B3 Register
Timer B4 Register
Timer B5 Register
SI/O6 Transmit/Receive Register
SI/O6 Control Register
(1)
SI/O6 Bit Rate Generator
(1)
(1)
SI/O3, 4, 5, 6 Transmit/Receive Register
Timer B3 Mode Register
Timer B4 Mode Register
Timer B5 Mode Register
Interrupt Cause Select Register 0
Interrupt Cause Select Register 1
SI/O3 Transmit/Receive Register
(2)
IFSR2
TB3
TB4
TB5
S6TRR
S6C
S6BRG
S3456TRR
TB3MR
TB4MR
TB5MR
IFSR0
IFSR1
S3TRR
01E1h
01E2h
01E3h
01E4h
SI/O3 Control Register
SI/O3 Bit Rate Generator
SI/O4 Transmit/Receive Register
S3C
S3BRG
S4TRR
01E5h
01E6h
01E7h
01E8h
01E9h
01EAh
01EBh
01ECh
01EDh
01EEh
01EFh
01F0h
01F1h
01F2h
01F3h
01F4h
01F5h
01F6h
01F7h
01F8h
01F9h
01FAh
01FBh
01FCh
01FDh
01FEh
01FFh
SI/O4 Control Register
SI/O4 Bit Rate Generator
SI/O5 Transmit/Receive Register
SI/O5 Control Register
(1)
SI/O5 Bit Rate Generator
(1)
(1)
UART0 Special Mode Register 4
UART0 Special Mode Register 3
UART0 Special Mode Register 2
UART0 Special Mode Register
UART1 Special Mode Register 4
UART1 Special Mode Register 3
UART1 Special Mode Register 2
UART1 Special Mode Register
UART2 Special Mode Register 4
UART2 Special Mode Register 3
UART2 Special Mode Register 2
UART2 Special Mode Register
UART2 Transmit/Receive Mode Register
UART2 Bit Rate Generator
UART2 Transmit Buffer Register
UART2 Transmit/Receive Control Register 0
UART2 Transmit/Receive Control Register 1
UART2 Receive Buffer Register
S4C
S4BRG
S5TRR
S5C
S5BRG
U0SMR4
U0SMR3
U0SMR2
U0SMR
U1SMR4
U1SMR3
U1SMR2
U1SMR
U2SMR4
U2SMR3
U2SMR2
U2SMR
U2MR
U2BRG
U2TB
U2C0
U2C1
U2RB
X: Undefined
000XXXXXb
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
00h
00h
XXh
XXh
X0000000b
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
01000000b
XXh
XXXX0000b
00XX0000b
00XX0000b
00XX0000b
00h
00h
XXh
01000000b
XXh
XXh
01000000b
XXh
XXh
01000000b
XXh
00h
000X0X0Xb
X0000000b
X0000000b
00h
000X0X0Xb
X0000000b
X0000000b
00h
000X0X0Xb
X0000000b
X0000000b
00h
XXh
XXh
XXh
00001000b
00000010b
XXh
XXh
NOTES:
1. These registers exist only in the 128-pin version.
2. The S5TRF and S6TRF bits in the S3456TRR register are used in the 128-pin version.
3. The blank areas are reserved and cannot be accessed by users.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 26 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 45

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.9 SFR Information (9)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0200h
0201h
0202h
0203h
0204h
0205h
0206h
0207h
0208h
0209h
020Ah
020Bh
020Ch
020Dh
020Eh
020Fh
0210h
0211h
0212h
0213h
0214h
0215h
0216h
0217h
0218h
0219h
021Ah
021Bh
021Ch
021Dh
021Eh
021Fh
0220h
0221h
0222h
0223h
0224h
0225h
0226h
0227h
0228h
0229h
022Ah
022Bh
022Ch
022Dh
022Eh
022Fh
0230h
0231h
0232h
0233h
0234h
0235h
0236h
0237h
0238h
0239h
023Ah
023Bh
023Ch
023Dh
023Eh
023Fh
X: Undefined
CAN0 Message Control Register 0
CAN0 Message Control Register 1
CAN0 Message Control Register 2
CAN0 Message Control Register 3
CAN0 Message Control Register 4
CAN0 Message Control Register 5
CAN0 Message Control Register 6
CAN0 Message Control Register 7
CAN0 Message Control Register 8
CAN0 Message Control Register 9
CAN0 Message Control Register 10
CAN0 Message Control Register 11
CAN0 Message Control Register 12
CAN0 Message Control Register 13
CAN0 Message Control Register 14
CAN0 Message Control Register 15
CAN0 Control Register
CAN0 Status Register
CAN0 Slot Status Register
CAN0 Interrupt Control Register
CAN0 Extended ID Register
CAN0 Configuration Register
CAN0 Receive Error Count Register
CAN0 Transmit Error Count Register
CAN0 Time Stamp Register
CAN1 Message Control Register 0
CAN1 Message Control Register 1
CAN1 Message Control Register 2
CAN1 Message Control Register 3
CAN1 Message Control Register 4
CAN1 Message Control Register 5
CAN1 Message Control Register 6
CAN1 Message Control Register 7
CAN1 Message Control Register 8
CAN1 Message Control Register 9
CAN1 Message Control Register 10
CAN1 Message Control Register 11
CAN1 Message Control Register 12
CAN1 Message Control Register 13
CAN1 Message Control Register 14
CAN1 Message Control Register 15
CAN1 Control Register
CAN1 Status Register
CAN1 Slot Status Register
CAN1 Interrupt Control Register
CAN1 Extended ID Register
CAN1 Configuration Register
CAN1 Receive Error Count Register
CAN1 Transmit Error Count Register
CAN1 Time Stamp Register
C0MCTL0
C0MCTL1
C0MCTL2
C0MCTL3
C0MCTL4
C0MCTL5
C0MCTL6
C0MCTL7
C0MCTL8
C0MCTL9
C0MCTL10
C0MCTL11
C0MCTL12
C0MCTL13
C0MCTL14
C0MCTL15
C0CTLR
C0STR
C0SSTR
C0ICR
C0IDR
C0CONR
C0RECR
C0TECR
C0TSR
C1MCTL0
C1MCTL1
C1MCTL2
C1MCTL3
C1MCTL4
C1MCTL5
C1MCTL6
C1MCTL7
C1MCTL8
C1MCTL9
C1MCTL10
C1MCTL11
C1MCTL12
C1MCTL13
C1MCTL14
C1MCTL15
C1CTLR
C1STR
C1SSTR
C1ICR
C1IDR
C1CONR
C1RECR
C1TECR
C1TSR
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
X0000001b
XX0X0000b
00h
X0000001b
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
X0000001b
XX0X0000b
00h
X0000001b
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
00h
00h
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 27 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 46

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.10 SFR Information (10)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0240h
0241h
0242h
0243h
0244h
0245h
0246h
0247h
0248h
0249h
024Ah
024Bh
024Ch
024Dh
024Eh
024Fh
0250h
0251h
0252h
0253h
0254h
0255h
0256h
0257h
0258h
0259h
025Ah
025Bh
025Ch
025Dh
025Eh
025Fh
0260h
0261h
0262h
0263h
0264h
0265h
0266h
0267h
0268h
0269h
026Ah
026Bh
026Ch
026Dh
026Eh
026Fh
0270h
0271h
0272h
0273h
0274h
0275h
0276h
0277h
0278h
0279h
027Ah
027Bh
027Ch
027Dh
027Eh
027Fh
X: Undefined
CAN0 Acceptance Filter Support Register
CAN1 Acceptance Filter Support Register
Peripheral Clock Select Register
CAN0/1 Clock Select Register
CAN1 Message Box 0: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 0: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 0:Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 1: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 1: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 1:Time Stamp
C0AFS
C1AFS
PCLKR
CCLKR
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
NOTE:
1. The blank areas are reserved and cannot be accessed by users.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 28 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 47

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.11 SFR Information (11)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0280h
0281h
0282h
0283h
0284h
0285h
0286h
0287h
0288h
0289h
028Ah
028Bh
028Ch
028Dh
028Eh
028Fh
0290h
0291h
0292h
0293h
0294h
0295h
0296h
0297h
0298h
0299h
029Ah
029Bh
029Ch
029Dh
029Eh
029Fh
02A0h
02A1h
02A2h
02A3h
02A4h
02A5h
02A6h
02A7h
02A8h
02A9h
02AAh
02ABh
02ACh
02ADh
02AEh
02AFh
02B0h
02B1h
02B2h
02B3h
02B4h
02B5h
02B6h
02B7h
02B8h
02B9h
02BAh
02BBh
02BCh
02BDh
02BEh
02BFh
X: Undefined
CAN1 Message Box 2: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 2: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 2: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 3: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 3: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 3: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 4: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 4: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 4: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 5: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 5: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 5: Time Stamp
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 29 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 48

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.12 SFR Information (12)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
02C0h
02C1h
02C2h
02C3h
02C4h
02C5h
02C6h
02C7h
02C8h
02C9h
02CAh
02CBh
02CCh
02CDh
02CEh
02CFh
02D0h
02D1h
02D2h
02D3h
02D4h
02D5h
02D6h
02D7h
02D8h
02D9h
02DAh
02DBh
02DCh
02DDh
02DEh
02DFh
02E0h
02E1h
02E2h
02E3h
02E4h
02E5h
02E6h
02E7h
02E8h
02E9h
02EAh
02EBh
02ECh
02EDh
02EEh
02EFh
02F0h
02F1h
02F2h
02F3h
02F4h
02F5h
02F6h
02F7h
02F8h
02F9h
02FAh
02FBh
02FCh
02FDh
02FEh
02FFh
X: Undefined
CAN1 Message Box 6: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 6: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 6: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 7: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 7: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 7: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 8: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 8: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 8: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 9: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 9: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 9: Time Stamp
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 30 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 49

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.13 SFR Information (13)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0300h
0301h
0302h
0303h
0304h
0305h
0306h
0307h
0308h
0309h
030Ah
030Bh
030Ch
030Dh
030Eh
030Fh
0310h
0311h
0312h
0313h
0314h
0315h
0316h
0317h
0318h
0319h
031Ah
031Bh
031Ch
031Dh
031Eh
031Fh
0320h
0321h
0322h
0323h
0324h
0325h
0326h
0327h
0328h
0329h
032Ah
032Bh
032Ch
032Dh
032Eh
032Fh
0330h
0331h
0332h
0333h
0334h
0335h
0336h
0337h
0338h
0339h
033Ah
033Bh
033Ch
033Dh
033Eh
033Fh
X: Undefined
CAN1 Message Box 10: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 10: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 10: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 11: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 11: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 11: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 12: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 12: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 12: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 13: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 13: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 13: Time Stamp
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 31 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 50
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.14 SFR Information (14)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0340h
0341h
0342h
0343h
0344h
0345h
0346h
0347h
0348h
0349h
034Ah
034Bh
034Ch
034Dh
034Eh
034Fh
0350h
0351h
0352h
0353h
0354h
0355h
0356h
0357h
0358h
0359h
035Ah
035Bh
035Ch
035Dh
035Eh
035Fh
0360h
0361h
0362h
0363h
0364h
0365h
0366h
0367h
0368h
0369h
036Ah
036Bh
036Ch
036Dh
036Eh
036Fh
0370h
0371h
0372h
0373h
0374h
0375h
0376h
0377h
0378h
0379h
037Ah
037Bh
037Ch
037Dh
037Eh
037Fh
X: Undefined
CAN1 Message Box 14: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 14: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 14: Time Stamp
CAN1 Message Box 15: Identifier / DLC
CAN1 Message Box 15: Data Field
CAN1 Message Box 15: Time Stamp
CAN1 Global Mask Register
CAN1 Local Mask A Register
CAN1 Local Mask B Register
C1GMR
C1LMAR
C1LMBR
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
NOTE:
1. The blank areas are reserved and cannot be accessed by users.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 32 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 51

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.15 SFR Information (15)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
0380h
0381h
0382h
0383h
0384h
0385h
0386h
0387h
0388h
0389h
038Ah
038Bh
038Ch
038Dh
038Eh
038Fh
0390h
0391h
0392h
0393h
0394h
0395h
0396h
0397h
0398h
0399h
039Ah
039Bh
039Ch
039Dh
039Eh
039Fh
03A0h
03A1h
03A2h
03A3h
03A4h
03A5h
03A6h
03A7h
03A8h
03A9h
03AAh
03ABh
03ACh
03ADh
03AEh
03AFh
03B0h
03B1h
03B2h
03B3h
03B4h
03B5h
03B6h
03B7h
03B8h
03B9h
03BAh
03BBh
03BCh
03BDh
03BEh
03BFh
X: Undefined
Count Start Flag
Clock Prescaler Reset Flag
One-Shot Start Flag
Trigger Select Register
Up/Down Flag
Timer A0 Register
Timer A1 Register
Timer A2 Register
Timer A3 Register
Timer A4 Register
Timer B0 Register
Timer B1 Register
Timer B2 Register
Timer A0 Mode Register
Timer A1 Mode Register
Timer A2 Mode Register
Timer A3 Mode Register
Timer A4 Mode Register
Timer B0 Mode Register
Timer B1 Mode Register
Timer B2 Mode Register
Timer B2 Special Mode Register
UART0 Transmit/Receive Mode Register
UART0 Bit Rate Generator
UART0 Transmit Buffer Register
UART0 Transmit/Receive Control Register 0
UART0 Transmit/Receive Control Register 1
UART0 Receive Buffer Register
UART1 Transmit/Receive Mode Register
UART1 Bit Rate Generator
UART1 Transmit Buffer Register
UART1 Transmit/Receive Control Register 0
UART1 Transmit/Receive Control Register 1
UART1 Receive Buffer Register
UART Transmit/Receive Control Register 2
DMA0 Request Cause Select Register
DMA1 Request Cause Select Register
CRC Data Register
CRC Input Register
TABSR
CPSRF
ONSF
TRGSR
UDF
TA0
TA1
TA2
TA3
TA4
TB0
TB1
TB2
TA0MR
TA1MR
TA2MR
TA3MR
TA4MR
TB0MR
TB1MR
TB2MR
TB2SC
U0MR
U0BRG
U0TB
U0C0
U0C1
U0RB
U1MR
U1BRG
U1TB
U1C0
U1C1
U1RB
UCON
DM0SL
DM1SL
CRCD
CRCIN
00h
0XXXXXXXb
00h
00h
(1)
00h
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
00h
00h
00h
00XX0000b
00XX0000b
00XX0000b
XXXXXX00b
00h
XXh
XXh
XXh
00001000b
00XX0010b
XXh
XXh
00h
XXh
XXh
XXh
00001000b
00XX0010b
XXh
XXh
X0000000b
00h
00h
XXh
XXh
XXh
NOTES:
1. The TA2P to TA4P bits in the UDF register are set to "0" after reset. However, the contents in these bits are indeterminate when read.
2. The blank areas are reserved and cannot be accessed by users.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 33 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 52

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 4. Special Function Register (SFR)
Table 4.16 SFR Information (16)
Address Register Symbol After Reset
03C0h
03C1h
03C2h
03C3h
03C4h
03C5h
03C6h
03C7h
03C8h
03C9h
03CAh
03CBh
03CCh
03CDh
03CEh
03CFh
A/D Register 0
A/D Register 1
A/D Register 2
A/D Register 3
A/D Register 4
A/D Register 5
A/D Register 6
A/D Register 7
AD0
AD1
AD2
AD3
AD4
AD5
AD6
AD7
03D0h
03D1h
03D2h
03D3h
03D4h
A/D Control Register 2
ADCON2
03D5h
03D6h
03D7h
03D8h
A/D Control Register 0
A/D Control Register 1
D/A Register 0
ADCON0
ADCON1
DA0
03D9h
03DAh
D/A Register 1
DA1
03DBh
03DCh
03DDh
03DEh
03DFh
03E0h
03E1h
03E2h
03E3h
03E4h
03E5h
03E6h
03E7h
03E8h
03E9h
03EAh
03EBh
03ECh
03EDh
03EEh
03EFh
03F0h
03F1h
03F2h
03F3h
03F4h
03F5h
03F6h
03F7h
03F8h
03F9h
03FAh
03FBh
03FCh
03FDh
03FEh
03FFh
D/A Control Register
Port P14 Control Register
Pull-Up Control Register 3
Port P0 Register
Port P1 Register
Port P0 Direction Register
Port P1 Direction Register
Port P2 Register
Port P3 Register
Port P2 Direction Register
Port P3 Direction Register
Port P4 Register
Port P5 Register
Port P4 Direction Register
Port P5 Direction Register
Port P6 Register
Port P7 Register
Port P6 Direction Register
Port P7 Direction Register
Port P8 Register
Port P9 Register
Port P8 Direction Register
Port P9 Direction Register
Port P10 Register
Port P11 Register
(1)
Port P10 Direction Register
Port P11 Direction Register
Port P12 Register
Port P13 Register
(1)
(1)
Port P12 Direction Register
Port P13 Direction Register
Pull-up Control Register 0
Pull-up Control Register 1
Pull-up Control Register 2
Port Control Register
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
DACON
PC14
PUR3
P0
P1
PD0
PD1
P2
P3
PD2
PD3
P4
P5
PD4
PD5
P6
P7
PD6
PD7
P8
P9
PD8
PD9
P10
P11
PD10
PD11
P12
P13
PD12
PD13
PUR0
PUR1
PUR2
PCR
X: Undefined
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
XXh
00h
00000XXXb
00h
00h
00h
00h
XX00XXXXb
00h
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
XXh
XXh
00X00000b
00h
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
XXh
XXh
00h
00h
00h
00000000b
00000010b
00h
00h
(1)
NOTES:
1. At hardware reset, the register is as follows:
"00000000b" where "L" is input to the CNVSS pin
"00000010b" where "H" is input to the CNVSS pin (CNVSS pin = H is not available in T/V-ver..)
At software reset, watchdog timer reset and oscillation stop detection reset, the register is as follows:
"00000000b" where the PM01 to PM00 bits in the PM0 register are "00b" (single-chip mode)
"00000010b" where the PM01 to PM00 bits in the PM0 register are "01b" (memory expansion mode) or "11b" (microprocessor mode)
* Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
2. These registers exist only in the128-pin version.
3. The blank areas are reserved and cannot be accessed by users.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 34 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 53
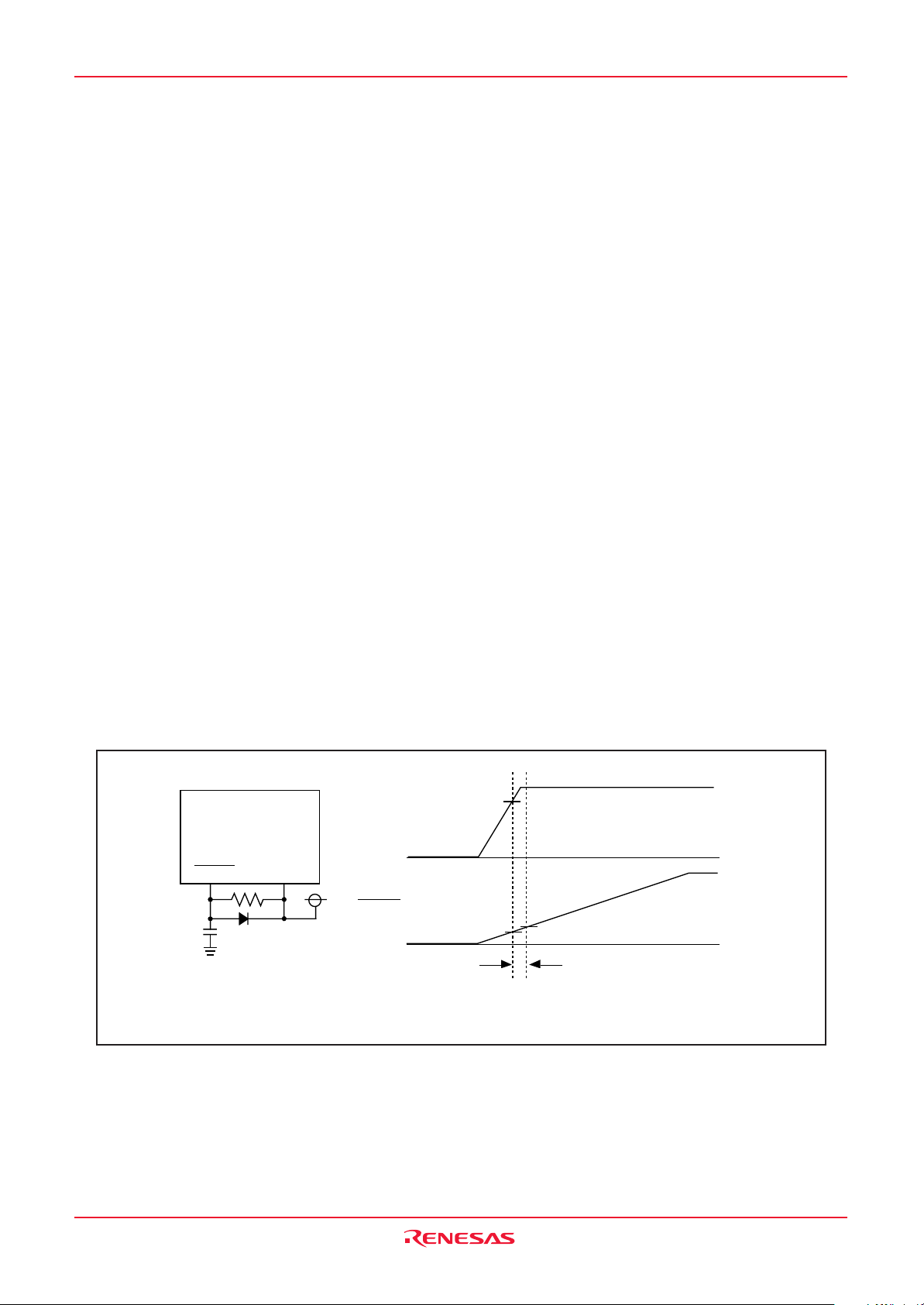
Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 5. Reset
5. Reset
Hardware reset, software reset, watchdog timer reset and oscillation stop detection reset are available to
reset the microcomputer.
5.1 Hardware Reset
____________
The microcomputer resets pins, the CPU and SFR by setting the RESET pin. If the supply voltage meets
the recommended operating conditions, the microcomputer resets all pins when an “L” signal is applied to
___________ ____________
the RESET pin (see Table 5.1 Pin Status When RESET Pin Level is “L”). The oscillation circuit is also
reset and the main clock starts oscillation. The microcomputer resets the CPU and SFR when the signal
____________
applied to the RESET pin changes low (“L”) to high (“H”). The microcomputer executes the program in an
address indicated by the reset vector. The internal RAM is not reset. When an “L” signal is applied to the
____________
RESET pin while writing data to the internal RAM, the internal RAM is in an indeterminate state.
Figure 5.1 shows an example of the reset circuit. Figure 5.2 shows a reset sequence. Table 5.1 lists pin
____________
states while the RESET pin is held low (“L”).
5.1.1 Reset on a Stable Supply Voltage
____________
(1) Apply “L” to the RESET pin
(2) Apply 20 or more clock cycles to the XIN pin
____________
(3) Apply “H” to the RESET pin
5.1.2 Power-on Reset
____________
(1) Apply “L” to the RESET pin
(2) Raise the supply voltage to the recommended operating level
(3) Insert td(P-R) ms as wait time for the internal voltage to stabilize
(4) Apply 20 or more clock cycles to the XIN pin
____________
(5) Apply “H” to the RESET pin
RESET
NOTE
1. Use the shortest possible wiring to connect external circuit.
VCC
Figure 5.1 Example Reset Circuit
VCC
0 V
R E S E T
0 V
v o l t a g
Re c o m m e n d e d
operation
e
0.2VCC or
below
0.2VCC or below
Supply a clock with td(P-R) +20
or more cycles to the XIN pin
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 35 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 54

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 5. Reset
VCC
XIN
td(P-R) More than
20 cycles
are needed
RESET
BCLK
Microprocessor
mode BYTE = H
Address
RD
WR
CS0
Microprocessor
mode BYTE = L
Address
RD
(1)
(1)
BCLK 28cycles
Content of reset vector
FFFFCh FFFFDh FFFFEh
Content of reset vector
FFFFCh FFFFEh
WR
CS0
Single-chip
mode
Addres
s
NOTE:
1. Not available in T/V-ver.
FFFFCh
Content of reset vector
FFFFEh
Figure 5.2 Reset Sequence
____________
Table 5.1 Pin Status When RESET Pin Level is “L”
Status
Pin Name
CNVSS = VSS
CNVSS = VCC
BYTE = VSS BYTE = VCC
(1)
P0 Input port Data input Data input
P1 Input port Data input Input port
P2, P3, P4_0 to P4_3 Input port Address output (undefined) Address output (undefined)
P4_4 Input port
P4_5 to P4_7 Input port Input port (Pulled high) Input port (Pulled high)
P5_0 Input port
P5_1 Input port
P5_2 Input port
P5_3 Input port BCLK output BCLK output
P5_4 Input port
P5_5 Input port
P5_6 Input port ALE output (“L” is output) ALE output (“L” is output)
P5_7 Input port
______
CS0 output (“H” is output)
______
WR output (“H” is output)
________
BHE output (undefined)
______
RD output (“H” is output)
___________
HLDA output
(The output value depends on (The output value depends on
the input to the HOLD pin)
__________
__________
HOLD input
________
RDY input
______
CS0 output (“H” is output)
______
WR output (“H” is output)
________
BHE output (undefined)
______
RD output (“H” is output)
___________
HLDA output
__________
the input to the HOLD pin)
__________
HOLD input
________
RDY input
P6, P7, P8_0 to P8_4, Input port Input port Input port
P8_6, P8_7, P9, P10
P11, P12, P13, Input port Input port Input port
P14_0, P14_1
(2)
NOTES:
1. Shown here is the valid pin state when the internal power supply voltage has stabilized after power-on.
When CNVSS = VCC, the pin state is indeterminate until the internal power supply voltage stabilizes.
* CNVSS = VCC is not available in T/V-ver..
2. P11, P12, P13, P14_0 and P14_1 pins are only in the 128-pin version.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 36 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 55

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 5. Reset
5.2 Software Reset
The microcomputer resets pins, the CPU and SFR when the PM03 bit in the PM0 register is set to “1”
(microcomputer reset). Then the microcomputer executes the program in an address determined by the reset vector.
Set the PM03 bit to “1” while the main clock is selected as the CPU clock and the main clock oscillation is stable.
In the software reset, the microcomputer does not reset a part of the SFR. Refer to 4. Special Function
Register (SFR) for details.
Processor mode remains unchanged since the PM01 to PM00 bits in the PM0 register are not reset.
5.3 Watchdog Timer Reset
The microcomputer resets pins, the CPU and SFR when the PM12 bit in the PM1 register is set to “1” (reset
when watchdog timer underflows) and the watchdog timer underflows. Then the microcomputer executes
the program in an address determined by the reset vector.
In the watchdog timer reset, the microcomputer does not reset a part of the SFR. Refer to 4. Special
Function Register (SFR) for details.
Processor mode remains unchanged since the PM01 to PM00 bits in the PM0 register are not reset.
5.4 Oscillation Stop Detection Reset
The microcomputer resets and stops pins, the CPU and SFR when the CM27 bit in the CM2 register is “0”
(reset at oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection), if it detects main clock oscillation circuit stop. Refer to 8.5
Oscillation Stop and Re-Oscillation Detection Function for details.
In the oscillation stop detection reset, the microcomputer does not reset a part of the SFR. Refer to 4. Special
Function Register (SFR) for details.
Processor mode remains unchanged since the PM01 to PM00 bits in the PM0 register are not reset.
5.5 Internal Space
Figure 5.3 shows CPU register status after reset. Refer to 4. Special Function Register (SFR) for SFR
states after reset.
b15 b0
0000h
0000h
0000h
0000h
0000h
0000h
0000h
b19
00000h
Content of addresses FFFFEh to FFFFCh
b15 b0
0000h
0000h
0000h
b15 b0
0000h
b15 b0
b7b8
Data Register (R0)
Data Register (R1)
Data Register (R2)
Data Register (R3)
Address Register (A0)
Address Register (A1)
Frame Base Register (FB)
b0
Interrupt Table Register (INTB)
Program Counter (PC)
User Stack Pointer (USP)
Interrupt Stack Pointer (ISP)
Static Base Register (SB)
Flag Register (FLG)
IPL U I O B S Z D C
Figure 5.3 CPU Register Status After Reset
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 37 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 56

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 6. Processor Mode
6. Processor Mode
Note
6. Processor Mode explains as an example of a Normal-ver..
T/V-ver. is available single-chip mode only. Not available memory expansion mode and microprocessor
mode.
6.1 Types of Processor Mode
Three processor modes are available to choose from: single-chip mode, memory expansion mode, and
microprocessor mode. (Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..)
Table 6.1 shows the features of these processor modes.
Table 6.1 Features of Processor Modes
Processor Mode Access Space Pins Which are Assigned I/O Ports
Single-chip Mode SFR, internal RAM, internal ROM All pins are I/O ports or
peripheral function I/O pins
Memory Expansion Mode
Microprocessor Mode
NOTES:
1. Refer to 7. Bus.
2. Not available in T/V-ver..
(2)
SFR, internal RAM, internal ROM, Some pins serve as bus control pins
external area
(2)
SFR, internal RAM, external area
(1)
(1)
Some pins serve as bus control pins
(1)
(1)
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 38 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 57

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 6. Processor Mode
6.2 Setting Processor Modes
Processor mode is set by using the CNVSS pin and the PM01 to PM00 bits in the PM0 register.
Table 6.2 shows the processor mode after hardware reset. Table 6.3 shows the PM01 to PM00 bits set
values and processor modes.
Table 6.2 Processor Mode After Hardware Reset
CNVSS Pin Input Level Processor Mode
VSS Single-chip mode
(1) (2) (3)
VCC
NOTES:
1. If the microcomputer is reset in hardware by applying VCC to the CNVSS pin, the internal ROM
cannot be accessed regardless of PM01 to PM00 bits.
2.
The multiplexed bus cannot be assigned to the entire CS space.
3. Not available in T/V-ver.. Do not set a value.
Table 6.3 PM01 to PM00 Bits Set Values and Processor Modes
PM01 to PM 00 Bits Processor Mode
00b Single-chip mode
(1)
01b
10b Do not set a value
(1)
11b
NOTE:
1. Not available in T/V-ver.. Do not set a value.
Microprocessor mode
_____
Memory expansion mode
Microprocessor mode
Rewriting the PM01 to PM00 bits places the microcomputer in the corresponding processor mode regardless of
whether the input level on the CNVSS pin is “H” or “L”. Note, however, that the PM01 to PM00 bits cannot
be rewritten to “01b” (memory expansion mode) or “11b” (microprocessor mode)
(1)
at the same time the
PM07 to PM02 bits are rewritten. Note also that these bits cannot be rewritten to enter microprocessor
mode in the internal ROM, nor can they be rewritten to exit microprocessor mode in areas overlapping the
internal ROM.
NOTE:
1. Not available memory expansion and mocroprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
If the microcomputer is reset in hardware by applying VCC to the CNVSS pin (hardware reset), the internal
ROM cannot be accessed regardless of PM01 to PM00 bits.
Figures 6.1 and 6.2 show the processor mode related registers. Figure 6.3 shows the memory map in
_____
single-chip mode. Figures 6.4 to 6.7 show the memory map and CS area in memory expansion mode and
microprocessor mode (Normal-ver. only).
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 39 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 58

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 6. Processor Mode
Processor Mode Register 0
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
(1)
Symbol Address
PM0 0004h
Bit symbol
Bit name Function
PM00
Processor Mode Bit
PM01
PM02
PM03
R/W Mode Select Bit
Software Reset Bit
PM04
Multiplexed Bus Space
Select Bit
(3)
PM05
PM06
PM07
Port P4_0 to P4_3 Function
Select Bit
(3))
BCLK Output Disable
(3)
Bit
(2)
After reset
00000000b (CNVSS pin = L)
00000011b (CNVSS pin = H)
b1 b0
0 0 : Single-chip mode
0 1 : Memory expansion mode
1 0 : Do not set a value
1 1 : Microprocessor mode
0 : RD, BHE, WR
(3)
1 : RD, WRH, WRL
Setting this bit to "1" resets the
microcomputer. When read, its
.
content is "0"
b5 b4
0 0 : Multiplexed bus is unused
(Separate bus in the entire CS space)
0 1 : Allocated to CS2 space
1 0 : Allocated to CS1 space
1 1 :
Allocated to the entire CS space
0 : Address output
1 : Port function
(Address is not output)
0 : BCLK is output
1 : BCLK is not output
(Pin is left high-impedance)
(2)
(5)
(5)
(5)
NOTES:
1. Write to this register after setting the PRC1 bit in the PRCR register to "1" (write enable).
2. The PM01 to PM00 bits do not change at software reset, watchdog timer reset and oscillation stop detection reset.
* Effective in memory expansion and microprocessor modes (= Normal-ver.)
3. Effective when the PM01 to PM00 bits are set to "01b" (memory expansion mode) or "11b" (microprocessor mode).
* Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver.. These bits are reserved bit in
T/V-ver., and set to "0".
4. To set the PM01 to PM00 bits are "01b" and the PM05 to PM04 bits are "11b" (multiplexed bus assigned to
the entire CS space), apply an "H" signal to the BYTE pin (external data bus is 8-bit width).
While the CNVSS pin is held "H" (VCC), do not rewrite the PM05 to PM04 bits to "11b" after reset.
If the PM05 to PM04 bits are set to "11b" during memory expansion mode, P3_1 to P3_7 and P4_0 to P4_3
become I/O ports, in which case the accessible area for each CS is 256 bytes.
* Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
5. Not available in T/V-ver.. Do not set a value.
(4)
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Figure 6.1 PM0 Register
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 40 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 59

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 6. Processor Mode
Processor Mode Register 1
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
000
(1)
Symbol Address After reset
PM1 0005h 00001000b
Bit symbol
PM10
PM11
PM12
PM13
-
(b6-b4)
PM17
CS2 Area Switch Bit
(Data Block Enable Bit)
Port P3_7 to P3_4 Function
Select Bit
Watchdog Timer Function
Select Bit
Internal Reserved Area
Expansion Bit
Reserved Bit
Wait Bit
Bit name Function
0 :
08000h to 26FFFh
(2)
1 :
10000h to 26FFFh
(3)
(5)
(6)
0 : Address output
1 : Port function
0 : Watchdog timer interrupt
1 : Watchdog timer reset
See NOTE 7
Set to "0"
0 : No wait state
1 : With wait state (1 wait)
(Block A disable)
(Block A enable)
(4)
NOTES:
1. Write to this register after setting the PRC1 bit in the PRCR register to "1" (write enable).
2. For the mask ROM version, this bit must be set to "0".
For the flash memory version, the PM10 bit also controls block A by enabling or disabling it. When the PM10
bit is set to "1", 0F000h to 0FFFFh (block A) can be used as internal ROM area.
In addition, the PM10 bit is automatically set to "1" when the FMR01 bit in the FMR0 register is "1" (CPU rewrite
mode).
3. Effective when the PM01 to PM00 bits are set to "01b" (memory expansion mode) or "11b" (microprocessor mode).
* Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver.. This bit is reserved bit in T/V-ver.,
and set to "0".
4. The PM12 bit is set to "1" by writing a "1" in a program. (Writing a "0" has no effect.)
5. Be sure to set this bit to "0" except for products with internal ROM area over 192 Kbytes.
The PM13 bit is automatically set to "1" when the FMR01 bit in the FMR0 register is "1" (CPU rewrite mode).
6. When the PM17 bit is set to "1" (with wait state), one wait state is inserted when accessing the internal RAM
or internal ROM.
When the PM17 bit is set to "1" and accesses an external area, set the CSiW bit (i = 0 to 3) in the CSR register
to "0" (with wait state).
7. The access area is changed by the PM13 bit as listed in the table below.
Access area PM13 = 0 PM13 = 1
Internal
External
RAM
ROM
Up to addresses 00400h to 03FFFh (15 Kbytes)
Up to addresses D0000h to FFFFFh (192 Kbytes)
Addresses 04000h to 07FFFh are usable
Addresses 80000h to CFFFFh are usable
The entire area is usable
The entire area is usable
Addresses 04000h to 07FFFh are reserved
Addresses 80000h to CFFFFh are reserved
(Memory expansion mode)
* External area is not available in T/V-ver..
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Figure 6.2 PM1 Register
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 41 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 60

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 6. Processor Mode
Single-chip mode
00000h
SFR
00400h
Internal RAM
XXXXXh
Can not use
YYYYYh
Internal ROM
FFFFFh
NOTES:
1. If the PM13 bit in the PM1 register is set to "0", 15 Kbytes of the internal RAM and 192
Kbytes of the internal ROM can be used.
2. For the mask ROM version, set the PM10 bit in the PM1 register to "0" (block A disabled,
addresses 08000h to 26FFFh for CS2 area).
PM13 bit in PM1 register = 0
Capacity
16 Kbytes
20 Kbytes
31 Kbytes
PM13 bit = 1
Capacity
16 Kbytes
20 Kbytes
31 Kbytes
Figure 6.3 Memory Map in Single-chip Mode
(1)
Internal RAM
Address XXXXXh
03FFFh
03FFFh
03FFFh
Internal RAM Internal ROM
Address XXXXXh
043FFh
053FFh
07FFFh
Internal ROM
Capacity
192 Kbytes
256 Kbytes
384 Kbytes
512 Kbytes
Capacity
192 Kbytes
256 Kbytes
384 Kbytes
512 Kbytes
Address YYYYYh
D0000h
D0000h
D0000h
D0000h
Address YYYYYh
D0000h
C0000h
A0000h
80000h
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 42 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 61

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 6. Processor Mode
When PM13 = 0 and PM10 = 0
Memory expansion mode Microprocessor mode
00000h
00400h
XXXXXh
04000h
08000h
27000h
28000h
30000h
80000h
YYYYYh
FFFFFh
SFR
Internal RAM
Reserved area
Reserved area
External area
Reserved area
Internal ROM
SFR
Internal RAM
Reserved area
Reserved area
External area
CS3
(16 Kbytes)
CS2
(124 Kbytes)
CS1
(32 Kbytes)
CS0
Memory expansion mode: 320 Kbytes
Microprocessor mode: 832 Kbytes
Capacity
16 Kbytes
20 Kbytes
31 Kbytes
Internal RAM
Address XXXXXh
03FFFh
03FFFh
03FFFh
(1)
Capacity
192 Kbytes
256 Kbytes
384 Kbytes
512 Kbytes
Internal ROM
Address YYYYYh
D0000h
D0000h
D0000h
D0000h
(1)
NOTES:
1. If the PM13 bit in the PM1 register is set to "0", 192 Kbytes of the internal ROM can be used.
2. Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
_____
Figure 6.4 Memory Map and CS Area in Memory Expansion Mode and Microprocessor Mode (1)
When PM13 = 1 and PM10 = 0
Memory expansion mode Microprocessor mode
00000h
00400h
XXXXXh
08000h
27000h
28000h
30000h
80000h
YYYYYh
FFFFFh
SFR
Internal RAM
Reserved area
Reserved area
External area
Reserved area
Internal ROM
SFR
Internal RAM
Reserved area
Reserved area
External area
CS2
(124 Kbytes)
CS1
(32 Kbytes)
CS0
Memory expansion mode: 320 Kbytes
Microprocessor mode: 832 Kbytes
16 Kbytes
20 Kbytes
31 Kbytes
Internal RAM
Address XXXXXhCapacity
043FFh
053FFh
07FFFh
192 Kbytes
256 Kbytes
384 Kbytes
512 Kbytes
Internal ROM
Address YYYYYhCapacity
D0000h
C0000h
A0000h
80000h
NOTE:
1. Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
_____
Figure 6.5 Memory Map and CS Area in Memory Expansion Mode and Microprocessor Mode (2)
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 43 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 62

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 6. Processor Mode
When PM13 = 0 and PM10 = 1
Memory expansion mode Microprocessor mode
00000h
00400h
XXXXXh
04000h
08000h
10000h
27000h
28000h
30000h
80000h
YYYYYh
FFFFFh
SFR
Internal RAM
Reserved area
Reserved area
Reserved area
External area
Reserved area
Internal ROM
SFR
Internal RAM
Reserved area
CS3
(2)
Reserved area
Reserved area
External area
(2)
(16 Kbytes)
CS2
(92 Kbytes)
CS1
(32 Kbytes)
CS0
Memory expansion mode: 320 Kbytes
Microprocessor mode: 832 Kbytes
Capacity
16 Kbytes
20 Kbytes
31 Kbytes
Internal RAM
Address XXXXXh
03FFFh
03FFFh
03FFFh
(1)
Capacity
192 Kbytes
256 Kbytes
384 Kbytes
512 Kbytes
Internal ROM
Address YYYYYh
D0000h
D0000h
D0000h
D0000h
(1)
NOTES:
1. If the PM13 bit in the PM1 register is set to "0", 192 Kbytes of the internal ROM can be used.
2. For the flash memory version, when the PM10 bit is set to "1", 0F000h to 0FFFFh (block A)
can be used as internal ROM area.
3. Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
_____
Figure 6.6 Memory Map and CS Area in Memory Expansion Mode and Microprocessor Mode (3)
When PM13 = 1 and PM10 = 1
Memory expansion mode Microprocessor mode
00000h
00400h
XXXXXh
10000h
27000h
28000h
30000h
80000h
YYYYYh
FFFFFh
SFR
Internal RAM
Reserved
(1)
area
Reserved area
External area
Reserved area
Internal ROM
SFR
Internal RAM
Reserved
(1)
area
Reserved area
External area
CS2
(92 Kbytes)
CS1
(32 Kbytes)
CS0
Memory expansion mode: 320 Kbytes
Microprocessor mode: 832 Kbytes
16 Kbytes
20 Kbytes
31 Kbytes
Internal RAM
Address XXXXXhCapacity
043FFh
053FFh
07FFFh
192 Kbytes
256 Kbytes
384 Kbytes
512 Kbytes
Internal ROM
Address YYYYYhCapacity
D0000h
C0000h
A0000h
80000h
NOTES:
1. For the flash memory version, when the PM10 bit is set to "1", 0F000h to 0FFFFh (block A)
can be used as internal ROM area.
2. Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
_____
Figure 6.7 Memory Map and CS Area in Memory Expansion Mode and Microprocessor Mode (4)
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 44 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 63

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
7. Bus
Note
7. Bus explains as an example of a Normal-ver..
Not available the bus control pins in T/V-ver..
During memory expansion or microprocessor mode, some pins serve as the bus control pins to perform data
input/output to and from external devices. These bus control pins include A0 to A19, D0 to D15, CS0 to CS3,
_____ ________ ______ ________ ________ ________ __________ _________
_______ _______
RD, WRL/WR, WRH/BHE, ALE, RDY, HOLD, HLDA and BCLK.
7.1 Bus Mode
The bus mode, either multiplexed or separate, can be selected using the PM05 to PM04 bits in the PM0
register.
7.1.1 Separate Bus
In this bus mode, data and address are separate.
7.1.2 Multiplexed Bus
In this bus mode, data and address are multiplexed.
7.1.2.1 When the input level on BYTE pin is high (8-bit data bus)
D0 to D7 and A0 to A7 are multiplexed.
7.1.2.2 When the input level on BYTE pin is low (16-bit data bus)
D0 to D7 and A1 to A8 are multiplexed. D8 to D15 are not multiplexed. Do not use D8 to D15.
External devices connecting to a multiplexed bus are allocated to only the even addresses of the
microcomputer. Odd addresses cannot be accessed.
Table 7.1 shows the difference between a separate bus and multiplexed bus.
Table 7.1 Difference between Separate Bus and Multiplexed Bus
Pin Name
(1)
Separate Bus
BYTE = H BYTE = L
Multiplexed Bus
P0_0 to P0_7/D0 to D7 D0 to D7 (NOTE 2) (NOTE 2)
P1_0 to P1_7/D8 to D15 D8 to D15
I/O Port
P1_0 to P1_7
(NOTE 2)
P2_0/A0(/D0/-) A0 A0 D0 A0
P2_1 to P2_7/A1 to A7
(/D1 to D7/D0 to D6)
A1 to A7 A1 to A7 D1 to D7 A1 to A7 D0 to D6
P3_0/A8(/-/D7) A8 A8 A8 D7
NOTES :
1. See Table 7.6 Pin Functions for Each Processor Mode for bus control signals other than the above.
2. It changes with a setup of PM05 to PM04, and area to access. See Table 7.6 Pin Functions for Each
Processor Mode for details.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 45 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 64

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
7.2 Bus Control
The following describes the signals needed for accessing external devices and the functionality of software
wait.
7.2.1 Address Bus
The address bus consists of 20 lines, A0 to A19.
The address bus width can be chosen to be 12,
16 or 20 bits by using the PM06 bit in the PM0
register and the PM11 bit in the PM1 register.
Table 7.2 shows the PM06 and PM11 bits set
values and address bus widths.
When processor mode is changed from single-chip
mode to memory expansion mode, the address
bus is indeterminate until any external area is
accessed.
Table 7.2 PM06 and PM11 Bits Set Value and
Address Bus Width
Set Value
(1)
Pin Function Address Bus Width
PM11 = 1 P3_4 to P3_7 12 bits
PM06 = 1 P4_0 to P4_3
PM11 = 0 A12 to A15 16 bits
PM06 = 1 P4_0 to P4_3
PM11 = 0 A12 to A15 20 bits
PM06 = 0 A16 to A19
NOTE:
1. No values other than those shown above can
be set.
7.2.2 Data Bus
When input on the BYTE pin is high (data bus is an 8-bit width), 8 lines D0 to D7 comprise the data bus;
when input on the BYTE pin is low (data bus is a 16-bit width), 16 lines D0 to D15 comprise the data bus.
Do not change the input level on the BYTE pin while in operation.
7.2.3 Chip Select Signal
The chip select (hereafter referred to as the CS) signals are output from the CSi (i = 0 to 3) pins. These
pins can be chosen to function as I/O ports or as CS by using the CSi bit in the CSR register.
Figure 7.1 shows the CSR register.
During 1 Mbyte mode, the external area can be separated into up to 4 by the CSi signal which is output
from the CSi pin.
Figure 7.2 shows the example of address bus and CSi signal output.
______
_____ ______
_____
______
______
Chip Select Control Register
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
NOTES:
1. Where the RDY signal is used in the area indicated by CSi (i = 0 to 3) or the multiplexed bus is used, set the
CSiW bit to "0" (Wait state).
2. If the PM17 bit in the PM1 register is set to "1" (with wait state), set the CSiW bit to "0" (with wait state).
3. When the CSiW bit = 0 (with wait state), the number of wait states (in terms of clock cycles) can be selected
using the CSEi1W to CSEi0W bits in the CSE register.
4. Not available this register in T/V-ver..
Figure 7.1 CSR Register
(4)
Symbol Address After Reset
CSR 0008h 00000001b
Bit Symbol
CS0
CS1
CS2
CS3
CS0W
CS1W
CS2W
CS3W
Bit Name Function
CS0 Output Enable Bit
CS1 Output Enable Bit
CS2 Output Enable Bit
CS3 Output Enable Bit
CS0 Wait Bit
CS1 Wait Bit
CS2 Wait Bit
CS3 Wait Bit
0 : Chip select output disabled
1 : Chip select output enabled
0 : With wait state
1 : Without wait state
(functions as I/O port)
(1) (2) (3)
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 46 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 65

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
Example 1
To access the external area indicated by CSj in the next cycle
after accessing the external area indicated by CSi.
The address bus and the chip select signal both change state
between these two cycles.
Access to the external
area indicated by CSi
BCLK
Read signal
Data bus
Address bus
CSi
CSj
Example 3
To access the external area indicated by CSi in the next cycle
after accessing the external area indicated by the same CSi.
The address bus changes state but t he chip select signal
does not change state.
Address
Access to the external
area indicated by CSj
Data
Data
Address
Example 2
To access the internal ROM or internal RAM in the next cycle
after accessing the external area indicated by CSi.
The chip select s ignal changes state but the address bus
does not change state.
Access to the external
area indicated by CSi
BCLK
Read signal
Data bus
Address bus
CSi
Example 4
Not to access any area (nor instruction prefetch generated)
in the next cycle after accessing the external area indicated
by CSi.
Neither the address bus nor the chip select signal changes
state between these two cycles.
Access to the internal
ROM or internal RAM
Data
Address
Access to the external
area indicated by CSi
BCLK
Read signal
Data bus
Address bus
CSi
NOTE:
1. These examples show the address bus and chip select signal when accessing areas in two successive cycles. The chip select bus cycle may be
extended more than two cycles depending on a combination of these examples.
Shown above is the case where separate bus is selected and the area is accessed for read without wait states. i = 0 to 3, j = 0 to 3 (not including i, however)
Address
Access to the same
external area
Data Data
Address
Read signal
Address bus
______
Access to the external
area indicated by CSi
BCLK
Data bus
CSi
No access
Data
Address
Figure 7.2 Example of Address Bus and CSi Signal Output
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 47 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 66

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
7.2.4 Read and Write Signals
When the data bus is 16-bit width, the read and write signals can be chosen to be a combination of RD,
______ ________ _____ ________ ________
WR and BHE or a combination of RD, WRL and WRH by using the PM02 bit in the PM0 register. When
the data bus is 8-bit width, use a combination of RD, WR and BHE.
Table 7.3 shows the operation of RD, WRL, and WRH signals. Table 7.4 shows the operation of RD, WR,
________
_____ ________ _________ _____ ______
and BHE signals.
_____ ________ _________
Table 7.3 Operation of RD, WRL and WRH Signals
Data Bus Width
16 Bits
(BYTE pin
input = L)
Table 7.4 Operation of RD, WR and BHE Signals
Data Bus Width
16 Bits
(BYTE pin
input = L)
8 Bits
(BYTE pin input = H)
_____
RD
L
H
H
H
_____ ______ ________
_____
RD
______
WR
H
L
H
L
H
L
H
L
________
WRL
H
L
H
L
________
BHE
L
H
L
H
L
H
L
H
L
L
H
H
L
L
Not used
Not used
_____ ______ ________
_________
WRH Status of External Data Bus
H
H
L
L
A0
H
H
L
L
L
L
H to L
H to L
Read data
Write 1 byte of data to an even address
Write 1 byte of data to an odd address
Write data to both even and odd addresses
Status of External Data Bus
Write 1 byte of data to an odd address
Read 1 byte of data from an odd address
Write 1 byte of data to an even address
Read 1 byte of data from an even address
Write data to both even and odd addresses
Read data from both even and odd addresses
Write 1 byte of data
Read 1 byte of data
_____
7.2.5 ALE Signal
The ALE signal latches the address when accessing the multiplexed bus space. Latch the address when
the ALE signal falls. Figure 7.3 shows the ALE signal, address bus and data bus.
When BYTE pin input = H When BYTE pin input = L
ALE
A0/D0 to A7/D7
A8 to A19
NOTE:
1. If the entire CS space is assigned a multiplexed bus, these pins function as I/O ports.
Address Data
Address
(1)
Figure 7.3 ALE Signal, Address Bus, Data Bus
A1/D0 to A8/D7
ALE
A0
A9 to A19
Address
Address Data
Address
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 48 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 67

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
________
7.2.6 RDY Signal
This signal is provided for accessing external devices which need to be accessed at low speed. If input on
________
the RDY pin is asserted low at the last falling edge of BCLK of the bus cycle, one wait state is inserted in
the bus cycle. While in a wait state, the following signals retain the state in which they were when the RDY
signal was acknowledged.
_______ _______ _____ ________ ________ ______ ________ __________
A0 to A19, D0 to D15, CS0 to CS3, RD, WRL, WRH, WR, BHE, ALE, HLDA
________
Then, when the input on the RDY pin is detected high at the falling edge of BCLK, the remaining bus cycle
is executed. Figure 7.4 shows example in which the wait state was inserted into the read cycle by the
________ ________
RDY signal. To use the RDY signal, set the corresponding bit (CS3W to CS0W bits) in the CSR register
________ ________
to “0” (with wait state). When not using the RDY signal, the RDY pin must be pulled-up.
In an instance of separate bus
BCLK
________
RD
CSi
(i=0 to 3)
RDY
Accept timing of RDY signal
In an instance of multiplexed bus
BCLK
RD
CSi
(i=0 to 3)
RDY
: Wait using RDY signal
: Wait using software
tsu(RDY - BCLK)
tsu(RDY - BCLK)
Accept timing of RDY signal
tsu(RDY-BCLK): RDY input setup time
Shown above is the case where CSEi1W to CSEi0W (i = 0 to 3) bits in the CSE register are
"00b" (one wait state).
________
Figure 7.4 Example in which Wait State was Inserted into Read Cycle by RDY Signal
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 49 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 68

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
__________
7.2.7 HOLD Signal
This signal is used to transfer control of the bus from CPU or DMAC to an external circuit. When the input
__________
on HOLD pin is pulled low, the microcomputer is placed in a hold state after the bus access then in
process finishes. The microcomputer remains in a hold state while the HOLD pin is held low, during which
__________
__________
time the HLDA pin outputs a low-level signal.
Table 7.5 shows the microcomputer status in the hold state.
__________
Bus-using priorities are given to HOLD, DMAC, and CPU in order of decreasing precedence (see Figure
7.5 Bus-using Priorities). However, if the CPU is accessing an odd address in word units, the DMAC
cannot gain control of the bus during two separate accesses.
__________
HOLD > DMAC > CPU
Figure 7.5 Bus-using Priorities
Table 7.5 Microcomputer Status in Hold State
Item Status
BCLK Output
A0 to A19, D0 to D15, CS0 to CS3, RD, WRL, WRH, High-impedance
______ ________
WR, BHE
I/O Ports P0, P1, P3, P4
__________
HLDA Output “L”
Internal Peripheral Circuits ON (but watchdog timer stops
ALE Signal Undefined
NOTES:
1. When I/O port function is selected.
2. The watchdog timer does not stop when the PM22 bit in the PM2 register is set to “1” (the count source
for the watchdog timer is the on-chip oscillator clock).
_______ _______ ______ _________ _________
P6 to P10 Maintains status when hold signal is received
(1)
High-impedance
(2)
)
7.2.8 BCLK Output
If the PM07 bit in the PM0 register is set to “0” (output enable), a clock with the same frequency as that
of the CPU clock is output as BCLK from the BCLK pin. Refer to 8.2 CPU Clock and Peripheral Function
Clock.
Table 7.6 shows the pin functions for each processor mode.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 50 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 69

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
Table 7.6 Pin Functions for Each Processor Mode
Processor Mode Memory Expansion Mode or Microprocessor Mode
_______
01b (CS2 is for multiplexed bus and
others are for separate bus)
PM05 to PM04 Bits 00b (separate bus)
_______
10b (CS1 is for multiplexed bus and
others are for separate bus)
Memory Expansion Mode
11b
(multiplexed bus for
the entire space)
(1)
Data Bus Width 8 bits 16 bits 8 bits 16 bits 8 bits
BYTE Pin “H”“L”“H”“L” “H”
P0_0 to P0_7 D0 to D7 D0 to D7
P1_0 to P1_7 I/O ports D8 to D15 I/O ports
P2_0 A0 A0/D0
P2_1 to P2_7 A1 to A7 A1 to A7 A1 to A7
/D1 to D7
P3_0 A8 A8/D7
(4)
D8 to D15
(2)
A0 A0/D0
(4)
I/O ports
I/O ports
A1 to A7/D1 to D7
(2)
/D0 to D6
(2)
(2)
A8
P3_1 to P3_3 A9 to A11 I/O ports
P3_4 PM11 = 0 A12 to A15 I/O ports
to P3_7 PM11 = 1 I/O ports
P4_0 PM06 = 0 A16 to A19 I/O ports
to P4_3 PM06 = 1 I/O ports
P4_4 CS0 = 0 I/O ports
CS0 = 1
P4_5 CS1 = 0 I/O ports
CS1 = 1
P4_6 CS2 = 0 I/O ports
CS2 = 1
P4_7 CS3 = 0 I/O ports
CS3 = 1
P5_0 PM02 = 0
PM02 = 1-
P5_1 PM02 = 0
PM02 = 1P5_2
P5_3 BCLK
P5_4
P5_5
P5_6 ALE
P5_7
_______
CS0
_______
CS1
_______
CS2
_______
CS3
_______
WR
(3)
________
BHE
(3)
_____
RD
__________
HLDA
__________
HOLD
________
RDY
________
WRL
_________
WRH
(3)
-
(3)
-
________
WRL
_________
WRH
(3)
-
(3)
-
I/O ports: Function as I/O ports or peripheral function I/O pins.
NOTES:
1. For setting the PM01 to PM00 bits to “01b” (memory expansion mode) and the PM05 to PM04 bits to
_____
“11b” (multiplexed bus assigned to the entire CS space), apply “H” to the BYTE pin (external data bus is
an 8-bit width). While the CNVSS pin is held “H” (VCC), do not rewrite the PM05 to PM04 bits to “11b”
after reset. If the PM05 to PM04 bits are set to “11b” during memory expansion mode, P3_1 to P3_7
_____
and P4_0 to P4_3 become I/O ports, in which case the accessible area for each CS is 256 bytes.
2. In separate bus mode, these pins serve as the address bus.
3.
If the data bus is 8-bit width, make sure the PM02 bit is set to “0” (RD, BHE, WR).
_____ ________ ______
4. When accessing the area that uses a multiplexed bus, these pins output an indeterminate value during
a write.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 51 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 70

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
7.2.9 External Bus Status When Internal Area Accessed
Table 7.7 shows the external bus status when the internal area is accessed.
Table 7.7 External Bus Status When Internal Area Accessed
Item SFR Accessed Internal ROM, Internal RAM Accessed
A0 to A19 Address output Maintain status before accessed address
of external area or SFR
D0 to D15 When read High-impedance High-impedance
_____ ______ ________ _________
RD, WR, WRL, WRH
________
BHE
_______ _______
When write Output data Undefined
_____ ______ _________ __________
RD, WR, WRL, WRH output Output “H”
________
BHE output Maintain status before accessed status of
external area or SFR
CS0 to CS3 Output “H” Output “H”
ALE Output “L” Output “L”
7.2.10 Software Wait
Software wait states can be inserted by using the PM17 bit in the PM1 register, the CS0W to CS3W bits
in the CSR register, and the CSE register. The SFR area is unaffected by these control bits. This area is
always accessed in 2 BCLK or 3 BCLK cycles as determined by the PM20 bit in the PM2 register. See
Table 7.8 Bit and Bus Cycle Related to Software Wait for details.
To use the RDY signal, set the corresponding CS3W to CS0W bit to “0” (with wait state). Figure 7.6 shows
the CSE register. Table 7.8 shows the software wait related bits and bus cycles. Figures 7.7 and 7.8 show
the typical bus timings using software wait.
________
Chip Select Expansion Control Register
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
NOTES:
1. Set the CSiW bit (i = 0 to 3) in the CSR register to "0" (with wait state) before writing to the CSEi1W to CSEi0W
bits. If the CSiW bit needs to be set to "1" (without wait state), set the CSEi1W to CSEi0W bits to "00b" before
setting it.
2. Not available this register in T/V-ver..
Symbol Address After Reset
CSE 001Bh 00h
Bit Symbol
CSE00W
CS0 Wait Expansion Bit
CSE01W
CSE10W
CS1 Wait Expansion Bit
CSE11W
CS20WE
CS2 Wait Expansion Bit
CSE21W
CSE30W
CS3 Wait Expansion Bit
CSE31W
(2)
Bit Name Function
b1 b0
0 0 : 1 wait
0 1 : 2 waits
(1)
1 0 : 3 waits
1 1 : Do not set a value
b3 b2
0 0 : 1 wait
0 1 : 2 waits
(1)
1 0 : 3 waits
1 1 : Do not set a value
b5 b4
0 0 : 1 wait
0 1 : 2 waits
(1)
1 0 : 3 waits
1 1 : Do not set a value
b7 b6
0 0 : 1 wait
0 1 : 2 waits
(1)
1 0 : 3 waits
1 1 : Do not set a value
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Figure 7.6 CSE Register
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 52 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 71

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
Table 7.8 Software Wait Related Bits and Bus Cycles
0
1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
PM1 Register
PM17 Bit
-
0
1
0
-
-
1
-
-
1
Area
SFR
Bus Mode
PM2 Register
PM20 Bit
-
Internal
ROM, RAM
External
Area
-
-
Separate
Bus
Multiplexed
(2)
Bus
NOTES:
1.
To use the RDY signal, set this bit to “0 ”.
________
CSR Register
CS3W Bit
CS2W Bit
(5)
CS1W Bit
CS0W Bit
-
-
-
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
CSE Register
(1)
CS31W to CS30W Bits
(1)
CS21W to CS20W Bits
(1)
CS11W to CS10W Bits
(1)
CS01W to CS00W Bits
-
-
-
-
00b
00b
01b
10b
00b
00b
01b
10b
00b
Software
Wait
-
-
No wait
1 wait
No wait
1 wait
2 waits
3 waits
1 wait
1 wait
2 waits
3 waits
1 wait
Bus Cycle
3 BCLK cycles
2 BCLK cycles
1 BCLK cycle
(4)
(4)
(3)
2 BCLK cycles
1 BCLK cycle (read)
2 BCLK cycles (write)
2 BCLK cycles
(3)
3 BCLK cycles
4 BCLK cycles
2 BCLK cycles
3 BCLK cycles
3 BCLK cycles
4 BCLK cycles
3 BCLK cycles
2. To access in multiplexed bus mode, set the corresponding bit of CS0W to CS3W to “0” (with wait state).
3. After reset, the PM17 bit is set to “0” (without wait state), all of the CS0W to CS3W bits are set to “0”
_______ _______
(with wait state), and the CSE register is set to “00h” (one wait state for CS0 to CS3). Therefore, the
internal RAM and internal ROM are accessed with no wait state, and all external areas are accessed
with one wait state.
4. When the selected CPU clock source is the PLL clock, the number of wait cycles can be altered by the
PM20 bit in the PM2 register. When using PLL clock over 16 MHz, be sure to set the PM20 bit to “0”
(2 wait cycles).
5. When the PM17 bit is set to “1” and access an external area, set the CSiW bits (i = 0 to 3) to “0” (with
wait sate).
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 53 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 72

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
(1) Separate bus, No wait setting
BCLK
Write signal
Read signal
Data bus
Address bus
CS
(2) Separate bus, 1-wait setting
BCLK
Write signal
Read signal
Bus cycle
Output
Address
Bus cycle
(1)
Bus cycle
(1)
Input
Address
(1)
Bus cycle
(1)
Data bus
Address bus
Address
Output
Address
Input
CS
(3) Separate bus, 2-wait setting
Bus cycle
(1)
Bus cycle
(1)
BCLK
Write signal
Read signal
Address
Output
Address
Data bus
Address bus
CS
NOTE:
1. These example timing charts indicate bus cycle length. After this bus cycle sometimes come read and
write cycles in succession.
Input
Figure 7.7 Typical Bus Timings Using Software Wait (1)
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 54 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 73

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 7. Bus
(1) Separate bus, 3-wait setting
BCLK
Write signal
Read signal
Bus cycle
(1)
Bus cycle
(1)
Data bus
Address bus
CS
(2)Multiplexed bus, 1- or 2-wait setting
BCLK
Write signal
Read signal
ALE
Address bus
Address bus/
Data bus
Address
CS
(3)Multiplexed bus, 3-wait setting
Address
Bus cycle
Address
Data output
Bus cycle
Output
(1)
Bus cycle
Address
Address
(1)
(1)
Input
Address
Bus cycle
Input
(1)
BCLK
Write signal
Read signal
ALE
Address bus
Address bus/
Data bus
Address
Address
Data output
CS
NOTE:
1. These example timing charts indicate bus cycle length. After this bus cycle sometimes come read and
write cycles in succession.
Figure 7.8 Typical Bus Timings Using Software Wait (2)
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 55 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Address
Address
Input
Page 74

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.1 Types of Clock Generating Circuit
Four circuits are incorporated to generate the system clock signal:
• Main clock oscillation circuit
• Sub clock oscillation circuit
• On-chip oscillator
• PLL frequency synthesizer
Table 8.1 lists the clock generating circuit specifications. Figure 8.1 shows the clock generating circuit.
Figures 8.2 to 8.8 show the clock-related registers.
Table 8.1 Clock Generating Circuit Specifications
Item
Use of Clock
Clock
Frequency
Usable
Oscillator
Pins to Connect
Oscillator
Oscillation Stop
and Re-Oscillation
Detection Function
Oscillation Status
After Reset
Main Clock
Oscillation Circuit
• CPU clock source
• Peripheral function
clock source
0 to 16 MHz
•Ceramic oscillator
•Crystal oscillator
XIN, XOUT
Available
Oscillating
Sub Clock
Oscillation Circuit
• CPU clock source
• Clock source of Timer
A, B
32.768 kHz
•Crystal oscillator
XCIN, XCOUT
Available
Stopped
On-chip Oscillator
• CPU clock source
• Peripheral function
clock source
• CPU and peripheral
function clock sources
when the main clock
stops oscillating
About 1 MHz
-
-
Available
Stopped
PLL Frequency
Synthesizer
• CPU clock source
• Peripheral function
clock source
16 MHz, 20 MHz,
24 MHz
(1)
-
-
Available
Stopped
Other
Externally derived clock can be input
NOTE:
1. 24 MHs is available Normal-ver. only.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 56 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
-
-
Page 75

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
WAIT instruction
Sub clock oscillation circuit
CM04
CM10=1
(stop mode)
Software reset
Interrupt request level
QS
R
CM05
QS
R
RESET
NMI
judgment output
PM00, PM01 : Bits in PM0 register
CM00, CM01, CM02, CM04, CM05, CM06, CM07 : BIts in CM0 register
CM10, CM11, CM16, CM17 : Bits in CM1 register
PCLK0, PCLK1 : Bits in PCLKR register
CM21, CM27 : Bits in CM2 register
CCLK0 to CCLK2, CCLK4 to CCLK6 : Bits in CCLKR register
XCOUTXCIN
CM21
XOUTXIN
Main clock
oscillation circuit
Main clock
Sub clock
On-chip
oscillator
Oscillation stop,
re-oscillation
detection circuit
PLL frequency
synthesizer
PLL clock
1
0 CM11
CM02
On-chip oscillator
clock
CM21=1
CM21=0
I/O ports
PM01-PM00=00b, CM01-CM00=01b
PM01-PM00=00b, CM01-CM00=10b
fC32
1/32
f
C
Divider
Divider
bcd
a
Divider
b
1/2 1/2 1/2 1/2 1/2
a
CM06=0
CM17-CM16=10b
CM06=0
CM17-CM16=01b
CM06=0
CM17-CM16=00b
CM01-CM00=00b
PM01-PM00=00b,
CM01-CM00=11b
fCAN0
By CCLK0,1 and 2
f
CAN1
By CCLK4,5 and 6
f
1
PCLK0=1
f
2
PCLK0=0
f
8
f
32
PCLK0=1
PCLK0=0
f
1SIO
PCLK1=1
f
2SIO
PCLK1=0
f
8SIO
f
32SIO
CM07=0
e
f
C
CM07=1
cd
1/32
1/16
1/81/41/2
CM06=0
CM17-CM16=11b
CM06=1
e
Details of divider
CPU clock
CLKOUT
f
AD
BCLK
Oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection circuit
Main clock
Pulse generating circuit
for clock edge detection
and charge,
discharge control
Charge,
discharge
circuit
PLL frequency synthesizer
Programmable
counter
Main clock
Figure 8.1 Clock Generating Circuit
CM27 = 0
CM27 = 1
Phase
comparator
Reset
generating
circuit
Oscillation stop,
re-oscillation detection
interrupt generating
circuit
Charge
pump
oscillator
lowpass filter
Oscillation stop
detection reset
Oscillation stop,
re-oscillation detection
interrupt signal
CM21 switch signal
Voltage
control
(VCO)
Internal
1/2
PLL clock
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 57 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 76

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
System Clock Control Register 0
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
Symbol Address After Reset
(1)
CM0 0006h 01001000b
Bit Name FunctionBit Symbol
CM00
CM01
CM02
CM03
CM04
CM05
CM06
CM07
Clock Output Function
Select Bit
(Valid only in single-chip
mode)
WAIT Mode Peripheral
Function Clock Stop Bit
XCIN-XCOUT Drive
Capacity Select Bit
Port XC Select Bit
Main Clock Stop Bit
Main Clock Division Select
(7) (10) (12)
Bit 0
System Clock Select
(6) (11)
Bit
(3)
(3)
(5) (6) (7)
NOTES:
1. Write to this register after setting the PRC0 bit in the PRCR register to "1" (write enable).
2. The fC32 clock does not stop. During low-speed or low power dissipation mode, do not set this bit to "1"
(peripheral clock turned off when in wait mode).
3. The CM03 bit is set to "1" (high) while the CM04 bit is set to "0" (I/O port) or when entered to stop mode.
4. To use a sub clock, set this bit to "1". Also make sure ports P8_6 and P8_7 are directed for input, with no
pull-ups.
5. This bit is provided to stop the main clock when the low power dissipation mode or on-chip oscillator low
power dissipation mode is selected. This bit cannot be used for detection as to whether the main clock stopped
or not. To stop the main clock, set bits in the following order.
(1) Set the CM07 bit to "1" (sub clock select) or the CM21 bit in the CM2 register to "1" (on-chip oscillator select)
with the sub clock stably oscillating.
(2) Set the CM20 bit in the CM2 register to "0" (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection function disabled).
(3) Set the CM05 bit to "1" (stop).
6. To use the main clock as the clock source for the CPU clock, set bits in the following order.
(1) Set the CM05 bit to "0" (oscillate)
(2) Wait until the main clock oscillation stabilizes.
(3) Set the CM11, CM21 and CM07 bits all to "0".
7. When the CM21 bit = 0 (on-chip oscillator turned off) and the CM05 bit = 1 (main clock turned off), the CM06
bit is fixed to "1" (divide-by-8 mode) and the CM15 bit is fixed to "1" (drive capability High).
8. During external clock input, set the CM05 bit to "0" (oscillate).
9. When the CM05 bit is set to "1", the XOUT pin goes "H". Furthermore, because the internal feedback resistor
remains connected, the XIN pin is pulled "H" to the same level as XOUT via the feedback resistor.
10. When entering stop mode from high- or medium-speed mode, on-chip oscillator mode or on-chip oscillator
low power dissipation mode, the CM06 bit is set to "1" (divide-by-8 mode).
11. After setting the CM04 bit to "1" (XCIN-XCOUT oscillator function), wait until the sub clock oscillates stably
before switching the CM07 bit from "0" to "1" (sub clock).
12. To return from on-chip oscillator mode to high-speed or medium-speed mode, set the CM06 and CM15 bits
both to "1".
b1 b0
0 0 : I/O port P5_7
0 1 : fC output
1 0 : f8 output
1 1 : f32 output
0 : Do not stop peripheral function
clock in wait mode
1 : Stop peripheral function clock
in wait mode
(2)
0 : LOW
1 : HIGH
0 : I/O port P8_6, P8_7
1 : XCIN-XCOUT generation
function
0 : On
1 : Off
(4)
(8) (9)
0 : CM16 and CM17 valid
1 : Divide-by-8 mode
0 : Main clock, PLL clock,
or on-chip oscillator clock
1 : Sub clock
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Figure 8.2 CM0 Register
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 58 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 77

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
System Clock Control Register 1
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
000
Symbol
CM1 0007h 00100000b
(1)
Address After Reset
Bit Name FunctionBit Symbol
CM10
CM11
-
(b4-b2)
CM15
CM16
CM17
All Clock Stop Control
(2) (3)
Bit
System Clock Select Bit 1
Reserved Bit
XIN-XOUT Drive Capacity
Select Bit
Main Clock Division
Select Bit 1
(6)
(7)
NOTES:
1. Write to this register after setting the PRC0 bit in the PRCR register to "1" (write enable)
2. If the CM10 bit is "1" (stop mode), XOUT goes "H" and the internal feedback resistor is disconnected.
The XCIN and XCOUT pins are placed in the high-impedance state. When the CM11 bit is set to "1" (PLL
clock), or the CM20 bit in the CM2 register is set to "1" (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection function enabled),
do not set the CM10 bit to "1".
3. When the PM22 bit in the PM2 register is set to "1" (watchdog timer count source is on-chip oscillator clock),
writing to the CM10 bit has no effect.
4. Effective when the CM07 bit is "0" and the CM21 bit is "0".
5. After setting the PLC07 bit in the PLC0 register to "1" (PLL operation), wait until tsu(PLL) elapses before
setting the CM11 bit to "1" (PLL clock).
6. When entering stop mode from high- or medium-speed mode, or when the CM05 bit is set to "1" (main clock
turned off) in low-speed mode, the CM15 bit is set to "1" (drive capability high).
7. Effective when the CM06 bit is "0" (CM16 and CM17 bits enabled).
0 : Clock on
1 : All clocks off (stop mode)
0 : Main clock
(4)
1 : PLL clock
(5)
Set to "0"
0 : LOW
1 : HIGH
b7 b6
0 0 : No division mode
0 1 : Divide-by-2 mode
1 0 : Divide-by-4 mode
1 1 : Divide-by-16 mode
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Figure 8.3 CM1 Register
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 59 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 78

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
Oscillation Stop Detection Register
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
00
Symbol
CM2 000Ch 0X000000b
Bit Symbol
CM20
CM21
CM22
CM23
-
(b5-b4)
-
(b6)
CM27
(1)
Address
Bit Name
Oscillation Stop,
Re-Oscillation Detection
Enable Bit
System Clock Select
Bit 2
Oscillation Stop,
Re-Oscillation Detection
Flag
XIN Monitor Flag
(2) (3) (4)
(2) (5) (6) (7) (8) (11)
(9)
After Reset
(10)
Function
0 : Oscillation stop, re-oscillation
detection function disabled
1 : Oscillation stop, re-oscillation
detection function enabled
0 : Main clock or PLL clock
1 : On-chip oscillator clock
(On-chip oscillator oscillating)
0 : Main clock stop, re-oscillation
not detected
1 : Main clock stop, re-oscillation
detected
0 : Main clock oscillating
1 : Main clock turned off
Reserved Bit Set to "0"
Nothing is assigned. When write, set to "0".
When read, its content is indeterminate.
Operation Select Bit
behavior if oscillation stop,
(
re-oscillation is detected)
0 : Oscillation stop detection reset
1 : Oscillation stop, re-oscillation
(2)
detection interrupt
(2)
NOTES:
1. Write to this register after setting the PRC0 bit in the PRCR register to "1" (write enable).
2. The CM20, CM21 and CM27 bits do not change at oscillation stop detection reset.
3. Set the CM20 bit to "0" (disable) before entering stop mode. After exiting stop mode, set the CM20 bit back
to "1" (enable).
4. Set the CM20 bit to "0" (disable) before setting the CM05 bit in the CM0 register.
5. When the CM20 bit is "1" (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection function enabled), the CM27 bit is "1"
(oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt), and the CPU clock source is the main clock, the CM21 bit
is set to "1" (on-chip oscillator clock) if the main clock stop is detected.
6. If the CM20 bit is "1" and the CM23 bit is "1" (main clock turned off), do not set the CM21 bit to "0".
7. Effective when the CM07 bit in the CM0 register is "0".
8. Where the CM20 bit is "1" (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection function enabled), the CM27 bit is "1"
(oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt), and the CM11 bit is "1" (the CPU clock source is PLL clock),
the CM21 bit remains unchanged even when main clock stop is detected. If the CM22 bit is "0" under these
conditions, an oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt request is generated at main clock stop detection;
it is, therefore, necessary to set the CM21 bit to "1" (on-chip oscillator clock) inside the interrupt routine.
9. This bit is set to "1" when the main clock is detected to have stopped and when the main clock is detected to
have restarted oscillating. When this bit changes state from "0" to "1", an oscillation stop and re-oscillation
detection interrupt request is generated. Use this bit in an interrupt routine to discriminate the causes of
interrupts between the oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection interrupt and the watchdog timer interrupt.
This bit is set to "0" by writing "0" in a program. (Writing "1" has no effect. Nor is it set to "0" by an oscillation
stop and re-oscillation detection interrupt request acknowledged.)
If an oscillation stop or a re-oscillation is detected when the CM22 bit = 1, no oscillation stop and re-oscillation
detection interrupt requests are generated.
10. Read the CM23 bit in an oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection interrupt handling routine to determine
the main clock status.
11. When the CM21 bit = 0 (on-chip oscillator turned off) and the CM05 bit = 1 (main clock turned off), the CM06
bit is fixed to "1" (divide-by-8 mode) and the CM15 bit is fixed to "1" (drive capability High).
RW
RW
RW
RW
RO
RW
-
RW
Figure 8.4 CM2 Register
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 60 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 79

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
Peripheral Clock Select Register
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
000
Symbol Address After Reset
PCLKR 025Eh 00h
(1)
Bit Name FunctionBit Symbol
Timers A, B, and A/D Clock
PCLK0
Select Bit
(Clock source for the timers A, B,
the dead time timer and A/D)
SI/O Clock Select Bit
PCLK1
-
(b4-b2)
PCLK5
PCLK6
PCLK7
(Clock source for UART0 to UART2,
SI/O3 to SI/O6)
(5)
Reserved Bit
Pin Function Swirch Bit
Software Interrupt Number/SFR
Location Switch Bit
A/D Clock Direct Input Bit
NOTES:
1. Write to this register after setting the PRC0 bit in the PRCR register to "1" (write enable).
2. If this bit is set to "1", the software interrupt number and SFR location can be changed as follows.
(1) Software interrupt number of the key input interrupt in the vector table can be changed from 14 to 13.
- No.13 is changed from the CAN0/1 error interrupt to the CAN0/1 error/key input interrupt.
- No.14 is changed from the A/D/key input interrupt to the A/D interrupt.
(2) Address of the KUPIC register in the SFR can be changed from 004Eh to 004Dh.
- Address 004Dh is changed from the C01ERRIC register to the C01ERRIC/KUPIC register.
- Address 004Eh is changed from the ADIC/KUPIC register to the ADIC register.
3. When this bit = 1, the A/D clock is set to divide-by-1 of fAD mode regardless of whether the PCLK0 bit is set.
4. When the PCLK5 bit and the SM43 bit in the S4C register = 1, the pin function of SI/O4 can be changed as follows.
P8_0/TA4OUT/U/(SIN4)
P7_5/TA2IN/W/(SOUT4)
P7_4/TA2OUT/W/(CLK4)
5. SI/O5 and SI/O6 are only in the 128-pin version.
0 : Divide-by-2 of fAD, f2
1 : fAD, f1
0 : f2SIO
1 : f1SIO
Set to "0"
0: Normal mode
1: Swiching mode
0: Normal mode
1: Swiching mode
0: Normal mode
1: Swiching mode
(4)
(2)
(3)
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Figure 8.5 PCLKR Register
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 61 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 80

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
CAN0/1 Clock Select Register
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
(1)
Symbol Address After Reset
CCLKR 025Fh 00h
Bit Name FunctionBit Symbol
b2 b1 b0
CCLK0
CCLK1
CAN0 Clock Select Bits
CCLK2
CCLK3
CAN0 CPU Interface
Sleep Bit
(3)
CCLK4
CCLK5
CAN1 Clock Select Bits
CCLK6
CCLK7
CAN1 CPU Interface
Sleep Bit
(3)
NOTES:
1. Write to this register after setting the PRC0 bit in the PRCR register to "1" (Write enabled).
2. Set only when the Reset bit in the CiCTLR register (i = 0, 1) = 1 (Reset/Initialization mode).
3. Before setting this bit to "1", set the Sleep bit in the CiCTLR register to "1" (Sleep mode enabled).
0 0 0 No division
0 0 1 : Divide-by-2
0 1 0 : Divide-by-4
(2)
0 1 1 : Divide-by-8
1 0 0: Divide-by-16
1 0 1 :
1 1 0 : Do not set a value
1 1 1 :
0: CAN0 CPU interface operating
1: CAN0 CPU interface in sleep
b6 b5 b4
0 0 0 No division
0 0 1 : Divide-by-2
0 1 0 : Divide-by-4
(2)
0 1 1 : Divide-by-8
1 0 0: Divide-by-16
1 0 1 :
1 1 0 : Do not set a value
1 1 1 :
0: CAN1 CPU interface operating
1: CAN1 CPU interface in sleep
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
Figure 8.6 CCLKR Register
Processor Mode Register 2
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
000
NOTES:
1. Write to this register after setting the PRC1 bit in the PRCR register to "1" (write enable).
2. The PM20 bit become effective when the PLC07 bit in the PLC0 register is set to "1" (PLL on). Change the PM20
bit when the PLC07 bit is set to "0" (PLL off). Set the PM20 bit t "0" (2 waits) when PLL clock > 16MHz.
3. Once this bit is set to "1", it cannot be set to "0" in a program.
4. Setting the PM22 bit to "1" results in the following conditions:
The on-chip oscillator starts oscillating, and the on-chip oscillator clock becomes the watchdog timer count source.
The CM10 bit in the CM1 register is disabled against write. (Writing a "1" has no effect, nor is stop mode entered.)
The watchdog timer does not stop when in wait mode or hold state.
(1)
Symbol Address After Reset
PM2 001Eh XXX00000b
Bit Symbol
Bit Name Function
Specifying Wait when
PM20
-
(b1)
PM22
-
(b4-b3)
-
(b7-b5)
Accessing SFR at PLL
Operation
(2)
Reserved Bit Set to "0"
WDT Count Source
Protective Bit
(3) (4)
Reserved Bit
Nothing is assigned. When write, set to "0".
When read, their contents are indeterminate.
0 : 2 waits
1 : 1 wait
0 : CPU clock is used for the
watchdog timer count source
1 : On-chip oscillator clock is used for
the watchdog timer count source
Set to "0"
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
-
Figure 8.7 PM2 Register
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 62 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 81

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
PLL Control Register 0
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
0 10
(1)
Symbol Address After Reset
PLC0 001Ch 0001X010b
PLC00
PLC01
PLC02
-
(b3)
-
(b4)
-
(b6-b5)
PLC07
Bit NameBit Symbol
b2 b1 b0
0 0 0 : Do not set a value
0 0 1 : Multiply by 2
PLL Multiplying Factor
Select Bit
(2)
0 1 0 : Multiply by 4
0 1 1 : Multiply by 6
1 0 0 :
1 0 1 :
1 1 0 :
1 1 1 :
Nothing is assigned. When write, set to "0".
When read, its content is indeterminate.
Reserved Bit Set to "1"
Reserved Bit Set to "0"
0 : PLL Off
Operation Enable Bit
(3)
1 : PLL On
Function
Do not set a value
(4)
NOTES:
1. Write to this register after setting the PRC0 bit in the PRCR register to "1" (write enable).
2. This bit can only be modified when the PLC07 bit = 0 (PLL turned off). The value once written to this bit
cannot be modified.
3. Before setting this bit to "1", set the CM07 bit in the CM0 register to "0" (main clock), set the CM17 to
CM16 bits in the CM1 register to "00b" (main clock undivided mode), and set the CM06 bit in the CM0
register to "0" (CM16 and CM17 bits enable).
4. Multiply by 6 is available Normal-ver. only.
RW
RW
RW
RW
-
RW
RW
RW
Figure 8.8 PLC0 Register
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 63 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 82

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
The following describes the clocks generated by the clock generating circuit.
8.1.1 Main Clock
The main clock is generated by the main clock oscillation circuit. This clock is used as the clock source for
the CPU and peripheral function clocks. The main clock oscillator circuit is configured by connecting a
resonator between the XIN and XOUT pins. The main clock oscillator circuit contains a feedback resistor,
which is disconnected from the oscillator circuit during stop mode in order to reduce the amount of power
consumed in the chip. The main clock oscillator circuit may also be configured by feeding an externally
generated clock to the XIN pin. Figure 8.9 shows the examples of main clock connection circuit.
After reset, the main clock divided by 8 is selected for the CPU clock.
The power consumption in the chip can be reduced by setting the CM05 bit in the CM0 register to “1”
(main clock oscillator circuit turned off) after switching the clock source for the CPU clock to a sub clock or
on-chip oscillator clock. In this case, XOUT goes “H”. Furthermore, because the internal feedback resistor remains on, XIN is pulled “H” to XOUT via the feedback resistor. Note, that if an externally generated
clock is fed into the XIN pin, the main clock cannot be turned off by setting the CM05 bit to “1” unless the
sub clock is selected as a CPU clock. If necessary, use an external circuit to turn off the clock.
During stop mode, all clocks including the main clock are turned off. Refer to 8.4 Power Control.
Microcomputer
(Built-in feedback resistor)
CIN
XIN
Oscillator
XOUT
VSS
NOTE:
1.Place a damping resistor if required. The resistance will vary depending on the oscillator
and the oscillation drive capacity setting. Use the value recommended by each oscillator
the oscillator manufacturer.
When the oscillation drive capacity is set to low, check that oscillation is stable.
Also, place a feedback resistor between XIN and XOUT if the oscillator manufacturer
recommends placing the resistor externally.
Rd
(1)
COUT
Microcomputer
(Built-in feedback resistor)
Figure 8.9 Examples of Main Clock Connection Circuit
XIN
XOUT
External clock
VCC
VSS
Open
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 64 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 83

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.1.2 Sub Clock
The sub clock is generated by the sub clock oscillation circuit. This clock is used as the clock source for
the CPU clock, as well as the timer A and timer B count sources. In addition, an fC clock with the same
frequency as that of the sub clock can be output from the CLKOUT pin.
The sub clock oscillator circuit is configured by connecting a crystal resonator between the XCIN and
XCOUT pins. The sub clock oscillator circuit contains a feedback resistor, which is disconnected from the
oscillator circuit during stop mode in order to reduce the amount of power consumed in the chip. The sub
clock oscillator circuit may also be configured by feeding an externally generated clock to the XCIN pin.
Figure 8.10 shows the examples of sub clock connection circuit.
After reset, the sub clock is turned off. At this time, the feedback resistor is disconnected from the oscillator circuit.
To use the sub clock for the CPU clock, set the CM07 bit in the CM0 register to “1 ” (sub clock) after the
sub clock becomes oscillating stably.
During stop mode, all clocks including the sub clock are turned off. Refer to 8.4 Power Control.
Microcomputer
(Built-in feedback resistor)
CCIN
XCIN
Oscillator
XCOUT
VSS
NOTE:
1.Place a damping resistor if required. The resistance will vary depending on the oscillator
and the oscillation drive capacity setting. Use the value recommended by each oscillator
the oscillator manufacturer.
When the oscillation drive capacity is set to low, check that oscillation is stable.
Also, place a feedback resistor between XCIN and XCOUT if the oscillator manufacturer
recommends placing the resistor externally.
RCd
(1)
CCOUT
Microcomputer
(Built-in feedback resistor)
Figure 8.10 Examples of Sub Clock Connection Circuit
XCIN
XCOUT
External clock
VCC
VSS
Open
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 65 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 84

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.1.3 On-chip Oscillator Clock
This clock, approximately 1 MHz, is supplied by a on-chip oscillator. This clock is used as the clock
source for the CPU and peripheral function clocks. In addition, if the PM22 bit in the PM2 register is “1”
(on-chip oscillator clock for the watchdog timer count source), this clock is used as the count source for
the watchdog timer (refer to 11.1 Count Source Protective Mode).
After reset, the on-chip oscillator is turned off. It is turned on by setting the CM21 bit in the CM2 register
to “1” (on-chip oscillator clock), and is used as the clock source for the CPU and peripheral function
clocks, in place of the main clock. If the main clock stops oscillating when the CM20 bit in the CM2 register
is “1” (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection function enabled) and the CM27 bit is “1” (oscillation stop,
re-oscillation detection interrupt), the on-chip oscillator automatically starts operating, supplying the necessary clock for the microcomputer.
8.1.4 PLL Clock
The PLL clock is generated by a PLL frequency synthesizer. This clock is used as the clock source for the
CPU and peripheral function clocks. After reset, the PLL clock is turned off. The PLL frequency synthesizer is activated by setting the PLC07 bit to “1” (PLL operation). When the PLL clock is used as the clock
source for the CPU clock, wait a fixed period of tsu(PLL) for the PLL clock to be stable, and then set the
CM11 bit in the CM1 register to “1”.
Before entering wait mode or stop mode, be sure to set the CM11 bit to “0” (CPU clock source is the main
clock). Furthermore, before entering stop mode, be sure to set the PLC07 bit in the PLC0 register to “0”
(PLL stops). Figure 8.11 shows the procedure for using the PLL clock as the clock source for the CPU.
The PLL clock frequency is determined by the equation below. When the PLL clock frequency is 16 MHz
or more, set the PM20 bit in the PM2 register to “0” (2 waits).
PLL clock frequency = f(XIN) ✕ (multiplying factor set by the PLC02 to PLC00 bits in the PLC0 register)
(However, PLL clock frequency = 16 MHz, 20 MHz or 24 MHz
(1)
)
NOTE:
1. 24 MHz is available Normal-ver. only.
The PLC02 to PLC00 bits can be set only once after reset. Table 8.2 shows the example for setting PLL
clock frequencies.
Table 8.2 Example for Setting PLL Clock Frequencies
XIN
(MHz)
8
4
10
5
12
6
4
PLC02
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
PLC01 PLC00
0
1
0
1
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
Multiply
Factor
2
4
2
4
2
4
(3)
6
PLL Clock
(1)
(MHz)
16
20
(2)
24
NOTES:
1. PLL clock frequency = 16 MHz , 20 MHz or 24 MHz
2. 24 MHz is available Normal-ver. only.
3. Multiply by 6 is available Normal-ver. only.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 66 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 85

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
Using the PLL clock as the clock source for the CPU
Set the CM07 bit to "0" (main clock), the CM17 to CM16
bits to "00b" (main clock undivided), and the CM06 bit to "0"
(CM16 and CM17 bits enabled).
(1)
Set the PLC02 to PLC00 bits (multiplying factor).
(When PLL clock > 16 MHz)
Set the PM20 bit to "0" (2-wait state).
Set the PLC07 bit to "1" (PLL operation).
Wait until the PLL clock becomes stable (tsu(PLL)).
Set the CM11 bit to "1" (PLL clock for the CPU clock source).
END
NOTE:
1. PLL operation mode can be entered from high-speed mode.
Figure 8.11 Procedure to Use PLL Clock as CPU Clock Source
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 67 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 86

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.2 CPU Clock and Peripheral Function Clock
Two type clocks: CPU clock to operate the CPU and peripheral function clocks to operate the peripheral
functions.
8.2.1 CPU Clock and BCLK
These are operating clocks for the CPU and watchdog timer.
The clock source for the CPU clock can be chosen to be the main clock, sub clock, on-chip oscillator clock
or the PLL clock.
If the main clock or on-chip oscillator clock is selected as the clock source for the CPU clock, the selected
clock source can be divided by 1 (undivided), 2, 4, 8 or 16 to produce the CPU clock. Use the CM06 bit in
the CM0 register and the CM17 to CM16 bits in the CM1 register to select the divide-by-n value.
When the PLL clock is selected as the clock source for the CPU clock, the CM06 bit should be set to “0”
and the CM17 to CM16 bits to “00b” (undivided).
After reset, the main clock divided by 8 provides the CPU clock.
During memory expansion or microprocessor mode
CPU clock can be output from the BCLK pin by setting the PM07 bit of PM0 register to “0” (output enabled).
Note that when entering stop mode from high- or medium-speed mode, on-chip oscillator mode or on-chip
oscillator low power dissipation mode, or when the CM05 bit in the CM0 register is set to “1” (main clock
turned off) in low-speed mode, the CM06 bit in the CM0 register is set to “1” (divide-by-8 mode).
(1)
, a BCLK signal with the same frequency as the
NOTE:
1. Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
8.2.2 Peripheral Function Clock
(f1, f2, f8, f32, f1SIO, f2SIO, f8SIO, f32SIO, fAD, fCAN0, fCAN1, fC32)
These are operating clocks for the peripheral functions.
Two of these, fi (i = 1, 2, 8, 32) and fiSIO are derived from the main clock, PLL clock or on-chip oscillator
clock by dividing them by i. The clock fi is used for timers A and B, and fiSIO is used for serial interface.
The f8 and f32 clocks can be output from the CLKOUT pin.
The fAD clock is produced from the main clock, PLL clock or on-chip oscillator clock, and is used for the
A/D converter.
The fCANi (i =0, 1) clock is derived from the main clock, PLL clock or on-chip oscillator clock by dividing
them by 1 (undivided), 2, 4, 8 or 16, and is used for the CAN module.
When the WAIT instruction is executed after setting the CM02 bit in the CM0 register to “1” (peripheral
function clock turned off during wait mode), or when the microcomputer is in low power dissipation mode,
the fi, fiSIO, fAD, fCAN0 and fCAN1 clocks are turned off
(1)
.
The fC32 clock is derived from the sub clock, and is used for timers A and B. This clock can be used when
the sub clock is activated.
NOTE:
1. fCAN0 and fCAN1 clocks stop at “H” in CAN0, 1 sleep mode.
8.3 Clock Output Function
During single-chip mode, the f8, f32 or fC clock can be output from the CLKOUT pin. Use the CM01 to
CM00 bits in the CM0 register to select.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 68 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 87

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.4 Power Control
Normal operation mode, wait mode and stop mode are provided as the power consumption control.
All mode states, except wait mode and stop mode, are called normal operation mode in this document.
8.4.1 Normal Operation Mode
Normal operation mode is further classified into seven sub modes.
In normal operation mode, because the CPU clock and the peripheral function clocks both are on, the
CPU and the peripheral functions are operating. Power control is exercised by controlling the CPU clock
frequency. The higher the CPU clock frequency, the greater the processing capability. The lower the CPU
clock frequency, the smaller the power consumption in the chip. If the unnecessary oscillator circuits are
turned off, the power consumption is further reduced.
Before the clock sources for the CPU clock can be switched over, the new clock source to which switched
must be oscillating stably. If the new clock source is the main clock, sub clock or PLL clock, allow a
sufficient wait time in a program until it becomes oscillating stably.
Note that operation modes cannot be changed directly from low speed or low power dissipation mode to
on-chip oscillator or on-chip oscillator low power dissipation mode. Nor can operation modes be changed
directly from on-chip oscillator or on-chip oscillator low power dissipation mode to low-speed or low power
dissipation mode. Where the CPU clock source is changed from the on-chip oscillator to the main clock,
change the operation mode to the medium-speed mode (divide-by-8 mode) after the clock was divided by
8 (the CM06 bit in the CM0 register was set to “1”) in the on-chip oscillator mode.
8.4.1.1 High-speed Mode
The main clock divided by 1 provides the CPU clock. If the sub clock is activated, fC32 can be used as
the count source for timers A and B.
8.4.1.2 PLL Operation Mode
The main clock multiplied by 2, 4 or 6
(1)
provides the PLL clock, and this PLL clock serves as the CPU
clock. If the sub clock is activated, fC32 can be used as the count source for timers A and B. PLL
operation mode can be entered from high speed mode. If PLL operation mode is to be changed to wait
or stop mode, first go to high speed mode before changing.
NOTE:
1. The main clock multiplied by 6 is available Normal-ver. only.
8.4.1.3 Medium-speed Mode
The main clock divided by 2, 4, 8 or 16 provides the CPU clock. If the sub clock is activated, fC32 can be
used as the count source for timers A and B.
8.4.1.4 Low-speed Mode
The sub clock provides the CPU clock. The main clock is used as the clock source for the peripheral
function clock when the CM21 bit in the CM2 register is set to “0” (on-chip oscillator turned off), and the
on-chip oscillator clock is used when the CM21 bit is set to “1” (on-chip oscillator oscillating).
The fC32 clock can be used as the count source for timers A and B.
8.4.1.5 Low Power Dissipation Mode
In this mode, the main clock is turned off after being placed in low speed mode. The sub clock provides
the CPU clock. The fC32 clock can be used as the count source for timers A and B.
Simultaneously when this mode is selected, the CM06 bit in the CM0 register becomes “1” (divide-by-8
mode). In the low power dissipation mode, do not change the CM06 bit. Consequently, the medium
speed (divide-by-8) mode is to be selected when the main clock is operated next.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 69 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 88

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.4.1.6 On-chip Oscillator Mode
The on-chip oscillator clock divided by 1 (undivided), 2, 4, 8 or 16 provides the CPU clock. The on-chip
oscillator clock is also the clock source for the peripheral function clocks. If the sub clock is activated,
fC32 can be used as the count source for timers A and B. When the operation mode is returned to the
high- and medium-speed modes, set the CM06 bit in the CM0 register to “1” (divide-by-8 mode).
8.4.1.7 On-chip Oscillator Low Power Dissipation Mode
The main clock is turned off after being placed in on-chip oscillator mode. The CPU clock can be
selected like in the on-chip oscillator mode. The on-chip oscillator clock is the clock source for the
peripheral function clocks. If the sub clock is activated, fC32 can be used as the count source for timers
A and B.
Table 8.3 lists the setting clock related bit and modes.
Table 8.3 Setting Clock Related Bit and Modes
Modes
CM2 Register
CM21 CM11
CM1 Register CM0 Register
CM17, CM16
CM07 CM06 CM05 CM04
PLL Operation Mode 0 1 00b 0 0 0 -
High-Speed Mode 0 0 00b 0 0 0 -
Medium-
Speed
Mode
Divide-by-2
Divide-by-4
Divide-by-8
Divide-by-16
0 0 01b 0 0 0 -
0 0 10b 0 0 0 -
00-0 10-
0 0 11b 0 0 0 -
Low-Speed Mode - 0 - 1 - 0 1
Low Power 0 0 - 1 1
(1)
1
(1)
1
Dissipation Mode
On-chip
Oscillator
Mode
Divide-by-1
Divide-by-2
Divide-by-4
Divide-by-8
Divide-by-16
1 0 00b 0 0 0 -
1 0 01b 0 0 0 -
1 0 10b 0 0 0 -
10-0 10-
1 0 11b 0 0 0 -
On-chip Oscillator 1 0 (NOTE 2) 0 (NOTE 2) 1 Low power Dissipation
Mode
-: “0” or “1”
NOTES:
1. When the CM05 bit is set to “1” (main clock turned off) in low-speed mode, the mode goes to low power
dissipation mode and the CM06 bit is set to “1” (divide-by-8 mode) simultaneously.
2. The divide-by-n value can be selected the same way as in on-chip oscillator mode.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 70 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 89

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.4.2 Wait Mode
In wait mode, the CPU clock is turned off, so are the CPU (because operated by the CPU clock) and the
watchdog timer. However, if the PM22 bit in the PM2 register is “1” (on-chip oscillator clock for the watchdog
timer count source), the watchdog timer remains active. Because the main clock, sub clock and on-chip
oscillator clock all are on, the peripheral functions using these clocks keep operating.
8.4.2.1 Peripheral Function Clock Stop Function
If the CM02 bit in the CM0 register is “1” (peripheral function clocks turned off during wait mode), the f1,
f2, f8, f32, f1SIO, f8SIO, f32SIO, fAD, fCAN0 and fCAN1 clocks are turned off when in wait mode, with
the power consumption reduced that much. However, fC32 remains on.
8.4.2.2 Entering Wait Mode
The microcomputer is placed into wait mode by executing the WAIT instruction.
When the CM11 bit = 1 (CPU clock source is the PLL clock), be sure to set the CM11 bit in the CM1
register to “0” (CPU clock source is the main clock) before going to wait mode. The power consumption
of the chip can be reduced by setting the PLC07 bit in the PLC0 register to “0” (PLL stops).
8.4.2.3 Pin Status During Wait Mode
Table 8.4 lists the pin status during wait mode.
Table 8.4 Pin Status During Wait Mode
Pin
A0 to A19, D0 to D15, Retains status before wait mode Does not become a bus control pin
_______ _______ ________
CS0 to CS3, BHE
______ _______ _________ _________
RD, WR, WRL, WRH
___________
HLDA, BCLK
(2)
ALE
(2)
(2)
(2)
Memory Expansion Mode
Microprocessor Mode
“H”
“H”
“L”
(1)
Single-chip Mode
I/O ports Retains status before wait mode Retains status before wait mode
CLKOUT Does not become a CLKOUT pin Does not stop
When fC selected
When f8, f32
selected
•CM02 bit = 0: Does not stop
•CM02 bit = 1: Retains status before
wait mode
NOTES:
1. Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
2. Not available the bus control pins in T/V-ver..
8.4.2.4 Exiting Wait Mode
The microcomputer is moved out of wait mode by a hardware reset, NMI interrupt or peripheral function
interrupt.
If the microcomputer is to be moved out of wait mode by a hardware reset or NMI interrupt, set the
peripheral function interrupt priority ILVL2 to ILVL0 bits to “000b” (interrupt disabled) before executing
the WAIT instruction.
The peripheral function interrupts are affected by the CM02 bit. If the CM02 bit is “0” (peripheral function
clocks not turned off during wait mode), peripheral function interrupts can be used to exit wait mode. If
the CM02 bit is “1” (peripheral function clocks turned off during wait mode), the peripheral functions
using the peripheral function clocks stop operating, so that only the peripheral functions clocked by
external signals can be used to exit wait mode.
Table 8.5 lists the interrupts to exit wait mode.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 71 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
______
______
Page 90

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
Table 8.5 Interrupts to Exit Wait Mode and Use Conditions
_______
Interrupt CM02 Bit = 0 CM02 Bit = 1
NMI Interrupt Can be used Can be used
Serial Interface Interrupt Can be used when operating with Can be used when operating with
internal or external clock external clock
Key Input Interrupt Can be used Can be used
A/D Conversion Interrupt Can be used in one-shot mode or - (Do not use)
single sweep mode
Timer A Interrupt Can be used in all modes Can be used in event counter mode
Timer B interrupt or when the count source is fc32
______
INT Interrupt Can be used Can be used
CAN0/1 Wake-up Interrupt Can be used in CAN sleep mode Can be used in CAN sleep mode
If the microcomputer is to be moved out of wait mode by a peripheral function interrupt, set up the
following before executing the WAIT instruction.
(1) Set the ILVL2 to ILVL0 bits in the interrupt control register, for peripheral function interrupts used to
exit wait mode.
The ILVL2 to ILVL0 bits in all other interrupt control registers, for peripheral function interrupts not
used to exit wait mode, are set to “000b” (interrupt disable).
(2) Set the I flag to “1”.
(3) Start operating the peripheral functions used to exit wait mode.
When the peripheral function interrupt is used, an interrupt routine is performed as soon as an
interrupt request is acknowledged and the CPU clock is supplied again.
When the microcomputer exits wait mode by the peripheral function interrupt, the CPU clock is the same
clock as the CPU clock executing the WAIT instruction.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 72 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 91

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.4.3 Stop Mode
In stop mode, all oscillator circuits are turned off, so are the CPU clock and the peripheral function clocks.
Therefore, the CPU and the peripheral functions clocked by these clocks stop operating. The least
amount of power is consumed in this mode. If the voltage applied to VCC is VRAM or more, the internal
RAM is retained.
However, the peripheral functions clocked by external signals keep operating.
Table 8.6 lists the interrupts to stop mode and use conditions.
Table 8.6 Interrupts to Stop Mode and Use Conditions
_______
NMI Interrupt Can be used
Key Input Interrupt Can be used
______
INT Interrupt Can be used
Timer A Interrupt Can be used
Timer B interrupt (when counting external pulses in event counter mode)
Serial Interface Interrupt Can be used (when external clock is selected)
CAN0/1 Wake-up Interrupt Can be used (when CAN sleep mode is selected)
Interrupt Condition
8.4.3.1 Entering Stop Mode
The microcomputer is placed into stop mode by setting the CM10 bit in the CM1 register to “1” (all clocks
turned off). At the same time, the CM06 bit in the CM0 register is set to “1” (divide-by-8 mode) and the
CM15 bit in the CM1 register is set to “1” (main clock oscillator circuit drive capability high).
Before entering stop mode, set the CM20 bit in the CM2 register to “0” (oscillation stop, re-oscillation
detection function disabled).
Also, if the CM11 bit in the CM1 register is “1” (PLL clock for the CPU clock source), set the CM11 bit to
“0” (main clock for the CPU clock source) and the PLC07 bit in the PLC0 register to “0” (PLL turned off)
before entering stop mode.
8.4.3.2 Pin Status in Stop Mode
Table 8.7 lists the pin status in stop mode.
Table 8.7 Pin Status in Stop Mode
Pin
A0 to A19, D0 to D15, Retains status before stop mode Does not become a bus control pin
_______ _______ ________
CS0 to CS3, BHE
______ _______ _________ _________
RD, WR, WRL, WRH
___________
HLDA, BCLK
(2)
ALE
(2)
(2)
(2)
Memory Expansion Mode
Microprocessor Mode
“H”
“H”
indeterminate
(1)
Single-chip Mode
I/O ports Retains status before stop mode Retains status before stop mode
CLKOUT Does not become a CLKOUT pin “H”
When fC selected
When f8, f32
Retains status before stop mode
selected
NOTES:
1. Not available memory expansion and microprocessor modes in T/V-ver..
2. Not available the bus control pins in T/V-ver..
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 73 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 92

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.4.3.3 Exiting Stop Mode
Stop mode is exited by a hardware reset, NMI interrupt or peripheral function interrupt.
_______
_______
When the hardware reset or NMI interrupt is used to exit wait mode, set all ILVL2 to ILVL0 bits in the
interrupt control registers for the peripheral function interrupt to “000b” (interrupt disabled) before setting
the CM10 bit in the CM1 register to “1”.
When the peripheral function interrupt is used to exit stop mode, set the CM10 bit to “1” after the following
settings are completed.
(1) The ILVL2 to ILVL0 bits in the interrupt control registers, for the peripheral function interrupt used to
exit stop mode, must have larger value than that of the RLVL2 to RLVL0 bits.
The ILVL2 to ILVL0 bits in all other interrupt control registers, for the peripheral function interrupts
which are not used to exit stop mode, must be set to “000b” (interrupt disabled).
(2) Set the I flag to “1”.
(3) Start operation of peripheral function being used to exit wait mode.
When exiting stop mode by the peripheral function interrupt, the interrupt routine is performed when
an interrupt request is generated and the CPU clock is supplied again.
_______
When stop mode is exited by the peripheral function interrupt or NMI interrupt, the CPU clock source is
as follows, in accordance with the CPU clock source setting before the microcomputer had entered stop
mode.
• When the sub clock is the CPU clock before entering stop mode: Sub clock
• When the main clock is the CPU clock source before entering stop mode: Main clock divided by 8
• When the on-chip oscillator clock is the CPU clock source before entering stop mode:
On-chip oscillator clock divided by 8
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 74 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 93

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
Figure 8.12 shows the state transition from normal operation mode to stop mode and wait mode. Figure
8.13 shows the state transition in normal operation mode.
Table 8.8 shows a state transition matrix describing allowed transition and setting. The vertical line shows
current state and horizontal line show state after transition.
Reset
CPU operation stoppedAll oscillators stopped
Wait Mode
Wait Mode
Wait Mode
Wait Mode
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 1
CM05 = 0
CM11 = 0
CM10 = 1
(5)
CM10 = 1
Stop Mode
(3)
Stop Mode
Stop Mode
Stop Mode
Interrupt
Interrupt
CM10 = 1
CM10 = 1
Interrupt
CM10 = 1
Interrupt
(5)
(5)
(5)
(4)
When
power
dissipation
mode
Medium-Speed Mode
(divided-by-8 mode)
High-Speed Mode,
Medium-Speed Mode
When
low
low-
speed
mode
PLL Operation Mode
Low-Speed Mode,
Low Power Dissipation Mode
On-chip Oscillator Mode,
On-chip Oscillator Dissipation Mode
(NOTES 1, 2)
WAIT
instruction
Interrupt
WAIT
instruction
Interrupt
WAIT
instruction
Interrupt
WAIT
instruction
Interrupt
Normal Mode
CM05, CM06, CM07: Bits in CM0 register
CM10, CM11: Bits in CM1 register
NOTES:
Do not go directly from PLL operation mode to wait or stop mode.
1.
2.PLL operation mode can be entered from high-speed mode. Similarly, PLL operation mode can be changed back to high-speed mode.
3.Write to the CM0 and CM1 registers per 16 bits with the CM21 bit in the CM2 register = 0 (on-chip oscillator stops).
Since the operation starts from the main clock after exiting stop mode, the time until the CPU operates can be reduced.
4.The on-chip oscillator clock divided by 8 provides the CPU clock.
5.Before entering stop mode, be sure to set the CM20 bit in the CM2 register to "0" (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection function disabled).
Figure 8.12 State Transition to Stop Mode and Wait Mode
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 75 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 94

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
Main Clock Oscillation
PLL operation mode
: f(PLL)
: f(PLL)
PLC07 = 1
CM11 = 1
PLC07 = 0
CM11 = 0
PLC07 = 1
CM11 = 1
PLC07 = 0
CM11 = 0
CPU clock
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 0
CM17 = 0
CM16 = 0
CPU clock
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 0
CM17 = 0
CM16 = 0
PLL operation mode
High-Speed Mode
CPU clock
(6)
: f(XIN)
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 0
CM17 = 0
CM16 = 0
High-Speed mode
CPU clock
(6)
: f(XIN)
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 0
CM17 = 0
CM16 = 0
Medium-Speed Mode
(divide by 2)
CPU clock
: f(XIN)/2
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 0
CM17 = 0
CM16 = 1
Medium-Speed Mode
(divide by 2)
CPU clock
: f(XIN)/2
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 0
CM17 = 0
CM16 = 1
Medium-Speed Mode
(divide by 4)
CPU clock
: f(XIN)/4
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 0
CM17 = 1
CM16 = 0
CM04 = 1CM04 = 1 CM04 = 0 CM04 = 0
Medium-Speed Mode
(divide by 4)
CPU clock
: f(XIN)/4
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 0
CM17 = 1
CM16 = 0
(3)
CM07 =1
CPU clock: f(XCIN)
CM07 = 0
(1) (8)
CM05 = 1
Low Power Dissipation Mode
CPU clock: f(XCIN)
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 1
CM15 = 1
Medium-Speed Mode
(divide by 8)
CPU clock
: f(XIN)/8
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 1
Medium-Speed Mode
(divide by 8)
CPU clock
: f(XIN)/8
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 1
CM07 = 0
CM05 = 0
Medium-Speed Mode
Medium-Speed Mode
(2) (4)
(divide by 16)
CPU clock
: f(XIN)/16
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 0
CM17 = 1
CM16 = 1
(divide by 16)
CPU clock
: f(XIN)/16
CM07 = 0
CM06 = 0
CM17 = 1
CM16 = 1
CM21 = 0
CM21 = 1
CM21 = 0
CM21 = 1
CM21 = 0
CM21 = 1
On-chip Oscillator
Mode
CPU clock
(7)
f(Ring)
f(Ring)/2
f(Ring)/4
f(Ring)/8
f(Ring)/16
CM04 = 1
CM04 = 0
CPU clock
(7)
f(Ring)
f(Ring)/2
f(Ring)/4
f(Ring)/8
f(Ring)/16
On-chip Oscillator
Mode
Low-Speed ModeLow-Speed Mode
CPU clock: f(XCIN)
CM07 = 0
On-chip Oscillator
Clock Oscillation
On-chip Oscillator
Low Power Dissipation Mode
CPU clock
CM05 = 0
f(Ring)
f(Ring)/2
f(Ring)/4
(1)
CM05 = 1
f(Ring)/8
f(Ring)/16
CM04 = 1
CM04 = 0
CPU clock
CM05 = 0
f(Ring)
f(Ring)/2
f(Ring)/4
(1)
CM05 = 1
f(Ring)/8
f(Ring)/16
On-chip Oscillator
Low Power Dissipation Mode
Sub clock oscillation
CM04, CM05, CM06, CM07: Bits in CM0 register
CM11, CM15, CM16, CM17: Bits in CM1 register
CM20, CM21 : Bits in CM2 register
PLC07 : Bit in PLC0 register
NOTES:
1. Avoid making a transition when the CM20 bit is set to "1" (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection function enabled).
Set the CM20 bit to "0" (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection function disabled) before transiting.
2. Wait for the main clock oscillation stabilization time.
3. Switch clock after oscillation of sub clock is sufficiently stable.
4. Change the CM17 and CM16 bits before changing the CM06 bit.
5. Transit in accordance with arrow.
6. The PM20 bit in the PM2 register become effective when the PLC07 bit is set to "1" (PLL on). Change the PM20 bit when the PLC07 bit is
set to "0" (PLL off). Set the PM20 bit to "0" (2 waits) when PLL clock > 16 MHz.
PM20 bit to "0" (SFR accessed with two wait states) before setting the PLC07 bit to "1" (PLL operation).
7. Set the CM06 bit to "1" (divide-by-8 mode) before changing back the operation mode from on-chip oscillator mode to high- or middle-speed mode.
8. When the CM21 bit = 0 (on-chip oscillator turned off) and the CM05 bit = 1 (main clock turned off), the CM06 bit is fixed to "1" (divide-by-8 mode)
and the CM15 bit is fixed to "1" (drive capability High).
Figure 8.13 State Transition in Normal Operation Mode
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 76 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 95

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
Table 8.8 Allowed Transition and Setting
(9)
State after transition
High-Speed Mode,
Medium-Speed
Mode
High-Speed Mode,
Medium-Speed Mode
(NOTE 8) (9)
Low-Speed
(2)
Mode
Low Power
Dissipation Mode
PLL Operation
(2)
Mode
On-chip Oscillator
Mode
Current state
On-chip Oscillator Low
(12)
(14)
Power Dissipation Mode
Stop Mode
Wait Mode
-: Cannot transit
NOTES:
1. Avoid making a transition when the CM20 bit = 1 (oscillation stop, reoscillation detection function enabled). Set the CM20 bit to “0” (oscillation
stop, re-oscillation detection function disabled) before transiting.
2. On-chip oscillator clock oscillates and stops in low-speed mode. In this
mode, the on-chip oscillator can be used as peripheral function clock. Sub
clock oscillates and stops in PLL operation mode. In this mode, sub clock
can be used as peripheral function clock.
3. PLL operation mode can only be entered from and changed to high-speed
mode.
4. Set the CM06 bit to “1” (divide-by-8 mode) before transiting from on-chip
oscillator mode to high- or medium-speed mode.
5. When exiting stop mode, the CM06 bit is set to “1” (divide-by-8 mode).
6. If the CM05 bit is set to “1” (main clock stop), then the CM06 bit is set to “1”
(divide-by-8 mode).
7. A transition can be made only when sub clock is oscillating.
8. State transitions within the same mode (divide-by-n values changed or sub
clock oscillation turned on or off) are shown in the table below.
(18)
(18) (18) (18)
Sub Clock Oscillating Sub Clock Turned Off
Divide- Divide- Divide- Divide-NoDivide- Divide- Divide- Divide-
No
Division
by-2 by-4 by-8 by-16
No Division
Divide-by-2
Divide-by-4
Divide-by-8
Divide-by-16
Sub Clock Oscillating
No Division
Divide-by-2-(2)
Divide-by-4
Divide-by-8
Divide-by-16
Sub Clock Turned Off
9. ( ):setting method. See right table.
(4) (5) (7) (6) (1)
(3) (5) (7) (6)
(3) (4) (7) (6)
(3) (4) (5) (6)
(3) (4) (5) (7)
(2)
----
---
--
(2)
---
----
Low-Speed Low Power
(2)
Mode
Dissipation Mode
(7)
-
(8) (11)
-
(10)
(3)
(4)
-- ----
---
----
(5)
(18) (18)
Division
by-2 by-4 by-8 by-16
----
-
(1)
--
---
---(4) (5) (7) (6)
(3) (5) (7) (6)
--
(2)
(3) (4) (7) (6)
-
(3) (4) (5) (6)
(2) (3) (4) (5) (7)
PLL Operation
(1) (6)
---
(1)
On-chip Oscillator
Mode (2) Mode
(3)
(13)
(15)
---
---
(NOTE 8) (11)
(10) (NOTE 8) (16)
-
-
(18)
(18) (18)
(1) CM04=0 Sub clock turned off
(2) CM04=1 Sub clock oscillating
(
3) CM06=0 CPU clock no division
(
4) CM06=0 CPU clock divide-by-2
(
5) CM06=0 CPU clock divide-by-4
(
6) CM06=0 CPU clock divide-by-16
(7) CM06=1
(8) CM07=0 Main clock, PLL clock
(9) CM07=1 Sub clock selected
(10)
(11)
(12)
(
--
(1)
13)
-
(14)
(1)
(
15)
(16)
(17)
(18)
CM04, CM05, CM06, CM07: Bits in CM0 register
CM10, CM11, CM16, CM17: Bits in CM1 register
CM20, CM21 : Bits in CM2 register
PLC07 : Bit in PLC0 register
On-chip Oscillator
Low Power
Dissipation Mode
-
(5)
(18)
Stop Wait
Mode Mode
(16)
(16)
(16)
(1)
(16)
(5)
(1)
(17)
(1)
(17)
(1)
(17)
(1)
(17)
(1)
(17)
-
-
Setting Operation
CM17=0 mode
CM16=0
CM17=0 mode
CM16=1
CM17=1 mode
CM16=0
CM17=1 mode
CM16=1
CPU clock divide-by-8 mode
or on-chip oscillator
clock selected
CM05=0 Main clock oscillating
CM05=1 Main clock turned off
PLC07=0 Main clock selected
CM11=0
PLC07=1 PLL clock selected
CM11=1
CM21=0 Main clock or
PLL clock selected
CM21=1 On-chip oscillator clock
selected
CM10=1 Transition to stop mode
WAIT Transition to wait mode
instruction
Hardware Exit stop mode or wait
interrupt mode
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 77 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 96

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.5 Oscillation Stop and Re-oscillation Detection Function
The oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection function is such that main clock oscillation circuit stop and
re-oscillation are detected. At oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection, reset or oscillation stop, re-oscillation
detection interrupt request are generated. Which one is to be generated can be selected using the CM27 bit
in the CM2 register.
The oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection function can be enabled or disabled using the CM20 bit in
the CM2 register.
Table 8.9 lists a specification overview of the oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection function.
Table 8.9 Specification Overview of Oscillation Stop and Re-oscillation Detection Function
Item Specification
Oscillation Stop Detectable Clock and f(XIN) ≥ 2 MHz
Frequency Bandwidth
Enabling Condition for Oscillation Stop Set CM20 bit to “1” (enable)
and Re-oscillation Detection Function
Operation at Oscillation Stop, •Reset occurs (when CM27 bit = 0)
Re-oscillation Detection •
Oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt occurs (when the CM27 bit =1)
8.5.1 Operation When CM27 Bit = 0 (Oscillation Stop Detection Reset)
Where main clock stop is detected when the CM20 bit is “1” (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection
function enabled), the microcomputer is initialized, coming to a halt (oscillation stop reset; refer to
4. Special Function Register (SFR), 5. Reset).
This status is reset with hardware reset. Also, even when re-oscillation is detected, the microcomputer
can be initialized and stopped; it is, however, necessary to avoid such usage (During main clock stop, do
not set the CM20 bit to “1” and the CM27 bit to “0”).
8.5.2 Operation When CM27 Bit = 1 (Oscillation Stop, Re-oscillation Detection Interrupt)
Where the main clock corresponds to the CPU clock source and the CM20 bit is “1” (oscillation stop, re-oscillation
detection function enabled), the system is placed in the following state if the main clock comes to a halt:
• Oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt request is generated.
• The on-chip oscillator starts oscillation, and the on-chip oscillator clock becomes the clock source for
CPU clock and peripheral functions in place of the main clock.
• CM21 bit = 1 (on-chip oscillator clock is the clock source for CPU clock)
• CM22 bit = 1 (main clock stop detected)
• CM23 bit = 1 (main clock stopped)
Where the PLL clock corresponds to the CPU clock source and the CM20 bit is “1”, the system is placed
in the following state if the main clock comes to a halt: Since the CM21 bit remains unchanged, set it to “1”
(on-chip oscillator clock) inside the interrupt routine.
• Oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt request is generated.
• CM22 bit = 1 (main clock stop detected)
• CM23 bit = 1 (main clock stopped)
• CM21 bit remains unchanged
Where the CM20 bit is “1”, the system is placed in the following state if the main clock re-oscillates from
the stop condition:
• Oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt request is generated.
• CM22 bit = 1 (main clock re-oscillation detected)
• CM23 bit = 0 (main clock oscillation)
• CM21 bit remains unchanged
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 78 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 97

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 8. Clock Generating Circuit
8.5.3 How to Use Oscillation Stop and Re-oscillation Detection Function
• The oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt shares the vector with the watchdog timer interrupt.
If the oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection and watchdog timer interrupts both are used, read the
CM22 bit in an interrupt routine to determine which interrupt source is requesting the interrupt.
• Where the main clock re-oscillated after oscillation stop, the clock source for CPU clock and peripheral
function must be switched to the main clock in the program. Figure 8.14 shows the procedure to switch
the clock source from the on-chip oscillator to the main clock.
• Simultaneously with oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt request occurrence, the CM22 bit
becomes “1”. When the CM22 bit is set at “1”, oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt are
disabled. By setting the CM22 bit to “0” in the program, oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection interrupt
are enabled.
• If the main clock stops during low speed mode where the CM20 bit is “1”, an oscillation stop, re-oscillation
detection interrupt request is generated. At the same time, the on-chip oscillator starts oscillating. In this
case, although the CPU clock is derived from the sub clock as it was before the interrupt occurred, the
peripheral function clocks now are derived from the on-chip oscillator clock.
• To enter wait mode while using the oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection function, set the CM02
bit to “0” (peripheral function clocks not turned off during wait mode).
• Since the oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection function is provided in preparation for main clock
stop due to external factors, set the CM20 bit to “0” (oscillation stop, re-oscillation detection function
disabled) where the main clock is stopped or oscillated in the program, that is where the stop mode is
selected or the CM05 bit is altered.
• This function cannot be used if the main clock frequency is 2 MHz or less. In that case, set the CM20 bit to “0”.
Switch the main clock
NO
CM06 bit : Bit in CM0 register
CM21, CM22, CM 23 bits: Bits in CM2 register
NOTE:
1. If the clock source for CPU clock is to be changed to PLL clock,
set to PLL operation mode after set to high-speed mode.
Determine several times
whether the CM23 bit is set to "0"
(main clock oscillates)
YES
Set the CM06 bit to "1" (divide-by-8)
Set the CM22 bit to "0" (main clock stop,
re-oscillation not detected)
Set the CM21 bit to "0"
(main clock for the CPU clock source)
End
(1)
Figure 8.14 Procedure to Switch Clock Source from On-chip Oscillator to Main Clock
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 79 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 98

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 9. Protection
9. Protection
In the event that a program runs out of control, this function protects the important registers so that they will
not be rewritten easily. Figure 9.1 shows the PRCR register. The following lists the registers protected by the
PRCR register.
• The PRC0 bit protects the CM0, CM1, CM2, PLC0, PCLKR and CCLKR registers;
• The PRC1 bit protects the PM0, PM1, PM2, TB2SC, INVC0 and INVC1 registers;
• The PRC2 bit protects the PD7, PD9, S3C, S4C, S5C and S6C registers
NOTE:
1. The S5C and S6C registers are only in the 128-pin version.
Set the PRC2 bit to “1” (write enabled) and then write to any address, and the PRC2 bit will be set to “0” (write
protected). The registers protected by the PRC2 bit should be changed in the next instruction after setting
the PRC2 bit to “1”. Make sure no interrupts or DMA transfers will occur between the instruction in which the
PRC2 bit is set to “1” and the next instruction. The PRC0 and PRC1 bits are not automatically set to “0” by
writing to any address. They can only be set to “0” in a program.
(1)
.
Protect Register
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
0 0 0
NOTES:
1. The PRC2 bit is set to "0" by writing to any address after setting it to "1". Other bits are not set to "0" by writing
to any address, and must therefore be set in a program.
2. The S5C and S6C registers are only in the 128-pin version.
Symbol Address After Reset
PRCR 000Ah XX000000b
Bit NameBit Symbol Function
Enable write to CM0, CM1, CM2,
PRC0
PRC1
PRC2
-
(b5-b3)
-
(b7-b6)
Protect Bit 0
Protect Bit 1
Protect Bit 2
Reserved Bit Set to "0"
Nothing is assigned. When write, set to "0".
When read, their contents are indeterminate.
PLC0, PCLKR, CCLKR
registers
0 : Write protected
1 : Write enabled
Enable write to PM0, PM1, PM2,
TB2SC, INVC0, INVC1
registers
0 : Write protected
1 : Write enabled
Enable write to PD7, PD9, S3C,
S4C, S5C, S6C registers
0 : Write protected
1 : Write enabled
(2)
(1)
RW
RW
RW
RW
RW
-
Figure 9.1 PRCR Register
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 80 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 99

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 10. Interrupt
10. Interrupt
10.1 Type of Interrupts
Figure 10.1 shows the types of interrupts.
Undefined instruction (UND instruction)
Overflow (INTO instruction)
Software
(Non-maskable interrupt)
BRK instruction
INT instruction
Interrupt
Hardware
Special
(Non-maskable interrupt)
Peripheral function
(Maskable interrupt)
(1)
_______
NMI
________
(2)
DBC
Oscillation stop and re-oscillation detection
Watchdog timer
Single step
Address match
(2)
NOTES:
1. The peripheral functions in the microcomputer are used to generate the peripheral interrupt.
2. Do not normally use this interrupt because it is provided exclusively for use by development
tools.
Figure 10.1 Interrupts
• Maskable Interrupt: An interrupt which can be enabled (disabled) by the interrupt enable flag
(I flag) or whose interrupt priority can be changed by priority level.
• Non-Maskable Interrupt: An interrupt which cannot be enabled (disabled) by the interrupt enable flag
(I flag) or whose interrupt priority cannot be changed by priority level.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 81 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
Page 100

Under development
This document is under development and its contents are subject to change.
M16C/6N Group (M16C/6NK, M16C/6NM) 10. Interrupt
10.2 Software Interrupts
A software interrupt occurs when executing certain instructions. Software interrupts are non-maskable
interrupts.
10.2.1 Undefined Instruction Interrupt
An undefined instruction interrupt occurs when executing the UND instruction.
10.2.2 Overflow Interrupt
An overflow interrupt occurs when executing the INTO instruction with the O flag in the FLG register set to
“1” (the operation resulted in an overflow). The following are instructions whose O flag changes by arithmetic:
ABS, ADC, ADCF, ADD, CMP, DIV, DIVU, DIVX, NEG, RMPA, SBB, SHA, SUB
10.2.3 BRK Interrupt
A BRK interrupt occurs when executing the BRK instruction.
10.2.4 INT Instruction Interrupt
An INT instruction interrupt occurs when executing the INT instruction. Software interrupt Nos. 0 to 63 can
be specified for the INT instruction. Because software interrupt Nos. 1 to 31 are assigned to peripheral
function interrupts, the same interrupt routine as for peripheral function interrupts can be executed by
executing the INT instruction.
In software interrupt Nos. 0 to 31, the U flag is saved to the stack during instruction execution and is set
to “0” (ISP selected) before executing an interrupt sequence. The U flag is restored from the stack when
returning from the interrupt routine. In software interrupt Nos. 32 to 63, the U flag does not change state
during instruction execution, and the SP then selected is used.
Rev.2.00 Nov 28, 2005 page 82 of 378
REJ09B0124-0200
 Loading...
Loading...