Page 1

User’s Manual
V850ES/JF3-L
32
RENESAS MCU
V850ES/JF3-L Microcontrollers
μ PD70F3735
μPD70F3736
User’s Manual: Hardware
All information contained in these materials, including products and product specifications,
represents information on the product at the time of publication and is subject to change by
Renesas Electronics Corp. without notice. Please review the latest information published by
Renesas Electronics Corp. through various means, including the Renesas Electronics Corp.
website (http://www.renesas.com).
www.renesas.com
Rev.4.00 Sep 2010
Page 2

Notice
1. All information included in this document is current as of the date this document is issued. Such information, however, is
subject to change without any prior notice. Before purchasing or using any Renesas Electronics products listed herein, please
confirm the latest product information with a Renesas Electronics sales office. Also, please pay regular and careful attention to
additional and different information to be disclosed by Renesas Electronics such as that disclosed through our website.
2. Renesas Electronics does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights, or other intellectual property rights
of third parties by or arising from the use of Renesas Electronics products or technical information described in this document.
No license, express, implied or otherwise, is granted hereby under any patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights
of Renesas Electronics or others.
3. You should not alter, modify, copy, or otherwise misappropriate any Renesas Electronics product, whether in whole or in part.
4. Descriptions of circuits, software and other related information in this document are provided only to illustrate the operation of
semiconductor products and application examples. You are fully responsible for the incorporation of these circuits, software,
and information in the design of your equipment. Renesas Electronics assumes no responsibility for any losses incurred by
you or third parties arising from the use of these circuits, software, or information.
5. When exporting the products or technology described in this document, you should comply with the applicable export control
laws and regulations and follow the procedures required by such laws and regulations. You should not use Renesas
Electronics products or the technology described in this document for any purpose relating to military applications or use by
the military, including but not limited to the development of weapons of mass destruction. Renesas Electronics products and
technology may not be used for or incorporated into any products or systems whose manufacture, use, or sale is prohibited
under any applicable domestic or foreign laws or regulations.
6. Renesas Electronics has used reasonable care in preparing the information included in this document, but Renesas Electronics
does not warrant that such informatio n is error free. Renesas Electronics assumes no liab ility whatsoever for any damages
incurred by you resulting from errors in or omissions from the information included herein.
7. Renesas Electronics products are classified according to the following three quality grades: “Standard”, “High Quality”, and
“Specific”. The recommended applications for each Renesas Electronics product depends on the product’s quality grade, as
indicated below. You must check the quality grade of each Renesas Electronics product before using it in a particular
application. You may not use any Renesas Electronics product for any application categorized as “Specific” without the prior
written consent of Renesas Electronics. Further, you may not use any Renesas Electronics product for any application for
which it is not intended without the prior written consent of Renesas Electronics. Renesas Electronics shall not be in any way
liable for any damages or losses incurred by you or third parties arising from the use of any Renesas Electronics product for an
application categorized as “Specific” or for which the product is not intended where you have failed to obtain the prior written
consent of Renesas Electronics. The quality grade of each Renesas Electronics product is “Standard” unless otherwise
expressly specified in a Ren esas E lectronics data sheets or data books, et c.
“Standard”: Computers; office equipment; communications equipment; test and measurement equipment; audio and visual
equipment; home electron ic appliances; machine tools; personal electronic equipment; and industrial robots.
“High Quality”: Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.); traffic control systems; anti-disaster systems; anti-
crime systems; safety equipment; and medical equipment not specifically designed for life support.
“Specific”: Aircraft; aerospace equipment; submersible repeaters; nuclear react or control systems; medical equipmen t or
systems for life support (e.g. artificial life support devices or systems), surgical implantations, or healthcare
intervention (e.g. excision, etc.), and any other applicat io ns or purposes that pose a direct threat to human life.
8. You should use the Renesas Electronics products described in this document within the range specified by Renesas Electronics,
especially with respect to the maximum rating, operating supply voltage range, movement power voltage range, heat radiation
characteristics, installation and other product characteristics. Renesas Electronics shall have no liability for malfunctions or
damages arising out of the use of Renesas Electronics products beyond such specified ranges.
9. Although Renesas Electronics endeavors to improve the quality and reliability of its products, semiconductor products have
specific characteristics such as t he occu rrence o f failure at a certai n rate an d malfunct io ns under cert ain u se con dition s. Further,
Renesas Electronics prod ucts are not subject to radiation resistance design. Please be sure to implement safet y measures to
guard them against the possibility of physical injury, and injury or damage caused by fire in the event of the failure of a
Renesas Electronics product, such as safety design for hardware and software including but not limited to redundancy, fire
control and malfunction prevention, appropriate treatment for aging degradation or any other appropriate measures. Because
the evaluation of microcomputer software alone is very difficult, please evaluate the safety of the final products or system
manufactured by you.
10. Please contact a Renesas Electronics sales office for details as to environmental matters such as the envi ronmental
compatibility of each Renesas Electronics product. Please use Renesas Electronics products in compliance with all applicable
laws and regulations that regulate the inclusion or use of controlled substances, including without limitation, the EU RoHS
Directive. Renesas Electronics assumes no liability for damages or losses occurring as a result of your noncompliance with
applicable laws and regulations.
11. This document may not be reproduced or duplicated, in any form, in whole or in part, without prior written consent of Renesas
Electronics.
12. Please contact a Renesas Electronics sales office if you have any questions regarding the information contained in this
document or Renesas Electronics products, or if you have any other inquiries.
(Note 1) “Renesas Electronics” as used in this document means Renesas Electronics Corporation and also includes its majorit y-
owned subsidiaries.
(Note 2) “Renesas Electronics product(s)” means any product developed or manufactured by or for Renesas Electronics.
Page 3

NOTES FOR CMOS DEVICES
1
VOLTAGE APPLICATION WAVEFORM AT INPUT PIN
Waveform distortion due to input noise or a reflected wave may cause malfunction. If the input of the
IL
CMOS device stays in the area between V
malfunction. Take care to prevent chattering noise from entering the device when the input level is fixed,
and also in the transition period when the input level passes through the area between V
IH
(MIN).
V
HANDLING OF UNUSED INPUT PINS
2
Unconnected CMOS device inputs can be cause of malfunction. If an input pin is unconnected, it is
possible that an internal input level may be generated due to noise, etc., causing malfunction. CMOS
devices behave differently than Bipolar or NMOS devices. Input levels of CMOS devices must be fixed
high or low by using pull-up or pull-down circuitry. Each unused pin should be connected to V
via a resistor if there is a possibility that it will be an output pin. All handling related to unused pins must
be judged separately for each device and according to related specifications governing the device.
3
PRECAUTION AGAINST ESD
A strong electric field, when exposed to a MOS device, can cause destruction of the gate oxide and
ultimately degrade the device operation. Steps must be taken to stop generation of static electricity as
much as possible, and quickly dissipate it when it has occurred. Environmental control must be
adequate. When it is dry, a humidifier should be used. It is recommended to avoid using insulators that
easily build up static electricity. Semiconductor devices must be stored and transported in an anti-static
container, static shielding bag or conductive material. All test and measurement tools including work
benches and floors should be grounded. The operator should be grounded using a wrist strap.
Semiconductor devices must not be touched with bare hands. Similar precautions need to be taken for
PW boards with mounted semiconductor devices.
(MAX) and VIH (MIN) due to noise, etc., the device may
IL
(MAX) and
DD
or GND
4
STATUS BEFORE INITIALIZATION
Power-on does not necessarily define the initial status of a MOS device. Immediately after the power
source is turned ON, devices with reset functions have not yet been initialized. Hence, power-on does
not guarantee output pin levels, I/O settings or contents of registers. A device is not initialized until the
reset signal is received. A reset operation must be executed immediately after power-on for devices
with reset functions.
5
POWER ON/OFF SEQUENCE
In the case of a device that uses different power supplies for the internal operation and external
interface, as a rule, switch on the external power supply after switching on the internal power supply.
When switching the power supply off, as a rule, switch off the external power supply and then the
internal power supply. Use of the reverse power on/off sequences may result in the application of an
overvoltage to the internal elements of the device, causing malfunction and degradation of internal
elements due to the passage of an abnormal current.
The correct power on/off sequence must be judged separately for each device and according to related
specifications governing the device.
6
INPUT OF SIGNAL DURING POWER OFF STATE
Do not input signals or an I/O pull-up power supply while the device is not powered. The current
injection that results from input of such a signal or I/O pull-up power supply may cause malfunction and
the abnormal current that passes in the device at this time may cause degradation of internal elements.
Input of signals during the power off state must be judged separately for each device and according to
related specifications governing the device.
Page 4

How to Use This Manual
Readers This manual is intended for users who wish to understand the functions of the
V850ES/JF3-L and design application systems using these products.
Purpose This manual is intended to give users an understanding of the hardware functions of the
V850ES/JF3-L shown in the Organization below.
Organization This manual is divided into two parts: Hardware (this manual) and Architecture (V850ES
Architecture User’s Manual).
Hardware Architecture
• Pin functions • Data types
• CPU function • Register set
• On-chip peripheral functions • Instruction format and instruction set
• Flash memory programming • Interrupts and exceptions
• Electrical specifications • Pipeline operation
How to Read This Manual It is assumed that the readers of this manual have general knowledge in the fields of
electrical engineering, logic circuits, and microcontrollers.
To understand the overall functions of the V850ES/JF3-L
→ Read this manual according to the CONTENTS.
To find the details of a register where the name is known
→ Use APPENDIX B REGISTER INDEX.
Register format
→ The name of the bit whose number is in angle brackets (<>) in the figure of the register
format of each register is defined as a reserved word in the device file.
To understand the details of an instruction function
→ Refer to the V850ES Architecture User’s Manual available separately.
To know the electrical specifications of the V850ES/JF3-L
→ See CHAPTER 30 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS.
The “yyy bit of the xxx register” is described as the “xxx.yyy bit” in this manual. Note with
caution that if “xxx.yyy” is described as is in a program, however, the compiler/assembler
cannot recognize it correctly.
The mark <R> shows major revised points. The revised points can be easily searched by
copying an “<R>” in the PDF file and specifying it in the "Find what:" field.
Page 5

Conventions Data significance: Higher digits on the left and lower digits on the right
Active low representation: xxx (overscore over pin or signal name)
Memory map address: Higher addresses on the top and lower addresses on the
bottom
Note: Footnote for item marked with Note in the text
Caution: Information requiring particular attention
Remark: Supplementary information
Numeric representation: Binary ... xxxx or xxxxB
Decimal ... xxxx
Hexadecimal ... xxxxH
Prefix indicating power of 2 (address space, memory capacity):
K (kilo): 2
M (mega): 2
G (giga): 230 = 1,024
10
= 1,024
20
= 1,024
2
3
Page 6

Related Documents The related documents indicated in this publication may include preliminary versions.
However, preliminary versions are not marked as such.
Documents related to V850ES/JF3-L
Document Name Document No.
V850ES Architecture User’s Manual U15943E
V850ES/JF3-L Hardware User’s Manual This manual
Documents related to development tools
Document Name Document No.
QB-V850ESSX2 In-Circuit Emulator U17091E
QB-V850MINI On-Chip Debug Emulator U17638E
QB-MINI2 On-Chip Debug Emulator with Flash Programming Function U18371E
CA850 Ver. 3.20 C Compiler Package
PM+ Ver. 6.30 Project Manager U18416E
ID850QB Ver. 3.40 Integrated Debugger Operation U18604E
SM850 Ver. 2.50 System Simulator Operation U16218E
SM850 Ver. 2.00 or Later System Simulator External Part User Open
RX850 Ver. 3.20 Real-Time OS
RX850 Pro Ver. 3.21 Real-Time OS
AZ850 Ver. 3.30 System Performance Analyzer U17423E
PG-FP4 Flash Memory Programmer U15260E
PG-FP5 Flash Memory Programmer U18865E
Operation U18512E
C Language U18513E
Assembly Language U18514E
Link Directives U18515E
U14873E
Interface Specification
Operation U18601E SM+ System Simulator
User Open Interface U18212E
Basics U13430E
Installation U17419E
Task Debugger U17420E
Basics U18165E
Installation U17421E
Task Debugger U17422E
Page 7

Caution: This product uses SuperFlash
®
technology licensed from Silicon Storage Technology, Inc.
IECUBE is a registered trademark of Renesas Electronics Corporation in Japan and Germany.
MINICUBE is a registered trademark of Renesas Electronics Corporation in Japan and Germany or a trademark in
the United States of America.
EEPROM is a trademark of Renesas Electronics Corporation.
Applilet is a registered trademark of Renesas Electronics in Japan, Germany, Hong Kong, China, the Republic of
Korea, the United Kingdom, and the United States of America.
Windows and Windows NT are either registered trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United
States and/or other countries.
SuperFlash is a registered trademark of Silicon Storage Technology, Inc. in several countries including the United
States and Japan.
PC/AT is a trademark of International Business Machines Corporation.
SPARCstation is a trademark of SPARC International, Inc.
Solaris and SunOS are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc.
TRON is an abbreviation of The Realtime Operating System Nucleus.
ITRON is an abbreviation of Industrial TRON.
Page 8

CONTENTS
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION....................................................................................................................1
1.1 General .......................................................................................................................................1
1.2 Features......................................................................................................................................3
1.3 Application Fields......................................................................................................................4
1.4 Ordering Information.................................................................................................................4
1.5 Pin Configuration (Top View) ...................................................................................................5
1.6 Function Block Configuration ..................................................................................................7
1.6.1 Internal block diagram..................................................................................................................7
1.6.2 Internal units ................................................................................................................................8
CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS ................................................................................................................11
2.1 List of Pin Functions ...............................................................................................................11
2.2 Pin States .................................................................................................................................18
2.3 Pin I/O Circuit Types, I/O Buffer Power Supplies, and Connection of Unused Pins ........19
2.4 Cautions ...................................................................................................................................22
CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION .................................................................................................................23
3.1 Features....................................................................................................................................23
3.2 CPU Register Set .....................................................................................................................24
3.2.1 Program register set ..................................................................................................................25
3.2.2 System register set ....................................................................................................................26
3.3 Operation Modes .....................................................................................................................32
3.3.1 Specifying operation mode ........................................................................................................32
3.4 Address Space.........................................................................................................................33
3.4.1 CPU address space ................................................................................................................... 33
3.4.2 Wraparound of CPU address space ..........................................................................................34
3.4.3 Memory map..............................................................................................................................35
3.4.4 Areas .........................................................................................................................................37
3.4.5 Recommended use of address space........................................................................................ 40
3.4.6 Peripheral I/O registers .............................................................................................................. 43
3.4.7 Special registers ........................................................................................................................52
3.4.8 Cautions.....................................................................................................................................56
CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS ............................................................................................................59
4.1 Features....................................................................................................................................59
4.2 Basic Port Configuration ........................................................................................................59
4.3 Port Configuration ...................................................................................................................60
4.3.1 Port 0 .........................................................................................................................................65
4.3.2 Port 1 .........................................................................................................................................68
4.3.3 Port 3 .........................................................................................................................................69
4.3.4 Port 4 .........................................................................................................................................75
4.3.5 Port 5 .........................................................................................................................................77
4.3.6 Port 7 .........................................................................................................................................81
4.3.7 Port 9 .........................................................................................................................................82
4.3.8 Port CM .....................................................................................................................................88
4.3.9 Port CT ......................................................................................................................................90
4.3.10 Port DH...................................................................................................................................... 92
4.3.11 Port DL ......................................................................................................................................93
Page 9

4.4 Block Diagrams........................................................................................................................96
4.5 Port Register Settings When Alternate Function Is Used ................................................ 124
4.6 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 131
4.6.1 Cautions on setting port pins ...................................................................................................131
4.6.2 Cautions on bit manipulation instruction for port n register (Pn)............................................... 134
4.6.3 Cautions on on-chip debug pins............................................................................................... 135
4.6.4 Cautions on P05/INTP2/DRST pin...........................................................................................135
4.6.5 Cautions on P10 and P53 pins when power is turned on......................................................... 135
4.6.6 Hysteresis characteristics ........................................................................................................135
CHAPTER 5 BUS CONTROL FUNCTION .......................................................................................... 136
5.1 Features................................................................................................................................. 136
5.2 Bus Control Pins................................................................................................................... 137
5.2.1 Pin status when internal ROM, internal RAM, or on-chip peripheral I/O is accessed...............137
5.2.2 Pin status in each operation mode...........................................................................................137
5.3 Memory Block Function....................................................................................................... 138
5.4 Bus Access ........................................................................................................................... 139
5.4.1 Number of clocks for access....................................................................................................139
5.4.2 Bus size setting function ..........................................................................................................139
5.4.3 Access by bus size ..................................................................................................................140
5.5 Wait Function ........................................................................................................................ 147
5.5.1 Programmable wait function ....................................................................................................147
5.5.2 External wait function...............................................................................................................148
5.5.3 Relationship between programmable wait and external wait ...................................................149
5.5.4 Programmable address wait function.......................................................................................150
5.6 Idle State Insertion Function ............................................................................................... 151
5.7 Bus Hold Function................................................................................................................ 152
5.7.1 Functional outline.....................................................................................................................152
5.7.2 Bus hold procedure..................................................................................................................153
5.7.3 Operation in power save mode ................................................................................................153
5.8 Bus Priority ........................................................................................................................... 154
5.9 Bus Timing ............................................................................................................................ 155
CHAPTER 6 CLOCK GENERATION FUNCTION .............................................................................. 158
6.1 Overview................................................................................................................................ 158
6.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 159
6.3 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 161
6.4 Operation............................................................................................................................... 166
6.4.1 Operation of each clock ...........................................................................................................166
6.4.2 Clock output function ...............................................................................................................166
6.5 PLL Function......................................................................................................................... 167
6.5.1 Overview..................................................................................................................................167
6.5.2 Registers.................................................................................................................................. 167
6.5.3 Usage ......................................................................................................................................171
CHAPTER 7 16-BIT TIMER/EVENT COUNTER P (TMP) ................................................................ 172
7.1 Overview................................................................................................................................ 172
7.2 Functions............................................................................................................................... 172
7.3 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 173
7.4 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 175
7.5 Operation............................................................................................................................... 187
7.5.1 Interval timer mode (TPnMD2 to TPnMD0 bits = 000) .............................................................188
Page 10

7.5.2 External event count mode (TPnMD2 to TPnMD0 bits = 001) .................................................198
7.5.3 External trigger pulse output mode (TPnMD2 to TPnMD0 bits = 010) .....................................206
7.5.4 One-shot pulse output mode (TPnMD2 to TPnMD0 bits = 011)............................................... 218
7.5.5 PWM output mode (TPnMD2 to TPnMD0 bits = 100) .............................................................. 225
7.5.6 Free-running timer mode (TPnMD2 to TPnMD0 bits = 101) ....................................................234
7.5.7 Pulse width measurement mode (TPnMD2 to TPnMD0 bits = 110)......................................... 251
7.5.8 Timer output operations ........................................................................................................... 257
7.6 Selector Function ................................................................................................................. 258
7.7 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 259
CHAPTER 8 16-BIT TIMER/EVENT COUNTER Q (TMQ)................................................................ 260
8.1 Overview................................................................................................................................ 260
8.2 Functions............................................................................................................................... 260
8.3 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 261
8.4 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 263
8.5 Operation............................................................................................................................... 279
8.5.1 Interval timer mode (TQ0MD2 to TQ0MD0 bits = 000) ............................................................280
8.5.2 External event count mode (TQ0MD2 to TQ0MD0 bits = 001) ................................................289
8.5.3 External trigger pulse output mode (TQ0MD2 to TQ0MD0 bits = 010) ....................................298
8.5.4 One-shot pulse output mode (TQ0MD2 to TQ0MD0 bits = 011)..............................................311
8.5.5 PWM output mode (TQ0MD2 to TQ0MD0 bits = 100) .............................................................320
8.5.6 Free-running timer mode (TQ0MD2 to TQ0MD0 bits = 101) ................................................... 331
8.5.7 Pulse width measurement mode (TQ0MD2 to TQ0MD0 bits = 110)........................................351
8.5.8 Timer output operations ........................................................................................................... 357
8.6 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 358
CHAPTER 9 16-BIT INTERVAL TIMER M (TMM) ............................................................................ 359
9.1 Overview................................................................................................................................ 359
9.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 360
9.3 Register ................................................................................................................................. 361
9.4 Operation............................................................................................................................... 362
9.4.1 Interval timer mode ..................................................................................................................362
9.4.2 Cautions................................................................................................................................... 366
CHAPTER 10 WATCH TIMER FUNCTIONS ...................................................................................... 367
10.1 Functions............................................................................................................................... 367
10.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 368
10.3 Control Registers ................................................................................................................. 370
10.4 Operation............................................................................................................................... 374
10.4.1 Operation as watch timer.........................................................................................................374
10.4.2 Operation as interval timer....................................................................................................... 375
10.4.3 Cautions...................................................................................................................................376
CHAPTER 11 FUNCTIONS OF WATCHDOG TIMER 2 ................................................................... 377
11.1 Functions............................................................................................................................... 377
11.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 378
11.3 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 379
11.4 Operation............................................................................................................................... 381
CHAPTER 12 REAL-TIME OUTPUT FUNCTION (RTO)................................................................... 382
12.1 Function................................................................................................................................. 382
12.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 383
Page 11

12.3 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 385
12.4 Operation............................................................................................................................... 387
12.5 Usage..................................................................................................................................... 388
12.6 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 388
CHAPTER 13 A/D CONVERTER ......................................................................................................... 389
13.1 Overview................................................................................................................................ 389
13.2 Functions............................................................................................................................... 389
13.3 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 390
13.4 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 393
13.5 Operation............................................................................................................................... 404
13.5.1 Basic operation........................................................................................................................404
13.5.2 Conversion operation timing ....................................................................................................405
13.5.3 Trigger mode ...........................................................................................................................406
13.5.4 Operation mode.......................................................................................................................408
13.5.5 Power-fail compare mode........................................................................................................412
13.6 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 417
13.7 How to Read A/D Converter Characteristics Table........................................................... 421
CHAPTER 14 D/A CONVERTER ......................................................................................................... 425
14.1 Functions............................................................................................................................... 425
14.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 425
14.3 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 426
14.4 Operation............................................................................................................................... 428
14.4.1 Operation in normal mode .......................................................................................................428
14.4.2 Operation in real-time output mode..........................................................................................428
14.4.3 Cautions...................................................................................................................................429
CHAPTER 15 ASYNCHRONOUS SERIAL INTERFACE A (UARTA) ............................................. 430
15.1 Mode Switching of UARTA2 and I2C00 ............................................................................... 430
15.2 Features................................................................................................................................. 431
15.3 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 432
15.4 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 434
15.5 Interrupt Request Signals.................................................................................................... 440
15.6 Operation............................................................................................................................... 441
15.6.1 Data format..............................................................................................................................441
15.6.2 SBF transmission/reception format.......................................................................................... 443
15.6.3 SBF transmission.....................................................................................................................445
15.6.4 SBF reception..........................................................................................................................446
15.6.5 UART transmission.................................................................................................................. 447
15.6.6 Continuous transmission procedure.........................................................................................448
15.6.7 UART reception ....................................................................................................................... 450
15.6.8 Reception errors ......................................................................................................................451
15.6.9 Parity types and operations .....................................................................................................453
15.6.10 Receive data noise filter........................................................................................................... 454
15.7 Dedicated Baud Rate Generator ......................................................................................... 455
15.8 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 463
CHAPTER 16 3-WIRE VARIABLE-LENGTH SERIAL I/O (CSIB).................................................... 464
16.1 Mode Switching of CSIB0 and I2C01 ................................................................................... 464
16.2 Features................................................................................................................................. 465
16.3 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 466
Page 12

16.4 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 468
16.5 Interrupt Request Signals.................................................................................................... 475
16.6 Operation............................................................................................................................... 476
16.6.1 Single transfer mode (master mode, transmission mode)........................................................476
16.6.2 Single transfer mode (master mode, reception mode).............................................................478
16.6.3 Single transfer mode (master mode, transmission/reception mode)........................................480
16.6.4 Single transfer mode (slave mode, transmission mode) .......................................................... 482
16.6.5 Single transfer mode (slave mode, reception mode)................................................................484
16.6.6 Single transfer mode (slave mode, transmission/reception mode)...........................................486
16.6.7 Continuous transfer mode (master mode, transmission mode) ...............................................488
16.6.8 Continuous transfer mode (master mode, reception mode)..................................................... 490
16.6.9 Continuous transfer mode (master mode, transmission/reception mode)................................ 493
16.6.10 Continuous transfer mode (slave mode, transmission mode) ..................................................497
16.6.11 Continuous transfer mode (slave mode, reception mode) .......................................................499
16.6.12 Continuous transfer mode (slave mode, transmission/reception mode) ..................................502
16.6.13 Reception error ........................................................................................................................506
16.6.14 Clock timing .............................................................................................................................507
16.7 Output Pins ........................................................................................................................... 509
16.8 Baud Rate Generator............................................................................................................ 510
16.8.1 Baud rate generation ...............................................................................................................511
16.9 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 512
CHAPTER 17 I2C BUS .......................................................................................................................... 513
17.1 Mode Switching of I2C Bus and Other Serial Interfaces ................................................... 513
17.1.1 UARTA2 and I2C00 mode switching.........................................................................................513
17.1.2 CSIB0 and I2C01 mode switching ............................................................................................514
17.2 Features................................................................................................................................. 515
17.3 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 516
17.4 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 520
17.5 I2C Bus Mode Functions....................................................................................................... 536
17.5.1 Pin configuration......................................................................................................................536
17.6 I2C Bus Definitions and Control Methods .......................................................................... 537
17.6.1 Start condition.......................................................................................................................... 537
17.6.2 Addresses................................................................................................................................ 538
17.6.3 Transfer direction specification ................................................................................................539
17.6.4 ACK .........................................................................................................................................540
17.6.5 Stop condition..........................................................................................................................541
17.6.6 Wait state.................................................................................................................................542
17.6.7 Wait state cancellation method................................................................................................544
17.7 I2C Interrupt Request Signals (INTIICn) .............................................................................. 545
17.7.1 Master device operation...........................................................................................................545
17.7.2 Slave device operation (when receiving slave address data (address match))........................ 548
17.7.3 Slave device operation (when receiving extension code) ........................................................552
17.7.4 Operation without communication............................................................................................556
17.7.5 Arbitration loss operation (operation as slave after arbitration loss).........................................556
17.7.6 Operation when arbitration loss occurs (no communication after arbitration loss) ................... 558
17.8 Interrupt Request Signal (INTIICn) Generation Timing and Wait Control....................... 565
17.9 Address Match Detection Method ...................................................................................... 567
17.10 Error Detection...................................................................................................................... 567
17.11 Extension Code..................................................................................................................... 567
17.12 Arbitration ............................................................................................................................. 568
17.13 Wakeup Function.................................................................................................................. 569
Page 13

17.14 Communication Reservation............................................................................................... 570
17.14.1 When communication reservation function is enabled (IICFn.IICRSVn bit = 0) .......................570
17.14.2 When communication reservation function is disabled (IICFn.IICRSVn bit = 1)....................... 574
17.15 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 575
17.16 Communication Operations ................................................................................................ 576
17.16.1 Master operation in single master system................................................................................ 577
17.16.2 Master operation in multimaster system ..................................................................................577
17.16.3 Slave operation........................................................................................................................581
17.17 Timing of Data Communication .......................................................................................... 584
CHAPTER 18 DMA FUNCTION (DMA CONTROLLER) ................................................................... 591
18.1 Features................................................................................................................................. 591
18.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 592
18.3 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 593
18.4 Transfer Targets ................................................................................................................... 600
18.5 Transfer Modes..................................................................................................................... 600
18.6 Transfer Types...................................................................................................................... 601
18.7 DMA Channel Priorities........................................................................................................ 602
18.8 Time Related to DMA Transfer ............................................................................................ 602
18.9 DMA Transfer Start Factors................................................................................................. 603
18.10 DMA Abort Factors ............................................................................................................... 604
18.11 End of DMA Transfer ............................................................................................................ 604
18.12 Operation Timing .................................................................................................................. 604
18.13 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 609
CHAPTER 19 INTERRUPT/EXCEPTION PROCESSING FUNCTION............................................... 614
19.1 Features................................................................................................................................. 614
19.2 Non-Maskable Interrupts ..................................................................................................... 618
19.2.1 Operation.................................................................................................................................620
19.2.2 Restore .................................................................................................................................... 621
19.2.3 NP flag..................................................................................................................................... 622
19.3 Maskable Interrupts.............................................................................................................. 623
19.3.1 Operation.................................................................................................................................623
19.3.2 Restore .................................................................................................................................... 625
19.3.3 Priorities of maskable interrupts...............................................................................................626
19.3.4 Interrupt control register (xxICn) .............................................................................................. 630
19.3.5 Interrupt mask registers 0 to 3 (IMR0 to IMR3)........................................................................632
19.3.6 In-service priority register (ISPR)............................................................................................. 634
19.3.7 ID flag ......................................................................................................................................635
19.3.8 Watchdog timer mode register 2 (WDTM2) .............................................................................635
19.4 Software Exception .............................................................................................................. 636
19.4.1 Operation.................................................................................................................................636
19.4.2 Restore .................................................................................................................................... 637
19.4.3 EP flag..................................................................................................................................... 638
19.5 Exception Trap...................................................................................................................... 639
19.5.1 Illegal opcode...........................................................................................................................639
19.5.2 Debug trap...............................................................................................................................641
19.6 External Interrupt Request Input Pins (NMI and INTP0 to INTP7) ................................... 643
19.6.1 Noise elimination .....................................................................................................................643
19.6.2 Edge detection......................................................................................................................... 643
19.7 Interrupt Acknowledge Time of CPU .................................................................................. 648
19.8 Periods in Which Interrupts Are Not Acknowledged by CPU.......................................... 649
Page 14

19.9 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 649
CHAPTER 20 KEY INTERRUPT FUNCTION ..................................................................................... 650
20.1 Function................................................................................................................................. 650
20.2 Register ................................................................................................................................. 651
20.3 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 651
CHAPTER 21 STANDBY FUNCTION .................................................................................................. 652
21.1 Overview................................................................................................................................ 652
21.2 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 654
21.3 HALT Mode............................................................................................................................ 659
21.3.1 Setting and operation status ....................................................................................................659
21.3.2 Releasing HALT mode............................................................................................................. 659
21.4 IDLE1 Mode ........................................................................................................................... 661
21.4.1 Setting and operation status ....................................................................................................661
21.4.2 Releasing IDLE1 mode............................................................................................................661
21.5 IDLE2 Mode ........................................................................................................................... 663
21.5.1 Setting and operation status ....................................................................................................663
21.5.2 Releasing IDLE2 mode............................................................................................................663
21.5.3 Securing setup time when releasing IDLE2 mode ...................................................................665
21.6 STOP Mode/Low-Voltage STOP Mode................................................................................ 666
21.6.1 Setting and operation status ....................................................................................................666
21.6.2 Releasing STOP mode/low-voltage STOP mode ....................................................................670
21.6.3 Re-setting after release of low-voltage STOP mode................................................................671
21.6.4 Securing oscillation stabilization time when releasing STOP mode.........................................672
21.7 Subclock Operation Mode/Low-Voltage Subclock Operation Mode............................... 673
21.7.1 Setting and operation status ....................................................................................................673
21.7.2 Releasing subclock operation mode ........................................................................................ 677
21.7.3 Releasing low-voltage subclock operation mode ..................................................................... 677
21.8 Sub-IDLE Mode/Low-Voltage Sub-IDLE Mode................................................................... 678
21.8.1 Setting and operation status ....................................................................................................678
21.8.2 Releasing sub-IDLE mode/low-voltage sub-IDLE mode ..........................................................681
CHAPTER 22 RESET FUNCTIONS ..................................................................................................... 682
22.1 Overview................................................................................................................................ 682
22.2 Registers to Check Reset Source....................................................................................... 683
22.3 Operation............................................................................................................................... 684
22.3.1 Reset operation via RESET pin ...............................................................................................684
22.3.2 Reset operation by watchdog timer 2.......................................................................................687
22.3.3 Reset operation by low-voltage detector.................................................................................. 689
22.3.4 Operation after reset release ................................................................................................... 690
22.3.5 Reset function operation flow...................................................................................................691
22.4 Cautions ................................................................................................................................ 692
CHAPTER 23 CLOCK MONITOR ........................................................................................................ 693
23.1 Functions............................................................................................................................... 693
23.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 693
23.3 Register ................................................................................................................................. 694
23.4 Operation............................................................................................................................... 695
CHAPTER 24 LOW-VOLTAGE DETECTOR (LVI) ............................................................................. 698
24.1 Functions............................................................................................................................... 698
Page 15

24.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 698
24.3 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 699
24.4 Operation............................................................................................................................... 701
24.4.1 To use for internal reset signal.................................................................................................701
24.4.2 To use for interrupt ..................................................................................................................702
CHAPTER 25 CRC FUNCTION............................................................................................................ 703
25.1 Functions............................................................................................................................... 703
25.2 Configuration ........................................................................................................................ 703
25.3 Registers ............................................................................................................................... 704
25.4 Operation............................................................................................................................... 705
25.5 Usage Method ....................................................................................................................... 706
CHAPTER 26 REGULATOR ................................................................................................................. 708
26.1 Outline ................................................................................................................................... 708
26.2 Operation............................................................................................................................... 709
CHAPTER 27 OPTION BYTE............................................................................................................... 710
CHAPTER 28 FLASH MEMORY.......................................................................................................... 712
28.1 Features................................................................................................................................. 712
28.2 Memory Configuration ......................................................................................................... 713
28.3 Functional Outline ................................................................................................................ 714
28.4 Rewriting by Dedicated Flash Programmer....................................................................... 717
28.4.1 Programming environment.......................................................................................................717
28.4.2 Communication mode..............................................................................................................718
28.4.3 Flash memory control ..............................................................................................................723
28.4.4 Selection of communication mode ........................................................................................... 724
28.4.5 Communication commands .....................................................................................................725
28.4.6 Pin connection .........................................................................................................................726
28.5 Rewriting by Self Programming.......................................................................................... 730
28.5.1 Overview..................................................................................................................................730
28.5.2 Features...................................................................................................................................731
28.5.3 Standard self programming flow ..............................................................................................732
28.5.4 Flash functions.........................................................................................................................733
28.5.5 Pin processing .........................................................................................................................733
28.5.6 Internal resources used ...........................................................................................................734
CHAPTER 29 ON-CHIP DEBUG FUNCTION ..................................................................................... 735
29.1 Debugging with DCU............................................................................................................ 736
29.1.1 Connection circuit example...................................................................................................... 736
29.1.2 Interface signals.......................................................................................................................736
29.1.3 Maskable functions .................................................................................................................. 738
29.1.4 Register ...................................................................................................................................738
29.1.5 Operation.................................................................................................................................740
29.1.6 Cautions...................................................................................................................................741
29.2 Debugging Without Using DCU........................................................................................... 742
29.2.1 Circuit connection examples....................................................................................................742
29.2.2 Maskable functions .................................................................................................................. 744
29.2.3 Securement of user resources................................................................................................. 744
29.2.4 Cautions...................................................................................................................................750
29.3 ROM Security Function........................................................................................................ 751
Page 16

29.3.1 Security ID ............................................................................................................................... 751
29.3.2 Setting .....................................................................................................................................752
CHAPTER 30 ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS................................................................................. 753
CHAPTER 31 PACKAGE DRAWINGS ................................................................................................ 783
CHAPTER 32 RECOMMENDED SOLDERING CONDITIONS........................................................... 785
APPENDIX A DEVELOPMENT TOOLS............................................................................................... 786
A.1 Software Package................................................................................................................. 788
A.2 Language Processing Software.......................................................................................... 788
A.3 Control Software................................................................................................................... 788
A.4 Debugging Tools (Hardware) .............................................................................................. 789
A.4.1 When using IECUBE® QB-V850ESSX2 ..................................................................................789
A.4.2 When using MINICUBE QB-V850MINI ....................................................................................792
A.4.3 When using MINICUBE2 QB-MINI2 ........................................................................................793
A.5 Debugging Tools (Software)................................................................................................ 794
A.6 Embedded Software ............................................................................................................. 795
A.7 Flash Memory Writing Tools ............................................................................................... 796
APPENDIX B REGISTER INDEX ......................................................................................................... 797
APPENDIX C INSTRUCTION SET LIST ............................................................................................. 806
C.1 Conventions .......................................................................................................................... 806
C.2 Instruction Set (in Alphabetical Order) .............................................................................. 809
APPENDIX D REVISION HISTORY ..................................................................................................... 816
D.1 Major Revisions in This Edition.............................................................................................. 816
D.2 Revision History of Previous Editions................................................................................... 816
Page 17

V850ES/JF3-L
RENESAS MCU
R01UH0017EJ0400
Rev.4.00
Sep 30, 2010
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
The V850ES/JF3-L is one of the products in the Renesas Electronics V850 single-chip microcontrollers designed for
low-power operation for real-time control applications.
1.1 General
The V850ES/JF3-L is a 32-bit single-chip microcontroller that includes the V850ES CPU core and peripheral functions
such as ROM/RAM, a timer/counter, serial interfaces, an A/D converter, and a D/A converter.
In addition to high real-time response characteristics and 1-clock-pitch basic instructions, the V850ES/JF3-L features
multiply instructions, saturated operation instructions, bit manipulation instructions, etc., realized by a hardware multiplier,
as optimum instructions for digital servo control applications. Moreover, as a real-time control system, the V850ES/JF3-L
enables an extremely high cost-performance for applications that require ultra low power consumption, such as digital
cameras, power meters, and mobile terminals.
Table 1-1 lists the products of the V850ES/JF3-L and V850ES/JG3-L.
The V850ES/JG3-L is a model of the V850ES/JF3-L with expanded I/O, timer/counter, and serial interface functions.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 1 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 18

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
Generic Name V850ES/JF3-L V850ES/JG3-L
Part Number
Flash memory 128 KB 256 KB 128 KB 256 KB Internal
memory
RAM 8 KB 16 KB 8 KB 16 KB
Logical space 64 MB Memory
space
External memory area 15 MB
External bus interface Address bus: 18
General-purpose register 32 bits × 32 registers
Clock
Main clock
(oscillation frequency)
Subclock
(oscillation frequency)
Internal oscillator fR = 220 kHz (TYP.)
Minimum instruction
execution time
DSP function 32 × 32 = 64: 200 to 250 ns (at 20 MHz)
I/O port I/O: 66 (5 V tolerant/N-ch open-drain output
Timer
16-bit TMP 4 channels 6 channels
16-bit TMQ 1 channel 1 channel
16-bit TMM 1 channel 1 channel
Watch timer 1 channel 1 channel
WDT 1 channel 1 channel
Real-time output port 4 bits × 1 channel, 2 bits × 1 channel, or 6 bits × 1 channel
10-bit A/D converter 8 channels 12 channels
8-bit D/A converter 1 channel 2 channels
Serial interface CSIB: 2 channels
DMA controller 4 channels (transfer target: on-chip peripheral I/O, internal RAM, external memory)
External 9 (9)
Internal 40 48
Power save function HALT/IDLE1/IDLE2/STOP/subclock/sub-IDLE/
Reset source RESET pin input, watchdog timer 2 (WDT2), clock monitor (CLM), low-voltage detector (LVI)
CRC function 16-bit error detection code generated for 8-bit unit data
On-chip debug MINICUBE®, MINICUBE2 supported
Operating power supply voltage 2.2 to 3.6 V @5 MHz, 2.7 to 3.6 V @20 MHz
Operating ambient temperature −40 to +85°C
Package 80-pin LQFP (12 × 12 mm)
Note The figure in parentheses indicates the number of external interrupts that can release STOP mode.
Table 1-1. V850ES/Jx3-L Product List
μ
PD70F3735
Address data bus: 16
Multiplexed bus mode output supported
Ceramic/crystal
(in PLL mode: f
X = 2.5 to 5 MHz (multiplied by 4), in clock through mode: fX = 2.5 to 10 MHz)
External clock
(in PLL mode: f
X = 2.5 to 5 MHz (multiplied by 4), in clock through mode: fX = 2.5 to 5 MHz)
Crystal (fXT = 32.768 kHz)
50 ns (main clock (fXX) = 20 MHz)
32 × 32 + 32 = 32: 300 ns (at 20 MHz)
16 × 16 = 32: 50 to 100 ns (at 20 MHz)
16 × 16 + 32 = 32: 150 ns (at 20 MHz)
selectable: 25)
UARTA: 2 channels
2
CSIB/I
C bus: 1 channel
2
UARTA/I
C bus: 1 channel
low-voltage STOP/low-voltage subclock/low-voltage sub-IDLE mode
80-pin LQFP (14 × 14 mm)
μ
PD70F3736
μ
PD70F3737
Address bus: 22
Address data bus: 16
Separate bus/multiplexed bus mode selectable
I/O: 84 (5 V tolerant/N-ch open-drain output
selectable: 31)
CSIB: 3 channels
UARTA/CSIB: 1 channel
2
CSIB/I
C bus: 1 channel
2
UARTA/I
Note
9 (9)
C bus: 2 channels
100-pin LQFP (14 × 14 mm)
100-pin LQFP (14 × 20 mm)
μ
PD70F3738
Note
Interrupt source
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 2 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 19

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.2 Features
{ Minimum instruction execution time: 50 ns (operating with main clock (f
200 ns (operating with main clock (f
30.5 μs (operating with subclock (fXT) of 32.768 kHz)
{ General-purpose registers: 32 bits × 32 registers
{ CPU features: Signed multiplication (16 × 16 → 32): 1 to 2 clocks
Signed multiplication (32 × 32 → 64): 1 to 5 clocks
Saturated operations (overflow and underflow detection functions included)
32-bit shift instruction: 1 clock
Bit manipulation instructions
Load/store instructions with long/short format
{ Memory space: 64 MB of linear address space (for programs and data)
External expansion: Up to 16 MB (including 1 MB used as internal ROM/RAM)
• Internal memory: RAM: 8/16 KB (see Table 1-1)
Flash memory: 128/256 KB (see Table 1-1)
• External bus interface: Multiplexed bus output
8/16 bit data bus sizing function
Wait function
• Programmable wait function
• External wait function
Idle state function
Bus hold function
{ Interrupts and exceptions: Non-maskable interrupts: 2 sources
Maskable interrupts: 47 sources
Software exceptions: 32 sources
Exception trap: 2 sources
{ I/O lines: I/O ports: 66
{ Timer function: 16-bit interval timer M (TMM): 1 channel
16-bit timer/event counter P (TMP): 4 channels
16-bit timer/event counter Q (TMQ): 1 channel
Watch timer: 1 channel
Watchdog timer: 1 channel
{ Real-time output port: 6 bits × 1 channel
{ Serial interface: Asynchronous serial interface A (UARTA)
3-wire variable-length serial interface B (CSIB)
I
2
C bus interface (I2C)
UARTA: 2 channels
UARTA/I
CSIB/I
2
C: 1 channel
2
C: 1 channel
CSIB: 2 channels
{ A/D converter: 10-bit resolution: 8 channels
{ D/A converter: 8-bit resolution: 1 channel
{ DMA controller: 4 channels
{ DCU (debug control unit): JTAG interface
{ Clock generator: During main clock or subclock operation
7-level CPU clock (f
XX, fXX/2, fXX/4, fXX/8, fXX/16, fXX/32, fXT)
Clock-through mode/PLL mode selectable
XX) of 20 MHz: VDD = 2.7 to 3.6 V)
XX) of 5 MHz: VDD = 2.2 to 3.6 V)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 3 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 20

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
{ Internal oscillation clock: 220 kHz (TYP.)
{ Power-save functions: HALT/IDLE1/IDLE2/STOP/low-voltage STOP mode/subclock/sub-IDLE/
low-voltage subclock/low-voltage sub-IDLE mode
{ Package: 80-pin plastic LQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12)
80-pin plastic LQFP (14 × 14)
1.3 Application Fields
Digital cameras, power meters, mobile terminals, digital home electronics, and other consumer devices
1.4 Ordering Information
Part Number Package Internal Flash Memory
μ
PD70F3735GK-GAK-AX
μ
PD70F3736GK-GAK-AX
μ
PD70F3735GC-GAD-AX
μ
PD70F3736GC-GAD-AX
Remark V850ES/JF3-L microcontrollers are lead-free products.
80-pin plastic LQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12)
80-pin plastic LQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12)
80-pin plastic LQFP (14 × 14)
80-pin plastic LQFP (14 × 14)
128 KB
256 KB
128 KB
256 KB
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 4 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 21

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.5 Pin Configuration (Top View)
80-pin plastic LQFP (fine pitch) (12 × 12)
80-pin plastic LQFP (14 × 14)
μ
PD70F3735GK-GAK-AX
μ
PD70F3736GK-GAK-AX
P70/ANI0
μ
PD70F3735GC-GAD-AX
μ
PD70F3736GC-GAD-AX
P71/ANI1
P72/ANI2
P73/ANI3
P74/ANI4
P75/ANI5
P76/ANI6
P77/ANI7
PDH1/A17
PDL15/AD15
PDL14/AD14
PDH0/A16
PDL13/AD13
PDL12/AD12
PDL11/AD11
PDL10/AD10
PDL9/AD9
PDL8/AD8
PDL7/AD7
PDL6/AD6
REF0
AV
AV
P10/ANO0
AV
REF1
P03/INTP0/ADTRG
P04/INTP1
P06/INTP3
Note 1
FLMD0
V
Note 2
REGC
V
X1
X2
RESET
XT1
XT2
P02/NMI
P05/INTP2/DRST
P40/SIB0/SDA01
P41/SOB0/SCL01
80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61
1
ss
DD
SS
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40
SS
DD
EV
EV
60
59
58
57
56
55
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
PDL5/AD5/FLMD1
PDL4/AD4
PDL3/AD3
PDL2/AD2
PDL1/AD1
PDL0/AD0
PCT6/ASTB
PCT4/RD
PCT1/WR1
PCT0/WR0
PCM3/HLDRQ
PCM2/HLDAK
PCM1/CLKOUT
PCM0/WAIT
P915/INTP6/TIP50/TOP50
P914/INTP5/TIP51/TOP51
P913/INTP4
P99/SCKB1
P98/SOB1
P97/SIB1/TIP20/TOP20
P30/TXDA0
P42/SCKB0
P90/KR6/TXDA1
P35/TIP11/TOP11
P33/TIP01/TOP01
P31/RXDA0/INTP7
P34/TIP10/TOP10
P38/TXDA2/SDA00
P32/ASCKA0/TIP00/TOP00
P39/RXDA2/SCL00
P50/TIQ01/KR0/TOQ01/RTP00
P51/TIQ02/KR1/TOQ02/RTP01
P54/SOB2/KR4/RTP04/DCK
P52/TIQ03/KR2/TOQ03/RTP02/DDI
P53/SIB2/TIQ00/KR3/TOQ00/RTP03/DDO
P91/KR7/RXDA1
P96/TIP21/TOP21
P55/SCKB2/KR5/RTP05/DMS
Notes 1. Connect this pin to V
2. Connect the REGC pin to V
SS in the normal mode.
SS via a 4.7
μ
F (recommended value) capacitor.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 5 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 22

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
Pin names
A16, A17:
AD0 to AD15:
ADTRG:
ANI0 to ANI7:
ANO0:
ASCKA0:
ASTB:
AV
REF0, AVREF1:
AVSS:
CLKOUT:
DCK:
DDI:
DDO:
DMS:
DRST:
EV
DD:
EV
SS:
FLMD0, FLMD1:
HLDAK:
HLDRQ:
INTP0 to INTP7:
KR0 to KR7:
NMI:
P02 to P06:
P10:
P30 to P35:
P38, P39
P40 to P42:
P50 to P55:
P70 to P77:
P90, P91:
P96 to P99,
P913 to P915
Address bus
Address/data bus
A/D trigger input
Analog input
Analog output
Asynchronous serial clock
Address strobe
Analog reference voltage
Analog V
SS
Clock output
Debug clock
Debug data input
Debug data output
Debug mode select
Debug reset
Power supply for external pin
Ground for external pin
Flash programming mode
Hold acknowledge
Hold request
External interrupt input
Key return
Non-maskable interrupt request
Port 0
Port 1
Port 3
Port 4
Port 5
Port 7
Port 9
PCM0 to PCM3:
PCT0, PCT1,
PCT4, PCT6:
PDH0, PDH1:
PDL0 to PDL15:
RD:
REGC:
RESET:
RTP00 to RTP05:
RXDA0 to RXDA2:
SCKB0 to SCKB2:
SCL00, SCL01:
SDA00, SDA01:
SIB0 to SIB2:
SOB0 to SOB2:
TIP00, TIP01,
TIP10, TIP11,
TIP20, TIP21,
TIP50, TIP51,
TIQ00 to TIQ03:
TOP00, TOP01,
TOP10, TOP11,
TOP20, TOP21,
TOP50, TOP51,
TOQ00 to TOQ03:
TXDA0 to TXDA2:
V
DD:
V
SS:
WAIT:
WR0:
WR1:
X1, X2:
XT1, XT2:
Port CM
Port CT
Port DH
Port DL
Read strobe
Regulator control
Reset
Real-time output port
Receive data
Serial clock
Serial clock
Serial data
Serial input
Serial output
Timer input
Timer output
Transmit data
Power supply
Ground
Wait
Lower byte write strobe
Upper byte write strobe
Crystal for main clock
Crystal for subclock
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 6 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 23

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.6 Function Block Configuration
1.6.1 Internal block diagram
INTP to INTP7
TIQ00 to TIQ03
TOQ00 to TOQ03
TIP00 to TIP20, TIP50
TIP01 to TIP21, TIP51
TOP00 to TOP20, TOP50
TOP01 to TOP21, TOP51
NMI
INTC
16-bit timer/
counter Q:
1 ch
16-bit timer/
counter P:
4 ch
16-bit interval
timer M:
1 ch
Flash
memory
Note 1
RAM
Note 2
DMAC
PC
32-bit barrel
shifter
System
registers
General-purpose
registers 32 bits × 32
CPU
Multiplier
16 × 16 → 32
ALU
Instruction
queue
BCU
HLDRQ
HLDAK
ASTB
RD
WAIT
WR0, WR1
A16, A17
AD0 to AD15
RTP00 to RTP05
SOB0/SCL01
SIB0/SDA01
SCKB0
SOB1
SIB1
SCKB1
SOB2
SIB2
SCKB2
TXDA0
RXDA0
ASCKA0
TXDA1
RXDA1
TXDA2/SDA00
RXDA2/SCL00
RTO
CSIB0 I2C01
CSIB1
CSIB2
UARTA0
UARTA1
UARTA2
I2C00
Ports
P70-P77
P50-P55
P40-P42
PDH0, PDH1
PDL0-PDL15
PCM0b to PCM3
PCT0, PCT1, PCT4, PCT6
P90, P91, P96-P99, P913-P915
A/D
converter
D/A
converter
Key return
function
Watchdog
timer 2
Watch timer
Internal
oscillator
P10
P02-P06
P30-P35, P38, P39
ANI0 to ANI7
AV
SS
AV
REF0
ADTRG
AV
REF1
ANO0
KR0 to KR7
CLM
CRC
DCU
CG
CG
PLL
LVI
Regulator
CLKOUT
XT1
XT2
X1
X2
RESET
V
DD
V
SS
REGC
FLMD0
FLMD1
EV
DD
EV
SS
DRST
DMS
DDI
DCK
DDO
Notes 1.
μ
PD70F3735: 128 KB
μ
PD70F3736: 256 KB
2. μPD70F3735: 8 KB
μ
PD70F3736: 16 KB
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 7 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 24

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
1.6.2 Internal units
(1) CPU
The CPU uses five-stage pipeline control to enable single-clock execution of address calculations, arithmetic logic
operations, data transfers, and almost all other instruction processing.
Other dedicated on-chip hardware, such as a multiplier (16 bits × 16 bits → 32 bits) and a barrel shifter (32 bits)
contribute to faster complex processing.
(2) Bus control unit (BCU)
The BCU starts a required external bus cycle based on the physical address obtained by the CPU. When an
instruction is fetched from external memory space and the CPU does not send a bus cycle start request, the BCU
generates a prefetch address and prefetches the instruction code. The prefetched instruction code is stored in an
instruction queue.
(3) Flash memory (ROM)
This is a 256/128 KB flash memory mapped to addresses 0000000H to 003FFFFH/0000000H to 001FFFFH.
It can be accessed from the CPU in one clock during instruction fetch.
(4) RAM
This is a 16/8 KB RAM mapped to addresses 3FFB000H to 3FFEFFFH/3FFD000H to 3FFEFFFH. It can be
accessed from the CPU in one clock during data access.
(5) Interrupt controller (INTC)
This controller handles hardware interrupt requests (NMI, INTP0 to INTP7) from on-chip peripheral hardware and
external hardware. Eight levels of interrupt priorities can be specified for these interrupt requests, and multiplexed
servicing control can be performed.
(6) Clock generator (CG)
A main clock oscillator and subclock oscillator are provided and generate the main clock oscillation frequency (f
and subclock frequency (f
clock frequency (f
XX) as is. In the PLL mode, fX is used multiplied by 4.
XT), respectively. There are two modes: In the clock-through mode, fX is used as the main
The CPU clock frequency (fCPU) can be selected from among fXX, fXX/2, fXX/4, fXX/8, fXX/16, fXX/32, and fXT.
(7) Internal oscillator
An internal oscillator is provided on chip. The oscillation frequency is 220 kHz (TYP). The internal oscillator
supplies the clock for watchdog timer 2 and timer M.
(8) Timer/counter
Four-channel 16-bit timer/event counter P (TMP), one-channel 16-bit timer/event counter Q (TMQ), and one-
channel 16-bit interval timer M (TMM), are provided on chip.
(9) Watch timer
This timer counts the reference time period (0.5 s) for counting the clock (the 32.768 kHz subclock or the 32.768
kHz clock f
BRG from prescaler 3). The watch timer can also be used as an interval timer for the main clock.
X)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 8 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 25

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
(10) Watchdog timer 2
A watchdog timer is provided on chip to detect inadvertent program loops, system abnormalities, etc.
The internal oscillation clock, the main clock, or the subclock can be selected as the source clock.
Watchdog timer 2 generates a non-maskable interrupt request signal (INTWDT2) or a system reset signal
(WDT2RES) after an overflow occurs.
(11) Serial interface
The V850ES/JF3-L includes three kinds of serial interfaces: asynchronous serial interface A (UARTA), 3-wire
variable-length serial interface B (CSIB), and an I
In the case of UARTA, data is transferred via the TXDA0 to TXDA2 pins and RXDA0 to RXDA2 pins.
In the case of CSIB, data is transferred via the SOB0 to SOB2 pins, SIB0 to SIB2 pins, and SCKB0 to SCKB2
pins.
In the case of I
2
C, data is transferred via the SDA00, SDA01, SCL00, and SCL01 pins.
(12) A/D converter
This 10-bit A/D converter includes 8 analog input pins. Conversion is performed using the successive
approximation method.
(13) D/A converter
A one-channel, 8-bit-resolution D/A converter that uses the R-2R ladder method is provided on chip.
(14) DMA controller
A 4-channel DMA controller is provided on chip. This controller transfers data between the internal RAM and on-
chip peripheral I/O devices in response to interrupt requests sent by on-chip peripheral I/O.
(15) Key interrupt function
A key interrupt request signal (INTKR) can be generated by inputting a falling edge to the key input pins (8
channels).
(16) Real-time output function
The real-time output function transfers preset 6-bit data to output latches upon the occurrence of a timer compare
register match signal.
(17) CRC function
A CRC operation circuit that generates a 16-bit CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) code upon setting of 8-bit data
is provided on-chip.
(18) DCU (debug control unit)
An on-chip debug function that uses the JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) communication specifications is provided.
Switching between the normal port function and on-chip debugging function is done with the control pin input
level and the OCDM register.
2
C bus interface (I2C).
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 9 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 26

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
(19) Ports
The following general-purpose port functions and control pin functions are available.
Port I/O Alternate Function
P0 5-bit I/O NMI, external interrupt, A/D converter trigger, debug reset
P1 1-bit I/O D/A converter analog output
P3 8-bit I/O External interrupt, serial interface, timer I/O
P4 3-bit I/O Serial interface
P5 6-bit I/O Timer I/O, real-time output, key interrupt input, serial interface, debug I/O
P7 8-bit I/O A/D converter analog input
P9 9-bit I/O Serial interface, key interrupt input, timer I/O, external interrupt
PCM 4-bit I/O External control signal
PCT 4-bit I/O External control signal
PDH 2-bit I/O External address bus
PDL 16-bit I/O External address/data bus
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 10 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 27

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.1 List of Pin Functions
The names and functions of the pins in the V850ES/JF3-L are described below.
There are three types of pin I/O buffer power supplies: AV
supplies and the pins is described below.
Table 2-1. Pin I/O Buffer Power Supplies
Power Supply Corresponding Pins
AVREF0 Port 7
AVREF1 Port 1
EVDD RESET, ports 0, 3 to 5, 9, CM, CT, DH, DL
REF0, AVREF1, and EVDD. The relationship between these power
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 11 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 28
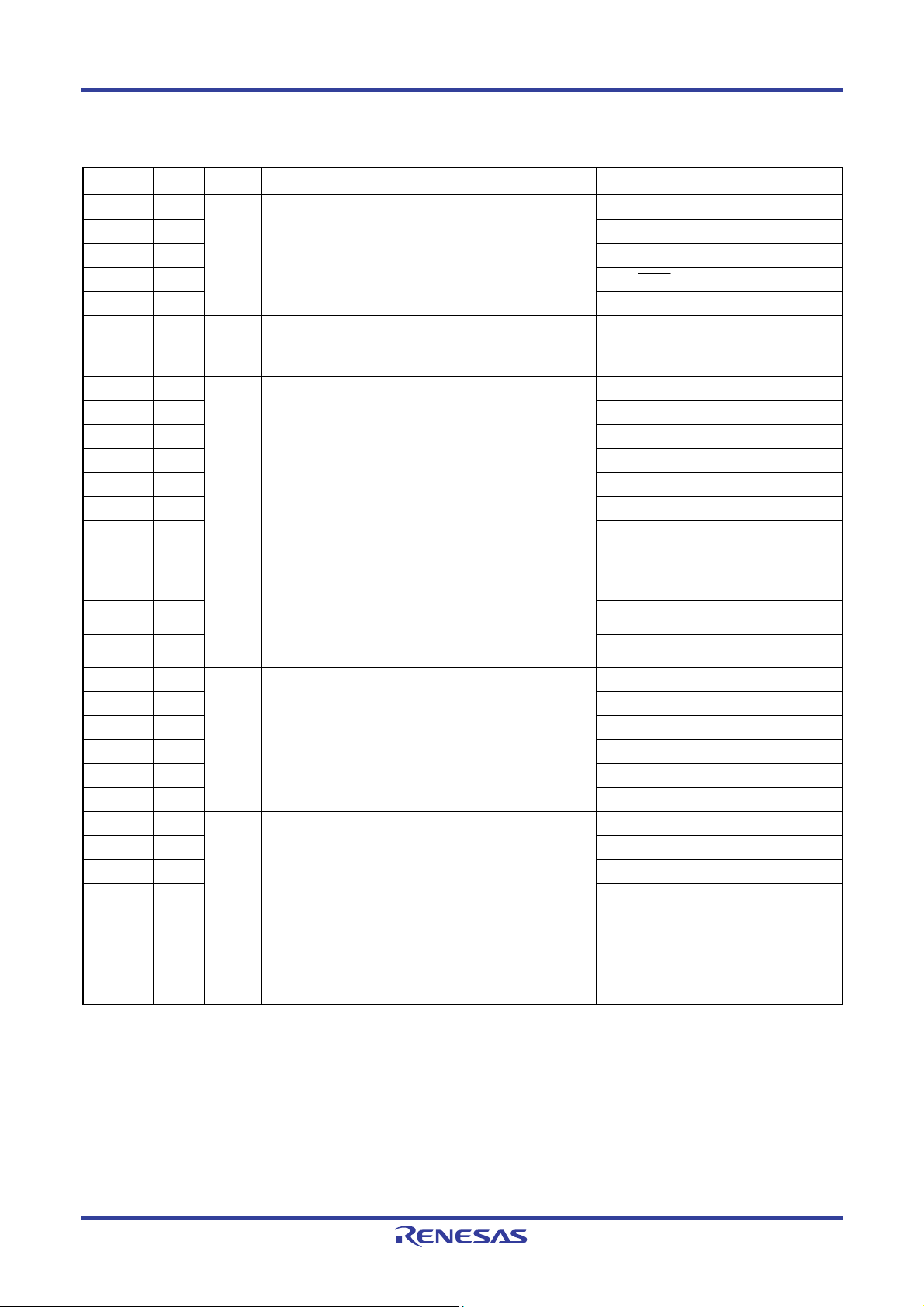
V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
(1) Port pins
(1/2)
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Function Alternate Function
P02 17 NMI
P03 5 INTP0/ADTRG
P04 6 INTP1
Note
P05
18 INTP2/DRST
P06 7
P10 3 I/O
P30
P31
P32
P33
P34
P35
P38
P39
P40 19 SIB0/SDA01
P41 20 SOB0/SCL01
P42 21
P50 32 TIQ01/KR0/TOQ01/RTP00
P51 33 TIQ02/KR1/TOQ02/RTP01
P52 34 TIQ03/KR2/TOQ03/RTP02/DDI
P53 35 SIB2/KR3/TIQ00/TOQ00/RTP03/DDO
P54 36 SOB2/KR4/RTP04/DCK
P55 37
P70 80 ANI0
P71 79 ANI1
P72 78 ANI2
P73 77 ANI3
P74 76 ANI4
P75 75 ANI5
P76 74 ANI6
P77 73
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Por t 0
5-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
N-ch open-drain output can be specified in 1-bit units.
5 V tolerant.
Por t 1
1-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
Por t 3
10-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
N-ch open-drain output can be specified in 1-bit units.
5 V tolerant.
Por t 4
3-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
N-ch open-drain output can be specified in 1-bit units.
5 V tolerant.
Por t 5
6-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
N-ch open-drain output can be specified in 1-bit units.
5 V tolerant.
Por t 7
8-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
INTP3
ANO0
TXDA0
RXDA0/INTP7
ASCKA0/TIP00/TOP00
TIP01/TOP01
TIP10/TOP10
TIP11/TOP11
TXDA2/SDA00
RXDA2/SCL00
SCKB0
SCKB2/KR5/RTP05/DMS
ANI7
Note Incorporates a pull-down resistor. It can be disconnected by clearing the OCDM.OCDM0 bit to 0.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 12 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 29

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Function Alternate Function
P90 38 KR6/TXDA1
P91 39 KR7/RXDA1
P96 40 TIP21/TOP21
P97 41 SIB1/TIP20/TOP20
P98 42 SOB1
P99 43 SCKB1
P913 44 INTP4
P914 45 INTP5/TIP51/TOP51
P915 46
PCM0 47 WAIT
PCM1 48 CLKOUT
PCM2 49 HLDAK
PCM3 50
PCT0 51 WR0
PCT1 52 WR1
PCT4 53 RD
PCT6 54
PDH0 71 A16
PDH1 72
PDL0 55 AD0
PDL1 56 AD1
PDL2 57 AD2
PDL3 58 AD3
PDL4 59 AD4
PDL5 60 AD5/FLMD1
PDL6 61 AD6
PDL7 62 AD7
PDL8 63 AD8
PDL9 64 AD9
PDL10 65 AD10
PDL11 66 AD11
PDL12 67 AD12
PDL13 68 AD13
PDL14 69 AD14
PDL15 70
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
I/O
Por t 9
9-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
N-ch open-drain output can be specified in 1-bit units.
5 V tolerant. (only P90, P91, P96)
Por t CM
4-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
Por t CT
4-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
Port DH
2-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
Por t DL
16-bit I/O port
Input/output can be specified in 1-bit units.
INTP6/TIP50/TOP50
HLDRQ
ASTB
A17
AD15
(2/2)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 13 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 30

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
(2) Non-port pins
(1/4)
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Function Alternate Function
A16 89 PDH0
A17 90
AD0 55 PDL0
AD1 56 PDL1
AD2 57 PDL2
AD3 58 PDL3
AD4 59 PDL4
AD5 60 PDL5/FLMD1
AD6 61 PDL6
AD7 62 PDL7
AD8 63 PDL8
AD9 64 PDL9
AD10 65 PDL10
AD11 66 PDL11
AD12 67 PDL12
AD13 68 PDL13
AD14 69 PDL14
AD15 70
ADTRG 5 Input A/D converter external trigger input. 5 V tolerant. P03/INTP0
ANI0 80 P70
ANI1 79 P71
ANI2 78 P72
ANI3 77 P73
ANI4 76 P74
ANI5 75 P75
ANI6 74 P76
ANI7 73
ANO0 3 Output Analog voltage output for D/A converter P10
ASCKA0 24 Input UARTA0 baud rate clock input. 5 V tolerant. P32/TIP00/TOP00
ASTB 54 Output Address strobe signal output for external memory PCT6
AVREF0 1 Reference voltage input for A/D converter/positive power
AVREF1 4
AVSS 2 − Ground potential for A/D and D/A converters (same
CLKOUT 48 Output Internal system clock output PCM1
DCK 36 Input Debug clock input. 5 V tolerant. P54/SOB2/KR4/RTP04
DDI 34 Input Debug data input. 5 V tolerant. P52/TIQ03/KR2/TOQ03/RTP02
Note
DDO
35 Output Debug data output. N-ch open-drain output selectable.
DMS 37 Input Debug mode select input. 5 V tolerant. P55/SCKB2/KR5/RTP05
Note In the on-chip debug mode, high-level output is forcibly set.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 14 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Output Address bus for external memory
I/O Address bus/data bus for external memory
Input Analog voltage input for A/D converter
−
supply for port 7
Reference voltage input for D/A converter/positive power
supply for port 1
potential as V
5 V tolerant.
SS)
PDH1
PDL15
P77
−
−
−
P53/SIB2/KR3/TIQ00/TOQ00/
RTP03
Page 31

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Function Alternate Function
DRST 18 Input Debug reset input. 5 V tolerant. P05/INTP2
EVDD 31 − Positive power supply for external (same potential as VDD)
EVSS 30 − Ground potential for external (same potential as VSS)
FLMD0 8
FLMD1 60
HLDAK 49 Output Bus hold acknowledge output PCM2
HLDRQ 50 Input Bus hold request input PCM3
INTP0 5 P03/ADTRG
INTP1 6 P04
INTP2 18 P05/DRST
INTP3 7 P06
INTP4 44 P913
INTP5 45 P914/TIP51/TOP51
INTP6 46 P915/TIP50/TOP50
INTP7 23
KR0 32 P50/TIQ01/TOQ01/RTP00
KR1 33 P51/TIQ02/TOQ02/RTP01
KR2 34 P52/TIQ03/TOQ03/RTP02/DDI
KR3 35
KR4 36 P54/SOB2/RTP04/DCK
KR5 37 P55/SCKB2/RTP05/DMS
KR6 38 P90/TXDA1
KR7 39
NMI 17 Input
RD 53 Output Read strobe signal output for external memory PCT4
REGC 10
RESET 14 Input System reset input
RTP00 32 P50/TIQ01/KR0/TOQ01
RTP01 33 P51/TIQ02/KR1/TOQ02
RTP02 34 P52/TIQ03/KR2/TOQ03/DDI
RTP03 35
RTP04 36 P54/SOB2/KR4/DCK
RTP05 37
RXDA0 23 P31/INTP7
RXDA1 39 P91/KR7
RXDA2 29
Input Flash memory programming mode setting pin
Input
Input
Output
Input Serial receive data input (UARTA0 to UARTA2)
External interrupt request input (maskable, analog noise
elimination).
Analog noise elimination or digital noise elimination
selectable for INTP3 pin.
5 V tolerant.
Key interrupt input (on-chip analog noise eliminator)
5 V tolerant.
External interrupt input (non-maskable, analog noise
elimination). 5 V tolerant.
Connection of regulator output stabilization capacitance
−
μ
F (recommended value))
(4.7
Real-time output port
N-ch open-drain output selectable.
5 V tolerant.
5 V tolerant.
PDL5/AD5
P31/RXDA0
P53/SIB2/TIQ00/TOQ00/
RTP03/DDO
P91/RXDA1
P02
P53/SIB2/TIQ00/KR3/TOQ00/
DDO
P55/SCKB2/KR5/DMS
P39/SCL00
−
−
−
−
−
(2/4)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 15 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 32

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Function Alternate Function
SCKB0 21 P42
SCKB1 43 P99
SCKB2 37
SCL00 29 P39/RXDA2
SCL01 20
SDA00 28 P38/TXDA2
SDA01 19
SIB0 19 P40/SDA01
SIB1 41 P97/TIP20/TOP20
SIB2 35
SOB0 20 P41/SCL01
SOB1 42 P98
SOB2 36
TIP00 24 External event count input/capture trigger input/external
TIP01 25 Capture trigger input (TMP0). 5 V tolerant. P33/TOP01
TIP10 26 External event count input/capture trigger input/external
TIP11 27 Capture trigger input (TMP1). 5 V tolerant. P35/TOP11
TIP20 41 External event count input/capture trigger input/external
TIP21 40 Capture trigger input (TMP2). 5 V tolerant.
TIP50 46
TIP51 45
TIQ00 35
TIQ01 32 P50/KR0/TOQ01/RTP00
TIQ02 33 P51/KR1/TOQ02/RTP01
TIQ03 34
TOP00 24 P32/ASCKA0/TIP00
TOP01 25
TOP10 26 P34/TIP10
TOP11 27
TOP20 41 P97/SIB1/TIP20
TOP21 40
TOP50 46 P915/INTP6/TIP50
TOP51 45
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 16 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
I/O Serial clock I/O (CSIB0 to CSIB2)
N-ch open-drain output selectable.
5 V tolerant (SCKB0, SCKB2 only).
I/O Serial clock I/O (I
N-ch open-drain output selectable.
5 V tolerant.
I/O Serial transmit/receive data I/O (I
N-ch open-drain output selectable.
5 V tolerant.
Input Serial receive data input (CSIB0 to CSIB2)
5 V tolerant (SIB0, SIB2 only).
Output Serial transmit data output (CSIB0 to CSIB2)
N-ch open-drain output selectable.
5 V tolerant (SOB0, SOB2 only).
Input
trigger input (TMP0). 5 V tolerant.
trigger input (TMP1). 5 V tolerant.
trigger input (TMP2)
External event count input/capture trigger input/external
trigger input (TMP5)
Capture trigger input (TMP5).
External event count input/capture trigger input/external
trigger input (TMQ0). 5 V tolerant.
Capture trigger input (TMQ0). 5 V tolerant.
Output
Timer output (TMP0)
N-ch open-drain output selectable. 5 V tolerant.
Timer output (TMP1)
N-ch open-drain output selectable. 5 V tolerant.
Timer output (TMP2)
N-ch open-drain output selectable. 5 V tolerant (TOP21
only).
Timer output (TMP5)
N-ch open-drain output selectable.
2
C00, I2C01)
2
C00, I2C01)
P55/KR5/RTP05/DMS
P41/SOB0
P40/SIB0
P53/TIQ00/KR3/TOQ00/
RTP03/DDO
P54/KR4/RTP04/DCK
P32/ASCKA0/TOP00
P34/TOP10
P97/SIB1/TOP20
P96/TOP21
P915/INTP6/TOP50
P914/INTP5/TOP51
P53/SIB2/KR3/TOQ00/RTP03/DDO
P52/KR2/TOQ03/RTP02/
DDI
P33/TIP01
P35/TIP11
P96//TIP21
P914/INTP5/TIP51
(3/4)
Page 33

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Pin Name Pin No. I/O Function Alternate Function
TOQ00 35
TOQ01 32 P50/TIQ01/KR0/RTP00
TOQ02 33 P51/TIQ02/KR1/RTP01
TOQ03 34
TXDA0 22 P30
TXDA1 38 P90/KR6
TXDA2 28
VDD 9 − Positive power supply pin for internal
VSS 11 − Ground potential for internal
WAIT 47 Input External wait input PCM0
WR0 51 Write strobe for external memory (lower 8 bits) PCT0
WR1 52
X1 12 Input
X2 13
XT1 15 Input
XT2 16
Output
Output
Output
Timer output (TMQ0)
N-ch open-drain output selectable. 5 V tolerant.
Serial transmit data output (UARTA0 to UARTA2)
N-ch open-drain output selectable.
5 V tolerant.
Write strove for external memory (higher 8 bits) PCT1
Connection of resonator for main clock
−
Connection of resonator for subclock
−
P53/SIB2/TIQ00/KR3/RTP03/
DDO
P52/TIQ03/KR2/RTP02/DDI
P38/SDA00
−
−
−
−
−
−
(4/4)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 17 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 34

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.2 Pin States
The operation states of pins in the various modes are described below.
Table 2-2. Pin Operation States in Various Modes
Pin Name
When Power
Is Turned
Note 1
On
During Reset
(Except When
Powe r I s
HALT Mode
Turned On)
P05/DRST Pulled down Pulled down
P10/ANO0 Hi-Z Held Held Hi-Z Held Held
Undefined
P53/DDO
Note 6
AD0 to AD15
Hi-Z
Hi-Z
Note 4
Held Held Held Held Held
Note 5
Hi-Z
Held Held Held Held Held
Note 6
Undefined
A16, A17
WAIT
CLKOUT Operating L L Operating Operating
WR0, WR1
RD
ASTB
HLDAK
Operating
HLDRQ
Other port pins Hi-Z Hi-Z Held Held Held Held Held
Notes 1. Duration until 1 ms elapses after the supply voltage reaches the operating supply voltage range (lower limit)
when the power is turned on.
2. Operates while an alternate function is operating.
3. The state of the pins in the idle state inserted after the T3 state is shown.
4. Pulled down during external reset. During internal reset by the watchdog timer, clock monitor, etc., the state
of this pin differs according to the OCDM.OCDM0 bit setting.
5. DDO output is specified in the on-chip debug mode.
6. The bus control pins function alternately as port pins, so they are initialized to the input mode (port mode).
7. Operates even in the HALT mode, during DMA operation.
Remark Hi-Z: High impedance
Held: The state during the immediately preceding external bus cycle is held.
L: Low-level output
H: High-level output
−: Input without sampling (not acknowledged)
Note 2
Note 7
IDLE1, IDLE2,
Sub-IDLE
Note 2
Mode
Hi-Z Hi-Z Held Hi-Z
STOP
Mode
Note 2
Idle
State
Note 3
Bus Hold
− − − − −
Note 7
Hi-Z
H
Note 7
H H H
− − −
Operating
L
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 18 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 35

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.3 Pin I/O Circuit Types, I/O Buffer Power Supplies, and Connection of Unused Pins
(1/2)
Pin No.Pin Alternate Function
P02 NMI 17
P03 INTP0/ADTRG 5
P04 INTP1 6
P05 INTP2/DRST 18 10-N
P06 INTP3 7 10-D
P10 ANO0 3 12-D
P30 TXDA0 22 10-G
P31 RXDA0/INTP7 23
P32 ASCKA0/TIP00 24
P33 TIP01/TOP01 25
P34 TIP10/TOP10 26
P35 TIP11/TOP11 27
P38 TXDA2/SDA00 28
P39 RXDA2/SCL00 29
P40 SIB0/SDA01 19
P41 SOB0/SCL01 20
P42 SCKB0 21
P50 TIQ01/KR0/TOQ01/RTP00 32
P51 TIQ02/KR1/TOQ02/RTP01 33
P52 TIQ03/KR2/TOQ03/RTP02/DDI 34
P53
SIB2/KR3/TIQ00/TOQ00/RTP03/
DDO
P54 SOB2/KR4/RTP04/DCK 36
P55 SCKB2/KR5/RTP05/DMS 37
P70 to P77 ANI0 to ANI7 100-73 11-G
I/O Circuit Type Recommended Connection
GC
10-D
Input: Independently connect to EV
resistor.
Output: Leave open.
Input: Independently connect to EV
Fixing to V
DD level is prohibited.
Output: Leave open.
Internally pull-down after reset by RESET pin.
Input: Independently connect to EV
resistor.
Output: Leave open.
Input: Independently connect to AV
resistor.
Output: Leave open.
Input: Independently connect to EV
10-D
resistor.
Output: Leave open.
35
Input: Independently connect to AV
resistor.
Output: Leave open.
DD or EVSS via a
SS via a resistor.
DD or EVSS via a
REF1 or AVSS via a
DD or EVSS via a
REF0 or AVSS via a
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 19 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 36

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Pin Alternate Function Pin No. I/O Circuit Type Recommended Connection
P90 KR6/TXDA1 38
P91 KR7/RXDA1 39
P96 TIP21/TOP21 40
P97 SIB1/TIP20/TOP20 41
P98 SOB1 42 10-G
P99 SCKB1 43
P913 INTP4 44
P914 INTP5/TIP51/TOP51 45
P915 INTP6/TIP50/TOP50 46
PCM0 WAIT 47
PCM1 CLKOUT 48
PCM2 HLDAK 49
PCM3 HLDRQ 50
PCT0, PCT1 WR0, WR1 51, 52
PCT4 RD 53
PCT6 ASTB 54
PDH0, PDH1 A16, A17 71, 72
PDL0 to
PDL4
PDL5 AD5/FLMD1 60
PDL6 to
PDL15
AVREF0
AVREF1
AVSS
EVDD
EVSS
FLMD0
REGC
RESET
VDD
VSS
X1
X2
XT1
XT2
AD0 to AD4 55, 59
AD6 to AD15 61, 70
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
1
4
2
31
30
8
10
14 2
9
11
12
13
15 16-C Connect to VSS.
16 16-C Leave open.
10-D
10-D
5
−
−
−
−
− −
−
−
− −
− −
− −
− −
Input: Independently connect to EV
resistor.
Output: Leave open.
Directly connect to VDD and always supply power.
Directly connect to VDD and always supply power.
Directly connect to VSS and always supply power.
Directly connect to VDD and always supply power.
Directly connect to V
memory programming mode.
Connect regulator output stabilization capacitance (4.7
μ
F (recommended value)).
SS in a mode other than the flash
−
DD or EVSS via a
(2/2)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 20 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 37

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
Type 2
Figure 2-1. Pin I/O Circuits
Type 10-N
EV
DD
IN
Schmitt-triggered input with hysteresis characteristics
Type 5
Data
Output
disable
Input
enable
Type 10-D
Data
Open drain
Output
disable
Note
EV
EV
DD
P-ch
N-ch
SS
EV
EV
DD
P-ch
N-ch
SS
IN/OUT
IN/OUT
IN/OUT
Data
Open drain
Output
disable
Input
enable
Type 11-G
Data
Output
disable
Comparator
(Threshold voltage)
Input enable
Note
OCDM0 bit
+
_
REF0
V
AV
P-ch
IN/OUT
N-ch
EV
SS
N-ch
AV
REF0
P-ch
N-ch
AV
SS
P-ch
N-ch
SS
IN/OUT
Type 10-G
Data
Open drain
Output
disable
Input
enable
Input
enable
EV
EV
DD
P-ch
IN/OUT
N-ch
SS
Type 12-D
Data
Output
disable
Input
enable
Analog output
Type 16-C
Feedback cut-off
XT1 XT2
voltage
P-ch
P-ch
N-ch
AV
AV
REF1
P-ch
N-ch
SS
IN/OUT
Note Hysteresis characteristics are not available in port mode.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 21 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 38

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 2 PIN FUNCTIONS
2.4 Cautions
When the power is turned on, the following pins may output an undefined level temporarily even during reset.
• P10/ANO0 pin
• P53/SIB2/KR3/TIQ00/TOQ00/RTP03/DDO pin
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 22 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 39

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
The CPU of the V850ES/JF3-L is based on RISC architecture and executes almost all instructions with one clock by
using a 5-stage pipeline.
3.1 Features
Minimum instruction execution time: 50 ns (operating with main clock (fXX) of 20 MHz: VDD = 2.7 to 3.6 V)
200 ns (operating with main clock (f
30.5 μs (operating with subclock (fXT) of 32.768 kHz)
Memory space Program (physical address) space: 64 MB linear
Data (logical address) space: 4 GB linear
General-purpose registers: 32 bits × 32 registers
Internal 32-bit architecture
5-stage pipeline control
Multiplication/division instruction
Saturation operation instruction
32-bit shift instruction: 1 clock
Load/store instruction with long/short format
Four types of bit manipulation instructions
• SET1
• CLR1
• NOT1
• TST1
XX) of 5 MHz: VDD = 2.2 to 3.6 V)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 23 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 40

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.2 CPU Register Set
The registers of the V850ES/JF3-L can be classified into two types: general-purpose program registers and dedicated
system registers. All the registers are 32 bits wide.
For details, refer to the V850ES Architecture User’s Manual.
(1) Program register set
(2) System register set
31 0 31 0
r0
(Zero register)
(Assembler-reserved register)
r1
r2
r3
(Stack pointer (SP))
r4
(Global pointer (GP))
r5
(Text pointer (TP))
r6
r7
r8
r9
r10
r11
r12
r13
r14
r15
r16
r17
r18
r19
r20
r21
r22
r23
r24
r25
r26
r27
r28
r29
r30
(Element pointer (EP))
r31
(Link pointer (LP))
EIPC
EIPSW
FEPC
FEPSW
ECR (Interrupt source register)
PSW (Program status word)
CTPC
CTPSW
DBPC
DBPSW
CTBP (CALLT base pointer)
(Interrupt status saving register)
(Interrupt status saving register)
(NMI status saving register)
(NMI status saving register)
(CALLT execution status saving register)
(CALLT execution status saving register)
(Exception/debug trap status saving register)
(Exception/debug trap status saving register)
31 0
PC (Program counter)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 24 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 41

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.2.1 Program register set
The program registers include general-purpose registers and a program counter.
(1) General-purpose registers (r0 to r31)
Thirty-two general-purpose registers, r0 to r31, are available. Any of these registers can be used to store a data
variable or an address variable.
However, r0 and r30 are implicitly used by instructions and care must be exercised when these registers are used.
r0 always holds 0 and is used for an operation that uses 0 or addressing of offset 0. r30 is used by the SLD and
SST instructions as a base pointer when these instructions access the memory. r1, r3 to r5, and r31 are implicitly
used by the assembler and C compiler. When using these registers, save their contents for protection, and then
restore the contents after using the registers. r2 is sometimes used by the real-time OS. If the real-time OS does
not use r2, it can be used as a register for variables.
Table 3-1. Program Registers
Name Usage Operation
r0 Zero register Always holds 0.
r1 Assembler-reserved register Used as working register to create 32-bit immediate data
r2 Register for address/data variable (if real-time OS does not use r2)
r3 Stack pointer Used to create a stack frame when a function is called
r4 Global pointer Used to access a global variable in the data area
r5 Text pointer Used as register that indicates the beginning of a text area (area
where program codes are located)
r6 to r29 Register for address/data variable
r30 Element pointer Used as base pointer to access memory
r31 Link pointer Used when the compiler calls a function
PC Program counter Holds the instruction address during program execution
Remark For further details on the r1, r3 to r5, and r31 that are used in the assembler and C compiler, refer to the
CA850 (C Compiler Package) Assembly Language User’s Manual.
(2) Program counter (PC)
The program counter holds the instruction address during program execution. The lower 32 bits of this register are
valid. Bits 31 to 26 are fixed to 0. A carry from bit 25 to 26 is ignored even if it occurs.
Bit 0 is fixed to 0. This means that execution cannot branch to an odd address.
31 2625 1 0
PC
Fixed to 0 Instruction address during program execution
0
Default value
00000000H
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 25 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 42

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.2.2 System register set
The system registers control the status of the CPU and hold interrupt information.
These registers can be read or written by using system register load/store instructions (LDSR and STSR), using the
system register numbers listed below.
Table 3-2. System Register Numbers
System Register Name
Register
Number
Note 1
Note 1
Note 1
Note 1
0 Interrupt status saving register (EIPC)
1 Interrupt status saving register (EIPSW)
2 NMI status saving register (FEPC)
3 NMI status saving register (FEPSW)
4 Interrupt source register (ECR)
5 Program status word (PSW)
6 to 15 Reserved for future function expansion (operation is not guaranteed if these
Operand Specification System
LDSR Instruction STSR Instruction
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
× √
√ √
× ×
registers are accessed)
16 CALLT execution status saving register (CTPC)
17 CALLT execution status saving register (CTPSW)
18 Exception/debug trap status saving register (DBPC) √
19 Exception/debug trap status saving register (DBPSW) √
20 CALLT base pointer (CTBP)
21 to 31 Reserved for future function expansion (operation is not guaranteed if these
√ √
√ √
Note 2
√
Note 2
√
√ √
× ×
Note 2
Note 2
registers are accessed)
Notes 1. Because only one set of these registers is available, the contents of these registers must be saved by
program if multiple interrupts are enabled.
2. These registers can be accessed only during the interval between the execution of the DBTRAP instruction
or illegal opcode and DBRET instruction execution.
Caution Even if EIPC or FEPC, or bit 0 of CTPC is set to 1 by the LDSR instruction, bit 0 is ignored when
execution is returned to the main routine by the RETI instruction after interrupt servicing (this is
because bit 0 of the PC is fixed to 0). Set an even value to EIPC, FEPC, and CTPC (bit 0 = 0).
Remark √: Can be accessed
×: Access prohibited
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 26 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 43

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(1) Interrupt status saving registers (EIPC and EIPSW)
EIPC and EIPSW are used to save the status when an interrupt occurs.
If a software exception or a maskable interrupt occurs, the contents of the program counter (PC) are saved to EIPC,
and the contents of the program status word (PSW) are saved to EIPSW (these contents are saved to the NMI
status saving registers (FEPC and FEPSW) if a non-maskable interrupt occurs).
The address of the instruction next to the instruction under execution, except some instructions (see 19.8 Periods
in Which Interrupts Are Not Acknowledged by CPU), is saved to EIPC when a software exception or a maskable
interrupt occurs.
The current contents of the PSW are saved to EIPSW.
Because only one set of interrupt status saving registers is available, the contents of these registers must be saved
by program when multiple interrupts are enabled.
Bits 31 to 26 of EIPC and bits 31 to 8 of EIPSW are reserved for future function expansion (these bits are always
fixed to 0).
The value of EIPC is restored to the PC and the value of EIPSW to the PSW by the RETI instruction.
31 0
EIPC
EIPSW
00
31 0
00
26 25
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0
(Contents of saved PC)
87
(Contents of
saved PSW)
Default value
0xxxxxxxH
(x: Undefined)
Default value
000000xxH
(x: Undefined)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 27 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 44

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(2) NMI status saving registers (FEPC and FEPSW)
FEPC and FEPSW are used to save the status when a non-maskable interrupt (NMI) occurs.
If an NMI occurs, the contents of the program counter (PC) are saved to FEPC, and those of the program status
word (PSW) are saved to FEPSW.
The address of the instruction next to the one of the instruction under execution, except some instructions, is saved
to FEPC when an NMI occurs.
The current contents of the PSW are saved to FEPSW.
Because only one set of NMI status saving registers is available, the contents of these registers must be saved by
program when multiple interrupts are enabled.
Bits 31 to 26 of FEPC and bits 31 to 8 of FEPSW are reserved for future function expansion (these bits are always
fixed to 0).
The value of FEPC is restored to the PC and the value of FEPSW to the PSW by the RETI instruction.
31 0
FEPC
FEPSW
00
31 0
00
(3) Interrupt source register (ECR)
The interrupt source register (ECR) holds the source of an exception or interrupt if an exception or interrupt occurs.
This register holds the exception code of each interrupt source. Because this register is a read-only register, data
cannot be written to this register using the LDSR instruction.
31 0
ECR
Bit position Bit name Meaning
31 to 16 FECC Exception code of non-maskable interrupt (NMI)
15 to 0 EICC Exception code of exception or maskable interrupt
26 25
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0
FECC EICC
(Contents of saved PC)
16 15
87
(Contents of
saved PSW)
Default value
0xxxxxxxH
(x: Undefined)
Default value
000000xxH
(x: Undefined)
Default value
00000000H
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 28 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 45

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(4) Program status word (PSW)
The program status word (PSW) is a collection of flags that indicate the status of the program (result of instruction
execution) and the status of the CPU.
If the contents of a bit of this register are changed by using the LDSR instruction, the new contents are validated
immediately after completion of LDSR instruction execution. However if the ID flag is set to 1, interrupt requests will
not be acknowledged while the LDSR instruction is being executed.
Bits 31 to 8 of this register are reserved for future function expansion (these bits are fixed to 0).
(1/2)
31 0
PSW
RFU
Bit position Flag name Meaning
31 to 8 RFU Reserved field. Fixed to 0.
7 NP Indicates that a non-maskable interrupt (NMI) is being serviced. This bit is set to 1 when an
NMI request is acknowledged, disabling multiple interrupts.
0: NMI is not being serviced.
1: NMI is being serviced.
6 EP Indicates that an exception is being processed. This bit is set to 1 when an exception
occurs. Even if this bit is set, interrupt requests are acknowledged.
0: Exception is not being processed.
1: Exception is being processed.
5 ID Indicates whether a maskable interrupt can be acknowledged.
0: Interrupt enabled
1: Interrupt disabled
4 SAT
3 CY Indicates whether a carry or a borrow occurs as a result of an operation.
2 OV
1 S
0 Z Indicates whether the result of an operation is 0.
Note
Indicates that the result of a saturation operation has overflowed and is saturated. Because
this is a cumulative flag, it is set to 1 when the result of a saturation operation instruction is
saturated, and is not cleared to 0 even if the subsequent operation result is not saturated.
Use the LDSR instruction to clear this bit. This flag is neither set to 1 nor cleared to 0 by
execution of an arithmetic operation instruction.
0: Not saturated
1: Saturated
0: Carry or borrow does not occur.
1: Carry or borrow occurs.
Note
Indicates whether an overflow occurs during operation.
0: Overflow does not occur.
1: Overflow occurs.
Note
Indicates whether the result of an operation is negative.
0: The result is positive or 0.
1: The result is negative.
0: The result is not 0.
1: The result is 0.
87NP6EP5ID4
SAT3CY2OV
1
SZ
Default value
00000020H
Remark Also read Note on the next page.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 29 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 46

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
Note The result of the operation that has performed saturation processing is determined by the contents of the
OV and S flags. The SAT flag is set to 1 only when the OV flag is set to 1 when a saturation operation is
performed.
SAT OV S
Maximum positive value is exceeded 1 1 0 7FFFFFFFH
Maximum negative value is exceeded 1 1 1 80000000H
Positive (maximum value is not exceeded) 0
Negative (maximum value is not exceeded)
Holds value
before operation
Flag Status Status of Operation Result
0
1
Result of Operation of
Saturation Processing
Operation result itself
(5) CALLT execution status saving registers (CTPC and CTPSW)
CTPC and CTPSW are CALLT execution status saving registers.
When the CALLT instruction is executed, the contents of the program counter (PC) are saved to CTPC, and those
of the program status word (PSW) are saved to CTPSW.
The contents saved to CTPC are the address of the instruction next to CALLT.
The current contents of the PSW are saved to CTPSW.
Bits 31 to 26 of CTPC and bits 31 to 8 of CTPSW are reserved for future function expansion (fixed to 0).
CTPC
CTPSW
31 0
00
31 0
00
26 25
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0
(Saved PC contents)
87
(Saved PSW
contents)
Default value
0xxxxxxxH
(x: Undefined)
Default value
000000xxH
(x: Undefined)
(2/2)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 30 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 47

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(6) Exception/debug trap status saving registers (DBPC and DBPSW)
DBPC and DBPSW are exception/debug trap status registers.
If an exception trap or debug trap occurs, the contents of the program counter (PC) are saved to DBPC, and those
of the program status word (PSW) are saved to DBPSW.
The contents to be saved to DBPC are the address of the instruction next to the one that is being executed when
an exception trap or debug trap occurs.
The current contents of the PSW are saved to DBPSW.
This register can be read or written only during the interval between the execution of the DBTRAP instruction or
illegal opcode and the DBRET instruction.
Bits 31 to 26 of DBPC and bits 31 to 8 of DBPSW are reserved for future function expansion (fixed to 0).
The value of DBPC is restored to the PC and the value of DBPSW to the PSW by the DBRET instruction.
31 0
DBPC
DBPSW
00
31 0
00
(7) CALLT base pointer (CTBP)
The CALLT base pointer (CTBP) is used to specify a table address or generate a target address (bit 0 is fixed to 0).
Bits 31 to 26 of this register are reserved for future function expansion (fixed to 0).
31 0
CTBP
00
0 0 0 0 0
26 25
0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0 00 0 0 0 0
26 25
(Saved PC contents)
(Base address)
87
(Saved PSW
contents)
Default value
0xxxxxxxH
(x: Undefined)
Default value
000000xxH
(x: Undefined)
Default value
0xxxxxxxH
(x: Undefined)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 31 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 48

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.3 Operation Modes
The V850ES/JF3-L has the following operation modes.
(1) Normal operation mode
In this mode, each pin related to the bus interface is set to the port mode after system reset has been released.
Execution branches to the reset entry address of the internal ROM, and then instruction processing is started.
(2) Flash memory programming mode
In this mode, the internal flash memory can be programmed by using a flash programmer.
(3) On-chip debug mode
The V850ES/JF3-L is provided with an on-chip debug function that employs the JTAG (Joint Test Action Group)
communication specifications.
For details, see CHAPTER 29 ON-CHIP DEBUG FUNCTION.
3.3.1 Specifying operation mode
Specify the operation mode by using the FLMD0 and FLMD1 pins.
In the normal mode, make sure that a low level is input to the FLMD0 pin when reset is released.
In the flash memory programming mode, a high level is input to the FLMD0 pin from the flash programmer if a flash
programmer is connected, but it must be input from an external circuit in the self-programming mode.
Operation When Reset Is Released
FLMD0 FLMD1
Operation Mode After Reset
L
H L Flash memory programming mode
H H Setting prohibited
×
Normal operation mode
Remark L: Low-level input
H: High-level input
×: Don’t care
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 32 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 49

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.4 Address Space
3.4.1 CPU address space
For instruction addressing, up to a combined total of 16 MB of external memory area and internal ROM area, plus an
internal RAM area, are supported in a linear address space (program space) of up to 64 MB. For operand addressing
(data access), up to 4 GB of a linear address space (data space) is supported. The 4 GB address space, however, is
viewed as 64 images of a 64 MB physical address space. This means that the same 64 MB physical address space is
accessed regardless of the value of bits 31 to 26.
Figure 3-1. Image on Address Space
Image 63
16 MB
Program space
Use-prohibited area
Internal RAM area
Use-prohibited area
External memory area
4 GB
64 MB
Image 1
Image 0
Data space
Peripheral I/O area
Internal RAM area
Use-prohibited area
64 MB
External memory area
Internal ROM area
(external memory area)
Internal ROM area
(external memory area)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 33 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 50

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.4.2 Wraparound of CPU address space
(1) Program space
Of the 32 bits of the PC (program counter), the higher 6 bits are fixed to 0 and only the lower 26 bits are valid. The
higher 6 bits ignore a carry or borrow from bit 25 to 26 during branch address calculation.
Therefore, the highest address of the program space, 03FFFFFFH, and the lowest address, 00000000H, are
contiguous addresses. That the highest address and the lowest address of the program space are contiguous in
this way is called wraparound.
Caution Because the 4 KB area of addresses 03FFF000H to 03FFFFFFH is an on-chip peripheral I/O area,
instructions cannot be fetched from this area. Therefore, do not execute an operation in which
the result of a branch address calculation affects this area.
00000001H
00000000H
03FFFFFFH
03FFFFFEH
Program space
(+) direction (−) direction
Program space
(2) Data space
The result of an operand address calculation operation that exceeds 32 bits is ignored.
Therefore, the highest address of the data space, FFFFFFFFH, and the lowest address, 00000000H, are
contiguous, and wraparound occurs at the boundary of these addresses.
00000001H
00000000H
FFFFFFFFH
Data space
(+) direction (−) direction
FFFFFFFEH
Data space
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 34 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 51

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.4.3 Memory map
The areas shown below are reserved in the V850ES/JF3-L.
Figure 3-2. Data Memory Map (Physical Addresses)
03FFFFFFH
03FF0000H
03FEFFFFH
On-chip peripheral I/O area
(4 KB)
(64 KB)
Internal RAM area
(60 KB)
Use prohibited
03FFFFFFH
03FFF000H
03FFEFFFH
03FF0000H
01000000H
00FFFFFFH
External memory area
(14 MB)
00200000H
001FFFFFH
(2 MB)
00000000H
Note 1
External memory area
(1 MB)
Internal ROM area
(1 MB)
Note 1
Note 2
001FFFFFH
00100000H
000FFFFFH
00000000H
Notes 1. The V850ES/JF3-L has 18 address pins, so the external memory area appears as a repeated 256 KB
image.
2. Fetch access and read access to addresses 00000000H to 000FFFFFH is made to the internal ROM
area. However, data write access to these addresses is made to the external memory area.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 35 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 52

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
Figure 3-3. Program Memory Map
03FFFFFFH
03FFF000H
03FFEFFFH
03FF0000H
03FEFFFFH
01000000H
00FFFFFFH
Use prohibited
(program fetch prohibited area)
Internal RAM area (60 KB)
Use prohibited
(program fetch prohibited area)
Note
Note
00200000H
001FFFFFH
00100000H
000FFFFFH
00000000H
External memory area
External memory area
(14 MB)
(1 MB)
Internal ROM area
(1 MB)
Note The V850ES/JF3-L has 18 address pins, so the external memory area appears as a repeated 256 KB
image.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 36 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 53

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.4.4 Areas
(1) Internal ROM area
Up to 1 MB is reserved as an internal ROM area.
(a) Internal ROM (128 KB)
128 KB are allocated to addresses 00000000H to 0001FFFFH in the
Accessing addresses 00020000H to 000FFFFFH is prohibited.
Figure 3-4. Internal ROM Area (128 KB)
000FFFFFH
Access-prohibited
area
μ
PD70F3735.
(b) Internal ROM (256 KB)
256 KB are allocated to addresses 00000000H to 0003FFFFH in the
Accessing addresses 00040000H to 000FFFFFH is prohibited.
00020000H
0001FFFFH
00000000H
Internal ROM
(128 KB)
μ
Figure 3-5. Internal ROM Area (256 KB)
000FFFFFH
Access-prohibited
area
00040000H
0003FFFFH
Internal ROM
(256 KB)
PD70F3736.
00000000H
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 37 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 54

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(2) Internal RAM area
Up to 60 KB are reserved as the internal RAM area.
(a) Internal RAM (8 KB)
8 KB are allocated to addresses 03FFD000H to 03FFEFFFH of the
Accessing addresses 03FF0000H to 03FFCFFFH is prohibited.
Figure 3-6. Internal RAM Area (8 KB)
Physical address space
μ
PD70F3735.
Logical address space
(b) Internal RAM (16 KB)
16 KB are allocated to addresses 03FFB000H to 03FFEFFFH of the
Accessing addresses 03FF0000H to 03FFAFFFH is prohibited.
03FFEFFFH
03FFD000H
03FFCFFFH
03FF0000H
Figure 3-7. Internal RAM Area (16 KB)
Physical address space
Internal RAM
(8 KB)
Access-prohibited
area
FFFFEFFFH
FFFFD000H
FFFFCFFFH
FFFF0000H
μ
PD70F3736.
Logical address space
03FFEFFFH
Internal RAM
(16 KB)
03FFB000H
03FFAFFFH
Access-prohibited
area
03FF0000H
FFFFEFFFH
FFFFB000H
FFFFAFFFH
FFFF0000H
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 38 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 55

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(3) On-chip peripheral I/O area
4 KB of addresses 03FFF000H to 03FFFFFFH are reserved as the on-chip peripheral I/O area.
Figure 3-8. On-Chip Peripheral I/O Area
Physical address space Logical address space
03FFFFFFH
On-chip peripheral I/O area
(4 KB)
03FFF000H
FFFFFFFFH
FFFFF000H
Peripheral I/O registers that have functions to specify the operation mode for and monitor the status of the on-chip
peripheral I/O are mapped to the on-chip peripheral I/O area. Program cannot be fetched from this area.
Cautions 1. When a register is accessed in word units, a word area is accessed twice in halfword units in
the order of lower area and higher area, with the lower 2 bits of the address ignored.
2. If a register that can be accessed in byte units is accessed in halfword units, the higher 8 bits
are undefined when the register is read, and data is written to the lower 8 bits.
3. Addresses not defined as registers are reserved for future expansion. The operation is
undefined and not guaranteed when these addresses are accessed.
4. The internal ROM/RAM area and on-chip peripheral I/O area are assigned to successive
addresses.
When accessing the internal ROM/RAM area by incrementing or decrementing addresses
using a pointer operation or such, be careful not to access the on-chip peripheral I/O area by
mistakenly extending over the internal ROM/RAM area boundary.
(4) External memory area
15 MB (00100000H to 00FFFFFFH) are allocated as the external memory area. For details, see CHAPTER 5
BUS CONTROL FUNCTION.
Caution The V850ES/JF3-L has 18 address pins (AD0 to AD15, A16, A17), so the external memory area
appears as a repeated 256 KB image.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 39 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 56

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.4.5 Recommended use of address space
The architecture of the V850ES/JF3-L requires that a register that serves as a pointer be secured for address
generation when operand data in the data space is accessed. The address stored in this pointer ±32 KB can be directly
accessed by an instruction for operand data. Because the number of general-purpose registers that can be used as a
pointer is limited, however, by keeping the performance from dropping during address calculation when a pointer value is
changed, as many general-purpose registers as possible can be secured for variables, and the program size can be
reduced.
(1) Program space
Of the 32 bits of the PC (program counter), the higher 6 bits are fixed to 0, and only the lower 26 bits are valid.
Regarding the program space, therefore, a 64 MB space of contiguous addresses starting from 00000000H
unconditionally corresponds to the memory map.
To use the internal RAM area as the program space, access the following addresses.
Caution If a branch instruction is at the upper limit of the internal RAM area, a prefetch operation (invalid
fetch) straddling the on-chip peripheral I/O area does not occur.
RAM Size Access Address
16 KB 03FFB000H to 03FFEFFFH
8 KB 03FFD000H to 03FFEFFFH
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 40 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 57

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(2) Data space
With the V850ES/JF3-L, it seems that there are sixty-four 64 MB address spaces on the 4 GB CPU address space.
Therefore, the least significant bit (bit 25) of a 26-bit address is sign-extended to 32 bits and allocated as an
address.
(a) Application example of wraparound
If R = r0 (zero register) is specified for the LD/ST disp16 [R] instruction, a range of addresses 00000000H ±32
KB can be addressed by sign-extended disp16. All the resources, including the internal hardware, can be
addressed by one pointer.
The zero register (r0) is a register fixed to 0 by hardware, and practically eliminates the need for registers
dedicated to pointers.
Example:
μ
PD70F3736
0003FFFFH
00007FFFH
(R = )
00000000H
FFFFF000H
FFFFEFFFH
FFFFB000H
FFFFAFFFH
FFFF8000H
Internal ROM area
On-chip peripheral
I/O area
Internal RAM area
Access
prohibited area
32 KB
4 KB
16 KB
12 KB
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 41 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 58

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
FFFFFFFFH
FFFFF000H
FFFFEFFFH
FFFF0000H
FFFEFFFFH
04000000H
03FFFFFFH
03FFF000H
03FFEFFFH
03FFB000H
03FFAFFFH
03FF0000H
03FEFFFFH
Figure 3-9. Recommended Memory Map
Data spaceProgram space
On-chip
peripheral I/O
Internal RAM
Use prohibited
Internal RAM
On-chip
peripheral I/O
Internal RAM
Use prohibited
FFFFFFFFH
FFFFF000H
FFFFEFFFH
FFFFB000H
FFFFAFFFH
FFFF0000H
FFFEFFFFH
Program space
64 MB
01000000H
00FFFFFFH
00100000H
000FFFFFH
00040000H
0003FFFFH
00000000H
Use prohibited
External
Note
memory
Internal ROM
Internal ROM
External
Note
memory
Internal ROM
00100000H
000FFFFFH
00000000H
Note The V850ES/JF3-L has 18 address pins, so the external memory area appears as a repeated 256 KB
image.
Remarks 1. indicates the recommended area.
μ
2. This figure is the recommended memory map of the
PD70F3736.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 42 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 59

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.4.6 Peripheral I/O registers
(1/9)
Manipulatable Bits Address Function Register Name Symbol R/W
1 8 16
FFFFF004H Port DL register PDL √ 0000H
FFFFF004H Port DL register L PDLL
FFFFF005H Port DL register H PDLH
FFFFF006H Port DH register PDH
FFFFF00AH Port CT register PCT
FFFFF00CH Port CM register PCM
R/W
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
FFFFF024H Port DL mode register PMDL
FFFFF024H Port DL mode register L PMDLL
FFFFF025H Port DL mode register H PMDLH
FFFFF026H Port DH mode register PMDH
FFFFF02AH Port CT mode register PMCT
FFFFF02CH Port CM mode register PMCM
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
FFFFF044H Port DL mode control register PMCDL
FFFFF044H Port DL mode control register L PMCDLL
FFFFF045H Port DL mode control register H PMCDLH
FFFFF046H Port DH mode control register PMCDH
FFFFF04AH Port CT mode control register PMCCT
FFFFF04CH Port CM mode control register PMCCM
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
FFFFF066H Bus size configuration register BSC
FFFFF06EH System wait control register VSWC
√
FFFFF080H DMA source address register 0L DSA0L
FFFFF082H DMA source address register 0H DSA0H
FFFFF084H DMA destination address register 0L DDA0L
FFFFF086H DMA destination address register 0H DDA0H
FFFFF088H DMA source address register 1L DSA1L
FFFFF08AH DMA source address register 1H DSA1H
FFFFF08CH DMA destination address register 1L DDA1L
FFFFF08EH DMA destination address register 1H DDA1H
FFFFF090H DMA source address register 2L DSA2L
FFFFF092H DMA source address register 2H DSA2H
FFFFF094H DMA destination address register 2L DDA2L
FFFFF096H DMA destination address register 2H DDA2H
FFFFF098H DMA source address register 3L DSA3L
FFFFF09AH DMA source address register 3H DSA3H
FFFFF09CH DMA destination address register 3L DDA3L
FFFFF09EH DMA destination address register 3H DDA3H
FFFFF0C0H DMA transfer count register 0 DBC0
FFFFF0C2H DMA transfer count register 1 DBC1
FFFFF0C4H DMA transfer count register 2 DBC2
FFFFF0C6H DMA transfer count register 3 DBC3
FFFFF0D0H DMA addressing control register 0 DADC0
√ 0000H
Note The output latch is 00H or 0000H. When these registers are in the input mode, the pin statuses are read.
Default Value
Note
00H
Note
00H
Note
00H
Note
00H
Note
00H
FFFFH
√
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
0000H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
5555H
√
77H
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Undefined
√
Note
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 43 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 60

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
Manipulatable Bits Address Function Register Name Symbol R/W
1 8 16
FFFFF0D2H DMA addressing control register 1 DADC1
FFFFF0D4H DMA addressing control register 2 DADC2
FFFFF0D6H DMA addressing control register 3 DADC3
FFFFF0E0H DMA channel control register 0 DCHC0
FFFFF0E2H DMA channel control register 1 DCHC1
FFFFF0E4H DMA channel control register 2 DCHC2
FFFFF0E6H DMA channel control register 3 DCHC3
FFFFF100H Interrupt mask register 0 IMR0
FFFFF100H Interrupt mask register 0L IMR0L
FFFFF101H Interrupt mask register 0H IMR0H
FFFFF102H Interrupt mask register 1 IMR1
FFFFF102H Interrupt mask register 1L IMR1L
FFFFF103H Interrupt mask register 1H IMR1H
FFFFF104H Interrupt mask register 2 IMR2
FFFFF104H Interrupt mask register 2L IMR2L
FFFFF105H Interrupt mask register 2H IMR2H
FFFFF106H Interrupt mask register 3 IMR3
FFFFF106H Interrupt mask register 3L IMR3L
FFFFF107H Interrupt mask register 3H IMR3H
FFFFF110H Interrupt control register LVIIC
FFFFF112H Interrupt control register PIC0
FFFFF114H Interrupt control register PIC1
FFFFF116H Interrupt control register PIC2
FFFFF118H Interrupt control register PIC3
FFFFF11AH Interrupt control register PIC4
FFFFF11CH Interrupt control register PIC5
FFFFF11EH Interrupt control register PIC6
FFFFF120H Interrupt control register PIC7
FFFFF122H Interrupt control register
FFFFF124H Interrupt control register TQ0CCIC0
FFFFF126H Interrupt control register TQ0CCIC1
FFFFF128H Interrupt control register TQ0CCIC2
FFFFF12AH Interrupt control register TQ0CCIC3
FFFFF12CH Interrupt control register TP0OVIC
FFFFF12EH Interrupt control register TP0CCIC0
FFFFF130H Interrupt control register TP0CCIC1
FFFFF132H Interrupt control register TP1OVIC
FFFFF134H Interrupt control register TP1CCIC0
FFFFF136H Interrupt control register TP1CCIC1
FFFFF138H Interrupt control register TP2OVIC
FFFFF13AH Interrupt control register TP2CCIC0
FFFFF13CH Interrupt control register TP2CCIC1
FFFFF14AH Interrupt control register TP5OVIC
TQ0OVIC
R/W
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
Default Value
0000H
√
0000H
√
0000H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
FFFFH
√
FFH
FFH
FFFFH
√
FFH
FFH
FFFFH
√
FFH
FFH
FFFFH
√
FFH
FFH
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
(2/9)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 44 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 61

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
Manipulatable Bits Address Function Register Name Symbol R/W
1 8 16
FFFFF14CH Interrupt control register TP5CCIC0
FFFFF14EH Interrupt control register TP5CCIC1
FFFFF150H Interrupt control register TM0EQIC0
FFFFF152H Interrupt control register CB0RIC/IICIC1
FFFFF154H Interrupt control register CB0TIC
FFFFF156H Interrupt control register CB1RIC
FFFFF158H Interrupt control register CB1TIC
FFFFF15AH Interrupt control register CB2RIC
FFFFF15CH Interrupt control register CB2TIC
FFFFF162H Interrupt control register UA0RIC
FFFFF164H Interrupt control register UA0TIC
FFFFF166H Interrupt control register UA1RIC
FFFFF168H Interrupt control register UA1TIC
FFFFF16AH Interrupt control register UA2RIC/IICIC0
FFFFF16CH Interrupt control register UA2TIC
FFFFF16EH Interrupt control register ADIC
FFFFF170H Interrupt control register DMAIC0
FFFFF172H Interrupt control register DMAIC1
FFFFF174H Interrupt control register DMAIC2
FFFFF176H Interrupt control register DMAIC3
FFFFF178H Interrupt control register KRIC
FFFFF17AH Interrupt control register WTIIC
FFFFF17CH Interrupt control register WTIC
FFFFF1FAH In-service priority register ISPR R
FFFFF1FCH Command register PRCMD W
FFFFF1FEH Power save control register PSC
FFFFF200H A/D converter mode register 0 ADA0M0
FFFFF201H A/D converter mode register 1 ADA0M1
FFFFF202H A/D converter channel specification register ADA0S
FFFFF203H A/D converter mode register 2 ADA0M2
FFFFF204H Power-fail compare mode register ADA0PFM
FFFFF205H Power-fail compare threshold value register ADA0PFT
FFFFF210H A/D conversion result register 0 ADA0CR0
FFFFF211H A/D conversion result register 0H ADA0CR0H
FFFFF212H A/D conversion result register 1 ADA0CR1
FFFFF213H A/D conversion result register 1H ADA0CR1H
FFFFF214H A/D conversion result register 2 ADA0CR2
FFFFF215H A/D conversion result register 2H ADA0CR2H
FFFFF216H A/D conversion result register 3 ADA0CR3
FFFFF217H A/D conversion result register 3H ADA0CR3H
FFFFF218H A/D conversion result register 4 ADA0CR4
FFFFF219H A/D conversion result register 4H ADA0CR4H
FFFFF21AH A/D conversion result register 5 ADA0CR5
FFFFF21BH A/D conversion result register 5H ADA0CR5H
R/W
R/W
R
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
47H
00H
Undefined
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
√
Undefined
√
√
Undefined
√
√
Undefined
√
√
Undefined
√
√
Undefined
√
√
Undefined
√
Default Value
Undefined
Undefined
Undefined
Undefined
Undefined
Undefined
(3/9)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 45 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 62

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
Note
Note
(4/9)
Manipulatable Bits Address Function Register Name Symbol R/W
1 8 16
FFFFF21CH A/D conversion result register 6 ADA0CR6
FFFFF21DH A/D conversion result register 6H ADA0CR6H
R
√
FFFFF21EH A/D conversion result register 7 ADA0CR7
FFFFF21FH A/D conversion result register 7H ADA0CR7H
FFFFF280H D/A conversion value setting register 0 DA0CS0
R/W
FFFFF282H D/A converter mode register DA0M
FFFFF300H Key return mode register KRM
FFFFF308H Selector operation control register 0 SELCNT0
FFFFF310H CRC input register CRCIN
√ √
√ √
√ √
√
√
√
FFFFF312H CRC data register CRCD
FFFFF318H Noise elimination control register NFC
FFFFF320H Prescaler mode register 1 PRSM1
FFFFF321H Prescaler compare register 1 PRSCM1
FFFFF324H Prescaler mode register 2 PRSM2
FFFFF325H Prescaler compare register 2 PRSCM2
FFFFF331H Regulator protection register REGPR
FFFFF332H Regulator output voltage level control register REGOVL0
FFFFF340H IIC division clock select register OCKS0
FFFFF344H IIC division clock select register OCKS1
FFFFF400H Port 0 register P0
FFFFF402H Port 1 register P1
√
√ √
√
√ √
√
√
√
√
√
√ √
√ √
FFFFF406H Port 3 register P3 √ 0000H
FFFFF406H Port 3 register L P3L
FFFFF407H Port 3 register H P3H
FFFFF408H Port 4 register P4
FFFFF40AH Port 5 register P5
FFFFF40EH Port 7 register L P7L
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
FFFFF412H Port 9 register P9 √ 0000H
FFFFF412H Port 9 register L P9L
FFFFF413H Port 9 register H P9H
FFFFF420H Port 0 mode register PM0
FFFFF422H Port 1 mode register PM1
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
FFFFF426H Port 3 mode register PM3
FFFFF426H Port 3 mode register L PM3L
FFFFF427H Port 3 mode register H PM3H
FFFFF428H Port 4 mode register PM4
FFFFF42AH Port 5 mode register PM5
FFFFF42EH Port 7 mode register L PM7L
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
FFFFF432H Port 9 mode register PM9
FFFFF432H Port 9 mode register L PM9L
FFFFF433H Port 9 mode register H PM9H
FFFFF440H Port 0 mode control register PMC0
√ √
√ √
√ √
Default Value
Undefined
√
Undefined
Undefined
√
Undefined
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
FFH
FFH
FFFFH
√
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFH
FFFFH
√
FFH
FFH
00H
Note The output latch is 00H or 0000H. When these registers are input, the pin statuses are read.
Note
Note
Note
Note
Note
Note
Note
Note
Note
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 46 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 63

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
Manipulatable Bits Address Function Register Name Symbol R/W
1 8 16
FFFFF446H Port 3 mode control register PMC3
FFFFF446H Port 3 mode control register L PMC3L
FFFFF447H Port 3 mode control register H PMC3H
FFFFF448H Port 4 mode control register PMC4
FFFFF44AH Port 5 mode control register PMC5
FFFFF452H Port 9 mode control register PMC9
FFFFF452H Port 9 mode control register L PMC9L
FFFFF453H Port 9 mode control register H PMC9H
FFFFF460H Port 0 function control register PFC0
FFFFF466H Port 3 function control register PFC3
FFFFF466H Port 3 function control register L PFC3L
FFFFF467H Port 3 function control register H PFC3H
FFFFF468H Port 4 function control register PFC4
FFFFF46AH Port 5 function control register PFC5
FFFFF472H Port 9 function control register PFC9
FFFFF472H Port 9 function control register L PFC9L
FFFFF473H Port 9 function control register H PFC9H
FFFFF484H Data wait control register 0 DWC0
FFFFF488H Address wait control register AWC
FFFFF48AH Bus cycle control register BCC
FFFFF540H TMQ0 control register 0 TQ0CTL0
FFFFF541H TMQ0 control register 1 TQ0CTL1
FFFFF542H TMQ0 I/O control register 0 TQ0IOC0
FFFFF543H TMQ0 I/O control register 1 TQ0IOC1
FFFFF544H TMQ0 I/O control register 2 TQ0IOC2
FFFFF545H TMQ0 option register 0 TQ0OPT0
FFFFF546H TMQ0 capture/compare register 0 TQ0CCR0
FFFFF548H TMQ0 capture/compare register 1 TQ0CCR1
FFFFF54AH TMQ0 capture/compare register 2 TQ0CCR2
FFFFF54CH TMQ0 capture/compare register 3 TQ0CCR3
FFFFF54EH TMQ0 counter read buffer register TQ0CNT R
FFFFF590H TMP0 control register 0 TP0CTL0
FFFFF591H TMP0 control register 1 TP0CTL1
FFFFF592H TMP0 I/O control register 0 TP0IOC0
FFFFF593H TMP0 I/O control register 1 TP0IOC1
FFFFF594H TMP0 I/O control register 2 TP0IOC2
FFFFF595H TMP0 option register 0 TP0OPT0
FFFFF596H TMP0 capture/compare register 0 TP0CCR0
FFFFF598H TMP0 capture/compare register 1 TP0CCR1
FFFFF59AH TMP0 counter read buffer register TP0CNT R
FFFFF5A0H TMP1 control register 0 TP1CTL0
FFFFF5A1H TMP1 control register 1 TP1CTL1
R/W
R/W
R/W
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ 0000H
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ 0000H
√ √
√ √
Note The output latch is 00H or 0000H. When these registers are input, the pin statuses are read.
Default Value
0000H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
√
00H
00H
00H
0000H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
√
00H
00H
7777H
√
FFFFH
√
AAAAH
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
√
0000H
√
0000H
√
0000H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
√
0000H
√
00H
00H
(5/9)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 47 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 64

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
Manipulatable Bits Address Function Register Name Symbol R/W
FFFFF5A2H TMP1 I/O control register 0 TP1IOC0
FFFFF5A3H TMP1 I/O control register 1 TP1IOC1
FFFFF5A4H TMP1 I/O control register 2 TP1IOC2
FFFFF5A5H TMP1 option register 0 TP1OPT0
FFFFF5A6H TMP1 capture/compare register 0 TP1CCR0
FFFFF5A8H TMP1 capture/compare register 1 TP1CCR1
FFFFF5AAH TMP1 counter read buffer register TP1CNT R
FFFFF5B0H TMP2 control register 0 TP2CTL0
FFFFF5B1H TMP2 control register 1 TP2CTL1
FFFFF5B2H TMP2 I/O control register 0 TP2IOC0
FFFFF5B3H TMP2 I/O control register 1 TP2IOC1
FFFFF5B4H TMP2 I/O control register 2 TP2IOC2
FFFFF5B5H TMP2 option register 0 TP2OPT0
FFFFF5B6H TMP2 capture/compare register 0 TP2CCR0
FFFFF5B8H TMP2 capture/compare register 1 TP2CCR1
FFFFF5BAH TMP2 counter read buffer register TP2CNT R
FFFFF5E0H TMP5 control register 0 TP5CTL0
FFFFF5E1H TMP5 control register 1 TP5CTL1
FFFFF5E2H TMP5 I/O control register 0 TP5IOC0
FFFFF5E3H TMP5 I/O control register 1 TP5IOC1
FFFFF5E4H TMP5 I/O control register 2 TP5IOC2
FFFFF5E5H TMP5 option register 0 TP5OPT0
FFFFF5E6H TMP5 capture/compare register 0 TP5CCR0
FFFFF5E8H TMP5 capture/compare register 1 TP5CCR1
FFFFF5EAH TMP5 counter read buffer register TP5CNT R
FFFFF680H Watch timer operation mode register WTM
FFFFF690H TMM0 control register 0 TM0CTL0
FFFFF694H TMM0 compare register 0 TM0CMP0
FFFFF6C0H Oscillation stabilization time select register OSTS
FFFFF6C1H PLL lockup time specification register PLLS
FFFFF6D0H Watchdog timer mode register 2 WDTM2
FFFFF6D1H Watchdog timer enable register WDTE
FFFFF6E0H Real-time output buffer register 0L RTBL0
FFFFF6E2H Real-time output buffer register 0H RTBH0
FFFFF6E4H Real-time output port mode register 0 RTPM0
FFFFF6E5H Real-time output port control register 0 RTPC0
FFFFF706H Port 3 function control expansion register L PFCE3L
FFFFF70AH Port 5 function control expansion register PFCE5
FFFFF712H Port 9 function control expansion register PFCE9
FFFFF712H Port 9 function control expansion register L PFCE9L
FFFFF713H Port 9 function control expansion register H PFCE9H
FFFFF802H System status register SYS
FFFFF80CH Internal oscillation mode register RCM
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
Default Value
1 8 16
√
√
√
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
√
0000H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
√
0000H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
√
0000H
√
00H
00H
0000H
√
06H
03H
67H
9AH
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
0000H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ 0000H
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ 0000H
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ 0000H
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
(6/9)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 48 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 65

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
FFFFF810H DMA trigger factor register 0 DTFR0
FFFFF812H DMA trigger factor register 1 DTFR1
FFFFF814H DMA trigger factor register 2 DTFR2
FFFFF816H DMA trigger factor register 3 DTFR3
FFFFF820H Power save mode register PSMR
FFFFF822H Clock control register CKC
FFFFF824H Lock register LOCKR R
FFFFF828H Processor clock control register PCC
FFFFF82CH PLL control register PLLCTL
FFFFF82EH CPU operation clock status register CCLS R
FFFFF870H Clock monitor mode register CLM
FFFFF888H Reset source flag register RESF
FFFFF890H Low-voltage detection register LVIM
FFFFF891H Low-voltage detection level select register LVIS
FFFFF8B0H Prescaler mode register 0 PRSM0
FFFFF8B1H Prescaler compare register 0 PRSCM0
FFFFF9FCH On-chip debug mode register OCDM
FFFFFA00H UARTA0 control register 0 UA0CTL0
FFFFFA01H UARTA0 control register 1 UA0CTL1
FFFFFA02H UARTA0 control register 2 UA0CTL2
FFFFFA03H UARTA0 option control register 0 UA0OPT0
FFFFFA04H UARTA0 status register UA0STR
FFFFFA06H UARTA0 receive data register UA0RX R
FFFFFA07H UARTA0 transmit data register UA0TX
FFFFFA10H UARTA1 control register 0 UA1CTL0
FFFFFA11H UARTA1 control register 1 UA1CTL1
FFFFFA12H UARTA1 control register 2 UA1CTL2
FFFFFA13H UARTA1 option control register 0 UA1OPT0
FFFFFA14H UARTA1 status register UA1STR
FFFFFA16H UARTA1 receive data register UA1RX R
FFFFFA17H UARTA1 transmit data register UA1TX
FFFFFA20H UARTA2 control register 0 UA2CTL0
FFFFFA21H UARTA2 control register 1 UA2CTL1
FFFFFA22H UARTA2 control register 2 UA2CTL2
FFFFFA23H UARTA2 option control register 0 UA2OPT0
FFFFFA24H UARTA2 status register UA2STR
FFFFFA26H UARTA2 receive data register UA2RX R
FFFFFA27H UARTA2 transmit data register UA2TX
FFFFFC00H External interrupt falling edge specification register 0 INTF0
FFFFFC06H External interrupt falling edge specification register 3 INTF3
FFFFFC13H External interrupt falling edge specification register 9H INTF9H
FFFFFC20H External interrupt rising edge specification register 0 INTR0
FFFFFC26H External interrupt rising edge specification register 3 INTR3
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
Manipulatable Bits Address Function Register Name Symbol R/W
1 8 16
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√
√ √
√
√ √
√ √
√
√
√ √
√ √
√
√
√ √
√
√
√ √
√ √
√
√
√ √
√
√
√ √
√ √
√
√
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
Default Value
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
0AH
00H
03H
01H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
01H
10H
00H
FFH
14H
00H
FFH
FFH
10H
00H
FFH
14H
00H
FFH
FFH
10H
00H
FFH
14H
00H
FFH
FFH
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
(7/9)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 49 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 66

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
Manipulatable Bits Address Function Register Name Symbol R/W
FFFFFC33H External interrupt rising edge specification register 9H INTR9H
FFFFFC60H Port 0 function register PF0
FFFFFC66H Port 3 function register PF3
FFFFFC66H Port 3 function register L PF3L
FFFFFC67H Port 3 function register H PF3H
FFFFFC68H Port 4 function register PF4
FFFFFC6AH Port 5 function register PF5
FFFFFC72H Port 9 function register PF9
FFFFFC72H Port 9 function register L PF9L
FFFFFC73H Port 9 function register H PF9H
FFFFFD00H CSIB0 control register 0 CB0CTL0
FFFFFD01H CSIB0 control register 1 CB0CTL1
FFFFFD02H CSIB0 control register 2 CB0CTL2
FFFFFD03H CSIB0 status register CB0STR
FFFFFD04H CSIB0 receive data register CB0RX
FFFFFD04H CSIB0 receive data register L CB0RXL
FFFFFD06H CSIB0 transmit data register CB0TX
FFFFFD06H CSIB0 transmit data register L CB0TXL
FFFFFD10H CSIB1 control register 0 CB1CTL0
FFFFFD11H CSIB1 control register 1 CB1CTL1
FFFFFD12H CSIB1 control register 2 CB1CTL2
FFFFFD13H CSIB1 status register CB1STR
FFFFFD14H CSIB1 receive data register CB1RX
FFFFFD14H CSIB1 receive data register L CB1RXL
FFFFFD16H CSIB1 transmit data register CB1TX
FFFFFD16H CSIB1 transmit data register L CB1TXL
FFFFFD20H CSIB2 control register 0 CB2CTL0
FFFFFD21H CSIB2 control register 1 CB2CTL1
FFFFFD22H CSIB2 control register 2 CB2CTL2
FFFFFD23H CSIB2 status register CB2STR
FFFFFD24H CSIB2 receive data register CB2RX
FFFFFD24H CSIB2 receive data register L CB2RXL
FFFFFD26H CSIB2 transmit data register CB2TX
FFFFFD26H CSIB2 transmit data register L CB2TXL
FFFFFD80H IIC shift register 0 IIC0
FFFFFD82H IIC control register 0 IICC0
FFFFFD83H Slave address register 0 SVA0
FFFFFD84H IIC clock select register 0 IICCL0
FFFFFD85H IIC function expansion register 0 IICX0
FFFFFD86H IIC status register 0 IICS0 R
FFFFFD8AH IIC flag register 0 IICF0 R/W
R/W
R
R/W
R
R/W
R
R/W
1 8 16
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
√
00H
00H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
√
00H
00H
01H
00H
00H
00H
√
00H
√
00H
01H
00H
00H
00H
√
00H
√
00H
01H
00H
00H
00H
√
00H
√
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
Default Value
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
0000H
(8/9)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 50 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 67

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
FFFFFD90H IIC shift register 1 IIC1
FFFFFD92H IIC control register 1 IICC1
FFFFFD93H Slave address register 1 SVA1
FFFFFD94H IIC clock select register 1 IICCL1
FFFFFD95H IIC function expansion register 1 IICX1
FFFFFD96H IIC status register 1 IICS1 R
FFFFFD9AH IIC flag register 1 IICF1 R/W
R/W
Manipulatable Bits Address Function Register Name Symbol R/W
1 8 16
√
√ √
√
√ √
√ √
√ √
√ √
Default Value
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
00H
(9/9)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 51 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 68

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.4.7 Special registers
Special registers are registers that are protected from being written with illegal data due to a program hang-up. The
V850ES/JF3-L has the following seven special registers.
• Power save control register (PSC)
• Clock control register (CKC)
• Processor clock control register (PCC)
• Clock monitor mode register (CLM)
• Reset source flag register (RESF)
• Low-voltage detection register (LVIM)
• On-chip debug mode register (OCDM)
In addition, the PRCDM register is provided to protect against a write access to the special registers so that the
application system does not inadvertently stop due to a program hang-up. A write access to the special registers is made
in a specific sequence, and an illegal store operation is reported to the SYS register.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 52 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 69

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(1) Setting data to special registers
Set data to the special registers in the following sequence.
<1> Disable DMA operation.
<2> Prepare data to be set to the special register in a general-purpose register.
<3> Write the data prepared in <2> to the PRCMD register.
<4> Write the setting data to the special register (by using the following instructions).
• Store instruction (ST/SST instruction)
• Bit manipulation instruction (SET1/CLR1/NOT1 instruction)
(<5> to <9> Insert NOP instructions (5 instructions).)
<10> Enable DMA operation if necessary.
[Example] With PSC register (setting standby mode)
ST.B r11, PSMR[r0] ; Set PSMR register (setting IDLE1, IDLE2, and STOP modes).
<1>CLR1 0, DCHCn[r0] ; Disable DMA operation. n = 0 to 3
<2>MOV0x02, r10
<3>ST.B r10, PRCMD[r0] ; Write PRCMD register.
<4>ST.B r10, PSC[r0] ; Set PSC register.
<5>NOP
<6>NOP
<7>NOP
<8>NOP
<9>NOP
Note
; Dummy instruction
Note
; Dummy instruction
Note
; Dummy instruction
Note
; Dummy instruction
Note
; Dummy instruction
<10>SET1 0, DCHCn[r0] ; Enable DMA operation. n = 0 to 3
(next instruction)
There is no special sequence to read a special register.
Note Five NOP instructions or more must be inserted immediately after setting the IDLE1 mode, IDLE2 mode, or
STOP mode (by setting the PSC.STP bit to 1).
Cautions 1. When a store instruction is executed to store data in the command register, interrupts are not
acknowledged. This is because it is assumed that steps <3> and <4> above are performed by
successive store instructions. If another instruction is placed between <3> and <4>, and if an
interrupt is acknowledged by that instruction, the above sequence may not be established,
causing malfunction.
2. Although dummy data is written to the PRCMD register, use the same general-purpose
register used to set the special register (<4> in Example) to write data to the PRCMD register
(<3> in Example). The same applies when a general-purpose register is used for addressing.
Note
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 53 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 70

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(2) Command register (PRCMD)
The PRCMD register is an 8-bit register that protects the registers that may seriously affect the application system
from being written, so that the system does not inadvertently stop due to a program hang-up. The first write access
to a special register is valid after data has been written in advance to the PRCMD register. In this way, the value of
the special register can be rewritten only in a specific sequence, so as to protect the register from an illegal write
access.
The PRCMD register is write-only, in 8-bit units (undefined data is read when this register is read).
After reset: Undefined W Address: FFFFF1FCH
7
REG7PRCMD
6
REG65REG54REG43REG32REG21REG10REG0
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 54 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 71

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(3) System status register (SYS)
Status flags that indicate the operation status of the overall system are allocated to this register.
This register can be read or written in 8-bit or 1-bit units.
Reset sets this register to 00H.
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFF802H
< >
SYS 0 0 0 0 0 0 PRERR
0
PRERR
0
Protection error did not occur
1
Protection error occurred
The PRERR flag operates under the following conditions.
(a) Set condition (PRERR flag = 1)
(i) When data is written to a special register without writing anything to the PRCMD register (when <4> is
executed without executing <3> in 3.4.7 (1) Setting data to special registers)
(ii) When data is written to an on-chip peripheral I/O register other than a special register (including execution
of a bit manipulation instruction) after writing data to the PRCMD register (if <4> in 3.4.7 (1) Setting data
to special registers is not the setting of a special register)
Remark Even if an on-chip peripheral I/O register is read (except by a bit manipulation instruction) between
an operation to write the PRCMD register and an operation to write a special register, the PRERR
flag is not set, and the set data can be written to the special register.
(b) Clear condition (PRERR flag = 0)
(i) When 0 is written to the PRERR flag
(ii) When the system is reset
Cautions 1. If 0 is written to the PRERR bit of the SYS register, which is not a special register,
immediately after a write access to the PRCMD register, the PRERR bit is cleared to 0 (the
write access takes precedence).
2. If data is written to the PRCMD register, which is not a special register, immediately after a
write access to the PRCMD register, the PRERR bit is set to 1.
Detects protection error
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 55 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 72

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
3.4.8 Cautions
(1) Registers to be set first
Be sure to set the following registers first when using the V850ES/JF3-L.
• System wait control register (VSWC)
• On-chip debug mode register (OCDM)
• Watchdog timer mode register 2 (WDTM2)
After setting the VSWC, OCDM, and WDTM2 registers, set the other registers as necessary.
When using the external bus, set each pin to the alternate-function bus control pin mode by using the port-related
registers after setting the above registers.
(a) System wait control register (VSWC)
The VSWC register controls wait of bus access to the on-chip peripheral I/O registers.
Three clocks are required to access an on-chip peripheral I/O register (without a wait cycle). The V850ES/JF3-
L requires wait cycles according to the operating frequency. Set the following value to the VSWC register in
accordance with the frequency used.
The VSWC register can be read or written in 8-bit units (address: FFFFF06EH, default value: 77H).
Operating Frequency (fCLK) Set Value of VSWC Number of Waits
32 kHz ≤ fCLK < 16.6 MHz 00H 0 (no waits)
16.6 MHz ≤ fCLK ≤ 20 MHz 01H 1
(b) On-chip debug mode register (OCDM)
For details, see CHAPTER 29 ON-CHIP DEBUG FUNCTION.
(c) Watchdog timer mode register 2 (WDTM2)
The WDTM2 register sets the overflow time and the operation clock of watchdog timer 2.
Watchdog timer 2 automatically starts in the reset mode after reset is released. Write the WDTM2 register to
activate this operation.
For details, see CHAPTER 11 FUNCTIONS OF WATCHDOG TIMER 2.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 56 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 73

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(2) Accessing specific on-chip peripheral I/O registers
This product has two types of internal system buses.
One is a CPU bus and the other is a peripheral bus that interfaces with low-speed peripheral hardware.
The clock of the CPU bus and the clock of the peripheral bus are asynchronous. If an access to the CPU and an
access to the peripheral hardware conflict, therefore, unexpected illegal data may be transferred. If there is a
possibility of a conflict, the number of cycles for accessing the CPU changes when the peripheral hardware is
accessed, so that correct data is transferred. As a result, the CPU does not start processing of the next instruction
but enters the wait status. If this wait status occurs, the number of clocks required to execute an instruction
increases by the number of wait clocks shown below.
This must be taken into consideration if real-time processing is required.
When specific on-chip peripheral I/O registers are accessed, more wait states may be required in addition to the
wait states set by the VSWC register.
The access conditions and how to calculate the number of wait states to be inserted (number of CPU clocks) at this
time are shown below.
Peripheral Function Register Name Access k
16-bit timer/event counter P (TMP)
(n = 0 to 2, 5)
16-bit timer/event counter Q (TMQ)
Watchdog timer 2 (WDT2) WDTM2
Real-time output function (RTO) RTBL0, RTBH0
A/D converter
I2C00, I2C01 IICS0, IICS1 Read 1
CRC CRCD Write 1
Number of clocks necessary for access = 3 + i + j + (2 + j) × k
Caution Accessing the above registers is prohibited in the following statuses. If a wait cycle is generated,
it can only be cleared by a reset.
• When the CPU operates with the subclock and the main clock oscillation is stopped
• When the CPU operates with the internal oscillation clock
Remark i: Values (0) of higher 4 bits of VSWC register
j: Values (0 or 1) of lower 4 bits of VSWC register
TPnCNT Read 1 or 2
TPnCCR0, TPnCCR1
TQ0CNT Read 1 or 2
TQ0CCR0 to TQ0CCR3
ADA0M0 Read 1 or 2
ADA0CR0 to ADA0CR7 Read 1 or 2
ADA0CR0H to ADA0CR7H Read 1 or 2
Write
Read 1 or 2
Write
Read 1 or 2
Write
(when WDT2 operating)
Write
(RTPC0.RTPOE0 bit = 0)
• 1st access: No wait
• Continuous write: 3 or 4
• 1st access: No wait
• Continuous write: 3 or 4
3
1
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 57 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 74

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 3 CPU FUNCTION
(3) Restriction on conflict between sld instruction and interrupt request
(a) Description
If a conflict occurs between the decode operation of an instruction in <2> immediately before the sld instruction
following an instruction in <1> and an interrupt request before the instruction in <1> is complete, the execution
result of the instruction in <1> may not be stored in a register.
Instruction <1>
• ld instruction: ld.b, ld.h, ld.w, ld.bu, ld.hu
• sld instruction: sld.b, sld.h, sld.w, sld.bu, sld.hu
• Multiplication instruction: mul, mulh, mulhi, mulu
Instruction <2>
satsub reg1, reg2
xor reg1, reg2
sub reg1, reg2
cmp imm5, reg2
shl imm5, reg2
<Example>
<i> ld.w [r11], r10 If the decode operation of the mov instruction <ii> immediately before the sld
<ii> mov r10, r28
<iii> sld.w 0x28, r10
(b) Countermeasure
<1> When compiler (CA850) is used
Use CA850 Ver. 2.61 or later because generation of the corresponding instruction sequence can be
<2> For assembler
When executing the sld instruction immediately after instruction <ii>, avoid the above operation using
mov reg1, reg2
satadd reg1, reg2
and reg1, reg2
add reg1, reg2
mulh reg1, reg2
•
•
•
not reg1, reg2
satadd imm5, reg2
tst reg1, reg2
add imm5, reg2
shr imm5, reg2
instruction <iii> and an interrupt request conflict before execution of the ld instruction
<i> is complete, the execution result of instruction <i> may not be stored in a register.
satsubr reg1, reg2
or reg1, reg2
subr reg1, reg2
cmp reg1, reg2
sar imm5, reg2
automatically suppressed.
either of the following methods.
• Insert a nop instruction immediately before the sld instruction.
• Do not use the same register as the sld instruction destination register in the above instruction <ii>
executed immediately before the sld instruction.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 58 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 75

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.1 Features
{ I/O ports: 66
• 5 V tolerant/N-ch open-drain output selectable: 25 (ports 0, 3 to 5, 9 (P90, P91, P96))
{ Input/output specifiable in 1-bit units
4.2 Basic Port Configuration
The V850ES/JF3-L features a total of 66 I/O ports consisting of ports 0, 1, 3 to 5, 7, 9, CM, CT, DH, and DL. The port
configuration is shown below.
Figure 4-1. Port Configuration Diagram
Port 0
Port 1
Port 3
Port 4
Port 5
Port 7
P02
P06
P10
P30
P35
P38
P39
P40
P42
P50
P55
P70
P77
P90
P91
P96
P99
P913
P915
PCM0
PCM3
PCT0
PCT1
PCT4
PCT6
PDH0
PDH1
PDL0
PDL15
Port 9
Port CM
Port CT
Port DH
Port DL
Caution Ports 0, 3 to 5, and 9 (P90, P91, P96) are 5 V tolerant.
Table 4-1. I/O Buffer Power Supplies for Pins
Power Supply Corresponding Pins
AVREF0 Port 7
AVREF1 Port 1
EVDD RESET, ports 0, 3 to 5, 9, CM, CT, DH, DL
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 59 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 76

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.3 Port Configuration
Table 4-2. Port Configuration
Item Configuration
Control register
Ports I/O: 66
(1) Port n register (Pn)
Data is input from or output to an external device by writing or reading the Pn register.
The Pn register consists of a port latch that holds output data, and a circuit that reads the status of pins.
Each bit of the Pn register corresponds to one pin of port n, and can be read or written in 1-bit units.
Port n mode register (PMn: n = 0, 1, 3 to 5, 7, 9, CM, CT, DH, DL)
Port n mode control register (PMCn: n = 0, 3 to 5, 9, CM, CT, DH, DL)
Port n function control register (PFCn: n = 0, 3 to 5, 9)
Port n function control expansion register (PFCEn: n = 3, 5, 9)
Port n function register (PFn: n = 0, 3 to 5, 9)
After reset: 00H (output latch) R/W
01237567
Pn
Pn7
Pnm
0
1
Pn6 Pn5 Pn4 Pn3 Pn2 Pn1 Pn0
Control of output data (in output mode)
Output 0.
Output 1.
Data is written to or read from the Pn register as follows, regardless of the setting of the PMCn register.
Table 4-3. Writing/Reading Pn Register
Setting of PMn Register Writing to Pn Register Reading from Pn Register
Note
Note
.
.
The value of the output latch is read.
The pin status is read.
Output mode
(PMnm = 0)
Input mode
(PMnm = 1)
Data is written to the output latch
In the port mode (PMCn = 0), the contents of the output
latch are output from the pins.
Data is written to the output latch.
The pin status is not affected
Note The value written to the output latch is retained until a new value is written to the output latch.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 60 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 77

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(2) Port n mode register (PMn)
The PMn register specifies the input or output mode of the corresponding port pin.
Each bit of this register corresponds to one pin of port n, and the input or output mode can be specified in 1-bit
units.
After reset: FFH R/W
PMn
PMn7
PMnm
0
1
PMn6 PMn5 PMn4 PMn3 PMn2 PMn1 PMn0
Control of input/output mode
Output mode
Input mode
(3) Port n mode control register (PMCn)
The PMCn register specifies the port mode or alternate function.
Each bit of this register corresponds to one pin of port n, and the mode of the port can be specified in 1-bit units.
After reset: 00H R/W
PMCn
PMCn7 PMCn6 PMCn5 PMCn4 PMCn3 PMCn2 PMCn1 PMCn0
PMCnm
0
1
Port mode
Alternate function mode
Specification of operation mode
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 61 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 78

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(4) Port n function control register (PFCn)
The PFCn register specifies the alternate function of a port pin to be used if the pin has two alternate functions.
Each bit of this register corresponds to one pin of port n, and the alternate function of a port pin can be specified in
1-bit units.
After reset: 00H R/W
PFCn
PFCn7 PFCn6 PFCn5 PFCn4 PFCn3 PFCn2 PFCn1 PFCn0
PFCnm
0
1
Alternate function 1
Alternate function 2
Specification of alternate function
(5) Port n function control expansion register (PFCEn)
The PFCEn register specifies the alternate function of a port pin to be used if the pin has three or more alternate
functions.
Each bit of this register corresponds to one pin of port n, and the alternate function of a port pin can be specified in
1-bit units.
After reset: 00H R/W
PFCEn
PFCn
PFCEn7 PFCEn6 PFCEn5 PFCEn4 PFCEn3 PFCEn2 PFCEn1 PFCEn0
PFCn7 PFCn6 PFCn5 PFCn4 PFCn3 PFCn2 PFCn1 PFCn0
PFCEnm
PFCnm
0
0
1
1
0
Alternate function 1
1
Alternate function 2
0
Alternate function 3
1
Alternate function 4
Specification of alternate function
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 62 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 79

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(6) Port n function register (PFn)
The PFn register specifies normal output or N-ch open-drain output.
Each bit of this register corresponds to one pin of port n, and the output mode of the port pin can be specified in 1-
bit units.
After reset: 00H R/W
PFn
PFn7 PFn6 PFn5 PFn4 PFn3 PFn2 PFn1 PFn0
PFnm
Note
0
Normal output (CMOS output)
1
N-ch open-drain output
Control of normal output/N-ch open-drain output
Note The PFnm bit of the PFn register is valid only when the PMnm bit of the PMn register is 0 (when the
output mode is specified) in port mode (PMCnm bit = 0). When the PMnm bit is 1 (when the input mode
is specified), the set value of the PFn register is invalid.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 63 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 80

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(7) Port setting
Set a port as illustrated below.
Figure 4-2. Setting of Each Register and Pin Function
Port mode
Output mode
Input mode
Alternate function
(when two alternate
functions are available)
Alternate function 1
Alternate function 2
Alternate function
(when three or more alternate
functions are available)
Alternate function 1
Alternate function 2
Alternate function 3
Alternate function 4
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
“0”
“1”
“0”
“1”
PMn register
PFCn register
PFCn register
PFCEn register
“0”
“1”
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
PMCn register
PFCEnm
0
0
1
1
PFCnm
0
1
0
1
Remark Set the alternate functions in the following sequence.
<1> Set the PFCn and PFCEn registers.
<2> Set the PFCn register.
<3> Set the INTRn or INTFn register (to specify an external interrupt pin).
If the PMCn register is set first, an unintended function may be set while the PFCn and PFCEn
registers are being set.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 64 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 81

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.3.1 Port 0
Port 0 is a 5-bit port for which I/O settings can be controlled in 1-bit units.
Port 0 includes the following alternate-function pins.
Table 4-4. Port 0 Alternate-Function Pins
Pin Name Pin No. Alternate-Function Pin Name I/O Remark Block Type
P02 17 NMI Input L-1
P03 5 INTP0/ADTRG Input N-1
P04 6 INTP1 Input L-1
P05 18 INTP2/DRST
P06 7 INTP3 Input
Note
Input AA-1
Note The DRST pin is used for on-chip debugging.
If on-chip debugging is not used, fix the P05/INTP2/DRST pin to low level between when the reset signal of the
RESET pin is released and when the OCDM.OCDM0 bit is cleared (0).
For details, see 4.6.3 Cautions on on-chip debug pins.
Caution The P02 to P06 pins have hysteresis characteristics in the input mode of the alternate function, but
do not have hysteresis characteristics in the port mode.
(1) Port 0 register (P0)
After reset: 00H (output latch) R/W Address: FFFFF400H
Selectable as N-ch open-drain output
L-1
P0 P06 P05 P04 P03 P02 0 0
0
P0n
0
1
Outputs 0
Outputs 1
Output data control (in output mode) (n = 2 to 6)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 65 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 82

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(2) Port 0 mode register (PM0)
After reset: FFH R/W Address: FFFFF420H
PM0 PM06 PM05 PM04 PM03 PM02 1 1
1
PM0n
0
1
Output mode
Input mode
(3) Port 0 mode control register (PMC0)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFF440H
0PMC0 PMC06 PMC05 PMC04 PMC03 PMC02 0 0
PMC06
0
I/O port
1
INTP3 input
PMC05
0
I/O port
1
INTP2 input
I/O mode control (n = 2 to 6)
Specification of P06 pin operation mode
Specification of P05 pin operation mode
PMC04
0
1
PMC03
0
1
PMC02
0
1
I/O port
INTP1 input
I/O port
INTP0 input/ADTRG input
I/O port
NMI input
Specification of P04 pin operation mode
Specification of P03 pin operation mode
Specification of P02 pin operation mode
Caution The P05/INTP2/DRST pin becomes the DRST pin regardless of the value of the PMC05 bit
when the OCDM.OCDM0 bit = 1.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 66 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 83

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(4) Port 0 function control register (PFC0)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFF460H
PFC0
0 0 0 0 PFC03 0 0 0
PFC03
0
INTP0 input
1
ADTRG input
(5) Port 0 function register (PF0)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFFC60H
PF0 PF06 PF05 PF04 PF03 PF02 0 0
0
PF0n
0
1
Control of normal output or N-ch open-drain output (n = 2 to 6)
Normal output (CMOS output)
N-ch open drain output
Caution When an output pin is pulled up at EV
Specification of P03 pin alternate function
DD or higher, be sure to set the PF0n bit to 1.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 67 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 84

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.3.2 Port 1
Port 1 is a 1-bit port for which I/O settings can be controlled in 1-bit units.
Port 1 includes the following alternate-function pin.
Table 4-5. Port 1 Alternate-Function Pin
Pin Name Pin No. Alternate-Function Pin Name I/O Remark Block Type
P10 3 ANO0 Output
−
Caution When the power is turned on, the P10 pin may output an undefined level temporarily even during
reset.
(1) Port 1 register (P1)
After reset: 00H (output latch) R/W Address: FFFFF402H
A-2
P1 0 0 0 0 0 0 P10
0
P10
0
1
Output data control (in output mode)
Outputs 0
Outputs 1
Cautions 1. Do not read or write the P1 register during D/A conversion (see 14.4.3 Cautions).
2. Be sure to set bits 7 to 1 to “0”.
(2) Port 1 mode register (PM1)
After reset: FFH R/W Address: FFFFF422H
PM1 1 1 1 1 1 1 PM10
1
PM10
0
1
I/O mode control
Output mode
Input mode
Cautions 1. When using P10 as the alternate function (ANO0 pin output), set the PM10 bit to 1.
2. Be sure to set bits 7 to 1 to “1”.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 68 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 85

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.3.3 Port 3
Port 3 is an 8-bit port for which I/O settings can be controlled in 1-bit units.
Port 3 includes the following alternate-function pins.
Table 4-6. Port 3 Alternate-Function Pins
Pin Name Pin No. Alternate-Function Pin Name I/O Remark Block Type
P30 22 TXDA0 Output E-2
P31 23 RXDA0/INTP7
P32 24 ASCKA0/TIP00/TOP00
P33 25 TIP01/TOP01
P34 26 TIP10/TOP10
P35 27 TIP11/TOP11
P38 28 TXDA2/SDA00
P39 29 RXDA2/SCL00
Caution The P31 to P35, P38, and P39 pins have hysteresis characteristics in the input mode of the alternate-
function pin, but do not have the hysteresis characteristics in the port mode.
Selectable as N-ch open-drain output
Input N-4
I/O U-16
I/O G-1
I/O G-1
I/O G-1
I/O G-12
I/O
G-6
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 69 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 86

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(1) Port 3 register (P3)
After reset: 0000H (output latch) R/W Address: P3 FFFFF406H,
P3 (P3H)
0 0 0 0 0 0 P39 P38
P3L FFFFF406H, P3H FFFFF407H
89101112131415
(P3L)
0 0 P35 P34 P33 P32 P31 P30
P3n
0
1
Outputs 0
Outputs 1
Output data control (in output mode) (n = 0 to 5, 8, 9)
Caution Be sure to set bits 15 to 10, 7, and 6 to “0”.
Remarks 1. The P3 register can be read or written in 16-bit units.
However, when using the higher 8 bits of the P3 register as the P3H register and the lower 8
bits as the P3L register, P3 can be read or written in 8-bit or 1-bit units.
2. To read/write bits 8 to 15 of the P3 register in 8-bit or 1-bit units, specify them as bits 0 to 7 of
the P3H register.
(2) Port 3 mode register (PM3)
After reset: FFFFH R/W Address: PM3 FFFFF426H,
PM3 (PM3H)
1
1 1 1 1 1 PM39 PM38
PM3L FFFFF426H, PM3H FFFFF427H
89101112131415
(PM3L)
1 1 PM35 PM34 PM33 PM32 PM31 PM30
PM3n
0
1
Output mode
Input mode
I/O mode control (n = 0 to 5, 8, 9)
Caution Be sure to set bits 15 to 10, 7, and 6 to “1”.
Remarks 1. The PM3 register can be read or written in 16-bit units.
However, when using the higher 8 bits of the PM3 register as the PM3H register and the
lower 8 bits as the PM3L register, PM3 can be read or written in 8-bit or 1-bit units.
2. To read/write bits 8 to 15 of the PM3 register in 8-bit or 1-bit units, specify them as bits 0 to 7
of the PM3H register.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 70 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 87

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(3) Port 3 mode control register (PMC3)
After reset: 0000H R/W Address: PMC3 FFFFF446H,
PMC3 (PMC3H)
0 0 0 0 0 0 PMC39 PMC38
PMC3L FFFFF446H, PMC3H FFFFF447H
89101112131415
(PMC3L)
0 0 PMC35 PMC34 PMC33 PMC32 PMC31 PMC30
PMC39
0
1
PMC38
0
1
PMC35
0
1
PMC34
0
1
PMC33
0
1
I/O port
RXDA2 input/SCL00 I/O
I/O port
TXDA2 output/SDA00 I/O
I/O port
TIP11 input/TOP11 output
I/O port
TIP10 input/TOP10 output
I/O port
TIP01 input/TOP01 output
Specification of P39 pin operation mode
Specification of P38 pin operation mode
Specification of P35 pin operation mode
Specification of P34 pin operation mode
Specification of P33 pin operation mode
PMC32
0
1
PMC31
0
1
PMC30
0
1
I/O port
ASCKA0 input/TIP00 input/TOP00 output
I/O port
RXDA0 input/INTP7 input
I/O port
TXDA0 output
Specification of P32 pin operation mode
Specification of P31 pin operation mode
Specification of P30 pin operation mode
Caution Be sure to clear bits 15 to 10, 7, and 6 to “0”.
Remarks 1. The PMC3 register can be read or written in 16-bit units.
However, when using the higher 8 bits of the PMC3 register as the PMC3H register and the
lower 8 bits as the PMC3L register, PMC3 can be read or written in 8-bit or 1-bit units.
2. To read/write bits 8 to 15 of the PMC3 register in 8-bit or 1-bit units, specify them as bits 0 to
7 of the PMC3H register.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 71 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 88

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(4) Port 3 function control register (PFC3)
PFC3 (PFC3H)
After reset: 0000H R/W Address: PFC3 FFFFF466H,
PFC3L FFFFF466H, PFC3L FFFFF467H
0 0 0 0 0 0 PFC39 PFC38
89101112131415
(PFC3L)
0 0 PFC35 PFC34 PFC33 PFC32 0 0
Caution Be sure to set bits 15 to 10, 7, 6, 1, and 0 to “0”.
Remarks 1. For details of alternate function specification, see 4.3.3 (6) Port 3 alternate function
specifications.
2. The PFC3 register can be read or written in 16-bit units.
However, when using the higher 8 bits of the PFC3 register as the PFC3H register and the
lower 8 bits as the PFC3L register, PFC3 can be read or written in 8-bit and 1-bit units.
3. To read/write bits 8 to 15 of the PFC3 register in 8-bit or 1-bit units, specify them as bits 0 to 7
of the PFC3H register.
(5) Port 3 function control expansion register L (PFCE3L)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFF706H
PFCE3L
0 0 0 0 0 PFCE32 0 0
Remark For details of alternate function specification, see 4.3.3 (6) Port 3 alternate function
specifications.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 72 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 89

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(6) Port 3 alternate function specifications
PFC39 Specification of P39 pin alternate function
0 RXDA2 input
1 SCL00 I/O
PFC38 Specification of P38 pin alternate function
0 TXDA2 output
1 SDA00 I/O
PFC35 Specification of P35 pin alternate function
0 TIP11 input
1 TOP11 output
PFC34 Specification of P34 pin alternate function
0 TIP10 input
1 TOP10 output
PFC33 Specification of P33 pin alternate function
0 TIP01 input
1 TOP01 output
PFCE32 PFC32 Specification of P32 pin alternate function
0 0 ASCKA0 input
0 1 Setting prohibited
1 0 TIP00 input
1 1 TOP00 output
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 73 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 90

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(7) Port 3 function register (PF3)
After reset: 0000H R/W Address: PF3 FFFFFC66H,
PF3 (PF3H)
0 0 0 0 0 0 PF39 PF38
PF3L FFFFFC66H, PF3H FFFFFC67H
89101112131415
(PF3L)
0 0 PF35 PF34 PF33 PF32 PF31 PF30
PF3n
0
1
Control of normal output or N-ch open-drain output (n = 0 to 5, 8, 9)
Normal output (CMOS output)
N-ch open-drain output
Cautions 1. When a pull-up resistor at EVDD or higher is connected to an output pin, be sure to set the
PF3n bit to 1.
2. Be sure to set bits 15 to 10, 7, and 6 to “0”.
Remarks 1. The PF3 register can be read or written in 16-bit units.
However, when using the higher 8 bits of the PF3 register as the PF3H register and the lower
8 bits as the PF3L register, PF3 can be read or written in 8-bit or 1-bit units.
2. To read/write bits 8 to 15 of the PF3 register in 8-bit or 1-bit units, specify them as bits 0 to 7
of the PF3H register.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 74 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 91

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.3.4 Port 4
Port 4 is a 3-bit port that controls I/O in 1-bit units.
Port 4 includes the following alternate-function pins.
Table 4-7. Port 4 Alternate-Function Pins
Pin Name Pin No. Alternate-Function Pin Name I/O Remark Block Type
P40 19 SIB0/SDA01 I/O G-6
P41 20 SOB0/SCL01 I/O G-12
P42 21 SCKB0 I/O
Caution The P40 to P42 pins have hysteresis characteristics in the input mode of the alternate-function pin,
but do not have the hysteresis characteristics in the port mode.
(1) Port 4 register (P4)
After reset: 00H (output latch) R/W Address: FFFFF408H
Selectable as N-ch open-drain output
E-3
P4 0 0 0 0 P42 P41 P40
0
P4n
0
1
(2) Port 4 mode register (PM4)
After reset: FFH R/W Address: FFFFF428H
PM4 1 1 1 1 PM42 PM41 PM40
1
PM4n
0
1
Outputs 0
Outputs 1
Output mode
Input mode
Output data control (in output mode) (n = 0 to 2)
I/O mode control (n = 0 to 2)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 75 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 92

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(3) Port 4 mode control register (PMC4)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFF448H
0PMC4 0 0 0 0 PMC42 PMC41 PMC40
PMC42
0
I/O port
1
SCKB0 I/O
PMC41
0
I/O port
1
SOB0 output/SCL01 I/O
PMC40
0
I/O port
1
SIB0 input/SDA01 I/O
(4) Port 4 function control register (PFC4)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFF468H
PFC4
0 0 0 0 0 0 PFC41 PFC40
PFC41
0
SOB0 output
1
SCL01 I/O
Specification of P42 pin operation mode
Specification of P41 pin operation mode
Specification of P40 pin operation mode
Specification of P41 pin alternate function
PFC40
0
1
SIB0 input
SDA01 I/O
Specification of P40 pin alternate function
(5) Port 4 function register (PF4)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFFC68H
PF4 0 0 0 0 PF42 PF41 PF40
Caution When a pull-up resistor at EV
0
PF4n
0
1
Control of normal output or N-ch open-drain output (n = 0 to 2)
Normal output (CMOS output)
N-ch open-drain output
DD or higher is connected to an output pin, be sure to set the
PF4n bit to 1.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 76 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 93

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.3.5 Port 5
Port 5 is a 6-bit port that controls I/O in 1-bit units.
Port 5 includes the following alternate-function pins.
Table 4-8. Port 5 Alternate-Function Pins
Pin Name Pin No. Alternate-Function Pin Name I/O Remark Block Type
Note
Note
Note
Note
P50 32 TIQ01/KR0/TOQ01/RTP00
P51 33 TIQ02/KR1/TOQ02/RTP01
P52 34 TIQ03/KR2/TOQ03/RTP02/DDI
P53 35 SIB2/KR3/TIQ00/TOQ00/RTP03/DDO
P54 36 SOB2/KR4/RTP04/DCK
P55 37 SCKB2/KR5/RTP05/DMS
Note The DDI, DDO, DCK, and DMS pins are used for on-chip debugging.
If on-chip debugging is not used, fix the P05/INTP2/DRST pin to low level between when the reset signal of the
RESET pin is released and when the OCDM.OCDM0 bit is cleared (0).
For details, see 4.6.3 Cautions on on-chip debug pins.
Cautions 1. When the power is turned on, the P53 pin may output undefined level temporarily even during
reset.
2. The P50 to P55 pins have hysteresis characteristics in the input mode of the alternate function,
but do not have hysteresis characteristics in the port mode.
(1) Port 5 register (P5)
After reset: 00H (output latch) R/W Address: FFFFF40AH
Selectable as N-ch open-drain output
I/O U-5
I/O U-5
I/O U-6
I/O U-7
I/O U-8
I/O
U-9
P5 0 P55 P54 P53 P52 P51 P50
0
P5n
0
1
Outputs 0
Outputs 1
Output data control (in output mode) (n = 0 to 5)
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 77 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 94

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(2) Port 5 mode register (PM5)
After reset: FFH R/W Address: FFFFF42AH
PM5 1 PM55 PM54 PM53 PM52 PM51 PM50
1
PM5n
0
1
Output mode
Input mode
(3) Port 5 mode control register (PMC5)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFF44AH
0PMC5 0 PMC55 PMC54 PMC53 PMC52 PMC51 PMC50
PMC55
0
I/O port
1
SCKB2 I/O/KR5 input/RTP05 output
PMC54
0
I/O port
1
SOB2 output/KR4 input/RTP04 output
I/O mode control (n = 0 to 5)
Specification of P55 pin operation mode
Specification of P54 pin operation mode
PMC53
0
1
PMC52
0
1
PMC51
0
1
PMC50
0
1
I/O port
SIB2 input/KR3 input/TIQ00 input/TOQ00 output/RTP03 output
I/O port
TIQ03 input/KR2 input/TOQ03 output/RTP02 output
I/O port
TIQ02 input/KR1 input/TOQ02 output/RTP01 output
I/O port
TIQ01 input/KR0 input/TOQ01 output/RTP00 output
Specification of P53 pin operation mode
Specification of P52 pin operation mode
Specification of P51 pin operation mode
Specification of P50 pin operation mode
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 78 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 95

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(4) Port 5 function control register (PFC5)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFF46AH
0PFC5 0 PFC55 PFC54 PFC53 PFC52 PFC51 PFC50
Remark For details of alternate function specification, see 4.3.5 (6) Port 5 alternate function
specifications.
(5) Port 5 function control expansion register (PFCE5)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFF70AH
0PFCE5 0 PFCE55 PFCE54 PFCE53 PFCE52 PFCE51 PFCE50
Remark For details of alternate function specification, see 4.3.5 (6) Port 5 alternate function
specifications.
(6) Port 5 alternate function specifications
PFCE55 PFC55 Specification of P55 pin alternate function
0 0 SCKB2 I/O
0 1 KR5 input
1 0 Setting prohibited
1 1 RTP05 output
PFCE54 PFC54 Specification of P54 pin alternate function
0 0 SOB2 output
0 1 KR4 input
1 0 Setting prohibited
1 1 RTP04 output
PFCE53 PFC53 Specification of P53 pin alternate function
0 0 SIB2 input
0 1 TIQ00 input/KR3
1 0 TOQ00 output
1 1 RTP03 output
Note
input
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 79 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 96

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
PFCE52 PFC52 Specification of P52 pin alternate function
0 0 Setting prohibited
0 1 TIQ03 input/KR2
1 0 TOQ03 input
1 1 RTP02 output
PFCE51 PFC51 Specification of P51 pin alternate function
0 0 Setting prohibited
0 1 TIQ02 input/KR1
1 0 TOQ02 output
1 1 RTP01 output
PFCE50 PFC50 Specification of P50 pin alternate function
0 0 Setting prohibited
0 1 TIQ01 input/KR0
1 0 TOQ01 output
1 1 RTP00 output
Note KRn and TIQ0m are alternate functions. When using the pin as the TIQ0m pin, disable KRn pin key return
detection, which is the alternate function. (Clear the KRM.KRMn bit to 0.) Also, when using the pin as the
KRn pin, disable TIQ0m pin edge detection, which is the alternate function (n = 0 to 3, m = 0 to 3).
Pin Name Use as TIQ0m Pin Use as KRn Pin
KR0/TIQ01 KRM.KRM0 bit = 0 TQ0IOC1. TQ0TIG2, TQ0IOC1. TQ0TIG3 bits = 0
KR1/TIQ02 KRM.KRM1 bit = 0 TQ0IOC1.TQ0TIG4, TQ0IOC1.TQ0TIG5 bits = 0
KR2/TIQ03 KRM.KRM2 bit = 0 TQ0IOC1.TQ0TIG6, TQ0IOC1.TQ0TIG7 bits = 0
KR3/TIQ00 KRM.KRM3 bit = 0
(7) Port 5 function register (PF5)
After reset: 00H R/W Address: FFFFFC6AH
Note
input
Note
input
Note
input
TQ0IOC1.TQ0TIG0, TQ0IOC1.TQ0TIG1 bits = 0
TQ0IOC2.TQ0EES0, TQ0IOC2.TQ0EES1 bits = 0
TQ0IOC2.TQ0ETS0, TQ0IOC2.TQ0ETS1 bits = 0
PF5 0 PF55 PF54 PF53 PF52 PF51 PF50
0
PF5n
0
1
Control of normal output or N-ch open-drain output (n = 0 to 5)
Normal output (CMOS output)
N-ch open-drain output
Caution When an output pin is pulled up at EV
DD or higher, be sure to set the PF5n bit to 1.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 80 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 97

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.3.6 Port 7
Port 7 is a 8-bit port for which I/O settings can be controlled in 1-bit units.
Port 7 includes the following alternate-function pins.
Table 4-9. Port 7 Alternate-Function Pins
Pin Name Pin No. Alternate-Function Pin Name I/O Remark Block Type
P70 80 ANI0 Input A-1
P71 79 ANI1 Input A-1
P72 78 ANI2 Input A-1
P73 77 ANI3 Input A-1
P74 76 ANI4 Input A-1
P75 75 ANI5 Input A-1
P76 74 ANI6 Input A-1
P77 73 ANI7 Input
(1) Port 7 register L (P7L)
After reset: 00H (output latch) R/W Address: FFFFF40EH
−
A-1
P7L
P77 P76 P75 P74 P73 P72 P71 P70
P7n
0
1
Outputs 0
Outputs 1
Output data control (in output mode) (n = 0 to 7)
Caution Do not read or write the P7L register during A/D conversion (see 13.6 (4) Alternate I/O).
(2) Port 7 mode register L (PM7L)
After reset: FFH R/W Address: FFFFF42EH
PM7L
PM77 PM76 PM75 PM74 PM73 PM72 PM71 PM70
PM7n
0
1
Output mode
Input mode
I/O mode control (n = 0 to 7)
Caution When using the P7n pin as its alternate function (ANIn pin), set the PM7n bit to 1.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 81 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 98

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
4.3.7 Port 9
Port 9 is a 16-bit port for which I/O settings can be controlled in 1-bit units.
Port 9 includes the following alternate-function pins.
Table 4-10. Port 9 Alternate-Function Pins
Pin Name Pin No. Alternate-Function Pin Name I/O Remark Block Type
P90 38 KR6/TXDA1 I/O U-17
P91 39 KR7/RXDA1 I/O U-18
P96 40 TIP21/TOP21 I/O U-19
P97 41 SIB1/TIP20/TOP20 I/O U-20
P98 42 SOB1 Output G-3
P99 43 SCKB1 I/O G-5
P913 44 INTP4 Input N-2
P914 45 INTP5/TIP51/TOP51 I/O U-15
P915 46 INTP6/TIP50/TOP50 I/O
Caution The P90, P91, P96, P99, and P913 to P915 pins have hysteresis characteristics in the input mode of
the alternate-function pin, but do not have the hysteresis characteristics in the port mode.
(1) Port 9 register (P9)
After reset: 0000H (output latch) R/W Address: P9 FFFFF412H,
P9 (P9H)
P915
P914 P913 0 0 0 P99 P98
Selectable as N-ch open-drain output
U-15
P9L FFFFF412H, P9H FFFFF413H
89101112131415
(P9L)
P97 P96 0 0 0 0 P91 P90
P9n
0
1
Output data control (in output mode) (n = 0, 1, 6 to 9, 13 to 15)
Outputs 0
Outputs 1
Caution Be sure to set bits 12 to 10 and 5 to 2 to “0”.
Remarks 1. The P9 register can be read or written in 16-bit units.
However, when using the higher 8 bits of the P9 register as the P9H register and the lower 8
bits as the P9L register, P9 can be read or written in 8-bit or 1-bit units.
2. To read/write bits 8 to 15 of the P9 register in 8-bit or 1-bit units, specify them as bits 0 to 7 of
the P9H register.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 82 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 99

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(2) Port 9 mode register (PM9)
After reset: FFFFH R/W Address: PM9 FFFFF432H,
PM9 (PM9H)
PM915 PM914 PM913 1 1 1 PM99 PM98
PM9L FFFFF432H, PM9H FFFFF433H
89101112131415
(PM9L)
PM97
PM9n
0
1
PM96 1 1 1 1 PM91 PM90
I/O mode control (n = 0, 1, 6 to 9, 13 to 15)
Output mode
Input mode
Caution Be sure to set bits 12 to 10 and 5 to 2 to “1”.
Remarks 1. The PM9 register can be read or written in 16-bit units.
However, when using the higher 8 bits of the PM9 register as the PM9H register and the
lower 8 bits as the PM9L register, PM9 can be read or written in 8-bit and 1-bit units.
2. To read/write bits 8 to 15 of the PM9 register in 8-bit or 1-bit units, specify them as bits 0 to 7
of the PM9H register.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 83 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
Page 100

V850ES/JF3-L CHAPTER 4 PORT FUNCTIONS
(3) Port 9 mode control register (PMC9)
PMC9 (PMC9H)
After reset: 0000H R/W Address: PMC9 FFFFF452H,
PMC9L FFFFF452H, PMC9H FFFFF453H
89101112131415
PMC915 PMC914 PMC913 0 0 0 PMC99 PMC98
(PMC9L)
PMC97 PMC96 0 0 0 0 PMC91 PMC90
PMC915
0
1
PMC914
0
1
PMC913
0
1
PMC99
0
1
PMC98
0
1
PMC97
0
1
I/O port
INTP6 input/TIP50 input/TOP50 output
I/O port
INTP5 input/TIP51 input/TOP51 output
I/O port
INTP4 input
I/O port
SCKB1 I/O
I/O port
SOB1 output
I/O port
SIB1 input/TIP20 input/TOP20 output
Specification of P915 pin operation mode
Specification of P914 pin operation mode
Specification of P913 pin operation mode
Specification of P99 pin operation mode
Specification of P98 pin operation mode
Specification of P97 pin operation mode
PMC96
0
1
PMC91
0
1
PMC90
0
1
I/O port
TIP21 input/TOP21 output
I/O port
KR7 input/RXDA1 input
I/O port
KR6 input/TXDA1 output
Specification of P96 pin operation mode
Specification of P91 pin operation mode
Specification of P90 pin operation mode
Caution Be sure to set bits 12 to 10 and 5 to 2 to “0”.
Remarks 1. The PMC9 register can be read or written in 16-bit units.
However, when using the higher 8 bits of the PMC9 register as the PMC9H register and the
lower 8 bits as the PMC9L register, PMC9 can be read or written in 8-bit or 1-bit units.
2. To read/write bits 8 to 15 of the PMC9 register in 8-bit or 1-bit units, specify them as bits 0 to
7 of the PMC9H register.
R01UH0017EJ0400 Rev.4.00 Page 84 of 816
Sep 30, 2010
 Loading...
Loading...