Page 1
REJ10J1822-0101
Renesas Microcomputer Development Environment System
Stub Generator
V.1.00
User’s Manual
Rev.1.01
Revision Date: Mar. 17, 2008
Page 2

Page 3
Notes regarding these materials
1. This document is provided for reference purposes only so that Renesas customers may select the appropriate
Renesas products for their use. Renesas neither makes warranties or representations with respect to the
accuracy or completeness of the information contained in this document nor grants any license to any
intellectual property rights or any other rights of Renesas or any third party with respect to the information in
this document.
2. Renesas shall have no liability for damages or infringement of any intellectual property or other rights arising
out of the use of any information in this document, including, but not limited to, product data, diagrams, charts,
programs, algorithms, and application circuit examples.
3. You should not use the products or the technology described in this document for the purpose of military
applications such as the development of weapons of mass destruction or for the purpose of any other military
use. When exporting the products or technology described herein, you should follow the applicable export
control laws and regulations, and procedures required by such laws and regulations.
4. All information included in this document such as product data, diagrams, charts, programs, algorithms, and
application circuit examples, is current as of the date this document is issued. Such information, however, is
subject to change without any prior notice. Before purchasing or using any Renesas products listed in this
document, please confirm the latest product information with a Renesas sales office. Also, please pay regular
and careful attention to additional and different information to be disclosed by Renesas such as that disclosed
through our website. (http://www.renesas.com )
5. Renesas has used reasonable care in compiling the information included in this document, but Renesas
assumes no liability whatsoever for any damages incurred as a result of errors or omissions in the information
included in this document.
6. When using or otherwise relying on the information in this document, you should evaluate the information in
light of the total system before deciding about the applicability of such information to the intended application.
Renesas makes no representations, warranties or guaranties regarding the suitability of its products for any
particular application and specifically disclaims any liability arising out of the application and use of the
information in this document or Renesas products.
7. With the exception of products specified by Renesas as suitable for automobile applications, Renesas
products are not designed, manufactured or tested for applications or otherwise in systems the failure or
malfunction of which may cause a direct threat to human life or create a risk of human injury or which require
especially high quality and reliability such as safety systems, or equipment or systems for transportation and
traffic, healthcare, combustion control, aerospace and aeronautics, nuclear power, or undersea communication
transmission. If you are considering the use of our products for such purposes, please contact a Renesas
sales office beforehand. Renesas shall have no liability for damages arising out of the uses set forth above.
8. Notwithstanding the preceding paragraph, you should not use Renesas products for the purposes listed below:
(1) artificial life support devices or systems
(2) surgical implantations
(3) healthcare intervention (e.g., excision, administration of medication, etc.)
(4) any other purposes that pose a direct threat to human life
Renesas shall have no liability for damages arising out of the uses set forth in the above and purchasers who
elect to use Renesas products in any of the foregoing applications shall indemnify and hold harmless Renesas
Technology Corp., its affiliated companies and their officers, directors, and employees against any and all
damages arising out of such applications.
9. You should use the products described herein within the range specified by Renesas, especially with respect
to the maximum rating, operating supply voltage range, movement power voltage range, heat radiation
characteristics, installation and other product characteristics. Renesas shall have no liability for malfunctions or
damages arising out of the use of Renesas products beyond such specified ranges.
10. Although Renesas endeavors to improve the quality and reliability of its products, IC products have specific
characteristics such as the occurrence of failure at a certain rate and malfunctions under certain use
conditions. Please be sure to implement safety measures to guard against the possibility of physical injury, and
injury or damage caused by fire in the event of the failure of a Renesas product, such as safety design for
hardware and software including but not limited to redundancy, fire control and malfunction prevention,
appropriate treatment for aging degradation or any other applicable measures. Among others, since the
evaluation of microcomputer software alone is very difficult, please evaluate the safety of the final products or
system manufactured by you.
11. In case Renesas products listed in this document are detached from the products to which the Renesas
products are attached or affixed, the risk of accident such as swallowing by infants and small children is very
high. You should implement safety measures so that Renesas products may not be easily detached from your
products. Renesas shall have no liability for damages arising out of such detachment.
12. This document may not be reproduced or duplicated, in any form, in whole or in part, without prior written
approval from Renesas.
13. Please contact a Renesas sales office if you have any questions regarding the information contained in this
document, Renesas semiconductor products, or if you have any other inquiries.
Page 4

Page 5

Preface
This manual describes how to use the stub generator. Read this manual and understand it well
before using the stub generator.
Notes on Descriptions
RPCGEN Abbreviation for the stub generator
Prefix Prefix 0x indicates a hexadecimal number. Numbers with no prefix are
decimal.
\ ‘\’ is the directory delimiter.
[Menu -> Menu item] ‘->’ leads to the menu item (e.g. File -> Save).
$(xxxx) Custom placeholder in the High-performance Embedded Workshop
i
Page 6

Trademarks
All trademarks and registered trademarks belong to their respective owners.
1. TRON is an acronym formed from "The Real Time Operating system Nucleus". ITRON is
short for "Industrial TRON" and µITRON is short for "Micro Industrial TRON".
TRON, ITRON, and µITRON are the names of computer specifications and do not indicate
specific products or groups of products.
The µITRON4.0 specification is an open realtime-kernel specification defined by the TRON
Association. The µITRON4.0 specification can be downloaded from the TRON Association
homepage (
http://www.assoc.tron.org).
The copyright of the µITRON specification belongs to the TRON Association.
2. Microsoft® and Windows® are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United
States and/or other countries. The formal name of Windows® is Microsoft Windows Operating
System.
3. All other product names are trademarks or registered trademarks of the respective holders.
Renesas Technology Homepage
Various support information are available on the following Renesas Technology homepage:
http://www.renesas.com/en/tools/
ii
Page 7

Contents
Section 1 Overview..................................................................................................1
1.1 Overview............................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Operating Environment......................................................................................................... 2
Section 2 Installation................................................................................................3
2.1 Downloading......................................................................................................................... 3
2.2 Installing RPCGEN...............................................................................................................3
Section 3 Functions and Files Generated by RPCGEN...........................................5
3.1 Functions Generated by RPCGEN........................................................................................ 5
3.1.1 Client..................................................................................................................... 6
3.1.2 Server.................................................................................................................... 6
3.2 Files Generated by RPCGEN................................................................................................ 7
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN ................................................................................9
4.1 Executing RPCGEN ............................................................................................................. 9
4.2 Options................................................................................................................................ 10
4.2.1 PUBI ...................................................................................................................10
4.2.2 CLNTS................................................................................................................ 10
4.2.3 CLNTI................................................................................................................. 10
4.2.4 SVRS .................................................................................................................. 11
4.2.5 SVRI ...................................................................................................................11
4.3 Executing RPCGEN as a Build Phase in the High-performance Embedded Workshop..... 12
Section 5 Specifications of a Config File ..............................................................23
5.1 Definition............................................................................................................................ 23
5.2 Comments ........................................................................................................................... 24
5.3 File Locations ..................................................................................................................... 25
5.3.1 PUB_INCPATH ................................................................................................. 25
5.3.2 CLNT_SOURCEPATH...................................................................................... 26
5.3.3 CLNT_INCPATH............................................................................................... 26
5.3.4 SVR_SOURCEPATH......................................................................................... 27
5.3.5 SVR_INCPATH ................................................................................................. 27
5.4 Controlling the Output of #include Directives.................................................................... 28
5.4.1 Order of #Include Directives............................................................................... 29
5.4.2 GLOBAL_INCFILE ........................................................................................... 30
iii
Page 8

5.4.3 CLNT_INCFILE................................................................................................. 30
5.4.4 SVR_INCFILE ...................................................................................................31
5.5 Server Information..............................................................................................................32
5.5.1 SVR_NAME....................................................................................................... 32
5.5.2 SVR_ID .............................................................................................................. 33
5.5.3 SVR_VERSION ................................................................................................. 34
5.5.4 SVR_NOINIT..................................................................................................... 34
5.5.5 SVR_NOSTUBTBL ........................................................................................... 35
5.5.6 SVR_NOSHUTDOWN ...................................................................................... 36
5.5.7 SVR_STATIC..................................................................................................... 37
5.5.8 SVR_AUTH ....................................................................................................... 38
5.5.9 SVR_SECTION.................................................................................................. 42
5.6 Client Information ..............................................................................................................43
5.6.1 CLNT_NOINIT .................................................................................................. 43
5.6.2 CLNT_NOSHUTDOWN ................................................................................... 44
5.6.3 CLNT_CALLCHK ............................................................................................. 45
5.6.4 CLNT_SECTION ............................................................................................... 46
5.7 Server Functions ................................................................................................................. 47
5.7.1 RPC_FUNC ........................................................................................................ 47
Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions.............................................................49
6.1 Format................................................................................................................................. 49
6.2 Function-Type Directives ................................................................................................... 52
6.2.1 Function with a Return Value............................................................................. 52
6.2.2 Function without a Return Value........................................................................ 53
6.2.3 When the Return Value is not Representable as a 4-Byte Integer ...................... 54
6.3 Function Names..................................................................................................................55
6.4 Parameters........................................................................................................................... 56
6.5 Keywords for Input/Output................................................................................................. 57
6.5.1 IN (Input)............................................................................................................ 57
6.5.2 OUT (Output) ..................................................................................................... 58
6.5.3 INOUT (Input and Output)................................................................................. 59
6.5.4 REF (Passing by Reference)............................................................................... 60
6.5.5 DESC (Specified Parameter is not Passed from the Client to the Server) .......... 62
6.6 Keywords for Data Types................................................................................................... 63
6.6.1 DFLT (Default)................................................................................................... 63
6.6.2 STR (String)........................................................................................................ 64
6.6.3 PTR (Pointer)...................................................................................................... 65
6.6.4 ARY (Array)....................................................................................................... 66
6.6.5 COUNT (Number of Elements in an Array)....................................................... 67
iv
Page 9

6.7 Optional Keywords............................................................................................................. 83
6.7.1 SVRSTUB (Server Stub) .................................................................................... 84
6.7.2 SVRFUNC (Server Function Name) ..................................................................85
6.7.3 CLNTSTUB (Client Stub) .................................................................................. 86
6.7.4 UNACK (Asynchronous Call)............................................................................ 87
6.7.5 CLNTCOPYCBK (RPC Call by rpc_call_copycbk())........................................ 88
Section 7 Server Functions Not Supported by RPCGEN ......................................89
7.1 Parameter ............................................................................................................................ 89
7.2 Return Value....................................................................................................................... 91
Section 8 Application Interface .............................................................................93
8.1 Client-Stub Functions Generated by RPCGEN .................................................................. 93
8.2 Server-Stub Functions Generated by RPCGEN.................................................................. 95
8.3 Server-Initialization Function ............................................................................................. 96
8.4 Server-Stub Function Table ................................................................................................ 97
8.5 Server-Shutdown Function .................................................................................................99
8.6 Client-Initialization Function............................................................................................ 100
8.7 Client-Shutdown Function................................................................................................ 101
8.8 rpc_retval_adr() ................................................................................................................102
8.9 <Config file>_public.h...................................................................................................... 104
8.10 Local Variables Used in the Source Code Created by RPCGEN......................................104
Section 9 Notes ....................................................................................................105
Section 10 Error Messages...................................................................................107
10.1 Format............................................................................................................................... 107
10.2 General.............................................................................................................................. 108
10.3 Definition Errors (other than RPC_FUNC) ...................................................................... 108
10.4 Definition Errors (RPC_FUNC) ....................................................................................... 108
Section 11 Samples..............................................................................................109
11.1 Config File (sample.x) ...................................................................................................... 110
11.2 sample_clnt.h .................................................................................................................... 112
11.3 sample_private.h............................................................................................................... 113
11.4 sample_clnt.c .................................................................................................................... 114
11.5 sample_svr.h ..................................................................................................................... 120
11.6 sample_svr.c .....................................................................................................................122
11.7 sample_public.h................................................................................................................ 127
v
Page 10

vi
Page 11
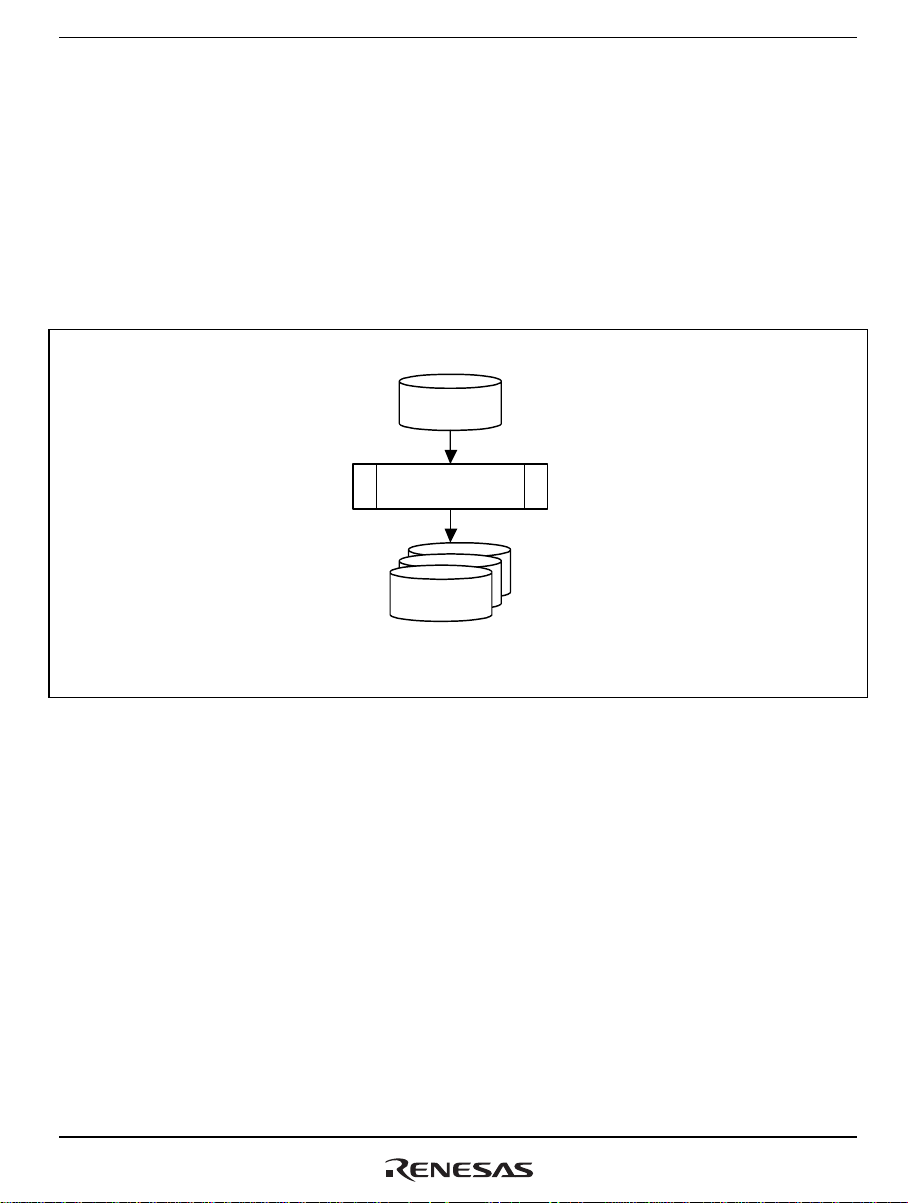
Section 1 Overview
Section 1 Overview
1.1 Overview
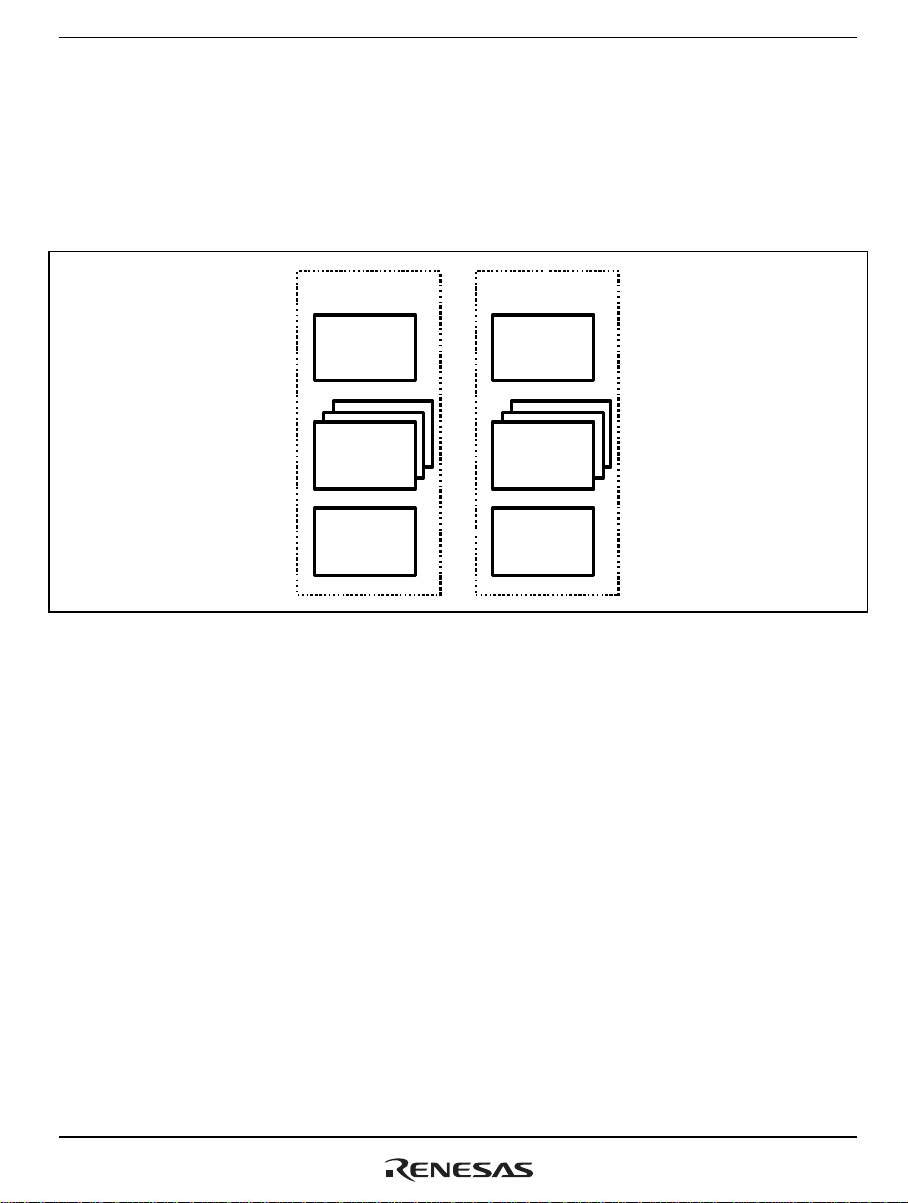
The stub generator (hereafter referred to as RPCGEN) is a tool used to generate the source code of
the client and server stubs that are required whenever the remote procedure call (RPC) facility of
the HI7200/MP realtime operating system is to be used. A config file is created by using a text
editor and then input to RPCGEN, which creates the source code of the client and server stubs.
C o n fig file
RPCGEN
Source code of the client
and server stubs
Figure 1.1 Overview of RPCGEN
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 1 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 12

Section 1 Overview
1.2 Operating Environment
RPCGEN is provided as a Perl script file. Table 1.1 shows the operating environment.
Table 1.1 Operating Environment
Item Operating Environment
Realtime OS HI7200/MP V.1.00 Release 00 or later
Perl environment We have confirmed correct execution of RPCGEN by ActivePerl
5.8.8.820 (for Windows® (x86)) produced by ActiveState Software Inc.
ActivePerl is available for free download from the following Web site:
http://www.activestate.com/Products/activeperl/
Host machine Any machine with Windows® XP (32 bits) or Windows® 2000 as the
operating system
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 2 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 13
Section 2 Installation
Section 2 Installation
2.1 Downloading
RPCGEN can be downloaded for free from the Renesas Web site at the following URL.
http://www.renesas.com
2.2 Installing RPCGEN
The file for downloading has been compressed in the zip format. Expanding the zip file generates
the files listed in table 2.1. These files must be stored in a suitable folder.
Table 2.1 Files Provided as RPCGEN
Filename Description
rpcgen.pl Main body of RPCGEN
rpcgen_clnt.pm
rpcgen_svr.pm
rpcgen_info.pm
rpcgen_misc.pm
Package modules for use by the main body of RPCGEN
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 3 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 14

Section 2 Installation
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 4 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 15
Section 3 Functions and Files Generated by RPCGEN
Section 3 Functions and Files Generated by RPCGEN
3.1 Functions Generated by RPCGEN
Figure 3.1 shows the functions generated by RPCGEN.
Client
Client-
init ia lizatio n
function
Server
Server-
init ialization
function
C lient-s t u b
functions
Client-
shutdown
fun ctio n
Figure 3.1 Functions Generated by RPCGEN
Server-stub
functions
Server-
shutdown
fun ctio n
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 5 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 16

Section 3 Functions and Files Generated by RPCGEN
3.1.1 Client
(1) Client-initialization function
This function initiates the connection with the server. Specifying CLNT_NOINIT prevents the
creation of the client-initialization function.
(2) Client-shutdown function
This function ends the connection with the server. Specifying CLNT_NOSHUTDOWN prevents
the creation of the client-shutdown function.
(3) Client-stub functions
Each of these functions makes an RPC call and has the same API as or an API similar to the server
function. If SVRAUTH has not been specified, the API will be the same as that of the server
function. Specifying CLNTSTUB prevents the creation of a specific client-stub function.
3.1.2 Server
(1) Server-initialization function
This function starts up the server. Specifying SVR_NOINIT prevents the creation of the serverinitialization function.
(2) Server-shutdown function
This function shuts the server down. Specifying SVR_NOSHUTDOWN prevents the creation of
the server-shutdown function.
(3) Server-stub functions
Each of these functions is called back from the RPC library and then calls a server function.
Specifying SVRSTUB prevents the creation of a specific server-stub function, while specifying
SVRFUNC allows the name of the called server function to be replaced.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 6 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 17

Section 3 Functions and Files Generated by RPCGEN
3.2 Files Generated by RPCGEN
RPCGEN generates the files listed in table 3.1 in accord with the name of the config file.
Table 3.1 Files Generated by RPCGEN
Filename Description Definition of the File Location
<config file>_clnt.c Client-stub source file CLNTS option or
CLNT_SOURCEPATH in the config file
<config file>_clnt.h Client-stub header file
<config file>_private.h Internal header file for the
client stub
<config file>_svr.c Server-stub source file SVRS option or SVR_SOURCEPATH
<config file>_svr.h Server-stub header file SVRI option or SVR_INCPATH in the
<config file>_public.h Header file for the client and
server stubs
When the config file is “sample.x,” for example, RPCGEN will generate the following files:
sample_clnt.c, sample_clnt.h, sample_svr.c, sample_svr.h, sample_private.h, and sample_public.h.
CLNTI option or CLNT_INCPATH in
the config file
in the config file
config file
PUBI option or PUB_INCPATH in the
config file
To temporarily save information during the process of file generation, RPCGEN also generates
intermediate files in the current directory. The names of these intermediate files consist of two
underscores (“__”) appended before the filenames given in the table above.
(1) <config file>_clnt.c (client-stub source file)
This file contains the client-stub functions, client-initialization function, and client-shutdown
function.
(2) <config file>_clnt.h (client-stub header file)
This file contains definitions required for use of the client-stub functions, client-initialization
function, and client-shutdown function. The definitions include prototype declarations of the
client-stub functions, client-initialization function, and client-shutdown function.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 7 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 18

Section 3 Functions and Files Generated by RPCGEN
(3) <config file>_private.h (internal header file for the client stub)
This is a header file included by <config file>_clnt.c only.
(4) <config file>_svr.c (server-stub source file)
This file contains the server-stub functions, server-initialization function, server-shutdown
function, and server-stub function table.
(5) <config file>_svr.h (server-stub header file)
This file contains definitions required for use of the server-initialization function and servershutdown function. The definitions include prototype declarations of the server-stub functions,
server-initialization function, and server-shutdown function.
(6) <config file>_public.h (header file for the client and server stubs)
This is a header file for the client and server applications. For details, refer to section 8.9, <config
file>_public.h.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 8 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 19

Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
4.1 Executing RPCGEN
RPCGEN must be executed from the command prompt as follows.
perlΔ-I<rpcgen path>Δ<rpcgen path>\rpcgen.plΔ
<config file>[Δ<option>...](RET)
<rpcgen path> is a path to the directory where RPCGEN has been installed.
<config file> refers to a file describing the specifications of the client and server stubs to be
generated. This file must be created by the user. The standard filename extension for the config
file is “.x”, which must not be omitted when the name is entered in a command line.
After execution of the above command, RPCGEN will generate the C-language source files and
header files for the client and server stubs in accord with the information contained in the config
file.
If <config file> and <option> are omitted, the command syntax will be shown.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 9 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 20

Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
4.2 Options
4.2.1 PUBI
Format:
PUBI="<path>"
Description:
This option is used to specify the path for output of <config file>_public.h. If this option is used, a
definition of PUB_INCPATH in the config file is ignored.
4.2.2 CLNTS
Format:
CLNTS="<path>"
Description:
This option is used to specify the path for output of <config file>_clnt.c. If this option is used, a
definition of CLNT_SOURCEPATH in the config file is ignored.
4.2.3 CLNTI
Format:
CLNTI="<path>"
Description:
This option is used to specify the path for output of <config file>_clnt.h and
<config file>_private.h. If this option is used, a definition of CLNT_INCPATH in the config file
is ignored.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 10 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 21

Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
4.2.4 SVRS
Format:
SVRS="<path>"
Description:
This option is used to specify the path for output of <config file>_svr.c. If this option is used, a
definition of SVR_SOURCEPATH in the config file is ignored.
4.2.5 SVRI
Format:
SVRI="<path>"
Description:
This option is used to specify the path for output of <config file>_svr.h. If this option is used, a
definition of SVR_INCPATH in the config file is ignored.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 11 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 22
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
4.3 Executing RPCGEN as a Build Phase in the High-performance
Embedded Workshop
After RPCGEN has been registered as a custom build phase in the workspace, it will be
automatically executed at the time of building.
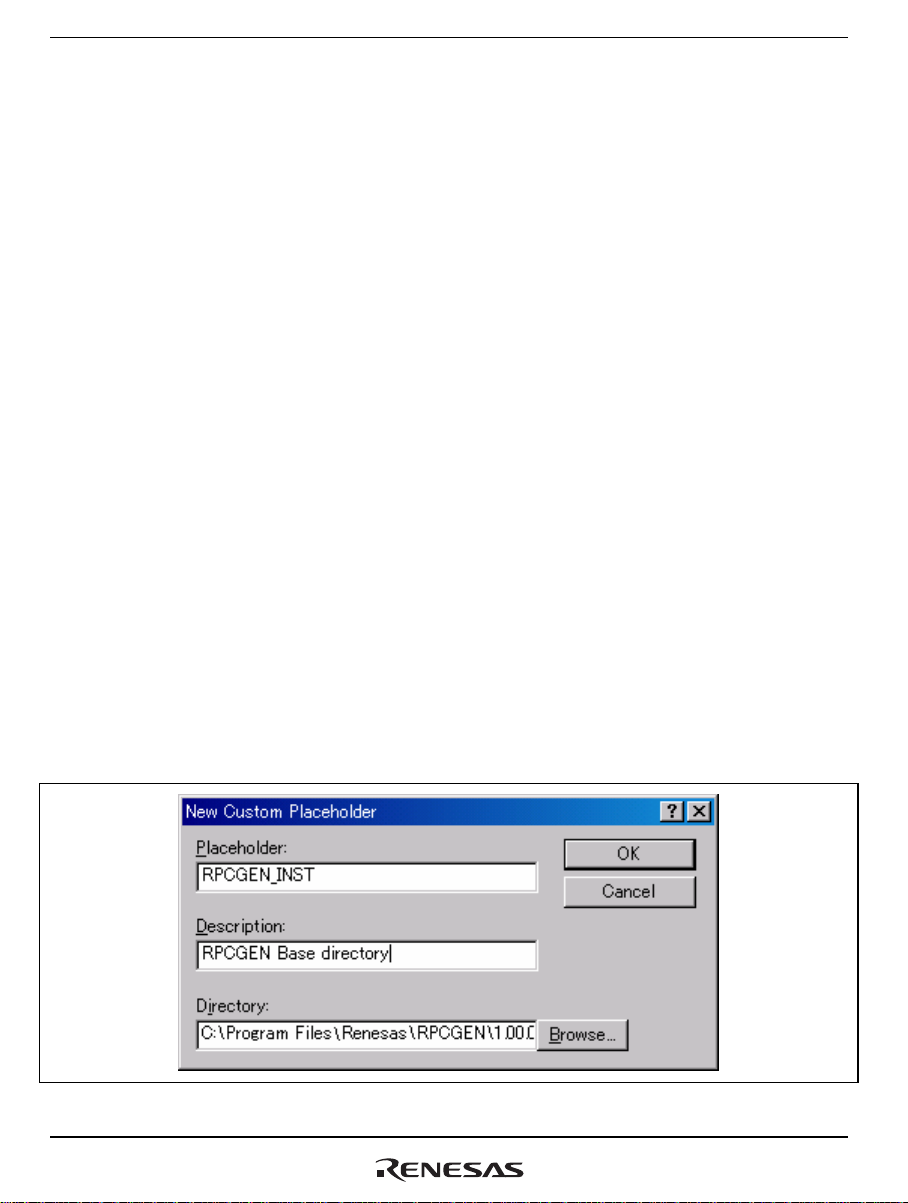
(1) Defining Custom Placeholders
The following two custom placeholders must be defined.
• Path to RPCGEN
[Placeholder]: RPCGEN_INST
[Description]: RPCGEN Base directory
[Directory]: Directory under which RPCGEN is stored
• Path to Perl.exe
[Placeholder]: PERL_INST
[Description]: Perl Base directory
[Directory]: Directory under which perl.exe is stored
To define a custom placeholder, follow the procedure below.
Select [Setup->Customize] from the menu bar of the High-performance Embedded Workshop.
Then select the [Placeholders] tab of the [Customize] dialog box. Choose either [Application wide
custom placeholders] or [Workspace wide custom placeholders] and click on the [Add] button.
This opens the [New Custom Placeholder] dialog box shown in figure 4.1. Define the two custom
placeholders in this dialog box by filling in the information given above.
Figure 4.1 [New Custom Placeholder] Dialog Box
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 12 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 23
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
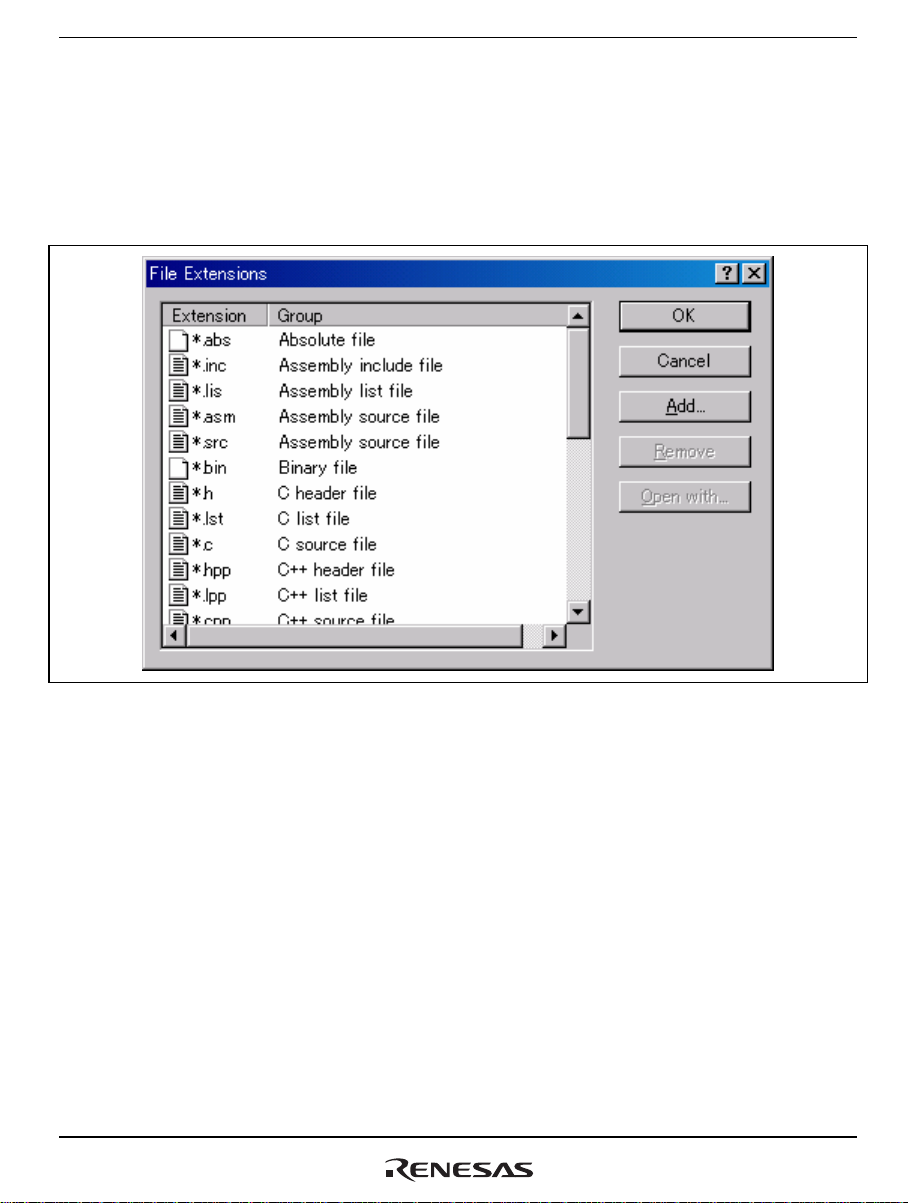
(2) Adding a File Extension
To make execution as a custom build phase work, the filename extension “.x” for config files must
be added as a filename extension to be used in custom build phases. Select [Project->File
Extensions] from the menu bar of the High-performance Embedded Workshop. This opens the
[File Extensions] dialog box shown in figure 4.2.
Figure 4.2 [File Extensions] Dialog Box
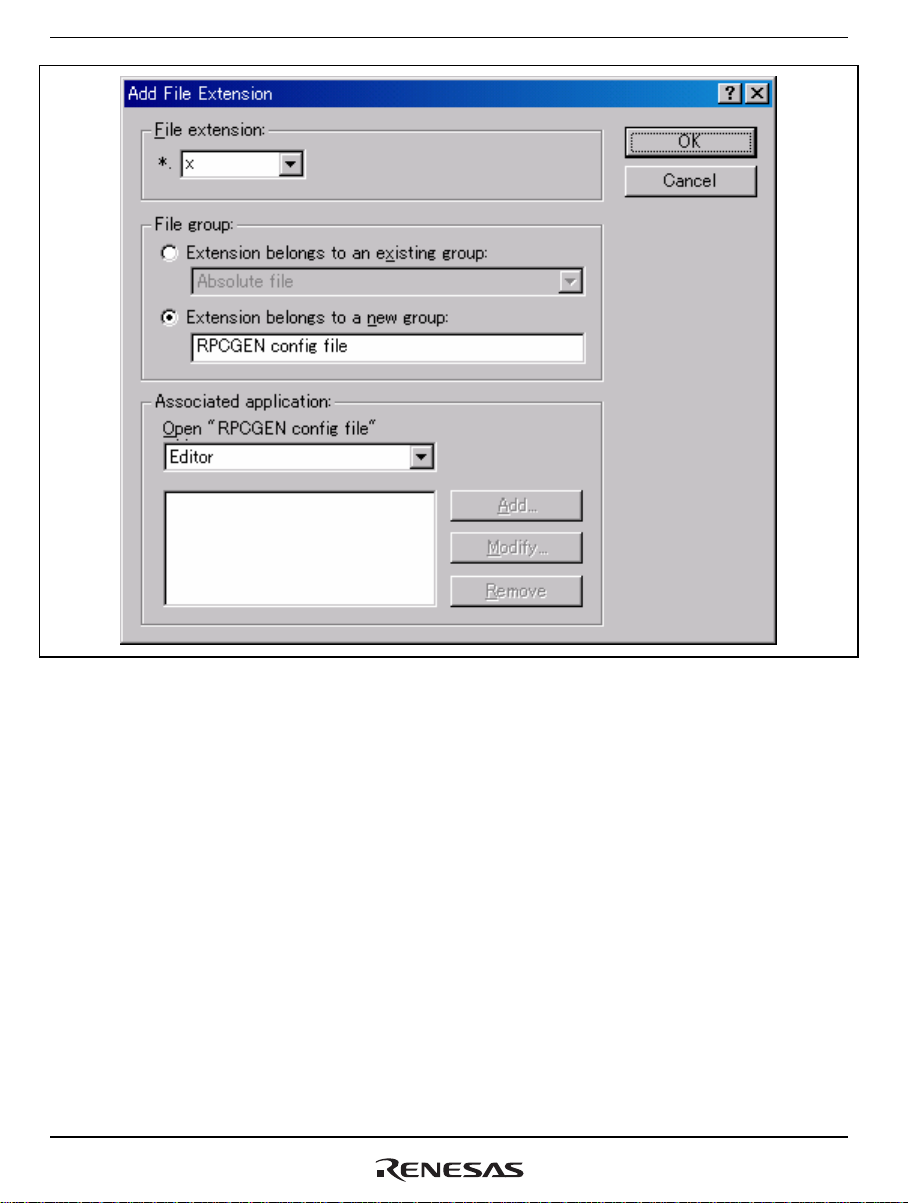
Clicking the [Add] button opens the [Add File Extension] dialog box shown in figure 4.3. Add the
extension “.x” as shown in the figure.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 13 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 24
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
Figure 4.3 [Add File Extension] Dialog Box
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 14 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 25
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
(3) Creating the RPCGEN Custom Build Phase
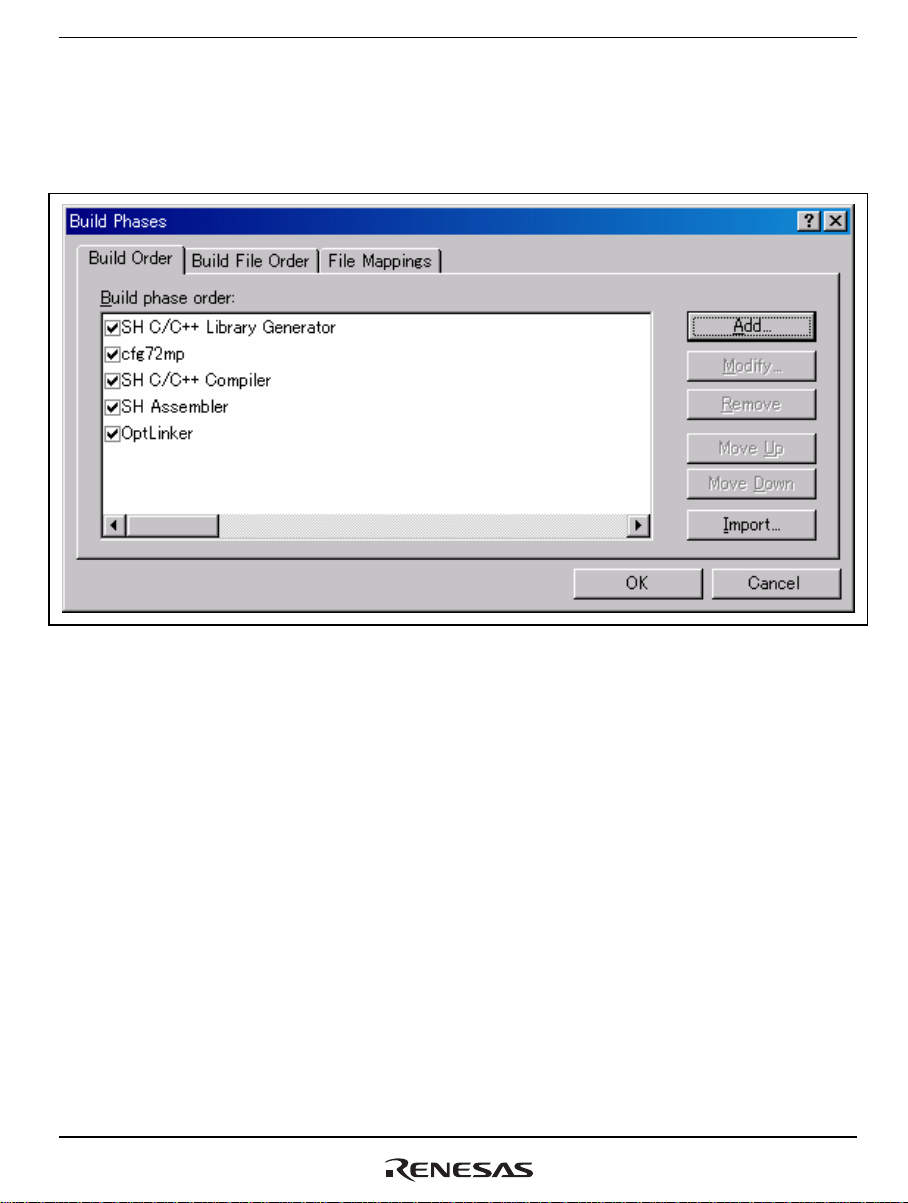
Select [Build->Build Phases] from the menu bar of the High-performance Embedded Workshop.
This opens the [Build Phases] dialog box shown in figure 4.4.
Figure 4.4 [Build Phases] Dialog Box
Clicking on the [Add] button invokes the [New Build Phase] wizard (figure 4.5).
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 15 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 26
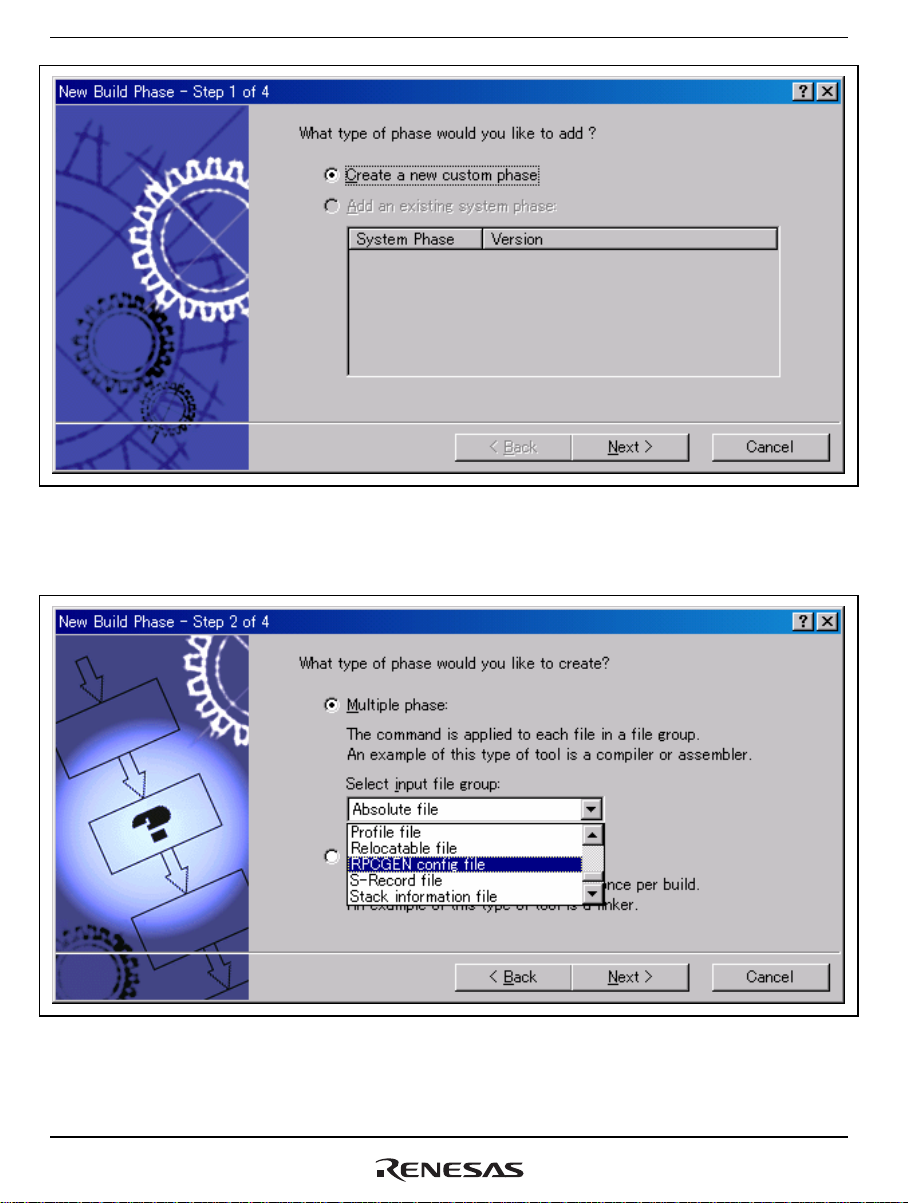
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
Figure 4.5 [New Build Phase - Step 1 of 4] Dialog Box
Click on [Next] to go to step 2.
Figure 4.6 [New Build Phase - Step 2 of 4] Dialog Box
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 16 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 27
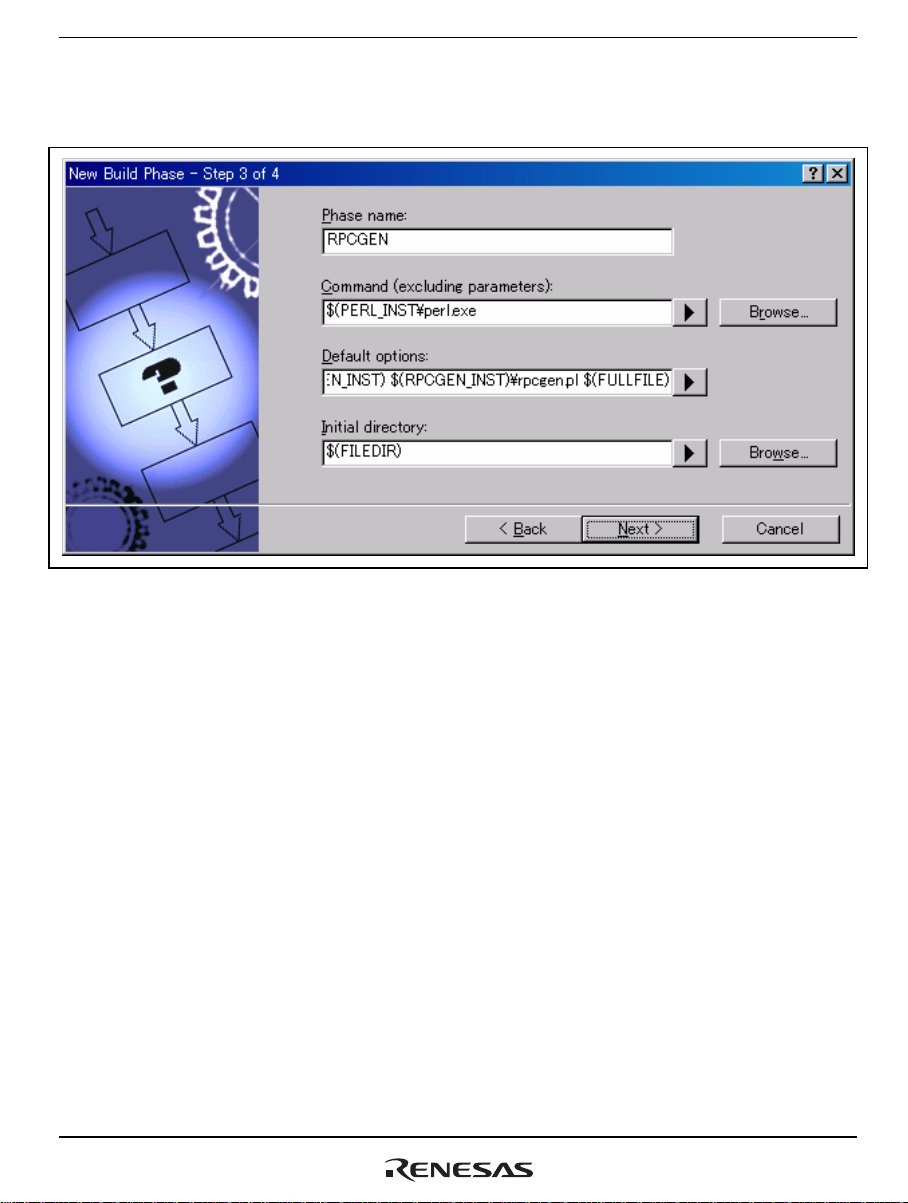
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
At step 2, select [Multiple phase]. Then select [RPCGEN config file] for [Select input file group].
Click on [Next] to go to step 3.
Figure 4.7 [New Build Phase - Step 3 of 4] Dialog Box
[Phase name]: Any name defined by the user (“rpcgen” in this example)
[Command]: $(PERL_INST)\perl.exe
[Default options]: -I $(RPCGEN_INST) $(RPCGEN_INST)\rpcgen.pl $(FULLFILE)
[Initial directory]: $(FILEDIR)
Click on [Next] to go to step 4.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 17 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 28
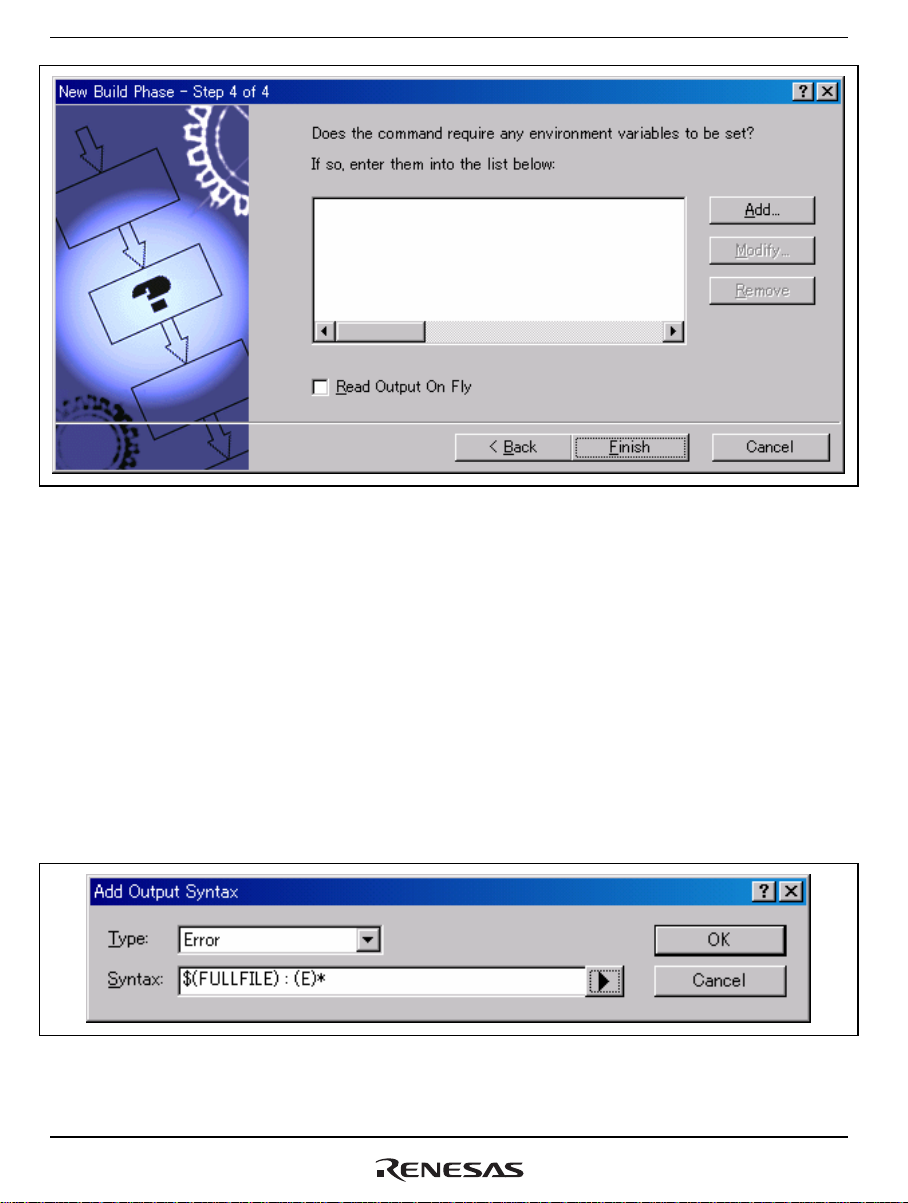
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
Figure 4.8 [New Build Phase - Step 4 of 4] Dialog Box
Although no environment variables need to be added for RPCGEN, you can add environment
variables for the Perl environment as required.
Creation of the RPCGEN custom build phase is now complete.
Next, the syntax for messages about RPCGEN must be defined. After the syntax has been defined,
the corresponding config file (*.x) will be opened in response to double-clicking on an RPCGEN
error message output in the [Build] window of the High-performance Embedded Workshop.
In the [Build Phases] dialog box shown in figure 4.4, select “rpcgen” and click on the [Modify]
button. The [Modify rpcgen] dialog box opens. Select the [Output Syntax] tab and type in the
syntax for errors shown in figure 4.9.
Figure 4.9 [Add Output Syntax] Dialog Box
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 18 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 29
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
Now settings must be made so that the files output by RPCGEN will be deleted by
[Build->Clean Current Project] or [Build->Clean All Projects] from the High-performance
Embedded Workshop.
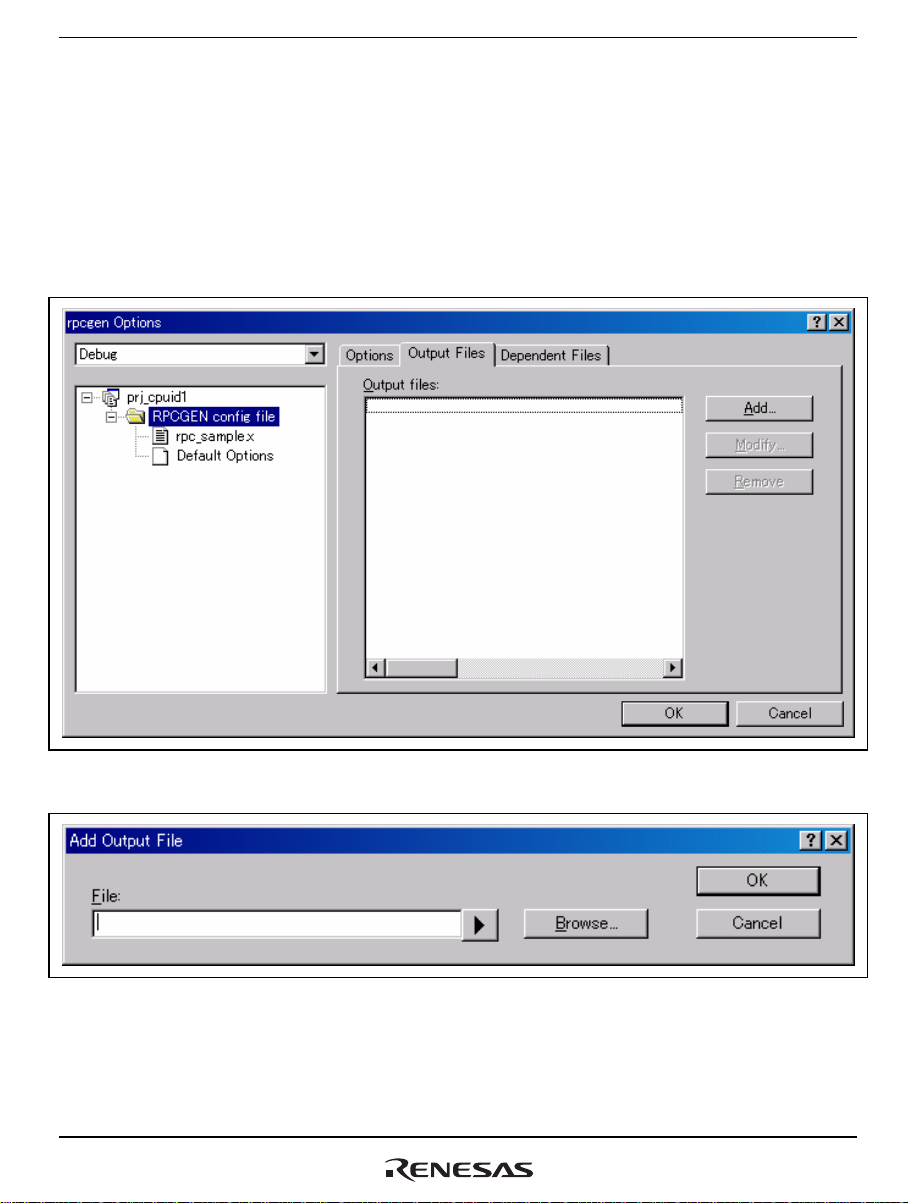
Select [Build->rpcgen] to open the [rpcgen Options] dialog box (figure 4.10). Select the [Output
Files] tab, check that the “RPCGEN config file” folder icon is active, and click on the [Add]
button. This opens the [Add Output File] dialog box, in which the names of the files output by
RPCGEN should be entered. For the filenames, refer to section 3.2, Files Generated by RPCGEN.
Figure 4.10 [rpcgen Options] Dialog Box
Figure 4.11 [Add Output File] Dialog Box
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 19 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 30
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
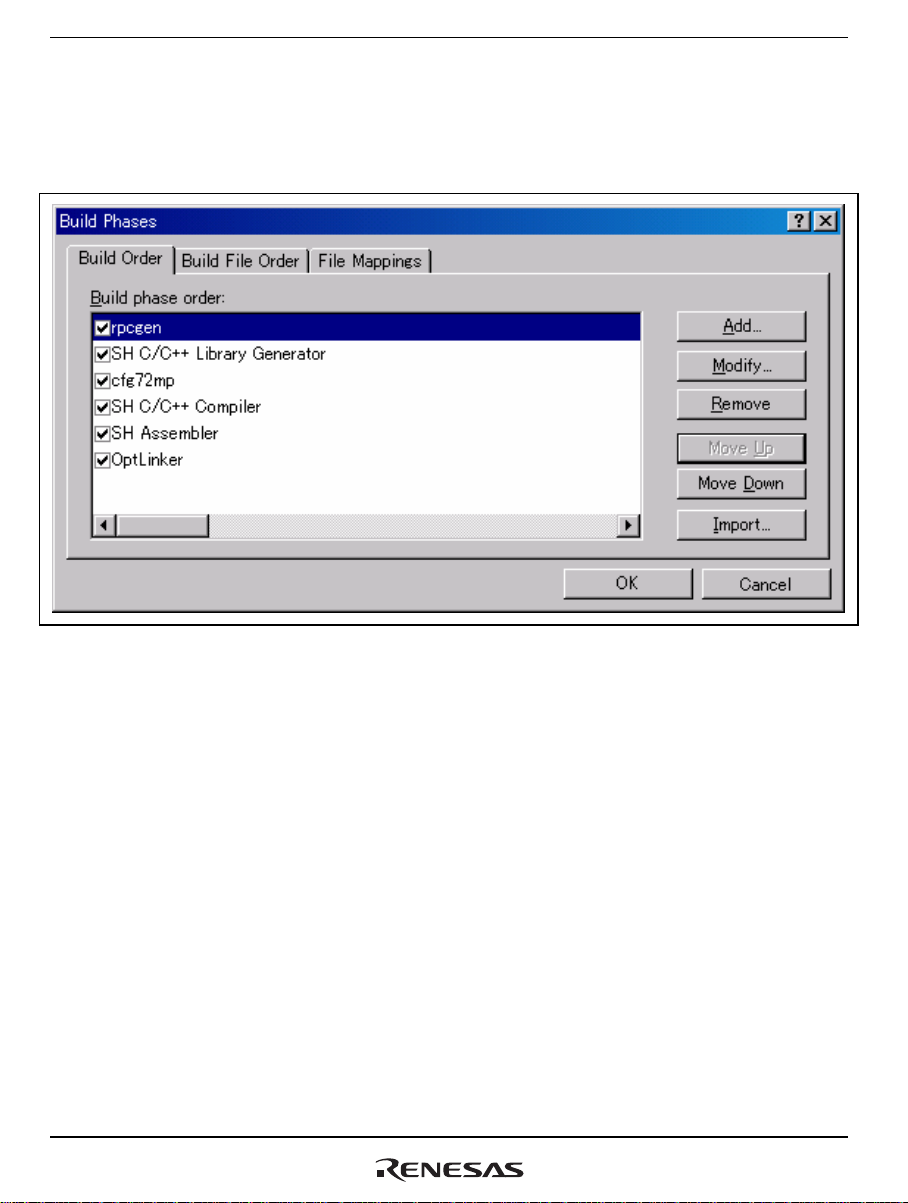
(4) Settings in the [Build Phases] Dialog Box
The created RPCGEN custom build phase is shown at the bottom of the [Build Phases] dialog box.
Use the [Move Up] button to move “rpcgen” so that it is above “SH C/C++ Library Generator.”
Figure 4.12 [Build Phases] Dialog Box - [Build Order] Tab
Open the [Build File Order] tab. Select “RPCGEN config file” under [File group] and check the
box for [rpcgen] under [Phase order].
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 20 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 31

Figure 4.13 [Build Phases] Dialog Box - [Build File Order] Tab
Setting of the RPCGEN build phase is now complete.
Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 21 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 32

Section 4 Executing RPCGEN
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 22 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 33

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
A config file contains definitions used for creation of the client and server stubs. Specifically, such
definitions are made by appending keywords for passing to RPCGEN to the API of the server
functions (as described in section 6, Definitions of Server Functions). Read this section carefully
before creating your own config file. The extension for config files is “.x.”
One config file corresponds to the definition of one server. Do not attempt to define multiple
servers within a single config file.
5.1 Definition
Definitions must be written in either of the following formats.
<keyword>{...};
<keyword>;
For certain definitions, two or more items can be entered between the braces {...}.
Example:
GLOBAL_INCFILE { “types.h” “rpc_public.h” };
A config file can include the following definitions.
(1) Locations where the files created by RPCGEN will be stored
• PUB_INCPATH{…}; Path to <config file>_public.h
• CLNT_SOURCEPATH{…}; Path to <config file>_clnt.c
• CLNT_INCPATH{…}; Path to <config file>_clnt.h and <config file>_private.h
• SVR_SOURCEPATH{…}; Path to <config file>_svr.c
• SVR_INCPATH{…}; Path to <config file>_svr.h
(2) Controlling output of the #include directive to the files created by RPCGEN
• GLOBAL_INCFILE{…}; Include file common to the client and server stubs
• CLNT_INCFILE{…}; Include file for the client stub
• SVR_INCFILE{…}; Include file for the server stub
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 23 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 34

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
(3) Server information
• SVR_NAME{…}; Server name
• SVR_ID{…}; Server ID
• SVR_VERSION{…}; Server version
• SVR_NOINIT; The server-initialization function is not to be created.
• SVR_NOSHUTDOWN; The server-shutdown function is not to be created.
• SVR_NOSTUBTBL; The server-stub function table is not to be created.
• SVR_STATIC{…}; Use of a static server
• SVR_SECTION{…}; Section name to be given to the server stub
• SVR_AUTH; How the server ID and server version will be assigned
(4) Client information
• CLNT_NOINIT; The client-initialization function is not to be created.
• CLNT_NOSHUTDOWN; The client-shutdown function is not to be created.
• CLNT_CALLCHK; Facilitates saving the return values of RPC calls
• CLNT_SECTION{…}; Section name to be given to the client stub
(5) Server functions
• RPC_FUNC{…}; Server functions
Server functions are only defined within the braces of RPC_FUNC; multiple server functions can
be defined.
5.2 Comments
Comments in config files should be written in the same way as in the C and C++ languages. The
comments that are written before the first valid definition of a keyword will be output to the
beginning of all source and header files generated by RPCGEN.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 24 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 35

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.3 File Locations
Use the statements listed below to define paths to the files generated by RPCGEN. If these
definitions are omitted, RPCGEN will generate the source or header files in the current directory.
If a definition is otherwise correct but the defined path does not exist or the directory already
contains read-only files, RPCGEN displays an error message and terminates the processing.
The following definitions of file locations are available.
• PUB_INCPATH{…}; Path to <config file>_public.h
• CLNT_SOURCEPATH{…}; Path to <config file>_clnt.c
• CLNT_INCPATH{…}; Path to <config file>_clnt.h and <config file>_private.h
• SVR_SOURCEPATH{…}; Path to <config file>_svr.c
• SVR_INCPATH{…}; Path to <config file>_svr.h
5.3.1 PUB_INCPATH
Format:
PUB_INCPATH{"<path>"};
Description:
This statement defines the path under which <config file>_public.h will be generated. When the
PUBI option is used, a definition of PUB_INCPATH is ignored.
Example:
PUB_INCPATH{"public_include"};
<config file>_public.h will be generated in the public_include directory under the current
directory.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 25 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 36

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.3.2 CLNT_SOURCEPATH
Format:
CLNT_SOURCEPATH{"<path>"};
Description:
This statement defines the path under which <config file>_clnt.c will be generated. When the
CLNTS option is used, a definition of CLNT_SOURCEPATH is ignored.
Example:
CLNT_SOURCEPATH{"clnt\source"};
<config file>_clnt.c will be generated in the clnt\source directory under the current directory.
5.3.3 CLNT_INCPATH
Format:
CLNT_INCPATH{"<path>"};
Description:
This statement defines the path under which <config file>_clnt.h and <config file>_private.h will
be generated. When the CLNTI option is used, a definition of CLNT_INCPATH is ignored.
Example:
CLNT_INCPATH{"C:\clnt\include"};
<config file>_clnt.h and <config file>_private.h will be generated in the C:\clnt\include directory.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 26 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 37

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.3.4 SVR_SOURCEPATH
Format:
SVR_SOURCEPATH{"<path>"};
Description:
This statement defines the path under which <config file>_svr.c will be generated. When the
SVRS option is used, a definition of SVR_SOURCEPATH is ignored.
Example:
SVR_SOURCEPATH{"svr\source"};
<config file>_svr.c will be generated in the svr\source directory under the current directory.
5.3.5 SVR_INCPATH
Format:
SVR_INCPATH{"<path>"};
Description:
This statement defines the path under which <config file>_svr.h will be generated. When the
SVRI option is used, a definition of SVR_INCPATH is ignored.
Example:
SVR_INCPATH{"svr\include"};
<config file>_svr.h will be generated in the svr\include directory under the current directory.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 27 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 38

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.4 Controlling the Output of #include Directives
Use the statements listed below to output #include directives for user files to the files generated by
RPCGEN.
Note, however, that #include directives for the following include files will always be output.
Table 5.1 Default Include Files
Filename Description
string.h Standard include file for the compiler
types.h Header file of data-type definitions; comes with Renesas
operating systems (such as the HI7200/MP)
rpc_public.h RPC header file that comes with Renesas operating systems
(such as the HI7200/MP)
The following definitions are available for controlling the output of #include directives.
• GLOBAL_INCFILE{…}; Include file common to the client and server stubs
• CLNT_INCFILE{…}; Include file for the client stub
• SVR_INCFILE{…}; Include file for the server stub
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 28 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 39

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.4.1 Order of #Include Directives
RPCGEN outputs #include directives to files in the following order.
(1) <config file>_clnt.c
1. Default include files (in the order given in table 5.1)
2. File(s) defined with GLOBAL_INCFILE (in the order of file definition)
3. File(s) defined with CLNT_INCFILE (in the order of file definition)
4. <config file>_public.h generated by RPCGEN (only if SVR_AUTH has not been defined)
5. <config file>_clnt.h generated by RPCGEN
6. <config file>_private.h generated by RPCGEN
(2) <config file>_svr.c
1. Default include files (in the order given in table 5.1)
2. File(s) defined with GLOBAL_INCFILE (in the order of file definition)
3. File(s) defined with SVR_INCFILE (in the order of file definition)
4. <config file>_public.h generated by RPCGEN (only if SVR_AUTH has not been defined)
5. <config file>_svr.h generated by RPCGEN
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 29 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 40

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.4.2 GLOBAL_INCFILE
Format:
GLOBAL_INCFILE{<file>[Δ<file>...]};
Description:
This statement is for the output of #include directives for the specified files to <config file>_clnt.c
and <config file>_svr.c. File(s) must be specified in the form "filename" or <filename>. The
difference between these two formats is as defined in the specification of the #include directive.
When two or more files are to be specified, they must be separated by a space.
Example:
GLOBAL_INCFILE{<math.h> "import\include\user_public.h"};
5.4.3 CLNT_INCFILE
Format:
CLNT_INCFILE{<file>[Δ<file>...]};
Description:
This statement is for the output of #include directives for the specified files to <config file>_clnt.c.
File(s) must be specified in the form "filename" or <filename>. The difference between these two
formats is as defined in the specification of the #include directive.
When two or more files are to be specified, they must be separated by a space.
Example:
CLNT_INCFILE{<math.h> "import\include\user_clnt.h"};
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 30 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 41

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.4.4 SVR_INCFILE
Format:
SVR_INCFILE{<file>[Δ<file>...]};
Description:
This statement is for the output of #include directives for the specified files to <config file>_svr.c.
File(s) must be specified in the form "filename" or <filename>. The difference between these two
formats is as defined in the specification of the #include directive.
When two or more files are to be specified, they must be separated by a space.
Example:
SVR_INCFILE{<math.h> "import\include\user_svr.h"};
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 31 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 42

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.5 Server Information
The following types of definitions are available for defining server information.
• SVR_NAME{…}; Server name
• SVR_ID{…}; Server ID
• SVR_VERSION{…}; Server version
• SVR_NOINIT; The server-initialization function is not to be created.
• SVR_NOSHUTDOWN; The server-shutdown function is not to be created.
• SVR_NOSTUBTBL; The server-stub function table is not to be created.
• SVR_STATIC{…}; Use of a static server
• SVR_SECTION{…}; Section name to be given to the server stub
• SVR_AUTH; How the server ID and server version will be assigned
5.5.1 SVR_NAME
Format:
SVR_NAME {<server name>};
Description:
This statement defines the server name. The defined server name will be applied to the names of
stub functions, etc. generated by RPCGEN. This definition cannot be omitted; if it is omitted,
RPCGEN reports the error and terminates processing.
Example:
SVR_NAME{EXAMPLE};
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 32 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 43

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.5.2 SVR_ID
Format:
SVR_ID {<ID number>};
Description:
This statement defines the server ID. The ID number can only be specified as a 4-byte integer
constant that can be represented as UINT32 or a C-language macro name to be replaced by such a
4-byte integer constant. If a C-language macro is used, this macro must have been defined in a file
specified by GLOBAL_INCFILE.
The server ID must, of course, be consistent across the entire system due to the specifications of
the HI7200/MP. RPCGEN does not detect duplication of server IDs.
The ID number is output to <config file>_public.h in the following format.
#define RPCSVR_ID_<server name> <ID number>
<Server name> refers to the server name defined with SVR_NAME.
SVR_ID cannot be omitted if a definition of SVR_AUTH has been omitted. Also refer to section
5.5.8, SVR_AUTH.
Example:
SVR_ID{1UL};
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 33 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 44

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.5.3 SVR_VERSION
Format:
SVR_VERSION {<server version>};
Description:
This statement defines the server version. The server version can only be specified as a 4-byte
integer constant that can be represented as UINT32 or a C-language macro name to be replaced by
such a 4-byte integer constant. If a C-language macro is used, this macro must have been defined
in a file specified by GLOBAL_INCFILE.
The server version is output to <config file>_public.h in the following format.
#define RPCSVR_VERS_<server name> <server version>
SVR_VERSION cannot be omitted if SVR_AUTH has been omitted. Also refer to section 5.5.8,
SVR_AUTH.
Example:
SVR_VERSION{1UL};
5.5.4 SVR_NOINIT
Format:
SVR_NOINIT;
Description:
If this statement is present, RPCGEN will not create the server-initialization function. Use
SVR_NOINIT when the server-initialization function is provided as part of the application. Also
refer to sections 8.3, Server-Initialization Function, and 8.4, Server-Stub Function Table.
Example:
SVR_NOINIT;
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 34 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 45

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.5.5 SVR_NOSTUBTBL
Format:
SVR_NOSTUBTBL;
Description:
The server-stub function table is rpc_server_info.ServerStubList, the table defined by
rpc_start_server() or rpc_start_server_with_paramarea() called by the server-initialization
function.
If this statement is present, RPCGEN will not create the server-stub function table. Use
SVR_NOSTUBTBL when the server-initialization function is provided as part of the application.
Also refer to section 8.4, Server-Stub Function Table.
Example:
SVR_NOSTUBTBL;
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 35 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 46

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.5.6 SVR_NOSHUTDOWN
Format:
SVR_NOSHUTDOWN;
Description:
If this statement is present, RPCGEN will not create the server-shutdown function. Use
SVR_NOSHUTDOWN when the server-shutdown function is provided as part of the application.
The server-shutdown function generated by RPCGEN calls rpc_stop_server() to stop the server.
Although rpc_stop_server() generally allows specification of a callback function to be executed at
the time the server is stopped, no callback function is specifiable for the server-shutdown function
generated by RPCGEN. If you wish to use a callback function, specify SVR_NOSHUTDOWN
and implement the server-shutdown function on the user side.
Also refer to section 8.5, Server-Shutdown Function.
Example:
SVR_NOSHUTDOWN;
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 36 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 47

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.5.7 SVR_STATIC
Format:
SVR_STATIC{<size>Δ<section name>};
Description:
This statement defines the server as static. If this definition is omitted, the server will be dynamic.
Note that SVR_STATIC cannot be used in conjunction with SVR_NOINIT.
<Size> indicates the size of the server parameter area. Specify an integer constant that can be
represented as UINT32. The specified value is rounded up to the nearest multiple of four.
<Section name> indicates the section name to be given to the server parameter area. Note,
however, that the actual section name will be ‘B’ followed by the section name given here. This
<section name> is not affected by definition of SVR_SECTION.
The server-parameter area information is output to <config file>_svr.c in the following format.
#pragma section <section name>
#pragma pack 4
static UINT8 ucServerArea_<server name>[ ALIGNUP4(<size>) ];
#pragma unpack
#pragma section
Note:
Since the SH2A-DUAL does not have a facility for the CPU cores to snoop on each other’s
caches, the server parameter area must be allocated in a non-cacheable area. Specify a section
name that can be distinguished from those of sections to be allocated in cacheable areas.
Example:
SVR_STATIC{ 512 D_SVRAREA};
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 37 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 48

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.5.8 SVR_AUTH
Format:
SVR_AUTH;
Description:
There are two ways to assign the server ID and server version.
(1) Model 1
Model 1 applies when SVR_AUTH has not been specified.
In this model, the application does not recognize the server ID or server version. The server ID
and server version are determined within the client and server stubs generated by RPCGEN.
Each of the client-stub functions has the same API as the original server function. Server IDs and
server version information passed to the following functions will be ignored.
• Server-initialization function
• Server-shutdown function
• Client-initialization function
• Client-shutdown function
RPCGEN outputs the definitions of the server ID and server version to <config file>_public.h.
Since the client-stub functions and server- and client- initialization and shutdown functions
generated by RPCGEN have include statements for <config file>_public.h, the server ID and
server version information is passed to the RPC library.
If RPCGEN-generated files for the client and server are from different generations, the RPC
library treats any RPC call as an error.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 38 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 49

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
Client application
Any server IDs and
server versions in
parameters are ignored
Client-
initializatio n
function
Client-
shutdown
fun c tio n
Server ID and server version
R PC lib r a ry
fun c ( ...) ( s a me A P I
as the original
server function)
???
Client stub
???
Figure 5.1 Model 1
<c o n f ig file >_pu blic.h
Server ID
Server version
Server application
Any server IDs and
se rv e r v e rs io n s in
parameters are ignored
Server-
initializ a tio n
function
Server ID and server version
RPC library
Check that the s e rver ID a n d
server version specifications
on the client match the server
Server-
initializ a tio n
function
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 39 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 50

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
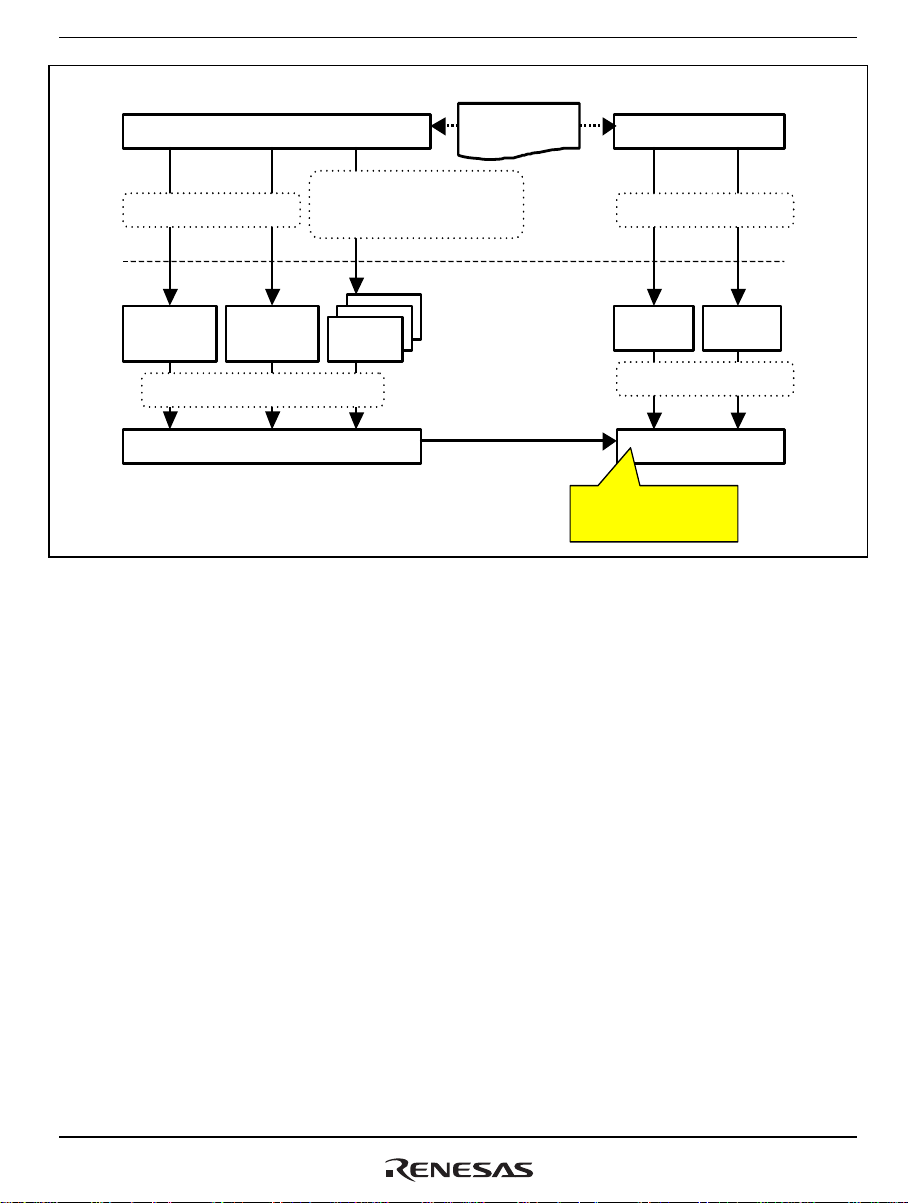
(2) Model 2
Model 2 applies when SVR_AUTH has been specified.
In this model, the application assigns the server ID and server version. RPCGEN outputs
definitions of the server ID and server version in <config file>_public.h so that the application is
able to acquire this information.
Each of the client-stub functions is in the form of rpcclnt_<server name>_<server function name>
and its first and second parameters are the server ID and server version, respectively. The third and
subsequent parameters are the parameters of the actual server function. In other words, all of the
client-stub functions have APIs that differ from the server functions. To make the client-stub
functions have the same APIs as the original server functions, the user must implement wrapper
functions for the client-stub functions.
RPCGEN outputs definitions of the server ID and server version to <config file>_public.h.
Applications that call client-stub functions and the server-initialization function must thus include
<config file>_public.h so that the server ID and version are specified.
If <config file>_public.h for the client and server are from different generations, the RPC library
treats any RPC call as an error.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 40 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 51
Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
<c o n f ig file > _public.h
C lie n t a p plicat io n Server application
Server ID
Server version
Example:
SVR_AUTH;
Server ID and server version
Client-
initializatio n
function
Client-
shutdown
fun c tio n
Server ID and server version
R PC lib r a ry
rpcclnt_<server name>_func
(se rv er ID , s e rv e r ve r sio n , ...)
???
Client stub
???
Figure 5.2 Model 2
Server ID and server version
Server-
initializ a tio n
function
Server ID and server version
RPC library
Ch eck tha t th e s erver ID a n d
server version specifications
on the client match the server
Server-
initializ a tio n
function
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 41 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 52

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.5.9 SVR_SECTION
Format:
SVR_SECTION{<section name>};
Description:
This statement specifies the section to which the server stubs will be assigned. When this
definition is omitted, one of the section names (alphabetical characters) listed below will
automatically be assigned. If SVR_SECTION has been defined, the actual section name will be
one of the letters listed below followed by <section name>.
• Program section: ‘P’
• Constant section: ‘C’
• Non-initialized data section: ‘B’
• Initialized data section: ‘D’
Example:
SVR_SECTION{ C_EXAMPLE };
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 42 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 53

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.6 Client Information
The following definitions of client information are available.
• CLNT_NOINIT; The client-initialization function is not to be created.
• CLNT_NOSHUTDOWN; The client-shutdown function is not to be created.
• CLNT_CALLCHK; Facilitates saving the return value in RPC calls
• CLNT_SECTION{…}; Section name to be given to the client stub
5.6.1 CLNT_NOINIT
Format:
CLNT_NOINIT;
Description:
RPCGEN creates the following client-initialization function in <config file>_clnt.c as the
standard:
INT32 rpcclnt_<server name>_init(UINT32 __ulRPCServerID, UINT32
__ulRPCServerVersion );
If the CLNT_NOINIT statement is present, RPCGEN will not create the client-initialization
function. Use CLNT_NOINIT when the client-initialization function is provided as part of the
application. Also refer to section 8.6, Client-Initialization Function.
Example:
CLNT_NOINIT;
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 43 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 54

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.6.2 CLNT_NOSHUTDOWN
Format:
CLNT_NOSHUTDOWN;
Description:
RPCGEN creates the following client-shutdown function in <config file>_clnt.c as the standard:
INT32 rpcclnt_<server name>_shutdown(UINT32 __ulRPCServerID, UINT32
__ulRPCServerVersion );
If the CLNT_NOSHUTDOWN statement is present, RPCGEN will not create the client-shutdown
function. Use CLNT_NOSHUTDOWN when the client-shutdown function is provided as part of
the application.
The client-shutdown function generated by RPCGEN calls rpc_disconnect() to disconnect the
client from the server. Although rpc_disconnect() generally allows specification of a callback
function to be executed at the time the client is disconnected from the server, no callback function
is specifiable for the client-shutdown function generated by RPCGEN. If you wish to use a
callback function, specify CLNT_NOSHUTDOWN and implement the client-shutdown function
on the user side.
In the current HI7200/MP specification, a callback function is ignored even if one has been
specified for rpc_disconnect().
Also refer to section 8.7, Client-Shutdown Function.
Example:
CLNT_NOSHUTDOWN;
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 44 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 55

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.6.3 CLNT_CALLCHK
Format:
CLNT_CALLCHK;
Description:
RPCGEN creates the following code in <config file>_clnt.c to facilitate saving of the return values
of RPC calls (rpc_call() or rpc_call_copycbk()) and outputs the API of *rpc_retval_adr() in
<config file>_clnt.h.
*rpc_retval_adr() = rpc_call(...);
rpc_retval_adr() must be implemented by the user. If this definition is omitted, the following code,
which discards the return value of an RPC call, will be created.
rpc_call(...);
For how to implement rpc_retval_adr(), refer to section 8.8, rpc_retval_adr().
Example:
CLNT_CALLCHK;
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 45 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 56

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.6.4 CLNT_SECTION
Format:
CLNT_SECTION{<section name>};
Description:
This statement specifies the section to which the client stubs will be assigned. When this definition
is omitted, one of the section names (alphabetical characters) listed below will automatically be
assigned. If CLNT_SECTION has been defined, the actual section name will be one of the letters
listed below followed by the <section name>.
• Program section: ‘P’
• Constant section: ‘C’
• Non-initialized data section: ‘B’
• Initialized data section: ‘D’
Example:
CLNT_SECTION{ C_EXAMPLE };
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 46 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 57

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
5.7 Server Functions
The following definition statement is available for defining server functions.
• RPC_FUNC{…}; Server functions
5.7.1 RPC_FUNC
Format:
RPC_FUNC
{
<definitions of server functions>;
...
};
Description:
Enter definitions of server functions between the braces {} of RPC_FUNC. For information on
definition statements for server functions, refer to section 6, Definitions of Server Functions.
Example:
RPC_FUNC
{
int ret = func1([IN DFLT]int par);
func2([OUT PTR]struct ST *ptr);
};
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 47 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 58

Section 5 Specifications of a Config File
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 48 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 59

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.1 Format
Server functions must be defined in one of the following formats.
(1) <specification of the return value> <variable to be returned> =
<function name>(<parameter>, ...)[<option>Δ...];
(2) <function name> (<parameter>, ...)[<option>Δ...];
(3) <directive to extend the return value><specification of the return
value> <variable to be returned> = <function name>(<parameter>, ...)
[<option>Δ...];
RPCGEN keywords enclosed by [] are specified in <parameter>, <option>, and <directive to
extend the return value>.
Example 1:
Specification of a server function
int func(int par);
The function takes par as an input and returns a value of type int.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN DFLT]int par);
Description
• Directive to extend the return value: None
• Specification of the return value: int ret =
• Function name: func
• Parameter directive: [IN DFLT]
• Parameter specification: int par
• Option: None
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 49 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 60

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Example 2:
Specification of a server function
void func(struct ST *ptr);
The function takes ptr, a pointer to a structure of type ST, as an input and does not return a
value.
Definition of the server function
func([IN PTR]struct ST *ptr)[UNACK];
Description
• Directive to extend the return value: None
• Specification of the return value: None
• Function name: func
• Parameter directive: [IN PTR]
• Parameter specification: struct ST *ptr
• Option: [UNACK]
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 50 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 61

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Example 3:
Specification of a server function
double func(double inf);
The input is inf and a value of type double will be returned.
Definition of the server function
[RETEXT]double dret = func([IN DFLT]double inf);
Description
• Directive to extend the return value: [RETEXT]
• Specification of the return value: double dret =
• Function name: func
• Parameter directive: [IN DFLT]
• Parameter specification: double inf
• Option: None
For details on each of the descriptions, refer to the following sections.
• Function-type directives: 6.2, Function-Type Directives
• Specifying the return value: 6.2, Function-Type Directives
• Function name: 6.3, Function Names
• Parameter: 6.4, Parameters
• Option: 6.7, Optional Keywords
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 51 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 62

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.2 Function-Type Directives
6.2.1 Function with a Return Value
Format:
<type of the return value>Δ<variable to hold the return value>=
Description:
<Variable to hold the return value> refers to a local variable used to store the return value in both
client and server stubs. A parameter of the function may be specified as this variable.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(int par);
The function takes par as an input and returns a value of type int.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN DFLT]int par);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 52 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 63

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.2.2 Function without a Return Value
Description:
For a function that doesn’t have a return value, a return-value specification must not be made.
Example:
Specification of a server function
void func(struct ST *ptr);
The function has no input and returns a value in the ST structure indicated by *ptr.
Definition of the server function
func([OUT PTR]struct ST *ptr);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 53 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 64

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.2.3 When the Return Value is not Representable as a 4-Byte Integer
Format:
[RETEXT]Δ<type of the return value>Δ
<variable to hold the return value>=
Description:
By default, the return value is cast into UINT32 in the server stub and then transferred to the
client. This value is cast back into the original type in the client stub and is then returned.
When the return value is of the following types, however, the definition must have an RETEXT
directive because the default behavior above is not applicable in these cases.
• 64-bit integer
• Floating point
• Structure-type object
• Union-type object
When a definition has an RETEXT directive, code will be generated such that a value is returned
from the server to the client by using the structure IOVEC.
Example:
Specification of a server function
double func(int par);
The function takes par as an input and returns a value of type double.
Definition of the server function
[RETEXT]double ret = func([IN DFLT]int par);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 54 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 65

6.3 Function Names
Description:
Type the name of the function you wish to use.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(int par);
The function takes par as an input and returns a value of type int.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN DFLT]int par);
Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 55 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 66

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.4 Parameters
Parameters must be defined in the following format.
[parameter directive]<parameter specification>
The parameter directive is a declaration of the following parameter specification and has the form
given below.
[<type of input/output>Δ<data type>]
<type of input/output>: Specify one of the keywords given in section 6.5, Keywords for
Input/Output.
<data type>: Specify one of the keywords given in section 6.6, Keywords for Data Types.
<parameter specification>: Define the specification of the original function.
Table 6.1 lists the available combinations of keywords although details on input/output and data
types will be described in later sections. Note, however, that REF and DESC cannot be used at the
same time.
Table 6.1 Input/Output and Data Types
Input/Output Data Type
Option DFLT STR PTR ARY
IN
OUT
INOUT
9: Available
⎯: Not available (RPCGEN reports an error and terminates the processing)
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 56 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
None 9 9 9 9
REF ⎯ 9 9 9
DESC 9 9 9 9
None ⎯ ⎯ 9 9
REF ⎯ ⎯ ⎯ ⎯
DESC ⎯ ⎯ ⎯ ⎯
None ⎯ ⎯ 9 9
REF ⎯ ⎯ ⎯ ⎯
DESC ⎯ ⎯ ⎯ ⎯
Page 67

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.5 Keywords for Input/Output
The following three keywords are available for setting the input/output attributes of parameters.
• IN: Input
• OUT: Output
• INOUT: Input and output
The following optional keywords can also be attached to the keywords listed above (note,
however, that REF and DESC cannot be used at the same time).
• REF: Passing by reference
• DESC: The parameter is not passed from the client to the server
Each of these keywords, specified with one of the data-type keywords listed in section 6.6, works
as a declaration of the subsequent parameter specification.
6.5.1 IN (Input)
Description:
This keyword defines a parameter as an input to the server function. The parameter is transferred
from the client to the server and is then passed to the server function.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(int par);
The function takes par as an input and returns a value of type int.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN DFLT]int par);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 57 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 68

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.5.2 OUT (Output)
Description:
This keyword defines a parameter as an output from the server function. The data output by the
server function to the area specified by the parameter are returned to the client. This keyword can
only be used with the data-type keywords PTR and ARY.
Example:
Specification of a server function
void func(struct ST *ptr);
The function has no input and returns a value in the ST structure indicated by *ptr.
Definition of the server function
func([OUT PTR]struct ST *ptr);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 58 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 69

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.5.3 INOUT (Input and Output)
Description:
This keyword defines a parameter as an input to and output from the server function. The data in
the area specified by the parameter are transferred from the client to the server and then passed to
the server function. After that, the data output by the server function to the area specified by the
parameter are returned to the client. This keyword can only be used with the data-type keywords
PTR and ARY.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr);
The function takes *ptr, a pointer to a structure of type ST, as an input and returns a value in the
same area.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([INOUT PTR]struct ST *ptr);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 59 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 70

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.5.4 REF (Passing by Reference)
Description:
This keyword specifies that only the address of the parameter will be passed between the client
and the server. REF is useful when the size of the parameter to be passed is large.
This keyword can be used in conjunction with IN and with the data-type keywords PTR, STR, and
ARY.
Figure 6.1 illustrates the difference between cases with and without REF.
[IN PTR] struct ST *ptr
P ar a mete r s p e c ifie d in th e clie n t
ptr
Copying
struct ST
Client area
[IN REF PTR] stru c t ST *p t r
Parameter specified in the client
ptr
*Note: When the device in use does not provide a facility for cache-snooping
between the CPU cores (as is the case for the SH2A-DUAL etc.), the server
parameter area must be allocated in a non-cacheable area.
Copying
struct ST
Client area*
Se rve r p ara m e te r are a
(in a non-cacheable area)
struct ST
Server parameter area
(in a non-cacheable area)
ptr
Pa ra m e ter to be
Pa ra m e te r to b e
passed to the
server function
passed to the
server function
ptr
Figure 6.1 REF
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 60 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 71

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Without the REF specification, the data indicated by the pointer variable specified with PTR, STR,
or ARY are transferred. The transferred pointer points to a different area from that before the
transfer.
With the REF specification, the pointer variable is transferred. In this case, the pointer points to
the same area even after the transfer.
Note:
When the device in use does not provide a facility for cache-snooping between the CPU cores (as
is the case for the SH2A-DUAL etc.), the server parameter area must be allocated in a noncacheable area.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr);
*ptr is passed to func as the input. ptr is sure to keep pointing to a non-cacheable area.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN REF PTR]struct ST *ptr);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 61 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 72

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.5.5 DESC (Specified Parameter is not Passed from the Client to the Server)
Description:
This keyword specifies that the parameter will not be passed from the client to the server. This
keyword can also be used with IN.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(void);
While the actual server function has no parameter, the client application calls an old API
function, func, which does have a parameter (int par).
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN DESC PTR]int par);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 62 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 73

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.6 Keywords for Data Types
Select one of the following four available keywords.
• DFLT: Default
• PTR: Pointer
• STR: String
• ARY: Array
When ARY is selected, the parameter for COUNT must also be specified.
6.6.1 DFLT (Default)
Input/Output Keywords Available for Use in Combination with DFLT:
IN
Description:
The parameter itself is transferred between the client and server. DFLT is only specifiable when
the parameter has any of the following types.
• Integer (signed short, unsigned short, signed long, unsigned long, signed int, or unsigned int)
• Character (signed char or unsigned char)
• Real number (float or double)
• Structure-type or union-type object that is not an array
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(int par);
The function takes par as an input and returns a value of type int.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN DFLT]int par);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 63 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 74

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.6.2 STR (String)
Input/Output Keywords Available in Combination with STR:
IN
Description:
The string specified as the parameter is transferred from the client to the server. STR is only
specifiable when the parameter is of the character type.
When STR is used with REF, the pointer to the string is transferred instead of the string itself. For
details, refer to section 6.5.4, REF (Passing by Reference).
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(const char *s);
The function takes string s as an input and returns a value of type int.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN STR]const char *s);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 64 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 75

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.6.3 PTR (Pointer)
Input/Output Keywords Available in Combination with PTR:
All
Description:
The data pointed to by a specified pointer are transferred between the client and the server. PTR is
only specifiable when the parameter is of the pointer type.
When IN has been selected and REF is used with PTR, the pointer value is transferred instead of
the data it indicates. For details, refer to section 6.5.4, REF (Passing by Reference).
Example:
Specification of a server function
void func(struct ST *ptr);
The function has no input and returns the structure of type ST that is indicated by *ptr.
Definition of the server function
func([OUT PTR]struct ST *ptr);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 65 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 76

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.6.4 ARY (Array)
Input/Output Keywords Available in Combination with ARY:
All
Description:
The data of a specified array are transferred between the client and the server. ARY is only
specifiable when the parameter is of the array type. As the parameter specification that follows this
keyword, define a parameter that expresses the first address of the array.
When ARY is used, it must be followed by a definition of COUNT, which indicates the number of
elements in the array to be passed between the client and the server. For details, refer to section
6.6.5, COUNT (Number of Elements in an Array).
When IN has been selected and REF is used with ARY, the pointer to the array is transferred
instead of the array it indicates. For details, refer to section 6.5.4, REF (Passing by Reference).
Example:
Refer to section 6.6.5, COUNT (Number of Elements in an Array).
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 66 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 77

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.6.5 COUNT (Number of Elements in an Array)
Description:
When ARY is used, it must be followed by a definition of COUNT, which indicates the number of
elements in the array to be passed between the client and the server.
(1) When the input/output keyword selected for ARY is IN
In this case, a parameter specification that includes ARY must be followed by a single definition
of COUNT to indicate the number of elements in the array.
<parameter including ARY>,<definition of COUNT>
COUNT is an expression that specifies the number of elements in the array to be passed from the
client to the server.
RPCGEN creates client-stub code that makes an RPC call after setting the size of an input IOVEC
structure by using an expression of the kind specified in figure 6.2. This must be taken into
account when COUNT is defined. For example, the expression for COUNT must not contain any
variables that hold the return value of a function. Figures 6.2 and 6.3 show the code for example 5
(without SVR_AUTH) of the examples introduced following the figures.
int func (struct INF * inf, struct ST * ptr )
{
IOVEC __input[2];
...
__input[ __ulInputParamCount ].pBaseAddress = (UINT8 *)(inf);
__input[ __ulInputParamCount++ ].ulSize = sizeof(*inf);
...
if (((UINT32)(inf->count)) > 0UL)
{
__input[ __ulInputParamCount ].pBaseAddress = (UINT8 *)(ptr);
__input[ __ulInputParamCount++ ].ulSize = sizeof(*ptr) * ((UINT32)(inf->count));
}
...
rpc_call(...);
}
Figure 6.2 Code Output to the Client Stub (IN) for COUNT
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 67 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 78

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
UINT32 rpcsvr_SMPL_func( rpc_server_stub_info * __pInfo )
{
...
inf = (struct INF *)( __pInfo->pucParamArea + __ulInputParamOffset);
__ulInputParamOffset += ALIGNUP4(sizeof(*inf));
if (((UINT32)(inf->count)) > 0UL)
{
ptr = (struct ST *)( __pInfo->pucParamArea + __ulInputParamOffset);
}
...
ret = func( inf, ptr );
...
return ((UINT32)ret);
}
Figure 6.3 Code Output to the Server Stub (IN) for COUNT
Examples:
Example 1
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr);
Pointer ptr to an array of 10 elements of the structure type (ST) will be passed.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN ARY]struct ST *ptr, [COUNT]10);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 68 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 79

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Example 2
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr, int count);
Pointer ptr to an array of count elements of the structure type (ST) will be passed.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN ARY]struct ST *ptr, [COUNT]count,[IN DFLT]int
count);
Example 3
Specification of a server function
int func(int count , struct ST *ptr);
Pointer ptr to an array of count elements of the structure type (ST) will be passed.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN DFLT]int count, [IN ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
]count);
Example 4
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr, int *p_count);
Pointer ptr to an array of *p_count elements of the structure type (ST) will be passed.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN ARY]struct ST *ptr, [COUNT]*p_count, [IN PTR]int
*p_count);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 69 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 80

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Example 5
Specification of a server function
int func(struct INF *inf, struct ST *ptr);
ptr points to an array to be given to the server function and inf indicates other input information.
It has a type-int member count, which indicates the number of elements in the array pointed to
by ptr.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN PTR]struct INF *inf, [IN ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
]inf->count);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 70 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 81

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
(2) When the input/output keyword selected for ARY is OUT
In this case, a parameter specification that includes ARY must be followed by two definitions of
COUNT to indicate the number of elements in the array.
<parameter including ARY>,<definition of first COUNT>,
<definition of second COUNT>
The first COUNT is the COUNT keyword followed by an expression that specifies the number of
elements in the array for storage of output by the client.
The second COUNT is the COUNT keyword followed by an expression that specifies the number
of elements in the array to be actually output by the server. This value must be less than or equal
to that specified for the first COUNT.
RPCGEN creates client-stub code that makes an RPC call after setting the size of an input IOVEC
structure by using an expression of the kind specified in figure 6.4. RPCGEN also creates serverstub code that makes a server-function call before setting the size of an output IOVEC structure by
using an expression of the kind specified in figure 6.5. This must be taken into account in defining
the first and second COUNT. For example, an expression for the first COUNT must not contain
any variables that hold the return value of a function. Figures 6.4 and 6.5 show the code for
example 8 (without SVR_AUTH) of the examples introduced following the figures.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 71 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 82

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
int func (struct INF * inf, struct ST * ptr )
{
IOVEC __input[1];
IOVEC __output[1];
...
__input[ __ulInputParamCount ].pBaseAddress = (UINT8 *)(inf);
__input[ __ulInputParamCount++ ].ulSize = sizeof(*inf);
if (((UINT32)(inf->count)) > 0UL)
{
__output[ __ulOutputParamCount ].pBaseAddress = (UINT8 *)(ptr);
__output[ __ulOutputParamCount++ ].ulSize = sizeof(*ptr) * ((UINT32)(inf->count));
}
...
rpc_call(...);
}
Figure 6.4 Code Output to the Client Stub (OUT) for First COUNT
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 72 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 83

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
UINT32 rpcsvr_SMPL_func( rpc_server_stub_info * __pInfo )
{
...
inf = (struct INF *)( __pInfo->pucParamArea + __ulInputParamOffset);
__ulInputParamOffset += ALIGNUP4(sizeof(*inf));
if (((UINT32)(inf->count)) > 0UL)
{
ptr = (struct ST *)( __pInfo->pucParamArea + __ulInputParamOffset);
}
ret = func( inf, ptr );
__pInfo->pOutputIOVectorTable[ __ulOutputParamCount ].pBaseAddress = ptr;
if (((UINT32)(ret )) > 0UL)
{
__pInfo->pOutputIOVectorTable[ __ulOutputParamCount++ ].ulSize = sizeof(*ptr) *
((UINT32)(ret ));
}
else
{
__pInfo->pOutputIOVectorTable[ __ulOutputParamCount++ ].ulSize = 0UL;
}
__pInfo->ulOutputIOVectorTableSize = 1UL;
return ((UINT32)ret);
}
Figure 6.5 Code Output to the Server Stub (OUT) for Second COUNT
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 73 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 84

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Examples:
Example 1
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr);
ptr points to an array for output that has 10 elements. func outputs all 10 elements.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([OUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,[COUNT]10, [COUNT]10));
Example 2
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr, int *p_count);
ptr points to an array for output that has 10 elements. *p_count, which is the return parameter of
func, indicates the number of elements to be output.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([OUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
]10,[COUNT]*p_count,[OUT PTR]int *p_count);
Example 3
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr);
ptr points to an array for output that has 10 elements. The return value from func indicates the
number of elements to be output.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([OUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,[COUNT]10, [COUNT]ret);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 74 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 85

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Example 4
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr, int *p_count);
ptr points to an array for output that has *p_count elements. func outputs the return parameter
*p_count as the number of elements.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([OUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
]*p_count, [COUNT]*p_count,[INOUT PTR]int *p_count);
Example 5
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr, int count);
ptr points to an array for output that has count elements. func outputs all count elements.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([OUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 75 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
]count, [COUNT]count,[IN DFLT]int count);
Page 86

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Example 6
Specification of a server function
int func(struct INF *inf, struct ST *ptr, int *p_count);
ptr points to an array for output and inf indicates other input information. It has a type-int
member count, which indicates the number of elements in the array pointed to by ptr. func
outputs the return parameter *p_count as the number of elements.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN PTR]struct INF *inf, [OUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
]inf->count, [COUNT]*p_count, [OUT PTR]int *p_count);
Example 7
Specification of a server function
int func(struct INF *inf, struct ST *ptr);
ptr points to an array for output and inf indicates other input information. It has a type-int
member count, which indicates the number of elements in the array pointed to by ptr. func
outputs all inf -> count elements.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN PTR]struct INF *inf, [OUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 76 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
]inf->count, [COUNT]inf->count );
Page 87

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Example 8
Specification of a server function
int func(struct INF *inf, struct ST *ptr);
ptr points to an array for output and inf indicates other input information, including a type-int
member count, which indicates the number of elements in the array pointed to by ptr. The return
value indicates the number of elements to be output.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN PTR]struct INF *inf, [OUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
]inf->count, [COUNT]ret );
(3) When the input/output keyword selected for ARY is INOUT
In this case, a parameter specification that includes ARY must be followed by two definitions of
COUNT to indicate the number of elements in the array.
<parameter including ARY>,<definition of first COUNT>,
<definition of second COUNT>
The first COUNT is the COUNT keyword followed by an expression that specifies the number of
elements in the array to be passed from the client to the server.
The second COUNT is the COUNT keyword followed by an expression that specifies the number
of elements in the array to be actually output by the server. This value must be less than or equal
to that specified for the first COUNT.
RPCGEN creates client-stub code that makes an RPC call after setting the size of an input IOVEC
structure by using an expression of the kind specified in figure 6.6. RPCGEN also creates serverstub code that makes a server-function call before setting the size of an output IOVEC structure by
using an expression of the kind specified in figure 6.7. This must be taken into account in defining
the first and second COUNT. For example, an expression for the first COUNT must not contain
any variables that hold the return value of a function. Figures 6.6 and 6.7 show the code for
example 8 (without SVR_AUTH) of the examples introduced following the figures.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 77 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 88

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
int func (struct INF * inf, struct ST * ptr )
{
IOVEC __input[2];
IOVEC __output[1];
...
__input[ __ulInputParamCount ].pBaseAddress = (UINT8 *)(inf);
__input[ __ulInputParamCount++ ].ulSize = sizeof(*inf);
if (((UINT32)(inf->count)) > 0UL)
{
__input[ __ulInputParamCount ].pBaseAddress = (UINT8 *)(ptr);
__input[ __ulInputParamCount++ ].ulSize = sizeof(*ptr) * ((UINT32)(inf->count));
}
if (((UINT32)(inf->count)) > 0UL)
{
__output[ __ulOutputParamCount ].pBaseAddress = (UINT8 *)(ptr);
__output[ __ulOutputParamCount++ ].ulSize = sizeof(*ptr) * ((UINT32)(inf->count));
}
...
rpc_call(...);
}
Figure 6.6 Code Output to the Client Stub (INOUT) for First COUNT
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 78 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 89

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
UINT32 rpcsvr_SMPL_func( rpc_server_stub_info * __pInfo )
{
...
inf = (struct INF *)( __pInfo->pucParamArea + __ulInputParamOffset);
__ulInputParamOffset += ALIGNUP4(sizeof(*inf));
if (((UINT32)(inf->count)) > 0UL)
{
ptr = (struct ST *)( __pInfo->pucParamArea + __ulInputParamOffset);
__ulInputParamOffset += ALIGNUP4(sizeof(*ptr) * ((UINT32)(inf->count)));
}
...
ret = func( inf, ptr );
__pInfo->pOutputIOVectorTable[ __ulOutputParamCount ].pBaseAddress = ptr;
if (((UINT32)(ret )) > 0UL)
{
__pInfo->pOutputIOVectorTable[ __ulOutputParamCount++ ].ulSize = sizeof(*ptr) *
((UINT32)(ret ));
}
else
{
__pInfo->pOutputIOVectorTable[ __ulOutputParamCount++ ].ulSize = 0UL;
}
__pInfo->ulOutputIOVectorTableSize = 1UL;
return ((UINT32)ret);
}
Figure 6.7 Code Output to the Server Stub (INOUT) for Second COUNT
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 79 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 90

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Examples:
Example 1
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr);
ptr points to an array for input and output that has 10 elements. func outputs all 10 elements.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([INOUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,[COUNT]10, [COUNT]10);
Example 2
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr, int *p_count);
ptr points to an array for input and output that has 10 elements. *p_count, which is the return
parameter of func, indicates the number of elements to be output.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([INOUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
]10,[COUNT]*p_count,[OUT PTR]int *p_count);
Example 3
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr);
ptr points to an array for input and output that has 10 elements. The return value from func
indicates the number of elements to be output.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([INOUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,[COUNT]10, [COUNT]ret);
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 80 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 91

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Example 4
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr, int *p_count);
ptr points to an array for input and output that has *p_count elements. func outputs the return
parameter *p_count as the number of elements.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([INOUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
]*p_count,[COUNT]*p_count,[INOUT PTR]int *p_count);
Example 5
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr, int count);
ptr points to an array for input and output that has count elements. func outputs all count
elements.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([INOUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 81 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
]count, [COUNT]count, [IN DFLT]int count);
Page 92

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Example 6
Specification of a server function
int func(struct INF *inf, struct ST *ptr, int *p_count);
ptr points to an array for input and output and inf indicates other input information, including a
type-int member count, which indicates the number of elements in the array pointed to by ptr.
func outputs the return parameter *p_count as the number of elements.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN PTR]struct INF *inf, [INOUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
]inf->count, [COUNT]*p_count, [OUT PTR]int *p_count);
Example 7
Specification of a server function
int func(struct INF *inf, struct ST *ptr);
ptr points to an array for input and output and inf indicates other input information, including a
type-int member count, which indicates the number of elements in the array pointed to by ptr.
func outputs all inf -> count elements.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN PTR]struct INF *inf, [INOUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 82 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
]inf->count, [COUNT]inf->count );
Page 93

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Example 8
Specification of a server function
int func(struct INF *inf, struct ST *ptr);
ptr points to an array for input and output and inf indicates other input information, including a
type-int member count, which indicates the number of elements in the array pointed to by ptr.
The return value indicates the number of elements to be output.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN PTR]struct INF *inf, [INOUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,
[COUNT
]inf->count, [COUNT]ret );
6.7 Optional Keywords
The following optional keywords are available to control output to the client or server stub for the
individual server functions.
• SVRSTUB: Server stub
• SVRFUNC: Server function name
• CLNTSTUB: Client stub
• UNACK: Asynchronous call
• CLNTCOPYCBK: RPC call by rpc_call_copycbk()
Two or more optional keywords may be specifiable. Note, however, that the same keyword must
not be used more than once. When a combination of keywords specified by the user is not valid,
RPCGEN shows an error message and terminates processing.
Multiple keywords must be delimited by commas.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 83 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 94

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
Table 6.2 shows the available combinations of optional keywords.
Table 6.2 Combinations of Optional Keywords
SVRSTUB SVRFUNC CLNTSTUB UNACK CLNTCOPYCBK
SVRSTUB ⎯ 9 9 9
SVRFUNC 9 9 9
CLNTSTUB ⎯ ⎯
UNACK 9
CLNTCOPYCBK
9: Available
⎯: Not available (RPCGEN reports an error and terminates processing)
6.7.1 SVRSTUB (Server Stub)
Format:
[SVRSTUB] <server-stub function name>
Description:
A server stub provided by the user is to be used, so RPCGEN does not create a server stub.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(int par);
The function takes par as an input and returns a value of type int. RPCGEN will not create a
server stub for func (i.e. will not create func_svrstub) because the user will provide this server
stub.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN DFLT]int par)[SVRSTUB]func_svrstub;
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 84 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 95

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.7.2 SVRFUNC (Server Function Name)
Format:
[SVRFUNC]<replacement server function name>
Description:
RPCGEN replaces the name of the server function to be called by the server stub with a specific
name. Use SVRFUNC when the name of a function as called by the client does not match the
name of the function as called by the server.
SVRFUNC cannot be used with SVRSTUB.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(int par);
The function takes par as an input and returns a value of type int. func on the server, however, is
named func_main.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN DFLT]int par)[SVRFUNC]func_main;
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 85 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 96

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.7.3 CLNTSTUB (Client Stub)
Format:
[CLNTSTUB]
Description:
A client stub provided by the user is to be used, so RPCGEN does not create a client stub.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(int par);
The function takes par as an input and returns a value of type int. RPCGEN will not create a
client stub for func because the user will provide this client stub.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN DFLT]int par)[CLNTSTUB];
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 86 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 97

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.7.4 UNACK (Asynchronous Call)
Format:
[UNACK]
Description:
The client makes RPC calls in asynchronous mode. When UNACK is not used, RPC calls are
made in synchronous mode.
UNACK cannot be used with CLNTSTUB.
Note:
When UNACK is used, the return value of the server function must be of type void and the
input/output keyword for parameters must be IN.
Example:
Specification of a server function
void func(int par);
The function takes par as an input. The client makes RPC calls in asynchronous mode.
Definition of the server function
func([IN DFLT]int par)[UNACK];
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 87 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 98

Section 6 Definitions of Server Functions
6.7.5 CLNTCOPYCBK (RPC Call by rpc_call_copycbk())
Format:
[CLNTCOPYCBK]<function 1> <function 2>
Description:
RPC calls are started by rpc_call_copycbk(). <function 1> and <function 2> are copy callback
functions specified in rpc_call_copycbk(). Specification of the two callback functions is
mandatory.
The prototype for the callback functions must conform with the RPC specifications and has to be
declared in a file included by the client stub.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(struct ST *ptr);
ptr is an array for output and has 10 elements, all of which are output by func. copy1() is used
for transfer from the client to the server while copy2() is used for transfer from the server to the
client.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([OUT ARY]struct ST *ptr,[COUNT]10,
[COUNT]10)[CLNTCOPYCBK] copy1 copy2
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 88 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
;
Page 99

Section 7 Server Functions Not Supported by RPCGEN
Section 7 Server Functions Not Supported by RPCGEN
This section gives the types of functions not supported by RPCGEN. If a server function you are
using falls under the definitions in this section, use SVRSTUB or CLNTSTUB so that RPCGEN
will not create a server or client stub for the server function. A substitute server or client stub must
be implemented by the user.
7.1 Parameter
RPCGEN is not capable of correctly creating a client or server stub for server functions that have
parameters of the following types.
(1) Parameters with data types of undefined size
RPCGEN cannot handle parameters with data types that have undefined size. When such a
parameter is a pointer, however, using REF allows the creation of stub code for passing of the
pointer itself.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(void *par);
The function takes ptr, a pointer to data of undefined size, as an input and returns an int-type
value.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN PTR]void *par);
In this case, an error will occur in compilation of the client stub.
int ret = func([IN REF PTR]void *par);
In this case, code to pass the value of par to the server will be created.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 89 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
Page 100

Section 7 Server Functions Not Supported by RPCGEN
(2) Multiple-level pointers
RPCGEN only recognizes the first level of multiple-level pointers.
Example:
Specification of a server function
int func(int **ptr);
The function takes ptr, a pointer to a pointer to int-type data, as an input.
Definition of the server function
int ret = func([IN PTR] int **ptr);
In this case, RPCGEN creates code to transfer *ptr from the client to the server. *ptr is a pointer
to the target int-type data, but this data (**ptr) will not be transferred.
(3) Function pointer
RPCGEN does not support server functions whose parameters are pointers to functions.
Rev. 1.01 Mar. 17, 2008 Page 90 of 128
REJ10J1822-0101
 Loading...
Loading...