Page 1
REG10J0052-0200
Renesas Starter Kit Ethernet & USB
Application Board User's Manual
RENESAS STARTER KIT
Rev.2.00 Renesas Technology Europe Ltd.
Revision date:17.Jan.2008 www.renesas.com
D007133_11
Page 2

Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Preface..................................................................................................................................................3
Chapter 2. Purpose.................................................................................................................................................4
Chapter 3. Board Layout.........................................................................................................................................5
3.1. Component References ...............................................................................................................................5
3.2. Board Component functions.........................................................................................................................6
3.3. Board Dimensions........................................................................................................................................7
Chapter 4. User Circuitry.........................................................................................................................................8
4.1. Fitting the Target RSK to the RSK application board...................................................................................8
4.2. Network Controller........................................................................................................................................8
4.3. USB Controller..............................................................................................................................................9
4.4. SRAM.........................................................................................................................................................11
4.5. Option Links................................................................................................................................................12
Chapter 5. Headers...............................................................................................................................................13
5.1. Application Headers ...................................................................................................................................13
Chapter 6. Code Development .............................................................................................................................17
Chapter 7. Additional Information..........................................................................................................................18
ii
Page 3

Chapter 1. Preface
Cautions
This document may be, wholly or partially, subject to change without notice.
All rights reserved. Duplication of this document, either in whole or part is prohibited without the written permission of Renesas
Technology Europe Limited.
Trademarks
All brand or product names used in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or
organisations.
Copyright
© Renesas Technology Europe Ltd. 2007. All rights reserved.
Website:
Glossary
CPU Central Processing Unit RTE Renesas Technology Europe Ltd.
HEW High-performance Embedded Workshop RSO Renesas Solutions Organisation.
USB Universal Serial Bus RSK Renesas Starter Kit
PC Program Counter NIC Network Interface Controller
E10A ‘E10A for Starter Kits’ Emulator
http://www.eu.renesas.com/
3
Page 4

Chapter 2.Purpose
This RSK Application Board is an evaluation tool for using Renesas microcontrollers with Ethernet and USB interfaces. It is used in
conjunction with the RSK for the microcontroller to be evaluated.
Features include:
• Mounting connections to allow RSK to be added to top of board.
• Interface to standard RSK ‘Application Interface’ connectors.
• Interface to Memory Expansion connectors.
• Power connector for +5V (reverse polarity protected), with on-board regulated 3.3V conversion and level translation to
allow operation with RSK boards working at either +5V or +3.3V.
• LAN9118-MT NIC and RJ45 Ethernet connector with integral status LEDs.
• ISP1761BE USB Hi-Speed 2.0 Host Controller with:
o 1 Host/Slave USB (Mini AB) connector and
o 2 Host USB (Standard A) connectors.
• 512 kByte Static Ram arranged as 256k x 16 bit words.
4
Page 5
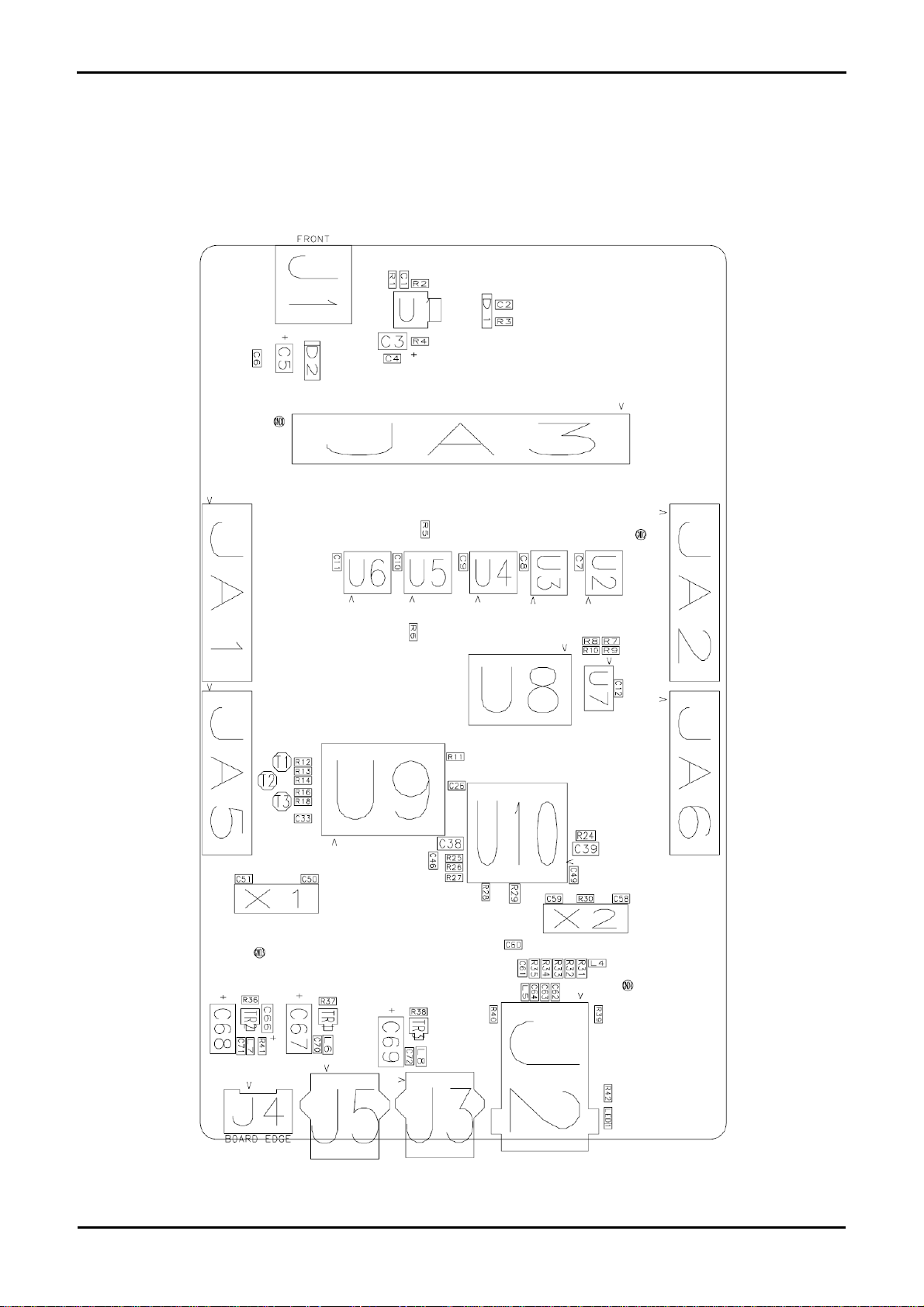
Chapter 3.Board Layout
3.1.Component References
The following diagram shows the component references for the board.
Figure 3-1: Component References
5
Page 6
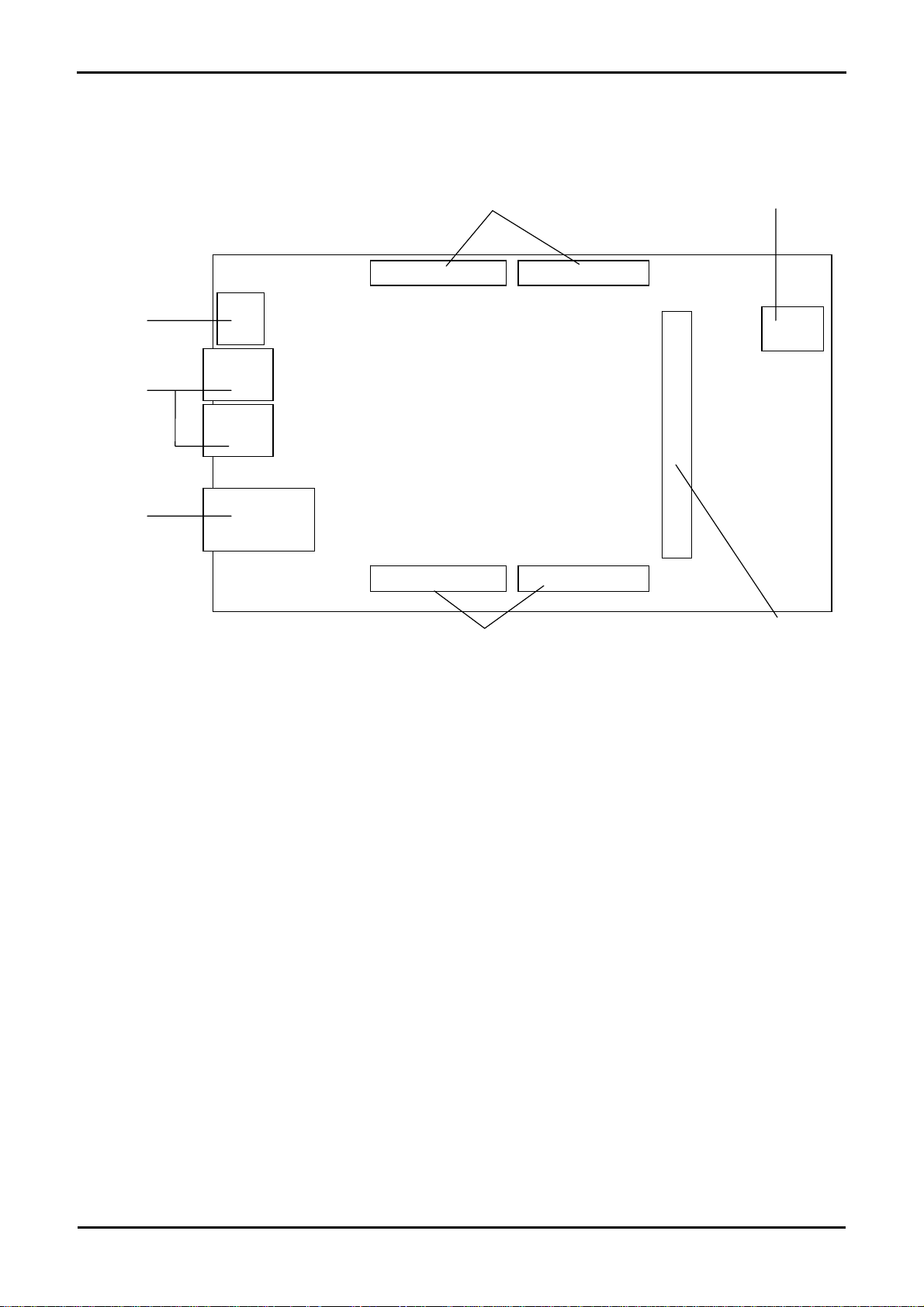
3.2.Board Component functions
The following diagram the shows the functions of the components on the board.
USB
Mini AB
USB
Std A
RJ45
J4
J5
J3
J2
Application Board Interface
JA5 JA1
JA6 JA2
Application Board Interface
+5V DC
J1
JA3
Memory Extension Interface
Figure 3-2: Board Layout
6
Page 7

3.3.Board Dimensions
The following diagram gives the board dimensions and connector positions. All through hole connectors are on a common 0.1” grid for easy
interfacing.
Figure 3-3 : Board Dimensions
7
Page 8

Chapter 4.User Circuitry
4.1.Fitting the Target RSK to the RSK application board
The board is supplied with 2x 24 way sockets, 2x 26 way sockets and 1 x 50 way socket.
These should be soldered on the underside of the host RSK in JA1, JA2, JA5, JA6 and JA3 positions.
The RSK should be plugged into the equivalent connectors on the RSK LCD application board.
A separate application note is available to explain how to configure the host RSK to enable it to connect to this
application board.
The board is designed to be 5V I/O tolerant. Therefore this board can be connected to an RSK with 5V I/O.
4.2.Network Controller
The network functionality is provided by the SMCS LAN9118-MT non-PCI Ethernet controller.
Refer to the manufacturer’s datasheet for more information on this peripheral.
The Ethernet controller is configured to use a 16 bit data bus. It uses single 16 bit read and write strobes.
Byte or long word accesses are not available for this device.
The chip select used for the network controller is CS1 which is on JA3 pin 27.
Please note the timing. This will require programming the bus controller for the Host RSK.
5ns
A[7:1]
0ns
CSn,RDn
35ns
Data
40ns
0ns
Valid
Figure 4-1: Ethernet controller read timing
8
Page 9

A[7:1]
5ns
5ns
CSn,WRn
Data
35ns
10ns
Valid
5ns
Figure 4-2: Ethernet controller write timing
The Ethernet controller can drive two interrupts.
IRQ0 is the IRQ from the Ethernet controller.
IRQ2 is the PME output from the Ethernet controller. PME interrupts can be enabled on the IRQ pin, so this can
be disabled for host RSKs with fewer interrupt lines, if the PME interrupt is required.
Both interrupts are pulled high to 3.3V by 1K resistors.
4.3.USB Controller
The Universal Serial Bus functionality is provided by the Philips ISP1761 controller.
Refer to the manufacturer’s datasheet for more information on this peripheral.
This peripheral provides 2 Host type A and one On the Go Host/Peripheral mini AB type USB controller.
The ISP1761 controller is configured to use a 16 bit data bus. It uses single 16 bit read and write strobes.
Byte or long word accesses are not available for this device.
The chip select used for the USB controller is CS2 which is o n JA3 pin 28.
Please note the timing. This will require programming the bus controller for the Host RSK.
9
Page 10

A[17:1]
5ns
CSn,RDn
Data
A[17:1]
5ns
35ns
40ns
Valid
Figure 4-3: USB controller read timing
5ns
20ns
0ns
5ns
CSn,WRn
Data
8ns
Valid
5ns
Figure 4-4: USB controller write timing
The ISP1761 controller can drive two interrupts.
IRQ1 is the HC_IRQ from the ISP1761 controller.
IRQ3 is the DC_IRQ output from the ISP1761 controller. DC_IRQ interrupts can be enabled on the HC_IRQ pin,
so this can be disabled for host RSKs with fewer interrupt lines, if the DC_IRQ interrupt is required.
Both interrupts are pulled high to 3.3V by 1K resistors.
10
Page 11

4.4.SRAM
The board is provided with 512 kilobytes of static RAM arranged as 256k x 16 b i t words.
This RAM is byte addressable, provided the host RSK supports this.
The chip select used for the RAM is CS3 which is on JA3 pin 45.
Please note the timing. This will require programming the bus controller for the Host RSK.
5ns
A[18:1]
CSn,RDn
Data
A[18:1]
5ns
15ns
20ns
Figure 4-5: SRAM read timing
5ns
20ns
0ns
Valid
5ns
CSn,WRn
Data
Figure 4-6: SRAM write timing
11
8ns
Valid
5ns
Page 12

4.5.Option Links
Table 4-1 below describes the function of the option links contained on this CPU board. The default configuration is indicated by BOLD
text.
Option Link Settings
Reference Function Fitted Alternative (Removed) Related To
R2 3V power select
R7 Write Strobe Select
R8 Write Strobe Select High Byte writes from WR1n
R9 Write Strobe Select
R10 Write Strobe Select Low Byte writes from WR0n
Regulator drives Board_3V3
High Byte writes from WR1n
Low Byte writes from WR0n
Table 4-1: JA1 Option Link Settings
Board_3V from RSK
WR1n not connected R8, R9, R10
WR1n not connected
WR0n not connected R7, R8, R10
WR0n not connected
R7, R9, R10
R7, R8, R9
12
Page 13

Chapter 5.Headers
5.1.Application Headers
This information is supplied for reference. Only pins marked are connected on this board.
These connections are
Table 5-1 and belowTable 5-2 show the standard application header connections.
Pin Generic Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
1 Regulated Supply 1 5V 2 Regulated Supply 1 GROUND
3 Regulated Supply 2 3V3 4 Regulated Supply 2 GROUND
5 Analogue Supply AVcc 6 Analogue Supply AVss
7 Analogue Reference AVref 8 ADTRG ADTRG
ADC0 I0
9
ADC2 I2
11
DAC0
13
IOPort
15
IOPort
17
IOPort
19
IOPort
21
AD0 10 ADC1 I1 AD1
AD2 12 ADC3 I3 AD3
DAC0 14 DAC1 DAC1
IO_0 16 IOPort IO_1
IO_2 18 IOPort IO_3
IO_4 20 IOPort IO_5
IO_6 22 IOPort IO_7
not level translated.
JA1
Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
23 Open drain IRQAEC IRQ3 24 I²C Bus - (3rd pin) IIC_EX
I²C Bus
25
IIC_SDA 26 I²C Bus IIC_SCL
Table 5-1: JA1 Standard Generic Header
13
Page 14

JA2
Pin Generic Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
1 Open drain RESn 2 External Clock Input EXTAL
3 Open drain NMIn 4 Regulated Supply 1 Vss1
5 Open drain output WDT_OVF 6 Serial Port SCIaTX
7 Open drain WUP IRQ0 8 Serial Port SCIaRX
9 Open drain IRQ1 10 Serial Port SCIaCK
11 Up/down MO_UD 12 Serial Port Handshake CTS/RTS
13 Motor control MO_Up 14 Motor control MO_Un
15 Motor control MO_Vp 16 Motor control MO_Vn
17 Motor control MO_Wp 18 Motor control MO_Wn
19 Output TMR0 20 Output TMR1
21 Input TRIGa 22 Input TRIGb
23 Open drain IRQ2 24 Tristate Control TRSTn
25 SPARE - 26 SPARE -
Table 5-2: JA2 Standard Generic Header
Table 5-3 and Table 5-4 below show the optional generic header connections
JA5
Pin Generic Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
1 ADC4 I4 AD4 2 ADC5 I5 AD5
3 ADC6 I6 AD6 4 ADC7 I7 AD7
5 CAN CAN1TX 6 CAN CAN1RX
7 CAN CAN2TX 8 CAN CAN2RX
9 Reserved 10 Reserved
11 Reserved 12 Reserved
13 Reserved 14 Reserved
15 Reserved 16 Reserved
17 Reserved 18 Reserved
19 Reserved 20 Reserved
21 Reserved 22 Reserved
23 Reserved 24 Reserved
Table 5-3: JA5 Optional Generic Header
14
Page 15

JA6
Pin Generic Header Name CPU board
Signal
Pin Header Name CPU board
Signal Name
Name
1 DMA DREQ 2 DMA DACK
3 DMA TEND 4 Standby (Open drain) STBYn
5 Host Serial SCIdTX RS232TX 6 Host Serial SCIdRX RS232RX
7 Serial Port SCIbRX 8 Serial Port SCIbTX
9 Serial Port Synchronous SCIcTX 10 Serial Port SCIbCK
11 Serial Port Synchronous SCIcCK 12 Serial Port Synchronous SCIcRX
13 Reserved 14 Reserved
15 Reserved 16 Reserved
17 Reserved 18 Reserved
19 Reserved 20 Reserved
21 Reserved 22 Reserved
23 Reserved 24 Reserved
Table 5-4: JA6 Optional Generic Header
15
Page 16

Table 5-5 below shows the Memory Expansion connections
These connections support 5 to 3.3V level translation.
Pin Generic Header Name Signal Name Pin Header Name Signal Name
1 A(0) A(0) 2 A(1) A(1)
3 A(2) A(2) 4 A(3) A(3)
5 A(4) A(4) 6 A(5) A(5)
7 A(6) A(6) 8 A(7) A(7)
9 A(8) A(8) 10 A(9) A(9)
11 A(10) A(10) 12 A(11) A(11)
13 A(12) A(12) 14 A(13) A(13)
15 A(14) A(14) 16 A(15) A(15)
17 D(0) D(0) 18 D(1) D(1)
19 D(2) D(2) 20 D(3) D(3)
JA3
21 D(4) D(4) 22 D(5) D(5)
23 D(6) D(6) 24 D(7) D(7)
25 RDn RDn 26 WRn WRn
27 CS1n CS1n 28 CS2n CS2n
29 D(8) D(8) 30 D(9) D(9)
31 D(10) D(10) 32 D(11) D(11)
33 D(12) D(12) 34 D(13) D(13)
35 D(14) D(14) 36 D(15) D(15)
37 A(16) A(16) 38 A(17) A(17)
39 A(18) A(18) 40 A(19) A(19)
41 A(20) A(20) 42 A(21) A(21)
43 A(22) A(22) 44 SDCLK SDCLK
45 CS3n CS3n 46 ALE ALE
47 WR1n WR1n 48 WR0n WR0n
49 CASn CASn 50 RASn RASn
Table 5-5: JA3 Memory Expansion connector
16
Page 17

Chapter 6.Code Development
RSKs with appropriate connections will include suitable sample software to drive the interfaces on this board.
17
Page 18

Chapter 7.Additional Information
For details on how to use High-performance Embedded Workshop (HEW), refer to the HEW manual available on the CD or from the web
site.
Online technical support and information is available at:
Technical Contact Details
America: techsupport.rta@renesas.com
Europe:
Japan:
General information on Renesas Microcontrollers can be found on the Renesas website at:
tools.support.eu@renesas.com
csc@renesas.com
http://www.renesas.com/renesas_starter_kits
http://www.renesas.com/
18
Page 19

Renesas St arter Kit Ethernet & USB Application Board
User's Manual
Publication Date Rev.2.00 17.Jan.2008
Published by:
Renesas Technology Europe Ltd.
Duke’s Meadow, Millboard Road, Bourne End
Buckinghamshire SL8 5FH, United Kingdom
©2007 Renesas T echnology Europe and Renesas Solutions Corp., All Rights Reserved.
Page 20

Renesas Starter Ethernet & USB
Application Board User's Manual
Renesas Technology Europe Ltd.
Duke’s Meadow, Millboard Road, Bourne End
Buckinghamshire SL8 5FH, United Kingdom
 Loading...
Loading...