Page 1
REJ10J1242-0200
Renesas Starter Kit for R8C/25
User’s Manual
RENESAS SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER
M16C FAMILY / R8C/Tiny SERIES
Rev.2.00 Renesas Solutions Corp.
Revision date: 15.OCT.2007 www.renesas.com
i
Page 2

Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Preface..................................................................................................................................................1
Chapter 2. Purpose.................................................................................................................................................2
Chapter 3. Power Supply........................................................................................................................................3
3.1. Requirements...............................................................................................................................................3
3.2. Power – Up Behaviour .................................................................................................................................3
Chapter 4. Board Layout.........................................................................................................................................4
4.1. Component Layout.......................................................................................................................................4
4.2. Board Dimensions........................................................................................................................................5
Chapter 5. Block Diagram.......................................................................................................................................6
Chapter 6. User Circuitry.........................................................................................................................................7
6.1. Switches.......................................................................................................................................................7
6.2. LEDs.............................................................................................................................................................7
6.3. Potentiometer...............................................................................................................................................7
6.4. Serial port.....................................................................................................................................................8
6.5. LCD Module..................................................................................................................................................8
6.6. Option Links..................................................................................................................................................9
6.7. Oscillator Sources ......................................................................................................................................11
6.8. Reset Circuit...............................................................................................................................................11
Chapter 7. Modes..................................................................................................................................................12
7.1. Boot mode..................................................................................................................................................12
7.2. Single chip mode........................................................................................................................................12
Chapter 8. Programming Methods........................................................................................................................13
Chapter 9. Headers...............................................................................................................................................14
9.1. Microcontroller Headers.............................................................................................................................14
9.2. Application Headers ...................................................................................................................................16
Chapter 10. Code Development ...........................................................................................................................18
10.1. Overview...................................................................................................................................................18
10.2. Mode Support...........................................................................................................................................18
10.3. Breakpoint Support...................................................................................................................................18
10.4. Memory Map.............................................................................................................................................19
Chapter 11. Component Placement......................................................................................................................20
Chapter 12. Additional Information........................................................................................................................21
ii
Page 3

Chapter 1. Preface
Cautions
This document may be, wholly or partially, subject to change without notice.
All rights reserved. Duplication of this document, either in whole or part is prohibited without the written permission of Renesas
Solutions Corp.
Trademarks
All brand or product names used in this manual are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies or
organisations.
Copyright
© Renesas Solutions Corp. 2007. All rights reserved.
© Renesas Technology Europe Ltd. 2007. All rights reserved.
© Renesas Technology Corp. 2007. All rights reserved.
Website:
Glossary
CPU Central Processing Unit RTE Renesas Technology Europe Ltd.
HEW High-performance Embedded Workshop RSO Renesas Solutions Organisation.
LED Light Emitting Diode RSK Renesas Starter Kit
PC Program Counter
http://www.eu.renesas.com/
1
Page 4

Chapter 2. Purpose
This RSK is an evaluation tool for Renesas microcontrollers.
Features include:
• Renesas Microcontroller Programming.
• User Code Debugging.
• User Circuitry such as Switches, LEDs and potentiometer(s).
• User or Example Application.
• Sample peripheral device initialisation code.
The RSK board contains all the circuitry required for microcontroller operation.
2
Page 5

Chapter 3. Power Supply
3.1. Requirements
This RSK operates from a 3V to 5V power supply.
A diode provides reverse polarity protection only if a current limiting power supply is used.
All RSK boards are supplied with an E8a debugger module. This product is able to power the RSK board with up to 300mA. When the RSK
is connected to another system then that system should supply power to the RSK.
All RSK boards have an optional centre positive supply connector using a 2.1mm barrel power jack.
Warning
The RSK is neither under nor over voltage protected. Use a centre positive supply for this board.
3.2. Power – Up Behaviour
When the RSK is purchased the RSK board has the ‘Release’ or stand alone code from the example tutorial code pre-programmed into the
Renesas microcontroller. On powering up the board the user LEDs will start to flash. After 200 flashes, or after pressing a switch the LEDs
will flash at a rate controlled by the potentiometer.
3
Page 6
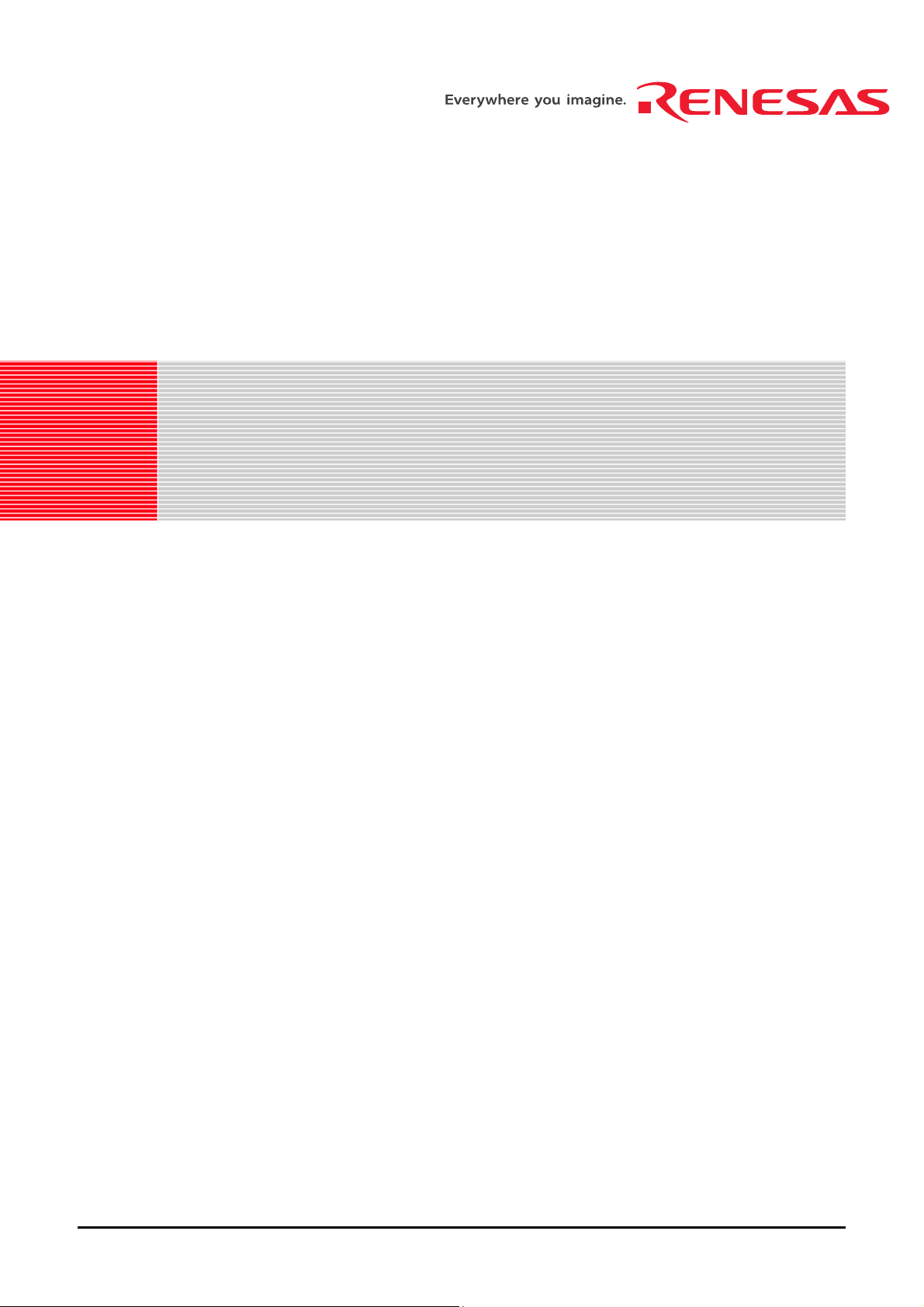
Chapter 4. Board Layout
r
r
A
A
r
r
4.1. Component Layout
The following diagram shows the top layer component layout of the board.
LCD Display
Microcontroller Pin Headers
(J1 to J4)
pplication Board Interface
JA1
MCU
JA2
pplication Board Interface
Figure 4-1: Board Layout
Reset Switch
RS232 Serial
Power
Power LED
E8 Heade
User LED
Power Connecto
for LIN
LIN Connecto
Boot LED
User/Boot Switch
User Switches
Potentiomete
4
Page 7
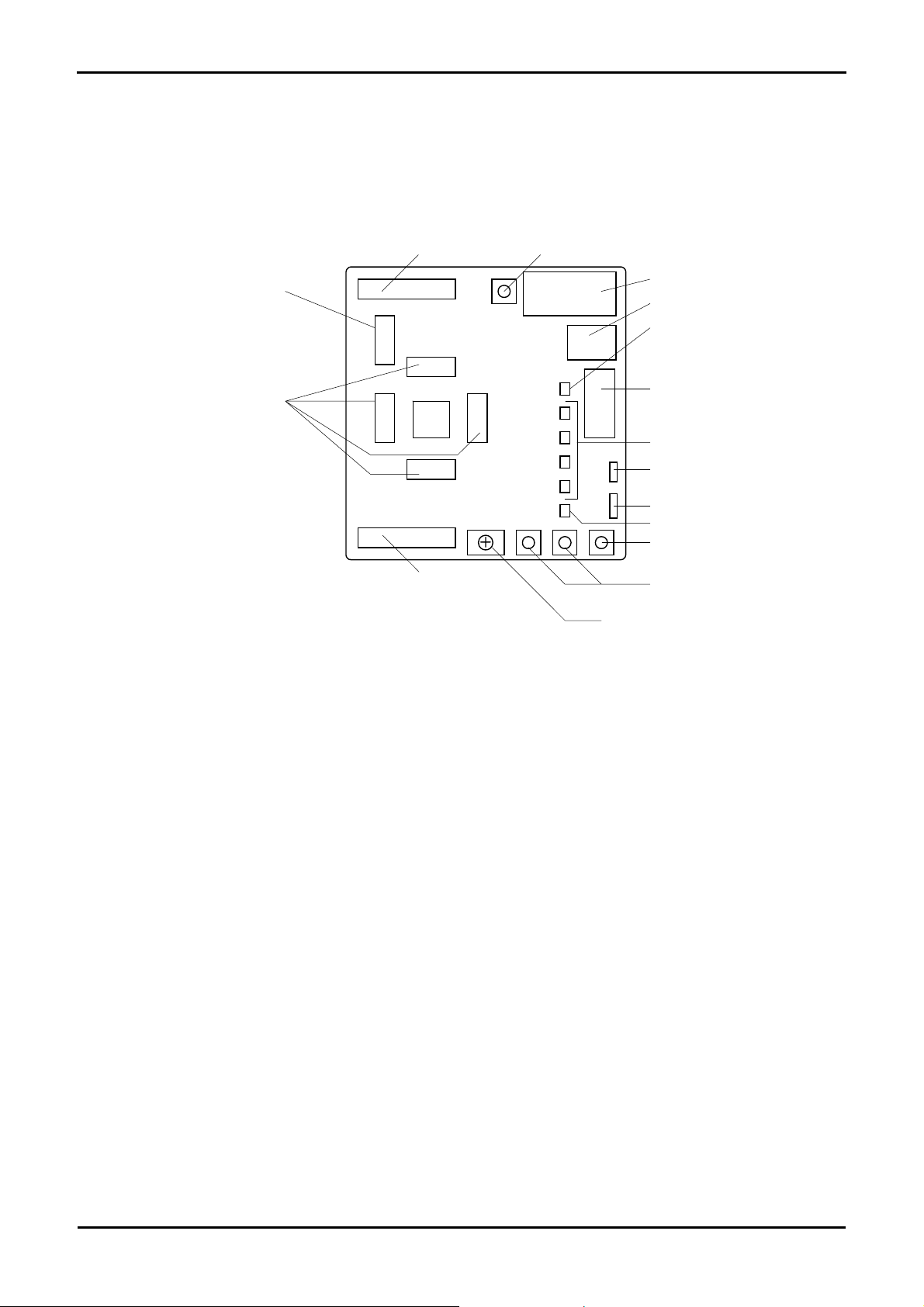
4.2. Board Dimensions
The following diagram gives the board dimensions and connector positions. All through hole connectors are on a common 0.1” grid for easy
interfacing.
3.81mm
5.00mm
45.00mm
JA1
14.00mm
92.71mm
85.00mm
100.00mm
MCU
JA2
27.00mm
50.80mm
80.00mm
85.00mm
Figure 4-2 : Board Dimensions
5
Page 8
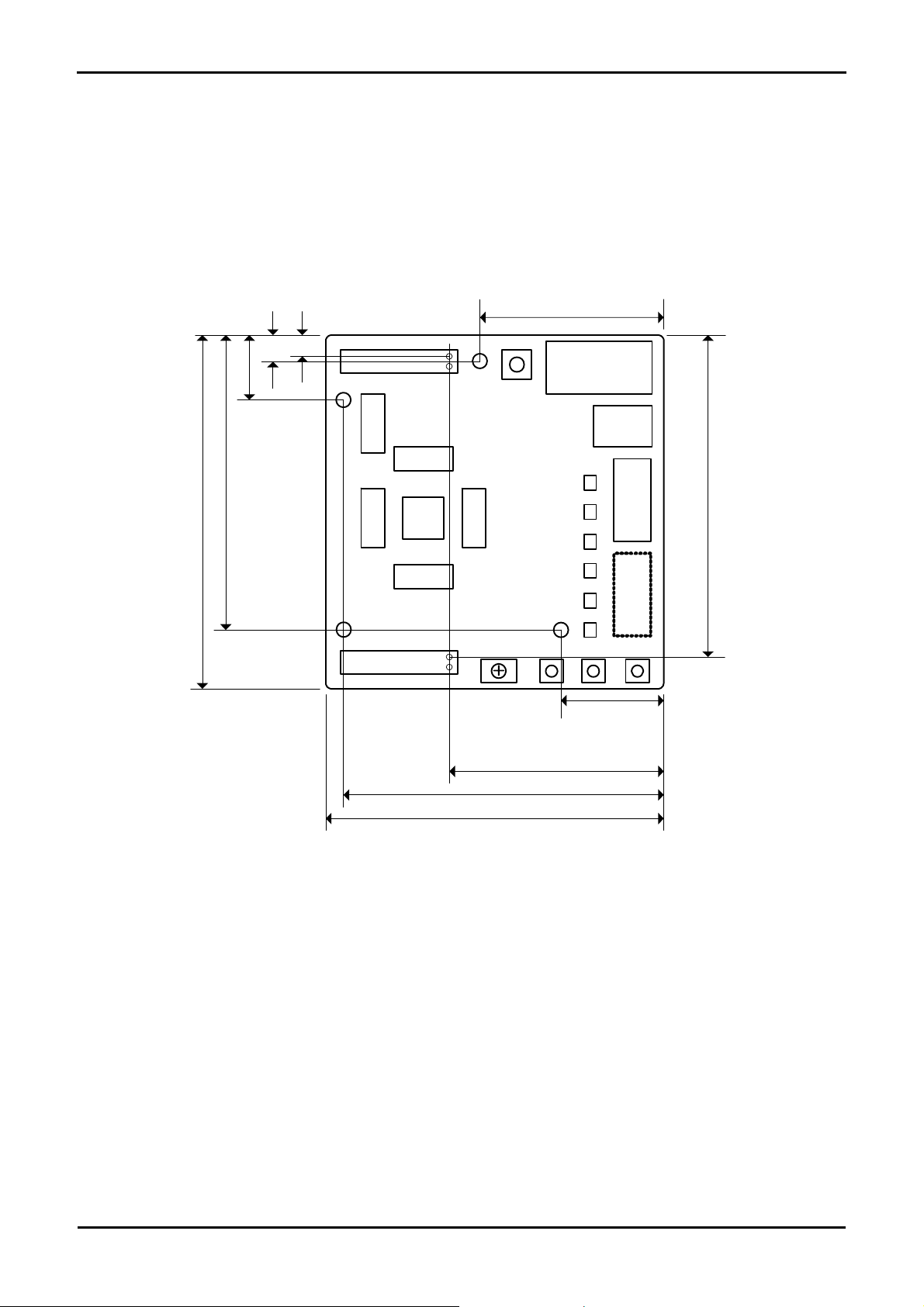
Chapter 5. Block Diagram
Figure 5-1 is representative of the CPU board components and their connectivity.
Pow er J ack Op tion
Application Board
Inter face
Mi crocontrol le r Pin
Headers
E8
LI N Connector,
Power Co nn ector f o r LIN
Serial Connect or Opt i on
Potentimeter
Boot mode pins
RESET p i n
Microcontroller
LCD Di sp l ay
Figure 5-1: Block Diagram
Figure 5-2 is representative of the connections required to the RSK.
IRQ pins
I/OADC Inp ut
Control x2
Data x4
Sw itches
User LED x4
1Green, 1Orage, 2Red
LEDs
BOOT
Circuitry
D-ty pe
Latch
SW1
BOOT
RES
PO W ER: Green
BOOT: Ora n ge
SW2SW3
BOOT & BOOTn signals
Host PC
MCU
USB Cable
E8a module
User Interface Cable
Pin 1
E8
CPU Board
Figure 5-2 : RSK Connections
6
Page 9

Chapter 6. User Circuitry
6.1. Switches
There are four switches located on the RSK. The function of each switch and its connection are shown in Table 6-1.
Switch Function Microcontroller
RES When pressed, the RSK microcontroller is reset. RESET Pin8
SW1/BOOT* Connects to an IRQ input for user controls.
The switch is also used in conjunction with the RES switch to place
the device in BOOT mode when not using the E8a debugger.
SW2* Connects to an IRQ Interrupt input line for user controls. INT1 Pin21
SW3* Connects to a Key In Interrupt input line for user controls KI3 Pin25
Table 6-1: Switch Functions
*Refer to schematic for detailed connectivity information.
INT0 Pin27
(Port 4, pin 5)
(Port 1, pin 7)
(Port 1, pin 3)
6.2. LEDs
There are six LEDs on the RSK board. The green ‘POWER’ LED lights when the board is powered. The orange BOOT LED indicates the
device is in BOOT mode when lit. The four user LEDs are connected to an IO port and will light when their corresponding port pin is set low.
Table 6-2, below, shows the LED pin references and their corresponding microcontroller port pin connections.
LED Reference (As
shown on silkscreen)
LED0 Green Port 2.4 16
LED1 Orange Port 2.5 15
LED2 Red Port 2.6 14
LED3 Red Port 2.7 13
Colour Microcontroller Port Pin function Microcontroller Pin
Number
Table 6-2: LED Port
6.3. Potentiometer
A single turn potentiometer is connected to AN8 (P1.0) of the microcontroller. This may be used to vary the input analogue voltage value to
this pin between VREF and Ground.
7
Page 10

6.4. Serial port
The microcontroller programming serial port 1 is connected to the RS232 transceiver. This serial port can optionally be connected to the
RS232 transceiver as well by fitting option resistors. The connections to be fitted are listed in the table 6-3.
Description Function Fit for RS232
TxD1 Programming Serial Port R45
RxD1 Programming Serial Port R46
Table 6-3: Serial Port settings
A Secondary serial port is connected to the application headers. This is shared with the LIN module.
6.5. LCD Module
A LCD module is supplied to be connected to the connector J8. This should be fitted so that the LCD module lies over J1. Care should be
taken to ensure the pins are inserted correctly into J8.The LCD module uses a 4 bit interface to reduce the pin allocation. No contrast
control is provided; this is set by a resistor on the supplied display module. The module supplied with the RSK only supports 5V operation.
Table 6-4 shows the pin allocation and signal names used on this connector.
J8
Pin Circuit Net Name Device
Pin
1 Ground - 2 5V Only 3 No Connection - 4 LCD_RS 31
5 R/W (Wired to Write only) - 6 LCD_E 30
7 No Connection - 8 No Connection 9 No Connection - 10 No Connection 11 LCD_D4 51 12 LCD_D5 50
13 LCD_D6 49 14 LCD_D7 48
Table 6-4: LCD Module Connections
Pin Circuit Net Name Device
Pin
8
Page 11

6.6.Option Links
Table 6-5 below describes the function of the option links contained on this RSK board.
Option Link Settings
Reference Function Fitted Alternative (Removed) Related To
R7 Reference Voltage
R8 Oscillator
(Main clock)
R10 Oscillator
(Main clock)
R11 Oscillator
(Main clock)
R12 Oscillator
(Main clock)
R13 Oscillator
(Sub clock)
R14 Oscillator
Connects Reference Voltage
to microcontroller
Connects External
Microcontroller header pins to
microcontroller
Connects External
Microcontroller header pins to
microcontroller
Connects main clock (X1) to
microcontroller
Connects main clock (X1) to
microcontroller
Connects sub clock (X2) to
microcontroller
Connects sub clock (X2) to
Reference Voltage
disconnected from
microcontroller
Disconnects sensitive
microcontroller signals from
external pins
Disconnects sensitive
microcontroller signals from
external pins
Main clock disconnected from
microcontroller
Main clock disconnected from
microcontroller
Sub clock disconnected from
microcontroller
Sub clock disconnected from
R19
R10, R11, R12
R8, R11, R12
R8, R10, R12
R8, R10, R11
R14, R15, R16,
R17
R13, R15, R16,
(Sub clock)
R15 Oscillator
(Sub clock)
R16 Oscillator
(Sub clock)
R17 Oscillator
(Sub clock)
R18 Board VCC
R19 Reference Voltage
R20 Board VCC
microcontroller
Connects External
Microcontroller header pins to
microcontroller
Connects External
Microcontroller header pins to
microcontroller
Parallel resister for sub clock
(X2)
Supply to board from DC
Power Jack (J5)
Connects Board_VCC supply
to Reference Voltage supply
Connects Board_VCC supply
to board voltage line
microcontroller
Disconnects sensitive
microcontroller signals from
external pins
Disconnects sensitive
microcontroller signals from
external pins
Not fitted
Disconnected R20
Reference Voltage MUST be
provided from external
interface
Board_VCC disconnected from
board voltage line
R17
R13, R14, R16
R13, R14, R15
R13, R14
R7
R18, R19, R21,
R22, R23
R21 Board VCC
Connects External 5V
(CON_5V) to Board_VCC
9
External 5V disconnected from
Board_VCC
R20, R22
Page 12

Option Link Settings
Reference Function Fitted Alternative (Removed) Related To
R22 Board VCC Connects External 3V3
(CON_3V3) to Board_VCC
R23 Microcontroller
Supply to microcontroller
VCC
R30 User I/O Power
Supply
R31 SW1
Connects Board_VCC supply
to SW2, 3 and LED0-3
Connects SW1 to INT0 Input
R44 RS232 Transceiver Disables RS232 Serial
Transceiver
R45 Programming
Serial Port
R46 Programming
Serial Port
R47 E8
R50 Microcontroller pin
Connects RS232 port to
Programming SCI port
Connects RS232 port to
Programming SCI port
Enables E8a Connection
Connects microcontroller pin
External 3V3 disconnected
R20, R21
from Board_VCC
Fit Low ohm resister to
measure current
Board_VCC disconnected from
SW2, 3 and LED0-3
Disconnected
Enables RS232 Serial
R45, R46
Transceiver
Disconnected
Disconnected
Do not connect a option
R44, R46
R44, R45
resister
MUST be removed if R51 fitted R51
function select
R51 Microcontroller pin
function select
R52 Microcontroller pin
function select
R53 Microcontroller pin
function select
R54 Microcontroller pin
function select
R55 Microcontroller pin
function select
R56 LIN
R59 LIN
28 to IRQ1
Connects microcontroller pin
28 to IO_6
Connects microcontroller pin
29 to IRQ2
Connects microcontroller pin
28 to IO_7
Connects microcontroller pin
27 to IRQ0
Connects microcontroller pin
27 to TRIGa
For Master Mode
Connects microcontroller pin
22 to LIN-NSLP
R60 LIN
Connects microcontroller pin
23 to LIN-RXD0
Should be removed if R50
R50
fitted
MUST be removed if R53 fitted R53
Should be removed if R52
R52
fitted
MUST be removed if R55 fitted R55
Should be removed if R54
R54
fitted
For Slave Mode R59, R60, R61
Disconnected R56, R60, R61
Disconnected R56, R59, R61
R61 LIN
Connects microcontroller pin
23 to LIN-TXD0
R62 CAN Do not use CAN function,
R8C/25 Microcontroller do not
have CAN function
10
Disconnected R56, R59, R60
Do not use CAN function,
R8C/25 Microcontroller do not
have CAN function
Page 13

Option Link Settings
Reference Function Fitted Alternative (Removed) Related To
R64 CAN Do not use CAN function,
R8C/25 Microcontroller do not
have CAN function
R66 CAN Do not use CAN function,
R8C/25 Microcontroller do not
have CAN function
Table 6-5: Option Links
Do not use CAN function,
R8C/25 Microcontroller do not
have CAN function
Do not use CAN function,
R8C/25 Microcontroller do not
have CAN function
6.7.Oscillator Sources
A crystal oscillator is fitted on the RSK and used to supply the main and sub clock input to the Renesas microcontroller.
Table 6-6: Oscillators / Resonators
details the oscillators that are fitted and alternative footprints provided on this RSK:
Component
Crystal (X1) Fitted 20 MHz (HC/49U package)
Sub clock (X2) Fitted 32.768 kHz (90SMX package)
Table 6-6: Oscillators / Resonators
6.8.Reset Circuit
The CPU Board includes a simple latch circuit that links the mode selection and reset circuit. This provides an easy method for swapping
the device between Boot Mode, User Boot Mode and User mode. This circuit is not required on customers boards as it is intended for
providing easy evaluation of the operating modes of the device on the RSK. Please refer to the hardware manual for more information
on the requirements of the reset circuit.
The Reset circuit operates by latching the state of the boot switch on pressing the reset button. This control is subsequently used to
modify the mode pin states as required.
The mode pins should change state only while the reset signal is active to avoid possible device damage.
The reset is held in the active state for a fixed period by a pair of resistors and a capacitor. Please check the reset requirements carefully
to ensure the reset circuit on the user’s board meets all the reset timing requirements.
11
Page 14

Chapter 7. Modes
The RSK supports Boot mode and Single chip mode.
Details of programming the FLASH memory is described in the R8C/25 Group Hardware Manual.
7.1. Boot mode
The boot mode settings for this RSK are shown in Table 7-1: Boot Mode pin settings below:
MODE LSI State after Reset End
Low Boot Mode
Table 7-1: Boot Mode pin settings
The software supplied with this RSK supports Boot mode using an E8a and HEW only. However, hardware exists to enter boot mode
manually, do not connect the E8a in this case. Press and hold the SW1/BOOT. The mode pin is held in its boot state while reset is pressed
and released. Release the boot button. The BOOT LED will be illuminated to indicate that the microcontroller is in boot mode.
When neither the E8a is connected nor the board is placed in boot mode as above, the Mode pin is pulled high by a 4.7k resistor.
When an E8a is used the Mode pin is controlled by the E8a.
7.2. Single chip mode
Because the Mode pin is pulled high, this RSK will always boot in Single Chip mode when the E8a is not connected and the boot switch is
not depressed. Refer to R8C/25 Group Hardware Manual for details of Single chip mode.
MODE LSI State after Reset End
High Single Chip Mode
Table 7-2: Single Chip Mode pin settings
12
Page 15

Chapter 8. Programming Methods
The board is intended for use with HEW and the supplied E8a debugger. Refer to R8C/25 Group Hardware Manual for details of
programming the microcontroller without using these tools.
13
Page 16

Chapter 9. Headers
9.1. Microcontroller Headers
Table 9-1 to Table 9-4 show the microcontroller pin headers and their corresponding microcontroller connections. The header pins connect
directly to the microcontroller pins.
Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin
1 No Connection - 2 IIC_SCL 2
3 TRISTn 3 4 IIC_SDA 4
5 MODE_E8B 5 6 RING_P4_3 6
7 RING_P4_4 7 8 RESn 8
9 CON_XOUT 9 10 VSS 10
11 CON_XIN 11 12 UC_VCC 12
13 MO_Wn 13 14 No Connection -
Pin Circuit Net Name Device
1 MO_Vn 14 2 MO_Wp 15
3 MO_Vp 16 4 MO_Un 17
* Marked pins are subject to option links.
J1
Table 9-1: J1
J2
Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin
Pin
5 TMR0 18 6 MO_Up 19
7 P2_0 20 8 TRIGb 21
9 SCIaCK 22 10 SCIaRX 23
11 SCIaTX 24 12 IRQ3 25
13 No Connection - 14 No Connection -
Table 9-2: J2
14
Page 17

J3
Pin Circuit Net Name Device
Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin
Pin
1 IRQ0/TRIGa* 27 2 IRQ1/IO_6* 28
3 IRQ2/IO_7* 29 4 LCD_E 30
5 LCD_RS 31 6 AD_POT 32
7 P3_1 33 8 TMR1 34
9 IO_5 35 10 IO_4 36
11 IO_3 37 12 AD0 38
13 No Connection - 14 No Connection -
Table 9-3: J3
J4
Pin Circuit Net Name Device
Pin Circuit Net Name Device Pin
Pin
1 No Connection - 2 AD1 41
3 AD2 42 4 AD3 43
5 P4_2/VREF 44 6 IO_0 45
7 IO_2 46 8 IO_1 47
9 LCD_D7 48 10 LCD_D6 49
11 LCD_D5 50 12 LCD_D4 51
13 MO_UD 52 14 No Connection -
Table 9-4: J4
15
Page 18

9.2. Application Headers
Table 9-5 and Table 9-6 below show the standard application header connections. * Marked pins are subject to option links.
JA1
Pin Header Name RSK Signal
Name
1 Regulated Supply 1 CON_5V - 2 Regulated Supply 1 GROUND 3 Regulated Supply 2 CON_3V3 - 4 Regulated Supply 2 GROUND 5 Analogue Supply NC - 6 Analogue Supply NC 7 Analogue Reference CON_VREF 44 8 ADTRG NC 9 ADC0 AD0 38 10 ADC1 AD1 41
11 ADC2 AD2 42 12 ADC3 AD3 43
13 DAC0 NC - 14 DAC1 NC 15 IOPort0 IO_0 45 16 IOPort1 IO_1* 47
17 IOPort2 IO_2 46 18 IOPort3 IO_3 37
19 IOPort4 IO_4 36 20 IOPort5 IO_5 35
21 IOPort8 IO_6* 28 22 IOPort7 IO_7* 29
23 IRQ3 IRQ3 25 24 I2C Bus (3rd pin) NC 25 I²C Bus IIC_SDA 4 26 I²C Bus IIC_SCL 2
Table 9-5: JA1 Standard Generic Header
Device
Pin
Pin Header Name RSK Signal
Name
Device
Pin
JA2
Pin Header Name RSK Signal
Name
1 Reset RESn 8 2 External Clock Input CON_XIN 11
3 Interrupt NC - 4 Regulated Supply 1 GND 5 SPARE NC - 6 Serial Port SCIaTX 24
7 Interrupt IRQ0* 27 8 Serial Port SCIaRX 23
9 Interrupt IRQ1* 28 10 Serial Port SCIaCK 22
11 Motor up/down MO_UD* 52 12 Serial Port Handshake NC 13 Motor control MO_Up 19 14 Motor control MO_Un 17
15 Motor control MO_Vp 16 16 Motor control MO_Vn 14
17 Motor control MO_Wp 15 18 Motor control MO_W 13
19 Timer Output TMR0 18 20 Timer Output TMR1 34
21 Timer Input TRIGa* 27 22 Timer Input TRIGb 21
23 Interrupt IRQ2* 29 24 Tristate Control TRISTn 3
25 SPARE P2_0 20 26 SPARE P3_1 33
Device
Pin
Pin Header Name RSK Signal
Name
Device
Pin
Table 9-6: JA2 Standard Generic Header
16
Page 19

J9
Pin Function Signal Name
1 Power Supply (for LIN module) VBAT
2 GROUND GND
J10
Pin Function Signal Name
1 Power Supply (for LIN module) VBAT
2 LIN Bus Line LIN
3 GROUND GND
Table 9-7: LIN Headers
17
Page 20

Chapter 10.Code Development
10.1. Overview
Note: For all code debugging using Renesas software tools, the RSK board must be connected to a PC USB port via an E8a. An E8a is
supplied with the RSK product.
10.2. Mode Support
HEW connects to the Microcontroller and programs it via the E8a. Mode support is handled transparently to the user.
10.3. Breakpoint Support
HEW supports breakpoints on the user code, both in RAM and ROM.
Double clicking in the breakpoint column in the code sets the breakpoint. Breakpoints will remain unless they are double clicked to remove
them.
18
Page 21

10.4. Memory Map
00000h
002FFh
00400h
SFR
00BFFh
02400h
02BFFh
08000h
0FFFFh
Internal RAM
In t er nal ROM
(Data Area)
In t er nal ROM
(Program Area)
User RA M A rea
Emulator Firmware
Area
Note: E8 Firmware area
selected via HEW
Emulator Firmware
Area
08800h
User ROM Area
0FFDCh
Fixed Vector Tables
Figure 10-1: Memory Map
19
Page 22

Chapter 11. Component Placement
Figure 11-1: Component Placement
20
Page 23

Chapter 12. Additional Information
For details on how to use High-performance Embedded Workshop (HEW, refer to the HEW manual available on the CD or from the web
site.
For information about the R8C/25 group microcontrollers refer to the R8C/25 Group Hardware Manual
For information about the R8C/25 assembly language, refer to the R8C/Tiny Series Software Programming Manual.
Online technical support and information is available at:
Technical Contact Details
America:
Europe:
Japan:
General information on Renesas Microcontrollers can be found on the Renesas website at:
techsupport.rta@renesas.com
tools.support.eu@renesas.com
csc@renesas.com
http://www.renesas.com/rsk
http://www.renesas.com/.
21
Page 24

Renesas Starter Kit for R8C/25
User's Manual
Publication Date Rev.1.01 29.05.2006
Published by:
Renesas Solutions Corp.
4-1-6, Miyahara, Yodogawa-ku, Osaka City, 532-0003, Japan
©2006 Renesas Solutions Corp., Renesas Technology Europe Ltd. and Renesas Technology Corp.,
All Rights Reserved.
Page 25

Renesas Starter Kit for R8C/25
User's Manual
Renesas Solutions Corp.
4-1-6, Miyahara, Yodogawa-ku, Osaka City, 532-0003, Japan
 Loading...
Loading...