Page 1
M34514T-MCU
MCU Board for 4513/4514 Group MCUs
User's Manual
Rev.1.00
September 1, 2003
REJ10J0274-0100Z
Page 2

* MS-DOS is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
* IBM and AT are registered trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation.
* NQPACK, YQPACK, YQSOCKET, YQ-GUIDE, HQPACK, TQPACK and TQSOCKET are trademarks of Tokyo Eletech Corporation.
• Renesas Technology Corporation and Renesas Solutions Corporation put the maximum effort into making semiconductor products better
and more reliable, but there is always the possibility that trouble may occur with them. Trouble with semiconductors may lead to personal
injury, fire or property damage. Remember to give due consideration to safety when making your circuit designs, with appropriate
measures such as (i) placement of substitutive, auxiliary circuits, (ii) use of nonflammable material or (iii) prevention against any
malfunction or mishap.
• These materials are intended as a reference to assist our customers in the selection of the Renesas Technology product best suited to
the customer's application; they do not convey any license under any intellectual property rights, or any other rights, belonging to Renesas
Technology Corporation, Renesas Solutions Corporation or a third party.
• Renesas Technology Corporation and Renesas Solutions Corporation assume no responsibility for any damage, or infringement of any
third-party's rights, originating in the use of any product data, diagrams, charts, programs, algorithms, or circuit application examples
contained in these materials.
• All information contained in these materials, including product data, diagrams, charts, programs and algorithms represents information
on products at the time of publication of these materials, and are subject to change by Renesas Technology Corporation and Renesas
Solutions Corporation without notice due to product improvements or other reasons. It is therefore recommended that customers contact
Renesas Technology Corporation, Renesas Solutions Corporation or an authorized Renesas Technology product distributor for the latest
product information before purchasing a product listed herein. The information described here may contain technical inaccuracies or
typographical errors. Renesas Technology Corporation and Renesas Solutions Corporation assume no responsibility for any damage,
liability, or other loss rising from these inaccuracies or errors. Please also pay attention to information published by Renesas Technology
Corporation and Renesas Solutions Corporation by various means, including the Renesas home page (http://www.renesas.com).
• When using any or all of the information contained in these materials, including product data, diagrams, charts, programs, and algorithms,
please be sure to evaluate all information as a total system before making a final decision on the applicability of the information and
products. Renesas Technology Corporation and Renesas Solutions Corporation assume no responsibility for any damage, liability or
other loss resulting from the information contained herein.
• Renesas Technology semiconductors are not designed or manufactured for use in a device or system that is used under circumstances
in which human life is potentially at stake. Please contact Renesas Technology Corporation, Renesas Solutions Corporation or an
authorized Renesas Technology product distributor when considering the use of a product contained herein for any specific purposes,
such as apparatus or systems for transportation, vehicular, medical, aerospace, nuclear, or undersea repeater use.
• The prior written approval of Renesas Technology Corporation and Renesas Solutions Corporation is necessary to reprint or reproduce
in whole or in part these materials.
• If these products or technologies are subject to the Japanese export control restrictions, they must be exported under a license from the
Japanese government and cannot be imported into a country other than the approved destination. Any diversion or reexport contrary to
the export control laws and regulations of Japan and/or the country of destination is prohibited.
• Please contact Renesas Technology Corporation or Renesas Solutions Corporation for further details on these materials or the products
contained therein.
Keep safety first in your circuit designs!
Notes regarding these materials
• This product is a development supporting unit for use in your program development and evaluation stages. In mass-producing your
program you have finished developing, be sure to make a judgment on your own risk that it can be put to practical use by performing
integration test, evaluation, or some experiment else.
• In no event shall Renesas Solutions Corporation be liable for any consequence arising from the use of this product.
• Renesas Solutions Corporation strives to renovate or provide a workaround for product malfunction at some charge or without charge.
However, this does not necessarily mean that Renesas Solutions Corporation guarantees the renovation or the provision under any
circumstances.
• This product has been developed by assuming its use for program development and evaluation in laboratories. Therefore, it does not fall
under the application of Electrical Appliance and Material Safety Law and protection against electromagnetic interference when used in
Japan.
For inquiries about the contents of this document or product, fill in the text file the installer of the emulator debugger generates in the
following directory and email to your local distributor.
\SUPPORT\Product-name\SUPPORT.TXT
Renesas Tools Homepage http://www.renesas.com/en/tools
Precautions to be taken when using this product
( 2 / 42 )
Page 3

Contents
Preface ....................................................................................................................................4
1. Precautions for Safety.........................................................................................................5
1.1 Safety Symbols and Meanings ..............................................................................5
2. Handling Precautions..........................................................................................................9
3. Contents of the M34514T-MCU Package ........................................................................11
3.1 Things to Check When Unpacking .....................................................................11
3.2 Other Necessary Products ...................................................................................11
4. M34514T-MCU................................................................................................................13
4.1 Outline.................................................................................................................13
4.2 Specifications ......................................................................................................15
4.3 Description of Switches ......................................................................................16
4.4 Description of Connectors...................................................................................18
4.5 Connection to the Target System ........................................................................21
4.6 LED .....................................................................................................................27
5. Precautions to Be Taken When Debugging......................................................................29
5.1 Reset ....................................................................................................................29
5.2 System Clock ......................................................................................................29
5.3 Real-time Capability of Timer ............................................................................29
5.4 Watchdog Timer..................................................................................................30
5.5 Pullup Transistor Control ....................................................................................30
5.6 Port I/O Timing ...................................................................................................31
5.7 Port I/O Characteristics .......................................................................................32
5.8 Power-down Mode ..............................................................................................33
5.9 Program Execution (G, GB)................................................................................34
5.10 External Trigger Signal .....................................................................................36
6. Connection Circuit Diagram.............................................................................................37
7. Pitch Converter Board External Dimensions ...................................................................39
7.1 M34513T-PTCA .................................................................................................39
7.2 M34513T-PTCB .................................................................................................39
7.3 M34513T-PTCC .................................................................................................39
Appendix A. How to Request for Repair .............................................................................40
( 3 / 42 )
Page 4
Preface
This user's manual describes the specifications of the M34514T-MCU emulator board for Renesas
4513/4514 Group of 4-bit single-chip microcomputers. M34514T-MCU is an MCU board for the
PC4504 emulator. For the PC4504 emulator main unit and the M3T-PD45 emulator debugger, refer
to each user's manual.
To use the product properly
Precautions for Safety
• In both this User's Manual and on the product itself, several icons are used to insure
proper handling of this product and also to prevent injuries to you or other persons,
or damage to your properties.
• The icons' graphic images and meanings are given in "Chapter 1. Precautions for
Safety". Be sure to read this chapter before using the product.
( 4 / 42 )
Page 5
Chapter 1. Precautions for Safety
In both the user's manual and on the product itself, several icons are used to insure proper handling
of this product and also to prevent injuries to you or other persons, or damage to your properties.
This chapter describes the precautions which should be taken in order to use this product safely and
properly. Be sure to read this chapter before using this product.
1.1 Safety Symbols and Meanings
If the requirements shown in the "WARNING"
WARNING
CAUTION
IMPORTANT
In addition to the three above, the following are also used as appropriate.
sentences are ignored, the equipment may
cause serious personal injury or death.
If the requirements shown in the "CAUTION"
sentences are ignored, the equipment may
malfunction.
It means important information on using this
product.
means WARNING or CAUTION.
Example: CAUTION AGAINST AN ELECTRIC SHOCK
means PROHIBITION.
Example: DISASSEMBLY PROHIBITED
means A FORCIBLE ACTION.
Example:
The following pages describe the symbols "WARNING", "CAUTION", and "IMPORTANT".
UNPLUG THE POWER CABLE FROM THE RECEPTACLE.
( 5 / 42 )
Page 6

WARNING
Warning for Installation:
• Do not set this product in water or areas of high humidity. Make sure that the main unit does not
get wet. Spilling water or some other liquid into the main unit can cause an unrepairable damage.
Warning for Use Environment:
• This equipment is to be used in an environment with a maximum ambient temperature of 35 °C. Care
should be taken that this temperature is not exceeded.
CAUTION
Cautions to Be Taken for This Product:
• Do not disassemble or modify this product. Disassembling or modifying this product can cause
damage. Disassembling and modifying the product will void your warranty.
• Use caution when handling the main unit. Be careful not to apply a mechanical shock.
• Do not pull the emulator probe (100-wire half-pitch cable or 50-wire normal-pitch cable) to
disconnect from the emulator main unit.
•Do not use inch-size screws for this equipment. The screws used in this equipment are all ISO
(meter-size) type screws. When replacing screws, use same type screws as equipped before.
( 6 / 42 )
Page 7

IMPORTANT
Notes on Differences between Actual MCU and Emulator:
• Emulator operation differs from emulation of a mask MCU, as listed below. For details refer to
"Chapter 5. Precautions to Be Taken When Debugging".
(1) Reset condition
(2) Initial values of internal resource data at power-on
(3) Internal ROM and RAM capacities, etc.
(4) Electrical characteristics
(5) Operation in the power-down mode
(6) Operation of the watchdog timer function
(7) Port I/O Timing
(8) Pullup transistor control
• Therefore, always be sure to evaluate your system with an evaluation MCU (onetime version).
Also, be sure to perform board-mounted evaluation with ES (Engineering Sample) version MCU
to make final confirmation of device operation before starting mask production.
Note on the Target System:
• Make sure that the target's supply voltage is + 3.0 V or + 5.0 V. Therefore the target's supply voltage
should be in the range of + 3.0 V ±10% or + 5.0 V ±10%.
Notes on Connecting the Target System:
• When connecting the emulator probe, be careful to the wrong connection.
• When connecting the emulator probe, be careful to the warp of the cable. The warp may cause
breaking the wire.
( 7 / 42 )
Page 8

MEMO
( 8 / 42 )
Page 9
2. Handling Precautions
When using the M34514T-MCU board, pay attention to the following:
(1) About the emulator
To use the M34514T-MCU board, you always need to install it on the PC4504 emulator main unit.
(2) About the MCU board installation
Before installing (and removing) the MCU board, always be sure to power off the PC4504
emulator main unit and unplug its power cord from the outlet. For details on how to install and
remove the MCU board, see "Chapter 2. Setup" in the PC4504 System User's Manual.
(3) Emulator debugger (M3T-PD45)
When using the M34514T-MCU board to debug your program, you need the M3T-PD45
emulator debugger (sold separately). Be sure to use the data file for 4513 or 4514 Group included
with the M3T-PD45 emulator debugger.
(4) Registers that can be operated from M3T-PD45
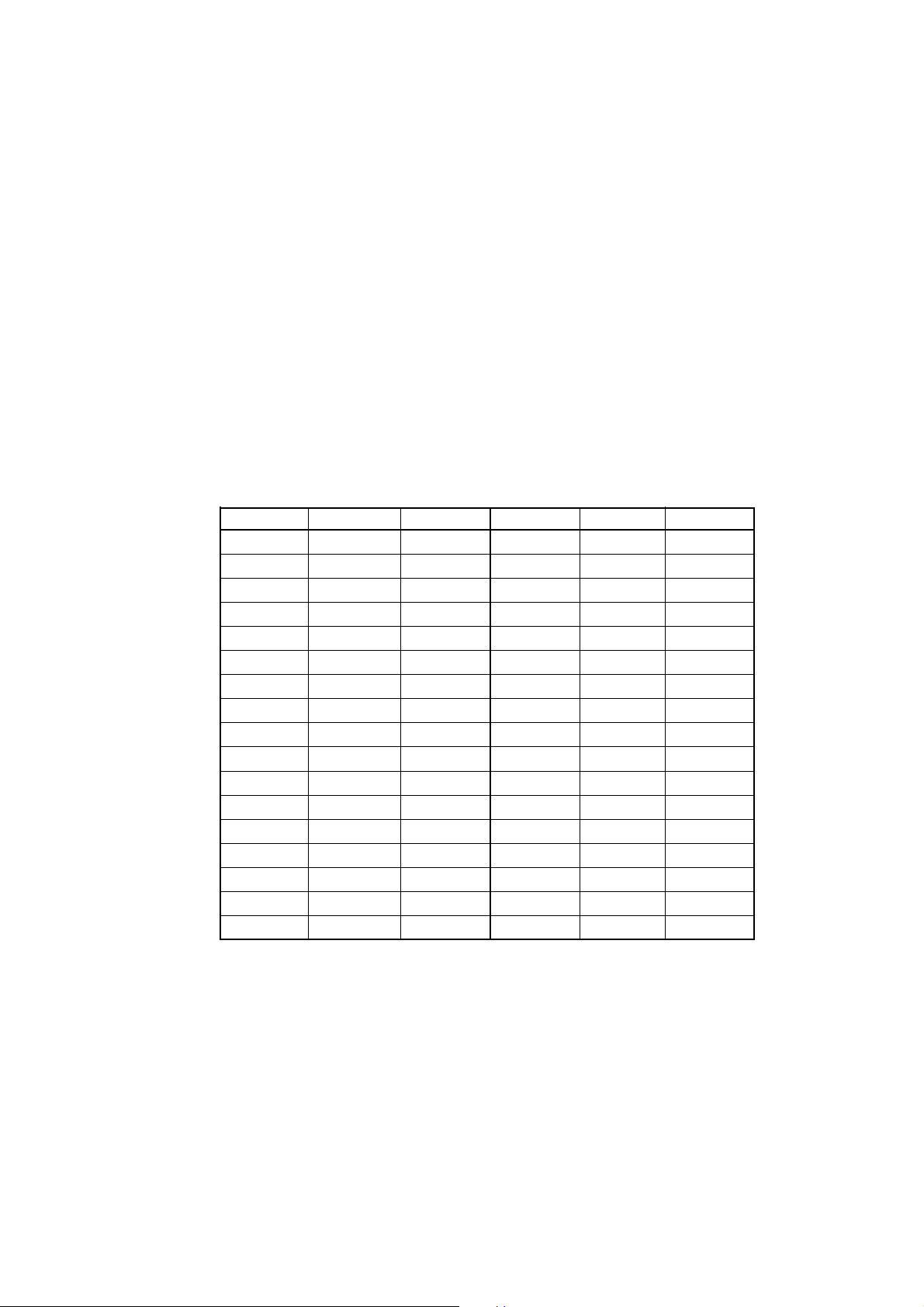
Table 2.1 lists the registers that can be operated from M3T-PD45 for 4514 Group MCUs. The
"Yes" in the table means that the register can be operated; the "No" means that the register can
not be operated.
Table 2.1 Registers that can be operated for 4514 Group MCUs
Register Reference Modification Register Reference Modification
PC Yes Yes W1 Yes Yes
CY Yes Yes W2 Yes Yes
A Yes Yes W3 Yes Yes
B Yes Yes W4 Yes Yes
X Yes Yes W6 Yes Yes
Y Yes Yes J1 Yes Yes
Z Yes Yes Q1 Yes Yes
D Yes Yes Q2 Yes Yes
E Yes Yes Q3 Yes Yes
SP Yes No K0 Yes Yes
V1 Yes Yes PU0 Yes Yes
V2 Yes Yes FR0 No Yes
I1 Yes Yes MR Yes Yes
I2 Yes Yes R1 No Yes
SI Yes Yes R2 No Yes
LA Yes No R3 No Yes
HA Yes Yes R4 No Yes
( 9 / 42 )
Page 10
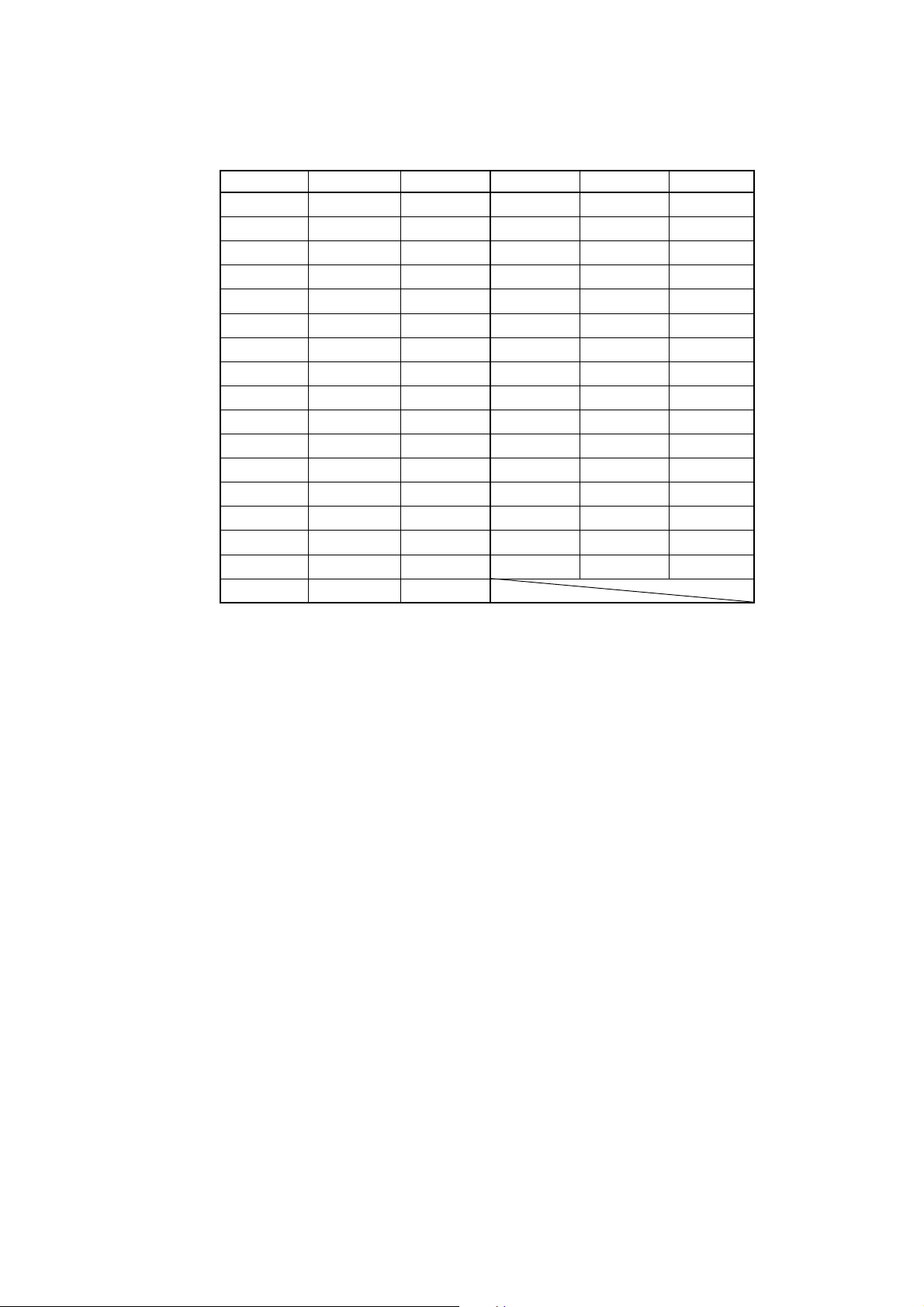
Table 2.2 lists the registers that can be operated from M3T-PD45 for 4513 Group MCUs. The "Yes"
in the table means that the register can be operated; the "No" means that the register can not be
operated.
Table 2.2 Registers that can be operated for 4513 Group MCUs
Register Reference Modification Register Reference Modification
PC Yes Yes W1 Yes Yes
CY Yes Yes W2 Yes Yes
A Yes Yes W3 Yes Yes
B Yes Yes W4 Yes Yes
X Yes Yes W6 Yes Yes
Y Yes Yes J1 Yes Yes
Z Yes Yes Q1 Yes Yes
D Yes Yes Q2 Yes Yes
E Yes Yes Q3 Yes Yes
SP Yes No K0 Yes Yes
V1 Yes Yes PU0 Yes Yes
V2 Yes Yes MR Yes Yes
I1 Yes Yes R1 No Yes
I2 Yes Yes R2 No Yes
SI Yes Yes R3 No Yes
LA Yes No R4 No Yes
HA Yes Yes
( 10 / 42 )
Page 11
3. Contents of the M34514T-MCU Package
3.1 Things to Check When Unpacking
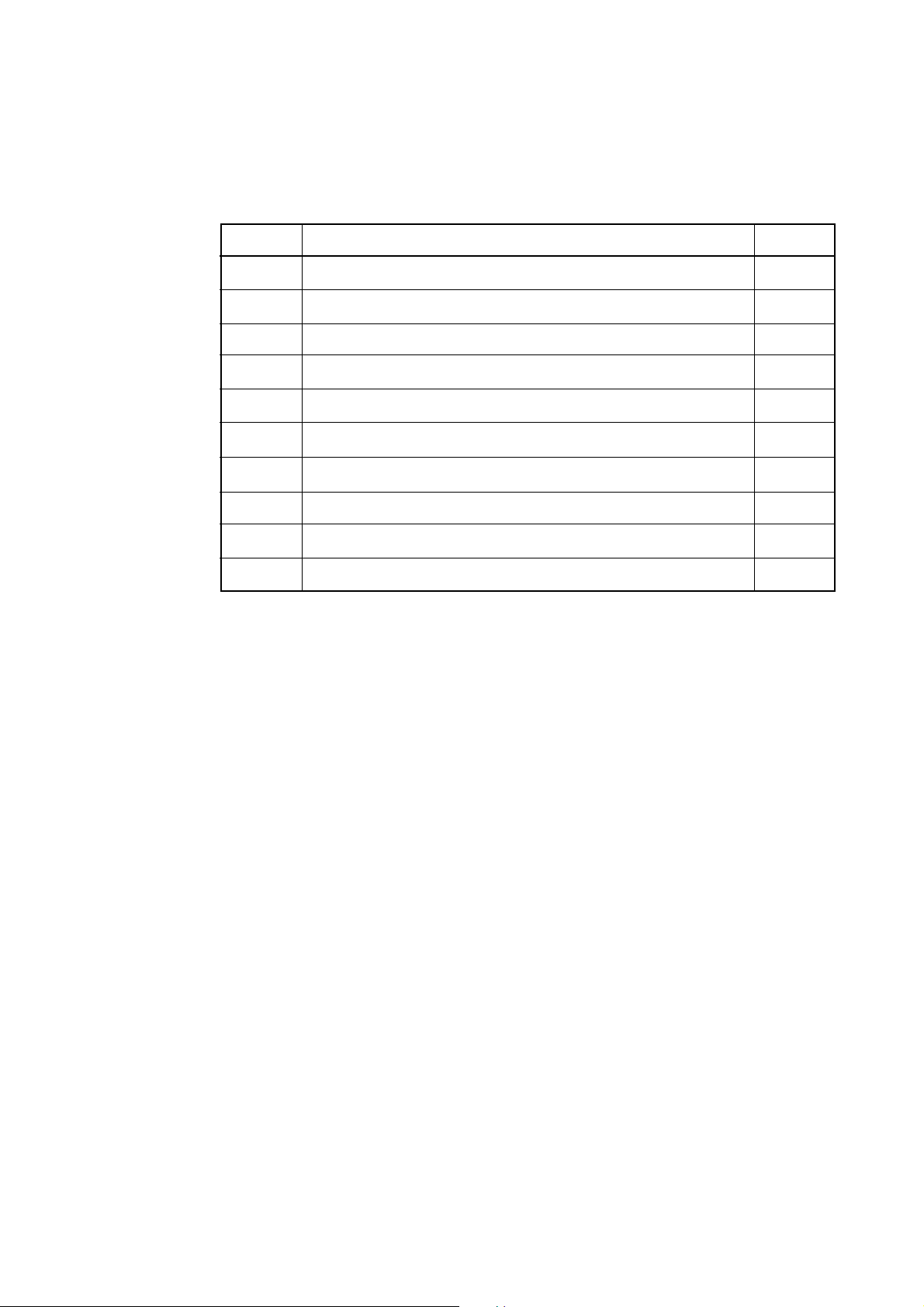
Table 3.1 shows the contents of the M34514T-MCU package. When unpacking your M34514TMCU package, check to see that all of these components are included.
Table 3.1 Contents of M34514T-MCU
Item
Product name
Quantity
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
M34514T-MCU
100-wire half-pitch cable (40 cm)
50-wire normal-pitch cable (10 cm)
2-wire cable for external trigger signal (50 cm)
PCA4029 pitch converter board
OSC-2 oscillator circuit board (J1 connector mounted) *
M34513T-PTCA pitch converter board
M34513T-PTCB pitch converter board
M34513T-PTCC pitch converter board *
M34514T-MCU English user's manual (this manual)
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
*1 M34514T-MCU has an oscillator circuit board OSC-2 (for 4.19 MHz) that is incorporated when
shipped from the factory. In addition, it comes with an oscillator circuit board OSC-2, with only
a connector J1 mounted.
*2 M34513T-PTCC consists of M34513T-PTCC and TQPACK.
*3 Keep the packaging carton and cushion material of the M34514T-MCU to transport it for repair
or for other purposes in the future.
*4 If you find any item missing or faulty, or any suggestion, contact your local distributor.
3.2 Other Necessary Products
To bring forward programs development on the 4513/4514 Group of 4-bit microcomputers, the
products given below are necessary in addition to those contained in the package above. Get them
separately to be ready when necessary.
(1) Emulator main unit: PC4504
(2) Emulator debugger: M3T-PD45
(3) Programming adapter: PCA7441 (for 4514 Group SSOP)
PCA7442FP (for 4513 Group LQFP)
PCA7442SP (for 4513 Group SDIP)
( 11 / 42 )
Page 12

MEMO
( 12 / 42 )
Page 13
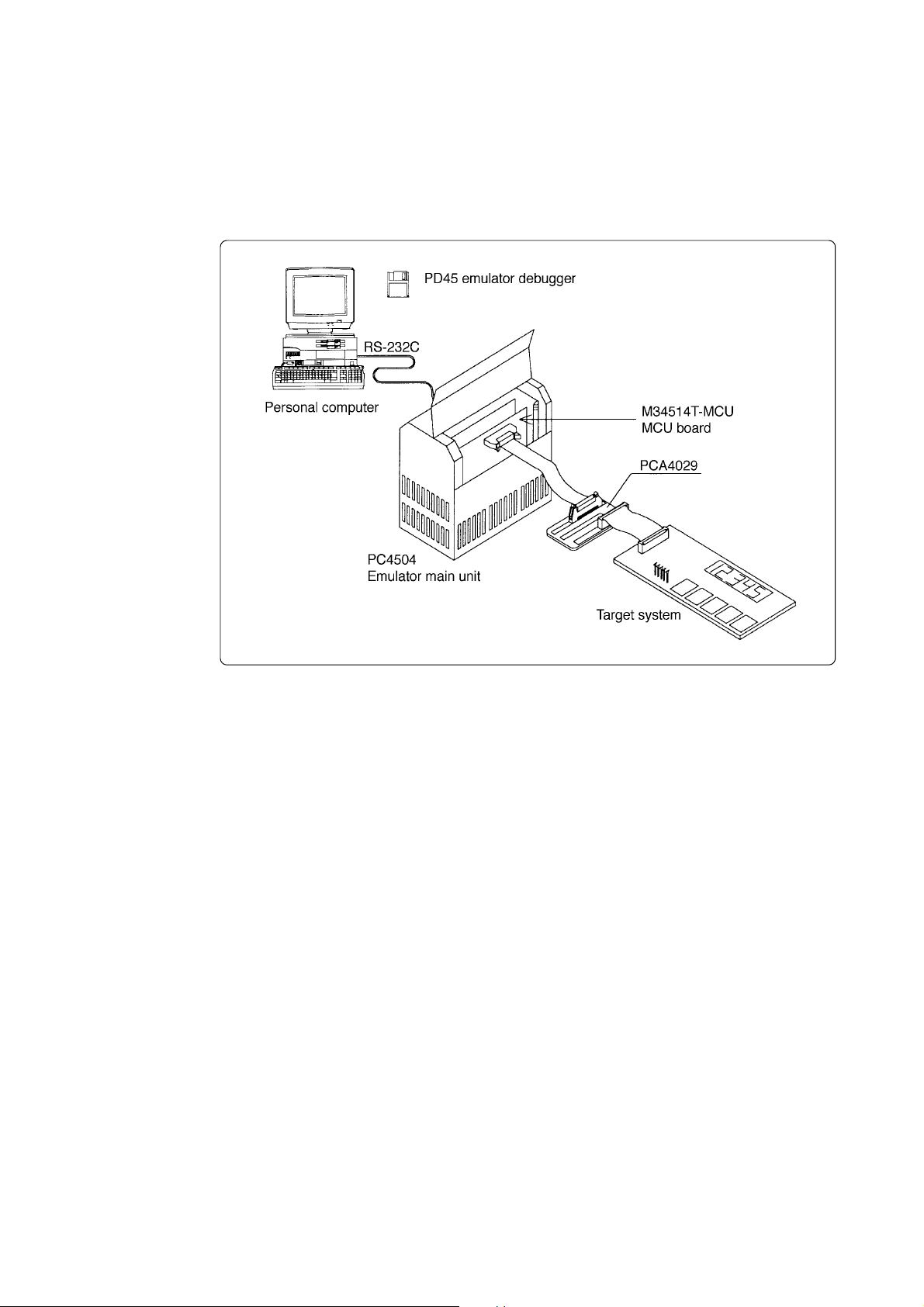
4. M34514T-MCU
4.1 Outline
By using with the PC4504 emulator main unit, M34514T-MCU can make up an emulator system
which can be operated by a personal computer.
Figure 4.1 shows the development support system configuration for 4514 Group MCUs.
Figure 4.1 Development support system configuration for 4514 Group MCUs
( 13 / 42 )
Page 14

Figure 4.2 shows the development support system configuration for 4513 Group MCUs.
Figure 4.2 Development support system configuration for 4513 Group MCUs
*1 Use the M34513T-PTCA pitch converter board for 32SDIP.
*2 Use the M34513T-PTCA, M34513T-PTCB and M34513T-PTCC pitch converter boards for
32LQFP.
For more details, refer to "4.5 Connection to the Target System".
( 14 / 42 )
Page 15

4.2 Specifications
Table 4.1 lists specifications of M34514T-MCU.
Table 4.1 M34514T-MCU Specifications
Applicable MCUs
Evaluation MCU
Maximum operating
clock frequency
Target system voltage
Power supply
Port emulation
M34513MX-XXXFP/SP, M34513EX-XXXFP/SP
M34514MX-XXXFP, M34514E8-XXXFP
M34514E8FP (mounted)
1
3 V
5 V
3 V or 5 V
Supplied by the PC4504's internal power supply (+5 V, +12 V)
Port
D0 to D5
P00 to P03
P10 to P13
P21/SOUT
P22/SIN
Medium-speed mode*
High-speed mode: 2.0 MHz
Medium-speed mode*1: 4.2 MHz
High-speed mode: 4.2 MHz
Output type
N-channel
open drain
-
: 4.2 MHz
Direction
Input/output
Input
Device used
Input: 74HC4050
Output: 74LS06
Input/Output: 74HC4066
Input: 74HC4050
Board dimensions
Operating temperature
Product configuration
233 (L) x 135 (W) x 26 (H) mm
5 to 35°C (non-condensing)
M34514T-MCU
100-wire half-pitch cable
50-wire normal-pitch cable
External trigger cable
PCA4029
OSC-2 (for changing frequencies) *
M34513T-PTCA
M34513T-PTCB
M34513T-PTCC*
3
2
*1 M34514T-MCU operates at the medium-speed mode (instruction-clock f (XIN)/6) immediately
after a RESET is released.
*2 M34514T-MCU has an oscillator circuit board OSC-2 (for 4.19 MHz) that is incorporated when
shipped from the factory. In addition, it comes with an oscillator circuit board OSC-2, with only
a connector J1 mounted.
*3 M34513T-PTCC consists of M34513T-PTCC and TQPACK.
( 15 / 42 )
Page 16

4.3 Description of Switches
The M34514T-MCU board has eight switches. Figure 4.3 shows the positions of these switches.
Tables 4.2 and 4.3 list the functions of the switches and the preset switch positions that are set before
the MCU board is shipped from the factory.
For the products with the following lot numbers, the position of SW8 is here:
8FS001 - 8FS005, 8GS006 - 8GS020, 8KS021 - 8KS040, 9AS001 - 9AS020,
9CS021 - 9CS060, 9GS061 - 9GS090, 9JS091 - 9JS140
Figure 4.3 Positions of switches
Table 4.2 Functions of switches (1/2)
Switch position
ON
ON
SW1
SW2
Label
OFF
ON
ROMSIZE
Description
Does not connect the VDD of the M34514T-
OFF
MCU to the VDD of the target system.
Connects the VDD of the M34514T-MCU
OFF
to the VDD of the target system.
Set the MCU’s ROM size.
• Set "2" (M2)
• Set "4" (M4)
• Set "6" (M6)
• Set "8" (M8)
Factory-setting
OFF
8
SW3
5 V
3 V
3V
3V
5V
Operates the target MCU at +5 V.
5V
Operates the target MCU at + 3 V.
5V
( 16 / 42 )
Page 17

Table 4.3 Functions of switches (2/2)
Label
OFF
Switch position
ON
Description
Does not connect the pullup resistor 68
kΩ to the ports P00 and P01.
Factory-setting
SW4
SW5
SW6
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
Connects the pullup resistor 68 kΩ to
the ports P0
0 and P01.
Does not connect the pullup resistor 68
kΩ to the ports P0
2 and P03.
Connects the pullup resistor 68 kΩ to
the ports P02 and P03.
Does not connect the pullup resistor 68
kΩ to the ports P10 and P11.
Connects the pullup resistor 68 kΩ to
the ports P10 and P11.
OFF
OFF
OFF
SW7
SW8
OFF
ON
514
513
513
513
OFF
ON
OFF
Does not connect the pullup resistor 68
kΩ to the ports P1
2 and P13.
Connects the pullup resistor 68 kΩ to
the ports P12 and P13.
Operates for 4514 Group.
514
Operates for 4513 Group.
514
OFF
514
( 17 / 42 )
Page 18

4.4 Description of Connectors
The M34514T-MCU board has five connectors. Table 4.4 lists the functions of these connectors.
Figure 4.4 shows the positions of connectors on the MCU board.
Table 4.4 Connectors
Connector
Function
J1
J2
J3
J4
J6
Connects the evaluation MCU bus.
Connects the monitor CPU bus.
Connects the target system. (100-pin)
Connects the external trigger signal. (2-pin)
Connects the oscillator circuit board. (4-pin)
Figure 4.4 Positions of the connectors
( 18 / 42 )
Page 19

(1) Connector J3
Table 4.5 lists the pin assignments of the 100-wire half-pitch connector (J3) for connecting the
PCA4029. And Figure 4.5 shows the connector J3 pin layout.
Table 4.5 Pin assignments of the connector J3
Line A Line B Line C Line D
Pin No.
Signal I/O
Pin No.
Signal I/O
Pin No.
Signal I/O
Pin No.
Signal I/O
1 GND 1 GND 1 EP13 I/O 1 EP12 I/O
2 GND 2 GND 2 ED0 I/O 2 EP11 I/O
3 GND 3 GND 3 ED1 I/O 3 EP10 I/O
4 GND 4 GND 4 ED2 I/O 4 EP03 I/O
5 GND 5 GND 5 ED3 I/O 5 EP02 I/O
6 GND 6 GND 6 ED4 I/O 6 EP01 I/O
7 GND 7 GND 7 ED5 I/O 7 EP00 I/O
8 GND 8 GND 8
9 GND 9 GND 9
D6/CNTR0
D7/CNTR1
I/O 8 P43/AIN7 I/O
I/O 9 P42/AIN6 I/O
10 GND 10 GND 10 P50 I/O 10 P41/AIN5 I/O
11 GND 11 GND 11 P51 I/O 11 P40/AIN4 I/O
12 GND 12 GND 12 P52 I/O 12
13 GND 13 GND 13 P53 I/O 13
14 GND 14 GND 14 P20/SCK I/O 14
15 GND 15 GND 15 P21/SOUT I/O 15
A
IN3
/COM1+
A
IN2
/COM1-
A
IN1
/COM0+
A
IN0
/COM016 GND 16 GND 16 P22/SIN I16P33 I/O
17 GND 17 GND 17 RESET I 17 P32 I/O
18 GND 18 GND 18 CNVSS -18P31/INT1 I/O
19 GND 19 GND 19 XOUT -19P30/INT0 I/O
20 GND 20 GND 20 XIN -20VDCE I
21 GND 21 GND 21 VSS 21 VDD
22 GND 22 GND 22 NC - 22 NC 23 GND 23 GND 23 NC - 23 NC 24 GND 24 GND 24 NC - 24 NC 25 GND 25 GND 25 NC - 25 NC -
I
I
I
I
Note: "I" in the direction column denotes "Input"; "O" denotes "Output"; "I/O" denotes "Input/
output"; "-" denotes "Not connected".
Figure 4.5 Connector J3 pin layout
( 19 / 42 )
Page 20

(2) Connector J4
To use the external trigger signal as event input of trigger breaks or trace points, connect the 2wire external trigger signal cable included with your M34514T-MCU board to the connector J4.
Connect the black clip of the external trigger cable to GND, and use the white clip for external
trigger signal input. Table 4.6 lists the pin assignments of the connector J4.
Table 4.6 Pin assignments of connector J4
Pin No.
Signal
Function
1
2
TRIG
GND
External trigger signal input
GND input
(3) Connector J6
The connector J6 is a connector used to connect an oscillator circuit board OSC-2. Table 4.7 lists
the pin assignments of the connector J6. Figure 4.6 shows the pin layout of the connector J6. For
the 4.19 MHz operation with the oscillator circuit board OSC-2, see Figure 4.7.
Table 4.7 Pin assignments of connector J6
Pin No.
1
2
3
4
Signal
VCC
GND
CLK
GND
Function
Power supply
GND
Clock input
GND
Figure 4.6 Pin layout of connector J6
Figure 4.7 Circuit diagram of OSC-2 oscillator circuit board (4.19 MHz)
( 20 / 42 )
Page 21

4.5 Connection to the Target System
(1) For 4514 Group
When connecting the M34514T-MCU board to the target system:
a. Connecting to 2.54-mm-pitch Dual-in-line Pins on the Target System
Use the 50-wire normal-pitch cable (included) to connect the 50-pin dual-in-line pins on the
target system. Following products are required for connection to the target system.
• 100-wire half-pitch cable (40 cm)
• PCA4029 pitch converter board
• 50-wire normal-pitch cable (10 cm)
Figure 4.8 depicts the M34514T-MCU board connected to the target system using the 50-wire
normal-pitch cable. Table 4.8 lists the connector signal assignments of the 50-wire normal-pitch
cable. Figure 4.9 shows the pin layout of the 50-wire normal-pitch cable.
Figure 4.8 Connection to the target system using dual-in-line pins
( 21 / 42 )
Page 22

Table 4.8 50-wire normal-pitch cable pin assignments
50-wire normal-pitch cable
Pin No.
1 EP13 50 EP12
2ED0 49 EP11
3ED1 48 EP10
4ED2 47 EP03
5ED3 46 EP02
6ED4 45 EP01
7ED5 44 EP00
8D6/CNTR0 43 P43/AIN7
9D7/CNTR1 42 P42/AIN6
10 P50 41 P41/AIN5
11 P51 40 P40/AIN4
12 P52 39 AIN3/COM1+
13 P53 38 AIN2/COM114 P20/SCK 37 AIN1/COM0+
15 P21/SOUT 36 AIN0/COM016 P22/SIN 35 P33
17 RESET 34 P32
18 NC (CNVSS)33 P31/INT1
19 NC (XOUT)32P30/INT0
20 NC (XIN)31 VDCE
21 VSS 30 VDD
22 NC 29 NC
23 NC 28 NC
24 NC 27 NC
25 NC 26 NC
Signal
Pin No.
Signal
Figure 4.9 Pin layout of 50-wire normal-pitch cable
( 22 / 42 )
Page 23

(2) For 4513 Group
When connecting the M34514T-MCU board to the target system (for 4513 Group):
a. Connecting to the IC socket for 32-pin SDIP on the Target System
Connect the M34514T-MCU board with the IC socket for 32-pin SDIP on the target system
using the 50-wire normal-pitch cable (included) with the M34513T-PTCA pitch converter
board attached. Figure 4.10 depicts the connection between the M34513T-PTCA pitch converter board and the target system. Following products are required for connection to the target
system.
• 100-wire half-pitch cable (40 cm)
• PCA4029 pitch converter board
• 50-wire normal-pitch cable (10 cm)
•M34513T-PTCA pitch converter board
Table 4.9 shows the connector signal assignments of the M34513T-PTCA pitch converter
board. The pin assignments of M34513T-PTCA is the same as for the 32SDIP in 4513 Group.
When connecting the M34513T-PTCA pitch converter board, make sure the No. 1 pin position
of each connector is aligned with that of cable. To avoid damage to the emulator and target
system, be careful of the connection.
Figure 4.10 Connecting to IC socket for 32-pin SDIP
( 23 / 42 )
Page 24

Table 4.9 M34513T-PTCA pin assignments
M34513T-PTCA J2
Pin No.
1ED0 32 EP13
2ED1 31 EP12
3ED2 30 EP11
4ED3 29 EP10
5ED4 28 EP03
6ED5 27 EP02
7D6/CNTR0 26 EP01
8D7/CNTR1 25 EP00
9P20/SCK 24 AIN3/COM1+
10 P21/SOUT 23 AIN2/COM111 P22/SIN 22 AIN1/COM0+
12 RESET 21 AIN0/COM013 CNVSS 20 P31/INT1
14 XOUT 19 P30/INT0
15 XIN 18 VDCE
16 V
Signal
SS 17 VDD
Pin No.
Signal
( 24 / 42 )
Page 25

b. When Connecting to a 32-pin LQFP Foot Pattern on the Target System
Attach the pitch converter boards M34513T-PTCA and M34513T-PTCB to the 50-pin normalpitch cable (included with this product). Then connect the cable via the M34513T-PTCC to the
TQPACK032SA that has been soldered to the 32-pin LQFP foot pattern on the target system.
Figure 4.11 shows an example of how to connect to the target system using the M34513T-PTCA,
M34513T-PTCB, and M34513T-PTCC. Following products are required for connection to the
target system:
• 100-wire half-pitch cable (40 cm)
• PCA4029 pitch converter board
• 50-wire normal-pitch cable (10 cm)
• M34513T-PTCA pitch converter board
• M34513T-PTCB pitch converter board
• M34513T-PTCC pitch converter board (TQPACK* included)
* TQPACK consists of TQSOCKET032AF, TQSOCKET032SAP and TQPACK032SA.
Table 4.10 shows the connector signal assignments of the TQPACK032SA. When the
TQPACK032SA and M34513T-PTCC are used for target system connection, the pin assignments are the same as for the 32LQFP in 4513 Group.
Solder the TQPACK032SA to the 32-pin LQFP foot pattern on the target system. The No. 1 pin
of the TQPACK032SA is located at its corner-cut part of package. Attach the M34513T-PTCC
to the TQPACK032SA with its No. 1 pin position (marked by a white dot) aligned with that of
the TQPACK032SA. After attaching the pitch converter boards M34513T-PTCA and M34513TPTCB to the 50-pin normal-pitch cable, connect the cable to the M34513T-PTCC. To avoid
damage to the emulator and target system, be careful of the connection.
When connecting cable and attaching the pitch converter boards, make sure the No. 1 pin
position of each connector is aligned with that of cable. Figure 4.12 shows the external view of
the TQPACK032SA and M34513T-PTCC.
Figure 4.11 Connecting to 32-pin LQFP foot pattern on target system
( 25 / 42 )
Page 26

Table 4.10 TQPACK032SA pin assignments
TQPACK pin No.
Pin No.
1ED3 32 ED2
2ED4 31 ED1
3ED5 30 ED0
4D6/CNTR0 29 EP13
5D7/CNTR1 28 EP12
6P20/SCK 27 EP11
7P21/SOUT 26 EP10
8P22/SIN 25 EP03
9 RESET 24 EP02
10 CNVSS 23 EP01
11 XOUT 22 EP00
12 XIN 21 AIN3/COM1+
13 VSS 20 AIN2/COM114 VDD 19 AIN1/COM0+
15 VDCE 18 AIN0/COM016 P3
Signal
0/INT0 17 P31/INT1
Pin No.
Signal
Figure 4.12 External view of TQPACK032SA and M34513T-PTCC
( 26 / 42 )
Page 27

Some signals connected to the target system are emulated on the M34514T-MCU board. For
details, see "Chapter 6. Connection Circuit Diagram".
(1) Pins connected directly to the target system (8 types, 21 lines)
•P30 to P33
•P40 to P43
•P50 to P53
*1
*1
*1
•P20
•D6, D7
•AIN0 to AIN3
• VDCE
•VSS
*1 For 4513 Group MCUs, the ports P32, P33, P40 to P43 and P50 to P53 can not be connected to
the target system.
(2) Pins connected to the target system via emulation circuits etc. (6 types, 18 lines)
•P00 to P03
•P10 to P13
•P21 to P22
•D0 to D5
• RESET*
•VDD
(3) Pins not connected to the target system (3 types, 3 lines)
4.6 LED
•XIN
•XOUT
• CNVSS
Figure 4.13 shows the LED layout of M34514T-MCU. The LED lights in green when the power is
supplied to the MCU board.
Figure 4.13 Layout of LED
( 27 / 42 )
Page 28

MEMO
( 28 / 42 )
Page 29

5. Precautions to Be Taken When Debugging
5.1 Reset
The M34514T-MCU uses a 74AC14 for its RESET signal input buffer, so that its electrical
characteristics differ from those of the actual chip. Table 5.1 lists the RESET signal input
characteristics of the M34514T-MCU.
Table 5.1 RESET signal input characteristics
H-level threshold voltage
L-level threshold voltage
5.2 System Clock
Depending on the supply voltage and operation mode, use one of the following frequencies for the
system clock:
• Supply voltage 5 V: 4.2 MHz or less (medium-speed/high-speed mode)
• Supply voltage 3 V: 4.2 MHz or less (medium-speed mode), 2.0 MHz or less (high-speed mode)
Item Symbol
Hysteresis voltage
V
VN
VH
P
Voltage
VCC = 3.0 V
VCC = 4.5 V
VCC = 5.5 V
VCC = 3.0 V
VCC = 4.5 V
VCC = 5.5 V
VCC = 3.0 V
VCC = 4.5 V
VCC = 5.5 V
Minimum
-
-
-
0.5 V
0.9 V
1.1 V
0.3 V
0.4 V
0.5 V
Maximum
2.2 V
3.2 V
3.9 V
-
-
-
1.2 V
1.4 V
1.6 V
To change this clock frequency to suit that of the target system, attach the necessary parts to the
oscillator circuit board OSC-2 that are included with the M34514T-MCU package.
For details about the oscillation circuit constant, consult your oscillator manufacturer.
5.3 Real-time Capability of Timer
The PC4504 and M34514T-MCU have their internal clock operating even during emulation, so that
the timer values keep changing.
Example: (1) When single-stepping the program
(2) When registers or internal RAM are referenced or modified
( 29 / 42 )
Page 30

5.4 Watchdog Timer
The M34514T-MCU does not have an operational watchdog timer. Therefore, use an evaluation
MCU (OTP version) to verify the operation associated with a watchdog timer.
The M34514T-MCU outputs a signal whose waveform is shown below from the check pin TP5
during WRST instruction execution cycles. This signal allows you to check the initialization cycle
of a watchdog timer.
System clock
XIN
WRST
Figure 5.1 Waveform output from check pin TP5
5.5 Pullup Transistor Control
Since ports P0 and P1 contain emulation circuits, you can not control the pullup resistors using the
pullup control register PU0. If you want to use the internal pullup resistors, turn on switches SW4 to
SW7 to activate the pullup resistors on the M34514T-MCU board.
The port's resistance value of the pullup resistor (RA1) is 68 kΩ.
WRST instruction
Next WRST instruction
( 30 / 42 )
Page 31

5.6 Port I/O Timing
(1) Port input timing
(2) Port output timing
Port input timings are the same as with the actual MCUs.
When using the M34514T-MCU, output timings are different from those of the actual MCUs for
the following ports that are configured with port emulation circuits:
• Ports P00 to P03
• Ports P10 to P13
• Ports D0 to D5
With the actual MCUs, changes occur at the beginning of the T3 state of an output instruction.
With the M34514T-MCU, changes occur at the beginning of the T2 state of the next output
instruction. Figure 5.2 shows the port output timings of the actual MCUs and M34514T-MCU.
For the other ports, the output timings are the same as with the actual MCUs.
Next output instructionOutput instruction
System clock
X
IN
P0, P1, D port
output timings
on actual MCUs
P0, P1, D port
output timings of
M34514T-MCU
Figure 5.2 P0, P1 and D port output timings
( 31 / 42 )
Page 32

5.7 Port I/O Characteristics
With the M34514T-MCU, port I/O characteristics are different from actual MCUs because there is
an emulation circuit in ports P0, P1, P2 and D0 to D5. Table 5.2 lists port I/O characteristics of the
M34514T-MCU.
Table 5.2 Emulation port I/O characteristics
Port
Input 74HC4050
P0, P1
Output
P2
5 to D0
D
Input/
output
Input
Output
Device Item Voltage
IH
VCC = 2.0 V
V
CC = 4.5 V
VCC = 2.0 V
V
CC = 4.5 V
V
VIL
IOH
IOL
V
74LS06
CC = 4.75 V
VOL
CC = 2.0 V
V
RON
V
CC = 4.5 V
74HC4066
RON
VIH
74HC4050
VIL
CC = 4.5 V
V
V
CC = 2.0 V
VCC = 4.5 V
V
CC = 2.0 V
VCC = 4.5 V
IOH
74LS06
IOL
V
CC = 4.75 V
VOL
Min.
1.5 V
3.15 V
-
-
-
-
-
-
160 Ω
70 Ω
96 Ω
10 Ω
1.5 V
3.15 V
-
-
-
-
-
-
Max.
-
-
0.5 V
1.35 V
250 µA
40 mA
0.4 V
0.7 V
-
130 Ω
200 Ω
-
-
-
0.5 V
1.35 V
250 µA
40 mA
0.4 V
0.7 V
Remarks
V
OH = MAX
I
OL = 16 mA
I
OL = MAX
VI/O = VCC to GND
I
I/O ≤ 1 mA
VI/O = VCC or GND
I
I/O ≤ 1 mA
VI/O = VCC to GND
I
I/O ≤ 1 mA
OH = MAX
V
I
OL = 16 mA
I
OL = MAX
( 32 / 42 )
Page 33

5.8 Power-down Mode
In the power-down mode, the M34514T-MCU operates differently from the actual chip of each
MCU.
(1) Power-down operation of M34514T-MCU
Although the actual chip of each MCU is placed in the power-down mode by executing a
combination of EPOF and POF instructions, the M34514T-MCU is placed in the power-down
mode by only the POF instruction.
In the M34514T-MCU, the EPOF instruction does not have any effect.
Program example 5.1
RC
INY
EPOF
POF
•
•
Program example 5.2
RC
INY
POF
•
•
•
Actual MCU
The power-down mode works.
M34514T-MCU
The power-down mode works.
Actual MCU
The power-down mode does NOT work.
M34514T-MCU
The power-down mode works.
( 33 / 42 )
Page 34

5.9 Program Execution (G, GB)
The PC4504 and M34514T-MCU’s hardware are subject to the following restrictions with respect
to the operation of the program execution commands (G and GB).
(1) Continuous description of instructions
Hardware breakpoints set in a continuous description of instructions following one after another
do not cause a break to occur in the continuous description of instructions. A break occurs only
after fetching the address where the continuous description of instructions is discontinued. (See
Program example 5.3)
However, a break does occur even in a continuous description of instructions when an external
trigger break or forced break is encountered. For execution to be resumed in this case, you need
to make sure that the execution start address is next to the continuous description of instructions.
(See Program example 5.4)
Program example 5.3
POINT: LA 1 ; Continuous description of instructions
POINT+2: XAM 3
If a break is set at POINT, execution is halted immediately before the XAM instruction at
address POINT+2.
LA 0
LA 2
Program example 5.4
LA 0
POINT: LA 1 ; Continuous description of instructions
POINT+1: LA 2
POINT+2: XAM 3
If a forced or external trigger break is applied at POINT, execution is halted at POINT +1.
When resuming program execution after the break, make sure that the start address is at
POINT+2, an address immediately after the continuous description of instructions is
discontinued.
( 34 / 42 )
Page 35

(2) Skip instructions (e.g. SNZP, INY, DEY, SZB, SEAM, SZC and RTS)
When a skip instruction skips the next instruction, a breakpoint set in the skipped instruction does
not cause execution to halt. (See Program examples 5.5 and 5.6)
Program example 5.5
RC SC
SZC SZC
POINT: TABP POINT: TABP
POINTA: TAM 0 POINTA: TAM 0
• •
• •
A breakpoint set at address POINT causes execution to halt immediately before address
POINTA in only the case of the instruction shown on the right side.
Program example 5.6
RC ; Skip instructions
INY
POINT: TABP
LA 0
•
•
If a break with pass count is set at address POINT, the count is taken and execution is
halted only when the instruction at address POINT is executed.
( 35 / 42 )
Page 36

5.10 External Trigger Signal
(1) External trigger signal input timing
The latch timing of the external trigger signal is shown in Figure 5.3.
Instruction
System clock
XIN
External trigger signal
TRIG
Next Instruction
Figure 5.3 Latch timing of external trigger signal
(2) External trigger signal input characteristics
Trigger breaks work according to the condition (leading edge/trailing edge) of signals input from
the external trace cable. The external trigger signals of the trace points and the external trigger
signals of the break points use the same signals. The input characteristics of the external trigger
signals are shown in Table 5.3 below. See the table before using external trigger signals.
Table 5.3 External trigger signal input characteristics
Item
H-level input voltage
L-level input voltage
Symbol
VIH
VIL
Voltage Maximum
VCC = 2.0 V
V
CC = 4.5 V
VCC = 2.0 V
CC = 4.5 V
V
-
-
0.5 V
1.35 V
Minimum
1.5 V
3.15 V
-
-
( 36 / 42 )
Page 37

6. Connection Circuit Diagram
Figure 6.1 shows the connection circuit diagram of M34514T-MCU. This circuit diagram depicts the
M34514T-MCU connection centering on circuits connected to the target system. Emulator control
blocks and other similar circuits that are not connected to the target system are omitted in this diagram.
denotes control signal
Figure 6.1 Connection circuit diagram
( 37 / 42 )
Page 38

MEMO
( 38 / 42 )
Page 39

7. Pitch Converter Board External Dimensions
7.1 M34513T-PTCA
Figure 7.1 M34513T-PTCA external dimensions
7.2 M34513T-PTCB
Figure 7.2 M34513T-PTCB external dimensions
7.3 M34513T-PTCC
Figure 7.3 M34513T-PTCC external dimensions
( 39 / 42 )
Page 40

Appendix A. How to Request for Repair
If your product is found faulty, follow the procedure below to send your product for repair.
Customer Fill in the Repair Request Sheet included with this product, then send it
along with this product for repair to your local distributor. Make sure
that information in the Repair Request Sheet is written in as much detail
as possible to facilitate repair.
Distributor After checking the contents of fault, the distributor should please send
the faulty product along with the Repair Request Sheet to Renesas
Solutions Corp.
Renesas Solutions When the faulty product is repaired, it will be returned to the customer
at the earliest convenience.
CAUTION
Note on Transporting the Product:
•When sending your product for repair, use the packing box and cushion material supplied with this
product when delivered to you and specify handling caution for it to be handled as precision
equipment. If packing of your product is not complete, it may be damaged during transportation.
When you pack your product in a bag, make sure to use conductive polyvinyl supplied with this
product (usually a blue bag). When you use other bags, they may cause a trouble on your product
because of static electricity.
( 40 / 42 )
Page 41

M34514T-MCU User's Manual
Rev.1.00
September 1, 2003
REJ10J0274-0100Z
COPYRIGHT ©2003 RENESAS TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
AND RENESAS SOLUTIONS CORPORATION ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Page 42

 Loading...
Loading...