Remote Automation Solutions Guide: OpenEnterprise Calculation Server Reference Guide Manuals & Guides
Page 1

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010
OE Version: 2.82
Calculation Serve
Bristol OpenEnterprise Reference Guide
Calculation Server
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 2

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 2
Calculation Serve
Contents
1 Calculation Server...................................................................................................................5
1.1 Calculation Server Overview...............................................................................................5
1.2 Calculation Components Diagram ......................................................................................5
1.2.1 Calculation Components Diagram................................................................................ 5
1.2.2 The Database...............................................................................................................5
1.2.3 The Scheduler..............................................................................................................6
1.2.4 The Calculation Server.................................................................................................6
1.2.5 Calculation Interface.....................................................................................................6
1.2.5.1 Properties...............................................................................................................6
1.2.5.2 Methods .................................................................................................................6
1.2.6 The Calculations...........................................................................................................7
1.2.7 The OESyncAccessMDI...............................................................................................7
1.2.7.1 OESynchAccess Interface .....................................................................................7
1.2.7.1.1 Properties.........................................................................................................7
1.2.7.1.2 Methods............................................................................................................8
1.2.7.1.3 Read method parameter lists........................................................................... 8
1.2.7.1.4 Write methods parameter lists..........................................................................8
1.2.8 ODBC ...........................................................................................................................9
1.2.9 The OECalculationUtils Class Library ..........................................................................9
1.2.9.1 OECalculationUtils Classes ...................................................................................9
1.2.9.1.1 AttributeObject class.........................................................................................9
1.2.9.1.1.1 Properties...................................................................................................9
1.2.9.1.1.2 Methods......................................................................................................9
1.2.9.1.2 Utilities class...................................................................................................10
1.2.9.1.2.1 Properties.................................................................................................10
1.2.9.1.2.2 Methods....................................................................................................10
1.3 Starting the Calculation Components ...............................................................................10
1.3.1 Starting the Calculation Server...................................................................................10
1.3.1.1 Program Arguments.............................................................................................10
1.3.1.1.1 DataService....................................................................................................10
1.3.1.1.2 ServerID..........................................................................................................10
1.3.2 Starting the Calculation Server...................................................................................11
1.3.2.1 Program Arguments.............................................................................................11
1.3.2.1.1 DataService....................................................................................................11
1.3.2.1.2 ServerID..........................................................................................................11
1.3.3 Starting the OESyncAccessMDI.................................................................................11
1.4 Configuring a Calculation..................................................................................................12
1.4.1 Configuring a Calculation ...........................................................................................12
1.4.2 Temporarily Stopping a Calculation ...........................................................................12
1.4.3 Monitoring the Status of a Calculation........................................................................12
1.4.4 Specifying Calculation Arguments..............................................................................12
1.4.4.1 ActiveX DLL .........................................................................................................12
1.4.4.1.1 Executable......................................................................................................13
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 3

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 3
Running a Calculation ................................................................................................13
1.4.5
1.4.5.1 Diary.....................................................................................................................13
1.4.5.2 Attribute Trigger ...................................................................................................13
1.4.5.3 Manually...............................................................................................................14
1.4.6 Executing a Calculation When an Alarm Occurs........................................................14
1.4.7 Configuring Calculation Cascades.............................................................................15
1.4.8 Status Codes..............................................................................................................15
1.4.9 Calculation DLLs ........................................................................................................16
1.4.9.1 Writing a Calculation............................................................................................16
1.4.9.2 DLL Example Code..............................................................................................16
1.5 Generating Calculation Alarms .........................................................................................18
1.5.1.1.1.1 Control Alarms..........................................................................................19
1.5.1.1.1.2 Monitor Alarms.........................................................................................19
2 Index .......................................................................................................................................20
Calculation Serve
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 4

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 4
Calculation Serve
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 5
Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 5
Calculation Serve
1 Calculation Server
1.1 Calculation Server Overview
The OpenEnterprise Calculation Server executes calculations and runs applications (executables and
Windows command files). Calculations can be run on a timed basis, at user request and follo wing a
signal value change. Calculations can also be chained together to form a squence of calcul ations.
Its main use is to run programmable calculations to be performed on data from the OpenEnterprise
Server Database. The Server Side Calculation DLL, provided with OpenEnterprise should be
sufficient for most calculation requirements.
However, user defined calculations can be written in any language that can access the Calculation
Server's Calculation and OECalculationUtils interfaces, such as Visual C++ or Visual BASIC.
1.2 Calculation Components Diagram
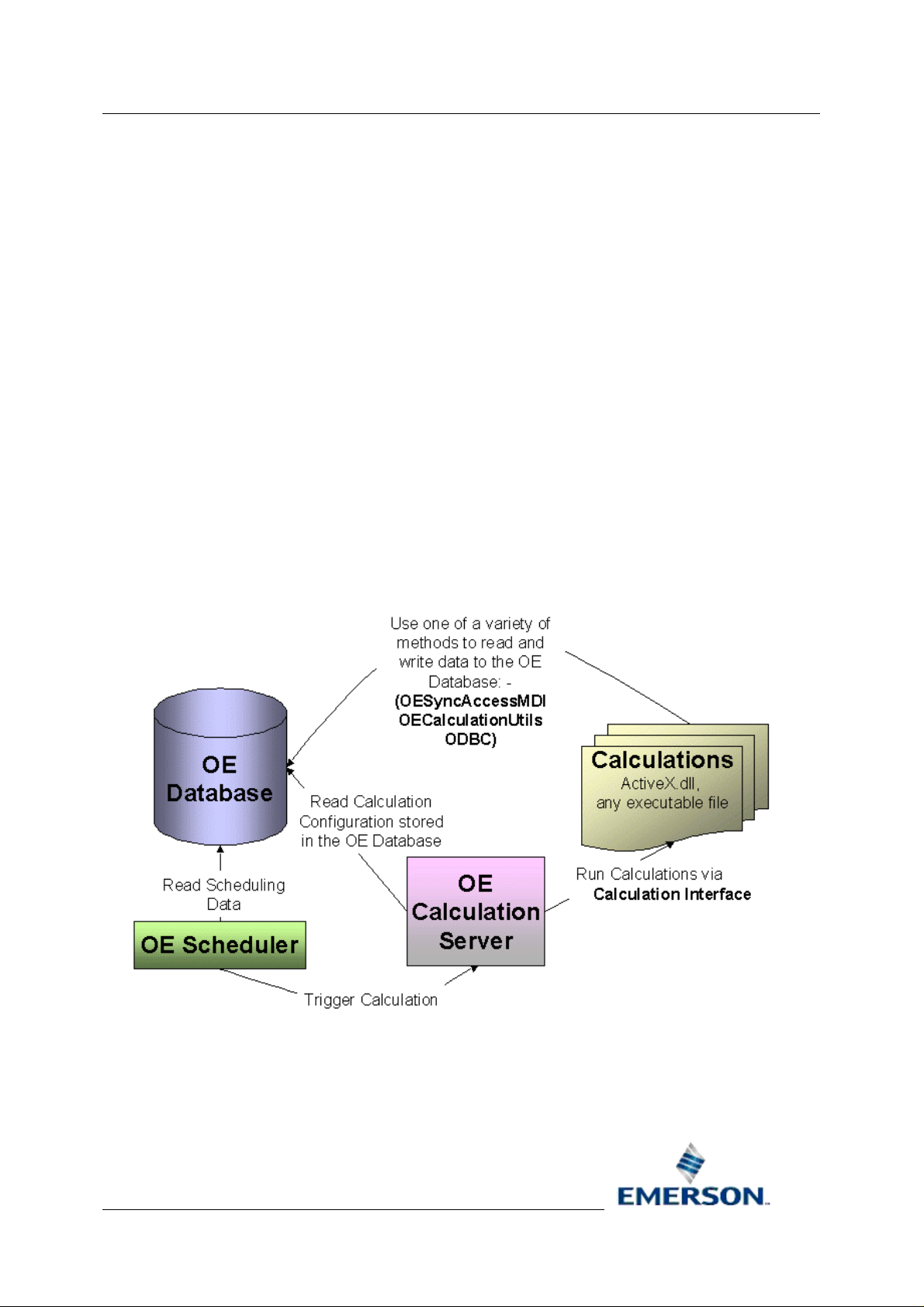
1.2.1 Calculation Components Diagram
This is a diagram of how diary triggered calculations are managed within OpenEnterprise. The
Scheduler notifies the Calculation server that it is time to run a calculation. The Calculation server
runs the DLL specified for the calculation, which reads and/or writes the necessary values to the
Database.
1.2.2 The Database
Calculations can access the data in the database and update values according to the algorith ms
employed by the calculation program and user provided 'arguments'.
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 6

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 6
The database stores calculation configuration details in the Calculation table. The Calculation table
contains the name of each calculation, the time when the calculation will run, whether it should use a
diary or attribute triggers, and any optional command line parameters that will be passed to the
calculation.
The calculations are scheduled (triggered) by the Scheduler or internally by the database if using
attribute triggers.
It is the Calculation Server that actually runs the calculations.
Calculation Serve
1.2.3 The Scheduler
The OpenEnterprise Scheduler is the component that is used to trigger calculations based on a diary.
When the diary time is due, the Scheduler sets the 'due' attribute of the calculation that is using the
diary to 'True', which activates the Calculation Server to run the calculation.
1.2.4 The Calculation Server
The Calculation Server is a component that is used to run calculations. It sources all of its
configuration data from the Database's Calculation table. The Calculation table's 'Calculate' attribute
is monitored to determine when to run a calculation. The Calculation Server itself performs no
calculation scheduling.
The Calculation Server uses the Server Security component to logon to the database.
1.2.5 Calculation Interface
The Calculation interface is defined by the Calculation Server for the use of ActiveX DLL calculations.
The ActiveX DLL will implement the Calculation interface. When browsing with Visual Basic this
interface will be seen as 'CalculationServer.Calculation'.
The interface simply consists of a single method, Execute. The Visual BASIC calculation will
implement the Execute method by placing the calculation specific code within the body of the Execute
method. Note that the Execute method must be implemented as a synchronous method. Once the
Execute method returns, the Calculation Server will deem the calculation as complete.
1.2.5.1 Properties
There are
1.2.5.2 Methods
The Execute
long Execute(
VARIANT FAR* Arg1,
VARIANT FAR* Arg2,
currently no properties declared.
method is defined as follows.
VARIANT FAR* Arg3)
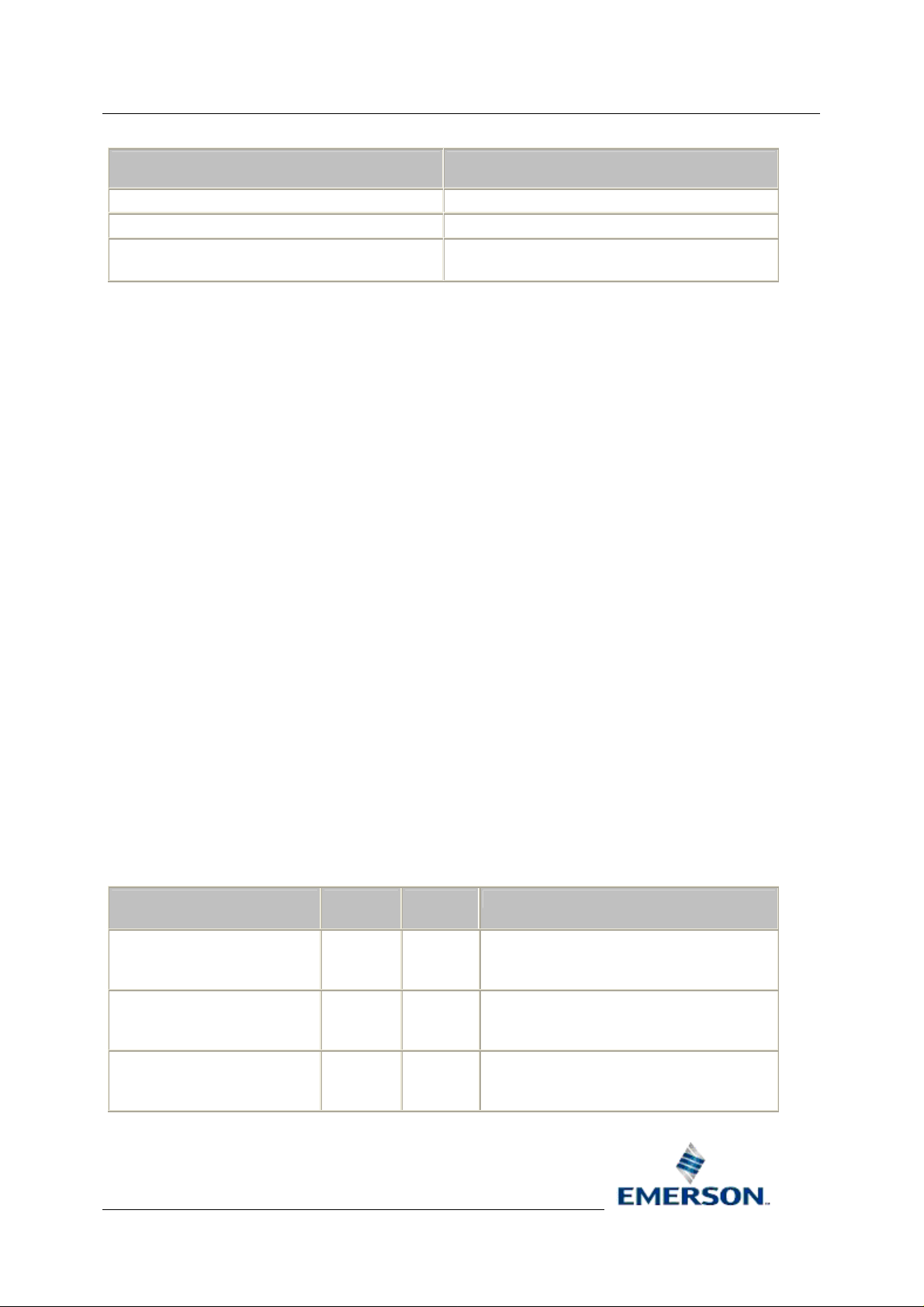
The return value for the Execute function should indicate the status of the calculation. The following
rules should be used when returning a status code.
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 7
Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 7
Status Code Description
> 0 Application (calculation) specific error code.
0 Success
< 0 Internal error and status codes. Calculations
should not return a value less than zero.
Calculation Components Diagram
Calculation Serve
1.2.6 The Calculations
The OpenEnterprise Server Side Calculation DLL, which comes with the product is sophisticated
enough for most calculation needs. It also enables the user to specify Calculation arguments by
using the 'calculator' like Editor, which is part of the Calculation Configuration tool.
Those wishing to create their own calculations, should write them as ActiveX DLLs in Visual C++ or
Visual BASIC implementing the Calculation interface. A calculation may be set up to use the
OECalculationUtils or ODBC to interface with the database.
The Calculation Server will actually run any executable application. It can be used to run anything
(with the exception of an NT Service). For example, if the user wishes to run Microsoft® Excel to
generate and print a report on a scheduled basis then the Calculation Server will run Excel as the
target.
Of course, in order for the Server to find the executables, especially if they are DLLs, they must be
registered on the Server.
1.2.7 The OESyncAccessMDI
The OESynchAccessMDI is a component that runs on the OpenEnterprise Server and provides
methods to read and write to an OpenEnterprise database in a synchronous manner. When browsing
with Visual BASIC this interface will be seen as 'OpenEnterprise Synchronous database access'. As
an alternative to this interface, the OECalculationUtils interface can be used instead. Note that
OESynchAccessMDI uses the Server Security component to logon to the database.
1.2.7.1 OESynchAccess Interface
The OESynchAccess inte
1.2.7.1.1 Properties
Name Direction Data
DefaultTimeout [in] short The default timeout, specified in seconds,
DefaultNameIdentifier [in] BSTR Specifies the default name used to identify
DefaultNameIdentifierType [in] BSTR The data type of the
rface provides the following properties and methods .
Explanation
Type
applied to all synchronous database reads
and writes. Default 45 seconds.
a signal object within the database.
Default value is 'name'.
DefaultNameIdentifier. Default value is
'string'
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 8

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 8
DefaultDataService [in] BSTR The default database data service for all
database read and write requests. This by
default is 'rtrdb1'.
1.2.7.1.2 Methods
Method Name Return Value Type Table Read from / Written to
ReadInteger(parameter list) long IntegerAnalog table
WriteInteger(parameter list) long IntegerAnalog table
ReadAnalog(parameter list) long RealAnalog table
WriteAnalog(parameter list) long RealAnalog table
ReadDigital(parameter list) long Digital table
WriteDigital(parameter list) long Digital table
ReadTime(parameter list) long Time table
WriteTime(parameter list) long Time table
ReadString(parameter list) long StringSignal table
WriteString(parameter list) long StringSignal table
Calculation Serve
These functions are used to read from and write values to the database. All the Read and Write calls
act, by default, on the corresponding signal tables. For example, the ReadInteger will default to
reading the readvalue from the IntegerAnalog table. A limitation of the calls is that they only support
objects that can be identified by a single attribute primary key. Composite primary keys are not
supported. Also, a single Read or Write will act on a single attribute only. In other words, a call to
ReadInteger can only retrieve the value of a single column.
1.2.7.1.3 Read method parameter lists
<> denotes optional attributes:
[in] LPCTSTR name,
[out] <base data type> FAR* value,
<[in] const VARIANT FAR& dataService = 'rtrdb1',>
<[in] const VARIANT FAR& tableName = 'signal table name',>
<[in] const VARIANT FAR& attributeName = 'readvalue',>
<[in] const VARIANT FAR& objectAttributeName = 'name',>
<[in] const VARIANT FAR& objectAttributeType = 'string'>
1.2.7.1.4 Write methods parameter lists.
Note: <> den
otes optional attributes
[in] LPCTSTR name,
[in] <base data type> value,
<[in] const VARIANT FAR& dataService = 'rtrdb1',>
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 9

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 9
<[in] const VARIANT FAR& tableName = 'signal table name',>
<[in] const VARIANT FAR& attributeName = 'readvalue',>
<[in] const VARIANT FAR& objectAttributeName = 'name',>
<[in] const VARIANT FAR& objectAttributeType = 'string'>
Note that all the optional parameters, whilst they are all string attributes, are declared as VARIANTS
within an automation interface. This allows the value VT_ERROR to be passed as the value,
indicating the value has not been supplied by the call.
Calculation Components Diagram
Calculation Serve
1.2.8 ODBC
ODBC is the industry standard method of reading and writing data to remote data sources. It is also
one of the ways to interact with the Server database when writing a calculation using VB.
1.2.9 The OECalculationUtils Class Library
The OECalculationUtils Class Library provides an object based method of synchronously reading and
writing data to an OpenEnterprise database. When browsing Objects within Visual BASIC this
interface will be seen as 'OpenEnterprise Calculation Utilities'.
The OECalculationUtils Class Library uses the IOESynchAccess interface but wraps the interface into
an object- oriented design. The user can create attribute objects that can be used to query and
update the database multiple times.
1.2.9.1 OECalculationUtils Classes
Two mai
1.2.9.1.1 AttributeObject class
Obje
specific object. Thereafter it can be used to query and update that object's attribute value.
1.2.9.1.1.1 Properties
1. dataservice As Variant - data service of the database
2. tableName As Variant
3. attributeName As Variant
4. objectName As Variant
5. attributeType As OEDataTypes
6. ObjectIDName As Variant
7. ObjectIDType As OEDataTypes
8. Value As Variant - value last read or written
1.2.9.1.1.2 Methods
1. Initialise(
n classes are provided: AttributeObject and Utilities.
cts of the AttributeObject class can be created and initialized to reference a specific attribute of a
name As String, _
Optional tableName As String = "integeranalog", _
Optional attributeName As String = "value", _
Optional attributeType As OEDataTypes = OEReal, _
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 10

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 10
Optional objectName As String = "name", _
Optional objectType As OEDataTypes = OEString, _
Optional dataservice As String = "rtrdb1")
2. ReadValue() As Long
3. WriteValue() As Long
1.2.9.1.2 Utilities class
Calculation Serve
The Utility cla
1.2.9.1.2.1 Properties
1. DefaultDataService(ByVal vNewValue As Variant)
2. DefaultTimeout(ByVal vNewValue As Variant)
1.2.9.1.2.2 Methods
Sleep(seconds As Long) As Long
Cal
culation Components Diagram
ss object provides the following utility properties and methods.
1.3 Starting the Calculation Components
1.3.1 Starting the Calculation Server
If calculations are going to be used, the Calculation Server should be started by the Session Manager
as part of an OpenEnterprise Server Session. To edit the Calculation Server task, select it from the
task list in the Session Manager's interface. Then select the Stop option from the context menu. When
the task has stopped select the Properties option from the same context menu. This will open the
Task Properties dialog.
On the Task page of this dialog, the following command line options should be provided in the
'Program Arguments' field.
1.3.1.1 Program Arguments
[/DataService=<dataservice>] [/ServerID=<serverid>] Whe
OESyncAccessMDI
E.g: CalculationServer /DataService=oeserv1:rtrdb1,oeserv2:rtrdb1
1.3.1.1.1 DataService
This optio
configuration. If it is not present, then the Calculation Server will not connect to any dataservice.
1.3.1.1.2 ServerID
Optional p
Servers from the same Calculation table (database). E.g. ServerID=HOSTA.
n is mandatory. It specifies the data service of the database that holds the calculation
arameter. Specifies the ID of the Calculation Server when supporting multiple Calculation
re:Starting the
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 11

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 11
Calculation Serve
1.3.2 Starting the Calculation Server
If calculations are going to be used, the Calculation Server should be started by the Session Manager
as part of an OpenEnterprise Server Session. To edit the Calculation Server task, select it from the
task list in the Session Manager's interface. Then select the Stop option from the context menu. When
the task has stopped select the Properties option from the same context menu. This will open the
Task Properties dialog.
On the Task page of this dialog, the following command line options should be provided in the
'Program Arguments' field.
1.3.2.1 Program Arguments
[/DataService=<dataservice>] [/ServerID=<serverid>] Whe
OESyncAccessMDI
E.g: CalculationServer /DataService=oeserv1:rtrdb1,oeserv2:rtrdb1
1.3.2.1.1 DataService
This optio
configuration. If it is not present, then the Calculation Server will not connect to any dataservice.
1.3.2.1.2 ServerID
Optional p
Servers from the same Calculation table (database). E.g. ServerID=HOSTA.
n is mandatory. It specifies the data service of the database that holds the calculation
arameter. Specifies the ID of the Calculation Server when supporting multiple Calculation
re:Starting the
1.3.3 Starting the OESyncAccessMDI
It is recommended that you start the OESynchAccessMDI component as part of an OpenEnterprise
Server Session so it will already be connected to the database when the first calculation is run. To
edit the OESynchAccessMDI task, select it from the task list in the Session Manager's interface. Then
select the Stop option from the context menu. When the task has stopped select the Properties option
from the same context menu. This will open the Task Properties dialog.
On the Task page of this dialog, the following command line options should be provided in the
'Program Arguments' field.
Program Arguments
OESynchAccessMDI [/DataService=<dataservice>]
Where:
DataService
Specifies the data service of the database that holds the calculation configuration. If not
present the default will be rtrdb1.E.g. DataService=rtrdb1
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 12

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 12
Calculation Serve
1.4 Configuring a Calculation
1.4.1 Configuring a Calculation
Configuration of Calculations is best done using the Calculation Config Tool, found within the Toolbox.
Calculations created with the tool are inserted into the calculation_table.
The Configuration tool provides access to all of the methods of running and controlling calculat ions.
However, the topics listed below give further insight into the attributes of the calculation table that are
used to control and trouble shoot calculations. The Status Codes are particularly useful in tracking
down problems.
• Temporarily Stopping a Calculation
• Monitoring the Status of a Calculation
• Specifying Calculation Arguments
• Running a Calculation
• Executing a Calculation When an Alarm Occurs
• Calculation Cascading
• Status Codes
1.4.2 Temporarily Stopping a Calculation
Set the calculation's Disable attribute to TRUE. To resume the calculations set the Disable attribute to
FALSE.
1.4.3 Monitoring the Status of a Calculation
The following attributes can be used to monitor a calculation. Status, Disable, LastDueTime,
LastCalculateTime and CompletionTime.
1.4.4 Specifying Calculation Arguments
The Calculation Configuration tool provides a Calculation Editor for use with the product's own Server
Side Calculation DLL, which will meet most needs. However, user defined calculations can optionally
be passed arguments by typing them directly into the 'Arguments' field on the Action Details dialog of
the Configuration tool. The Calculation Server treats command line arguments differently for an
ActiveX DLL and an EXE calculation.
1.4.4.1 ActiveX DLL
An ActiveX DLL that imple
command line parameters. When specifying the Calculation.Args attribute the arguments should be
specified as a comma separated list.
For example,
ments the Execute method can be configured to receive up to three
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 13

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 13
Args = 'Argument1'
...will set Execute.Arg1 to "Argument1". Arg2 and Arg3 will have the value VT_EMPTY.
Args = 'Argument1,Argument2'
...will set Execute.Arg1 to "Argument1" and Arg2 to "Argument2". Arg3 will have the value
VT_EMPTY.
1.4.4.1.1 Executable
Calculation Serve
An Executabl
and hence only has meaning to the calculation itself.
The calculation EXE will be invoked as follows:
<Calculation.ProgramID> <Calculation.Args>
For example:-
ProgramID = 'C:\MyApps\Calculation.exe'
Args = 'Argument1 Argument2' Will be invoked as
C:\MyApps\Calculation.exe Argument1 Argument2
Database Configuration
e calculation can be passed any number of arguments as the argument list is parsed
1.4.5 Running a Calculation
A calculation can be triggered or run from a Diary, from one or more attribute triggers, or manually.
1.4.5.1 Diary
To run the
attribute.
1.4.5.2 Attribute Trigger
calculation from a Diary specify the appropriate diary name in the Calculation.Diary
A calcul
Tool for information on how to configure attribute triggers the easy way. Attribute triggers can be
configured such that a calculation will run whenever a given attribute within a given object changes
value. Note that the calculation will always be triggered for every change to the attribute trigger's
value. It is recommended to use the MinimumInterval attribute if there are concerns about the
calculation running too frequently.
Also note that attribute triggers can only be placed on objects within the local database. Remo te
attribute triggers are not supported.
The following is an example SQL statement showing how an attribute trigger could be configured
using the SQL Client:-
INSERT INTO realanalogsignaltrigger_table(id,calculationname,objectvalue)
VALUES (0, 'Calculation1', 'REAL.ANALOG.1');
ation can be triggered by one or more attribute triggers. See the Calculation Configuration
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 14

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 14
This will result in the Calculation1 running for every change in the RealAnalog.Value of the
RealAnalog object whose name is REAL.ANALOG.1. Calculationname should refer to the
Calculation.Name attribute of the calculation you want to run.
1.4.5.3 Manually
Calculation Serve
To run a
to TRUE.
Setting the Calculate attribute will always result in the Calculation Server running the calculation. This
is recommended for testing the calculation.
Setting the Due attribute will look at the Disable and MinimumInterval attributes before deciding
whether to trigger the calculation or not. This is recommended for normal running.
Database Configuration
calculation manually then, set either the Calculation.Calculate or Calculation.Due attributes
1.4.6 Executing a Calculation When an Alarm Occurs
An Alarm Action is defined as an action that is to be performed when an alarm occurs. Alarm actions
can be configured to run a Calculation.
Alarm action programs are configured on a per alarm condition basis. For NW3000 remote al arms a
signal will only have a single alarm condition. Other signals may have more than one ala rm co ndition.
The base table for alarm conditions is the AlarmCondition_table whic h holds all the alarm action
configuration. However, in order to configure the appropriate alarm condition entries the user must
configure the derived alarm condition tables as these reference the source objects.
For example, with NW3000 remote alarms, the RealAnalogAlarmCondition and DigitalAlarmCondition
tables should be used when configuring alarm actions.
In order to configure an Alarm Action, the following attributes can be used.
ATTRIBUTE TYPE MEANING
AlarmAction STRING The name of the Calculation to run. This should reference a
calculation.name attribute.
AlarmActionOptions INTEGER Optional options to control how the AlarmAction is triggered.
The various bits refer to the following:
BIT0 - Set to 1 to trigger the AlarmAction when alarm is
updated to 'cleared'. Default behavior is to trigger alarm
actions only when an alarm condition is updated to 'not
cleared'.
BIT1 to 31 - Reserved for future use.
AlarmActionEnable BOOL Enable or disable the AlarmAction from being triggered.
TRUE - AlarmAction is enabled.FALSE - AlarmAction is
disabled.The default value is TRUE.
By default, Alarm Actions will only be triggered when an alarm condition is updated to 'not cleared'.
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 15

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 15
Calculation Serve
1.4.7 Configuring Calculation Cascades
Calculation cascades enable the completion of a calculation to automatically trigger another
calculation. This can be useful if a calculation requires another calculation to manipulate database
data before it can run itself.
Two Calculation_table attributes control calculation cascades, namely NextCalculation and
IgnoreCompletionStatus.
The NextCalculation attribute identifies the next calculation to run and refers to the name of the
calculation. When the current calculation completes successfully (Calculate = FALSE and Status = 0),
if the NextCalculation is not NULL then the calculation is located and triggered (Due = TRUE ). If the
next calculation should be run regardless of the completion status then the IgnoreCompletionStatus
should be set to TRUE.
1.4.8 Status Codes
All internally generated status codes are negative or zero. Application specific status code s should be
positive. Each calculation component has unique status codes within the following ranges.
General Code Ranges
Range Component
>= 1 Application specific.
0 General status code for Okay.
-1 to -99 Calculation CL.
-100 to -199 Calculation Server.
-200 to -299 OESynchAccessMDI
Some Individual status codes:
Value Meaning
0 Okay.
-1 Calculation is currently running.
-2 No calculation has been supplied.
-3 The attribute is unrecognized. This error may occur when setting up an
attribute trigger for a calculation when the attribute does not exist.
-4 Failed to link to the attribute trigger. Check the parameters for the attribute
trigger.
-5 Not implemented.
-6 The minimum frequency for the calculation has been exceeded.
-7 The calculation is due but is already calculating.
-8 The calculation is disabled.
-100 The calculation is disabled.
-101 Not implemented.
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 16

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 16
-102 Unknown calculation type. The Calculation Server was unable to determin e
the calculation type (EXE, DLL or BAT).
-103 Failed to create thread.
-104 Invalid Program ID. The supplied ActiveX DLL program id could not be
converted to a Class ID. Check spelling and that the ActiveX DLL has been
registered successfully.
-105 ActiveX DLL does not support the unknown interface.
-106 ActiveX DLL does not implement the IOECalculation interface.
-107 ActiveX DLL does not implement the IOECalculation.Execute method.
-108 Failed to call the Execute function of the ActiveX DLL.
-109 Failed to create a process. Specific to EXE and Bat calculations.
-110 File does not exist.
-111 The path does not exist.
-112 Access denied.
-113 Argument list is too long.
-114 Bad file format.
-115 Not enough memory.
-200 Not implemented.
-201 Failed to connect to the database.
-202 Read error occurred.
-203 Data type mismatch.
-204 Write error occurred.
Calculation Serve
Database Configuration
1.4.9 Calculation DLLs
1.4.9.1 Writing a Calculation
These are the tasks required to write a calculation as a DLL using Visual BASIC.
Tasks
1. Create a new project using the ActiveX DLL template.
2. Choose "Project", "References" and select "OpenEnterprise Calculation Server" and
"OpenEnterprise Calculation Utilities".
3. Use the "Implements" keyword to implement the Calculation Server interface.
4. Declare the Execute function and use the OpenEnterprise Calculation Utilities classes,
methods and properties to interact with the database.
1.4.9.2 DLL Example Code
This exam
only if another signal allows the calculation:
ple reads two signal values, adds them together and writes the result to another signal, but
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 17

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 17
Option Explicit
Implements CalculationServer.Calculation
' declare an object so we can use the Calculation utilities (Sleep)
Dim Utils As New OECalculationUtils.Utilities
' declare the signal objects
Dim INPUT1 As New OECalculationUtils.AttributeObject
Dim INPUT2 As New OECalculationUtils.AttributeObject
Dim CONTROL As New OECalculationUtils.AttributeObject
Dim OUTPUT As New OECalculationUtils.AttributeObject
Private Sub Class_Initialize()
' place any specific initialisation here
Calculation Serve
End Sub
'this method is called by the calculation server to run the calculation
Public Function Calculation_Execute(
ByRef Arg1 As Variant, _
ByRef Arg2 As Variant, _
ByRef Arg3 As Variant) As Long
Dim error As Long
' setup the global exception handling
On Error GoTo Error_Label
' initialise the signal objects with name and table details
INPUT1.Initialise "Input.1.", "nw3000RealAnalog", "value", OEReal
INPUT2.Initialise "Input.2.", "nw3000RealAnalog", "value", OEReal
CONTROL.Initialise "Control..", "nw3000Digital", "value", OEBoolean
OUTPUT.Initialise "Output..", "nw3000RealAnalog", "value", OEReal
' read the control signal to see if we can proceed
error = CONTROL.ReadValue()
if ((error = 0) AND (CONTROL.Value)) Then
error = INPUT1.ReadValue()
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 18

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 18
error = INPUT2.ReadValue()
OUTPUT.Value = INPUT1.Value + INPUT2.Value
OUTPUT.WriteValue()
End If
' finish by storing the last error code (zero == success)
Calculation_Execute = error
Exit Function
Error_Label:
' capture the latest error value to send back to the calculation
Calculation_Execute = error
End Function
Calculation Serve
Private Sub Class_Terminate()
' delete the Calculation utilities object
Set Utils = Nothing
' now delete all the objects
Set INPUT1 = Nothing
Set INPUT2 = Nothing
Set CONTROL = Nothing
Set OUTPUT = Nothing
End Sub
1.5 Generating Calculation Alarms
The system can be optionally configured to generate alarms based on the Calculation.Status attribute.
By default, no alarms will be generated. Alarms are configured on a per calculation basis.
In order to generate an alarm for a given calculation, an entry needs to be created within the
CalculationStatusAlarmCondition_table.
For example, the following SQL statement will create an alarm condition for the calculation named
'Calculation1' using priority 252. The 'condition' value of 9 refers to a change of state alarm but is
ignored by the calculation alarm sub-system. The id field should always be set to zero:
INSERT INTO CalculationStatusAlarmCondition_Table (id,priority,condition
,name) VALUES (0, 252, 9, 'Calculation1');
Each configured calculation alarm can be either a control alarm or a monitor alarm. By default the
alarm will be a control alarm.
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 19

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 19
1.5.1.1.1.1 Control Alarms
A control al
failures and will not regenerate alarms, or update existing alarms, when the same error is continually
repeating.
For example, if the user has configured a calculation with a program id that does not exist then an
alarm will be generated when the calculation is first triggered to indicate Invalid Program ID. The next
time the calculation is triggered, if the program id is still invalid then no new alarm will be generated as
the previous alarm will still be current.
1.5.1.1.1.2 Monitor Alarms
A monitor ala
statuses. A monitor alarm should be used if you wish to record every running of the calculation. In
order to create a Monitor Alarm, when creating the alarm condition, the MonitorAlarm attribute must
be set to TRUE. By default its value is FALSE.
For example,
INSERT INTO CalculationStatusAlarmCondition_Table (id ,priority ,condition
,name, MonitorAlarm) values (0, 252, 9, 'Calculation1', TRUE);
arm is an intelligent alarm condition that will attempt to only generate alarms given actual
rm records all changes to the status attribute including all transient and non-alarm
Calculation Serve
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 20

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010 - Page 20
Calculation Serve
2 Index
A
Alarm Occurs ............................................13
C
Calculation ....................................11, 12, 16
Running................................................. 12
Temporarily Stopping............................ 11
Writing ...................................................16
Calculation Components Diagram..............1
Calculation Server...............................3, 8, 9
Starting ................................................ 8, 9
Calculation Server Overview.......................1
Calculation When......................................13
Executing...............................................13
Calculations................................................. 4
Configuring Calculation Cascades............14
D
Database Configuration ............................10
DLL Example Code................................... 16
Scheduler.....................................................2
Specifying Calculation Arguments.............11
Starting ....................................................8, 9
Calculation Server................................8, 9
OESyncAccessMDI..................................9
Status.........................................................11
Monitoring ..............................................11
Status Codes.............................................14
T
Temporarily Stopping ................................11
Calculation .............................................11
W
Writing........................................................16
Calculation .............................................16
E
Executing...................................................13
Calculation When ..................................13
G
Generating Calculation Alarms .................19
I
IOCalculation Interface................................3
M
Monitoring..................................................11
Status.....................................................11
O
ODBC.......................................................... 6
OECalculationUtils...................................... 6
OESyncAccessMDI.................................4, 9
Starting .................................................... 9
OpenEnterprise Database...........................2
R
Running.....................................................12
Calculation.............................................12
S
Remote Automation Solutions
Website: www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
Page 21

Reference Guide
r
D301483X412
23-Feb-2010
DISCLAIMER
Bristol, Inc., Bristol Babcock Ltd, Bristol Canada, BBI SA de CV and the Flow Computer Division , are wholly owned subsidiaries of Emerson Electric Co. doing business
as Remote Automation Solutions (“RAS”), a division of Emerson Process Management. ROC, FloBoss, ROCLINK, Bristol, Bristol Babcock, ControlWave, TeleFlow and
Helicoid are trademarks of RAS. AMS, PlantWeb and the PlantWeb logo are marks of Emerson Electric Co. The Emerson logo is a trademark and service mark of the
Emerson Electric Co. All other marks are property of their respective owners.
The contents of this publication are presented for informational purposes only. While every effort has been made to ensure informational accuracy, they are not to be
construed as warranties or guarantees, express or implied, regarding the products or services described herein or their use or applicability. RAS reserves the right to
modify or improve the designs or specifications of such products at any time without notice. All sales are governed by RAS’ terms and conditions which are available upon
request. RAS does not assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any product. Responsibility for proper selection, us e and maint en ance of any RAS
product remains solely with the purchaser and end-user.
Engineered and supported by:
Remote Automation Solutions,
Blackpole Road, Worcester, WR3 8YB, UK
Registered office: Meridian East, Leicester, LE19 1UX
Calculation Serve
Registered in England and Wales, Registration No. 00671801
VAT Reg No. GB 705 353 652
Emerson Process Management
Remote Automation Solutions
1100 Buckingham St
Watertown, CT 06795
T 1 (860) 945 2200
F 1 (860) 945 2278
www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
binfo@EmersonProcess.com
© 2010 Remote Automation Solutions, division of Emerson Process Management. All rights reserved.
Emerson Process Management
Remote Automation Solutions
Blackpole Road
Worcester, WR3 8YB
T 44 (0) 1905 856848
F 44 (0) 1905 856930
www.EmersonProcess.com/Remote
oedsupport@EmersonProcess.com
 Loading...
Loading...