Red Hat CERTIFICATE SYSTEM 6.0, Certificate System 6.1, Certificate System 6.2, Certificate System 7.3 User Manual
Page 1

Red Hat Certificate System
Migration Guide: 6.x to 7.3
6.0
Matthew Harmsen
ISBN: N/A
Publication date: March 12, 2008
Page 2

This migration guide provides in-depth procedures to migrate subsystems, user information, and
certificate and key materials from Netscape Certificate Management System 6.0, 6.1, and 6.2 to
Red Hat Certificate System 7.3.
Red Hat Certificate System
Page 3

Red Hat Certificate System: Migration Guide: 6.x to 7.3
Author Matthew Harmsen <mharmsen@redhat.com>
Editor Ella Deon Lackey <dlackey@redhat.com>
Copyright © 2008 Red Hat, Inc.
Copyright © 2008 Red Hat. This material may only be distributed subject to the terms and conditions set forth in the
Open Publication License, V1.0 or later with the restrictions noted below (the latest version of the OPL is presently
available at http://www.opencontent.org/openpub/).
Distribution of substantively modified versions of this document is prohibited without the explicit permission of the
copyright holder.
Distribution of the work or derivative of the work in any standard (paper) book form for commercial purposes is
prohibited unless prior permission is obtained from the copyright holder.
Red Hat and the Red Hat "Shadow Man" logo are registered trademarks of Red Hat, Inc. in the United States and other
countries.
All other trademarks referenced herein are the property of their respective owners.
The GPG fingerprint of the security@redhat.com key is:
CA 20 86 86 2B D6 9D FC 65 F6 EC C4 21 91 80 CD DB 42 A6 0E
1801 Varsity Drive
Raleigh, NC 27606-2072
USA
Phone: +1 919 754 3700
Phone: 888 733 4281
Fax: +1 919 754 3701
PO Box 13588
Research Triangle Park, NC 27709
USA
Page 4

Red Hat Certificate System
Page 5

1. Introduction to Red Hat Certificate System Migration ................................................ 1
1. Certificate System Migration Overview ............................................................ 1
1.1. Migration Scripts ................................................................................. 2
1.2. Certificate System Subsystems ............................................................ 3
2. Considerations before Migration ...................................................................... 4
2. Step 1: Preparing the 6.x Server Instance for Migration ............................................ 7
3. Step 2: Installing the New Certificate System ........................................................... 9
4. Step 3: Stopping the New Certificate System Servers ..............................................11
5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases .....................................................................13
1. Certificate Authority (CA) Migration ................................................................13
1.1. Option 1: Security Databases to Security Databases Migration ..............13
1.2. Option 2: Security Databases to HSM Migration ...................................15
1.3. Option 3: HSM to Security Databases Migration ...................................19
1.4. Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration .........................................................21
2. Data Recovery Manager (DRM) Migration ......................................................23
2.1. Option 1: Security Databases to Security Databases Migration ..............24
2.2. Option 2: Security Databases to HSM Migration ...................................26
2.3. Option 3: HSM to Security Databases Migration ...................................30
2.4. Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration .........................................................33
3. Online Certificate Status Protocol Manager (OCSP) Migration .........................37
3.1. Option 1: Security Databases to Security Databases Migration ..............37
3.2. Option 2: Security Databases to HSM Migration ...................................39
3.3. Option 3: HSM to Security Databases Migration ...................................43
3.4. Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration .........................................................46
6. Step 5: Migrating Password Cache Data .................................................................51
7. Step 6: Migrating Internal Databases ......................................................................53
8. Step 7: Customizing User Data (Non-Console) ........................................................59
9. Step 8: Starting All Certificate System 7.3 Instances ................................................61
10. Step 9: Generate New Certificate System Server Certificates .................................63
1. Self-Signing an SSL Server Certificate for a CA ..............................................63
2. Requesting a New SSL Server Certificate from a Third-Party CA .....................64
3. Generating a New DRM, OCSP, or TKS SSL Server Certificate .......................65
11. Step 10: Customizing User Data (Console) ...........................................................67
12. Step 11: Verifying Migration .................................................................................69
v
Page 6

vi
Page 7

Introduction to Red Hat Certificate
System Migration
Netscape Certificate Management System (CMS) versions 6.0x, 6.1, and 6.2 can be migrated to
Red Hat Certificate System version 7.3 using the Red Hat Certificate System migration utility.
Certificate System has the ability to extract data from the installation of a previous version and
migrate this data to 7.3. Each Certificate System subsystem is migrated independently.
• Product downgrade, extracting information from a newer version to import into an older
version, is not supported by the migration utility in any version of the Certificate System.
• Certificate System 7.3 does not support in-place upgrades. This is true even when the
installations are on the same machine, running the same platform. For example, a Certificate
Management System 6.2 installation on a machine named delta.example.com running Red
Hat Enterprise Linux has to be migrated to Certificate System 7.3 installation, even if the 7.3
installation is on the same machine named delta.example.com running Red Hat Enterprise
Linux. This is accomplished simply by supplying a different installation directory for each
instance.
NOTE
Throughout this manual, all system instances are referred to as Certificate
System, unless the specific version or product name is required.
1. Certificate System Migration Overview
The migration process is staged to migrate the different subsets of Certificate System
information separately. The general process is as follows:
1. Install the Certificate System 7.3 subsystem instances.
2. Migrate the Certificate Management System 6.x security databases, which contains the key
and certificate materials for the server, to the Certificate System 7.3 instances.
3. Migrate the password database information for Certificate Management System 6.x to the
Certificate System 7.3 password file.
4. Migrate the Certificate Management System 6.x internal databases, which contain user and
group entries, to the Certificate System 7.3 server.
5. Migrate customized server configuration data from the 6.x server to Certificate System 7.3.
Chapter 1.
1
Page 8

6. Renew all migrated certificates.
1.1. Migration Scripts
The Certificate System migration utility contains several separate platform-independent tools,
but only two are required for migrating a Certificate System installation: one program to convert
all of the data in an LDIF that was exported from the 6.x installation into a normalized LDIF text
file, and another program to convert the normalized LDIF text file into an LDIF data file that can
be imported into the newer Certificate System.
NOTE
The major version number of the migration export/import package is applied to all
service packs for that version. (This also applies to installations which contain
hot-fixes, individual bug fixes made after a service pack is released.) For
example, migrating from Certificate Management System 6.01 uses the 60ToTxt
program to export data.
Certificate System migration export utilities are files named versionToTxt. For migrating 6.0x,
6.1, and 6.2 servers to Certificate System 7.3, there are three files which are used, depending
on your 6.x version: 60ToTxt, 61ToTxt, and 62ToTxt. Each export tool contains the following
files:
• Two precompiled Java™ classes
• An tool shell script
• An tool batch script
• The Java™ source file that produced the precompiled Java™ classes
• A sample shell script that can compile the source file
• A sample batch script that can compile the source file
The export file to use is determined by the older version of the Certificate System being
migrated.
NOTE
Each compilation batch and shell script is dependent on a specific version of the
Java software development kit defined in its comments.
Chapter 1. Introduction to Red Hat Certificate System Migration
2
Page 9

Certificate System migration import utilities are files named TxtToversion. To migrate the
Certificate Management System 6.x servers to Certificate System 7.3, use the TxtTo73 script.
The import tool contains the following files:
• Three precompiled Java™ classes
• An tool shell script
• An tool batch script
• The Java™ source file that produced the precompiled Java™ classes
• A sample shell script that can compile the source file
• A sample batch script that can compile the source file
Each compilation batch and shell script is dependent upon a specific version of the Java™
software development kit as defined in the comments.
1.2. Certificate System Subsystems
Certificate System installations may exist on different platforms. Additionally, each Certificate
System installation may contain more than one type of subsystem or more than one instance of
a type of subsystem. The following subsystems may be present in a Certificate System
installation:
• Certificate Authority (CA)
• Data Recovery Manager (DRM)
• Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) Manager
• Registration Authority (RA)
• Token Key Service (TKS)
• Token Processing System (TPS)
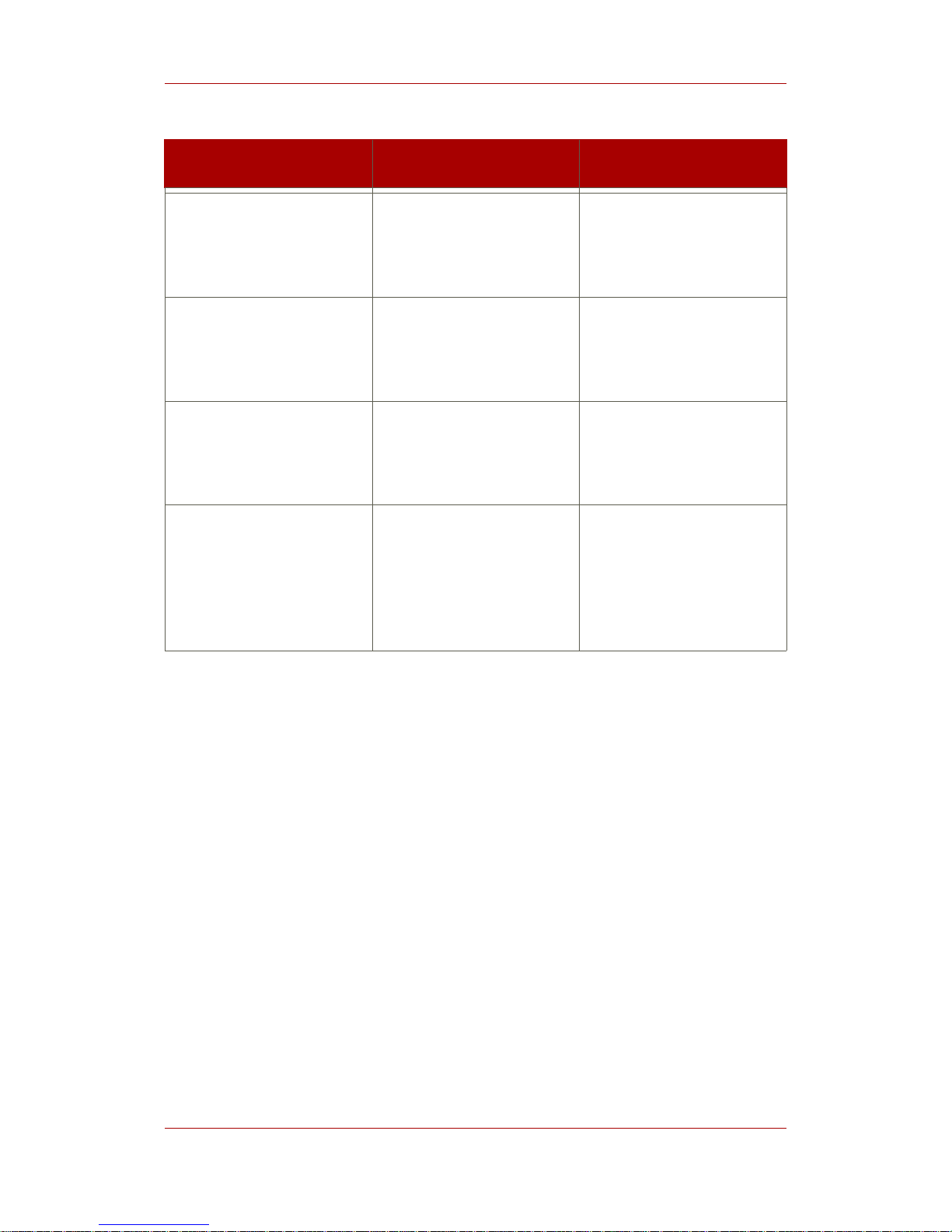
The following table defines the platforms and subsystems supported by different versions of
Certificate System:
Product (including service
packs and hot-fixes)
Subsystems Platforms
Netscape Certificate
Management System 6.0
CA
DRM
OCSP
RA
Solaris 8
Windows 2000 (SP 2)
Certificate System Subsystems
3
Page 10
Product (including service
packs and hot-fixes)
Subsystems Platforms
Netscape Certificate
Management System 6.01
a
CA
DRM
OCSP
RA
Red Hat Linux 7.2
Red Hat Enterprise Linux AS
2.1
Solaris 8
Netscape Certificate
Management System 6.1
CA
DRM
OCSP
RA
Solaris 8
Netscape Certificate
Management System 6.2
CA
DRM
OCSP
RA
Red Hat Enterprise Linux AS
2.1
Solaris 8
Red Hat Certificate System
7.3
CA
DRM
OCSP
RA
TKS
TPS
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
AS/ES 4 (i386)
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
AS/ES 4 (for AMD64 and Intel
EM64T)
Solaris 9 (64-bit)
a
Although Certificate Management System 6.01 was considered a service pack of version 6.0, Certificate Management
System 6.01 is listed separately in this table because it is supported on different platforms.
Table 1.1. Certificate System Subsystem Types and Platforms
2. Considerations before Migration
Since all migrations are unique to a deployment, it is strongly recommended that the entire
migration process be planned in advance. Here are some common issues related to migration.
The Migration Procedure.
• Not all steps in the migration processes apply to every deployment. Follow only the steps
which apply to the deployment being migrated.
• Perform all steps in the migration procedure for every instance of each subsystem being
migrated. Always follow the steps for migration in the order which they are presented in the
manual, even if not every step needs to be performed.
• Perform each subsystem migration as a separate migration. Wait until one subsystem
Chapter 1. Introduction to Red Hat Certificate System Migration
4
Page 11

migration is complete before starting the migration of the next subsystem.
Setting File Permissions.
• On Linux and UNIX systems, make sure that the file owner (user and group) and the file
permissions are correct when the file is copied between two instances. Also make sure that
the target machine allows the file transfer.
• The chmod command used in the examples have the permissions 00600 (octal, no sticky bit
permissions, user read/write permissions, no group permissions, no other permissions).
These are the recommended permissions, but are not required.
Extracting Data from a Hardware Security Module.
While the migration procedure refers to extracting data from a hardware security module (HSM),
no Certificate System tool can extract public/private key pairs from an HSM because of Federal
Information Processing Standard (FIPS) 140-1, which protects the private key portion of an
entry. Contact the HSM vendor for information on how to extract data from an old HSM.
Extracted keys should not have any dependencies, such as nickname prefixes, on the old HSM.
Changing Subsystem Names and Port Numbers.
It is possible to change the names of migrated Certificate System subsystem instances, but
greater care must be taken when extracting and renaming certain portions of the data. Because
port numbers are stored in the server.xml file, which is unaffected by subsystem migration,
port numbers can be changed between instances without difficulty.
About Usage Examples.
All examples assume that the new passwords are the same as the old passwords.
Subsystem and Version Related Considerations.
• The default key-splitting scheme used by the DRM subsystem in Certificate System 7.1 and
later is not the scheme required by the DRM subsystem key recovery feature in 6.x versions.
There is no way to migrate from the old key-splitting scheme to the new scheme. Therefore,
DRM instances in Certificate Management System 6.x versions cannot be successfully
migrated to version 7.3.
• The RA subsystem was deprecated in Certificate Management System 7.0 and redesigned in
Red Hat Certificate System 7.3, so it is not possible to migrate RA subsystems into Certificate
System version 7.3. All RA request queues should be processed by the 6.x-version servers
into their existing CAs before beginning any CA migrations.
Considerations before Migration
5
Page 12

6
Page 13

Step 1: Preparing the 6.x Server
Instance for Migration
Before migrating a Certificate System instance, back up the Certificate System instance. When
the backup process is complete, then stop the old Certificate System, Directory Server, and
Administration Server instances.
1. Stop all server instances running in the Certificate System, including all Certificate System
subsystems; the Directory Server, including all internal databases; and the Administration
Server instances on the local machine.
2. Run the backup facility (either the included Certificate Management System utility or a
commercial utility) to back up all data associated with the Certificate Management System
6.0x, 6.1, or 6.2 installation. For example, using the Certificate Management System utility:
cd /usr/netscape/servers/cert-instance
./cmsbackup
For more information on using the 6.x backup utility, see chapter 8, "Backing Up and
Restoring Data," in the Netscape Certificate Management System 6.x Command-Line Tools
Guide.
Additionally, RA subsystems in Certificate Management System 6.x cannot be migrated to
Certificate System 7.3. The RA subsystem was deprecated in Certificate Management System
7.0 and redesigned in Red Hat Certificate System 7.3 and is not compatible with 6.x versions of
the RA subsystem. To preserve the data in the RA subsystem, flush all data in RA request
queues by processing it on the CA subsystem. Then stop the RA subsystem and database so
that no further data can be gathered by it.
1. Stop the RA instance.
cd /usr/netscape/servers/cert-ra
./stop-cert
2. Stop the corresponding RA internal database instance.
cd /usr/netscape/servers/slapd-ra-db
./stop-slapd
Chapter 2.
7
Page 14

8
Page 15

Step 2: Installing the New Certificate
System
Install a new Certificate System 7.3 instance. All subsystem instances are installed separately;
make sure that every subsystem type which will be migrated has a corresponding new
subsystem instance.
1. Obtain the appropriate packages either through the up2date command or by downloading
the ISO image from the Certificate System 7.3 Red Hat Network channel.
2. If installing from an ISO image, run the installation utility to install the packages. This is done
automatically when using up2date.
rhpki-install -pki_subsystem=subsystem_type -pki_package_path=/path/to/ISO
image -force
3. Go through the HTML configuration wizard for each subsystem.
When the installation process is completed, the server returns a URL pointing to the
configuration wizard. Click that link to open the configuration wizard. For example:
http://server.example.com:9080/ca/admin/console/config/login?pin=Yc6EuvuY2OeezKeX7REk
The configuration wizard will fully configure the new subsystem instance and will generate all
required certificates. Make sure to have all necessary information when going through this
wizard. All subsystems require information to an external Red Hat Directory Server, including
bind information. DRM, OCSP, TKS, and subordinate CAs require information for the CA
which will generate their subsystem certificates.
NOTE
It is possible to change the names of migrated Certificate System subsystem
instances, but greater care must be taken when extracting and renaming certain
portions of the data. Because port numbers are stored in the server.xml file,
which is unaffected by subsystem migration, port numbers can be changed
between instances without difficulty.
For more information on the panels in the configuration wizard, see chapter 2, "Installation
and Configuration," in the Certificate System Administration Guide.
Chapter 3.
9
Page 16

10
Page 17

Step 3: Stopping the New Certificate
System Servers
1. First, stop all new Certificate System instances.
/etc/init.d/instance_ID stop
2. Then stop the Directory Server instance used by the Certificate System 7.3 servers.
cd /opt/redhat-ds/slapd-DS-instance
./stop-slapd
Chapter 4.
11
Page 18

12
Page 19

Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
For every Red Hat Certificate System subsystem instance migration, the data from the
certificate (cert7.db or cert8.db) and key (key3.db) security databases for the Netscape
Certificate Management System 6.x instances must be extracted and copied into the Red Hat
Certificate System 7.3 subsystem's /alias directory. Follow the migration procedure
corresponding to the subsystem being migrated.
There are three subsystems which can be migrated from Certificate Management System 6.x to
Red Hat Certificate System 7.3 — the CA, DRM, and OCSP — each with a different migration
procedure.
• Section 1, “Certificate Authority (CA) Migration”
• Section 2, “Data Recovery Manager (DRM) Migration”
• Section 3, “Online Certificate Status Protocol Manager (OCSP) Migration”
1. Certificate Authority (CA) Migration
Determine if the migration to be performed involves software security databases, an HSM, or
both, and follow the appropriate process for the deployment scenario being migrated.
• Section 1.1, “Option 1: Security Databases to Security Databases Migration”
• Section 1.2, “Option 2: Security Databases to HSM Migration”
• Section 1.3, “Option 3: HSM to Security Databases Migration”
• Section 1.4, “Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration”
1.1. Option 1: Security Databases to Security Databases
Migration
1. Remove all the security databases in the Certificate System 7.3 server which will receive
migrated data.
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
Chapter 5.
13
Page 20

NOTE
On Certificate Management System 6.0x, the certificate database is cert7.db,
not cert8.db.
2. Copy the certificate and key security databases from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_CA_instance-cert8.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_CA_instance-key3.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
3. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
4. Log in as root.
5. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group cert8.db
# chown user:group key3.db
6. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
7. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 cert8.db
chmod 00600 key3.db
8. List the contents of the certificate database using the certutil tool. In this example, -L lists
the certificates in the database.
certutil -L -d .
Server-Cert cert-old_CA_instance cu,cu,cu
caSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance cu,cu,cu
ocspSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance CTu,Cu,Cu
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
14
Page 21

NOTE
For Certificate Management System version 6.0x, the certificate database is
automatically converted from cert7.db to cert8.db.
9. Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
10.Edit the ca.signing.cacertnickname and ca.ocsp_signing.cacertnickaname attributes
to reflect the 7.3 CA instance.
ca.signing.cacertnickname=caSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance
ca.ocsp_signing.cacertnickname=ocspSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance
11.If there is CA-DRM connectivity, then also modify the ca.connector.KRA.nickname
attribute.
ca.connector.KRA.nickname=caSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance
12.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
Server-Cert cert-old_CA_instance
1.2. Option 2: Security Databases to HSM Migration
1. Remove all the security databases in the Certificate System 7.3 which will receive migrated
data.
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
NOTE
On Certificate Management System 6.0x, the certificate database is cert7.db,
not cert8.db.
2. Copy the certificate and key security databases from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
Option 2: Security Databases to HSM
15
Page 22

cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_CA_instance-cert8.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_CA_instance-key3.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
3. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
4. Log in as root.
5. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group cert8.db
# chown user:group key3.db
6. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
7. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 cert8.db
chmod 00600 key3.db
8. List the certificates stored in the old security databases by using the certutil command; -L
lists the certificates.
certutil -L -d .
Server-Cert cert-old_CA_instance cu,cu,cu
caSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance cu,cu,cu
ocspSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance CTu,Cu,Cu
NOTE
For Certificate Management System version 6.0x, the certificate database is
automatically converted from cert7.db to cert8.db.
9. Export the public/private key pairs of each entry in the Certificate System databases using
the pk12util tool; -o exports the key pairs to file, and -n sets the name of the certificate and
the old database prefix.
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
16
Page 23

pk12util -o ServerCert.p12 -n "Server-Cert cert-old_CA_instance" -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
Re-enter password: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 EXPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -o caSigningCert.p12 -n "caSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance" -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
Re-enter password: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 EXPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -o ocspSigningCert.p12 -n "ocspSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance"
-d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
Re-enter password: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 EXPORT SUCCESSFUL
NOTE
The old security databases may contain additional public/private key pairs; these
can also be extracted using pk12util.
10.Delete the old security databases.
rm cert8.db
rm key3.db
11.Register the new HSM in the 7.3 token database.
modutil -nocertdb -dbdir . -add new_HSM_token_name -libfile
new_HSM_library_path/new_HSM_library
12.Identify the new HSM slot name.
modutil -dbdir . -nocertdb -list
13.Create new security databases.
certutil -N -d .
Migration
17
Page 24

14.Import the public/private key pairs of each entry from the PKCS #12 files into the new HSM.
pk12util -i ServerCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i caSigningCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i ocspSigningCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
15.Optionally, delete the PKCS #12 files.
rm ServerCert.p12
rm caSigningCert.p12
rm ocspSigningCert.p12
16.Set the trust bits on the public/private key pairs that were imported into the new HSM.
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_CA_instance"
-t "cu,cu,cu" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance"
-t "CTu,CTu,CTu" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:ocspSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance"
-t "CTu,Cu,Cu" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
17.Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
18.Edit the ca.signing.cacertnickaname and ca.ocsp_signing.cacertnickname attributes
to reflect the 7.3 CA instance.
ca.signing.cacertnickname=new_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert
cert-old_CA_instance
ca.ocsp_signing.cacertnickname=new_HSM_slot_name:ocspSigningCert
cert-old_CA_instance
19.If there is CA-DRM connectivity, then also modify the ca.connector.KRA.nickname
attribute.
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
18
Page 25

ca.connector.KRA.nickname=new_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert
cert-old_CA_instance
20.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_CA_instance
1.3. Option 3: HSM to Security Databases Migration
1. Extract the public/private key pairs from the HSM. The format for the extracted key pairs
should be portable, such as a PKCS #12 file.
The pk12util tool provided by Certificate System cannot extract public/private key pairs
from an HSM because of requirements in the FIPS 140-1 standard which protect the private
key. To extract this information, contact the HSM vendor. The extracted keys should not have
any dependencies, such as nickname prefixes, on the HSM.
2. Copy the extracted key pairs from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/ServerCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/ServerCert.p12
cp old_server_root/alias/caSigningCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/caSigningCert.p12
cp old_server_root/alias/ocspSigningCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/ocspSigningCert.p12
3. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
4. Log in as root.
5. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group ServerCert.p12
# chown user:group caSigningCert.p12
# chown user:group ocspSigningCert.p12
Option 3: HSM to Security Databases
19
Page 26

6. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
7. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 ServerCert.p12
chmod 00600 caSigningCert.p12
chmod 00600 ocspSigningCert.p12
8. Import the public/private key pairs of each entry from the PKCS #12 files into the 7.3 security
databases.
pk12util -i ServerCert.p12 -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i caSigningCert.p12 -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i ocspSigningCert.p12 -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
9. Optionally, delete the PKCS #12 files.
rm ServerCert.p12
rm caSigningCert.p12
rm ocspSigningCert.p12
10.Set the trust bits on the public/private key pairs that were imported into the 7.3 security
databases.
certutil -M -n "Server-Cert cert-old_CA_instance" -t "cu,cu,cu" -d .
certutil -M -n "caSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance" -t "CTu,CTu,CTu" -d .
certutil -M -n "ocspSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance" -t "CTu,Cu,Cu" -d .
11.Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
12.Edit the ca.signing.cacertnickname and ca.ocsp_signing.cacertnickname attributes to
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
20
Page 27

reflect the 7.3 CA instance.
ca.signing.cacertnickname=caSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance
ca.ocsp_signing.cacertnickname=ocspSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance
13.If there is CA-DRM connectivity, then also modify the ca.connector.KRA.nickname
attribute.
ca.connector.KRA.nickname=caSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance
14.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
Server-Cert cert-old_CA_instance
1.4. Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration
1. Extract the public/private key pairs from the HSM. The format for the extracted key pairs
should be portable, such as a PKCS #12 file.
The pk12util tool provided by Certificate System cannot extract public/private key pairs
from an HSM because of requirements in the FIPS 140-1 standard which protect the private
key. To extract this information, contact the HSM vendor. The extracted keys should not have
any dependencies, such as nickname prefixes, on the HSM.
2. Copy the extracted key pairs from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/ServerCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/ServerCert.p12
cp old_server_root/alias/caSigningCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/caSigningCert.p12
cp old_server_root/alias/ocspSigningCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/ocspSigningCert.p12
3. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
4. Log in as root.
5. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
Migration
21
Page 28

# chown user:group ServerCert.p12
# chown user:group caSigningCert.p12
# chown user:group ocspSigningCert.p12
6. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
7. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 ServerCert.p12
chmod 00600 caSigningCert.p12
chmod 00600 ocspSigningCert.p12
8. Register the new HSM in the 7.3 token database.
modutil -nocertdb -dbdir . -add new_HSM_token_name -libfile
new_HSM_library_path/new_HSM_library
9. Identify the new HSM slot name.
modutil -dbdir . -nocertdb -list
10.Import the public/private key pairs of each entry from the PKCS #12 files into the new HSM.
pk12util -i ServerCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i caSigningCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i ocspSigningCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
11.Optionally, delete the PKCS #12 files.
rm ServerCert.p12
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
22
Page 29

rm caSigningCert.p12
rm ocspSigningCert.p12
12.Set the trust bits on the public/private key pairs that were imported into the new HSM.
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_CA_instance"
-t "cu,cu,cu" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance"
-t "CTu,CTu,CTu" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:ocspSigningCert cert-old_CA_instance"
-t "CTu,Cu,Cu" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
13.Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
14.Edit the ca.signing.cacertnickname and ca.ocsp_cacertnickname attributes to reflect
the 7.3 CA instance.
ca.signing.cacertnickname=new_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert
cert-old_CA_instance
ca.ocsp_signing.cacertnickname=new_HSM_slot_name:ocspSigningCert
cert-old_CA_instance
15.If there is CA-DRM connectivity, then also modify the ca.connector.KRA.nickname
attribute.
ca.connector.KRA.nickname=new_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert
cert-old_CA_instance
16.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_CA_instance
2. Data Recovery Manager (DRM) Migration
Determine if the migration to be performed involves software security databases, an HSM, or
both, and follow the appropriate process for the deployment scenario being migrated.
• Section 2.1, “Option 1: Security Databases to Security Databases Migration”
Data Recovery Manager (DRM) Migration
23
Page 30

• Section 2.2, “Option 2: Security Databases to HSM Migration”
• Section 2.3, “Option 3: HSM to Security Databases Migration”
• Section 2.4, “Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration”
NOTE
Archived keys stored in a 6.0x or 6.1 DRM cannot be migrated to Certificate
System 7.3 because the old key-splitting scheme is not supported in versions
later than 6.1 (SP4). To be able to recover these keys, obtain a migration patch
from Red Hat services.
2.1. Option 1: Security Databases to Security Databases
Migration
1. Remove all the security databases in the Certificate System 7.3 server which will receive
migrated data.
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
NOTE
On Certificate Management System 6.0x, the certificate database is cert7.db,
not cert8.db.
2. Copy the certificate and key security databases from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_DRM_instance-cert8.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_DRM_instance-key3.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
3. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
24
Page 31

4. Log in as root.
5. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group cert8.db
# chown user:group key3.db
6. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
7. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 cert8.db
chmod 00600 key3.db
8. List the certificates in the old security databases by using the certutil tool; -L lists the
certificates.
certutil -L -d .
Server-Cert cert-old_DRM_instance cu,cu,cu
caSigningCert cert-old_DRM_instance CT,c,
kraStorageCert cert-old_DRM_instance u,u,u
kraTransportCert cert-old_DRM_instance u,u,u
NOTE
For Certificate Management System version 6.0x, the certificate database is
automatically converted from cert7.db to cert8.db.
9. Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
10.Edit the kra.storageUnit.nickname and kra.transportUnit.nickname attribute to reflect
the 7.3 DRM instance.
kra.storageUnit.nickname=kraStorageCert cert-old_DRM_instance
kra.transportUnit.nickname=kraTransportCert cert-old_DRM_instance
NOTE
The caSigningCert is not referenced in the CS.cfg file.
Option 1: Security Databases to Security
25
Page 32

11.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
Server-Cert cert-old_DRM_instance
2.2. Option 2: Security Databases to HSM Migration
1. Remove all the security databases in the Certificate System 7.3 which will receive migrated
data.
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
NOTE
On Certificate Management System 6.0x, the certificate database is cert7.db,
not cert8.db.
2. Copy the certificate and key security databases from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_DRM_instance-cert8.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_DRM_instance-key3.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
3. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
4. Log in as root.
5. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group cert8.db
# chown user:group key3.db
6. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
26
Page 33

7. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 cert8.db
chmod 00600 key3.db
8. List the certificates stored in the old security databases by using the certutil command; -L
lists the certificates.
certutil -L -d .
Server-Cert cert-old_DRM_instance cu,cu,cu
caSigningCert cert-old_DRM_instance cT,c,
kraStorageCert cert-old_DRM_instance u,u,u
kraTransportCert cert-old_DRM_instance u,u,u
NOTE
For Certificate Management System version 6.0x, the certificate database is
automatically converted from cert7.db to cert8.db.
9. Export the public/private key pairs of each entry in the Certificate System databases using
the pk12util tool; -o exports the key pairs to a PKCS #12 file, and -n sets the name of the
certificate and the old database prefix.
pk12util -o ServerCert.p12 -n "Server-Cert cert-old_DRM_instance" -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
Re-enter password: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 EXPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -o kraStorageCert.p12 -n "kraStorageCert cert-old_DRM_instance" -d
.
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
Re-enter password: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 EXPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -o kraTransportCert.p12 -n "kraTransportCert
cert-old_DRM_instance" -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
Re-enter password: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 EXPORT SUCCESSFUL
Databases Migration
27
Page 34

NOTE
The old security databases may contain additional public/private key pairs; these
can also be extracted using pk12util.
10.Export the public key using the certutil tool; -L lists the named certificate, -n sets the
name of the file and the old prefix, and -a outputs the information to a base-64 file.
certutil -L -n "caSigningCert cert-old_DRM_instance" -d . -a >
caSigningCert.b64
NOTE
The old security databases may contain additional public keys; these can also be
extracted using certutil.
11.Delete the old security databases.
rm cert8.db
rm key3.db
12.Register the new HSM in the 7.3 token database.
modutil -nocertdb -dbdir . -add new_HSM_token_name -libfile
new_HSM_library_path/new_HSM_library
13.Identify the new HSM slot name.
modutil -dbdir . -nocertdb -list
14.Create new security databases.
certutil -N -d .
15.Import the public/private key pairs of each entry from the PKCS #12 files into the new HSM.
pk12util -i ServerCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
28
Page 35

Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i kraStorageCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i kraTransportCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
16.Optionally, delete the PKCS #12 files.
rm ServerCert.p12
rm kraStorageCert.p12
rm kraTransportCert.p12
17.Set the trust bits on the public/private key pairs that were imported into the new HSM.
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_DRM_instance"
-t "cu,cu,cu" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:kraStorageCert cert-old_DRM_instance"
-t "u,u,u" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:kraTransportCert cert-old_DRM_instance"
-t "u,u,u" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
18.Import the public key from the base-64 file into the new HSM, and set the trust bits.
certutil -A -n "new_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert cert-old_DRM_instance"
-t "CT,c," -d . -h new_HSM_token_name -i caSigningCert.b64
19.Optionally, delete the base-64 file.
rm caSigningCert.b64
20.Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
21.Edit the kra.storageUnit.nickname and kra.transportUnit.nickname attributes to
reflect the 7.3 DRM information.
Option 2: Security Databases to HSM
29
Page 36

kra.storageUnit.nickname=new_HSM_slot_name:kraStorageCert
cert-old_DRM_instance
kra.transportUnit.nickname=new_HSM_slot_name:kraTransportCert
cert-old_DRM_instance
NOTE
The caSigningCert is not referenced in the CS.cfg file.
22.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_DRM_instance
2.3. Option 3: HSM to Security Databases Migration
1. Extract the public/private key pairs from the HSM. The format for the extracted key pairs
should be portable, such as a PKCS #12 file.
The pk12util tool provided by Certificate System cannot extract public/private key pairs
from an HSM because of requirements in the FIPS 140-1 standard which protect the private
key. To extract this information, contact the HSM vendor. The extracted keys should not have
any dependencies, such as nickname prefixes, on the HSM.
2. Copy the extracted key pairs from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/ServerCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/ServerCert.p12
cp old_server_root/alias/kraStorageCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/kraStorageCert.p12
cp old_server_root/alias/kraTransportCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/kraTransportCert.p12
3. Extract the public key of the CA signing certificate from the old security databases and save
the base-64 encoded output to a file called caSigningCert.b64.
a. Open the Certificate Management System 6.x /alias directory.
cd old_server_root/alias
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
30
Page 37

b. Set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable to search the Certificate System libraries.
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=old_server_root/bin/cert/lib
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH
c. Use the Certificate Management System 6.x certutil tool to identify the old HSM slot
name.
old_server_root/bin/cert/tools/certutil -U -d .
d. Use the Certificate Management System 6.x certutil tool to extract the public key from
the security databases and save the base-64 output to a file.
old_server_root/bin/cert/tools/certutil -L
-n "old_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert cert-old_DRM_instance"
-d . -h old_HSM_token_name -a > caSigningCert.b64
e. Copy the key information from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/caSigningCert.b64
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/caSigningCert.b64
4. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
5. Log in as root.
6. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group ServerCert.p12
# chown user:group kraStorageCert.p12
# chown user:group kraTransportCert.p12
# chown user:group caSigningCert.b64
7. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
8. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 ServerCert.p12
Migration
31
Page 38

chmod 00600 kraStorageCert.p12
chmod 00600 kraTransportCert.p12
chmod 00600 caSigningCert.b64
9. Import the public/private key pairs of each entry from the PKCS #12 files into the 7.3 security
databases.
pk12util -i ServerCert.p12 -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i kraStorageCert.p12 -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i kraTransportCert.p12 -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
10.Optionally, delete the PKCS #12 files.
rm ServerCert.p12
rm kraStorageCert.p12
rm kraTransportCert.p12
11.Set the trust bits on the public/private key pairs that were imported into the 7.3 security
databases.
certutil -M -n "Server-Cert cert-old_DRM_instance" -t "cu,cu,cu" -d .
certutil -M -n "kraStorageCert cert-old_DRM_instance" -t "u,u,u" -d .
certutil -M -n "kraTransportCert cert-old_DRM_instance" -t "u,u,u" -d .
12.Import the public key from the base-64 file, and set the trust bits.
certutil -A -n "caSigningCert cert-old_DRM_instance" -t "CT,c," -d . -i
caSigningCert.b64
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
32
Page 39
13.Optionally, delete the base-64 file.
rm caSigningCert.b64
14.Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
15.Edit the kra.storageUnit.nickname and kra.transportUnit.nickname attributes to
reflect the 7.3 DRM instance.
kra.storageUnit.nickname=kraStorageCert cert-old_DRM_instance
kra.transportUnit.nickname=kraTransportCert cert-old_DRM_instance
NOTE
The caSigningCert is not referenced in the CS.cfg file.
16.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
Server-Cert cert-old_DRM_instance
2.4. Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration
1. Extract the public/private key pairs from the HSM. The format for the extracted key pairs
should be portable, such as a PKCS #12 file.
The pk12util tool provided by Certificate System cannot extract public/private key pairs
from an HSM because of requirements in the FIPS 140-1 standard which protect the private
key. To extract this information, contact the HSM vendor. The extracted keys should not have
any dependencies, such as nickname prefixes, on the HSM.
2. Copy the extracted key pairs from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/ServerCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/ServerCert.p12
cp old_server_root/alias/kraStorageCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/kraStorageCert.p12
cp old_server_root/alias/kraTransportCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/kraTransportCert.p12
Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration
33
Page 40

3. Extract the public key of the CA signing certificate from the old security databases and save
the base-64 encoded output to a file called caSigningCert.b64.
a. Open the Certificate Management System 6.x /alias directory.
cd old_server_root/alias
b. Set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable to search the Certificate System libraries.
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=old_server_root/bin/cert/lib
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH
c. Use the Certificate Management System 6.x certutil tool to identify the old HSM slot
name.
old_server_root/bin/cert/tools/certutil -U -d .
d. Use the Certificate Management System 6.x certutil tool to extract the public key from
the security databases and save the base-64 output to a file.
old_server_root/bin/cert/tools/certutil -L
-n "old_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert cert-old_DRM_instance"
-d . -h old_HSM_token_name -a > caSigningCert.b64
e. Copy the key information from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/caSigningCert.b64
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/caSigningCert.b64
4. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
5. Log in as root.
6. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group ServerCert.p12
# chown user:group kraStorageCert.p12
# chown user:group kraTransportCert.p12
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
34
Page 41

# chown user:group caSigningCert.b64
7. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
8. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 ServerCert.p12
chmod 00600 kraStorageCert.p12
chmod 00600 kraTransportCert.p12
chmod 00600 caSigningCert.b64
9. Register the new HSM in the 7.3 token database.
modutil -nocertdb -dbdir . -add new_HSM_token_name -libfile
new_HSM_library_path/new_HSM_library
10.Identify the new HSM slot name.
modutil -dbdir . -nocertdb -list
11.Import the public/private key pairs of each entry from the PKCS #12 files into the new HSM.
pk12util -i ServerCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i kraStorageCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i kraTransportCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
12.Optionally, delete the PKCS #12 files.
rm ServerCert.p12
rm kraStorageCert.p12
rm kraTransportCert.p12
Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration
35
Page 42

13.Set the trust bits on the public/private key pairs that were imported into the new HSM.
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_DRM_instance"
-t "cu,cu,cu" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:kraStorageCert cert-old_DRM_instance"
-t "u,u,u" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:kraTransportCert cert-old_DRM_instance"
-t "u,u,u" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
14.Import the public key from the base-64 file into the new HSM, and set the trust bits.
certutil -A -n "new_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert cert-old_DRM_instance"
-t "CT,c," -d . -h new_HSM_token_name -i caSigningCert.b64
15.Optionally, delete the base-64 file.
rm caSigningCert.b64
16.Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
17.Edit the kra.storageUnit.nickname and kra.transportUnit.nickname attributes to
reflect the 7.3 DRM information.
kra.storageUnit.nickname=new_HSM_slot_name:kraStorageCert
cert-old_DRM_instance
kra.transportUnit.nickname=new_HSM_slot_name:kraTransportCert
cert-old_DRM_instance
NOTE
The caSigningCert is not referenced in the CS.cfg file.
18.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_DRM_instance
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
36
Page 43

3. Online Certificate Status Protocol Manager (OCSP)
Migration
Determine if the migration to be performed involves software security databases, an HSM, or
both, and follow the appropriate process for the deployment scenario being migrated.
• Section 3.1, “Option 1: Security Databases to Security Databases Migration”
• Section 3.2, “Option 2: Security Databases to HSM Migration”
• Section 3.3, “Option 3: HSM to Security Databases Migration”
• Section 3.4, “Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration”
NOTE
Migrating from a hardware module to another hardware module is not possible
for Certificate Management System 6.0x versions, only Certificate Management
System 6.1 or 6.2.
3.1. Option 1: Security Databases to Security Databases
Migration
1. Remove all the security databases in the Certificate System 7.3 server which will receive
migrated data.
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
NOTE
On Certificate Management System 6.0x, the certificate database is cert7.db,
not cert8.db.
2. Copy the certificate and key security databases from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_OCSP_instance-cert8.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_OCSP_instance-key3.db
Option 1: Security Databases to Security
37
Page 44

/alias/key3.db
3. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
4. Log in as root.
5. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group cert8.db
# chown user:group key3.db
6. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
7. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 cert8.db
chmod 00600 key3.db
8. List the certificates in the security databases using the certutil command; -L lists the
certificates.
certutil -L -d .
Server-Cert cert-old_OCSP_instance cu,cu,cu
caSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance CT,c,
ocspSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance cu,cu,cu
NOTE
For Certificate Management System version 6.0x, the certificate database is
automatically converted from cert7.db to cert8.db.
9. Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
10.Edit the ocsp.signing.certnickname attribute to reflect the 7.3 OCSP instance.
ocsp.signing.certnickname=ocspSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
38
Page 45

NOTE
The caSigningCert is not referenced in the CS.cfg file.
11.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
Server-Cert cert-old_OCSP_instance
3.2. Option 2: Security Databases to HSM Migration
1. Remove all the security databases in the Certificate System 7.3 server which will receive
migrated data.
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
rm /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
NOTE
On Certificate Management System 6.0x, the certificate database is cert7.db,
not cert8.db.
2. Copy the certificate and key security databases from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_OCSP_instance-cert8.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/cert8.db
cp old_server_root/alias/cert-old_OCSP_instance-key3.db
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/key3.db
3. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
4. Log in as root.
5. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
Databases Migration
39
Page 46

# chown user:group cert8.db
# chown user:group key3.db
6. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
7. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 cert8.db
chmod 00600 key3.db
8. List the certificates in the old security databases using the certutil command; -L lists the
certificates.
certutil -L -d .
Server-Cert cert-old_OCSP_instance cu,cu,cu
caSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance CT,c,
ocspSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance cu,cu,cu
NOTE
For Certificate Management System version 6.0x, the certificate database is
automatically converted from cert7.db to cert8.db.
9. Export the public/private key pairs of each entry in the Certificate System databases using
the pk12util tool; -o exports the key pairs to a PKCS #12 file, and -n sets the name of the
certificate and the old database prefix.
pk12util -o ServerCert.p12 -n "Server-Cert cert-old_OCSP_instance" -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
Re-enter password: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 EXPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -o ocspSigningCert.p12 -n "ocspSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance"
-d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
Re-enter password: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 EXPORT SUCCESSFUL
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
40
Page 47

NOTE
The old security databases may contain additional public/private key pairs; these
can also be extracted using pk12util.
10.Export the public key using the certutil tool; -L lists the named certificate, -n sets the
name of the file and the old prefix, and -a outputs the information to a base-64 file.
certutil -L -n "caSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance" -d . -a >
caSigningCert.b64
NOTE
The old security databases may contain additional public keys; these can also be
exported using the certutil tool.
11.Delete the old security databases.
rm cert8.db
rm key3.db
12.Register the new HSM in the 7.3 token database.
modutil -nocertdb -dbdir . -add new_HSM_token_name -libfile
new_HSM_library_path/new_HSM_library
13.Identify the new HSM slot name.
modutil -dbdir . -nocertdb -list
14.Create new security databases.
certutil -N -d .
15.Import the public/private key pairs of each entry from the PKCS #12 files into the new HSM.
pk12util -i ServerCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
Option 2: Security Databases to HSM
41
Page 48

pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i ocspSigningCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
16.Optionally, delete the PKCS #12 files.
rm ServerCert.p12
rm ocspSigningCert.p12
17.Set the trust bits on the public/private key pairs that were imported into the new HSM.
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_OCSP_instance" -t
"cu,cu,cu" -d .
-h new_HSM_token_name
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:ocspSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance" -t
"cu,cu,cu" -d .
-h new_HSM_token_name
18.Import the public key from the base-64 file into the new HSM, and set the trust bits.
certutil -A -n "new_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance"
-t "CT,c," -d . -h new_HSM_token_name -i caSigningCert.b64
19.Optionally, delete the base-64 file.
rm caSigningCert.b64
20.Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
21.Edit the ocsp.signing.certnickname attribute to reflect the 7.3 OCSP instance.
ocsp.signing.certnickname=new_HSM_slot_name:ocspSigningCert
cert-old_OCSP_instance
NOTE
The caSigningCert is not referenced in the CS.cfg file.
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
42
Page 49

22.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_OCSP_instance
3.3. Option 3: HSM to Security Databases Migration
1. Extract the public/private key pairs from the HSM. The format for the extracted key pairs
should be portable, such as a PKCS #12 file.
The pk12util tool provided by Certificate System cannot extract public/private key pairs
from an HSM because of requirements in the FIPS 140-1 standard which protect the private
key. To extract this information, contact the HSM vendor. The extracted keys should not have
any dependencies, such as nickname prefixes, on the HSM.
2. Copy the extracted key pairs from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/ServerCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/ServerCert.p12
cp old_server_root/alias/ocspSigningCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/ocspSigningCert.p12
3. Extract the public key of the CA signing certificate from the old security databases and save
the base-64 encoded output to a file called caSigningCert.b64.
a. Open the Certificate Management System 6.x /alias directory.
cd old_server_root/alias
b. Set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable to search the Certificate System libraries.
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=old_server_root/bin/cert/lib
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH
c. Use the Certificate Management System 6.x certutil tool to identify the old HSM slot
name.
old_server_root/bin/cert/tools/certutil -U -d .
d. Use the Certificate Management System 6.x certutil tool to extract the public key from
the security databases and save the base-64 output to a file.
Migration
43
Page 50

old_server_root/bin/cert/tools/certutil -L -n
"old_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert
cert-old_OCSP_instance" -d . -h old_HSM_token_name -a >
caSigningCert.b64
e. Copy the key information from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/caSigningCert.b64
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/caSigningCert.b64
4. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
5. Log in as root.
6. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group ServerCert.p12
# chown user:group ocspSigningCert.p12
# chown user:group caSigningCert.b64
7. Log out as root, and log back into the system as the Certificate System user.
8. Set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 ServerCert.p12
chmod 00600 ocspSigningCert.p12
chmod 00600 caSigningCert.b64
9. Import the public/private key pairs of each entry from the PKCS #12 files into the 7.3 security
databases.
pk12util -i ServerCert.p12 -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i ocspSigningCert.p12 -d .
Enter Password or Pin for "NSS Certificate DB":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
44
Page 51

10.Optionally, delete the PKCS #12 files.
rm ServerCert.p12
rm ocspSigningCert.p12
11.Set the trust bits on the public/private key pairs that were imported into the 7.3 security
databases.
certutil -M -n "Server-Cert cert-old_OCSP_instance" -t "cu,cu,cu" -d .
certutil -M -n "ocspSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance" -t "cu,cu,cu" -d .
12.Import the public key from the base-64 file, and set the trust bits.
certutil -A -n "caSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance" -t "CT,c," -d . -i
caSigningCert.b64
13.Optionally, delete the base-64 file.
rm caSigningCert.b64
14.Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
15.Edit the ocsp.signing.certnickname attribute to reflect the 7.3 OCSP instance.
ocsp.signing.certnickname=ocspSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance
NOTE
The caSigningCert is not referenced in the CS.cfg file.
16.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
Server-Cert cert-old_OCSP_instance
Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration
45
Page 52

3.4. Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration
NOTE
Migrating from a hardware module to another hardware module is not possible
for Certificate Management System 6.0x versions, only Certificate Management
System 6.1 or 6.2.
1. Extract the public/private key pairs from the HSM. The format for the extracted key pairs
should be portable, such as a PKCS #12 file.
The pk12util tool provided by Certificate System cannot extract public/private key pairs
from an HSM because of requirements in the FIPS 140-1 standard which protect the private
key. To extract this information, contact the HSM vendor. The extracted keys should not have
any dependencies, such as nickname prefixes, on the HSM.
2. Copy the extracted key pairs from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/ServerCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/ServerCert.p12
cp old_server_root/alias/ocspSigningCert.p12
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/ocspSigningCert.p12
3. Extract the public key of the CA signing certificate from the old security databases and save
the base-64 encoded output to a file called caSigningCert.b64.
a. Open the Certificate Management System 6.x /alias directory.
cd old_server_root/alias
b. Set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH environment variable to search the Certificate System libraries.
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=old_server_root/bin/cert/lib
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH
c. Use the Certificate Management System 6.x certutil tool to identify the old HSM slot
name.
old_server_root/bin/cert/tools/certutil -U -d .
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
46
Page 53

d. Use the Certificate Management System 6.x certutil tool to extract the public key from
the security databases and save the base-64 output to a file.
old_server_root/bin/cert/tools/certutil -L
-n "old_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance"
-d . -h old_HSM_token_name -a > caSigningCert.b64
e. Copy the key information from the 6.x server to the 7.3 server.
cp old_server_root/alias/caSigningCert.b64
/var/lib/instance_ID/alias/caSigningCert.b64
4. Open the Certificate System /alias directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/alias/
5. Log in as root.
6. Set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group ServerCert.p12
# chown user:group ocspSigningCert.p12
# chown user:group caSigningCert.b64
7. Log out as root. As the Certificate System user, set the file permissions.
chmod 00600 ServerCert.p12
chmod 00600 ocspSigningCert.p12
chmod 00600 caSigningCert.b64
8. Register the new HSM in the new token database.
modutil -nocertdb -dbdir . -add new_HSM_token_name -libfile
new_HSM_library_path/new_HSM_library
9. Identify the new HSM slot name.
modutil -dbdir . -nocertdb -list
Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration
47
Page 54

10.Import the public/private key pairs of each entry from the PKCS #12 files into the new HSM.
pk12util -i ServerCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
pk12util -i ocspSigningCert.p12 -d . -h new_HSM_slot_name
Enter Password or Pin for "new_HSM_slot_name":********
Enter password for PKCS12 file: ********
pk12util: PKCS12 IMPORT SUCCESSFUL
11.Optionally, delete the PKCS #12 files.
rm ServerCert.p12
rm ocspSigningCert.p12
12.Set the trust bits on the public/private key pairs that were imported into the new HSM.
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_OCSP_instance
-t "cu,cu,cu" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
certutil -M -n "new_HSM_slot_name:ocspSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance"
-t "cu,cu,cu" -d . -h new_HSM_token_name
13.Import the public key from the base-64 file into the new HSM, and set the trust bits.
certutil -A -n "new_HSM_slot_name:caSigningCert cert-old_OCSP_instance"
-t "CT,c," -d . -h new_HSM_token_name -i caSigningCert.b64
14.Optionally, delete the base-64 file.
rm caSigningCert.b64
15.Open the CS.cfg configuration file in the /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/ directory.
16.Edit the ocsp.signing.certnickname attribute to reflect the 7.3 subsystem information.
ocsp.signing.certnickname=new_HSM_slot_name:ocspSigningCert
cert-old_OCSP_instance
Chapter 5. Step 4: Migrating Security Databases
48
Page 55

NOTE
The caSigningCert is not referenced in the CS.cfg file.
17.In the same directory, edit the serverCertNick.conf file to contain the old certificate
nickname. For example:
new_HSM_slot_name:Server-Cert cert-old_OCSP_instance
Option 4: HSM to HSM Migration
49
Page 56

50
Page 57

Step 5: Migrating Password Cache
Data
The password information for the Certificate System subsystems are saved in a special
password file. In Certificate System 6.x versions, these were kept in the pwcache.db file. The
contents of the password file must be decrypted and listed using the PasswordCache tool in the
6.x subsystem instance. Then, this information must be used to build the contents of the 7.3
password.conf file.
Every subsystem password file must be migrated separately, but the migration procedure is the
same for all Certificate System subsystem instances.
1. Log into the 6.x server as the Certificate System user for that machine, and open the
config/ directory.
cd old_server_root/cert-old_instance/config/
2. Run the PasswordCache tool from the tools directory to retrieve the passwords from the
database.
old_server_root/bin/cert/tools/PasswordCache old_passwordcache_password -d
old_server_root/alias
-P cert-old_instance-old_hostname- -c pwcache.db list
This lists the information stored in the password cache.
cert/key prefix = cert-old_instance-old_hostnamepath = old_server_root/alias
about to read password cache
----- Password Cache Content ----internal : password
Internal LDAP Database : passwordldap
3. Use the listed tags and passwords to create the password.conf file. For example:
internal=password
Internal LDAP Database=passwordldap
4. If the 6.x server instance used the password.conf file to start the server instance
automatically, then this file must also be migrated to the 7.3 server instance.
cp old_server_root/cert-old_instance/config/password.conf
/var/lib/instance_ID/conf/password.conf
Chapter 6.
51
Page 58

5. Log into the 7.3 server as the Certificate System user, and open the Certificate System
configuration directory.
cd /var/lib/instance_ID/conf/
6. Log in as root, and set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
chown user:group password.conf
7. Log out as root. As the Certificate System user, change the permissions on the password
file.
chmod 00600 password.conf
8. Copy the tags and passwords that were listed from the 6.x pwdcache.db file into the
password.conf file.
Chapter 6. Step 5: Migrating Password Cache Data
52
Page 59

Step 6: Migrating Internal Databases
Every Certificate Management System 6.x subsystem contains LDIF data in an associated
internal database which must be migrated to the corresponding Certificate System 7.3
subsystem internal database. The procedure is the same for each subsystem type. The only
difference between Certificate Management System 6.x versions is which import and export
utility to use; these are version specific.
1. Copy the newest version of the migration utility from the Certificate System 7.3 server to the
Certificate Management System 6.x server.
The migration utility is available as an independent RPM, which can be downloaded through
the Certificate System Red Hat Network channel. The migration utilities are installed in the
directory /usr/share/rhpki/migrate.
a. Open the Certificate System instance directory. The migration utilities are in the migrate
directory.
cd /usr/share/rhpki
b. Package the latest version of the Certificate System migration utility using zip or tar.
tar -cvf migrate.tar migrate
NOTE
Regardless of the packaging tool used, the corresponding tool must be present
on the 6.x server machine. If the platforms are identical and the zip utility is
used, copy the zip tool from the 7.3 server to the 6.x server so that the zip and
unzip versions match.
c. Copy the package from the 7.3 server to the 6.x server, and then remove the package
from the 7.3 server. (You can use any copy tool, such as sftp, scp, mv.)
cp /usr/share/rhpki/migrate.tar old_server_root/bin/cert
rm /usr/share/rhpki/migrate.tar
d. Log into the 6.x server as the Certificate Management System user for that machine, and
open the Certificate Management System bin/cert/ directory.
cd old_server_root/bin/cert
Chapter 7.
53
Page 60

e. Log in as root, and set the file user and group to the Certificate Management System user
and group.
# chown user:group migrate.tar
f. Log out as root. As the Certificate System user, change the permissions on the file.
chmod 00600 migrate.tar
g. Since the old Certificate Management System 6.x migration utility will not be used, remove
the Certificate Management System 6.x's upgrade/ directory. This ensures that only the
newest migration scripts, in the copied migrate directory, are available.
rm -rf old_server_root/bin/cert/upgrade
h. Unpackage the latest version of the migration utility using unzip or tar.
tar -xvf migrate.tar
i. Remove the migration utility package and any additional utilities, such as the unzip utility,
that were copied to the Certificate Management System 6.x server.
rm migrate.tar
2. Log into the Directory Server for the Certificate System 7.3 instance, and export the internal
database content to LDIF. The internal database name for the Certificate System instance is
in the internaldb.database parameter in the CS.cfg file. Name the output file new.ldif.
For example:
/opt/redhat-ds/slapd-DS-instance/db/db2ldif -n server.example.com-rhpki-ca
-a /opt/redhat-ds/slapd-DS-instance/ldif/new.ldif
3. Log into the 6.x Certificate System instance, and export the database contents to LDIF.
Name the output file old.ldif.
For example:
cd old_server_root/slapd-old_instance-db/db/db2ldif -n userRoot
-a old_server_root/slapd-old_instance-db/ldif/old.ldif
Chapter 7. Step 6: Migrating Internal Databases
54
Page 61

4. Modify the content of old.ldif.
NOTE
When using a text editor to perform the substitution instead of a script, use an
editor that supports file sizes greater than 4 gigabytes, such as vim, because the
LDIF files may be larger than 2 gigabytes and even 4 gigabytes in some
deployments.
a. Open the Certificate Management System 6.x LDIF directory.
cd old_server_root/slapd-old_instance-db/ldif
b. Open the old.ldif file.
vi old.ldif
c. Replace cn=aclResources entry in the old.ldif file with the cn=aclResources entry
from the new.ldif file. For example:
... replace with ...
dn: cn=aclResources,dc=server.example.com-rhpki-ca
resourceACLS: certServer.usrgrp.administration:read,modify:allow (read)
group=
"Administrators" || group="Auditors" || group="Certificate Manager
Agents" |
| group="Registration Manager Agents" || group="Data Recovery Manager
Agents
" || group="Online Certificate Status Manager Agents";allow (modify)
group="
Administrators":Administrators, auditors, and agents are allowed to
read user
and group configuration but only administrators are allowed to modify
... list of ACLs ...
objectClass: top
objectClass: CertACLS
cn: aclResources
d. Add new groups for the the security domains to the old.ldif file. Security domains were
not a feature in 6.x versions of Certificate System, so it is necessary to add all of the group
entries; for 7.2, it is only necessary to add the RA group entry.
dn: cn=Security Domain Administrators,ou=groups,basedn
description: People who are the Security Domain administrators
objectClass: top
objectClass: groupOfUniqueNames
55
Page 62

cn: Security Domain Administrators
uniqueMember: uid=admin,ou=People,basedn
dn: cn=Enterprise CA Administrators,ou=groups,basedn
description: People who are the administrators for the security domain for
CA
objectClass: top
objectClass: groupOfUniqueNames
cn: Enterprise CA Administrators
uniqueMember: uid=admin,ou=People,basedn
dn: cn=Enterprise KRA Administrators,ou=groups,basedn
description: People who are the administrators for the security domain for
KRA
objectClass: top
objectClass: groupOfUniqueNames
cn: Enterprise KRA Administrators
uniqueMember: uid=admin,ou=People,basedn
dn: cn=Enterprise OCSP Administrators,ou=groups,basedn
description: People who are the administrators for the security domain for
OCSP
objectClass: top
objectClass: groupOfUniqueNames
cn: Enterprise OCSP Administrators
uniqueMember: uid=admin,ou=People,basedn
dn: cn=Enterprise TKS Administrators,ou=groups,basedn
description: People who are the administrators for the security domain for
TKS
objectClass: top
objectClass: groupOfUniqueNames
cn: Enterprise TKS Administrators
uniqueMember: uid=admin,ou=People,basedn
dn: cn=Enterprise RA Administrators,ou=groups,basedn
description: People who are the administrators for the security domain for
RA
objectClass: top
objectClass: groupOfUniqueNames
cn: Enterprise RA Administrators
uniqueMember: uid=admin,ou=People,basedn
dn: cn=Enterprise TPS Administrators,ou=groups,basedn
description: People who are the administrators for the security domain for
TPS
objectClass: top
objectClass: groupOfUniqueNames
cn: Enterprise TPS Administrators
uniqueMember: uid=admin,ou=People,basedn
5. Convert the old.ldif file to a text file.
a. Open the version-to-text directory in the migration directory copied to the Certificate
Chapter 7. Step 6: Migrating Internal Databases
56
Page 63

Management System 6.x server. Each 6.x major version has its own migration directory.
For 6.0x, use 60ToTxt; for 6.1, use 61ToTxt; and for 6.2, use 62ToTxt. For example:
cd old_server_root/bin/cert/migrate/62ToTxt
b. Edit the appropriate run.sh script; uncomment and set the values for the following lines:
SERVER_ROOT=old_server_root
export SERVER_ROOT
INSTANCE=old_instance
export INSTANCE
c. Run the run.sh to use the old.ldif file to create a text file.
run.sh old_server_root/slapd-old_instance-db/ldif/old.ldif >
old_server_root/slapd-old_instance-db/ldif/old.txt
6. Open the Certificate Management System 6.x LDIF directory, and copy the old.txt file into
the Certificate System 7.3 server instance's internal database LDIF directory. (You can use
any copy tool, such as sftp, scp, and mv.)
cd old_server_root/slapd-old_instance-db/ldif
cp old_server_root/slapd-old_instance-db/ldif/old.txt
/opt/redhat-ds/slapd-DS-instance/ldif
7. Log into the 7.3 server as the Certificate System user, and open the Certificate System
ldif/ directory.
cd /opt/redhat-ds/slapd-DS-instance/ldif
8. Log in as root, and set the file user and group to the Certificate System user and group.
# chown user:group old.txt
9. Log out as root. As the Certificate System user, change the permissions on the file.
chmod 00600 old.txt
10.Convert the old.txt file to LDIF.
a. Open the 7.3 text-conversion migration directory in the Certificate System 7.3 server.
57
Page 64

cd /usr/share/rhpki/migrate/TxtTo73
b. Edit the run.sh script; uncomment and set the values for the following lines. For example:
SERVER_ROOT=/var/lib
export SERVER_ROOT
INSTANCE=rhpki-ca
export INSTANCE
c. Run run.sh to use old.txt to create an LDIF file.
run.sh /opt/redhat-ds/slapd-DS-instance/ldif/old.txt >
/opt/redhat-ds/slapd-DS-instance/ldif/old.ldif
11.Import the old.ldif LDIF file into the Certificate System 7.3 server instance's internal
database.
a. Open the Certificate System 7.3 database directory.
cd /opt/redhat-ds/slapd-DS-instance/db
b. Run the ldif2db tool to import the LDIF file into the Certificate System database. The
internal database name for the Certificate System instance is in the
internaldb.database parameter in the CS.cfg file. For example:
ldif2db -n server.example.com-rhpki-ca -i
/opt/redhat-ds/slapd-DS-instance/ldif/old.ldif
c. Force the virtual list views (VLV) indexes to be re-indexed.
db2index
Chapter 7. Step 6: Migrating Internal Databases
58
Page 65

Step 7: Customizing User Data
(Non-Console)
Copy all customized plug-ins, profiles, and forms to the Certificate System 7.3 server, and apply
any hand-edited changes to the Certificate System 7.3 CS.cfg file.
In this example, the profile configuration in the old_CA_instance has been changed to enable
S/MIME support. To migrate the configuration, make the same changes to the
new_CA_instance. In Certificate Management System 6.x, S/MIME support is enabled by
editing the caTokenUserEncryptionKeyEnrollment profile. Duplicate these changes over to
the corresponding new_CA_instance profile.
1. Log into the 6.x server as the Certificate Management System user for that machine, and
open the Certificate Management System profiles/ca/ directory.
2. Copy the p1 policy set in the caTokenUserEncryptionKeyEnrollment.cfg file, as shown:
policyset.set1.p1.constraint.class_id=noConstraintImpl
policyset.set1.p1.constraint.name=No Constraint
policyset.set1.p1.default.class_id=nsTokenUserKeySubjectNameDefaultImpl
policyset.set1.p1.default.name=nsTokenUserKeySubjectNameDefault
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.dnpattern=UID=$request.uid$,OU=Engineering,O=Example
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.enable=true
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.searchName=uid
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldapStringAttributes=uid,mail
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.basedn=dc=example,dc=com
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.maxConns=4
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.minConns=1
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.ldapconn.Version=2
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.ldapconn.host=ldaphostA.example.com
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.ldapconn.port=389
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.ldapconn.secureConn=false
This configuration enables S/MIME support for services that use this profile to obtain
certificates, such as token management systems.
3. Log into the new server as the Certificate System user, and open the Certificate System
profiles/ca/ directory.
4. Manually change the configuration in the new_CA_instance configuration to mimic the
old_CA_instance configuration by editing the p1 policy set in the
caTokenUserEncryptionKeyEnrollment.cfg file, as shown:
policyset.set1.p1.constraint.class_id=noConstraintImpl
policyset.set1.p1.constraint.name=No Constraint
policyset.set1.p1.default.class_id=nsTokenUserKeySubjectNameDefaultImpl
policyset.set1.p1.default.name=nsTokenUserKeySubjectNameDefault
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.dnpattern=UID=$request.uid$,
Chapter 8.
59
Page 66
OU=Engineering,O=Example
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.enable=true
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.searchName=uid
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldapStringAttributes=uid,mail
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.basedn=dc=example,dc=com
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.maxConns=4
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.minConns=1
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.ldapconn.Version=2
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.ldapconn.host=ldaphostA.example.com
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.ldapconn.port=389
policyset.set1.p1.default.params.ldap.ldapconn.secureConn=false
The altered profile serves certificate requests with S/MIME support enabled.
Chapter 8. Step 7: Customizing User Data (Non-Console)
60
Page 67

Step 8: Starting All Certificate
System 7.3 Instances
1. Restart the Directory Server for the Certificate System 7.3 instance.
cd /opt/redhat-ds/slapd-DS-instance
./start-slapd
2. Start all of the Certificate System 7.3 instances.
/etc/init.d/instance_ID start
Chapter 9.
61
Page 68

62
Page 69

Step 9: Generate New Certificate
System Server Certificates
If the Certificate System 7.3 server is on a different machine than the Certificate Management
System 6.x server, then an SSL server certificate associated with each newly-migrated
Certificate System server instance must be created.
There are three procedures to generate new server certificates, depending on the subsystem:
generating self-signed CA server certificates; generating a CA certificate request which is
signed by another CA; and generating DRM, OCSP, or TKS server certificates.
1. Self-Signing an SSL Server Certificate for a CA
1. Open the Certificate System 7.3 CA directory. For example:
cd /var/lib/rhpki-ca
2. Open the CA Console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:9443/ca
3. Select the Configuration tab.
4. Select the System Keys and Certificates option from the menu on the left.
5. Select the Local Certificates tab on the right.
6. Press the Add/Renew button to launch the Certificate Setup Wizard.
7. Follow the wizard prompts, and fill in the appropriate information.
a. In the Type of Operation panel, select the Request a certificate option (the default).
b. In the Certificate Selection panel, select SSL Server Certificate from the pull-down
menu.
Choose the Sign this SSL Certificate with my CA Signing Certificate option (the
default). The SSL server certificate is automatically generated at the end of the process.
c. In the Key-Pair Information for the SSL Server Certificate panel, select Create new
key pair.
Fill in information in the other fields on this panel as necessary.
d. Select the desired hashing algorithm or use the default of SHA-1 in the Message Digest
Chapter 10.
63
Page 70

Algorithm panel.
e. The next panel is Subject Name for the SSL Certificate. For the cn component, enter the
fully qualified domain name, such as zeta.example.com, of the Certificate System 7.3 CA
instance machine. Fill in information in the other fields on this panel as necessary (Red
Hat strongly recommends filling in the o and c components).
f. For the rest of the panels in the wizard, click next, and either fill in the options as desired
or accept all of the default settings.
8. Restart the Certificate System 7.3 CA instance.
/etc/init.d/rhpki-ca restart
2. Requesting a New SSL Server Certificate from a
Third-Party CA
1. Start the CA Console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:9443/ca
2. Select the newly-migrated Certificate System instance, and open the Console for that
instance.
3. In the Certificate System Console, select the Configuration tab.
4. In the left menu, select the Keys and Certificates option.
5. Select the Local Certificates tab on the right.
6. Press the Add/Renew button to launch the Certificate Setup Wizard.
7. Go through the screens in the wizard to request the certificate.
a. In the Type of Operation panel, select the Request a Certificate option (the default).
b. In the Certificate Selection panel, select SSL Server Certificate from the pull-down
menu, and choose the Create a request for submission to another CA option. An SSL
server certificate request is generated to submit to a CA for approval.
c. In the Key-Pair Information for the SSL Server Certificate panel, select Create new
key pair. Fill in information in the other fields on this panel.
d. The next panel is Subject Name for the SSL Certificate. For the cn component, enter the
fully qualified domain name of the Certificate System 7.3 CA instance machine, such as
Chapter 10. Step 9: Generate New Certificate System Server Certificates
64
Page 71

omega.example.com. Fill in information in the other fields on this panel; it is strongly
recommended that the o and c components also be filled in.
e. Go through the remaining panels in the Certificate Setup Wizard, and fill in the different
fields or use the defaults.
8. Obtain the SSL server certificate request, and store it in a base-64 file.
9. Submit the SSL server certificate request to another CA and wait for approval of the request.
10.Once the SSL server certificate has been approved, press the Add/Renew button to
relaunch the Certificate Setup Wizard.
a. In the Type of Operation panel, select the Install a certificate option.
b. In the Certificate Selection panel, select SSL Server Certificate from the pull-down
menu.
c. Enter in any necessary information in the Location of Certificate panel.
d. Go through the remaining panels in the Certificate Setup Wizard to install the updated SSL
server certificate.
11.Restart the Certificate System CA instance.
/etc/init.d/rhpki-ca restart
3. Generating a New DRM, OCSP, or TKS SSL Server
Certificate
1. Open the subsystem instance's administrative console. For example, for the DRM
subsystem:
pkiconsole https://server.example.com:10043/kra
2. Select the newly-imported Certificate System instance, and log into the Console for the
instance.
3. Open the Configuration tab.
4. Select the System Keys and Certificates option from the menu on the left.
5. Select the Local Certificates tab on the right.
6. Click the Add/Renew button to launch the Certificate Setup Wizard.
Generating a New DRM, OCSP, or TKS SSL
65
Page 72

a. In the Type of Operation panel, select the Request a certificate option (the default).
b. In the Certificate Selection panel, select SSL Server Certificate from the pull-down
menu. An SSL server certificate request is generated, which can be submitted to a CA for
approval.
c. In the Key-Pair Information for the SSL Server Certificate, select Create new key pair.
Fill in information in the other fields.
d. The next panel is Subject Name for the SSL Certificate. For the cn component, enter the
fully qualified domain name of the Certificate System subsystem machine, such as
omega.example.com. Fill in information in the other fields on this panel; Red Hat strongly
recommends filling in the o and c components also.
e. Click through the remaining panels in the Certificate Setup Wizard.
7. Obtain the SSL server certificate request, and store it in a base-64 file.
8. Submit the SSL server certificate request to a CA, and wait for approval of the request.
9. After the SSL server certificate is approved, click the Add/Renew button to relaunch the
Certificate Setup Wizard.
a. In the Type of Operation panel, select the Install a certificate option.
b. In the Certificate Selection panel, select SSL Server Certificate from the pull-down
menu.
c. Set the location information in the Location of Certificate if required.
d. Click through the remaining panels in the Certificate Setup Wizard to install the new SSL
server certificate for the migrated subsystem instance.
10.Restart the Certificate System subsystem instance.
/etc/init.d/rhpki-kra restart
Chapter 10. Step 9: Generate New Certificate System Server Certificates
66
Page 73

Step 10: Customizing User Data
(Console)
Use the Console to configure any custom behavior of the different subsystems, such as
customized plug-ins, logging, and auditing. A subsystem may have to be restarted once all
configuration changes have been applied.
Chapter 11.
67
Page 74

68
Page 75

Step 11: Verifying Migration
After migrating all Certificate Management System 6.x subsystems to the corresponding
Certificate System 7.3 subsystem instances, open the CA end-entities services page and each
subsystem agent services pages for the Certificate System 7.3 server to ensure that everything
is working properly. For example:
http://server.example.com:9080/ca/ee/ca
https://server.example.com:9443/ca/agent/ca
Then log into the Certificate System Console and verify that the new server can be managed
through the Console.
pkiconsole https://server.example.com/ca
The port numbers for all the agent services interfaces can be found in the server.xml in the
conf/ directory for the Certificate System 7.3 installation.
Chapter 12.
69
Page 76

70
 Loading...
Loading...