Page 1

Best Practices
for the use of
Bed Occupancy Sensors (BOS) and
Chair Occupancy Sensors (COS)
To clean the sensors wipe with a clean, dry cloth. Avoid holding any sensor by its
connection wire while wiping.
Test for correct activation of the BOS or COS using a resistance meter like a FLUKE
Model 175. When not activated, the resistance should be greater than 10 Mohms, when
activated, the resistance should be less than 10 ohms.
In the pictured test the resistance meter is reading beyond its capability to record a
resistance reading. Interpret this as much greater than 10 Mohms.
Page 2
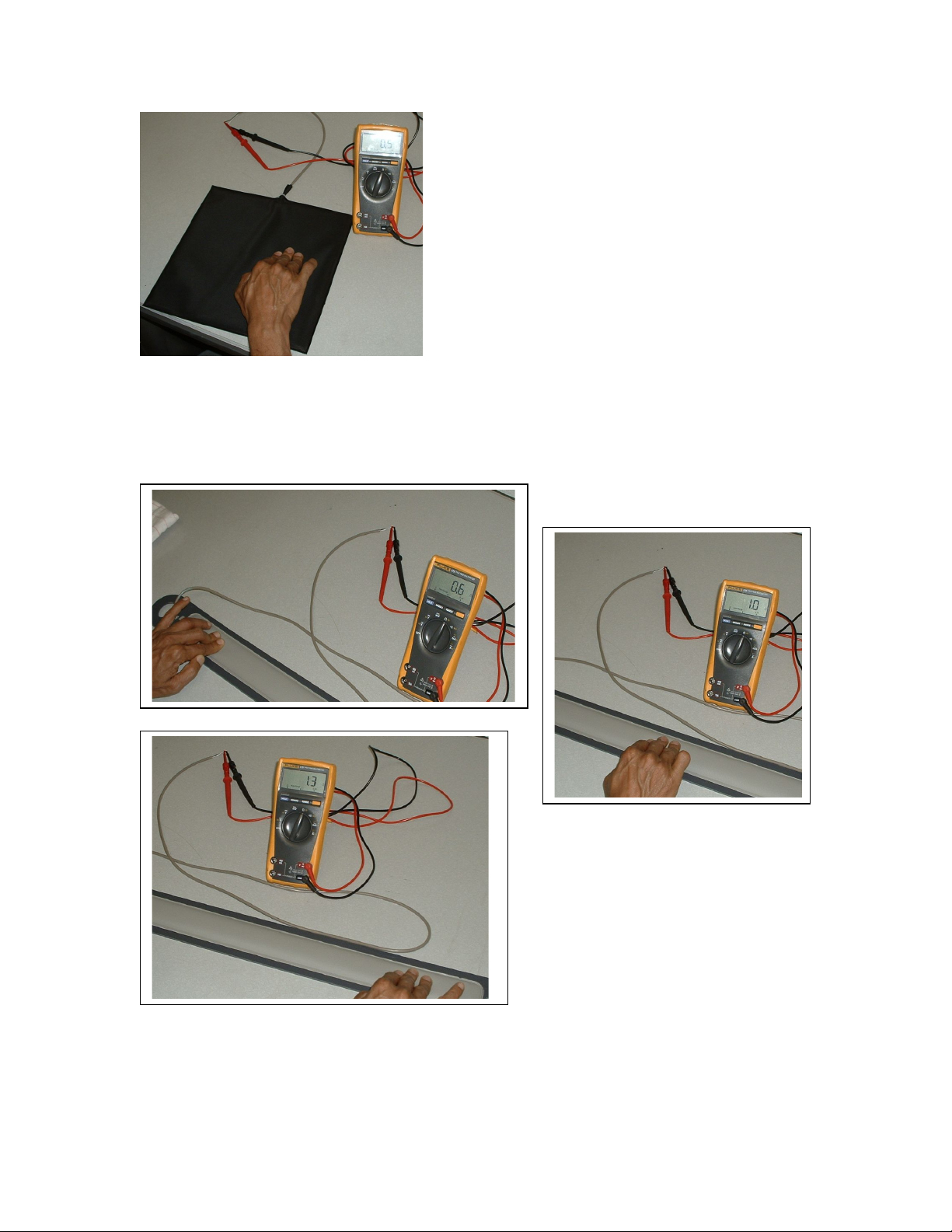
When the sensor is activated the reading should be less than 10 ohms. In this picture the
resistance indicated as the sensor is activated is 0.5 ohms, which is less than 10 ohms,
indicating a functional sensor.
In testing the sensor, be sure to activate it in multiple positions as shown above left,
middle and right.
Page 3

The correct activation force may be tested by placing a five (5) pound weight on to the
center of the BOS. The weight should have a pressure foot of one square inch to
accurately test the BOS activation.
Place the COS onto the chair seat so that
the maximum weight of the chair
occupant is directly over the sensor.
Position the BOS so that the person’s
weight is centered on the sensor. In
general the best position for the sensor is
under the buttocks or shoulders. In either
case the sensor must be on a firm flat
surface.
Page 4

When placing the sensor be sure to have the
wire exit the bed opposite the patient bed exit.
Shown in this photo is the WRONG orientation
for the bed sensor. Having the wire exit directly
under a person’s feet will encourage tripping
and potential premature failure of the sensor due
to accidental pulls on the wire.
NEVER remove the sensor from the bed or chair by
pulling on the wire. The wire can pull out of the sensor.
This breaks the sensor and cannot be restored.
Shown here is the correct way
to remove the BOS from the
bed. Grasp the sensor carrier
and remove the sensor
without pulling on the wire.
 Loading...
Loading...