Page 1

RDA5856TE
Features
Bluetooth v4.2 specification compliant,
supports BR/EDR
Bluetooth radio includes integrated balun
Support A2DP 1.2, HFP 1.5 and AVRCP1.5
104MHz RISC MCU and 104MHz Voice
Co-Processor(VoC) DSP core
Internal MCU ROM and RAM, VoC memory
and in-package serial flash memory.
Various serial interfaces: USB OTG 2.0 HS,
UART, I2C Master and SD Card Interface
Support analog key
Up to 4 PWM output
Independent powered Real-Time Clock
One channel 16 bits voice ADC and 16 bits
stereo DAC
Audio interfaces: analog stereo line in
Support MP3/SBC/WMA/ACC decoder
Support audio playback from SD/USB card
Integrated broadcast FM tuner which can
be tuned word-wide frequency band
Debug host interface allowing non-intrusive
in depth investigation GDB debugger
Internal 32K OSC for standby, shutoff and
sleep state
Integrated LDO
RDA5856TE
High performance, highly integrated
multi-media system-on-chip solution
with bluetooth connectivity
General Description
RDA5856TE is a high performance, highly
integrated multi-media system-on-chip solution
with Bluetooth connectivity, which specialized
in music and audio applications.
Integrating all essential electronic components,
including baseband, bluetooth transceiver,
power management, FM receiver onto a single
system on chip, RDA5856TE offers best in class
bill of material, space requirement and
cost/feature ratio for bluetooth music and
Applications
Bluetooth speakers
Bluetooth music box
Bluetooth headset or headphone
The 104MHz Voice Co-Processor supports
various audio applications. The integrated
audio codec supports two channels DAC and
one channel ADC. Playback form SD card and
USB card are also supported.
audio application.
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 1 / 17
Page 2

RDA5856TE
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ......................................................................................................................................... 2
1. Product Details ................................................................................................................................... 3
2. Package and Pinout ............................................................................................................................ 4
2.1. Pin Assignment ........................................................................................................................... 4
2.2. Pin Description ............................................................................................................................ 4
2.3. Package Dimensions ................................................................................................................... 5
3. Function Block Diagram ..................................................................................................................... 6
4. Clock and reset ................................................................................................................................... 6
5. MCU .................................................................................................................................................... 6
6. USB ..................................................................................................................................................... 7
7. VoC ..................................................................................................................................................... 7
8. Flash Controller .................................................................................................................................. 7
9. DMA .................................................................................................................................................... 8
10. AIF ....................................................................................................................................................... 8
11. SDMMC Controller ............................................................................................................................. 8
12. Timer .................................................................................................................................................. 8
13. GPIO .................................................................................................................................................... 8
14. UART ................................................................................................................................................... 9
15. Debug Host ......................................................................................................................................... 9
16. I2C Master .......................................................................................................................................... 9
17. Calendar ........................................................................................................................................... 10
18. PWM ................................................................................................................................................. 10
19. Audio Codec ..................................................................................................................................... 10
20. Power Management ......................................................................................................................... 10
20.1. Power on/off control ............................................................................................................. 11
20.2. Power Mode .......................................................................................................................... 11
21. Bluetooth Transceiver ...................................................................................................................... 11
22. FM ..................................................................................................................................................... 12
23. Electrical Characteristics .................................................................................................................. 13
23.1. BT RF Specifications ............................................................................................................... 13
23.2. FM RF Specifications ............................................................................................................. 15
23.3. Audio Characteristics............................................................................................................. 15
23.4. Recommended Operating Conditions ................................................................................... 15
24. Software ........................................................................................................................................... 16
25. Revision History ................................................................................................................................ 17
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 2 / 17
Page 3

1. Product Details
RDA5856TE
Bluetooth Radio
Fully compliant with Bluetooth radio
specification 4.2 including basic rate and
EDR.
On-chip Balun which combines the
balanced outputs of the PA on transmit and
produces the balanced input signals for the
LNA.
Microcontrollers
RDA in house developed 16/32 bit
processor
Reduced Instruction Set Architecture
Efficient 6-stage instruction pipeline
Voice Co-Processor
RDA Internal designed Voice DSP core
Two 16x16 -> 32 Multipliers
Bi-MAC (two accumulations on the same
register per cycle)
Eight 16 bit general purpose registers and
four 32 bit general purpose registers
Low power mode supported
Package Options
TSSOP24-EP
Audio Interface
Audio codec with 16 bits stereo DAC and
one channel 16 bits ADC
Support sample rate of 8, 11.025, 12, 16,
22.05, 32, 44.1 and 48 KHz.
Peripheral and Interfaces
Debug host for debug and normal UART
UART interface
USB 2.0 OTG high speed interface, support
USB audio
SDMMC controller for SD card
I2C master for internal and external
modules access
Up to 8 GPIOs
Integrated Power Management
Multiple LDOs
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 3 / 17
Page 4
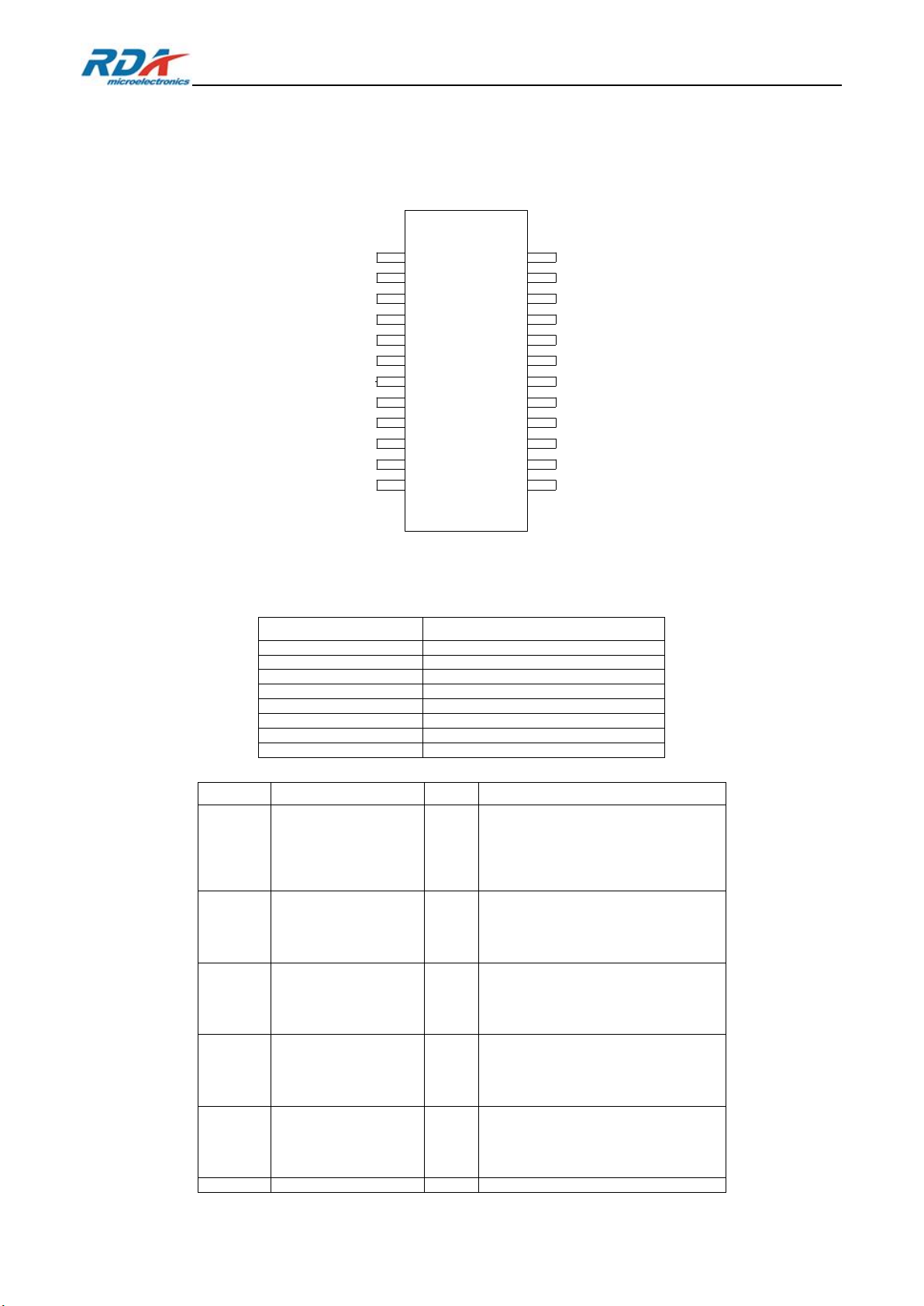
2. Package and Pinout
RDA5856TE
TSSOP24-EP
1
2
3
4
5
6
SD_DAT/GPIO_4<3>
SD_CMD/GPIO_4<5>
GPIO_3<7>
DVSS
DVDD
SD_CLK/GPIO_4<4>
7
8
9
10
11
12
AVSS_3V3
USB_DN/GPIO_0<0>
USB_DP/GPIO_0<1>
GPIO_4<0>
VBAT
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
AVDD_3V3
XTAL2
KEYSENSE/
GPIO_0<4>
AVDD_RF
BT_ANT
AVSS_RF
XTAL1
AVSS_CODEC
MIC_IN
DACOUT
LINEIN
AVDD_CODEC
FM_ANT
Pin Type
Description
I/O
Digital input/output
I
Digital input
O
Digital output
A, I
Analog input
A, O
Analog output
A, I/O
Analog input/output
PWR
Power
GND
Ground
PIN NO
NAME
TYPE
DESCRIPTION
1
GPIO_3<7>
I/O
Multiple functions configured by p37_cfg.
0: General purpose input/output
1: PWM output0
2: UART TXD
4: Debug Host TXD
7: GPIO interrupt input 6
2
GPIO_4<0>
I/O
Multiple functions configured by p40_cfg.
0: General purpose input/output
1: PWM output 1
4: Debug Host RXD
7: GPIO interrupt input 5
3
SD_DAT/GPIO_4<3>
I/O
Multiple functions configured by p43_cfg.
0: Debug Host Clock
3: General purpose input/output
5: SD data
7: GPIO interrupt input 2
4
SD_CLK/GPIO_4<4>
I/O
Multiple functions configured by p44_cfg.
0: Debug Host RXD
3: General purpose input/output
5: SD clock
7: GPIO interrupt input 1
5
SD_CMD/GPIO_4<5>
I/O
Multiple functions configured by p45_cfg.
0: Debug Host TXD
3: General purpose input/output
5: SD command
7: GPIO interrupt input 0
6
AVDD_3V3
PWR
Power of analogue 3.3V
2.1. Pin Assignment
RDA5856TE
2.2. Pin Description
Figure 1 Pin Assignment
Table 1 Pin Types
Table 2 pin description
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 4 / 17
Page 5
RDA5856TE
7
AVSS_3V3
GND
Ground of analogue 3.3V
8
DVSS
GND
Ground of digital core
9
DVDD
PWR
Power of digital code
10
VBAT
PWR
Battery power supply
11
USB_DN/GPIO_0<0>
A, I/O
Or
I/O
Multiple functions configured by p00_cfg.
0: General purpose input/output
2: UART RXD
6: USB negative input
7: USB detect negative input
12
USB_DP/GPIO_0<1>
A, I/O
Or
I/O
Multiple functions configured by p01_cfg.
0: General purpose input/output
2: UART TXD
6: USB positive input
7: USB detect positive input
13
LINEIN
A, I
Line input
14
DACOUT
A, O
DAC output
15
MIC_IN
A, I
Microphone input
16
AVDD_CODEC
PWR
Analogue power supply of headphone
17
AVSS_CODEC
GND
Analogue ground of headphone
18
FM_ANT
A, I
FM receiver input
19
AVDD_RF
PWR
Analogue power supply of bluetooth RF
20
AVSS_RF
GND
Analogue ground of bluetooth RF
21
BT_ANT
AI/O
Bluetooth transmitter output/receiver input
22
KEYSENSE/GPIO_0<4>
A, I
or
I/O
Multiple functions configured by p04_cfg.
0: General purpose input/output
4: Debug Host RXD
5: Key input
23
XTAL1
A, I
XTAL input
24
XTAL2
A, O
XTAL output
2.3. Package Dimensions
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 5 / 17
Page 6
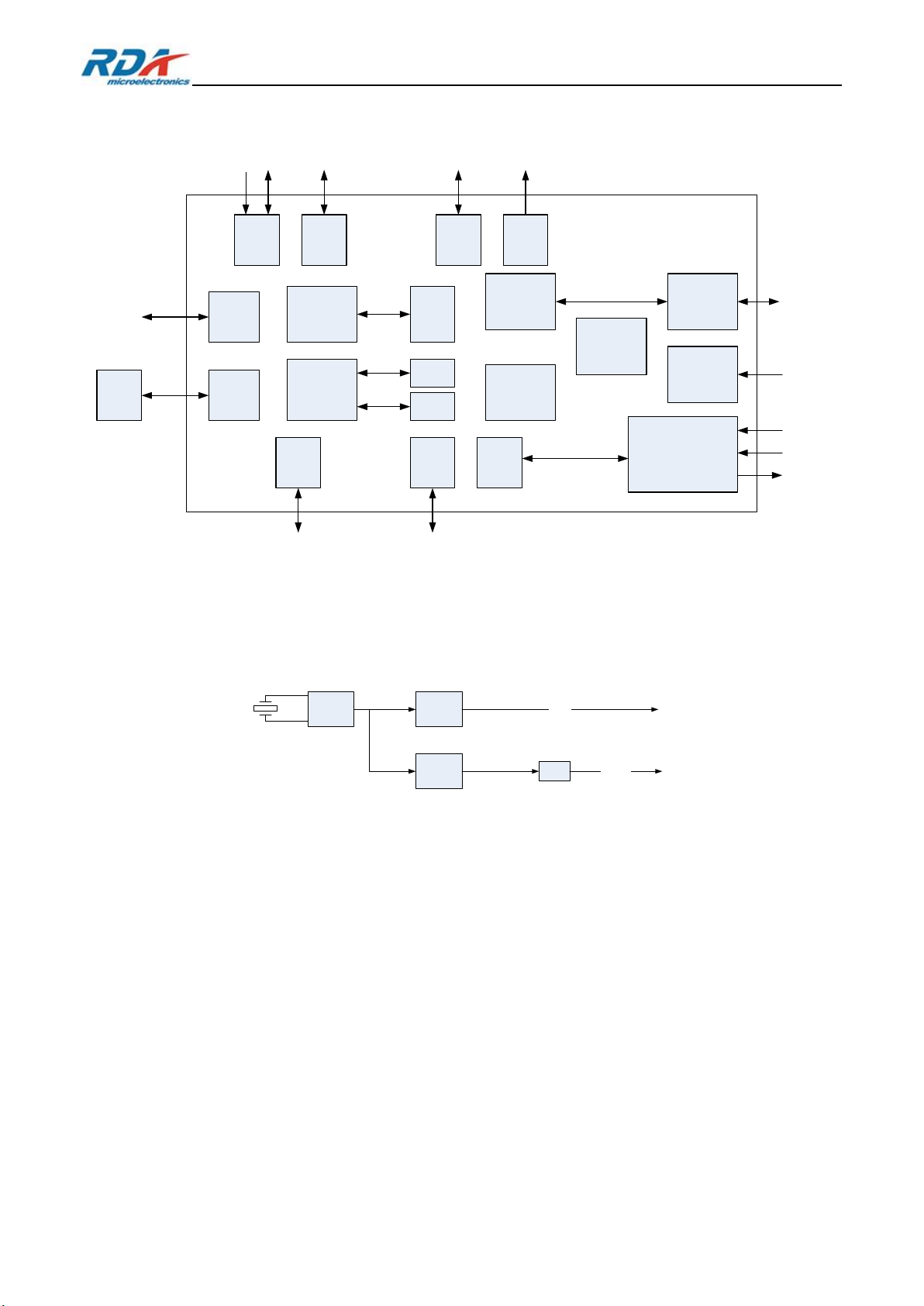
3. Function Block Diagram
I2C
Master
Debug
Host
UART SD/MMC PWM
USB 2.0
OTG
GPIO AIF
VOC
MCU
VOC
MEM
MCU
RAM
MCU
RAM
DMA
BT
Baseband
FM
Analog Audio
CODEC
BT
Radio
BT_ANT
FM_ANT
Line In
MIC In
DAC Out
PMU
Flash
Controller
DP/DN
PMW
out x4
SD UARTUARTHST_CLK
I2C
GPIO
Serial
Flash
SYSPLL
AUDPLL DIV
clk_codec
clk_sys
XTAL
RDA5856TE
Figure 2 RDA5856TE Block Diagram
4. Clock and reset
RDA5856TE has a reference clock input from either a crystal or an external clock source. There are
two internal PLL which use XTAL clock as reference. They are used for system and audio
applications.
Figure 3 Clock Structure
RDA5856TE has several reset sources, as following:
POR
Entire SoC is reset after power supply ramping from 0v to VBAT.
External Pin Reset
Entire SoC is reset except PMU.
Warm Reset
Global soft reset
DBB can be reset by set soft reset register in system control register map.
Watch Dog Reset
DBB will be reset when watch dog timer expired.
5. MCU
RDA RISC is a 16/32-bits processor which using a Reduced Instruction Set Architecture, an efficient
6-stage instruction pipeline, it provides high performance to the system.
RDA RISC Core.
32x32-bit Multiplier.
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 6 / 17
Page 7

RDA5856TE
32x32-bit -> 64-bit Multiplier Accumulator (MAC) in 2 cycles (pipelined).
Read / Write Buffer.
16/32 bit instruction set.
32 interrupt sources.
TCM interface for ROM and flash code read
6. USB
RDA5856TE has a high-speed USB OTG interface for communicating with other devices, such as PC
or USB card. Bothe USB PHY and Link layer is integrated. It supports both host and device. USB role
detection is included to support USB Type A.
Operates either as the host/peripheral in point-to-point communications with another USB
function or as a function controller for a USB peripheral
Complies with the USB 2.0 standard for high-speed (480 Mbps) functions
Supports point-to-point communications with one high-, full- or low-speed device
Integrated USB PHY with ESD protection circuits
Supports Control, Interrupt, Bulk and Isochronous transfer
5 Endpoint with FIFOs
One Bi-directional Control Endpoint (EP0)
Four soft configurable Bi-directional Endpoints
Certified compliant with the On-The-Go supplement
Supports Session Request Protocol (SRP) and Host Negotiation Protocol (HNP)
7. VoC
The VoC is designed to process different vocoders. It is developed as a target-specific DSP core,
including basic function-call support. It executes the code with very little control intervention from
the MCU. It is controlled and configured by the CPU through the AMBA bus.
Bi-MAC, single test/logic Computational Unit with two 16x16 -> 32-bit multipliers
Eight 16-bit general purpose registers that can be combined in four 32-bit general purpose
registers.
All 16-bit registers can be used as pointers; four of them are incremental (for easy array
addressing).
Four 32-bit general purpose registers.
Double stack with random access: for 32-bit & 16-bit values (push, pop).
Functions call support (jal, return).
Two zero-cycle loop counters.
Pointer & Direct addressing modes.
DMA sub-module for block transfers between external memory and VoC memories.
8. Flash Controller
The Flash controller provides instruction/data management on serial Flash devices. A command poll
is used to support variable commands for variable flash devices. Up to one 512/256Mb Flash or two
128Mb (16MB) Flash devices are supported using Standard, or Dual or Quad SPI. Besides the
normal Flash read mode using register address through RX FIFO, the Flash controller provides an
XIP mode, in which CPU can read Flash address range as RAMs.
Flash size up to 512Mb x 1, or 256Mb x 1, or 128Mb x 2
Standard, Dual, Quad SPI.
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 7 / 17
Page 8

RDA5856TE
Up to 52MHz SPI clock.
Command poll to support variable Flash commands, including advanced read commands.
Normal Read & XIP mode.
9. DMA
RDA5856TE support various DMA functions. It supports memory to memory, memory to peripheral,
peripheral to memory transfers. For transfers between memory and peripheral, hardware
handshake is supported and multiple DMA channels shared with peripherals.
Support for linear memory transfers.
Multiple DMA channels
Support for word, half-word and byte aligned addresses.
Burst transfer supported
Interrupt generation at completion of the transaction.
Can fill a part of the memory with a 32-bit pattern.
Frame Check Sequence computation
10. AIF
The Audio Interface (AIF) module is the audio interface between the system and internal audio
codec.
All common DTMF and Comfort Tones can be generated and gained from -15 dB to 0 dB
Side Tone fully configurable: Mute or amplification from -36 dB to +6 dB
Loop back capabilities for test purposes.
16-bit mono samples from ADC.
16-bit stereo samples to stereo DAC.
Separate TX and RX strobe lines for synchronization.
11. SDMMC Controller
This module connects inner bus and outer SD or MMC card. It receives the inner command and
data, transfers it to outer SD or MMC card, and transfer response or data back.
SD Card Specification Version 2.0
SDIO Version 1.10
MMC specification Version 3.1
Hot insertion and removal of media cards will be considered by GPIO module
12. Timer
There are three different timers.
1 24-bit decremental timer for OS, ticks of 16384Hz.
1 32-bit incremental hardware delay timer, ticks of 16384Hz.
1 24-bit decremental watchdog timer, ticks of 32768Hz.
Multiple IRQ sources: timers wrap, interval arrives.
13. GPIO
GPIO module has configurable number of General Purpose Input or Output ports (GPIO).
Up to 8 GPIOs configurable as input or output.
Up to 5 GPIOs can generate interrupt.
Various interrupt triggered mode.
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 8 / 17
Page 9

RDA5856TE
Rising/Falling edge.
High/Low level.
14. UART
RDA5856TE includes UART which can be used as a serial interface or as an IrDA interface.
Smooth stop feature (the UART stops after the end of the current word transfer).
Break generation and detection.
Supports low speed IrDA 1.0 SIR mode by adding external hardware.
DMA capabilities to allow fully automated data transfers.
Wide selection of programmable interrupts to allow interrupt driven data transfer
management.
Loop Back capabilities for test purposes.
15. Debug Host
Debug Host module contains 1 normal Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter channels
(UART) and 1 Debug UART. The two UARTs share the same TX/RX engines, which sends and receives
byte data from serial interface. Each UART has its own control sub-module and own APB interface.
Debug Host module parses the incoming data from serial interface to switch between the normal
UART and the Debug UART.
Normal UART
The normal UART can be used for traces and other purposes. For APB interface, it is exactly the
same to the other UARTs in the system. However, if Debug UART is enabled, it should have the
same serial interface configuration as the Debug UART. Some of its configuration options will be
masked in this case. To adapt different clock frequency, the normal UART uses asynchronous FIFO,
which uses gray code to represent the read and write pointer positions.
Debug UART
The Debug UART is specially designed for communicating debug information with a PC host. The
serial interface of Debug UART is a simplified version of the normal UART and is less configurable.
Each sample is sent serially, has 1 start bit (always zero), 8 data bits, and 1 stop bits (always one).
Breaks (data line held low) can be generated and detected allowing resynchronizing the two
devices.
16. I2C Master
RDA5856TE has I2C master which supports 100Kbps and 400Kbps.
Compatible with Philips I2C standard
Multi Master Operation
Software programmable clock frequency
Clock stretching and wait state generation
Software programmable acknowledge bit
Interrupt or bit-polling driven byte-by-byte data-transfers
Arbitration lost interrupt, with automatic transfer cancellation
Start/Stop/Repeated Start/Acknowledge generation
Start/Stop/Repeated Start detection
Bus busy detection
Supports 7 and 10bit addressing mode
Operates from a wide range of input clock frequencies
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 9 / 17
Page 10

RDA5856TE
17. Calendar
The calendar module provides date and time information. It works on the 32.768 KHz oscillator with
independent power supply. In addition to provide timing data, alarm interrupt is generated and it is
also used to power-up the baseband core by sending wakeup signal.
Independent power supply.
Counters for second, minute, hour, day, month, year and day of week.
Maxim day of each month stored in module, leap year supported.
Alarm generate, wakeup triggered by alarm. Alarm IRQ.
Periodical IRQ for certain intervals.
18. PWM
The PWM module generates 4 independent PWM outputs, utilizing 3 specialized modulation
schemes. All PWM outputs can be configured to PWL, PWT and LGP mode.
Pulse Width Tone (PWT)
Generates square wave output capable of driving piezo electric speaker
Variable frequency between 349Hz and 5276Hz with 12 half-tone frequencies per
octave
Volume control
Light Pulse Generation (LPG)
Adjustable PWM frequency is from 0.01Hz ~ 6.5MHz
Adjustable on-time/off-time is from 0.77us to 50s.
Customized output mode for square wave
Pulse Width Light (PWL)
Pseudo random bit sequence with output on-time proportional to a programmed
threshold value
Minimizes flicker
19. Audio Codec
The audio codec has one channel voice ADC and audio DAC, which supports mono voice input and
stereo audio output. It also has flexible mixing and loopback paths to support variable scenario
requirements, such as side tone, FM recording, etc.
One channel 16 bits ADC and 16 bits stereo DAC
Mono input for voice and audio band, input resistance is typically 4KΩ.
Integrated mic bias which don’t need external load capacitor with configurable output
voltage
Stereo outputs are supported, could drive 16Ω/32Ω headphone, or act as line-out.
Support sample rate of 8, 11.025, 12, 16, 22.05, 32, 44.1 and 48 KHz.
Configurable gain for audio input and output path, gains control is implemented in both
digital and analog.
Stereo FM playback.
Flexible audio/voice path mixing/loopback.
20. Power Management
PMU integrated multiple LDOs.
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 10 / 17
Page 11

RDA5856TE
Low Power Mode
Power Off Mode
Active Power Mode
1
0
LP_MODE
0
1
Software control register:
Default value:0, reset to 0 when
PowerOn goes low
To LDOs and
DCDC control
Power On Mode
1
0
PowerOn
20.1. Power on/off control
PMU performs a POR once battery is connected which resets all components in chip. PMU can be
configured to support either hard mode power on or soft mode power on.
Hard mode
No power key implementation is needed. System is powered on once battery is connected.
Soft mode
An extra key press (i.e. Power on key pressed) is needed to power on the system.
20.2. Power Mode
The PMU implements multiple power mode defining the LDOs activation in various modes.
Power Off Mode
Used when the system is off (system has been shut-off or first time battery is plugged...). In
this case only V_RTC is provided.
Power On Mode
After Power Up sequence, all LDOs that have “reset state ON” are activated.
Active Power Mode
Used once system has booted and decides to switch from “Power On Mode”. This mode is
programmable.
Low Power Mode
Used when the system goes to low-power mode. This mode is programmable.
Figure 4 Principle schematic for Power-profile usage
21. Bluetooth Transceiver
RDA5856TE integrated bluetooth baseband and radio which has been designed to provide low
power, low cost and robust communications for Bluetooth application. It is fully compliant with
Bluetooth radio specification 4.2 including basic rate, EDR to 3MHz. RDA5856TE contains an on-chip
Balun which combines the balanced outputs of the PA on transmit and produces the balanced input
signals for the LNA.
Baseband
The BT baseband core handles packet and bit stream processing including packing/unpacking
for different packet types, error checking, whitening/de-whitening, error correction, and
encryption/decryption and so on。
Compliant with Bluetooth 4.2 + EDR specification
- Support BR, EDR 2M/3M
- Support SCO/eSCO
Bluetooth Piconet and Scatternet support
Low power support and optimization
- Support AFH
- Sniff Subrating
- Enhance Inquiry Response
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 11 / 17
Page 12

RDA5856TE
- Sleep on 32.768KHz clock
Test Mode support
- BR/EDR Transmitter test and Loopback test
- Fixed pattern, PRBS-9, PRBS-15 or user defined pattern
RF Receiver
The receiver features a low-IF architecture that enables the channel select filters to be
integrated onto the die. The down converted signal is digitalized by a sigma-delta AD and
further processed by a digital demodulator. The receiver path provides a low noise figure, a
high degree of linearity and an extended dynamic range.
RF Transmitter
The transmitter features a direct IQ modulator to minimize frequency drift during a packet,
which results in a well-controlled modulation index. The digital modulator performs the data
modulation and filtering required for the Bluetooth signal. The internal PA has a programmable
output power that meets Class 2 and class3 Bluetooth radio requirements without an external
RF PA.
RF Synthesizer
The radio synthesizer is fully integrated onto the die with no requirement for external LC
resonators or loop filter. The synthesizer provides fast frequency locking and low phase noise
to meet Bluetooth specification.
22. FM
RDA5856TE integrates a broadcast FM stereo radio tuner with fully integrated synthesizer and MPX
decoder. The tuner requires the least external component. It has a powerful low-IF digital audio
processor, this make it has optimum sound quality with varying reception conditions. It can be
tuned to the worldwide frequency band.
Low Power Consumption
Support worldwide frequency band
65-108MHz
Digital low-IF tuner
Image-reject down-converter
High performance A/D converter
Fully integrated digital frequency synthesizer
Fully integrated on-chip RF and IF VCO
Fully integrated on-chip loop filter
Autonomous search tuning
Auto gain control (AGC)
Digital adaptive noise cancellation
Mono/stereo switch
Soft mute
Soft blending
Programmable de-emphasis (50/75 us)
Receive signal strength indicator (RSSI)
Bass boost
Volume control
32.768 KHz Reference Clock
I2C control bus interface
Directly support 32Ω resistance loading
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 12 / 17
Page 13

RDA5856TE
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITION
MIN
TYP.
MAX
UNIT
General Specification
Sensitivity @ 0.1% BER
/
-93 / dBm
Maximum input @ 0.1% BER
0 / /
dBm
C/I co-channel
/ / 9
dB
Adjacent channel selectivity C/I
F = F0 + 1 MHz
/ / -12
dB
F = F0 – 1 MHz
/ / -10
dB
F = F0 + 2 MHz
/ / -40
dB
F = F0 – 2 MHz
/ / -40
dB
F = F0 + 3 MHz
/ / -45
dB
F = F0 – 3 MHz
/ / -45
dB
F = F_image
/ / -10
dB
Out-of-band blocking
30MHz–2000MHz
-10 / /
dBm
2000MHz–2400MHz
-20 / /
dBm
2500MHz–3000MHz
-20 / /
dBm
3000MHz–12.5GHz
-10 / /
dBm
Inter-modulation
-34 / /
dBm
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITION
MIN
TYP.
MAX
UNIT
General Specification
Max RF output power
/ 8 /
dBm
Power control step
/ 3 /
dB
20dB bandwidth
/
0.92
/
MHz
Adjacent channel transmitter power
|M – N| = 2 MHz
/ / -52
dBm
|M – N| >= 3 MHz
/ / -55
dBm
△ f1avg Maximum modulation
/
152 / kHz
△ f2avg/△f1avg
/
0.97
/ / ICFT
/ / 10
kHz
Drift (1 slot packet)
/
10 / kHz
Drift (5 slot packet)
/
10 / kHz
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITION
MIN
TYP.
MAX
UNIT
π/4 DQPSK
Sensitivity @0.01% BER
/
-92.5
/
dBm
Maximum input @ 0.1% BER
-3 / /
dBm
C/I co-channel
/ / 10
dB
Adjacent channel selectivity C/I
F = F0 + 1 MHz
/ / -10
dB
F = F0 – 1 MHz
/ / -8
dB
23. Electrical Characteristics
23.1. BT RF Specifications
Receiver Characteristics --- Basic Data Rate (VBAT = 4.0 V, TA = +27℃, unless otherwise specified)
Transmitter Characteristics --- Basic Data Rate (VBAT = 4.0 V, TA = +27℃, unless otherwise specified)
Receiver Characteristics --- Enhanced Data Rate (VBAT = 4.0 V, TA = +27℃, unless otherwise specified)
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 13 / 17
Page 14

RDA5856TE
F = F0 + 2 MHz
/ / -39
dB
F = F0 – 2 MHz
/ / -39
dB
F = F0 + 3 MHz
/ / -45
dB
F = F0 – 3 MHz
/ / -45
dB
F = F_image
/ / -8
dB
8DPSK
Sensitivity @0.01% BER
/
-82.5
/
dBm
Maximum input @ 0.1% BER
-5 / /
dBm
C/I co-channel
/ / 20
dB
Adjacent channel selectivity C/I
F = F0 + 1 MHz
/ / -2
dB
F = F0 – 1 MHz
/ / 0
dB
F = F0 + 2 MHz
/ / -28
dB
F = F0 – 2 MHz
/ / -28
dB
F = F0 + 3 MHz
/ / -38
dB
F = F0 – 3 MHz
/ / -38
dB
F = F_image
/ / 0
dB
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITION
MIN
TYP.
MAX
UNIT
General Specification
Max RF output power
/ 4 /
dBm
Relative transmit power
/
-1.5
/
dB
π/4 DQPSK max w0
/
-5 / kHz
π/4 DQPSK max wi
/
20 / kHz
π/4 DQPSK max |wi + w0|
/
17 / kHz
8DPSK max w0
/
-2 / kHz
8DPSK max wi
/
17 / kHz
8DPSK max |wi + w0|
/
17 / kHz
π/4 DQPSK Modulation Accuracy
RMS DEVM
/
10 / %
DEVM < 30%
/
100 / %
Peak DEVM
/ / 24
%
8DPSK Modulation Accuracy
RMS DEVM
/
10 / %
DEVM < 30%
/
99.8
/ % Peak DEVM
/ / 22
%
π/4 DQPSK In-band spurious emissions
|M – N| =1 MHz
/ / -38
dBc
|M – N| =2 MHz
/ / -36
dBm
|M – N| >= 3 MHz
/ / -41
dBm
8DPSK In-band spurious emissions
|M – N| =1 MHz
/ / -37
dBc
|M – N| =2 MHz
/ / -36
dBm
|M – N| >= 3 MHz
/ / -40
dBm
EDR Differential Phase Coding
/
100 / %
Transmitter Characteristics --- Enhanced Data Rate (VBAT = 4.0 V, TA = +27℃, unless otherwise specified)
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 14 / 17
Page 15

RDA5856TE
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
General Parameters
F
in
FM Input Frequency
BAND=00
87 108
MHz
BAND=01
76 91
MHz
BAND=02
76 106
MHz
BAND=03
65 76
MHz
V
rf
Sensitivity
1,2,3
(S+N)/N=26dB
2 µV EMF
R
in
LNA Input Resistance
7
150 Ω
C
in
LNA Input Capacitance
7
2 4 6
pF
(S+N)/N
Maximum Signal Plus Noise to
Noise Ratio
1,2
55
60 - dB
THD
Audio Total Harmonic
Distortion
1,3,6
0.15
0.2
%
R
L
Audio Output Loading Resistance
Single-ended
32
Ω
Pins LNAN, LNAP
V
com_rfin
Pins LNAN and LNAP Input
Common Mode Voltage
0
V
V
com
Audio Output Common Mode
Voltage
0.95 1 1.05
V
Parameter
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
SNR
-
92.5 - dB
THD
-
-80 - dB
Output Voltage
-
590
-
mV rms
Operating Condition
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
Operating Temperature Range
-20
20
65
℃
VBAT
3.4
3.8
4.35 V AVDDHP
2.22
2.48
2.76
V
AVDD33
2.88
3.25
3.3
V
DVDD
1.02
1.2
1.44 V AVDD_RF
2.23
2.37
2.53
V
23.2. FM RF Specifications
(VDD = 2,7 to 5,5V, TA = -25°C to 85 °C, unless otherwise specified)
Notes:
1. Fin=65 to 115MHz; Fmod=1KHz; de-emphasis=75 s; MONO=1; L=R unless noted otherwise;
2. f=22.5KHz; 3. BAF = 300Hz to 15KHz, RBW <=10Hz; 4. |f2-f1|>1MHz, f0=2xf1-f2, AGC disable, Fin=76 to 108MHz;
5. PRF=60dBUV; 6. F=75KHz,fpilot=10% 7. Measured at VEMF = 1 m V, f RF = 65 to 108MHz
8. At LOUT and ROUT pins
9. Adjustable
23.3. Audio Characteristics
23.4. Recommended Operating Conditions
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 15 / 17
Page 16

RDA5856TE
24. Software
The software development of RDA5856TE is support by RDA R-IOT SDK.
R-IoT is the IOT development platform of RDA, it composed of SDK, Eclipse IDE and some other
auxiliary tools for debugging and audio calibration, etc. The SDK provides all the necessary
components and standard APIs for the platform. The SDK is based on Eclipse which includes the
cross-compile tools, connector to deploy and debug your software on the chip, basic library and
sample code needed for embedded software development.
RDA has a variety of IoT chips for different requirements and scenarios. It has single bluetooth, WIFI
chip; also it has SoC combined with bluetooth, WIFI and GSM for wireless network connection, and
GPIO, I2C and etc. pins to connect sensor and peripheral device. What’s more, RDA IoT chip supports
co-exist technology which allows bluetooth and WIFI work simultaneously. Via HAL (hardware
abstract layer) R-IoT provides the support of all RDA IoT chips.
Meanwhile, R-IoT offers “micro-services” style architecture to facilitate software development and
maintenance. IoT applications are based on these “micro-services”, for instance, if we build a
bluetooth music player, we need to program with “BT micro-services”. In most cases, these
“micro-services” running in its own COS task and communicating with other services by sending or
receiving COS event. The COS (Common OS) is an OS wrapper over C interface, it provides developers
unified API so that developers could program with such interface without having to consider the
native OS details.
Below is the diagram of R-IoT software architecture:
Figure 5 R-IoT Software Architecture
There are 5 layers:
Chip and Device Layer
HAL Layer
HAL is the module to configure chip and device; it tries to be common for all chips and devices, so
the configuration must be very similar.
OS and Driver Layer
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 16 / 17
Page 17

RDA5856TE
Revision
Date
Description
0.01
2016/05/13
Initial draft
0.02
2016/07/12
Add “Recommended Operation Conditions”
0.03
2016/08/04
1. Update “Package and Pinout”
2. Update “Audio Characteristics”
R-IoT tries to support more Oses like RT-Thread, etc. without jeopardizing high layer service and
application by introducing Common OS wrapper. Drivers are all external chip driver as opposed to
chip drivers.
Service Layer
These services are small building blocks, highly decoupled and provide user interface to application
layer.
Application Layer
In conclusion, R-IoT is almost a “turn-key” platform for IoT application development. The original
SDK already had rich features for many mainstream IoT applications including home appliances and
automation, asset tracking systems and consumer electronics devices, this enables the customer to
rapid delivery its unique product to the market. Beyond that, its modularized and scalable software
architecture makes it easier to support more Oses, chip, micro-services and cloud vendors, all these
bring not only technical advantages but cost advantages as well.
For more information, please refer to RDA IOT SDK Development Manual and RDA IOT BT
Development Manual.
25. Revision History
Copyright@2016 RDA Microelectronics. CONFIDENTIAL 17 / 17
 Loading...
Loading...