Page 1
RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
RDA5851S Bluetooth Multi-Media Single-Chip Terminal
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 1 / 72
FEATURES
● External Memory Interface
Integrated 8Mbit(or 1MByte) Flash on chip
Power efficient using retention technology to
avoid floating lines
Flexible IO voltage
● Power Management
Power On reset control
Internal 32K OSC for standby/ shutoff/ sleep
state
Battery charger (from USB or AC charger)
Integrated all internal voltages from VBAT
Provide all LDOs for external components
● User Interface
ADC serial interface Keypad
● Connectivity
USB 1.1 Device
UART interface
1 SD controller
I2C controller
I2S controller
General Purpose I/Os
1 GPADC, 10bits, 1 channel
● Audio
1 channel voice ADC, 8kHz, 13 bits/sample
for microphone
Voice DAC, 8kHz, 13 bits/sample for
receiver
High fidelity Stereo DAC, up to 48kHz, 16
bits per sample
Stereo analog audio line input
● Debug
Host debug interface allowing non intrusive
in depth investigation
GDB debugger
Execution logger and profiling through debug
port
High level text based debugging using Host
debug or USB
● FM
Integrated Broadcast FM tuner which can be
tuned world-wide frequency band
● Bluetooth
Integrated Bluetooth SoC complaint with 2.1
+ EDR standard
APPLICATIONS
The high level of integration achieved on RDA5851S
allows for highly integrated bluetooth music box and
stereo headset without increasing the BOM.
Page 2

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
A high performance, high integrated multi-media system-on-chip
solution with Bluetooth connectivity.
RDA5851S is a high performance, highly integrated multi-media system-on-chip solution with bluetooth
connectivity. This is a newer generation than 5851, which specialized in music and audio applications, such as
bluetooth music boom box, bluetooth stereo headset, etc.
Integrating all essential electronic components, including baseband, bluetooth transceiver, power management,
FM receiver onto a single system on chip, RDA5851S offers best in class bill of material, space requirement and
cost/feature ratio for bluetooth music and audio application.
Built around a cost effective 32-bit XCPU RISC core running at up to 312MHz with 4k of Instruction cache and
4k of Data cache, RDA5851S offers plenty of processing power for multimedia applications. A high performance
proprietary 16/32-bit digital signal processing engine can further improve overall performance and user
experience when performing complex multimedia tasks.
It is also packed with impressive connectivity for easy scalability of the system, allowing glue less interfaces to
SDMMC Memory Cards and USB (slave, full speed).
Additionally, RDA5851S integrates a FM tuner and a Bluetooth module which completely include digital,
analogue and RF function. And they can easily work only with a few passive components as filter or matching
network.
RDA5851S is available in a small footprint, fine pitch, 6.5 X 6.5, 81 ball TFBGA package.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 2 / 72
Page 3

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Table of Contents
Features ................................................................................................................................................................ 1
Applications ........................................................................................................................................................... 1
General Description ..............................................................................................................................................2
A. Architecture Overview ......................................................................................................................................6
B. Block Description ........................................................................................................................................... 10
B.I System Modules ......................................................................................................................................10
B.I.1 System CPU (XCPU) ....................................................................................................................... 10
B.I.2 Memory Bridge ................................................................................................................................ 19
Operations ........................................................................................................................................... 20
B.I.3 Direct Memory Access (DMA) .......................................................................................................... 21
B.I.4 Page Spy ......................................................................................................................................... 21
B.I.5 System Intelligent Flow Controller (Sys IFC) ....................................................................................21
AHB2APB bridge operation ..................................................................................................................22
DMA Operations .................................................................................................................................. 22
Debug channel operations ................................................................................................................... 23
B.II System Peripherals ................................................................................................................................. 24
B.II.1 System and Clock Control ..............................................................................................................24
B.II.2 Trace (Normal UART) and Host (Debug UART) Port .....................................................................26
B.II.3 I2C .................................................................................................................................................. 32
B.II.4 General Purpose Input Output .......................................................................................................34
B.II.5 Keypad ........................................................................................................................................... 34
B.II.6 Timers ............................................................................................................................................ 34
B.II.7 Debug Port (EXL, PXTS, Signal Spy) .............................................................................................35
B.II.8 General Purpose Analog to Digital Converter (GP ADC) ................................................................ 35
B.II.9 Timing Control Unit and Low Power Synchronizer (TCU+LPS) ....................................................... 36
B.II.10 System AHB Monitor (Sys AHBC Mon) ........................................................................................36
B.II.11 System IRQ Controller (Sys IRQ) ................................................................................................. 37
B.II.12 USB Controller ..............................................................................................................................37
B.II.13 SD/MMC Controller ....................................................................................................................... 38
B.II.14 Audio Interface Analog + I2S (AIF) ...............................................................................................38
B.III Digital Modules ......................................................................................................................................39
B.III.1 Voice Coprocessor (VoC) .............................................................................................................. 39
B.IV Analog Modules ..................................................................................................................................... 39
SPI Interface for Analog IP control ....................................................................................................... 39
Power Management Unit ...................................................................................................................... 40
Analog module (ABB) ..........................................................................................................................45
B.V FM .......................................................................................................................................................... 47
General Description ............................................................................................................................. 47
Features ............................................................................................................................................... 47
Block Description ................................................................................................................................. 47
Receiver Characteristics ......................................................................................................................48
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 3 / 72
Page 4

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
B.VI Bluetooth ...............................................................................................................................................49
General Description ............................................................................................................................. 49
Features ............................................................................................................................................... 50
Block Description ................................................................................................................................. 50
Performance Characteristics ................................................................................................................51
C. Memory Map .................................................................................................................................................. 54
D. Pins Description ............................................................................................................................................. 56
D.I Pin-out ..................................................................................................................................................... 56
E. Electrical Characteristics ...............................................................................................................................60
E.I Absolute Maximum Rating ....................................................................................................................... 60
E.II Temperature Characteristics ..................................................................................................................60
E.III Audio Characteristics .............................................................................................................................60
E.V DC Characteristics .................................................................................................................................62
E.VI Digital IO DC Characteristics ................................................................................................................. 67
E.VII Digital IO AC Characteristics (SPI Interface Timing) ............................................................................68
F. Packaging ...................................................................................................................................................... 70
G. Ball Out ......................................................................................................................................................... 71
H. Glossary ........................................................................................................................................................ 72
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 4 / 72
Page 5

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Figure Index
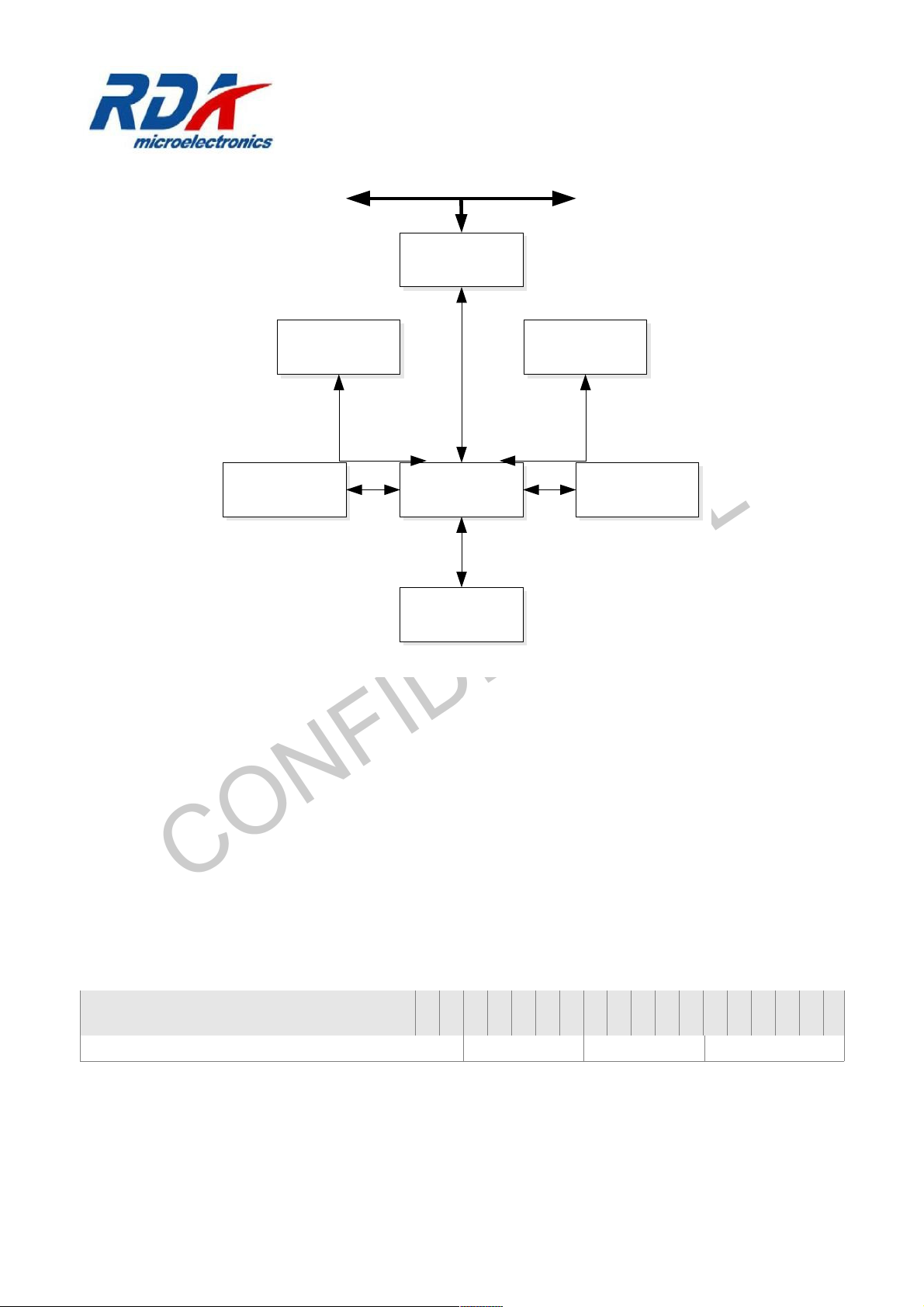
Figure B.1: XCPU Block Diagram ..............................................................................................................11
Figure B.2: Typical transfer operation ........................................................................................................ 22
Figure B.3: Debug channel block diagram .................................................................................................24
Figure B.4: General Message Format ........................................................................................................28
Figure B.5: Read Return Message Format ................................................................................................ 28
Figure B.6: Event Message Format ........................................................................................................... 28
Figure B.7: Tx Switch STM ........................................................................................................................ 30
Figure B.8: IrDA SIR Data Format ............................................................................................................. 30
Figure B.9: YUV 4:2:2 Subsampling ...........................................................................................................42
Figure B.10: SPI Write & Read Timing .......................................................................................................46
Figure B.11: PMU Power ON ..................................................................................................................... 47
Figure B.12: POR triggered by POWKEY press ........................................................................................48
Figure B.13: Principle schematic for Power-Profiles usage ........................................................................ 49
Figure B.14: Charging I-V Curve ................................................................................................................51
Figure B.15: PLL Clock Path ...................................................................................................................... 52
Figure B.16: USB PHY FS 1.1 .................................................................................................................. 53
Figure B.17: GPADC Timing Diagram ....................................................................................................... 54
Figure B.18: FM Tuner Block Diagram .......................................................................................................55
Figure B.19: Bluetooth Block Diagram ....................................................................................................... 57
Figure E.1: SCLK Timing Diagram ............................................................................................................. 83
Figure E.2: SPI Write Timing Diagram ......................................................................................................83
Figure E.3: SPI Read Timing Diagram .......................................................................................................84
Figure G.1: RDA5851 Ball out diagram ..................................................................................................... 86
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 5 / 72
Page 6

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
A. ARCHITECTURE OVERVIEW
RDA5851S is a single chip multi-media solution which integrates PMIC, Audio CODEC, FM, and Bluetooth, as
well as all the system requirements for a multi-media platform.
1. Analog modules
○ Analog block:
■ PLL generates 624MHz from 26MHz
■ Differential 13 bit Audio ADC and 16 bit stereo DAC
■ Audio line in
■ Full Speed USB PHY 1.1
■ 1 Channel General Purpose ADC
○ PMU
■ Complete integrated power management system
■ Integrated LDO voltage regulators
○ FM Tuner:
■ Support worldwide frequency band 65-108MHz
■ Digital low-IF tuner
■ Fully integrated digital frequency synthesizer
■ Autonomous search tuning
■ Digital auto gain control (AGC)
■ Digital adaptive noise cancellation
■ Programmable de-emphasis (50/75 ms)
■ Receive signal strength indicator (RSSI)
■ Bass boost
■ Volume control
○ Bluetooth:
■ Completely integrates bluetooth radio transceiver and baseband processor
■ Also includes sub-controller software stack
■ Compliant with Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR specification
2. Digital Module
RDA5851S Digital Baseband is based on two processors: the system processor (XCPU) and the multimedia dedicated processor (BCPU). Each of these processor is on an AHB bus (AMBA AHB
compliant). Those buses can communicate through an AHB to AHB interface module. Each AHB bus
has a dedicated APB bus (AMBA APB compliant).
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 6 / 72
Page 7

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
● Memory Bridge
○ internal ROM 20kB for critical constants and code, XCPU boot monitor
○ internal SRAM 64kB for critical data and code. Shared communication memory between the 2
CPUs
○ External Bus Controller (EBC)
16 bit data bus, up to 32MB memory space
● System Modules
○ System CPU (XCPU)
RDA RISC Core
32x32 bits Multiplier Accumulator (MAC)
16/32 bit instruction set
4 kByte Instruction Cache
4 kByte Data Cache
○ DSP Co-Processor (VoC)
Bi-MAC, dual operation unit
16-bit instruction set with 32-bit extension
20 kByte + 20 kByte data RAM on 32 bits
32 kByte instruction RAM on 32 bits
○ Direct Memory Access (DMA)
All size, all alignment and all source and destination possible
32-bit word pattern mode
○ Page Spy
Six memory spaces can be spied
○ System Intelligent Flow Controller (Sys IFC) 7 channels
AHB2APB bridge
Four 8-bit or 32-bit DMA channels to accelerate data transfer between peripherals and
memory
Dedicated specialized channels for DBG Host
○ Audio Interface (AIF)
Tone generator
4 samples In and Out Fifos
I2S / DAI Interface
Serial Input / Output at 8/16 ks/s
Can be used for test purpose in DAI mode
Audio Interface
13 bit RX Data from audio ADC
16 bit TX Data to stereo DAC
○ SPI Flash Controller
Up to size 512Mb x 1, or 256Mb x 1, or 128Mb x 2
● System Peripherals
○ System, PLL and Clock Control (Sys & PLL & Clk Ctrl)
Provides general controls over the whole system, including:
Reset controls
Power management controls
Clock selection
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 7 / 72
Page 8

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Some debug features
○ Host Port
Software Flow Control (XON/XOFF)
Host Port auto-reseted when a break is detected
Multiplexed trace mechanism
Clock input allowing up to 1840kbps baud rate independent from the system clock
Secured protocol with 8 bits CRC (no error correction)
○ Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
Master interface with multi-chip selects
16 bytes FIFO
○ I2C Master Peripheral Interface (I2C)
Master interface
○ General Purpose Input Output (GPIO)
○ ADC serial Keypad
○ SD/MMC Card Controller
can support 2 peripherals
SD Card specification Version 2.0
SDIO Version 1.10
MMC specification Version 3.1
○ Timers
1 Real Time Clock Timer (Calendar)
1 24 bits general purpose interval Timers at 16384Hz
1 32 bits uptime counter at 16384Hz
1 Watchdog Timer
○ Debug Port
CPU Execution Logger (EXL): Generate strobe and output the selected CPU's program
counter
Program Execution Time Stamp (PXTS): Allow to profile running code
Hardware Signal Spy, selection of several hardware signal connected to pins.
Access to the last PC of the selected CPU when a watchdog reset occurs
○ General Purpose Analog to Digital Converter (GP ADC)
1 channel inputs
generate IRQ when programmed threshold is passed
○ Timing Control Unit (TCU)
Quarter bit precision
60 entries event table
○ System AHB Monitor (Sys AHB Monitor)
Measure some bandwidth information from the System AHB bus:
Global Bus usage
Master Bus usage and latency
Slave Bus usage and access duration
Special resource measurement
Write detection to a single word location
○ System IRQ Controller (Sys IRQ)
Several masking levels:
Module level
IRQ Control level
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 8 / 72
Page 9

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
○ BIST
Internal RAMs and ROM test to reduce testing cost in production
○ USB Controller
Fully compliant to USB Specification Version 1.1
Slave Full Speed (12Mbps) Device
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 9 / 72
Page 10

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
B. BLOCK DESCRIPTION
B.I System Modules
B.I.1 System CPU (XCPU)
The XCPU RISC is a 16/32-bits processor. Using a Reduced Instruction Set Architecture, an efficient 6-stage
instruction pipeline and separated Instruction and Data caches, it provides high performance to the system. The
Pipeline Stages are as follows:
● PC. Program Counter. Calculate the address of the next instruction and send it to the instruction cache.
● IF. Instruction Fetch. In this stage the instruction cache is being accessed and the instruction
information is retrieved.
● RF. Register File. The register file is being accessed and the instruction is decoded.
● EX. Execution. The instruction is executed
● DC. Data Memory read and write access.
● WB. Write Back. Results are written back to the register file.
Features
● RDA RISC Core.
○ 32x32-bit Multiplier.
○ 32x32-bit -> 64-bit Multiplier Accumulator (MAC) in 2 cycles (pipelined).
○ Read / Write Buffer.
○ 16/32 bit instruction set.
● 32 interrupt sources.
● 4 kByte Instruction Cache.
● 4 kByte Data Cache.
● 16 byte streaming buffer to accelerate uncached instruction accesses.
Block Diagram
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 10 / 72
Page 11
RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
32-bit Instruction Set
Instruction Formats
The RISC processor supports three instruction formats:
R – Register base instruction format
● RD –Target register
● RS – First operand
● RT – Second operand
● SHAMT – Shift amount for shift instructions
● S Code – Instruction code for R type Instructions
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
0 RS RT RD SHAMT S Code
I – Immediate operand instruction format
● Opcode –Instruction Code
● RS – Source or Base register
● RT – Target Register or Reg-Immediate
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 11 / 72
AMBA AHB
System Interface
System Interface
& Rd / Wr Buffer
& Rd / Wr Buffer
Instruction Cache
Instruction Cache
Exception
Exception
Co-processor
Co-processor
Data Cache
Data Cache
Address TranslationExceptions
Integer Pipeline
Integer Pipeline
Multiply Instructions
and Operands
Multiplier
Multiplier
Divider
Divider
Figure B.1: XCPU Block Diagram
Memory
Memory
Management
Management
Page 12
RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
● Immediate – 16 bit Immediate or Displacement
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Opcode RS RT Immediate
J – Jump instruction format
● Opcode –Instruction Code
● Jump Immediate – Immediate 26 bit for jump instruction address
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Opcode Jump Immediate
Supported Instructions
Arithmetic Instructions.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
ADD R RD = RS + RT 0x00 0x20
ADDU R Unsigned[RD = RS + RT] 0x00 0x21
SUB R RD = RS – RT 0x00 0x22
SUBU R Unsigned[ RD = RS – RT] 0x00 0x23
ADDI I RT = RS + Signed(Immediate) 0x08 n/a
ADDIU I RT = RS + Unsigned(Immediate) 0x09 n/a
Logical Instructions. Logical instructions are all bit wise operations.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
AND R RD = RS and RT 0x00 0x24
OR R RD = RS or RT 0x00 0x25
XOR R RD = RS xor RT 0x00 0x26
NOR R RD = not(RS or RT) 0x00 0x27
ANDI I RT = RS and Zero-extend(Immediate) 0x0c n/a
ORI I RT = RS or Zero-extend(Immediate) 0x0d n/a
XORI I RT = RS xor Zero-extend(Immediate) 0x0e n/a
Shift Instructions.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 12 / 72
Page 13
RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
SLL R RD = RS << SHAMT 0x00 0x00
SRL R RD = RS >> SHAMT 0x00 0x02
SRA R RD = signed(RS) >> SHAMT 0x00 0x03
SLLV R RD = RS << (RT) 0x00 0x04
SRLV R RD = RS >> (RT) 0x00 0x06
SRAV R RD = signed(RS) >> (RT) 0x00 0x07
Conditional Set Instructions. These instructions are used for magnitude conditional test. If the condition is
true, the result register is set to 0x1 otherwise it is set to 0x0.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
SLT R RD = 0x1 if(RS < RT) 0x00 0x2a
SLTU R RD = 0x1 when unsigned (RS < RT) 0x00 0x2b
SLTI I RD = 0x1 when (RS < signed(Immediate)) 0x0a n/a
SLTIU I RD = 0x1 when unsigned (RS < signed(Immediate)) 0x0b n/a
Branch Instructions. BEQ and BNE test 2 operands for equal and non equal conditions. The rest of the branch
instructions test a single operand with 0. BLTZAL and BGEZAL save the address of the instruction following the
delay slot in R31.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
BEQ I Branch to ((Immediate + 1) << 2) when RS = RT 0x04
BNE I Branch to ((Immediate + 1) << 2) when RS != RT 0x05
BGEZ I Branch to ((Immediate + 1) << 2) when RS >= 0 0x01 0x01
BLEZ I Branch to ((Immediate + 1) << 2) when RS <= 0 0x06 n/a
BGTZ I Branch to ((Immediate + 1) << 2) when RS > 0 0x07 n/a
BLTZ I Branch to ((Immediate + 1) << 2) when RS < 0 0x01 0x00
BLTZAL I Branch to ((Immediate + 1) << 2) when RS < 0 0x01 0x10
BGEZAL I Branch to ((Immediate + 1) << 2) when RS >= 0 0x01 0x11
Jump Instructions. Jump is performed by combining bit (31:28) of PC with the
J_IMME field of the instructions and 0b00 to form the target address. Link instructions
also save the address of the instruction following the branch delay slot in R31.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
J J Jump 0x02 n/a
JAL J Jump and link 0x03 n/a
JR R Jump register 0x00 0x08
JALR R Jump register and link 0x00 0x09
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 13 / 72
Page 14
RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Move To and From Multiply and Divide registers.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
MFHI R Move from High 0x00 0x10
MTHI R Move to High 0x00 0x11
MFLO R Move from Low (RS = Low) 0x00 0x12
MTLO R Move to Low (Low = RS) 0x00 0x13
Multiply and Divide Instructions.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
MULT R Multiply (Low, High) = RS x RT 0x00 0x18
MULTU R Multiply unsigned (Low, High) = RS x RT 0x00 0x19
DIV R Divide (Low, High) = RS x RT 0x00 0x1a
DIVU R Divide unsigned (Low, High) = RS x RT 0x00 0x13
Load Upper Immediate.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
LUI I RT[31:16] = Immediate 0x0f
Load and Store Instructions. The address for the load or store is calculated by adding the DISP field to the
content of RS. The value read from or written to the memory is from RT.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
LB I Load Byte (sign extend) 0x20
LH I Load Half (sign extend) 0x21
LW I Load Word 0x23
LBU I Load Byte (unsigned) 0x24
LHU I Load Half (unsigned) 0x25
SB I Store Byte 0x28
SH I Store Half 0x29
SW I Store Word 0x2b
Miscellaneous. In addition to the standard instructions described above, the RISC processor supports the
following instructions.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
CACHE n/a See the code below. 0x2f
Cache instruction format:
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 14 / 72
Page 15
RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Opcode OP1 Address Code
Name Description
Code
Bits [2:0]
Command code as follows:
"000" invalidate all lines of both caches ('A' is ignored)
"001" invalidate all lines of icache ('A' is ignored, dcache is unaffected)
"010" invalidate all lines of dcache ('A' is ignored, icache is unaffected)
“011” not specified, do not use.
"100" invalidate an Icache line whos address is specified by register OP1
"101" invalidate a single line specified by 'A' from icache
"110" invalidate a single line specified by 'A' from dcache
"111" invalidate a Dcache line whos address is specified by register OP1
Address
Bits [13:3]
or bits [11:3]
or bits [9:3]
The cache line byte address to invalidate. The actual bits used are (RAM_HIGH
downto TAG_LOW).
The XCPU has a 4K of data and instruction cache with 4W line, so the bits used are
(11 downto 3). The BCPU has a 1K of data and instruction cache with 4W line, so the
bits used are (9 downto 3).
OP1
Bits [25:21]
Register operand. The content of the CPU register is used as the Address parameter.
Opcode
Bits [31:26]
Value: 0x2f.
MAC Instructions. The multiply and accumulate (MAC) option adds supports for the following instructions.
Name Type Description Opcode S-Code
MADD R
Signed multiply and accumulate.
{hi, lo} = {hi, lo} + RS * RT
0x00 0x1c
MADDU R
Unsigned multiply and accumulate.
{hi, lo} = {hi, lo} + RS * RT
0x00 0x1d
MSUB R
Signed multiply and subtract.
{hi, lo} = {hi, lo} - RS * RT
0x00 0x1e
MSUBU R
Unsigned multiply and subtract.
{hi, lo} = {hi, lo} - RS * RT
0x00 0x1f
16-bit Instruction Set
The 16 Bit Instruction mode is an option in the configuration file. This chapter assumes that the user chose to
enable this mode. The 16 bit instruction set is provided for situations where reducing code size is a priority.
16 Bit and 32 Bit Instruction Modes
The processor determines the Instruction Mode base on bit 0 of the address of the instruction. When bit 0 of the
address of the instruction is 0, the processor is in 32 bit mode, and it interprets the instruction as a 32 bit
instruction. When bit 0 of the address of the instruction is set, the processor is in 16 bit mode, and it interprets
the instruction as a 16 bit instruction.
In this 32 bit mode:
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 15 / 72
Page 16
RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
1. The instruction counter is incremented by 4 from 1 instruction to the next.
2. For Branch and Link instructions, the processor save the address of the instruction + 8 as the return address.
This is the instruction after the delay slot.
3. The processor will take an Illegal Instruction Exception, if either bit 0 or bit 1 are set.
In this 16 bit mode:
1. The instruction counter is incremented by 2 from 1 instruction to the next.
2. For Branch and Link instructions, the processor save the address of the instruction + 4 as the return address.
This is the instruction after the delay slot.
3. The processor passes bit 1 of the instruction address to the memory subsystem.
Bit 0 is always sent as 0 to the memory subsystem.
Switching between 32 Bit and 16 Bit modes.
To switch between the modes, bit 0 of the instruction address must be changed from 1 to 0 and back. There are
2 basic mechanisms to achieve this.
JALX instruction. This instruction exists in both 32 bit and 16 bit modes. In addition to changing the execution
path to the target address, it also toggles bit 0 of the instruction and hence the mode.
JR, JALR instructions. These instructions take the 32 bit contents of a register and use it as the target
address. Bit 0 of the register can be set to reflect the mode of the instructions at the target address.
The 16 Bit Mode Instructions
The following instructions are supported:
Name 15 .. 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
ADDIU2 0 1 0 0 1 rx imm8
ADDIU3 0 1 0 0 0 rx ry 0 imm4
ADDIUPC 0 0 0 0 1 rx imm8
ADDIU2SP 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 imm8
ADDIU3SP 0 0 0 0 0 rx imm8
ADDU3 1 1 1 0 0 rx ry rz 0 1
AND 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 1 1 0 0
B 0 0 0 1 0 offset
BEQZ 0 0 1 0 0 rx offset
BNEZ 0 0 1 0 1 rx offset
BREAK 1 1 1 0 1 code 0 0 1 0 1
BTEQZ 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 offset
BTNEZ 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 offset
CMP 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 1 0 1 0
CMPI 0 1 1 1 0 rx imm8
DIV 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 1 1 0 1 0
DIVU 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 1 1 0 1 1
EXTEND 1 1 1 1 0 imm(10:5) imm(15:11)
JAL 0 0 0 1 1 0 target(20:16) target(25:21)
JAL 2nd target(15:0)
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 16 / 72
Page 17
RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Name 15 .. 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
JALR 1 1 1 0 1 rx 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
JALRC 1 1 1 0 1 rx 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
JALX 0 0 0 1 1 1 target(20:16) target(25:21)
JALX 2nd target(15:0)
JRRA 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
JRRAC 1 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
JRRX 1 1 1 0 1 rx 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
JRRXC 1 1 1 0 1 rx 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
LI 0 1 1 0 1 rx offset
LB 1 0 0 0 0 rx ry offset
LBU 1 0 1 0 0 rx ry offset
LH 1 0 0 0 1 rx ry offset
LHU 1 0 1 0 1 rx ry offset
LW 1 0 0 1 1 rx ry offset
LWPC 1 0 1 1 0 rx offset
LWSP 1 0 0 1 0 rx offset
MFHI 1 1 1 0 1 rx 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
MFLO 1 1 1 0 1 rx 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
MOVEmt32 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 r32(2:0) r32(4:3) rz
MOVEmf32 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 ry r32
MULT 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 1 1 0 0 0
MULTU 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 1 1 0 0 1
NEG 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 1 0 1 1
NOT 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 1 1 1 1
OR 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 1 1 0 1
RESTORE 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 ra s0 s1 frame size
SAVE 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 ra s0 s1 frame size
SB 1 1 0 0 0 rx ry offset
SDBBP 1 1 1 1 0 code 0 0 0 0 1
SEB 1 1 1 0 1 rx 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
SEH 1 1 1 0 1 rx 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1
SH 1 1 0 0 1 rx ry offset
SLL 0 0 1 1 0 rx ry sa 0 0
SLLV 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 0 1 0 0
SLT 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 0 0 1 0
SLTI 0 1 0 1 0 rx imm8
SLTIU 0 1 0 1 1 rx imm8
SLTU 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 0 0 1 1
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 17 / 72
Page 18
RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Name 15 .. 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
SRA 0 0 1 1 0 rx ry sa 1 1
SRAV 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 0 1 1 1
SRL 0 0 1 1 0 rx ry sa 1 0
SRLV 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 0 1 1 0
SUBU 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry rz 1 1
SW 1 1 0 1 1 rx ry offset
SWSPRX 0 1 1 0 0 rx offset
SWSPRA 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 offset
XOR 1 1 1 0 1 rx ry 0 1 1 1 0
ZEB 1 1 1 0 1 rx 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
ZEH 1 1 1 0 1 rx 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1
Memory Map
Processor Address Mapping
The addresses are all byte addresses. The Size description is also in byte. The processor offers four different
memory spaces.
Segment Name Base Address Size Description
kseg2 0xc000,0000 0x4000,0000 1 GB mapped and cached
kseg1 0xa000,0000 0x2000,0000 0,5 GB unmapped and uncached
kseg0 0x8000,0000 0x2000,0000 0,5 GB unmapped and cached
kuseg 0x0000,0000 0x8000,0000 2 GB mapped and cached
Note that kuseg and kseg2 are available only with the use of a MMU. As there is no MMU in RDA5851S,
attempts to access those memory segments will trigger an exception.
Memory Access Types
In case of cache miss, a cached access will occur and a full line of 4 x 32 bits ( = 16 bytes) will be loaded.
An uncached access will be a single access or a streaming buffer fill (16 bytes), in case of a streaming buffer
miss, if this feature is enabled. A configuration bit allows to enable / disable the streaming feature.
Multiplier & Divider
The RISC processor’s multiplier unit implements a 2 cycle fall through algorithm.
The divider uses a step divide algorithm, which takes 36 cycles to complete a divide operation.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 18 / 72
Page 19

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
B.I.2 Memory Bridge
The memory bridge is the interface to general memory used by the system, including internal rom, internal sram
and access to external memory.
Features
● Dual AHB Slave
○ A rom/sram controller
○ An Asynchronous FIFO to external controller
● The bridge is implemented as a crossbar between the 2 AHB and the 2 controller (rom/sram and FIFO)
● The rom/sram controller can insert wait cycle to the AHB Slave (to manage read/write conflicts and to
allow using slower instance if needed).
● The rom/sram controller integrate a BIST engine to test the ROM by computing a CRC and test the
rams with the March C algorithm
● All AHB burst size are supported
○ Wrap will be split at wrap address
○ Burst longer than the data buffer size of the FIFO will be split
○ Read INCR will read a fixed data size
● FIFO data buffer can store 2 requests either read or write (each 4x32 bytes) from either AHB slave
interface.
● APB slave for configuration
External Bus Controller Features
● The controller handles 16 bits data bus width only, however 8 bit memory chips can still be used; by
groups of 2. 8 bit peripherals must be connected to the 8 LSBs of data and accessed through even
addresses only.
● Manage page mode SRAM or FLASH.
● Manage burst mode PseudoSRAM.
● Manage AD-Mux and AD-Mux burst mode PseudoSRAM.
● 1 Control Register Enable (M_CRE) Output pin in same power domain than other memory IO for
PseudoSRAM register control.
● FIFO interface for address/data path
● APB interface for configuration (subset of the mem bridge APB address space)
AHB Master Features
● AHB Compliant master
● except the 1K crossing limit defined by AMBA (additional logic required)
● Memory space divided in 5 spaces with a base address for each (aligned on n Word address, n=FIFO
data buffer size)
● Do not use WRAP (due to FIFO organization)
● use INCR4, SINGLE or INCR (for 2 or 3 data only) burst type
● FIFO interface for address/data path
● APB interface for configuration (subset of the mem bridge APB address space)
● External clock is provided from outside the IP (and synthesized in the outside clock tree)
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 19 / 72
Page 20

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Operations
Dual AHB Operation
The Slave allow simultaneous access to rom/sram controller and FIFO from the two slaves.
Access to the rom/sram controller are sequenced using WAIT on AHB (HReady low).
Access to the FIFO are sequenced using split when the FIFO busy on the other AHB slave (other split conditions
are described bellow in FIFO Operation section).
Arbitration in case of simultaneous access to the same controller: Should try to serve each side (BB and Sys)
alternatively.
Simultaneous access to rom/sram controller: memorize the last accepted burst. when the two arrives exactly
simultaneously reply wait to the memorized side and process the other side.
Simultaneous access to FIFO: First serve read of data if data are available for this read. Serve the side that did
not enter the FIFO on last Burst in priority.
FIFO Operation
The FIFO can store 2 requests either read or write from either AHB Slave interface. But only one at a time.
For each request there is an associated Write Data Buffer and a Read Data Buffer.
If the FIFO is full the master is split, this master will be released when one spot is free in the FIFO (all masters
split because FIFO was full are released at the same time).
Write
A burst is stored to the Data buffer until the burst is finished. If the Data buffer is full or the Wrap address of a
wrap burst is reached, the Split response is send (the master will be released in the same condition as above).
Read
The request is stored (address, length ...) and the master is split.
The master will be released when the Data buffer has been filled by the external controller (EBC or AHB Master).
When the Master comes back, the Data are provided, if the master end the burst the transfer is complete (even
if there is still some data in the buffer, in this case they are lost) if the master request more than the available
Data it receive the Split response and will be released in the same conditions as for FIFO full: the request is not
stored.
FIFO Flush status: Read in FIFO at special address space does not impact the external controller but returns
when the command has reached the end of the FIFO (so the read returns only when previous writes are done,
no pooling is required)
If external controller has error (disabled space for EBC or AHB Error response for master) the FIFO data reads
as and error code. “0xD15AB1ED”
EBC Operation
FIFO access are translated to external memory access.
Configuration of Chip select are validated only between access (atomic change)
● Flash block address remapping and M_CRE control registers are placed in the FIFO space to keep
accesses in sequence and avoid using FIFO Flush each time.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 20 / 72
Page 21

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
B.I.3 Direct Memory Access (DMA)
The DMA controller relieve the CPU from doing generic memory transfers. A data FIFO is integrated to allow
burst transfers. It can generate an interrupt to the system CPU at transfer completion.
Read and Write transfers are supported from and to any memory mapped location (external memory, internal
SRAM, modules FIFO…). The addresses can be word, halfword or byte aligned. The DMA can also be used in
pattern mode. In this case, a 32-bit word will be used to fill the destination memory zone.
Features
● Support for linear memory transfers.
● Support for word, halfword and byte aligned addresses.
● Burst transfer mode and internal FIFO for best performances.
● Autonomous transfer up to 64K byte per transfer.
● Interrupt generation at completion of the transaction.
● Can fill a part of the memory with a 32-bit pattern.
B.I.4 Page Spy
This module is a System spy that detects read or write access into predefined ranges of memory addresses and
triggers an interrupt in case of selected access.
Features
● Six memory spaces can be spied.
● Memory space described with a start address (inclusive) and an end address (exclusive) and mode
(detect read, write or both).
● For each space a status register gives the master that triggered the spy, the address that caused it and
the mode.
B.I.5 System Intelligent Flow Controller (Sys IFC)
The System Intelligent Flow Controller (SYS_IFC) is a bridge between the system bus and the peripheral bus.
The IFC also provides DMA capabilities to allow data transfer from or to peripherals. It supports 7 DMA standard
channels for 8-bit or 32-bit and a dedicated DMA channel for the RF SPI module.
Features
● 7 independent DMA channels. internal FIFO of four 32-bit words per channel.
● 1 dedicated DMA channel for the debug host
● Burst mode on AHB bus to enhance transfer rate
● Support 2 types of transfer: memory to peripheral and peripheral to memory
● Incremental address for AHB master access and non-incremental address for APB access.
● Dynamic allocation of the 7 DMA channels, request lines among the following peripherals:
a) SCI
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 21 / 72
Page 22

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
b) SPI1
c) SPI2
d) SPI3
e) TRACE UART (DBG Host)
f) UART
g) UART2
h) SDMMC
● Hardware semaphore registers which indicate to the CPU which channel must be used and a global
status register indicating which channel is free.
● AHB to APB bridge, write buffer for a single write access the master isn't stalled, no wait state inserted
AHB2APB bridge operation
The SYS_IFC include a bridge between the AHB bus and the APB bus. The SYS_IFC bus is the only one master
on the APB bus. The APB bus is a low bandwidth and low power bus mainly used to configure peripheral register
or transfer data with the IFC DMA.
Arbitration
The IFC includes some DMA capability which can access to APB bus, in case of 2 accesses simultaneously
(AHB slave and DMA channel), request from the AHB has the highest priority. But if processor requests an
access to the APB, and the DMA already have an access in progress, the processor will be stalled until the DMA
access is finished.
DMA Operations
The SYS IFC includes 7 DMA channels. Each channel can perform data movements between devices in the
AHB bus and peripheral on the APB bus.
Typical transfer
The DMA feature is used to automatically transfer data from memory to peripheral or from peripheral to memory.
A typical transfer is defined by a start address, the number of bytes to transfer (TC), a direction (Rx or Tx) and a
peripheral address.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 22 / 72
start_addr
memory
TC
Figure B.2: Typical transfer
operation
Page 23

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
START_ADDR register gives the first address of the data to transfer.
TC register gives the number of bytes to transfer.
The direction and the peripheral to access is given by the field REQ_SRC in the control register.
Typical data flow for memory to peripheral transfer
1. Check which channel to use and which channel is busy.
2. Configure in the given channel of the IFC, the AHB start address.
3. Configure in the given channel of the IFC, the number of bytes to transfer (TC register)
4. Program the peripheral in which to write and enable the IFC channel to start.
5. The IFC start a read burst access on its AHB master interface.
6. If the programmable DMA request line (of the peripheral associated to this transfer) is high (meaning the
7. peripheral needs data), writes are performed on the APB interface and the current transfer counter (TC)
is decremented. This sequence is made until the FIFO of the IFC is empty.
8. When the FIFO of the IFC is empty; another read burst access is performed on the AHB bus and return
to the step (6).
9. If the transfer is complete (current transfer counter reaches zero), the associated Done signals goes
high and the channel is disabled (if the autodisable bit is set)
This is the same flow for peripheral to memory transfer.
Auto-disable bit
At the end of the transfer when TC=0 the channel is not necessary disabled. The state of the autodisable bit
determines whether or not the channel is automatically disabled. This allows for one resource to keep the
channel, and this resource can launch a new transfer just by writing a new value to the TC.
Incremental TC
It is possible during the transfer to write several time in the TC register. The new TC value will be added to the
current value of the TC and the total number of bytes transferred is a the addition of all writes in TC.
For example, at first the processor programs the IFC with TC=50, and the IFC start the transfer.
Later during the transfer the processor again writes TC=30. The total number of transfers will be 80 bytes which
is 80=50+30.
Debug channel operations
The SYS IFC includes an additional channel dedicated for debug purpose only. This feature allows access to all
the resources of the chip through the Debug Host Port.
The debug channel receive request from the host port. A typical debug request is composed of an address, a
command (read or write), a size and a data to write. The read/write command is the MSB bit of the address (0
for read, 1 for write). The size of the transfer is given by bit 30 and 29 of the address.
The debug channel include a 2 words receive FIFO for receiving debug request from a peripheral and a one
word transmit FIFO.
The following figure shows a brief diagram of the architecture.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 23 / 72
Page 24

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
For a write debug command, the host peripheral transmits by a first DMA request the Address, the R/W bit and
the Size and by a second DMA request the DATA to write. Then the debug channel makes an AHB write access
to desired resource.
For a read debug command, the host peripheral transmits by a first DMA request the Address, the R/W bit and
the Size and by a second DMA request a data to only fill the internal debug command FIFO. The data loaded in
the FIFO during this second access is not used. With the address loaded, the IFC performs an AHB read
access, the recovered data is stored in the transmit FIFO. When the host peripheral performs a DMA transmit
request, a write access is performed on the APB bus for sending data to the peripheral.
B.II System Peripherals
B.II.1 System and Clock Control
The system control provides general controls over the whole system, including reset controls, power
management controls, clock selection, and some debug features.
Features
● Registers for reset control, clock control, fast clock div control, AHBC, some debug feature(like Debug
Breakpoints,Lock / Unlock the protected registers),.
● Automatic clock gating signal generation for APB module (PCLK_DATA and PCLK_CONF)
● XCPU and CPU special signals for clock management and breakpoint management
Reset Control
After a hardware reset, the XCPU will automatically boot and perform the system initialization. The CPU is held
in reset until released by the XCPU.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 24 / 72
Debug
Channel
data to write
Address + R/W
Peripheral
AHB
master
read data
Figure B.3: Debug channel block
diagram
Page 25

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
The reset control allows resetting independently most of the modules of the design. In normal use, there should
be no need to reset an individual module and caution must be taken when doing so to avoid crashing the
system. This is provided mainly for debug purposes.
A global software reset feature is provided. This feature allows resetting the whole system from the software
running on any of the CPUs. The effect of the software reset is the same as a hardware reset except that it does
not reset the host interface.
A watchdog timer allows recovering from software crashes. Once enabled, the watchdog timer must be reloaded
periodically by the software. If the software fails to do so because of a software crash, the watchdog timer will
reach 0 and trigger a software reset automatically. The system will then restart. When the XCPU reboots, it can
detect that a watchdog has triggered a reset and can save the context at the time of the watchdog
expiration(Program counter, register values, stack location), this should allow for easier software debug.
It is also possible to trigger a software reset from the host interface. A special feature allows preventing the
XCPU from booting after this reset. This allows avoiding the XCPU to set the system in an invalid configuration
in case the boot code is not valid (flash not programmed or badly programmed) and gaining access to the whole
system from the host port to find the cause of the issue or reprogram the boot code in flash.
Clock management
The system has three main sources for the internal clocks generation:
● a 32.768kHz generated by 26MHz clock
● a 26MHz clock from the RF transceiver
● a PLL that generates 624MHz from 26MHz provided by the clock Squarer, this PLL allows to generate a
26MHz, 39MHz, 52MHz, 78MHz, 89MHz, 104MHz, 113MHz, 125MHz, 139MHz, 156MHz, 178MHz,
208MHz, 250MHz, 312MHz;
The other clock source can go only to some part of the design:
● a dedicated clock input for the HST clock : used by the host module.
● an audio clock input (BCK) : used for the I2S audio module, note that this pin is actually bidirectional
(depending on the connection to a I2S master or I2S slave, this pin is configured as a clock input i_BCK
or a clock output o_BCK).
All internal clocks in the design except the clocks for host and in some case audio, derive from one of the three
main clock sources. The selection is made through configuration registers. Thanks to glitch free muxes, it is
possible to change the internal clock frequency on the fly. Caution must be taken when changing the main clock
frequency as some interfaces clocks are divided versions of this main clock. For example, the SPI baud rate
directly depends on the main clock frequency so when changing the main clock, it is recommended to make
sure that the SPI is not transmitting during the change.
To reduce the power consumption, it is possible to gate the clock signal going to most of the modules individually
when a module is not in use. Enabling or disabling the clock going to a module can be automatic (all the
modules needing to run over short period of times are able to control their clock themselves. For example the
DMA only has a clock while doing a transfer) or manual (for the modules running all the time once they are
enabled. For example, the audio interface which needs to output samples continuously once enabled)
Debug features
Hardware breakpoints
This feature allows defining one hardware breakpoint for each CPU. This breakpoint can be either on an
instruction fetch, a data read or a data write.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 25 / 72
Page 26

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
When the breakpoint is reached, the CPU is stalled. A status bit allows to know if the breakpoint has been
reached or not. When the CPU is stalled, all its internal registers are accessible through the host port. If the
breakpoint is released, the CPU resumes its execution.
Debug clock
It is possible to output any internal clock of the design on the pin DBG_CLK (also used for EXL/PXTS Clock) for
debug purposes (check frequency, power saving feature...).
The Debug clock register is defined in the debug_port module.
B.II.2 Trace (Normal UART) and Host (Debug UART) Port
RDA5851S Debug Host module contains 1 normal Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter channels
(UART) and 1 Debug UART. The two UARTs share the same Tx/Rx engines, which sends and receives byte
data from serial interface. Each UART has its own control sub-module and own APB interface. RDA5851S
Debug Host module parses the incoming data from serial interface to switch between the normal UART and the
Debug UART.
● Normal UART
The normal UART can be used for traces and other purposes. For APB interface, it is exactly the same to the
other UARTs in the RDA5851S system. However, if Debug UART is enabled, it should have the same serial
interface configuration as the Debug UART. Some of its configuration options will be masked in this case. To
Adapt different clock frequency, the normal UART uses asynchronous FIFO, which uses gray code to represent
the read and write pointer positions.
● Debug UART
The Debug UART is specially designed for communicating debug information with a PC host. The serial
interface of Debug UART is a simplified version of the normal UART and is less configurable. Each sample is
sent serially, has 1 start bit (always zero), 8 data bits, and 1 stop bits (always one). Breaks (data line held low)
can be generated and detected allowing resynchronizing the two devices.
Features
● Auto normal/Debug UART select by parsing incoming message.
● Separate UART APB and Debug UART APB interfaces.
Normal UART features:
● Fully programmable transfer word format.
○ 7 or 8 data bits.
○ 1 or 2 stop bits.
○ Odd, even, mark, space or none parity.
● Smooth stop feature (the UART stops after the end of the current word transfer).
● Break generation and detection.
○ Break length programmable.
○ Interrupt can be generated.
● Supports Automatic Software Flow Control (XON/XOFF).
● Programmable receive and transmit fifos (16 bytes deep).
● Supports low speed IrDA 1.0 SIR mode by adding external hardware.
● DMA capabilities (through the System IFC) to allow fully automated data transfers.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 26 / 72
Page 27

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
● Wide selection of programmable interrupts to allow interrupt driven data transfer management.
○ Rx or Tx Fifo trigger reached.
○ Timeout: No characters in or out of the Rx Fifo during the last 4 character times and there is at
least one character in the Rx Fifo during this time.
○ DMA timeout: After Rx Sys IFC DMA is started, no characters in or out of the Rx Fifo during the
last 4 character times.
○ End of the Sys IFC DMA transfer.
○ CTS detection.
○ Tx or Rx overflow, parity or framing (bad sample format received) error or break.
● Loop Back capabilities for test purposes.
● Up to 1843.2 Kbit/s for serial and 115.2 Kbit/s for IrDA.
Debug UART features:
● Transfer word format.
○ 1 start bit.
○ 8 data bits.
○ 1 stop bit.
● Tx Break generation when pin reset and Rx break detection.
● HW reset event.
● Programmable events allowing CPU directly write to Debug UART.
● Some serial interface read/write internal registers.
● DMA capabilities (through the System IFC Debug Channel) for automated data transfers.
● Up to 1843.2 Kbit/s for serial.
Message Frame
In case of Debug UART is disabled, the message has no format requirement. If Debug UART is enabled, the
General message received by the Debug Host should be of the following format:
○ 1 Start byte.
○ 2 Size bytes.
○ 1 Flow Identification byte.
○ N Message Body bytes.
○ 1 CRC byte.
The start byte is 0xAD, which starts a message frame. The 2 size bytes indicates the length of the message ( the
length of how many bytes after SIZE field, equals to N Message Body byte + 1 CRC byte = N+1). The Flow
Identification byte identifies what kind of Flow is this message, the definition of the Flow Ids can be found in the
REMOTE specifications. The message body field length is variable, and has different data structure according to
the Flow ID. The CRC field is calculated by an XOR between the Flow ID and each Message body byte.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 27 / 72
0xAD Message Body IDSize CRC
1 byte 2 bytes 1 byte n bytes 1 byte
CMD Addr Data
1 byte 4 bytes 1/2/4/4m bytes
Debug
Page 28

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Figure B.4: General Message Format
For Debug Messages, the Flow_ID = 255, and the Message Body field is composed of:
○ 1 command byte ( bit 7,bits 2 to 0 used).
○ x00 for byte.
○ x01 for half word.
○ x10 for word.
○ x11 for block.
○ 1xx for internal registers.
○ Bit 7 for Write_H (0 for read, 1 for write)
○ 4 address bytes (bits 28 to 0 used).
○ Byte, half word, word or 4m data bytes(block) in case of write, 1 data byte in case of read (RID).
● Block mode is only for write, in case of read, only byte, half word and word data is supported. The read
return message of Debug Message is:
Figure B.5: Read Return Message Format
● If the CPU send an event, the RID is 0, the format will be:
Figure B.6: Event Message Format
IFC DMA Data
The Debug UART read and write data from memory by using the IFC DMA. It will encapsulate the received
message into a 4-byte command and a 4-byte data. The 4-byte command includes the read or write indicator (bit
31), the type(bit 30 to 29) and the address(bit 28 to 0). The 4-byte data is formed from data field in the message
(in case of byte and half word, replicate the data to fill the 4 bytes). When the Command and Data is ready, the
Debug UART will generate an IFC Debug Request. In case of block data, the address is recalculate for each 4byte data.
Normal/Debug UART Select
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 28 / 72
0xAD Data RIDSize CRC
1 byte 2 bytes 1 byte 1 byte 4/2/1 bytes 1 byte
255
0xAD Data0Size CRC
1 byte 2 bytes 1 byte 1 byte 4 bytes 1 byte
255
Page 29

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
● Clock Select
The Debug Host detects if there is a host clock. If the host clock exists (an UART Dongle is plugged), it will
enable the Debug UART and use this clock for both Debug UART and normal UART. There is also a software
configure Force_Host_On signal, which force to enable the Debug UART, in this case, if no host clock is
detected, the CLK_UART will be used for the both 2 UARTs. If no host clock is detected and Force_Host_On
signal is inactive low, the Debug UART will be disabled, and CLK_UART is used for the normal UART. The
following table illustrates the clock selection and the enabling of different function groups. In the table, the
columns on left have the priority.
HST_CLK Plugged Force_HST_ON UART_CLK only
HOST_Func Enabled Yes Yes No
Clock used CLK_Host CLK_UART CLK_UART
Mask UART Config Yes Yes No
● RX UART Select
If host clock exists, the Debug Host parses the Incoming Data from Rx engine permanently. The
messages with Flow ID = 255 is a Debug flow and thus host will select the Debug UART, otherwise, the
normal UART. The Rx parser will send to Debug Uart only the message body, but if Normal Uart is
destined, the Rx parser will send the whole package including the head and CRC.
The Debug Uart has separate Rx and Tx state machines. By de-assert UART RTS, The Rx state machine will
be blocked before the next command if previous Debug IFC channel DMA is not finished, to avoid lost of the old
command's address and data.
Another case which needs to block Rx is: a new read command comes but previous read has not finished
sending its data. In fact, each read operation uses both Rx and Tx machines: The Rx state machine finishes by
sending the read request to IFC. On the other side, Tx state machine is triggered either by a event sending
request or by read data ready signal. If the current Tx state machine has not finishes, the Rx process will need to
wait in order not to lose the old RID and read data.
A CRC checker is enabled if the Rx flow is for Debug UART. When command is Read, if the CRC is bad, the
command received will be rejected and not be sent to IFC. When Write, if the destination is host internal register
and CRC is bad, the command will be ignored. If the destination is memory, the command will be executed
before CRC is calculated. The CRC check result will be put to the CRC check result internal register and can be
read through the serial interface. For normal UART, the CRC is checked by software.
● TX UART Select
By default, The Debug UART TX is given priority, so if the normal UART continues to send messages, the TX
will switch to Debug UART once the current message is finished. Further more, there is an internal register bit
Debug_Force_Prio which is by default to be active high. In this case, whenever the host wants to send anything,
it can insert them into the normal Uart package.
If the Debug_force_prio is inactive low, A parser in the normal UART TX path analyzes if the current read
operation for normal UART is finished or not, in order that the process is not disturbed by a read request or
event from Debug UART. In this case, the arbitration process for TX UART select can be illustrated in the
following:
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 29 / 72
Page 30

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Figure B.7: Tx Switch STM
When the normal UART receives any data from the APB, it will clear the status to 0 which no more grant the
Debug UART for TX and waits for start byte 0xAD. Once it founds a 0xAD, the parser will count until number of
data declared in SIZE field has been received before it checks the CRC. The CRC result will be put in an internal
register and can be read from the host interface. Then the status will be reset to 1, and the Debug UART can
send its data if there is a request.
IrDA SIR Operation
IrDA 1.0 SIR mode is available only if the Debug UART is not enabled and can be activated when the user
opens a UART. IrDA 1.0 SIR mode supports bi-directional data communications with remote devices using
infrared radiation as the transmission medium. IrDA 1.0 SIR mode specifies a maximum baud rate of 115.2
KBaud.
Transmitting an infrared pulse corresponds to a zero, while one is represented by not sending any pulse. The
width of a infrared pulse is 3/16 th of a normal serial bit time (depending on the baudrate). Each sample begins
with a pulse (the start bit)
Received data is inverted (due to the IrDA physical purposes). Therefore, the Uart_Rx port, has the correct
UART polarity. See the following figure for more details.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 30 / 72
Uart_Tx
Uart_Tx (IrDA mode)
Uart_Rx (IrDA mode)
Uart_Rx
Start
Start
Stop
Stop
3/16
bit period
0xAD
Yes, status=0
Recv
N=SIZE
N=N+1
CRC
No
Any byte,
Status=0
HOST
TX
Host
Req
YES
NO
Figure B.8: IrDA SIR Data Format
Page 31

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
The UART module operation when IrDA SIR mode is enabled is similar to when the mode is disabled, with one
exception: data transfers can only occur in half-duplex fashion when IrDA SIR mode is enabled. This is because
the IrDA SIR physical layer specifies a minimum of 10ms delay between transmission and reception. This 10ms
delay must be handled by the software.
Break Generation and Reset
A break is generated by the sending UART holds the TXD line to 0 for quite a long time. It can be used to avoid
the case RTS line is always inactive and thus blocks the data to be sent any more. When a break is detected, it
will reset the state machine of the Rx/Tx engines. If Host is enabled, the break will be sent to both two UART.
For debug UART, It will write into the CFG internal register bit Disable_UART to temporarily disconnect the
normal UART to the serial interface (in this state, all data destined for normal UART received by RX engine will
be discarded, all data in the normal UART FIFO are still kept but will not send to the TX engine, the RTS from
normal UART will also be disconnected to the RX engine), this will allow the Debug UART to diagnostic what
happens in case of normal UART errors. It will also reset the Debug Host baud-rate. For normal UART, the
break will also generate an error IRQ, which can ask soft to perform operations such as a reset for the FIFO etc.
The normal UART can be enabled later by clear the Disable UART bit.
If the reset source is coming from pin reset, a break should be sent by the debug host to let the other-side UART
configure the baud-rate. This break lasts at least 12 bit long in 115.2K baud-rate, which should be the lowest
baud-rate. A hardware reset event should be sent by the debug host in case of system reset.
Clock Detector
This sub-module detects if the Host clock is present or not. This module is located in clock control module, it will
generate a Host_Clock_On signal. The Host_Clock_On signal helps to select the system clock or host clock as
the input for debug host. When Host_Clock_On is active high, host clock is used, otherwise, UART clock. The
Host_Clock_On signal is also send to Debug host to enable or disable the host functionality.
The clock Detector uses 32.768KHz clock to detect 14.7468MHz host clock. There is a 10 bit counter in the host
clock domain, and the highest bit is used to generate a 14.4KHz slow clock. The 32KHz clock detects the rising
edge of this slow clock, and launch a 2-bit incremental counter. Every time a rising edge detected, the counter
will be added by one, until the counter reaches 3. At this moment, the Host_clock_on signal will be asserted and
host clock is considered to be connected. There is another 6-bit timeout counter, each time a new rising edge is
detected, the timeout counter will be reset to “111111”, otherwise, it will be decremented by one at each 32KHz
clock rising edge. If the timeout counter reaches 0, the incremental counter will be reset and Host_clock_on
signal will be de-asserted, the host clock is considered to be disconnected.
Software flow control
If sending of characters must be postponed, the character XOFF is sent on the line, to restart the
communication again XON is used. Sending the XOFF character only stops the communication in the direction
of the device which issued the XOFF.
The XON/XOFF character can be programmed by register bits. However, two bytes have been predefined in the
ASCII character set to be used with software flow control. These bytes are named XOFF and XON, because
they can stop and restart transmitting. The byte value of XOFF is 19, it can be simulated by pressing Ctrl-S on
the keyboard. XON has the value 17 assigned which is equivalent to Ctrl-Q.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 31 / 72
Page 32

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Backslash '/' can be added before XON, XOFF and '/' to signifies their original values instead of flow control
marks.
B.II.3 I2C
I2C is a two-wire, bi-directional serial bus that provides a simple and efficient method of data exchange between
devices. It is most suitable for applications requiring occasional communication over a short distance between
many devices. The I2C standard is a true multi-master bus including collision detection and arbitration that
prevents data corruption if two or more masters attempt to control the bus simultaneously.
The interface defines 3 transmission speeds:
• Normal: 100Kbps
• Fast: 400Kbps
• High speed: 3.5Mbps
Only 100Kbps and 400Kbps modes are supported directly.
Features
• Compatible with Philips I2C standard
• Multi Master Operation
• Software programmable clock frequency
• Clock Stretching and Wait state generation
• Software programmable acknowledge bit
• Interrupt or bit-polling driven byte-by-byte data-transfers
• Arbitration lost interrupt, with automatic transfer cancellation
• Start/Stop/Repeated Start/Acknowledge generation
• Start/Stop/Repeated Start detection
• Bus busy detection
• Supports 7 and 10bit addressing mode
• Operates from a wide range of input clock frequencies
Operations
• I2C System configuration
The I2C system uses a serial data line (SDA) and a serial clock line (SCL) for data transfers. All devices
connected to these two signals must have open drain or open collector outputs. The logic AND function is
exercised on both lines with external pull-up resistors.
Data is transferred between a Master and a Slave synchronously to SCL on the SDA line on a byte-by-byte
basis. Each data byte is 8 bits long. There is one SCL clock pulse for each data bit with the MSB being
transmitted first. An acknowledge bit follows each transferred byte. Each bit is sampled during the high period of
SCL; therefore, the SDA line may be changed only during the low period of SCL and must be held stable during
the high period of SCL. A transition on the SDA line while SCL is high is interpreted as a command (see START
and STOP signals).
• I2C protocol
START signal
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 32 / 72
Page 33

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
When the bus is free/idle, meaning no master device is engaging the bus (both SCL and SDA lines are high), a
master can initiate a transfer by sending a START signal. A START signal, usually referred to as the S-bit, is
defined as a high-to-low transition of SDA while SCL is high. The START signal denotes the beginning of a new
data transfer. A Repeated START is a START signal without first generating a STOP signal. The master uses
this method to communicate with another slave or the same slave in a different transfer direction (e.g. from
writing to a device to reading from a device) without releasing the bus.
The I2C master generates a START signal when the STA-bit in the Command Register is set and the RD or WR
bits are set. Depending on the current status of the SCL line, a START or Repeated START is generated.
Slave address transfer
The first byte of data transferred by the master immediately after the START signal is the slave address. This is
a seven-bits calling address followed by a RW bit. The RW bit signals the slave the data transfer direction. No
two slaves in the system can have the same address. Only the slave with an address that matches the one
transmitted by the master will respond by returning an acknowledge bit by pulling the SDA low at the 9th SCL
clock cycle.
Note: The I2C master supports 10bit slave addresses by generating two address transfers. See the Philips I2C
specifications for more details.
The I2C master treats a Slave Address Transfer as any other write action. Store the slave device’s address in
the Transmit Register and set the WR bit. The I2C master will then transfer the slave address on the bus.
Data Transfer
Once successful slave addressing has been achieved, the data transfer can proceed on a byte-by-byte basis in
the direction specified by the RW bit sent by the master. Each transferred byte is followed by an acknowledge bit
on the 9th SCL clock cycle. If the slave signals a No Acknowledge, the master can generate a STOP signal to
abort the data transfer or generate a Repeated START signal and start a new transfer cycle.
If the master, as the receiving device, does not acknowledge the slave, the slave releases the SDA line for the
master to generate a STOP or Repeated START signal.
To write data to a slave, store the data to be transmitted in the Transmit Register and set the WR bit. To read
data from a slave, set the RD bit. During a transfer the core set the TIP flag, indicating that a Transfer is In
Progress. When the transfer is done the TIP flag is reset, the IF flag set and, when enabled, an interrupt
generated. The Receive Register contains valid data after the IF flag has been set. The user may issue a new
write or read command when the TIP flag is reset.
Stop signal
The master can terminate the communication by generating a STOP signal. A STOP signal, usually referred to
as the P-bit, is defined as a low-to-high transition of SDA while SCL is at logical ‘1’.
• Arbitration Procedure
Clock Synchronization
The I2C bus is a true multi-master bus that allows more than one master to be connected on it. If two or more
masters simultaneously try to control the bus, a clock synchronization procedure determines the bus clock.
Because of the wired-AND connection of the I2C signals a high to low transition affects all devices connected to
the bus. Therefore a high to low transition on the SCL line causes all concerned devices to count off their low
period. Once a device clock has gone low it will hold the SCL line in that state until the clock high state is
reached. Due to the wired-AND connection the SCL line will therefore be held low by the device with the longest
low period, and held high by the device with the shortest high period.
Clock stretching
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 33 / 72
Page 34

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Slave devices can use the clock synchronization mechanism to slow down the transfer bit rate. After the master
has driven SCL low, the slave can drive SCL low for the required period and then release it. If the slave’s SCL
low period is greater than the master’s SCL low period, the resulting SCL bus signal low period is stretched, thus
inserting wait-states.
B.II.4 General Purpose Input Output
RDA5851S GPIO modules has configurable number of General Purpose Input or Output ports (GPIO) and
General Purpose Output port(GPO). There are 3 GPIOs are used to get external events. They can be used as
inputs or outputs.
B.II.5 Keypad
The RDA5851S keypad is realized using ADC serial keypad detection
B.II.6 Timers
RDA5851S includes 1 OS timer, 1 watchdog timer and 1 hardware delay timers. The OS timer serves for OS,
and has Ticks of 16384 Hz. It is a decrement timer and the initial value can be programmed. When the OS timer
reaches 0, it will cause an interruption. After that, the OS timer will either stop or restart with the initial value (loop
mode) or wrap to maximum value (wrap mode).
The watchdog timer can be used to protect against system failure or software mistakes by reinitializing the
system. When it’s no longer servicing the watchdog timer, the Watchdog Timer operations are almost identical
to the OS Timer. In addition when the counter reaches 0 it can trigger a System Reset. To use the Watchdog
function, the software should reload the Watchdog Timer on a periodic basis to avoiding the Watchdog Timer to
reach 0 and trigger an interrupt or a system reset (depending on configuration).
The hardware delay timer is an incremental timer. It has Ticks of 16384 Hz. This timer is free running, and the
value will be reset to 0. The timer value will wrap to 0 after 0xfffffff, and will generate an IRQ when wrap. The
hardware delay timer can also generate an interval IRQ which can be configured to every 1/8 second,1/4
second, 1/2 second, or 1 second.
The timers module has two IRQs. One dedicated for OS timer, the other is used by all the other timers.
(including watchdog timer, hardware delay timer)
Features
● 1 24-bit decremental timer for OS.
● 1 32-bit incremental hardware delay timer.
● 1 24-bit decremental watchdog timer.
● Multiple IRQ sources: timers wrap, interval arrives.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 34 / 72
Page 35

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
B.II.7 Debug Port (EXL, PXTS, Signal Spy)
The DEBUG_PORT module:
- Provide 4 watches.
- Storing the last execution address of the selected CPU in the event of a watchdog reset.
This value is not reset on any system reset and can be read when the system was recovered
from the watchdog reset.
- Data packet transfer: debugging tool configurable in 4 different modes:
Features
● Access to the last PC of the selected CPU when a watchdog reset occurs.
● Mode Debug_Port_Off : This mode switch off the module
● Mode Exl : This mode record all the CPU Jump start address send to the Romulator. Generate a
strobe and output the selected CPU's PC.
● Mode Pxts : This mode record all the serial events analyzed by Coolprofile. Generate a Strobe and
output the Pxts tag.Through Pxts Enable decoding, we will be able to select one Pxts_tag into 16
Pxts_tag defined.
● Mode Pxts_Exl: this mode enable both mode PXTS and EXL. PXTS mode has a highest priority
compare to mode EXL.
● Mode Signal_Spy : This mode spy the signals for the debug purpose(Describe the IOCore muxing for
IO mode configuration)
B.II.8 General Purpose Analog to Digital Converter (GP ADC)
The GPADC module controls the analog module of general purpose analog to digital converter, which is capable
of measuring analog external inputs of the chip. The one external input can be connected to sensors to measure
battery voltage, battery temperature, temperature, accessory ID, remote control, or other low frequency analog
signal within the specified voltage range.
The GPADC is active periodically at a variable rate if at least one channel is enabled. The value of each channel
is readable through the APB interface.
Features
● 1 analog external channels.
● Automatic measurement at variable rate.
● Interrupt when programmed threshold is passed.
Operation
By default, GPADC works in functional mode, GPADC is active periodically at a variable rate and measures all
the enabled channel each time.
There is also a test mode for debug purpose, in which GPADC receives a start measure command from APB,
and do a measurement once.
Usually, the one GPADC is used for mic detect, and another is for user defined function.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 35 / 72
Page 36

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
B.II.9 Timing Control Unit and Low Power Synchronizer
(TCU+LPS)
The Timing Control Unit handle the scheduling of individual events with a quarter bit precision.
The TCU is based on a quarter bit counter (13/12 MHz = 1.083 MHz), which wraps at a programmable value. An
interruption is generated when the counter wraps (Frame interrupt). The current value of this counter is available
at any time. The wrap value can be set at any time. To assure a predictable behavior this value should only be
set by the programmer “far” from the wrap time, to make sure this new value will be taken into account the next
time.
The programmer can define events associated to particular counter values (dates). When the counter equals the
given date, the action associated to the event will take place.
The event are contained in a table of events split into a programming table and an active table. Only the events
in the active table are compared to the counter value. The programming table table allows to prepare a full
sequence of events which will be transfered to the active table when the counter wraps.
A force signal allows to transfer events from the programming table to the active table immediately.
The LPS Low Power Synchronizer is a part of the TCU, it is responsible for maintaining the time base while
running at a slower clock (32kHz) for power saving.
TCU Features
● Quarter bit precision.
● 60 entries event table.
● Programmable counter wrap value.
LPS Features
● Allow skipping frames by masking the TCU Frame Interrupt.
● Calibration of the 32kHz clock against the System Clock with an accuracy of 4 System clocks during a
programmable time to reach wanted rate accuracy.
● Low power counters (32kHz) can maintain timebase while System clock is suspended.
● A hardware state machine can assist the CPU for the power up after each exit of the low power mode.
B.II.10 System AHB Monitor (Sys AHBC Mon)
This monitor connected to the System AHB bus can measure several bandwidth and latency information.
Features
● 8 configurable time windows:
● 4 asynchronous for gradually going from accuracy to reactivity of the measures.
● 4 based on frame for GMS related measurements
● Peak or mean measures.
● Selection between several resources:
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 36 / 72
Page 37

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
● Global bus usage.
● Bus usage and latency of access for a particular master.
● Bus usage, number of access and duration of access for a slave.
● High time, number of rise and duration of high time for a resource selected via the signal select of the
debug port.
Mean calculation
Measures are always relative to the time window. Mean latency or duration has to be calculated by dividing the
total latency / duration measured by the number of accesses.
Special resource monitoring
The Signal_Select0 and Signal_Select1 signals can be monitored to estimate latency of IRQ handling, or
measure any latency/usage of software part. This last case can be achieved by setting Signal_Select0 to
Watch(n) in the debug port configuration, monitoring the Signal_Select0 signal; by setting and clearing the
Watch(n) during code to profile, you can measure the mean time spent.
B.II.11 System IRQ Controller (Sys IRQ)
In RDA5851S, the interruptions are generated by the modules, they can be filtered at the module level (the mask
must be configured in each corresponding module's registers), then they are filtered by the System or Base
Band IRQ Controller (the mask is set in System IRQ Control or Base Band IRQ Control registers). The
interrupts must be cleared in the corresponding module.
For power saving, one CPU can shut down its own clock. A special wakeup mask allows re-enabling the clock
when an interruption enabled in this mask is triggered..
Features
● A mask at the module level.
● A mask at the IRQ Control level.
● A second Mask for Pulse IRQ (that are not masked in the module)
● Wakeup mask.
● Sleep Register
● Driving IRQ inputs to the CPU (6 lines)
B.II.12 USB Controller
Features
● Fully compliant to USB Specification Version 1.1
● Slave Full Speed (12Mbps) Device
● Integrated USB Transceiver
● Supports Control, Interrupt, Bulk and Isochronous transfer
● 4 Endpoint with FIFO:
○ One Bi-directional Control Endpoint (EP0)
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 37 / 72
Page 38

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
○ Three soft configurable Bi-directional Endpoints
● SRAM FIFO : 264 words (32bits)
B.II.13 SD/MMC Controller
This module connects inner bus and outer SD or MMC card. It receives the inner command and data, transfers it
to outer SD or MMC card, and transfer response or data back.
Features
● SD Card Specification Version 2.0
● SDIO Version 1.10
● MMC specification Version 3.1
● Hot insertion and removal of media cards will be considered by GPIO module
B.II.14 Audio Interface Analog + I2S (AIF)
The Audio Interface (AIF) module is the audio interface between the RDA5851S system and multimedia chip.
AIF can work in master mode in which it generates synchronization signals needed by the multimedia chip,
which contains the audio ADC and DAC to convert the serial digital output data to analog audio signal and the
input analog signal to serial digital audio data. It can also works in slave mode which uses synchronization
signals sent from multimedia chip. Please see below for more details about serial data format.
AIF includes both serious and parallel interface. It is able to support multiple sample rate including 8 kHz, 11.025
kHz, 12kHz, 16 kHz, 22,05 kHz, 24kHz, 32kHz, 44,1 kHz, 48kHz and various data format. AIF can also generate
common DTMF, comfort tones and side tone with a configurable gain.
Features
● Common features.
○ 4*32-bit RX and 4*32-bit TX FIFO.
○ All common DTMF and Comfort Tones can be generated and gained from -15 dB to 0 dB.
○ Side Tone fully configurable: Mute or amplification from -36 dB to +6 dB.
○ Loop back capabilities for test purposes.
● Serial Interfaces.
○ 16-bit mono or stereo samples.
○ MSB/LSB configurable.
○ Configurable as master or slave.
○ LRCK/BCLK ratio from 16 to 31.
○ Supports multiple sample rates (8 kHz; 11.025 kHz; 12kHz; 16 kHz; 22,05 kHz; 24kHz; 32kHz;
44,1 kHz; 48kHz).
○ Fully configurable clock polarity: Data can be sampled or sent independently at either rising edge
or falling edge of the clock.
○ Configurable TX/RX data delays: Digital audio data in can be aligned or 1/2/3 cycles delayed to
LRCK edge. Digital audio data out can be aligned or 1 cycle delayed to LRCK edge. 1 cycle
supplementary delay is possible for TX data in slave mode.
○ Support Audio mode: I2S compatible but can have more configurations.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 38 / 72
Page 39

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
○ Support voice mode: One cycle strobe pulse at the beginning of each new sample. Compatible to
Maxim 9851/9853 voice mode.
● DAI interface.
○ 13-bit mono sample.
○ Generate 104 kHz master clock.
○ Starts after a pulse on the DAI_RST line.
● Parallel Interface
○ 13-bit mono samples from ADC.
○ 16-bit x 2 stereo samples to stereo DAC.
○ Separate TX and RX strobe lines for synchronization.
B.III Digital Modules
B.III.1 Voice Coprocessor (VoC)
The Voice Co-Processor (VoC) is designed to process different Vocoders (FR, HR, EFR, AMR)It is developed
as a target-specific DSP core, including basic function-call support, able to execute the code with very little (or
no) control intervention from the CPU. It is controlled and configured by the CPU through the AMBA bus.
Features
● Bi-MAC, single test/logic Computational Unit with two 16x16 -> 32-bit multipliers
● Eight 16-bit general purpose registers, that can be combined in four 32-bit general purpose registers.
● All 16-bit registers can be used as pointers, four of them are incremental (for easy array addressing).
● Four 32-bit general purpose registers.
● 2 x 20 Kbytes data RAM + 32 Kbytes instruction RAM.
● Double stack with random access: for 32-bit & 16-bit values (push, pop).
● Function call support (jal, return).
● Two zero-cycle loop counters.
● Pointer & Direct addressing modes.
● DMA sub-module for block transfers between external memory and VoC memories.
● Simple DAI Interface for Analog test Audio Loop (Loop between DAI interface and Analog Interface
designed to test the Audio Filters implemented by VoC)
● Clock speed : 26MHz, 39MHz, 52MHz, 78MHz, 89MHz, 104MHz, 113MHz, 125MHz, 139MHz,
156MHz, 178MHz, 208MHz, 250MHz, 312MHz.
B.IV Analog Modules
SPI Interface for Analog IP control
All the IPs connected to DBB feature an SPI interface dedicated to IP control.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 39 / 72
Page 40

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
The Power Management Unit(PMU) and the Analog module(ABB) are controlled by the same SPI of DBB (with
different chip-select).
For simplicity sake and ease of use, the SPI protocol settings for PMU and ABB.
The chosen SPI setting is the following:
– Data from DBB are issued on falling edge of clock and can be latched on rising edge by the slave.
– Data from the slave are issued on rising edge of the clock and will be latched on falling edge of
clock.
– the SPI frame is 26 bits long : first bit is the R/W selection, then 9 bits of address A
8
to A0, then 16
bits of data D15 to D0.
– Maximum SPI_CLK frequency : 26 MHz
Power Management Unit
The PMU is controlled from the DBB through SPI.
B.IV.0.0.a Power System Management
The PMU performs a POR either when POWKEY is asserted (i.e. Power-ON/OFF button pressed) or when then
WAKEUP line is raised (RTC Alarm) or when the charger (or USB) is plugged.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 40 / 72
A0
D15
D0
SPI_CLK
SPI_CS_X
SPI_DO
R/W
A0
D15 D0
SPI_CLK
SPI_DO
SPI_DI_X
SPI Write Timing
SPI Read Timing
A8->1
A8->1
R/W
SPI_CS_X
Figure B.9: SPI Write & Read Timing
Page 41

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
In the presented principle schematic, PowerON is an internal signal of the PMU that reflects that the system
needs power. It can either be raised when the Power-ON key is pressed, when the WAKEUP line from DBB is
raised or when the charger (or USB) is plugged. When a rising edge of PowerON is detected, the PMU should
go through its POR sequence.
The POR sequence consists in turning ON the relevant power supplies then wait for RST delay that is be long
enough to ensure that all LDOs are in steady state and that all the chip is correctly powered, then raise the
RESETB signal.
In case the POR is trigged by POWKEY, It's DBB responsibility to set the WAKEUP line high when it considers
that POWKEY has been pressed long enough. As POWKEY is a VBAT level input, a V_CORE version of
POWKEY (named KEYON) is generated for DBB.
POR can also be initiated when the WAKEUP line is being raised directly because of an RTC Alarm (the
POWKEY is not pressed).
As long as PowerON is high, the PMU provides voltages supplies that are specified by the current Power-Profile
that describes the LDO and DC/DC settings.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 41 / 72
POWKEY
WAKEUP
PowerON
CHG_MASK
PMU
KEYON
Charger / USB
Detect
V_CORE
CHG_IN
ChargerON
Figure B.10: PMU Power ON
Page 42

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
B.IV.0.0.b
The PMU implements multiple power profiles defining the LDOs and DC/DC activation in various modes.
• Default_powerOFF_profile: used when the system is OFF( system has been shut-off or first time battery
is plugged...). In this case only V_RTC is provided.
• Default_powerON_profile: used when PowerON is asserted and the POR is trigged, all LDOs that have
“reset state ON” are activated.
• Active_power_profile: used once system has booted and decided to switch from
Default_powerON_profile. This profile is programmable.
• LP_power_profile: used when the system goes to low-power mode (switch from Active to Low-power
through LP_MODE line). This profile is programmable.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 42 / 72
POWKEY
LDO's supplies
RESETB
WAKEUP
RSTdelay
DBB boots and sets WAKEUP
PowerON
Figure B.11: POR triggered by POWKEY press
Page 43

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
If the PowerON line goes low, the RESETB signal will be set to Low level then all power supplies excepted
V_RTC are switched OFF.
It can be useful to be able to go back to Default_powerOFF_profile (i.e. shut-off all supplies except RTC) even
when a charger is plugged. The CHG_MASK (RTC domain) line is used for this purpose, by masking the
ChargerON line.
V_USB is not power-on automatically when USB is detected. The USB PHY remains OFF until the software
decides to turn it ON.
B.IV.0.0.c LDOs
Name Type Voltage Max Current Usage (power domain)
V_CORE DC-DC 1.2V 300mA Core
V_CORE LDO 1.2V 20mA Core
V_PAD LDO 1.8V / 2.8V 200mA Digital IO
V_ANA LDO 200mA Analog module
V_MEM LDO 1.8V / 2.8V 200mA External Combo flash / ram
V_SPIMEM LDO 1.8V / 2.8V 200mA External SPI Memory
V_MMC LDO 2.8V / 3.2V 150mA Memory Card
V_USB LDO 3.3V 300mA USB PHY
V_MIC LDO 1.4V/1.75V 200mA Microphone
V_RTC LDO 1.2V 0.6mA Real time clock
B.IV.0.0.d Charger Circuit
The RDA5851S integrates the most of charger circuits, except for a few components such as one PMOS, one
accurate resistor and one diode, which should be applied externally.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 43 / 72
Defaut_powerON_profile
LP_power_profile
Active_power_profile
LP_MODE
Software selectable:
default to '0', reset to '0'
when PowerON goes low.
To LDOs and
DC/DC control
Defaut_powerOFF_profile
PowerON
0
1
0
1
0
1
Figure B.12: Principle schematic for Power-Profiles usage
Page 44

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
When the charger is on, this block controls the charging phase and turns on the appropriate LDOs according to
the battery status. If the voltage is greater than 4.2~ 4.4 V, charging is stopped immediately to prevent
permanent damage to the battery.
Battery charging states include No Charge mode, Constant Current (CC) charge mode (pre-charge, constant
current), and Constant Voltage (CV) charge mode. No matter what state the phone is in, the PMIC charger
handles the charging state transition. A typical charging process is described as what the Figure 5 shows.
The charge current is calculated by the following expression,
I_charge = I_ref * (200/0.2)
I_ref is 0.05mA in pre_charge mode and 0.5mA in constant mode, and these two mode can be switched by
internal charger circuit.
B.IV.0.0.e Interrupt management
The PMU has two lines of interruption to DBB:
• the PENIRQ line dedicated to touchscreen
• the PMU_INT line that handles several other causes of interruption.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 44 / 72
Pre
charging
t(pre-charge) t(charge)
CC mode CV mode
Charge curre nt
Charge voltag e
Li-ion cell voltage
Figure B.13: Charging I-V Curve
Page 45

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Analog module (ABB)
B.IV.0.0.f PLL and clock squarer
ABB includes a PLL that generates 624MHz from a 26MHz input (x24 integer frequency multiplier). It also
includes a “clock squarer” that buffers the clock coming from the internal transceiver to provide a clean version
(at VCORE levels) of this clock.
The following drawing summarizes the PLL clock path:
B.IV.0.0.g AUDIO
The Audio part includes ADC, DAC, Audio Amplifiers and Audio Muxes. The following diagram provides a global
view of audio blocks. Voice data can be input from microphone. Voice and audio data can be output to a stereo
DAC and connected to peripherals such as receiver, headset and loudspeaker. It is able to support multiple
sample rate audio data including 8 kHz, 11.025 kHz, 12kHz, 16 kHz, 22,05 kHz, 24kHz, 32kHz, 44,1 kHz,
48kHz.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 45 / 72
XCVR
ABB
PLL
BBCLK_OUT_624M
Clock_Squarer
CLK_PLL_IN
CLK_RF_26M
Figure B.14: PLL Clock Path
Page 46

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
B.IV.0.0.h USB PHY
DIP and DIM pins are really reflecting DP and DM, therefore the following decoding must be done in DBB USB
controller:
B.IV.0.0.i General Purpose ADC
ABB includes an A to D converter. A functional timing diagram is given below:
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 46 / 72
USB_OEN
USB_DIP
USB_DIM
USB_SUSPEND
USB_RXD
USB_RXDP
USB_RXDM
USB_DP
USB_DM
USB PHY
Figure B.15: USB PHY FS 1.1
Figure B.16: GPADC Timing Diagram
Page 47

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
B.V FM
General Description
RDA5851S Integrates a broadcast FM stereo radio tuner with fully integrated synthesizer, IF selectivity and MPX
decoder. The tuner requires the least external component. It has a powerful low-IF digital audio processor, this
make it have optimum sound quality with varying reception conditions. It can be tuned to the worldwide
frequency band.
Features
● Low Power Consumption
➢ Total Current consumption Lower than 22 mA at 3.0 V power supply
● Support worldwide frequency band
➢ 65-108MHz
● Digital low-IF tuner
➢ Image-reject down-converter
➢ High performance A/D converter
➢ IF selectivity performed internally
● Fully integrated digital frequency synthesizer
➢ Fully integrated on-chip RF and IF VCO
➢ Fully integrated on-chip loop filter
● Autonomous search tuning
● Support 32.768KHz crystal oscillator
● Digital auto gain control (AGC)
● Digital adaptive noise cancellation
➢ Mono/stereo switch
➢ Soft mute
➢ High cut
● Programmable de-emphasis (50/75 ms)
● Receive signal strength indicator (RSSI)
● Bass boost
● Volume control
● FM Record through digital audio interface
● Line-level analog output voltage
● 32.768 KHz 12M,24M,13M,26M,19.2M,38.4MHz Reference Clock
● SPI control bus interface
● Directly support 32Ω resistance loading
Block Description
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 47 / 72
Page 48

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
The FM receiver uses a digital low-IF architecture that avoids the difficulties associated with direct conversion
while delivering lower solution cost and reduces complexity, and integrates a low noise amplifier (LNA)
supporting the FM broadcast band (65 to 108MHz), a quadrature image-reject mixer, a programmable gain
control (PGA), a high resolution analog-to-digital converters (ADCs).
The LNA has differential input ports (LNAP and LNAN) and supports any input port by set according registers
bits. It default input common mode voltage is GND.
The limiter prevents overloading and limits the amount of intermodulation products created by strong adjacent
channels.
The quadrature mixer down converts the LNA output differential RF signal to low-IF, it also has image-reject
function.
The PGA amplifies the mixer output IF signal and then digitized with ADCs.
The DSP core finishes the channel selection, FM demodulation, stereo MPX decoder and output audio signal.
The MPX decoder can autonomous switch from stereo to mono to limit the output noise.
The frequency synthesizer generates the local oscillator signal which divide to quadrature, then be used to downconvert the RF input to a constant low intermediate frequency (IF). The synthesizer reference clock is 32.768
kHz. The synthesizer frequency is defined by register bits with the range from 65MHz to 108MHz.
Receiver Characteristics
(VDD = 2,7 to 5,5V, TA = -25°C to 85 °C, unless otherwise specified)
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
General Parameters
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 48 / 72
Figure B.17: FM Tuner Block Diagram
Page 49

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN TYP MAX UNIT
F
in
FM Input Frequency
BAND=00 87 108 MHz
BAND=01 76 91 MHz
BAND=02 76 106 MHz
BAND=03 65 76 MHz
V
rf
Sensitivity
1,2,3
(S+N)/N=26dB 1 1.5 µV EMF
R
in
LNA Input Resistance
7
150 Ω
C
in
LNA Input Capacitance
7
2 4 6 pF
IP3
in
Input IP3
4
AGCD=1 80 - dBµV
a
am
AM Suppression
1,2
M=0.3 40 - dB
S
200
Adjacent Channel Selectivity ± 200kHz 45 - dB
V
AFL;VAFL
Left and Right Audio
Frequency output Voltage
Volume [3:0]=1111 200 mV
(S+N)/N Maximum Signal Plus Noise to
Noise Ratio
1,2
55 60 - dB
a
SCS
Stereo Channel Separation 35 - - dB
THD Audio Total Harmonic
Distortion
1,3,6
0.03 0.05 %
a
AOI
Audio Output L/R Imbalance 0.1 dB
R
L
Audio Output Loading
Resistance
Single-ended 32 - - Ω
Pins LNAN, LNAP
V
com_rfin
Pins LNAN and LNAP Input
Common Mode Voltage
0 V
V
com
Audio Output Common Mode
Voltage
0.95 1 1.05 V
Notes:
1. Fin=65 to 108MHz, F
mod
=1KHz, de-emphasis=75µS,MONO=1;L=R unless noted otherwise.
2. Δf =22.5KHz.
3. BA =300Hz to 15KHz, RBW <= 10Hz.
4. | f2-f1|>1MHz, f0=2xf1-f2, AGC disable, Fin=76 to 108MHz.
5. PRF=60dbµV.
6. Δf =75KHz.
7. Measured at V
EMF
=1mV, FRF=65 to 108MHz.
B.VI Bluetooth
General Description
RDA5851S Integrates a highly integrated Bluetooth SoC with radio transceiver and baseband processor, which
is compliant with Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR specification and provides an optimal solution for data and voice
application.
It has been designed on highest level of integration to extremely reduce the number of external component.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 49 / 72
Page 50

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Features
● CMOS single-chip fully-integrated radio and baseband
● Compliant with Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR specification
● Bluetooth Piconet and Scatternet support
● Support AFH
● Meet class1, class2 and class3 transmitting power requirement
● Provides +4dbm transmitting power
● NZIF receiver with -90dBm sensitivity
● Up to 4Mbps high speed UART HCI support
● Low power consumption
● Minimum external component
Block Description
As shown in Figure above, the Bluetooth module on-chip integrates radio unit, baseband core, ARM7 core and
memory which provides a complete lower Bluetooth protocol stack including the LC, LM and HCI interface.
The description of individual section is following,
● Radio Front
◦ Build-in TX/RX switch
◦ Fully integrated synthesizer without any external component
◦ Support DCXO or external reference clock direct input
◦ Class1,class2 and class3 transmit output power supported and over 30dB dynamic control range
◦ Supports π/4 DQPSK and 8DPSK modulation
◦ High performance in receiver sensitivity and over 80dB dynamic range
◦ Integrated channel filter
● Baseband
◦ Internal RAM allows fully speed data transfer, mixed voice and data, and fully piconet operation
◦ Logic for forward error correction, header error control, access code correlation, CRC, demodulation
, encryption bit stream generation, whitening and transmit pulse shaping
◦ Support eSCO and AFH
◦ Support up to Bluetooth v2.1 + EDR
◦ Support A-law, μ-law and CVSD digitize audio CODEC in PCM interface
● Stack
◦ Compliant with Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR specification
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 50 / 72
Figure B.18: Bluetooth Block Diagram
Page 51

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Performance Characteristics
Power consumption specification (VBAT = 4.0 V, TA = +27 , unless otherwise specified)℃
STATE DESCRIPION Condition TYP. UNIT
DH1 / DM1 26 mA
DH3 / DM3 28 mA
DH5 / DH5 29 mA
HCI only active 5.5 mA
Sleep 100 uA
Shut off 15 uA
Receiver Characteristics --- Basic Data Rate (VBAT = 4.0 V, TA = +27 , unless otherwise specified)℃
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITION MIN TYP. MAX UNIT
General Specification
Sensitivity @ 0.1% BER / -90 / dBm
Maximum input @ 0.1% BER 0 / / dBm
C/I co-channel / 10 / dB
Adjacent channel selectivity C/I
F = F0 + 1 MHz / / -5 dB
F = F0 - 1 MHz / / 0 dB
F = F0 + 2 MHz / / -33 dB
F = F0 - 2 MHz / / -30 dB
F = F0 + 3 MHz / / -45 dB
F = F0 - 3 MHz / / -40 dB
F = F_image / / 0 dB
Out-of-band blocking
30MHz–2000MHz -10 / / dBm
2000MHz–2400MHz -27 / / dBm
2500MHz–3000MHz -27 / / dBm
3000MHz–12.5GHz -10 / / dBm
Inter-modulation -35 / / dBm
Spurious output level -150 / / dBm
Transmitter Characteristics --- Basic Data Rate (VBAT = 4.0 V, TA = +27 , unless otherwise specified)℃
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITION MIN TYP. MAX UNIT
General Specification
Max RF output power / 4 / dBm
Power control range 30 / / dB
20dB bandwidth / 0.9 / MHz
Adjacent channel transmitter power F = F0 + 1 MHz / -35 / dBm
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 51 / 72
Page 52

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
F = F0 - 1 MHz / -34 / dBm
F = F0 + 2 MHz / -55 / dBm
F = F0 - 2 MHz / -55 / dBm
F = F0 + 3 MHz / -58 / dBm
F = F0 - 3 MHz / -58 / dBm
F = F0+ > 3 MHz -58 / / dBm
F = F0- > 3 MHz -58 / / dBm
△f1avg Maximum modulation
/ 164 / kHz
△f2max Minimum modulation
/ 145 / kHz
△f2avg/ f1avg△
0.8 / / /
ICFT / 4 / kHz
Drift rate / 0.1 / kHz/50
us
Drift (1 slot packet) / -2 / kHz
Drift (5 slot packet) / -2 / kHz
Receiver Characteristics --- Enhanced Data Rate (VBAT = 4.0 V, TA = +27 , unless otherwise specified)℃
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITION MIN TYP. MAX UNIT
π/4 DQPSK
Sensitivity @0.01% BER / -89 / dBm
Maximum input @ 0.1% BER 0 / / dBm
C/I co-channel / / 13 dB
Adjacent channel selectivity C/I
F = F0 + 1 MHz / / 5 dB
F = F0 - 1 MHz / / 0 dB
F = F0 + 2 MHz / / -30 dB
F = F0 - 2 MHz / / -20 dB
F = F0 + 3 MHz / / -40 dB
F = F0 - 3 MHz / / -40 dB
F = F_image / / -7 dB
8DPSK
Sensitivity @0.01% BER / -83 / dBm
Maximum input @ 0.1% BER 0 / / dBm
C/I co-channel / / 18 dB
Adjacent channel selectivity C/I F = F0 + 1 MHz / / 5 dB
F = F0 - 1 MHz / / 5 dB
F = F0 + 2 MHz / / -25 dB
F = F0 - 2 MHz / / -13 dB
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 52 / 72
Page 53

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
F = F0 + 3 MHz / / -33 dB
F = F0 - 3 MHz / / -33 dB
F = F_image / / 0 dB
Transmitter Characteristics --- Enhanced Data Rate (VBAT = 4.0 V, TA = +27 , unless otherwise specified)℃
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITION MIN TYP. MAX UNIT
General Specification
Max RF output power / 2 / dBm
Relative transmit control / 1.6 / dB
π/4 DQPSK max w0 / 7.4 / kHz
π/4 DQPSK max wi / 6.7 / kHz
π/4 DQPSK max |wi + w0| / 2.4 / kHz
8DPSK max w0 / 7.1 / kHz
8DPSK max wi / 4.4 / kHz
8DPSK max |wi + w0| / 2.7 / kHz
π/4 DQPSK Modulation Accuracy
RMS DEVM / 4.7 / %
99% DEVM / / 30 %
Peak DEVM / 8.8 / %
8PSK Modulation Accuracy
RMS DEVM / 4.6 / %
99% DEVM / / 20 %
Peak DEVM / 11.3 / %
In-band spurious emissions F = F0 + 1 MHz / -14.7 / dBm
F = F0 - 1 MHz / -15.2 / dBm
F = F0 + 2 MHz / -51 / dBm
F = F0 - 2 MHz / -52.2 / dBm
F = F0 + 3 MHz / -55.5 / dBm
F = F0 - 3 MHz / -55.8 / dBm
F = F0+ > 3 MHz / / -55 dBm
F = F0- > 3 MHz / / -55 dBm
EDR Differential Phase Coding / 100 / %
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 53 / 72
Page 54

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
C. MEMORY MAP
Memory Name Description Address Size
External CS1 External memory 0x02000000 ~ 0x03ffffff 32MB
FIFO_regs Internal register 0x018c0000 ~ 0x018fffff 256KB
VOC Voice codec 0x01940000 ~ 0x0197fffff 256KB
CPU SRAM CPU internal sram 0x01980000 ~ 0x01987fff 32KB
SYS APB Sys apb slave 0x01a00000 ~ 0x01a7ffff 512KB
USB Usb controller 0x01a80000 ~ 0x01abffff 256KB
XCPU RAM Xcpu internal sram 0x01ac0000 ~ 0x01adffff 128KB
MPMC REG MPMC REG 0x01ae4000~0x01ae7ffff 16KB
MAILBOX MAILBOX 0x01b00000~0x01b00800 2KB
Internal sram Internal sram 0x01c00000 ~ 0x01c0ffff 64KB
Regs for bcpu patch Regs for bcpu patch 0x01d00000~0x01d00100 256B
Internal rom Internal rom 0x01e00000 ~ 0x01e04fff 20KB
External spi flash External spi flash 0x08000000 ~ 0x0fffffff 128MB
External psram External psram 0x02000000 ~ 0x03ffffff 32MB
XCPU APB
Sys_ctrl 0x01A00000
Irq 0x01A01000
Timer 0x01A02000
Gpio 0x01A03000
Ebc 0x01A04000
Pwm 0x01A06000
I2c 0x01A07000
Dma 0x01A08000
Ifc 0x01A09000
Comregs 0x01A0b000
Page_spy 0x01A0c000
Debug_port 0x01A0d000
Tcu 0x01A0f000
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 54 / 72
Page 55

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Sci 0x01A10000
Spi 0x01A11000
Spi2 0x01A12000
Spi3 0x01A13000
Debug_uart 0x01A14000
Uart2 0x01A16000
Sdmmc 0x01A17000
Xcpu_reg 0x01A19000
Xcpu_tag 0x01A1a000
Xcpu_idata 0x01A1b000
Xcpu_ddata 0x01A1c000
Sys_ahb_mon 0x01A1d000
Bb_ahb_mon 0x01A1e000
Bist 0x01A1f000
IFC2 0x01A20000
I2C2 0x01A22000
I2C3 0x01A23000
EXT_APB 0x01A24000
Spi Flash Reg 0x01A25000
Nand Flash Cs0 0x01A26000
Nand Flash Cs1 0x01A27000
Nand Flash Cs2 0x01A28000
Nand Flash Cs3 0x01A29000
Nand Flash RS 0x01A2a000
Sdmmc2 0x01A2b000
Debug_host 0x01A3f000
AIF 0x01907000
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 55 / 72
Page 56

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
D. PINS DESCRIPTION
D.I Pin-out
Pin Name I/O Type First Usage Second Usage Third
Usage
Power
Domain
Ball
No
I2C2
I2C2_SCL I/O D I2C2 Clock GPIO_24 STD G7
I2C2_SDA I/O D I2C2 Data GPIO_25 STD G8
I2S
I2S_BCK I D I2S Clock CAM_DATA_4 GPIO_18 STD E8
I2S_LRCK I D I2S L/R Channel Clock CAM_DATA_5 GPIO_19 STD B9
I2S_DI I D I2S Data In CAM_DATA_6 GPIO_26 STD D9
I2S_DO O D I2S Data Out CAM_DATA_7 GPIO_27 STD C9
Memory Card Interface
SSD_CLK O D SD Clock MMC F6
SSD_CMD I/O D SD Command MMC E7
SDAT_0 I/O D SD data bit 0 MMC E6
SDAT_1 I/O D SD data bit 1 MMC F5
SDAT_2 I/O D SD data bit 2 MMC D7
SDAT_3 I/O D SD data bit 3 MMC C7
Debug Host
HST_CLK I D Host Clock input STD D3
HST_RXD I D Host data receive. STD H7
HST_TXD O D Host data transmit. STD J7
KEYPAD
KEYIN_SENSE I A Key input GPADC sense ABB C3
KEY_P O A Key sense P ABB B1
KEY_N O A Key sense N ABB B2
UART
UART2_RXD I/O D UART2 receive data GPIO_8 STD F8
UART2_TXD I/O D UART2 transmit data GPIO_13 STD F7
General Purpose I/O
GPIO_1 I/O D GPIO_1 KEYIN_6 STD H9
GPIO_3 I/O D GPIO_3 STD H8
GPIO_21 I/O D GPIO_21 KEYIN_4 STD E5
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 56 / 72
Page 57

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Pin Name I/O Type First Usage Second Usage Third
Usage
Power
Domain
Ball
No
GPIO_17 I/O D GPIO_17 STD F1
GPIO_11 I/O D GPIO_11 KEYOUT_2 STD E4
GPIO_7 I/O D GPIO_7 KEYOUT_3 STD E3
GPIO_8 I/O D GPIO_8 KEYOUT_4 STD D5
Miscellaneous Pins
RESETB_EXT I D External Reset for chip STD B7
TST_H ID D Test Mode RTC A7
BBPLL_TEST O D Digital CLK output for test ABB D6
XVR_XTAL1 I A 26MHz Crystal port Input ABB J9
XVR_XTAL2 O A 26MHz Crystal port Output ABB J8
ANA_TEST_EN I A test mode ABB A8
General Purpose ADC
GP_ADC_IN_0 I A GPADC input channel 0 ABB C2
USB
USB_DM I/O A USB D- ABB H5
USB_DP I/O A USB D+ ABB G5
AUDIO
LINE_IN_L I A Stereo Line input ABB F3
LINE_IN_R I A Stereo Line input ABB F4
AU_MIC_P I A Audio In+ ABB H4
AU_MIC_N I A Audio In- ABB H3
AU_RCV_P O A Receiver Out + ABB G6
AU_RCV_N O A Receiver Out - ABB H6
AU_HPL O A Headset Left Out ABB G3
AU_HPR O A Headset Right Out ABB G4
FM
FMRFIN I A FM RF differential input FM H1
FMRFIP I A FM RF differential input FM G1
FM_GND A FM GND FM H2
Bluetooth
BT_RFIP I A BT RF signal input BT G9
DECAP_BTDVDD A BT DECAP BT J6
Power Management Control
POWERKEY I A
Power-on switch enable
signal. Active High.
PMU D4
AC_R I A
Input from the AC
charger or USB inlet
PMU C1
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 57 / 72
Page 58

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Pin Name I/O Type First Usage Second Usage Third
Usage
Power
Domain
Ball
No
GDRV O A Charger drive PMU E2
IS_CHG I A Current Sens for Charger
Control
PMU D1
VBAT_SENSE I A Battery voltage ADC detect PMU D2
PROG_EFUSE I A High voltage input for
OTP/EFUSE programming
PMU C4
POWER
VBAT_PMU1 I A PMU Battery Power Supply PMU A5
VBAT_PMU2 I A PMU Battery Power Supply PMU B5
V_CORE O A
Supplies BB Core. Out
for decoupling / debug /
backup
PMU A2
VBUCK2_2V4 O A
DCDC power supply
PMU B3
V_ANA O A
Out for decoupling /
debug / backup
PMU J1
V_PAD O A
Supplies Standard
PADs I/O ring. Out for
decoupling / debug /
backup
PMU J5
V_MMC O A
Supplies MMC PADs
I/O ring
PMU J4
V_USB O A
Supplies USB PHY. Out
for debug / backup /
decoupling
PMU E1
V_MIC O A
Microphone Biasing
PMU J3
V_NEG O A Negative Voltage generator PMU J2
SW_BUCK I A PMU A1
SW_BUCK2 I A PMU A3
GROUND
SW_GND A DC/DC Switch GND PMU A4
SW_GND A DC/DC Switch GND PMU B4
BT_GND A BT_GND PMU E9
BT_GND A BT_GND PMU F9
CORE_GND A CORE_GND PMU A6
CORE_GND A CORE_GND PMU B6
CORE_GND A CORE_GND PMU C6
CORE_GND A CORE_GND PMU C5
NC
NC TEST1 QN_RXTXDATA STD A9
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 58 / 72
Page 59

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Pin Name I/O Type First Usage Second Usage Third
Usage
Power
Domain
Ball
No
NC TEST2 QP_RXTXEN STD B8
NC TEST3 IP STD C8
NC TEST4 IN_STROBE STD D8
NC TEST5 KEYIN_1 STD G2
NC TEST6 KEYIN_3 STD F2
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 59 / 72
Page 60

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
E. ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
E.I Absolute Maximum Rating
Name Min Typical Max Usage (power domain)
VBAT_ABB,
VBAT_XCVR
VBAT_PMU
/ 3.8V 4.5V For chip
DC Charger 5V 7V For charger circuit
E.II Temperature Characteristics
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Work Temperature -25 25 70 °C
Storage Temperature -40 / 125 °C
E.III Audio Characteristics
Headphone
OUT RMS
ON
THD SINAD
OUT RMS
OFF
OUT PWR SNR
Battery
Voltage
(v) % (dB) (v)
0.23615 0.00844 46.353 0.000024 0.001743 79.86 4
0.32909 0.01013 46.3297 0.000036 0.003384 79.22 4
0.46948 0.01152 46.3691 0.000046 0.006888 80.18 4
0.6456 2.45938 31.9825 0.000066 0.013025 79.81 4
0.82236 13.9234 17.1464 0.000091 0.021134 79.12 4
1.02057 21.5071 13.3848 0.000127 0.032549 78.1 4
1.11581 26.4702 11.5432 0.000193 0.038907 75.24 4
1.16341 30.8232 10.1984 0.000326 0.042298 71.05 4
Receiver
OUT RMS
ON
THD SINAD
OUT RMS
OFF
OUT PWR SNR
Battery
Voltage
(v) % (dB) (v)
0.131718 0.02263 46.29659 0.000019 0.002169 76.82 4
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 60 / 72
Page 61

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
0.186607 0.032254 46.29754 0.000023 0.004353 78.18 4
0.261563 0.046055 46.2518 0.000029 0.008552 79.1 4
0.370479 0.066329 46.17642 0.00004 0.017157 79.33 4
0.519742 0.096372 46.15026 0.000053 0.033766 79.83 4
0.731471 0.162468 45.74333 0.000074 0.066881 79.9 4
0.978627 4.08141 27.70084 0.000106 0.119714 79.31 4
1.121201 14.80495 16.579 0.000143 0.157136 77.89 4
E.IV
E.V DC Characteristics
Name Min.(V) Typical(V) Max.(V) Description
VBAT 3.4 3.8 4.2 Normal work
VCORE 0.9 1.2 1.8 Normal work
V_BUCK_2V4 1.4 2.4 2.8 Normal work
AVDD_2V4 2.4 2.4 2.7 Normal work
V_BOOST 4.1 4.3 4.5 Normal work
V_ANA 2.6 2.8 3.0 Normal work
V_RTC 1.1 1.2 1.5 Normal work
V_MIC 1.3 1.4 1.5 Normal work
V_USB 3.3 Normal work
V_PAD,V_MEM,
V_SPIMEM,
V_ASW,
V_MMC
1.7 1.8 1.9 When 1.8V mode
2.6 2.8 3.0 When 3.0V mode
V_CORE
Vcore_DCDC
2FH[15:12]
Vbat=4.2V Vbat=3.4V
PWM PFM PWM PFM
Voltage(V) Voltage(V) Voltage(V) Voltage(V)
0000 0.734343 0.851079 0.734317 0.851287
0001 0.803534 0.913479 0.803521 0.917133
0010 0.873937 0.982545 0.87401 0.986022
0011 0.945415 1.046256 0.94553 1.054174
0100 1.018249 1.125916 1.018255 1.123417
0101 1.086779 1.185644 1.086697 1.187782
0110 1.154799 1.245822 1.154695 1.253376
0111 1.245088 1.331853 1.244965 1.338222
1000 1.323666 1.408776 1.323419 1.412903
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 61 / 72
Page 62

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
1001 1.42365 1.502113 1.423239 1.5059
1010 1.484614 1.560248 1.484106 1.561996
1011 1.554532 1.622902 1.554064 1.625002
1100 1.636774 1.693612 1.636572 1.696991
1101 1.683802 1.732771 1.683665 1.735503
1110 1.735693 1.776002 1.735418 1.775653
1111 1.792848 1.822333 1.792613 1.803393
V_BUCK2
Vbuck2_DCDC
2FH[7:4]
Vbat=4.2V Vbat=3.4V
PWM PFM PWM PFM
Voltage(V) Voltage(V) Voltage(V) Voltage(V)
0000 1.372298 1.326017 1.372103 1.326514
0001 1.462675 1.418426 1.462358 1.415203
0010 1.554009 1.495003 1.553642 1.489541
0011 1.646787 1.583869 1.646447 1.569516
0100 1.74188 1.672534 1.741347 1.654777
0101 1.830813 1.751696 1.830326 1.743785
0110 1.919983 1.835457 1.919578 1.836826
0111 2.036944 1.951065 2.036566 1.94758
1000 2.139276 2.060935 2.138946 2.041343
1001 2.268955 2.171742 2.268683 2.16727
1010 2.347893 2.252698 2.347531 2.242021
1011 2.439514 2.338851 2.439071 2.342576
1100 2.548583 2.448924 2.547497 2.451623
1101 2.609603 2.512368 2.60867 2.505622
1110 2.676921 2.570107 2.675591 2.56608
1111 2.750746 2.649165 2.749533 2.629614
V_PAD
VIO_Vsel
04H[12] 05H[5:3]
Vbat=4.2V Vbat=3.4V
Output Voltage(V) Output Voltage(V)
1
000 1.727 1.724
001 1.744 1.740
010 1.761 1.758
011 1.780 1.776
100 1.800 1.796
101 1.820 1.817
110 1.844 1.840
111 1.868 1.865
0 000 2.667251 2.666588
001 2.666319 2.665895
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 62 / 72
Page 63

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
010 2.679315 2.673723
011 2.727957 2.722229
100 2.780148 2.774493
101 2.835819 2.829775
110 2.896831 2.89022
111 2.960846 2.953016
V_MMC
VMC_vsel
04H[8] 06H[5:3]
Vbat=4.2V Vbat=3.4V
Output Voltage
(V)
Output Voltage
(V)
1
000 3.011621 3.003268
001 3.063471 3.047207
010 3.119571 3.080525
011 3.177808 3.101405
100 3.238899 3.115282
101 3.283025 3.124006
110 3.309923 3.129626
111 3.310144 3.133079
0
000 2.663742 2.655401
001 2.705838 2.696863
010 2.751196 2.741702
011 2.798733 2.788834
100 2.852021 2.836747
101 2.905989 2.874893
110 2.965718 2.900944
111 3.02769 2.917139
V_RTC
04H[15:13]
Vbat=4.2V Vbat=3.4V
Output Voltage(V) Output Voltage(V)
000 1.186234 1.184931
001 1.230272 1.229045
010 1.274606 1.273073
011 1.318833 1.317157
100 1.36277 1.360878
101 1.406876 1.404861
110 1.451079 1.448805
111 1.494915 1.492837
V_ASW
Vasw_vsel
04H[11] 06H[14:12]
Vbat=4.2V Vbat=3.4V
Output
Voltage(V)
Output
Voltage(V)
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 63 / 72
Page 64

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
1
000 1.898296 1.892917
001 1.914543 1.909376
010 1.932078 1.926779
011 1.950724 1.945268
100 1.97053 1.965045
101 1.991559 1.986128
110 2.014514 2.00895
111 2.038958 2.033227
0
000 2.597639 2.591382
001 2.640999 2.63448
010 2.686948 2.680374
011 2.735839 2.729014
100 2.7881 2.78095
101 2.843998 2.836121
110 2.904497 2.894896
111 2.96897 2.956203
V_ANA
07H[8:6]
Vbat=4.2V Vbat=3.4V
Output
Voltage(V)
Output
Voltage(V)
000 2.268517 2.266341
001 2.318284 2.315792
010 2.374201 2.372018
011 2.435136 2.433037
100 2.502894 2.500666
101 2.577594 2.575412
110 2.664263 2.662017
111 2.760628 2.758421
V_USB
07H[11:9]
Vbat=4.2V Vbat=3.4V
Output Voltage
(V)
Output Voltage
(V)
000 2.947253 2.946909
001 3.026925 3.026907
010 3.116152 3.114516
011 3.212047 3.209178
100 3.317436 3.314619
101 3.433383 3.386186
110 3.564778 3.386197
111 3.711378 3.386196
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 64 / 72
Page 65

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
V_MIC
ABB
Mb_sel_bit05H[15:14]
Vbat=4.2V Vbat=3.4V
Output Voltage(V) Output Voltage(V)
00 1.60 1.60
01 1.71 1.71
10 1.83 1.83
11 1.97 1.97
Charge Characteristics
CC
current
13H[9:7]=chr_cc_i_bit chr_current (mA)
000 41
001 70
010 109
011 166
100 223
101 329
110 474
111 580
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 65 / 72
Page 66

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
E.VI Digital IO DC Characteristics
Symbol Description Min.(V) Typical(V) Max.(V)
VDD All of power for digital usage VDD-0.2 1.8/2.8 VDD+0.2
VIL CMOS Low Level Input Voltage 0 - 0.3*VDD
VIH CMOS High Level Input Voltage 0.7*VDD - VDD
VTH CMOS Threshold Voltage - 0.5*VDD -
E.VII Digital IO AC Characteristics (SPI Interface Timing)
Symbol Description Min. Typ. Max. Unit
t
CLK
SCLK Cycle Time 35 - - ns
t
R
SCLK Rise Time - - 50 ns
t
F
SCLK Fall Time - - 50 ns
t
HI
SCLK High Time 10 - - ns
t
LO
SCLK Low Time 10 - - ns
t
SU
SDI Setup Time to SCLK↑ 15 - - ns
t
HOLD
SDI Hold Time to SCLK↑ 10 - - ns
t
EN1
SEN↓ to SCLK↑ Delay Time
10 - - ns
t
EN2
SCLK↑ to SEN↑ Delay Time
12 - - ns
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 66 / 72
Page 67

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Symbol Description Min. Typ. Max. Unit
t
EN3
SEN↑ to SCLK↑ Delay Time
12 - - ns
t
W
SEN Pulse Width 10 - - ns
t
CA
SCLK↑ to SDO Delay Time
- - 27 ns
C
load
Digital Input Pin Capacitance - - 5 pF
f
REF
Crystal Reference Frequency - 26 - MHz
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 67 / 72
Figure E.1: SCLK Timing Diagram
Figure E.2: SPI Write Timing Diagram
Page 68

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 68 / 72
Figure E.3: SPI Read Timing Diagram
Page 69

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
F. PACKAGING
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 69 / 72
Page 70

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
G. BALL OUT
Figure G.1: RDA5851S Ball out diagram
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 70 / 72
Page 71

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
H. GLOSSARY
Name Description
AHB AMBA Advanced High-performance Bus.
AHB2AHB Bridge allowing Sys AHB to communicate with BB AHB, and vice versa.
AIF RDA5851S's Audio Interface, including PCM, DAI and Audio Analog Interface.
APB AMBA Advanced Peripheral Bus, slow bandwidth bus.
ATR Answer To Reset, see SCI module for details.
Comfort Tone Tone generated by the AIF, used to indicate ringing, occupied...
CS Chip Select.
DAI Digital Audio Interface, part of the AIF used for test purpose.
DMA Direct Memory Access, can copy a part of the memory at an other address.
DTMF Dual Tone Multi Frequency generated by the AIF when a number is dialed.
EBC External Bus Controller, to connect external RAM, polyphonic chips, MMC...
ETU Elementary Time Unit, see SCI module for details.
GP ADC General Purpose Analog to Digital Converter.
IFC Base Band Intelligent Flow Controller, a bridge between AHB and APB buses.
IrDA Infra Red communication protocol used by RDA5851S's UART infra red mode.
Mailbox Communication module between the Sys AHB bus and the BB AHB bus.
MMC Multi Media Chips.
PCM Pulse Code Modulation, the part of the AIF that outputs samples in serial.
PLL Phase-Locked Loop.
SPI Serial Peripheral Interface.
Sys System side of RDA5851S, dedicated to the application, MMI.
TCU Timing Control Unit, handle the scheduling of individual events.
UART Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter, asynchronous serial port.
VCO Voltage Controlled Oscillator.
XCPU System RDA's 16/32-bit RISC CPU.
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 71 / 72
Page 72

RDA5851S Datasheet V1.01
Document History
The evolution of this document is described in the following table:
Version Date Description
1.00 2013-05-24 Initial version.
1.01 2013-10-25 Update pinout
RDA Microelectronics Inc. CONFIDENTIAL 72 / 72
 Loading...
Loading...