Raytheon RMWP23001 Datasheet
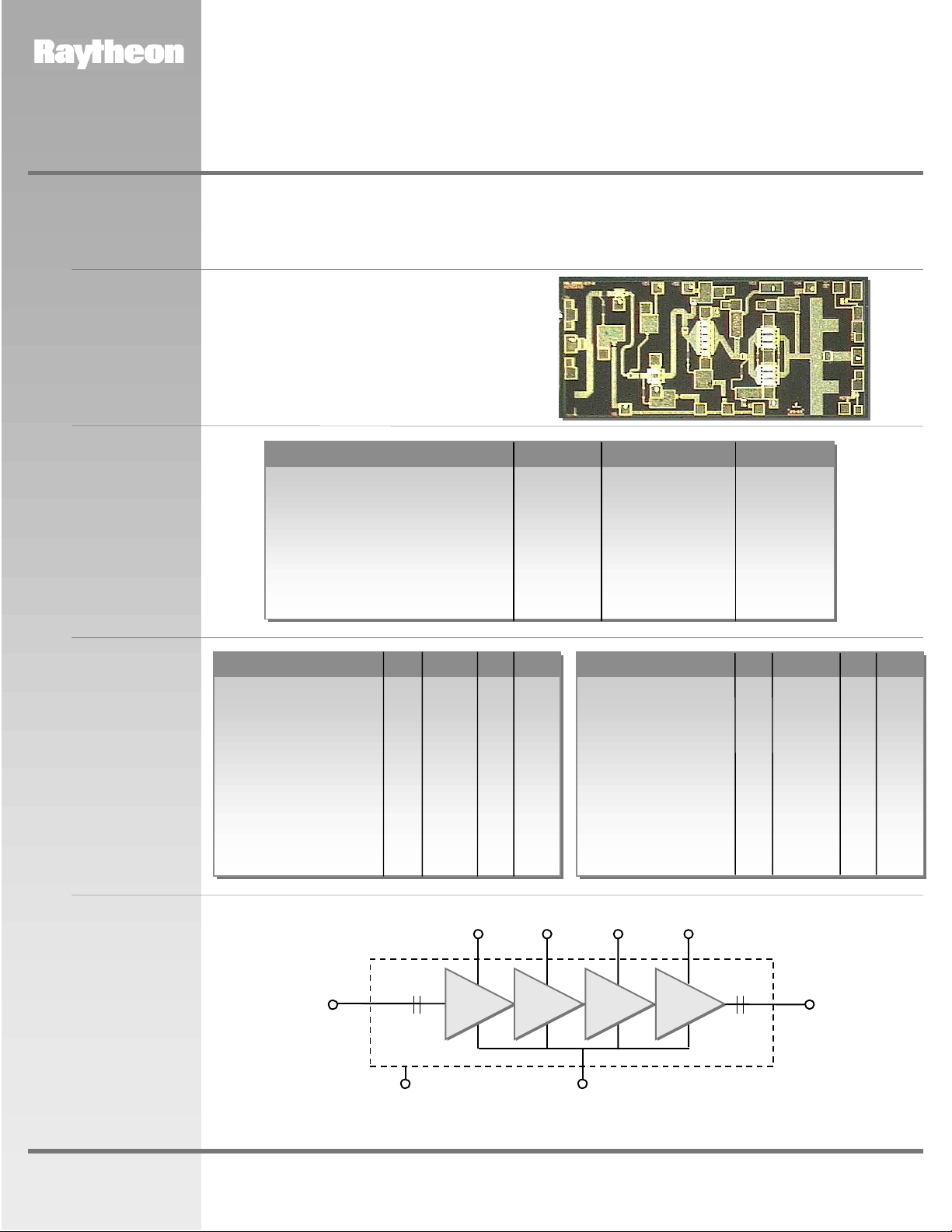
RMWP23001
21-24 GHz Power Amplifier MMIC
PRODUCT INFORMATION
Description
Features
Absolute
Maximum
Ratings
The RMWP23001 is a 4-stage GaAs MMIC amplifier designed as a 21 to 24 GHz Power Amplifier for use in point to
point radios, point to multi-point communications, LMDS, and other millimeter wave applications. In conjunction
with other Raytheon amplifiers, multipliers and mixers it forms part of a complete 23 GHz transmit/receive chipset.
The RMWP23001 utilizes Raytheon’s 0.25µm power PHEMT process and is sufficiently versatile to serve in a
variety of power amplifier applications.
4 mil substrate
Small-signal gain 22.5 dB (typ.)
1dB compressed Pout 23.5 dBm (typ.)
Chip size 2.6 mm x 1.2 mm
Parameter Symbol Value Units
Positive DC voltage (+4 V Typical) Vd +6 Volts
Negative DC voltage Vg -2 Volts
Simultaneous (Vd - Vg) Vdg 8 Volts
Positive DC Current I
RF Input Power (from 50 Ω source) P
Operating Baseplate Temperature T
Storage Temperature Range T
Thermal Resistance (Channel to Backside) R
D
IN
C
stg
jc
607 mA
+8 dBm
-30 to +85 °C
-55 to +125 °C
36.5 °C/W
Electrical
Characteristics
(At 25°C),
Ω system,
50
Vd = +4 V,
Quiescent Current
Idq = 400 mA
Functional
Block Diagram
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Frequency Range 21 24 GHz
Gate Supply Voltage (Vg)
Gain Small Signal at
Pi n= -8 dBm 20 22.5 dB
Gain Variation vs. Frequency 1.0 dB
Gain at 1dB Compression 21.5 dB
Power Output at 1dB
Compression 24 dBm
Power Output Saturated:
Pin = +3 dBm 22 25 dBm
Drain Current at Pin = -8 dBm 400 mA
RF IN RF OUT
Note:
1. Typical range of gate voltage is -0.7 to -0.05 V to set Idq of 400 mA.
Characteristic performance data and specifications are subject to change without notice.
1
MMIC Chip
-0.3 V
Drain
Supply
Vd1
Ground
(Back of Chip)
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
Drain Current at 1 dB
Compression 430 mA
Drain Current at Saturated:
Pin = +3 dBm 410 mA
Power Added Efficiency
(PAE): at P1 dB 15 %
Input Return Loss
(Pin = -8 dBm) 14 dB
Output Return Loss
(Pin = -8 dBm) 12 dB
OIP3 33 dBm
Noise Figure 8 dB
Drain
Supply
Vd2
Drain
Supply
Vd3
Gate Supply
Vg
Drain
Supply
Vd4
www.raytheon.com/micro
Revised March 14, 2001
Page 1
Raytheon RF Components
362 Lowell Street
Andover, MA 01810
RMWP23001
21-24 GHz Power Amplifier MMIC
PRODUCT INFORMATION
Application
Information
Recommended
Procedure
for Biasing and
Operation
CAUTION: THIS IS AN ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE.
Chip carrier material should be selected to have GaAs compatible thermal coefficient of expansion and high
thermal conductivity such as copper molybdenum or copper tungsten. The chip carrier should be machined,
finished flat, plated with gold over nickel and should be capable of withstanding 325°C for 15 minutes.
Die attachment should utilize Gold/Tin (80/20) eutectic alloy solder and should avoid hydrogen environment for
PHEMT devices. Note that the backside of the chip is gold plated and is used as RF and DC ground.
These GaAs devices should be handled with care and stored in dry nitrogen environment to prevent
contamination of bonding surfaces. These are ESD sensitive devices and should be handled with appropriate
precaution including the use of wrist grounding straps. All die attach and wire/ribbon bond equipment must be
well grounded to prevent static discharges through the device.
Recommended wire bonding uses 3 mils wide and 0.5 mil thick gold ribbon with lengths as short as practical
allowing for appropriate stress relief. The RF input and output bonds should be typically 0.012” long
corresponding to a typically 2 mil between the chip and the substrate material.
CAUTION: LOSS OF GATE VOLTAGES (Vg) WHILE DRAIN VOLTAGES (Vd) IS PRESENT MAY DAMAGE THE
AMPLIFIER CHIP.
The following sequence of steps must be followed to properly test the amplifier.
Step 1: Turn off RF input power.
Step 2: Connect the DC supply grounds to the grounds
of the chip carrier. Slowly apply negative gate
bias supply voltage of -1.5 V to Vg.
Step 3: Slowly apply positive drain bias supply voltage
of +4 V to Vd.
Step 4: Adjust gate bias voltage to set the quiescent
current of Idq = 400 mA.
Step 5: After the bias condition is established, RF input
signal may now be applied at the appropriate
frequency band.
Step 6: Follow turn-off sequence of:
(i) Turn off RF input power,
(ii) Turn down and off drain voltage (Vd),
(iii) Turn down and off gate bias voltage (Vg).
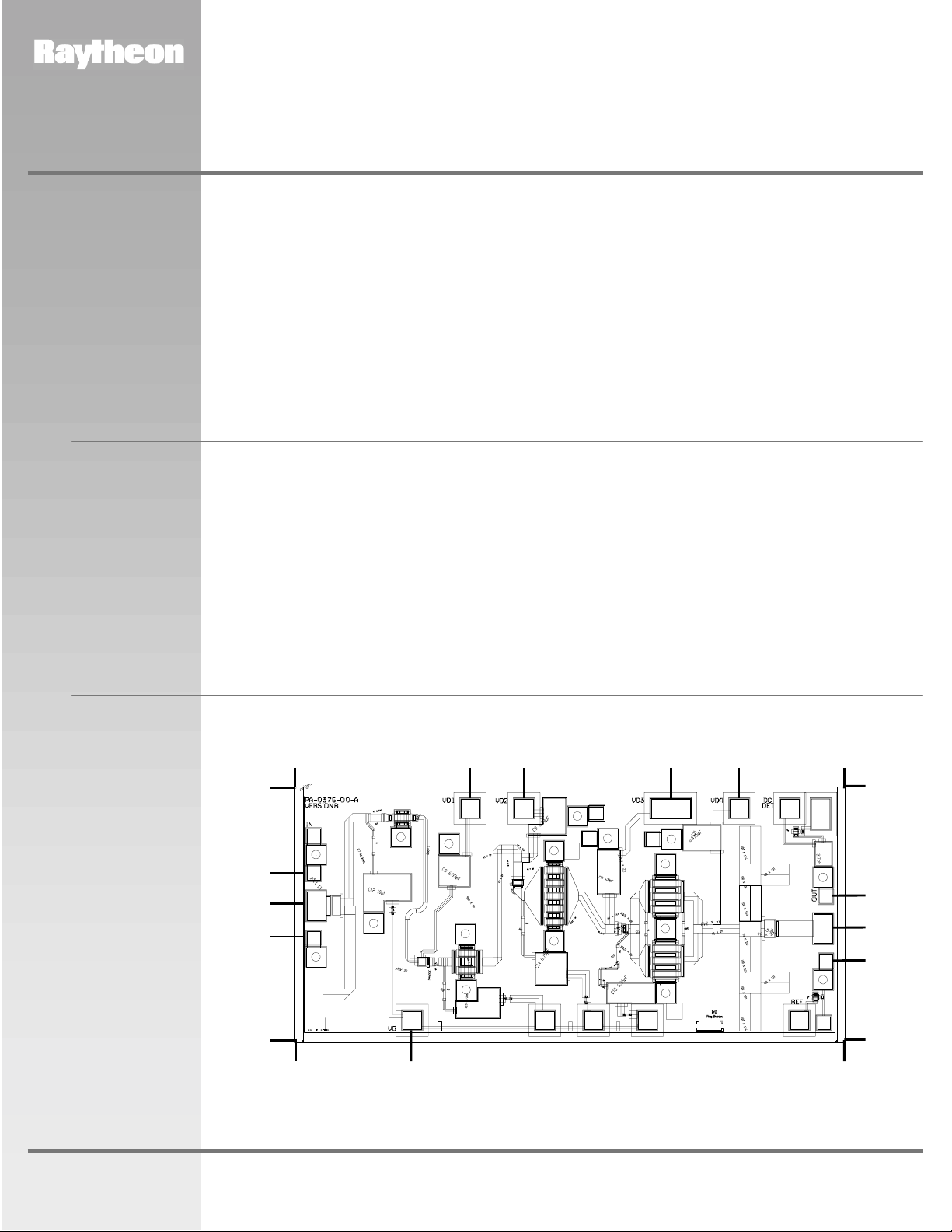
Chip Layout and
Bond Pad
Locations
Chip Layout and Bond
Pad Locations
Chip Size is 2.6 mm x
1.2 mm x 100
Back of chip is RF and
µm.
DC ground
Dimensions in mm
0.0
1.2
0.791
0.637
0.482
0.0
0.0
Characteristic performance data and specifications are subject to change without notice.
0.55
0.82 1.072 1.756 2.076
2.6
1.2
0.685
0.53
0.376
0.0
2.6
www.raytheon.com/micro
Revised March 14, 2001
Page 2
Raytheon RF Components
362 Lowell Street
Andover, MA 01810
RMWP23001
21-24 GHz Power Amplifier MMIC
PRODUCT INFORMATION
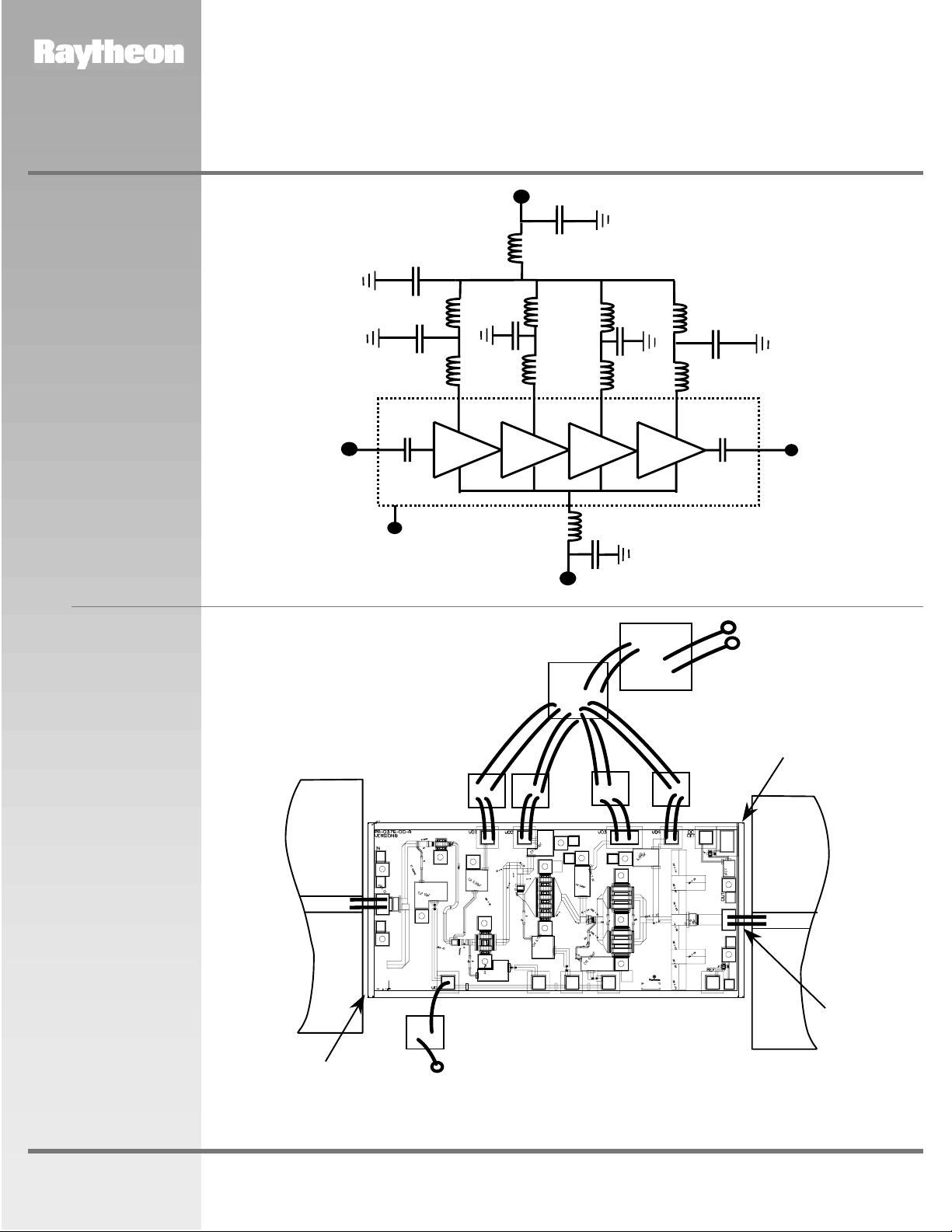
Recommended
Application
Schematic Circuit
Diagram
Recommended
Assembly
Diagram
10,000pF
RF IN
Ground
(Back of Chip)
100pF
MMIC Chip
Drain Supply
Vd = +4 V
L
100pF
L
Gate Supply
L
L
L
10,000pF
Vg
1 µF
L
L
100pF
100pF
L
L = Bond Wire
Inductance
L
100pF
L
RF OUT
Vd
(Positive)
1µF
www.raytheon.com/micro
Die-Attach
80Au/20Sn
100pF
5mil Thick
Alumina
50-Ohm
RF
Input
100pF
2 mil Gap
Note: Use 0.003” by 0.0005” Gold Ribbon for bonding. RF input and output bonds should be less than 0.015” long with stress relief.
Characteristic performance data and specifications are subject to change without notice.
Revised March 14, 2001
Page 3
Vg
(Negative)
100pF
100pF
100pF
5 mil Thick
Alumina
50-Ohm
RF
Output
L< 0.015”
(4 Places)
Raytheon RF Components
362 Lowell Street
Andover, MA 01810
 Loading...
Loading...