Page 1

KX II-101
User Guide
2.0.20
Copyright © 2008 Raritan, Inc.
KX2101-v2.20-0B-E
July 2008
255-62-4031-00
Page 2
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. All rights reserved. No
part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated into another language without
express prior written consent of Raritan, Inc.
© Copyright 2008 Raritan, Inc., CommandCenter®, Dominion®, Paragon® and the Raritan company
logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Raritan, Inc. All rights reserved. Java® is a
registered trademark of Sun Microsystems, Inc. Internet Explorer® is a registered trademark of
Microsoft Corporation. Netscape® and Netscape Navigator® are registered trademarks of Netscape
Communication Corporation. All other trademarks or registered tradema rks a re the prope rty of their
respective holders.
FCC Information
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a commercial installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential
environment may cause harmful interference.
VCCI Information (Japan)
Raritan is not responsible for damage to this product resulting from accident, disaster, misuse, abuse,
non-Raritan modification of the product, or other events outside of Raritan's rea son able control or not
arising under normal operating conditions.
C
U
L
US
1F61
I.T.E.
LISTED
Page 3
Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction 1
What's New in the User Guide.......................................................................................................1
KX II-101 Overview........................................................................................................................2
Product Photos ..............................................................................................................................4
Product Features ...........................................................................................................................5
Interfaces.............................................................................................................................5
Network Configuration.........................................................................................................5
System Management Features ...........................................................................................5
Administration Features.......................................................................................................5
User Features......................................................................................................................6
Power...................................................................................................................................6
Video Resolution .................................................................................................................6
Mounting..............................................................................................................................6
Terminology...................................................................................................................................6
Package Contents..........................................................................................................................7
Optional Accessories.....................................................................................................................7
User Guide.....................................................................................................................................7
Related Documentation.......................................................................................................8
Chapter 2 Installation and Configuration 9
Overview........................................................................................................................................9
Default Logon Information .............................................................................................................9
Getting Started.............................................................................................................................10
Step 1: Configure the Target Server..................................................................................10
Step 2: Configure Network Firewall Settings.....................................................................16
Step 3: Connect the KX II-101...........................................................................................17
Step 4: Configure the KX II-101.........................................................................................24
Chapter 3 Working with Target Servers 32
Interfaces.....................................................................................................................................32
KX II-101 Remote Console Interface.................................................................................32
Multi-Platform Client Interface...........................................................................................41
Virtual KVM Client........................................................................................................................41
Overview............................................................................................................................41
Connecting to a KVM Target Server .................................................................................41
VKC Toolbar......................................................................................................................42
Power Controlling a KVM Target Server...........................................................................42
Disconnecting a KVM Target Server.................................................................................43
VKC Connection Properties...............................................................................................43
Connection Information .....................................................................................................45
iii
Page 4

Contents
Keyboard Options..............................................................................................................46
Video Properties................................................................................................................49
Mouse Options...................................................................................................................52
VKC Virtual Media.............................................................................................................56
Tool Options ......................................................................................................................57
View Options......................................................................................................................59
Help Options......................................................................................................................59
Multi-Platform Client (MPC).........................................................................................................60
Requirements and Installation...........................................................................................60
Operation...........................................................................................................................60
Administrative Functions ...................................................................................................99
Chapter 4: Virtual Media 106
Overview....................................................................................................................................107
Prerequisites for Using Virtual Media........................................................................................110
File Server Setup (File Server ISO Images Only)......................................................................111
Connecting to Virtual Media.......................................................................................................113
Local Drives.....................................................................................................................113
Conditions when Read/Write is Not Available.................................................................114
CD-ROM/DVD-ROM/ISO Images....................................................................................114
Disconnecting Virtual Media......................................................................................................115
Chapter 5 User Management 116
User Groups...............................................................................................................................116
User Group List................................................................................................................117
Relationship Between Users and Groups .......................................................................117
Adding a New User Group...............................................................................................118
Modifying an Existing User Group...................................................................................123
Users..........................................................................................................................................123
User List...........................................................................................................................124
Adding a New User..........................................................................................................124
Modifying an Existing User..............................................................................................125
Blocking and Unblocking Users.......................................................................................125
Authentication Settings..............................................................................................................126
Implementing LDAP/LDAPS Remote Authentication......................................................127
Returning User Group Information from Active Directory Server....................................129
Implementing RADIUS Remote Authentication...............................................................130
Returning User Group Information via RADIUS..............................................................133
RADIUS Communication Exchange Specifications.........................................................133
User Authentication Process...........................................................................................135
Changing a Password................................................................................................................137
Chapter 6 Device Management 138
Network Settings........................................................................................................................138
Network Basic Settings....................................................................................................139
LAN Interface Settings.....................................................................................................140
iv
Page 5

Contents
Device Services.........................................................................................................................141
Keyboard/Mouse Setup .............................................................................................................143
Serial Port Settings....................................................................................................................144
Admin Port.......................................................................................................................144
Raritan Power Strip Control.............................................................................................145
Modem.............................................................................................................................146
Date/Time Settings ....................................................................................................................148
Event Management....................................................................................................................149
Configuring Event Management - Settings......................................................................150
Event Management - Destinations ..................................................................................151
Port Configuration......................................................................................................................154
Managing KVM Target Servers (Port Page)....................................................................155
Power Control..................................................................................................................157
v
Page 6

Contents
Analog KVM Switch ...................................................................................................................162
Resetting the KX II-101 Using the Reset Button .......................................................................163
Chapter 7 Managing USB Connections 165
Overview....................................................................................................................................166
Basic USB Connection Settings ................................................................................................166
Advanced USB Connection Settings.........................................................................................168
Known USB Profiles...................................................................................................................169
Chapter 8 Security Management 184
Security Settings........................................................................................................................184
Logon Limitations.......................................................................................................................185
Strong Passwords......................................................................................................................186
User Blocking.............................................................................................................................188
Encryption & Share....................................................................................................................190
Checking Your Browser for AES Encryption .............................................................................192
IP Access Control ......................................................................................................................193
Chapter 9 Maintenance 195
Audit Log....................................................................................................................................195
Device Information.....................................................................................................................196
Backup and Restore ..................................................................................................................197
Upgrading Firmware ..................................................................................................................198
Upgrade History.........................................................................................................................200
Rebooting...................................................................................................................................201
Chapter 10 Diagnostics 202
Network Interface Page .............................................................................................................202
Network Statistics Page.............................................................................................................203
Ping Host Page..........................................................................................................................206
Trace Route to Host Page .........................................................................................................206
Device Diagnostics ....................................................................................................................208
Chapter 11 Command Line Interface (CLI) 210
Overview....................................................................................................................................210
Accessing the KX II-101 Using the CLI......................................................................................211
SSH Connection to the KX II-101..............................................................................................211
SSH Access from a Windows PC....................................................................................211
SSH Access from a UNIX/Linux Workstation..................................................................212
Logging On ................................................................................................................................212
Navigation of the CLI .................................................................................................................212
CLI Prompts.....................................................................................................................213
Completion of Commands...............................................................................................213
vi
Page 7
Contents
CLI Syntax -Tips and Shortcuts.......................................................................................214
Common Commands for All Command Line Interface Levels........................................214
CLI Commands..........................................................................................................................214
Diagnostics......................................................................................................................215
Configuration ...................................................................................................................216
Listports Command .........................................................................................................218
Userlist Command...........................................................................................................218
Chapter 12 CC Unmanage 219
Overview....................................................................................................................................219
Removing a KX II-101 from CC-SG Management.....................................................................220
Using CC-SG in Proxy Mode.....................................................................................................221
Appendix A Specifications 222
KX II-101 Specifications.............................................................................................................222
Supported Video Resolutions....................................................................................................223
Supported Keyboard Languages...............................................................................................224
Supported Operating Systems (Clients)....................................................................................225
Supported Browsers ..................................................................................................................225
Certified Modems.......................................................................................................................226
Connectors.................................................................................................................................226
TCP and UDP Ports Used.........................................................................................................226
Network Speed Settings ............................................................................................................228
Admin Port Pinout Information...................................................................................................229
9 Pin Pinout................................................................................................................................230
Appendix B Updating the LDAP Schema 231
Returning User Group Information.............................................................................................231
From LDAP......................................................................................................................231
From Microsoft Active Directory ......................................................................................231
Setting the Registry to Permit Write Operations to the Schema ...............................................232
Creating a New Attribute............................................................................................................232
Adding Attributes to the Class ...................................................................................................233
Updating the Schema Cache.....................................................................................................235
Editing rciusergroup Attributes for User Members.....................................................................235
Appendix C AC-DC Adapter and Rack Mount 239
AC-DC Adapter Clip Fitting........................................................................................................239
Identify the Clip Type.......................................................................................................239
Remove the Attachment Cover from AC-DC Power Adapter..........................................240
Attach the Clip to AC-DC Power Adapter........................................................................241
Bracket Installation.....................................................................................................................241
KX II-101 Bracket Parts...................................................................................................243
Attach the Brackets to KX II-101 for Horizontal Mount....................................................243
vii
Page 8

Contents
Attach the Brackets to KX II-101 for Vertical Mount........................................................244
Appendix D Informational Notes 246
Java Runtime Environment (JRE) .............................................................................................246
Keyboard, Video and Mouse Notes...........................................................................................246
Sun Blade™ Video, Keyboard, and Mouse Support Limitation.......................................246
Sun Keyboard Key Support Limitations...........................................................................247
BIOS Access Limitation from a Local Keyboard..............................................................247
HP UX RX 1600 Keyboard and Mouse Configuration.....................................................248
Compaq Alpha and IBM P Server Mouse Mode Limitation.............................................248
Windows 2000 and 2003 Server Keyboard Limitations...................................................249
Index 251
viii
Page 9

Chapter 1
Introduction
In This Chapter
What's New in the User Guide ..................................................................1
KX II-101 Overview....................................................................................2
Product Photos..........................................................................................4
Product Features.......................................................................................5
Terminology...............................................................................................6
Package Contents.....................................................................................7
Optional Accessories
User Guide
................................................................................................7
What's New in the User Guide
The following sections of the user guide have changed or information
has been added to based on enhancements and changes to the
equipment and/or user documentation.
• Managing USB Connections (formerly managing target server
settings). See Managing USB Connections (on page 165).
• Analog KVM Switch
page 162).
• Pinout and
to the user guide. See Specifications (on page 222).
.................................................................................7
config
uration. See Analog KVM Switch (on
su
pported operating system information has been added
Please se
changes applied to this version of the user guide.
e the rele
ase notes for a more detailed explanation of the
1
Page 10

Chapter 1: Introduction
KX II-101 Overview
Thank you for purchasing the Dominion the KX II-101. The KX II-101
provides a single keyboard, video, and mouse (KVM) port for connection
to a target server and a single IP port for connection to an IP network.
Within the KX II-101 device, KVM signals from your server are converted
to IP format and compressed for transmission over an IP network.
The KX II-101 dongle form-factor makes it easy to install near the target
server, and each individual KX II-101 device has its own IP
address. Each device is powered via Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) or an
external AC-DC power pack.
The KX II-101 can operate as a standalone appliance or integrated into a
single logical solution, along with other Raritan access products, using
Raritan's CommandCenter Secure Gateway (CC-SG) manage ment unit.
2
Page 11
Chapter 1: Introduction
Diagram key
KX II-101
LAN
Windows, Linux, and Sun servers
TCP/IP
LAN
Remote (network) access
3
Page 12
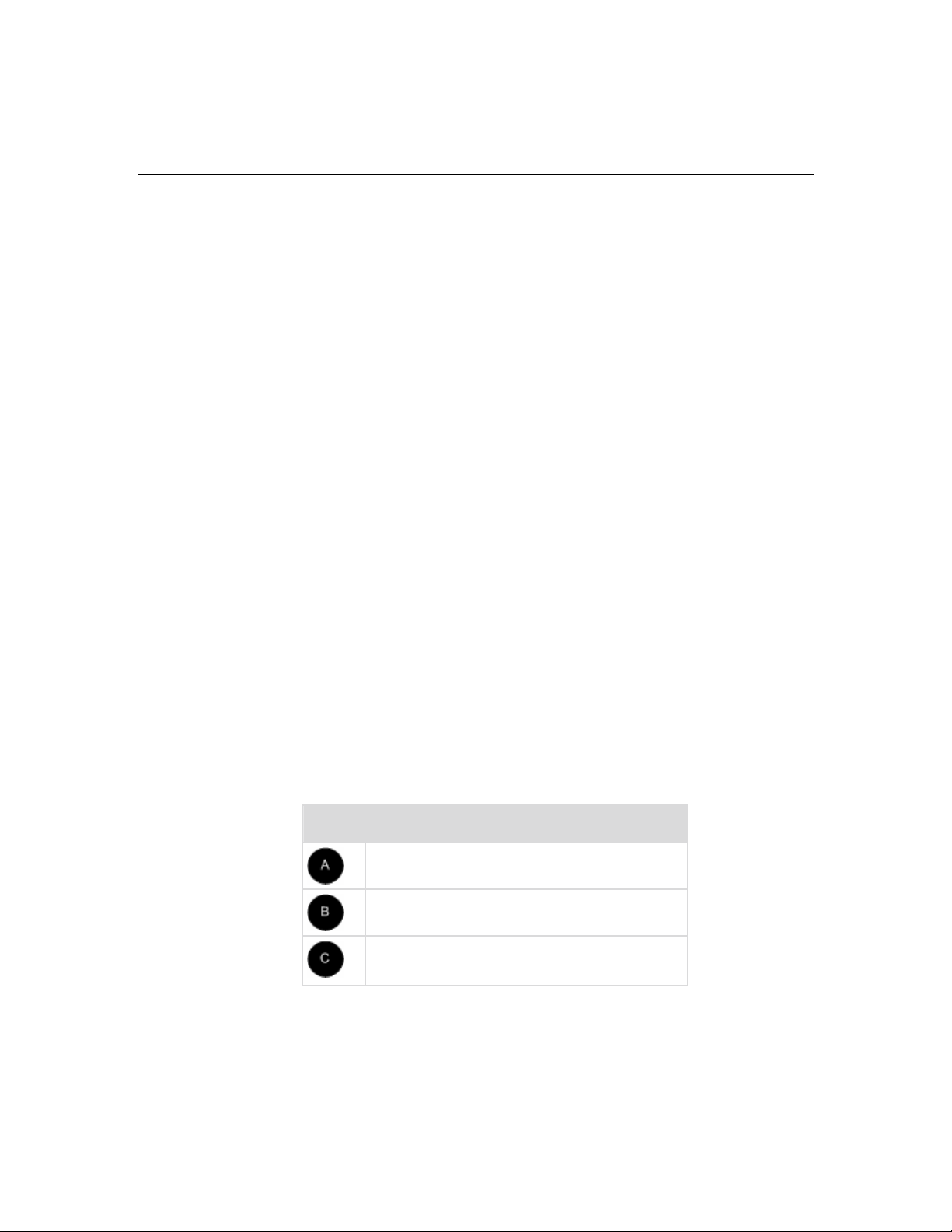
Chapter 1: Introduction
Product Photos
Diagram key
KX II-101
Mini-USB to USB cable
Optional local port cable
4
Page 13

Chapter 1: Introduction
Product Features
Interfaces
• Integrated PS/2 KVM connection
• USB connection for control and virtual media
• Serial Admin port for initial device configuration and diagnostics, as
well as use with an external modem access and Raritan power strip
control
• Ethernet LAN port supporting 10/100-base-T autosensing, full duplex
• LED network activity indicator and status
• Backlit LED power ON indicator
Network Configuration
• DHCP or static IP device address
System Management Features
• Firmware upgradable over Ethernet
• Failsafe firmware upgrade capability
• Clock that can be set manually or via synchronization with Network
Time Protocol (NTP/SNTP)
• Local, timestamped, administrator activity log SNMP V2 agent that
can be disabled by the administrator
• Support for RADIUS and LDAP/LDAPS authentication protocols
Administration Features
• Web-based management
• LDAP, Active Directory, RADIUS, or internal authentication and
authorization
• DHCP or fixed IP addressing
• Integration with Raritan's CommandCenter Secure Gateway (CC-
SG) management unit
5
Page 14

Chapter 1: Introduction
User Features
• Web-based access through common browsers
• Intuitive graphical user interface (GUI)
• PC Share mode, which enables more than one remote user
• TCP communication
• English user interface
• Virtual media access
™
• Absolute Mouse Synchronization
• Plug-and-play
• 256-bit encryption of complete KVM signal, including video and
virtual media
Power
• Powered via Class 2 Power over Ethernet (PoE) provision
• Alternately powered by an external AC/DC power pack
Video Resolution
• Up to 1600X1200 at up to 60 Hz resolution
Mounting
• Rack mounting bracket
See AC-DC Adapter and Rack Mount (on page 239).
Terminology
Term Description
Target Server Server to be accessed remotely via the KX II-101
and its connected KVM configuration.
Remote PC A Windows, Linux, or Apple Macintosh® computer
used to access and control target servers
connected to the KX II-101.
Admin serial
port
Use the Admin serial port to connect to the serial
port on the PC using the included Mini-DIN to DB9
cable. Then use a standard emulation software
package (for example, HyperTerminal) to access
the Admin serial port. The Admin serial port is used
for network configuration.
6
Page 15

Chapter 1: Introduction
Term Description
Local User port Enables a user in immediate proximity to the target
server to use the native keyboard and mouse
without unplugging the KX II-101.
Virtual media Enables a KVM target server to remotely access
media from client PC and network file servers.
Package Contents
Each KX II-101 device ships with:
• KX II-101 - KVM over IP
• USB Type A to Type B miniconnector
• Power Adaptor Kit - AC-DC 6VDC
• Three additional power outlet plugs for worldwide use
• Mini-DIN to DB9 serial cable
• Mounting bracket kit
• CD containing the Raritan User Guide & Quick Setup Guide
• Printed Quick Setup Guide
• Printed application release notes (if applicable)
• Printed technical notes (if applicable)
Optional Accessories
• DB15 to PS/2 and VGA Local User Cable
See Connectors (on page 226).
User Guide
The KX II-101 User Guide provides information on how to install, set up,
and configure the KX II-101. It also includes information on accessing
target servers and power strips, using virtual media, managing users and
security, and maintaining and diagnosing the KX II-101.
7
Page 16

Chapter 1: Introduction
Related Documentation
The KX II-101 User Guide is accompanied by a KX II-101 Quick Setup
Guide, which can be found on the CD included with the device or on the
Support page of Raritan's website (www.raritan.com). Installation
requirements and instructions for client applications used with the KX II101 can be found in the KVM and Serial Client User Guide, also found
on the Raritan website. Where applicable, specific client functions used
with the KX II-101 are included in this user guide.
8
Page 17

Chapter 2
Overview
Installation and Configuration
In This Chapter
Overview....................................................................................................9
Default Logon Information.........................................................................9
Getting Started ........................................................................................10
This chapter describes how to install and configure the KX II-101.
Installation and configuration consists of the following steps:
• Step 1: Configure the Target Server (on page 10)
• Step 2: Con
• Step 3: Con
• Step 4: Con
figure Network Firewall Settings (on page 16)
nect the KX II-101 (on page 17)
figure the KX II-101 (on page 24)
Before installi
first configure the target server you want to access via the KX II-101.
Note that the following configuration requirements apply only to the
target server, not to the computers that you will be using to access the
KX II-101 remotely.
ng the KX II-101, in order to ensure optimum performance,
Default Logon Information
Default Value
User name The default user name is admin. This user has
administrative privileges.
Password The default password is raritan.
Passwords are case sensitive and must be entered
in the exact case combination in which they were
created. For example, the default password raritan
must be entered entirely in lowercase letters.
The first time you start the KX II-101, you are
required to change the default password.
IP address The KX II-101 ships with the default IP address of
192.168.0.192.
Important: For backup and business continuity purposes, it is
strongly recommended that you create a backup administrator
user name and password and keep that information in a secure
location.
9
Page 18

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Getting Started
KX II-101 users with Microsoft Internet Explorer version 6 or Windows
2000 must upgrade to Service Pack 4 (SP4) or higher.
The KX II-101 ships with a static default IP address. On a network
without a DHCP server, you must configure a new static IP address, net
mask, and gateway address using either the KX II-101 serial admin
console or the KX II-101 Remote Console.
See Assigning an IP Address (on page 25) for information on assigning
an IP addre
Configure the KX II-101 Using a Terminal Emulation Program
(Optional) (on page 29) for information on setting an IP address using
the Serial Ad
Step 1: Configure the Target Server
Before installing the KX II-101, first configure the target server you want
to access via the KX II-101 in order to ensure optimum performance.
Note that the following configuration requirements apply only to the
target server, not to the computers that you will be using to access the
KX II-101 remotely.
s
s to the KX II-101 using the Remote Console. See
min Co
nsole.
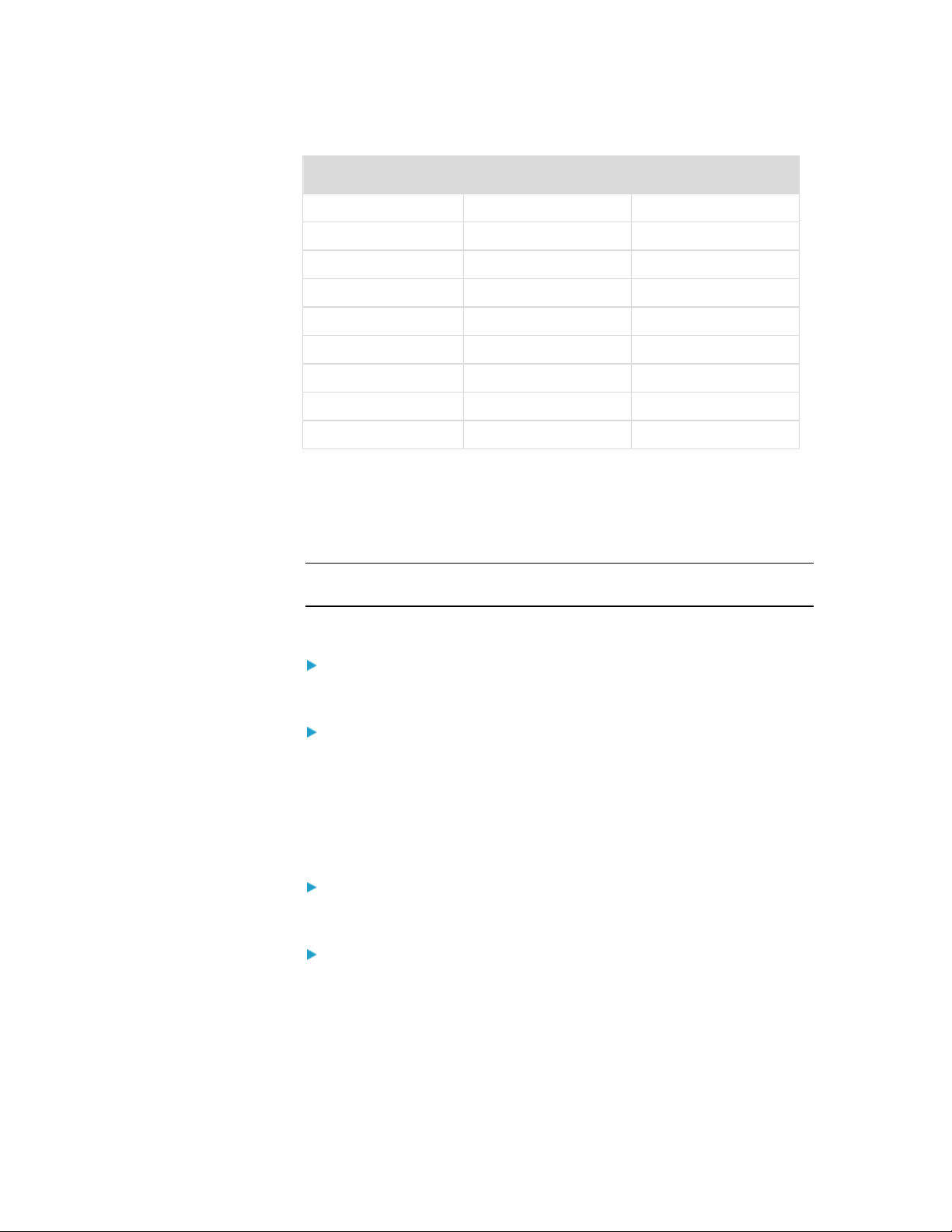
Setting the Server Video Resolution
For optimal bandwidth efficiency and video performance, a target server
running a graphical user interface such as Windows, X-Windows,
Solaris, and KDE should be configured with desktop backgrounds set to
a predominantly solid, light-colored graphic. Backgrounds featuring
photos or complex gradients should be avoided.
Ensure that the server's video resolution and refresh rate are supported
by the KX II-101 and that the signal is non-interlaced. The KX II-101
supports the following video resolutions:
Resolutions
640x350 @70 Hz 720x400 @85 Hz 1024x768 @90 Hz
640x350 @85 Hz 800x600 @56 Hz 1024x768 @100 Hz
640x400 @56 Hz 800x600 @60 Hz 1152x864 @60 Hz
640x400 @84 Hz 800x600 @70 Hz 1152x864 @70 Hz
640x400 @85 Hz 800x600 @72 Hz 1152x864 @75 Hz
640x480 @60 Hz 800x600 @75 Hz 1152x864 @85 Hz
10
Page 19
Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Resolutions
640x480 @66.6 Hz 800x600 @85 Hz 1152x870 @75.1 Hz
640x480 @72 Hz 800x600 @90 Hz 1152x900 @66 Hz
640x480 @75 Hz 800x600 @100 Hz 1152x900 @76 Hz
640x480 @85 Hz 832x624 @75.1 Hz 1280x960 @60 Hz
640x480 @90 Hz 1024x768 @60 Hz 1280x960 @85 Hz
640x480 @100 Hz 1024x768 @70 Hz 1280x1024 @60 Hz
640x480 @120 Hz 1024x768 @72 Hz 1280x1024 @75 Hz
720x400 @70 Hz 1024x768 @75 Hz 1280x1024 @85 Hz
720x400 @84 Hz 1024x768 @85 Hz 1600x1200 @60 Hz
Sun™ Video Resolution
Sun systems have two resolution settings, a command line resolution
and a GUI resolution. For information about the resolutions supported by
the KX II-101, see Setting the Server Video Resolution (on page 10).
ort
Note: If none of the supp
ed resolutions work, make sure the monitor is
multisync. Some monitors will not work with an H&V sync.
Command Line Resolution
To check the command line resolution:
1. Run the following command as the root: # eeprom output-device
To change the command line resolution:
1. Run the following command: # eeprom output-
device=screen:r1024x768x75 where 1024x768x75 is any resolution
that the KX II-101 supports.
2. Restart the computer.
GUI Resolution/32 Bit
To check the GUI resolution on 32 bit cards:
1. Run the following command: # /usr/sbin/pgxconfig –prconf
To change the GUI resolution on 32 bit cards:
1. Run the following command: # /usr/sbin/pgxconfig –
res1024x768x75 where 1024x768x75 is any resolution that the KX II101 supports.
2. Restart the computer.
11
Page 20

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
GUI Resolution/64 Bit
To check the GUI resolution on 64 bit cards:
1. Run the following command: # /usr/sbin/m64config –prconf
To change the resolution on 64 bit cards:
1. Run the following command: # /usr/sbin/m64config –
res1024x768x75 where 1024x768x75 is any resolution that the KX II101 supports.
2. Restart the computer.
GUI Resolution/Solaris 8
To check the resolution on Solaris 8 for 32 bit and 64 bit cards:
1. Run the following command: # /usr/sbin/fbconfig –prconf
To change the resolution on Solaris 8 for 32 and 64 bit cards:
1. Run the following command: # /usr/sbin/fbconfig –res1024x768x75
where 1024x768x75 is any resolution that the KX II-101 supports.
2. Restart the computer.
Mouse Modes
The KX II-101 operates in several mouse modes: Absolute Mouse
Synchronization™, Intelligent Mouse mode (do not use an animated
mouse), and Standard Mouse mode.
Mouse parameters do not have to be altered for Absolute Mouse
Synchronization. For both the Standard and Intelligent Mouse modes,
mouse parameters must be set to specific values, which are described in
this section.
Mouse configurations will vary on different target operating systems.
Consult your OS documentation for additional details.
Windows 2000® Settings
To configure the mouse:
1. Choose Start > Control Panel > Mouse.
2. On the Motion tab, set the acceleration to None and set the mouse
motion speed setting to exactly the middle speed. Click OK.
To disable transition effects:
1. Select the Display option from Control Panel.
2. On the Effects tab, deselect the Use the following transition effect for
menus and tooltips checkbox. Click OK.
12
Page 21

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Windows XP®/Windows 2003® Settings
To configure the mouse:
1. Select Start > Control Panel > Mouse.
2. On the Pointer Options tab in the Motion group, set the mouse
motion speed setting to exactly the middle speed and deselect the
Enhanced pointer precision checkbox. Click OK.
To disable transition effects:
1. Select Start > Control Panel > Display.
2. On the Appearance tab, click the Effects button.
3. Deselect the Use the following transition effect for menus and
tooltips checkbox. Click OK.
Windows 2000 and XP Setting Notes
For a target server running Windows 2000 or XP, you may want to create
a username to be used only for remote connections through the KX II-
101. This allows you to keep the Target Server's slow mouse pointer
motion/acceleration settings exclusive to the KX II-101 connection only,
as other users may desire faster mouse speeds.
Windows 2000 or XP login screens revert to preset mouse parameters
that differ from those suggested for optimal KX II-101 performance.
Therefore, mouse sync will not be optimal at these screens. If you are
comfortable adjusting the registry on Windows target servers, you can
obtain better KX II-101 mouse synchronization at login screens by using
the Windows registry editor to change the following settings:
• Default user mouse motion speed = 0; mouse threshold 1= 0; mouse
threshold 2 = 0.
Windows Vista® Settings
To configure the mouse:
1. Select Start > Settings > Control Panel > Mouse.
2. On the Pointer Options tab in the Motion group, set the mouse
motion speed setting to exactly the middle speed and deselect the
Enhanced pointer precision option. Click OK.
To disable animation and fade effects:
1. Select Start > Settings >Control Panel > System > Advanced system
settings. The System Properties dialog appears.
2. Click the Advanced tab and click the Settings button in the
Performance group. The Performance Options dialog appears.
3. Under Custom options, deselect the following checkboxes:
13
Page 22

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Animate controls and elements inside windows
Animate windows when minimizing and maximizing
Fade or slide menus into view
Fade or slide ToolTips into view
Fade out menu items after clicking
4. Click OK.
Linux® Settings
On a target server running Linux graphical interfaces, set the mouse
acceleration to exactly 1 and set threshold to exactly 1. Enter the
command xset mouse 1 1.
Ensure that a target server running Linux is using a resolution supported
by the KX II-101 at a standard VESA resolution and refresh rate. A Linux
target server should also be set so the blanking times are within +/- 40%
of VESA standard values.
To check for these parameters:
1. Go to the Xfree86 Configuration file XF86Config.
2. Using a text editor, disable all non-KX II-101 supported resolutions.
3. Disable the virtual desktop feature, which is not supported by the KX
II-101.
4. Check blanking times (+/- 40% of VESA standard).
5. Restart the computer.
Note: In many Linux graphical environments, the command Ctrl+Alt+ +
(plus sign) changes the video resolution, scrolling through all available
resolutions that remain enabled in the XF86Config file.
Sun® Solaris™ Settings
A Solaris target server must be configured to one of the display
resolutions supported by the KX II-101. The most popular supported
resolutions for Sun machines are:
Resolution
1024x768@60Hz
1024x768@70Hz
1024x768@75Hz
1024x768@85Hz
1280x1024@60Hz
14
Page 23

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Set the mouse acceleration value to exactly 1 and the threshold to
exactly 1. A target server running the Solaris operating system must
output VGA video (H-and-V sync, not composite sync). Set this at the
graphical user interface or with the command line xset mouse a t where
a is the acceleration and t is the threshold.
To change your Sun video card output from composite sync to
the non-default VGA output:
1. Issue the Stop+A command to drop to bootprom mode.
2. Issue the #eeprom output-device=screen:r1024x768x75 command to
change the output resolution.
3. Issue the boot command to reboot the server.
Alternatively, contact your Raritan representative to purchase a video
output adapter. Suns with composite sync output require APSSUN II
Raritan guardian for use with the KX II-101. HD15 Suns with separate
sync output require an APKMSUN Raritan guardian for use with the KX
II-101.
Apple Macintosh® Settings
Mac works with the KX II-101 'out of the box.' However, you must use
Absolute Mouse Synchronization and enable Absolute Mouse mode and
mouse scaling for Mac servers on the KX II-101 Port page.
To enable this setting:
1. Choose Device Settings > Port Configuration. The Port Configuration
Page opens.
2. Click the Port Name for the port you want to edit.
3. In the USB Connection Settings section, select the Enable Absolute
Mouse checkbox and the "Enable Absolute mouse scaling for MAC
server" checkbox. Click OK.
See Port Configuration (on page 154).
IBM AIX® Settings
1. Go to the Style Manager.
15
Page 24

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
2. Click on Mouse Settings and set the Mouse Acceleration to 1.0 and
Threshold to 3.0.
Step 2: Configure Network Firewall Settings
To access the KX II-101 through a network firewall, your firewall must
allow communication on TCP Port 5000. Alternatively, the KX II-101 can
be configured to use a different TCP port of your own designation.
To take advantage of the KX II-101's web-access capabilities, the firewall
must allow inbound communication on TCP Port 443 - the standard TCP
port for HTTPS communication. To take advantage of the KX II-101's
redirection of HTTP requests to HTTPS (so that users may type the more
common, http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, instead of https://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx), the
firewall must also allow inbound communication on TCP Port 80 - the
standard TCP port for HTTP communication.
16
Page 25

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Step 3: Connect the KX II-101
The KX II-101 has the physical connections described in the diagram.
17
Page 26

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Diagram key
Admin port Use to do one of the following:
• Configure and manage the device with a
terminal emulation program on your PC.
• Configure and manage a power strip.
• Connect an external modem to dial into the
device.
Monitor and
PS/2 cable
Mini-USB
port
Power
indicator
Monitor and
PS/2 cable
Power
connector
Local user
port
Ethernet
LAN/PoE
port
Attached Monitor and PS/2 cable (see E).
Use to connect the device to the target server
with the included USB cable if not using the
attached PS/2 cable. A USB connection must
be used to utilize the Absolute Mouse
Synchronization or virtual media features.
Backlit LED power ON and boot-up indicator.
Provides feedback on the operating status of
the device.
Attached Monitor and PS/2 cable. Use to
connect the device to a monitor and to a target
server if not using the USB cable.
Connects the power supply if you are not using
a PoE (Power over Ethernet) LAN connection.
Use to connect a local keyboard, video, and
mouse directly to the target server using an
optional PS/2 cable.
Provides LAN connectivity and power if using a
PoE LAN connection.
18
Power
The KX II-101 can be powered with either the included standard AC
power pack or by PoE (Power over Ethernet).
• For standard AC power, plug the included AC power adaptor kit into
the Power port and plug the other end into a nearby AC power outlet.
• For PoE, attach a 10/100Mbps cable to the LAN port and plug the
other end into a PoE-provisioned LAN.
After the KX II-101 is powered ON, it goes through a boot-up sequence,
during which the blue Raritan-logo LED will blink for about 45
seconds. Upon successful boot-up, the back-lit LED remains lit.
Page 27

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Target Server
The KX II-101 can use either the included USB cable or integrated PS/2
cables to connect to the target server. Before connecting, configure your
target server's video to a supported resolution.
Note: For PS/2 configurations that require virtual media connectivity, the
USB connector is also necessary.
USB Configuration
To configure the KX II-101 for use with a USB target server:
1. Connect the mini-USB connector to the KX II-101 and the USB
connector to a USB port on the target server.
2. Use the attached video cable to connect the KX II-101 to the target
video port.
3. Use the optional PS/2 DKX2-101-LPKVMC cabling to attach only the
local video to the Local User port of the KX II-101. Optional
Note: The KX II-101 must be powered for the Local User port to
function.
19
Page 28

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Use USB cables to connect the keyboard and mouse directly to the
target server.
20
Diagram key
Target server
Included mini-USB to USB cable from the KX II-101 to the
target server
KX II-101
Local monitor, keyboard, and mouse
USB connection from the target server to mouse
Page 29

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Diagram key
USB connection from the target server to keyboard
Video connection to the local monitor (optional cable)
PS/2 Configuration
To configure the KX II-101 for use with a PS/2 target server:
1. Use the attached PS/2 keyboard, video, and mouse cabling to
connect the KX II-101 to the target server.
2. Use the PS/2 cabling to attach the local keyboard, video, and mouse
to the Local User port of the KX II-101.
Note: The KX II-101 must be powered for the Local User port to
function.
21
Page 30

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
3. If you require Virtual Media (VM) connectivity, connect the mini-USB
connector to the KX II-101 and the USB connector to any USB port
on the target server.
22
Diagram key
Target server
Included mini-USB to USB connector from the KX II-101 to
the target server for Virtual Media connectivity
KX II-101
Local monitor, keyboard, and mouse
Integrated PS/2 keyboard, video, and mouse connections
from the KX II-101 to the target server
Page 31

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Diagram key
PS/2 connection from the KX II-101 to the mouse (optional
cable)
PS/2 connection from the KX II-101 to the keyboard
(optional cable)
Video connection to the local monitor (optional cable)
Network
Connect a standard Ethernet cable from the network port labeled LAN to
an Ethernet switch, hub, or router. The LAN LEDs that appear above the
Ethernet connection indicate Ethernet activity. The yellow one blinks
while the KX II-101 is in use, indicating IP traffic at 10 Mbps. The green
light indicates a 100 Mbps connection speed.
Admin Port
The Admin port enables you to perform configuration and setup for the
KX II-101 using a terminal emulation program like HyperTerminal. Plug
the min-DIN end of the included serial cable into the Admin port of the
KX II-101 and plug the DB9 end into a serial port on your PC or laptop.
The serial port communication settings should be configured to the
following:
• 115,200 Baud
• 8 data bits
• 1 stop bit
• No parity
• No flow control
See Configure the KX II-101 Using a Terminal Emulation Program
(Optional) (on page 29) for additional information on using a terminal
n pro
emulatio
gram.
23
Page 32

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Local User Port
The KX II-101 is available with optional video and PS/2 cables (KX II101-LPKVMC) that enable you to attach a keyboard and mouse to the
target server through the Local User port. The Local User port serves as
a pass-through to the target server to which the KX II-101 is attached
and has no other purpose. The KX II-101 must be powered on to use the
Local User port.
For USB configurations, only the local video connects to the target server
at the Local User port. The keyboard and mouse connect directly to the
target server using USB ports.
Note: Only PS/2 host interface connectivity is supported on the Local
User port and you must restart the target server after connecting to the
KX II-101 using PS/2 connectors.
Step 4: Configure the KX II-101
The KX II-101 can be configured in two ways:
• Using the web-based KX II-101 Remote Console, which requires the
device to have a network connection to your workstation.
• Using a terminal emulation program like HyperTerminal, which
requires a direct connection from the device's Admin port to your
workstation. The cable for this connection is included with the KX II-
101.
This section describes both ways of configuring the KX II-101.
Configure the KX II-101 Using the Remote Console
The KX II-101 Remote Console is a web-based application that enables
you to configure the device prior to use and manage it after it has been
configured. Before configuring the KX II-101 using the Remote Console,
you must have both your workstation and the device connected to a
network.
You can also use a terminal emulation program to configure the KX II-
101. See Configure the KX II-101 Using a Terminal Emulation
Program (Optional) (on page 29).
Setting a New Password
When you first log into the Remote Console, you are prompted to set a
new password to replace the default. Then you can configure the KX II-
101.
1. Log into a workstation with network connectivity to your KX II-101
device.
24
Page 33

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
2. Launch a supported web browser such as Internet Explorer (IE) or
Firefox.
3. In the address field of the browser, enter the default IP address of
the device: 192.168.0.192.
4. Press Enter. The login page opens.
5. Enter the user name admin and the password raritan.
6. Click Login. The Change Password page is displayed.
7. Type raritan in the Old Password field.
8. Type a new password in the New Password field and the Confirm
New Password field. Passwords can be up to 64 characters long and
can consist of English alphanumeric and printable special
characters.
9. Click Apply. You will receive confirmation that the password was
successfully changed.
10. Click OK. The Port Access page opens.
Assigning an IP Address
1. In the KX II-101 Remote Console, choose Device Settings >
Network. The Network Settings page opens.
2. In the Device Name field, specify a meaningful name for your KX II101 device. You can enter up to 16 alphanumeric and special
characters with no spaces.
3. Select the IP configuration from the IP auto configuration drop-down
list:
None (Static IP) - This is the default and recommended option
because the KX II-101 is an infrastructure device and its IP
address should not change. This option requires that you
manually specify the network parameters.
25
Page 34

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
DHCP - With this option, network parameters are assigned by the
DHCP server each time the KX II-101 is booted.
26
Configuring Direct Port Access
To configure direct port access:
1. Choose Device Settings > Device Services. The Device Services
page opens.
2. Select the Enable Direct Port Access via URL checkbox.
3. Enable global TELNET or SSH access.
Select the Enable TELNET Access checkbox to enable TELNET
access.
Select the Enable SSH Access checkbox to enable SSH access.
Page 35

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
4. Specify a valid TCP port for the selected access type. For example,
direct port access via Telnet TCP port can be configured as 7770.
5. Click OK.
See Device Management (on page 138) for more information.
Naming the Target Server
1. Attach the KX II-101 to the target server.
2. Choose Device Settings > Port Configuration. The Port Configuration
page opens.
3. Click the Port Name for the target server. The Port page opens.
4. Type a name, up to 32 alphanumeric and special characters.
27
Page 36

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
5. Click OK.
28
Remote Authentication
Note to CC-SG Users
When the KX II-101 is controlled by CommandCenter Secure Gateway,
CC-SG authenticates users and groups.
For additional information about CC-SG authentication, see the
CommandCenter Secure Gateway User Guide, Administrator Guide,
or Deployment Guide, which can be downloaded from the Support
section of the Raritan website (www.raritan.com).
Supported Protocols
To simplify management of usernames and passwords, the KX II-101
provides the ability to forward authentication requests to an external
authentication server. Two external authentication protocols are
supported: LDAP/LDAPS and RADIUS.
Page 37

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
Note on Microsoft Active Directory
Microsoft Active Directory uses the LDAP/LDAPS protocol natively, and
can function as an LDAP/LDAPS server and authentication source for
the KX II-101. If it has the IAS (Internet Authorization Server) component,
a Microsoft Active Directory server can also serve as a RADIUS
authentication source.
Create User Groups and Users
As part of the initial configuration, you must define user groups and users
in order for users to access the KX II-101.
The KX II-101 uses system-supplied default user groups and allows you
to create groups and specify the appropriate permissions to suit your
needs.
User names and passwords are required to gain access to the KX II-101.
This information is used to authenticate users attempting to access your
KX II-101.
See User Management (on page 116) for details on adding and editing
groups and users.
r
use
Configure the KX II-101 Using a Terminal Emulation Program (Optional)
You can use the Admin serial console with a terminal emulation program
like HyperTerminal to set the following configuration parameters for the
KX II-101:
• IP address
• Subnet mask address
• Gateway address
• IP access control
• LAN speed
• LAN interface mode
To use a terminal emulation program with the KX II-101, you must first
connect the included RS-232 serial cable from the Admin port on the KX
II-101 to the COM1 port on your PC. See Admin Port (on page 23).
stration purposes, the terminal emulation program described
mon
For de
in this section is HyperTerminal. You can use any terminal emulation
program.
To use a terminal emulation program to configure the KX II-101:
1. Connect the KX II-101 to a local PC using the included RS-232 serial
cable.
2. Connect to the Admin port on the KX II-101 and the COM1 port on
the PC.
29
Page 38

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
3. Launch the terminal emulation program you want to use to configure
the KX II-101.
4. Set the following port settings in the terminal emulation program:
Bits per second - 115200
Data bits - 8
Parity - None
Stop bits - 1
Flow control - None
30
5. Connect to the KX II-101. The login page opens.
6. Type the administrator user name and press Enter. You are
prompted to enter your password.
7. Type your password and press Enter. The Admin Port prompt
appears.
8. At the Admin Port > prompt, type config and press Enter.
9. At the Config > prompt, type network and press Enter.
10. To view the current interface settings, at the Interface > prompt, type
interface and press Enter. The current interface settings appear.
Page 39

Chapter 2: Installation and Configuration
11. To configure new network settings, at the Network prompt, type
interface followed by one of the following commands and its
appropriate argument (option), then press Enter.
Command Argument Options
ipauto none|dhcp none - Enables you to manually specify
an IP address for the device. You must
follow this option with the ip command
and the IP address, as shown in the
following example:
interface ipauto none ip
192.168.50.12
dhcp - Automatically assign an IP address
to the device on startup.
ip IP address The IP address to assign to the device. To
manually set an IP address for the first
time, this command must be used with the
ipauto command and the none option.
See ipauto for information. After you have
manually assigned an IP address once,
you can use the ip command alone to
change the IP address.
mask subnetmask The subnet mask IP address.
gw IP address The gateway IP address
mode mode The Ethernet mode. You have the
following choices:
auto - Automatically sets speed and
interface mode based on the network.
10hdx - 10 MB/s, half duplex.
10fdx - 10 MB/s, full duplex
100hdx - 100 MB/s, half duplex
100fdx - 100 MB/s, full duplex
• When you have successfully changed a setting, you see a
confirmation message like the following:
1. When you are finished configuring the KX II-101, type logout at the
command prompt and press Enter.
You are logged out of the command line interface.
31
Page 40

Chapter 3
Interfaces
Working with Target Servers
In This Chapter
Interfaces.................................................................................................32
Virtual KVM Client ...................................................................................41
).....................................................................60
Multi-Platform Client
KX II-101 Remote Console Interface
The KX II-101 Remote Console is a browser-based graphical user
interface that allows you to log into KVM target servers and serial targets
connected to the KX II-101 and to remotely administer the KX II-101.
The KX II-101 Remote Console provides a digital connection to your
connected KVM target servers. When you log into a KVM target server
using the KX II-101 Remote Console, a Virtual KVM Client window
opens.
(MPC
Note: If you are using IE 7, you may run into permission issues when
trying to connect to a target server. To avoid this, do the following:
1. In IE7, click Tools > Internet Options to open the Internet Options
dialog.
2. In the "Temporary Internet files" section, click the Settings button. The
Settings dialog opens.
3. In the "Check for newer versions of stored pages" section, select
Automatically.
4. Click OK to apply the settings.
Enable Direct Port Access
Direct port access enables you to access the KX II-101 Remote Client
without having to go through the usual login page. With direct port
access enabled, you can define an URL to navigate directly to the Port
Access page.
To enable direct port access:
1. Launch the KX II-101 Remote Console.
2. Choose Device Settings > Device Services. The Device Services
page opens.
3. Select the Enable Direct Port Access via URL checkbox.
32
Page 41

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
4. Click Save.
To define a direct port access URL:
• Define a URL with the IP address, user name, password, and if
necessary, port number of the KX II-101.
If you have only one KVM port, the port number is not needed.
The format for a direct port access URL is:
https://IP
address/dpa.asp?username=username&password=password&port=
port number
Tip: Define a direct port access URL once, then save it in your web
browser as a bookmark to make reusing it easier.
KX II-101 Remote Console Interface
The KX II-101 Remote Console is a browser-based graphical user
interface that allows you to log into KVM target servers and serial
targets connected to the KX II-101 and to remotely administer the KX II-
101.
The KX II-101 Remote Console provides a digital connection to your
connected KVM target servers. When you log into a KVM target server
using the KX II-101 Remote Console, a Virtual KVM Client window
opens.
KX II-101 Console Navigation
The KX II-101 Console interfaces provide many methods for navigation
and making your selections.
To select an option (use any of the following):
• Click on a tab. A page of available options appears.
• Hover over a tab and select the appropriate option from the menu.
• Click the option directly from the menu hierarchy displayed
(breadcrumbs).
To scroll through pages longer than the screen:
• Use Page Up and Page Down keys on your keyboard.
• Use the scroll bar on the right.
33
Page 42

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Port Access Page
After successfully logging in to the KX II-101 Remote Console, the Port
Access page appears. This page lists the KX II-101 port, the connected
KVM target server, and its status and availability. The Port Access page
provides access to the KVM target server connected to the KX II-101. A
KVM target server is a server that you want to control through the KX II101 device. They are connected to the KX II-101 ports at the back of the
device.
To use the Port Access page:
1. From the KX II-101 Remote Console, click the Port Access tab. The
Port Access page opens.
The KVM target servers are initially sorted by Port Number. You can
change the display to sort on any of the columns.
Port Number - The port available for the KX II-101 device.
Port Name - The name of the KX II-101 port. Initially, this is set to
Dominion_KX2_101_Port1 but you can change the name to
something more descriptive. When you click a Port Name link,
the Port Action Menu appears.
Status - The status is either up or down.
Availability - The Availability can be Idle, Connected, Busy, or
Unavailable.
2. Click the Port Name of the target server you want to access. The
Port Action Menu appears. See Port Action Menu (on page 34) for
details o
3. Choose the desired menu command from the Port Action Menu.
Port Action Menu
available menu options.
n
When you click a Port Name in the Port Access list, the Port Action menu
appears. Choose the desired menu option for that port to execute it. Note
that only options available for the selected port are listed in the Port
Action menu:
• Connect - Creates a new connection to the target server. For the KX
II-101 Remote Console, a new Virtual KVM Client (on page 41)
ppe
page a
ars.
Note: This option is not available from the KX II-101 Remote Console
for an available port if all connections are busy.
34
Page 43

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
• Disconnect - Disconnects this port and closes the Virtual KVM Client
page for this target server. This menu item is available only when the
port status is up and connected, or up and busy.
• Power On - Powers on the target server through the associated
outlet. This option is visible only when there are one or more power
associations to the target.
• Power Off - Powers off the target server through the associated
outlets. This option is visible only when there are one or more power
associations to the target, when the target power is on (port status is
up), and when user has permission to operate this service.
• Power Cycle - Power cycles the target server through the associated
outlets. This option is visible only when there are one or more power
associations to the target, and when the user has permission to
operate this service.
35
Page 44

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Managing Favorites
A Favorites feature is provided so you can organize and quickly access
the devices you use frequently. The Favorite Devices section is located
in the lower left side (sidebar) of the Port Access page and provides the
ability to:
• Create and manage a list of favorite devices
• Quickly access frequently-used devices
• List your favorites either by Device Name, IP Address, or DNS
hostname
• Discover KX II-101 devices on its subnet (before and after login)
• Retrieve discovered KX II-101 devices from the connected KX device
(after login)
To access a favorite KX II-101 device:
• Click the device name (listed beneath Favorite Devices). A new
browser opens to that device.
To display favorites by name:
• Click Display by Name.
To display favorites by IP Address:
• Click Display by IP.
To display favorites by the host name:
• Click Display by Host Name.
36
Page 45

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Manage Favorites Page
To open the Manage Favorites page:
• Click the Manage button in the left panel. The Manage Favorites
page appears and contains the following:
Use: To:
Favorites List Manage your list of favorite
devices.
Discover Devices - Local Subnet Discover Raritan devices on the
client PC's local subnet.
Discover Devices - KX II-101
Subnet
Discover the Raritan devices on
the KX II-101 device subnet.
Add New Device to Favorites Add, edit, and delete devices from
your list of Favorites.
Favorites List Page
From the Favorites List page, you can add, edit, and delete devices from
your list of favorites.
To open the Favorites List page:
• Choose Manage > Favorites List. The Favorites List page opens.
Discovering Raritan Devices on the Local Subnet
This option discovers the devices on your local subnet, which is the
subnet where the KX II-101 Remote Console is running. These devices
can be accessed directly from this page or you can add them to your list
of favorites. See Favorites List Page (on page 37).
To discover devices on the local subnet:
1. Choose Manage > Discover Devices - Local Subnet. The Discover
Devices - Local Subnet page appears.
2. Choose the appropriate discovery port:
To use the default discovery port, select the Use Default Port
5000 checkbox.
To use a different discovery port:
a. Deselect the Use Default Port 5000 checkbox.
b. Type the port number in the Discover on Port field.
c. Click Save.
37
Page 46

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
3. Click Refresh. The list of devices on the local subnet is refreshed.
To add devices to your Favorites List:
1. Select the checkbox next to the device name/IP address.
2. Click Add.
Tip: Use the Select All and Deselect All buttons to quickly select all (or
deselect all) devices in the remote console subnet.
To access a discovered device:
• Click the device name or IP address for that device. A new browser
opens to that device.
38
Page 47

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Discovering Raritan Devices on the KX II-101 Subnet
This option discovers devices on the device subnet, which is the subnet
of the KX II-101 device IP address itself. You can access these devices
directly from this the Subnet page or add them to your list of favorites.
See Favorites List Page (on page 37).
r
This featu
e allows multiple KX II-101 devices to interoperate and scale
automatically. The KX II-101 Remote Console automatically discovers
the KX II-101 devices, and any other Raritan device, in the subnet of the
KX II-101.
To discover devices on the device subnet:
1. Choose Manage > Discover Devices - KX II-101 Subnet. The
Discover Devices - KX II-101 Subnet page appears.
2. Click Refresh. The list of devices on the local subnet is refreshed.
To add devices to your Favorites List:
1. Select the checkbox next to the device name/IP address.
2. Click Add.
Tip: Use the Select All and Deselect All buttons to quickly select all (or
deselect all) devices in the KX II-101 device subnet.
To access a discovered device:
• Click the device name or IP address for that device. A new browser
opens to that device.
Adding, Deleting, and Editing Favorites
To add a device to your favorites list:
1. Choose Manage > Add New Device to Favorites. The Add New
Favorite page appears.
2. Type a meaningful description.
3. Type the IP Address/Host Name for the device.
39
Page 48

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
4. Change the discovery Port (if necessary).
5. Select the Product Type.
6. Click OK. The device is added to your list of favorites.
To edit a favorite:
1. From the Favorites List page, select the checkbox next to the
appropriate KX II-101 device.
2. Click the Edit button. The Edit page appears.
3. Update the fields as necessary:
Description
IP Address/Host Name - Type the IP address of the KX II-101
device
Port (if necessary)
Product Type
4. Click OK.
To delete a favorite:
Important: Exercise caution in the removal of favorites. You are not
prompted to confirm their deletion.
40
Page 49

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
1. Select the checkbox next to the appropriate KX II-101 device.
2. Click the Delete button. The favorite is removed from your list of
favorites.
Logging off
To quit the KX II-101 Remote Console:
• Click Logout in the upper right-hand corner of the page.
Note: Logging off also closes any open Virtual KVM Client and serial
client sessions.
Multi-Platform Client Interface
See Multi-Platform Client (MPC) (on page 60).
Virtual KVM Client
Overview
Whenever you access a target server using the KX II-101 Remote
Console, a Virtual KVM Client (VKC) window opens. There is one Virtual
KVM Client for each target server connected. These windows can be
accessed via the Windows task bar.
Virtual KVM Client windows can be minimized, maximized, and moved
around your computer desktop.
Note: Refreshing your HTML browser will close the Virtual KVM Client
connection, so exercise caution.
Connecting to a KVM Target Server
To connect to a KVM target server:
1. From the KX II-101 Remote Console, click the Port Access tab to
open it. The Port Access page opens.
2. Click the Port Name of the target you want to access. The Port
Action menu appears.
3. Click Connect. A Virtual KVM Client (on page 41) window opens to
the target server conne
cted to that port.
41
Page 50

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
VKC Toolbar
Button Description
Properties
Video settings
Calibrate color
Synchronize the target mouse cursor
Refresh screen
Auto-sense video
Send Ctrl+Alt+Delete
Single mouse cursor
Full screen
Resize video to fit screen
Power Controlling a KVM Target Server
Note: These features are available only when you have made power
associations. See Power Control (on page 157).
To power cycle a KVM target server:
1. From the KX II-101 Remote Console, click the Port Access tab. The
Port Access page opens.
2. Click the Port Name of the appropriate target server. The Port Action
menu appears.
3. Choose Power Cycle. A confirmation message appears.
To power on a target server:
1. From the KX II-101 Remote Console, click the Port Access tab. The
Port Access page opens.
2. Click the port name of the appropriate target server. The Port Action
menu appears.
3. Choose Power On. A confirmation message appears.
42
Page 51

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
To power off a target server:
1. From the KX II-101 Remote Console, click the Port Access tab to
open it. The Port Access page opens.
2. Click the port name of the appropriate target server. The Port Action
menu appears.
3. Choose Power Off. A confirmation message appears.
Disconnecting a KVM Target Server
To disconnect a target server:
1. Click the port name of the target you want to disconnect. The Port
Action menu appears.
2. Choose Disconnect.
Tip: You can also close the Virtual KVM Client window by selecting
Connection > Exit from the Virtual KVM menu.
VKC Connection Properties
The KX II-101 dynamic video compression algorithms maintain KVM
console usability under varying bandwidth constraints. The KX II-101
devices optimize KVM output not only for LAN use, but also for WAN
use. These devices can also control color depth and limit video output,
offering an optimal balance between video quality and system
responsiveness for any bandwidth.
The parameters in the Properties dialog can be optimized to suit your
needs for different operating environments.
To set the connection properties:
1. Choose Connection > Properties or click the Connection Properties
button
in the toolbar. The Properties dialog appears.
43
Page 52

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
2. Choose the Connection Speed from the drop-down list. The device
can automatically detect available bandwidth and not limit bandwidth
use. However, you can also adjust this usage according to
bandwidth limitations.
Auto
100 Mb Ethernet
10 Mb Ethernet
1.5 Mb (MAX DSL/T1)
1 Mb (Fast DSL/T1)
512 Kb (Medium DSL/T1)
384 Kb (Slow DSL/T1)
256 Kb (Cable)
128 Kb (Dual ISDN)
56 kb (ISP Modem)
33 kb (Fast Modem)
24 kb (Slow Modem)
Note that these settings are an optimization for specific conditions
rather than an exact speed. The client and server always attempt to
deliver video as quickly as possible on the network regardless of the
current network speed and encoding setting. But the system will be
most responsive when the settings match the real world environment.
3. Choose the Color Depth from the drop-down list. The device can
dynamically adapt the color depth transmitted to remote users in
order to maximize usability in all bandwidths.
15-bit RGB Color
8-bit RGB Color
4-bit Color
4-bit Gray
3-bit Gray
2-bit Gray
Black and White
Important: For most administrative tasks (server monitoring,
reconfiguring, and so on), the full 24-bit or 32-bit color spectrum
made available by most modern video graphics cards is not
necessary. Attempting to transmit such high color depths wastes
network bandwidth.
44
Page 53

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
4. Use the slider to select the desired level of Smoothing (15-bit color
mode only). The level of smoothing determines how aggressively to
blend screen regions with small color variation into a single smooth
color. Smoothing improves the appearance of target video by
reducing displayed video noise.
5. Click OK to set these properties.
Connection Information
To obtain information about your Virtual KVM Client
connection:
• Choose Connection > Connection Info. The Connection Info window
opens.
The following information is displayed about the current connection:
• Device Name - The name of the KX II-101 device.
• IP Address - The IP address of the KX II-101 device.
• Port - The KVM communication TCP/IP port used to access the
target device.
• Data In/Second - Data rate in.
• Data Out/Second - Data rate out.
• Connect Time - The duration of the connect time.
• FPS - The frames per second transmitted for video.
• Horizontal Resolution - The screen resolution horizontally.
• Vertical Resolution - The screen resolution vertically.
• Refresh Rate - How often the screen is refreshed.
• Protocol Version - RFB Protocol version.
To copy this information:
• Click Copy to Clipboard. The information is available to be pasted
into the program of your choice.
45
Page 54

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Keyboard Options
Keyboard Macros
Keyboard macros ensure that keystroke combinations intended for the
target server are sent to and interpreted only by the target server.
Otherwise, they might be interpreted by the computer on which the
Virtual KVM Client is running (your client PC).
Macros are stored on the client PC and are PC-specific. Therefore, if you
use another PC, you will not see your macros. In addition, if another
person uses your PC and logs in under a different name, that user will
see your macros since they are computer-wide. Keyboard macros
created in the Virtual KVM Client are available in MPC and vice versa.
Building a Keyboard Macro
To build a macro:
1. Click Keyboard > Keyboard Macros. The Keyboard Macros dialog
appears.
2. Click Add. The Add Keyboard Macro dialog then appears.
3. Type a name for the macro in the Keyboard Macro Name field. This
name will appear in the Keyboard menu after it is created.
4. From the Hot-Key Combination field, select a keyboard combination
from the drop-down list. This allows you to execute the macro with a
predefined keystroke. Optional
5. In the Keys to Press drop-down list:
a. Select each key you would like to use to emulate keystrokes.
Select the keys in the order by which they are to be pressed.
b. After each selection, select Press Key. As each key is selected,
it will appear in the Keys to Release field.
For example, select the Windows key and the letter D key. When
these keys are selected in the client, the macro will be executed.
Add a key release attribute to the macro if needed (see next
step).
6. In the Keys to Release field:
a. Choose each key for which you would like to emulate a key
release. Define the keys you want released in order to run the
macro.
For example, specify that the keys to be pressed must also be
released in order for the macro to be executed. Select the keys in
the order by which they are to be released.
46
b. Click Release Key after each selection.
Page 55

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
7. Review the Macro Sequence field to be sure the macro sequence is
defined correctly.
The contents of this field are automatically generated and are based
on the selections made in the Keys to Press and Keys to Release
fields.
a. To remove a step in the sequence, select it and click Remove.
b. To change the order of steps in the sequence, click the step and
then click the up or down arrow buttons to reorder them as
needed.
8. Click OK to save the macro. Click Clear to clear all field and start
over. When you click OK, the Keyboard Macros dialog appears and
lists the new keyboard macro.
47
Page 56

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
9. Click Close to close the Keyboard Macros dialog. The macro will now
appear on the Keyboard menu in the application. Select the new
macro on the menu to run it or use the keystrokes you assigned to
the macro.
Running a Keyboard Macro
Once you have created a keyboard macro, execute it using the keyboard
macro you assigned to it or by choosing it from the Keyboard menu.
Run a Macro from the Menu Bar
When you create a macro, it appears under the Keyboard menu.
Execute the keyboard macro by clicking on it in the Keyboard menu.
Run a Macro Using a Keyboard Combination
If you assigned a keyboard combination to a macro when building it, you
can execute the macro by pressing its assigned keystro kes. For
example, press the keys Ctrl+Alt+0 simultaneously to minimize all
windows on a Windows target server.
Modifying and Removing Keyboard Macros
To modify a macro:
1. Choose Keyboard > Keyboard Macros. The Keyboard Macros dialog
appears.
2. Choose the macro from among those listed.
48
3. Click Modify. The Add/Edit Macro dialog appears.
4. Make your changes.
Page 57

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
5. Click OK.
To remove a macro:
1. Choose Keyboard > Keyboard Macros. The Keyboard Macros dialog
appears.
2. Choose the macro from among those listed.
3. Click Remove. The macro is deleted.
Video Properties
Refresh Screen
The Refresh Screen command forces a refresh of the video screen.
Video settings can be refreshed automatically in several ways:
• The Refresh Screen command forces a refresh of the video screen.
• The Auto-sense Video Settings command automatically detects the
target server's video settings.
• The Calibrate Color command calibrates the video to enhance the
colors being displayed.
In addition, you can manually adjust the settings using the Video Settings
command.
To refresh the video settings, do one of the following:
• Choose Video > Refresh Screen or click the Refresh Screen button
Auto-Sense Video Settings
from toolbar.
The Auto-sense Video Settings command forces a re-sensing of the
video settings (resolution, refresh rate) and redraws the video screen.
To automatically detect the video settings, do the following:
• Choose Video > Auto-sense Video Settings or click the Auto-Sense
Video Settings button
auto adjustment is in progress appears.
in the toolbar. A message stating that the
49
Page 58

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Calibrate Color
Use the Calibrate Color command to optimize the color levels (hue,
brightness, saturation) of the transmitted video images. The KX II-101
color settings are on a target server-basis.
Note: The Calibrate Color command applies to the current connection
only.
To calibrate the color, do the following:
• Choose Video > Calibrate Color or click the Calibrate Color button
calibration.
VKC Video Settings
Use the Video Settings command to manually adjust the video settings.
To change the video settings:
1. Choose Video > Video Settings or click the Video Settings button
in the toolbar. The target device screen updates its color
in the toolbar to open the Video Settings dialog.
2. Adjust the following settings as required. As you adjust the settings
the effects are immediately visible:
a. Noise Filter
The KX II-101 device can filter out the electrical interference of
video output from graphics cards. This feature optimizes picture
quality and reduces bandwidth. Higher settings transmit variant
pixels only if a large color variation exists in comparison to the
neighboring pixels. However, setting the threshold too high can
result in the unintentional filtering of desired screen changes.
Lower settings transmit most pixel changes. Setting this
threshold too low can result in higher bandwidth use.
b. Brightness: Use this setting to adjust the brightness of the target
server display.
c. Brightness Red - Controls the brightness of the target server
display for the red signal.
d. Brightness Green - Controls the brightness of the green signal.
e. Brightness Blue - Controls the brightness of the blue signal.
f. Contrast Red - Controls the red signal contrast.
g. Contrast Green - Controls the green signal.
h. Contrast Blue - Controls the blue signal.
50
Page 59

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
If the video image looks extremely blurry or unfocused, the
settings for clock and phase can be adjusted until a better image
appears on the active target server.
Warning: Exercise caution when changing the Clock and Phase
settings. Doing so may result in lost or distorted video and you may
not be able to return to the previous state. Contact Raritan Technical
Support before making any changes.
i. Clock - Controls how quickly video pixels are displayed across
the video screen. Changes made to clock settings cause the
video image to stretch or shrink horizontally. Odd number
settings are recommended. Under most circumstances this
setting should not be changed because the autodetect is usually
quite accurate.
j. Phase - Phase values range from 0 to 31 and will wrap around.
Stop at the phase value that produces the best video image for
the active target server.
k. Horizontal Offset - Controls the horizontal positioning of the
target server display on your monitor.
3. Vertical Offset - Controls the vertical positioning of the target server
display on your monitor.
4. Select the video sensing mode:
Best possible video mode
The KX II-101 device will perform the full Auto Sense process
when switching targets or target resolutions. Selecting this option
calibrates the video for the best image quality.
Quick sense video mode
With this option, the KX II-101 device will use a quick video Auto
Sense in order to show the target's video sooner. This option is
especially useful for entering a target server's BIOS configuration
right after a reboot.
5. Click OK to apply the settings and close the dialog. Click Apply to
apply the settings without closing the dialog.
51
Page 60

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Note: Some Sun background screens, such as screens with very dark
borders, may not center precisely on certain Sun servers. Use a different
background or place a lighter colored icon in the upper left corner of the
screen.
52
Mouse Options
When controlling a target server, the KX II-101 Remote Console displays
two mouse cursors: one belonging to your client workstation and the
other belonging to the target server.
You can operate in either single mouse mode or dual mouse mode.
When in dual mouse mode, and provided the option is properly
configured, the mouse cursors will align.
When there are two mouse cursors, the KX II-101 device offers several
mouse modes:
• Absolute (Mouse Synchronization)
• Intelligent (Mouse Mode)
• Standard (Mouse Mode)
Page 61

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Mouse Pointer Synchronization
When remotely viewing a target server that uses a mouse, you will see
two mouse cursors: one belonging to your remote client workstation and
the other belonging to the target server. When the mouse pointer lies
within the Virtual KVM Client target server window, mouse movements
and clicks are directly transmitted to the connected target server. While
in motion, the client mouse pointer slightly leads the target mouse pointer
due to mouse acceleration settings.
On fast LAN connections, you may want to disable the Virtual KVM
Client mouse pointer and view only the target server's pointer. You can
toggle between these two modes (single mouse and dual mouse).
Mouse Synchronization Tips
Be sure to follow these steps when configuring mouse synchronization:
1. Verify that the selected video resolution and refresh rate are among
those supported by the KX II-101 device. The Virtual KVM Client
Connection Info dialog displays the actual values that the KX II-101
is seeing.
2. Verify that the cable length is within the specified limits for the
selected video resolution.
3. Verify that the mouse and video have been properly configured
during the installation process.
4. Force an auto-sense by clicking the Virtual KVM Client auto-sense
button.
5. If that does not improve the mouse synchronization (for Linux, UNIX,
and Solaris KVM target servers):
a. Open a terminal window.
b. Enter the xset mouse 1 1 command.
53
Page 62

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
c. Close the terminal window.
6. Click the "Virtual KVM Client mouse synchronization" button
Additional Notes for Intelligent Mouse Mode
.
• Be sure that there are no icons or applications in the upper left
section of the screen since that is where the synchronization routine
takes place.
• Do not use an animated mouse.
• Disable active desktop on KVM target servers.
Synchronize Mouse
In dual mouse mode, the Synchronize Mouse command forces
realignment of the target server mouse pointer with Virtual KVM Client
mouse pointer.
To synchronize the mouse, do one of the following:
• Choose Mouse > Synchronize Mouse or click the Synchronize
Mouse button
Standard Mouse Mode
in the toolbar.
Standard Mouse mode uses a standard mouse synchronization
algorithm using relative mouse positions. Standard Mouse mode requires
that mouse acceleration is disabled and other mouse parameters are set
correctly in order for the client and server mouse to stay synchronized.
Standard Mouse mode is the default.
54
To enter standard mouse mode:
• Choose Mouse > Standard.
Absolute Mouse Mode
In this mode, absolute coordinates are used to keep the client and target
cursors in sync, even when the target mouse is set to a different
acceleration or speed. This mode is supported on servers with USB
ports.
To enter absolute mouse mode:
• Choose Mouse > Absolute.
Note: The absolute mouse setting requires a USB target system and is
the recommended mouse setting for KX II-101.
Page 63

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Intelligent Mouse Mode
In Intelligent Mouse mode, the KX II-101 device can detect the target
mouse settings and synchronize the mouse cursors accordingly, allowing
mouse acceleration on the target. In this mode, the mouse cursor does a
“dance” in the top left corner of the screen and calculates the
acceleration. For this mode to work properly, certain conditions must be
met.
To enter intelligent mouse mode:
• Choose Mouse > Intelligent.
Intelligent Mouse Synchronization Conditions
The Intelligent Mouse Synchronization command, available on the
Mouse menu, automatically synchronizes mouse cursors during
moments of inactivity. For this to work properly, however, the following
conditions must be met:
• The active desktop should be disabled on the target.
• No windows should appear in the top left corner of the target page.
• There should not be an animated background in the top left corner of
the target page.
• The target mouse cursor shape should be normal and not animated.
• The target mouse speeds should not be set to very slow or very high
values.
• Advanced mouse properties such as “Enhanced pointer precision" or
“Snap mouse to default button in dialogs” should be disabled.
• Choose “Best Possible Video Mode” in the Video Settings window.
• The edges of the target video should be clearly visible (that is, a
black border should be visible between the target desktop and the
remote KVM console window when you scroll to an edge of the
target video image).
• When using the intelligent mouse synchronization function, having a
file icon or folder icon located in the upper left corner of your desktop
may cause the function not to work properly. To be sure to avoid any
problems with this function, Raritan recommends you do not have file
icons or folder icons in the upper left corner of your desktop.
After autosensing the target video, manually initiate mouse
synchronization by clicking the Synchronize Mouse button on the toolbar.
This also applies when the resolution of the target changes if the mouse
cursors start to desync from each other.
If intelligent mouse synchronization fails, this mode will revert to standard
mouse synchronization behavior.
55
Page 64

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Please note that mouse configurations will vary on different target
operating systems. Consult your OS guidelines for further details. Also
note that intelligent mouse synchronization does not work with UNIX
targets.
Single Mouse Cursor
Single Mouse mode uses only the target server mouse cursor and the
local mouse pointer no longer appears onscreen. While in single mouse
mode, the Synchronize Mouse command is not available (there is no
need to synchronize a single mouse cursor).
To enter single mouse mode, do the following:
1. Choose Mouse > Single Mouse Cursor.
2. Click the Single/Double Mouse Cursor button
in the toolbar.
To exit single mouse mode:
1. Press Ctrl+Alt+O on your keyboard to exit single mouse mode.
VKC Virtual Media
See the chapter on Virtual Media (on page 106) for complete
information about setting up and using virtual media.
56
Page 65

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Tool Options
From the Tools menu, you can specify certain options for use with the
Virtual KVM Client, including logging, setting the keyboard type, and
defining hot keys for exiting target screen resolution mode and single
cursor mode.
To set the tools options:
1. Choose Tools > Options. The Options dialog appears.
2. Select the Enable Logging checkbox only if directed to by Technical
Support. This option creates a log file in your home directory.
3. Choose the Keyboard Type from the drop-down list (if necessary).
The options include:
US/International
French (France)
German (Germany)
Japanese
United Kingdom
Korean (Korea)
Belgian (Belgium)
Norwegian (Norway)
Danish (Denmark)
Swedish (Sweden)
German (Switzerland)
Hungarian (Hungary)
Spanish (Spain)
57
Page 66

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Italian (Italy)
Slovenian
4. Exit Target Screen Resolution Mode - Hotkey. When you enter target
screen resolution mode, the display of the target server becomes full
screen and acquires the same resolution as the target server. This is
the hot key used for exiting this mode.
5. Exit Single Cursor Mode - Hotkey. When you enter single cursor
mode, only the target server mouse cursor is visible. This is the hot
key used to exit single cursor mode and bring back the client mouse
cursor.
6. Click OK.
Keyboard Limitations
Slovenian Keyboards
The < key does not work on Slovenian keyboards due to a JRE
limitation.
Language Configuration on Linux
Because the Sun JRE on Linux has problems generating the correct Key
Events for foreign-language keyboards configured using System
Preferences, Raritan recommends that you configure foreign keyboards
using the methods described in the following table.
Language Configuration method
US Intl Default
French Keyboard Indicator
German System Settings (Control Center)
Japanese System Settings (Control Center)
UK System Settings (Control Center)
Korean System Settings (Control Center)
Belgian Keyboard Indicator
Norwegian Keyboard Indicator
Danish Keyboard Indicator
Swedish Keyboard Indicator
Hungarian System Settings (Control Center)
Spanish System Settings (Control Center)
Italian System Settings (Control Center)
Slovenian System Settings (Control Center)
58
Page 67

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Note: The Keyboard Indicator should be used on Linux systems using
Gnome as a desktop environment.
View Options
View Toolbar
You can use the Virtual KVM client with or without the toolbar display.
To toggle the display of the toolbar (on and off):
• Choose View > View Toolbar.
Scaling
Scaling your target window allows you to view the entire contents of the
target server window. This feature increases or reduces the size of the
target video to fit the Virtual KVM Client window size, and maintains the
aspect ratio so that you see the entire target server desktop without
using the scroll bar.
To toggle scaling (on and off):
• Choose View > Scaling.
Target Screen Resolution
When you enter target screen resolution mode, the display of the target
server becomes full screen and acquires the same resolution as the
target server. The hot key used for exiting this mode is specified in the
Options dialog (the default is Ctrl+Alt+M).
To enter target screen resolution:
• Choose View > Target Screen Resolution.
To exit target screen resolution mode:
Press the hot key configured in the Tools Options dialog. The default is
Ctrl+Alt+M.
Help Options
About Raritan Virtual KVM Client
This menu command provides version information about the Virtual KVM
Client, in case you require assistance from Raritan Technical Support.
To obtain version information:
• Choose Help > About Raritan Virtual KVM Client.
59
Page 68

Chapter 3: Working with Target Servers
Multi-Platform Client (MPC)
Raritan Multi-Platform Client (MPC) is a graphical user interface for the
Raritan product lines, providing remote access to target servers
connected to Raritan KVM over IP devices.
Requirements and Installation
If you do not have MPC installed, for information on MPC installation
requirements and directions on how to install MPC, see the KVM and
Serial Client User Guide. This guide can be accessed on the Raritan
website http://www.raritan.com on the Support page.
Operation
MPC Interface
MPC functions are grouped into six general sections on the page. As a
standalone product or using a web browser, the MPC window contains
these main sections.
60
 Loading...
Loading...